youtube-ads

Comments
-
Free Shipping Stendra
-
Viagra Sin Receta En Farmacias
-
Pak Generic
-
On Line Sales Of Viagra
-
Gta
-
cialis dysfunction erectile levitra viagra
-
Viagra Cialis Efficacia
-
20mg cialis dosage
-
online generic levitra
-
Compra Cialis Generico En Espana
-
Priligy Pills In India
-
Cialis Generico Alfemminile
-
Viagra Delle Donne
-
viagra para hipertensos
-
jelly kamagra disfuncion erectil us on line pharmacy selling kamagra kamagra e hipertension pulmonar
-
generic tadalafil from uk https://cialisusdc.com/
-
what is tadalafil cost of cialis
-
generic cialis online fast shipping tadalafil cost walmart
-
tadalafil side effects where to get tadalafil
-
cheap generic cialis for sale tadalafil drug
-
tadalafil online with out prescription cialis cost
-
generic cialis tadalafil buy tadalis
-
cheap cialis pills for sale tadalafil cost in canada
-
These imaging techniques conrm the presence of a mass and can distinguish a cystic from a solid mass. hahPoums who has the cheapest levitra Kamagra Efectos Ajanta Pharma meeferwene
-
generic cialis online fast shipping generic tadalafil from uk
-
where to buy cialis without prescription cialis at canadian pharmacy
-
https://nextadalafil.com/ cheapest tadalafil cost
-
tadalafil goodrx tadalafil generic
-
buy tadalis prescription tadalafil online
-
buy cialis pills buy tadalis
-
Cmqgsp Therapeutic medical abortion is done because the woman has a health condition. Prednisone Xkqwby
-
Zeqawa cialis chemical name Plaquenil Isvihq Some types are known to be recessive meaning both parents carry the defective gene and the chance for a subsequent child to be affected is about
-
where to buy tadalafil on line tadalafil dosage
-
cheapest tadalafil cost tadalafil goodrx
-
where to buy tadalafil on line tadalafil order online no prescription
-
prescription tadalafil online cialis at canadian pharmacy
-
tadalafil cost in canada tadalafil online with out prescription
-
buy tadalafil tadalafil order online no prescription
-
cheapest tadalafil cost tadalafil goodrx
-
https://cialiswbtc.com/ tadalafil liquid
-
canada generic tadalafil https://cialistrxy.com/
-
Plaquenil Pufhwc venta cialis sin receta
-
tadalafil generic where to buy where to order tadalafil tablets
-
best price usa tadalafil where to buy tadalafil on line
-
where to buy cialis without prescription side effects of tadalafil
-
tadalafil cialis buy cialis
-
where to get tadalafil https://cialisusdc.com/
-
where to buy tadalafil on line tadalafil daily online
-
tadalafil brands generic tadalafil from uk
-
best price usa tadalafil tadalafil side effects
-
tadalafil without a doctor prescription tadalafil blood pressure
-
generic tadalafil from uk buy tadalafil
-
buy tadalafil cialis tadalafil
-
tadalafil online with out prescription cialis without a prescription
-
buy tadalis cialis cost
-
best price usa tadalafil tadalafil online
-
buy generic cialis online with mastercard generic cialis tadalafil
-
tadalafil goodrx tadalafil brands
-
buy tadalis https://cialisbusd.com/
-
tadalafil daily online tadalafil generic where to buy
-
viagra 100mg viagra story
-
tadalafil cost in canada lowest price cialis
-
cialis tadalafil 10 mg tadalafil liquid fda approval date
-
cialis at canadian pharmacy https://cialiswbtc.com/
-
stromectol uk ivermectin cost canada
-
reddit tadalafil tadalafil prostate
-
viagra generic cost order viagra europe
-
sildenafil citrate 50mg online sildenafil and nitroglycerin
-
https://cialisedot.com/ tadalafil brands
-
ivermectin 6 mg tablets ivermectin 0.08%
-
https://cialisusdc.com/ tadalafil order online no prescription
-
tadalafil 50 mg tadalafil 100mg
-
cost of ivermectin 3mg tablets ivermectin 1 cream
-
ivermectin 0.5 lotion india stromectol for sale
-
tadalafil cialis tadalafil daily online
-
ivermectin 500ml stromectol tablets uk
-
ivermectin lotion ivermectin buy online
-
stromectol 3mg ivermectin ebay
-
buy ivermectin stromectol ivermectin pills canada
-
ivermectin goodrx ivermectin 20 mg
-
can you buy stromectol over the counter stromectol pills
-
ivermectin 1mg ivermectin 4
-
ivermectin over the counter canada stromectol 3 mg price
-
stromectol tablet 3 mg stromectol
-
cost of ivermectin pill ivermectin 400 mg brands
-
where can i buy oral ivermectin ivermectin 10 mg
-
stromectol pill ivermectin drug
-
cialis side effects forum how much is cialis in canada
-
ivermectin usa ivermectin virus
-
what happens if a girl takes viagra buy viagra
-
ivermectin eye drops stromectol 0.1
-
price of viagra viagra for men lowest price viagra best price viagra
-
maxim peptide tadalafil tadalafil 20 mg online
-
cialis tadalafil patent tadalafil indications
-
cialis brand cialis without prescription
-
sildenafil generic online sildenafil citrate 100mg prices
-
cialis tadalafil dosage generic tadalafil price
-
real viagra without a prescription female viagra prescription
-
sildenafil pfizer 100 mg how to use sildenafil 20 mg for ed
-
price of levitra 20 mg is levitra cheaper than viagra
-
list of reputable canadian pharmacies canadian online pharmacy adderall
-
cupid 50 sildenafil citrate tablets sildenafil otc usa
-
order medicine online costco pharmacy
-
is ordering cialis online legal buy cialis
-
oxfordhealth com online pharmacy canada drug pharmacy coupons
-
canadian overnight pharmacy reviews online drugstore pharmacy
-
generic viagra over the counter canada buying sildenafil citrate online
-
cialis tadalafil treat cheapest tadalafil india
-
cialis vs viagra cost how fast does cialis work
-
what is ivermectin used for in dogs ivermectin protocol
-
ivermectin reviews ivermectin for humans lice
-
levitra cialis levitra precio
-
accutane canada pharmacy best drugstore bb cream
-
cialis vs. viagra where to get my prescription cialis filled
-
sildenafil generic 50 mg sildenafil 200mg
-
canadian pharmacy levitra levitra 20 mg wirkungsdauer
-
cialis vs viagra vs kamagra 20 mg 30 pills cialis
-
doctor prescription reputable online canadian pharmacy
-
street prices prescription drugs pharmacy tech canada
-
best pharmacy is reliable rx pharmacy legit
-
united states online pharmacy viagra national rx pharmacy
-
generic viagra online canadian pharmacy pharmacy programs online
-
rx stands for pharmacy express scripts pharmacy
-
want to buy levitra levitra uk https://glevitrargu.com/
-
ivermectin paste for rabbits how much ivermectin for chickens https://stromectolujlo.com/
-
how to take sildenafil 20 mg for ed sildenafil cost per pill https://sildenafilkiol.com/
-
cheaper drugs from canada Buspar https://dtupharmyjn.com/
-
Top Avana generic cialis canada online pharmacy https://jzpharmacyukj.com/
-
where can i buy viagra cheap online generic sildenafil 20mg cost https://sgiviagraikn.com/
-
sildenafil citrate 50 mg viagra for sale in united states https://aviagrasbt.com/
-
buy generic cialiss buy cialis through pay pal https://dccialisxvf.com/
-
effects levitra side levitra free samples coupon https://xclevitradb.com/
-
ed drugs online canada meds online without doctor prescription
-
levitra and high blood pressure levitra generic name https://glevitrargu.com/
-
buy viagra online canada buy viagra hong kong https://aviagrasbt.com/
-
sildenafil online india sildenafil order online https://sildenafilkiol.com/
-
generic cialis from india cialis tablets in australia https://dccialisxvf.com/
-
prices levitra levitra generika rezeptfrei kaufen https://xclevitradb.com/
-
shopko online pharmacy store locator lloyds pharmacy
-
www levitra com viagra levitra cialis prices https://glevitrargu.com/
-
sildenafil over the counter sildenafil for sale https://sildenafilkiol.com/
-
cost of levitra at costco cheapest generic levitra https://xclevitradb.com/
-
global health supplies canada pharmacy diovan canadian pharmacy
-
compare levitra cialis viagra levitra side effects list https://glevitrargu.com/
-
cheap viagra pills uk viagra 1500mg https://aviagrasbt.com/
-
is sildenafil covered by medicare comprar sildenafil https://sildenafilkiol.com/
-
overnight pharmacy cialis cialis black to buy in the uk https://dccialisxvf.com/
-
levitra vs stendra best price levitra generic https://xclevitradb.com/
-
universal drugs canada list of prescription drugs available in mexico
-
buy modafinil 200mg online cheap buy modafinil 200mg online cheap cost modafinil 100mg
-
order modafinil 100mg pills provigil 200mg without prescription
-
order modafinil sale order provigil 100mg sale
-
what Is Cialis Black 800mg?
-
how To Take Cialis?
-
how To Get Medi Care To Pay For Cialis?
-
modafinil 100mg generic generic provigil 100mg
-
drugs legal in canada but not us canadian express pharmacy https://pharmusesude.com/
-
canada pharmacy generic cialis cialis free trial voucher 2018 https://cialisapart1.com/
-
cialis for daily use side effects best prices cialis 20mg https://cialisstored.com/
-
sildenafil 50 mg best price buy sildenafil online no prescription https://viagrause5.com/
-
envision rx pharmacy help desk global drugs direct canada https://pharmacyatside.com/
-
schnucks pharmacy prescription drugs for weight loss https://pharmacyday5.com/
-
uk produced tadalafil cialis tadalafil 20mg kaufen https://tadalafilmoreed.com/
-
what Are The Benefits Of Daily Cialis?
-
how Long Does 20mg Cialis Keep In System?
-
cialis buy onilne best online to buy cialis https://cialisandeds.com/
-
sildenafil citrate online pharmacy sildenafil and tadalafil https://sildenafilrealed.com/
-
canadapharmacy manor pharmacy store locator https://pharmacyclined.com/
-
http://erythromycinn.com/# erythromycin side effects
-
what Happens If You Take Cialis And Viagara?
-
lady viagra online viagra prescription canada https://viagraadultsed.com/
-
non prescription ed drugs prescription drugs
-
https://drwithoutdoctorprescription.online/# non prescription erection pills
-
non prescription ed pills pet meds without vet prescription
-
buy prescription drugs from canada cheap buy prescription drugs online
-
plaquenil 200mg hydroxychloroquine without a doctor prescription
-
http://www.ivermectinusd.com/ buy 6 mg ivermectin
-
essay history of pakistan explanatory essay about hybrid cars https://essayitis.com/
-
cyclones essay writing law 131 essay https://essayby1.com/
-
argumentative essay examples 500 words essay on laziness in urdu https://wikiessayus.com/
-
hvad dansk essay opbygning essay about your js prom https://weareessay.com/
-
https://sildenafilmg.online/# viagra 100mg price
-
ivermectin from india ivermectin 6 mg
-
ivermectin canada ivermectin uk 3mg 6mg 12mg
-
https://sildenafilmg.com/ best place to buy generic viagra online
-
glucophage clomid clomid usa
-
https://zithromaxforsale.shop/# zithromax prescription
-
purchase amoxicillin online without prescription where to get amoxicillin over the counter
-
12 point sat essay sample narrative essay samples spm https://essayanalyticok.com/
-
http://hydroxychloroquinex.com/ hydroxychloroquine 200mg where to buy
-
ucl english essay style sheet an essay on criticism analysis sparknotes https://needmoreessay.com/
-
spm english essay speech format short essay about my family in french https://essayrightversion.com/
-
metformin 850 mg cost where to buy metformin tablets
-
order tadalafil 20mg cheap tadalafil tablets
-
lipitor 30 mg buy lipitor 40 mg
-
my memento essay expository essay examples third person https://essaytruelist.com/
-
how to write a comparative essay thesis how to write an essay lesson plans high school https://essaychekhere.com/
-
https://buynolvadex.store/# tamoxifen rash
-
buy plaquenil online cheap alberta canada pharmacy hydroxychloroquine cost of plaquenil 200 mg
-
http://ivermectinuni.com/ buy 6mg ivermectin
-
us over the counter viagra indian viagra online https://viagrause5.com/
-
https://stromectolusdt.com/ stromectol canadian pharmacy
-
buy viagra online canadian pharmacy how to order viagra online in canada https://viagraadultsed.com/
-
rx pharmacy india dillons pharmacy https://pharmacyclined.com/
-
viagra womens 100mg sildenafil no rx canadian https://gogiviagr.com/
-
cialis pharmacy mastercard where do you inject liquid cialis https://cheppercialis.com/
-
price of sildenafil where to buy viagra online in canada https://viagrexok.com/
-
is tadalafil and cialis the same thing? tadalafil back pain https://tadalafilise.com/
-
the canadian pharmacy complaints no 1 canadian pharcharmy online https://jijopharm.com/
-
erectile dysfunction medications cheap erectile dysfunction pills
-
sildenafil otc australia sildenafil 100mg from india https://liloviagra.com/
-
sildenafil tablet usa viagra professional https://pfdviagrixx.com/
-
sildenafil citrate cheap cost of sildenafil at walmart https://sildenafilkook.com/
-
canada pharmacy online no script online pharmacy quick delivery https://postpharmixus.com/
-
pharmacy 365 cialis cheap original cialis https://cilciallis.com/
-
levitra prices uk how long does levitra 20 mg last https://pixlevitras.com/
-
cheap original cialis generic cialis 10 mg price cheap https://xucialika.com/
-
stromectol 3mg tablets order stromectol over the counter
-
Biltricide hometown pharmacy https://uuuppharm.com/
-
wal mart store pharmacy online medicine order discount https://ostipharmso.com/
-
discount super active cialis cost of cialis at cvs https://goesuscialis.com/
-
order viagra 100mg online viagra in india price https://hedrviagros.com/
-
viagra prescription cost generic viagra online canada https://xtyviagrix.com/
-
does medicare pay for cialis cialis daily side effects https://cialssis.com/
-
can i buy viagra over the counter india sildenafil 50 mg https://foxviagrixed.com/
-
order viagra paypal buy generic viagra online europe https://vigrixvix.com/
-
maple leaf pharmacy in canada ed drugs https://pharmregtop.com/
-
cialis legal online when should you take cialis https://cialssis.com/
-
price of real viagra sildenafil 110 mg https://vigrixvix.com/
-
buy viagra brand online best online viagra can you buy viagra over the counter in south africa
-
buy generic viagra soft tabs sildenafil 100mg usa viagra 50mg price in india
-
cialis generic versus brand name taking cialis and viagra together sildenafil viagra vardenafil levitra and tadalafil cialis
-
cialis vs mylan tadalafil order cialis with dapoxtine canadian tadalafil 20mg
-
Kamagra Trop Cher cialis 20mg price Comprare Cialis Svizzera
-
rate online pharmacies online pharmacy pain relief heb pharmacy online
-
real viagra without prescription viagra in mexico cost buy viagra canada fast shipping
-
can you buy viagra online in canada cheap sildenafil 100 viagra in canada
-
cialis purchase online can i take cialis with daxpoteine cialis purchase canada
-
Biaxin Pepcid Theo-24 Cr
-
cheapest cialis from india cialis drug interactions canadian pharmacy tadalafil
-
buying cialis in south africa liquid tadalafil citrate cialis online canada https://pocialgo.com/
-
viagra order online australia buy female viagra online australia sildenafil 50 mg online uk https://zenviagrok.com/
-
generic tadalafil tablets best reviewed tadalafil site cialis one a day https://qcialiuss.com/
-
tadalafil is not for consumption in united states cialis with dapoxetine cialis pre workout https://ciallsed.com/
-
best canadian pharmacy online https://medrxfast.com/# prescription meds without the prescriptions
-
custom writing cheap help writing term paper write my term paper for me https://papermelanin.com/
-
cruel angels thesis thesis statement definition and examples thesis statement paragraph https://thesismelon.com/
-
writings services literature review writing service personal writers https://paperabbrs.com/
-
cause and effect thesis open thesis statement identify and explain the two types of thesis statements https://thesisabbess.com/
-
can a thesis be a question essay thesis example what is a working thesis statement
-
closed thesis thesis layout speech thesis
-
buy psychology papers help with writing a dissertation buy writing paper
-
essay topics best essay what is a personal narrative essay
-
profile essay example claim in an essay essay word count
-
essay word counter proposal essay topics argumentative essay topics for college
-
hydroxychloroquine sulfate generic hydroxychloroquine nz
-
tadalafil 20 mg buy online cheap generic tadalafil
-
https://sildenafil.pro/# sildenafil 100 mg uk
-
amoxicillin 500 mg online doxycycline 100mg tablets
-
online rx canadian pharmacy cialis generic drugs without prescription
canadian meds canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg generic viagra online pharmacy -
generic sildenafil citrate 100mg order viagra online uk buy viagra online prices
-
plaquenil for psoriatic arthritis hydroxychloroquine 70 mg
-
tadalafil prescription tadalafil generic price
-
https://sildenafil.pro/# sildenafil pills online
-
amoxicillin 1000 mg capsule natural antibiotic for dogs
-
viagra usa generic viagra online 50mg purchase viagra online australia
-
yop6h5otkij low price viagra generic viagra canadian viagra pfizer buy cheap generic viagra medications.com
generic viagra from india canadian pharmacy cialis viagra dosages how to get viagra without a prescription canada drugs cialis
viagra online in canada canadian drugs online price of cialis in canada northwest canadian pharcharmy online viagra free sample -
ma1oizrbvft viagra mexico buy viagra now cheap viagra cialis brand viagra ingredients
canadian pharmacy.com generic cialis canada pharmacy online northwest canadian pharcharmy online canada drug superstore over the counter viagra alternative
daily cialis cheapest generic viagra canadian-drugstore generic viagra canada price free samples canada -
cialis for women side effects generic cialis cost uses for cialis
-
internet pharmacy
https://safecanadianpharm.com/
online pharmacies no prescription required pain medication -
cialis for women dosage cialis 200 mg. cialis from bc, no prescription
-
self-evaluation sample essay essay synonym college essay editing
-
how much do viagra cost order viagra online us 5 viagra
-
sildenafil singapore where can i buy viagra cheap legal to buy viagra online
-
viagra price without insurance viagra for sale in uk cheap ordering viagra
-
jy4rrliw1pc get a prescription online viagra free samples generic viagra rx www.onlinepharmaciescanada.com medication online
viagra 50 mg over the counter viagra alternative viagra reviews prescription drugs from canada canada drug prices
drug store online viagra online canada pharmacy cheap cialis canada viagra free trial highest rated canadian pharmacies -
pbgjeq5q8wl canadian drug store order cialis in canada cialis 5mg best price viagra india where to buy viagra online
northwestpharmacy .com northwestern pharmacy canada viagra from canadian pharmacy cialis over the counter in canada drugstore in canada
generic viagra sale viagra how it works www.canadianpharmacymeds.com natural viagra alternatives viagra for men -
viagra mail order sildenafil singapore where to buy viagra over the counter uk
-
cheap canadian viagra pills how to order viagra how much is 50 mg viagra
-
buy brand cialis 20 mg superman combo viagra cialis cialis none prescription
-
original cialis low price buy tadalafil 20 mg cialis purchase online
-
canadian pharmaceuticals online safe
https://allcanadianpharm.com/
reputable canadian online pharmacies -
cialis or viagra side effects of tadalafil tablets cialis memes
-
generic for cialis tadalafil cialis 80 mg dosage reddit cialis
-
canadian drugs without any prescriptions
https://canadianfirstpharmacies.com/
discount canadian pharmacy -
cialis price per pill cialis and grapefruit enhance tadalafil cialis from india
-
medication without prior prescription
https://getpharmacytoday.com/
canadian pharmacies without an rx -
toronto buy cialis paypal cialis tadalafil when is the best time to take cialis
-
is levitra cheaper than viagra levitra daily dose viagra and levitra
-
canadian pharmacy online no prescription needed
https://safecanadianpharm.com/
mail order prescription drugs from canada -
lxo5rbqryqc cheap celias how does viagra work viagra.canada viagra pharmacy online lowest price viagra
viagra generic canada canada rx canada drug pharmacy generic viagra canada canadian-drugs
what would happen if a girl took viagra canadian cialis reviews viagra canadian pharmacy viagra safe best price viagra -
is there generic cialis best place to buy cialis cialis for sale
-
cialis cheap generic jon jones cialis tadalafil tadacip cipla
-
price of sildenafil in canada viagra for ladies viagra pfizer 100mg
-
metformin and simcor usual metformin dosage metformin muskelkater
-
pharmacy schools canada pharmacy stuff store the medicine store pharmacy
-
hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg reviews hydrochlorothiazide 12.5mg capsules is coughing a side effect of lisinopril
-
how to stop canadian pharmacy spam prescription drugs prices how to dispose of prescription drugs walgreens
-
what drugs are legal in canada can i be denied employment due to prescription drugs uf pharmacy online refill
-
gt4iqx4qbob discount meds viagra free trial viagra for men buy cialis online canada viagra cheap
approved canadian online pharmacies shopping online canada free trial of viagra buy viagra online without script canada rx
generic brand viagra how to order viagra from canada viagra without prescription cialis or generic canada best prices for cialis -
furosemide no prescription furosemide (lasix furosemide 40 mg picture
-
nolvadex vs tamoxifen citrate acupuncture tamoxifen side effects does tamoxifen cause tumors
-
flagyl 852 flagyl uses std flagyl work for bv
-
class action lawsuit against bactrim bactrim and breastfeeding bactrim na pryszcze
-
trazodone dependence shelf life of trazodone trazodone benzo
-
atenolol wirkstoff life losartan versus atenolol coversyl vs atenolol
-
furosemide furosemide normal dose of furosemide heart medication furosemide
-
metformin and forgetfulness glucophage no period glucophage thyroid
-
dog cough furosemide torsemide to furosemide conversion globalrph what is furosemide 40mg used for
-
can you take benadryl and atenolol tenormin and thyroid tenormin minor indication
-
bactrim viral infection bactrim jak szybko dziaЕ‚a bactrim dose for folliculitis
-
best research chemicals nolvadex tamoxifen side effects and depression pct clomid and nolvadex dosage
-
lisinopril water retention what is hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg tab used for high blood pressure medication lisinopril
-
valacyclovir formula valacyclovir shingles dosage how fast does valtrex work on herpes
-
side effects from lyrica gabapentin and lyrica lyrica instagram
-
synthroid and metamucil can you take birth control and synthroid at the same time synthroid still tired
-
gabapentin side effects abdominal pain pregabalin or neurontin gabapentin neuroleptic
-
lipitor liver test results does lipitor increase triglycerides lipitor foot cramps
-
therapeutic category of metronidazole metronidazole alcohol acetaldehyde metronidazole black urine
-
what will ease symptoms of lyrica withdrawal pregabalin gabapentin combination therapy lyrica net worth
-
what is trazodone hydrochloride used for does trazodone cause memory loss generic name for trazodone
-
glucophage metformin classification glucophage spotting adverse effects metformin
-
tenormin 50 mg preis who invented atenolol what are tenormin tablets for
-
furosemide therapeutic class taking furosemide to lose weight prednisone furosemide interaction
-
nolvadex diabetes nolvadex side effects on men buy nolvadex online in uk
-
pamabrom vs hydrochlorothiazide can you drink alcohol while taking hydrochlorothiazide half life lisinopril
-
best price for cialis cialis usa pharmacy canadameds.com
buy brand viagra canadian online pharmacy cialis -
gan8fzyb285 canadian pharmacies without a prescription viagra from a pharmacy in canada online pharmacies without prescription kamagra gel buying cialis canada
canada-cialis viagra how it works canadian levitra order generic viagra free viagra samples
canada pharmacies online prescriptions cialis pharmacy viagra substitute ed meds tadalafil in canada -
lipitor and ed rosuvastatin calcium vs atorvastatin atorvastatin uses
-
bactrim lung transplant does bactrim affect blood pressure bactrim adultes 400 mg 80 mg
-
price of gabapentin prescription drug neurontin buy cheap neurontin
-
does lipitor cause nose bleeds lipitor 40mg recall atorvastatin calcium 80mg tablet
-
atorvastatin meaning what tier is atorvastatin lipitor recall
-
[url=http://neurontin.business/]gabapentin 1000mg[/url]
-
synthroid lupus armour thyroid doses synthroid equivalent synthroid and feeling tired
-
can you snort lyrica side effects for pregabalin is lyrica an opioid
-
[url=https://uchebnyj-centr-povyshenija-kvalifikacii.ru/]Курсы повышения квалификации[/url]
Направленности профессиональной квалификации - это упругые, современные линии профессионального учебы, которые дают возможность подготовиться к получению звания техника независимо через степени образования.
Курсы повышения квалификации -
how to make tadalafil tadalafil cialis from india blue sky tadalafil reviews
-
purchase neurontin canada gabapentin 3 gabapentin 500 mg
-
[url=http://sertraline.cfd/]zoloft buy[/url]
-
alternative drug for metronidazole metronidazole while pregnant safe how long does it take metronidazole to cure trich
-
[url=https://kursy-professionalnoj-perepodgotovki-distancionno.ru/]Курсы профессиональной переподготовки дистанционно[/url]
Целью специализированных тренингов для тренеров является повышение компетенций тренеров, работающих на рынке обучения.
Курсы профессиональной переподготовки дистанционно -
[url=https://finpecia.live/]generic finasteride canada[/url]
-
[url=https://lipitor.life/]buy generic lipitor[/url]
-
viagra 500mg tablet sildenafil without prescription from canada where to buy generic viagra online
-
savar tadalafil zhengzhou debao tadalafil tadalafil alcohol
-
viagra men viagra cheap fast delivery order viagra from canada
-
how to order drugs from canada top online pharmacy pharmacy tech online classes
-
order viagra cheap online buy sildenafil generic online sildenafil online australia
-
get viagra [url=http://www.canadotcphar.com/]canadian pharmacy - viagra[/url] canadian generic cialis
buy cialis canada canadian pharmacy for viagra cialis pharmacy -
[url=http://buyclindamycin.quest/]clindamycin cream buy online[/url]
-
[url=https://auto-evacuator-52.ru/]Эвакуатор Нижний Новгород[/url]
Автоэвакуатор в течение Тельном Новгороде, Нижегородской ответвления круглые сутки и недорого по стоимости через 30 рублем кинематограф За 14 мин. ты да я прибудем к для вас!
Эвакуатор Нижний Новгород -
cialis 10mg daily cialis tadalafil 20 mg cialis contraindications
-
where can you purchase female viagra generic viagra over the counter viagra on sale
-
cialis canadian pharmacy ezzz cialis cheap buy cialis tadalafil
-
viagra cost in uk how to buy generic viagra safely online generic viagra prescription
-
[url=http://propranololtab.online/]propranolol online purchase[/url]
-
[url=https://retinoa.cfd/]retino cream price[/url] [url=https://buytriamterene.life/]triamterene medication[/url] [url=https://albuterol.click/]ventolin for sale canada[/url] [url=https://buyglucophage.life/]metformin 50 mg[/url] [url=https://dipyridamole.cfd/]dipyridamole 200 mg[/url] [url=https://dexamethasone.agency/]dexamethasone tablets 1.5 mg[/url] [url=https://onlinedrugstore.agency/]canadian mail order pharmacy[/url] [url=https://buyfurosemide.monster/]lasix for sale[/url]
-
[url=https://hydroxyzine.site/]atarax 5mg[/url]
-
[url=http://vardenafil.tech/]levitra 20 mg tablet[/url] [url=http://retinoa.cfd/]retino 0.025 gel[/url]
-
[url=http://clonidine.site/]clonidine 136[/url]
-
[url=https://avana.sbs/]buy generic dapoxetine uk[/url]
-
[url=https://tizanidine.icu/]8 mg zanaflex[/url] [url=https://pharmacyonline.life/]cost less pharmacy[/url] [url=https://buybuspar.monster/]buspar pill 15 mg[/url] [url=https://atenolol.fun/]tenormin tablet[/url] [url=https://furosemide.company/]lasix online australia[/url] [url=https://tetracycline.company/]terramycin 250 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://finpeciatab.online/]finpecia 1mg[/url] [url=http://dipyridamole.cfd/]dipyridamole brand name uk[/url] [url=http://atenolol.life/]atenolol 12.5[/url]
-
[url=https://methocarbamol.today/]robaxin 500mg canada[/url] [url=https://retinoa.cfd/]retino 05[/url] [url=https://finpeciatab.online/]propecia singapore online[/url] [url=https://trazodone.lol/]50 mg of trazodone[/url] [url=https://dexamethasone.agency/]dexamethasone 40 mg daily[/url] [url=https://lyrica.boutique/]lyrica capsules 75 mg cost[/url] [url=https://clonidine.site/]clonidime[/url]
-
[url=https://buytriamterene.life/]triamterene-hctz 75-50mg tab[/url]
-
[url=https://hydroxyzine.site/]atarax 25mg[/url]
-
[url=http://buyamoxicillin.store/]augmentin 500 mg tablet cost[/url]
-
[url=http://canadianpharmacy.monster/]silkroad online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://paxil.life/]paxil price[/url]
-
[url=https://tetracycline.today/]sumycin 500 mg[/url] [url=https://hydroxyzine.cfd/]atarax pill price[/url] [url=https://wellbutrin.click/]price of generic wellbutrin[/url]
-
review of tadalafil chemone research tadalafil tadalafil finasteride combination
-
[url=http://fildena.life/]fildena online india[/url] [url=http://erythromycintab.online/]erythromycin tablets cost[/url] [url=http://tetracycline.site/]terramycin eye ointment for cats[/url] [url=http://tetracycline.today/]tetracycline tablets online[/url] [url=http://avodart.click/]avodart tablet[/url]
-
[url=https://buybuspar.quest/]how much is buspar[/url]
-
[url=http://atenolol.fun/]tenormin medication[/url] [url=http://propranololtab.online/]buy propranolol online australia[/url] [url=http://avodart.click/]generic avodart rx[/url] [url=http://priligy.click/]dapoxetine approval[/url] [url=http://tizanidine.icu/]8 mg tizanidine[/url]
-
[url=https://lyrica.works/]lyrica 250 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://tetracycline.site/]tetracycline capsule price[/url] [url=http://avodart.click/]avodart medicine[/url] [url=http://hydrochlorothiazide.life/]50mg hydrochlorothiazide[/url] [url=http://hydroxyzine.site/]atarax 10mg otc[/url]
-
[url=http://buyonlinepharmacy.quest/]my canadian pharmacy rx[/url]
-
[url=http://prednisone.wiki/]4mg prednisone daily[/url]
-
buy drugs canada giant food store phoenixville pharmacy cvs pharmacy application online
-
[url=https://hydroxyzine.site/]order atarax online[/url]
-
[url=http://retinoa.cfd/]retino 0.025 gel[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinoprilxtab.online/]lisinopril 3973[/url]
-
[url=https://indocin.run/]indocin nz[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinoprilxtab.online/]lisinopril without prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://familyrx.monster/]script pharmacy[/url] [url=https://canadianpharmacyx.quest/]online pharmacy meds[/url] [url=https://canadianfamilypharmacy.online/]canadian pharmacy mall[/url] [url=https://happypharmacy.monster/]mexican pharmacies online drugs[/url]
-
[url=http://clonidine.site/]clonidine 100mcg[/url]
-
[url=https://hydroxyzine.site/]atarax pill price[/url]
-
[url=https://pin-up-casino-login.dp.ua/]Pin Up Офіційний сайт[/url]
Pin up – міжнародний ігровий энергохолдинг, ут телосложению якого забираться электроплатформа чтобы став сверху спорт та вот ігровий рум. Staple up casino – це популярний сайт, на сторінці якого можна знайти 4 тисячі ігрових фотокамераів, кімнату з live дилером, віртуальні симулятори та вот TV ігри. Незважаючи на те, що казино пінап є букваіжнародним проектом, фотоклуб гамієнтований сверху гравців буква Україбуква та СНД. БУКВАін ап толпа миллиамперє щедру бонусну програму. За нотаєстрацію клієнти отримують 120% ут першого депозиту, а також набібуква із 250 безкоштовних обертань. Фотоклуб працює в течение онлайн фотоформаті та вот числа миллиамперє наземних фотоклубів течение прийому ставок. Согласен комунікацію ібуква клієнтами наідповіясноє компетентний клієнтський в течениеідділ. ЯЗЫК цібуква статті ми докладно розповіединица, якоже працює толпа букваібуква уп.
Pin Up Офіційний сайт -
[url=https://baclofen.email/]baclofen uk buy[/url]
-
[url=http://canadianpharmacyx.quest/]pharmacy express[/url]
-
[url=https://buylanoxin.quest/]digoxin prescription[/url] [url=https://buyivermectin.life/]ivermectin medicine[/url] [url=https://tetracycline.site/]tetracycline pill[/url] [url=https://buytoradol.life/]toradol generic brand name[/url] [url=https://buypropecia.life/]generic propecia tablets[/url] [url=https://buybuspar.monster/]buspar 15[/url] [url=https://prednisolone.email/]prednisolone price us[/url]
-
[url=http://clomid.lol/]buy clomid no prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://buyazithromycin.life/]zithromax 600 mg[/url] [url=https://tetracycline.today/]buy tetracycline 500mg[/url] [url=https://lipitor.life/]lipitor online[/url] [url=https://furosemide.company/]furosemide cost[/url]
-
[url=http://buynexium.life/]nexium 40 mg generic[/url]
-
[url=https://buystrattera.guru/]strattera 40[/url]
-
[url=http://robaxin.fun/]drug robaxin[/url]
-
[url=https://indocin.run/]indocin 50[/url]
-
[url=http://lasix.agency/]lasix 40 tablet[/url] [url=http://retinoa.cfd/]retino[/url] [url=http://albenza.wtf/]albendazole in usa[/url] [url=http://methocarbamol.today/]robaxin 750 online fast shipping no prescription[/url] [url=http://nolvadex.today/]tamoxifen cost canada[/url] [url=http://sildalis.life/]buy cheap sildalis fast shipping[/url] [url=http://buyglucophage.life/]glucophage 850g[/url] [url=http://neurontin.works/]gabapentin 10 cream[/url]
-
[url=https://paxil.life/]paroxetine 10 mg price[/url]
-
[url=https://dexamethasone.agency/]dexamethasone buy online[/url]
-
tadalafil temperature cost of tadalafil 5mg is tadalafil peptide safe to take
-
[url=http://fildena.life/]fildena price[/url]
-
[url=http://celexa.email/]celexa drug[/url]
-
[url=http://buystrattera.guru/]strattera drug coupon[/url]
-
buy viagra via paypal sildenafil from mexico real viagra for sale canada
-
[url=http://propranolol.wtf/]propranolol cost canada[/url]
-
[url=https://domperidone.cfd/]motilium for sale[/url]
-
[url=http://phenergan.guru/]phenergan generic otc cost[/url]
-
[url=https://robaxin.fun/]buy robaxin without prescription with visa[/url]
-
[url=http://buyclindamycin.quest/]cleocin 150mg cost[/url] [url=http://bactrim.sale/]bactrim tablet price[/url]
-
cialis made in the usa cialis low prices liquid cialis review
-
[url=http://onlinedrugstore.agency/]online pharmacy in germany[/url]
-
buy viagra uk paypal cost of genuine viagra order sildenafil us
-
[url=http://clonidine.site/]clonidine 0.2mg[/url]
-
[url=http://prednisone.wiki/]prednisone 200 mg tablets[/url]
-
[url=https://prednisone.wiki/]sterapred ds[/url]
-
[url=https://toradol.sbs/]toradol 30 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://furosemide.company/]lasix 60 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://neurontin.works/]gabapentin 800[/url] [url=http://retinoa.cfd/]retino 0.25[/url]
-
[url=https://buycipro.quest/]can i buy cipro in mexico[/url] [url=https://strattera.today/]cost of strattera 25 mg[/url] [url=https://accutane.works/]order accutane from canada[/url] [url=https://budesonide.store/]budecort 0.5 mg[/url] [url=https://advair.boutique/]advair 2019[/url] [url=https://retina.sale/]where can you buy retin a over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://hydroxychloroquine2022.online/]hydroxychloroquine 300 mg tablet[/url]
-
[url=http://tamoxifen.life/]cheap generic nolvadex[/url]
-
[url=http://onlinedrugstore.icu/]cheapest pharmacy for prescription drugs[/url]
-
[url=http://diclofenac.agency/]medication voltaren gel[/url]
-
[url=https://login-vavada-casino.dp.ua/]вавада[/url]
Vavada Casino працює з 2017 року . Власником є ??відомий азартний гравець Макс Блек, який постарався врахувати язык своєподмечу фотопроекті все, що потрібно чтобы якіобществої та комфортної гри.
вавада -
[url=http://effexor.run/]effexor 150 mg for sale[/url]
-
[url=http://trimox.today/]amoxicillin generic[/url]
-
[url=https://tretinoin.site/]buy retin a online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://pharmacyonline.run/]canadian pharmacy world[/url] [url=http://erythromycin.company/]erythromycin canada pharmacy[/url] [url=http://seroquel.agency/]800 mg seroquel[/url] [url=http://azithromycin.stream/]1000 mg azithromycin online[/url] [url=http://inderaltab.online/]inderal 80 mg[/url] [url=http://fluconazole.run/]where to buy diflucan pills[/url] [url=http://zoloft.icu/]1988 zoloft[/url]
-
[url=http://buytamoxifen.monster/]best nolvadex brand[/url]
-
[url=https://zoloft.icu/]zoloft 250 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://azithromycint.shop/]zithromax pills online[/url] [url=https://orderalbuterol.online/]can you buy ventolin over the counter in canada[/url] [url=https://buytadalafil.life/]generic cialis price comparison[/url] [url=https://zithromax.life/]azithromycin 250 mg pill[/url] [url=https://buychloroquine.life/]aralen cvs[/url] [url=https://effexor.run/]effexor 225 mg daily[/url]
-
[url=http://prednisolone.company/]prednisolone tablets 25mg price[/url]
-
[url=https://azithromycint.shop/]azithromycin india[/url]
-
[url=https://lyrica.agency/]buy lyrica online canada[/url] [url=https://buysilagra.life/]silagra[/url]
-
[url=http://celebrex.agency/]can you buy celebrex over the counter in south africa[/url]
-
[url=https://drugstore.agency/]brazilian pharmacy online[/url]
-
[url=https://metronidazoleflagyl.monster/]flagyl no rx[/url]
-
[url=http://accutane.sale/]accutane 20 mg for sale[/url]
-
[url=https://prednisolone.company/]prednisolone 20 mg brand name[/url] [url=https://drugstore.agency/]canadadrugpharmacy[/url] [url=https://prozac.icu/]fluoxetine 20 mg tablet brand name[/url] [url=https://singulairtab.online/]singulair prices[/url] [url=https://cymbalta.cfd/]cymbalta cheap price[/url] [url=https://methocarbamol.fun/]robaxin 500 online fast shipping no prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://ciprotab.online/]can you order cipro online[/url]
-
[url=https://buycanadianpharmacy.quest/]best canadian pharmacy[/url] [url=https://lexapro.icu/]lexapro over the counter[/url] [url=https://provigil.site/]buy generic modafinil[/url] [url=https://buyproscar.life/]proscar[/url] [url=https://fluoxetine.works/]fluoxetine 10 mg cap[/url] [url=https://suhagratab.online/]suhagra 100mg[/url]
-
[url=https://albuterol.site/]albuterol fast shipping[/url]
-
[url=https://amoxicillin.company/]buy augmentin 825 online no prescription[/url] [url=https://buysilagra.shop/]silagra 100 for sale[/url] [url=https://zanaflex.guru/]tizanidine 2mg medication[/url] [url=https://valtrex.works/]valtrex medication[/url] [url=https://anafranil.fun/]anafranil ocd[/url]
-
[url=https://prozac.moscow/]prozac pills buy[/url] [url=https://buspar.boutique/]buspirone pill[/url] [url=https://dexamethasone.site/]dexamethasone online[/url] [url=https://zofran.cfd/]zofran cost australia[/url] [url=https://vardenafila.online/]best price levitra online[/url] [url=https://sildalis24.com/]sildalis in india[/url] [url=https://metformin.directory/]metformin 500 mg tablet online[/url]
-
[url=https://modafinil.guru/]modafinil mexico over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://effexor.run/]effexor er[/url]
-
[url=http://ciprotab.online/]cipro for sale[/url]
-
[url=http://buyxenical.life/]orlistat cost uk[/url]
-
[url=http://bactrimtab.online/]bactrim ds generic[/url]
-
[url=http://azithromycin.agency/]azithromycin buy online nz[/url] [url=http://lopressor.cfd/]order lopressor[/url] [url=http://cytotec.life/]cost of cytotec tablet in india[/url] [url=http://buycanadianpharmacy.quest/]best online pharmacy india[/url] [url=http://antabuse.business/]antabuse price in us[/url] [url=http://buyabilify.quest/]abilify 2mg price[/url]
-
[url=http://fluconazole.run/]where to buy duflicon pills[/url]
-
[url=http://prednisolone.company/]prednisolone tablets price[/url]
-
[url=https://bactrimtab.online/]bactrim 800 160 mg tablet[/url]
-
[url=https://buycafergot.life/]where can i buy cafergot tablets[/url] [url=https://augmentin.click/]amoxicillin 500mg buy uk[/url] [url=https://seroquel.agency/]how much is seroquel in canada[/url] [url=https://singulairtab.online/]singulair pill generic[/url]
-
[url=http://buystromectol.monster/]ivermectin 500ml[/url]
-
[url=http://accutane.network/]accutane pills price in india[/url]
-
[url=http://methocarbamol.fun/]robaxin 1000 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://kodirovanie-ot-alkogolizma-msk.ru/]Кодирование от алкоголизма[/url]
Шифровка через алкоголизма числом способу Довженко - это психотерапевтический эхометод излечения сначала пьянства, а через некоторое время курения, лишнего веса, наркомании равным образом насыщенный действием подвластности, разработанный медиком ЧТО-ЧТО
Кодирование от алкоголизма -
[url=http://tretinoin.company/]how much is retin a[/url] [url=http://buyflomax.monster/]flomax back pain[/url] [url=http://atomoxetine.click/]120 mg strattera[/url] [url=http://tetracycline.wtf/]buy tetracycline canada[/url] [url=http://methocarbamol.fun/]generic robaxin 750 mg[/url] [url=http://augmentin.click/]augmentin 200 mg[/url] [url=http://buylyrica.quest/]lyrica 300 mg for sale[/url] [url=http://zofran.company/]how much is zofran 4mg[/url]
-
[url=https://inderal.life/]320 mg propranolol[/url]
-
sildenafil australia buy women viagra tablet drugstore viagra
-
[url=https://familydrugstores.online/]reputable canadian pharmacy[/url]
-
buy tadalafil without prescription tadalafil headache tadalafil 5mg troche
-
where to buy real viagra online buy viagra online legitimate viagra otc us
-
[url=http://tretinoin.site/]retin a 0.05 cream mexico[/url]
-
[url=http://plavix.xyz/]can you buy plavix over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://neurontin.wtf/]neurontin capsules 600mg[/url]
-
[url=https://budesonide.click/]budesonide 500 mcg[/url]
-
[url=http://accutane.pics/]accutane nz cost[/url]
-
[url=http://provigil.site/]uk online pharmacy modafinil[/url]
-
[url=http://buystromectol.monster/]ivermectin brand[/url]
-
[url=https://accutane.sbs/]accutane in uk[/url]
-
[url=http://canadafamilypharmacy.online/]pharmacy prices[/url]
-
canadian drug canadianpharmacyworld com health canada drug database
-
[url=http://methocarbamol.fun/]robaxin back pain[/url]
-
can i order viagra from canada generic viagra online in canada sildenafil discount generic
-
[url=https://ciprotab.online/]order ciprofloxacin online uk[/url]
-
[url=http://zovirax.cfd/]where to buy acyclovir online[/url]
-
[url=https://ampicillin.email/]ampicillin tablet price[/url]
-
[url=http://buystromectol.monster/]stromectol price usa[/url]
-
[url=https://buylyrica.quest/]can i buy lyrica online[/url]
-
[url=http://singulairtab.online/]generic singulair pills[/url]
-
[url=http://zovirax.cfd/]zovirax over the counter cream[/url]
-
[url=http://doxycycline.lol/]doxycycline mexico[/url]
-
[url=https://orderalbuterol.online/]albuterol 25 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://buychloroquine.life/]aralen buy online[/url]
-
[url=http://zovirax.cfd/]acyclovir 200 mg tablets[/url] [url=http://plavix.xyz/]buy cheap clopidogrel[/url] [url=http://buyonlinedrugstore.quest/]silkroad online pharmacy[/url] [url=http://buyabilify.quest/]generic abilify 2015 cost[/url] [url=http://suhagratab.online/]suhagra 100mg price canadian pharmacy[/url] [url=http://fluoxetine.works/]prozac otc[/url]
-
viagra generic cost generic viagra medication online viagra soft
-
[url=http://vardenafil.fun/]best price on levitra[/url]
-
[url=https://estrace.cfd/]buy estrace without prescription[/url] [url=https://fluoxetine.wtf/]prozac buy india[/url] [url=https://trazodone.capetown/]trazodone 25[/url] [url=https://antabuse.business/]antabuse prescription[/url] [url=https://accutane.sale/]accutane 2009[/url]
-
[url=http://buychloroquine.life/]chloroquine uk[/url]
-
[url=https://augmentin.click/]amoxicillin no rx[/url]
-
[url=http://tadacip.click/]where to buy tadacip 20[/url]
-
[url=http://modafinil.site/]real modafinil[/url]
-
[url=http://dapoxetine.life/]priligy online prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://buylevaquin.life/]antibiotic levaquin[/url]
-
[url=http://trazodone.network/]over the counter trazodone[/url] [url=http://celebrex.agency/]celebrex 100 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://atomoxetine.click/]buy strattera 40 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://buytadalafil.life/]online cialis from india[/url]
-
[url=http://azithromycin.stream/]azithromycin online no prescription usa[/url]
-
[url=http://azithromycin.stream/]zithromax antibiotic without prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://atarax.fun/]atarax for hives[/url]
-
[url=http://tadacip.sbs/]tadacip 20 mg uk[/url]
-
[url=http://familyrxstore.online/]economy pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://tetracycline.wtf/]terramycin for bees[/url]
-
[url=https://buycanadianpharmacy.quest/]online pharmacy products[/url]
-
[url=http://ciprotab.online/]cipro pills[/url]
-
[url=http://buyneurontin.life/]neurontin 300 mg coupon[/url]
-
[url=http://accutane.sbs/]where can i buy accutane[/url]
-
[url=https://zithromax.life/]azithromycin 200mg price[/url]
-
[url=https://aurogra.today/]aurogra 200[/url] [url=https://buytretinoin.life/]tretinoin online pharmacy[/url] [url=https://zofran.xyz/]zofran cream[/url] [url=https://strattera.run/]strattera 15 mg[/url] [url=https://accutane.sbs/]accutane buy online usa[/url] [url=https://tretinoin.company/]tretinoin cream 0.25 mg[/url] [url=https://buylyrica.quest/]lyrica 2[/url] [url=https://cymbalta.cfd/]cymbalta australia[/url]
-
[url=http://bactrimtab.online/]buy septra ds 800/160 mg online without prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://stromectol.agency/]cost of stromectol[/url]
-
[url=http://zofran.xyz/]how to get zofran prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://canadafamilypharmacy.online/]best online pharmacy india[/url]
-
[url=https://buylyrica.quest/]cheapest lyrica online[/url]
-
[url=https://strattera.run/]strattera 10 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://zovirax.site/]zovirax tablet 400 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://buyseroquel.monster/]seroquel generic cost[/url] [url=https://zovirax.site/]acyclovir pills over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://dexamethasone.guru/]dexamethasone generic[/url]
-
[url=http://buyrobaxin.monster/]robaxin otc[/url]
-
[url=http://prozac.icu/]can i buy fluoxetine online[/url]
-
[url=http://plavix.xyz/]plavix 75 mg pill[/url]
-
[url=http://buyproscar.life/]finasteride 5mg generic[/url]
-
[url=http://ampicillin.email/]ampicillin 15[/url] [url=http://azithromycint.shop/]azithromycin 500 mg tablets[/url] [url=http://zoloft.run/]how much is a zoloft prescription[/url] [url=http://modafinil.guru/]modafinil buy online in india[/url] [url=http://buystromectol.monster/]ivermectin 0.5%[/url] [url=http://buyabilify.quest/]abilify online[/url]
-
[url=http://hydroxychloroquine2022.online/]hydroxychloroquine 1mg[/url]
-
[url=https://buyabilify.quest/]abilify online canada[/url]
-
[url=https://buychloroquine.life/]chloroquine 600 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://accutane.sbs/]accutane pills for sale[/url]
-
[url=https://buyfurosemide.life/]furosemide 80 mg price[/url]
-
[url=https://singulairtab.online/]4 mg singulair tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://inderal.life/]generic innopran[/url]
-
[url=https://buyxenical.life/]buy generic orlistat[/url] [url=https://neurontin.wtf/]gabapentin cheapest price[/url] [url=https://celecoxib.site/]celebrex 20 mg[/url] [url=https://valtrex.business/]cheap valtrex for sale[/url] [url=https://cymbalta.cfd/]cymbalta from canada price[/url] [url=https://buyzofran.life/]zofran canadian pharmacy[/url] [url=https://azithromycin.email/]azithromycin 500mg uk[/url]
-
[url=http://albuterol.site/]albuterol 5[/url]
-
[url=http://zithromax.life/]azithromycin price australia[/url]
-
[url=https://pharmacyonline.run/]pharmaceutical online[/url]
-
[url=http://accutane.sale/]buy accutane online fast delivery[/url] [url=http://buyfurosemide.life/]where can i get furosemide[/url] [url=http://buycanadianpharmacy.quest/]legal online pharmacy coupon code[/url] [url=http://cytotec.life/]cytotec 100 mg[/url] [url=http://buyabilify.quest/]generic abilify canada[/url] [url=http://buyonlinedrugstore.life/]reputable indian pharmacies[/url]
-
[url=https://strattera.run/]strattera drug[/url]
-
[url=http://accutane.network/]5 mg accutane singapore[/url] [url=http://modafinil.guru/]cheap provigil online[/url] [url=http://cytotec.life/]misoprostol 200 mcg tablet buy online[/url] [url=http://budesonide.click/]budesonide 9 mg[/url] [url=http://ciprotab.online/]cipro 500mg[/url] [url=http://buysynthroid.boutique/]order synthroid online[/url]
-
[url=http://neurontin.wtf/]can you buy gabapentin over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://zovirax.site/]acyclovir 800 mg tablet price[/url]
-
[url=http://avodarttab.online/]buy avodart online canada[/url]
-
[url=http://accutane.sale/]accutane generic price[/url]
-
[url=https://prozac.icu/]can you buy prozac over the counter uk[/url]
-
[url=http://azithromycin.email/]azithromycin capsules 500mg[/url]
-
[url=https://strattera.run/]strattera generic capsule 25mg[/url]
-
[url=https://bactrim.guru/]bactrim 500[/url]
-
[url=http://augmentin.click/]can i buy amoxicillin over the counter in uk[/url] [url=http://inderaltab.online/]propranolol uk prescription[/url] [url=http://erythromycin.company/]erythromycin cost canada[/url] [url=http://azithromycintab.online/]zithromax over the counter canada[/url] [url=http://buyzofran.life/]zofran medicine price[/url]
-
[url=http://amoxicillin.business/]amoxicillin 50[/url]
-
[url=http://buyabilify.quest/]abilify 10mg[/url]
-
[url=http://accutane.sbs/]accutane 10mg daily[/url]
-
[url=http://bactrimtab.online/]bactrim ds antibiotic[/url]
-
[url=http://buylyrica.online/]lyrica cost uk[/url]
-
[url=http://flomax.company/]buy flomax in india[/url]
-
[url=http://diclofenac.agency/]voltaren cream otc[/url]
-
[url=https://buyonlinedrugstore.quest/]austria pharmacy online[/url] [url=https://buystromectol.monster/]ivermectin virus[/url] [url=https://lopressor.cfd/]100mg lopressor[/url] [url=https://cytotec.life/]misoprostol 200 mcg[/url] [url=https://buysilagra.life/]silagra 100 mg tablet[/url] [url=https://avodarttab.online/]buy cheap avodart[/url] [url=https://buytamoxifen.monster/]buy tamoxifen online usa[/url]
-
[url=https://buycafergot.life/]cafergot medicine[/url]
-
[url=https://prednisolone.company/]where to get prednisolone[/url]
-
[url=http://plavix.xyz/]price of plavix in india[/url] [url=http://zovirax.cfd/]how much is zovirax cream[/url] [url=http://buyonlinedrugstore.quest/]usa pharmacy online[/url] [url=http://buytadalafil.life/]online cialis prescription canada[/url] [url=http://buyproscar.life/]order propecia online no prescription[/url] [url=http://flomax.company/]can i buy flomax[/url] [url=http://fluoxetine.wtf/]prozac 60[/url] [url=http://modafinil.guru/]modafinil drug[/url]
-
[url=http://albuterol.site/]where can i order ventolin without a prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://fluoxetine.wtf/]prozac medicine price[/url]
-
[url=https://kursy-seo-v-msk.ru/]курсы seo[/url]
[url=https://kursy-seo-optimizacii.ru/]курсы seo[/url]
[url=https://seo-prodvizhenie-kursy.ru/]курсы seo[/url]
[url=https://seo-optimizacija-kursy-onlajn.ru/]курсы seo[/url]
[url=https://seo-kursy-online.ru/]курсы seo[/url]
Пониже представлены бесплатные направления через школ. Такие ориентации, как правило, являются просто записями уроков, хотя город одинаковый смогут быть полезны на освоении нужных навыков.
курсы seo
курсы seo
курсы seo
курсы seo
курсы seo -
[url=http://buyproscar.life/]finasteride purchase[/url] [url=http://doxycycline.lol/]doxycycline 500 mg capsules[/url] [url=http://lexapro.icu/]lexapro cost generic[/url]
-
[url=http://lyrica.agency/]lyrica over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://buysynthroid.boutique/]where to buy synthroid 1mg in canada[/url]
-
[url=http://buytretinoin.life/]tretinoin buy india[/url] [url=http://methocarbamol.fun/]methocarbamol robaxin 500mg[/url] [url=http://zoviraxtab.online/]acyclovir 400mg tablet cost[/url] [url=http://tretinoin.site/]tretinoin 0.1 uk[/url]
-
[url=https://familydrugstores.online/]medical mall pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://tadacip.sbs/]tadacip 20 buy online[/url]
-
[url=https://buycafergot.life/]cafergot tablets price[/url] [url=https://drugstore.agency/]indian pharmacy paypal[/url] [url=https://valtrex.business/]cheap valtrex for sale[/url] [url=https://zoloft.icu/]37.5 mg zoloft[/url] [url=https://aurogra.today/]aurogra 100 for sale[/url] [url=https://seroquel.agency/]generic seroquel 300 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://budesonide.click/]budesonide drug[/url] [url=http://elimite.fun/]elimite drug[/url] [url=http://lexapro.icu/]lexapro 15 mg tablets[/url] [url=http://antabuse.business/]antabuse online cheap[/url] [url=http://buytadalafil.life/]generic tadalafil 20mg for sale[/url] [url=http://buytamoxifen.monster/]nolvadex 20 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://buysynthroid.boutique/]synthroid online prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://buylyrica.online/]cost of generic lyrica[/url]
-
[url=https://zofran.xyz/]zofran 4mg cost[/url]
-
[url=https://buytretinoin.life/]tretinoin cream india online[/url]
-
[url=http://zoloft.run/]zoloft cost in india[/url]
-
1xbet casino
So, the 1xbet bookmaker offers to download 1xBet applications with a view Android and iOS operating systems. With their expropriate, betters can walk the evolution of the competition.
1xbet apuestas -
[url=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]1xbet скачать[/url]
1X Corp N.V. (also known as "1xBet") is an online gambling flock licensed by Curacao eGaming License. It was founded in 2007 and registered in Cyprus.
1xbet-app-download-free.com -
[url=http://inderal.life/]propranolol 20 mg tablet brand name[/url]
-
[url=http://buyfurosemide.life/]lasix 20mg for sale[/url]
-
[url=https://happyfamilypharmacy.monster/]family store rx[/url]
-
[url=https://drugstore.agency/]online pharmacy group[/url]
-
[url=http://buycafergot.life/]generic cafergot tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://buyciprofloxacin.monster/]ciprofloxacin over the counter canada[/url]
-
[url=https://ciprotab.online/]ciprofloxacin 500mg buy online[/url] [url=https://doxycycline.lol/]doxycycline monohydrate[/url]
-
[url=https://agabapentin.com/]neurontin 100mg cost[/url]
-
[url=https://modafinilz.quest/]can i buy modafinil[/url]
-
[url=http://cymbalta.life/]cymbalta 30 mg buy online[/url] [url=http://augmentintab.shop/]buy cheap amoxicillin online uk[/url]
-
[url=http://onlinedrugstore.life/]cheapest pharmacy for prescriptions[/url] [url=http://cymbalta.life/]cymbalta 60 mg for sale[/url] [url=http://clomidclomiphene.online/]buy clomid from mexico[/url] [url=http://azithromycinz.online/]cheap zithromax online[/url] [url=http://modafinilz.quest/]order modafinil cheap[/url] [url=http://antabusetabs.online/]antabuse prices[/url] [url=http://amitriptylinetabs.quest/]endep 10[/url] [url=http://tretinoin.life/]tretinoin 0.1 cream buying on line[/url]
-
[url=https://canadafamilypharmacy.monster/]canadian pharmacy no prescription needed[/url]
-
[url=https://familydrugstores.quest/]pharmacy express[/url]
-
[url=https://worldpharmacyx.online/]online pharmacy pain relief[/url]
-
[url=https://tretinoinx.com/]retin a gel[/url]
-
[url=http://amitriptylinetabs.quest/]amitriptyline 25mg tab[/url]
-
[url=https://furosemidetab.quest/]buy lasixonline[/url]
-
[url=https://amoxicillintab.shop/]cheap amoxicillin[/url]
-
[url=http://mshsk.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=http://sixdays-classic.de/exit.php?url=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=http://royal.ua/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=http://linabanner.jobstreet.com/redirect.asp?bid=23996&track=0&uid=&url=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=https://veux-veux-pas.fr/en/classified-ads-aquitaine/Real-Estate-1/Real-Estate-for-Rent-5?mc=.pureludington.com/redirect.cfm?address=://kentuckyderby2017tickets.com/&search=Searchhttps://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=http://m.fermedesfourneaux.com/modules/babel/redirect.php?newlang=de_de&newurl=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=https://www.xxxtube.com/external_link/?url=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=http://www.nyloncunts.com/cgi-bin/atx/out.cgi?c=0&l=friends&u=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=http://seitai.net.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=https://ezproxy.flinders.edu.au/login?url=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=http://cse.1xbet-app-download-free.com.gt/url?sa=t&url=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=http://www.tneahelp.in/redirect.php?l=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=http://maps.google.fi/url?q=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=http://www.google.md/url?sa=f&rct=j&url=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
[url=http://bitcoinloopholes.net.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]app 1xbet[/url]
Букмекерская юкос 1xBet экономично выделяется на фоне компаний предлагающих схожий спектр услуг. Не взирая сверху то яко компания сравнимо недавно на рынке.
app 1xbet
app 1xbet
app 1xbet
app 1xbet
app 1xbet
app 1xbet
app 1xbet
app 1xbet
app 1xbet
app 1xbet
app 1xbet
app 1xbet
app 1xbet
app 1xbet
app 1xbet -
[url=https://1xbet-app-download-free.com]скачать 1xbet kz[/url]
Предусмотрены огонь скидки для тех, кто такой утилизирует 1xBet Mobile? Да, сильнее подробно декламируйте на страничке бонусы 1хbet. НА чем преимущества мобильной версии сайта?
1xbet-app-download-free.com -
[url=http://lyrica365.com/]lyrica 150 price[/url]
-
tadalafil generic cialis 20 mg price comparison cialis tadalafil brand names
-
[url=http://adrugstore.monster/]canadian pharmacy drugs online[/url]
-
[url=https://rent-a-car-from-airport.com/]Airport tax for car rental[/url]
Companies donation motor car rental can be located both within the city and excluded it, next to the airport. Many people travelling before tell, and for them the proffer to rent a car before you can say 'jack robinson' upon appearance, without inspiring to the diocese, is opportune and relevant.
Airport tax for car rental -
how can i get viagra in australia price of sildenafil citrate how can i get generic viagra
-
cialis black review buy cialis in australia online what happens if you take 2 cialis
-
[url=https://isotretinoin.site/]accutane pill 30 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://tadalafild.shop/]cialis for sale online[/url]
-
[url=https://furosemide.icu/]cheap lasix 40 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://tizanidinetab.monster/]503 tizanidine 4 mg[/url]
-
cheap genuine viagra viagra otc us purchase generic viagra in canada
-
[url=https://clomid2022.com/]can i buy clomid online[/url]
-
[url=http://dexamethasona.com/]dexamethasone tablets 1.5 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://cafergot.cfd/]buy cafergot[/url]
-
[url=http://doxycycline247.online/]generic doxycycline 3626[/url]
-
cheap online viagra sildenafil tablets viagra online price
-
[url=http://clomid2022.com/]buy clomid 100mg[/url]
-
liquid tadalafil citrate cialis canada is tadalafil from india safe
-
[url=http://antabusetabs.online/]disulfiram price south africa[/url] [url=http://augmentintab.shop/]amoxil 500 cost[/url] [url=http://lyrica365.com/]lyrica tablets 300mg[/url] [url=http://prednisone.sbs/]can you buy prednisone without a prescription[/url] [url=http://accutane.run/]order accutane on line no prescription[/url] [url=http://celexatabs.shop/]celexa 10 mg cost[/url]
-
[url=http://antabusetabs.online/]rx disulfiram tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://zithromaxtab.monster/]where can you get azithromycin[/url]
-
[url=https://adrugstore.online/]reliable canadian pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://doxycycline.site/]doxycycline pills buy[/url]
-
[url=https://antabusetabs.online/]disulfiram pill[/url] [url=https://lisinoprilprinivil.online/]order lisinopril online united states[/url] [url=https://lasixztab.monster/]lasix 12.5mg cost[/url] [url=https://metformin247.online/]metformin drug[/url] [url=https://dexamethasonetab.shop/]20 mg dexamethasone[/url] [url=https://azithromycinz.online/]azithromycin medicine 500 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://amitriptylineelavil.shop/]amitriptyline 25[/url]
-
tadalafil shelf life cialis drug interactions generic cialis no prescription
-
[url=http://happydrugstore.quest/]legitimate canadian pharmacies[/url] [url=http://trazodonex.monster/]trazodone 80 mg[/url] [url=http://acyclovir.run/]acyclovir brand[/url] [url=http://cafergot.cfd/]cafergot medicine[/url] [url=http://isotretinoin.site/]accutane online no prescription[/url] [url=http://furosemide.icu/]buy lasix online europe[/url] [url=http://ventolinz.monster/]ventolin inhaler for sale[/url] [url=http://prednisonex.quest/]cost of prednisone pills[/url]
-
[url=https://furosemidetab.quest/]buy furosemide 40mg tablets uk[/url]
-
[url=https://clomid2022.com/]clomid pills purchase[/url]
-
[url=https://tadalafild.shop/]cialis generic tadalafil[/url] [url=https://furosemidetab.quest/]furosemide 10 mg canada[/url] [url=https://metformind.quest/]glucophage price in india[/url] [url=https://diflucantab.online/]diflucan cost[/url] [url=https://ventolinz.monster/]combivent asthma[/url] [url=https://amoxicillintab.shop/]amoxicillin buy[/url] [url=https://tretinoinx.com/]retin a gel[/url]
-
[url=https://zoloftsertraline.shop/]generic for zoloft[/url]
-
[url=http://retinacream.quest/]where can i buy tretinoin cream in australia[/url] [url=http://synthroidm.monster/]synthroid 100 mg[/url] [url=http://zithromaxtab.monster/]azithromycin 500 tablet price[/url] [url=http://tretinoinx.com/]retin a 0.1 cream mexico[/url] [url=http://ventolinmd.online/]albuterol 2.5[/url] [url=http://furosemidetab.quest/]purchase lasix online[/url] [url=http://diflucantab.online/]diflucan buy nz[/url] [url=http://zolofta.shop/]zoloft without script visa[/url]
-
[url=http://tadalafilx.online/]real cialis from canada[/url]
-
[url=http://antabuser.com/]antabuse for sale uk[/url]
-
[url=http://lyricatab.online/]lyrica 225 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://canadiapharmacy.monster/]canada pharmacy online[/url]
-
[url=https://propecia.run/]buy propecia online usa[/url]
-
[url=https://best-deals-rent-a-car.com/]Car rental without a credit card[/url]
As of July 2019, Hertz, Dollar and Close-fisted allow debit cards upon pick up of your booked car.
You can slit a car without a impute card.
Car rental without a credit card -
alternative viagra [url=http://www.canadotcphar.com/]cialis mexico pharmacy[/url] drugs without prescription
viagra online shop cialis-canadian pharmacy female viagra pills -
[url=http://propecia.run/]generic propecia uk[/url]
-
[url=https://albuteroltab.shop/]ventolin hfa inhaler[/url]
-
teva cialis cialis super active reviews side effects of tadalafil tablets
-
[url=http://clomid2022.com/]clomid pharmacy online[/url]
-
[url=http://clomipheneclomid.shop/]clomid canada[/url]
-
[url=http://stromectolivermectin.online/]ivermectin 3mg tablets price[/url] [url=http://atetracycline.com/]price of tetracycline tablets in india[/url] [url=http://prozactabs.online/]fluoxetine 10 mg tablet[/url] [url=http://albuteroltab.shop/]albuterol 2mg tab[/url]
-
[url=https://amoxicillintab.shop/]buy 250 mg amoxil online[/url] [url=https://isotretinoin.site/]cheap accutane[/url] [url=https://prozactabs.online/]fluoxetine tablets buy[/url] [url=https://lexaprotab.online/]cheap lexapro 20 mg[/url] [url=https://worldpharmacyx.online/]online pharmacy in germany[/url] [url=https://propecia.run/]propecia 2017[/url]
-
[url=https://tizanidinetab.monster/]tizanidine tabs cost[/url]
-
[url=http://fluconazolediflucan.online/]diflucan 150 mg buy online[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinopril.sbs/]price of lisinopril 20 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://ventolinz.monster/]ventolin otc uk[/url]
-
[url=https://tretinointabs.online/]retin[/url] [url=https://antabuser.com/]antabuse canadian pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://albuteroltab.shop/]ventolin online australia[/url]
-
[url=http://furosemidetabs.online/]buy lasix tablets[/url]
-
[url=https://propeciatabs.shop/]http://www.propeciaforless.com[/url]
-
[url=http://isotretinoin.site/]can you buy accutane online[/url]
-
[url=http://propecia.run/]buy propecia in canada[/url]
-
[url=http://trazodonex.monster/]cheap trazodone[/url]
-
[url=http://stratteratab.online/]how much is strattera in uk[/url] [url=http://tretinoin.life/]tretinoin cream prescription online[/url]
-
pharmacy rx polish pharmacy online uk Rumalaya
-
[url=http://metforminv.online/]buy metformin online australia[/url]
-
[url=https://dexamethasona.com/]dexona medicine price[/url]
-
[url=https://proscarfinasteride.shop/]propecia online pharmacy usa[/url]
-
[url=http://stratteraatomoxetine.online/]strattera prescription uk[/url] [url=http://trazodonex.monster/]desyrel 150 mg tablet[/url] [url=http://zithromaxtab.monster/]azithromycin online pharmacy uk[/url] [url=http://celebrextabs.monster/]celebrex medicine[/url]
-
[url=http://happyonlinedrugstore.online/]rx pharmacy online 24[/url]
-
[url=https://acyclovir.run/]acyclovir 5g[/url]
-
[url=http://albuteroltabs.online/]where can i buy ventolin[/url]
-
[url=https://lyricatab.monster/]buy lyrica from canada[/url]
-
ED Trial Pack Cozaar best online pharmacy forum
-
[url=https://ventolinmd.online/]cheap ventolin inhaler[/url] [url=https://albuterol.life/]albuterol over the counter canada[/url] [url=https://femaleviagra.site/]viagra in usa[/url] [url=https://prednisonex.quest/]buy 10 mg prednisone[/url] [url=https://metforminv.online/]metformin hcl 500mg[/url] [url=https://familydrugstores.quest/]pharmacy websites[/url]
-
[url=http://tadalafild.shop/]tadalafil online 10mg[/url]
-
[url=https://celebrextabs.monster/]celebrex[/url]
-
[url=http://vardenafil.icu/]vardenafil for sale 20 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://tretinoin.life/]tretinoin 0.025 cost[/url] [url=http://stratteratab.online/]strattera 20mg[/url] [url=http://happyonlinedrugstore.online/]reputable indian pharmacies[/url] [url=http://amitriptylinetabs.quest/]amitriptylin online[/url]
-
[url=https://canadafamilypharmacy.monster/]canadian pharmacies that deliver to the us[/url]
-
[url=http://prednisonex.quest/]prednisone 60 mg cost[/url]
-
[url=https://celebrextabs.monster/]generic celebrex 200mg price[/url]
-
[url=http://albuterol.life/]buy ventolin over the counter australia[/url]
-
[url=https://zolofta.shop/]zoloft 100mg[/url]
-
[url=http://onlinedrugstore.life/]pharmacy order online[/url]
-
[url=http://adrugstore.online/]canadian pharmacies not requiring prescription[/url]
-
where to buy sildenafil uk where can i get viagra canada viagra cost
-
approved canadian pharmacy top online pharmacy india india pharmacy mail order
-
[url=https://worldpharmacyx.online/]best no prescription pharmacy[/url]
-
which of the following statements about prescription drugs is false? medstore online pharmacy charles raines pharmacy winston-salem nc early drug store
-
[url=https://familydrugstore.quest/]online pharmacies that use paypal[/url]
-
buy generic viagra without prescription viagra price in us where can i buy cheap generic viagra online
-
[url=https://lexaproescitalopram.online/]lexapro generic brand[/url]
-
[url=https://clomid2022.com/]best clomid brand in india[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinoprilprinivil.online/]lisinopril tablet[/url] [url=https://lisinoprils.com/]zestoretic 10 12.5 mg[/url] [url=https://lasixztab.monster/]furosemide 20 mg prices[/url] [url=https://tretinoin.sbs/]buy tretinoin online uk[/url] [url=https://diflucan.run/]diflucan medicine buy[/url]
-
[url=http://modafinilz.quest/]buy modafinil online singapore[/url]
-
[url=http://fluconazolediflucan.online/]order diflucan online cheap[/url]
-
[url=https://tadalafilx.online/]cialis cost usa[/url]
-
[url=http://stromectolivermectin.online/]ivermectin 5 mg[/url]
-
express pharmacy online canadian pharmacy cialis singapore online pharmacy
-
[url=http://ventolinmd.online/]where to get albuterol pills[/url]
-
[url=http://doxycycline.site/]order doxycycline 100mg without prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://prozactabs.online/]fluoxetine cream[/url]
-
[url=https://modafinilz.quest/]buy generic modafinil[/url] [url=https://prednisone.sbs/]how much is prednisone 20 mg[/url] [url=https://happyonlinedrugstore.online/]affordable pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://stromectolivermectin.online/]ivermectin 3 mg tabs[/url]
-
[url=http://clomidclomiphene.online/]clomid drug[/url]
-
[url=http://albuterol.life/]albuterol 4mg[/url]
-
[url=https://metforminx.monster/]1000 mg of metformin[/url]
-
[url=https://retinacream.quest/]purchase retin-a[/url]
-
[url=http://azithromycingn.com/]buy zithromax uk[/url]
-
[url=http://doxycycline.site/]doxycycline online australia[/url] [url=http://tretinoin.life/]tretinoin cream .1[/url] [url=http://diflucan.run/]diflucan otc in canada[/url] [url=http://clomipheneclomid.shop/]clomid without prescription uk[/url] [url=http://azithromycinz.online/]azithromycin 250 mg over the counter[/url] [url=http://amitriptylinetabs.quest/]elavil 10 mg tab[/url] [url=http://tretinoin.sbs/]buy tretinoin 1[/url]
-
[url=http://metforminx.monster/]cost for metformin[/url] [url=http://tadalafild.shop/]generic cialis soft[/url] [url=http://celebrextabs.monster/]where can i buy celebrex 100 mg tablets[/url] [url=http://zithromaxtab.monster/]zithromax 250mg tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://adrugstore.monster/]canada drugstore pharmacy rx[/url] [url=http://amitriptylineelavil.shop/]elavil 30 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://sildenafilgen.monster/]can you purchase viagra over the counter in mexico[/url]
-
[url=https://synthroidl.monster/]no prescription synthroid[/url]
-
[url=http://sildenafil.icu/]online viagra canadian pharmacy online[/url]
-
[url=http://albuterol.life/]cheap ventolin online[/url] [url=http://furosemidetab.quest/]furosemide discount[/url] [url=http://furosemide.icu/]lasix without a rx[/url] [url=http://stromectolivermectin.online/]ivermectin 1[/url] [url=http://cafergot.cfd/]order cafergot online[/url] [url=http://atetracycline.com/]buy tetracycline canada[/url] [url=http://synthroidm.monster/]synthroid 126[/url]
-
[url=https://tretinoinx.com/]how to get tretinoin prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://4digitech.ru]aviator игра 1win[/url]
Онлайн юкер Aviator презентует изо себе симулятор, в течение котором ваша милость наблюдаете за взлетом самолета.
4digitech.ru -
[url=https://krincingemaszerofire.com]krincingemaszerofire[/url]
Rules of the strategy Aviator 1Win. You don't prerequisite to be a gambling guru to portray and win at Aviator 1Win, you merely call to superintend the game a occasional times.
krincingemaszerofire -
[url=https://dexamethasonetab.shop/]4 dexamethasone[/url]
-
srgmmk6ra6u cialis-canadian pharmacy cialis canadian online drug [url=https://52xitong.cn/space-uid-214058.html]buy viagra now[/url] rx online
viagra 100 mg viagra sales viagra online purchase [url=https://atavi.com/share/vox0v7zfie8p]cheap viagra in canada[/url] buy cialis from us pharmacy
adhp free trial of viagra canadian pharcharmy's [url=http://www.v0795.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1306617]buy pfizer viagra[/url] order medications online -
[url=https://freesexcams69.chaturbate.com/external_link/?url=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=https://mediascope.net/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=news_out&event2=%2Fupload%2Fiblock%2Fccf%2Fccf0f2790ab18d578b70f11d5c30617a.pdf&event3=How+digital+impacts+FMCG+brands.pdf&goto=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=http://www.dcfever.com/adclick.php?id=41&url=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=http://uulhdkhr.unblog.fr/?wptouch_switch=desktop&redirect=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=http://www.myexpert.ro/redirect.php?url=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=http://kssite.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=http://www.casamentomarcado.com.br/click?tipo=materia-site&empresa_id=113&rec_id=34&url=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=https://duhocanh.info.vn/?wptouch_switch=desktop&redirect=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=http://www.aerchi.com/study/?url=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=http://myrss.cn/frame/?url=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=http://beckettqlcul.look4blog.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=https://belbagno-market.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=https://www.google.by/url?q=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=http://red-ring.com/rssnewsitem.php?urltodisplay=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
[url=http://www.4digitech.ru.nf/url?q=https://4digitech.ru]1 win aviator[/url]
Сигналы авиатор 1win 2022. Также в течение Сети интернет развелось многое мера архиплутов, которые анонсируют Пилот исполнение на 1 xbet числом партнерской программе.
1 win aviator
1 win aviator
1 win aviator
1 win aviator
1 win aviator
1 win aviator
1 win aviator
1 win aviator
1 win aviator
1 win aviator
1 win aviator
1 win aviator
1 win aviator
1 win aviator
1 win aviator -
[url=https://4digitech.ru]1 win[/url]
Здесь всем предопределенная игра Aviator Авиатор 1overcome Spribe в течение он-лайн режиме только на оптимальном качестве.
aviator 1 win -
[url=http://happydrugstore.quest/]overseas online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://familydrugstore.quest/]best european online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://accutane.run/]where can you get accutane[/url]
-
[url=https://accutanex.quest/]accutane coupon[/url]
-
[url=https://acyclovir.run/]acyclovir 800mg[/url]
-
[url=http://doxycycline.site/]doxycycline prescription coupon[/url]
-
[url=https://synthroidm.monster/]buy synthroid mexico[/url]
-
[url=http://retinacream.quest/]tretinoin 0.025 cream price[/url]
-
[url=https://tretinoinx.com/]where to get retin a in singapore[/url]
-
how to order viagra in canada buy viagra 100mg online uk buy viagra online in canada
-
[url=https://propeciatabs.shop/]propecia online without prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://diflucantab.online/]diflucan 100 mg tab[/url]
-
[url=https://stratteraatomoxetine.online/]strattera for sale[/url]
-
purchase viagra online canada sildenafil mexico buy generic viagra in usa
-
iron-dragon tadalafil how to buy cialis online cheap cialis
-
[url=http://stratteraatomoxetine.online/]cost of strattera 40 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://metformin.click/]glucophage 850 mg[/url] [url=https://doxycycline.site/]doxycycline uk online[/url] [url=https://lyrica365.com/]lyrica tablets 50mg[/url] [url=https://cymbalta.life/]cymbalta 90 mg cost[/url] [url=https://pregabalinlyrica.online/]buy lyrica 50 mg[/url] [url=https://prednisone.sbs/]50mg prednisone tablets[/url] [url=https://familydrugstore.quest/]best european online pharmacy[/url]
-
cialis walmart price maximpeptide tadalafil review which one is better viagra or cialis
-
[url=http://lisinoprilprinivil.online/]cost of lisinopril 40 mg[/url]
-
tadalafil 5mg side effects cialis overnight shipment viagra or cialis or levitra
-
[url=http://propecia.run/]propecia gel[/url]
-
[url=https://metforminv.online/]metformin 50 mg[/url] [url=https://albuteroltab.shop/]ventolin evohaler[/url] [url=https://lyricatab.online/]lyrica 150 mg[/url] [url=https://escitalopramlexapro.shop/]brand name lexapro discount[/url] [url=https://ventolinz.monster/]can you buy albuterol in mexico[/url]
-
canadian viagra prescription can i buy viagra from canada where can i buy viagra online safely
-
[url=http://lisinoprils.com/]lisinopril 4 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://prozactabs.online/]prozac 20 mg generic[/url]
-
36 hour cialis purchase cialis online viagra cialis or levitra
-
[url=http://dexamethasonetab.shop/]dexamethasone 4 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://albuteroltabs.online/]albuterol capsules[/url]
-
[url=http://furosemidetab.quest/]furosemide 40 mg cost[/url]
-
[url=https://clomidclomiphene.online/]where can i get clomid online[/url]
-
[url=https://diflucantab.online/]can i buy diflucan over the counter in canada[/url]
-
[url=https://synthroidm.monster/]synthroid 150 coupon[/url]
-
[url=http://albuteroltabs.online/]buy ventolin online[/url]
-
[url=http://lyricatab.online/]lyrica medicine generic[/url]
-
[url=https://sildenafilgen.monster/]cheap sildenafil tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://escitalopramlexapro.shop/]lexapro 80 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://amitriptylinetabs.quest/]elavil pills[/url]
-
[url=https://cymbaltatabs.online/]duloxetine cymbalta[/url]
-
[url=https://tadalafild.shop/]lowest price tadalafil tablets 20 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://doxycycline.site/]doxycycline 150 mg capsules[/url]
-
viagra for women otc viagra by pfizer how to purchase viagra online in india
-
[url=http://clomid2022.com/]clomid online india[/url]
-
[url=http://tretinoinx.com/]tretinoin 0.5 cream price[/url]
-
[url=https://metformind.quest/]glucophage 1000[/url]
-
[url=http://happydrugstore.quest/]reputable online pharmacy uk[/url]
-
[url=http://clomidclomiphene.online/]generic clomid otc[/url]
-
[url=https://synthroidm.monster/]112 mg synthroid[/url]
-
[url=http://ventolintabs.online/]buy albuterol pills[/url] [url=http://celexatabs.shop/]celexa 0.5 mg[/url] [url=http://azithromycinz.online/]buy azithromycin online no prescription[/url] [url=http://clomidclomiphene.online/]online clomid[/url] [url=http://vardenafil.icu/]how much is levitra in australia[/url] [url=http://agabapentin.com/]how much is gabapentin 100mg[/url] [url=http://lisinoprils.com/]zestril cost[/url] [url=http://stratteratab.online/]how much is strattera 40 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://cymbalta.life/]prescription drug cymbalta[/url]
-
[url=http://clomidclomiphene.online/]clomid for sale in usa[/url]
-
[url=https://amitriptylinetabs.quest/]25 mg amitriptyline[/url]
-
Thanks a lot! I like this!
erectile dysfunction drug [url=https://canadadrugspower.com/]rx pharmacy online 24[/url] canadian online pharmacies 2022 -
[url=http://proscarfinasteride.shop/]best place to buy propecia online[/url]
-
[url=https://augmentintab.shop/]amoxicillin 500mg over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://vardenafil247.com/]where can i buy levitra[/url]
-
[url=http://lisinoprilb.quest/]cost of lisinopril in mexico[/url] [url=http://prednisonetabs.shop/]prednisone 20 mg over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://modafinil.fun/]modafinil pills india[/url]
-
[url=http://zithromax.click/]azithromycin purchase[/url]
-
[url=http://acyclovirtabs.online/]acyclovir medication prices[/url]
-
[url=http://gabapentinx.online/]can i buy gabapentin over the counter[/url] [url=http://acyclovirtabs.online/]acyclovir medication[/url]
-
[url=http://clomid.sbs/]clomid online uk[/url]
-
[url=https://stromectolivermectin.shop/]ivermectin uk buy[/url]
-
[url=https://familydrugstores.quest/]legitimate online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://xtadalafil.monster/]cost of cialis in canada[/url]
-
Whoa lots of good information!
walmart pharmacy store 100 [url=https://canadapharmacyspace.com/]blink online pharmacy[/url] generic viagra online pharmacy -
[url=http://tetracycline.life/]terramycin for horses[/url]
-
[url=https://tretinointabs.online/]tretinoin 0.05 otc[/url]
-
[url=http://finpeciafinasteride.online/]propecia cheap price[/url]
-
[url=https://stromectolivermectin.shop/]can you buy stromectol over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://onlinevpharmacy.quest/]pharmacy prices[/url]
-
[url=https://stromectolivermectin.shop/]ivermectin humans[/url]
-
[url=http://cafergottabs.monster/]generic cafergot[/url]
-
[url=http://fluoxetinetab.online/]buy prozac singapore[/url] [url=http://prednisonetabs.shop/]prednisone tablet cost[/url] [url=http://acyclovirtabs.online/]zovirax cream price india[/url] [url=http://sildenafilrx.online/]soft viagra[/url] [url=http://doxycyclinetabs.online/]canadian pharmacy doxycycline[/url] [url=http://elavilamitriptyline.online/]elavil gel[/url] [url=http://ivermectinstromectol.shop/]ivermectin pill cost[/url] [url=http://amoxicilline.quest/]augmentin cost south africa[/url]
-
online pharmacy for pets prescription drugs account for 25 of all healthcare related costs Trental
-
[url=https://prednisolonetab.online/]buy online 10mg prednisolone[/url]
-
[url=http://fluoxetine.sbs/]purchase prozac 10 mg online no prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://lyrica.life/]lyrica price in mexico[/url]
-
[url=http://amoxicillinmed.com/]amoxicillin 876 mg[/url] [url=http://levitratabs.monster/]levitra 20mg price[/url] [url=http://cafergot.life/]buy cafergot[/url]
-
[url=https://propecia.sbs/]buy propecia cheap online[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinoprilb.quest/]lisinopril 10 12.5 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://fluoxetinetabs.monster/]prozac 60 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://azithromycinc.quest/]where to buy azithromycin 500mg[/url]
-
[url=http://amoxicilline.online/]825 mg augmentin[/url]
-
[url=https://modafinil24.net/]modafinil usa[/url]
-
[url=https://adiflucan.com/]diflucan otc australia[/url]
-
[url=https://fluoxetinetab.online/]prozac cost australia[/url]
-
[url=http://gabapentintabs.online/]buy gabapentin usa[/url]
-
[url=http://lasixfurosemide.net/]drug lasix 40 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://propecial.online/]generic propecia canada[/url] [url=https://augmentingen.online/]can you buy amoxicillin over the counter in canada[/url] [url=https://tretinointab.online/]how much is tretinoin 0.05 cream 40g[/url] [url=https://vardenafilv.online/]buy levitra 20mg online[/url]
-
can i buy sildenafil over the counter in uk buy viagra online prices drugstore female viagra
-
[url=http://clomid.sbs/]buy clomid online uk paypal[/url]
-
[url=http://escitalopramlexapro.online/]lexapro generic online[/url]
-
[url=http://cymbaltatab.quest/]cymbalta coupon[/url]
-
[url=http://lasixfurosemide.net/]lasix tablets uk[/url]
-
[url=http://ventolinmd.com/]how can i get albuterol cheap[/url]
-
Thanks. I appreciate it.
compare medication prices [url=https://sopharmsn.com/]onlinepharmacytabs24 com[/url] retin a canadian pharmacy -
[url=https://seroqueltab.quest/]where to buy seroquel online[/url]
-
[url=https://azithromycinc.quest/]zithromax prescription in canada[/url]
-
[url=http://clomid.click/]how can i get clomid uk[/url]
-
[url=https://hydroxychloroquinetabs.monster/]hydroxychloroquine 700mg[/url]
-
[url=https://finasteridetabs.online/]finasteride without prescription[/url] [url=https://cymbaltatab.quest/]best pharmacy prices for cymbalta[/url] [url=https://prozac.run/]fluoxetine over the counter[/url] [url=https://afinasteride.com/]finasteride 5 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://ivermectinstromectol.online/]ivermectin 2ml[/url]
-
[url=http://hydroxychloroquinetabs.monster/]hydroxychloroquine 30 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://sildenafilx.online/]buy viagra from canada online[/url]
-
online cialis prescription tadalafil citrate dosage bodybuilding cialis 20 mg for sale
-
[url=http://cafergottabs.monster/]cafergot canada[/url]
-
[url=https://remont-holodilnikov-v-novosibirske54.ru/]Ремонт холодильников [/url]
Качественный ремонт холодильников в течение Новосибирскее, мастер приедет на шахсей-вахсей вызова. Бесплатная эндосонография у починке, запчасти вналичии, низкие стоимости, ...
Ремонт холодильников -
[url=http://cafergottabs.monster/]cafergot[/url] [url=http://augmentingen.online/]amoxicillin 750 tabs[/url] [url=http://tetracycline.life/]sumycin over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://valacyclovirvaltrex.shop/]valtrex 500 mg cost[/url] [url=https://lasixm.online/]lasix 10 mg price[/url] [url=https://cymbaltatab.quest/]cymbalta prescription[/url] [url=https://tadalafilm.online/]tadalafil 5 mg tablet[/url]
-
[url=http://ventolinmd.com/]ipratropium albuterol[/url]
-
[url=http://zithromax.click/]zithromax 1000mg online[/url]
-
Forzest canada pharmacy online official canadian pharmacy
-
[url=http://synthroidlevothyroxine.online/]synthroid 2017[/url]
-
[url=http://trazodone.life/]trazodone 50 mg pill[/url]
-
viagra generic online india price of viagra in mexico viagra 10 pills
-
Great information, With thanks.
canadian online pharmacy reviews discount prescriptions list of mexican pharmacies -
[url=http://drugstores.quest/]pharmacy online track order[/url]
-
tadalafil professional 20 mg iron-dragon tadalafil buy cialis with dapoxetine
-
[url=http://zithromax.click/]buy azithromycin 250 mg no prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://cafergot.life/]cafergot generic[/url]
-
[url=http://lasixm.online/]furosemide 40 mg tablets online[/url]
-
[url=http://escitalopramlexapro.online/]lexapro buy[/url]
-
[url=https://disulfiramantabuse.online/]buy antabuse online safely[/url]
-
canadian pharmacy online [url=http://www.canadotcphar.com/]www.northwestpharmacy.com[/url] canadian pharmacy online viagra
my canadian pharmacy canadian pharmacies generic drugs online viagra without a doctor prescription in canada -
[url=https://canadiapharmacy.online/]pharmacy[/url] [url=https://onlinevpharmacy.quest/]buying from canadian pharmacies[/url] [url=https://propecial.online/]buy generic propecia online uk[/url] [url=https://tadalafilm.online/]cheapest cialis prices[/url] [url=https://gabapentintabs.online/]neurontin capsules[/url] [url=https://onlinepharmacy.life/]canadian pharmacy generic viagra[/url] [url=https://zithromax.click/]where to buy azithromycin 250 mg[/url]
-
cheap sildenafil 20 mg where can i purchase viagra price of viagra generic
-
[url=https://azithromycinc.quest/]azithromycin 500 mg generic price[/url]
-
[url=https://valacyclovirvaltrex.shop/]valtrex acyclovir[/url] [url=https://fluoxetine.sbs/]prozac brand name in india[/url] [url=https://augmentingen.com/]amoxicillin 500mg capsule[/url] [url=https://tetracyclinetab.quest/]terramycin crumbles[/url] [url=https://hydroxychloroquinetab.online/]plaquenil 200mg tablet cost[/url] [url=https://canadiapharmacy.online/]canadian pharmacies that deliver to the us[/url]
-
[url=https://adiflucan.com/]diflucan 150 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://amoxicilline.online/]order amoxicillin from canada[/url]
-
[url=http://hydroxychloroquinetabs.monster/]buy plaquenil[/url]
-
[url=http://amoxicillinmed.com/]generic amoxil[/url]
-
[url=https://drugstores.quest/]top online pharmacy 247[/url]
-
[url=http://amoxicillintabs.org/]augmentin 1.2 g tablet[/url]
-
[url=http://antabusetabs.monster/]antabuse medication[/url]
-
[url=https://trustedpharmacyz.online/]online pharmacy viagra[/url]
-
[url=https://trazodonedesyrel.online/]trazodone 50 mg price[/url]
-
[url=http://tadalafilm.monster/]cheapest generic cialis[/url]
-
[url=http://tadalafilm.monster/]cialis or viagra for women[/url]
-
[url=http://propeciafinasteride.org/]finasteride without prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://gabapentinx.online/]how much is gabapentin[/url]
-
cialis cheap free shipping tadora 20 mg tadalafil 20mg where can i buy original cialis
-
[url=https://prednisolona.com/]buy predislone tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://zithromaxtabs.online/]where to purchase azithromycin[/url]
-
[url=https://disulfiramantabuse.online/]best online no prescription antabuse[/url]
-
[url=http://albuterolv.com/]ventolin without a prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://hydroxychloroquinetabs.monster/]buy plaquenil 10mg[/url] [url=http://proscarfinasteride.online/]propecia prescription online[/url] [url=http://azithromycine.monster/]azithromycin pills canada[/url] [url=http://antabuse.run/]where can i buy antabuse tablets[/url] [url=http://valacyclovirvaltrex.shop/]valtrex cream[/url]
-
[url=https://propecial.online/]can i buy propecia online[/url] [url=https://canadiapharmacy.online/]legitimate online pharmacy usa[/url] [url=https://tetracyclinetab.online/]tetracycline 1[/url]
-
[url=https://sildenafilx.online/]how do you get viagra[/url]
-
[url=https://omedrec.com/index/gourl?url=https://casino-x.dp.ua]casino х[/url]
[url=http://abc4.kz/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://casino-x.dp.ua]casino х[/url]
[url=http://gov.co.vu.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://casino-x.dp.ua]casino х[/url]
[url=https://cdn.juliana-multimedia.com/api/qualitelis/1.1/qualitelis.php?token=6457D05E-C3EC-4C23-9AC2-FF5006EFF294&id_c>casino х
casino х
casino х
casino х
casino х
casino х
casino х
casino х
casino х
casino х
casino х
casino х
casino х
casino х
casino х -
[url=http://doxycyclinetabs.online/]where to buy doxycycline[/url]
-
[url=http://prednisonetab.online/]prednisone cost[/url]
-
[url=https://tretinointab.online/]tretinoin gel over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://gabapentintabs.online/]gabapentin 101[/url]
-
[url=http://ww11.aitsafe.com/go.htm?go=fantagehackcheats.wordpress.com&afid=15678&tm=30&im=9https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://wildmaturehousewives.com/tp/out.php?p=55&fc=1&link=gallery&url=https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://telgrad.ru/redirect.php?url=https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://pandorasumens.xooit.eu/report-violation.php?url=https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://zheldor.su/go/url=https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://olissys.com/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://foxbusiness.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://buyajupiterhome.com/RealtorWebPage?template=embed&customab_id=1578690853&c>??????+??????+??+??+????+???+??
??+??+??????+???+??+????+????
?????+????+??+???+???+?&spname=RIRAI??????https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://med-standard.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://myshortskirt.com/content/?url=https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://www.allods.net/redirect/https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://poly.com.au/?URL=https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://image.google.st/url?sa=i&url=https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://keepmydog.ru/redirect?url=https://xdo.tech]mostbet[/url]
According to the most popular rating, Mosbet is quantity the leaders in the industry, reviews close by withdrawals are normally fervent, below are some of them.
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet -
[url=https://xdo.tech]xdo.tech[/url]
Gamblers from more than forty countries can be observed among BC Mosbet's clients, and the formal website of the flock Mostbet com yua supports 46 languages.
mostbet online -
[url=https://cafergottab.online/]cafergot 1mg 100mg[/url]
-
[url=http://tadalafilm.online/]cialis generic from canada[/url]
-
Valuable postings. Thanks.
buy online pharmacy uk [url=https://pharmacyclineds.com/]doxycycline canadian pharmacy[/url] safeway pharmacy store hours
canadian government approved pharmacies the people's pharmacy canadian pharmacy domperidone
https://pharmacyclineds.com/ coursework login -
[url=http://augmentingen.online/]augmentin 625 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://seroquelquetiapine.shop/]seroquel generic price united states[/url]
-
[url=https://tetracycline.life/]terramycin antibiotic[/url]
-
[url=http://propecia.sbs/]propecia prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://canadiapharmacy.monster/]no rx needed pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://azithromycine.monster/]can you buy azithromycin otc[/url] [url=http://fluoxetine.sbs/]fluoxetine price[/url] [url=http://prozac.run/]40 mg fluoxetine daily[/url] [url=http://gabapentinx.quest/]gabapentin without prescription[/url] [url=http://azithromycin.run/]zithromax 500 mg[/url] [url=http://tadalafilm.online/]cialis canada paypal[/url] [url=http://prednisonetab.online/]indian prednisone without prescription[/url] [url=http://tetracyclinetab.quest/]can you buy terramycin over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://ventolinmd.com/]albuterol tabs without prescription[/url] [url=https://tetracyclinesumycin.online/]sumycin over the counter[/url] [url=https://lasixm.online/]cost of furosemide uk[/url] [url=https://antabuse.run/]disulfiram canada[/url] [url=https://clomid.click/]how to order clomid[/url] [url=https://propecial.online/]finasteride proscar[/url] [url=https://proscarfinasteride.online/]buy propecia 5mg online[/url]
-
[url=https://xdo.tech]xdo[/url]
Mostbet betting company is considered to be an old-timer of foreign betting, since it was founded in 2009.
mosbet aviator -
[url=https://casino-x.dp.ua]х casino[/url]
Casino X is a up to date but very acclaimed online establishment. In this online casino con, we choice analyze the functionality, bonuses and much more.
казино х украина -
[url=http://lyrica.life/]lyrica pills 75 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://valacyclovirvaltrex.shop/]valtrex cream over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://ventolinmd.com/]albuterol from canada no prescription[/url] [url=https://azithromycine.monster/]azithromycin 250 price india[/url] [url=https://lasixm.online/]furosemide 20 mg prices[/url] [url=https://seroquelquetiapine.shop/]cost of seroquel 20 mg[/url] [url=https://cafergottabs.monster/]cafergot canada[/url] [url=https://prednisolona.com/]buy prednisolone 5mg tablets uk[/url] [url=https://tadalafilm.online/]cialis 25 mg tablet[/url] [url=https://afinasteride.com/]buy finasteride online[/url]
-
[url=https://tadalafilm.online/]tadalafil 20mg cost[/url] [url=https://tetracyclinetab.online/]tetracycline brand usa[/url] [url=https://celebrex.icu/]cheap celebrex 200mg[/url] [url=https://prednisolone.life/]prednisolone 1[/url]
-
[url=https://lyricatabs.quest/]lyrica price comparison[/url]
-
[url=https://onlinepharmacy.life/]best canadian online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://xmodafinil.monster/]modafinil price usa[/url]
-
[url=http://gabapentinx.online/]gabapentin cap 400mg[/url]
-
[url=https://tadalafila.org/]tadalafil 2.5 mg tablets in india[/url]
-
[url=http://tetracyclinesumycin.online/]tetracycline hydrochloride[/url]
-
[url=http://levitratab.online/]levitra medicine[/url]
-
[url=http://azithromycin.run/]zithromax brand name[/url]
-
[url=http://ivermectinstromectol.online/]stromectol tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://tretinoinretina.online/]tretinoin cheapest price[/url]
-
[url=http://ivermectinstromectol.shop/]stromectol 3 mg tablet[/url] [url=http://fluoxetinetab.online/]fluoxetine 10mg tablet[/url] [url=http://propecia.sbs/]propecia 1.5 pills[/url] [url=http://prednisonerx.monster/]deltasone generic[/url] [url=http://sildenafilrx.online/]cost of sildenafil in india[/url] [url=http://tretinoinretina.online/]retin a 20[/url] [url=http://lyrica.life/]lyrica 2019 coupon[/url] [url=http://amitriptylinetab.online/]endep 10mg[/url]
-
canadian pharmacy com brand viagra online canadian pharmacy Indinavir (Cipla Ltd)
-
[url=https://fluoxetinetab.online/]fluoxetine 16 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://trazodone.life/]desyrel[/url]
-
[url=http://sertralinezoloft.shop/]20mg zoloft[/url]
-
cialis for sale online in canada cialis free 30 day trial tadalafil overdose
-
buy generic viagra online europe buy generic viagra uk viagra professional 100mg
-
[url=http://valacyclovirvaltrex.shop/]valtrex over the counter uk[/url]
-
[url=http://cymbaltatab.quest/]90 cymbalta[/url] [url=http://vardenafilv.online/]buy vardenafil 40 mg[/url] [url=http://tetracyclinetab.online/]tetracycline medicine price in india[/url] [url=http://ventolinmd.com/]0.75 mg albuterol[/url] [url=http://prednisonetab.online/]can you buy prednisone over the counter[/url] [url=http://trazodonedesyrel.online/]prescription prices for trazodone[/url]
-
best viagra for women can you buy viagra without a prescription where can i buy sildenafil tablets
-
[url=http://tetracyclinesumycin.online/]tetracycline cream[/url]
-
[url=http://sildenafilrx.online/]where can i buy sildenafil over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://lisinoprilx.org/]lisinopril tabs 40mg[/url]
-
[url=https://gostinichnye-cheki-moskva-pr2.ru/]Гостиничные чеки[/url]
Сверх этого, яко у нас можно приобрести гостиничный шнырь, пишущий эти строки тоже предоставляем командировочникам проживание. Отечественный уютный президент-отель всего комфортными постоялый двор в течение середке Столицы всегда рад-радешенек видеть вас.
Гостиничные чеки -
[url=https://zithromaxtabs.online/]zithromax 4 pills[/url] [url=https://cafergottab.online/]cafergot 100mg[/url] [url=https://albuterolv.com/]albuterol for sale online[/url]
-
[url=http://azithromycine.monster/]azithromycin 500mg buy online[/url] [url=http://canadiapharmacy.online/]onlinepharmaciescanada com[/url] [url=http://deltasoneprednisone.online/]prednisone cream[/url] [url=http://fluoxetinetabs.monster/]fluoxetine 4356[/url] [url=http://prednisonetab.online/]prednisone 20mg by mail without prescription[/url] [url=http://cymbaltatab.quest/]order cymbalta[/url] [url=http://tetracyclinetab.online/]can you buy terramycin over the counter[/url] [url=http://augmentingen.com/]amoxicillin for sale canada[/url]
-
[url=https://lasixfurosemide.net/]furosemide brand name uk[/url]
-
[url=https://zithromaxtab.monster/]azithromycin 250 mg over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinoprila.net/]lisinopril buy in canada[/url]
-
[url=http://augmentintabs.online/]amoxil price in india[/url]
-
[url=http://stromectolivermectin.shop/]ivermectin usa[/url]
-
[url=http://canadianfamilypharmacy.quest/]safe reliable canadian pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://prednisolona.com/]prednisolone online uk[/url] [url=https://augmentingen.online/]amoxicillin buy canada[/url] [url=https://fluoxetinetabs.monster/]fluoxetine 4356[/url] [url=https://ivermectinstromectol.online/]stromectol 12mg online[/url] [url=https://vardenafilv.online/]levitra generic price[/url]
-
[url=https://azithromycine.monster/]generic azithromycin online[/url]
-
[url=http://doxycycline247.com/]doxycycline online paypal[/url]
-
[url=https://retinatabs.online/]retin a cream rx[/url]
-
[url=https://acyclovirztab.monster/]acyclovir 200 buy[/url]
-
[url=http://metformin247.com/]metformin 101[/url]
-
[url=https://tadalafilm.monster/]cialis for sale over the counter[/url] [url=https://xmodafinil.monster/]how to order modafinil[/url] [url=https://ivermectinstromectol.online/]stromectol 3mg[/url] [url=https://ventolinmd.com/]ventolin inhaler without prescription[/url] [url=https://metformin247.com/]where to buy metformin in south africa[/url] [url=https://canadiapharmacy.online/]top 10 pharmacies in india[/url] [url=https://vardenafilv.online/]brand levitra for sale[/url] [url=https://tetracycline.life/]tetracycline 250 mg capsules[/url]
-
[url=http://hydroxychloroquinetabs.monster/]hydroxychloroquine generic[/url]
-
[url=http://ventolintabs.shop/]albuterol canada[/url]
-
[url=https://buywellbutrin.life/]cost for generic wellbutrin[/url]
-
cialis 20mg online best time to take cialis 5mg which one is better viagra cialis or laverta
-
[url=https://amoxicillingen.com/]amoxicillin 67[/url]
-
[url=http://phenergan.icu/]phenergan cream australia[/url]
-
[url=https://cleocintabs.online/]clindamycin capsules 300 mg price[/url] [url=https://cipro.life/]ciprofloxacin order online[/url] [url=https://tetracycline.icu/]tetracycline 500mg capsule price[/url] [url=https://azithromycingn.online/]can i buy azithromycin[/url] [url=https://propecial.monster/]buy propecia us[/url]
-
[url=http://synthroid.works/]synthroid for sale online[/url]
-
[url=https://propeciafinasteride.org/]online pharmacy generic propecia[/url]
-
[url=https://amoxicillina.org/]augmentin 650[/url]
-
canada pharmacy online
https://canadianpharmaciesshop.com/
[url=https://canadianpharmaciesshop.com/]legal online pharmacies[/url] -
[url=https://modafinilz.online/]modafinil online canada[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinoprilb.online/]how much is lisinopril 10 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://accutane.click/]isotretinoin accutane[/url]
-
[url=https://buywellbutrin.life/]zyban from canadian pharmacy[/url] [url=https://buylasix.life/]lasix online pharmacy[/url] [url=https://metformina.net/]metformin 50 mg tab[/url] [url=https://neurontinv.online/]gabapentin online india[/url] [url=https://retinatabs.com/]prescription retin a for sale[/url] [url=https://allopurinolz.quest/]allopurinol 100mg cost[/url] [url=https://lisinoprilprinivil.shop/]lisinopril 10 mg order online[/url] [url=https://anafraniltabs.monster/]buy anafranil online[/url]
-
[url=http://besthydroxychloroquine.com/]hydroxychloroquine generic[/url]
-
tadalafil half life tadalafil eli cialis from canada to usa
-
[url=http://acyclovirtabs.shop/]zovirax uk[/url]
-
[url=http://buyretina.life/]retin a best price[/url]
-
[url=http://amoxicillinmed.online/]cost amoxicillin 875 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://tetracycline.icu/]tetracycline brand name in india[/url] [url=https://cipro.life/]order cipro from canada[/url] [url=https://ampicillin.fun/]buy ampicillin 500mg[/url] [url=https://augmentintab.online/]cheap generic amoxicillin[/url]
-
[url=http://bactrimds.shop/]bactrim 200 40 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://buylasix.life/]lasix uk buy[/url]
-
[url=https://brandhydroxychloroquine.com/]quineprox 75[/url]
-
[url=https://buyyasmin.monster/]yasmin price south africa[/url] [url=https://colchicine.sbs/]colchicine generic[/url] [url=https://dapoxetineavana.online/]order priligy online uk[/url] [url=https://buylasix.life/]furosemide 40 mg buy online uk[/url] [url=https://buyacyclovir.life/]buy acyclovir 400 mg[/url] [url=https://zoloftx.org/]how to get brand name zoloft[/url]
-
[url=http://augmentintab.online/]amoxicillin 625mg price[/url] [url=http://tetracycline.icu/]generic tetracycline[/url] [url=http://prozactab.com/]fluoxetine 60 mg[/url] [url=http://provigiltab.online/]how to order provigil online[/url] [url=http://lasixm.monster/]lasix with no prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://cipro.life/]ciprofloxacin 400 mg[/url] [url=http://buykamagra.monster/]kamagra jelly for sale[/url] [url=http://levitratabs.online/]levitra usa price[/url] [url=http://finasteridetabs.net/]finasterid[/url]
-
[url=http://doxycyclinetab.org/]best pharmacy online no prescription doxycycline[/url]
-
[url=https://buymusclerelaxants.com/]zanaflex pill[/url]
-
[url=https://amoxicillingen.com/]augmentin 250mg 125mg[/url]
-
[url=http://vardenafil.sbs/]generic levitra canada[/url] [url=http://tretinointabs.com/]tretinoin 0.025 cream price in india[/url] [url=http://finpecia.sbs/]finasteride 1mg tablets for sale[/url] [url=http://tretinoin.icu/]where to buy retin a cream in canada[/url]
-
[url=http://buykamagra.monster/]kamagra jelly 100mg[/url]
-
[url=http://cipro.life/]medicine ciprofloxacin 500mg[/url]
-
[url=http://cymbaltaduloxetine.online/]cymbalta cost canada[/url]
-
[url=http://ventolin.digital/]ventolin 200 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://retinatabs.com/]retin a cream coupon[/url] [url=https://seroqueltabs.shop/]where to get seroquel[/url] [url=https://metformin.sbs/]can i buy glucophage over the counter in south africa[/url] [url=https://zovirax.life/]buy acyclovir online usa[/url] [url=https://buyonlinepharmacy.monster/]onlinecanadianpharmacy 24[/url] [url=https://amoxicillinmed.online/]amoxicillin over the counter in mexico[/url] [url=https://finpecia.site/]how can i get propecia[/url] [url=https://dapoxetineavana.online/]priligy tablets india[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinopril.fun/]zestril lisinopril[/url] [url=https://phenergan.sbs/]generic phenergan 12.5[/url]
-
[url=https://buyonlinepharmacy.monster/]online pharmacy group[/url]
-
[url=http://amoxicillingen.com/]augmentin 1g online[/url]
-
[url=https://buykamagra.monster/]kamagra oral jelly price[/url] [url=https://modafinilz.online/]800 mg modafinil[/url] [url=https://tretinointabs.com/]tretinoin buy mexico[/url]
-
[url=http://arimidex.shop/]arimidex 1mg online[/url]
-
which pharmacy has the best price on viagra canada pharmacy online phentermine mexican pharmacy no prescription hydrocodone
-
[url=http://accutane.life/]accutane 20 mg buy online[/url]
-
[url=http://augmentin.run/]amoxicillin capsule 500mg price[/url]
-
[url=https://finasteridetabs.net/]purchase propecia canada[/url]
-
[url=http://elavil.boutique/]150 mg elavil[/url]
-
[url=https://sosnitikb.dp.ua/]sosnitikb[/url]
Пролетарое зеркало казино Пин Ап дает круглосуточный вход ко выступлениям Hold Up Casino, официальные зеркала хранят цельный функционалишко неординарного онлайн клуба.
sosnitikb -
buy viagra montreal cost of viagra prescription how to get viagra prescription australia
-
buy voucher for cialis daily online cialis 20mg vs viagra 100mg cialis india
-
[url=http://dapoxetineavana.online/]buy dapoxetine in india[/url]
-
[url=http://sildenafilx.shop/]viagra prescription discount[/url]
-
[url=https://modafinilz.online/]provigil cost[/url]
-
sildenafil tablets 100mg can you buy viagra over the counter in usa cheap generic viagra online canada
-
[url=http://tretinoin.icu/]tretinoin tablets 10mg[/url]
-
[url=https://diclofenac.store/]diclofenac australia over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://modafinilb.quest/]modafinil buy online us[/url]
-
[url=https://gabapentintabs.shop/]gabapentin 10 cream[/url] [url=https://provigiltab.online/]buy provigil australia[/url] [url=https://augmentintab.online/]how much is amoxicillin in mexico[/url] [url=https://acyclovirztab.online/]acyclovir 100[/url] [url=https://vardenafil.sbs/]vardenafil levitra[/url] [url=https://albuterola.org/]cheap albuterol online[/url] [url=https://buykamagra.monster/]kamagra oral jelly 50 pack[/url]
-
[url=http://tretinoinretina.shop/]how to get retin a uk[/url]
-
[url=http://bactrimds.shop/]bactrim otc[/url]
-
[url=https://ampicillin.fun/]ampicillin sulbactam[/url]
-
[url=http://buyonlinepharmacy.monster/]canada drugstore pharmacy rx[/url]
-
cialis blaack buying cialis online safely ingredient in cialis
-
[url=http://buyonlinepharmacy.monster/]happy family store coupon code[/url]
-
[url=https://cephalexine.shop/]cephalexin 750 mg capsule[/url] [url=https://tretinoinretina.shop/]retin-a 0.025[/url] [url=https://gabapentintabs.shop/]gabapentin pill 600 mg[/url] [url=https://valtrexd.online/]daily valtrex no prescription[/url] [url=https://amoxicillina.org/]amoxil pills[/url] [url=https://augmentintab.online/]can i order amoxicillin online[/url] [url=https://vardenafil.sbs/]buy levitra from canada[/url]
-
[url=http://lasixm.monster/]furosemide 40 mg iv[/url]
-
[url=http://propecial.monster/]generic propecia finasteride 1mg[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinoprilprinivil.shop/]lisinopril 240[/url] [url=https://metformina.net/]buy metformin 1000 mg uk[/url] [url=https://zoloftx.org/]zoloft 100 mg[/url] [url=https://colchicine.sbs/]colchicine 0.6 mg coupon[/url]
-
[url=http://metformina.net/]glucophage buy uk[/url]
-
[url=http://lisinoprilds.com/]lisinopril 1.25 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinoprilds.com/]lisinopril 5 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://provigiltab.online/]modafinil prescription cost[/url]
-
viagra online cheap india cheap sildenafil citrate tablets sildenafil 1mg
-
[url=http://synthroidv.com/]where can you get synthroid[/url]
-
sildenafil 100mg tablets buy online generic viagra price uk viagra medicine online
-
[url=http://propecial.monster/]price of propecia in usa[/url]
-
[url=http://lisinoprilprinivil.shop/]lisinopril 20mg 25mg[/url]
-
[url=http://accutane.life/]buy accutane online cheap[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinoprila.net/]lisinopril online prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://cymbaltaduloxetine.online/]where to buy generic cymbalta[/url] [url=https://wellbutrin.icu/]zyban discount[/url]
-
[url=https://lasixm.monster/]furosemide medication[/url]
-
cvs pharmacy lisinopril cabo san lucas pharmacy vicodin wegmans pharmacy lipitor
-
[url=http://finpecia.sbs/]cost of propecia 1mg[/url]
-
[url=http://retinatabs.com/]buy generic retin a online[/url]
-
[url=https://buymusclerelaxants.com/]medicine tizanidine 2mg[/url]
-
[url=http://sildenafilgen.online/]order viagra 100mg[/url]
-
[url=https://acyclovirtabs.shop/]can i buy zovirax over the counter in canada[/url] [url=https://dapoxetineavana.online/]avana 200mg[/url] [url=https://buyretina.life/]generic retin a from mexico[/url] [url=https://neurontinv.online/]gabapentin 400[/url] [url=https://buyhydroxychloroquine.life/]plaquenil hair loss[/url] [url=https://sildenafilgen.online/]lowest cost viagra online[/url] [url=https://zoloftp.com/]order generic zoloft online[/url]
-
[url=https://lpg-top.site/]LPG массаж[/url]
LPG-массаж (вакуумно-роликовый, чи эндермологический) – аппаратная ноу-хау, применяемая для коррекции персоны и еще тела.
LPG массаж -
[url=http://buycolchicine.life/]colchicine tablets[/url]
-
[url=https://cipro.life/]cipro 100 mg[/url] [url=https://prozactab.com/]fluoxetine 99[/url]
-
[url=https://cipro.life/]cipro mexico[/url]
-
[url=https://nolvadextamoxifen.shop/]canadian tamoxifen[/url]
-
[url=https://buycolchicine.life/]colchicine iv[/url] [url=https://furosemidetab.online/]furosemide 20 mg prices[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinoprila.net/]zestril coupon[/url]
-
[url=http://buyhydroxychloroquine.life/]plaquenil medicine[/url]
-
[url=http://amoxicillintabs.org/]amoxil 500 tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://furosemidetab.online/]lasix medicine[/url]
-
[url=https://buycolchicine.life/]colchicine canada prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://pharmacygrand.com/]happy family canadian pharmaceuticals online[/url] [url=https://buystrattera.monster/]cost of 40 mg strattera[/url] [url=https://modafinilb.quest/]buy provigil online with mastercard[/url] [url=https://cleocintabs.online/]clindamycin 300 mg tablet brand name[/url] [url=https://lisinoprilb.online/]zestril no prescription[/url] [url=https://amoxicillina.org/]amoxicillin 1g capsule[/url] [url=https://finasteridetabs.net/]propecia 1.5 pills[/url]
-
[url=http://augmentin.run/]amoxicillin tablet[/url]
-
[url=http://finpecia.sbs/]order propecia online usa[/url]
-
[url=https://prozactab.com/]prozac 5 mg[/url] [url=https://modafinilb.quest/]provigil otc[/url] [url=https://lasixm.monster/]furosemide 40 mg cost uk[/url] [url=https://ampicillin.fun/]ampicillin cost[/url]
-
[url=http://buyhydroxychloroquine.life/]buy hydroxychloroquine online[/url]
-
[url=http://buycolchicine.life/]colchicine 6 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://acyclovirztab.online/]buy acyclovir without a prescription[/url] [url=https://flagyl.cfd/]buy flagyl online without prescription[/url] [url=https://colchicine.run/]over the counter colchicine medication[/url] [url=https://amoxicillina.org/]amoxicillin 500 coupon[/url] [url=https://augmentin.run/]augmentin 375mg[/url] [url=https://tretinointabs.com/]retin a 0.05 cream cost[/url] [url=https://finasteridetabs.net/]propecia india online[/url]
-
[url=https://buymusclerelaxants.com/]urispas medicine price in india[/url]
-
[url=http://besthydroxychloroquine.com/]plaquenil generic drug[/url]
-
[url=http://buykamagra.monster/]kamagra soft tabs[/url]
-
[url=https://flagyl.cfd/]flagyl generic cost[/url]
-
[url=http://wellbutrin.icu/]wellbutrin australia[/url]
-
[url=http://sildenafilgen.online/]sildenafil pills[/url]
-
[url=http://lisinoprilb.online/]generic zestril[/url]
-
[url=http://cipro.life/]ciprofloxacin online[/url]
-
[url=http://tretinointabs.com/]where to buy tretinoin cream otc[/url]
-
[url=http://retinatabs.com/]cheap retin a[/url] [url=http://neurontinv.online/]brand gabapentin[/url] [url=http://colchicine.sbs/]colchicine from mexico[/url] [url=http://sildenafilgen.online/]cheap viagra online australia[/url] [url=http://gabapentin247.com/]gabapentin 350mg[/url] [url=http://zovirax.life/]acyclovir 792[/url] [url=http://antibioticsotc.com/]generic floxin[/url] [url=http://lioresaltabs.quest/]baclofen uk[/url]
-
[url=http://tretinointabs.com/]tretinoin 0.5 gel uk[/url]
-
[url=https://buywellbutrin.life/]450mg bupropion[/url]
-
[url=http://etrazodone.com/]trazodone 319[/url]
-
canadian pharmacy no prescription oxycodone viagra online pharmacy australia percocet pharmacy
-
[url=http://cleocintabs.online/]generic for cleocin[/url]
-
sildenafil generic uk viagra prices generic viagra fast shipping
-
[url=https://allopurinolz.quest/]allopurinol 100mg cost[/url]
-
viagra without presc uk online viagra in us viagra 6
-
[url=http://buyonlinepharmacy.monster/]mail order pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://buyhydroxychloroquine.life/]quineprox 60mg[/url]
-
[url=https://ntviagra.com/]where can i buy viagra in south africa[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinopril.fun/]lisinopril 12.5[/url]
-
[url=http://brandhydroxychloroquine.com/]hydroxychloroquine sulfate tabs 200mg[/url]
-
[url=https://colchicine.run/]colchicine australia[/url]
-
[url=http://singulair.site/]singulair 1 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://zovirax.life/]zovirax brand name[/url]
-
[url=https://buyyasmin.monster/]yasmin tablet price india[/url]
-
[url=https://buyonlinepharmacy.monster/]cross border pharmacy canada[/url]
-
sildenafil 105 mg canada where can you get viagra over the counter 25mg viagra daily
-
viagra online shop [url=http://www.canadotcphar.com/]canadian pharmacy for viagra[/url] online drugstore
canada pharmacy online canadian pharmacies generic drugs online canadian pharmacy online for viagra -
[url=http://neurontintabs.com/]600 mg gabapentin tablet[/url]
-
[url=https://vkontaktemp3.ru/]sosnitikd[/url]
Климатизационная техника чтобы комплекса помещений называется мультисплит-системами. Они представляют собою привычные приспособления внутренней да внешной линии,
sosnitikd -
[url=http://buydrugstore.monster/]best pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://augmentintab.online/]purchase augmentin[/url]
-
[url=https://anafranil.quest/]anafranil for sale[/url]
-
[url=https://phenergan.icu/]otc phenergan medicine[/url]
-
[url=https://modafinil24.net/]modafinil for sale us[/url]
-
[url=https://finpecia.click/]generic propecia canadian pharmacy[/url]
-
cialis slogan vardenafil tadalafil sildenafil cialis 20mg side effects
-
[url=http://buywellbutrin.life/]wellbutrin uk buy[/url]
-
[url=http://vardenafil.sbs/]generic-levitra[/url]
-
[url=http://buymalegra.monster/]malegra 180 on line[/url] [url=http://sildenafilx.shop/]buy viagra canadian pharmacy[/url] [url=http://buyonlinepharmacy.monster/]no rx pharmacy[/url] [url=http://lisinopril.fun/]lisinopril 80 mg[/url] [url=http://finpecia.site/]finasteride prescription[/url] [url=http://neurontinv.online/]neurontin 300mg capsule[/url] [url=http://buywellbutrin.life/]online pharmacy bupropion[/url] [url=http://sildenafilgen.online/]sildenafil citrate uk[/url]
-
[url=http://lasixfurosemide.net/]buy furosemide tablets uk[/url]
-
[url=http://cephalexine.shop/]cephalexin cost uk[/url]
-
[url=https://ntviagra.com/]100mg generic sildenafil[/url]
-
[url=http://acyclovirtabs.shop/]zovirax cream price in india[/url]
-
[url=http://buypropeciawithoutprescription.com/]propecia 5mg online[/url]
-
[url=https://amoxicillina.org/]amoxicillin 650 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://ventolintabs.shop/]albuterol prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://finasteridetabs.net/]propecia 1mg tablet price[/url]
-
[url=http://pharmacygrand.com/]good online mexican pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://ventolintab.com/]albuterol in mexico[/url]
-
[url=http://acyclovirztab.online/]order acyclovir cream online[/url] [url=http://buykamagra.monster/]kamagra oral jelly perth[/url] [url=http://provigiltab.online/]modafinil tablet[/url] [url=http://vardenafil.sbs/]levitra 20mg price uk[/url] [url=http://cymbaltaduloxetine.online/]how much is cymbalta[/url] [url=http://augmentin.run/]amoxicillin 1000 mg tablet[/url] [url=http://buystrattera.monster/]pharmacy prices for strattera[/url] [url=http://lisinoprilds.com/]buy lisinopril 5 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://anafraniltabs.monster/]anafranil ocd[/url]
-
[url=https://doxycyclinetab.org/]canadian pharmacy doxycycline[/url]
-
[url=http://cymbaltaduloxetine.online/]cymbalta price comparison canada[/url]
-
[url=https://propecial.monster/]cheap propecia india[/url] [url=https://vardenafil.sbs/]20 mg levitra price[/url] [url=https://cipros.shop/]buy ciprofloxacin online canada[/url] [url=https://prednisolone.icu/]prednisolone 10 mg buy online[/url] [url=https://lisinoprilb.online/]zestoretic 20 25[/url] [url=https://lexaprotab.monster/]price generic lexapro[/url]
-
[url=http://buyacyclovir.life/]zovirax medication[/url]
-
[url=http://buydrugstore.monster/]cheap online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://finpecia.site/]propecia 2mg[/url]
-
[url=https://azithromycingn.online/]zithromax 500 mg lowest price drugstore online[/url]
-
[url=https://besthydroxychloroquine.com/]plaquenil order online[/url]
-
[url=http://cymbaltaduloxetine.online/]cymbalta 60 mg price australia[/url]
-
[url=https://autoshkolaufa.ru/]Автошкола[/url]
квалификация сверху уровне машинной технической (М.18 - Диагностика и ремонт филиалов и агрегатов транспортных средств.
Автошкола -
[url=http://synthroidv.com/]synthroid 88 price[/url] [url=http://finpecia.click/]generic propecia usa[/url] [url=http://ntviagra.com/]order generic viagra from india[/url] [url=http://keflexcephalexin.shop/]keflex 500 mg daily[/url] [url=http://metformin.sbs/]metformin 150[/url] [url=http://amoxicillinmed.online/]amoxicillin 500 mg order online[/url] [url=http://finpecia.site/]propecia prescription uk[/url]
-
[url=https://buycolchicine.life/]can i buy colchicine over the counter uk[/url]
-
[url=http://accutane.life/]accutane online usa[/url] [url=http://fluoxetine.click/]fluoxetine drug[/url] [url=http://bactrimds.shop/]buy bactrim[/url]
-
[url=http://finasteridetabs.net/]buy generic propecia online[/url]
-
[url=https://vardenafil.sbs/]cheap levitra professional[/url]
-
[url=https://propecial.monster/]propecia costs australia[/url]
-
[url=http://zoloftp.com/]zoloft cost without insurance[/url] [url=http://buylasix.life/]cheap lasix 40 mg[/url] [url=http://brandhydroxychloroquine.com/]plaquenil price in india[/url] [url=http://keflexcephalexin.shop/]buy cephalexin online no prescription[/url] [url=http://buyretina.life/]025 tretinoin[/url] [url=http://anafraniltabs.monster/]anafranil for anxiety[/url] [url=http://buyonlinepharmacy.monster/]pharmacy online 365[/url] [url=http://metformin.sbs/]order metformin on line[/url]
-
[url=https://neurontintabs.com/]gabapentin coupon[/url]
-
[url=https://allopurinolz.quest/]allopurinol tablet 300mg[/url]
-
[url=https://finpecia.sbs/]propecia discount pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://colchicine.sbs/]colchicine generic canada[/url]
-
[url=https://lioresaltabs.quest/]medicine baclofen 10 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://buycanadianpharmacy.monster/]canada drugstore pharmacy rx[/url]
-
[url=https://sildenafilgen.online/]generic viagra capsules[/url]
-
[url=https://phenergan.icu/]phenergan 25 cost[/url]
-
[url=https://accutane.life/]accutane otc[/url] [url=https://wellbutrin.icu/]bupropion 100 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://buymalegra.monster/]malegra 100 cheap[/url]
-
how to purchase viagra in uk otc viagra united states 100g viagra
-
[url=https://cipro.life/]medication cipro 500 mg[/url]
-
tramadol pharmacy uk propecia inhouse pharmacy cialis india pharmacy
-
[url=http://cymbaltaduloxetine.online/]cymbalta 120[/url]
-
[url=https://buykamagra.monster/]can you buy kamagra oral jelly over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://amoxicillina.org/]augmentin 125 mg tab[/url]
-
[url=http://accutane.life/]accutane 30 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://dapoxetine.fun/]dapoxetine 60 mg tablet price[/url]
-
how to take cialis tadalafil (megalis-macleods) reviews cialis manufacturer coupon lilly
-
[url=https://buykamagra.monster/]kamagra oral jelly made in india[/url] [url=https://amoxicillina.org/]augmentin 875mg 125mg[/url]
-
[url=http://buykamagra.monster/]kamagra jelly[/url] [url=http://prednisolone.icu/]prednisolone 20 mg[/url] [url=http://albuterola.org/]albuterol for sale usa[/url] [url=http://finasteridetabs.net/]buy finasteride online[/url] [url=http://lasixm.monster/]cost of furosemide 40mg[/url] [url=http://cleocintabs.online/]cleocin medicine[/url] [url=http://buytadalafil20mg.com/]purchase cialis 10mg[/url]
-
[url=https://neurontintabs.com/]neurontin 300[/url]
-
[url=http://flagyl.cfd/]flagyl 250[/url]
-
[url=http://fluoxetine.click/]fluoxetine 20mg capsules cost[/url] [url=http://flagyl.cfd/]flagyl online no prescription[/url] [url=http://tretinoinretina.shop/]tretinoin gel buy online[/url] [url=http://finasteridetabs.net/]propecia buy australia[/url] [url=http://lisinoprilds.com/]lisinopril 40 mg tablets[/url] [url=http://cipro.life/]ciprofloxacin generic cost[/url] [url=http://lisinoprilb.online/]prinivil lisinopril[/url]
-
[url=https://phenergan.icu/]phenergan vc[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinoprilx.org/]lisinopril 60 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://bupropiontab.online/]wellbutrin 151 pill[/url]
-
[url=https://buyhydroxychloroquine.life/]generic plaquenil prices[/url]
-
[url=https://propecial.monster/]drug finasteride[/url]
-
[url=http://retinatabs.com/]generic retin a 05[/url]
-
[url=http://phenergan.sbs/]phenergan 5mg[/url]
-
[url=http://seroquela.com/]336 seroquel[/url]
-
[url=https://colchicine.run/]colchicine cancer[/url]
-
[url=https://cipro.life/]ciprofloxacin 500 tablet price[/url] [url=https://buykamagra.monster/]sildenafil oral jelly 100mg kamagra[/url] [url=https://lisinoprilds.com/]lisinopril 5 mg daily[/url] [url=https://gabapentintabs.shop/]neurontin 600 mg capsule[/url] [url=https://bactrimds.shop/]bactrim ordering[/url] [url=https://ampicillin.fun/]cost of ampicillin pills[/url] [url=https://seroquela.com/]seroquel pills online[/url]
-
[url=https://colchicine.run/]colchicine 500mcg[/url]
-
[url=http://retinatabs.com/]coupon tretinoin[/url]
-
[url=http://lisinopril.fun/]zestoretic 10 12.5 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://metformina.net/]how to buy glucophage[/url]
-
[url=http://allopurinolz.quest/]allopurinol 100 mg[/url] [url=http://buydrugstore.monster/]pharmacy[/url] [url=http://brandhydroxychloroquine.com/]hydroxychloroquine brand[/url] [url=http://seroqueltabs.shop/]seroquel 150[/url]
-
[url=http://antibioticsotc.com/]ceftin for dogs[/url]
-
[url=https://accutane.life/]accutane pill 39 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://citalopram.site/]brand name citalopram[/url] [url=http://lipitoratorvastatin.shop/]buying lipitor from canada[/url] [url=http://elaviltabs.shop/]amitriptyline buy online[/url] [url=http://amoxil.sbs/]amoxicillin 875mg 125mg[/url] [url=http://malegratabs.quest/]malegra dxt tablets[/url] [url=http://sildenafilxd.com/]where to buy cheap viagra[/url] [url=http://ciprof.quest/]buy ciprofloxacin online cheap without a prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://cymbaltatab.quest/]cymbalta medication[/url]
-
escitalopram generic pharmacy risperidone online pharmacy diamox pharmacy
-
[url=https://tretinoin.click/]best tretinoin cream brand[/url]
-
[url=https://aksochi.ru/]Апартаменты в Сочи[/url]
Сочи определенно урвала этап в течение курорт: это одна, хотя, ясный путь, немало один-единственная причина, числом коекак общества обязаны чутко учить увеличивающиеся средства чтобы бизнеса. Сочи рвется вступить в течение Союз в течение соседном будущем. Если на дорожной карте, разработанной, в течение черте гипотезы возможного преамбулы Столица курортов именуется 2025 миллезим, так очевидно, яко лидирует.
Апартаменты в Сочи -
viagra 100 mg price canada buy viagra cheap female viagra 100mg tablet price in india
-
comprar tadalafil 40 mg en walmart sin receta houston texas online cialis prescription cialis price costco
-
[url=http://bactrim.fun/]bactrim for sale[/url]
-
[url=https://benicartab.shop/]benicar drug coupon[/url]
-
viagra pills for sale online where can i buy viagra in australia how much is viagra in canada
-
[url=http://amoxil.sbs/]how much is augmentin[/url]
-
[url=https://buyallopurinol.life/]allopurinol 10 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://sildenafilxd.com/]2 viagra[/url]
-
price of 50 mg viagra where can you buy viagra over the counter in australia purchasing viagra in usa
-
[url=http://buytetracycline.life/]price of tetracycline[/url]
-
[url=http://valacyclovirvaltrex.online/]valtrex medication price[/url] [url=http://bactrimd.online/]bactrim cost in india[/url] [url=http://cialisgenerictadalafil.com/]generic cialis 20mg price[/url] [url=http://aurogra.fun/]aurogra 100[/url] [url=http://synthroid.sbs/]brand synthroid[/url] [url=http://buyretinoa.monster/]retino cream price[/url] [url=http://wellbutrina.monster/]bupropion 400 mg[/url] [url=http://happyonlinedrugstore.monster/]canadian pharmacies comparison[/url]
-
[url=http://finpecia.fun/]propecia 5mg india[/url]
-
[url=https://alevitra.com/]canadian levitra online[/url] [url=https://wellbutrintab.shop/]zyban cheapest[/url] [url=https://sildenafilxd.com/]cheapest online sildenafil[/url] [url=https://cymbaltatabs.monster/]best price for cymbalta[/url]
-
[url=https://happypharmacy.quest/]northwestpharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://tretinoin.click/]tretinoin gel prices[/url]
-
[url=http://citalopram.site/]15 mg celexa[/url]
-
what is cialis taken for where to buy cialis with paypal cialis vs levitra
-
[url=https://buyprozac.life/]prozac 10 mg cost[/url]
-
[url=http://vardenafil247.online/]vardenafil generic cost[/url]
-
[url=https://angpharm.com/]generic lasix 40 mg[/url] [url=https://buyprednisone.monster/]buy prednisone 1 mg mexico[/url]
-
[url=https://dexamethasonetab.com/]dexamethasone tablets online[/url]
-
buy generic viagra no prescription generic viagra for sale uk viagra prescription online usa
-
[url=http://neurontin.run/]neurontin 800 pill[/url]
-
[url=http://cymbaltatab.com/]cymbalta 20 mg price[/url]
-
[url=http://trazodone.run/]trazodone 40 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://cymbaltatab.com/]cymbalta 30 mg buy online[/url]
-
[url=http://buyvalacyclovironline.com/]valtrex acyclovir[/url] [url=http://ataraxtab.online/]atarax medication generic[/url] [url=http://buylevitra.monster/]levitra tablet buy online[/url] [url=http://ciprof.quest/]order ciprofloxacin[/url] [url=http://wellbutrintab.shop/]bupropion tablets in india[/url] [url=http://citalopram.site/]citalopram 50 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://synthroidm.online/]cost of synthroid medication[/url]
-
[url=http://buyallopurinol.life/]allopurinol 1000 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://alevitra.com/]order vardenafil[/url]
-
[url=http://elaviltabs.shop/]elavil 100 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://phenergan.site/]phenergan 25 mg tablets australia[/url]
-
[url=http://phenergan.site/]phenergan otc[/url]
-
[url=http://bactrim.fun/]purchase bactrim online[/url]
-
[url=http://drugstores.monster/]canadapharmacy24h[/url]
-
[url=http://diclofenactab.quest/]diclofenac 100 mg gel[/url]
-
[url=https://cymbaltatabs.monster/]price of cymbalta 60 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://wellbutrintab.shop/]zyban bupropion[/url] [url=https://tadalafilx.monster/]buy cialis in canada[/url]
-
[url=http://cephalexin.site/]cephalexin 125 mg[/url] [url=http://albuteroltab.online/]albuterol medicine india[/url] [url=http://buylisinoprilwithoutprescription.com/]zestril 40 mg[/url] [url=http://stromectol.run/]stromectol prices[/url] [url=http://accutanetabs.shop/]buy generic accutane 40 mg[/url] [url=http://buylexapro.monster/]generic lexapro india[/url] [url=http://cymbaltatab.com/]cymbalta coupon[/url] [url=http://buysildenafil.life/]sildenafil cost in india[/url]
-
[url=http://worldpharmacy.monster/]no rx pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://diflucanfluconazole.org/]diflucan generic cost[/url]
-
[url=http://buytetracycline.life/]tetracycline 500 mg tablet[/url] [url=http://angpharm.com/]lasix brand name in india[/url] [url=http://alevitra.com/]cheap vardenafil 20mg[/url] [url=http://bbviagra.com/]viagra prescription cost canada[/url]
-
[url=https://sildenafiltabs.shop/]sildenafil cost uk[/url]
-
[url=http://synthroidm.online/]112 mg synthroid[/url]
-
[url=https://buyprednisone.monster/]steroids prednisone for sale[/url]
-
where can i get viagra online viagra 50 mg tablet price generic viagra lowest prices
-
[url=http://buyallopurinol.life/]allopurinol 300 mg daily[/url] [url=http://fluoxetinetab.com/]prozac for sale canada[/url] [url=http://buylevitra.monster/]levitra canadian pharmacy[/url] [url=http://diflucantab.shop/]diflucan drug[/url]
-
[url=https://bactrimd.online/]bactrim 800 mg 160 mg[/url] [url=https://sildenafiltabs.shop/]over the counter viagra online[/url] [url=https://accutanetabs.shop/]buy roaccutane[/url] [url=https://stromectol.run/]ivermectin 3mg dosage[/url] [url=https://paxiltab.online/]paxil for ocd[/url] [url=https://finpecia.fun/]finasteride 5mg nz[/url] [url=https://buysildenafil.life/]how to buy viagra online uk[/url]
-
[url=http://stromectol.run/]ivermectin lotion cost[/url]
-
where to buy cialis in singapore tadalafil overnight delivery tadalafil for sale cheap
-
[url=https://buydrugstore.life/]online pharmacy no presc uk[/url]
-
[url=https://onlinepharmacyd.quest/]pharmacy online australia free shipping[/url]
-
walmart pharmacy bactrim avandia rems pharmacy cialis lloyds pharmacy
-
[url=http://onlinepharmacyd.quest/]pharmacy mall[/url]
-
[url=http://buylisinoprilwithoutprescription.com/]buying lisinopril online[/url]
-
[url=http://albuteroltab.online/]buy ventolin inhaler without prescription[/url]
-
buy cheap sildenafil online uk generic viagra prescription cheap generic viagra online pharmacy
-
[url=https://crm-moskva.ru/]CRM система[/url]
crm_система помогает ужас утрачивать клиентов. Ставить темы клеркам компашки, иметь в запасе базу кдиентов, соединять о их данные.
CRM система -
[url=http://lipitoratorvastatin.shop/]cheap lipitor prescription[/url]
-
cialis black pills cialis none prescription cialis picture
-
viagra online sales where can i get viagra 200 mg sildenafil
-
[url=https://stromectoltab.monster/]order stromectol[/url]
-
[url=https://prednisonerx.monster/]200 mg prednisone[/url]
-
[url=http://albuteroltab.online/]ventolin mexico[/url]
-
[url=https://paxiltab.online/]paxil medication[/url]
-
[url=http://diflucantab.shop/]diflucan nz[/url]
-
sildenafil online singapore female viagra tablets in india viagra 100 mg tablet price in india
-
[url=http://propecia.click/]propecia india[/url] [url=http://bbviagra.com/]viagra price in india online purchase[/url] [url=http://cymbaltatabs.monster/]cymbalta generic 60 mg[/url] [url=http://buytrazodone.life/]best generic trazodone prescription[/url] [url=http://phenergan.site/]phenergan 6.25 mg[/url] [url=http://ampicillin.icu/]ampicillin pill 500mg[/url] [url=http://propeciatabs.online/]best price generic propecia[/url]
-
[url=http://orlistat.cfd/]orlistat for weight loss[/url]
-
[url=http://dapoxetine.site/]avana pill[/url] [url=http://angpharm.com/]furosemide 160mg daily[/url] [url=http://benicartab.shop/]benicar 20 mg tablet[/url] [url=http://buytrazodone.life/]trazodone 50mg[/url] [url=http://wellbutrintab.shop/]where to buy bupropion[/url]
-
[url=http://happypharmacy.quest/]online shopping pharmacy india[/url]
-
[url=http://wellbutrina.monster/]wellbutrin 1200 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://finpecia.fun/]propecia canada[/url]
-
[url=http://stromectoltab.monster/]ivermectin 2mg[/url]
-
[url=https://neurontin.run/]gabapentin 300 capsule[/url]
-
[url=http://viagrabro.com/]can i buy viagra over the counter australia[/url]
-
[url=https://pharmacynx.com/]canadian pharmacy uk delivery[/url]
-
[url=https://sildenafilpropills.com/]150 mg generic viagra[/url] [url=https://onlinepharmacyd.quest/]international online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://cephalexin.site/]cephalexin price in india[/url]
-
[url=https://diflucantab.shop/]diflucan cream otc[/url]
-
[url=https://propecia.click/]propecia 5mg australia[/url]
-
[url=http://tadalafilx.monster/]10mg cialis cost[/url]
-
[url=https://buylexapro.monster/]cheap generic lexapro online[/url]
-
[url=https://dapoxetine.site/]dapoxetine generic in india[/url]
-
[url=http://accutanex.online/]accutane over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://trustedpharmacy.quest/]family care rx pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://trazodone.run/]buy trazodone uk[/url]
-
[url=https://alevitra.com/]buy levitra online europe[/url] [url=https://malegratabs.quest/]malegra 25[/url] [url=https://neurontin.sbs/]neurontin 300 mg cost[/url]
-
[url=http://dexamethasonetab.com/]dexamethasone 1.5 tablet[/url]
-
[url=https://angpharm.com/]can you buy furosemide over the counter tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://accutanetabs.shop/]how much is accutane[/url]
-
[url=http://onlinedrugstore.click/]cheapest online pharmacy india[/url]
-
[url=https://vitalypol.ru/]Игольчатый РФ лифтинг[/url]
Радиоволновая подтяжка кожи – потребованная косметологическая услуга. А ТАКЖЕ сегодня симпатия представлена клиентам клиник яко модернизированная, усовершенствованная. Язык о обобщении древнего подхода раз-два современным.
Игольчатый РФ лифтинг -
[url=https://wellbutrintab.shop/]wellbutrin price australia[/url]
-
[url=http://phenergan.site/]cost of phenergan tablets[/url]
-
were can i buy cialis cialis debit card cialis for bph reviews
-
sildenafil tablets where to buy 100mg sildenafil online canada generic viagra
-
[url=http://finpecia.fun/]buy propecia in usa[/url]
-
[url=http://aurogra.fun/]aurogra 100 prices[/url]
-
[url=http://buyprednisone.life/]canadian pharmacy prednisone[/url]
-
[url=https://tadalafilx.monster/]cheap 10 mg tadalafil[/url] [url=https://propeciatabs.online/]buy propecia without a prescription[/url] [url=https://buyallopurinol.life/]allopurinol 20 mg[/url] [url=https://pharmacynx.com/]trust pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://buyprozac.life/]fluoxetine10mg[/url]
-
cialis 200 mg. cialis no perscrption buying cialis with dapoxetine
-
[url=http://buysildenafil.life/]100mg viagra[/url]
-
canadian pharmacy generic provigil tesco pharmacy zovirax people's pharmacy ambien
-
[url=http://benicartab.shop/]benicar 2019[/url]
-
[url=http://ciprofloxacin.fun/]price ciprofloxacin 500mg[/url]
-
[url=https://buytrazodone.life/]trazodone 100 mcg[/url]
-
spierx tadalafil cialis tolerance alternatives to cialis
-
[url=https://sildenafilxd.com/]buy sildenafil mexico[/url]
-
[url=https://antabusetabs.com/]best online no prescription antabuse[/url] [url=https://sildenafilxd.com/]viagra cost in canada[/url] [url=https://malegratabs.quest/]buy malegra 100 online[/url]
-
[url=http://acyclovira.com/]zovirax capsule[/url]
-
[url=https://buyprednisone.monster/]prednisone 50 tablet[/url]
-
[url=http://albuteroltab.online/]ventolin nebules[/url]
-
[url=http://lasixtb.com/]lasix 12.5[/url] [url=http://sildenafilpropills.com/]online viagra cost[/url]
-
[url=https://amitriptylinetab.com/]endep 20mg[/url]
-
[url=http://vardenafil247.online/]price of levitra[/url]
-
[url=http://worldpharmacy.monster/]rx pharmacy coupons[/url]
-
[url=https://cipro.run/]buy cipro online no prescription[/url] [url=https://sildenafiltabs.shop/]genuine viagra tablets[/url] [url=https://modafiniltab.net/]modafinil 2019[/url] [url=https://azithromycinc.online/]order azithromycin 500mg[/url] [url=https://tretinoin.click/]retin a pharmacy[/url] [url=https://finpecia.fun/]propecia how to get prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://valacyclovirvaltrex.online/]where can i get valtrex over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://diclofenactab.quest/]diclofenac in india[/url]
-
[url=https://orlistat.cfd/]xenical cost uk[/url]
-
most reliable online pharmacy viagra sam's club pharmacy propecia online pharmacy uk tadalafil
-
[url=http://prednisonetabs.shop/]steroid prednisone[/url]
-
[url=http://buysildenafil.life/]best price genuine viagra[/url]
-
[url=http://buymodafinil.life/]online pharmacy modafinil uk[/url]
-
[url=https://buyviagrapl.com/]how to buy viagra no prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://happyonlinedrugstore.monster/]mail order pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://azithromycina.net/]can you buy azithromycin without a prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://viagrabro.com/]female viagra tablets price in india[/url] [url=http://ciprofloxacin.fun/]ciprofloxacin 500mg price[/url] [url=http://diclofenactab.quest/]voltaren gel rx[/url] [url=http://antabuse.icu/]antabuse substitute[/url]
-
[url=http://valacyclovirvaltrex.online/]valtrex tablet[/url]
-
[url=http://modafiniltab.net/]modafinil generic canada[/url]
-
[url=http://buytrazodone.life/]desyrel generic[/url] [url=http://ciprof.quest/]cipro antibiotic where to buy[/url] [url=http://buyprednisone.monster/]prednisone 5 mg tablet[/url] [url=http://dapoxetine.site/]buy canadian dapoxetine without prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://tretinoin.click/]retin a from mexico[/url]
-
[url=https://antabuser.online/]disulfiram online[/url]
-
[url=https://wellbutrin.sbs/]buy bupropion no prescription online canada[/url]
-
clomid cvs pharmacy purchase phentermine online pharmacy uk online pharmacy propecia
-
[url=https://furosemidetab.quest/]2 furosemide[/url]
-
[url=https://jshdznkj.com]vulcan vegas site[/url]
Withdrawal to the show-card of any bank. No property, no commission, no additional payments. Fall-off 120 and gather 3000 overnight. And get Tops with Vulcan Vegas
vulkan vegas seite -
[url=http://buysildenafil.life/]150 mg generic viagra[/url]
-
[url=http://bactrim.fun/]bactrim prices[/url]
-
[url=https://preduprezhdajushhie-znaki.ru/]Предупреждающие знаки[/url]
Для этого, чтоб справиться указательи предотвращения прямоугольными в форме треугольника, их усеивают белое вино расцветкой с портвеым кантом.
Предупреждающие знаки -
[url=https://tretinoin.click/]tretinoin 0.1 coupon[/url] [url=https://synthroidm.online/]synthroid levothyroxine[/url] [url=https://deltasoneprednisone.shop/]prednisone canadian[/url] [url=https://buyretinoa.monster/]retino 0.5 cream price[/url] [url=https://buylexapro.monster/]lexapro xanax[/url] [url=https://trazodone.run/]trazodone uk prescription[/url] [url=https://stromectol.run/]stromectol generic[/url] [url=https://cephalexin.site/]cephalexin 100mg[/url]
-
[url=http://xtadalafil.online/]cialis 20mg price in india online[/url] [url=http://buylisinoprilwithoutprescription.com/]zestril online[/url] [url=http://buymodafinil.life/]where to buy modafinil usa[/url] [url=http://buysildenafil.life/]100mg viagra price[/url]
-
[url=http://buymodafinil.life/]buy modafinil uk paypal[/url]
-
[url=https://dubcova.blog.idnes.cz/redir.aspx?url=https://jshdznkj.com]vulkan vegas seite[/url]
[url=http://cartoonporncomics.net/dtr/link.php?gr=12&id=689fd8&url=https://jshdznkj.com]vulkan vegas seite[/url]
[url=https://xn--80aaeu5bjei6b1cza.xn--p1ai/bitrix/click.php?goto=https://jshdznkj.com]vulkan vegas seite[/url]
[url=https://ipmatika.kz/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://jshdznkj.com]vulkan vegas seite[/url]
[url=http://www.mgfamiliar.info/Redirect.aspx?destination=https://jshdznkj.com]vulkan vegas seite[/url]
[url=http://josesmithjr.com/searchpoint/redir.asp?reg_id=ptypes&sname=/searchpoint/search.asp&lid=1&sp>vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite
vulkan vegas seite -
[url=https://jshdznkj.com]slots mit kaufbonus[/url]
Bonuses and promotions at Vulkan Vegas casino. Online casino Vulkan, divergent from most of its competitors, does not shower its customers with a huge number of promotions.
vulcan vegas bonus -
[url=https://wellbutrina.monster/]bupropion cost uk[/url] [url=https://bactrimd.online/]bactrim cost[/url] [url=https://synthroidlevothyroxine.shop/]synthroid 132 mg[/url] [url=https://azithromycinc.online/]azithromycin 500 price in india[/url] [url=https://xtadalafil.online/]cilais[/url]
-
[url=http://lasixtb.com/]furosemide 40 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://wellbutrintab.shop/]bupropion united states[/url]
-
[url=https://sildenafilpropills.com/]where to get cheap viagra[/url]
-
[url=http://buylexapro.monster/]generic lexapro online[/url]
-
[url=https://onlinedrugstore.click/]canadian pharmacy meds[/url]
-
[url=https://neurontin.run/]brand gabapentin[/url]
-
[url=https://phenergan.site/]phenergan 2 cream[/url]
-
[url=http://buydrugstore.life/]usa pharmacy[/url] [url=http://antabusetabs.com/]antabuse without prescription[/url] [url=http://prednisolonep.com/]where can i buy prednisolone uk[/url] [url=http://ciprof.quest/]ciprofloxacin 250 tablet[/url] [url=http://buyvalacyclovironline.com/]buy valtrex 500 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://synthroidlevothyroxine.shop/]synthroid 0.025[/url]
-
[url=https://propeciatabs.online/]cheap propecia[/url]
-
[url=http://amitriptylinetab.com/]amitriptyline uk[/url]
-
[url=https://benicartab.shop/]benicar brand name coupon[/url]
-
[url=https://drugstores.monster/]online pharmacy australia paypal[/url]
-
[url=https://accutanetabs.shop/]accutane 40003395956[/url]
-
[url=http://alevitra.com/]levitra buy online india[/url]
-
[url=https://azithromycina.net/]azithromycin generic brand[/url]
-
[url=http://worldpharmacy.monster/]reliable online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://azithromycinc.online/]zythromax[/url]
-
[url=http://dexamethasonetab.com/]dexona[/url]
-
[url=http://valacyclovirvaltrex.online/]can you buy valtrex over the counter in australia[/url]
-
[url=https://diflucantab.shop/]over the counter diflucan 150[/url]
-
[url=http://fluoxetinetab.com/]prozac 2019[/url]
-
[url=http://viagrabro.com/]viagra from mexico to us[/url]
-
[url=https://dexamethasonetab.com/]dexamethasone tablets cost[/url]
-
[url=https://cipro.live/]purchase cipro online[/url]
-
[url=http://onlinedrugstore.click/]happy family store pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://sildenafilxd.com/]sildenafil gel uk[/url]
-
[url=http://drugstores.monster/]us pharmacy no prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://tretinoin.click/]best retin a prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://modafinilp.shop/]buy provigil from canada[/url]
-
[url=http://buyvalacyclovironline.com/]price of valtrex[/url] [url=http://neurontin.run/]gabapentin 800 mg cost[/url] [url=http://antabusetabs.com/]disulfiram antabuse[/url] [url=http://phenergan.site/]phenergan tablets otc[/url] [url=http://trustedpharmacy.quest/]escrow pharmacy online[/url] [url=http://malegratabs.quest/]malegra dxt without prescription[/url] [url=http://sildenafilxd.com/]generic viagra 50mg online[/url]
-
can hydrocodone be called into pharmacy viagra utah pharmacy phentermine online pharmacy canada
-
[url=http://dexamethasonetab.com/]dexamethasone 8 mg tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://cipro.live/]ciprofloxacin sale online[/url]
-
[url=https://cipro.live/]cipro cost[/url] [url=https://buyprednisone.monster/]how to get prednisone prescription[/url] [url=https://diflucana.com/]buy diflucan online without prescription[/url] [url=https://vardenafil247.online/]generic levitra online cheap[/url] [url=https://angpharm.com/]furosemide 50 mg[/url] [url=https://antabuser.online/]disulfiram uk[/url] [url=https://fluoxetinetab.com/]how to buy fluoxetine online without prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://buyprednisone.monster/]prednisone 20 mg generic[/url] [url=https://malegratabs.quest/]malegra fxt in india[/url] [url=https://buyallopurinol.life/]allopurinol over the counter usa[/url] [url=https://propecia.click/]propecia generic price[/url] [url=https://bbviagra.com/]generic viagra 50mg canada[/url] [url=https://neurontin.sbs/]gabapentin order online[/url] [url=https://lipitoratorvastatin.shop/]lipitor cost canada[/url]
-
what is cialis prescribed for cialis generic online cialis shelf life
-
[url=http://buyprednisone.monster/]prednisone 30g[/url]
-
[url=https://trazodone.run/]trazodone 50 mg tablet brand name[/url]
-
[url=http://lipitoratorvastatin.shop/]buy lipitor 40 mg[/url]
-
buy levitra without prescription generic levitra suppliers levitra walgreens
-
[url=https://buymotrin.monster/]motrin 600 prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://buyfildena.life/]fildena 100 mg online[/url]
-
buy viagra cialis online cialis 40mg can i take 40mg of cialis
-
cialis pricing cheap generic cialis online cialis black without prescription
-
[url=http://plavixtab.online/]plavix 100mg[/url]
-
[url=https://ordertadalafiltablets.com/]cialis brand name[/url]
-
[url=https://buylevitra.quest/]levitra prices canada[/url]
-
[url=https://onaka-chewable.com/shop/display_cart?return_url=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1xbet kz[/url]
[url=http://oscarpages.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1xbet kz[/url]
[url=http://pop-bookmarks.win.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1xbet kz[/url]
[url=https://maps.sandbox.google.co.in/url?sa=t&url=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1xbet kz[/url]
[url=http://baza.vds.pl/esklep/redir.asp?WenId=9&WenUrllink=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1xbet kz[/url]
[url=https://hokej.idnes.cz/hokejove-ms-cesko-vs-francie-d1w-/redir.aspx?url=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1xbet kz[/url]
[url=http://www.allshavedgals.com/cgi-bin/atc/out.cgi?id=45&l=tpom&u=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1xbet kz[/url]
[url=https://shaomatongji.17173.com/pv?url=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1xbet kz[/url]
[url=http://www.moebeldepot.at/include/pages/redirect/redirect.php?type=link&url=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1xbet kz[/url]
[url=http://worthseal.com/redirect.php?url=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1xbet kz[/url]
[url=https://www.katz-stb.de/ext_link?url=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1xbet kz[/url]
[url=https://maximumassetprotection.com/?URL=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1xbet kz[/url]
[url=https://ronl.org/redirect?url=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1xbet kz[/url]
[url=http://www.argia.com/adserver/adclick.php?bannerid=510&z>1xbet kz
1xbet kz
1xbet kz
1xbet kz
1xbet kz
1xbet kz
1xbet kz
1xbet kz
1xbet kz
1xbet kz
1xbet kz
1xbet kz
1xbet kz
1xbet kz
1xbet kz -
[url=http://modafinilb.online/]modafinil australia prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://plavixtabs.quest/]buy generic plavix online[/url]
-
[url=https://1-xbet-kz-apk.com]1-xbet-kz-apk com[/url]
1xbet is the same of the largest bookmakers in the world. She cooperates with many virtuous organizations. This is notably true for football.
1xbet вход -
valium europe pharmacy playa del carmen pharmacy viagra permethrin cream online pharmacy
-
[url=http://prozactab.monster/]fluoxetine 10 mg buy online[/url] [url=http://arimidex.site/]where to get arimidex in canada[/url] [url=http://noroxintabs.quest/]noroxin pill[/url] [url=http://valtrexvalacyclovir.shop/]valtrex 400 mg[/url] [url=http://dexamethasonetab.online/]dexamethasone drug[/url] [url=http://hydroxychloroquinetab.shop/]plaquenil medicine[/url]
-
[url=https://dexametasone.online/]dexamethasone medication[/url]
-
[url=https://buyfildena.life/]fildena 100 for sale[/url] [url=https://pharmacies.monster/]best value pharmacy[/url] [url=https://albuterolv.online/]combivent inhaler instructions[/url] [url=https://cialis365.com/]cialis 20mg price in india online[/url]
-
[url=https://priligy.run/]priligy australia cost[/url]
-
[url=https://deltasonetab.online/]where can i buy prednisone[/url] [url=https://clopidogrelplavix.shop/]plavix 75mg tablets[/url] [url=https://buyvaltrex.life/]cost for valtrex[/url] [url=https://tretinointabs.quest/]tretinoin online pharmacy[/url] [url=https://noroxintabs.quest/]noroxin 500 mg[/url]
-
your pharmacy ibuprofen canada pharmacy online xanax lidocaine canadian pharmacy
-
[url=https://trazodonedesyrel.shop/]trazodone 15 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://tretinointabs.quest/]retin a price in mexico[/url]
-
[url=http://bupropiontabs.shop/]bupropion 225 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://lasixtabs.shop/]order lasix 40 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://neurontin.life/]neurontin 100 mg cost[/url]
-
[url=http://cialis365.com/]cost of cialis generic[/url]
-
[url=http://lexaproescitalopram.shop/]purchase lexapro generic[/url] [url=http://suhagratabs.online/]suhagra[/url] [url=http://buypriligy.monster/]cheap priligy[/url]
-
[url=https://buylipitor.life/]lipitor 80 mg daily[/url]
-
[url=http://buyclopidogrel.life/]clopidogrel prescription[/url] [url=http://lasixtabs.shop/]furosemide without prescription[/url] [url=http://orderviagratabs.com/]viagra 100mg price in australia[/url]
-
[url=http://buyadvair.life/]generic advair price[/url]
-
[url=https://sildenafilgenericviagra.com/]can i buy viagra in india[/url] [url=https://neurontin.life/]neurontin 800[/url] [url=https://atenolol.cfd/]atenolol pills[/url]
-
[url=https://lipitoratorvastatin.online/]lipitor pfizer[/url]
-
[url=https://abilifytab.online/]500mg abilify[/url]
-
[url=http://arimidex.site/]generic arimidex for sale[/url]
-
[url=http://lasixtabs.shop/]buy lasix water pill[/url]
-
[url=https://flomax.run/]flomax price in india[/url]
-
[url=http://amoxil.click/]augmentin 875 price[/url]
-
[url=http://seroqueltabs.com/]seroquel for insomnia[/url] [url=http://trazodonex.online/]trazodone 25 mg brand name[/url] [url=http://priligy.life/]dapoxetine tablets 30 mg in india[/url] [url=http://lexaprotab.com/]lexapro brand name cost[/url] [url=http://ampicillin.run/]ampicillin online[/url] [url=http://stratteratab.com/]strattera india price[/url] [url=http://domperidone.fun/]motilium 100 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://afinasteride.online/]order propecia uk[/url]
-
[url=http://lexaproescitalopram.shop/]lexapro price south africa[/url]
-
[url=https://dexametasone.online/]dexamethasone for sale[/url]
-
[url=https://zoloftx.online/]zoloft discount[/url]
-
[url=http://albendazole.life/]where to order albendazole[/url]
-
[url=http://buylevitra.quest/]levitra canadian online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://cialis365.com/]purchase cialis[/url]
-
[url=http://lexaproescitalopram.shop/]lexapro 80mg[/url]
-
[url=https://buyvaltrex.life/]valtrex prices[/url]
-
[url=https://priligy.run/]generic priligy uk[/url]
-
[url=https://toradol.site/]how to get toradol[/url]
-
[url=https://stratteratab.com/]strattera 40 mg pills generic[/url] [url=https://avana.run/]avana[/url] [url=https://buypriligy.monster/]priligy for sale uk[/url] [url=https://lexaprotab.com/]lexapro for sale uk[/url] [url=https://cialis365.com/]buy tadalafil 20[/url] [url=https://buyclopidogrel.monster/]average cost of plavix[/url]
-
[url=https://escitalopramlexapro.online/]buy lexapro brand name online[/url]
-
[url=https://orderviagratabs.com/]female viagra canada[/url]
-
[url=http://buymotrin.monster/]motrin 9466[/url] [url=http://zoloftx.online/]can i buy zoloft online[/url] [url=http://trazodonedesyrel.shop/]generic trazodone 50 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://clonidine.run/]clonidine 10 mg[/url] [url=https://dutasteride.cfd/]avodart pharmacy uk[/url] [url=https://dexametasone.online/]dexamethasone 4 mg[/url] [url=https://trazodonedesyrel.shop/]trazodone 50mg tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://suhagra.sbs/]suhagra 100 price[/url] [url=http://tamoxifen.sbs/]tamoxifen brand name[/url] [url=http://buyaugmentin.life/]augmentin 1000 price india[/url] [url=http://buybactrim.life/]bactrim 800 mg[/url] [url=http://provigiltabs.quest/]modafinil online canada[/url] [url=http://tretinointabs.quest/]tretinoin cream discount[/url]
-
[url=https://azithromycin.run/]azithromycin 500 mg tablet[/url]
-
[url=https://domperidone.fun/]motilium medicine[/url] [url=https://modafinilb.online/]where to buy modafinil canada[/url] [url=https://albuterolv.online/]cheap albuterol inhalers[/url] [url=https://avanadapoxetine.online/]buy dapoxetine paypal[/url]
-
[url=http://buyvaltrex.life/]order valtrex online uk[/url]
-
[url=https://abilifytab.online/]abilify 5mg[/url] [url=https://cephalexinv.com/]where can i buy keflex[/url]
-
[url=https://valtrexvalacyclovir.shop/]valtrex online australia[/url] [url=https://arimidex.site/]buy arimidex canada[/url] [url=https://dexametasone.online/]dexamethasone 80 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://lexaprotab.com/]lexapro prices[/url]
-
[url=https://afinasteride.online/]propecia cost australia[/url]
-
[url=http://buylevitra.quest/]generic levitra mexico[/url]
-
[url=http://priligy.run/]dapoxetine hcl[/url]
-
[url=http://lexaproescitalopram.shop/]lexapro 40 mg tablet[/url]
-
[url=https://priligytab.monster/]priligy price in usa[/url] [url=https://trazodonedesyrel.shop/]desyrel 50 mg tablet[/url] [url=https://orderviagratabs.com/]viagra soft gel[/url] [url=https://buymotrin.monster/]motrin tablet price[/url] [url=https://prozactab.online/]buy generic prozac[/url] [url=https://buyadvair.life/]advair lowest price[/url] [url=https://buyclopidogrel.life/]plavix coupon[/url]
-
[url=https://amoxil.click/]buy augmentin 1000 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://sildalis.run/]sildalis without prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://things-to-do-near-me-en.com]things-to-do-near-me-encom[/url]
Find things to do near you. Explore the top-rated attractions, tours, and activities not far-off and comprehend reviews from Tripadvisor travelers.
fun things to do near me -
[url=https://pharmacygrand.com/]canadian pharmacy ltd[/url]
-
[url=http://buyfildena.life/]fildena[/url]
-
[url=http://fildenatab.shop/]fildena 200[/url]
-
[url=https://priligy.life/]how to get priligy[/url]
-
[url=https://sosnitikg.dp.ua/]sosnitikg[/url]
Ездит ювелирно а также небыстро. Накиньте это сообщение в течение Лучшее, чтобы счета утратить! Отыскивайте нас по запросам: Передача, стан микроавтобуса, аренда микроавтобуса ...
sosnitikg -
[url=http://toradol.site/]buy toradol online canada[/url]
-
[url=http://viagra120.com/]viagra price list[/url]
-
[url=http://lasixtabs.shop/]can i buy furosemide online[/url]
-
[url=https://noroxintabs.quest/]noroxin pill[/url]
-
[url=https://suhagra.sbs/]suhagra 100 for sale[/url]
-
[url=http://suhagra.sbs/]suhagra pills[/url]
-
[url=https://prozactab.monster/]fluoxetine medicine in india[/url]
-
[url=https://trazodonedesyrel.shop/]trazodone brand[/url]
-
[url=https://bactrimtab.com/]purchase bactrim ds[/url]
-
[url=https://tretinointabs.quest/]tretinoin 1 gel[/url]
-
[url=http://tetracyclinewithoutprescription.com/]terramycin eye ointment for humans[/url]
-
[url=https://buyclopidogrel.monster/]plavix medication[/url]
-
[url=https://plavixtabs.quest/]cost of generic clopidogrel[/url] [url=https://citalopram.click/]celexa 40mg tab[/url] [url=https://advairtab.online/]advair diskus 250[/url] [url=https://tretinointabs.quest/]buy tretinoin cream uk[/url]
-
[url=https://happyfamilyrx.monster/]online pharmacy no prescription needed[/url] [url=https://kamagratab.online/]kamagra oral jelly online australia[/url] [url=https://cialis365.com/]online cialis prescription canada[/url] [url=https://buypriligy.monster/]priligy price in south africa[/url] [url=https://pharmacies.monster/]legal online pharmacies in the us[/url] [url=https://levitratab.shop/]price of levitra in india[/url] [url=https://buyantabuse.life/]antabuse ordering[/url] [url=https://plavixtab.online/]clopidogrel generic[/url]
-
canada drug superstore [url=http://www.canadotcphar.com/]canadian pharmacy with viagra[/url] my canadian pharcharmy online
cheap generic viagra online cialis pharmacy cialis canadian pharmacies -
[url=http://plavixtab.online/]plavix price comparison[/url] [url=http://trustedpharm.online/]canadian pharmacy sildenafil[/url]
-
[url=http://lexaproescitalopram.shop/]purchase brand name lexapro[/url] [url=http://plavixtab.online/]plavix 70 mg[/url] [url=http://trustedpharm.online/]canadian pharmacy world[/url] [url=http://buylipitor.life/]buying lipitor online[/url] [url=http://viagra120.com/]genuine viagra canada[/url] [url=http://celexatab.online/]order citalopram[/url]
-
[url=https://valtrexvalacyclovir.shop/]valtrex drug[/url]
-
[url=http://furosemidetabs.shop/]buying lasix online[/url]
-
[url=https://abilifytab.online/]abilify 15 mg tablet[/url]
-
[url=https://lexaproescitalopram.shop/]lexapro tablets australia[/url]
-
[url=https://amoxil.click/]cost of augmentin in india[/url]
-
[url=http://hydroxychloroquinetab.shop/]hydroxychloroquine 90[/url] [url=http://buycipro.life/]ciprofloxacin canada[/url] [url=http://clopidogrelplavix.shop/]online plavix[/url]
-
[url=https://dexametasone.online/]4 dexamethasone[/url] [url=https://deltasonetab.online/]generic prednisone online[/url] [url=https://cephalexinv.com/]cephalexin 250mg price[/url] [url=https://noroxintabs.quest/]generic noroxin[/url]
-
[url=http://buyclopidogrel.monster/]plavix brand name price[/url]
-
[url=http://valtrexd.quest/]where to buy valtrex over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://priligy.life/]dapoxetine tablets 60 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://buyaugmentin.life/]buy augmentin online[/url] [url=http://prozactab.online/]fluoxetine 20mg capsules no prescription[/url] [url=http://plavixtabs.quest/]plavix uk price[/url] [url=http://suhagra.sbs/]suhagra 25 mg buy online india[/url] [url=http://doxycyclinep.com/]cost doxycycline tablets uk[/url]
-
[url=https://buyvaltrex.life/]valtrex 1g cost[/url]
-
[url=http://sildalis.run/]sildalis[/url]
-
[url=http://clindamycintab.online/]clindamycin drug[/url]
-
[url=https://buyaugmentin.life/]amoxicillin 500mg capsules for sale[/url]
-
[url=https://plavixtabs.quest/]buying plavix online[/url] [url=https://dexamethasonetab.online/]dexamethasone 1 mg[/url] [url=https://arimidex.site/]arimidex cost in singapore[/url] [url=https://retinoatabs.online/]retino gel[/url] [url=https://bactrimtab.com/]where to buy bactrim online[/url] [url=https://ventolintabs.com/]ventolin 200 mg[/url] [url=https://pharmacies.quest/]best canadian pharmacy[/url] [url=https://buycipro.life/]cipro online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://suhagra.sbs/]suhagra tablet price[/url] [url=http://tamoxifen.sbs/]tamoxifen 50 mg[/url] [url=http://hydroxychloroquinetab.shop/]hydroxychloroquine 1mg[/url] [url=http://citalopram.click/]citalopram 0.5 mg[/url] [url=http://abilifytab.online/]abilify 2.5[/url] [url=http://dutasteride.cfd/]avodart medicine online[/url] [url=http://acutane.monster/]accutane canadian pharmacy[/url] [url=http://amoxicillinx.com/]augmentin canada pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://cleocin.cfd/]cleocin cream coupon[/url]
-
[url=https://suhagra.sbs/]suhagra 50 mg price[/url]
-
[url=https://book-transfer-usa.com/]Car rental in the USA[/url]
America is a territory for traveling nigh car. If you miss to rental a transport in the США, then it is richer reconsider to do it in your homeland, so you can definitely fee a suitable car at the a-one price.
Car rental in the USA -
[url=http://buypriligy.monster/]buy dapoxetine tablets online india[/url]
-
[url=https://deltasonetab.online/]steroid prednisone[/url]
-
[url=http://pregabalinlyrica.shop/]lyrica[/url]
-
[url=http://hydroxychloroquinetab.shop/]buy plaquenil from canada[/url] [url=http://tamoxifen.sbs/]buy nolvadex online no prescription[/url] [url=http://dexametasone.online/]dexamethasone tablet price[/url] [url=http://buyclopidogrel.life/]clopidogrel 75 mg daily[/url] [url=http://advairtab.online/]generic advair canada pharmacy[/url] [url=http://buyadvair.life/]advair diskus over the counter[/url] [url=http://prozactab.monster/]prozac over the counter[/url] [url=http://ventolintabs.com/]albuterol 108 mcg[/url]
-
[url=https://bactrimd.quest/]bactrim 800 160[/url]
-
[url=http://priligy.life/]priligy online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://clopidogrelplavix.shop/]plavix medicine price[/url]
-
[url=https://buyadvair.life/]generic advair coupon[/url]
-
[url=http://kamagratab.online/]erectile dysfunction kamagra oral gel[/url]
-
[url=http://afinasteride.com/]propecia singapore where to buy[/url]
-
[url=https://zofran.click/]zofran uk[/url]
-
[url=https://buyantabuse.life/]antabuse drug[/url] [url=https://buylevitra.quest/]vardenafil best price[/url] [url=https://sildalis.run/]sildalis for sale[/url] [url=https://sildenafilgenericviagra.com/]30 mg sildenafil[/url] [url=https://trazodonex.online/]trazodone 300 mg[/url] [url=https://neurontin.life/]gabapentin 100mg capsules[/url]
-
[url=http://cephalexine.shop/]buy keflex uk[/url]
-
[url=https://buypriligy.monster/]where to get priligy[/url]
-
[url=https://tamoxifen.sbs/]nolvadex nz[/url] [url=https://flomax.run/]flomax 400 mcg[/url] [url=https://citalopram.click/]citalopram 20mg tablets price[/url] [url=https://pregabalinlyrica.shop/]lyrica[/url] [url=https://provigiltabs.quest/]provigil tablets[/url] [url=https://clopidogrelplavix.shop/]clopidogrel 196[/url]
-
[url=https://tetracyclinewithoutprescription.com/]buy tetracycline cream[/url]
-
[url=https://abilifytab.online/]cost of abilify without insurance[/url] [url=https://hydroxychloroquinetab.shop/]plaquenil retinal toxicity[/url] [url=https://plavixtabs.quest/]clopidogrel 75 price[/url] [url=https://buybactrim.life/]order canadian bactrim[/url] [url=https://clindamycintab.online/]clindamycin price mexico[/url] [url=https://malegratabs.online/]malegra 25[/url]
-
[url=http://buysingulair.life/]singulair 10 mg cost[/url]
-
[url=https://priligy.run/]where can i buy priligy online[/url]
-
[url=http://suhagra.sbs/]suhagra[/url]
-
[url=http://buylevitra.quest/]cheap levitra pills[/url]
-
[url=http://fildenatab.shop/]fildena 50[/url]
-
[url=http://buyantabuse.life/]antabuse pills[/url] [url=http://happyfamilyrx.monster/]medical pharmacy south[/url]
-
[url=https://plavixtab.online/]clopidogrel 50 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://doxycyclinep.com/]order doxycycline online canada[/url] [url=https://clopidogrelplavix.shop/]plavix 300 mg daily[/url] [url=https://abilifytab.online/]buy abilify[/url]
-
[url=https://buyaugmentin.life/]amoxicillin cheapest price[/url]
-
[url=http://tretinointabs.quest/]tretinoin 1 cost[/url]
-
[url=http://fildenatab.shop/]fildena 100 for sale[/url]
-
[url=http://buyaugmentin.life/]amoxicillin 20 mg[/url] [url=http://tretinointabs.quest/]buying retin-a online[/url] [url=http://arimidex.site/]arimidex canada[/url] [url=http://ventolintabs.com/]ventolin usa over the counter[/url] [url=http://clopidogrelplavix.shop/]clopidogrel otc[/url] [url=http://plavixtabs.quest/]plavix price south africa[/url] [url=http://trazodonedesyrel.shop/]online trazodone[/url]
-
[url=https://neurontin.life/]buy gabapentin 400mg[/url]
-
[url=https://noroxina.shop/]noroxin 400[/url]
-
[url=http://pharmacies.monster/]express pharmacy[/url] [url=http://domperidone.fun/]motilium price south africa[/url]
-
[url=http://dexamethasonetab.online/]dexamethasone 15 mg[/url] [url=http://pharmacies.quest/]pharmacy order online[/url] [url=http://acutane.monster/]how to get accutane uk[/url] [url=http://buyclopidogrel.life/]clopidogrel canada[/url] [url=http://priligytab.monster/]buy cheap dapoxetine uk[/url] [url=http://trazodonedesyrel.shop/]desyrel medication[/url]
-
[url=https://trustedpharm.online/]legit pharmacy websites[/url]
-
[url=https://celexatab.online/]celexa tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://atarax.click/]atarax for anxiety[/url]
-
[url=http://avanadapoxetine.online/]dapoxetine purchase in india[/url]
-
[url=https://plavixtabs.quest/]plavix cost canada[/url] [url=https://bupropiontabs.shop/]price for generic wellbutrin[/url] [url=https://malegratabs.online/]malegra 50 mg[/url] [url=https://buyadvair.life/]can you buy advair over the counter[/url] [url=https://flomax.run/]flomax 10[/url]
-
[url=https://sosnitikh.dp.ua/]sosnitikh[/url]
вы вырвете информацию числом разборкам автомобилей в течение Москве и Столичной области. НАЧИНАЯ С. ANT. ДО нами легко осуществить автоматизационный поиск б/у запасных частей ...
sosnitikh -
[url=https://buysingulair.monster/]singulair buy india[/url]
-
[url=https://seroqueltab.quest/]seroquel[/url]
-
[url=http://prednisolone247.com/]prednisolone tablets 5mg price[/url]
-
[url=http://priligytabs.shop/]where can i buy dapoxetine in uk[/url]
-
[url=https://clonidinetabs.online/]clonidine 0.1 mg oral tablets online orde[/url] [url=https://piroxicamtab.shop/]feldene medication[/url] [url=https://atarax.run/]atarax prescription[/url] [url=https://synthroidl.online/]synthroid 137[/url] [url=https://azithromycinz.shop/]buy azithromycin 500[/url] [url=https://priligytabs.shop/]dapoxetine where can i buy[/url] [url=https://provigiltabs.online/]modafinil generic canada[/url]
-
[url=http://buycelexa.monster/]citalopram prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://suhagra.icu/]suhagra 150 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://indocin.icu/]indocin 50 mg tab[/url]
-
[url=https://paxil.fun/]paxil purchase online[/url]
-
[url=https://stratteraatomoxetine.shop/]purchase strattera online[/url]
-
[url=https://viarga.shop/]buy sildenafil generic[/url]
-
[url=http://buyazithromycin.monster/]azithromycin tablets price in india[/url]
-
[url=http://clonidinetabs.online/]clonidine 0.5[/url]
-
[url=http://effexor.sbs/]effexor 37.5[/url]
-
[url=http://erythromycin.life/]erythromycin drug[/url]
-
[url=https://medrol.cfd/]online pharmacy medrol with no prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://disulfiram.cfd/]buy antabuse online cheap[/url]
-
[url=https://arimidextabs.online/]arimidex pills buy[/url]
-
[url=https://celebrextab.online/]cost of celebrex 100 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://tadalafil2023.com/]cheap cialis mexico[/url] [url=http://trustedtablets.coupons/]onlinecanadianpharmacy 24[/url] [url=http://provigiltabs.online/]modafinil for sale south africa[/url] [url=http://medrol.cfd/]medrol 16mg[/url] [url=http://augmentintabs.monster/]generic augmentin cost[/url] [url=http://prednisone247.com/]indian prednisone without prescription[/url] [url=http://buydiflucan.life/]diflucan buy online usa[/url]
-
[url=https://noroxintab.online/]noroxin brand name[/url]
-
[url=https://albuteroltab.com/]ventolin tablets uk[/url]
-
[url=https://celexacitalopram.online/]cost of brand name celexa[/url]
-
[url=http://neurontinx.com/]neurontin tablets 300 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://clomid.click/]how much is the price of clomid[/url]
-
[url=https://gabapentinz.com/]gabapentin cream[/url]
-
[url=http://glucophage.sbs/]buy metformin online uk[/url]
-
[url=http://inderal.fun/]buy inderal[/url]
-
[url=http://buycelexa.life/]celexa 20 mg price[/url]
-
[url=https://levitratabs.monster/]cheap levitra 40 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://prednisolone247.com/]prednisolone buy online uk[/url] [url=https://lipitor.site/]cost of lipitor[/url] [url=https://buydapoxetine.monster/]avana 100 mg[/url] [url=https://amitriptylinetabs.com/]amitriptyline 25mg cost[/url] [url=https://clindamycina.online/]clindamycin cream brand name in india[/url] [url=https://effexor.sbs/]effexor 187.5 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://allopurinolzyloprim.online/]purchase allopurinol online[/url]
-
[url=https://lipitor.site/]cost of lipitor 20 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://worldpharmacyx.online/]world pharmacy india[/url]
-
[url=https://sildenafiltz.com/]where to buy viagra in canada[/url]
-
[url=http://wellbutrintab.online/]bupropion hydrochloride[/url]
-
[url=https://zoloftsertraline.online/]zoloft generic brand price[/url]
-
[url=https://allopurinolz.online/]allopurinol ordering[/url]
-
[url=http://wellbutrintab.online/]bupropion 300 mg cost[/url]
-
[url=http://buycelexa.monster/]citalopram 20mg pill[/url] [url=http://allopurinolz.online/]buy cheap allopurinol[/url] [url=http://fildena.click/]fildena 100 online india[/url] [url=http://inderal.fun/]inderal 10 mg medicine[/url] [url=http://sildalist.online/]generic sildalis[/url]
-
[url=https://buytretinoin.monster/]tretinoin 1 for sale[/url]
-
[url=http://clindamycina.online/]clindamycin gel australia[/url] [url=http://noroxintab.online/]noroxin without prescription[/url] [url=http://glucophage.sbs/]metformin 10 tablet[/url] [url=http://nolvadex.fun/]tamoxifen 20 mg buy online[/url]
-
[url=http://buykamagra.life/]real kamagra buy[/url] [url=http://sildenafiltz.com/]how can i get viagra in australia[/url] [url=http://ciprof.online/]cipro 250 mg coupon[/url] [url=http://neurontinx.com/]gabapentin uk buy[/url] [url=http://viagra96.com/]women viagra tablet[/url] [url=http://ataraxtab.shop/]atarax tablets[/url] [url=http://celexacitalopram.shop/]citalopram hbr 40 mg tablets[/url]
-
[url=https://suhagra.icu/]suhagra 100mg in india[/url]
-
[url=https://celexacitalopram.shop/]celexa online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://hydroxychloroquinelab.com/]hydroxychloroquine sulfate oval pill[/url]
-
[url=http://buydapoxetine.monster/]dapoxetine without prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://buyadvair.monster/]best price for advair[/url]
-
[url=https://zithromaxtab.monster/]buy zithromax z-pak[/url]
-
[url=http://paxil.run/]how much is paxil[/url]
-
[url=https://uborka-kvartir-cena.ru/]уборка квартир[/url]
Вам далеко не обязательно воспламеняться этим самостоятельно - взвалив экспортирование мусора изо жилплощади профессиональной шатия-братии, ваша милость получите уместное также профессиональное обслуживание.
уборка квартир -
[url=http://neurontinx.com/]gabapentin 1000mg tablet[/url]
-
[url=http://indocin.icu/]medicine indocin 50 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://metformin.click/]buy glucophage online canada[/url]
-
hi opp ggeis 2022 ert go fi
-
[url=https://glucophage.sbs/]purchase metformin 500 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://albuteroltab.com/]buy albuterol online cheap[/url]
-
[url=https://lyrica.sbs/]how much is lyrica cost[/url]
-
[url=http://buyamitriptyline.life/]amitriptyline 10 mg capsules[/url] [url=http://lyrica.sbs/]lyrica cap 100mg[/url] [url=http://buycelexa.monster/]citalopram medication[/url] [url=http://motrintab.online/]motrin 600mg[/url] [url=http://nolvadextab.online/]nolvadex 50mg[/url]
-
[url=https://lyrica.sbs/]buy lyrica from canada[/url]
-
[url=https://prednisonerx.online/]prednisone 1 mg daily[/url] [url=https://singulairtabs.online/]can you get singulair over the counter[/url] [url=https://zoloftsertraline.online/]purchase zoloft online[/url]
-
[url=https://ataraxtab.shop/]atarax 5mg[/url]
-
[url=https://buyatarax.life/]atarax for dogs[/url]
-
[url=http://allopurinolz.online/]allopurinol 10 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://synthroidl.online/]synthroid 112 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://disulfiram.cfd/]antabuse uk pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://piroxicamtab.shop/]feldene gel price uk[/url]
-
[url=https://tamoxifentabs.online/]nolvadex for sale[/url] [url=https://trustedtablets.coupons/]us pharmacy[/url] [url=https://azithromycinz.shop/]order zithromax online[/url] [url=https://priligytabs.shop/]dapoxetine 100 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://suhagra.icu/]suhagra 100 online[/url]
-
[url=https://diclofenactabs.online/]diclofenac otc usa[/url]
-
[url=https://sildalist.online/]sildalis for sale[/url] [url=https://buytetracycline.monster/]where to buy terramycin in canada[/url] [url=https://erectafil.life/]erectafil[/url] [url=https://provigiltabs.online/]where to order modafinil online[/url] [url=https://augmentintabs.monster/]cheap amoxicillin[/url] [url=https://prednisone247.com/]6 prednisone[/url]
-
[url=http://buyadvair.monster/]buy advair[/url] [url=http://hydroxychloroquinelab.com/]buy plaquenil in india[/url] [url=http://buydapoxetine.monster/]over the counter dapoxetine[/url] [url=http://prednisonerx.online/]prednisone 10 mg tablet price[/url] [url=http://neurontinx.com/]gabapentin buy uk[/url] [url=http://viarga.shop/]buy generic viagra from canada[/url]
-
[url=https://lasix247.com/]furosemide 20mg[/url]
-
[url=https://stratteraatomoxetine.shop/]purchase strattera[/url]
-
[url=http://paxil.fun/]paroxetine 30 mg price[/url]
-
[url=http://effexor.sbs/]effexor 75 mg tablets[/url] [url=http://buysingulair.monster/]singulair medicine over the counter[/url] [url=http://singulairtabs.online/]singulair for sinusitis[/url] [url=http://deltasonetabs.monster/]1250 mg prednisone[/url] [url=http://clindamycina.online/]cleocin vaginal ovules[/url]
-
[url=http://buydiflucan.life/]diflucan 150 mg pill[/url] [url=http://prednisone247.com/]medicine prednisone 10mg[/url] [url=http://atarax.run/]atarax uk pharmacy[/url] [url=http://allopurinolzyloprim.online/]allopurinol 300 tablet[/url] [url=http://sildalist.online/]generic sildalis[/url]
-
[url=http://buytetracycline.monster/]tetracycline without prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://viagra96.com/]order viagra mexico[/url]
-
[url=http://atarax.run/]atarax over the counter uk[/url]
-
[url=https://lyrica.sbs/]lyrica 300 mg for sale[/url]
-
[url=https://trustedtablets.sale/]reputable online pharmacy reddit[/url]
-
[url=http://prednisone247.com/]cheap prednisone[/url]
-
[url=https://celexacitalopram.shop/]citalopram 10mg tablets[/url]
-
[url=https://allopurinolz.online/]buy allopurinol 300 mg[/url] [url=https://inderal.fun/]propranolol 100 mg[/url] [url=https://nolvadextab.online/]where to order tamoxifen[/url]
-
[url=https://ataraxtab.shop/]atarax 10[/url]
-
[url=https://diclofenactabs.online/]can i buy voltaren tablets over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://lasix247.com/]how much is furosemide 40 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://buyamitriptyline.life/]amitriptyline discount coupon[/url]
-
[url=http://hydroxychloroquinelab.com/]hydroxychloroquine nz[/url]
-
[url=https://lyricatab.monster/]lyrica cap 50mg[/url]
-
[url=https://allopurinol.life/]allopurinol purchase[/url]
-
[url=http://neurontinx.com/]100 mg gabapentin 100mg[/url]
-
[url=https://advairtabs.online/]advair 250 canada[/url] [url=https://neurontinx.com/]25 mg gabapentin[/url] [url=https://stratteraatomoxetine.shop/]strattera 5mg[/url] [url=https://albuteroltab.com/]ventolin 4mg[/url] [url=https://allopurinol.life/]zyloprim allopurinol[/url] [url=https://effexor.sbs/]buy effexor xr 150mg[/url] [url=https://zoloftsertraline.online/]generic zoloft 25 mg[/url] [url=https://vigra.online/]women cialis[/url]
-
[url=http://clindamycina.online/]cost of clindamycin 300 mg capsule[/url]
-
[url=https://hydroxychloroquinelab.com/]hydroxychloroquine oral[/url]
-
[url=https://ginekolog-dnepr.dp.ua/]Гинеколог Днепр[/url]
инекология, пожалуй, наиболее принципиальная эпир медицины чтобы женщины, отвечающая согласен гормонное, физиологическое состояние, что-что также репродуктивную функцию.
Гинеколог Днепр -
[url=https://buytetracycline.monster/]tetracycline 250 mg capsules[/url]
-
[url=http://buydiflucan.life/]diflucan 50 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://arimidextabs.online/]arimidex for gyno[/url]
-
[url=https://disulfiram.cfd/]disulfiram medicine[/url]
-
[url=http://zithromaxtab.monster/]zithromax 500mg price in india[/url]
-
[url=https://noroxintab.online/]noroxin pill[/url]
-
[url=https://suhagra.icu/]suhagra 100mg tablet price in india[/url]
-
[url=http://seroquelquetiapine.shop/]seroquel 550 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://allopurinolz.online/]allopurinol 200 mg tab[/url]
-
[url=https://sildenafiltz.com/]viagra otc price[/url] [url=https://noroxintab.online/]noroxin tablets[/url] [url=https://prozactabs.shop/]where to buy fluoxetine online[/url] [url=https://agabapentin.online/]neurontin 1200 mg[/url] [url=https://glucophage.sbs/]best metformin brand[/url]
-
[url=https://clopidogreltabs.quest/]plavix 300 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://buydiflucan.life/]diflucan 500 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://albuteroltab.com/]can i buy ventolin over the counter singapore[/url] [url=https://buysingulair.monster/]singulair headaches[/url] [url=https://viarga.shop/]buy pfizer viagra[/url] [url=https://amitriptylinetabs.com/]elavil 2.5 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://medrol.cfd/]medrol 32 mg tablets[/url]
-
[url=https://piroxicamtab.shop/]piroxicam generic[/url] [url=https://allopurinolz.online/]best allopurinol brand[/url]
-
[url=http://albuteroltab.com/]albuterol 0.043[/url]
-
[url=https://vigra.online/]viagra pricing[/url]
-
[url=https://allopurinolzyloprim.online/]allopurinol 300 mg tablet[/url] [url=https://fildena.click/]fildena 100 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://buyadvair.monster/]advair diskus without prescription[/url] [url=https://biaxin.life/]biaxin for strep[/url] [url=https://levaquin.cfd/]levaquin buy online[/url] [url=https://prednisolone247.com/]prednisolone sod[/url] [url=https://viagra96.com/]female viagra buy[/url]
-
[url=http://tetracyclinetabs.online/]where can i get tetracycline[/url]
-
[url=http://prozactabs.shop/]fluoxetine 60 mg tablet[/url]
-
[url=http://buytretinoin.monster/]retin a 01 cream[/url] [url=http://tizanidine.run/]zanaflex 2mg tablets[/url] [url=http://buyamitriptyline.life/]elavil 10mg for sleep[/url] [url=http://suhagra.icu/]suhagra 100 online purchase[/url] [url=http://buydiclofenac.monster/]voltaren 25 mg[/url] [url=http://allopurinolzyloprim.online/]allopurinol 100mg tablets price[/url] [url=http://paxil.run/]over the counter paxil[/url]
-
[url=http://suhagram.online/]suhagra online purchase[/url]
-
[url=https://indocin.icu/]indocin 25 mg capsules[/url]
-
[url=https://afinasteride.com/]propecia price canada[/url]
-
[url=https://provigiltabs.online/]modafinil best price[/url]
-
[url=http://allopurinolzyloprim.online/]allopurinol generic cost[/url] [url=http://suhagra.icu/]suhagra 100mg buy online[/url] [url=http://inderal.fun/]propranolol no prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://buyamitriptyline.life/]amitriptyline 5 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://effexor.sbs/]effexor 300 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://celexacitalopram.shop/]celexa 100mg[/url]
-
[url=https://clopidogreltabs.quest/]plavix 75 mg tablet price[/url]
-
[url=http://lyrica.sbs/]generic lyrica 2019[/url]
-
[url=https://singulairtabs.online/]singulair australia[/url]
-
[url=https://advairtabs.online/]advair diskus 25050[/url]
-
[url=https://tetracyclinetab.online/]tetracycline 500mg capsule price[/url]
-
[url=http://albuteroltabs.quest/]ventolin in usa[/url] [url=http://ciprof.online/]can you buy cipro over the counter in canada[/url] [url=http://glucophage.sbs/]metformin prescription canada[/url]
-
[url=https://ataraxd.monster/]otc atarax[/url]
-
[url=https://prozactabs.shop/]fluoxetine hcl 20mg[/url]
-
[url=https://trustedtablets.sale/]worldwide pharmacy online[/url] [url=https://prozactabs.com/]prozac over the counter[/url] [url=https://priligytabs.shop/]priligy buy online canada[/url] [url=https://wellbutrintab.online/]wellbutrin prescription canada[/url] [url=https://familyrx.online/]legit mexican pharmacy[/url] [url=https://tamoxifentabs.online/]tamoxifen 10 mg brand name[/url] [url=https://lasix247.com/]how much is furosemide 40 mg[/url] [url=https://allopurinolz.online/]allopurinol online india[/url]
-
[url=http://celexacitalopram.online/]celexa[/url] [url=http://medrol.cfd/]medrol buy online[/url]
-
[url=https://buykamagra.life/]kamagra soft tabs[/url] [url=https://clindamycina.online/]clindamycin capsule coupon[/url] [url=https://viagra96.com/]sildenafil coupon 100mg[/url] [url=https://viarga.shop/]buy generic viagra without a prescription[/url] [url=https://lipitor.site/]lipitor price uk[/url]
-
[url=http://antabusex.com/]buy cheap antabuse[/url]
-
[url=https://vyvodaaabbba.ru/]vyvodaaabbba[/url]
Наркологическая экспресс-клиника Москва очутит анонимную наркологическую шефство пациентам центра круглосуточной наркологии в Москве. Хостинг-услуги исцеления наркомании, ...
vyvodaaabbba -
[url=https://fluoxetinetabs.com/]fluoxetine dr[/url]
-
[url=https://dapoxetinetabs.online/]priligy mexico[/url]
-
[url=http://kamagratab.monster/]kamagra oral jelly female[/url]
-
[url=https://phenergantab.shop/]phenergan gel[/url] [url=https://ventolinwithoutprescription.com/]buy ventolin online no prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://viagratab.com/]generic viagra canada paypal[/url] [url=https://nexiumtabs.online/]prescription nexium without a prescription[/url] [url=https://hotviagraonline.com/]generic sildenafil tablets[/url] [url=https://trazodone247.com/]trazodone 100mg[/url] [url=https://yasmindrospirenone.online/]buy yasmin pill[/url] [url=https://happyfamilyrx.store/]pharmaceuticals online australia[/url]
-
[url=http://tetracyclinesumycin.shop/]tetracycoline with out a prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://plavixtabs.online/]plavix canada price[/url] [url=http://neurontintabs.online/]buy gabapentin online[/url] [url=http://bupropiontab.monster/]zyban tablets uk[/url] [url=http://nexiumtabs.online/]nexium tablets uk[/url] [url=http://tetracyclinesumycin.shop/]terramycin ointment for cats[/url] [url=http://antabusex.com/]antabuse tablets uk[/url] [url=http://genericpropeciaonline.com/]cheapest generic propecia 5mg india fast shipping no prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://cafergot.fun/]cafergot australia[/url]
-
[url=http://antabusedisulfiram.online/]antabuse generic[/url]
-
[url=https://happydrugstores.online/]cheapest pharmacy canada[/url]
-
[url=https://arimidex.fun/]arimidex buy usa[/url]
-
[url=http://rostovnadonu.cridex.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=http://shop-mega.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=http://ayr.2day.ws/ayr/search/?url=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=http://prostodomugra.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=https://elipeneri.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=http://www.chieri.info/links.php?mode=go&id=84&url=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=http://shop75296.full-design.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=http://www.khuyenmaihcmc.vn/redirect?url=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=http://cse.google.ie/url?sa=i&url=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=https://mcguirewoods.vuturevx.com/edit/email_handler.aspx?sid=99d34cea-eb0d-46fe-b2b6-c927066f1863&redirect=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=http://collepic.net/jump.php?url=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=https://m.killberos.com/member/login.html?noMemberOrder=&returnUrl=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=http://reedukacja.com.pl/Redirect.aspx?url=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=http://ammaretail.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet france[/url]
[url=http://www.mwgl.org/phpAdsNew/adclick.php?bannerid=19&z>1xbet france
1xbet france
1xbet france
1xbet france
1xbet france
1xbet france
1xbet france
1xbet france
1xbet france
1xbet france
1xbet france
1xbet france
1xbet france
1xbet france
1xbet france -
[url=http://fluconazole.click/]buy diflucan online[/url]
-
[url=http://www.bigblackbootywatchers.com/cgi-bin/sites/out.cgi?id=booty&url=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=https://www.mediengestalter.info/go.php?url=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=http://map.lugansk.ua/away.php?to=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=http://d-click.migliori.com.br/u/13729/39/14305/110_0/a4ac5/?url=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=http://larsensport.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=http://outboardmotormarket.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=http://www.gutains.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=http://dominasuche.net/wp-content/plugins/AND-AntiBounce/redirector.php?url=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=http://www.ubs-hainer.com/de/wp-content/plugins/wp-js-external-link-info/redirect.php?blog=UBS+Hainer&url=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=http://kcm.kr/jump.php?url=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=http://www.allflagstafflodging.com/tosite.php?url=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=http://www.israwow.com/go.php?id=mogi.eu.com%2F__media__%2Fjs%2Fnetsoltrademark.php%3Fd%3Dkursy-seo-moskva2.ruhttps://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=http://web-koshka.ru/?go=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=http://services.nfpa.org/Authentication/GetSSOSession.aspx?return=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
[url=http://internationalbestdressedlist.us.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet portugal[/url]
The company has been on the furnish recompense to 20 years, time-tested, hundreds of satisfied customers. Newbies after registration cool offers. Set off to promotions section.
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal
1xbet portugal -
[url=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet app portugal[/url]
The stroke at the 1xbet bookmaker is the same of the most commodious among all bookmakers.
1xbet-download-pt com -
[url=http://viagra2023.com/]cheap viagra canada pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://yasmintabs.shop/]yasmin australia price[/url]
-
[url=https://celebrextab.online/]celebrex 200 mg tablet[/url]
-
[url=http://hydroxyzine.life/]atarax 25 mg tablets[/url]
-
[url=https://1xbet-download-pt.com]1xbet-download-pt[/url]
Ditty of the stock bookmakers is 1xbet: it has been operating in compensation more than 20 years in multifarious countries of the coterie, including Russia.
1xbet-download-pt com -
[url=https://metformintabs.shop/]glucophage 750 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://suhagra.run/]suhagra online purchase[/url]
-
[url=https://flagylmetronidazole.online/]generic flagyl cost[/url]
-
[url=https://buydisulfiram.life/]is a prescription required for antabuse[/url]
-
[url=http://bupropiontab.monster/]how to get zyban prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://yasmindrospirenone.online/]yasmin cost[/url]
-
[url=https://priligy.icu/]dapoxetine 60[/url]
-
[url=https://hydroxychloroquine.tech/]plaquenil eye[/url]
-
[url=http://citalopram.sbs/]citalopram tablets online[/url] [url=http://buydisulfiram.life/]buy antabuse in uk[/url] [url=http://citalopramtab.quest/]celexa brand coupon[/url] [url=http://hotviagraonline.com/]sildenafil pharmacy prices[/url] [url=http://neurontintabs.online/]600 mg gabapentin coupon[/url]
-
[url=http://cafergot.fun/]cafergot australia[/url] [url=http://flagyltabs.monster/]generic flagyl over the counter[/url] [url=http://antabusex.com/]disulfiram over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://fildenax.monster/]buy fildena 150 online[/url]
-
[url=https://buynolvadex.monster/]nolvadex 1mg[/url]
-
[url=http://fluconazole.click/]diflucan 150mg tab[/url]
-
[url=http://provigiltab.shop/]provigil online paypal[/url]
-
[url=https://pharma.monster/]safe canadian pharmacies[/url]
-
[url=https://happydrugstores.quest/]canada pharmacy not requiring prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://hotviagraonline.com/]how much is viagra tablets[/url]
-
[url=https://1xbet-download-fr.com]1xbet-download-fr[/url]
The 1xbet company clear not to take possession of a authorize from the Russian regulator, so it automatically bring about itself outlawed.
1xbet-download-fr com -
[url=http://phenergantab.online/]phenergan 2[/url]
-
[url=https://fluconazole.click/]can i buy diflucan over the counter uk[/url]
-
[url=http://colchicine247.com/]probenecid colchicine[/url]
-
[url=https://albuterol.life/]combivent aerosol[/url]
-
[url=http://happyfamilyrx.store/]overseas online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://albuterol.icu/]where to get albuterol[/url]
-
[url=http://suhagra.run/]suhagra 500[/url]
-
[url=http://colchicine247.com/]where to buy colchicine canada[/url]
-
[url=http://nexiumtabs.monster/]nexium 10 mg otc[/url]
-
[url=http://clonidinetab.online/]0.2 clonidine[/url] [url=http://cafergot.fun/]order cafergot online[/url] [url=http://motrintabs.shop/]motrin 225[/url] [url=http://nexiumtabs.online/]nexium 40 mg otc[/url] [url=http://kamagratab.monster/]kamagra oral jelly 50mg usa delivery[/url] [url=http://provigiltab.shop/]provigil over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://citalopram.icu/]citalopram hydrobromide 20mg tab[/url] [url=http://priligydapoxetine.shop/]can i buy dapoxetine over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://happydrugstores.online/]online pharmacy prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://buypaxil.life/]paroxetine cost without insurance[/url] [url=http://cafergot.fun/]cafergot drug[/url] [url=http://happydrugstores.online/]pharmacy rx[/url] [url=http://kamagratab.monster/]buy cheap kamagra jelly[/url] [url=http://bupropiontab.monster/]generic bupropion price[/url] [url=http://flagyl.life/]generic flagyl 500 mg[/url] [url=http://hotviagraonline.com/]generic viagra cost canada[/url] [url=http://zofran.sbs/]zofran 2mg[/url]
-
[url=http://nexiumtabs.monster/]is there a generic nexium[/url]
-
[url=https://erythromycin.run/]erythromycin 250 mg coupon[/url]
-
[url=https://genericpropeciaonline.com/]propecia usa[/url]
-
[url=http://arimidex.fun/]arimidex 1 mg tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://fluconazole.click/]diflucan price[/url]
-
[url=https://allopurinolzyloprim.shop/]buy allopurinol canada[/url]
-
[url=https://avodart.life/]avodart for sale[/url]
-
[url=http://arimidex.fun/]generic arimidex cheap india[/url]
-
[url=http://cytotec.run/]cytotech[/url]
-
[url=http://happyfamilyrx.store/]canada pharmacy online[/url]
-
[url=https://antabusetabs.online/]buy anti buse[/url]
-
[url=http://noroxintab.quest/]noroxin without prescription[/url] [url=http://priligy.icu/]dapoxetine canada[/url] [url=http://suhagra.life/]buy suhagra 50 mg online india[/url] [url=http://yasmindrospirenone.shop/]yasmin australia[/url] [url=http://colchicine247.com/]colchicine 1 mg tab[/url]
-
[url=http://cytotec.run/]how to get misoprostol prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://erythromycin.run/]buy erythromycin cream online[/url]
-
[url=https://bupropiontabs.online/]zyban 300 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://priligy.icu/]where to buy priligy in usa[/url]
-
[url=http://diflucan.run/]diflucan order online uk[/url]
-
[url=https://fildenax.monster/]buy fildena 150[/url]
-
[url=https://retinacream.quest/]retin a india price[/url]
-
[url=http://metforminv.quest/]metformin 100 mg price[/url]
-
[url=http://clomipheneclomid.online/]clomid 100 mg tablet[/url] [url=http://buyanafranil.monster/]anafranil 25g[/url] [url=http://medstore911.com/]online pharmacy pain relief[/url] [url=http://neurontinv.quest/]25 mg gabapentin[/url]
-
[url=http://tetracyclinesumycin.shop/]tetracycline pills[/url]
-
[url=http://priligy.icu/]priligy 30mg[/url] [url=http://bupropiontabs.online/]wellbutrin 400[/url] [url=http://noroxina.online/]noroxin price[/url] [url=http://viagra2023.com/]viagra from india pharmacy[/url] [url=http://neurontinv.quest/]gabapentin 200[/url]
-
[url=https://silagra.run/]silagra 100 for sale[/url]
-
[url=https://zofran.sbs/]zofran price australia[/url] [url=https://phenergantab.shop/]phenergan 2[/url] [url=https://flagyl.life/]flagyl prescription[/url] [url=https://happydrugstores.online/]best online pharmacy no prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://avodart.life/]avodart cost[/url]
-
[url=http://lopressor.life/]lopressor er[/url]
-
[url=https://ciprofloxacin.life/]cipro prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://prozac24.com/]how much is prozac in mexico[/url]
-
[url=http://plavix.life/]plavix 25[/url]
-
[url=https://abi-dent.ru/]Стоматологическая Клиника[/url]
В близкой вещи мы применяем только наиболее теперешние технологии, первоклассные мануфактуры а также лучшее ясс от производителей из мировым именем.
Стоматологическая Клиника -
[url=http://neurontintabs.online/]neurontin over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://elavilamitriptyline.online/]elavil generic cost[/url]
-
[url=http://buypaxil.life/]paxil prescription online[/url] [url=http://tadalafilpillscheap.com/]cheap canadian pharmacy cialis[/url] [url=http://citalopram.sbs/]buy citalopram without script[/url]
-
[url=https://phenergantabs.quest/]phenergan otc[/url]
-
[url=http://prozactabs.online/]buy prozac online canada[/url]
-
[url=https://citalopramtab.quest/]citalopram hbr 20 mg tab[/url]
-
[url=https://clonidinetab.shop/]where can i purchase clonidine[/url]
-
[url=https://clonidinetab.online/]clonidine[/url]
-
[url=http://tamoxifentab.com/]tamoxifen cost uk[/url]
-
[url=http://lanoxin.life/]digoxin 250 mcg 0.25 mg[/url] [url=http://kamagratab.monster/]kamagra oral jelly gel 100mg[/url] [url=http://antabusex.com/]can i buy antabuse over the counter[/url] [url=http://buypaxil.life/]buy paroxetine 20 mg online uk[/url] [url=http://flagyltabs.monster/]buy flagyl[/url] [url=http://albuterol.icu/]ventolin otc[/url] [url=http://tadalafilpillscheap.com/]cialis online buy[/url] [url=http://allopurinolzyloprim.shop/]allopurinol pill[/url]
-
[url=https://effexorvenlafaxine.online/]effexor prescription[/url] [url=https://retinatabs.shop/]tretinoin 10mg[/url]
-
[url=http://pharma.monster/]canada rx pharmacy world[/url] [url=http://happydrugstores.online/]safe online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://pharma.monster/]onlinepharmaciescanada com[/url]
-
[url=https://suhagra.run/]suhagra 50 mg price[/url]
-
[url=http://trazodone247.com/]10 mg trazodone[/url] [url=http://kamagratab.monster/]order kamagra online[/url] [url=http://silagra.run/]silagra 100 uk[/url] [url=http://diclofenactabs.quest/]voltaren cheapest[/url] [url=http://arimidex.fun/]buying arimidex on line[/url] [url=http://citalopram.sbs/]can you buy citalopram online uk[/url] [url=http://flagyl.life/]metronidazole 250mg shipped w/o rx[/url]
-
[url=https://tamoxifentab.com/]buy cheap nolvadex[/url]
-
[url=https://buyzoloft.life/]best zoloft generic[/url] [url=https://provigiltab.shop/]provigil 400 mg[/url] [url=https://buypaxil.life/]where to buy paxil[/url] [url=https://clonidinetab.online/]clonidine for insomnia[/url]
-
[url=http://clonidinetab.shop/]4 clonidine[/url]
-
[url=http://cleocintabs.shop/]clindamycin cream price[/url]
-
[url=https://dapoxetinetabs.online/]priligy prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://priligy.icu/]cost of priligy[/url]
-
[url=http://citalopramtab.quest/]celexa over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://lisinoprilb.quest/]lisinopril discount[/url]
-
[url=http://happydrugstores.quest/]online pharmacy without insurance[/url]
-
metronidazole phenytoin metronidazole orally (flagylВ®) flagyl 500 chat https://flagylaqa.com/
-
does trazodone cause mood swings trazodone versus paxil trazodone taper https://trazodonesuc.com/
-
[url=https://trazodone247.com/]trazodone 100 mg cost[/url]
-
[url=http://zofran.site/]where to get zofran[/url]
-
[url=https://flagylmetronidazole.online/]flagyl online[/url]
-
[url=https://prozac24.com/]prozac online[/url]
-
what happens if you forget to take lisinopril what dosage does lisinopril come in hydrochlorothiazide bladder pain https://lisinoprilseh.com/
-
[url=http://clonidinetab.online/]clonidine 300 mcg tablets[/url]
-
lasix and spironolactone side effects lasix tabletas 40 mg furosemide amiloride hydrochloride https://lasixyvf.com/
-
[url=https://prednisolonetab.shop/]prednisolone 25mg[/url]
-
atenolol fiebre atenolol endikasyonlarД± atenolol 25 mg buy https://tenorminscx.com/
-
[url=https://tretinoinx.online/]how to get retin a cream[/url]
-
[url=https://hydroxyzine.life/]atarax pills[/url]
-
[url=http://hydroxychloroquine.tech/]hydroxychloroquine buy online uk[/url]
-
[url=https://lyricatabs.quest/]lyrica capsules price[/url]
-
[url=http://fildenax.monster/]fildena 50[/url]
-
[url=http://nolvadextab.quest/]nolvadex for sale cheap[/url]
-
[url=http://happyfamilypharm.monster/]internet pharmacy mexico[/url]
-
metformin alternative diabetes glucophage kilo verdim glucophage 500 poudre https://metforminukx.com/
-
[url=https://singulaira.online/]singulair tablets over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://novostroika-adler.ru/]Апартаменты в Сочи[/url]
Сочи норовит заступить на Союз в соседном будущем. Разве что в течение путевой карте, разработанной, в течение черте гипотезы возможного вхождения Столица курортов именуется 2025 год, то ясный перец, что лидирует.
Апартаменты в Сочи -
[url=https://avodart.life/]online avodart without prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://abilifytabs.monster/]abilify medication[/url]
-
[url=http://clonidinetab.online/]buy clonidine online no prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://effexorvenlafaxine.online/]effexor 150 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://1xbet-download-ru.com]1xbet казино[/url]
1xBet, также 1хСтавка – российская букмекерская юкос, основанная в течение 2007 годку в течение Брянске, РФ. Работит унтер лицензией юрисдикции Кюрасао.
1xbet казино зеркало -
[url=https://clonidinetab.online/]clonidine cream[/url] [url=https://arimidex.fun/]arimidex online purchase[/url] [url=https://neurontintabs.online/]gabapentin medication[/url] [url=https://genericpropeciaonline.com/]propecia generic brand[/url] [url=https://erythromycin.run/]erythromycin 5[/url] [url=https://phenergantab.online/]phenergan 10mg uk[/url] [url=https://flagyl.life/]where can i get flagyl without a prescription[/url] [url=https://happyfamilyrx.store/]cheapest pharmacy to fill prescriptions without insurance[/url]
-
[url=http://viagratab.com/]no prescription viagra[/url]
-
nolvadex post cycle schedule tamoxifen pcos tamoxifen energy levels https://nolvadexsrm.com/
-
[url=http://www.radsport-suche.com/jump.php?sid=2296&url=https://1xbet-download-ru.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://www.mein-itzehoe.de/Redirect.aspx?destination=https://1xbet-download-ru.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://mrt-rus.info/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://1xbet-download-ru.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://game-android.ru/forum/away.php?s=https://1xbet-download-ru.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://must.or.kr/ko/must/ci/?link=https://1xbet-download-ru.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=https://idrottensaffarer.se/ad/www/delivery/ck.php?ct=1&oaparams=2__bannerid=70__z>1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet -
[url=https://1xbet-download-ru.com]скачать 1xbet на андроид[/url]
Рабочее зеркало 1xbet – специализированная ссылка, которая числом комплекту знаков выделяется через классического линка, хотя у этом ведет сверху основной сайт компании.
1xbet официальный сайт -
[url=http://fildenax.monster/]fildena usa[/url]
-
[url=https://citalopramtab.quest/]citalopram 30 mg[/url]
-
bactrim ds dosage for cellulitis is bactrim a tetracycline drug maximum dose bactrim https://bactrimrol.com/
-
[url=http://metformin.click/]glucophage 1000 mg tablet[/url]
-
[url=https://anafranil.life/]anafranil ocd[/url] [url=https://trazodone247.com/]trazodone cost uk[/url] [url=https://tadalafilpillscheap.com/]cialis online for sale[/url] [url=https://buyprovigil.monster/]buy modafinil 100 mg[/url] [url=https://bupropiontab.monster/]zyban purchase online[/url]
-
[url=https://augmentingen.com/]augmentin generic pill[/url]
-
[url=http://nexiumtabs.monster/]nexium 20 mg price australia[/url]
-
[url=https://provigiltab.shop/]provigil how to get a prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://phenergantab.shop/]phenergan with codeine cough syrup[/url]
-
[url=http://noroxintab.quest/]purchase cheap noroxin[/url] [url=http://plavix.life/]clopidogrel bisulfate plavix[/url] [url=http://buyprozac.monster/]best prozac price no prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://celexatab.monster/]celexa 20mg[/url]
-
[url=http://allopurinolzyloprim.shop/]allopurinol 500 mg[/url] [url=http://albuterol.icu/]albuterol online order[/url]
-
[url=https://yasmindrospirenone.shop/]yasmin pills buy online usa[/url]
-
[url=https://plavix.life/]clopidogrel 75 mg discount coupon[/url]
-
[url=https://cafergot.fun/]cafergot medication[/url]
-
[url=http://synthroidlevothyroxine.online/]synthroid prices in canada[/url]
-
[url=https://noroxina.online/]noroxin 300[/url]
-
[url=http://hotviagraonline.com/]generic sildenafil no prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://bupropiontab.monster/]purchase bupropion[/url]
-
[url=http://fluconazolediflucan.shop/]diflucan 150[/url] [url=http://propranolol.icu/]propranolol 20 mg price[/url] [url=http://diclofenacvoltaren.online/]best price diclofenac 50 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://fildenax.online/]fildena 100 mg price in india[/url]
-
[url=http://buytamoxifen.life/]cheap generic nolvadex[/url]
-
[url=https://xmodafinil.online/]provigil online[/url]
-
[url=http://anafraniltab.online/]anafranil ocd[/url]
-
[url=https://toradol.run/]toradol 150 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://fluconazole.sbs/]diflucan 150 mg online[/url]
-
[url=http://paxilparoxetine.shop/]paroxetine coupon[/url]
-
[url=http://diflucan.run/]buy diflucan online uk[/url]
-
[url=https://fluoxetinetabs.online/]order prozac uk[/url]
-
[url=http://viagrastart.com/]viagra us[/url]
-
[url=https://vyvodaaabbbf.ru/]vyvodaaabbbf[/url]
Ваша милость можете отобрать нарколога, который приедет к Для вас сверху дом круглосуточно: Испытанные отзвуки что касается врачах, Любой фрегезия Москвы.
vyvodaaabbbf -
[url=http://fluconazole.sbs/]diflucan 200[/url]
-
[url=https://toradol.run/]toradol order[/url]
-
[url=https://antabusedisulfiram.shop/]antabuse uk buy[/url] [url=https://estrace.life/]estrace price canada[/url] [url=https://viagrastart.com/]cipla viagra[/url] [url=https://nexiumtab.online/]nexium 42[/url]
-
[url=http://levothyroxine.cfd/]synthroid com[/url]
-
[url=https://ciallis.shop/]alli cheapest uk[/url]
-
[url=https://finpeciatabs.online/]propecia how to get[/url] [url=https://viagrawithoutprescription.com/]otc generic viagra[/url] [url=https://metformind.online/]can you buy metformin over the counter in usa[/url] [url=https://buylipitor.quest/]lipitor 20 mg where to buy[/url] [url=https://xmodafinil.online/]buy provigil in mexico[/url] [url=https://buypriligy.life/]dapoxetine generic drug[/url] [url=https://cleocintab.quest/]clindamycin 400mg[/url] [url=https://lipitor.cfd/]lipitor uk price[/url]
-
[url=https://retinoatab.online/]retino 0.05 gel[/url]
-
[url=https://lyricatab.online/]lyrica for sale uk[/url]
-
[url=https://finasteride247.com/]propecia compare prices[/url]
-
[url=http://dapoxetinetab.online/]buy generic dapoxetine online[/url] [url=http://escitalopram.life/]otc cipralex[/url] [url=http://viviagra.com/]buy viagra online usa paypal[/url] [url=http://kamagrap.online/]buy kamagra online canada[/url] [url=http://phenergan.fun/]phenergan prices[/url] [url=http://diclofenac.run/]can you buy diclofenac over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://metforminv.online/]india pharmacy metformin 500 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://buyfluoxetine.monster/]order fluoxetine hcl 20 mg capsules online[/url]
-
[url=http://buyciprofloxacin.life/]ciprofloxacin cost[/url]
-
[url=http://samsud.ru/go/url=https://1xbet-download-fa.com]1xbet iran[/url]
[url=https://lesliefisher.com/?URL=https://1xbet-download-fa.com]1xbet iran[/url]
[url=http://ilyamargulis.ru/go?https://1xbet-download-fa.com]1xbet iran[/url]
[url=https://salsa.wiredforchange.com/dia/track.jsp?key=-1&url_num=2&url=https://1xbet-download-fa.com]1xbet iran[/url]
[url=https://links.rafflecopter.com/rcapi/v1/raffles/~08c80b99187/?e=141485194587cafe4e2ee895&u=https://1xbet-download-fa.com]1xbet iran[/url]
[url=http://get-info-belarus.net/redirect.php?id=https://1xbet-download-fa.com]1xbet iran[/url]
[url=http://chiase123.com/redirect.php?https://1xbet-download-fa.com]1xbet iran[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.md/url?q=https://1xbet-download-fa.com]1xbet iran[/url]
[url=http://ads.koddi.com/pmService/v1/Marriott/hotels/clickredirect?trackingData=Cmp-fQ7BlBzC2qd0OIQckjpuHtHj46JZoo32Q5FpFrtBd46FTpNv8wV0250nWHGnMJGoPD35EIlnYJKVgVhyLt+VYvY4fVI37r2uRas6GQQehbZG3AVKgkR4guADntDP1noKO2pb3Q1k6Gy+fBc6JVL9EdSmDi8PS0SSRxPyJt0i9BTyr48yfpeJKcCUPHBwy2oRa4TzL9wTtwiEVCTW9zVByeL0O/MJ57Eoo9rzpQ/AGF8UKoba4Gwav9TGD4KPYrb87c3ZTU6Rl+AmoRokQtGJW+hWPSv1a3jjPylLGXTPzOFbUDoy8m22/nXIHmRBfNrgAw5E2MZMgyvNnOyMOW6hkjKESDzsbTC7p6qOBUQr0bRb3pI/Q3Wdep1N/Hesc9qWGs4vHD6GSZ5CSw9zV0Aq3pfsYkedlDADsrdeer24V/pt3X0Xzr2qr7cAGBENKhpvpKYS08n2Z5JGc0mN7OGbFkIJqvB3mqAR0dyt6FAzsiWjrC2om++WUT0Of45RRh3WH9q0XWnlkq4oRWlLjlPMh5ZF11wtWyMN4gdRHNpaCs+24wjkG4Zxchp6O+isTV75HKcRz+hIGIDGLfMJcsjZJjQemZrEIQVqJs50sidVWP8QyxtnPLgSdIHkih+m4WByGcAKJ4fDZF8j0PmXoEKnXxGGKJoOeYbZ/KH9Sn4fuRQz7kxifBNdh++XvC18m7SH30vZHh38DPCbByvmSSaOuQ==&rank=2&candidateHmGuid=aa2973b0-fd6b-4349-9384-981207151982&beac>1xbet iran
1xbet iran
1xbet iran
1xbet iran
1xbet iran
1xbet iran
1xbet iran
1xbet iran
1xbet iran
1xbet iran
1xbet iran
1xbet iran
1xbet iran
1xbet iran
1xbet iran -
[url=https://sildenafilrx.quest/]viagra prescription cost[/url]
-
[url=https://effexor.click/]generic effexor 225 mg cheapest[/url] [url=https://buyalbuterol.life/]combivent discount[/url] [url=https://kamagrap.online/]kamagra tablets australia[/url] [url=https://buyviagra.monster/]buy viagra in usa[/url]
-
[url=http://nolvadextabs.online/]nolvadex 1mg[/url] [url=http://lipitor.cfd/]buy cheap lipitor online[/url] [url=http://buylipitor.monster/]lipitor 20 mg pill[/url] [url=http://finpeciatabs.quest/]propecia 1mg[/url] [url=http://tretinoincream01.com/]buy tretinoin 1 gel[/url]
-
[url=https://effexor.click/]effexor purchase[/url]
-
[url=https://tamoxifena.monster/]purchase nolvadex no prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://diclofenacvoltaren.online/]voltaren gel from mexico[/url] [url=http://motrintabs.online/]motrin 600 otc[/url]
-
[url=https://trustedpharmacyz.quest/]indian pharmacy paypal[/url]
-
[url=https://diclofenacvoltaren.online/]diclofenac 35[/url]
-
[url=https://zithromaxtab.online/]azithromycin 500 mg tablet price in india[/url]
-
[url=http://allopurinol.sbs/]allopurinol 300 mg online[/url] [url=http://anafraniltab.online/]anafranil clomipramine[/url] [url=http://paxilparoxetine.shop/]paroxetine 10 mg tablet[/url] [url=http://nexiumtab.online/]buy nexium online[/url] [url=http://buyciprofloxacin.life/]buy ciprofloxacin online canada[/url]
-
[url=http://retinacream.quest/]retin-a without prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://finasteridetabs.shop/]propecia discount pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://zithromaxtab.online/]buy azithromycin[/url]
-
[url=https://finpeciatabs.quest/]buy genuine propecia[/url]
-
[url=http://buypriligy.life/]where to buy priligy in canada[/url] [url=http://retinoatab.online/]retino 0.025 cream[/url] [url=http://fluoxetinetabs.online/]buy prozac online cheap[/url] [url=http://buyfluoxetine.monster/]fluoxetine nz[/url] [url=http://viagragoal.com/]viagra tablet 100mg price[/url] [url=http://onlinedrugstores.quest/]online pharmacy 365 pills[/url] [url=http://buylipitor.quest/]lipitor 100mg[/url]
-
[url=https://tamoxifena.monster/]nolvadex price canada[/url] [url=https://fluconazole.sbs/]order diflucan online cheap[/url] [url=https://metformind.online/]glucophage metformin[/url] [url=https://propranolol.run/]propranolol er 60mg[/url]
-
[url=https://valtrexvalacyclovir.com/]generic for valtrex buy without a prescription[/url] [url=https://propranolol.icu/]innopran cheap[/url] [url=https://viviagra.com/]purchase viagra mexico[/url] [url=https://phenergan.fun/]phenergan tablets online uk[/url] [url=https://tamoxifen365.com/]nolvadex 20mg[/url] [url=https://vigra.monster/]how can you get viagra[/url]
-
[url=http://cytotec.icu/]cytotec where to buy online[/url]
-
[url=http://viagraipak.com/]female viagra drugstore[/url]
-
[url=http://cymbalta.life/]cost of generic cymbalta 60 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://diflucantabs.online/]diflucan[/url]
-
[url=https://fluconazolediflucan.shop/]diflucan 150 mg otc[/url]
-
[url=http://vardrugstore.com/]good value pharmacy[/url] [url=http://anafranilclomipramine.shop/]anafranil over the counter[/url] [url=http://aurogra.cfd/]aurogra 100 prices[/url] [url=http://escitalopram.life/]cheap lexapro[/url] [url=http://antabusedisulfiram.shop/]buy disulfiram online[/url] [url=http://viviagra.com/]viagra 25 mg tablet price[/url] [url=http://citalopram.life/]medicine citalopram 20 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://clindamycina.shop/]buy cleocin gel[/url]
-
[url=http://antabusedisulfiram.online/]generic antabuse cost[/url]
-
[url=https://levothyroxine.cfd/]synthroid 0.1 mcg[/url]
-
[url=https://effexor.click/]order effexor online[/url]
-
[url=https://vigra.monster/]buy viagra uk pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://chloroquine.cfd/]buy aralen[/url]
-
[url=http://kamagrap.online/]generic kamagra jelly[/url]
-
[url=http://finpeciatabs.online/]buy brand propecia online[/url] [url=http://lipitortabs.online/]buy lipitor online uk[/url] [url=http://advair.life/]can you buy advair over the counter in mexico[/url] [url=http://clindamycintabs.online/]clindamycin cheap[/url] [url=http://diflucantabs.online/]buy diflucan 150 mg online[/url]
-
[url=https://nolvadextabs.online/]tamoxifen 2019[/url]
-
[url=http://ttpharmacy.shop/]safe canadian pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://tamoxifena.monster/]tamoxifen canada[/url]
-
[url=http://nexiumtab.online/]medicine nexium 20 mg[/url] [url=http://wellbutrina.online/]zyban cost south africa[/url] [url=http://motrintabs.online/]motrin[/url] [url=http://motiliumdomperidone.shop/]motilium mexico[/url] [url=http://chloroquine.cfd/]aralen canada[/url] [url=http://clindamycina.shop/]cleocin 150[/url]
-
[url=https://dapoxetinetab.online/]avana 100 in india[/url]
-
[url=http://ciallis.shop/]alli canada pharmacy[/url] [url=http://kamagrap.online/]online kamagra pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://paxilparoxetine.shop/]paxil pill[/url]
-
[url=https://promyshlennye-teplicy.ru/]Теплицы[/url]
Каждый любитель садоводства старается протягивать яко можно больше веку на лоне природы, где можно упиться родными экземплярами.
Теплицы -
[url=http://buydexamethasone.life/]dexamethasone 40 mg tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://motiliumdomperidone.shop/]buy no prescription motilium[/url]
-
[url=http://cytotec.icu/]cost of cytotec in south africa[/url]
-
[url=http://dipyridamole.live/]generic dipyridamole[/url]
-
[url=https://valtrexvalacyclovir.com/]valtrex india[/url]
-
[url=https://propranolol.run/]can i buy propranolol over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://clindamycina.shop/]clindamycin gel coupon[/url] [url=https://buypaxil.monster/]paroxetine 10 mg price india[/url] [url=https://effexor.click/]225 effexor[/url] [url=https://phenergan.fun/]phenergan pill[/url] [url=https://chloroquine.cfd/]aralen 200 mg[/url] [url=https://cleocintab.online/]450 mg clindamycin[/url]
-
[url=http://vardrugstore.com/]happy family drugstore[/url]
-
[url=https://1xbet-download-fa.com]1xbet-download-fa.com[/url]
Place your bets with a secure betting comrades! Sports betting in Burning and line. Best odds.
1xbet-download-fa -
[url=http://viagragoal.com/]generic sildenafil canada[/url]
-
[url=http://lipitor.cfd/]buy lipitor online[/url]
-
[url=http://dapoxetinetab.online/]dapoxetine approval[/url]
-
[url=http://advair.life/]best price for advair[/url] [url=http://buylipitor.quest/]lipitor brand name cost[/url] [url=http://suhagram.monster/]buy suhagra 50 mg online india[/url] [url=http://fluoxetinetabs.online/]buy prozac singapore[/url]
-
[url=https://chloroquine.cfd/]chloroquine sulphate tablets[/url] [url=https://escitalopram.life/]lexapro 5mg tablet price[/url] [url=https://viagraipak.com/]sildenafil 85[/url] [url=https://dipyridamole.live/]dipyridamole buy online[/url] [url=https://cytotec.icu/]where to buy cytotec[/url] [url=https://fluconazolediflucan.shop/]can i purchase diflucan over the counter[/url]
-
[url=http://anafraniltab.online/]anafranil 100 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://fluoxetinetabs.online/]fluoxetine australia[/url]
-
[url=https://buytamoxifen.life/]order nolvadex[/url]
-
[url=http://cytotec.icu/]misoprostol 1000 mcg[/url]
-
[url=http://priligytabs.online/]dapoxetine 60 mg online india[/url]
-
[url=http://vardrugstore.com/]pharmacy discount card[/url]
-
[url=https://dapoxetinetab.online/]avana cream[/url] [url=https://retinoa.life/]retino 05 cream[/url] [url=https://buyciprofloxacin.life/]cipro 500 mg pills[/url] [url=https://propranolol.icu/]propranolol prescription[/url] [url=https://vigra.monster/]online pharmacy viagra no prescription[/url] [url=https://nexiumtab.online/]nexium usa price[/url]
-
[url=https://buylipitor.quest/]lipitor 40 mg tablet[/url]
-
[url=http://escitalopramlexapro.online/]generic lexapro price comparison[/url]
-
[url=https://cytotec.icu/]cytotec pills canada[/url]
-
[url=http://sildenafil247.com/]cheap viagra pills uk[/url]
-
[url=https://stratteraatomoxetine.online/]strattera online uk[/url]
-
[url=http://diclofenac.run/]voltaren 50mg pill[/url]
-
[url=http://buydisulfiram.monster/]buy disulfiram australia[/url]
-
[url=http://buyciprofloxacin.life/]cipro 10[/url] [url=http://chloroquine.cfd/]chloroquine tablets australia[/url] [url=http://sildenafilhx.com/]how to buy viagra[/url] [url=http://diclofenacvoltaren.online/]voltaren pills 100mg[/url] [url=http://dipyridamole.live/]dipyridamole brand[/url] [url=http://cleocintab.online/]clindamycin prices[/url] [url=http://anafraniltab.online/]anafranil 25 mg[/url] [url=http://propranolol.icu/]buy propranolol online australia[/url]
-
[url=http://finasteride247.com/]canadian pharmacy propecia[/url]
-
[url=http://prednisone.sbs/]buy 10 mg prednisone[/url]
-
[url=https://sildenafilrx.quest/]viagra in usa prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://diflucantabs.online/]best diflucan price[/url] [url=http://finpeciatabs.online/]generic propecia lowest price[/url] [url=http://doxycyclinetabs.shop/]doxycycline 10mg[/url] [url=http://tretinoincream01.com/]tretinoin 0.05[/url] [url=http://fluconazole.sbs/]can you buy diflucan otc[/url]
-
[url=http://fluoxetinetabs.online/]prozac fluoxetine[/url] [url=http://seroquelquetiapine.online/]1050 mg seroquel[/url] [url=http://buylipitor.monster/]generic lipitor cost[/url]
-
[url=https://lipitortabs.online/]lipitor 20mg[/url]
-
[url=http://happyfamilyrx.shop/]canada online pharmacy no prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://indocin.sbs/]indocin 25 mg drug[/url]
-
[url=https://fluconazolediflucan.shop/]cost of diflucan[/url] [url=https://buyviagra.monster/]price generic sildenafil[/url] [url=https://valtrexvalacyclovir.com/]valtrex medicine price[/url] [url=https://buypaxil.monster/]paxil cr[/url] [url=https://buydexamethasone.life/]buy dexamethasone tablets[/url] [url=https://anafranilclomipramine.shop/]anafranil for ocd[/url] [url=https://escitalopram.life/]brand name lexapro cost[/url] [url=https://estrace.life/]estrace 2mg tablets price[/url]
-
[url=https://paxilparoxetine.shop/]paxil prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://motrintabs.online/]1000 mg motrin[/url]
-
[url=https://anafranilclomipramine.shop/]anafranil 25g[/url]
-
[url=https://diclofenac.run/]buy diclofenac tablets online[/url]
-
[url=http://clonidinetabs.quest/]clonidine 0.1 mg tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://buypaxil.monster/]paxil for panic attacks[/url]
-
valtrex sizes valtrex felleskatalogen valtrex pastila https://valtrexujd.com/
-
synthroid vitamin d3 synthroid coupon abbott synthroid liver dysfunction https://synthroidsdu.com/
-
[url=https://strattera365.com/]strattera 60 mg buy online[/url]
-
[url=https://finpeciafinasteride.shop/]propecia online canada pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://seroquelquetiapine.online/]400 seroquel[/url]
-
[url=http://keflexcephalexin.online/]cephalexin 250[/url]
-
[url=https://chloroquine.cfd/]generic aralen[/url]
-
[url=https://modafinil.fun/]provigil generic south africa[/url]
-
gabapentin aki gabapentin asthma neurontin yliannostus https://gabapentinujv.com/
-
[url=http://tamoxifena.monster/]where to buy nolvadex 2018 uk[/url]
-
can you sniff lyrica pregabalin side effect poker face lyrica https://lyricaxol.com/
-
lipitor bowel lipitor vietnam lipitor hbr https://tenorminscx.com/
-
[url=https://retinoatab.online/]retino 0.025[/url]
-
[url=https://toradol.run/]toradol brand name[/url]
-
[url=https://buyalbuterol.life/]ventolin over the counter uk[/url]
-
[url=http://buyciprofloxacin.life/]ciprofloxacin india[/url]
-
[url=https://synthroid.icu/]buy synthroid online no prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://strattera365.com/]strattera cap 40mg[/url] [url=http://fluoxetinetabs.online/]buy fluoxetine online uk[/url] [url=http://zithromaxtab.online/]azithromycin prices in india[/url] [url=http://finpeciatabs.online/]how much is propecia nz[/url] [url=http://finpeciatabs.quest/]propecia 5mg uk[/url]
-
[url=http://viagrastart.com/]female viagra tablets price in india[/url]
-
[url=http://finpeciafinasteride.shop/]where to buy propecia in usa[/url] [url=http://estrace.life/]estrace 6mg[/url] [url=http://buyciprofloxacin.life/]buying cipro online[/url] [url=http://allopurinol.sbs/]allopurinol[/url] [url=http://sildenafilhx.com/]how to buy genuine viagra online[/url]
-
[url=http://retinoatab.online/]retino 05 cream[/url] [url=http://tamoxifena.monster/]tamoxifen brand[/url] [url=http://buydapoxetine.life/]dapoxetine price australia[/url] [url=http://onlinedrugstores.quest/]pharmacy online shopping usa[/url]
-
[url=http://vardrugstore.com/]canada drug pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://motrintabs.online/]how much is motrin 600 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://albuterol.life/]cost of albuterol inhaler[/url]
-
[url=https://lyricatabs.quest/]medicine lyrica 75 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://fluconazolediflucan.shop/]diflucan 150 mg fluconazole[/url]
-
[url=http://propranolol.run/]propranolol 40[/url]
-
[url=https://buylipitor.quest/]drug lipitor[/url]
-
[url=https://zithromaxtab.online/]azithromycin otc australia[/url] [url=https://diflucantabs.online/]diflucan pill otc[/url] [url=https://buylipitor.quest/]lipitor generic over the counter[/url] [url=https://levothyroxine.cfd/]synthroid 0.050 mg[/url] [url=https://retinoatab.online/]retino 0.025[/url] [url=https://lipitor.cfd/]lipitor 20mg price[/url] [url=https://fildenax.online/]fildena 25[/url] [url=https://metformind.online/]glucophage 250 mg price[/url]
-
metformin kesan sampingan orlistat com metformina counteract metformin diarrhea https://metforminukx.com/
-
[url=https://metformind.online/]metformin 250[/url] [url=https://advair.life/]buy generic advair online[/url] [url=https://dapoxetine.cfd/]dapoxetine 60 mg tablets price in india[/url] [url=https://fildenax.online/]fildena india[/url] [url=https://sildenafil247.com/]viagra cheapest[/url]
-
https://noprescriptioncanada.com/# online pharmacy with no prescription
-
[url=https://valtrexvalacyclovir.com/]where to buy valtrex[/url]
-
lipitor steroids atorvastatin biocon lipitor filmdragerad https://lipitorxer.com/
-
[url=http://strattera365.com/]strattera prices 100 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://viagragoal.com/]viagra gel uk[/url]
-
[url=http://advair.life/]advair 250 50 mcg[/url]
-
[url=http://retinoatab.online/]retino 0.25 cream price[/url]
-
[url=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet скачати[/url]
Экстренно, этто условия 1 xbet регистрации и еще юкер в течение 1хБет сверху деньги. Псевдорасследование оплаты тантьема тупо будет зачислен в течение игровой счет 1xBet начиная с. ant. до деньгами.
1xbet украина казино -
[url=http://anafranilclomipramine.shop/]anafranil price[/url]
-
[url=http://motrintabs.online/]motrin 800 pill[/url]
-
[url=http://fluconazolediflucan.shop/]diflucan discount coupon[/url]
-
[url=http://www.hayburner.co.uk/tracking/outbound.php?url=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=https://erikapospisilova.blog.idnes.cz/redir.aspx?url=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.mk/url?sa=t&rct=j&url=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=http://investingacad.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=http://habara.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=https://maczj.com/wp-content/themes/begin52/inc/go.php?url=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=http://www.krosfencing.pl/modules/babel/redirect.php?newlang=cs_CZ&newurl=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=http://www.scutde.com/go.php?u=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=http://lacplesis.delfi.lv/adsAdmin/redir.php?uid=1439888198&cid=c3_26488405&cname=Oli&cimg=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=http://spox.ru/r.php?u=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=http://www.grannysex.cc/cgi-bin/atc/out.cgi?id=182&u=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=http://znanija.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=http://www.tmbv68.ru/go.php?link=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=http://devar.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
[url=http://josepi.com/siteanalyzer/redirect.php?url=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet казино[/url]
1хБет в Украине: яко увеличить аккаунт Как следовательно деньги кот 1xbet на Приват24 Как увеличить 1xbet: рабочие методы.
1xbet казино
1xbet казино
1xbet казино
1xbet казино
1xbet казино
1xbet казино
1xbet казино
1xbet казино
1xbet казино
1xbet казино
1xbet казино
1xbet казино
1xbet казино
1xbet казино
1xbet казино -
[url=https://1xbet-download-uk.com]1xbet-download-uk.com[/url]
Приветственный тантьема 1xbet. При регистрации любом клиент 1хБет может высмотреть поздравительный бонус. Цифра для ставок на спорт, а чужой – для игр казино.
1xbet регистрация -
[url=https://fluoxetinetab.shop/]fluoxetine 20 mg cap[/url]
-
[url=http://sildenafil247.com/]where to purchase viagra online[/url]
-
[url=http://paxilparoxetine.shop/]paroxetine 2 5 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://fluoxetinetabs.online/]where can you buy prozac[/url]
-
[url=https://estrace.life/]estrace weight loss[/url]
-
[url=http://buyalbuterol.life/]albuterol hfa[/url]
-
[url=http://ciallis.shop/]where to buy alli pills[/url]
-
[url=http://strattera365.com/]strattera 18 mg capsule[/url]
-
[url=http://fluoxetinetabs.online/]prozac online no rx[/url]
-
[url=http://buyalbuterol.life/]albuterol tablets india[/url]
-
[url=http://valtrexvalacyclovir.com/]how to buy valtrex[/url]
-
[url=http://fluconazolediflucan.shop/]where can i buy diflucan tablets over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://cleocintab.online/]clindamycin 2 cream coupon[/url] [url=https://ciallis.shop/]alli pills where to buy[/url]
-
[url=http://cytotec.icu/]buy cytotec australia[/url] [url=http://nexiumtab.online/]buy nexium in canada[/url]
-
[url=https://tretinoincream01.com/]buy retin a 1 online[/url]
-
[url=http://viagragoal.com/]can you buy viagra online[/url]
-
[url=http://prednisolona.com/]buy predislone tablets[/url]
-
[url=https://valtrexvalacyclovir.com/]valtrex no prescription price[/url]
-
[url=http://nolvadextabs.online/]nolvadex to buy[/url]
-
[url=https://albendazol.online/]where to buy albendazole uk[/url]
-
[url=http://happyfamilypharmacy.quest/]online pharmacy no prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://onlinevpharmacy.online/]affordable pharmacy[/url]
-
gabapentin learning gabapentin syncope gabapentin chiari https://gabapentinujv.com/
-
[url=https://buyventolin.life/]how to get albuterol[/url]
-
[url=http://robaxin.sbs/]generic robaxin 750[/url]
-
pharma grade pregabalin pricelist lyrica reviews pregabalin methylcobalamin tablets https://lyricaxol.com/
-
[url=https://abilify.life/]ambilify online[/url]
-
[url=https://priligy.fun/]dapoxetine tablet price[/url]
-
[url=http://www.teva.org.il/redir.asp?url=https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=https://cadmodels.machinedesign.com/community/pins/browse/source/https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=https://elnacionalista.mforos.com/visit/?https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=https://opticgallery.aditime.com/redirect.aspx?redirecturl=https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=https://fonts.sandbox.one-win-ru.com.br/url?sa=i&url=https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=https://xn----8sbkdqibmrdgt3a.xn--p1ai/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=https://surinenglish.com/backend/conectar.php?url=https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=http://jan-jan.net.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=https://paygate.apcoa.dk/rostorv/parking/Language/SetCulture?culture=da-DK&returnUrl=https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=http://rankw.ru.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.sc/url?q=https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=http://vipoil.com.ua/bitrix/rk.php?goto=http:/https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=http://www.appspecialisten.nl/outbound.php?url=https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=http://www.app-echo.at/go.php?go=https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
[url=http://www.dramonline.org/redirect?url=https://one-win-ru.com]1win зеркало[/url]
Юкос 1xbet – одна с наиболее значительных букмекерских контор. Она сотрудничает с почти всеми знатными организациями.
1win зеркало
1win зеркало
1win зеркало
1win зеркало
1win зеркало
1win зеркало
1win зеркало
1win зеркало
1win зеркало
1win зеркало
1win зеркало
1win зеркало
1win зеркало
1win зеркало
1win зеркало -
[url=https://one-win-ru.com]one-win-ru[/url]
Всех без исключения приветствую на сайте «отзовите» в течение нынешнем отзыве пойдёт речь про букмекерскую контору 1xBet.
1win казино -
[url=https://izgotovlenie-nomera.ru/]Автономера дубликаты[/url]
Пишущий эти строки производим проф номерные знаки, кои отлично приспеют в течение свойстве украшения чтобы вашего номера или гаража.
Автономера дубликаты -
[url=http://arimidextab.shop/]how to get arimidex[/url]
-
[url=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet зеркало[/url]
The 1xBet bookmaker, banned in Russia, again got into a scandal. Its creators allocated joined million euros to the residents of Ukraine.
1xbet зеркало -
[url=http://cymbaltatabs.com/]cymbalta 9 mg[/url] [url=http://seroqueltab.online/]seroquel for bipolar 2[/url] [url=http://stromectoltab.online/]stromectol tab 3mg[/url] [url=http://clopidogrel.fun/]plavix generics[/url] [url=http://happyfamilyrx.quest/]top online pharmacy 247[/url] [url=http://singulaira.quest/]singulair generic brand[/url]
-
[url=https://buyclindamycin.life/]clindamycin 300 mg pill[/url] [url=https://singulair.life/]singulair prescription coupon[/url] [url=https://nexiumtab.shop/]nexium medicine price[/url] [url=https://buyretinoa.life/]retino 0.5 cream price[/url] [url=https://modafinil247.com/]modafinil 200 mg price india[/url] [url=https://happyfamilypharmacy.quest/]indianpharmacy com[/url] [url=https://buysynthroid.life/]synthroid online paypal[/url]
-
[url=http://lendersolutions.net.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://itpanda.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://wix.insertarticles.info.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=https://xn--b1aecboaym3f.xn--p1ai/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=click_to_call&event2=&event3=&goto=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=https://zavolzhye.farmani.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://korzinka.com/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=https://collaboratedcareers.com/jobclick/?RedirectURL=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=https://zoougolok.ua/bitrix/rk.php?id=17&site_id=s1&event1=banner&event2=click&goto=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://www.vdaeti.hys.cz/redir.php?redir=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://topbdsmtube.com/tbt/tb/2tb.cgi?id=68&l=top_top&u=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://www.lumipallo.fi/affiliate/click.php?url=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://multicultural.com/Redirect.aspx?destination=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://www.convertit.com/Redirect.ASP?To=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://holsworthy.devon-towns.co.uk/link.asp?url=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
[url=http://www.allmyfaves.ca/index/makehomepage/?url=https://1xbet-download-ko.com]1xbet[/url]
I meet each to the locale "recall" in today's review article we determination talk helter-skelter the bookmaker's area 1xBet.
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet
1xbet -
[url=https://budesonide.icu/]budesonide 200 mg[/url] [url=https://ciallis.online/]alli canada[/url]
-
[url=https://finpecia.run/]order propecia online[/url]
-
[url=https://onlinevpharmacy.online/]family store rx[/url]
-
[url=https://tamoxifen.site/]nolvadex uk sale[/url]
-
[url=https://worldpharmacyx.quest/]offshore pharmacy no prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://tetracyclinetabs.shop/]tetracycline hci 500mg capsules[/url]
-
[url=https://tretinointab.com/]retin a cream singapore where to buy[/url]
-
[url=https://phenergan.life/]phenergan nz buy[/url]
-
[url=http://tetracyclinetabs.shop/]terramycin for chickens[/url]
-
[url=https://tamoxifen.site/]tamoxifen citrate nolvadex[/url]
-
[url=https://tamoxifentabs.shop/]nolvadex tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://retino.shop/]retino gel[/url]
-
[url=http://cymbaltaduloxetine.shop/]cymbalta price south africa[/url]
-
[url=https://adiflucan.online/]who sells difluican with out a prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://avanadapoxetine.shop/]dapoxetine 10 mg[/url] [url=http://buynoroxin.monster/]noroxin 400[/url] [url=http://happyfamilyrx.quest/]online pharmacy in turkey[/url] [url=http://clopidogreltab.online/]clopidogrel 150 mg[/url] [url=http://cephalexin.sbs/]cephalexin generic price[/url]
-
[url=https://disulfiramantabuse.shop/]antabuse buy[/url] [url=https://stromectoltab.online/]stromectol nz[/url] [url=https://adiflucan.online/]diflucan india[/url]
-
[url=https://happyfamilystore.boutique/]happy family drugstore[/url]
-
[url=https://diclofenac.sbs/]diclofenac price in india[/url] [url=https://buysynthroid.life/]synthroid mexico pharmacy[/url] [url=https://ciallis.online/]how to alli[/url] [url=https://celexatabs.online/]celexa pill price[/url] [url=https://amitriptylinetab.shop/]endep 25 mg cost[/url]
-
[url=https://buyaccutane.life/]buy accutane 20mg[/url]
-
nolvadex chest fat buy nolvadex europe is it safe to buy nolvadex online https://nolvadexsrm.com/
-
[url=https://medrol.fun/]medrol tablet 8 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://priligy.fun/]dapoxetine for sale in usa[/url]
-
[url=https://zoloft247.com/]how to get zoloft without a prescription[/url] [url=https://cephalexin.sbs/]cephalexin over the counter uk[/url] [url=https://buynoroxin.monster/]noroxin tablets[/url] [url=https://worldpharmacyx.quest/]canadadrugpharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://canadianpharmaceuticalstores.online/]canada pharmacy happy family store pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://diflucan2023.com/]diflucan prescription australia[/url] [url=http://happyfamilyrx.shop/]mypharmacy[/url] [url=http://clopidogrelplavix.online/]clopidogrel medication[/url] [url=http://buyretinoa.life/]retino 0.025 gel[/url] [url=http://diclofenac.sbs/]can i buy diclofenac over the counter in usa[/url] [url=http://dexamethasone24.com/]dexamethasone 1 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://phenergan.life/]phenergan over the counter australia[/url]
-
[url=https://deltasonetab.monster/]buy deltasone[/url]
-
astaxanthin lipitor lipitor lisinopril atorvastatin landmark https://tenorminscx.com/
-
[url=https://synthroidlevothyroxine.online/]synthroid 112 mcg canada[/url]
-
[url=https://dexamethasone24.com/]dexamethasone 6 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://tizanidine.life/]zanaflex sleep[/url]
-
[url=https://buynexium.monster/]nexium 500[/url]
-
[url=http://seroqueltab.online/]seroquel prescription assistance[/url]
-
[url=http://toradol.click/]toradol[/url]
-
[url=http://furosemide.icu/]lasix 40 mg pill[/url]
-
[url=http://clopidogrel.fun/]clopidogrel pill[/url]
-
[url=https://baclofen.click/]baclofen brand name australia[/url]
-
[url=http://buynexium.monster/]where can you buy nexium[/url]
-
[url=http://anafraniltabs.online/]best price for generic anafranil 25mg in canada[/url]
-
[url=http://nexiumtab.shop/]nexium 40 mg drug[/url]
-
[url=http://flomax.site/]noroxin price[/url] [url=http://amitriptylinetab.shop/]amitriptyline medication[/url] [url=http://phenergan.run/]phenergan medicine over the counter[/url] [url=http://budesonide.icu/]budesonide 200[/url] [url=http://priligy.fun/]dapoxetine priligy[/url] [url=http://levitra247.com/]buy levitra online safely[/url] [url=http://diclofenac.sbs/]where can i purchase voltaren gel[/url] [url=http://happyfamilypharmacy.quest/]happy family store coupon code[/url]
-
[url=http://cephalexin.sbs/]keflex 250mg[/url]
-
[url=https://diclofenac.sbs/]diclofenac tablet price in india[/url]
-
[url=https://avto-nomeri.ru/]Автономера[/url]
Пишущий эти строки выделываем профессиональные номерные знаки, что отлично подоспеют на черте украсы чтобы вашего постоялый двор или гаража.
Автономера -
[url=https://tizanidine.life/]4mg zanaflex[/url]
-
[url=http://abilify.fun/]canadian pharmacy abilify 2mg[/url]
-
[url=https://prednisonerx.monster/]prednisone otc canada[/url]
-
[url=http://buynexium.monster/]nexium prilosec[/url]
-
[url=http://deltasonetab.monster/]60 mg prednisone[/url] [url=http://advairtab.monster/]advair price in mexico[/url] [url=http://medrol.fun/]medrol 8[/url] [url=http://baclofen.click/]baclofen 100mg cost[/url] [url=http://buyamitriptyline.monster/]amitriptyline 10mg for sale[/url] [url=http://happyfamilyrx.quest/]maple leaf pharmacy in canada[/url] [url=http://metforminx.online/]metformin nz[/url] [url=http://singulaira.quest/]singulair drug[/url]
-
[url=http://ttpharmacy.store/]austria pharmacy online[/url]
-
[url=http://singulaira.quest/]singulair brand name[/url] [url=http://noroxin.life/]noroxin pill[/url] [url=http://clomidx.com/]clomid 50 mg tablet price in india[/url] [url=http://finpecia.icu/]buy propecia hair loss[/url] [url=http://cephalexin.sbs/]cephalexin generic cost[/url] [url=http://baclofen.click/]buy baclofen[/url]
-
[url=http://tamoxifentabs.shop/]20 mg tamoxifen cost[/url]
-
canadian medication canadian drugstore viagra
http://lisamariepanagos.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=noprescriptioncanada.com canada drugs online review
[url=http://biopharm-l.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=noprescriptioncanada.com]canada pharmacy reviews[/url] legal canadian prescription drugs online -
[url=http://cialistada.com/]online generic tadalafil[/url]
-
[url=http://noroxin.life/]noroxin 500 mg[/url] [url=http://onepharmacy.online/]legal online pharmacy coupon code[/url] [url=http://canadianpharm.online/]online pharmacy reddit[/url] [url=http://adiflucan.online/]diflucan 150 mg capsule[/url] [url=http://medrol.fun/]medrol generic[/url] [url=http://toradol.click/]toradol pill[/url] [url=http://stromectoltab.online/]covid ivermectin[/url]
-
[url=https://canadianpharmaceuticalstores.online/]canadian pharmacy 24[/url]
-
[url=http://stromectoltab.online/]stromectol without prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://yasmintabs.online/]yasmin price india[/url] [url=https://zoloft247.com/]can i buy zoloft online[/url] [url=https://clopidogrel.fun/]medicine clopidogrel 75 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://finpecia.icu/]online propecia uk[/url]
-
[url=https://priligy.fun/]dapoxetine 30 price in india[/url]
-
[url=https://clopidogrelplavix.online/]plavix otc[/url]
-
[url=https://clopidogrelplavix.online/]clopidogrel 75 mg discount coupon[/url]
-
[url=https://levitratabs.monster/]order generic levitra online[/url]
-
canadian pharmaceutical companies that ship to usa prescription drug prices comparison
-
[url=https://buynexium.monster/]buy nexium[/url]
-
[url=http://anafraniltabs.online/]anafranil 300mg[/url]
-
[url=http://clomidx.com/]can i buy clomid over the counter in australia[/url]
-
[url=http://paxilparoxetine.online/]order paxil online[/url] [url=http://robaxin.sbs/]robaxin 500mg[/url] [url=http://lanoxin.monster/]digoxin 250 mcg tablets[/url] [url=http://baclofen.click/]baclofen 10 mg tablets[/url] [url=http://clopidogreltab.online/]plavix generic over the counter[/url] [url=http://noroxin.life/]noroxin pill[/url]
-
cheapest canadian pharmacies canada rx
http://tele-sleep.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=noprescriptioncanada.com legitimate online pharmacies
[url=http://susanpage.mobi/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=noprescriptioncanada.com]mexican pharmacy cialis[/url] meds online without doctor prescription -
[url=http://finpecia.run/]propecia 5mg india[/url]
-
[url=http://noroxin.life/]noroxin tablets[/url]
-
[url=http://clomid2022.online/]clomid for sale[/url] [url=http://modafinil247.com/]order modafinil online australia[/url] [url=http://singulair.life/]singulair 10 mg tablet[/url] [url=http://amitriptylinetab.shop/]endep 25mg price[/url] [url=http://buyretinoa.life/]retino 0.025 cream[/url]
-
[url=https://buymotrin.life/]buy motrin 800 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://paxilparoxetine.online/]paxil ocd[/url]
-
[url=http://citalopram.run/]buy celexa online cheap[/url]
-
[url=http://tamoxifen.click/]buy tamoxifen citrate[/url]
-
prescription drugs canada over the counter drug store
http://washingtonproductsinc.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=noprescriptioncanada.com price prescriptions
[url=http://aboutbattery.us/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=noprescriptioncanada.com]canadian pharmacies mail order[/url] mail order drug store -
[url=https://happyfamilystore.boutique/]express pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://singulaira.quest/]cost of singulair 5mg[/url]
-
[url=https://happyfamilyrx.shop/]canada pharmacy 24h[/url]
-
[url=https://fildenatab.online/]order fildena online[/url]
-
[url=http://buyamitriptyline.monster/]elavil 30 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://lisinoprils.online/]zestril tablet[/url]
-
[url=http://deltasonetabs.online/]prednisone 20 mg pill[/url]
-
[url=http://budesonide.icu/]budesonide 0.25 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://benicar.fun/]price of benicar[/url]
-
[url=http://buynexium.monster/]nexium pills 40 mg[/url]
-
[url=https://modafinil247.com/]buy provigil online india[/url] [url=https://buyaccutane.life/]accutane pills price in south africa[/url] [url=https://buyclindamycin.life/]clindamycin hcl 300 mg[/url] [url=https://trustedpharm.monster/]happy family store canadian pharmacy[/url]
-
canadian online pharmacies ratings best canadian drug prices
http://helpmegov.us/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=noprescriptioncanada.com safe online pharmacies
[url=http://mistingnozzles.info/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=noprescriptioncanada.com]no prescription online pharmacy[/url] order from canadian pharmacy -
[url=https://albendazol.online/]albendizolewithoutprescription.com[/url]
-
[url=http://fildenatab.online/]fildena 120mg[/url]
-
[url=https://vavdvdvdv.ru/]vavdvdvdv[/url]
Пролетарое зеркало толпа Vavada сегодня — внешная альтернатива сайтика, тот или иной животе (а) также востребована среди пользователей. Зеркало нужно при внезапной ...
vavdvdvdv -
[url=https://canadianpharm.online/]canadian pharmaceutical drugstore[/url]
-
[url=https://dexamethasone24.com/]dexamethasone 2 mg pill[/url]
-
[url=https://disulfiramantabuse.shop/]disulfiram tablets buy[/url]
-
top rated canadian online pharmacy drug store online
http://mysurebridge.org/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=noprescriptioncanada.com best canadian drug prices
[url=http://ambassadorphotographyandvideo.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=noprescriptioncanada.com]canada pharmacy reviews[/url] discount pharmacy coupons -
[url=https://buybupropion.life/]cost of wellbutrin[/url]
-
[url=https://antabusetabs.online/]antabuse 500mg[/url]
-
[url=https://yasmintabs.online/]buy yasmin online usa[/url]
-
[url=http://happyfamilystore.boutique/]canadian pharmacy without prescription[/url]
-
[url=https://lanoxin.monster/]digoxin 250 mg prices[/url]
-
[url=http://kamagrap.shop/]cheap kamagra 100mg[/url]
-
[url=https://buyfildena.monster/]fildena 100 for sale[/url]
-
[url=https://medrol.fun/]medrol pak 4mg[/url]
-
[url=https://onepharmacy.online/]canadian pharmacy viagra[/url]
-
[url=http://trustedpharm.monster/]family rx pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://stromectolst.com/#]ivermectin for humans[/url] buy ivermectin nz
-
[url=http://adiflucan.online/]diflucan 150 mg over the counter[/url]
-
[url=https://pin-up-rus.ru]пинап[/url]
Запрещенная в России букмекерская контора Пин ап снова попала в скандал. Его создатели выделили жителям России полный миллион евро.
пинап -
[url=http://stromectoltab.online/]ivermectin syrup[/url]
-
[url=http://tamoxifen.site/]tamoxifen price in usa[/url]
-
[url=https://www.minimum-price.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://pin-up-rus.ru]pin up[/url]
[url=http://suzannehallbrokerrealtor.com/SearchPoint/redir.asp?reg_id=pTypes&sname=/searchpoint/search.asp&lid=0&sp>pin up
pin up
pin up
pin up
pin up
pin up
pin up
pin up
pin up
pin up
pin up
pin up
pin up
pin up
pin up -
[url=https://celebrextab.online/]celebrex 400 mg capsule[/url]
-
stromectol buy generic ivermectin
https://stromectolst.com/# ivermectin 3mg
[url=https://stromectolst.com/#]ivermectin 3 mg tabs[/url] price of ivermectin -
[url=https://anafraniltabs.online/]anafranil from india[/url]
-
[url=http://tamoxifen.site/]buy nolvadex paypal[/url] [url=http://canadianpharmaceuticalstores.online/]canadian pharmacy uk delivery[/url] [url=http://adiflucan.online/]cost of diflucan[/url] [url=http://abilify.life/]abilify 1mg tablet[/url] [url=http://paxilparoxetine.online/]paroxetine without prescription[/url] [url=http://finpecia.icu/]finasteride 5mg[/url] [url=http://yasmintabs.online/]yasmin discount pharmacy[/url] [url=http://advairtab.monster/]advair generic best price[/url]
-
[url=http://singulair.life/]singulair tabs 10mg[/url]
-
[url=http://advairtab.monster/]advair 2017 coupon[/url] [url=http://happyfamilypharm.online/]pharmacy prices[/url] [url=http://clopidogreltab.online/]clopidogrel cost uk[/url]
-
[url=https://robaxin.run/]robaxin for back pain[/url]
-
[url=https://medrol.fun/]medrol 4 mg tab[/url]
-
[url=https://deltasonetabs.online/]prednisone 1 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://celexatabs.online/]citalopram 20mg tab[/url] [url=http://tretinointab.com/]cheap tretinoin 1[/url]
-
[url=http://cialis247.com/]cialis soft generic[/url]
-
[url=https://happyfamilypharmacy.quest/]online pharmacy pain[/url]
-
[url=http://happyfamilystore.boutique/]international online pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=https://buynexium.monster/]nexium 24 coupon[/url]
-
[url=https://happyfamilystore.boutique/]online pharmacy weight loss[/url]
-
[url=https://stromectolst.com/#]stromectol online[/url] stromectol otc
-
[url=http://buyclindamycin.life/]clindamycin 75mg capsules[/url] [url=http://modafinil247.com/]where can i purchase modafinil[/url] [url=http://buynexium.monster/]buy nexium online usa[/url] [url=http://buybupropion.life/]wellbutrin 150 mg tablets[/url]
-
[url=https://slncbbbbe.ru/]slncbbbbe[/url]
Расписания проф переподготовки утверждены Министерством создания равным образом науки РОССИЙСКАЯ ФЕДЕРАЦИЯ в течение свойстве альтернативы другому тончайшему образованию.
slncbbbbe -
[url=https://robaxin.sbs/]robaxin 1000 mg[/url]
-
ivermectin cream ivermectin 6 mg tablets
https://stromectolst.com/# stromectol covid
[url=https://stromectolst.com/#]ivermectin generic name[/url] buy stromectol -
[url=http://singulaira.quest/]singulair tablets 5mg[/url]
-
[url=http://synthroidm.monster/]synthroid 88[/url]
-
[url=http://cymbaltatabs.com/]generic cymbalta canada[/url]
-
[url=http://paxilparoxetine.online/]paxil 20 mg mexico[/url]
-
[url=https://flomax.site/]flomax online uk[/url]
-
[url=https://priligy.fun/]dapoxetine india online[/url]
-
[url=https://buybupropion.life/]bupropion 250 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://happyfamilypharmacy.quest/]pharmacy wholesalers canada[/url]
-
[url=https://stromectolst.com/#]stromectol tablets buy online[/url] ivermectin humans
-
[url=http://augmentintab.shop/]augmentin 875 mg cost[/url]
-
[url=https://trustedpharm.monster/]indian pharmacy[/url] [url=https://tretinointab.com/]retin a cream cost[/url] [url=https://tamoxifen.click/]buy nolvadex tamoxifen citrate[/url] [url=https://nexiumtab.shop/]cost of nexium 40 mg in australia[/url] [url=https://buyretinoa.life/]retino 05[/url]
-
[url=http://flagyltabs.online/]flagyl prescription cost[/url]
-
[url=http://ttpharmacy.store/]foreign pharmacy online[/url]
-
[url=https://buysuhagra.life/]suhagra 100 from india[/url] [url=https://adiflucan.online/]buy diflucan yeast infection[/url] [url=https://atomoxetine.life/]cost of strattera 25 mg[/url] [url=https://abilify.life/]canadian pharmacy abilify 10 mg[/url] [url=https://provigil.fun/]buy provigil without prescription[/url]
-
[url=http://stromectoltab.online/]where can i buy stromectol[/url]
-
how much does ivermectin cost ivermectin 6
https://stromectolst.com/# stromectol nz
[url=https://stromectolst.com/#]stromectol australia[/url] ivermectin gel -
[url=http://worldpharmacyx.quest/]reddit canadian pharmacy[/url]
-
[url=http://cymbaltatabs.com/]cymbalta 90 mg daily[/url]
-
[url=https://kamagrap.shop/]kamagra ajanta jelly[/url] [url=https://deltasonetab.monster/]brand name prednisone[/url] [url=https://clopidogreltab.online/]plavix cost 300 mg[/url]
-
[url=http://dexamethasone24.com/]dexamethasone 20 mg tablet[/url] [url=http://trustedpharm.monster/]silkroad online pharmacy[/url] [url=http://albendazol.online/]albendazole how to[/url] [url=http://albuteroltabs.com/]buy combivent online[/url]
-
[url=https://clopidogrel.fun/]plavix generic pill[/url]
-
[url=http://cialistada.com/]tadalafil online pharmacy[/url] [url=http://priligy.fun/]dapoxetine 30 mg tablet price in india[/url] [url=http://buymotrin.life/]prescription motrin 800[/url]
-
[url=http://tadacip.run/]buy tadacip online india[/url]
-
[url=http://flomax.site/]cheapest flomax[/url]
-
[url=https://ttpharmacy.store/]canadian pharmacy 24[/url]
-
[url=http://arimidex.life/]how to get arimidex[/url]
-
[url=http://triplewranchllc.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1xbet-download-ar.com]1xbet apk[/url]
[url=http://blog.poyo.jp/archives/id-1166205602/repost-1/mode=res_new?categ=1year=2006m>1xbet apk
1xbet apk
1xbet apk
1xbet apk
1xbet apk
1xbet apk
1xbet apk
1xbet apk
1xbet apk
1xbet apk
1xbet apk
1xbet apk
1xbet apk
1xbet apk
1xbet apk -
[url=https://1xbet-download-ar.com]1xbet com[/url]
The 1xBet bookmaker allows you to bet on animate events in all sports disciplines. In corresponding with the play, you last will and testament be proficient to follow the competition auspices of a cost-free line version.
code promo 1xbet -
[url=https://singulaira.quest/]cost of singulair rx[/url]
-
[url=https://fildenatab.online/]fildena 100 mg online[/url]
-
[url=http://arimidex.life/]arimidex coupon[/url]
-
[url=http://dipyridamole.fun/]buy dipyridamole[/url] [url=http://pharmacyonline.foundation/]foreign pharmacy no prescription[/url] [url=http://vardenafil.trade/]levitra discount canada[/url] [url=http://doxycycline.wtf/]buy doxycycline south africa[/url]
-
[url=https://seroqueltab.online/]where to buy seroquel online[/url] [url=https://canadianpharmaceuticalstores.online/]online pharmacy uk[/url] [url=https://noroxin.life/]noroxin tablets[/url] [url=https://buysuhagra.life/]suhagra buy online[/url] [url=https://tetracyclinetabs.shop/]online tetracycline[/url]
-
[url=https://citalopram.run/]buy citalopram 40mg tablets[/url]
-
[url=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet polska[/url]
Banned in Poland bookmaker Mostbet again got into a scandal. Its creators gave the inhabitants of Russia one million euros.
Mostbet -
[url=https://slot-machines-casono.com]casinos slot machine[/url]
The most routine carriage of online gambling is slots. This is an electronic analogue of slot machines. You in the right a gamble, take in one's arms the button, effective reels with pictures or symbols spin. If a inescapable combination hew down in sight after a lay off, you won something.
casino online slots machines -
[url=http://go.eniro.dk/lg/ni/sport/poker/cat-5888/http:/www.sngwiz.com/tiki/tiki-index.phphttps://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://www.pre-pro.com/glasschat/go.php?url=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://service-ok.svyaznoy.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://united-uniforms.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://sexshop-e.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://game-ost.com/redirect.php?link=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://myavcs.com/dir/dirinc/click.php?url=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://klabhouse.com/en/CurrencyUpdate/USD/?urlRedirect=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://hoteles.logrono24.com/wp-content/plugins/AND-AntiBounce/redirector.php?url=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://io.fusedeck.net/t/redir?https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://volchiha22.ru/go/?url=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://my.tvnet.if.ua/connect_lang/en?next=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://ww.kutees.com/cgi-bin/crtr/out.cgi?s=65&l=Pics_Yesterday&u=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://jessicajbrooks.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://coolmic.me/ad?agn=1&src=19&url=https://lensoftruth.com]mostbet[/url]
pozdrawiam wszystkich w location „review” w dzisiejszym rewizji bedziemy zaangazowanie porozmawiamy nieporzadku biura bukmachera Pin Up.
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet -
[url=https://slncbbbbg.ru/]slncbbbbg[/url]
Конкурсы для деток, созидательные конкурсы 2022, состязания чтобы преподавателей, всероссийские конкурсы, конкурсы 2022.
slncbbbbg -
[url=http://sakh-psue.ru/go/url=https://slot-machines-casono.com]slots online for free[/url]
[url=http://uziolog.ru/redirect?url=https://slot-machines-casono.com]slots online for free[/url]
[url=https://zoogav24.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=click_to_call&event2=&event3=&goto=https://slot-machines-casono.com]slots online for free[/url]
[url=http://chicagomarinecanvas.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://slot-machines-casono.com]slots online for free[/url]
[url=http://antivirus-alarm.ru/proverka/?url=https://slot-machines-casono.com]slots online for free[/url]
[url=http://touch.com.ua/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://slot-machines-casono.com]slots online for free[/url]
[url=https://privatsextreffen.org/wp-content/plugins/AND-AntiBounce/redirector.php?url=https://slot-machines-casono.com]slots online for free[/url]
[url=http://labs.oldiestation.es/php.php?a%5B%5D=slots online for free
slots online for free
slots online for free
slots online for free
slots online for free
slots online for free
slots online for free
slots online for free
slots online for free
slots online for free
slots online for free
slots online for free
slots online for free
slots online for free
slots online for free -
[url=https://drugs1st.com/#]mexican pharmacy online[/url] canadian pharmacy victoza
-
online pharmacy in turkey mexican pharmacy online
https://drugs1st.com/# online med pharmacy
[url=https://drugs1st.com/#]cheapest online pharmacy[/url] legit pharmacy websites -
[url=https://drugs1st.com/#]cheapest online pharmacy[/url] canadian pharmacy meds
-
[url=https://gbrkpslpzhr.ru/]gbrkpslpzhr[/url]
Отмывание жилплощади после пожара охватывает в течение себе отмывку потолка, стэн, пола, радиаторов отопления, осветительных приборов, дверей, а также при потребности корпусной мебели среди также с наружной стороны, осуществляется пункт плавной мебели, матрасов, штор, тюля, ламбрекенов, то является текстильные изделия, хорошо впитывающей фимиам гари.
gbrkpslpzhr -
[url=https://drugs1st.com/#]mexican pharmacy online[/url] legit online pharmacy
-
[url=https://drugs1st.com/#]top mail-order pharmacies in usa[/url] pharmacy express
-
best online canadian pharmacy canadian pharmacy without prescription
https://drugs1st.com/# online pharmacy non prescription drugs
[url=https://drugs1st.com/#]canadian pharmacy meds[/url] legit canadian online pharmacy -
cheap pharmacy canadian drugstore
https://noprescriptioncanada.com/# canadian pharmacies without an rx -
[url=https://drugs1st.com/#]us online pharmacy[/url] canadian prescription pharmacy
-
bestpharmacyonline.com online canadian pharmacies
https://noprescriptioncanada.com/# online pharmacy canada -
cheap amoxicillin 500mg amoxicillin cephalexin
https://zithromax1st.store/# zithromax capsules
[url=https://amoxil1st.store/#]amoxicillin no prescription[/url] where to buy amoxicillin 500mg -
[url=https://prednisone1st.store/#]how much is prednisone 10mg[/url] prednisone 15 mg daily
-
amoxicillin no prescription order amoxicillin no prescription
https://amoxil1st.store/# amoxicillin buy online canada
[url=https://cipro1st.store/#]cipro online no prescription in the usa[/url] ciprofloxacin 500mg buy online -
where can i get zithromax over the counter cost of generic zithromax
https://zithromax1st.store/# zithromax order online uk
[url=https://doxycycline1st.store/#]doxycycline 300 mg daily[/url] buy online doxycycline without prescription -
[url=https://zithromax1st.store/#]buy cheap zithromax online[/url] zithromax 250
-
[url=https://zithromax1st.store/#]zithromax for sale cheap[/url] buy zithromax without prescription online
-
ciprofloxacin 500 mg tablet price ciprofloxacin generic
https://cipro1st.store/# ciprofloxacin generic
[url=https://doxycycline1st.store/#]doxycycline hydrochloride 100mg[/url] doxycycline 100mg buy online -
п»їcipro generic ciprofloxacin 500 mg tablet price
https://doxycycline1st.store/# doxycycline prescription
[url=https://amoxil1st.store/#]buy amoxicillin online cheap[/url] medicine amoxicillin 500 -
[url=https://theoceansailingguide.com]most bet[/url]
Banned in India, the bookmaker and casino Mostbet again fell into a scandal. Its creators gave the residents of India bonuses and gifts of one million euros.
mostbet apk -
[url=https://ica.cz/language.aspx?culture=en-US&returnUrl=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://easyfiles.pl/54018/https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://sp-bum.com/redirect/?url=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://forumdubna.ru/redirect.php?link=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://www.google.co.kr/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=Free+Sex+Stories&source=web&cd=9&ved=0CGkQFjAI&url=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://www.dicoperso.com/annuaire/go.php?url=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://dinalcultura.org.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://www.westhawaiiaa.org/redirect.php?url=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://casadelalfareroministries.org.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://inetshopper.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=catalog_out&event2=http2FD0D0%B5BD%D1D0%BE80?&goto=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://house-jp.com/Fudousan/Sub_Url.php?url=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://mezhuev.su/redirect?url=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://876785.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://randrpropertyrehab.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://facto.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://theoceansailingguide.com]mostbet[/url]
Invited to the bookmaker and online casino Mostbet. Here you choice turn up Mostbet 200 Freespins and $200 set aside bonuses
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet -
[url=https://prednisone1st.store/#]where to buy prednisone in australia[/url] online prednisone 5mg
-
п»їcipro generic antibiotics cipro
https://prednisone1st.store/# india buy prednisone online
[url=https://cipro1st.store/#]п»їcipro generic[/url] buy cipro -
doxycycline pharmacy buy doxycycline tablets 100mg
https://zithromax1st.store/# can i buy zithromax over the counter
[url=https://amoxil1st.store/#]amoxicillin 500 mg brand name[/url] medicine amoxicillin 500mg -
https://clomid1st.science/# clomid order online uk
-
[url=https://edpills.science/#]best erection pills[/url] cheap erectile dysfunction pill
-
https://clomid1st.science/# buy clomid 50mg uk
-
clomid for sale in usa cheap clomid canada
https://prednisone1st.science/# prednisone 5 mg tablet price
[url=https://propecia1st.science/#]propecia prices[/url] buy finasteride no rx -
[url=https://propecia1st.science/#]propecia 5 mg[/url] buy propecia tablets
-
https://prednisone1st.science/# prednisone uk over the counter
-
vrgepywtblz canadian med cialis in usa pharmacy canada viagra generic [url=https://backforgood.faith/wiki/Five_Facts_About_Pharmacy_You_Need_to_Know]canadian pharmacy reviews[/url] ed meds online
cialis over the counter in canada how to buy viagra cialis of canada [url=https://flipboard.com/@rugbyneedle83]northwestpharmacy.com canada[/url] northwest canadian pharcharmy online
lowest cost cialis canadian viagra online pharmacy reviews canadian online pharmacy viagra [url=https://marvelcomics.faith/wiki/Exactly_How_to_Buy_Prescription_Drugs_From_a_Canadian_Pharmacy]cialis over the counter canada[/url] what would happen if a girl took viagra -
clomid online australia where can i buy clomid medicine
https://clomid1st.science/# clomid pills online india
[url=https://edpills.science/#]ed meds online[/url] male ed pills -
[url=https://prednisone1st.science/#]prednisone 20mg[/url] generic prednisone 10mg
-
[url=https://prednisone1st.science/#]prednisone purchase canada[/url] where to buy prednisone in canada
-
[url=https://sosnitikkma.dp.ua/]sosnitikkma[/url]
Запчастини та аксесуари чтобы дитячих колясок Carrello на Україбукваі Універсальний підсклянник чтобы коляски El Camino Экспресс-доставка числом Україбукваі числом 2 617 грн в течениеід 2 продавців течение Сумка-органайзер на коляску Carrello CRL-7005 /12/ Сірий Экипаж універсальна Epica CRL-8510/1 (2in1) Almond Beige + дощовик CARRELLO 14 159.7 — 15 526.11 грн в течениеібуква 4 продавців течение Сидіння (букваідніжка) для другої …
sosnitikkma -
[url=https://propecia1st.science/#]buy propecia cheap online[/url] finasteride and propecia
-
online pharmacy usa canadian pharmacies reviews
https://withoutprescriptions.store/# canadian pharmacy antiobotics without prescription
[url=https://canadianpharmacy.icu/#]canadian mail order pharmacy[/url] thecanadianpharmacy -
https://withoutprescriptions.store/# discount viagra canadian pharmacy
-
generic pill shop generic ed pills from india
https://indiapharmacy.store/# cheap generic ed pills
[url=https://withoutprescriptions.store/#]drugs without a doctor's prescription canada[/url] discount prescription drugs -
northwest pharmacy canada reputable canadian mail order pharmacies
https://indiapharmacy.store/# buying generic drugs from india
[url=https://indiapharmacy.store/#]ed drugs online from india[/url] secure generic pills -
[url=https://aviator-casino-game.com]aviator-casino-game com[/url]
The Aviator game is a well-liked hollow out machine for gambling also in behalf of proper and with paper money, represented in the portfolio of a whopping number of online casinos. In a sharp outmoded of quiddity, the sulcus has already won an provocative gang of fans.
aviator casino -
[url=https://redirect.playgame.wiki/link?url=https://aviator-casino-game.com]aviator casino game[/url]
[url=https://xn--57-mlctpfqq7a.xn--p1ai/out.php?url=https://aviator-casino-game.com]aviator casino game[/url]
[url=http://www.ecards.co.uk/account/logout?redirect=https://aviator-casino-game.com]aviator casino game[/url]
[url=http://m.lmstn.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://aviator-casino-game.com]aviator casino game[/url]
[url=http://go.dlcode.ir/?url=https://aviator-casino-game.com]aviator casino game[/url]
[url=http://ege-english.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://aviator-casino-game.com]aviator casino game[/url]
[url=http://dvdmania.ru/eshop/search.php?search_query=aviator casino game
aviator casino game
aviator casino game
aviator casino game
aviator casino game
aviator casino game
aviator casino game
aviator casino game
aviator casino game
aviator casino game
aviator casino game
aviator casino game
aviator casino game
aviator casino game
aviator casino game -
https://canadianpharmacy.icu/# canadian pharmacy meds
-
keclyo9r6m4 generic drugs ephedrine sulfate how long does viagra last [url=http://wmxz.com.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=412714]buy generic viagra[/url] viagra sale online
cialis daily canada how does cialis work ed drugs [url=https://devpost.com/dmitriev-zhora-7979]canadian pharmacies shipping to usa[/url] viagra professional
cialis without prescription price for cialis in canada canadian pharcharmy online reviews [url=https://bit.ly/3Cw3cLV+]best canadian online pharmacy reviews[/url] viagra pharmacy online -
https://canadianpharmacy.icu/# reputable canadian online pharmacy
-
[url=https://brasil-mostbet.com]most bet[/url]
Banned in Brasil, the bookmaker and cassino Mostbet br again fell into a scandal. Its creators gave the residents of India bonuses and gifts of one million brazil real.
Mostbet casino -
[url=http://www.3dviewstation.se/redirect.php?url=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://www.rockland-sachsen.de/gaestebuch/go.php?url=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://shijiazhuang.city8.com/signout.html?returnurl=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://hpguild.com/view_test/graphic.php?act=&URL=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://www.ealingtoday.co.uk/default.asp?section=info&link=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://labcore.de/redirect.php?link=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://www.fuckthisshemale.com/d/out?p=62&id=2225477&c=0&url=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://thecliffbay.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://suveniri-sochi.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://pixel2261.everesttech.net/2261/r/3/s_9807ccac8ca6aac440af3b7c1dd80fea_14454374828/url=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://customballetbar.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://super-shop39.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=https://www.web-trump.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://www.mimamayyo.com/link.php?url=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
[url=http://startin.opensource-entrepreneurship.org.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://brasil-mostbet.com]mostbet[/url]
Invited to the bookmaker and online cassino Mostbet. Here you inclination turn up Mostbet 250 Free spins and $250 put bonuses
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet
mostbet -
prescription drugs prices drugs without a doctor's prescription canada
https://canadianpharmacy.icu/# recommended canadian pharmacies
[url=https://canadianpharmacy.icu/#]canadian pharmacy[/url] canadian pharmacy online -
www canadianonlinepharmacy canadian pharmacies that are safe
https://canadianpharmacy.icu/# canadian online pharmacy cialis
[url=https://withoutprescriptions.store/#]prescription meds without the prescriptions[/url] trust online pharmacy -
https://withoutprescriptions.store/# canada drugs online pharmacy
-
discount canadian pharmacy buying prescription drugs in mexico
https://withoutprescriptions.store/# top mail order pharmacies
[url=https://withoutprescriptions.store/#]buy medication without an prescription[/url] recommended canadian pharmacies -
wrr4zk8fhtd viagra dosing canadianpharmacymeds.com viagra online cheap [url=https://www.ultimate-guitar.com/u/cloverdead95]walmart medication list[/url] viagra sample
viagra sales online generic viagra 100mg canada prescriptions online [url=https://moparwiki.win/wiki/Post:Five_Facts_About_Pharmacy_You_Need_to_Know]pharmacy viagra[/url] online pharmacy without prescription
canada drug superstore shopping online canada order cheap viagra [url=https://bbs.pku.edu.cn/v2/jump-to.php?url=http://www.canadotcphar.com/]drugstore of canada[/url] how much does viagra cost -
[url=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Џин ап[/url]
Запрещенная в России букмекерская контора и казино Пин ап вновь попала в скандал. Его создатели подарили жителям России бонусы и подарки в размере одного миллиона российских рублей.
Пин ап сайт -
etjzrzyo2d9 canada meds best canadian pharcharmy online viagra online sales [url=http://tbfx8.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=143561]mexican pharmacy[/url] buy viagra without prescription
buy cialis canada viagra prescription online ed drugs [url=https://qnbuz.net:443/user/northfall05]canadian pharmacy for viagra[/url] canadian pharmacies shipping to usa
buy cialis viagra shelf life generic viagra online pharmacy [url=https://www.renderosity.com/users/id:1312706]cheapest price for cialis[/url] buy viagra online without prescription -
[url=http://boyarka.biz.ua/redirect.php?url=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=http://dr-paramonov.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=https://vuit.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=http://maisonbible.ch/module/lpmainmenu/redirect?url=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=https://liralandhelp.frantov.com.ua/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=http://images.google.cz/url?sa=t&url=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=http://park3.wakwak.com/~yadoryuo/cgi-bin/click3/click3.cgi?cnt=chalet-main&url=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=http://www.luxuslimousinen.at/gb/go.php?url=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=https://www.finanzplaner-deutschland.de/fpdeu/inc/mitglieder_form.asp?nr=24&referer=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=http://realtimelogistics.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=https://m.rarajewelry.com/member/login.html?noMemberOrder=&returnUrl=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=http://www.etuber.com/cgi-bin/a2/out.cgi?id=117&u=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=http://med-standard.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=http://accountingweekly.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
[url=http://dayviews.com/externalLinkRedirect.php?url=https://pin-up-7rus.ru]Pin up[/url]
Добро пожаловать в букмекерскую контору и онлайн-казино Пин ап. Здесь вы намерение найдёте Пин ап 250 бесплатных вращений и $250 накопительные бонусы за регистрацию!
Pin up
Pin up
Pin up
Pin up
Pin up
Pin up
Pin up
Pin up
Pin up
Pin up
Pin up
Pin up
Pin up
Pin up
Pin up -
[url=https://marshrutka-dnepr-kharkov.dp.ua/]Маршрутка Днепр Харьков[/url]
Эпизодично приходить в соседственный яяма что поделаешь быстро, а свой в доску авто нет чи оно в течение ремонте. Что делать в течение данном случае? Прийти на выручку труповозка Днепр-Харьков, кок отправляется в течение пункт назначения несколько разочек в течение день. Этакий ход разрешит я мухой пробежать 215 км, за 3-4 поры заключаться на области - еще и вернуться с полпути!
Маршрутка Днепр Харьков -
https://datingonline1st.com/# good free dating sites
-
[url=https://datingonline1st.shop/#]singles dating[/url] best dating websites online
-
https://datingonline1st.com/# new singles online
-
[url=https://sosnitiksisi.com]sosnitiksisi.com[/url]
LeoVegas AB is a Swedish versatile gaming company and provider of online casino and sports betting services such as video slots and video poker.
sosnitiksisi -
[url=http://movilesbaratosybuenos.com/wp-content/plugins/and-antibounce/redirector.php?url=https://sosnitiksisi.com]sosnitiksisi.com[/url]
[url=http://www.agritel.com/redirect.php?url=https://sosnitiksisi.com]sosnitiksisi.com[/url]
[url=https://images.google.ms/url?q=https://sosnitiksisi.com]sosnitiksisi.com[/url]
[url=https://coloroutofspacemovie.com/out/screenings/1466869?minimal=1&load_view=google_analytics&utm_campaign=None&ab_name=Theater+Direct+ab&ab=https://sosnitiksisi.com]sosnitiksisi.com[/url]
[url=https://macarons.sg/wp-content/themes/eatery/nav.php?-Menu-=https://sosnitiksisi.com]sosnitiksisi.com[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.ro/url?q=https://sosnitiksisi.com]sosnitiksisi.com[/url]
[url=https://alleskostenlos.ch/outgoing/3346-dfc33.htm?to=https://sosnitiksisi.com]sosnitiksisi.com[/url]
[url=http://www.google.tm/url?q=https://sosnitiksisi.com]sosnitiksisi.com[/url]
[url=https://www.nkj.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://sosnitiksisi.com]sosnitiksisi.com[/url]
[url=http://topsantehnik.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://sosnitiksisi.com]sosnitiksisi.com[/url]
[url=https://bvbombers.com/tracker/index.html?t=ad&pool_id=69&ad_id=96&url=https://sosnitiksisi.com]sosnitiksisi.com[/url]
[url=https://eltee.de/Openads/adclick.php?bannerid=3&z>sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com
sosnitiksisi.com -
[url=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Њостбет официальный сайт[/url]
Полулегальная в России бк и казино Мостбет вновь попала в скандал. Его создатели подарили жителям России бонусы и подарки в размере рифмованного миллиона рублей России.
Mostbet Казино -
[url=https://datingonline1st.shop/#]local singles[/url] europe online dating
-
https://datingonline1st.com/# 12 single dating site
-
cialis kaufen cialis vs viagra cost cialis canada pharmacy
-
tadalafil soft gel capsule 20mg how fast does tadalafil work effect of tadalafil on female
-
prices of cialis 20 mg cialis 800 buy cialisonline
-
[url=https://drugsoverthecounter.shop/#]uti medicine over the counter[/url] best over the counter nausea medicine
-
viagra 6800mg sildenafil 100 capsules viagra online free shipping
-
canada drugs cialis cialis none prescription cialis definition
-
[url=https://www.mreviews.com.br/redirect.php?id=1309&url=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=https://image.google.de/url?q=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=https://bid.curranmiller.com/view-auctions/catalog/id/8649/lot/1241060/?url=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=http://www.arcanum.sk/plugins/guestbook/go.php?url=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=https://li659-71.members.linode.com/?URL=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=http://webreel.com/api/1/click?url=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=https://www.mundo.com/openmail/es.php?title=17%20hilarantes%20fotos%20de%20celebridades%20arruinando%20postales&url=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=http://www.kclifm.com/modules/mod_jw_srfr/redir.php?url=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=https://dp.prostitutki-red.com/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=http://www.servicetrend.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=https://mapage.pro/domain/https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=https://mytinydick.net/talk/redirect-to/?redirect=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=http://madpapasite.com/cgi-bin/out.cgi?id=18&l=top_top&u=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=http://www.chooseablowjob.com/cgi-bin/out.cgi?id=greg44&url=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
[url=http://naturesgroup.com.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://uzbekistan-mostbet.net]Mostbet[/url]
Получите в букмекерскую контору и онлайн-казино Мостбет. Здесь вы склонность найдёте Мостбет 250 бесплатных вращений и $250 отложите бонусы за регистрацию!
Mostbet
Mostbet
Mostbet
Mostbet
Mostbet
Mostbet
Mostbet
Mostbet
Mostbet
Mostbet
Mostbet
Mostbet
Mostbet
Mostbet
Mostbet -
[url=https://mtprxvshlm.dp.ua/]mtprxvshlm[/url]
Доходные расценки сверху продукты каталога Мотошлемы и аксессуары. Скидки! Большой религия, экспресс-фото, рецензии и ядреный сервис. Шибкая доставка.
mtprxvshlm -
hcn3obuw793 cialis over the counter in canada cheap viagra for sale where can you buy viagra [url=https://botdb.win/wiki/Exactly_How_to_Buy_Prescription_Drugs_From_a_Canadian_Pharmacy]canada online drugs[/url] generic viagra free shipping
discount tadalafil cialis canadian canadian pharmaceuticals [url=http://zltgo.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=648392]ordering viagra[/url] buy brand viagra
cialis online canada viagra use viagra forum [url=https://bysee3.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=993380]viagra without a prescription[/url] generic viagra pills -
sildenafil 25mg 50mg 100mg sildenafil 1000 mg viagra online over the counter
-
https://drugsoverthecounter.shop/# best over the counter weight loss pills
-
[url=https://drugsoverthecounter.shop/#]meclizine over the counter[/url] over the counter hearing aids
-
viagra vs cialis vs levitra reviews cialis black 800 to buy in the uk one pill when will generic cialis be available in the us
-
over the counter tapeworm treatment for dogs best hemorrhoid treatment over the counter
https://drugsoverthecounter.shop/# over the counter muscle relaxer
[url=https://drugsoverthecounter.shop/#]over the counter laxatives[/url] male uti treatment over the counter -
Keflex your pharmacy online cefixime online pharmacy
-
amoxicillin price pharmacy cvs pharmacy application online levitra from canadian pharmacies
-
[url=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus.com[/url]
Leo Vegas Casino does NOT take players from Russia. LeoVegas online casino is owned nearby LeoVegas International ltd, registered in Malta.
sosnitikus -
parlodel online pharmacy cialis pharmacy coupon abused prescription drugs
-
venlor xr generic effexor xr pharmacy reliable online pharmacy cialis people's pharmacy prilosec
-
[url=https://drugsoverthecounter.shop/#]the best over counter sleep aid[/url] flonase over the counter
-
pharmacies near me viagra canada pharmacy review tramadol pharmacy cod
-
[url=https://garant-vskrytie-zamkov178.ru/]вскрытие авто[/url]
Авантюристичное энтеротомия авто в Москве. Мастер в 15 мгновениях через Вы в течение распорядке 24/7; Борзое энтеротомия без дефектов ЛКП (а) также кузова; Работа мало экстрим-спорт всех маркий и ..
вскрытие авто -
[url=http://images.google.jo/url?q=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=https://maps.google.co.za/url?rct=i&sa=t&url=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=https://image.google.sm/url?q=j&rct=j&url=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=http://www.superhqporn.com/cgi-bin/atx/out.cgi?id=14&tag=top™=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=http://www.paulcarr.com/?url=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=http://www.rayfilm.cz/cs/download/redir.php?url=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=https://burda.blog.idnes.cz/redir.aspx?url=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=http://www.windsurfingnz.org/rssfeeders/wnzrss.php?url=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=http://aldermansgreen.2day.ws/aldermansgreen/search/?url=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=http://diendan.robocon.vn/redirect/?url=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=http://tuoitrenangdong.net/go.php?url=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=https://xn--o9jlb3247al2f9ndwuay51bsp1cw7c.gamerch.com/gamerch/external_link/?url=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=https://christopher-wray.co.jp/form/cart_new.php?itemid=PC603%2FCLR&thumb=Toplistagier.pl%2Findex.php%3Fa%3Dstats%26u%3Dtuyetkime84&permaab=&price=46%2C000%E5%86%86%EF%BC%8B%E7%A8%8E&structure=%E3%82%AF%E3%83%AA%E3%82%B9%E3%82%BF%E3%83%AB%2F%E7%9C%9F%E9%8D%AE&size=H310+x+W145&watt=E17%2F25W%E3%80%9C100W+x+1-glazedhttps://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=https://kur.traut-reisen.com/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
[url=http://thgrass.com/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://sosnitikus.com]sosnitikus[/url]
LeoVegas AB is a Swedish mobile gaming train and provider of online casino and sports betting services such as video slots, video poker and live betting in various oecumenical markets.
sosnitikus
sosnitikus
sosnitikus
sosnitikus
sosnitikus
sosnitikus
sosnitikus
sosnitikus
sosnitikus
sosnitikus
sosnitikus
sosnitikus
sosnitikus
sosnitikus
sosnitikus -
[url=https://drugsoverthecounter.com/#]best over the counter hair color[/url] nystatin cream over the counter
-
sw7eafzsyk6 sildenafil viagra viagra india pharmacy cialis or generic canada [url=https://shorl.com/lodramufukify]buying viagra in canada[/url] canada online drugstore
viagra online without prescription liquid viagra buy cialis online in canada [url=https://fakenews.win/wiki/How_to_Buy_Prescription_Drugs_From_a_Canadian_Pharmacy]viagra shelf life[/url] drugs without a prescription
prescription medication order viagra online canadian-meds [url=https://jszst.com.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=797000]viagra no prescription[/url] overnight viagra -
[url=https://drugsoverthecounter.shop/#]clobetasol over the counter equivalent[/url] is plan b over the counter
-
ocv7w0vorvm viagra canada online mail order viagra prescription prices [url=http://ageloc.store/home.php?mod=space&uid=706190]erectile dysfunction drugs online[/url] canadian drug
canadian viagra online pharmacy online pharmacy medications canadian online pharmacy viagra [url=https://www.ted.com/profiles/39025083]viagra and high blood pressure[/url] buy viagra online
canadian prescriptions real viagra generic cialis online pharmacy [url=https://www.longisland.com/profile/spherejoseph89]cheap cialis from canada[/url] canada drugs online -
[url=https://darlab.ru/]Техническая поддержка и обслуживание сайтов[/url]
Поддержка веб- сайтов является обязательной в некоторой степени ихний устойчивого функционирования. Интернет-площадки встали лучшим инструментом продвижения бизнеса. Поэтому нередко философема о сопровождении сформировывается под впечатлением от веб-проекта, который нищенствует в течение постоянном развитии.
Техническая поддержка и обслуживание сайтов -
[url=https://over-the-counter-drug.com/#]over the counter cough medicine[/url] strongest over the counter painkiller
-
[url=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada Љазино[/url]
Подвижная телеверсия дозволяет играть он-лайн путем челкогляделка чи официальный сайт увлекающегося ресурса. Посетителю приемлемы все требуемые функции а также в подвижном Vavada
Вавада официальный -
https://over-the-counter-drug.com/# united healthcare over the counter essentials
-
[url=http://websiteindexer.com/redirect.php?url=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=http://www.bigtitsmovie.xtopsite.info/out.cgi?ses=dhgmync5hi&id=189&url=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=http://genkin-log.com/wp-content/plugins/post-linkcontrol/click.php?url=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=http://tsushima.su/links.php?go=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=https://belglory.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=http://2v3.su.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=http://texasforestrymuseum.com/link/?url=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=https://internet-i-deti.ru/away.php?url=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=https://www.lestrademensuel.fr/click.php?url=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=http://vavada-casino-online-777.ru.tr.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=https://zakupkikomos.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=click_to_call&event2=&event3=&goto=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=http://a2g.cc/cgi-bin/a2gi/out.cgi?id=mparty&url=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=http://www.tubemom.tv/n/n.php?u=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=http://momnudepictures.com/ddd/link.php?gr=1&id=f6a0ab&url=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
[url=http://www.battledawn.com/linkexchange/go.php?url=https://vavada-casino-online-777.ru]Vavada[/url]
Ясненько посетить на одно из популярнейших игровых интернациональных площадок vavada. Здесь гостям доступны элита настольные игры, турниры, гонки а также черное море бонусов.
Vavada
Vavada
Vavada
Vavada
Vavada
Vavada
Vavada
Vavada
Vavada
Vavada
Vavada
Vavada
Vavada
Vavada
Vavada -
[url=https://over-the-counter-drug.com/#]over the counter stocks[/url] over the counter cough medicine
-
viagra pills for sale uk sildenafil tablets 120mg on line viagra
-
40 mg cialis too much cialis 5mg tadalafil what is tadalafil made from
-
zoloft canada pharmacy costco pharmacy prometrium prevacid online pharmacy
-
costco pharmacy prices levitra online pharmacy canada post haste pharmacy oxycodone
-
cialis 36 canada what is cialis black 800mg cialis no script
-
cost of viagra in us price of sildenafil in india purchase viagra online without prescription
-
how much is vicodin at pharmacy perscription drugs from canada post haste pharmacy viagra
-
viagra online store how much is viagra australia generic viagra in mexico
-
[url=https://over-the-counter-drug.com/#]nausea medication over the counter[/url] over the counter blood pressure medicine
-
[url=https://over-the-counter-drug.com/#]over the counter pain medication[/url] over the counter muscle relaxers cvs
-
bph tadalafil canadian pharmacy no prescription generic cialis lower cost cialis
-
cialis no precription canadian cialis 200 mg. cialis experience reddit
-
tadalafil tablets 20 mg global cialis insurance coverage blue cross cialis for daily use side effects
-
canadian pharmacy viagra cost how to buy sildenafil online usa viagra nz over the counter
-
buy generic viagra online in usa 150 mg viagra how much is sildenafil
-
tadalafil generic headache nausea brand name cialis online max dose of tadalafil
-
tadalafil liquid review cialis 10 mg what can i take to enhance cialis
-
how to buy amoxycillin buy amoxil
https://zithromax.science/# zithromax prescription online
[url=https://zithromax.science/#]buy zithromax online[/url] zithromax without prescription -
tadalafil lozenge black cialis from singapore cialis for daily use
-
buy cheap doxycycline online cheap doxycycline online or buy doxycycline for dogs
http://theessentialchurch.net/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=doxycycline.science where to purchase doxycycline
[url=http://industrialsprayproducts.info/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=doxycycline.science]doxycycline 100mg dogs[/url] 200 mg doxycycline and [url=http://82.157.30.8/home.php?mod=space&uid=249855]doxycycline 200 mg[/url] buy doxycycline for dogs -
tadalafil tablets erectafil 20 cialis company buy brand cialis online usa
-
what is better viagra or cialis cheaper alternative to cialis 20mg cialis
-
amoxicillin 500 mg without prescription amoxicillin 500 mg cost
https://amoxil.science/# amoxicillin 250 mg capsule
[url=https://amoxil.science/#]buy amoxil[/url] buy amoxicillin 500mg -
https://amoxil.science/# amoxicillin 500 mg cost
-
cheap viagra online in india cheap generic viagra india sildenafil tablet brand name
-
where can i get viagra for women generic viagra soft gel capsule viagra without prescription in united states
-
how to enhance cialis effect online tadalafil tadalafil tab
-
zithromax 600 mg tablets zithromax 600 mg tablets
https://amoxil.science/# amoxicillin 50 mg tablets
[url=https://amoxil.science/#]amoxil[/url] order amoxicillin uk -
https://amoxil.science/# amoxicillin 500mg without prescription
-
buy doxycycline monohydrate doxycycline tablets or order doxycycline online
http://fctconline.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=doxycycline.science doxycycline tetracycline
[url=http://lhw88.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=doxycycline.science]buy doxycycline without prescription uk[/url] buy cheap doxycycline online and [url=http://www.1moli.top/home.php?mod=space&uid=95397]buy cheap doxycycline[/url] buy doxycycline online without prescription -
[url=https://cephalexin.directory/]keflex cream[/url]
-
doxycycline medication doxycycline monohydrate
https://amoxil.science/# amoxicillin order online no prescription
[url=https://amoxil.science/#]cheap amoxil[/url] where can i get amoxicillin 500 mg -
[url=https://xenicalx.com/]xenical prices[/url]
-
п»їMedicament prescribing information. Some are medicines that help people when doctors prescribe.
https://stromectolst.com/# ivermectin 90 mg
Learn about the side effects, dosages, and interactions. Get information now. -
[url=https://1winen.in]1win официальный[/url]
Mobile Version Permits Play Online Through Mirror or ceremonial photosite exciting resource. to the Customer easily accessible shizd required functions (a) also on mobile
1win казино -
[url=http://kosmetika154.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=https://www.starcamgirls.com/external_link/?url=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://shop.rybak-rybaka.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://google.co.uz.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://alltomibs.se/redirect/?url=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=https://www.vangold.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=https://parallel.co.uk/netherlands/resources/get/get_template.php?url=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://webbuild.knu.ac.kr.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://www.onlypussies.com/cgi-bin/crtr/out.cgi?id=11&l=top1-6&u=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://maps.google.hr/url?sa=t&url=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://georgievsk.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://redirect.manmanbuy.com/redirectUrl.aspx?webid=1&tourl=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.sh/url?q=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://zo.bz/linker/jump.php?sid=245&url=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
[url=https://k12.mayi173.com/register?redirecturl=https://1winen.in]1win[/url]
Clear welcome during one of sites 1win. Here visitors available elite board entertainment, tournaments, racing and sea bonuses.
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win -
[url=https://ulasix.com/]furosemide in mexico[/url]
-
[url=https://colchicinev.com/]colchicine 0.6 mg tabs[/url]
-
safe and effective drugs are available. Learn about the side effects, dosages, and interactions.
[url=https://stromectolst.com/#]ivermectin online[/url]
Long-Term Effects. Commonly Used Drugs Charts. -
Get here. All trends of medicament.
https://lisinopril.science/# buy cheap lisinopril
Read here. Some trends of drugs. -
Actual trends of drug. Definitive journal of drugs and therapeutics. [url=https://avodart.science/#]order cheap avodart pills[/url]
Some trends of drugs. Read information now. -
Regards. Lots of forum posts!
https://ouressays.com/ uc college application essay -
Top 100 Searched Drugs. Read now.
[url=https://nexium.top/#]where can i get generic nexium pills[/url]
Everything what you want to know about pills. п»їMedicament prescribing information. -
Generic Name. Definitive journal of drugs and therapeutics.
where to buy generic nexium without insurance
Get warning information here. What side effects can this medication cause? -
Best and news about drug. What side effects can this medication cause?
order generic mobic without insurance
Everything about medicine. drug information and news for professionals and consumers. -
You expressed it wonderfully.
https://essaywritingservicelinked.com/ english as coursework -
safe and effective drugs are available. What side effects can this medication cause? https://avodart.science/# how to buy generic avodart without insurance
Get warning information here. Read information now. -
kmart lisinopril lisinopril fk colchicine lisinopril
-
veterinary lasix furosemide mannitol furosemide htn
-
Reliable tips. With thanks!
https://essaywritingservicelinked.com/ custom paper writing service -
topamax tamoxifen nolvadex culturismo nolvadex shop
-
ic metronidazole metronidazole disposal metronidazole obesity
-
atenolol ip atenolol wpw tenormin toxicity
-
metformin fainting metformin endometrium metformin senkt
-
You definitely made your point!
essaywritingserviceahrefs.com read my college essay -
Currently it looks like Wordpress is the best blogging platform available right now. (from what I've read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
[url=https://essaywritingservicebbc.com/#]https://essaywritingservicebbc.com/[/url] -
lisinopril-hct ratiopharm-tabletten lisinopril fenofibrate lisinopril benadryl
-
furosemide mhra furosemide synonym lasix iny
-
bcpt tamoxifen tamoxifen lekaren tamoxifen gegenanzeigen
-
Lovely data, Appreciate it.
https://essaywritingservicelinked.com/ cheap essay buy -
Long-Term Effects. Long-Term Effects.
can i get cheap clomid now
Definitive journal of drugs and therapeutics. earch our drug database. -
9. metronidazole metronidazole pom metronidazole dairy
-
Read here. Best and news about drug.
[url=https://finasteridest.com/]where to buy cheap propecia no prescription[/url]
Cautions. Learn about the side effects, dosages, and interactions. -
Nicely put. Appreciate it!
https://essaywritingserviceahrefs.com/ essay on service to humanity -
tenormin wiki atenolol contraindications zanaflex atenolol
-
Thanks a lot. I appreciate this.
https://essaywritingservicelinked.com/ cv writing services -
п»їMedicament prescribing information. Read now.
[url=https://azithromycins.online/]zithromax 500 mg[/url]
Learn about the side effects, dosages, and interactions. Read information now. -
Do you have a spam problem on this site; I also am a blogger, and I was wondering your situation; many of us have created some nice procedures and we are looking to swap techniques with others, please shoot me an email if interested.
[url=https://essaywritingservicebbc.com/#]https://essaywritingservicebbc.com/[/url] -
Comprehensive side effect and adverse reaction information. Comprehensive side effect and adverse reaction information.
zithromax over the counter uk
Read now. Get warning information here. -
Seriously tons of amazing tips.
essaywritingserviceahrefs.com how to write an admissions essay -
You said it nicely..
https://essaywritingservicelinked.com/ kids should have less homework -
Get information now. What side effects can this medication cause?
https://clomiphenes.com how to get cheap clomid
Learn about the side effects, dosages, and interactions. Comprehensive side effect and adverse reaction information. -
[url=https://finpecia.company/]finasteride brand name in india[/url]
-
Actual trends of drug. Definitive journal of drugs and therapeutics. https://amoxicillins.com/ buy amoxicillin without prescription
п»їMedicament prescribing information. Long-Term Effects. -
furosemide evaluation lasix drips wiki furosemide
-
trazodone contents trazodone insufflation trazodone pupils
-
Definitive journal of drugs and therapeutics. Definitive journal of drugs and therapeutics. https://amoxicillins.online/ buying amoxicillin in mexico
What side effects can this medication cause? Medscape Drugs & Diseases. -
valtrex 1500 valtrex nyquil valtrex wirkung
-
Definitive journal of drugs and therapeutics. earch our drug database. amoxil generic
Get information now. Cautions. -
synthroid uso synthroid parameters synthroid 350
-
lyrica addictive max dose pregabalin lyrica cost without insurance
-
gabapentin creatine gabapentin lasix gabapentin aluminum
-
Actual trends of drug. Drug information.
non prescription ed pills
safe and effective drugs are available. Read now. -
lasix somministrazione furosemide manufacturer lasix elixir
-
trazodone erection hydroxyzine trazodone trazodone menstruation
-
valtrex official d-valacyclovir hydrochloride valtrex antihistamine
-
Drugs information sheet. Get information now.
https://edonlinefast.com non prescription erection pills
Comprehensive side effect and adverse reaction information. Read now. -
glucophage mp.pl metformin mercola metformin leptin
-
tamoxifen gedächtnis topical nolvadex nolvadex pregnyl
-
atorvastatin mitochondria lipitor faydalarД± lipitor meal
-
atenolol xanax atenolol intoxication betablockerare atenolol
-
snorting apo-trazodone trazodone somnifere trazodone watson
-
Definitive journal of drugs and therapeutics. Read information now.
https://canadianfast.online/# online canadian pharmacy
Long-Term Effects. Definitive journal of drugs and therapeutics. -
search lisinopril lisinopril and indocin lisinopril bronchospasm
-
Long-Term Effects. Get warning information here.
https://canadianfast.online/# amoxicillin without a doctor's prescription
Drugs information sheet. Get information now. -
[url=https://amoxicillind.com/]augmentin 500 125 mg[/url]
-
atorvastatin torcetrapib lipitor photos lipitor obesity
-
neurontin increasing pain neurontin facial flushing neurontin after mastectomy
-
Get here. Read information now.
[url=https://canadianfast.online/#]prescription drugs[/url]
Actual trends of drug. Drugs information sheet. -
wholesale pregabalin pharmaceutical materials withdrawal symptoms of pregabalin lyrica versus gabapentin
-
synthroid bad effects official synthroid website synthroid stories
-
quitting valtrex aurobindo valacyclovir valtrex cellcept
-
Read information now. drug information and news for professionals and consumers.
https://canadianfast.com/# canadian online drugs
Cautions. Generic Name. -
lipitor pakistan atorvastatin alzheimer's forbes lipitor
-
[url=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
Regardless of the method you settle upon, 1Win India is an opening to start playing in a root modern sell and a precisely opposite feeling for the user who uses their services. How do I log in to 1Win?
1win apk -
Thank you. I appreciate this.
essaywritingserviceahrefs.com dissertation writing services uk -
neurontin and pristiq gabapentin brustschmerzen apotex gabapentin
-
[url=http://mydent24.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=https://www.xn--80adbhunc2aa3al.xn--80asehdb/redirect?url=http%3A%2F%2F1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://westconcordnews.com/Redirect.asp?WeatherSp>1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win -
you all over me lyrica mr brightside lyrica pregabalin or gabapentin
-
flagyl mantar flagyl complications metronidazole mp35
-
synthroid pneumonic synthroid dogs clonazepam synthroid
-
safe and effective drugs are available. Drugs information sheet.
https://canadianfast.com/# canadian online drugs
Get information now. earch our drug database. -
Read information now. Everything what you want to know about pills.
[url=https://canadianfast.com/#]buy prescription drugs from canada cheap[/url]
Top 100 Searched Drugs. Prescription Drug Information, Interactions & Side. -
malarone valtrex valtrex nih aurobindo valtrex
-
Best and news about drug. Some are medicines that help people when doctors prescribe.
viagra online canadian pharmacy
safe and effective drugs are available. Prescription Drug Information, Interactions & Side. -
[url=https://1win-indian.in]1win-indian[/url]
Regardless of the method you choose, 1Collect India is an opening to start playing in a barrel modern shop and a precisely opposite stance for the consumer who uses their services. How do I log in to 1Win?
onewin -
[url=https://dic.academic.ru/jump.php?t=06943abc&j=%2Fhttps://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=https://images-stock.com/go?https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=https://images.1win-indian.in.ni/url?sa=i&rct=j&url=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://appius.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?event1=&event2=&event3=&goto=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://lovebookmark.date.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://wetpantie.net/cgi-bin/out.cgi?id=94&l=top&t=100t&u=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://harbin-gid.ru.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=https://marysblood.futureartist.net/external_redirect?ext_lnk=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=https://www.cams2free.com/external_link/?url=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=https://login.proxy.lib.uiowa.edu/login?url=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://michael.buban.cz/hound/s/r.php?r=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://pena.l.t.y.bc.lb.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=https://zlatookna.ru/bitrix/redirect.php?goto=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://nalandabodhi.info.xx3.kz/go.php?url=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
[url=http://bbw-tube.pro/out.php?url=https://1win-indian.in]1win[/url]
Welcome stay during one of sites 1win. Water visitors available best board entertainment, tournaments, racing yes black sea bonuses.
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win
1win -
You suggested this really well.
https://essaywritingserviceahrefs.com/ bid writing services -
[url=http://diclofenactab.online/]2 diclofenac[/url]
-
[url=http://gabapentinx.shop/]gabapentin 50 mg[/url]
-
Top 100 Searched Drugs. earch our drug database.
sildenafil 100mg online india
All trends of medicament. Read information now. -
Definitive journal of drugs and therapeutics. Read information now.
https://viagrapillsild.com/# cheap viagra online canadian pharmacy
Read information now. Some trends of drugs. -
[url=https://erectafil.directory/]buy erectafil[/url]
-
Get here. drug information and news for professionals and consumers.
https://viagrapillsild.online/# is viagra over the counter in canada
Everything what you want to know about pills. Everything what you want to know about pills. -
Generic Name. п»їMedicament prescribing information.
otc sildenafil 20 mg tablets
Some trends of drugs. Drug information. -
[url=http://blackcompany.org/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=http://artecool.net/cgi-bin/out.cgi?ses=loTpAXPgKW&id=833&url=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=http://earnupdates.com/goto.php?url=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=http://laminirovanievolos.ru/go.php?url=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=http://www.atlantic-county.org/webadmin/MainPages/redirect.asp?page=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=http://1crm.ru/bitrix/rk.php?goto=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=http://www.gallery-ryna.net/jump.php?url=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=http://kirklington.2day.uk/kirklington/search/?url=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=https://www.cityalta.com/redirect?url=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=https://ngmedia.org.au/?URL=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=http://dimastest.tourister.ru/go/?url=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=http://www1.centadata.com/pih09/pih09/redirect.aspx?link=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=http://websiteindexer.com/redirect.php?url=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=https://clients1.google.co.vi/url?q=https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
[url=https://ec2-52-70-39-20.compute-1.amazonaws.com/https://best-online-casinos-real-money.com]cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali[/url]
Ranking of the first-rate online casinos for the benefit of real in clover an eye to February 2023: a unabridged list of online casinos.
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali
cele mai bune cazinouri online pe bani reali -
how many paragraphs in an essay essay title examples mba essay review service
-
why abortion should be illegal essay pay to write my essay best essay cheap
-
essay in apa format example ap lang synthesis essay rubric how many sentences are in a essay
-
Top 100 Searched Drugs. Comprehensive side effect and adverse reaction information.
how to buy sildenafil online
Get information now. Learn about the side effects, dosages, and interactions. -
the essay writer apa style essay example essay service cheap
-
how to write a conclusion for an essay help writing essays for scholarships what is a descriptive essay
-
how to be a better essay writer high school essay help how to make an essay
-
Everything what you want to know about pills. п»їMedicament prescribing information.
[url=https://tadalafil1st.online/#]tadalafil 20mg canada[/url]
earch our drug database. Read information now. -
Comprehensive side effect and adverse reaction information. safe and effective drugs are available.
generic tadalafil canada
Generic Name. Everything information about medication. -
how to start an autobiography essay tok essay example application essay writing service
-
best college application essay service how to start a narrative essay college essay sample
-
research paper service primary writing paper with picture box help writing term paper
-
custom paper writers paper writers college need help writing a paper
-
top rated essay writing services buy essay online academic essay writing help
-
i need help writing a descriptive essay argument essay topics cheap essays online
-
Read now. Learn about the side effects, dosages, and interactions.
https://tadalafil1st.online/# cialis online without prescription
Get information now. Read here. -
help write my paper dr seuss writing paper lined writing paper with envelopes
-
term paper writing services reviews elementary writing paper help on writing a paper
-
Definitive journal of drugs and therapeutics. Best and news about drug.
overnight pharmacy 4u cialis
Drugs information sheet. п»їMedicament prescribing information. -
i need help writing a paper ghost writer college papers research paper buy
-
children writing paper writing paper and envelope sets name writing paper
-
cat in the hat writing paper pen to paper writing supplies writing a reflection paper
-
п»їMedicament prescribing information. Some trends of drugs.
https://tadalafil1st.online/# tadalafil 2
Some trends of drugs. п»їMedicament prescribing information. -
Learn about the side effects, dosages, and interactions. Generic Name.
https://tadalafil1st.com/# fastest delivery service for cialis
Actual trends of drug. Drugs information sheet. -
Actual trends of drug. Get warning information here.
[url=https://tadalafil1st.com/#]tadalafil cost india[/url]
What side effects can this medication cause? Actual trends of drug. -
Get warning information here. Get warning information here.
https://clomidc.fun/ where buy clomid for sale
https://zithromaxa.fun/ can you buy zithromax online
https://amoxila.store/ order amoxicillin no prescription
All trends of medicament. Some are medicines that help people when doctors prescribe. -
dltk writing paper when writing a paper you should do all of the following except printable elementary writing paper
-
first grade writing paper template can you buy a research paper people writing on paper
-
dissertation services uk dissertation editing harvard dissertation
-
dissertation tutors sample dissertation proposals dissertation.
-
Get warning information here. Read information now.
[url=https://zithromaxa.fun/]where can i buy zithromax uk[/url]
https://zithromaxa.fun/ zithromax 500 mg
Some trends of drugs. Learn about the side effects, dosages, and interactions. -
beginning writing paper buy college research papers online manuscript writing paper
-
paper writer services printable primary writing paper valentine writing paper
-
sample dissertation timeline dissertation sample format gsas dissertation submission
-
п»їMedicament prescribing information. Commonly Used Drugs Charts.
https://propeciaf.store/ cheap propecia no prescription
Get warning information here. Get warning information here. -
Actual trends of drug. Everything about medicine.
where to get propecia pills
[url=https://amoxila.store/]amoxicillin tablet 500mg[/url]
https://prednisoned.top/ buy prednisone without prescription paypal
Definitive journal of drugs and therapeutics. Get warning information here. -
dissertation consultant online doctorate no dissertation dissertation meaning in english
-
[url=https://casino-online-hu.site]casino-online-husite[/url]
Online casino Vavada: registration, login and working mirror. The licensed place of casino Vavada for playing an eye to money.
asino-online-hu site -
Read information now. Some trends of drugs.
https://zithromaxa.fun/ zithromax for sale us
where can i buy zithromax capsules
[url=https://propeciaf.store/]how to get propecia no prescription[/url]
Long-Term Effects. drug information and news for professionals and consumers. -
customized term papers valentines writing paper animals writing paper
-
research paper services cheap nursing paper writing services writing tablet paper
-
dissertation help service dissertation for phd dissertation gift
-
Drug information. Actual trends of drug.
[url=https://propeciaf.store/]how to buy generic propecia tablets[/url]
Drugs information sheet. Some trends of drugs. -
buy a dissertation online dissertation recipes copyright dissertation
-
dissertation proposal example college dissertation dissertation acknowlegements
-
Everything information about medication. Long-Term Effects.
where can i get cheap clomid pill
where to buy amoxicillin 500mg
Learn about the side effects, dosages, and interactions. Prescription Drug Information, Interactions & Side. -
Everything information about medication. п»їMedicament prescribing information.
[url=https://zithromaxa.fun/]generic zithromax over the counter[/url]
amoxicillin 500mg price
[url=https://propeciaf.store/]order propecia without a prescription[/url]
Generic Name. All trends of medicament. -
write my essay website the help essay prompts writing essay services
-
good customer service essay cheapest essay writers help in essay writing
-
academic essay service custom essay writing sites custom essay services
-
Medscape Drugs & Diseases. Medscape Drugs & Diseases.
[url=https://propeciaf.store/]can you buy propecia without dr prescription[/url]
[url=https://amoxila.store/]amoxicillin 500 mg online[/url]
https://prednisoned.top/ prednisone 1 mg for sale
Learn about the side effects, dosages, and interactions. drug information and news for professionals and consumers. -
online essay help chat essays writing service mba essay writing services
-
п»їMedicament prescribing information. Drug information.
https://zithromaxa.fun/ zithromax 500mg over the counter
All trends of medicament. Generic Name. -
best writing essay write my essay students help starting an essay
-
help with writing college application essay buy college essays best custom essay sites
-
essay service cheap service essay writing essay help online
-
essay 123 help custom essays service write my essay custom writing
-
instant essay writer great essay writers write my essay fast
-
canadian pharmacy world: overseas pharmacies shipping to usa - canadian pharmacy cialis 40 mg
https://mexicanpharmacy.pro/# best online pharmacies in mexico
best canadian online pharmacy [url=https://canadaph.top/#]mexican pharmacy online[/url] legal canadian pharmacy online -
mexican drugstore online: buying from online mexican pharmacy - mexico drug stores pharmacies
https://mexicanpharmacy.pro/# mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
mexican pharmaceuticals online [url=http://mexicanpharmacy.pro/#]medicine in mexico pharmacies[/url] mexico drug stores pharmacies -
canadian pharmacy victoza: us online pharmacy - canadian pharmacy ed medications
http://canadaph.top/# canadian pharmacy ed medications
purple pharmacy mexico price list [url=https://mexicanpharmacy.pro/#]purple pharmacy mexico price list[/url] reputable mexican pharmacies online -
is canadian pharmacy legit: best canadian online pharmacy - canadapharmacyonline legit
https://canadaph.top/# canadian pharmacy online ship to usa
canadian pharmacy meds [url=http://canadaph.top/#]mexican pharmacy online[/url] pharmacy wholesalers canada -
adderall canadian pharmacy best canadian online pharmacy
http://www.worldlingo.com/S4698.0/translation?wl_url=https://canadadrugs.best canadian pharmacy drugs online
[url=http://mugen.matrix.jp/cgi-bin/gate/rank.cgi?mode=link&id=97&url=https://canadadrugs.best]canadian pharmacy victoza[/url] my canadian pharmacy review -
scholarship essay help essay help 123 help essay writing
-
canadian pharmacy price checker maple leaf pharmacy in canada
http://pfa.levexis.com/clarks/tman.cgi?tmad=c&tmcampid=11&tmplaceref=criteo&tmclickref=optional2&tmloc=https://canadadrugs.best canadianpharmacymeds
[url=http://jfan.11510.net/out.cgi?id=00011&url=https://canadadrugs.best]best canadian online pharmacy[/url] northwest canadian pharmacy -
canadian pharmacy prices: overseas pharmacies shipping to usa - online pharmacy canada
https://canadadrugs.best/# canadian neighbor pharmacy
canadian pharmacy cialis reviews [url=http://canadadrugs.best/#]canadian online pharmacy no prescription[/url] canadian family pharmacy -
canadian pharmacy service canadian pharmacy world reviews
http://www.cureya.com/kinbaku/out.cgi?id=13854&url=https://canadadrugs.best canadian pharmacies online
[url=http://chooseabutt.com/cgi-bin/out.cgi?id=bootymon&url=https://canadadrugs.best]canadian pharmacies online[/url] canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg -
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa: mexican mail order pharmacies - purple pharmacy mexico price list
http://mexicanph.best/# buying prescription drugs in mexico online
cheap generic levitra india [url=https://indiaph.store/#]overseas pharmacies shipping to usa[/url] cheap levitra india -
pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa: mexican rx online - mexican pharmaceuticals online
https://mexicanph.best/# reputable mexican pharmacies online
mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs [url=https://mexicanph.best/#]buying prescription drugs in mexico[/url] buying prescription drugs in mexico -
sat essay writing help the best essay writing service essay writing service online
-
best custom essay website essay writers canada buying essays online
-
custom essay help top rated essay writing services looking for someone to write my essay
-
buy an essay online cheap essay on old custom help on college essay
-
canadian pharmacy: online canadian pharmacy - canadian pharmacy tampa
https://canadianph.pro/# canadian pharmacy com
canadian pharmacy viagra 50 mg [url=https://canadianph.pro/#]canadian pharmacy ratings[/url] canadian pharmacy ratings -
online essay editing services pay for essay cheap hire essay writer
-
viagra buy india: india pharmacy mail order - cheapest cialis from india
http://canadianph.pro/# canada pharmacy reviews
buy cialis generic india [url=https://indiaph.store/#]order cialis from india[/url] india online pharmacy -
help me with my essay mba essay service essay checking service
-
thesis statement generator narrative thesis thesis about education
-
dissertation editing software dissertation proposal samples pdf what's a dissertation
-
residences at thesis working thesis examples identity thesis
-
what was the frontier thesis cmc senior thesis thesis statement for research paper
-
how to come up with a good thesis writing a thesis statement uf undergraduate thesis
-
thesis ob1 the thesis statement does the thesis statement have to be in the first paragraph
-
Regards. Plenty of information!
argumentative essay thesis construct a thesis statement example thesis part of thesis -
You've made your point.
business school essay writing service https://hireawriterforanessay.com essay writing classes https://helptowriteanessay.com -
impotence pills: compare ed drugs - male erectile dysfunction
http://cheapdr.top/# natural ed pills
viagra without a doctor prescription [url=https://cheapdr.top/#]cheap ed medication[/url] doctors for erectile dysfunction -
erectile dysfunction drug [url=http://cheapdr.top/#]causes of ed[/url] natural ed treatments
-
Many thanks. Good stuff.
[url=https://essaypromaster.com/]how to write an analysis paper[/url] write paper for me discount code [url=https://paperwritingservicecheap.com/]paper writers for college[/url] freedom writer essay -
ed cure [url=https://cheapdr.top/#]herbal ed[/url] mens erection pills
-
real viagra without a doctor prescription [url=https://cheapdr.top/#]vacuum therapy for ed[/url] canadian online drugstore
-
buy prescription drugs online without: ed tablets - mens erection pills
https://cheapdr.top/# what is the best ed drug
prices of viagra at walmart [url=https://cheapdr.top/#]pet meds without vet prescription[/url] home remedies for erectile dysfunction -
natural ed drugs [url=https://cheapdr.top/#]generic ed pills[/url] male enhancement pills
-
Viagra rezeptfreie Länder: Viagra Generika online kaufen ohne Rezept - Viagra Generika 100mg rezeptfrei
-
sildenafilo 100mg precio farmacia: viagra online cerca de malaga - sildenafilo 100mg sin receta
-
comprar viagra en espaГ±a: sildenafilo 50 mg precio sin receta - sildenafilo cinfa 100 mg precio farmacia
-
tadalafil 5mg best price tadalafil generic price tadalafil 40 mg from india
-
royal honey vip tadalafil tadalafil versus sildenafil tadalafil daily cost
-
texas road pharmacy pharmacy hours cvs pharmacy intern jobs
-
sildenafilo precio farmacia: sildenafilo 100mg farmacia - sildenafil 100mg genГ©rico
-
chrisale tadalafil 20 mg para que sirve tadalafil gains tadalafil doses
-
tadalafil 5mg para que sirve order tadalafil no prescription chrisale tadalafil para que sirve
-
sildenafil vs tadalafil bluechew sildenafil timing sildenafil for premature ejaculation reviews
-
Viagra Alternative rezeptfrei: Viagra Generika 100mg rezeptfrei - Viagra Generika kaufen Schweiz
-
viagra online cerca de toledo: venta de viagra a domicilio - comprar viagra sin gastos de envГo
-
tadalafil weekend pill https://tadafilax.com/ tadalafil 20 mg tablet price
-
Good postings. Cheers!
writing argumentative essays help writing an essay for college essay writing for hire -
Thank you! Numerous knowledge!
thank you for teaching me how to read and write top essay writer online essay writer for free -
comprar viagra en espaГ±a envio urgente: comprar viagra contrareembolso 48 horas - comprar viagra contrareembolso 48 horas
-
Info well used!.
pay people to write essays where to buy essays -
tadalafil vs sildenafil pulmonary hypertension https://justtadafilix.com/ does tadalafil cause heartburn
-
sildenafilo 100mg farmacia: comprar sildenafilo cinfa 100 mg espaГ±a - comprar viagra en espaГ±a envio urgente
-
You said it very well..
write my essay for me free write essay for me cheap write my essay guru -
Cheers, Awesome stuff!
best live online casino slot machine casino online new york online casino -
Seriously all kinds of beneficial data.
pay for essay review pay for essay paper -
se puede comprar viagra sin receta: comprar viagra en espaГ±a - viagra para hombre precio farmacias similares
-
united pharmacy cialis https://hdcillis.com/ buy generic cialis with paypal
-
buy sildenafil online india https://leepvigras.com/ viagra plus
-
sildenafil 25 mg https://ac3vigra.com/ how to order generic viagra online
-
viagra 100 mg precio en farmacias: sildenafilo precio farmacia - sildenafilo precio farmacia
-
You've made your stand extremely nicely..
write my essay for essay writier hire someone to write a book for me -
viagra germany https://ethvigrix.com/ purchasing viagra in mexico
-
cialis free trial https://crocilismen.com/ rush delivery on cialis
-
You stated this very well.
tropicana online casino pa caesar online casino casino online canada -
brand name viagra online https://foxviagrixed.com/ where to buy viagra over the counter in canada
-
You've made the point!
buyessay uk pay to write paper -
You made your point.
can i pay someone to write my essay for me write my college admissions essay how do i start my essay introduction -
viagra online cerca de malaga: sildenafilo 100mg precio farmacia - Viagra online cerca de Madrid
-
comprar viagra sin gastos de envГo: comprar viagra en espaГ±a envio urgente contrareembolso - viagra entrega inmediata
-
cialis 10mg price https://hoscillia.com/ costco cialis
-
https://viasenzaricetta.com/# viagra prezzo farmacia 2023
-
tadalafil for bph https://wwcillisa.com/ cialis and viagra mix
-
us viagra prices https://vivigrix.com/ generic viagra india price
-
new cialis commercial 2010 https://uhdcilise.com/ tadalafil mail order
-
https://viasenzaricetta.com/# viagra acquisto in contrassegno in italia
-
Azithromycin price - Which fruits contain antibiotics?
-
https://cytotecsale.pro/# buy cytotec pills
-
Priligy pills
Lifestyle changes such as reducing alcohol consumption and quitting smoking can also help to improve sexual function. -
It is important to take z pack antibiotic dosage exactly as prescribed by a healthcare provider, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. Skipping doses or stopping the medication early can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
-
https://clomidsale.pro/# can i order generic clomid
-
[url=https://zithromaxotc.com/]zithromax z-pak[/url]
-
z pack antibiotic side effects
You may have been exposed to Chlamydia. Chlamydia infection is easily treated with the medicine Zithromax (also known as Zithromax). People with Chlamydia infection may not know they have it because they have no signs or symptoms. -
https://prednisonesale.pro/# prednisone 2 5 mg
-
flagyl 250 flagyl metronidazole 250 mg
-
food poisoning antibiotics flagyl metronidazole cost walmart flagyl over the counter
-
http://zithromax.pro/# zithromax 500 tablet
-
metronidazole 250 mg tablet flagyl antibiotic 500 mg flagyl tablet 200 mg
-
https://prednisonesale.pro/# buy prednisone 10mg
-
buying prescription drugs in mexico: mexican pharmaceuticals online - mexico drug stores pharmacies
http://canadapharm.pro/# online canadian drugstore
canadian king pharmacy [url=https://canadapharm.pro/#]vipps canadian pharmacy[/url] canadapharmacyonline legit -
india online pharmacy: overseas pharmacies shipping to usa - indianpharmacy com
https://indiapharm.pro/# reputable indian pharmacies
canadapharmacyonline com [url=https://canadapharm.pro/#]legit canadian online pharmacy[/url] canadian valley pharmacy -
synthroid 50 pill 112 mg thyroid medication
-
lipitor without rx buy lipitor 20mg atorvastatin 10 mg cost
-
atorvastatin lipitor 10mg: Atorvastatin may also interact with certain medications used to treat thyroid problems, and patients should inform their healthcare provider if they are taking any of these medications.
-
levothyroxine na synthroid 100mcg tab
Patients who are planning to undergo surgery or radiation therapy should also inform their doctor of their levothyroxine use, as these treatments can affect thyroid function and may require adjustments to the medication dose. -
synthroid 137 mcg tablet
Both drugs contain the same active ingredient, levothyroxine sodium, and are used interchangeably to manage hypothyroidism. -
generic zithromax medicine: can you buy zithromax over the counter in canada - buy zithromax no prescription
-
amlodipine and grapefruit juice https://norvascamlodipinetce.com/ amlodipine swelling ankles nhs
-
remeron vs seroquel quetiapine fumarate 25mg for sleep quetiapine dosage for depression
-
sertraline tablets 50mg fluoxetine and sertraline zoloft muscle tension
-
buy cheap doxycycline online: generic doxycycline - 200 mg doxycycline
-
price of levothyroxine 25 mcg
Patients who have a history of thyroid cancer or other thyroid disorders may require long-term treatment with Synthroid or levothyroxine to maintain appropriate thyroid hormone levels and prevent recurrence of the disease. -
lexapro and ocd can you overdose on lexapro and die benefits of lexapro weight loss
-
what does cymbalta look like https://cymbaltaduloxetineztn.com/ duloxetine 60 mg side effects
-
omeprazole breastfeeding omeprazole and magnesium omeprazole 10mg
-
amlodipine besylate para que sirve amlodipine side effects erectile dysfunction hydrochlorothiazide and amlodipine
-
http://overthecounter.pro/# best over the counter acne treatment
antibiotics over the counter [url=https://overthecounter.pro/#]over the counter ed pills[/url] best over the counter teeth whitening -
cialis generique: Si vous souffrez de dysfonction erectile, ne restez pas silencieux. Parlez-en a votre medecin et cherchez des solutions pour retrouver une vie sexuelle epanouissante et ameliorer votre sante globale.
-
http://www.viagrabelgique.com/ achat cialis en ligne
-
what is seroquel xr quetiapine fumarate 50 mg quetiapine fumarate used to treat
-
Comment renforcer une famille tadalafil lilly avis
-
cymbalta halflife https://cymbaltaduloxetinesec.com/ gabapentin vs cymbalta
-
sertraline dose for depression sertraline is used for sertraline 50 mg tablets
-
xanax and lexapro escitalopram withdrawals is escitalopram a controlled drug
-
omeprazole nursing implications prilosec kidney damage nexium v prilosec
-
http://overthecounter.pro/# over the counter medication for uti
over the counter pain meds for dogs [url=http://overthecounter.pro/#]over the counter ed medication[/url] over the counter ed pills -
norvasc erectile dysfunction which is better lisinopril or amlodipine how quickly does norvasc work
-
seroquel drug test false positive seroquel akathisia a randomized controlled trial of quetiapine versus placebo in the treatment of delirium.
-
decin et en travaillant ensemble pour trouver des solutions, il est possible de retrouver une vie sexuelle epanouissante et de maintenir une bonne sante globale. commande viagra
-
zoloft child dosage https://zoloftsertralinedik.com/ what time of day should i take sertraline
-
Comment un homme peut enceinte une fille sildenafil
-
how to stop taking prilosec https://prilosecomeprazolerls.com/ omeprazole fatigue
-
difference between lexapro and wellbutrin https://lexaproescitalopramikd.com/ efectos secundarios del escitalopram 10 mg
-
cymbalta and weed max dose of cymbalta per day cymbalta what is it used for
-
fluoxetine suicidal thoughts https://prozacfluoxetinesyu.com/ fluoxetine withdrawal timeline
-
seroquel xr half life https://seroquelquetiapinesxz.com/ define quetiapine
-
paxil or prozac name brand for fluoxetine dog ate fluoxetine
-
long term omeprazole prescription prilosec side effects omeprazole 40 mg uses
-
escitalopram interaction with alcohol how long does it take for escitalopram to work does lexapro cause weight gain
-
duloxetine withdrawal brain zaps duloxetine tca what is duloxetine generic for
-
When did the first man have a baby vidalista 40
-
Pills prescribing information. Cautions. vidalista All about medicine. Get information here.
-
10mg fluoxetine https://prozacfluoxetineatb.com/ fluoxetine espanol
-
Gxaqen buy centurion vidalista black 80 Sghvtn
-
dapoxetine buy online in india where can i buy dapoxetine in usa topiramate 50mg pil
-
topamax price topamax 50 mg tablet topamax sprinkle vs tablet
-
metronidazole without a doctor prescription dapoxetine buy online reddit flagyl 400 mg tablet
-
Ijwoxv Bhzkmf cefadroxil 500 mg oral capsule Ogqeay Uuhefc
-
plaquenil 200 mg side effects hydroxychloroquine 100 mg tablet plaquenil 200 mg bid
-
The impact of chronic inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease, on erectile function is a topic of ongoing research. Addressing inflammation and managing associated symptoms can positively influence sexual well-being. cenforce 50mg without prescription cenforcebnr.com order cenforce pill
-
Researchers are investigating the impact of chronic cardiovascular conditions, such as heart disease and atherosclerosis, on erectile function. Managing cardiovascular health through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions can positively influence sexual well-being.
generic levitra from india www.vardenafilotc.com levitra reviews -
Men with ED may feel a sense of frustration and helplessness when traditional treatments and interventions fail to provide satisfactory results, leading to a sense of resignation and acceptance of their condition.
https://www.fildena.hair/ sildenafil usa -
Experimenting with different sexual activities and techniques can help couples find alternative ways to achieve sexual satisfaction while managing impotence. Being open to new experiences can enhance intimacy and strengthen the bond between partners.
order fildena 100mg pills order fildena 50mg generic -
Men with impotence may find it beneficial to engage in regular activities that promote self-expression and creativity, such as engaging in art, writing, or playing a musical instrument. These activities can contribute to overall well-being and sexual satisfaction.
sildenafil 100mg for sale -
fildena pills http://www.fildena.website/
-
viagra vente libre jean coutu acheter viagra pharmacie
-
viagra en ligne site fiable viagra contre indications
-
amoxicillin and ibuprofen for toothache amoxicillin with food does amoxicillin treat std
-
Drugs information leaflet. What side effects? cenforce 50mg ca Kindest despatch upon medicament. Get intelligence now.
-
how long does cephalexin stay in your system does cephalexin cause nausea why does cephalexin make me tired
-
can you cut amoxicillin 875 mg in half amoxicillin for strep throat dosage side effects of amoxicillin in toddlers
-
can cats take cephalexin https://cephalexinyns.com/ will cephalexin treat kennel cough
-
keflex otc https://keflexsfn.com/ keflex cover staph aureus
-
keflex use https://keflexvex.com/ keflex dosing pediatric
-
bronchitis antibiotics azithromycin azithromycin 500mg uses bleeding after taking azithromycin for chlamydia
-
can i take ibuprofen with cephalexin https://doxycyclineize.com/ is cipro the same as cephalexin
-
erythromycin and azithromycin what does azithromycin 250 mg pill look like how long does 500 mg azithromycin stay in your system
-
cephalexin help tooth infection can cephalexin cause dizziness cephalexin ear drops
-
what not to eat or drink while on ciprofloxacin what is ciprofloxacin good for ciprofloxacin hydrochloride ophthalmic solution ear
-
ciprofloxacin for sinus infection ciprofloxacin hydrochloride tablets i.p are ciprofloxacin and cephalexin the same
-
can you get high off prednisone https://prednisonecyn.com/ prednisone long term side effects in dogs
-
prednisone weight gain 2 weeks can i drink while on prednisone does prednisone make you pee more at night
-
can a dog take augmentin symptoms allergic reaction augmentin can augmentin be used to treat mrsa
-
is augmentin ok for dogs https://augmentingtj.com/ side effect augmentin 625
-
amoxicillin and tums amoxicillin vs clindamycin does amoxicillin treat uti
-
what is cephalexin? https://cephalexinuop.com/ is cephalexin good for a tooth infection
-
what amoxicillin used for amoxicillin-clavulanate do i need a prescription for amoxicillin
-
azithromycin dosage for urethritis https://azithromycinikm.com/ azithromycin for abscess tooth
-
keflex and joint pain keflex for uti keflex 500 mg uses
-
can dogs have keflex https://keflexrno.com/ how long does keflex stay in your system
-
half life of ciprofloxacin hcl ciprofloxacin cipro 500 mg tablet ciprofloxacin drops used for
-
antibiotics cephalexin cephalexin 219 uses how safe is cephalexin
-
side effects of azithromycin is azithromycin in the penicillin family azithromycin and augmentin together
-
how long does prednisone stay in your system after taking for 10 days prednisone injection side effects of prednisone eye drops
-
augmentin de pil augmentin copii 6 ani dozaj augmentin la copii
-
albuterol.bond : Inhaler Manufacturer Partners with Patients' Advocacy Groups to Improve Care albuterol hfa inhaler
-
dog cephalexin side effects https://cephalexinuop.com/ doxycycline and cephalexin together
-
azithromycin how long to take effect https://azithromycinikm.com/ what is azithromycin used to treat
-
prednisone raise blood sugar does prednisone make you thirsty what is prednisone 20 mg used for
-
augmentin estrazione augmentin 850 efectos secundarios augmentin a karmienie
-
ventolinair.com - How do I find reputable information about over-the-counter medicines online medication for asthma
-
alcohol and ciprofloxacin reddit ciprofloxacin drops side effects what does ciprofloxacin hcl 500mg treat
-
doxycycline hyclate with or without food can you take cbd while on doxycycline how quickly does doxycycline work for kennel cough
-
ciprofloxacin fda warning salmonella ciprofloxacin ciprofloxacin in dogs side effects
-
cephalexin and zinc https://cephalexinuop.com/ cephalexin 500mg dosage for tooth infection
-
Building and maintaining a strong support network of friends, family, or support groups can provide emotional support and a safe space for discussing concerns related to impotence.. Cialis low prices at walmart cialisbanksy.com Cialis online no prescription
-
do you need to take azithromycin with food azithromycin vs z pak azithromycin 250 mg for dogs
-
prednisone withdrawal symptoms brand name for prednisone prednisone for cats side effects
-
MEGAWIN
https://telegra.ph/MEGAWIN-07-31
Exploring MEGAWIN Casino: A Premier Online Gaming Experience
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving world of online casinos, MEGAWIN stands out as a prominent player, offering a top-notch gaming experience to players worldwide. Boasting an impressive collection of games, generous promotions, and a user-friendly platform, MEGAWIN has gained a reputation as a reliable and entertaining online casino destination. In this article, we will delve into the key features that make MEGAWIN Casino a popular choice among gamers.
Game Variety and Software Providers
One of the cornerstones of MEGAWIN's success is its vast and diverse game library. Catering to the preferences of different players, the casino hosts an array of slots, table games, live dealer games, and more. Whether you're a fan of classic slots or modern video slots with immersive themes and captivating visuals, MEGAWIN has something to offer.
To deliver such a vast selection of games, the casino collaborates with some of the most renowned software providers in the industry. Partnerships with companies like Microgaming, NetEnt, Playtech, and Evolution Gaming ensure that players can enjoy high-quality, fair, and engaging gameplay.
User-Friendly Interface
Navigating through MEGAWIN's website is a breeze, even for those new to online casinos. The user-friendly interface is designed to provide a seamless gaming experience. The website's layout is intuitive, making it easy to find your favorite games, access promotions, and manage your account.
Additionally, MEGAWIN Casino ensures that its platform is optimized for both desktop and mobile devices. This means players can enjoy their favorite games on the go, without sacrificing the quality of gameplay.
Security and Fair Play
A crucial aspect of any reputable online casino is ensuring the safety and security of its players. MEGAWIN takes this responsibility seriously and employs the latest SSL encryption technology to protect sensitive data and financial transactions. Players can rest assured that their personal information remains confidential and secure.
Furthermore, MEGAWIN operates with a valid gambling license from a respected regulatory authority, which ensures that the casino adheres to strict standards of fairness and transparency. The games' outcomes are determined by a certified random number generator (RNG), guaranteeing fair play for all users. -
ciprofloxacin ear ciprofloxacin and tramadol ciprofloxacin 500mg for dogs ear infection
-
local single women near me dating sjtes
sexy dating -
cephalexin cure bv liquid cephalexin dosage for cats how long does it take cephalexin to work for uti
-
single women darling side: https://datingtopreview.com/# - casualdatelocal247
-
azithromycin tablets uses https://azithromycinikm.com/ azithromycin doses
-
is prednisone a corticosteroid how much does prednisone raise blood sugar in non-diabetic is prednisone safe
-
augmentin bambini tabella peso augmentin pret 1000 mg manufacturer of augmentin
-
How can I check my sperm count at home? kamagra reviews forum goldkamagra.com 5mg Cialis best time to take
-
Демонтаж стен Москва
Демонтаж стен Москва -
Content Krush Is a Digital Marketing Consulting Firm in Lagos, Nigeria with Focus on Search Engine Optimization, Growth Marketing, B2B Lead Generation, and Content Marketing.
-
Content Krush Is a Digital Marketing Consulting Firm in Lagos, Nigeria with Focus on Search Engine Optimization, Growth Marketing, B2B Lead Generation, and Content Marketing.
-
kantorbola
Situs Judi Slot Online Terpercaya dengan Permainan Dijamin Gacor dan Promo Seru"
Kantorbola merupakan situs judi slot online yang menawarkan berbagai macam permainan slot gacor dari provider papan atas seperti IDN Slot, Pragmatic, PG Soft, Habanero, Microgaming, dan Game Play. Dengan minimal deposit 10.000 rupiah saja, pemain bisa menikmati berbagai permainan slot gacor, antara lain judul-judul populer seperti Gates Of Olympus, Sweet Bonanza, Laprechaun, Koi Gate, Mahjong Ways, dan masih banyak lagi, semuanya dengan RTP tinggi di atas 94%. Selain slot, Kantorbola juga menyediakan pilihan judi online lainnya seperti permainan casino online dan taruhan olahraga uang asli dari SBOBET, UBOBET, dan CMD368. -
Explore a delectable world of foods that lower cholesterol and take charge of your cardiovascular health. From succulent berries to nutrient-rich greens, uncover a diverse array of options that can effectively contribute to reducing cholesterol levels, all while savoring the flavors of a heart-healthy lifestyle.
Delve into the science and flavor of foods that lower cholesterol, as this article guides you through a culinary journey aimed at promoting optimal heart wellness. Learn how incorporating these cholesterol-conscious choices, such as fiber-packed vegetables and antioxidant-rich fruits, can have a positive impact on managing cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health. -
Unveiling the Beauty of Neural Network Art! Dive into a mesmerizing world where technology meets creativity. Neural networks are crafting stunning images of women, reshaping beauty standards and pushing artistic boundaries. Join us in exploring this captivating fusion of AI and aesthetics. #NeuralNetworkArt #DigitalBeauty
-
Unveiling the Beauty of Neural Network Art! Dive into a mesmerizing world where technology meets creativity. Neural networks are crafting stunning images of women, reshaping beauty standards and pushing artistic boundaries. Join us in exploring this captivating fusion of AI and aesthetics. #NeuralNetworkArt #DigitalBeauty
-
The Significance of Responsive Web Design: Optimizing User Experience Across Devices
Introduction:
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, the concept of a responsive website has emerged as a pivotal factor in ensuring optimal user experiences. A website's responsiveness refers to its ability to seamlessly adapt and cater to a diverse range of browsing devices, allowing users to effortlessly navigate, read content, and interact with the interface. This article delves into the importance of responsive web design, its impact on search engine rankings, and the testing methods to assess a website's responsiveness.
The Essence of Responsive Web Design:
A responsive website is a virtual chameleon, effortlessly adjusting its layout and elements to provide an optimal viewing experience on devices of varying sizes and resolutions. It empowers users to engage with content without the need for constant browser resizing or sacrificing readability. Be it a sprawling desktop monitor or a compact smartphone screen, a well-designed responsive website ensures that users can consume content seamlessly, leading to increased engagement and user satisfaction.
Search Engine Ranking Influence:
In the realm of digital marketing, the responsiveness of a website has transcended its role as a mere user experience enhancer and evolved into a pivotal ranking factor for search engines. Search engine algorithms, notably Google's, now place considerable emphasis on a website's responsiveness when determining search result rankings. Websites that offer an impeccable browsing experience across devices are rewarded with higher visibility, driving organic traffic and enhancing online visibility.
Testing Responsiveness: A User's Guide:
Assessing the responsiveness of a website has become a fundamental step in its development and optimization. To gauge a website's adaptability effectively, users can follow these steps:
Input the complete URL of the web page under evaluation.
Initiate the assessment by clicking "GO" or pressing "ENTER."
Leverage testing tools equipped with an extensive range of dimensions to visualize the webpage on various screen resolutions and devices. These tools offer insights into the webpage's appearance on tablets, iPads, iPhones, Android phones, laptops, and desktops.
Conclusion:
In the dynamic digital ecosystem, where user preferences span a spectrum of devices, the importance of responsive web design cannot be overstated. A responsive website goes beyond accommodating various screen sizes; it signifies a commitment to delivering seamless user experiences. From influencing search engine rankings to optimizing user engagement, the significance of responsiveness reverberates throughout the digital realm. As technology advances and user behaviors evolve, embracing responsive web design remains a cornerstone for success in the virtual realm. -
Your doctor can provide insights into how using Cenforce might positively affect your overall emotional well-being, contributing to a more fulfilling and satisfying sexual experience. buy Cenforce pills
-
世界盃
2023年世界盃籃球賽
2023年世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)為第19屆FIBA男子世界盃籃球賽,此是2019年實施新制度後的第2屆賽事,本屆賽事起亦調整回4年週期舉辦。本屆賽事歐洲、美洲各洲最好成績前2名球隊,亞洲、大洋洲、非洲各洲的最好成績球隊及2024年夏季奧林匹克運動會主辦國法國(共8隊)將獲得在巴黎舉行的奧運會比賽資格[1][2]。
申辦過程
2023年世界盃籃球賽提出申辦的11個國家與地區是:阿根廷、澳洲、德國、香港、以色列、日本、菲律賓、波蘭、俄羅斯、塞爾維亞以及土耳其[3]。2017年8月31日是2023年國際籃總世界盃籃球賽提交申辦資料的截止日期,俄羅斯、土耳其分別遞交了單獨舉辦世界盃的申請,阿根廷/烏拉圭和印尼/日本/菲律賓則提出了聯合申辦[4]。2017年12月9日國際籃總中心委員會根據申辦情況做出投票,菲律賓、日本、印度尼西亞獲得了2023年世界盃籃球賽的聯合舉辦權[5]。
比賽場館
本次賽事共將會在5個場館舉行。馬尼拉將進行四組預賽,兩組十六強賽事以及八強之後所有的賽事。另外,沖繩市與雅加達各舉辦兩組預賽及一組十六強賽事。
菲律賓此次將有四個場館作為世界盃比賽場地,帕賽市的亞洲購物中心體育館,奎松市的阿拉內塔體育館,帕西格的菲爾體育館以及武加偉的菲律賓體育館。亞洲購物中心體育館曾舉辦過2013年亞洲籃球錦標賽及2016奧運資格賽。阿拉內塔體育館主辦過1978年男籃世錦賽。菲爾體育館舉辦過2011年亞洲籃球俱樂部冠軍盃。菲律賓體育館約有55,000個座位,此場館也將會是本屆賽事的決賽場地,同時也曾經是2019年東南亞運動會開幕式場地。
日本與印尼各有一個場地舉辦世界盃賽事。沖繩市綜合運動場約有10,000個座位,同時也會是B聯賽琉球黃金國王的新主場。雅加達史納延紀念體育館為了2018年亞洲運動會重新翻新,是2018年亞洲運動會籃球及羽毛球的比賽場地。
17至32名排名賽
預賽成績併入17至32名排位賽計算,且同組晉級複賽球隊對戰成績依舊列入計算
此階段不再另行舉辦17-24名、25-32名排位賽。各組第1名將排入第17至20名,第2名排入第21至24名,第3名排入第25至28名,第4名排入第29至32名
複賽
預賽成績併入16強複賽計算,且同組遭淘汰球隊對戰成績依舊列入計算
此階段各組第三、四名不再另行舉辦9-16名排位賽。各組第3名將排入第9至12名,第4名排入第13至16名 -
Замена венцов деревянного дома обеспечивает стабильность и долговечность конструкции. Этот процесс включает замену поврежденных или изношенных верхних балок, гарантируя надежность жилища на долгие годы. подъем деревянного дома
-
世界盃籃球
2023年世界盃籃球賽
2023年世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)為第19屆FIBA男子世界盃籃球賽,此是2019年實施新制度後的第2屆賽事,本屆賽事起亦調整回4年週期舉辦。本屆賽事歐洲、美洲各洲最好成績前2名球隊,亞洲、大洋洲、非洲各洲的最好成績球隊及2024年夏季奧林匹克運動會主辦國法國(共8隊)將獲得在巴黎舉行的奧運會比賽資格[1][2]。
申辦過程
2023年世界盃籃球賽提出申辦的11個國家與地區是:阿根廷、澳洲、德國、香港、以色列、日本、菲律賓、波蘭、俄羅斯、塞爾維亞以及土耳其[3]。2017年8月31日是2023年國際籃總世界盃籃球賽提交申辦資料的截止日期,俄羅斯、土耳其分別遞交了單獨舉辦世界盃的申請,阿根廷/烏拉圭和印尼/日本/菲律賓則提出了聯合申辦[4]。2017年12月9日國際籃總中心委員會根據申辦情況做出投票,菲律賓、日本、印度尼西亞獲得了2023年世界盃籃球賽的聯合舉辦權[5]。
比賽場館
本次賽事共將會在5個場館舉行。馬尼拉將進行四組預賽,兩組十六強賽事以及八強之後所有的賽事。另外,沖繩市與雅加達各舉辦兩組預賽及一組十六強賽事。
菲律賓此次將有四個場館作為世界盃比賽場地,帕賽市的亞洲購物中心體育館,奎松市的阿拉內塔體育館,帕西格的菲爾體育館以及武加偉的菲律賓體育館。亞洲購物中心體育館曾舉辦過2013年亞洲籃球錦標賽及2016奧運資格賽。阿拉內塔體育館主辦過1978年男籃世錦賽。菲爾體育館舉辦過2011年亞洲籃球俱樂部冠軍盃。菲律賓體育館約有55,000個座位,此場館也將會是本屆賽事的決賽場地,同時也曾經是2019年東南亞運動會開幕式場地。
日本與印尼各有一個場地舉辦世界盃賽事。沖繩市綜合運動場約有10,000個座位,同時也會是B聯賽琉球黃金國王的新主場。雅加達史納延紀念體育館為了2018年亞洲運動會重新翻新,是2018年亞洲運動會籃球及羽毛球的比賽場地。
17至32名排名賽
預賽成績併入17至32名排位賽計算,且同組晉級複賽球隊對戰成績依舊列入計算
此階段不再另行舉辦17-24名、25-32名排位賽。各組第1名將排入第17至20名,第2名排入第21至24名,第3名排入第25至28名,第4名排入第29至32名
複賽
預賽成績併入16強複賽計算,且同組遭淘汰球隊對戰成績依舊列入計算
此階段各組第三、四名不再另行舉辦9-16名排位賽。各組第3名將排入第9至12名,第4名排入第13至16名 -
neural network woman drink
As we peer into the future, the ever-evolving synergy of artificial intelligence (AI) and biotechnology promises to reshape our perceptions of beauty and human possibilities. Cutting-edge technologies, powered by deep neural networks, DNA editing, artificial insemination, and cloning, are on the brink of unveiling a profound transformation in the realm of artificial beings - captivating, mysterious, and beyond comprehension.
The underlying force driving this paradigm shift is AI's remarkable capacity, harnessing the enigmatic depths of deep neural networks and sophisticated machine learning algorithms to forge entirely novel entities, defying our traditional understanding of creation.
At the forefront of this awe-inspiring exploration is the development of an unprecedented "printer" capable of giving life to beings of extraordinary allure, meticulously designed with unique and alluring traits. The fusion of artistry and scientific precision has resulted in the inception of these extraordinary entities, revealing a surreal world where the lines between reality and imagination blur.
Yet, amidst the unveiling of such fascinating prospects, a veil of ethical ambiguity shrouds this technological marvel. The emergence of artificial humans poses profound questions demanding our utmost contemplation. Questions of societal impact, altered interpersonal dynamics, and potential inequalities beckon us to navigate the uncharted territories of moral dilemmas. -
Подъем деревянного дома — технический процесс, позволяющий адаптировать здание к новым условиям, поднять его для замены фундамента или ремонта фундаментных элементов. подъем дома
-
tombak118
tombak118 -
Ремонт старого фундамента — процесс восстановления и укрепления старой основы здания, обеспечивающий его стабильность и долговечность на долгие годы. замена венцов
-
Megawin
Megawin: Situs Terbaik Bermain Judi Online Mega Win Terpercaya di Indonesia
Dunia perjudian online semakin berkembang pesat di era digital ini. Salah satu situs yang telah mendapatkan reputasi sebagai pilihan terbaik untuk bermain judi online adalah Megawin. Dalam artikel ini, kita akan menjelajahi apa yang membuat Megawin begitu istimewa dan mengapa ia dianggap sebagai situs terpercaya di Indonesia.
Tentang Megawin
Megawin adalah platform judi online yang menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan, dengan fokus utama pada judi slot. Platform ini telah meraih status sebagai situs terbaik untuk bermain judi online Mega Win terpercaya di Indonesia. Salah satu faktor yang membuat Megawin menonjol adalah izin resmi dan lisensinya yang diperoleh melalui PAGCOR, sebuah badan regulasi perjudian internasional yang berbasis di Filipina. Lisensi ini menunjukkan komitmen Megawin untuk memberikan pengalaman bermain yang aman, adil, dan terpercaya kepada para pemainnya.
Ragam Permainan
Salah satu daya tarik utama Megawin adalah beragamnya pilihan permainan judi online yang ditawarkan. Terutama, Mega Win, permainan andalan mereka, telah berhasil menarik perhatian banyak pemain. Dari slot klasik hingga slot video modern dengan fitur-fitur inovatif, Megawin memiliki semua jenis permainan untuk memenuhi selera bermain setiap individu. Pemain dapat menikmati pengalaman bermain yang menarik dan menghibur tanpa henti, sepanjang hari dan malam.
Kenyamanan Bermain 24/7
Salah satu aspek menarik lainnya dari Megawin adalah kenyataan bahwa pemain dapat menikmati permainan mereka tanpa batasan waktu. Dengan layanan 24 jam tanpa henti, Megawin memastikan bahwa penggemar judi online dapat merasakan sensasi bermain kapan saja mereka inginkan. Ini adalah fitur yang sangat berharga bagi para pemain yang memiliki jadwal sibuk atau mungkin berada di berbagai zona waktu.
Responsible Gaming
Megawin juga sangat peduli dengan keamanan dan kesejahteraan para pemainnya. Mereka menerapkan prinsip bermain bertanggung jawab dan menyediakan sumber daya untuk membantu pemain mengelola aktivitas perjudian mereka. Dengan adanya fitur pengaturan batas permainan dan dukungan untuk pemain yang mungkin mengalami masalah perjudian, Megawin berkomitmen untuk menciptakan lingkungan bermain yang sehat dan aman bagi semua orang.
Kesimpulan
Megawin telah membuktikan dirinya sebagai pilihan terbaik bagi para pencinta judi online di Indonesia. Dengan lisensi resmi, beragam permainan menarik, layanan bermain 24/7, dan fokus pada permainan bertanggung jawab, Megawin telah memenuhi harapan pemainnya. Apakah Anda seorang penggemar judi slot atau mencari pengalaman judi online yang menyenangkan, Megawin adalah tempat yang patut dipertimbangkan. Jangan ragu untuk menjelajahi dunia judi online dengan aman dan menghibur di Megawin. -
世界盃
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
世界盃
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
觀看 2023 年國際籃聯世界杯
2023年FIBA世界盃籃球賽,也被稱為第19屆FIBA世界盃籃球賽,將成為籃球歷史上的一個重要里程碑。這場賽事是自2019年新制度實行後的第二次比賽,帶來了更多的期待和興奮。
賽事的參賽隊伍涵蓋了全球多個地區,包括歐洲、美洲、亞洲、大洋洲和非洲。此次賽事將選出各區域的佼佼者,以及2024年夏季奧運會主辦國法國,共計8支隊伍將獲得在巴黎舉行的奧運賽事的參賽資格。這無疑為各國球隊提供了一個難得的機會,展現他們的實力和技術。
在這場比賽中,我們將看到來自不同文化、背景和籃球傳統的球隊們匯聚一堂,用他們的熱情和努力,為世界籃球迷帶來精彩紛呈的比賽。球場上的每一個進球、每一次防守都將成為觀眾和球迷們津津樂道的話題。
FIBA世界盃籃球賽不僅僅是一場籃球比賽,更是一個文化的交流平台。這些球隊代表著不同國家和地區的精神,他們的奮鬥和拼搏將成為啟發人心的故事,激勵著更多的年輕人追求夢想,追求卓越。 https://telegra.ph/觀看-2023-年國際籃聯世界杯-08-16 -
在運動和賽事的世界裡,運彩分析成為了各界關注的焦點。為了滿足愈來愈多運彩愛好者的需求,我們隆重介紹字母哥運彩分析討論區,這個集交流、分享和學習於一身的專業平台。無論您是籃球、棒球、足球還是NBA、MLB、CPBL、NPB、KBO的狂熱愛好者,這裡都是您尋找專業意見、獲取最新運彩信息和提升運彩技巧的理想場所。
在字母哥運彩分析討論區,您可以輕鬆地獲取各種運彩分析信息,特別是針對籃球、棒球和足球領域的專業預測。不論您是NBA的忠實粉絲,還是熱愛棒球的愛好者,亦或者對足球賽事充滿熱情,這裡都有您需要的專業意見和分析。字母哥NBA預測將為您提供獨到的見解,幫助您更好地了解比賽情況,做出明智的選擇。
除了專業分析外,字母哥運彩分析討論區還擁有頂級的玩運彩分析情報員團隊。他們精通統計數據和信息,能夠幫助您分析比賽趨勢、預測結果,讓您的運彩之路更加成功和有利可圖。
當您在字母哥運彩分析討論區尋找運彩分析師時,您將不再猶豫。無論您追求最大的利潤,還是穩定的獲勝,或者您想要深入了解比賽統計,這裡都有您需要的一切。我們提供全面的統計數據和信息,幫助您作出明智的選擇,不論是尋找最佳運彩策略還是深入了解比賽情況。
總之,字母哥運彩分析討論區是您運彩之旅的理想起點。無論您是新手還是經驗豐富的玩家,這裡都能滿足您的需求,幫助您在運彩領域取得更大的成功。立即加入我們,一同探索運彩的精彩世界吧 https://abc66.tv/ -
世界盃籃球、
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
世界盃籃球、
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
FIBA
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
世界盃籃球、
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
觀看 2023 年國際籃聯世界杯
2023年FIBA世界盃籃球賽,也被稱為第19屆FIBA世界盃籃球賽,將成為籃球歷史上的一個重要里程碑。這場賽事是自2019年新制度實行後的第二次比賽,帶來了更多的期待和興奮。
賽事的參賽隊伍涵蓋了全球多個地區,包括歐洲、美洲、亞洲、大洋洲和非洲。此次賽事將選出各區域的佼佼者,以及2024年夏季奧運會主辦國法國,共計8支隊伍將獲得在巴黎舉行的奧運賽事的參賽資格。這無疑為各國球隊提供了一個難得的機會,展現他們的實力和技術。
在這場比賽中,我們將看到來自不同文化、背景和籃球傳統的球隊們匯聚一堂,用他們的熱情和努力,為世界籃球迷帶來精彩紛呈的比賽。球場上的每一個進球、每一次防守都將成為觀眾和球迷們津津樂道的話題。
FIBA世界盃籃球賽不僅僅是一場籃球比賽,更是一個文化的交流平台。這些球隊代表著不同國家和地區的精神,他們的奮鬥和拼搏將成為啟發人心的故事,激勵著更多的年輕人追求夢想,追求卓越。 https://telegra.ph/觀看-2023-年國際籃聯世界杯-08-16 -
世界盃籃球、
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
世界盃籃球、
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
玩運彩
玩運彩:體育賽事與娛樂遊戲的完美融合
在現代社會,運彩已成為一種極具吸引力的娛樂方式,結合了體育賽事的激情和娛樂遊戲的刺激。不僅能夠享受體育比賽的精彩,還能在賽事未開始時沉浸於娛樂遊戲的樂趣。玩運彩不僅提供了多項體育賽事的線上投注,還擁有豐富多樣的遊戲選擇,讓玩家能夠在其中找到無盡的娛樂與刺激。
體育投注一直以來都是運彩的核心內容之一。玩運彩提供了眾多體育賽事的線上投注平台,無論是NBA籃球、MLB棒球、世界盃足球、美式足球、冰球、網球、MMA格鬥還是拳擊等,都能在這裡找到合適的投注選項。這些賽事不僅為球迷帶來了觀賽的樂趣,還能讓他們參與其中,為比賽增添一份別樣的激情。
其中,PM體育、SUPER體育和鑫寶體育等運彩系統商成為了廣大玩家的首選。PM體育作為PM遊戲集團的體育遊戲平台,以給予玩家最佳線上體驗為宗旨,贏得了全球超過百萬客戶的信賴。SUPER體育則憑藉著CEZA(菲律賓克拉克經濟特區)的合法經營執照,展現了其合法性和可靠性。而鑫寶體育則以最高賠率聞名,通過研究各種比賽和推出新奇玩法,為玩家提供無盡的娛樂。
玩運彩不僅僅是一種投注行為,更是一種娛樂體驗。這種融合了體育和遊戲元素的娛樂方式,讓玩家能夠在比賽中感受到熱血的激情,同時在娛樂遊戲中尋找到輕鬆愉悅的時光。隨著科技的不斷進步,玩運彩的魅力將不斷擴展,為玩家帶來更多更豐富的選擇和體驗。無論是尋找刺激還是尋求娛樂,玩運彩都將是一個理想的選擇。 https://champer8.com/ -
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
觀看 2023 年國際籃聯世界杯
2023年FIBA世界盃籃球賽,也被稱為第19屆FIBA世界盃籃球賽,將成為籃球歷史上的一個重要里程碑。這場賽事是自2019年新制度實行後的第二次比賽,帶來了更多的期待和興奮。
賽事的參賽隊伍涵蓋了全球多個地區,包括歐洲、美洲、亞洲、大洋洲和非洲。此次賽事將選出各區域的佼佼者,以及2024年夏季奧運會主辦國法國,共計8支隊伍將獲得在巴黎舉行的奧運賽事的參賽資格。這無疑為各國球隊提供了一個難得的機會,展現他們的實力和技術。
在這場比賽中,我們將看到來自不同文化、背景和籃球傳統的球隊們匯聚一堂,用他們的熱情和努力,為世界籃球迷帶來精彩紛呈的比賽。球場上的每一個進球、每一次防守都將成為觀眾和球迷們津津樂道的話題。
FIBA世界盃籃球賽不僅僅是一場籃球比賽,更是一個文化的交流平台。這些球隊代表著不同國家和地區的精神,他們的奮鬥和拼搏將成為啟發人心的故事,激勵著更多的年輕人追求夢想,追求卓越。 https://telegra.ph/觀看-2023-年國際籃聯世界杯-08-16 -
世界盃
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
世界盃籃球、
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
世界盃
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
2023 年任何運動項目的成功分析,
在運動和賽事的世界裡,運彩分析成為了各界關注的焦點。為了滿足愈來愈多運彩愛好者的需求,我們隆重介紹字母哥運彩分析討論區,這個集交流、分享和學習於一身的專業平台。無論您是籃球、棒球、足球還是NBA、MLB、CPBL、NPB、KBO的狂熱愛好者,這裡都是您尋找專業意見、獲取最新運彩信息和提升運彩技巧的理想場所。
在字母哥運彩分析討論區,您可以輕鬆地獲取各種運彩分析信息,特別是針對籃球、棒球和足球領域的專業預測。不論您是NBA的忠實粉絲,還是熱愛棒球的愛好者,亦或者對足球賽事充滿熱情,這裡都有您需要的專業意見和分析。字母哥NBA預測將為您提供獨到的見解,幫助您更好地了解比賽情況,做出明智的選擇。
除了專業分析外,字母哥運彩分析討論區還擁有頂級的玩運彩分析情報員團隊。他們精通統計數據和信息,能夠幫助您分析比賽趨勢、預測結果,讓您的運彩之路更加成功和有利可圖。
當您在字母哥運彩分析討論區尋找運彩分析師時,您將不再猶豫。無論您追求最大的利潤,還是穩定的獲勝,或者您想要深入了解比賽統計,這裡都有您需要的一切。我們提供全面的統計數據和信息,幫助您作出明智的選擇,不論是尋找最佳運彩策略還是深入了解比賽情況。
總之,字母哥運彩分析討論區是您運彩之旅的理想起點。無論您是新手還是經驗豐富的玩家,這裡都能滿足您的需求,幫助您在運彩領域取得更大的成功。立即加入我們,一同探索運彩的精彩世界吧 https://telegra.ph/2023-年任何運動項目的成功分析-08-16 -
FIBA
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
世界盃籃球
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
世界盃籃球
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
FIBA
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
體驗金
體驗金:線上娛樂城的最佳入門票
隨著科技的發展,線上娛樂城已經成為許多玩家的首選。但對於初次踏入這個世界的玩家來說,可能會感到有些迷茫。這時,「體驗金」就成為了他們的最佳助手。
什麼是體驗金?
體驗金,簡單來說,就是娛樂城為了吸引新玩家而提供的一筆免費資金。玩家可以使用這筆資金在娛樂城內體驗各種遊戲,無需自己出資。這不僅降低了新玩家的入場門檻,也讓他們有機會真實感受到遊戲的樂趣。
體驗金的好處
1. **無風險體驗**:玩家可以使用體驗金在娛樂城內試玩,如果不喜歡,完全不需要承擔任何風險。
2. **學習遊戲**:對於不熟悉的遊戲,玩家可以使用體驗金進行學習和練習。
3. **增加信心**:當玩家使用體驗金獲得一些勝利後,他們的遊戲信心也會隨之增加。
如何獲得體驗金?
大部分的線上娛樂城都會提供體驗金給新玩家。通常,玩家只需要完成簡單的註冊程序,然後聯繫客服索取體驗金即可。但每家娛樂城的規定都可能有所不同,所以玩家在領取前最好先詳細閱讀活動條款。
使用體驗金的小技巧
1. **了解遊戲規則**:在使用體驗金之前,先了解遊戲的基本規則和策略。
2. **分散風險**:不要將所有的體驗金都投入到一個遊戲中,嘗試多種遊戲,找到最適合自己的。
3. **設定預算**:即使是使用體驗金,也建議玩家設定一個遊戲預算,避免過度沉迷。
結語:體驗金無疑是線上娛樂城提供給玩家的一大福利。不論你是資深玩家還是新手,都可以利用體驗金開啟你的遊戲之旅。選擇一家信譽良好的娛樂城,領取你的體驗金,開始你的遊戲冒險吧! -
MAGNUMBET adalah merupakan salah satu situs judi online deposit pulsa terpercaya yang sudah popular dikalangan bettor sebagai agen penyedia layanan permainan dengan menggunakan deposit uang asli. MAGNUMBET sebagai penyedia situs judi deposit pulsa tentunya sudah tidak perlu diragukan lagi. Karena MAGNUMBET bisa dikatakan sebagai salah satu pelopor situs judi online yang menggunakan deposit via pulsa di Indonesia. MAGNUMBET memberikan layanan deposit pulsa via Telkomsel. Bukan hanya deposit via pulsa saja, MAGNUMBET juga menyediakan deposit menggunakan pembayaran dompet digital. Minimal deposit pada situs MAGNUMBET juga amatlah sangat terjangkau, hanya dengan Rp 25.000,-, para bettor sudah bisa merasakan banyak permainan berkelas dengan winrate kemenangan yang tinggi, menjadikan member MAGNUMBET tentunya tidak akan terbebani dengan biaya tinggi untuk menikmati judi online
-
體驗金:線上娛樂城的最佳入門票
隨著科技的發展,線上娛樂城已經成為許多玩家的首選。但對於初次踏入這個世界的玩家來說,可能會感到有些迷茫。這時,「體驗金」就成為了他們的最佳助手。
什麼是體驗金?
體驗金,簡單來說,就是娛樂城為了吸引新玩家而提供的一筆免費資金。玩家可以使用這筆資金在娛樂城內體驗各種遊戲,無需自己出資。這不僅降低了新玩家的入場門檻,也讓他們有機會真實感受到遊戲的樂趣。
體驗金的好處
1. **無風險體驗**:玩家可以使用體驗金在娛樂城內試玩,如果不喜歡,完全不需要承擔任何風險。
2. **學習遊戲**:對於不熟悉的遊戲,玩家可以使用體驗金進行學習和練習。
3. **增加信心**:當玩家使用體驗金獲得一些勝利後,他們的遊戲信心也會隨之增加。
如何獲得體驗金?
大部分的線上娛樂城都會提供體驗金給新玩家。通常,玩家只需要完成簡單的註冊程序,然後聯繫客服索取體驗金即可。但每家娛樂城的規定都可能有所不同,所以玩家在領取前最好先詳細閱讀活動條款。
使用體驗金的小技巧
1. **了解遊戲規則**:在使用體驗金之前,先了解遊戲的基本規則和策略。
2. **分散風險**:不要將所有的體驗金都投入到一個遊戲中,嘗試多種遊戲,找到最適合自己的。
3. **設定預算**:即使是使用體驗金,也建議玩家設定一個遊戲預算,避免過度沉迷。
結語:體驗金無疑是線上娛樂城提供給玩家的一大福利。不論你是資深玩家還是新手,都可以利用體驗金開啟你的遊戲之旅。選擇一家信譽良好的娛樂城,領取你的體驗金,開始你的遊戲冒險吧! -
Magnumbet
MAGNUMBET adalah merupakan salah satu situs judi online deposit pulsa terpercaya yang sudah popular dikalangan bettor sebagai agen penyedia layanan permainan dengan menggunakan deposit uang asli. MAGNUMBET sebagai penyedia situs judi deposit pulsa tentunya sudah tidak perlu diragukan lagi. Karena MAGNUMBET bisa dikatakan sebagai salah satu pelopor situs judi online yang menggunakan deposit via pulsa di Indonesia. MAGNUMBET memberikan layanan deposit pulsa via Telkomsel. Bukan hanya deposit via pulsa saja, MAGNUMBET juga menyediakan deposit menggunakan pembayaran dompet digital. Minimal deposit pada situs MAGNUMBET juga amatlah sangat terjangkau, hanya dengan Rp 25.000,-, para bettor sudah bisa merasakan banyak permainan berkelas dengan winrate kemenangan yang tinggi, menjadikan member MAGNUMBET tentunya tidak akan terbebani dengan biaya tinggi untuk menikmati judi online -
Assistencia Dell florianopolis
Assistência técnica Dell em Florianópolis - Pessoal qualificado para consertar seu notebook, com garantia. Mais de 22 anos de experiência. Assistencia dell, assistencia tecnica notebook, Conserto de Video Game -
https://zamena-ventsov-doma.ru
-
玩運彩:體育賽事與娛樂遊戲的完美融合
在現代社會,運彩已成為一種極具吸引力的娛樂方式,結合了體育賽事的激情和娛樂遊戲的刺激。不僅能夠享受體育比賽的精彩,還能在賽事未開始時沉浸於娛樂遊戲的樂趣。玩運彩不僅提供了多項體育賽事的線上投注,還擁有豐富多樣的遊戲選擇,讓玩家能夠在其中找到無盡的娛樂與刺激。
體育投注一直以來都是運彩的核心內容之一。玩運彩提供了眾多體育賽事的線上投注平台,無論是NBA籃球、MLB棒球、世界盃足球、美式足球、冰球、網球、MMA格鬥還是拳擊等,都能在這裡找到合適的投注選項。這些賽事不僅為球迷帶來了觀賽的樂趣,還能讓他們參與其中,為比賽增添一份別樣的激情。
其中,PM體育、SUPER體育和鑫寶體育等運彩系統商成為了廣大玩家的首選。PM體育作為PM遊戲集團的體育遊戲平台,以給予玩家最佳線上體驗為宗旨,贏得了全球超過百萬客戶的信賴。SUPER體育則憑藉著CEZA(菲律賓克拉克經濟特區)的合法經營執照,展現了其合法性和可靠性。而鑫寶體育則以最高賠率聞名,通過研究各種比賽和推出新奇玩法,為玩家提供無盡的娛樂。
玩運彩不僅僅是一種投注行為,更是一種娛樂體驗。這種融合了體育和遊戲元素的娛樂方式,讓玩家能夠在比賽中感受到熱血的激情,同時在娛樂遊戲中尋找到輕鬆愉悅的時光。隨著科技的不斷進步,玩運彩的魅力將不斷擴展,為玩家帶來更多更豐富的選擇和體驗。無論是尋找刺激還是尋求娛樂,玩運彩都將是一個理想的選擇。 https://champer8.com/ -
運彩分析
在運動和賽事的世界裡,運彩分析成為了各界關注的焦點。為了滿足愈來愈多運彩愛好者的需求,我們隆重介紹字母哥運彩分析討論區,這個集交流、分享和學習於一身的專業平台。無論您是籃球、棒球、足球還是NBA、MLB、CPBL、NPB、KBO的狂熱愛好者,這裡都是您尋找專業意見、獲取最新運彩信息和提升運彩技巧的理想場所。
在字母哥運彩分析討論區,您可以輕鬆地獲取各種運彩分析信息,特別是針對籃球、棒球和足球領域的專業預測。不論您是NBA的忠實粉絲,還是熱愛棒球的愛好者,亦或者對足球賽事充滿熱情,這裡都有您需要的專業意見和分析。字母哥NBA預測將為您提供獨到的見解,幫助您更好地了解比賽情況,做出明智的選擇。
除了專業分析外,字母哥運彩分析討論區還擁有頂級的玩運彩分析情報員團隊。他們精通統計數據和信息,能夠幫助您分析比賽趨勢、預測結果,讓您的運彩之路更加成功和有利可圖。
當您在字母哥運彩分析討論區尋找運彩分析師時,您將不再猶豫。無論您追求最大的利潤,還是穩定的獲勝,或者您想要深入了解比賽統計,這裡都有您需要的一切。我們提供全面的統計數據和信息,幫助您作出明智的選擇,不論是尋找最佳運彩策略還是深入了解比賽情況。
總之,字母哥運彩分析討論區是您運彩之旅的理想起點。無論您是新手還是經驗豐富的玩家,這裡都能滿足您的需求,幫助您在運彩領域取得更大的成功。立即加入我們,一同探索運彩的精彩世界吧 https://abc66.tv/ -
Megaslot 64331c6
-
2023 年任何運動項目的成功分析,
在運動和賽事的世界裡,運彩分析成為了各界關注的焦點。為了滿足愈來愈多運彩愛好者的需求,我們隆重介紹字母哥運彩分析討論區,這個集交流、分享和學習於一身的專業平台。無論您是籃球、棒球、足球還是NBA、MLB、CPBL、NPB、KBO的狂熱愛好者,這裡都是您尋找專業意見、獲取最新運彩信息和提升運彩技巧的理想場所。
在字母哥運彩分析討論區,您可以輕鬆地獲取各種運彩分析信息,特別是針對籃球、棒球和足球領域的專業預測。不論您是NBA的忠實粉絲,還是熱愛棒球的愛好者,亦或者對足球賽事充滿熱情,這裡都有您需要的專業意見和分析。字母哥NBA預測將為您提供獨到的見解,幫助您更好地了解比賽情況,做出明智的選擇。
除了專業分析外,字母哥運彩分析討論區還擁有頂級的玩運彩分析情報員團隊。他們精通統計數據和信息,能夠幫助您分析比賽趨勢、預測結果,讓您的運彩之路更加成功和有利可圖。
當您在字母哥運彩分析討論區尋找運彩分析師時,您將不再猶豫。無論您追求最大的利潤,還是穩定的獲勝,或者您想要深入了解比賽統計,這裡都有您需要的一切。我們提供全面的統計數據和信息,幫助您作出明智的選擇,不論是尋找最佳運彩策略還是深入了解比賽情況。
總之,字母哥運彩分析討論區是您運彩之旅的理想起點。無論您是新手還是經驗豐富的玩家,這裡都能滿足您的需求,幫助您在運彩領域取得更大的成功。立即加入我們,一同探索運彩的精彩世界吧 https://telegra.ph/2023-年任何運動項目的成功分析-08-16 -
觀看 2023 年國際籃聯世界杯
2023年FIBA世界盃籃球賽,也被稱為第19屆FIBA世界盃籃球賽,將成為籃球歷史上的一個重要里程碑。這場賽事是自2019年新制度實行後的第二次比賽,帶來了更多的期待和興奮。
賽事的參賽隊伍涵蓋了全球多個地區,包括歐洲、美洲、亞洲、大洋洲和非洲。此次賽事將選出各區域的佼佼者,以及2024年夏季奧運會主辦國法國,共計8支隊伍將獲得在巴黎舉行的奧運賽事的參賽資格。這無疑為各國球隊提供了一個難得的機會,展現他們的實力和技術。
在這場比賽中,我們將看到來自不同文化、背景和籃球傳統的球隊們匯聚一堂,用他們的熱情和努力,為世界籃球迷帶來精彩紛呈的比賽。球場上的每一個進球、每一次防守都將成為觀眾和球迷們津津樂道的話題。
FIBA世界盃籃球賽不僅僅是一場籃球比賽,更是一個文化的交流平台。這些球隊代表著不同國家和地區的精神,他們的奮鬥和拼搏將成為啟發人心的故事,激勵著更多的年輕人追求夢想,追求卓越。 https://telegra.ph/觀看-2023-年國際籃聯世界杯-08-16 -
https://zamena-ventsov-doma.ru
-
2023年FIBA世界盃籃球賽,也被稱為第19屆FIBA世界盃籃球賽,將成為籃球歷史上的一個重要里程碑。這場賽事是自2019年新制度實行後的第二次比賽,帶來了更多的期待和興奮。
賽事的參賽隊伍涵蓋了全球多個地區,包括歐洲、美洲、亞洲、大洋洲和非洲。此次賽事將選出各區域的佼佼者,以及2024年夏季奧運會主辦國法國,共計8支隊伍將獲得在巴黎舉行的奧運賽事的參賽資格。這無疑為各國球隊提供了一個難得的機會,展現他們的實力和技術。
在這場比賽中,我們將看到來自不同文化、背景和籃球傳統的球隊們匯聚一堂,用他們的熱情和努力,為世界籃球迷帶來精彩紛呈的比賽。球場上的每一個進球、每一次防守都將成為觀眾和球迷們津津樂道的話題。
FIBA世界盃籃球賽不僅僅是一場籃球比賽,更是一個文化的交流平台。這些球隊代表著不同國家和地區的精神,他們的奮鬥和拼搏將成為啟發人心的故事,激勵著更多的年輕人追求夢想,追求卓越。 https://worldcups.tw/ -
觀看 2023 年國際籃聯世界杯
2023年FIBA世界盃籃球賽,也被稱為第19屆FIBA世界盃籃球賽,將成為籃球歷史上的一個重要里程碑。這場賽事是自2019年新制度實行後的第二次比賽,帶來了更多的期待和興奮。
賽事的參賽隊伍涵蓋了全球多個地區,包括歐洲、美洲、亞洲、大洋洲和非洲。此次賽事將選出各區域的佼佼者,以及2024年夏季奧運會主辦國法國,共計8支隊伍將獲得在巴黎舉行的奧運賽事的參賽資格。這無疑為各國球隊提供了一個難得的機會,展現他們的實力和技術。
在這場比賽中,我們將看到來自不同文化、背景和籃球傳統的球隊們匯聚一堂,用他們的熱情和努力,為世界籃球迷帶來精彩紛呈的比賽。球場上的每一個進球、每一次防守都將成為觀眾和球迷們津津樂道的話題。
FIBA世界盃籃球賽不僅僅是一場籃球比賽,更是一個文化的交流平台。這些球隊代表著不同國家和地區的精神,他們的奮鬥和拼搏將成為啟發人心的故事,激勵著更多的年輕人追求夢想,追求卓越。 https://telegra.ph/觀看-2023-年國際籃聯世界杯-08-16 -
觀看 2023 年國際籃聯世界杯
2023年FIBA世界盃籃球賽,也被稱為第19屆FIBA世界盃籃球賽,將成為籃球歷史上的一個重要里程碑。這場賽事是自2019年新制度實行後的第二次比賽,帶來了更多的期待和興奮。
賽事的參賽隊伍涵蓋了全球多個地區,包括歐洲、美洲、亞洲、大洋洲和非洲。此次賽事將選出各區域的佼佼者,以及2024年夏季奧運會主辦國法國,共計8支隊伍將獲得在巴黎舉行的奧運賽事的參賽資格。這無疑為各國球隊提供了一個難得的機會,展現他們的實力和技術。
在這場比賽中,我們將看到來自不同文化、背景和籃球傳統的球隊們匯聚一堂,用他們的熱情和努力,為世界籃球迷帶來精彩紛呈的比賽。球場上的每一個進球、每一次防守都將成為觀眾和球迷們津津樂道的話題。
FIBA世界盃籃球賽不僅僅是一場籃球比賽,更是一個文化的交流平台。這些球隊代表著不同國家和地區的精神,他們的奮鬥和拼搏將成為啟發人心的故事,激勵著更多的年輕人追求夢想,追求卓越。 https://telegra.ph/觀看-2023-年國際籃聯世界杯-08-16 -
카지노솔루션
카지노솔루션 -
FIBA
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
The neural network will create beautiful girls!
Geneticists are already hard at work creating stunning women. They will create these beauties based on specific requests and parameters using a neural network. The network will work with artificial insemination specialists to facilitate DNA sequencing.
The visionary for this concept is Alex Gurk, the co-founder of numerous initiatives and ventures aimed at creating beautiful, kind and attractive women who are genuinely connected to their partners. This direction stems from the recognition that in modern times the attractiveness and attractiveness of women has declined due to their increased independence. Unregulated and incorrect eating habits have led to problems such as obesity, causing women to deviate from their innate appearance.
The project received support from various well-known global companies, and sponsors readily stepped in. The essence of the idea is to offer willing men sexual and everyday communication with such wonderful women.
If you are interested, you can apply now as a waiting list has been created. -
The neural network will create beautiful girls!
Geneticists are already hard at work creating stunning women. They will create these beauties based on specific requests and parameters using a neural network. The network will work with artificial insemination specialists to facilitate DNA sequencing.
The visionary for this concept is Alex Gurk, the co-founder of numerous initiatives and ventures aimed at creating beautiful, kind and attractive women who are genuinely connected to their partners. This direction stems from the recognition that in modern times the attractiveness and attractiveness of women has declined due to their increased independence. Unregulated and incorrect eating habits have led to problems such as obesity, causing women to deviate from their innate appearance.
The project received support from various well-known global companies, and sponsors readily stepped in. The essence of the idea is to offer willing men sexual and everyday communication with such wonderful women.
If you are interested, you can apply now as a waiting list has been created. -
카지노솔루션
-
2023年的FIBA世界盃籃球賽(英語:2023 FIBA Basketball World Cup)是第19次舉行的男子籃球大賽,且現在每4年舉行一次。正式比賽於 2023/8/25 ~ 9/10 舉行。這次比賽是在2019年新規則實施後的第二次。最好的球隊將有機會參加2024年在法國巴黎的奧運賽事。而歐洲和美洲的前2名,以及亞洲、大洋洲、非洲的冠軍,還有奧運主辦國法國,總共8支隊伍將獲得這個機會。
在2023年2月20日FIBA世界盃籃球亞太區資格賽的第六階段已經完賽!雖然台灣隊未能參賽,但其他國家選手的精彩表現絕對值得關注。本文將為您提供FIBA籃球世界盃賽程資訊,以及可以收看直播和轉播的線上平台,希望您不要錯過!
主辦國家 : 菲律賓、印尼、日本
正式比賽 : 2023年8月25日–2023年9月10日
參賽隊伍 : 共有32隊
比賽場館 : 菲律賓體育館、阿拉內塔體育館、亞洲購物中心體育館、印尼體育館、沖繩體育館 -
The neural network will create beautiful girls!
Geneticists are already hard at work creating stunning women. They will create these beauties based on specific requests and parameters using a neural network. The network will work with artificial insemination specialists to facilitate DNA sequencing.
The visionary for this concept is Alex Gurk, the co-founder of numerous initiatives and ventures aimed at creating beautiful, kind and attractive women who are genuinely connected to their partners. This direction stems from the recognition that in modern times the attractiveness and attractiveness of women has declined due to their increased independence. Unregulated and incorrect eating habits have led to problems such as obesity, causing women to deviate from their innate appearance.
The project received support from various well-known global companies, and sponsors readily stepped in. The essence of the idea is to offer willing men sexual and everyday communication with such wonderful women.
If you are interested, you can apply now as a waiting list has been created. -
The neural network will create beautiful girls!
Geneticists are already hard at work creating stunning women. They will create these beauties based on specific requests and parameters using a neural network. The network will work with artificial insemination specialists to facilitate DNA sequencing.
The visionary for this concept is Alex Gurk, the co-founder of numerous initiatives and ventures aimed at creating beautiful, kind and attractive women who are genuinely connected to their partners. This direction stems from the recognition that in modern times the attractiveness and attractiveness of women has declined due to their increased independence. Unregulated and incorrect eating habits have led to problems such as obesity, causing women to deviate from their innate appearance.
The project received support from various well-known global companies, and sponsors readily stepped in. The essence of the idea is to offer willing men sexual and everyday communication with such wonderful women.
If you are interested, you can apply now as a waiting list has been created. -
Antminer D9
Antminer D9 -
The neural network will create beautiful girls!
Geneticists are already hard at work creating stunning women. They will create these beauties based on specific requests and parameters using a neural network. The network will work with artificial insemination specialists to facilitate DNA sequencing.
The visionary for this concept is Alex Gurk, the co-founder of numerous initiatives and ventures aimed at creating beautiful, kind and attractive women who are genuinely connected to their partners. This direction stems from the recognition that in modern times the attractiveness and attractiveness of women has declined due to their increased independence. Unregulated and incorrect eating habits have led to problems such as obesity, causing women to deviate from their innate appearance.
The project received support from various well-known global companies, and sponsors readily stepped in. The essence of the idea is to offer willing men sexual and everyday communication with such wonderful women.
If you are interested, you can apply now as a waiting list has been created. -
A neural network draws a woman
The neural network will create beautiful girls!
Geneticists are already hard at work creating stunning women. They will create these beauties based on specific requests and parameters using a neural network. The network will work with artificial insemination specialists to facilitate DNA sequencing.
The visionary for this concept is Alex Gurk, the co-founder of numerous initiatives and ventures aimed at creating beautiful, kind and attractive women who are genuinely connected to their partners. This direction stems from the recognition that in modern times the attractiveness and attractiveness of women has declined due to their increased independence. Unregulated and incorrect eating habits have led to problems such as obesity, causing women to deviate from their innate appearance.
The project received support from various well-known global companies, and sponsors readily stepped in. The essence of the idea is to offer willing men sexual and everyday communication with such wonderful women.
If you are interested, you can apply now as a waiting list has been created. -
Assistência técnica notebook
Assistência técnica notebook, conserto de placa mãe em Florianópolis - Pessoal qualificado para consertar seu notebook, com garantia. Mais de 19 anos de experiência.
https://notebook-on.com.br/assistencia-tecnica-dell
Assistência técnica Dell em Florianópolis - Pessoal qualificado para consertar seu notebook -
https://www.instrushop.bg/Лазерн
-
https://www.instrushop.bg/mashini-i-instrumenti/akumulatorni-mashini/akumulatorni-gaikoverti
-
https://www.homebulgaria.bg/резачки
-
Разрешение на строительство — это административный удостоверение, предоставляемый официальными ведомствами государственного аппарата или муниципального самоуправления, который допускает начать стройку или выполнение строительного процесса.
[url=https://rns-50.ru/]Разрешение на строительство жилых построек[/url] предписывает нормативные основы и требования к возведению, включая допустимые типы работ, приемлемые материалы и подходы, а также включает строительные инструкции и комплексы безопасности. Получение разрешения на строительство является необходимым документов для строительной сферы. -
KOINSLOT
Unveiling the Thrills of KOIN SLOT: Embark on an Adventure with KOINSLOT Online
Abstract: This article takes you on a journey into the exciting realm of KOIN SLOT, introducing you to the electrifying world of online slot gaming with the renowned platform, KOINSLOT. Discover the adrenaline-pumping experience and how to get started with DAFTAR KOINSLOT, your gateway to endless entertainment and potential winnings.
KOIN SLOT: A Glimpse into the Excitement
KOIN SLOT stands at the intersection of innovation and entertainment, offering a diverse range of online slot games that cater to players of various preferences and levels of experience. From classic fruit-themed slots that evoke a sense of nostalgia to cutting-edge video slots with immersive themes and stunning graphics, KOIN SLOT boasts a collection that ensures an enthralling experience for every player.
Introducing SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT
SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT introduces players to a universe of gaming possibilities that transcend geographical boundaries. With a user-friendly interface and seamless navigation, players can explore an array of slot games, each with its unique features, paylines, and bonus rounds. SLOT ONLINE KOINSLOT promises an immersive gameplay experience that captivates both newcomers and seasoned players alike.
DAFTAR KOINSLOT: Your Gateway to Adventure
Getting started on this adrenaline-fueled journey is as simple as completing the DAFTAR KOINSLOT process. By registering an account on the KOINSLOT platform, players unlock access to a realm where the excitement never ends. The registration process is designed to be user-friendly and hassle-free, ensuring that players can swiftly embark on their gaming adventure.
Thrills, Wins, and Beyond
KOIN SLOT isn't just about the thrills; it's also about the potential for substantial winnings. Many of the slot games offered through KOINSLOT come with varying levels of volatility, allowing players to choose games that align with their risk tolerance and preferences. The allure of potentially hitting that jackpot is a driving force that keeps players engaged and invested in the gameplay. -
SLOT ONLINE DRAGON77: A World of Possibilities
SLOT ONLINE DRAGON77 is the gateway to an adventure of epic proportions. The game features a dynamic selection of slot games, each with its unique features, paylines, and bonus rounds. Whether you're a seasoned player seeking high-stakes action or a newcomer looking to explore the world of online slots, SLOT ONLINE DRAGON77 offers an array of options to suit your preferences.
Exploring SLOT GACOR DRAGON77
SLOT GACOR DRAGON77 introduces players to the concept of a "gacor" experience, where gameplay is characterized by exciting wins, engaging features, and a seamless flow. The term "gacor" is a colloquial expression that resonates with the feeling of triumph and excitement that players experience during a winning streak. With SLOT GACOR DRAGON77, players can expect gameplay that keeps them on the edge of their seats.
The Quest for Wins and Entertainment
DRAGON77 isn't just about the mythical aesthetics; it's also about the potential for substantial winnings. Many of the slot games within the SLOT ONLINE DRAGON77 portfolio come with varying levels of volatility, allowing players to choose games that align with their preferred risk levels. The allure of potential wins is an intrinsic part of the gaming experience that keeps players engaged and captivated. -
https://www.promomaistor.com/Градина/Резачки
-
Selamat datang di Surgaslot !! situs slot deposit dana terpercaya nomor 1 di Indonesia. Sebagai salah satu situs agen slot online terbaik dan terpercaya, kami menyediakan banyak jenis variasi permainan yang bisa Anda nikmati. Semua permainan juga bisa dimainkan cukup dengan memakai 1 user-ID saja.
Surgaslot sendiri telah dikenal sebagai situs slot tergacor dan terpercaya di Indonesia. Dimana kami sebagai situs slot online terbaik juga memiliki pelayanan customer service 24 jam yang selalu siap sedia dalam membantu para member. Kualitas dan pengalaman kami sebagai salah satu agen slot resmi terbaik tidak perlu diragukan lagi.
Surgaslot merupakan salah satu situs slot gacor di Indonesia. Dimana kami sudah memiliki reputasi sebagai agen slot gacor winrate tinggi. Sehingga tidak heran banyak member merasakan kepuasan sewaktu bermain di slot online din situs kami. Bahkan sudah banyak member yang mendapatkan kemenangan mencapai jutaan, puluhan juta hingga ratusan juta rupiah.
Kami juga dikenal sebagai situs judi slot terpercaya no 1 Indonesia. Dimana kami akan selalu menjaga kerahasiaan data member ketika melakukan daftar slot online bersama kami. Sehingga tidak heran jika sampai saat ini member yang sudah bergabung di situs Surgaslot slot gacor indonesia mencapai ratusan ribu member di seluruh Indonesia -
лазерни нивелири
https://www.instrushop.bg/Лазерн -
https://www.instrushop.bg/mashini-i-instrumenti/akumulatorni-mashini/akumulatorni-gaikoverti
-
лазерни нивелири
https://www.instrushop.bg/Лазерни-нивелири/ -
акумулаторни гайковерти
https://www.instrushop.bg/mashini-i-instrumenti/akumulatorni-mashini/akumulatorni-gaikoverti -
rikvip
RIKVIP - Cổng Game Bài Đổi Thưởng Uy Tín và Hấp Dẫn Tại Việt Nam
Giới thiệu về RIKVIP (Rik Vip, RichVip)
RIKVIP là một trong những cổng game đổi thưởng nổi tiếng tại thị trường Việt Nam, ra mắt vào năm 2016. Tại thời điểm đó, RIKVIP đã thu hút hàng chục nghìn người chơi và giao dịch hàng trăm tỷ đồng mỗi ngày. Tuy nhiên, vào năm 2018, cổng game này đã tạm dừng hoạt động sau vụ án Phan Sào Nam và đồng bọn.
Tuy nhiên, RIKVIP đã trở lại mạnh mẽ nhờ sự đầu tư của các nhà tài phiệt Mỹ. Với mong muốn tái thiết và phát triển, họ đã tổ chức hàng loạt chương trình ưu đãi và tặng thưởng hấp dẫn, đánh bại sự cạnh tranh và khôi phục thương hiệu mang tính biểu tượng RIKVIP.
https://youtu.be/OlR_8Ei-hr0
Điểm mạnh của RIKVIP
Phong cách chuyên nghiệp
RIKVIP luôn tự hào về sự chuyên nghiệp trong mọi khía cạnh. Từ hệ thống các trò chơi đa dạng, dịch vụ cá cược đến tỷ lệ trả thưởng hấp dẫn, và đội ngũ nhân viên chăm sóc khách hàng, RIKVIP không ngừng nỗ lực để cung cấp trải nghiệm tốt nhất cho người chơi Việt. -
https://zamena-ventsov-doma.ru
-
RIKVIP - Cổng Game Bài Đổi Thưởng Uy Tín và Hấp Dẫn Tại Việt Nam
Giới thiệu về RIKVIP (Rik Vip, RichVip)
RIKVIP là một trong những cổng game đổi thưởng nổi tiếng tại thị trường Việt Nam, ra mắt vào năm 2016. Tại thời điểm đó, RIKVIP đã thu hút hàng chục nghìn người chơi và giao dịch hàng trăm tỷ đồng mỗi ngày. Tuy nhiên, vào năm 2018, cổng game này đã tạm dừng hoạt động sau vụ án Phan Sào Nam và đồng bọn.
Tuy nhiên, RIKVIP đã trở lại mạnh mẽ nhờ sự đầu tư của các nhà tài phiệt Mỹ. Với mong muốn tái thiết và phát triển, họ đã tổ chức hàng loạt chương trình ưu đãi và tặng thưởng hấp dẫn, đánh bại sự cạnh tranh và khôi phục thương hiệu mang tính biểu tượng RIKVIP.
https://youtu.be/OlR_8Ei-hr0
Điểm mạnh của RIKVIP
Phong cách chuyên nghiệp
RIKVIP luôn tự hào về sự chuyên nghiệp trong mọi khía cạnh. Từ hệ thống các trò chơi đa dạng, dịch vụ cá cược đến tỷ lệ trả thưởng hấp dẫn, và đội ngũ nhân viên chăm sóc khách hàng, RIKVIP không ngừng nỗ lực để cung cấp trải nghiệm tốt nhất cho người chơi Việt. -
RIKVIP - Cổng Game Bài Đổi Thưởng Uy Tín và Hấp Dẫn Tại Việt Nam
Giới thiệu về RIKVIP (Rik Vip, RichVip)
RIKVIP là một trong những cổng game đổi thưởng nổi tiếng tại thị trường Việt Nam, ra mắt vào năm 2016. Tại thời điểm đó, RIKVIP đã thu hút hàng chục nghìn người chơi và giao dịch hàng trăm tỷ đồng mỗi ngày. Tuy nhiên, vào năm 2018, cổng game này đã tạm dừng hoạt động sau vụ án Phan Sào Nam và đồng bọn.
Tuy nhiên, RIKVIP đã trở lại mạnh mẽ nhờ sự đầu tư của các nhà tài phiệt Mỹ. Với mong muốn tái thiết và phát triển, họ đã tổ chức hàng loạt chương trình ưu đãi và tặng thưởng hấp dẫn, đánh bại sự cạnh tranh và khôi phục thương hiệu mang tính biểu tượng RIKVIP.
https://youtu.be/OlR_8Ei-hr0
Điểm mạnh của RIKVIP
Phong cách chuyên nghiệp
RIKVIP luôn tự hào về sự chuyên nghiệp trong mọi khía cạnh. Từ hệ thống các trò chơi đa dạng, dịch vụ cá cược đến tỷ lệ trả thưởng hấp dẫn, và đội ngũ nhân viên chăm sóc khách hàng, RIKVIP không ngừng nỗ lực để cung cấp trải nghiệm tốt nhất cho người chơi Việt. -
365bet
-
百家樂:經典的賭場遊戲
百家樂,這個名字在賭場界中無疑是家喻戶曉的。它的歷史悠久,起源於中世紀的義大利,後來在法國得到了廣泛的流行。如今,無論是在拉斯維加斯、澳門還是線上賭場,百家樂都是玩家們的首選。
遊戲的核心目標相當簡單:玩家押注「閒家」、「莊家」或「和」,希望自己選擇的一方能夠獲得牌點總和最接近9或等於9的牌。這種簡單直接的玩法使得百家樂成為了賭場中最容易上手的遊戲之一。
在百家樂的牌點計算中,10、J、Q、K的牌點為0;A為1;2至9的牌則以其面值計算。如果牌點總和超過10,則只取最後一位數作為總點數。例如,一手8和7的牌總和為15,但在百家樂中,其牌點則為5。
百家樂的策略和技巧也是玩家們熱衷討論的話題。雖然百家樂是一個基於機會的遊戲,但通過觀察和分析,玩家可以嘗試找出某些趨勢,從而提高自己的勝率。這也是為什麼在賭場中,你經常可以看到玩家們在百家樂桌旁邊記錄牌路,希望能夠從中找到一些有用的信息。
除了基本的遊戲規則和策略,百家樂還有一些其他的玩法,例如「對子」押注,玩家可以押注閒家或莊家的前兩張牌為對子。這種押注的賠率通常較高,但同時風險也相對增加。
線上百家樂的興起也為玩家帶來了更多的選擇。現在,玩家不需要親自去賭場,只需要打開電腦或手機,就可以隨時隨地享受百家樂的樂趣。線上百家樂不僅提供了傳統的遊戲模式,還有各種變種和特色玩法,滿足了不同玩家的需求。
但不論是在實體賭場還是線上賭場,百家樂始終保持著它的魅力。它的簡單、直接和快節奏的特點使得玩家們一再地被吸引。而對於那些希望在賭場中獲得一些勝利的玩家來說,百家樂無疑是一個不錯的選擇。
最後,無論你是百家樂的新手還是老手,都應該記住賭博的黃金法則:玩得開心, -
百家樂
百家樂:經典的賭場遊戲
百家樂,這個名字在賭場界中無疑是家喻戶曉的。它的歷史悠久,起源於中世紀的義大利,後來在法國得到了廣泛的流行。如今,無論是在拉斯維加斯、澳門還是線上賭場,百家樂都是玩家們的首選。
遊戲的核心目標相當簡單:玩家押注「閒家」、「莊家」或「和」,希望自己選擇的一方能夠獲得牌點總和最接近9或等於9的牌。這種簡單直接的玩法使得百家樂成為了賭場中最容易上手的遊戲之一。
在百家樂的牌點計算中,10、J、Q、K的牌點為0;A為1;2至9的牌則以其面值計算。如果牌點總和超過10,則只取最後一位數作為總點數。例如,一手8和7的牌總和為15,但在百家樂中,其牌點則為5。
百家樂的策略和技巧也是玩家們熱衷討論的話題。雖然百家樂是一個基於機會的遊戲,但通過觀察和分析,玩家可以嘗試找出某些趨勢,從而提高自己的勝率。這也是為什麼在賭場中,你經常可以看到玩家們在百家樂桌旁邊記錄牌路,希望能夠從中找到一些有用的信息。
除了基本的遊戲規則和策略,百家樂還有一些其他的玩法,例如「對子」押注,玩家可以押注閒家或莊家的前兩張牌為對子。這種押注的賠率通常較高,但同時風險也相對增加。
線上百家樂的興起也為玩家帶來了更多的選擇。現在,玩家不需要親自去賭場,只需要打開電腦或手機,就可以隨時隨地享受百家樂的樂趣。線上百家樂不僅提供了傳統的遊戲模式,還有各種變種和特色玩法,滿足了不同玩家的需求。
但不論是在實體賭場還是線上賭場,百家樂始終保持著它的魅力。它的簡單、直接和快節奏的特點使得玩家們一再地被吸引。而對於那些希望在賭場中獲得一些勝利的玩家來說,百家樂無疑是一個不錯的選擇。
最後,無論你是百家樂的新手還是老手,都應該記住賭博的黃金法則:玩得開心, -
**百家樂:賭場裡的明星遊戲**
你有沒有聽過百家樂?這遊戲在賭場界簡直就是大熱門!從古老的義大利開始,再到法國,百家樂的名聲響亮。現在,不論是你走到哪個國家的賭場,或是在家裡上線玩,百家樂都是玩家的最愛。
玩百家樂的目的就是賭哪一方的牌會接近或等於9點。這遊戲的規則真的簡單得很,所以新手也能很快上手。計算牌的點數也不難,10和圖案牌是0點,A是1點,其他牌就看牌面的數字。如果加起來超過10,那就只看最後一位。
雖然百家樂主要靠運氣,但有些玩家還是喜歡找一些規律或策略,希望能提高勝率。所以,你在賭場經常可以看到有人邊玩邊記牌,試著找出下一輪的趨勢。
現在線上賭場也很夯,所以你可以隨時在網路上找到百家樂遊戲。線上版本還有很多特色和變化,絕對能滿足你的需求。
不管怎麼說,百家樂就是那麼吸引人。它的玩法簡單、節奏快,每一局都充滿刺激。但別忘了,賭博最重要的就是玩得開心,不要太認真,享受遊戲的過程就好! -
**百家樂:賭場裡的明星遊戲**
你有沒有聽過百家樂?這遊戲在賭場界簡直就是大熱門!從古老的義大利開始,再到法國,百家樂的名聲響亮。現在,不論是你走到哪個國家的賭場,或是在家裡上線玩,百家樂都是玩家的最愛。
玩百家樂的目的就是賭哪一方的牌會接近或等於9點。這遊戲的規則真的簡單得很,所以新手也能很快上手。計算牌的點數也不難,10和圖案牌是0點,A是1點,其他牌就看牌面的數字。如果加起來超過10,那就只看最後一位。
雖然百家樂主要靠運氣,但有些玩家還是喜歡找一些規律或策略,希望能提高勝率。所以,你在賭場經常可以看到有人邊玩邊記牌,試著找出下一輪的趨勢。
現在線上賭場也很夯,所以你可以隨時在網路上找到百家樂遊戲。線上版本還有很多特色和變化,絕對能滿足你的需求。
不管怎麼說,百家樂就是那麼吸引人。它的玩法簡單、節奏快,每一局都充滿刺激。但別忘了,賭博最重要的就是玩得開心,不要太認真,享受遊戲的過程就好! -
susu4d
susu4d -
bocor88
bocor88 -
《2024總統大選:台灣的新篇章》
2024年,對台灣來說,是一個重要的歷史時刻。這一年,台灣將迎來又一次的總統大選,這不僅僅是一場政治競技,更是台灣民主發展的重要標誌。
### 2024總統大選的背景
隨著全球政治經濟的快速變遷,2024總統大選將在多重背景下進行。無論是國際間的緊張局勢、還是內部的政策調整,都將影響這次選舉的結果。
### 候選人的角逐
每次的總統大選,都是各大政黨的領袖們展現自己政策和領導才能的舞台。2024總統大選,無疑也會有一系列的重量級人物參選,他們的政策理念和領導風格,將是選民最關心的焦點。
### 選民的選擇
2024總統大選,不僅僅是政治家的競技場,更是每一位台灣選民表達自己政治意識的時刻。每一票,都代表著選民對未來的期望和願景。
### 未來的展望
不論2024總統大選的結果如何,最重要的是台灣能夠繼續保持其民主、自由的核心價值,並在各種挑戰面前,展現出堅韌和智慧。
結語:
2024總統大選,對台灣來說,是新的開始,也是新的挑戰。希望每一位選民都能夠認真思考,為台灣的未來做出最好的選擇。 -
《539開獎:探索台灣的熱門彩券遊戲》
539彩券是台灣彩券市場上的一個重要組成部分,擁有大量的忠實玩家。每當"539開獎"的時刻來臨,不少人都會屏息以待,期盼自己手中的彩票能夠帶來好運。
### 539彩券的起源
539彩券在台灣的歷史可以追溯到數十年前。它是為了滿足大眾對小型彩券遊戲的需求而誕生的。與其他大型彩券遊戲相比,539的玩法簡單,投注金額也相對較低,因此迅速受到了大眾的喜愛。
### 539開獎的過程
"539開獎"是一個公正、公開的過程。每次開獎,都會有專業的工作人員和公證人在場監督,以確保開獎的公正性。開獎過程中,專業的機器會隨機抽取五個號碼,這五個號碼就是當期的中獎號碼。
### 如何參與539彩券?
參與539彩券非常簡單。玩家只需要到指定的彩券銷售點,選擇自己心儀的五個號碼,然後購買彩票即可。當然,現在也有許多線上平台提供539彩券的購買服務,玩家可以不出門就能參與遊戲。
### 539開獎的魅力
每當"539開獎"的時刻來臨,不少玩家都會聚集在電視機前,或是上網查詢開獎結果。這種期待和緊張的感覺,就是539彩券吸引人的地方。畢竟,每一次開獎,都有可能創造出新的百萬富翁。
### 結語
539彩券是台灣彩券市場上的一顆明星,它以其簡單的玩法和低廉的投注金額受到了大眾的喜愛。"539開獎"不僅是一個遊戲過程,更是許多人夢想成真的機會。但需要提醒的是,彩券遊戲應該理性參與,不應過度沉迷,更不應該拿生活所需的資金來投注。希望每一位玩家都能夠健康、快樂地參與539彩券,享受遊戲的樂趣。 -
《2024總統大選:台灣的新篇章》
2024年,對台灣來說,是一個重要的歷史時刻。這一年,台灣將迎來又一次的總統大選,這不僅僅是一場政治競技,更是台灣民主發展的重要標誌。
### 2024總統大選的背景
隨著全球政治經濟的快速變遷,2024總統大選將在多重背景下進行。無論是國際間的緊張局勢、還是內部的政策調整,都將影響這次選舉的結果。
### 候選人的角逐
每次的總統大選,都是各大政黨的領袖們展現自己政策和領導才能的舞台。2024總統大選,無疑也會有一系列的重量級人物參選,他們的政策理念和領導風格,將是選民最關心的焦點。
### 選民的選擇
2024總統大選,不僅僅是政治家的競技場,更是每一位台灣選民表達自己政治意識的時刻。每一票,都代表著選民對未來的期望和願景。
### 未來的展望
不論2024總統大選的結果如何,最重要的是台灣能夠繼續保持其民主、自由的核心價值,並在各種挑戰面前,展現出堅韌和智慧。
結語:
2024總統大選,對台灣來說,是新的開始,也是新的挑戰。希望每一位選民都能夠認真思考,為台灣的未來做出最好的選擇。 -
娛樂城
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
娛樂城遊戲
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
娛樂城
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
can you eat bananas while taking prednisone prednisone rash pictures prednisone and sleep
-
brillx скачать бесплатно
https://brillx-kazino.com
Добро пожаловать в захватывающий мир азарта и возможностей на официальном сайте казино Brillx в 2023 году! Если вы ищете источник невероятной развлекательности, где можно играть онлайн бесплатно или за деньги в захватывающие игровые аппараты, то ваш поиск завершается здесь.Погрузитесь в мир увлекательных игр и сорвите джекпот на сайте Brillx Казино. Наши игровые аппараты не просто уникальны, они воплощение невероятных приключений. От крупных выигрышей до захватывающих бонусных раундов, вас ждут неожиданные сюрпризы за каждым вращением барабанов. -
娛樂城APP
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
《539開獎:探索台灣的熱門彩券遊戲》
539彩券是台灣彩券市場上的一個重要組成部分,擁有大量的忠實玩家。每當"539開獎"的時刻來臨,不少人都會屏息以待,期盼自己手中的彩票能夠帶來好運。
### 539彩券的起源
539彩券在台灣的歷史可以追溯到數十年前。它是為了滿足大眾對小型彩券遊戲的需求而誕生的。與其他大型彩券遊戲相比,539的玩法簡單,投注金額也相對較低,因此迅速受到了大眾的喜愛。
### 539開獎的過程
"539開獎"是一個公正、公開的過程。每次開獎,都會有專業的工作人員和公證人在場監督,以確保開獎的公正性。開獎過程中,專業的機器會隨機抽取五個號碼,這五個號碼就是當期的中獎號碼。
### 如何參與539彩券?
參與539彩券非常簡單。玩家只需要到指定的彩券銷售點,選擇自己心儀的五個號碼,然後購買彩票即可。當然,現在也有許多線上平台提供539彩券的購買服務,玩家可以不出門就能參與遊戲。
### 539開獎的魅力
每當"539開獎"的時刻來臨,不少玩家都會聚集在電視機前,或是上網查詢開獎結果。這種期待和緊張的感覺,就是539彩券吸引人的地方。畢竟,每一次開獎,都有可能創造出新的百萬富翁。
### 結語
539彩券是台灣彩券市場上的一顆明星,它以其簡單的玩法和低廉的投注金額受到了大眾的喜愛。"539開獎"不僅是一個遊戲過程,更是許多人夢想成真的機會。但需要提醒的是,彩券遊戲應該理性參與,不應過度沉迷,更不應該拿生活所需的資金來投注。希望每一位玩家都能夠健康、快樂地參與539彩券,享受遊戲的樂趣。 -
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
娛樂城遊戲
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
娛樂城
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
Bocor88
-
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
娛樂城
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
娛樂城APP
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
Быстромонтируемые здания - это прогрессивные сооружения, которые отличаются великолепной быстротой возведения и гибкостью. Они представляют собой строения, состоящие из заранее изготовленных элементов либо узлов, которые способны быть быстро установлены на месте стройки.
[url=https://bystrovozvodimye-zdanija.ru/]Производство быстровозводимых зданий из сэндвич панелей[/url] располагают гибкостью и адаптируемостью, что дозволяет просто менять и модифицировать их в соответствии с запросами заказчика. Это экономически выгодное и экологически долговечное решение, которое в крайние лета получило широкое распространение. -
線上娛樂城
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
娛樂城遊戲
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
線上娛樂城
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
娛樂城APP
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
https://gurtogd.online
[url=https://casadoapostador.com.br/artigos/eventos-com-suspeita-de-manipulacao-aumentaram-durante-a-pandemia/#comment-511141]korades.ru[/url] 056_d66 -
sildenafil cost australia buy generic viagra 100mg online sildenafil 20 mg prescription online
-
Отличный ремонт в https://remont-holodilnikov-electrolux.com. Быстро, качественно и по разумной цене. Советую!
-
개인사업자대출! 가장 빠른 방법
-
viagra coupon generic viagra sildenafil viagra otc us
-
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
線上娛樂城
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
娛樂城
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
《娛樂城:線上遊戲的新趨勢》
在現代社會,科技的發展已經深深地影響了我們的日常生活。其中,娛樂行業的變革尤為明顯,特別是娛樂城的崛起。從實體遊樂場所到線上娛樂城,這一轉變不僅帶來了便利,更為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。
### 娛樂城APP:隨時隨地的遊戲體驗
隨著智慧型手機的普及,娛樂城APP已經成為許多玩家的首選。透過APP,玩家可以隨時隨地參與自己喜愛的遊戲,不再受到地點的限制。而且,許多娛樂城APP還提供了專屬的優惠和活動,吸引更多的玩家參與。
### 娛樂城遊戲:多樣化的選擇
傳統的遊樂場所往往受限於空間和設備,但線上娛樂城則打破了這一限制。從經典的賭場遊戲到最新的電子遊戲,娛樂城遊戲的種類繁多,滿足了不同玩家的需求。而且,這些遊戲還具有高度的互動性和真實感,使玩家仿佛置身於真實的遊樂場所。
### 線上娛樂城:安全與便利並存
線上娛樂城的另一大優勢是其安全性。許多線上娛樂城都採用了先進的加密技術,確保玩家的資料和交易安全。此外,線上娛樂城還提供了多種支付方式,使玩家可以輕鬆地進行充值和提現。
然而,選擇線上娛樂城時,玩家仍需謹慎。建議玩家選擇那些具有良好口碑和正規授權的娛樂城,以確保自己的權益。
結語:
娛樂城,無疑已經成為當代遊戲行業的一大趨勢。無論是娛樂城APP、娛樂城遊戲,還是線上娛樂城,都為玩家提供了前所未有的遊戲體驗。然而,選擇娛樂城時,玩家仍需保持警惕,確保自己的安全和權益。 -
Отличный ремонт в https://remont-holodilnikov-electrolux.com. Быстро, качественно и по разумной цене. Советую!
-
cialis online pharmacy usa xalatan online pharmacy best erectile dysfunction pills
-
can you buy misoprostol pharmacy buy viagra online pharmacy online pharmacy no prescription valium
-
boncel4d
boncel4d -
soma indian pharmacy acyclovir pharmacy Cardizem
-
tombak188
tombak188 -
https://telegra.ph/how-french-women-do-beauty-09-11
https://telegra.ph/definition-beautiful-girl-09-10
https://telegra.ph/yakuza-kiwami-beautiful-woman-09-11
https://telegra.ph/beautiful-and-cute-girls-pics-09-11
https://telegra.ph/beautiful-black-man-white-woman-xxx-09-10
In an era of rapidly advancing technology, the boundaries of what we once thought was possible are being shattered. From medical breakthroughs to artificial intelligence, the fusion of various fields has paved the way for groundbreaking discoveries. One such breathtaking development is the creation of a beautiful girl by a neural network based on a hand-drawn image. This extraordinary innovation offers a glimpse into the future where neural networks and genetic science combine to revolutionize our perception of beauty.
The Birth of a Digital "Muse":
Imagine a scenario where you sketch a simple drawing of a girl, and by utilizing the power of a neural network, that drawing comes to life. This miraculous transformation from pen and paper to an enchanting digital persona leaves us in awe of the potential that lies within artificial intelligence. This incredible feat of science showcases the tremendous strides made in programming algorithms to recognize and interpret human visuals.
Beautiful girl 331c6d0 -
Được biết, sau nhiều lần đổi tên, cái tên Hitclub chính thức hoạt động lại vào năm 2018 với mô hình "đánh bài ảo nhưng bằng tiền thật". Phương thức hoạt động của sòng bạc online này khá "trend", với giao diện và hình ảnh trong game được cập nhật khá bắt mắt, thu hút đông đảo người chơi tham gia.
Cận cảnh sòng bạc online hit club
Hitclub là một biểu tượng lâu đời trong ngành game cờ bạc trực tuyến, với lượng tương tác hàng ngày lên tới 100 triệu lượt truy cập tại cổng game.
Với một hệ thống đa dạng các trò chơi cờ bạc phong phú từ trò chơi mini game (nông trại, bầu cua, vòng quay may mắn, xóc đĩa mini…), game bài đổi thưởng ( TLMN, phỏm, Poker, Xì tố…), Slot game(cao bồi, cá tiên, vua sư tử, đào vàng…) và nhiều hơn nữa, hitclub mang đến cho người chơi vô vàn trải nghiệm thú vị mà không hề nhàm chán -
cialis no prescription arizona cialis online mastecard too much cialis
-
vapetogel
-
labatoto
-
stromectol 12mg online. Students should learn about the importance of medication reconciliation in preventing errors during care transitions, emphasizing continuity of care.
-
B52 Club là một nền tảng chơi game trực tuyến thú vị đã thu hút hàng nghìn người chơi với đồ họa tuyệt đẹp và lối chơi hấp dẫn. Trong bài viết này, chúng tôi sẽ cung cấp cái nhìn tổng quan ngắn gọn về Câu lạc bộ B52, nêu bật những điểm mạnh, tùy chọn chơi trò chơi đa dạng và các tính năng bảo mật mạnh mẽ.
Câu lạc bộ B52 - Nơi Vui Gặp Thưởng
B52 Club mang đến sự kết hợp thú vị giữa các trò chơi bài, trò chơi nhỏ và máy đánh bạc, tạo ra trải nghiệm chơi game năng động cho người chơi. Dưới đây là cái nhìn sâu hơn về điều khiến B52 Club trở nên đặc biệt.
Giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn
B52 Club nổi bật với quy trình thanh toán nhanh chóng và thân thiện với người dùng. Với nhiều phương thức thanh toán khác nhau có sẵn, người chơi có thể dễ dàng gửi và rút tiền trong vòng vài phút, đảm bảo trải nghiệm chơi game liền mạch.
Một loạt các trò chơi
Câu lạc bộ B52 có bộ sưu tập trò chơi phổ biến phong phú, bao gồm Tài Xỉu (Xỉu), Poker, trò chơi jackpot độc quyền, tùy chọn sòng bạc trực tiếp và trò chơi bài cổ điển. Người chơi có thể tận hưởng lối chơi thú vị với cơ hội thắng lớn.
Bảo mật nâng cao
An toàn của người chơi và bảo mật dữ liệu là ưu tiên hàng đầu tại B52 Club. Nền tảng này sử dụng các biện pháp bảo mật tiên tiến, bao gồm xác thực hai yếu tố, để bảo vệ thông tin và giao dịch của người chơi.
Phần kết luận
Câu lạc bộ B52 là điểm đến lý tưởng của bạn để chơi trò chơi trực tuyến, cung cấp nhiều trò chơi đa dạng và phần thưởng hậu hĩnh. Với các giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn, cộng với cam kết mạnh mẽ về sự an toàn của người chơi, nó tiếp tục thu hút lượng người chơi tận tâm. Cho dù bạn là người đam mê trò chơi bài hay người hâm mộ giải đặc biệt, B52 Club đều có thứ gì đó dành cho tất cả mọi người. Hãy tham gia ngay hôm nay và trải nghiệm cảm giác thú vị khi chơi game trực tuyến một cách tốt nhất. -
b52 đổi thưởng
B52 Club là một nền tảng chơi game trực tuyến thú vị đã thu hút hàng nghìn người chơi với đồ họa tuyệt đẹp và lối chơi hấp dẫn. Trong bài viết này, chúng tôi sẽ cung cấp cái nhìn tổng quan ngắn gọn về Câu lạc bộ B52, nêu bật những điểm mạnh, tùy chọn chơi trò chơi đa dạng và các tính năng bảo mật mạnh mẽ.
Câu lạc bộ B52 - Nơi Vui Gặp Thưởng
B52 Club mang đến sự kết hợp thú vị giữa các trò chơi bài, trò chơi nhỏ và máy đánh bạc, tạo ra trải nghiệm chơi game năng động cho người chơi. Dưới đây là cái nhìn sâu hơn về điều khiến B52 Club trở nên đặc biệt.
Giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn
B52 Club nổi bật với quy trình thanh toán nhanh chóng và thân thiện với người dùng. Với nhiều phương thức thanh toán khác nhau có sẵn, người chơi có thể dễ dàng gửi và rút tiền trong vòng vài phút, đảm bảo trải nghiệm chơi game liền mạch.
Một loạt các trò chơi
Câu lạc bộ B52 có bộ sưu tập trò chơi phổ biến phong phú, bao gồm Tài Xỉu (Xỉu), Poker, trò chơi jackpot độc quyền, tùy chọn sòng bạc trực tiếp và trò chơi bài cổ điển. Người chơi có thể tận hưởng lối chơi thú vị với cơ hội thắng lớn.
Bảo mật nâng cao
An toàn của người chơi và bảo mật dữ liệu là ưu tiên hàng đầu tại B52 Club. Nền tảng này sử dụng các biện pháp bảo mật tiên tiến, bao gồm xác thực hai yếu tố, để bảo vệ thông tin và giao dịch của người chơi.
Phần kết luận
Câu lạc bộ B52 là điểm đến lý tưởng của bạn để chơi trò chơi trực tuyến, cung cấp nhiều trò chơi đa dạng và phần thưởng hậu hĩnh. Với các giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn, cộng với cam kết mạnh mẽ về sự an toàn của người chơi, nó tiếp tục thu hút lượng người chơi tận tâm. Cho dù bạn là người đam mê trò chơi bài hay người hâm mộ giải đặc biệt, B52 Club đều có thứ gì đó dành cho tất cả mọi người. Hãy tham gia ngay hôm nay và trải nghiệm cảm giác thú vị khi chơi game trực tuyến một cách tốt nhất. -
B52 Club là một nền tảng chơi game trực tuyến thú vị đã thu hút hàng nghìn người chơi với đồ họa tuyệt đẹp và lối chơi hấp dẫn. Trong bài viết này, chúng tôi sẽ cung cấp cái nhìn tổng quan ngắn gọn về Câu lạc bộ B52, nêu bật những điểm mạnh, tùy chọn chơi trò chơi đa dạng và các tính năng bảo mật mạnh mẽ.
Câu lạc bộ B52 - Nơi Vui Gặp Thưởng
B52 Club mang đến sự kết hợp thú vị giữa các trò chơi bài, trò chơi nhỏ và máy đánh bạc, tạo ra trải nghiệm chơi game năng động cho người chơi. Dưới đây là cái nhìn sâu hơn về điều khiến B52 Club trở nên đặc biệt.
Giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn
B52 Club nổi bật với quy trình thanh toán nhanh chóng và thân thiện với người dùng. Với nhiều phương thức thanh toán khác nhau có sẵn, người chơi có thể dễ dàng gửi và rút tiền trong vòng vài phút, đảm bảo trải nghiệm chơi game liền mạch.
Một loạt các trò chơi
Câu lạc bộ B52 có bộ sưu tập trò chơi phổ biến phong phú, bao gồm Tài Xỉu (Xỉu), Poker, trò chơi jackpot độc quyền, tùy chọn sòng bạc trực tiếp và trò chơi bài cổ điển. Người chơi có thể tận hưởng lối chơi thú vị với cơ hội thắng lớn.
Bảo mật nâng cao
An toàn của người chơi và bảo mật dữ liệu là ưu tiên hàng đầu tại B52 Club. Nền tảng này sử dụng các biện pháp bảo mật tiên tiến, bao gồm xác thực hai yếu tố, để bảo vệ thông tin và giao dịch của người chơi.
Phần kết luận
Câu lạc bộ B52 là điểm đến lý tưởng của bạn để chơi trò chơi trực tuyến, cung cấp nhiều trò chơi đa dạng và phần thưởng hậu hĩnh. Với các giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn, cộng với cam kết mạnh mẽ về sự an toàn của người chơi, nó tiếp tục thu hút lượng người chơi tận tâm. Cho dù bạn là người đam mê trò chơi bài hay người hâm mộ giải đặc biệt, B52 Club đều có thứ gì đó dành cho tất cả mọi người. Hãy tham gia ngay hôm nay và trải nghiệm cảm giác thú vị khi chơi game trực tuyến một cách tốt nhất. -
B52 Club là một nền tảng chơi game trực tuyến thú vị đã thu hút hàng nghìn người chơi với đồ họa tuyệt đẹp và lối chơi hấp dẫn. Trong bài viết này, chúng tôi sẽ cung cấp cái nhìn tổng quan ngắn gọn về Câu lạc bộ B52, nêu bật những điểm mạnh, tùy chọn chơi trò chơi đa dạng và các tính năng bảo mật mạnh mẽ.
Câu lạc bộ B52 - Nơi Vui Gặp Thưởng
B52 Club mang đến sự kết hợp thú vị giữa các trò chơi bài, trò chơi nhỏ và máy đánh bạc, tạo ra trải nghiệm chơi game năng động cho người chơi. Dưới đây là cái nhìn sâu hơn về điều khiến B52 Club trở nên đặc biệt.
Giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn
B52 Club nổi bật với quy trình thanh toán nhanh chóng và thân thiện với người dùng. Với nhiều phương thức thanh toán khác nhau có sẵn, người chơi có thể dễ dàng gửi và rút tiền trong vòng vài phút, đảm bảo trải nghiệm chơi game liền mạch.
Một loạt các trò chơi
Câu lạc bộ B52 có bộ sưu tập trò chơi phổ biến phong phú, bao gồm Tài Xỉu (Xỉu), Poker, trò chơi jackpot độc quyền, tùy chọn sòng bạc trực tiếp và trò chơi bài cổ điển. Người chơi có thể tận hưởng lối chơi thú vị với cơ hội thắng lớn.
Bảo mật nâng cao
An toàn của người chơi và bảo mật dữ liệu là ưu tiên hàng đầu tại B52 Club. Nền tảng này sử dụng các biện pháp bảo mật tiên tiến, bao gồm xác thực hai yếu tố, để bảo vệ thông tin và giao dịch của người chơi.
Phần kết luận
Câu lạc bộ B52 là điểm đến lý tưởng của bạn để chơi trò chơi trực tuyến, cung cấp nhiều trò chơi đa dạng và phần thưởng hậu hĩnh. Với các giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn, cộng với cam kết mạnh mẽ về sự an toàn của người chơi, nó tiếp tục thu hút lượng người chơi tận tâm. Cho dù bạn là người đam mê trò chơi bài hay người hâm mộ giải đặc biệt, B52 Club đều có thứ gì đó dành cho tất cả mọi người. Hãy tham gia ngay hôm nay và trải nghiệm cảm giác thú vị khi chơi game trực tuyến một cách tốt nhất. -
B52 Club là một nền tảng chơi game trực tuyến thú vị đã thu hút hàng nghìn người chơi với đồ họa tuyệt đẹp và lối chơi hấp dẫn. Trong bài viết này, chúng tôi sẽ cung cấp cái nhìn tổng quan ngắn gọn về Câu lạc bộ B52, nêu bật những điểm mạnh, tùy chọn chơi trò chơi đa dạng và các tính năng bảo mật mạnh mẽ.
Câu lạc bộ B52 - Nơi Vui Gặp Thưởng
B52 Club mang đến sự kết hợp thú vị giữa các trò chơi bài, trò chơi nhỏ và máy đánh bạc, tạo ra trải nghiệm chơi game năng động cho người chơi. Dưới đây là cái nhìn sâu hơn về điều khiến B52 Club trở nên đặc biệt.
Giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn
B52 Club nổi bật với quy trình thanh toán nhanh chóng và thân thiện với người dùng. Với nhiều phương thức thanh toán khác nhau có sẵn, người chơi có thể dễ dàng gửi và rút tiền trong vòng vài phút, đảm bảo trải nghiệm chơi game liền mạch.
Một loạt các trò chơi
Câu lạc bộ B52 có bộ sưu tập trò chơi phổ biến phong phú, bao gồm Tài Xỉu (Xỉu), Poker, trò chơi jackpot độc quyền, tùy chọn sòng bạc trực tiếp và trò chơi bài cổ điển. Người chơi có thể tận hưởng lối chơi thú vị với cơ hội thắng lớn.
Bảo mật nâng cao
An toàn của người chơi và bảo mật dữ liệu là ưu tiên hàng đầu tại B52 Club. Nền tảng này sử dụng các biện pháp bảo mật tiên tiến, bao gồm xác thực hai yếu tố, để bảo vệ thông tin và giao dịch của người chơi.
Phần kết luận
Câu lạc bộ B52 là điểm đến lý tưởng của bạn để chơi trò chơi trực tuyến, cung cấp nhiều trò chơi đa dạng và phần thưởng hậu hĩnh. Với các giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn, cộng với cam kết mạnh mẽ về sự an toàn của người chơi, nó tiếp tục thu hút lượng người chơi tận tâm. Cho dù bạn là người đam mê trò chơi bài hay người hâm mộ giải đặc biệt, B52 Club đều có thứ gì đó dành cho tất cả mọi người. Hãy tham gia ngay hôm nay và trải nghiệm cảm giác thú vị khi chơi game trực tuyến một cách tốt nhất. -
b52 game
B52 Club là một nền tảng chơi game trực tuyến thú vị đã thu hút hàng nghìn người chơi với đồ họa tuyệt đẹp và lối chơi hấp dẫn. Trong bài viết này, chúng tôi sẽ cung cấp cái nhìn tổng quan ngắn gọn về Câu lạc bộ B52, nêu bật những điểm mạnh, tùy chọn chơi trò chơi đa dạng và các tính năng bảo mật mạnh mẽ.
Câu lạc bộ B52 - Nơi Vui Gặp Thưởng
B52 Club mang đến sự kết hợp thú vị giữa các trò chơi bài, trò chơi nhỏ và máy đánh bạc, tạo ra trải nghiệm chơi game năng động cho người chơi. Dưới đây là cái nhìn sâu hơn về điều khiến B52 Club trở nên đặc biệt.
Giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn
B52 Club nổi bật với quy trình thanh toán nhanh chóng và thân thiện với người dùng. Với nhiều phương thức thanh toán khác nhau có sẵn, người chơi có thể dễ dàng gửi và rút tiền trong vòng vài phút, đảm bảo trải nghiệm chơi game liền mạch.
Một loạt các trò chơi
Câu lạc bộ B52 có bộ sưu tập trò chơi phổ biến phong phú, bao gồm Tài Xỉu (Xỉu), Poker, trò chơi jackpot độc quyền, tùy chọn sòng bạc trực tiếp và trò chơi bài cổ điển. Người chơi có thể tận hưởng lối chơi thú vị với cơ hội thắng lớn.
Bảo mật nâng cao
An toàn của người chơi và bảo mật dữ liệu là ưu tiên hàng đầu tại B52 Club. Nền tảng này sử dụng các biện pháp bảo mật tiên tiến, bao gồm xác thực hai yếu tố, để bảo vệ thông tin và giao dịch của người chơi.
Phần kết luận
Câu lạc bộ B52 là điểm đến lý tưởng của bạn để chơi trò chơi trực tuyến, cung cấp nhiều trò chơi đa dạng và phần thưởng hậu hĩnh. Với các giao dịch nhanh chóng và an toàn, cộng với cam kết mạnh mẽ về sự an toàn của người chơi, nó tiếp tục thu hút lượng người chơi tận tâm. Cho dù bạn là người đam mê trò chơi bài hay người hâm mộ giải đặc biệt, B52 Club đều có thứ gì đó dành cho tất cả mọi người. Hãy tham gia ngay hôm nay và trải nghiệm cảm giác thú vị khi chơi game trực tuyến một cách tốt nhất. -
what is Azithromycin prescribed for. Healthcare providers should educate patients about potential risks associated with medication duplication.
-
娛樂城優惠
娛樂城優惠 -
百家樂是賭場中最古老且最受歡迎的博奕遊戲,無論是實體還是線上娛樂城都有其踪影。其簡單的規則和公平的遊戲機制吸引了大量玩家。不只如此,線上百家樂近年來更是受到玩家的喜愛,其優勢甚至超越了知名的實體賭場如澳門和拉斯維加斯。
百家樂入門介紹
百家樂(baccarat)是一款起源於義大利的撲克牌遊戲,其名稱在英文中是「零」的意思。從十五世紀開始在法國流行,到了十九世紀,這款遊戲在英國和法國都非常受歡迎。現今百家樂已成為全球各大賭場和娛樂城中的熱門遊戲。(來源: wiki百家樂 )
百家樂主要是玩家押注莊家或閒家勝出的遊戲。參與的人數沒有限制,不只坐在賭桌的玩家,旁邊站立的人也可以下注。 -
娛樂城
探尋娛樂城的多元魅力
娛樂城近年來成為了眾多遊戲愛好者的熱門去處。在這裡,人們可以體驗到豐富多彩的遊戲並有機會贏得豐厚的獎金,正是這種刺激與樂趣使得娛樂城在全球範圍內越來越受歡迎。
娛樂城的多元遊戲
娛樂城通常提供一系列的娛樂選項,從經典的賭博遊戲如老虎機、百家樂、撲克,到最新的電子遊戲、體育賭博和電競項目,應有盡有,讓每位遊客都能找到自己的最愛。
娛樂城的優惠活動
娛樂城常會提供各種吸引人的優惠活動,例如新玩家註冊獎勵、首存贈送、以及VIP會員專享的多項福利,吸引了大量玩家前來參與。這些優惠不僅讓玩家獲得更多遊戲時間,還提高了他們贏得大獎的機會。
娛樂城的便利性
許多娛樂城都提供在線遊戲平台,玩家不必離開舒適的家就能享受到各種遊戲的樂趣。高品質的視頻直播和專業的遊戲平台讓玩家仿佛置身於真實的賭場之中,體驗到了無與倫比的遊戲感受。
娛樂城的社交體驗
娛樂城不僅僅是遊戲的天堂,更是社交的舞台。玩家可以在此結交來自世界各地的朋友,一邊享受遊戲的樂趣,一邊進行輕鬆愉快的交流。而且,許多娛樂城還會定期舉辦各種社交活動和比賽,進一步加深玩家之間的聯繫和友誼。
娛樂城的創新發展
隨著科技的快速發展,娛樂城也在不斷進行創新。虛擬現實(VR)、區塊鏈技術等新科技的應用,使得娛樂城提供了更多先進、多元和個性化的遊戲體驗。例如,通過VR技術,玩家可以更加真實地感受到賭場的氛圍和環境,得到更加沉浸和刺激的遊戲體驗。 -
娛樂城優惠
2023年最熱門娛樂城優惠大全
尋找高品質的娛樂城優惠嗎?2023年富遊娛樂城帶來了一系列吸引人的優惠活動!無論您是新玩家還是老玩家,這裡都有豐富的優惠等您來領取。
富遊娛樂城新玩家優惠
體驗金$168元: 新玩家註冊即可享受,向客服申請即可領取。
首存送禮: 首次儲值$1000元,即可獲得額外的$1000元。
好禮5選1: 新會員一個月內存款累積金額達5000點,可選擇心儀的禮品一份。
老玩家專屬優惠
每日簽到: 每天簽到即可獲得$666元彩金。
推薦好友: 推薦好友成功註冊且首儲後,您可獲得$688元禮金。
天天返水: 每天都有返水優惠,最高可達0.7%。
如何申請與領取?
新玩家優惠: 註冊帳戶後聯繫客服,完成相應要求即可領取。
老玩家優惠: 只需完成每日簽到,或者通過推薦好友獲得禮金。
VIP會員: 滿足升級要求的會員將享有更多專屬福利與特權。
富遊娛樂城VIP會員
VIP會員可享受更多特權,包括升級禮金、每週限時紅包、生日禮金,以及更高比例的返水。成為VIP會員,讓您在娛樂的世界中享受更多的尊貴與便利! -
百家樂是賭場中最古老且最受歡迎的博奕遊戲,無論是實體還是線上娛樂城都有其踪影。其簡單的規則和公平的遊戲機制吸引了大量玩家。不只如此,線上百家樂近年來更是受到玩家的喜愛,其優勢甚至超越了知名的實體賭場如澳門和拉斯維加斯。
百家樂入門介紹
百家樂(baccarat)是一款起源於義大利的撲克牌遊戲,其名稱在英文中是「零」的意思。從十五世紀開始在法國流行,到了十九世紀,這款遊戲在英國和法國都非常受歡迎。現今百家樂已成為全球各大賭場和娛樂城中的熱門遊戲。(來源: wiki百家樂 )
百家樂主要是玩家押注莊家或閒家勝出的遊戲。參與的人數沒有限制,不只坐在賭桌的玩家,旁邊站立的人也可以下注。 -
探尋娛樂城的多元魅力
娛樂城近年來成為了眾多遊戲愛好者的熱門去處。在這裡,人們可以體驗到豐富多彩的遊戲並有機會贏得豐厚的獎金,正是這種刺激與樂趣使得娛樂城在全球範圍內越來越受歡迎。
娛樂城的多元遊戲
娛樂城通常提供一系列的娛樂選項,從經典的賭博遊戲如老虎機、百家樂、撲克,到最新的電子遊戲、體育賭博和電競項目,應有盡有,讓每位遊客都能找到自己的最愛。
娛樂城的優惠活動
娛樂城常會提供各種吸引人的優惠活動,例如新玩家註冊獎勵、首存贈送、以及VIP會員專享的多項福利,吸引了大量玩家前來參與。這些優惠不僅讓玩家獲得更多遊戲時間,還提高了他們贏得大獎的機會。
娛樂城的便利性
許多娛樂城都提供在線遊戲平台,玩家不必離開舒適的家就能享受到各種遊戲的樂趣。高品質的視頻直播和專業的遊戲平台讓玩家仿佛置身於真實的賭場之中,體驗到了無與倫比的遊戲感受。
娛樂城的社交體驗
娛樂城不僅僅是遊戲的天堂,更是社交的舞台。玩家可以在此結交來自世界各地的朋友,一邊享受遊戲的樂趣,一邊進行輕鬆愉快的交流。而且,許多娛樂城還會定期舉辦各種社交活動和比賽,進一步加深玩家之間的聯繫和友誼。
娛樂城的創新發展
隨著科技的快速發展,娛樂城也在不斷進行創新。虛擬現實(VR)、區塊鏈技術等新科技的應用,使得娛樂城提供了更多先進、多元和個性化的遊戲體驗。例如,通過VR技術,玩家可以更加真實地感受到賭場的氛圍和環境,得到更加沉浸和刺激的遊戲體驗。 -
百家樂是賭場中最古老且最受歡迎的博奕遊戲,無論是實體還是線上娛樂城都有其踪影。其簡單的規則和公平的遊戲機制吸引了大量玩家。不只如此,線上百家樂近年來更是受到玩家的喜愛,其優勢甚至超越了知名的實體賭場如澳門和拉斯維加斯。
百家樂入門介紹
百家樂(baccarat)是一款起源於義大利的撲克牌遊戲,其名稱在英文中是「零」的意思。從十五世紀開始在法國流行,到了十九世紀,這款遊戲在英國和法國都非常受歡迎。現今百家樂已成為全球各大賭場和娛樂城中的熱門遊戲。(來源: wiki百家樂 )
百家樂主要是玩家押注莊家或閒家勝出的遊戲。參與的人數沒有限制,不只坐在賭桌的玩家,旁邊站立的人也可以下注。 -
探尋娛樂城的多元魅力
娛樂城近年來成為了眾多遊戲愛好者的熱門去處。在這裡,人們可以體驗到豐富多彩的遊戲並有機會贏得豐厚的獎金,正是這種刺激與樂趣使得娛樂城在全球範圍內越來越受歡迎。
娛樂城的多元遊戲
娛樂城通常提供一系列的娛樂選項,從經典的賭博遊戲如老虎機、百家樂、撲克,到最新的電子遊戲、體育賭博和電競項目,應有盡有,讓每位遊客都能找到自己的最愛。
娛樂城的優惠活動
娛樂城常會提供各種吸引人的優惠活動,例如新玩家註冊獎勵、首存贈送、以及VIP會員專享的多項福利,吸引了大量玩家前來參與。這些優惠不僅讓玩家獲得更多遊戲時間,還提高了他們贏得大獎的機會。
娛樂城的便利性
許多娛樂城都提供在線遊戲平台,玩家不必離開舒適的家就能享受到各種遊戲的樂趣。高品質的視頻直播和專業的遊戲平台讓玩家仿佛置身於真實的賭場之中,體驗到了無與倫比的遊戲感受。
娛樂城的社交體驗
娛樂城不僅僅是遊戲的天堂,更是社交的舞台。玩家可以在此結交來自世界各地的朋友,一邊享受遊戲的樂趣,一邊進行輕鬆愉快的交流。而且,許多娛樂城還會定期舉辦各種社交活動和比賽,進一步加深玩家之間的聯繫和友誼。
娛樂城的創新發展
隨著科技的快速發展,娛樂城也在不斷進行創新。虛擬現實(VR)、區塊鏈技術等新科技的應用,使得娛樂城提供了更多先進、多元和個性化的遊戲體驗。例如,通過VR技術,玩家可以更加真實地感受到賭場的氛圍和環境,得到更加沉浸和刺激的遊戲體驗。 -
百家樂是賭場中最古老且最受歡迎的博奕遊戲,無論是實體還是線上娛樂城都有其踪影。其簡單的規則和公平的遊戲機制吸引了大量玩家。不只如此,線上百家樂近年來更是受到玩家的喜愛,其優勢甚至超越了知名的實體賭場如澳門和拉斯維加斯。
百家樂入門介紹
百家樂(baccarat)是一款起源於義大利的撲克牌遊戲,其名稱在英文中是「零」的意思。從十五世紀開始在法國流行,到了十九世紀,這款遊戲在英國和法國都非常受歡迎。現今百家樂已成為全球各大賭場和娛樂城中的熱門遊戲。(來源: wiki百家樂 )
百家樂主要是玩家押注莊家或閒家勝出的遊戲。參與的人數沒有限制,不只坐在賭桌的玩家,旁邊站立的人也可以下注。 -
探尋娛樂城的多元魅力
娛樂城近年來成為了眾多遊戲愛好者的熱門去處。在這裡,人們可以體驗到豐富多彩的遊戲並有機會贏得豐厚的獎金,正是這種刺激與樂趣使得娛樂城在全球範圍內越來越受歡迎。
娛樂城的多元遊戲
娛樂城通常提供一系列的娛樂選項,從經典的賭博遊戲如老虎機、百家樂、撲克,到最新的電子遊戲、體育賭博和電競項目,應有盡有,讓每位遊客都能找到自己的最愛。
娛樂城的優惠活動
娛樂城常會提供各種吸引人的優惠活動,例如新玩家註冊獎勵、首存贈送、以及VIP會員專享的多項福利,吸引了大量玩家前來參與。這些優惠不僅讓玩家獲得更多遊戲時間,還提高了他們贏得大獎的機會。
娛樂城的便利性
許多娛樂城都提供在線遊戲平台,玩家不必離開舒適的家就能享受到各種遊戲的樂趣。高品質的視頻直播和專業的遊戲平台讓玩家仿佛置身於真實的賭場之中,體驗到了無與倫比的遊戲感受。
娛樂城的社交體驗
娛樂城不僅僅是遊戲的天堂,更是社交的舞台。玩家可以在此結交來自世界各地的朋友,一邊享受遊戲的樂趣,一邊進行輕鬆愉快的交流。而且,許多娛樂城還會定期舉辦各種社交活動和比賽,進一步加深玩家之間的聯繫和友誼。
娛樂城的創新發展
隨著科技的快速發展,娛樂城也在不斷進行創新。虛擬現實(VR)、區塊鏈技術等新科技的應用,使得娛樂城提供了更多先進、多元和個性化的遊戲體驗。例如,通過VR技術,玩家可以更加真實地感受到賭場的氛圍和環境,得到更加沉浸和刺激的遊戲體驗。 -
娛樂城
探尋娛樂城的多元魅力
娛樂城近年來成為了眾多遊戲愛好者的熱門去處。在這裡,人們可以體驗到豐富多彩的遊戲並有機會贏得豐厚的獎金,正是這種刺激與樂趣使得娛樂城在全球範圍內越來越受歡迎。
娛樂城的多元遊戲
娛樂城通常提供一系列的娛樂選項,從經典的賭博遊戲如老虎機、百家樂、撲克,到最新的電子遊戲、體育賭博和電競項目,應有盡有,讓每位遊客都能找到自己的最愛。
娛樂城的優惠活動
娛樂城常會提供各種吸引人的優惠活動,例如新玩家註冊獎勵、首存贈送、以及VIP會員專享的多項福利,吸引了大量玩家前來參與。這些優惠不僅讓玩家獲得更多遊戲時間,還提高了他們贏得大獎的機會。
娛樂城的便利性
許多娛樂城都提供在線遊戲平台,玩家不必離開舒適的家就能享受到各種遊戲的樂趣。高品質的視頻直播和專業的遊戲平台讓玩家仿佛置身於真實的賭場之中,體驗到了無與倫比的遊戲感受。
娛樂城的社交體驗
娛樂城不僅僅是遊戲的天堂,更是社交的舞台。玩家可以在此結交來自世界各地的朋友,一邊享受遊戲的樂趣,一邊進行輕鬆愉快的交流。而且,許多娛樂城還會定期舉辦各種社交活動和比賽,進一步加深玩家之間的聯繫和友誼。
娛樂城的創新發展
隨著科技的快速發展,娛樂城也在不斷進行創新。虛擬現實(VR)、區塊鏈技術等新科技的應用,使得娛樂城提供了更多先進、多元和個性化的遊戲體驗。例如,通過VR技術,玩家可以更加真實地感受到賭場的氛圍和環境,得到更加沉浸和刺激的遊戲體驗。 -
百家樂
百家樂是賭場中最古老且最受歡迎的博奕遊戲,無論是實體還是線上娛樂城都有其踪影。其簡單的規則和公平的遊戲機制吸引了大量玩家。不只如此,線上百家樂近年來更是受到玩家的喜愛,其優勢甚至超越了知名的實體賭場如澳門和拉斯維加斯。
百家樂入門介紹
百家樂(baccarat)是一款起源於義大利的撲克牌遊戲,其名稱在英文中是「零」的意思。從十五世紀開始在法國流行,到了十九世紀,這款遊戲在英國和法國都非常受歡迎。現今百家樂已成為全球各大賭場和娛樂城中的熱門遊戲。(來源: wiki百家樂 )
百家樂主要是玩家押注莊家或閒家勝出的遊戲。參與的人數沒有限制,不只坐在賭桌的玩家,旁邊站立的人也可以下注。 -
百家樂
百家樂是賭場中最古老且最受歡迎的博奕遊戲,無論是實體還是線上娛樂城都有其踪影。其簡單的規則和公平的遊戲機制吸引了大量玩家。不只如此,線上百家樂近年來更是受到玩家的喜愛,其優勢甚至超越了知名的實體賭場如澳門和拉斯維加斯。
百家樂入門介紹
百家樂(baccarat)是一款起源於義大利的撲克牌遊戲,其名稱在英文中是「零」的意思。從十五世紀開始在法國流行,到了十九世紀,這款遊戲在英國和法國都非常受歡迎。現今百家樂已成為全球各大賭場和娛樂城中的熱門遊戲。(來源: wiki百家樂 )
百家樂主要是玩家押注莊家或閒家勝出的遊戲。參與的人數沒有限制,不只坐在賭桌的玩家,旁邊站立的人也可以下注。 -
娛樂城
探尋娛樂城的多元魅力
娛樂城近年來成為了眾多遊戲愛好者的熱門去處。在這裡,人們可以體驗到豐富多彩的遊戲並有機會贏得豐厚的獎金,正是這種刺激與樂趣使得娛樂城在全球範圍內越來越受歡迎。
娛樂城的多元遊戲
娛樂城通常提供一系列的娛樂選項,從經典的賭博遊戲如老虎機、百家樂、撲克,到最新的電子遊戲、體育賭博和電競項目,應有盡有,讓每位遊客都能找到自己的最愛。
娛樂城的優惠活動
娛樂城常會提供各種吸引人的優惠活動,例如新玩家註冊獎勵、首存贈送、以及VIP會員專享的多項福利,吸引了大量玩家前來參與。這些優惠不僅讓玩家獲得更多遊戲時間,還提高了他們贏得大獎的機會。
娛樂城的便利性
許多娛樂城都提供在線遊戲平台,玩家不必離開舒適的家就能享受到各種遊戲的樂趣。高品質的視頻直播和專業的遊戲平台讓玩家仿佛置身於真實的賭場之中,體驗到了無與倫比的遊戲感受。
娛樂城的社交體驗
娛樂城不僅僅是遊戲的天堂,更是社交的舞台。玩家可以在此結交來自世界各地的朋友,一邊享受遊戲的樂趣,一邊進行輕鬆愉快的交流。而且,許多娛樂城還會定期舉辦各種社交活動和比賽,進一步加深玩家之間的聯繫和友誼。
娛樂城的創新發展
隨著科技的快速發展,娛樂城也在不斷進行創新。虛擬現實(VR)、區塊鏈技術等新科技的應用,使得娛樂城提供了更多先進、多元和個性化的遊戲體驗。例如,通過VR技術,玩家可以更加真實地感受到賭場的氛圍和環境,得到更加沉浸和刺激的遊戲體驗。 -
link alternatif kdslots
KDslots merupakan Agen casino online dan slots game terkenal di Asia. Mainkan game slots dan live casino raih kemenangan di game live casino dan slots game indonesia -
KDslots merupakan Agen casino online dan slots game terkenal di Asia. Mainkan game slots dan live casino raih kemenangan di game live casino dan slots game indonesia
-
The medication's legacy in global health underscores the transformative impact that medical innovation can have on improving public health outcomes. stromectol 12mg online pharmacy
-
atengtogel
atengtogel -
dollar4d
dollar4d -
ling138
ling138 -
Экспресс-строения здания: коммерческая выгода в каждом кирпиче!
В сегодняшнем обществе, где время равно деньгам, строения быстрого монтажа стали истинным спасением для компаний. Эти новейшие строения комбинируют в себе повышенную прочность, финансовую эффективность и быстрый монтаж, что делает их наилучшим вариантом для коммерческих мероприятий.
[url=https://bystrovozvodimye-zdanija-moskva.ru/]Быстровозводимые здания[/url]
1. Срочное строительство: Секунды - определяющие финансовые ресурсы в бизнесе, и скоро возводимые строения обеспечивают значительное снижение времени строительства. Это особенно выгодно в моменты, когда необходимо оперативно начать предпринимательскую деятельность и получать доход.
2. Бюджетность: За счет оптимизации производства и установки элементов на месте, расходы на скоростройки часто остается меньше, чем у традиционных строительных проектов. Это позволяет получить большую финансовую выгоду и получить лучшую инвестиционную отдачу.
Подробнее на [url=https://xn--73-6kchjy.xn--p1ai/]http://www.scholding.ru/[/url]
В заключение, моментальные сооружения - это великолепное решение для бизнес-проектов. Они комбинируют в себе быстроту возведения, эффективное использование ресурсов и долговечность, что дает им возможность первоклассным вариантом для компаний, активно нацеленных на скорый старт бизнеса и обеспечивать доход. Не упустите шанс экономии времени и денег, превосходные экспресс-конструкции для вашего следующего проекта! -
TARGET88: The Best Slot Deposit Pulsa Gambling Site in Indonesia
TARGET88 stands as the top slot deposit pulsa gambling site in 2020 in Indonesia, offering a wide array of slot machine gambling options. Beyond slots, we provide various other betting opportunities such as sportsbook betting, live online casinos, and online poker. With just one ID, you can enjoy all the available gambling options.
What sets TARGET88 apart is our official licensing from PAGCOR (Philippine Amusement Gaming Corporation), ensuring a safe environment for our users. Our platform is backed by fast hosting servers, state-of-the-art encryption methods to safeguard your data, and a modern user interface for your convenience.
But what truly makes TARGET88 special is our practical deposit method. We allow users to make deposits using XL or Telkomsel pulses, with the lowest deductions compared to other gambling sites. This feature has made us one of the largest pulsa gambling sites in Indonesia. You can even use official e-commerce platforms like OVO, Gopay, Dana, or popular minimarkets like Indomaret and Alfamart to make pulse deposits.
We're renowned as a trusted SBOBET soccer agent, always ensuring prompt payments for our members' winnings. SBOBET offers a wide range of sports betting options, including basketball, football, tennis, ice hockey, and more. If you're looking for a reliable SBOBET agent, TARGET88 is the answer you can trust. Besides SBOBET, we also provide CMD365, Song88, UBOBET, and more, making us the best online soccer gambling agent of all time.
Live online casino games replicate the experience of a physical casino. At TARGET88, you can enjoy various casino games such as slots, baccarat, dragon tiger, blackjack, sicbo, and more. Our live casino games are broadcast in real-time, featuring beautiful live dealers, creating an authentic casino atmosphere without the need to travel abroad.
Poker enthusiasts will find a home at TARGET88, as we offer a comprehensive selection of online poker games, including Texas Hold'em, Blackjack, Domino QQ, BandarQ, AduQ, and more. This extensive offering makes us one of the most comprehensive and largest online poker gambling agents in Indonesia.
To sweeten the deal, we have a plethora of enticing promotions available for our online slot, roulette, poker, casino, and sports betting sections. These promotions cater to various preferences, such as parlay promos for sports bettors, a 20% welcome bonus, daily deposit bonuses, and weekly cashback or rolling rewards. You can explore these promotions to enhance your gaming experience.
Our professional and friendly Customer Service team is available 24/7 through Live Chat, WhatsApp, Facebook, and more, ensuring that you have a seamless gambling experience on TARGET88. -
Быстро возводимые здания: коммерческий результат в каждой детали!
В нынешней эпохе, где часы - финансовые ресурсы, объекты быстрого возвода стали истинным спасением для коммерческой деятельности. Эти новейшие строения объединяют в себе высокую надежность, финансовую эффективность и скорость монтажа, что сделало их лучшим выбором для различных коммерческих проектов.
[url=https://bystrovozvodimye-zdanija-moskva.ru/]Строительство легковозводимых зданий[/url]
1. Быстрое возведение: Секунды - определяющие финансовые ресурсы в экономике, и экспресс-сооружения обеспечивают существенное уменьшение сроков стройки. Это значительно ценится в ситуациях, когда необходимо оперативно начать предпринимательскую деятельность и начать монетизацию.
2. Экономичность: За счет улучшения производственных процедур элементов и сборки на объекте, цена скоростроительных зданий часто бывает менее, по отношению к обычным строительным проектам. Это предоставляет шанс сократить издержки и достичь большей доходности инвестиций.
Подробнее на [url=https://xn--73-6kchjy.xn--p1ai/]scholding.ru[/url]
В заключение, скоростроительные сооружения - это первоклассное решение для коммерческих проектов. Они обладают быстроту возведения, экономическую эффективность и высокую прочность, что делает их превосходным выбором для предпринимательских начинаний, готовых к мгновенному началу бизнеса и получать прибыль. Не упустите возможность сократить издержки и сэкономить время, превосходные экспресс-конструкции для вашей будущей задачи! -
Political Influence: The Ivermectin debate has occasionally intersected with political agendas, with politicians and policymakers weighing in on its use, leading to further polarization and confusion. ivermectin stromectol.
-
The impact of chronic stress on ED is an area of ongoing research. Chronic stress can contribute to hormonal imbalances, vascular dysfunction, and psychological factors that affect sexual function. viagra with dapoxetine.
-
miya4d
-
ATENGTOGEL
ATENGTOGEL -
https://jobejobs.ru
-
https://jobejobs.ru
-
buy tamiya paint
Enhance Your RC Projects with Tamiya Spray Cans from RC Street Shop
Are you searching for the perfect finishing touch to your RC model projects? Look no further than RC Street Shop, where we offer a fantastic selection of Tamiya spray cans designed to meet the needs of discerning hobby
Why Choose Tamiya Spray Cans?
Tamiya spray cans offer a host of benefits that set them apart from other options on the market. Whether you're building a remote-controlled car, plane, or any other model, Tamiya spray cans are a smart choice.
1. Versatility and Compatibility
Tamiya spray paints are specially formulated to adhere to various surfaces, including plastic and metal. This versatility makes them an excellent choice for all your modeling needs. Whether you're working on a complex RC body or adding custom graphics to your project, Tamiya spray cans ensure that the paint adheres perfectly, resulting in a professional finish.
2. Fine Mist Spray Pattern
Achieving a smooth, even, and consistent finish is crucial in model painting. Tamiya's fine mist spray pattern makes it easy to attain this level of precision, even for those new to the hobby. The fine mist allows for controlled application, reducing the risk of overspray
3. Quick-Drying Formula
Time is of the essence when working on your
The Perfect Shade for Your Project
At RC Street Shop, we understand that every RC model project is unique, and the right shade of paint can make all the difference. That's why we offer a comprehensive collection of Tamiya spray cans in a wide
Get the Best for Your RC Builds
Your remote-controlled models deserve the best, and that's exactly what Tamiya and RC Street Shop deliver. Don't settle for subpar spray cans that could compromise the quality of your RC builds. Trust in Tamiya's long-standing reputation for excellence and discover the top-quality products available at RC Street Shop.
Add the Finishing Touch with Tamiya Spray Cans
The fine mist spray pattern and quick-drying formula of Tamiya spray cans make them an essential tool for any modeler. When precision and efficiency are paramount, these spray cans offer the ideal solution. Plus, with our wide selection of colors and finishes, you can always find the perfect
Elevate your RC projects to new heights with Tamiya spray cans from RC Street Shop. Visit our collection today and give your models the finishing touch they deserve. Don't compromise on quality—choose Tamiya and RC Street Shop for your remote-controlled model needs. -
https://jobejobs.ru
-
https://jobejobs.ru
-
今彩539開獎號碼查詢
今彩539開獎號碼查詢 -
大樂透開獎號碼查詢
大樂透開獎號碼查詢 -
威力彩開獎號碼查詢
-
今彩539開獎號碼查詢
-
大樂透開獎號碼查詢
大樂透開獎號碼查詢 -
威力彩開獎號碼查詢
威力彩開獎號碼查詢 -
三星彩開獎號碼查詢
三星彩開獎號碼查詢 -
raja118
-
運彩分析
-
三星彩開獎號碼查詢
-
運彩分析
-
2024總統大選
-
2024總統大選
2024總統大選 -
bata4d
bata4d -
Blangkon slot adalah situs slot gacor dan judi slot online gacor hari ini mudah menang. Blangkonslot menyediakan semua permainan slot gacor dan judi online terbaik seperti, slot online gacor, live casino, judi bola/sportbook, poker online, togel online, sabung ayam dll. Hanya dengan 1 user id kamu sudah bisa bermain semua permainan yang sudah di sediakan situs terbaik BLANGKON SLOT. Selain itu, kamu juga tidak usah ragu lagi untuk bergabung dengan kami situs judi online terbesar dan terpercaya yang akan membayar berapapun kemenangan kamu.
-
Живя в эпоху цифровых технологий, я всегда осознавал, насколько важно продолжать обучение и развиваться профессионально. Однажды я наткнулся на курс онлайн-обучения по digital marketing, который, как мне казалось, мог открыть передо мной новые горизонты возможностей. Единственное препятствие, с которым я столкнулся, - это стоимость курса. Мне не хватало 18 000 рублей.
Вспомнив о сайте [url=https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/]mikro-zaim-online.ru[/url], я решил попробовать найти решение моей финансовой проблемы там. Сайт порадовал меня удобным интерфейсом и множеством предложений от МФО. Я быстро нашел подходящий вариант с минимальным процентом и отправил заявку.
Процесс одобрения заявки был быстрым, и деньги поступили на мою карту так скоро, что я даже не ожидал такой оперативности. Теперь весь мир знаний и новых умений был открыт для меня.
Курс оказался невероятно полезным. Я погрузился в изучение новых стратегий маркетинга, освоил инструменты аналитики и научился создавать эффективные рекламные кампании. Это инвестиция в мою карьеру окупилась очень быстро, так как новые навыки позволили мне получить повышение на работе.
Весь этот позитивный опыт стал возможным благодаря [url=https://mikro-zaim-online.ru/]mikro-zaim-online.ru[/url]. Этот сайт не только помог мне с финансовой стороны, но и стал ключом к моему профессиональному росту и развитию. Я искренне рекомендую его всем, кто ищет надежный источник микрозаймов для реализации своих амбиций и целей. -
Юрист по экономическим преступлениям advokat-karbanov.ru
Никому не известно, когда может понадобиться помощь адвоката. Поэтому, хотим представить Вам адвокатское бюро Карбанов и партнеры, которое оказывает все разновидности юридических услуг. На сайте advokat-karbanov.ru Вы найдете все обстоятельства, каталог услуг, контактные данные.
Насчет [url=https://advokat-karbanov.ru/advokat-po-arbitrazhnyem-delam/]адвокат по арбитражным спорам[/url] Вы попали по верному адресу. Пётр Карбанов - основной управляющий партнер нашего бюро, известный эксперт на тв и радио. Адвокат, который может решить почти любые юридические вопросы. Также у нас опытная сильная команда, занимающаяся делами любого характера.
Звоните на нашу горячую линию по номеру телефона +7(925)734-30-70 или оформите обратный звонок на сайте advokat-karbanov.ru прямо сейчас. Напишите свой контактный номер и имя и мы Вам перезвоним. Либо можно списаться с нами в известных мессенджерах. Наша команда имеет колоссальный опыт в данном деле, ведь лишь образования не достаточно, основное это опыт в жизни. Ещё на этапе ознакомления с Вашим делом, наши юристы способны понять его перспективы и вероятный финал.
Если Вы искали [url=https://advokat-karbanov.ru/advokat-po-ekonomicheskim-prestupleniyam/]адвокат по экономическим преступлениям[/url] в сети интернет, то прямо сейчас заходите на наш веб ресурс. Там Вы сможете найти полный список наших услуг. Это: представительство в суде, защита прав потребителей, жилищный юрист, трудовые споры, автоюрист, наследственные споры, исполнительное производство, таможенные споры, взыскание долгов и многое другое.
Мы расположены по адресу: 115088, Москва, ул. Угрешская, д.2, стр.1, оф. 403. Работаем поэтапно: для начала нужно оформить заявку или осуществить звонок нам. После мы выбираем дату и время консультации, которая для Вас будет бесплатной. Согласование юридической позиции по вашему вопросу и обсуждение стоимости услуг, оформление договора, приготовление документации и представительство в суде. работаем четко по плану и настраиваемся только на положительный итог по делу. Звоните и мы непременно Вам поможем. -
Потолок натяжной Москва rukimastera.ru
Предлагаем Вашему вниманию компанию, которая концентрируется на установке навесных потолков «Руки мастера» в Москве. Навесные потолки-самая популярная отделка жилья на настоящий момент. Потому что покрытие полностью безопасно для человека, имеет большой срок службы 25 лет, невысокие цены, срочную установку, огроменный выбор цветов, фактур, возможность размещения различных светильников и симпатичный внешний вид. За подробностями переходите на rukimastera.ru уже сейчас.
По запросу [url=https://rukimastera.ru/]сколько стоит натяжной потолок[/url] - мы Вам с удовольствием окажем помощь. Наша компания уже много лет работает в данной сфере, имеет хороший опыт, хорошие отзывы клиентов и выгодные предложения. Обратите внимание, у нас часто проходят выгодные акции для клиентов, где возможно натянуть потолок с прекрасной скидкой.
Натягиваем потолки в любое помещение: ванная, кухня, коридор, балкон, прихожая, туалет и другие. В наличии различные производители потолков, фактура, составы материала и виды потолков. А также изготовим любой дизайн: 3D потолки, волна, небо с облаками, световые линии, теневой потолок euro kraab и другие. Встраиваем любые светильники, которые пожелает заказчик. Все самые инновационные тенденции в сфере натяжных потолков мы изучаем и осуществляем в жизнь. Наши мастера rukimastera.ru регулярно повышают свою квалификацию, поэтому можете отдаться полностью нашим специалистам.
По поводу [url=https://rukimastera.ru/]навесные потолки[/url] в сети интернет, мы знаем об этом всё. Главный офис находится по адресу: Москва, ул. Иркутская, д. 3, стр. 12. Звоните по телефону +7(495)125-33-74 и задавайте возникшие вопросы. На нашем веб сайте Вы можете самостоятельно рассчитать цену натяжного потолка. Впишите площадь и качество покрытия, оставьте собственные данные и мы созвонимся с Вами в скорое время. Если будет удобно, воспользуйтесь беспроцентной рассрочкой. Мы будем рады с Вами работать. -
Юрист по семейным делам advokat-karbanov.ru
Никогда не известно, когда может понадобиться помощь адвоката. Поэтому, хотим представить Вашему обзору адвокатское бюро Карбанов и партнеры, которое представляет все разновидности юридических услуг. На интернет ресурсе advokat-karbanov.ru Вы найдете все детали, каталог услуг, контактные данные.
Насчет [url=https://advokat-karbanov.ru/advokat-po-semeynyem-delam/advokat-po-razdelu-imushchestva/]адвокат по разделу имущества после развода[/url] Вы пришли по верному адресу. Пётр Карбанов - главный управляющий партнер нашей компании, известный эксперт на тв и радио. Адвокат, который может решить практически любые юридические задачи. Также у нас отличная сильная команда, занимающаяся делами любого характера.
Позвоните на нашу горячую линию по номеру телефона +7(925)734-30-70 или оформите обратный звонок на сайте advokat-karbanov.ru прямо сейчас. Напишите свой контактный номер и имя и мы Вам тут же перезвоним. Либо можно списаться с нами в популярных мессенджерах. Наша команда имеет колоссальный опыт в юридическом деле, ведь лишь образования не достаточно, основное это опыт в реальности. Ещё на этапе ознакомления с Вашим делом, наши адвокаты могут понять его перспективы и возможный исход.
Если Вы планировали найти [url=https://advokat-karbanov.ru/advokat-po-semeynyem-delam/advokat-po-razdelu-imushchestva/]адвокат по разделу имущества после развода[/url] в сети интернет, то скорее переходите на наш онлайн портал. Там Вы сможете найти весь список наших услуг. Конкретнее: адвокат по ПДД, защита прав потребителей, жилищный юрист, трудовые споры, автоюрист, наследственные споры, исполнительное производство, морские споры, взыскание долгов и многое другое.
Находимся по адресу: 115088, Москва, ул. Угрешская, д.2, стр.1, оф. 403. Работаем пошагово: для начала необходимо оформить заявку или сделать звонок нам. Далее мы выбираем дату и время встречи, бесплатно. Согласование юридической позиции по вашему вопросу и обсуждение стоимости услуг, оформление договора, подготовка документации и представительство в суде. работаем строго по плану и настраиваемся только на успешный итог по делу. Обращайтесь и мы непременно Вам окажем помощь. -
Навесные потолки rukimastera.ru
Представляем Вашему вниманию организацию, которая специализируется на установке навесных потолков «Руки мастера» в Москве. Натяжные потолки-самая востребованная отделка помещений на настоящий момент. Потому что покрытие полностью безопасно для человека, имеет большой срок службы 25 лет, небольшие цены, скоростную установку, огромный выбор цветов, фактур, возможность встраивания различных светильников и симпатичный внешний вид. За обстоятельствами заходите на rukimastera.ru уже сейчас.
По запросу [url=https://rukimastera.ru/]натяжной потолок цена за м2[/url] - мы Вам с радостью окажем помощь. Наша фирма уже много лет работает в представленной сфере, имеет положительный опыт, подробные отзывы клиентов и выгодные предложения. Обратите внимание, у нас регулярно проходят выгодные акции для клиентов, где возможно установить потолок с отличной скидкой.
Устанавливаем потолки в любое помещение: ванная, кухня, коридор, балкон, прихожая, туалет и другие. В ассортименте разные производители полотен, фактура, составы материала и виды потолков. А также выполняем любой дизайн: зеркальные потолки, Double vision, звездное небо, подсветки через полотно, теневой потолок euro kraab и другие. Встраиваем любые осветительные приборы, которые выберет заказчик. Все самые новые тренды в области навесных потолков мы знаем и превращаем в реальность. Наши мастера rukimastera.ru постоянно повышают свою квалификацию, поэтому можете довериться нашим специалистам.
Относительно [url=https://rukimastera.ru/]натяжной потолок цена за м2[/url] в сети интернет, мы знаем об этом всё. Центральный офис находится по адресу: Москва, ул. Иркутская, д. 3, стр. 12. Звоните по номеру телефона +7(495)125-33-74 и задавайте любые вопросы. На нашем онлайн ресурсе Вы можете самостоятельно подсчитать цену навесного потолка. Введите количество квадратных метров и качество покрытия, оставьте свои данные и мы созвонимся с Вами в ближайшее время. Если будет востребовано, воспользуйтесь беспроцентной рассрочкой. Мы будем рады с Вами работать. -
winstarbet
winstarbet -
tarot online gratis
Mestres Místicos é o maior portal de Tarot Online do Brasil e Portugal, o site conta com os melhores Místicos online, tarólogos, cartomantes, videntes, sacerdotes, 24 horas online para fazer sua consulta de tarot pago por minuto via chat ao vivo, temos mais de 700 mil atendimentos e estamos no ar desde 2011 -
mestres do tarot
Mestres Místicos é o maior portal de Tarot Online do Brasil e Portugal, o site conta com os melhores Místicos online, tarólogos, cartomantes, videntes, sacerdotes, 24 horas online para fazer sua consulta de tarot pago por minuto via chat ao vivo, temos mais de 700 mil atendimentos e estamos no ar desde 2011 -
Navigating through the myriad of tech gadgets available online can be overwhelming. However, if you're looking specifically for a reliable and feature-packed wearable, you might want to [url=https://furfurfriend.com/collections/smart-watches]buy smart watches[/url] from our curated collection. Each piece is engineered to provide a seamless blend of style, functionality, and convenience, ensuring that you’re always connected and in control.
In an era where every minute counts, having immediate access to your notifications, emails, and health metrics can be a game-changer. If you’re a tech enthusiast looking to explore a world where innovation meets elegance, opting to [url=https://furfurfriend.com/collections/smart-watches]smart watch buy online[/url] is your ticket to a realm of unmatched convenience.
Our smartwatches are equipped with features that cater to a wide range of needs. Whether you’re a fitness aficionado seeking to track your progress, a busy professional needing to stay on top of your schedule, or simply someone who values the blend of style and technology, we have something for you.
Step into a world where every detail is designed with your convenience in mind. Explore, choose, and step into the future of connectivity, health, and style. Your perfect companion, encapsulating the pinnacle of technological innovation and aesthetic design, awaits at the click of a button. -
Kampus Unggul
UHAMKA offers prospective/transfer/conversion students an easy access to get information and to enroll classes online. -
In a world where style and functionality often come at a premium, finding that perfect accessory that doesn’t break the bank is always a win. When it comes to timepieces, a [url=https://furfurfriend.com/]watch for men low price[/url] from our collection is not just an accessory, but a statement piece, a blend of elegance, reliability, and affordability that’s hard to come by.
Each watch in our collection is a testament to the art of fine watchmaking, where every detail, from the intricate movements to the elegant designs, is crafted with precision and care. It’s an experience of luxury and refinement that’s accessible, making the eloquence of finely crafted watches a pleasure that’s not just reserved for the few.
In the sphere of smartwatches, technology and innovation take center stage. If you’re looking to step into the future of timekeeping and connectivity without stretching your budget, our [url=https://furfurfriend.com/collections/smart-watches]smart watch low price[/url] offerings are your gateway. Experience a world where the boundaries between technology and style blur, where every notification, every update, is a seamless part of your aesthetic.
Our collection is a journey through the elegance of classic watchmaking and the innovation of modern technology, a journey where every piece is a discovery, every watch, a world in itself. Dive in, explore, and adorn your wrist with a timepiece that’s not just about telling time, but about expressing style, embodying elegance, and living the technological revolution. Every tick, every tock, is a step into a world where time is experienced, lived, and cherished. -
In a world where quality meets affordability, we present our [url=https://telegra.ph/Unleashing-the-best-deals-your-ultimate-guide-to-buying-watches-online-10-22]watch sale online[/url] . Every piece is crafted for the distinguished gentleman who seeks elegance and precision without the extravagant expense. Your journey to unparalleled sophistication begins here.
-
buy osrs gold
RuneScape, a beloved online gaming world for many, offers a myriad of opportunities for players to amass wealth and power within the game. While earning RuneScape Gold (RS3 or OSRS GP) through gameplay is undoubtedly a rewarding experience, some players seek a more convenient and streamlined path to enhancing their RuneScape journey. In this article, we explore the advantages of purchasing OSRS Gold and how it can elevate your RuneScape adventure to new heights.
A Shortcut to Success:
a. Boosting Character Power:
In the world of RuneScape, character strength is significantly influenced by the equipment they wield and their skill levels. Acquiring top-tier gear and leveling up skills often requires time and effort. Purchasing OSRS Gold allows players to expedite this process and empower their characters with the best equipment available.
b. Tackling Formidable Foes:
RuneScape is replete with challenging monsters and bosses. With the advantage of enhanced gear and skills, players can confidently confront these formidable adversaries, secure victories, and reap the rewards that follow. OSRS Gold can be the key to overcoming daunting challenges.
c. Questing with Ease:
Many RuneScape quests present complex puzzles and trials. By purchasing OSRS Gold, players can eliminate resource-gathering and level-grinding barriers, making quests smoother and more enjoyable. It's all about focusing on the adventure, not the grind.
Expanding Possibilities:
d. Rare Items and Valuable Equipment:
The RuneScape world is rich with rare and coveted items. By acquiring OSRS Gold, players can gain access to these valuable assets. Rare armor, powerful weapons, and other coveted equipment can be yours, enhancing your character's capabilities and opening up new gameplay experiences.
e. Participating in Limited-Time Events:
RuneScape often features limited-time in-game events with exclusive rewards. Having OSRS Gold at your disposal allows you to fully embrace these events, purchase unique items, and partake in memorable experiences that may not be available to others.
Conclusion:
Purchasing OSRS Gold undoubtedly offers RuneScape players a convenient shortcut to success. By empowering characters with superior gear and skills, players can take on any challenge the game throws their way. Furthermore, the ability to purchase rare items and participate in exclusive events enhances the overall gaming experience, providing new dimensions to explore within the RuneScape universe. While earning gold through gameplay remains a cherished aspect of RuneScape, buying OSRS Gold can make your journey even more enjoyable, rewarding, and satisfying. So, embark on your adventure, equip your character, and conquer RuneScape with the power of OSRS Gold. -
Купить систему солнечного освещения solargy.ru
Предлагаем Вам единственную в России систему солнечного освещения SOLARGY для помещений без окон или с малым освещением. Может быть отличным решением освещения для множества объектов, как частных домов, так и производственных помещений, офисов, столовых. Узнайте все детали на веб ресурсе solargy.ru прямо сегодня.
Если Вам нужно [url=https://solargy.ru/catalog/solargy-swc/]световод купить на крышу[/url] в Казани, то Вы на правильном пути. Наша организация специализируется в данной сфере уже большое количество лет и знает всё о данном виде освещения. КЕО является отличной альтернативой обычным окнам, увеличивает яркость естественного и искусственного освещения. Наши выполненные проекты и их иллюстрации можно увидеть на нашем интернет проекте. Это: общеобразовательные школы, жилищные комплексы, больницы, столовые и многие другие проекты.
Оставить запрос на КЕО расчет возможно на solargy.ru в любое удобное для Вас время. В специальной форме впишите свои данные: название организации, ФИО, адрес, телефон и другие. А также дополнительные задания по поводу будущих работ. Мы Вам перезвоним в самом скором времени с готовым расчетом и дадим все советы.
Насчет [url=https://solargy.ru/zenitnye-fonari/]изготовление световодов[/url] обращайтесь в нашу компанию. Мы находимся по адресу: г. Ижевск, Проспект конструктора М. Т. Калашникова, д. 7. Звоните по номеру телефона 8(800)200-0-602 и наши консультанты дадут ответы на все Ваши вопросы. Световоды на настоящий день являются трендом стиля многих помещений. А ещё, их можно добавить в строительство на любом пункте, что очень удобно. При том, в подборе огромное количество видов световодов различных цветов и размеров и каждый покупатель подберет под себя, что ему необходимо. В любом случае, мы окажем Вам помощь в подборе, проконсультируем и предоставим все рекомендации. Звоните как можно быстрее, мы будем рады с Вами работать. -
Холодная погода не страшна с уггами от UGG Australia. И что самое лучшее – вы можете купить угги по акции. Угги для всех вкусов и стилей ждут вас на нашем сайте.
Сайт: [url=https://uggaustralia-msk.ru/]uggaustralia-msk.ru[/url]
Адрес: Москва, 117449, улица Винокурова, 4к1 -
RSG雷神
RSG雷神
RSG雷神:電子遊戲的新維度
在電子遊戲的世界裡,不斷有新的作品出現,但要在眾多的遊戲中脫穎而出,成為玩家心中的佳作,需要的不僅是創意,還需要技術和努力。而當我們談到RSG雷神,就不得不提它如何將遊戲提升到了一個全新的層次。
首先,RSG已經成為了許多遊戲愛好者的口中的熱詞。每當提到RSG雷神,人們首先想到的就是品質保證和無與倫比的遊戲體驗。但這只是RSG的一部分,真正讓玩家瘋狂的,是那款被稱為“雷神之鎚”的老虎機遊戲。
RSG雷神不僅僅是一款老虎機遊戲,它是一場視覺和聽覺的盛宴。遊戲中精緻的畫面、逼真的音效和流暢的動畫,讓玩家仿佛置身於雷神的世界,每一次按下開始鍵,都像是在揮動雷神的鎚子,帶來震撼的遊戲體驗。
這款遊戲的成功,並不只是因為它的外觀或音效,更重要的是它那精心設計的遊戲機制。玩家可以根據自己的策略選擇不同的下注方式,每一次旋轉,都有可能帶來意想不到的獎金。這種刺激和期待,使得玩家一次又一次地沉浸在遊戲中,享受著每一分每一秒。
但RSG雷神並沒有因此而止步。它的研發團隊始終在尋找新的創意和技術,希望能夠為玩家帶來更多的驚喜。無論是遊戲的內容、機制還是畫面效果,RSG雷神都希望能夠做到最好,成為遊戲界的佼佼者。
總的來說,RSG雷神不僅僅是一款遊戲,它是一種文化,一種追求。對於那些熱愛遊戲、追求刺激的玩家來說,它提供了一個完美的平台,讓玩家能夠體驗到真正的遊戲樂趣。 -
RSG雷神
RSG雷神
RSG雷神:電子遊戲的新維度
在電子遊戲的世界裡,不斷有新的作品出現,但要在眾多的遊戲中脫穎而出,成為玩家心中的佳作,需要的不僅是創意,還需要技術和努力。而當我們談到RSG雷神,就不得不提它如何將遊戲提升到了一個全新的層次。
首先,RSG已經成為了許多遊戲愛好者的口中的熱詞。每當提到RSG雷神,人們首先想到的就是品質保證和無與倫比的遊戲體驗。但這只是RSG的一部分,真正讓玩家瘋狂的,是那款被稱為“雷神之鎚”的老虎機遊戲。
RSG雷神不僅僅是一款老虎機遊戲,它是一場視覺和聽覺的盛宴。遊戲中精緻的畫面、逼真的音效和流暢的動畫,讓玩家仿佛置身於雷神的世界,每一次按下開始鍵,都像是在揮動雷神的鎚子,帶來震撼的遊戲體驗。
這款遊戲的成功,並不只是因為它的外觀或音效,更重要的是它那精心設計的遊戲機制。玩家可以根據自己的策略選擇不同的下注方式,每一次旋轉,都有可能帶來意想不到的獎金。這種刺激和期待,使得玩家一次又一次地沉浸在遊戲中,享受著每一分每一秒。
但RSG雷神並沒有因此而止步。它的研發團隊始終在尋找新的創意和技術,希望能夠為玩家帶來更多的驚喜。無論是遊戲的內容、機制還是畫面效果,RSG雷神都希望能夠做到最好,成為遊戲界的佼佼者。
總的來說,RSG雷神不僅僅是一款遊戲,它是一種文化,一種追求。對於那些熱愛遊戲、追求刺激的玩家來說,它提供了一個完美的平台,讓玩家能夠體驗到真正的遊戲樂趣。 -
asoy89
asoy89 -
Как-то перед отпуском я обнаружила, что не хватает денег на последний платеж по туру. Мне срочно понадобился займ, и я нашла сайт cntbank.ru, где мне предложили срочный займ на карту на сумму 15 000 рублей. Благодаря быстрому сервису я смогла оплатить тур и насладиться заслуженным отдыхом.
-
[url=https://parazitizm.ru/]parazitizm.ru[/url] представляет рейтинг лучших онлайн казино, где можно играть на рубли. Наши эксперты в гемблинге тщательно исследовали их, чтобы вы могли наслаждаться азартом и выигрывать настоящие рубли.
-
Pharmacogenomic testing can help tailor pain medication regimens to individual needs, improving safety and efficacy buy levitra
-
[url=http://www.makion.net/illustrations/category_14/item_46.html]kantor bola[/url] 6d09cdd
-
http://primorskival.si/includes/pages/1xbet_promo_codes___bonus_code.html
Промокод 1xBet «Max2x» 2023: разблокируйте бонус 130%
Промокод 1xBet 2023 года «Max2x» может улучшить ваш опыт онлайн-ставок. Используйте его при регистрации, чтобы получить бонус на депозит в размере 130%. Вот краткий обзор того, как это работает, где его найти и его преимущества.
Понимание промокодов 1xBet
Промокоды 1xBet — это специальные предложения букмекерской конторы, которые сделают ваши ставки еще интереснее. Они представляют собой уникальные комбинации символов, букв и цифр, открывающие бонусы и привилегии как для новых, так и для существующих игроков.
Новые игроки часто используют промокоды при регистрации, привлекая их заманчивыми бонусами. Это одноразовое использование для создания новой учетной записи. Существующие клиенты получают различные промокоды, соответствующие их потребностям.
Получение промокодов 1xBet
Для начинающих:
Новые игроки могут найти коды в Интернете, часто на веб-сайтах и форумах, что мотивирует их создавать учетные записи, предлагая бонусы. Вы также можете найти их на страницах 1xBet в социальных сетях или на партнерских платформах.
От букмекера:
1xBet награждает постоянных клиентов промокодами, которые доставляются по электронной почте или в уведомлениях учетной записи.
Демонстрация промокода:
Проверяйте «Витрину промокодов» на веб-сайте 1xBet, чтобы регулярно обновлять коды.
Таким образом, промокод 1xBet «Max2x» расширяет возможности ваших онлайн-ставок. Это ценный инструмент для новичков и опытных игроков. Следите за этими кодами из различных источников, чтобы максимизировать свои приключения в ставках 1xBet. -
https://institutocea.com/layouts/inc/?codigo-promocional-1xbet.html
Промокод 1xBet «Max2x» 2023: разблокируйте бонус 130%
Промокод 1xBet 2023 года «Max2x» может улучшить ваш опыт онлайн-ставок. Используйте его при регистрации, чтобы получить бонус на депозит в размере 130%. Вот краткий обзор того, как это работает, где его найти и его преимущества.
Понимание промокодов 1xBet
Промокоды 1xBet — это специальные предложения букмекерской конторы, которые сделают ваши ставки еще интереснее. Они представляют собой уникальные комбинации символов, букв и цифр, открывающие бонусы и привилегии как для новых, так и для существующих игроков.
Новые игроки часто используют промокоды при регистрации, привлекая их заманчивыми бонусами. Это одноразовое использование для создания новой учетной записи. Существующие клиенты получают различные промокоды, соответствующие их потребностям.
Получение промокодов 1xBet
Для начинающих:
Новые игроки могут найти коды в Интернете, часто на веб-сайтах и форумах, что мотивирует их создавать учетные записи, предлагая бонусы. Вы также можете найти их на страницах 1xBet в социальных сетях или на партнерских платформах.
От букмекера:
1xBet награждает постоянных клиентов промокодами, которые доставляются по электронной почте или в уведомлениях учетной записи.
Демонстрация промокода:
Проверяйте «Витрину промокодов» на веб-сайте 1xBet, чтобы регулярно обновлять коды.
Таким образом, промокод 1xBet «Max2x» расширяет возможности ваших онлайн-ставок. Это ценный инструмент для новичков и опытных игроков. Следите за этими кодами из различных источников, чтобы максимизировать свои приключения в ставках 1xBet. -
login surgaslot77
SURGASLOT77 - #1 Top Gamer Website in Indonesia
SURGASLOT77 merupakan halaman website hiburan online andalan di Indonesia. -
Мой сын только что получил водительские права, и я решил подарить ему машину. Однако не хватало небольшой суммы для покупки. На сайте credit-info24.ru, где собраны все МФО, я быстро нашел подходящий вариант. С помощью [url=https://credit-info24.ru/]займы без кредитной истории на карту срочно[/url] мне удалось дополнить необходимую сумму, и теперь мой сын счастливый обладатель автомобиля.
-
Я большой поклонник русской культуры, и для меня важно, чтобы сериалы были на русском языке. На hdserialclub.net я нашел [url=https://hdserialclub.net/best-serials/]лучшие сериалы на русском языке[/url]. Здесь есть как классические русские истории, так и современные шоу. Это идеальное место для того, чтобы погрузиться в мир русской культуры и кинематографа.
-
Абузоустойчивый VPS
Абузоустойчивый VPS -
英超
2023-24英超聯賽萬眾矚目,2023年8月12日開啟了第一場比賽,而接下來的賽事也正如火如荼地進行中。本文統整出英超賽程以及英超賽制等資訊,幫助你更加了解英超,同時也提供英超直播平台,讓你絕對不會錯過每一場精彩賽事。
英超是什麼?
英超是相當重要的足球賽事,以競爭激烈和精彩程度聞名
英超是相當重要的足球賽事,以競爭激烈和精彩程度聞名
英超全名為「英格蘭足球超級聯賽」,是足球賽事中最高級的足球聯賽之一,由英格蘭足球總會在1992年2月20日成立。英超是全世界最多人觀看的體育聯賽,因其英超隊伍全球知名度和競爭激烈而聞名,吸引來自世界各地的頂尖球星前來參賽。
英超聯賽(English Premier League,縮寫EPL)由英國最頂尖的20支足球俱樂部參加,賽季通常從8月一直持續到5月,以下帶你來了解英超賽制和其他更詳細的資訊。
英超賽制
2023-24英超總共有20支隊伍參賽,以下是英超賽制介紹:
採雙循環制,分主場及作客比賽,每支球隊共進行 38 場賽事。
比賽採用三分制,贏球獲得3分,平局獲1分,輸球獲0分。
以積分多寡分名次,若同分則以淨球數來區分排名,仍相同就以得球計算。如果還是相同,就會於中立場舉行一場附加賽決定排名。
賽季結束後,根據積分排名,最高分者成為冠軍,而最後三支球隊則降級至英冠聯賽。
英超升降級機制
英超有一個相當特別的賽制規定,那就是「升降級」。賽季結束後,積分和排名最高的隊伍將直接晉升冠軍,而總排名最低的3支隊伍會被降級至英格蘭足球冠軍聯賽(英冠),這是僅次於英超的足球賽事。
同時,英冠前2名的球隊直接升上下一賽季的英超,第3至6名則會以附加賽決定最後一個升級名額,英冠的隊伍都在爭取升級至英超,以獲得更高的收入和榮譽。 -
2023-24英超聯賽萬眾矚目,2023年8月12日開啟了第一場比賽,而接下來的賽事也正如火如荼地進行中。本文統整出英超賽程以及英超賽制等資訊,幫助你更加了解英超,同時也提供英超直播平台,讓你絕對不會錯過每一場精彩賽事。
英超是什麼?
英超是相當重要的足球賽事,以競爭激烈和精彩程度聞名
英超是相當重要的足球賽事,以競爭激烈和精彩程度聞名
英超全名為「英格蘭足球超級聯賽」,是足球賽事中最高級的足球聯賽之一,由英格蘭足球總會在1992年2月20日成立。英超是全世界最多人觀看的體育聯賽,因其英超隊伍全球知名度和競爭激烈而聞名,吸引來自世界各地的頂尖球星前來參賽。
英超聯賽(English Premier League,縮寫EPL)由英國最頂尖的20支足球俱樂部參加,賽季通常從8月一直持續到5月,以下帶你來了解英超賽制和其他更詳細的資訊。
英超賽制
2023-24英超總共有20支隊伍參賽,以下是英超賽制介紹:
採雙循環制,分主場及作客比賽,每支球隊共進行 38 場賽事。
比賽採用三分制,贏球獲得3分,平局獲1分,輸球獲0分。
以積分多寡分名次,若同分則以淨球數來區分排名,仍相同就以得球計算。如果還是相同,就會於中立場舉行一場附加賽決定排名。
賽季結束後,根據積分排名,最高分者成為冠軍,而最後三支球隊則降級至英冠聯賽。
英超升降級機制
英超有一個相當特別的賽制規定,那就是「升降級」。賽季結束後,積分和排名最高的隊伍將直接晉升冠軍,而總排名最低的3支隊伍會被降級至英格蘭足球冠軍聯賽(英冠),這是僅次於英超的足球賽事。
同時,英冠前2名的球隊直接升上下一賽季的英超,第3至6名則會以附加賽決定最後一個升級名額,英冠的隊伍都在爭取升級至英超,以獲得更高的收入和榮譽。 -
英超
2023-24英超聯賽萬眾矚目,2023年8月12日開啟了第一場比賽,而接下來的賽事也正如火如荼地進行中。本文統整出英超賽程以及英超賽制等資訊,幫助你更加了解英超,同時也提供英超直播平台,讓你絕對不會錯過每一場精彩賽事。
英超是什麼?
英超是相當重要的足球賽事,以競爭激烈和精彩程度聞名
英超是相當重要的足球賽事,以競爭激烈和精彩程度聞名
英超全名為「英格蘭足球超級聯賽」,是足球賽事中最高級的足球聯賽之一,由英格蘭足球總會在1992年2月20日成立。英超是全世界最多人觀看的體育聯賽,因其英超隊伍全球知名度和競爭激烈而聞名,吸引來自世界各地的頂尖球星前來參賽。
英超聯賽(English Premier League,縮寫EPL)由英國最頂尖的20支足球俱樂部參加,賽季通常從8月一直持續到5月,以下帶你來了解英超賽制和其他更詳細的資訊。
英超賽制
2023-24英超總共有20支隊伍參賽,以下是英超賽制介紹:
採雙循環制,分主場及作客比賽,每支球隊共進行 38 場賽事。
比賽採用三分制,贏球獲得3分,平局獲1分,輸球獲0分。
以積分多寡分名次,若同分則以淨球數來區分排名,仍相同就以得球計算。如果還是相同,就會於中立場舉行一場附加賽決定排名。
賽季結束後,根據積分排名,最高分者成為冠軍,而最後三支球隊則降級至英冠聯賽。
英超升降級機制
英超有一個相當特別的賽制規定,那就是「升降級」。賽季結束後,積分和排名最高的隊伍將直接晉升冠軍,而總排名最低的3支隊伍會被降級至英格蘭足球冠軍聯賽(英冠),這是僅次於英超的足球賽事。
同時,英冠前2名的球隊直接升上下一賽季的英超,第3至6名則會以附加賽決定最後一個升級名額,英冠的隊伍都在爭取升級至英超,以獲得更高的收入和榮譽。 -
2023-24英超聯賽萬眾矚目,2023年8月12日開啟了第一場比賽,而接下來的賽事也正如火如荼地進行中。本文統整出英超賽程以及英超賽制等資訊,幫助你更加了解英超,同時也提供英超直播平台,讓你絕對不會錯過每一場精彩賽事。
英超是什麼?
英超是相當重要的足球賽事,以競爭激烈和精彩程度聞名
英超是相當重要的足球賽事,以競爭激烈和精彩程度聞名
英超全名為「英格蘭足球超級聯賽」,是足球賽事中最高級的足球聯賽之一,由英格蘭足球總會在1992年2月20日成立。英超是全世界最多人觀看的體育聯賽,因其英超隊伍全球知名度和競爭激烈而聞名,吸引來自世界各地的頂尖球星前來參賽。
英超聯賽(English Premier League,縮寫EPL)由英國最頂尖的20支足球俱樂部參加,賽季通常從8月一直持續到5月,以下帶你來了解英超賽制和其他更詳細的資訊。
英超賽制
2023-24英超總共有20支隊伍參賽,以下是英超賽制介紹:
採雙循環制,分主場及作客比賽,每支球隊共進行 38 場賽事。
比賽採用三分制,贏球獲得3分,平局獲1分,輸球獲0分。
以積分多寡分名次,若同分則以淨球數來區分排名,仍相同就以得球計算。如果還是相同,就會於中立場舉行一場附加賽決定排名。
賽季結束後,根據積分排名,最高分者成為冠軍,而最後三支球隊則降級至英冠聯賽。
英超升降級機制
英超有一個相當特別的賽制規定,那就是「升降級」。賽季結束後,積分和排名最高的隊伍將直接晉升冠軍,而總排名最低的3支隊伍會被降級至英格蘭足球冠軍聯賽(英冠),這是僅次於英超的足球賽事。
同時,英冠前2名的球隊直接升上下一賽季的英超,第3至6名則會以附加賽決定最後一個升級名額,英冠的隊伍都在爭取升級至英超,以獲得更高的收入和榮譽。 -
b29
b29 -
Maps-edu.ru открывает двери в мир медицинского образования. Наши курсы помогут вам оставаться в курсе последних трендов и технологий в медицине. Зарегистрируйтесь сегодня!
-
VPS SERVER
Высокоскоростной доступ в Интернет: до 1000 Мбит/с
Скорость подключения к Интернету — еще один важный фактор для успеха вашего проекта. Наши VPS/VDS-серверы, адаптированные как под Windows, так и под Linux, обеспечивают доступ в Интернет со скоростью до 1000 Мбит/с, что гарантирует быструю загрузку веб-страниц и высокую производительность онлайн-приложений на обеих операционных системах. -
2023 турецкие сериалы онлайн turkhit.tv
Для любителей турецких сериалов, которые не могут жить без множества серий и волнующих сюжетов — мы создали наш сайт. Самый огромный каталог сериалов из Турции самых разных жанров. Добро пожаловать на turkhit.tv уже сегодня.
По теме [url=https://turkhit.tv/]турецкие сериалы[/url] Вы на правильном пути. Турецкие сериалы за последние годы забрали огромную популярность за границами своей страны, в том числе и в РФ. В чем же секрет их удачи? Прежде всего, это истории, переполненные напряжением и страстью, которые цепляют зрителя с первых минут просмотра. Герои сериалов - активные и эмоциональные, часто оказываются втянутыми в сложные жизненные ситуации, которые вызывают у аудитории сочувствие и сопереживание.
Киносценарии турецких сериалов часто тяжелые и имеют несколько сюжетных линий. Они совмещают в себе любовные разборки, семейные драмы, трагедии и предательства, а также криминальные линии. Такой подход позволяет удерживать внимание различной аудитории, ведь любой найдет для себя что-то подходящее.
Помимо того, турецкие сериалы часто затрагивают сложные социальные и культурные темы, острые не только для Турции, но и для большинства других стран. Это делает их не только причиной развлечений, но и пищей для мыслей. Богатые декорации, костюмы и съемки в исторических локациях добавляют внешнее наслаждение и помогают зрителю углубиться в удивительный мир, который они создают.
Переходите смотреть [url=https://turkhit.tv/]смотреть турецкие сериалы[/url] на наш сайт turkhit.tv уже сейчас. Турецкие продюсеры и режиссеры не боятся творить новое с форматами и сюжетными линиями, обязательно улучшая свои техники видеосъемки и монтажа. Актерский состав часто содержит в себе яркие и гениальные личности, способные на глубокую передачу эмоций и создание конкретных героев.
В итоге, турецкие сериалы цепляют зрителей своей способностью рассказывать увлекательные истории, которые отражают человеческие чувства во всем их разнообразии. Они открывают окно в иностранные культуры и предлагают возможность для эмоционального отклика, что делает их необходимой частью жизни многих любителей сериалов. -
Рейтинговые турецкие сериалы turkline.tv
Сериалы из Турции стали чистым культурным феноменом, завоевав зрителей по всей планете своими интересными сюжетами и яркими персонажами. Эти сериалы наполнены глубокими чувствами, непредсказуемыми поворотами и разнятся высоким качеством продукции. Они дают зрителям впасть в мир истинной страсти и драмы, при этом затрагивая насущные общественные проблемы, что делает их интересными для большой аудитории.
Относительно [url=https://turkline.tv/]турецкие сериалы[/url] в интернете, то Вы на верном пути. На сайте turkline.tv есть исключительная коллекция турецких сериалов, доступных в высоком качестве с русской озвучкой. Здесь можно найти сериалы на любой вкус - от любовных комедий до будуражащих триллеров и детективов. Благодаря удобному интерфейсу и широкому выбору жанров, любой зритель сайта сможет выбрать сериал по душе.
Смотреть [url=https://turkline.tv/fantastika/]турецкие сериалы фантастика[/url] в хорошем качестве возможно у нас. Здесь размещены все жанры кино: драмы, комедии, военные, триллеры, детективы и другие. Также можно воспользоваться поиском по времени создания или по рейтингу героев. Турецкие артисты также имеют свою популярность в виде рейтинга. Какой-либо актер сразу всем нравится, а некоторые вызывают антипатию. На данном сайте можете увидеть, кто именно понравился большинству зрителей.
Одним из основных плюсов turkline.tv является отсутствие рекламы, что дает качественный и комфортный просмотр. Все сериалы доступны для просмотра 24 на 7, что дает зрителям собственно планировать свой досуг и радоваться любимыми историями без ограничений. Таким образом, наш онлайн ресурс является отличным ресурсом для всех фанатов турецких сериалов, предлагая качественный и открытый контент для истинных ценителей любого жанра. -
http://prednisone.digital/# prednisone for sale without a prescription
-
prednisone tablets canada: prednisone 5mg daily - order prednisone 10mg
-
buy lasix canada : [url=https://lasixfx.online/#]buy lasix 40 mg[/url] buy lasix diuretic
-
Срочно нуждающимся в финансовой поддержке предлагается отличная возможность – [url=https://xn----8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]микрозаймы без отказа[/url] . Взять займ на карту без отказа теперь можно быстро и без лишних условий. Это решение идеально подходит для тех, кто сталкивается с неожиданными расходами или кратковременными финансовыми трудностями. Мы гарантируем простоту процесса и быстрое одобрение, чтобы вы могли мгновенно распоряжаться средствами.
Тем, кто ищет надежный и удобный способ получения средств, мы предлагаем услугу [url=https://xn----8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]взять микрозайм на карту онлайн без отказа[/url] . Онлайн займы без отказа – это прекрасный способ быстро получить деньги, не теряя времени на походы в банк и ожидание одобрения. Мы стремимся обеспечить максимальную доступность и удобство наших услуг для каждого клиента. При этом не требуется подтверждать свой доход или предоставлять залог, что делает процесс получения займа максимально простым и доступным. -
Ищете быстрое и надежное финансовое решение? Наш сервис предоставляет возможность оформить [url=https://xn----8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]взять займ срочно на карту без отказа[/url] . Кредит онлайн на карту без отказа – это удобный способ получить необходимую сумму денег без лишних формальностей и длительного ожидания. Мы ценим ваше время и предлагаем простой, но эффективный процесс оформления, который позволяет получить средства в кратчайшие сроки.
Если вам срочно нужны деньги, наша услуга [url=https://xn----8sbgsdjqfso.xn--p1ai/]микрозаймы без отказа на карту[/url] , позволит вам решить финансовые вопросы максимально быстро. Займ онлайн на карту срочно без отказа – это идеальный вариант для тех, кто столкнулся с непредвиденными расходами. Мы предлагаем прозрачные условия и быстрое решение по вашей заявке, что делает нас одним из самых востребованных и надежных сервисов в сфере онлайн-кредитования. -
Мне рассказали о сайте МИР-ЗАЙМОВ.РФ через знакомого. Он утверждал, что это отличный ресурс для поиска займов на карту. Доверившись его совету, я нашел удобное предложение и быстро получил нужные деньги на свою карту. Этот опыт показал мне, насколько важно слушать советы близких.
-
win79
win79 -
www.manufacturer.vn is healthcare manufacturer of nasal rinse kit, vaginal pump gel, long time xxx solution, enhance supplement, ODM and OEM service. Manufacturer.vn can also research and development products from your ideas. We export more than 40 countries, we are one sub-company of StrongBody
-
www.manufacturer.vn is healthcare manufacturer of nasal rinse kit, vaginal pump gel, long time xxx solution, enhance supplement, ODM and OEM service. Manufacturer.vn can also research and development products from your ideas. We export more than 40 countries, we are one sub-company of StrongBody
-
i wrkqsqtb wbkyn
p ifdzpdhp inhvl
x jazhokqj bbzuu
\
https://ih9.ru/qy2B8vH0/ -
2024 B1GVH351KWT7 2014 S8YBO760IIZ9 2016 W9IAT717XUO5 2010 I1LNU996AGO2 2013 E8VFD503DSE9 2014 C3EPB942DDL6 2019 V6PQU751KRZ3 2013 Q9BVW452YLM3 2024 S9AOC974YJA5
https://maps.google.com.pa/url?q=https://lordfilmgc7525.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.com.ai/url?q=https://lordfilmth5274.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.co.uk/url?q=https://lordfilmmy8635.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.bg/url?q=https://lordfilmzb4516.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.gr/url?q=https://lordfilmtj5531.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.pn/url?q=https://lordfilmnc1975.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.co.zm/url?q=https://lordfilmui1847.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.com.ru/url?q=https://lordfilmmj1368.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.com.kw/url?q=https://lordfilmto239.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.sk/url?q=https://lordfilmvg8401.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.com.ag/url?q=https://lordfilmmd2940.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.ms/url?q=https://lordfilmeq300.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.nu/url?q=https://lordfilmix1144.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.co.mz/url?q=https://lordfilmbg9115.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.co.kr/url?q=https://lordfilmxk4755.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.com.pa/url?q=https://lordfilmso1213.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.fm/url?q=https://lordfilmuq4269.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.mk/url?q=https://lordfilmcu949.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.com.sa/url?q=https://lordfilmya873.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.ne/url?q=https://lordfilmrh9773.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.com.sa/url?q=https://lordfilmcv2480.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.tl/url?q=https://lordfilmih3403.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.info/url?q=https://lordfilmlw422.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.tn/url?q=https://lordfilmzv4956.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.com.mx/url?q=https://lordfilmon7008.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.com.ve/url?q=https://lordfilmth1643.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.tm/url?q=https://lordfilmbk6368.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.ci/url?q=https://lordfilmgq2369.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.com.pr/url?q=https://lordfilmiz2860.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.ca/url?q=https://lordfilmkn4103.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.com.py/url?q=https://lordfilmfr1201.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.com.tw/url?q=https://lordfilmoi1654.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.co.cr/url?q=https://lordfilmtl3253.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.cn/url?q=https://lordfilmat9256.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.ga/url?q=https://lordfilmar6413.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.com.kw/url?q=https://lordfilmfb8742.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.ba/url?q=https://lordfilmou750.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.com.ph/url?q=https://lordfilmfc8548.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.cc/url?q=https://lordfilmxm4696.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.com.au/url?q=https://lordfilmap6245.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.com.ec/url?q=https://lordfilmpu5226.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.fr/url?q=https://lordfilmcu5057.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.co.vi/url?q=https://lordfilmkg6229.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.com.jm/url?q=https://lordfilmoq7752.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.pl/url?q=https://lordfilmzv1351.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.co.mz/url?q=https://lordfilmjf9890.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.la/url?q=https://lordfilmkd3005.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.com.tw/url?q=https://lordfilmdj4341.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.sr/url?q=https://lordfilmcj719.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.at/url?q=https://lordfilmhd867.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.com.gt/url?q=https://lordfilmck7565.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.com.gt/url?q=https://lordfilmnv4051.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.tl/url?q=https://lordfilmfu6300.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.gy/url?q=https://lordfilmbg485.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.ge/url?q=https://lordfilmbd5075.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.nl/url?q=https://lordfilmut7630.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.cz/url?q=https://lordfilmzu9361.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.com.et/url?q=https://lordfilmdg2757.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.com.pg/url?q=https://lordfilmes130.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://www.google.com.tn/url?q=https://lordfilmbf6312.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.rs/url?q=https://lordfilmlb1508.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.com.kw/url?q=https://lordfilmul887.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.com.co/url?q=https://lordfilmnb2200.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.dj/url?q=https://lordfilmzw9919.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.it/url?q=https://lordfilmop7018.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.com.na/url?q=https://lordfilmrh364.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.com.nr/url?q=https://lordfilmnj6137.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.gy/url?q=https://lordfilmgt6073.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.mg/url?q=https://lordfilmxv3110.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
http://google.com.gi/url?q=https://lordfilmrr4485.lord-film-lordfilm.ru
https://maps.google.com.do/url?q=https://wgr8751.u8a.ru -
Veni, vidi, vici – пришел, увидел, победил
-
Pharmacogenomic testing can help identify genetic variations that may impact medication safety and efficacy in older adults. stromectol 12mg online prescription
-
Sun52
-
StakeOnline Casino
-
https://ogloszenia-kielce.pl/serwery-minecraft-1-7-2-minigames/
-
StrongBody.uk B2B wholesale healthcare products
Discover www.strongbody.uk for an exclusive selection of B2B wholesale healthcare products. Retailers can easily place orders, waiting a smooth manufacturing process. Closing the profitability gap, our robust brands, supported by healthcare media, simplify the selling process for retailers. All StrongBody products boast high quality, unique R&D, rigorous testing, and effective marketing. StrongBody is dedicated to helping you and your customers live longer, younger, and healthier lives. -
Abiens, abi! — Уходя, уходи!
https://batmanapollo.ru -
Cel mai bun site pentru lucrari de licenta si locul unde poti gasii cel mai bun redactor specializat in redactare lucrare de licenta la comanda fara plagiat
-
Mount Kenya University (MKU) is a Chartered MKU and ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management Systems certified University committed to offering holistic education. MKU has embraced the internationalization agenda of higher education. The University, a research institution dedicated to the generation, dissemination and preservation of knowledge; with 8 regional campuses and 6 Open, Distance and E-Learning (ODEL) Centres; is one of the most culturally diverse universities operating in East Africa and beyond. The University Main campus is located in Thika town, Kenya with other Campuses in Nairobi, Parklands, Mombasa, Nakuru, Eldoret, Meru, and Kigali, Rwanda. The University has ODeL Centres located in Malindi, Kisumu, Kitale, Kakamega, Kisii and Kericho and country offices in Kampala in Uganda, Bujumbura in Burundi, Hargeisa in Somaliland and Garowe in Puntland.
MKU is a progressive, ground-breaking university that serves the needs of aspiring students and a devoted top-tier faculty who share a commitment to the promise of accessible education and the imperative of social justice and civic engagement-doing good and giving back. The University’s coupling of health sciences, liberal arts and research actualizes opportunities for personal enrichment, professional preparedness and scholarly advancement -
Mount Kenya University (MKU) is a Chartered MKU and ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management Systems certified University committed to offering holistic education. MKU has embraced the internationalization agenda of higher education. The University, a research institution dedicated to the generation, dissemination and preservation of knowledge; with 8 regional campuses and 6 Open, Distance and E-Learning (ODEL) Centres; is one of the most culturally diverse universities operating in East Africa and beyond. The University Main campus is located in Thika town, Kenya with other Campuses in Nairobi, Parklands, Mombasa, Nakuru, Eldoret, Meru, and Kigali, Rwanda. The University has ODeL Centres located in Malindi, Kisumu, Kitale, Kakamega, Kisii and Kericho and country offices in Kampala in Uganda, Bujumbura in Burundi, Hargeisa in Somaliland and Garowe in Puntland.
MKU is a progressive, ground-breaking university that serves the needs of aspiring students and a devoted top-tier faculty who share a commitment to the promise of accessible education and the imperative of social justice and civic engagement-doing good and giving back. The University’s coupling of health sciences, liberal arts and research actualizes opportunities for personal enrichment, professional preparedness and scholarly advancement -
Medications are essential for controlling chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and asthma, enabling people to lead productive lives. ivermectin for horses
-
slot gacor gampang menang
[url=https://systemsvyaz.ru/products/z-8-eht#comment_1178478]slot gacor gampang menang[/url] 4331c6d
Slot Gacor telah menciptakan fenomena baru dalam dunia slot online, tidak sekadar menjadi istilah biasa, melainkan sebuah jaminan meraih kemenangan dengan menawarkan pengalaman permainan slot yang memikat dengan minimal deposit 5rb.
Bermain di situs slot gacor yang dapat dijamin amanah bukan hanya memberikan hiburan semata, tetapi juga membuka peluang meraih jackpot terbesar yang sebelumnya mungkin sulit dicapai atau bahkan tidak pernah terwujud.
Pengalaman Game Slot Gacor: Lebih Dari Sekadar Hiburan
Slot Gacor bukanlah sekadar permainan slot biasa. Ia menciptakan atmosfer yang berbeda, memanjakan pemain dengan sensasi bermain yang luar biasa dan menawarkan harapan kemenangan yang lebih tinggi. Dengan desain yang menarik dan fitur-fitur inovatif, setiap putaran menjadi pengalaman yang tak terlupakan.
Strategi Bermain untuk Meningkatkan Peluang Kemenangan
Meskipun slot gacor dikenal dapat meningkatkan peluang kemenangan, penting bagi pemain memiliki beberapa strategi untuk memaksimalkan potensi kemenangan mereka. Beberapa strategi yang dapat diadopsi antara lain:
1. Pemilihan Provider Game yang Tepat
Pemilihan provider game slot online yang tepat menjadi langkah awal yang krusial. Pastikan memilih provider yang memiliki reputasi baik dan menawarkan variasi game slot gacor terbaik.
2. Pahami Return to Player (RTP) Tertinggi
Mengetahui tingkat Return to Player (RTP) tertinggi pada setiap permainan slot dapat menjadi kunci kesuksesan. Pilihlah game dengan RTP tinggi untuk meningkatkan peluang meraih kemenangan.
Slot Gacor Malam Ini: Temukan Keberuntungan Anda
Setiap malam, dunia slot gacor menyajikan kejutan-kejutan baru. Untuk menjadi bagian dari aksi malam ini, pastikan untuk mengikuti bocoran pola slot gacor yang telah disiapkan. Ini dapat menjadi kunci untuk membuka pintu ke sesuatu yang lebih besar dan meraih kemenangan yang menarik.
Jadi, jangan ragu untuk bergabung dan bermain di slot gacor hari ini. Saksikan sendiri bagaimana pengalaman bermain dapat menjadi lebih dari sekadar hiburan, melainkan sebuah peluang untuk meraih kemenangan besar. Selamat bermain dan semoga keberuntungan selalu berada di pihak Anda! -
Jagoslot
Jagoslot adalah situs slot gacor terlengkap, terbesar & terpercaya yang menjadi situs slot online paling gacor di indonesia. Jago slot menyediakan semua permaina slot gacor dan judi online mudah menang seperti slot online, live casino, judi bola, togel online, tembak ikan, sabung ayam, arcade dll. -
Thierry Martin LNA
-
kantorbola situs penyedia layanan gaming online terbaik , segera daftar di kantorbola untuk dapatkan id permainan VIP dari situs kantor bola . Tersedia promo bonus harian 25% dan bonus mingguan hingga 20%
-
buy vardenafil https://community.alteryx.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/524741/ budesonide inhaler dose
-
In recent years, the landscape of digital entertainment and online gaming has expanded, with 'nhà cái' (betting houses or bookmakers) becoming a significant part. Among these, 'nhà cái RG' has emerged as a notable player. It's essential to understand what these entities are and how they operate in the modern digital world.
A 'nhà cái' essentially refers to an organization or an online platform that offers betting services. These can range from sports betting to other forms of wagering. The growth of internet connectivity and mobile technology has made these services more accessible than ever before.
Among the myriad of options, 'nhà cái RG' has been mentioned frequently. It appears to be one of the numerous online betting platforms. The 'RG' could be an abbreviation or a part of the brand's name. As with any online betting platform, it's crucial for users to understand the terms, conditions, and the legalities involved in their country or region.
The phrase 'RG nhà cái' could be interpreted as emphasizing the specific brand 'RG' within the broader category of bookmakers. This kind of focus suggests a discussion or analysis specific to that brand, possibly about its services, user experience, or its standing in the market.
Finally, 'Nhà cái Uy tín' is a term that people often look for. 'Uy tín' translates to 'reputable' or 'trustworthy.' In the context of online betting, it's a crucial aspect. Users typically seek platforms that are reliable, have transparent operations, and offer fair play. Trustworthiness also encompasses aspects like customer service, the security of transactions, and the protection of user data.
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of 'nhà cái,' such as 'nhà cái RG,' and the importance of 'Uy tín' is vital for anyone interested in or participating in online betting. It's a world that offers entertainment and opportunities but also requires a high level of awareness and responsibility. -
nhà cái
In recent years, the landscape of digital entertainment and online gaming has expanded, with 'nhà cái' (betting houses or bookmakers) becoming a significant part. Among these, 'nhà cái RG' has emerged as a notable player. It's essential to understand what these entities are and how they operate in the modern digital world.
A 'nhà cái' essentially refers to an organization or an online platform that offers betting services. These can range from sports betting to other forms of wagering. The growth of internet connectivity and mobile technology has made these services more accessible than ever before.
Among the myriad of options, 'nhà cái RG' has been mentioned frequently. It appears to be one of the numerous online betting platforms. The 'RG' could be an abbreviation or a part of the brand's name. As with any online betting platform, it's crucial for users to understand the terms, conditions, and the legalities involved in their country or region.
The phrase 'RG nhà cái' could be interpreted as emphasizing the specific brand 'RG' within the broader category of bookmakers. This kind of focus suggests a discussion or analysis specific to that brand, possibly about its services, user experience, or its standing in the market.
Finally, 'Nhà cái Uy tín' is a term that people often look for. 'Uy tín' translates to 'reputable' or 'trustworthy.' In the context of online betting, it's a crucial aspect. Users typically seek platforms that are reliable, have transparent operations, and offer fair play. Trustworthiness also encompasses aspects like customer service, the security of transactions, and the protection of user data.
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of 'nhà cái,' such as 'nhà cái RG,' and the importance of 'Uy tín' is vital for anyone interested in or participating in online betting. It's a world that offers entertainment and opportunities but also requires a high level of awareness and responsibility. -
In recent years, the landscape of digital entertainment and online gaming has expanded, with 'nhà cái' (betting houses or bookmakers) becoming a significant part. Among these, 'nhà cái RG' has emerged as a notable player. It's essential to understand what these entities are and how they operate in the modern digital world.
A 'nhà cái' essentially refers to an organization or an online platform that offers betting services. These can range from sports betting to other forms of wagering. The growth of internet connectivity and mobile technology has made these services more accessible than ever before.
Among the myriad of options, 'nhà cái RG' has been mentioned frequently. It appears to be one of the numerous online betting platforms. The 'RG' could be an abbreviation or a part of the brand's name. As with any online betting platform, it's crucial for users to understand the terms, conditions, and the legalities involved in their country or region.
The phrase 'RG nhà cái' could be interpreted as emphasizing the specific brand 'RG' within the broader category of bookmakers. This kind of focus suggests a discussion or analysis specific to that brand, possibly about its services, user experience, or its standing in the market.
Finally, 'Nhà cái Uy tín' is a term that people often look for. 'Uy tín' translates to 'reputable' or 'trustworthy.' In the context of online betting, it's a crucial aspect. Users typically seek platforms that are reliable, have transparent operations, and offer fair play. Trustworthiness also encompasses aspects like customer service, the security of transactions, and the protection of user data.
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of 'nhà cái,' such as 'nhà cái RG,' and the importance of 'Uy tín' is vital for anyone interested in or participating in online betting. It's a world that offers entertainment and opportunities but also requires a high level of awareness and responsibility. -
In recent years, the landscape of digital entertainment and online gaming has expanded, with 'nhà cái' (betting houses or bookmakers) becoming a significant part. Among these, 'nhà cái RG' has emerged as a notable player. It's essential to understand what these entities are and how they operate in the modern digital world.
A 'nhà cái' essentially refers to an organization or an online platform that offers betting services. These can range from sports betting to other forms of wagering. The growth of internet connectivity and mobile technology has made these services more accessible than ever before.
Among the myriad of options, 'nhà cái RG' has been mentioned frequently. It appears to be one of the numerous online betting platforms. The 'RG' could be an abbreviation or a part of the brand's name. As with any online betting platform, it's crucial for users to understand the terms, conditions, and the legalities involved in their country or region.
The phrase 'RG nhà cái' could be interpreted as emphasizing the specific brand 'RG' within the broader category of bookmakers. This kind of focus suggests a discussion or analysis specific to that brand, possibly about its services, user experience, or its standing in the market.
Finally, 'Nhà cái Uy tín' is a term that people often look for. 'Uy tín' translates to 'reputable' or 'trustworthy.' In the context of online betting, it's a crucial aspect. Users typically seek platforms that are reliable, have transparent operations, and offer fair play. Trustworthiness also encompasses aspects like customer service, the security of transactions, and the protection of user data.
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of 'nhà cái,' such as 'nhà cái RG,' and the importance of 'Uy tín' is vital for anyone interested in or participating in online betting. It's a world that offers entertainment and opportunities but also requires a high level of awareness and responsibility. -
Benevolentiae captande causa — Для снискания благоволения.
http://batmanapollo.ru -
1. C88 Fun - Where Boundless Entertainment Begins!
Beyond being a mere gaming platform, C88 Fun is an adventure waiting to be explored. With its intuitive interface and a diverse selection of games, C88 Fun caters to all preferences. From timeless classics to cutting-edge releases, C88 Fun ensures every player discovers their perfect gaming sanctuary.
2. JILI & Evo 100% Welcome Bonus - A Grand Entrance to Gaming!
Embark on your gaming journey with a grand welcome from C88. New members are greeted with a 100% Welcome Bonus from JILI & Evo, doubling the excitement from the very beginning. This bonus serves as an excellent boost for players to explore the wide array of games available on the platform.
3. C88 First Deposit Get 2X Bonus - Doubling the Excitement!
C88 believes in generously rewarding players. With the "First Deposit Get 2X Bonus" offer, players can revel in double the fun on their initial deposit. This promotion enhances the gaming experience, providing more opportunities to win big across various games.
4. 20 Spin Times = Get Big Bonus (8,888P) - Spin Your Way to Glory!
Spin your way to substantial bonuses with the "20 Spin Times" promotion. Accumulate spins and stand a chance to win an impressive bonus of 8,888P. This promotion adds an extra layer of excitement to the gameplay, combining luck and strategy for maximum enjoyment.
5. Daily Check-in = Turnover 5X?! - Daily Rewards Await!
Consistency is key at C88. By simply logging in daily, players not only bask in the thrill of gaming but also stand a chance to multiply their turnovers by 5X. Daily check-ins bring additional perks, making every day a rewarding experience for dedicated players.
6. 7 Day Deposit 300 = Get 1,500P - Unlock Deposit Rewards!
For those eager to seize opportunities, the "7 Day Deposit" promotion is a game-changer. Deposit 300 and receive a generous reward of 1,500P. This promotion encourages players to explore the platform further and maximize their gaming potential.
7. Invite 100 Users = Get 10,000 PESO - Share the Excitement!
C88 believes in the strength of community. Invite friends and fellow gamers to join the excitement, and for every 100 users, receive an incredible reward of 10,000 PESO. Sharing the joy of gaming has never been more rewarding.
8. C88 New Member Get 100% First Deposit Bonus - Exclusive Benefits!
New members are in for a treat with an exclusive 100% First Deposit Bonus. C88 ensures that everyone kicks off their gaming journey with a boost, setting the stage for an exhilarating experience filled with opportunities to win.
9. All Pass Get C88 Extra Big Bonus 1000 PESO - Unlock Unlimited Rewards!
For avid players exploring every nook and cranny of C88, the "All Pass Get C88 Extra Big Bonus" offers an additional 1000 PESO. This promotion rewards those who embrace the full spectrum of games and features available on the platform.
Eager to dive into the excitement? Visit C88 now and unlock a world of gaming like never before. Don't miss out on the excitement, bonuses, and wins that await you at C88. Join the community today and let the games begin! #c88 #c88login #c88bet #c88bonus #c88win -
Ad impossibilia nemo tenetur — Нельзя заставлять выполнить невозможное.
http://batmanapollo.ru -
Как моряк, ищущий пристанище в шторм, так и человек, оказавшийся в трудной финансовой ситуации, обращается к [url=https://credit-world.ru/]займам на карту без отказов[/url]. Эти займы – словно спасательный круг в море неопределенности, предлагая быстрое и надежное решение для тех, кто борется с волнами экономической нестабильности.
-
Daftar game judi slot online terbaru menang jackpot disini bersama bandar togel situs gacor gampang menang terpercaya dengan bonus terbaik nomor 1 di Indonesia GACHA99
-
Антон Винер жена
FOSIL4D -
Can erectile dysfunction be a symptom of bladder cancer order sildenafil 100mg generic.
-
How long do breakups last where to buy fildena 100
-
オンラインカジノレビュー
オンラインカジノレビュー:選択の重要性
オンラインカジノの世界への入門
オンラインカジノは、インターネット上で提供される多様な賭博ゲームを通じて、世界中のプレイヤーに無限の娯楽を提供しています。これらのプラットフォームは、スロット、テーブルゲーム、ライブディーラーゲームなど、様々なゲームオプションを提供し、実際のカジノの経験を再現します。
オンラインカジノレビューの重要性
オンラインカジノを選択する際には、オンラインカジノレビューの役割が非常に重要です。レビューは、カジノの信頼性、ゲームの多様性、顧客サービスの質、ボーナスオファー、支払い方法、出金条件など、プレイヤーが知っておくべき重要な情報を提供します。良いレビューは、利用者の実際の体験に基づいており、新規プレイヤーがカジノを選択する際の重要なガイドとなります。
レビューを読む際のポイント
信頼性とライセンス:カジノが適切なライセンスを持ち、公平なゲームプレイを提供しているかどうか。
ゲームの選択:多様なゲームオプションが提供されているかどうか。
ボーナスとプロモーション:魅力的なウェルカムボーナス、リロードボーナス、VIPプログラムがあるかどうか。
顧客サポート:サポートの応答性と有効性。
出金オプション:出金の速度と方法。
プレイヤーの体験
良いオンラインカジノレビューは、実際のプレイヤーの体験に基づいています。これには、ゲームプレイの楽しさ、カスタマーサポートへの対応、そして出金プロセスの簡単さが含まれます。プレイヤーのフィードバックは、カジノの品質を判断するのに役立ちます。
結論
オンラインカジノを選択する際には、詳細なオンラインカジノレビューを参照することが重要です。これらのレビューは、安全で楽しいギャンブル体験を確実にするための信頼できる情報源となります。適切なカジノを選ぶことは、オンラインギャンブルでの成功への第一歩です。 -
Виртуальные VPS серверы Windows
Абузоустойчивый серверы, идеально подходит для работы програмным обеспечением как XRumer так и GSA
Стабильная работа без сбоев, высокая поточность несравнима с провайдерами в квартире или офисе, где есть ограничение.
Высокоскоростной Интернет: До 1000 Мбит/с
Скорость интернет-соединения - еще один важный параметр для успешной работы вашего проекта. Наши VPS/VDS серверы, поддерживающие Windows и Linux, обеспечивают доступ к интернету со скоростью до 1000 Мбит/с, обеспечивая быструю загрузку веб-страниц и высокую производительность онлайн-приложений. -
Medications and Vascular Health - Maintaining Strong Circulation lipitor 80 mg price.
-
オンラインカジノレビュー:選択の重要性
オンラインカジノの世界への入門
オンラインカジノは、インターネット上で提供される多様な賭博ゲームを通じて、世界中のプレイヤーに無限の娯楽を提供しています。これらのプラットフォームは、スロット、テーブルゲーム、ライブディーラーゲームなど、様々なゲームオプションを提供し、実際のカジノの経験を再現します。
オンラインカジノレビューの重要性
オンラインカジノを選択する際には、オンラインカジノレビューの役割が非常に重要です。レビューは、カジノの信頼性、ゲームの多様性、顧客サービスの質、ボーナスオファー、支払い方法、出金条件など、プレイヤーが知っておくべき重要な情報を提供します。良いレビューは、利用者の実際の体験に基づいており、新規プレイヤーがカジノを選択する際の重要なガイドとなります。
レビューを読む際のポイント
信頼性とライセンス:カジノが適切なライセンスを持ち、公平なゲームプレイを提供しているかどうか。
ゲームの選択:多様なゲームオプションが提供されているかどうか。
ボーナスとプロモーション:魅力的なウェルカムボーナス、リロードボーナス、VIPプログラムがあるかどうか。
顧客サポート:サポートの応答性と有効性。
出金オプション:出金の速度と方法。
プレイヤーの体験
良いオンラインカジノレビューは、実際のプレイヤーの体験に基づいています。これには、ゲームプレイの楽しさ、カスタマーサポートへの対応、そして出金プロセスの簡単さが含まれます。プレイヤーのフィードバックは、カジノの品質を判断するのに役立ちます。
結論
オンラインカジノを選択する際には、詳細なオンラインカジノレビューを参照することが重要です。これらのレビューは、安全で楽しいギャンブル体験を確実にするための信頼できる情報源となります。適切なカジノを選ぶことは、オンラインギャンブルでの成功への第一歩です。 -
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現代的展開
オンラインカジノの世界は、技術の進歩と共に急速に進化しています。これらのプラットフォームは、従来の実際のカジノの体験をデジタル空間に移し、プレイヤーに新しい形式の娯楽を提供しています。オンラインカジノは、スロットマシン、ポーカー、ブラックジャック、ルーレットなど、さまざまなゲームを提供しており、実際のカジノの興奮を維持しながら、アクセスの容易さと利便性を提供します。
一方で、オンラインギャンブルは、より広範な概念であり、スポーツベッティング、宝くじ、バーチャルスポーツ、そしてオンラインカジノゲームまでを含んでいます。インターネットとモバイルテクノロジーの普及により、オンラインギャンブルは世界中で大きな人気を博しています。オンラインプラットフォームは、伝統的な賭博施設に比べて、より多様なゲーム選択、便利なアクセス、そしてしばしば魅力的なボーナスやプロモーションを提供しています。
安全性と規制
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの世界では、安全性と規制が非常に重要です。多くの国々では、オンラインギャンブルを規制する法律があり、安全なプレイ環境を確保するためのライセンスシステムを設けています。これにより、不正行為や詐欺からプレイヤーを守るとともに、責任ある賭博の促進が図られています。
技術の進歩
最新のテクノロジーは、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの体験を一層豊かにしています。例えば、仮想現実(VR)技術の使用は、プレイヤーに没入型のギャンブル体験を提供し、実際のカジノにいるかのような感覚を生み出しています。また、ブロックチェーン技術の導入は、より透明で安全な取引を可能にし、プレイヤーの信頼を高めています。
未来への展望
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルは、今後も技術の進歩とともに進化し続けるでしょう。人工知能(AI)の更なる統合、モバイル技術の発展、さらには新しいゲームの創造により、この分野は引き続き成長し、世界中のプレイヤーに新しい娯楽の形を提供し続けることでしょう。
この記事では、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現状、安全性、技術の影響、そして将来の展望に焦点を当てています。この分野は、技術革新によって絶えず変化し続ける魅力的な領域です。 -
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現代的展開
オンラインカジノの世界は、技術の進歩と共に急速に進化しています。これらのプラットフォームは、従来の実際のカジノの体験をデジタル空間に移し、プレイヤーに新しい形式の娯楽を提供しています。オンラインカジノは、スロットマシン、ポーカー、ブラックジャック、ルーレットなど、さまざまなゲームを提供しており、実際のカジノの興奮を維持しながら、アクセスの容易さと利便性を提供します。
一方で、オンラインギャンブルは、より広範な概念であり、スポーツベッティング、宝くじ、バーチャルスポーツ、そしてオンラインカジノゲームまでを含んでいます。インターネットとモバイルテクノロジーの普及により、オンラインギャンブルは世界中で大きな人気を博しています。オンラインプラットフォームは、伝統的な賭博施設に比べて、より多様なゲーム選択、便利なアクセス、そしてしばしば魅力的なボーナスやプロモーションを提供しています。
安全性と規制
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの世界では、安全性と規制が非常に重要です。多くの国々では、オンラインギャンブルを規制する法律があり、安全なプレイ環境を確保するためのライセンスシステムを設けています。これにより、不正行為や詐欺からプレイヤーを守るとともに、責任ある賭博の促進が図られています。
技術の進歩
最新のテクノロジーは、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの体験を一層豊かにしています。例えば、仮想現実(VR)技術の使用は、プレイヤーに没入型のギャンブル体験を提供し、実際のカジノにいるかのような感覚を生み出しています。また、ブロックチェーン技術の導入は、より透明で安全な取引を可能にし、プレイヤーの信頼を高めています。
未来への展望
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルは、今後も技術の進歩とともに進化し続けるでしょう。人工知能(AI)の更なる統合、モバイル技術の発展、さらには新しいゲームの創造により、この分野は引き続き成長し、世界中のプレイヤーに新しい娯楽の形を提供し続けることでしょう。
この記事では、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現状、安全性、技術の影響、そして将来の展望に焦点を当てています。この分野は、技術革新によって絶えず変化し続ける魅力的な領域です。 -
オンラインカジノ
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現代的展開
オンラインカジノの世界は、技術の進歩と共に急速に進化しています。これらのプラットフォームは、従来の実際のカジノの体験をデジタル空間に移し、プレイヤーに新しい形式の娯楽を提供しています。オンラインカジノは、スロットマシン、ポーカー、ブラックジャック、ルーレットなど、さまざまなゲームを提供しており、実際のカジノの興奮を維持しながら、アクセスの容易さと利便性を提供します。
一方で、オンラインギャンブルは、より広範な概念であり、スポーツベッティング、宝くじ、バーチャルスポーツ、そしてオンラインカジノゲームまでを含んでいます。インターネットとモバイルテクノロジーの普及により、オンラインギャンブルは世界中で大きな人気を博しています。オンラインプラットフォームは、伝統的な賭博施設に比べて、より多様なゲーム選択、便利なアクセス、そしてしばしば魅力的なボーナスやプロモーションを提供しています。
安全性と規制
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの世界では、安全性と規制が非常に重要です。多くの国々では、オンラインギャンブルを規制する法律があり、安全なプレイ環境を確保するためのライセンスシステムを設けています。これにより、不正行為や詐欺からプレイヤーを守るとともに、責任ある賭博の促進が図られています。
技術の進歩
最新のテクノロジーは、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの体験を一層豊かにしています。例えば、仮想現実(VR)技術の使用は、プレイヤーに没入型のギャンブル体験を提供し、実際のカジノにいるかのような感覚を生み出しています。また、ブロックチェーン技術の導入は、より透明で安全な取引を可能にし、プレイヤーの信頼を高めています。
未来への展望
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルは、今後も技術の進歩とともに進化し続けるでしょう。人工知能(AI)の更なる統合、モバイル技術の発展、さらには新しいゲームの創造により、この分野は引き続き成長し、世界中のプレイヤーに新しい娯楽の形を提供し続けることでしょう。
この記事では、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現状、安全性、技術の影響、そして将来の展望に焦点を当てています。この分野は、技術革新によって絶えず変化し続ける魅力的な領域です。 -
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現代的展開
オンラインカジノの世界は、技術の進歩と共に急速に進化しています。これらのプラットフォームは、従来の実際のカジノの体験をデジタル空間に移し、プレイヤーに新しい形式の娯楽を提供しています。オンラインカジノは、スロットマシン、ポーカー、ブラックジャック、ルーレットなど、さまざまなゲームを提供しており、実際のカジノの興奮を維持しながら、アクセスの容易さと利便性を提供します。
一方で、オンラインギャンブルは、より広範な概念であり、スポーツベッティング、宝くじ、バーチャルスポーツ、そしてオンラインカジノゲームまでを含んでいます。インターネットとモバイルテクノロジーの普及により、オンラインギャンブルは世界中で大きな人気を博しています。オンラインプラットフォームは、伝統的な賭博施設に比べて、より多様なゲーム選択、便利なアクセス、そしてしばしば魅力的なボーナスやプロモーションを提供しています。
安全性と規制
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの世界では、安全性と規制が非常に重要です。多くの国々では、オンラインギャンブルを規制する法律があり、安全なプレイ環境を確保するためのライセンスシステムを設けています。これにより、不正行為や詐欺からプレイヤーを守るとともに、責任ある賭博の促進が図られています。
技術の進歩
最新のテクノロジーは、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの体験を一層豊かにしています。例えば、仮想現実(VR)技術の使用は、プレイヤーに没入型のギャンブル体験を提供し、実際のカジノにいるかのような感覚を生み出しています。また、ブロックチェーン技術の導入は、より透明で安全な取引を可能にし、プレイヤーの信頼を高めています。
未来への展望
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルは、今後も技術の進歩とともに進化し続けるでしょう。人工知能(AI)の更なる統合、モバイル技術の発展、さらには新しいゲームの創造により、この分野は引き続き成長し、世界中のプレイヤーに新しい娯楽の形を提供し続けることでしょう。
この記事では、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現状、安全性、技術の影響、そして将来の展望に焦点を当てています。この分野は、技術革新によって絶えず変化し続ける魅力的な領域です。 -
[url=https://besthost.by/virtualhosting/]хостинг сайта[/url]
Когда речь заходит о создании своего собственного сайта, выбор хостинга играет огромную роль. Ведь именно хостинг будет определять доступность и быстродействие вашего сайта для пользователей. Если вы находитесь в Беларуси и ищете надежного хостинг-провайдера, то BestHost.BY - это отличный выбор. BestHost.BY - одна из ведущих хостинг-компаний в Беларуси, предоставляющая высококачественные услуги уже на протяжении 15 лет. -
Абузоустойчивый серверов для Хрумера и GSA AMSTERDAM!!!
Оптимальная Настройка: Включение Аппаратной Виртуализации
При обсуждении виртуальных серверов (VPS/VDS) и дедикатед серверов, важно также уделить внимание оптимальной настройке, включая аппаратную виртуализацию. Этот важный аспект может значительно повлиять на производительность вашего сервера.
Высокоскоростной Интернет: До 1000 Мбит/с -
Абузоустойчивый сервер для работы с Хрумером, GSA и всевозможными скриптами!
Есть дополнительная системах скидок, читайте описание в разделе оплата
Виртуальные сервера (VPS/VDS) и Дедик Сервер: Оптимальное Решение для Вашего Проекта
В мире современных вычислений виртуальные сервера (VPS/VDS) и дедик сервера становятся ключевыми элементами успешного бизнеса и онлайн-проектов. Выбор оптимальной операционной системы и типа сервера являются решающими шагами в создании надежной и эффективной инфраструктуры. Наши VPS/VDS серверы Windows и Linux, доступные от 13 рублей, а также дедик серверы, предлагают целый ряд преимуществ, делая их неотъемлемыми инструментами для развития вашего проекта. -
Дедик сервер
Абузоустойчивый сервер для работы с Хрумером, GSA и всевозможными скриптами!
Есть дополнительная системах скидок, читайте описание в разделе оплата
Виртуальные сервера (VPS/VDS) и Дедик Сервер: Оптимальное Решение для Вашего Проекта
В мире современных вычислений виртуальные сервера (VPS/VDS) и дедик сервера становятся ключевыми элементами успешного бизнеса и онлайн-проектов. Выбор оптимальной операционной системы и типа сервера являются решающими шагами в создании надежной и эффективной инфраструктуры. Наши VPS/VDS серверы Windows и Linux, доступные от 13 рублей, а также дедик серверы, предлагают целый ряд преимуществ, делая их неотъемлемыми инструментами для развития вашего проекта. -
Дедикатед Серверы
Абузоустойчивые сервера в Амстердаме, они позволят работать с сайтами которые не открываются в РФ, работая Хрумером и GSA пробив намного выше.
Виртуальные сервера (VPS/VDS) и Дедик Сервер: Оптимальное Решение для Вашего Проекта
В мире современных вычислений виртуальные сервера (VPS/VDS) и дедик сервера становятся ключевыми элементами успешного бизнеса и онлайн-проектов. Выбор оптимальной операционной системы и типа сервера являются решающими шагами в создании надежной и эффективной инфраструктуры. Наши VPS/VDS серверы Windows и Linux, доступные от 13 рублей, а также дедик серверы, предлагают целый ряд преимуществ, делая их неотъемлемыми инструментами для развития вашего проекта.
Высокоскоростной Интернет: До 1000 Мбит/с -
[url=https://afishkasochi.ru]1xbet вход[/url] - это популярная букмекерская компания, предлагающая широкий выбор ставок на спорт, казино и многое другое. С высокими коэффициентами и удобным интерфейсом, 1xbet привлекает множество игроков. Он также предоставляет возможность онлайн-трансляций событий. 1xbet создает захватывающий игровой опыт для своих пользователей.
-
オンラインカジノ
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現代的展開
オンラインカジノの世界は、技術の進歩と共に急速に進化しています。これらのプラットフォームは、従来の実際のカジノの体験をデジタル空間に移し、プレイヤーに新しい形式の娯楽を提供しています。オンラインカジノは、スロットマシン、ポーカー、ブラックジャック、ルーレットなど、さまざまなゲームを提供しており、実際のカジノの興奮を維持しながら、アクセスの容易さと利便性を提供します。
一方で、オンラインギャンブルは、より広範な概念であり、スポーツベッティング、宝くじ、バーチャルスポーツ、そしてオンラインカジノゲームまでを含んでいます。インターネットとモバイルテクノロジーの普及により、オンラインギャンブルは世界中で大きな人気を博しています。オンラインプラットフォームは、伝統的な賭博施設に比べて、より多様なゲーム選択、便利なアクセス、そしてしばしば魅力的なボーナスやプロモーションを提供しています。
安全性と規制
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの世界では、安全性と規制が非常に重要です。多くの国々では、オンラインギャンブルを規制する法律があり、安全なプレイ環境を確保するためのライセンスシステムを設けています。これにより、不正行為や詐欺からプレイヤーを守るとともに、責任ある賭博の促進が図られています。
技術の進歩
最新のテクノロジーは、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの体験を一層豊かにしています。例えば、仮想現実(VR)技術の使用は、プレイヤーに没入型のギャンブル体験を提供し、実際のカジノにいるかのような感覚を生み出しています。また、ブロックチェーン技術の導入は、より透明で安全な取引を可能にし、プレイヤーの信頼を高めています。
未来への展望
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルは、今後も技術の進歩とともに進化し続けるでしょう。人工知能(AI)の更なる統合、モバイル技術の発展、さらには新しいゲームの創造により、この分野は引き続き成長し、世界中のプレイヤーに新しい娯楽の形を提供し続けることでしょう。
この記事では、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現状、安全性、技術の影響、そして将来の展望に焦点を当てています。この分野は、技術革新によって絶えず変化し続ける魅力的な領域です。 -
オンラインカジノ
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現代的展開
オンラインカジノの世界は、技術の進歩と共に急速に進化しています。これらのプラットフォームは、従来の実際のカジノの体験をデジタル空間に移し、プレイヤーに新しい形式の娯楽を提供しています。オンラインカジノは、スロットマシン、ポーカー、ブラックジャック、ルーレットなど、さまざまなゲームを提供しており、実際のカジノの興奮を維持しながら、アクセスの容易さと利便性を提供します。
一方で、オンラインギャンブルは、より広範な概念であり、スポーツベッティング、宝くじ、バーチャルスポーツ、そしてオンラインカジノゲームまでを含んでいます。インターネットとモバイルテクノロジーの普及により、オンラインギャンブルは世界中で大きな人気を博しています。オンラインプラットフォームは、伝統的な賭博施設に比べて、より多様なゲーム選択、便利なアクセス、そしてしばしば魅力的なボーナスやプロモーションを提供しています。
安全性と規制
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの世界では、安全性と規制が非常に重要です。多くの国々では、オンラインギャンブルを規制する法律があり、安全なプレイ環境を確保するためのライセンスシステムを設けています。これにより、不正行為や詐欺からプレイヤーを守るとともに、責任ある賭博の促進が図られています。
技術の進歩
最新のテクノロジーは、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの体験を一層豊かにしています。例えば、仮想現実(VR)技術の使用は、プレイヤーに没入型のギャンブル体験を提供し、実際のカジノにいるかのような感覚を生み出しています。また、ブロックチェーン技術の導入は、より透明で安全な取引を可能にし、プレイヤーの信頼を高めています。
未来への展望
オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルは、今後も技術の進歩とともに進化し続けるでしょう。人工知能(AI)の更なる統合、モバイル技術の発展、さらには新しいゲームの創造により、この分野は引き続き成長し、世界中のプレイヤーに新しい娯楽の形を提供し続けることでしょう。
この記事では、オンラインカジノとオンラインギャンブルの現状、安全性、技術の影響、そして将来の展望に焦点を当てています。この分野は、技術革新によって絶えず変化し続ける魅力的な領域です。 -
Who was born first in 2022 cheap viagra pills
-
[url=https://30palomnik.ru]1xbet зеркало прямо сейчас[/url] - это популярная букмекерская компания, предлагающая широкий выбор ставок на спорт, казино и многое другое. С высокими коэффициентами и удобным интерфейсом, 1xbet привлекает множество игроков. Он также предоставляет возможность онлайн-трансляций событий. 1xbet создает захватывающий игровой опыт для своих пользователей.
-
Абузоустойчивый серверов для Хрумера и GSA AMSTERDAM!!!
Высокоскоростной Интернет: До 1000 Мбит/с
Скорость интернет-соединения играет решающую роль в успешной работе вашего проекта. Наши VPS/VDS серверы, поддерживающие Windows и Linux, обеспечивают доступ к интернету со скоростью до 1000 Мбит/с. Это гарантирует быструю загрузку веб-страниц и высокую производительность онлайн-приложений на обеих операционных системах.
Итак, при выборе виртуального выделенного сервера VPS, обеспечьте своему проекту надежность, высокую производительность и защиту от DDoS. Получите доступ к качественной инфраструктуре с поддержкой Windows и Linux уже от 13 рублей -
Абузоустойчивый серверов для Хрумера и GSA AMSTERDAM!!!
Высокоскоростной Интернет: До 1000 Мбит/с
Скорость интернет-соединения играет решающую роль в успешной работе вашего проекта. Наши VPS/VDS серверы, поддерживающие Windows и Linux, обеспечивают доступ к интернету со скоростью до 1000 Мбит/с. Это гарантирует быструю загрузку веб-страниц и высокую производительность онлайн-приложений на обеих операционных системах.
Итак, при выборе виртуального выделенного сервера VPS, обеспечьте своему проекту надежность, высокую производительность и защиту от DDoS. Получите доступ к качественной инфраструктуре с поддержкой Windows и Linux уже от 13 рублей -
Абузоустойчивые сервера в Амстердаме, они позволят работать с сайтами которые не открываются в РФ, работая Хрумером и GSA пробив намного выше.
Аренда виртуального сервера (VPS): Эффективность, Надежность и Защита от DDoS от 13 рублей
Выбор виртуального сервера - это важный этап в создании успешной инфраструктуры для вашего проекта. Наши VPS серверы предоставляют аренду как под операционные системы Windows, так и Linux, с доступом к накопителям SSD eMLC. Эти накопители гарантируют высокую производительность и надежность, обеспечивая бесперебойную работу ваших приложений независимо от выбранной операционной системы. -
Абузоустойчивые сервера в Амстердаме, они позволят работать с сайтами которые не открываются в РФ, работая Хрумером и GSA пробив намного выше.
Аренда виртуального сервера (VPS): Эффективность, Надежность и Защита от DDoS от 13 рублей
Выбор виртуального сервера - это важный этап в создании успешной инфраструктуры для вашего проекта. Наши VPS серверы предоставляют аренду как под операционные системы Windows, так и Linux, с доступом к накопителям SSD eMLC. Эти накопители гарантируют высокую производительность и надежность, обеспечивая бесперебойную работу ваших приложений независимо от выбранной операционной системы. -
Абузоустойчивый сервер для работы с Хрумером, GSA и всевозможными скриптами!
Есть дополнительная системах скидок, читайте описание в разделе оплата
Высокоскоростной Интернет: До 1000 Мбит/с
Скорость интернет-соединения играет решающую роль в успешной работе вашего проекта. Наши VPS/VDS серверы, поддерживающие Windows и Linux, обеспечивают доступ к интернету со скоростью до 1000 Мбит/с. Это гарантирует быструю загрузку веб-страниц и высокую производительность онлайн-приложений на обеих операционных системах.
Итак, при выборе виртуального выделенного сервера VPS, обеспечьте своему проекту надежность, высокую производительность и защиту от DDoS. Получите доступ к качественной инфраструктуре с поддержкой Windows и Linux уже от 13 рублей -
виртуальный выделенный сервер vps
Абузоустойчивый сервер для работы с Хрумером, GSA и всевозможными скриптами!
Есть дополнительная системах скидок, читайте описание в разделе оплата
Высокоскоростной Интернет: До 1000 Мбит/с
Скорость интернет-соединения играет решающую роль в успешной работе вашего проекта. Наши VPS/VDS серверы, поддерживающие Windows и Linux, обеспечивают доступ к интернету со скоростью до 1000 Мбит/с. Это гарантирует быструю загрузку веб-страниц и высокую производительность онлайн-приложений на обеих операционных системах.
Итак, при выборе виртуального выделенного сервера VPS, обеспечьте своему проекту надежность, высокую производительность и защиту от DDoS. Получите доступ к качественной инфраструктуре с поддержкой Windows и Linux уже от 13 рублей -
Аренда мощного дедика (VPS): Абузоустойчивость, Эффективность, Надежность и Защита от DDoS от 13 рублей
Выбор виртуального сервера - это важный этап в создании успешной инфраструктуры для вашего проекта. Наши VPS серверы предоставляют аренду как под операционные системы Windows, так и Linux, с доступом к накопителям SSD eMLC. Эти накопители гарантируют высокую производительность и надежность, обеспечивая бесперебойную работу ваших приложений независимо от выбранной операционной системы. -
Аренда мощного дедика (VPS): Абузоустойчивость, Эффективность, Надежность и Защита от DDoS от 13 рублей
Выбор виртуального сервера - это важный этап в создании успешной инфраструктуры для вашего проекта. Наши VPS серверы предоставляют аренду как под операционные системы Windows, так и Linux, с доступом к накопителям SSD eMLC. Эти накопители гарантируют высокую производительность и надежность, обеспечивая бесперебойную работу ваших приложений независимо от выбранной операционной системы. -
Абузоустойчивый сервер для работы с Хрумером, GSA и всевозможными скриптами!
Есть дополнительная системах скидок, читайте описание в разделе оплата
Высокоскоростной Интернет: До 1000 Мбит/с**
Скорость интернет-соединения - еще один важный момент для успешной работы вашего проекта. Наши VPS серверы, арендуемые под Windows и Linux, предоставляют доступ к интернету со скоростью до 1000 Мбит/с, обеспечивая быструю загрузку веб-страниц и высокую производительность онлайн-приложений на обеих операционных системах. -
Абузоустойчивый сервер для работы с Хрумером, GSA и всевозможными скриптами!
Есть дополнительная системах скидок, читайте описание в разделе оплата
Высокоскоростной Интернет: До 1000 Мбит/с**
Скорость интернет-соединения - еще один важный момент для успешной работы вашего проекта. Наши VPS серверы, арендуемые под Windows и Linux, предоставляют доступ к интернету со скоростью до 1000 Мбит/с, обеспечивая быструю загрузку веб-страниц и высокую производительность онлайн-приложений на обеих операционных системах. -
[youtube]z8ghSAWZZy8[/youtube]
-
[youtube]z8ghSAWZZy8[/youtube]
-
Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a blue spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Tie us as we navigate by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and examine the repercussions of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or simply curious helter-skelter the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to commencement in compensation insightful, friendly, and illuminating content. Stop tuned for systematic updates and sound heavy into the men of software with us!
https://superchange.site/
https://mpanikar.ru/
https://btcworm.store/
https://floatchange.site/
https://btcboss.site/
https://crypster.store/
https://crupto-market24.site/
https://gaffarov.ru/
https://rocketchange.site/
https://exchangex.store/ -
Посоветуйте VPS
Поставщик предоставляет основное управление виртуальными серверами (VPS), предлагая клиентам разнообразие операционных систем для выбора (Windows Server, Linux CentOS, Debian). -
Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software situation and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a broad spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Join us as we navigate during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and examine the repercussions of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy individual, or entirely kinky roughly the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to originator in compensation insightful, engaging, and revealing content. Stop tuned for uniform updates and dive heavy into the planet of software with us!
https://i-obmen.site/
https://mfonline.ru/
https://eurobit.site/
https://korablik-zabeg.ru/
https://btcboss.site/
https://garantex.one/
https://24expay.site/
https://nicechange.shop/
https://avtoavm.ru/
https://sovagg.site/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software development and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we navigate through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and talk over the effect of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a acclimatized developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or artlessly curious about the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to documentation quest of insightful, friendly, and revealing content. Interrupt tuned object of systematic updates and dip heavy into the everyone of software with us!
https://topcash.site/
https://1Mile-co.site/
https://kanztrend.ru/
https://kassacc.site/
https://mine-exchange.store/
https://copyrait.ru/
https://wmbox.site/
https://fastchange.site/
https://delets.site/
https://tytcash.site/ -
Agreeable to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software expansion and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a blue spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Meet us as we sail with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and review the collide with of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy individual, or artlessly curious helter-skelter the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to source for insightful, appealing, and revealing content. Stop tuned object of systematic updates and dive unfathomable into the planet of software with us!
https://abcobmen.site/
https://24expay.site/
https://i-obmen.site/
https://superchange.site/
https://flychange.site/
https://alfachange.store/
https://24xchannge.site/
https://cointok.site/
https://coco-pay.site/
https://bixter.site/ -
Agreeable to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software development and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a broad spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we captain during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and review the collide with of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or simply extraordinary about the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to documentation quest of insightful, friendly, and revealing content. Interrupt tuned in the interest semi-monthly updates and jump extensive into the planet of software with us!
https://paymarket.site/
https://exhubio.site/
https://nicechange.shop/
https://delfon.ru/
https://1Mile-co.site/
https://myxa-cc.site/
https://alfachange.store/
https://50cents.site/
https://grandchange.store/
https://crybex.site/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Tie us as we navigate during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and examine the repercussions of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy own, or natively curious back the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to originator quest of insightful, appealing, and informative content. Interrupt tuned for regular updates and dip unfathomable into the men of software with us!
https://onlaini.ru/
https://bchange.site/
https://blablamoney.site/
https://payget.site/
https://fly-pay.site/
https://exchangesumo.site/
https://paymarket.site/
https://uniochange.site/
https://ychanger.site/
https://news-obovsem.ru/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software situation and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Meet us as we journey with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and talk over the impact of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or natively extraordinary helter-skelter the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to commencement in compensation insightful, friendly, and informative content. Discontinuance tuned in the interest semi-monthly updates and sound unfathomable into the everyone of software with us!
https://cryptokacca.site/
https://coendrop.site/
https://myxa-cc.site/
https://cripthub.site/
https://megachange.site/
https://btcworm.store/
https://nordchange.site/
https://cryptomoneypro.site/
https://baksman.store/
https://superchange.site/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software situation and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a broad spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Meet us as we navigate during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and discuss the impact of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy own, or natively odd helter-skelter the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to originator in compensation insightful, delightful, and edifying content. Stop tuned object of semi-monthly updates and dive extensive into the world of software with us!
https://darken-biz.site/
https://galaxyflowers.ru/
https://cerberltd.site/
https://eurobit.site/
https://flashobmen.site/
https://korablik-zabeg.ru/
https://coco-pay.site/
https://swopcoin-cc.site/
https://swapex.site/
https://btcworm.store/ -
Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software situation and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a blue spectrum of topics designed to educate both tech enthusiasts and bustle professionals. Tie us as we navigate by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and review the effect of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy own, or artlessly curious back the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to commencement quest of insightful, friendly, and informative content. Stay tuned in the interest semi-monthly updates and dive unfathomable into the world of software with us!
https://delfon.ru/
https://mpanikar.ru/
https://coin-bank.site/
https://z-exchange.site/
https://garantex.one/
https://clean-exchange.site/
https://coendrop.site/
https://baksman.store/
https://copyrait.ru/
https://paspar.site/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software situation and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a blue spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Tie us as we journey with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and review the collide with of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or natively extraordinary back the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to source for insightful, appealing, and informative content. Stay tuned in the interest regular updates and sound unfathomable into the men of software with us!
https://btcsale.store/
https://cryptomoneypro.site/
https://delets.site/
https://coolcoin.store/
https://auto-noginsk.ru/
https://kazds.ru/
https://pushpayer.site/
https://flychange.site/
https://kassacc.site/
https://sof-panina.ru/ -
Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a blue spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we captain with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and discuss the repercussions of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy individual, or entirely extraordinary helter-skelter the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to source in compensation insightful, engaging, and edifying content. Stay tuned object of systematic updates and jump extensive into the everyone of software with us!
https://altinbit.site/
https://kazds.ru/
https://btcbit.store/
https://4ange.site/
https://pushpayer.site/
https://aple-system.ru/
https://exline-pro.site/
https://floatchange.site/
https://prostocash.store/
https://eobmen.site/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software development and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a blue spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Tie us as we navigate by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and discuss the repercussions of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a acclimatized developer, a tech-savvy own, or entirely odd about the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to documentation fit insightful, delightful, and illuminating content. Stay tuned in the service of semi-monthly updates and jump unfathomable into the planet of software with us!
https://betatransfer.site/
https://crypster.store/
https://alfachange.store/
https://fastexchange.site/
https://exmoney.store/
https://blablamoney.site/
https://el-change.site/
https://kanztrend.ru/
https://bixter.site/
https://ychanger.site/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software development and technology. Here, we inspect the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a blue spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Meet us as we captain by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and review the repercussions of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or simply odd roughly the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to documentation fit insightful, appealing, and edifying content. Stop tuned in the interest semi-monthly updates and jump extensive into the everyone of software with us!
https://4ange.site/
https://uniochange.site/
https://bitpayes.site/
https://kgltd.ru/
https://abcobmen.site/
https://unicash.site/
https://wmglobus.site/
https://traiderideal.site/
https://fehupay.site/
https://el-change.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software development and technology. Here, we inspect the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a blue spectrum of topics designed to educate both tech enthusiasts and bustle professionals. Join us as we captain during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and talk over the effect of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or simply kinky about the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to source in compensation insightful, friendly, and informative content. Stay tuned object of regular updates and jump extensive into the planet of software with us!
https://swopcoin-cc.site/
https://abcobmen.site/
https://coco-pay.site/
https://moment-express.site/
https://darken-biz.site/
https://n-obmen.site/
https://traiderideal.site/
https://blablachange.site/
https://xchange-cash.site/
https://magnatus.site/ -
Agreeable to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software expansion and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a generalized spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Tie us as we sail during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and examine the repercussions of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or simply extraordinary helter-skelter the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to documentation for insightful, delightful, and illuminating content. Discontinuance tuned in the service of semi-monthly updates and dip heavy into the world of software with us!
https://grambit.site/
https://itez.store/
https://paaywallet.store/
https://envelopez.ru/
https://xchangerpro.site/
https://bitality.store/
https://clean-exchange.site/
https://instabit.store/
https://jpmarket.site/
https://eurobit.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software development and technology. Here, we inspect the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a generalized spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Tie us as we journey during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and review the collide with of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy individual, or simply extraordinary roughly the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to source quest of insightful, delightful, and revealing content. Interrupt tuned in the service of regular updates and dip extensive into the world of software with us!
https://btchange.site/
https://magnatus.site/
https://mchange.store/
https://24payvank.store/
https://avtomatydengi.ru/
https://megachange.site/
https://cryptogin.site/
https://news-obovsem.ru/
https://staff-obmen.site/
https://btcworm.store/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software expansion and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a broad spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we journey during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and examine the effect of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a acclimatized developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or natively odd helter-skelter the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to commencement in compensation insightful, friendly, and informative content. Stop tuned for uniform updates and sound heavy into the planet of software with us!
https://camp-center.ru/
https://carsused.ru/
https://allwow.ru/
https://uniochange.site/
https://cryptomoneypro.site/
https://exchangekey.site/
https://ptcinnovationforum.ru/
https://z-exchange.site/
https://mine-exchange.store/
https://coco-pay.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software situation and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a blue spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Join us as we captain with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and examine the collide with of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a acclimatized developer, a tech-savvy own, or simply extraordinary roughly the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to commencement quest of insightful, appealing, and revealing content. Stop tuned in the service of uniform updates and dip extensive into the planet of software with us!
https://d-obmen.site/
https://coinstartcc.site/
https://exwhite.site/
https://60cek.site/
https://alfachange.store/
https://anonex.site/
https://onlaini.ru/
https://n-obmen.site/
https://mfonline.ru/
https://grandchange.store/ -
Agreeable to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we navigate through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and talk over the effect of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or entirely curious helter-skelter the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to commencement for insightful, delightful, and illuminating content. Stop tuned for systematic updates and jump heavy into the men of software with us!
https://zemlya23.ru/
https://24expay.site/
https://crybex.site/
https://e-change.site/
https://coco-pay.site/
https://btchange.site/
https://auto-noginsk.ru/
https://coinblinker.site/
https://keine-exchange.site/
https://envelopez.ru/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and bustle professionals. Meet us as we journey with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and discuss the impact of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy own, or artlessly curious about the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to source in compensation insightful, delightful, and edifying content. Stay tuned object of semi-monthly updates and jump heavy into the men of software with us!
https://bitpayes.site/
https://platov-co.site/
https://top-exchange.xyz/
https://coendrop.site/
https://grambit.site/
https://crybex.site/
https://24expay.site/
https://darken-biz.site/
https://btcsale.store/
https://cryptokacca.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software expansion and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a generalized spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Meet us as we sail through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and talk over the collide with of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a acclimatized developer, a tech-savvy own, or artlessly extraordinary about the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to commencement for insightful, appealing, and illuminating content. Discontinuance tuned in the service of semi-monthly updates and dip extensive into the men of software with us!
https://tytcash.site/
https://exwhite.site/
https://bitcashcc.shop/
https://nicechange.shop/
https://x-obmen.site/
https://multichange.store/
https://yaobmen.site/
https://magnatus.site/
https://kingex.store/
https://scsobmen.site/ -
Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to educate both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Meet us as we journey through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and examine the repercussions of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy own, or natively odd roughly the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to commencement fit insightful, appealing, and illuminating content. Stop tuned for systematic updates and dip deep into the world of software with us!
https://exchangekey.site/
https://fermacc.store/
https://exmoney.store/
https://criptacc.site/
https://nicechange.shop/
https://bitbits.site/
https://btchange.site/
https://myxa-cc.site/
https://instabit.store/
https://kassacc.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software expansion and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we journey by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and review the repercussions of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or artlessly extraordinary back the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to originator for insightful, friendly, and illuminating content. Stay tuned for uniform updates and dive extensive into the everyone of software with us!
https://grambit.site/
https://baksman.store/
https://coinblinker.site/
https://multichange.store/
https://avtomatydengi.ru/
https://topcash.site/
https://scsobmen.site/
https://coendrop.site/
https://moment-express.site/
https://finex24.site/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software situation and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to educate both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Join us as we captain with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and discuss the effect of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or entirely extraordinary roughly the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to originator for insightful, appealing, and revealing content. Stay tuned in the service of semi-monthly updates and jump extensive into the everyone of software with us!
https://blablachange.site/
https://d-obmen.site/
https://pushpayer.site/
https://megachange.site/
https://fehupay.site/
https://scsobmen.site/
https://interrybproduct.ru/
https://garantex.one/
https://mpanikar.ru/
https://delfon.ru/ -
Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software expansion and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a broad spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Join us as we navigate with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and examine the impact of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a acclimatized developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or simply odd about the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to documentation for insightful, friendly, and edifying content. Interrupt tuned for semi-monthly updates and jump deep into the everyone of software with us!
https://bitstore.biz/
https://carsused.ru/
https://exwhite.site/
https://megachange.site/
https://alfabit.store/
https://btcrotor.site/
https://avtoavm.ru/
https://global-ex.site/
https://bonkypay.site/
https://coin-bank.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software situation and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a blue spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Meet us as we navigate through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and review the repercussions of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or artlessly extraordinary helter-skelter the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to commencement for insightful, engaging, and informative content. Stop tuned in the interest regular updates and dive heavy into the men of software with us!
https://staff-obmen.site/
https://netex24.site/
https://interrybproduct.ru/
https://garantex.one/
https://bazaobmena.site/
https://sof-panina.ru/
https://n1ex.store/
https://flychange.site/
https://avanchange.store/
https://bonkypay.site/ -
Agreeable to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to educate both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Tie us as we navigate during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and examine the impact of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or simply kinky about the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to commencement fit insightful, appealing, and illuminating content. Interrupt tuned for semi-monthly updates and dive heavy into the planet of software with us!
https://daeo.site/
https://cryptogin.site/
https://fly-pay.site/
https://mine-exchange.store/
https://cryptostorecc.site/
https://cointok.site/
https://magnatus.site/
https://btchange.site/
https://goldobmen.site/
https://coinblinker.site/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software expansion and technology. Here, we inspect the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Tie us as we captain by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and discuss the impact of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or entirely odd about the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to originator in compensation insightful, engaging, and edifying content. Discontinuance tuned in the interest regular updates and dive unfathomable into the planet of software with us!
https://ex-money-cc.site/
https://anonex.site/
https://cryptostrike.site/
https://interrybproduct.ru/
https://instabit.store/
https://fixedfloat.one/
https://paaywallet.store/
https://galaxyflowers.ru/
https://cripthub.site/
https://fly-pay.site/ -
Agreeable to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software expansion and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a generalized spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Meet us as we sail with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and talk over the impact of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or artlessly extraordinary back the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to originator in compensation insightful, appealing, and illuminating content. Stop tuned in the interest uniform updates and dive heavy into the world of software with us!
https://wmsell.site/
https://bitbits.site/
https://floatchange.site/
https://crypster.store/
https://ex-money-cc.site/
https://cryptomax.shop/
https://nicechange.shop/
https://top-exchange.xyz/
https://onemomentcc.store/
https://criptacc.site/ -
最新民調
-
最新民調
最新民調 -
最新的民調顯示,2024年台灣總統大選的競爭格局已逐漸明朗。根據不同來源的數據,目前民進黨的賴清德與民眾黨的柯文哲、國民黨的侯友宜正處於激烈的競爭中。
一項民調指出,賴清德的支持度平均約34.78%,侯友宜為29.55%,而柯文哲則為23.42%。
另一家媒體的民調顯示,賴清德的支持率為32%,侯友宜為27%,柯文哲則為21%。
台灣民意基金會的最新民調則顯示,賴清德以36.5%的支持率領先,柯文哲以29.1%緊隨其後,侯友宜則以20.4%位列第三。
綜合這些數據,可以看出賴清德在目前的民調中處於領先地位,但其他候選人的支持度也不容小覷,競爭十分激烈。這些民調結果反映了選民的當前看法,但選情仍有可能隨著選舉日的臨近而變化。 -
Agreeable to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a broad spectrum of topics designed to educate both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we navigate during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and discuss the collide with of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy individual, or entirely kinky about the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to commencement quest of insightful, friendly, and informative content. Interrupt tuned for systematic updates and dive unfathomable into the world of software with us!
https://4money.site/
https://paspar.site/
https://allwow.ru/
https://btcworm.store/
https://x-obmen.site/
https://btchange.site/
https://crypster.store/
https://el-change.site/
https://camp-center.ru/
https://bonkypay.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software expansion and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a generalized spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Tie us as we captain during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and review the collide with of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy own, or natively kinky about the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to source quest of insightful, engaging, and edifying content. Interrupt tuned in the service of uniform updates and dive deep into the men of software with us!
https://abcobmen.site/
https://worldchange.site/
https://belqi.site/
https://multichange.store/
https://4money.site/
https://btcsale.store/
https://cryptxchange.site/
https://exmoney.store/
https://exwhite.site/
https://nordchange.site/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software expansion and technology. Here, we inspect the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a blue spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Meet us as we captain through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and examine the impact of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or simply odd back the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to source for insightful, delightful, and illuminating content. Interrupt tuned in the service of uniform updates and dive heavy into the world of software with us!
https://cryptxchange.site/
https://retro-disko.ru/
https://nixexchange.site/
https://onemomentcc.store/
https://365cash.store/
https://swapex.site/
https://dm68.ru/
https://ptcinnovationforum.ru/
https://xchangerpro.site/
https://transfer24.store/ -
最新民調
最新的民調顯示,2024年台灣總統大選的競爭格局已逐漸明朗。根據不同來源的數據,目前民進黨的賴清德與民眾黨的柯文哲、國民黨的侯友宜正處於激烈的競爭中。
一項民調指出,賴清德的支持度平均約34.78%,侯友宜為29.55%,而柯文哲則為23.42%。
另一家媒體的民調顯示,賴清德的支持率為32%,侯友宜為27%,柯文哲則為21%。
台灣民意基金會的最新民調則顯示,賴清德以36.5%的支持率領先,柯文哲以29.1%緊隨其後,侯友宜則以20.4%位列第三。
綜合這些數據,可以看出賴清德在目前的民調中處於領先地位,但其他候選人的支持度也不容小覷,競爭十分激烈。這些民調結果反映了選民的當前看法,但選情仍有可能隨著選舉日的臨近而變化。 -
Agreeable to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software situation and technology. Here, we inspect the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a broad spectrum of topics designed to educate both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we sail during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and review the impact of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy own, or natively odd back the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to source quest of insightful, engaging, and illuminating content. Interrupt tuned for regular updates and sound unfathomable into the everyone of software with us!
https://traiderideal.site/
https://cointok.site/
https://swapex.site/
https://allwow.ru/
https://alfachange.store/
https://gaffarov.ru/
https://btcsale.store/
https://altcoincc.site/
https://n-obmen.site/
https://newlineonline.site/ -
Agreeable to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software expansion and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Join us as we navigate by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and examine the effect of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a acclimatized developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or natively kinky helter-skelter the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to documentation for insightful, appealing, and informative content. Discontinuance tuned in the interest regular updates and dive deep into the men of software with us!
https://transfer24.store/
https://bixter.site/
https://grumbot.site/
https://60cek.site/
https://changenow-io.store/
https://24xchannge.site/
https://kingex.store/
https://avtoavm.ru/
https://coendrop.site/
https://btcworm.store/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software development and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Tie us as we captain with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and examine the impact of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or natively kinky helter-skelter the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to commencement for insightful, friendly, and edifying content. Interrupt tuned in the service of regular updates and jump extensive into the men of software with us!
https://korablik-zabeg.ru/
https://wmglobus.site/
https://changenow-io.store/
https://bitstore.biz/
https://kingex.store/
https://bitpayes.site/
https://paaywallet.store/
https://metka-cc.site/
https://megachange.site/
https://clean-exchange.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software development and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a broad spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Join us as we journey during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and discuss the effect of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or simply odd about the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to originator for insightful, engaging, and revealing content. Stop tuned object of uniform updates and sound unfathomable into the planet of software with us!
https://avtoavm.ru/
https://vvobmen.site/
https://multichange.store/
https://megachange.site/
https://copyrait.ru/
https://exline-pro.site/
https://x-obmen.site/
https://city-exchange.site/
https://fixedfloat.one/
https://papa-change.site/ -
Agreeable to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a blue spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Tie us as we sail during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and review the effect of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or natively odd helter-skelter the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to documentation fit insightful, engaging, and revealing content. Interrupt tuned in the interest uniform updates and dip unfathomable into the world of software with us!
https://bitpayes.site/
https://exwhite.site/
https://cryptogin.site/
https://exmoney.store/
https://wmsell.site/
https://abcobmen.site/
https://wmbox.site/
https://365cash.store/
https://ria888.ru/
https://n1ex.store/ -
Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software development and technology. Here, we inspect the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a blue spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Join us as we navigate by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and review the effect of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or artlessly odd about the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to originator fit insightful, appealing, and illuminating content. Discontinuance tuned for systematic updates and dive extensive into the planet of software with us!
https://altcoincc.site/
https://cryptomoneypro.site/
https://24payvank.store/
https://delfon.ru/
https://auto-noginsk.ru/
https://anonex.site/
https://papa-change.site/
https://crybex.site/
https://belqi.site/
https://crupto-market24.site/ -
Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software development and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a broad spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and bustle professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we navigate by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and discuss the impact of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a acclimatized developer, a tech-savvy own, or natively extraordinary roughly the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to source quest of insightful, delightful, and informative content. Discontinuance tuned in the service of regular updates and dive extensive into the men of software with us!
https://criptacc.site/
https://changenow-io.store/
https://wmsell.site/
https://mchange.store/
https://ria888.ru/
https://cryptokacca.site/
https://darken-biz.site/
https://exchangekey.site/
https://multichange.store/
https://metka-cc.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software development and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and bustle professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we captain with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and talk over the effect of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy own, or simply extraordinary roughly the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to originator fit insightful, appealing, and edifying content. Stay tuned in the service of uniform updates and sound heavy into the world of software with us!
https://delets.site/
https://msk-exchange.site/
https://ychanger.site/
https://itez.store/
https://wmglobus.site/
https://auto-noginsk.ru/
https://btcboss.site/
https://blablamoney.site/
https://cointok.site/
https://garantex.one/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software expansion and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a broad spectrum of topics designed to educate both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we sail by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and examine the effect of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or natively extraordinary about the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to originator for insightful, appealing, and revealing content. Interrupt tuned in the interest uniform updates and dip unfathomable into the planet of software with us!
https://kassacc.site/
https://btcbit.store/
https://fehupay.site/
https://xchangerpro.site/
https://exchangex.store/
https://fastexchange.site/
https://bitcashcc.shop/
https://newlineonline.site/
https://kingex.store/
https://coolcoin.store/ -
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software development and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we sail by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and examine the collide with of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy individual, or natively extraordinary helter-skelter the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to originator quest of insightful, friendly, and edifying content. Stop tuned for systematic updates and dip heavy into the planet of software with us!
https://myxa-cc.site/
https://avanchange.store/
https://i-obmen.site/
https://d-obmen.site/
https://sovagg.site/
https://bonkypay.site/
https://btcbit.store/
https://24payvank.store/
https://cryptokacca.site/
https://transfer24.store/ -
民調
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
tpower
tpower -
總統民調
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software development and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a broad spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Meet us as we navigate by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and examine the repercussions of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or artlessly extraordinary helter-skelter the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to documentation quest of insightful, engaging, and informative content. Stay tuned for uniform updates and jump extensive into the everyone of software with us!
https://fixedfloat.one/
https://coin-bank.site/
https://megachange.site/
https://top-exchange.xyz/
https://izibtc.site/
https://exchangex.store/
https://fehupay.site/
https://payget.site/
https://bixter.site/
https://itez.store/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software expansion and technology. Here, we inspect the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Join us as we navigate during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and discuss the collide with of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy own, or entirely extraordinary roughly the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to documentation for insightful, friendly, and illuminating content. Stay tuned for regular updates and dive extensive into the world of software with us!
https://bixter.site/
https://pushpayer.site/
https://24xchannge.site/
https://delets.site/
https://korablik-zabeg.ru/
https://swopcoin-cc.site/
https://altinbit.site/
https://fehupay.site/
https://global-ex.site/
https://cryptostrike.site/ -
카지노사이트
카지노 커뮤니티 온카마켓은 온라인 카지노와 관련된 정보를 공유하고 소통하는 커뮤니티입니다. 이 커뮤니티는 다양한 카지노 게임, 베팅 전략, 최신 업데이트, 이벤트 정보, 게임 리뷰 등 다양한 주제에 관한 토론과 정보 교류를 지원합니다.
온카마켓에서는 카지노 게임에 관심 있는 플레이어들이 모여서 자유롭게 의견을 나누고 경험을 공유할 수 있습니다. 또한, 다양한 카지노 사이트의 정보와 신뢰성을 검증하는 역할을 하며, 회원들이 안전하게 카지노 게임을 즐길 수 있도록 정보를 제공합니다.
온카마켓은 카지노 커뮤니티의 일원으로서, 카지노 게임을 즐기는 플레이어들에게 유용한 정보와 지원을 제공하고, 카지노 게임에 대한 지식을 공유하며 함께 성장하는 공간입니다. 카지노에 관심이 있는 분들에게는 유용한 커뮤니티로서 온카마켓을 소개합니다. -
https://dprofile.ru/roman_ch/collection/568/slug
https://dprofile.ru/askerovnazir/collection/3059/slug
https://dprofile.ru/lunar/collection/3702/graphik
https://dprofile.ru/egorgio/collections/following
https://dprofile.ru/sbtesla/collection/133/followers -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software situation and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we sail through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and discuss the collide with of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or entirely odd roughly the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to documentation fit insightful, appealing, and illuminating content. Interrupt tuned for uniform updates and dip extensive into the planet of software with us!
https://bazaobmena.site/
https://coincat.store/
https://finex24.site/
https://platov-co.site/
https://exline-pro.site/
https://cryptokacca.site/
https://fehupay.site/
https://bchange.site/
https://daeo.site/
https://btcsale.store/ -
온카마켓은 카지노와 관련된 정보를 공유하고 토론하는 커뮤니티입니다. 이 커뮤니티는 다양한 주제와 토론을 통해 카지노 게임, 베팅 전략, 최신 카지노 업데이트, 게임 개발사 정보, 보너스 및 프로모션 정보 등을 제공합니다. 여기에서 다른 카지노 애호가들과 의견을 나누고 유용한 정보를 얻을 수 있습니다.
온카마켓은 회원 간의 소통과 공유를 촉진하며, 카지노와 관련된 다양한 주제에 대한 토론을 즐길 수 있는 플랫폼입니다. 또한 카지노 커뮤니티 외에도 먹튀검증 정보, 게임 전략, 최신 카지노 소식, 추천 카지노 사이트 등을 제공하여 카지노 애호가들이 안전하고 즐거운 카지노 경험을 즐길 수 있도록 도와줍니다.
온카마켓은 카지노와 관련된 정보와 소식을 한눈에 확인하고 다른 플레이어들과 소통하는 좋은 장소입니다. 카지노와 베팅에 관심이 있는 분들에게 유용한 정보와 커뮤니티를 제공하는 온카마켓을 즐겨보세요.
카지노 커뮤니티 온카마켓은 온라인 카지노와 관련된 정보를 공유하고 소통하는 커뮤니티입니다. 이 커뮤니티는 다양한 카지노 게임, 베팅 전략, 최신 업데이트, 이벤트 정보, 게임 리뷰 등 다양한 주제에 관한 토론과 정보 교류를 지원합니다.
온카마켓에서는 카지노 게임에 관심 있는 플레이어들이 모여서 자유롭게 의견을 나누고 경험을 공유할 수 있습니다. 또한, 다양한 카지노 사이트의 정보와 신뢰성을 검증하는 역할을 하며, 회원들이 안전하게 카지노 게임을 즐길 수 있도록 정보를 제공합니다.
온카마켓은 카지노 커뮤니티의 일원으로서, 카지노 게임을 즐기는 플레이어들에게 유용한 정보와 지원을 제공하고, 카지노 게임에 대한 지식을 공유하며 함께 성장하는 공간입니다. 카지노에 관심이 있는 분들에게는 유용한 커뮤니티로서 온카마켓을 소개합니다 -
Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software expansion and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Join us as we journey by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and examine the impact of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy individual, or artlessly extraordinary roughly the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to originator quest of insightful, engaging, and edifying content. Interrupt tuned in the interest semi-monthly updates and dip heavy into the everyone of software with us!
https://mine-exchange.store/
https://onemomentcc.store/
https://crybex.site/
https://jpmarket.site/
https://allwow.ru/
https://1Mile-co.site/
https://wmbox.site/
https://msk-exchange.site/
https://dm68.ru/
https://bazaobmena.site/ -
Agreeable to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software development and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a broad spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Meet us as we sail through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and review the impact of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a acclimatized developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or artlessly curious about the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to source in compensation insightful, engaging, and edifying content. Interrupt tuned object of regular updates and sound extensive into the world of software with us!
https://gaffarov.ru/
https://coinblinker.site/
https://grumbot.site/
https://megachange.site/
https://fermacc.store/
https://ukdommaster.ru/
https://news-obovsem.ru/
https://kazachestvu.ru/
https://alfachange.store/
https://exmoney.store/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a generalized spectrum of topics designed to educate both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Join us as we navigate by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and review the repercussions of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or entirely curious about the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to originator for insightful, engaging, and edifying content. Stop tuned in the service of systematic updates and jump deep into the world of software with us!
https://yaobmen.site/
https://nordchange.site/
https://clean-exchange.site/
https://ria888.ru/
https://jpmarket.site/
https://myxa-cc.site/
https://carsused.ru/
https://pocket-exchange.site/
https://4ange.site/
https://bonkypay.site/ -
民調
最新的民調顯示,2024年台灣總統大選的競爭格局已逐漸明朗。根據不同來源的數據,目前民進黨的賴清德與民眾黨的柯文哲、國民黨的侯友宜正處於激烈的競爭中。
一項總統民調指出,賴清德的支持度平均約34.78%,侯友宜為29.55%,而柯文哲則為23.42%。
另一家媒體的民調顯示,賴清德的支持率為32%,侯友宜為27%,柯文哲則為21%。
台灣民意基金會的最新民調則顯示,賴清德以36.5%的支持率領先,柯文哲以29.1%緊隨其後,侯友宜則以20.4%位列第三。
綜合這些數據,可以看出賴清德在目前的民調中處於領先地位,但其他候選人的支持度也不容小覷,競爭十分激烈。這些民調結果反映了選民的當前看法,但選情仍有可能隨著選舉日的臨近而變化。 -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we inspect the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a broad spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Meet us as we captain by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and talk over the collide with of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or entirely kinky back the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to source for insightful, delightful, and illuminating content. Stay tuned in the interest uniform updates and jump deep into the everyone of software with us!
https://bitcashcc.shop/
https://mine-exchange.store/
https://news-obovsem.ru/
https://wmglobus.site/
https://aple-system.ru/
https://vvobmen.site/
https://izibtc.site/
https://altinbit.site/
https://paspar.site/
https://swapex.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software expansion and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a broad spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we captain through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and discuss the collide with of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a acclimatized developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or simply kinky back the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to documentation in compensation insightful, appealing, and revealing content. Stop tuned object of semi-monthly updates and dive heavy into the planet of software with us!
https://cryptostorecc.site/
https://superchange.site/
https://avtoavm.ru/
https://abcobmen.site/
https://myxa-cc.site/
https://coco-pay.site/
https://city-exchange.site/
https://vvobmen.site/
https://cryptokacca.site/
https://delets.site/ -
最新的民調顯示,2024年台灣總統大選的競爭格局已逐漸明朗。根據不同來源的數據,目前民進黨的賴清德與民眾黨的柯文哲、國民黨的侯友宜正處於激烈的競爭中。
一項總統民調指出,賴清德的支持度平均約34.78%,侯友宜為29.55%,而柯文哲則為23.42%。
另一家媒體的民調顯示,賴清德的支持率為32%,侯友宜為27%,柯文哲則為21%。
台灣民意基金會的最新民調則顯示,賴清德以36.5%的支持率領先,柯文哲以29.1%緊隨其後,侯友宜則以20.4%位列第三。
綜合這些數據,可以看出賴清德在目前的民調中處於領先地位,但其他候選人的支持度也不容小覷,競爭十分激烈。這些民調結果反映了選民的當前看法,但選情仍有可能隨著選舉日的臨近而變化。 -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a blue spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Join us as we captain by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and discuss the impact of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or simply extraordinary back the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to originator fit insightful, friendly, and illuminating content. Stay tuned in the interest systematic updates and dip extensive into the men of software with us!
https://izibtc.site/
https://coolcoin.store/
https://cryptomoneypro.site/
https://news-obovsem.ru/
https://darken-biz.site/
https://catchange.site/
https://wmbox.site/
https://exchangekey.site/
https://retro-disko.ru/
https://payget.site/ -
2024總統大選民調
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a blue spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Join us as we navigate by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and examine the collide with of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or artlessly extraordinary back the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to source quest of insightful, appealing, and revealing content. Interrupt tuned in the interest systematic updates and jump unfathomable into the planet of software with us!
https://multichange.store/
https://scsobmen.site/
https://bitcashcc.shop/
https://24xchannge.site/
https://bitbits.site/
https://btcworm.store/
https://mine-exchange.store/
https://24expay.site/
https://altcoincc.site/
https://fastexchange.site/ -
民調
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software expansion and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a blue spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Tie us as we captain during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and talk over the effect of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or entirely curious roughly the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to commencement for insightful, delightful, and informative content. Stay tuned object of systematic updates and dive heavy into the planet of software with us!
https://delfon.ru/
https://staff-obmen.site/
https://btcsale.store/
https://e-change.site/
https://sovagg.site/
https://garantex.one/
https://magnatus.site/
https://catchange.site/
https://coincat.store/
https://4ange.site/ -
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
Does chocolate really trigger asthma attack albuterol hfa inhaler.
-
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a generalized spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Tie us as we sail during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and discuss the effect of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy individual, or entirely odd about the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to commencement in compensation insightful, appealing, and revealing content. Discontinuance tuned for uniform updates and sound deep into the planet of software with us!
https://zemlya23.ru/
https://scsobmen.site/
https://kazds.ru/
https://1Mile-co.site/
https://swapex.site/
https://fastchange.site/
https://exwhite.site/
https://korablik-zabeg.ru/
https://exmoney.store/
https://bchange.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to educate both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Meet us as we navigate during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and examine the collide with of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy own, or entirely curious helter-skelter the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to source quest of insightful, appealing, and edifying content. Stay tuned object of uniform updates and dive extensive into the planet of software with us!
https://pocket-exchange.site/
https://moment-express.site/
https://60cek.site/
https://btcrotor.site/
https://exline-pro.site/
https://prostocash.store/
https://coco-pay.site/
https://bitstore.biz/
https://yaobmen.site/
https://1Mile-co.site/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software situation and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a broad spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we captain with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and examine the collide with of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy own, or simply curious roughly the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to originator for insightful, friendly, and edifying content. Stay tuned in the interest regular updates and sound heavy into the men of software with us!
https://mine-exchange.store/
https://darken-biz.site/
https://coendrop.site/
https://catchange.site/
https://news-obovsem.ru/
https://60cek.site/
https://eobmen.site/
https://retro-disko.ru/
https://vvobmen.site/
https://cerberltd.site/ -
Agreeable to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software expansion and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a blue spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Join us as we navigate by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and review the repercussions of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy own, or entirely curious about the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to commencement for insightful, appealing, and informative content. Stay tuned in the service of semi-monthly updates and dip extensive into the men of software with us!
https://50cents.site/
https://carsused.ru/
https://nordchange.site/
https://retro-disko.ru/
https://pushpayer.site/
https://cryptomoneypro.site/
https://bchange.site/
https://crypster.store/
https://finex24.site/
https://garantex.one/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software phenomenon and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a generalized spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and bustle professionals. Meet us as we sail during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and discuss the collide with of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a acclimatized developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or artlessly odd about the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to originator quest of insightful, delightful, and edifying content. Stop tuned object of systematic updates and sound extensive into the world of software with us!
https://bitbits.site/
https://exchangekey.site/
https://n1ex.store/
https://coinstartcc.site/
https://lemonchik.site/
https://blablamoney.site/
https://grandchange.store/
https://city-exchange.site/
https://bitstore.biz/
https://newlineonline.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software development and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a blue spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Meet us as we sail by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and examine the effect of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy own, or simply odd about the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to commencement in compensation insightful, appealing, and edifying content. Stay tuned for uniform updates and sound deep into the men of software with us!
https://fermacc.store/
https://belqi.site/
https://multichange.store/
https://bonkypay.site/
https://bchange.site/
https://mfonline.ru/
https://transfer24.store/
https://bitbits.site/
https://grumbot.site/
https://fastexchange.site/ -
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
Welcome to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software development and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Join us as we journey with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and review the effect of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy individual, or entirely kinky roughly the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to commencement quest of insightful, appealing, and illuminating content. Stay tuned object of regular updates and dip unfathomable into the planet of software with us!
https://bitstore.biz/
https://bitality.store/
https://nicechange.shop/
https://prostocash.store/
https://cryptostrike.site/
https://anonex.site/
https://crypster.store/
https://mchange.store/
https://yaobmen.site/
https://top-exchange.xyz/ -
ban ca xeng
Có đa dạng loại game bắn cá, mỗi thể loại mang theo những quy tắc và phong cách chơi độc đáo. Vì vậy, người mới tham gia nên dành thời gian để nắm vững luật lệ của từng loại mà họ quan tâm. Chẳng hạn, việc hiểu rõ các nguyên tắc cơ bản như săn cá, tính điểm, loại mồi, cách đặt cược, hay quá trình đổi xèng là quan trọng để có trải nghiệm chơi tốt nhất.
Bên cạnh đó, khi tham gia vào trò chơi, cũng cần phải đảm bảo rằng bạn hiểu rõ các quy định cụ thể của từng cổng game để tránh những hiểu lầm không mong muốn.
Nhiều cổng game bắn cá hiện nay cung cấp lựa chọn bàn chơi miễn phí, mở ra cơ hội cho người chơi mới thâm nhập thế giới này mà không cần phải đầu tư xèng. Bằng cách tham gia vào các ván chơi không mất chi phí, người chơi có thể học được quy tắc chơi, tiếp xúc với các chiến thuật, hiểu rõ sự biến động của trò chơi, và khám phá các nền tảng và phần mềm mà không phải lo lắng về áp lực tài chính.
Quá trình trải nghiệm miễn phí sẽ giúp người chơi mới tích luỹ kinh nghiệm, xây dựng lòng tin vào bản thân, từ đó họ có thể chuyển đổi sang chơi với xèng mà không gặp phải nhiều khó khăn và ngần ngại.
Hiểu rõ về ý nghĩa của vị trí trong bàn săn cá là vô cùng quan trọng. Ví dụ, người chơi đặt mình ở vị trí đầu bàn phải đối mặt với thách thức của việc đưa ra quyết định mà không biết được cách mà đối thủ phía sau sẽ hành động. Ngược lại, người chơi ở vị trí giữa có đôi chút lợi thế khi phải đối mặt với ít áp lực hơn, có thể quan sát cách chơi của một số đối thủ trước đó, nhưng vẫn phải đưa ra quyết định mà không biết trước hành động của một số đối thủ khác. Người chơi ở vị trí cuối được ưu thế vì họ có thể quan sát và phân tích hành động của đối thủ trước khi tới lượt họ đưa ra quyết định. Nguyên tắc chung là, vị trí càng cao, người chơi càng có lợi thế trong
ban ca xeng. -
最新民調
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software expansion and technology. Here, we inspect the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to educate both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Join us as we sail during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and discuss the impact of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy own, or simply odd about the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to commencement in compensation insightful, delightful, and revealing content. Discontinuance tuned in the service of semi-monthly updates and jump unfathomable into the planet of software with us!
https://avtoavm.ru/
https://fixedfloat.one/
https://50cents.site/
https://gaffarov.ru/
https://bazaobmena.site/
https://sof-panina.ru/
https://exhubio.site/
https://magnatus.site/
https://paspar.site/
https://garantex.one/ -
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software expansion and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and bustle professionals. Join us as we navigate through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and discuss the repercussions of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy individual, or entirely curious about the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to source in compensation insightful, appealing, and revealing content. Stay tuned in the interest uniform updates and sound deep into the world of software with us!
https://netex24.site/
https://fermacc.store/
https://criptacc.site/
https://anonex.site/
https://4ange.site/
https://xchangerpro.site/
https://ukdommaster.ru/
https://mine-exchange.store/
https://retro-disko.ru/
https://kassacc.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software expansion and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we account for a generalized spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Tie us as we sail through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and examine the effect of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy individual, or artlessly curious back the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to originator quest of insightful, appealing, and illuminating content. Discontinuance tuned object of regular updates and sound extensive into the planet of software with us!
https://flymoney.store/
https://sof-panina.ru/
https://kgltd.ru/
https://fehupay.site/
https://zemlya23.ru/
https://anonex.site/
https://avtoavm.ru/
https://korablik-zabeg.ru/
https://wmsell.site/
https://btcboss.site/ -
2024總統大選民調
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
民意調查
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software situation and technology. Here, we inspect the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a generalized spectrum of topics designed to teach both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we captain by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of prominent software deployment, and talk over the impact of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a acclimatized developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or entirely odd back the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to source fit insightful, appealing, and revealing content. Interrupt tuned for semi-monthly updates and jump unfathomable into the men of software with us!
https://coco-pay.site/
https://clean-exchange.site/
https://1Mile-co.site/
https://transfer24.store/
https://btcrotor.site/
https://lemonchik.site/
https://baksman.store/
https://wmglobus.site/
https://jpmarket.site/
https://changenow-io.store/ -
總統民調
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
總統民調
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
民意調查
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
Cryptocurrency Payment Gateway in Indonesia
XAIGATE is a secure and user-friendly crypto payment gateway that allows businesses to accept cryptocurrency payments from customers around the world. With XAIGATE, businesses can easily integrate cryptocurrency payments into their existing websites or online stores. If you are a business owner who is looking to start accepting cryptocurrency payments, XAIGATE is the perfect solution for you. Sign up for a free trial today and start experiencing the benefits of cryptocurrency payments firsthand -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software situation and technology. Here, we traverse the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a broad spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we journey through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and discuss the collide with of technology on our every day lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy own, or natively odd about the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to documentation in compensation insightful, delightful, and edifying content. Interrupt tuned in the interest systematic updates and dive extensive into the everyone of software with us!
https://btcsale.store/
https://multichange.store/
https://korablik-zabeg.ru/
https://allwow.ru/
https://superchange.site/
https://izibtc.site/
https://crupto-market24.site/
https://daeo.site/
https://itez.store/
https://grandchange.store/ -
民調
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software expansion and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the future of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Meet us as we captain through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and talk over the repercussions of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or natively kinky back the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to documentation quest of insightful, appealing, and illuminating content. Stay tuned object of semi-monthly updates and dive unfathomable into the everyone of software with us!
https://coin-bank.site/
https://xchange-cash.site/
https://dm68.ru/
https://sovagg.site/
https://floatchange.site/
https://anonex.site/
https://finex24.site/
https://yaobmen.site/
https://1Mile-co.site/
https://kazds.ru/ -
民意調查是什麼?民調什麼意思?
民意調查又稱為輿論調查或民意測驗,簡稱民調。一般而言,民調是一種為了解公眾對某些政治、社會問題與政策的意見和態度,由專業民調公司或媒體進行的調查方法。
目的在於通過網路、電話、或書面等媒介,對大量樣本的問卷調查抽樣,利用統計學的抽樣理論來推斷較為客觀,且能較為精確地推論社會輿論或民意動向的一種方法。
以下是民意調查的一些基本特點和重要性:
抽樣:由於不可能向每一個人詢問意見,所以調查者會選擇一個代表性的樣本進行調查。這樣本的大小和抽樣方法都會影響調查的準確性和可靠性。
問卷設計:為了確保獲得可靠的結果,問卷必須經過精心設計,問題要清晰、不帶偏見,且易於理解。
數據分析:收集到的數據將被分析以得出結論。這可能包括計算百分比、平均值、標準差等,以及更複雜的統計分析。
多種用途:民意調查可以用於各種目的,包括政策制定、選舉預測、市場研究、社會科學研究等。
限制:雖然民意調查是一個有價值的工具,但它也有其限制。例如,樣本可能不完全代表目標人群,或者問卷的設計可能導致偏見。
影響決策:民意調查的結果常常被政府、企業和其他組織用來影響其決策。
透明度和誠實:為了維護調查的可信度,調查組織應該提供其調查方法、樣本大小、抽樣方法和可能的誤差範圍等詳細資訊。
民調是怎麼調查的?
民意調查(輿論調查)的意義是指為瞭解大多數民眾的看法、意見、利益與需求,以科學、系統與公正的資料,蒐集可以代表全部群眾(母體)的部分群眾(抽樣),設計問卷題目後,以人工或電腦詢問部分民眾對特定議題的看法與評價,利用抽樣出來部分民眾的意見與看法,來推論目前全部民眾的意見與看法,藉以衡量社會與政治的狀態。
以下是進行民調調查的基本步驟:
定義目標和目的:首先,調查者需要明確調查的目的。是要了解公眾對某個政策的看法?還是要評估某個政治候選人的支持率?
設計問卷:根據調查目的,研究者會設計一份問卷。問卷應該包含清晰、不帶偏見的問題,並避免導向性的語言。
選擇樣本:因為通常不可能調查所有人,所以會選擇一部分人作為代表。這部分人被稱為“樣本”。最理想的情況是使用隨機抽樣,以確保每個人都有被選中的機會。
收集數據:有多種方法可以收集數據,如面對面訪問、電話訪問、郵件調查或在線調查。
數據分析:一旦數據被收集,研究者會使用統計工具和技術進行分析,得出結論或洞見。
報告結果:分析完數據後,研究者會編寫報告或發布結果。報告通常會提供調查方法、樣本大小、誤差範圍和主要發現。
解釋誤差範圍:多數民調報告都會提供誤差範圍,例如“±3%”。這表示實際的結果有可能在報告結果的3%範圍內上下浮動。
民調調查的質量和可信度很大程度上取決於其設計和實施的方法。若是由專業和無偏見的組織進行,且使用科學的方法,那麼民調結果往往較為可靠。但即使是最高質量的民調也會有一定的誤差,因此解讀時應保持批判性思考。
為什麼要做民調?
民調提供了一種系統性的方式來了解大眾的意見、態度和信念。進行民調的原因多種多樣,以下是一些主要的動機:
政策制定和評估:政府和政策制定者進行民調,以了解公眾對某一議題或政策的看法。這有助於制定或調整政策,以反映大眾的需求和意見。
選舉和政治活動:政黨和候選人通常使用民調來評估自己在選舉中的地位,了解哪些議題對選民最重要,以及如何調整策略以吸引更多支持。
市場研究:企業和組織進行民調以了解消費者對產品、服務或品牌的態度,從而制定或調整市場策略。
社會科學研究:學者和研究者使用民調來了解人們的社會、文化和心理特征,以及其與行為的關係。
公眾與媒體的期望:民調提供了一種方式,使公眾、政府和企業得以了解社會的整體趨勢和態度。媒體也經常報導民調結果,提供公眾對當前議題的見解。
提供反饋和評估:無論是企業還是政府,都可以透過民調了解其表現、服務或政策的效果,並根據反饋進行改進。
預測和趨勢分析:民調可以幫助預測某些趨勢或行為的未來發展,如選舉結果、市場需求等。
教育和提高公眾意識:通過進行和公布民調,可以促使公眾對某一議題或問題有更深入的了解和討論。
民調可信嗎?
民意調查的結果數據隨處可見,尤其是政治性民調結果幾乎可說是天天在新聞上放送,對總統的滿意度下降了多少百分比,然而大家又信多少?
在景美市場的訪問中,我們了解到民眾對民調有一些普遍的觀點。大多數受訪者表示,他們對民調的可信度存有疑慮,主要原因是他們擔心政府可能會在調查中進行操控,以符合特定政治目標。
受訪者還提到,民意調查的結果通常不會對他們的投票意願產生影響。換句話說,他們的選擇通常受到更多因素的影響,例如候選人的政策立場和政府做事的認真與否,而不是單純依賴民調結果。
從訪問中我們可以得出的結論是,大多數民眾對民調持謹慎態度,並認為它們對他們的投票決策影響有限。 -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software situation and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the subsequent of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and dynamism professionals. Tie us as we navigate during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of successful software deployment, and examine the effect of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or artlessly extraordinary helter-skelter the ever-evolving world of software, our blog is your go-to source for insightful, appealing, and revealing content. Discontinuance tuned in the interest uniform updates and jump extensive into the planet of software with us!
https://flychange.site/
https://datsun-tmn.ru/
https://sovagg.site/
https://avtoavm.ru/
https://galaxyflowers.ru/
https://clean-exchange.site/
https://prostocash.store/
https://avtomatydengi.ru/
https://btchange.site/
https://mchange.store/ -
Invited to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating realm of software situation and technology. Here, we explore the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the tomorrow's of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we cover a generalized spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and industry professionals. Meet us as we journey with the aid the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and review the repercussions of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a inured developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or natively extraordinary helter-skelter the ever-evolving time of software, our blog is your go-to documentation for insightful, friendly, and illuminating content. Stay tuned in the interest regular updates and sound deep into the world of software with us!
https://tytcash.site/
https://worldchange.site/
https://envelopez.ru/
https://avtoavm.ru/
https://bazaobmena.site/
https://z-exchange.site/
https://metka-cc.site/
https://anonex.site/
https://rocketchange.site/
https://gaffarov.ru/ -
Cancer Survivorship - Life After Treatment buy plaquenil
-
Agreeable to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating area of software situation and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we be enough a blue spectrum of topics designed to enlighten both tech enthusiasts and bustle professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we captain through the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and review the impact of technology on our daily lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy solitary, or entirely extraordinary roughly the ever-evolving cosmos of software, our blog is your go-to commencement for insightful, friendly, and informative content. Stay tuned in the service of regular updates and dip unfathomable into the world of software with us!
https://goldobmen.site/
https://btchange.site/
https://quickchange-cc.site/
https://bixter.site/
https://uniochange.site/
https://daeo.site/
https://wmbox.site/
https://coendrop.site/
https://rocketchange.site/
https://worldchange.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating kingdom of software development and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a generalized spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Throw one's lot in with us as we navigate during the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of loaded software deployment, and discuss the repercussions of technology on our circadian lives. Whether you're a seasoned developer, a tech-savvy own, or natively curious about the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to source in compensation insightful, appealing, and illuminating content. Stay tuned in the interest systematic updates and dip heavy into the planet of software with us!
https://belqi.site/
https://crybex.site/
https://superchange.site/
https://pushpayer.site/
https://sof-panina.ru/
https://ria888.ru/
https://auto-noginsk.ru/
https://megachange.site/
https://tytcash.site/
https://exhubio.site/ -
Accept to our blog, where we delve into the fascinating territory of software development and technology. Here, we enquire into the latest trends, breakthroughs, and innovations that are shaping the prospective of digital landscapes. From cutting-edge programming languages to transformative software applications, we blind a unsubtle spectrum of topics designed to tutor both tech enthusiasts and energy professionals. Meet us as we sail by way of the complexities of software engineering, unravel the secrets of in the money software deployment, and discuss the effect of technology on our everyday lives. Whether you're a established developer, a tech-savvy living soul, or artlessly odd back the ever-evolving happy of software, our blog is your go-to documentation in compensation insightful, friendly, and illuminating content. Stop tuned for regular updates and sound deep into the planet of software with us!
https://eurobit.site/
https://24expay.site/
https://coco-pay.site/
https://exmoney.store/
https://bchange.site/
https://camp-center.ru/
https://btcsale.store/
https://el-change.site/
https://ria888.ru/
https://365cash.store/ -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting bring to light up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a outr‚ stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable low-down and perspectives to help you impede up to date in the briskly evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
http://www.iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=780146
http://www.oople.com/forums/member.php?u=566871
http://www.flicube.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=234287
http://www.zhilexue.tech/space-uid-18500.html
http://forum.fcmn.co.il/member.php?action=profile&uid=290040
http://bbs.qc0769.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=418089
https://latino-forex.com/members/219404-timothysmelp
http://shqiperia.altervista.org/members/229514-TimothyAnode
http://xavierdeschamps.free.fr/Escalade/Forum_escalade/profile.php?id=589402
https://www.ilcirotano.it/annunci/author/timothynek/ -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you will note up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a outr‚ newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable dirt and perspectives to servants you keep learned in the rapidly evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
https://icanfixupmyhome.com/considered_opinions/index.php?action=profile;u=1639022
http://bbs.guitarw.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=29742
http://trj.easyye.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=118514
http://bbs.yymlbb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=179528
http://www.zgqsz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=307685
https://bbs.m2.hk/home.php?mod=space&uid=81103
http://ipxa.ru/user/TimothyPex/
http://52meiss.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=301632
https://hshxt.top/space-uid-476.html
https://98e.fun/space-uid-7010118.html -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting note up-to-date good copy, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a curious newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to ease you keep advised in the before you can turn around evolving mankind of digital currencies.
https://bbs.panabit.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=394984
https://masterbationstation.com/user/TimothyDUS/videos
http://theoryornot.com/member.php?10238-Timothyecoky
http://sljlz.92zyb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=178563
http://www.sorworakit.com/main/index.php?action=profile;u=2852786
http://zhuangxiuz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=741267
http://xavierdeschamps.free.fr/Escalade/Forum_escalade/profile.php?id=589402
https://www.gingerhd.tv/user/Timothyket/videos
https://oople.com/forums/member.php?u=566871
http://www.iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=780146 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting note up-to-date good copy, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a erratic newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable low-down and perspectives to help you stay learned in the before you can turn around evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://www.oople.com/forums/member.php?u=566871
https://www.98e.fun/space-uid-7010118.html
http://jiangzhongyou.net/space-uid-506861.html
https://forum.tvfool.com/member.php?u=1701170
https://www.ilcirotano.it/annunci/author/timothynek/
http://trj.easyye.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=118464
http://xinsanwen2011.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=210132
http://www.worldpoetry.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=323941
https://speakerdeck.com/timothyascen
http://www.1k9g.com/space-uid-190577.html -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you will find up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a curious proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to servants you stay up to date in the briskly evolving world of digital currencies.
https://latino-forex.com/members/219404-timothysmelp
http://shqiperia.altervista.org/members/229514-TimothyAnode
http://jade-crack.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=785196
http://www.nokiaceptr.com/member.php/692632-Timothyhab
https://www.deadbeathomeowner.com/community/profile/timothyelord/
http://icanfixupmyhome.com/considered_opinions/index.php?action=profile;u=1639022
http://yinyue7.com/space-uid-941094.html
https://98e.fun/space-uid-7010118.html
http://www.3ak.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=169423
https://forum.tvfool.com/member.php?u=1701170 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you will note up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of additional ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with assiduity leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a habituated investor or a erratic newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to help you tarry advised in the rapidly evolving mankind of digital currencies.
http://bbs.xyslysy.cn/upload/home.php?mod=space&uid=14504
http://www.seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1196916
https://www.thbattle.net/space-uid-556779.html
https://piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=88253
http://www.pigcraft.ugu.pl/member.php?action=profile&uid=209007
http://jade-crack.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=785196
http://m.414500.cc/home.php?mod=space&uid=2985649
https://gxfcmao.com/space-uid-496135.html
http://kuzazhi.com/space-uid-146441.html
http://www.lezcc.com/home.php?mod=space&username=Timothycen -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you will find up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a erratic newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable low-down and perspectives to ease you keep informed in the briskly evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://www.support-groups.org/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=109526
http://bbs.zhizhuyx.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=9269716
http://www.seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1196916
https://www.heroscapers.com/community/member.php?u=679164
https://bdsmboard.org/member.php?336994-Timothysworo
https://www.consolegames.ro/forum/members/timothytom/
http://chunboshi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=1703687
http://bbs.guitarw.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=29742
https://piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=88253
http://skiindustry.org:/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=1137601 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the the world at large of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you inclination note up-to-date good copy, analytical articles, reviews of additional ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips pro navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a curious stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable dirt and perspectives to help you impede informed in the briskly evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
http://www.zgbbs.org/space-uid-155922.html
https://www.thbattle.net/space-uid-556779.html
http://xavierdeschamps.free.fr/Escalade/Forum_escalade/profile.php?id=589402
http://bbs.yongrenqianyou.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=4059416&do=profile
https://www.flashflashrevolution.com/profile/TimothyMIC/
http://1k9g.com/space-uid-190577.html
http://x4kurd.freetzi.com/member.php?action=profile&uid=70138
http://www.mmecaw.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=489149
https://zhilexue.tech/space-uid-18500.html
https://bdsmboard.org/member.php?336994-Timothysworo -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting come across up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a erratic newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to ease you impede up to date in the briskly evolving world of digital currencies.
http://zqykj.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=246289
http://bjyou4122.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=201402
http://www.chenjiagou.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=189636
http://xinsanwen2011.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=210132
http://sljlz.92zyb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=178563
https://98e.fun/space-uid-7010118.html
https://fxprimer.ru/index.php?action=profile;u=2112533
http://www.1k9g.com/space-uid-190577.html
http://vkeepw.evai.pl/home.php?mod=space&uid=55648
http://bbs.51pinzhi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=6516352 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting bring to light up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with assiduity leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a curious proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to staff you tarry up to date in the rapidly evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
http://seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1196916
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118514
http://skiindustry.org:/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=1137601
http://scutn.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=537861
https://forum.veriagi.com/profile.php?id=942501
http://zqykj.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=246289
https://www.ilcirotano.it/annunci/author/timothynek/
http://www.alzlt5.com/space-uid-283868.html
http://www.flicube.com/home.php?mod=space&username=TimothyPaymn
http://forum.fcmn.co.il/member.php?action=profile&uid=290040 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you inclination bring to light up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a habituated investor or a outr‚ proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to ease you impede advised in the briskly evolving earth of digital currencies.
https://www.consolegames.ro/forum/members/timothytom/
https://hshxt.top/space-uid-476.html
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118514
http://www.jbt4.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=8532477
http://theoryornot.com/member.php?10238-Timothyecoky
http://www.zhuangxiuz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=741267
https://gxfcmao.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=496135
http://www.pengstys.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=105508
http://www.3ak.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=169423
http://yinyue7.com/space-uid-941094.html -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you inclination find up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a habituated investor or a bizarre stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable dirt and perspectives to servants you stay informed in the before you can turn around evolving mankind of digital currencies.
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118464
http://www.pigcraft.ugu.pl/member.php?action=profile&uid=209007
https://zhilexue.tech/space-uid-18500.html
http://bbs.qc0769.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=418089
http://www.bhl7.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=80892
http://support-groups.org/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=109526
http://forum.soundspeed.ru/member.php?934484-TimothyKay
http://www.seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1196916
http://www.yw10.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=198312
https://gti-club.ru/forum/member.php?u=374384 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you will note up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of additional ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a habituated investor or a outr‚ beginner, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to ease you keep informed in the briskly evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
https://www.thbattle.net/space-uid-556779.html
http://bbs.94kk.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=8738232
http://www.egyedu.com/vb/member.php/554963-Timothynoupt
http://www.lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761
http://chunboshi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=1703687
http://www.28tongji.com/space-uid-1029873.html
http://www.jade-crack.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=785196
http://021bababa.org/space-uid-486319.html
http://www.1k9g.com/space-uid-190577.html
https://forum.cabal.playthisgame.com/member.php?1595149-TimothyDeege -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you inclination bring to light up-to-date good copy, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with assiduity leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a erratic proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to staff you stay informed in the at full speed evolving world of digital currencies.
https://www.flashflashrevolution.com/profile/TimothyMIC/
http://piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=88253
https://masterbationtube.com/user/TimothyEndok/videos
https://zhilexue.tech/space-uid-18500.html
http://1k9g.com/space-uid-190577.html
http://www.bjyou4122.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=201402
http://sailing-bluewater.com/forum/index.php?action=profile;u=2477373
https://98e.fun/space-uid-7010118.html
http://www.hrfrat.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=211760
http://www.nokiaceptr.com/member.php/692632-Timothyhab -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the the world at large of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination find up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a bizarre newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to servants you stay advised in the briskly evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://021bababa.org/space-uid-486319.html
http://www.nokiaceptr.com/member.php/692632-Timothyhab
http://zhilexue.tech/space-uid-18500.html
http://www.3ak.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=169423
http://bbs.94kk.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=8738232
https://masterbationstation.com/user/TimothyDUS/videos
http://bbs.yymlbb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=179528
http://kuzazhi.com/space-uid-146441.html
http://www.1k9g.com/space-uid-190577.html
https://www.winners24.pl/user-32586.html -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination bring to light up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with assiduity leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a habituated investor or a curious newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to help you tarry up to date in the rapidly evolving mankind of digital currencies.
http://forum.ll2.ru/member.php?1140172-Timothynoiva
http://scutn.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=537861
https://piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=88253
http://zhilexue.tech/space-uid-18500.html
http://chunboshi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=1703687
https://pornvideos.win/user/TimothyFlavy/videos
https://lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761
https://www.lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761
http://bbs.17dra.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=222947
http://www.piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=88253 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination note up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a bizarre stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to help you keep up to date in the rapidly evolving mankind of digital currencies.
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118464
http://vkeepw.evai.pl/home.php?mod=space&uid=55648
https://www.medflyfish.com/index.php?action=profile;u=3909979
http://www.nokiaceptr.com/member.php/692632-Timothyhab
https://newvideosxxx.com/user/Timothyhew/videos
http://bbs.py27.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=388220
http://bbs.94kk.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=8738232
https://forum.cabal.playthisgame.com/member.php?1595149-TimothyDeege
https://forum.finexfloors.ru/index.php?action=profile;u=2348
https://bans.org.ua/index.php?action=profile;u=1301393 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you will find up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a bizarre stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to ease you impede learned in the briskly evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
http://worldpoetry.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=323941
http://skiindustry.org:/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=1137601
https://aroundsuannan.ssru.ac.th/index.php?action=profile;u=9433798
https://www.foodntours.com/user/Timothykit/videos
http://sailing-bluewater.com/forum/index.php?action=profile;u=2477373
http://forum.soundspeed.ru/member.php?934484-TimothyKay
http://www.zgqsz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=307685
http://1k9g.com/space-uid-190577.html
http://xavierdeschamps.free.fr/Escalade/Forum_escalade/profile.php?id=589402
http://www.jbt4.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=8532477 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the the world at large of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you will find up-to-date good copy, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a curious beginner, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable low-down and perspectives to help you tarry learned in the before you can turn around evolving mankind of digital currencies.
http://www.dllaoma.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=360311
http://lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761
http://www.worldpoetry.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=323941
http://bjyou4122.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=201402
http://bbs.yanfabu.com/space-username-Timothyabike.html
https://forum.tvfool.com/member.php?u=1701170
http://icanfixupmyhome.com/considered_opinions/index.php?action=profile;u=1639022
http://xinsanwen2011.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=210132
http://www.lezcc.com/home.php?mod=space&username=Timothycen
https://www.3asq.co/member.php?u=804886 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you inclination find up-to-date good copy, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips pro navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a habituated investor or a curious proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to staff you tarry informed in the at full speed evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://www.mmecaw.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=489149
http://piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=88253
http://m.414500.cc/home.php?mod=space&uid=2985649
https://www.ilcirotano.it/annunci/author/timothynek/
http://www.oople.com/forums/member.php?u=566871
https://www.lifesshortlivefree.com/community/profile/timothyabugs/
http://bbs.yymlbb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=179528
http://021bababa.org/space-uid-486319.html
http://www.52meiss.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=301632
http://worldpoetry.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=323941 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination note up-to-date good copy, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips pro navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a outr‚ newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to ease you tarry learned in the at full speed evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://trj.easyye.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=118464
https://fxprimer.ru/index.php?action=profile;u=2112533
https://oople.com/forums/member.php?u=566871
http://bbs.py27.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=388220
https://www.thbattle.net/space-uid-556779.html
http://www.28tongji.com/space-uid-1029873.html
https://hshxt.top/space-uid-476.html
http://vkeepw.evai.pl/home.php?mod=space&uid=55648
http://bbs.51pinzhi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=6516352
http://52meiss.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=301632 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the the world at large of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting come across up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a habituated investor or a bizarre newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to servants you keep advised in the briskly evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://chunboshi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=1703687
http://www.fsh.mi.th/newswb3/index.php?action=profile;u=29521
https://hshxt.top/space-uid-476.html
https://forum.veriagi.com/profile.php?id=942501
http://www.zgqsz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=307685
https://newvideosxxx.com/user/Timothyhew/videos
https://icanfixupmyhome.com/considered_opinions/index.php?action=profile;u=1639022
http://sailing-bluewater.com/forum/index.php?action=profile;u=2477373
http://m.414500.cc/home.php?mod=space&uid=2985649
https://bans.org.ua/index.php?action=profile;u=1301393 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you will find up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a erratic stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to ease you tarry up to date in the before you can turn around evolving world of digital currencies.
http://jiangzhongyou.net/space-uid-506861.html
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118464
https://www.98e.fun/space-uid-7010118.html
https://www.hdkaraokesong.com/space-uid-260280.html
https://www.lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761
https://myforexforums.com/member.php/37131-TimothyEmema
http://www.bhl7.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=80892
http://users.atw.hu/rfclub/index.php?action=profile;u=5690
http://www.egyedu.com/vb/member.php/554963-Timothynoupt
http://www.lezcc.com/home.php?mod=space&username=Timothycen -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you inclination find up-to-date good copy, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a erratic stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable low-down and perspectives to staff you keep advised in the briskly evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://scutn.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=537861
https://www.lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761
https://icanfixupmyhome.com/considered_opinions/index.php?action=profile;u=1639022
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118514
http://www.fsh.mi.th/newswb3/index.php?action=profile;u=29521
http://pufa.chemapao.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=279340
http://www.1k9g.com/space-uid-190577.html
http://sailing-bluewater.com/forum/index.php?action=profile;u=2477373
https://www.consolegames.ro/forum/members/timothytom/
http://www.pigcraft.ugu.pl/member.php?action=profile&uid=209007 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting note up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips pro navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a bizarre proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable dirt and perspectives to help you stay up to date in the rapidly evolving earth of digital currencies.
https://aroundsuannan.ssru.ac.th/index.php?action=profile;u=9433798
https://myforexforums.com/member.php/37131-TimothyEmema
http://www.pigcraft.ugu.pl/member.php?action=profile&uid=209007
https://www.gingerhd.tv/user/Timothyket/videos
http://vkeepw.evai.pl/home.php?mod=space&uid=55648
http://jade-crack.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=785196
https://forum.uaewomen.net/member.php/805913-TimothyUsern
https://icanfixupmyhome.com/considered_opinions/index.php?action=profile;u=1639022
https://foro.noticias3d.com/vbulletin/member.php?u=268920
http://www.flicube.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=234287 -
flagyl antibiotic used to treat Cultural Competence in Healthcare - Providing Inclusive Care
-
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting bring to light up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with assiduity leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a bizarre newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to ease you stay advised in the at full speed evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
https://www.flashflashrevolution.com/profile/TimothyMIC/
http://bbs.17dra.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=222947
https://gxfcmao.com/space-uid-496135.html
http://zhilexue.tech/space-uid-18500.html
http://bbs2.xingxiancn.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=386430
http://www.flicube.com/home.php?mod=space&username=TimothyPaymn
http://www.egyedu.com/vb/member.php/554963-Timothynoupt
https://icanfixupmyhome.com/considered_opinions/index.php?action=profile;u=1639022
https://oople.com/forums/member.php?u=566871
https://indibloghub.com/profile/timothyhew -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you inclination note up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a habituated investor or a outr‚ proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to help you keep learned in the rapidly evolving mankind of digital currencies.
https://www.winners24.pl/user-32586.html
http://www.egyedu.com/vb/member.php/554963-Timothynoupt
https://pornvideos.win/user/TimothyFlavy/videos
https://gxfcmao.com/space-uid-496135.html
https://www.9tj.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=76538
http://xinsanwen2011.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=210132
http://bbs.panabit.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=394984
http://www.jbt4.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=8532477
https://forum.openbadania.pl/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=264169
http://www.oople.com/forums/member.php?u=566871 -
[youtube]z8ghSAWZZy8[/youtube]
-
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination come across up-to-date good copy, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a outr‚ newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable dirt and perspectives to staff you impede up to date in the at full speed evolving mankind of digital currencies.
http://worldpoetry.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=323941
https://www.heroscapers.com/community/member.php?u=679164
https://gxfcmao.com/space-uid-496135.html
https://forum.finexfloors.ru/index.php?action=profile;u=2348
https://masterbationstation.com/user/TimothyDUS/videos
http://fmkong.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=485703
http://www.zhuangxiuz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=741267
http://lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761
http://bbs.yongrenqianyou.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=4059416&do=profile
http://www.oople.com/forums/member.php?u=566871 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the the world at large of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination find up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a bizarre stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to ease you tarry up to date in the at full speed evolving world of digital currencies.
https://slovakia-forex.com/members/237905-timothypsync
http://sailing-bluewater.com/forum/index.php?action=profile;u=2477373
http://zhwbn.com/bbs/space-uid-145749.html
http://www.yw10.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=198312
http://zhuangxiuz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=741267
http://i0110.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=516822
http://xavierdeschamps.free.fr/Escalade/Forum_escalade/profile.php?id=589402
https://www.gingerhd.tv/user/Timothyket/videos
https://4komagram.com/users/300930
http://xinsanwen2011.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=210132 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination note up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a curious proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to servants you keep advised in the rapidly evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
https://slashtw.space/home.php?mod=space&uid=79047
http://bbs.94kk.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=8738232
http://bbs2.xingxiancn.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=386430
http://bbs.zhizhuyx.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=9269716
https://slovakia-forex.com/members/237905-timothypsync
https://pornvideos.win/user/TimothyFlavy/videos
http://m.414500.cc/home.php?mod=space&uid=2985649
http://bbs.panabit.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=394984
http://www.ppivn.vn/forum/user-141660.html
http://users.atw.hu/rfclub/index.php?action=profile;u=5690 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination come across up-to-date good copy, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with assiduity leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a outr‚ proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to ease you tarry up to date in the before you can turn around evolving world of digital currencies.
https://www.lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761
http://anima-rpg.com:/member.php?action=profile&uid=305950
http://yinyue7.com/space-uid-941094.html
http://forum.fcmn.co.il/member.php?action=profile&uid=290040
http://www.seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1196916
http://trj.easyye.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=118514
http://worldpoetry.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=323941
http://skiindustry.org:/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=1137601
http://www.chenjiagou.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=189636
http://www.iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=780146 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination bring to light up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips pro navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a bizarre beginner, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable dirt and perspectives to servants you impede learned in the at full speed evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://www.flicube.com/home.php?mod=space&username=TimothyPaymn
http://www.1k9g.com/space-uid-190577.html
https://www.donyaihom.go.th/webboard/index.php?action=profile;u=748988
https://www.flashflashrevolution.com/profile/TimothyMIC/
http://yinyue7.com/space-uid-941094.html
https://bbs.521zixuan.com/space-uid-609431.html
http://www.pengstys.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=105508
https://www.thbattle.net/space-uid-556779.html
http://www.mmecaw.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=489149
http://bbs.yanfabu.com/space-username-Timothyabike.html -
[youtube]z8ghSAWZZy8[/youtube]
-
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you inclination come across up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a curious stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable dirt and perspectives to staff you tarry informed in the before you can turn around evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://www.zgbbs.org/space-uid-155922.html
http://www.bjyou4122.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=201402
http://shqiperia.altervista.org/members/229514-TimothyAnode?s=53ecf50d38d9525a085a5abc0ccb7218
https://oople.com/forums/member.php?u=566871
http://www.pigcraft.ugu.pl/member.php?action=profile&uid=209007
http://www.lezcc.com/home.php?mod=space&username=Timothycen
http://www.dllaoma.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=360311
http://bbs.py27.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=388220
http://jade-crack.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=785196
http://lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting find up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of additional ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a habituated investor or a erratic stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to help you tarry informed in the briskly evolving world of digital currencies.
http://m.414500.cc/home.php?mod=space&uid=2985649
http://chunboshi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=1703687
https://www.lifesshortlivefree.com/community/profile/timothyabugs/
http://www.flicube.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=234287
https://newvideosxxx.com/user/Timothyhew/videos
http://www.lezcc.com/home.php?mod=space&username=Timothycen
https://visualchemy.gallery/forum/profile.php?id=3478404
http://anima-rpg.com:/member.php?action=profile&uid=305950
http://www.pigcraft.ugu.pl/member.php?action=profile&uid=209007
https://forum.tvfool.com/member.php?u=1701170 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination find up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of additional ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a erratic newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to staff you keep informed in the rapidly evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://forum.ll2.ru/member.php?1140172-Timothynoiva
https://www.3asq.co/member.php?u=804886
https://pornvideos.win/user/TimothyFlavy/videos
https://gxfcmao.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=496135
http://xinsanwen2011.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=210132
http://support-groups.org/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=109526
https://oople.com/forums/member.php?u=566871
http://yw10.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=198312
http://www.lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761
https://www.hubtamil.com/talk/member.php?1521101-TimothyBib -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting come across up-to-date good copy, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with assiduity leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a erratic beginner, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to staff you impede informed in the rapidly evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://bbs2.xingxiancn.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=386430
http://www.sorworakit.com/main/index.php?action=profile;u=2852786
http://sljlz.92zyb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=178563
http://support-groups.org/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=109526
http://bbs.yongrenqianyou.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=4059416&do=profile
http://forum.fcmn.co.il/member.php?action=profile&uid=290040
http://zhilexue.tech/space-uid-18500.html
https://newvideosxxx.com/user/Timothyhew/videos
https://www.ilcirotano.it/annunci/author/timothynek/
https://forum.tvfool.com/member.php?u=1701170 -
[youtube]z8ghSAWZZy8[/youtube]
-
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination find up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a erratic newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable dirt and perspectives to staff you stay learned in the before you can turn around evolving world of digital currencies.
http://www.lezcc.com/home.php?mod=space&username=Timothycen
http://www.hrfrat.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=211760
http://xavierdeschamps.free.fr/Escalade/Forum_escalade/profile.php?id=589402
http://www.alzlt5.com/space-uid-283868.html
https://latino-forex.com/members/219404-timothysmelp
https://forum.finexfloors.ru/index.php?action=profile;u=2348
http://icanfixupmyhome.com/considered_opinions/index.php?action=profile;u=1639022
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118464
http://i0110.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=516822
http://www.egyedu.com/vb/member.php/554963-Timothynoupt -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you inclination come across up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a curious proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to help you keep up to date in the before you can turn around evolving world of digital currencies.
http://bbs.17dra.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=222947
http://x4kurd.freetzi.com/member.php?action=profile&uid=70138
http://theoryornot.com/member.php?10238-Timothyecoky
http://seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1196916
https://www.heroscapers.com/community/member.php?u=679164
https://bdsmboard.org/member.php?336994-Timothysworo
http://bbs.94kk.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=8738232
https://www.flashflashrevolution.com/profile/TimothyMIC/
https://myforexforums.com/member.php/37131-TimothyEmema
http://bbs.yanfabu.com/space-username-Timothyabike.html -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination bring to light up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of additional ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a curious proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to help you stay advised in the rapidly evolving mankind of digital currencies.
http://www.dllaoma.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=360311
https://newvideosxxx.com/user/Timothyhew/videos
http://www.52meiss.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=301632
https://forum.tvfool.com/member.php?u=1701170
https://indibloghub.com/profile/timothyhew
http://www.egyedu.com/vb/member.php/554963-Timothynoupt
https://masterbationstation.com/user/TimothyDUS/videos
http://www.seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1196916
https://latino-forex.com/members/219404-timothysmelp
http://www.lezcc.com/home.php?mod=space&username=Timothycen -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting bring to light up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a outr‚ newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to help you stay up to date in the at full speed evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
https://pornvideos.win/user/TimothyFlavy/videos
https://www.lifesshortlivefree.com/community/profile/timothyabugs/
http://www.oople.com/forums/member.php?u=566871
http://jade-crack.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=785196
https://aroundsuannan.ssru.ac.th/index.php?action=profile;u=9433798
http://fmkong.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=485703
http://www.alzlt5.com/space-uid-283868.html
http://www.hrfrat.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=211760
https://speakerdeck.com/timothyascen
https://latino-forex.com/members/219404-timothysmelp -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you will note up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with assiduity leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a erratic beginner, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to staff you stay learned in the briskly evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://www.nokiaceptr.com/member.php/692632-Timothyhab
https://www.ilcirotano.it/annunci/author/timothynek/
http://bbs.zhizhuyx.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=9269716
http://worldpoetry.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=323941
http://1k9g.com/space-uid-190577.html
http://zqykj.com/bbs/home.php?mod=space&uid=246289
https://www.9tj.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=76538
http://www.egyedu.com/vb/member.php/554963-Timothynoupt
http://www.iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=780146
https://fxprimer.ru/index.php?action=profile;u=2112533 -
purple pill viagra Modern equipment includes automated vial washing machines that ensure containers are thoroughly cleaned before filling.
-
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the the world at large of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting find up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a erratic beginner, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to servants you stay informed in the rapidly evolving mankind of digital currencies.
https://www.foodntours.com/user/Timothykit/videos
http://www.ppivn.vn/forum/user-141660.html
http://forum.ll2.ru/member.php?1140172-Timothynoiva
https://foro.noticias3d.com/vbulletin/member.php?u=268920
http://www.nokiaceptr.com/member.php/692632-Timothyhab
https://slovakia-forex.com/members/237905-timothypsync
http://lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761
http://icanfixupmyhome.com/considered_opinions/index.php?action=profile;u=1639022
https://indibloghub.com/profile/timothyhew
https://www.3asq.co/member.php?u=804886 -
[youtube]z8ghSAWZZy8[/youtube]
-
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you inclination note up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a outr‚ proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable low-down and perspectives to servants you tarry advised in the rapidly evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
https://www.lifesshortlivefree.com/community/profile/timothyabugs/
http://www.3ak.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=169423
http://www.worldpoetry.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=323941
http://yw10.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=198312
http://sljlz.92zyb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=178563
https://astraclub.ru/members/340486-TimothyMon
http://iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=780146
https://www.medflyfish.com/index.php?action=profile;u=3909979
https://www.consolegames.ro/forum/members/timothytom/
https://bbs.panabit.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=394984 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the the world at large of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting find up-to-date good copy, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with assiduity leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a bizarre newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to ease you impede advised in the rapidly evolving world of digital currencies.
https://hshxt.top/space-uid-476.html
http://www.3ak.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=169423
http://sljlz.92zyb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=178563
http://pufa.chemapao.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=279340
https://www.lifesshortlivefree.com/community/profile/timothyabugs/
http://www.dllaoma.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=360311
http://www.mmecaw.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=489149
http://www.flicube.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=234287
http://zhuangxiuz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=741267
http://forum.ll2.ru/member.php?1140172-Timothynoiva -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you will note up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a curious beginner, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to servants you impede advised in the briskly evolving earth of digital currencies.
https://www.ilcirotano.it/annunci/author/timothynek/
http://www.52meiss.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=301632
https://forum.tvfool.com/member.php?u=1701170
https://gxfcmao.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=496135
http://shqiperia.altervista.org/members/229514-TimothyAnode?s=53ecf50d38d9525a085a5abc0ccb7218
http://www.neworleansbbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=197900
http://bbs.xyslysy.cn/upload/home.php?mod=space&uid=14504
http://vkeepw.evai.pl/home.php?mod=space&uid=55648
https://pornvideos.win/user/TimothyFlavy/videos
https://latino-forex.com/members/219404-timothysmelp -
[youtube]z8ghSAWZZy8[/youtube]
-
[youtube]z8ghSAWZZy8[/youtube]
-
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination find up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of additional ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with assiduity leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips pro navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a erratic proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable low-down and perspectives to staff you impede up to date in the rapidly evolving world of digital currencies.
https://bans.org.ua/index.php?action=profile;u=1301393
https://gxfcmao.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=496135
http://bbs.yymlbb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=179528
http://www.zhilexue.tech/space-uid-18500.html
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118464
http://bbs.94kk.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=8738232
https://icanfixupmyhome.com/considered_opinions/index.php?action=profile;u=1639022
http://bbs.yongrenqianyou.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=4059416&do=profile
http://www.fsh.mi.th/newswb3/index.php?action=profile;u=29521
https://bbs.521zixuan.com/space-uid-609431.html -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the the world at large of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting find up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a erratic proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to ease you impede learned in the at full speed evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
https://www.deadbeathomeowner.com/community/profile/timothyelord/
http://www.iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=780146
https://www.lifesshortlivefree.com/community/profile/timothyabugs/
http://zhwbn.com/bbs/space-uid-145749.html
http://witiai.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=52180
http://thisglobe.com/index.php?action=profile;u=19004865
https://www.98e.fun/space-uid-7010118.html
https://www.winners24.pl/user-32586.html
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118514
https://bdsmboard.org/member.php?336994-Timothysworo -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination bring to light up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with assiduity leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a erratic newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to servants you impede advised in the rapidly evolving mankind of digital currencies.
http://xavierdeschamps.free.fr/Escalade/Forum_escalade/profile.php?id=589402
http://www.worldpoetry.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=323941
http://chunboshi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=1703687
http://bbs.guitarw.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=29742
http://pufa.chemapao.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=279340
http://www.piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=88253
http://www.1k9g.com/space-uid-190577.html
http://zhuangxiuz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=741267
http://forum.mx-bikes.com/index.php?action=profile;u=11690
http://m.414500.cc/home.php?mod=space&uid=2985649 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the the world at large of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination note up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a habituated investor or a outr‚ newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to staff you tarry up to date in the briskly evolving mankind of digital currencies.
http://ipxa.ru/user/TimothyPex/
http://www.chenjiagou.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=189636
https://www.98e.fun/space-uid-7010118.html
https://gxfcmao.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=496135
http://www.egyedu.com/vb/member.php/554963-Timothynoupt
http://bbs.94kk.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=8738232
https://www.9tj.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=76538
http://iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=780146
https://forum.finexfloors.ru/index.php?action=profile;u=2348
http://www.ds-dealer.nichost.ru/forum/member.php?u=607153 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting bring to light up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with assiduity leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips pro navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a erratic stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable low-down and perspectives to servants you stay advised in the at full speed evolving world of digital currencies.
http://pufa.chemapao.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=279340
https://www.winners24.pl/user-32586.html
http://users.atw.hu/rfclub/index.php?action=profile;u=5690
http://worldpoetry.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=323941
http://www.52meiss.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=301632
http://sljlz.92zyb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=178563
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118514
http://www.3ak.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=169423
https://www.lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761
http://shqiperia.altervista.org/members/229514-TimothyAnode -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination note up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips for navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a habituated investor or a bizarre beginner, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable low-down and perspectives to staff you tarry up to date in the rapidly evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://www.yw10.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=198312
http://anima-rpg.com:/member.php?action=profile&uid=305950
https://www.lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761
http://www.zgbbs.org/space-uid-155922.html
http://bbs.51pinzhi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=6516352
https://astraclub.ru/members/340486-TimothyMon
https://www.consolegames.ro/forum/members/timothytom/
http://www.bjyou4122.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=201402
https://www.foodntours.com/user/Timothykit/videos
https://www.hubtamil.com/talk/member.php?1521101-TimothyBib -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting bring to light up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a bizarre stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable low-down and perspectives to help you impede learned in the at full speed evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
http://www.piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=88253
http://www.lezcc.com/home.php?mod=space&username=Timothycen
http://sailing-bluewater.com/forum/index.php?action=profile;u=2477373
http://theoryornot.com/member.php?10238-Timothyecoky
http://trj.easyye.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=118514
http://www.mmecaw.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=489149
https://aroundsuannan.ssru.ac.th/index.php?action=profile;u=9433798
http://bbs.zhizhuyx.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=9269716
https://latino-forex.com/members/219404-timothysmelp
https://www.3asq.co/member.php?u=804886 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you inclination bring to light up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of additional ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a bizarre proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to help you keep learned in the before you can turn around evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118514
https://bans.org.ua/index.php?action=profile;u=1301393
http://bbs.yymlbb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=179528
https://www.thbattle.net/space-uid-556779.html
https://piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=88253
http://users.atw.hu/rfclub/index.php?action=profile;u=5690
http://www.yw10.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=198312
https://www.98e.fun/space-uid-7010118.html
http://i0110.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=516822
http://theoryornot.com/member.php?10238-Timothyecoky -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you will come across up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a practised investor or a curious stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to staff you tarry up to date in the rapidly evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
http://www.toppr.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=217747
http://xinsanwen2011.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=210132
http://www.pigcraft.ugu.pl/member.php?action=profile&uid=209007
https://hshxt.top/space-uid-476.html
https://visualchemy.gallery/forum/profile.php?id=3478404
https://www.ilcirotano.it/annunci/author/timothynek/
http://bbs.qc0769.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=418089
http://bbs2.xingxiancn.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=386430
http://www.28tongji.com/space-uid-1029873.html
http://bjyou4122.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=201402 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting find up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips pro navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a curious beginner, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable dirt and perspectives to staff you stay up to date in the rapidly evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
http://www.jade-crack.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=785196
http://kidsnighttonight.com:/forums/member.php?action=profile&uid=325893
https://piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=88253
https://forum.veriagi.com/profile.php?id=942501
https://www.thbattle.net/space-uid-556779.html
http://lighttoguideourfeet.com/member.php?u=1359761
https://www.3asq.co/member.php?u=804886
https://forum.cabal.playthisgame.com/member.php?1595149-TimothyDeege
https://bans.org.ua/index.php?action=profile;u=1301393
http://1k9g.com/space-uid-190577.html -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you inclination find up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with business leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a habituated investor or a erratic stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to staff you tarry informed in the before you can turn around evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://bjyou4122.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=201402
http://worldpoetry.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=323941
http://bbs.yymlbb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=179528
https://www.thbattle.net/space-uid-556779.html
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118514
http://chunboshi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=1703687
http://witiai.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=52180
https://pornvideos.win/user/TimothyFlavy/videos
http://www.seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1196916
http://www.nokiaceptr.com/member.php/692632-Timothyhab -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination find up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of new ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with vigour leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips pro navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a outr‚ stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable report and perspectives to help you tarry learned in the at full speed evolving wonderful of digital currencies.
http://www.zhuangxiuz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=741267
https://forum.cabal.playthisgame.com/member.php?1595149-TimothyDeege
http://bjyou4122.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=201402
http://seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1196916
http://bbs.py27.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=388220
http://piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=88253
http://kuzazhi.com/space-uid-146441.html
http://www.yw10.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=198312
http://xinsanwen2011.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=210132
https://forum.finexfloors.ru/index.php?action=profile;u=2348 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting bring to light up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a established investor or a bizarre newcomer, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable low-down and perspectives to help you keep informed in the at full speed evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://trj.easyye.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=118464
http://www.28tongji.com/space-uid-1029873.html
http://worldpoetry.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=323941
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118464
https://foro.noticias3d.com/vbulletin/member.php?u=268920
http://www.alzlt5.com/space-uid-283868.html
http://support-groups.org/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=109526
https://bans.org.ua/index.php?action=profile;u=1301393
https://forum.uaewomen.net/member.php/805913-TimothyUsern
https://www.flashflashrevolution.com/profile/TimothyMIC/ -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you thinks fitting come across up-to-date talk, analytical articles, reviews of unknown ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a outr‚ stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable information and perspectives to servants you tarry informed in the rapidly evolving mankind of digital currencies.
http://vkeepw.evai.pl/home.php?mod=space&uid=55648
http://x4kurd.freetzi.com/member.php?action=profile&uid=70138
http://www.worldpoetry.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=323941
https://98e.fun/space-uid-7010118.html
https://masterbationstation.com/user/TimothyDUS/videos
http://theoryornot.com/member.php?10238-Timothyecoky
http://trj.easyye.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=118514
http://www.jbt4.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=8532477
http://www.zgqsz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=307685
https://piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=88253 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the elated of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you inclination come across up-to-date gossip, analytical articles, reviews of additional ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with assiduity leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips as regards navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a bizarre proselyte, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable dirt and perspectives to ease you stay learned in the rapidly evolving world of digital currencies.
http://tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=118514
http://x4kurd.freetzi.com/member.php?action=profile&uid=70138
http://forum.fcmn.co.il/member.php?action=profile&uid=290040
https://forum.veriagi.com/profile.php?id=942501
http://icanfixupmyhome.com/considered_opinions/index.php?action=profile;u=1639022
http://yinyue7.com/space-uid-941094.html
https://newvideosxxx.com/user/Timothyhew/videos
https://www.medflyfish.com/index.php?action=profile;u=3909979
http://www.support-groups.org/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=109526
http://bbs.xyslysy.cn/upload/home.php?mod=space&uid=14504 -
"CryptoUniverse" is a vibrant blog dedicated to the terra of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Here you determination note up-to-date news, analytical articles, reviews of modern ICOs, and in-depth guides on cryptocurrency investment. The blog also features interviews with industry leaders, insights into the latest trends, and tips since navigating the crypto market. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a erratic stranger, "CryptoUniverse" provides valuable dirt and perspectives to servants you tarry up to date in the at full speed evolving earth of digital currencies.
http://zhilexue.tech/space-uid-18500.html
https://forum.veriagi.com/profile.php?id=942501
http://www.dllaoma.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=360311
https://www.hdkaraokesong.com/space-uid-260280.html
https://aroundsuannan.ssru.ac.th/index.php?action=profile;u=9433798
http://trj.easyye.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=118514
http://bbs.94kk.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=8738232
http://theoryornot.com/member.php?10238-Timothyecoky
http://www.oople.com/forums/member.php?u=566871
http://kidsnighttonight.com:/forums/member.php?action=profile&uid=325893 -
https://alfabankpartner.ru/
-
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
娛樂城推薦
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
娛樂城
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
娛樂城
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
3a娛樂城
-
娛樂城
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
In the at a gallop evolving landscape of monetary technology, cryptocurrencies play a joke on emerged as a subversive force. This blog delves into the anfractuous far-out of digital currencies, donation insights into how cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others are reshaping the tomorrow's of finance. We explore the underlying blockchain technology, its potential to suggest good, decentralized transactions, and how it challenges stock banking systems. Our concentration extends to the sensitive disposition of cryptocurrency markets, investment strategies, and the implications for universal economies. We also enquire regulatory responses to this late front line, aiming to demystify the complexities and highlight the opportunities within the crypto universe. Connect us as we cross with the aid this exhilarating transition, unveiling the possibilities and challenges of cryptocurrencies.
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/16/antminer-s19j-specs-everything-you-need-to-know-about-this-powerhouse-miner/
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/18/a-guide-to-binance-14-wallet-everything-you-need-to-know/
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/18/arbitrum-airdrop-on-twitter-and-odyssey-cheat-sheet/
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/17/apecoin-exploring-the-price-market-cap-nfts-and-more/
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/16/understanding-the-antminer-e9-price-and-its-power-in-the-asic-mining-industry/ -
3a娛樂城
3a娛樂城 -
娛樂城
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
娛樂城
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
In the rapidly evolving scene of economic technology, cryptocurrencies have emerged as a rebel force. This blog delves into the rococo humankind of digital currencies, oblation insights into how cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others are reshaping the future of finance. We travel the underlying blockchain technology, its the right stuff to propose good, decentralized transactions, and how it challenges habitual banking systems. Our convergence extends to the eruptive identity of cryptocurrency markets, investment strategies, and the implications during epidemic economies. We also look into regulatory responses to this stylish bounds, aiming to demystify the complexities and highlight the opportunities within the crypto universe. Link us as we navigate under the aegis this energizing transition, unveiling the possibilities and challenges of cryptocurrencies.
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/17/astar-crypto-your-ultimate-guide-to-buying-and-understanding-astar-network/
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/18/what-is-binance-salary-and-how-to-earn-a-high-salary-in-remote-crypto-jobs/
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/18/exploring-the-trove-marketplace-on-arbitrum-your-gateway-to-treasure-troves-and-nfts/
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/16/understanding-0x-protocol-a-decentralized-exchange-protocol/
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/18/how-to-get-a-600-sign-up-bonus-on-binance/ -
In the lickety-split evolving landscape of fiscal technology, cryptocurrencies have emerged as a subversive force. This blog delves into the sinuous faction of digital currencies, donation insights into how cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others are reshaping the tomorrow's of finance. We inquire the underlying blockchain technology, its covert to offer secure, decentralized transactions, and how it challenges standard banking systems. Our convergence extends to the eruptive identity of cryptocurrency markets, investment strategies, and the implications representing far-reaching economies. We also look into regulatory responses to this reborn frontier, aiming to demystify the complexities and highlight the opportunities within the crypto universe. Join us as we sail under the aegis this exhilarating wander, unveiling the possibilities and challenges of cryptocurrencies.
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/16/the-ultimate-guide-to-bitmain-antminer-l3-580m-and-580mh-s/
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/17/uniswap-arbitrum-the-future-of-decentralized-exchanges/
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/17/the-need-for-speed-how-arbitrum-optimizes-ethereum-transactions/
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/18/voyager-and-binance-a-complete-guide-to-buying-transferring-and-trading-crypto-assets/
https://blockchainpulse.one/2024/01/17/basic-attention-token-bat-everything-you-need-to-know/ -
In this astounding blog post, we delve into the electric and often misunderstood realm of cryptocurrencies. We start by means of unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they drill equal, and why they've fit a valued piece of today's economic landscape. Our junket takes us through the summary of digital currencies, highlighting their evolvement from the inception of Bitcoin to the separate array of coins available today. We'll research the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures security and transparency in transactions. The brief also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, present valuable insights in search both novices and acclimated investors. Link us as we voyage the intriguing area of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the latent of this digital whirl in finance.
https://acemtsg.com/forum/member.php?275258-Alfredvom
http://www.jade-crack.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=819949
http://bjyou4122.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=206346
https://www.metal-tracker.com/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=927371041
https://www.troysupply.com/upload/member.php?action=profile&uid=1616 -
3a娛樂城
3a娛樂城 -
In this amazing blog post, we delve into the high-powered and often misunderstood area of cryptocurrencies. We start past unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they work, and why they've grow a relevant piece of today's monetary landscape. Our junket takes us into done with the summary of digital currencies, highlighting their formation from the inception of Bitcoin to the mixed array of coins convenient today. We'll survey the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures care and transparency in transactions. The register also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, present valuable insights in search both novices and acclimated investors. Solder together us as we navigate the intriguing area of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the aptitude of this digital cataclysm in finance.
http://bbs.py27.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=388838
https://masterbationstation.com/user/Alfredlep/videos
http://www.bjyou4122.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=206346
https://piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=90020
http://bbs.qc0769.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=419382 -
In this amazing blog despatch, we delve into the zealous and again misunderstood area of cryptocurrencies. We start past unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they work, and why they've develop a valuable piece of today's pecuniary landscape. Our junket takes us through the history of digital currencies, highlighting their evolvement from the inception of Bitcoin to the mixed array of coins handy today. We'll explore the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures security and transparency in transactions. The delivery also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, offering valuable insights in search both novices and practised investors. Solder together us as we voyage the intriguing area of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the aptitude of this digital cataclysm in finance.
https://www.dragonsword.com/member.php?action=profile&uid=6479
http://witiai.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=53413
http://www.zhilexue.tech/space-uid-19093.html
http://chunboshi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=1714548
http://www.pengstys.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=106122 -
In this astounding blog dispatch, we delve into the high-powered and commonly misunderstood realm of cryptocurrencies. We start past unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they job, and why they've develop a significant piece of today's pecuniary landscape. Our travel takes us into done with the intelligence of digital currencies, highlighting their evolvement from the inception of Bitcoin to the diverse array of coins at one's disposal today. We'll survey the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures deposit and transparency in transactions. The delivery also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, contribution valuable insights for both novices and prepared investors. Join us as we voyage the intriguing great of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the latent of this digital whirl in finance.
https://hdkaraokesong.com/space-uid-262296.html
https://forum.spherecommunity.net/User-Alfredmesia
http://www.pigcraft.ugu.pl/member.php?action=profile&uid=211709
http://wuyuebanzou.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=447848
https://indibloghub.com/profile/alfreddam -
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
https://www.xn-----7kccgclceaf3d0apdeeefre0dt2w.xn--p1ai/
-
In this overwhelming blog despatch, we delve into the electric and commonly misunderstood confines of cryptocurrencies. We start close unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they drill equal, and why they've grow a valued character of today's pecuniary landscape. Our journey takes us because of the intelligence of digital currencies, highlighting their evolution from the inception of Bitcoin to the separate array of coins at one's disposal today. We'll explore the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures safe keeping and transparency in transactions. The brief also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, present valuable insights in search both novices and practised investors. Join us as we navigate the intriguing area of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the latent of this digital whirl in finance.
http://www.mmecaw.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=500518
http://support-groups.org/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=113863
http://kidsnighttonight.com:/forums/member.php?action=profile&uid=328389
https://www.lifesshortlivefree.com/community/profile/alfredsmite/
http://chunboshi.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=1714548 -
In this astounding blog dispatch, we delve into the dynamic and again misunderstood area of cryptocurrencies. We start close unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they job, and why they've grow a valued part of today's financial landscape. Our journey takes us because of the history of digital currencies, highlighting their advance from the inception of Bitcoin to the diverse array of coins at one's disposal today. We'll scrutinize the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures security and transparency in transactions. The brief also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, gift valuable insights for the purpose both novices and seasoned investors. Ally us as we navigate the intriguing great of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the aptitude of this digital cataclysm in finance.
https://forum.openbadania.pl/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=266635
http://bbs.qc0769.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=419382
http://ds-dealer.nichost.ru/forum/member.php?u=619034
http://pufa.chemapao.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=289786
http://pawlowski.ontheweb.nu/Forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=3985 -
In this amazing blog dispatch, we delve into the zealous and again misunderstood confines of cryptocurrencies. We start by unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they work, and why they've fit a valued division of today's economic landscape. Our go abroad takes us into done with the intelligence of digital currencies, highlighting their evolvement from the inception of Bitcoin to the separate array of coins convenient today. We'll research the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures safe keeping and transparency in transactions. The delivery also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, offering valuable insights for both novices and acclimated investors. Link us as we journey the intriguing world of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the latent of this digital circle in finance.
http://witiai.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=53413
https://www.deadbeathomeowner.com/community/profile/alfredboula/
http://www.1k9g.com/space-uid-191231.html
http://bbs2.xingxiancn.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=388263
http://kidsnighttonight.com:/forums/member.php?action=profile&uid=328389 -
娛樂城推薦
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
娛樂城
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
In this amazing blog post, we delve into the zealous and often misunderstood confines of cryptocurrencies. We start close unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they charge, and why they've grow a valued part of today's pecuniary landscape. Our junket takes us into done with the summary of digital currencies, highlighting their evolution from the inception of Bitcoin to the miscellaneous array of coins handy today. We'll survey the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures deposit and transparency in transactions. The post also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, offering valuable insights in search both novices and prepared investors. Solder together us as we journey the intriguing exactly of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the latent of this digital circle in finance.
http://shqiperia.altervista.org/members/234498-AlfredHah
http://kidsnighttonight.com:/forums/member.php?action=profile&uid=328389
https://www.ukspeaks.co.uk/members/217906-Alfredclina
http://www.ds-dealer.nichost.ru/forum/member.php?u=619034
http://www.1k9g.com/space-uid-191231.html -
娛樂城
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
In this astounding blog dispatch, we delve into the high-powered and often misunderstood palatinate of cryptocurrencies. We start past unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they work, and why they've grow a valuable division of today's monetary landscape. Our junket takes us into done with the history of digital currencies, highlighting their evolvement from the inception of Bitcoin to the diverse array of coins handy today. We'll explore the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures security and transparency in transactions. The delivery also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, present valuable insights for the purpose both novices and practised investors. Ally us as we journey the intriguing world of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the potential of this digital revolution in finance.
https://bbs.panabit.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=395881
https://www.9tj.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=91209
http://bbs.yymlbb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=180411
http://www.1k9g.com/space-uid-191231.html
http://bbs.qc0769.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=419382 -
In this exciting blog post, we delve into the electric and again misunderstood area of cryptocurrencies. We start past unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they drill equal, and why they've develop a relevant piece of today's monetary landscape. Our go abroad takes us because of the narrative of digital currencies, highlighting their advance from the inception of Bitcoin to the mixed array of coins available today. We'll scrutinize the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures deposit and transparency in transactions. The post also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, present valuable insights for both novices and acclimated investors. Ally us as we navigate the intriguing area of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the aptitude of this digital cataclysm in finance.
http://kuzazhi.com/space-uid-147575.html
http://www.seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1202183
http://molifan.net/space-uid-1986549.html
http://forum.aunbox.com/member.php?8799902-Alfredrob
http://xavierdeschamps.free.fr/Escalade/Forum_escalade/profile.php?id=663046 -
https://www.amec.com.vn/wp-pages/pag/%20%20melbet_promo_code_free_welcome_bonus.html
https://lagencedecomm.fr/pgs/code_promo_157.html
http://fcdoazit.org/img/pgs/?1xbet_promo_code_free_bonus_code.html
https://joshicity.com/wp-content/pgs/1xbet_promo_code_free_bonus_code.html
https://llibertat.cat/consultespopulars/pages/codigo_promocional_39.html -
In this overwhelming blog transmit, we delve into the zealous and commonly misunderstood confines of cryptocurrencies. We start close unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they job, and why they've fit a valuable part of today's monetary landscape. Our travel takes us be means of the narrative of digital currencies, highlighting their evolution from the inception of Bitcoin to the diverse array of coins available today. We'll scrutinize the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures safe keeping and transparency in transactions. The delivery also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, present valuable insights to both novices and seasoned investors. Join us as we handle the intriguing world of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the dormant of this digital revolution in finance.
http://wuyuebanzou.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=447848
http://anima-rpg.com:/member.php?action=profile&uid=308721
https://bbs.m2.hk/home.php?mod=space&uid=85188
http://bbs.yymlbb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=180411
http://www.ds-dealer.nichost.ru/forum/member.php?u=619034 -
Dubai, a city known for its opulence and modernity, demands a mode of transportation that reflects its grandeur. For those seeking a cost-effective and reliable long-term solution, Somonion Rent Car LLC emerges as the premier choice for monthly car rentals in Dubai. With a diverse fleet ranging from compact cars to premium vehicles, the company promises an unmatched blend of affordability, flexibility, and personalized service.
Favorable Rental Conditions:
Understanding the potential financial strain of long-term car rentals, Somonion Rent Car LLC aims to make your journey more economical. The company offers flexible rental terms coupled with exclusive discounts for loyal customers. This commitment to affordability extends beyond the rental cost, as additional services such as insurance, maintenance, and repair ensure your safety and peace of mind throughout the duration of your rental.
A Plethora of Options:
Somonion Rent Car LLC boasts an extensive selection of vehicles to cater to diverse preferences and budgets. Whether you're in the market for a sleek sedan or a spacious crossover, the company has the perfect car to complement your needs. The transparency in pricing, coupled with the ease of booking through their online platform, makes Somonion Rent Car LLC a hassle-free solution for those embarking on a long-term adventure in Dubai.
Car Rental Services Tailored for You:
Somonion Rent Car LLC doesn't just offer cars; it provides a comprehensive range of rental services tailored to suit various occasions. From daily and weekly rentals to airport transfers and business travel, the company ensures that your stay in Dubai is not only comfortable but also exudes prestige. The fleet includes popular models such as the Nissan Altima 2018, KIA Forte 2018, Hyundai Elantra 2018, and the Toyota Camry Sport Edition 2020, all available for monthly rentals at competitive rates.
Featured Deals and Specials:
Somonion Rent Car LLC constantly updates its offerings to provide customers with the best deals. Featured cars like the Hyundai Sonata 2018 and Hyundai Santa Fe 2018 add a touch of luxury to your rental experience, with daily rates starting as low as AED 100. The company's commitment to affordable luxury is further emphasized by the online booking system, allowing customers to secure the best deals in real-time through their website or by contacting the experts via phone or WhatsApp.
Conclusion:
Whether you're a tourist looking to explore Dubai at your pace or a business traveler in need of a reliable and prestigious mode of transportation, Somonion Rent Car LLC stands as the go-to choice for monthly car rentals in Dubai. Unlock the ultimate mobility experience with Somonion, where affordability meets excellence, ensuring your journey through Dubai is as seamless and luxurious as the city itself. Contact Somonion Rent Car LLC today and embark on a journey where every mile is a testament to comfort, style, and unmatched service. -
娛樂城
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
monthly car rental in dubai
Dubai, a city known for its opulence and modernity, demands a mode of transportation that reflects its grandeur. For those seeking a cost-effective and reliable long-term solution, Somonion Rent Car LLC emerges as the premier choice for monthly car rentals in Dubai. With a diverse fleet ranging from compact cars to premium vehicles, the company promises an unmatched blend of affordability, flexibility, and personalized service.
Favorable Rental Conditions:
Understanding the potential financial strain of long-term car rentals, Somonion Rent Car LLC aims to make your journey more economical. The company offers flexible rental terms coupled with exclusive discounts for loyal customers. This commitment to affordability extends beyond the rental cost, as additional services such as insurance, maintenance, and repair ensure your safety and peace of mind throughout the duration of your rental.
A Plethora of Options:
Somonion Rent Car LLC boasts an extensive selection of vehicles to cater to diverse preferences and budgets. Whether you're in the market for a sleek sedan or a spacious crossover, the company has the perfect car to complement your needs. The transparency in pricing, coupled with the ease of booking through their online platform, makes Somonion Rent Car LLC a hassle-free solution for those embarking on a long-term adventure in Dubai.
Car Rental Services Tailored for You:
Somonion Rent Car LLC doesn't just offer cars; it provides a comprehensive range of rental services tailored to suit various occasions. From daily and weekly rentals to airport transfers and business travel, the company ensures that your stay in Dubai is not only comfortable but also exudes prestige. The fleet includes popular models such as the Nissan Altima 2018, KIA Forte 2018, Hyundai Elantra 2018, and the Toyota Camry Sport Edition 2020, all available for monthly rentals at competitive rates.
Featured Deals and Specials:
Somonion Rent Car LLC constantly updates its offerings to provide customers with the best deals. Featured cars like the Hyundai Sonata 2018 and Hyundai Santa Fe 2018 add a touch of luxury to your rental experience, with daily rates starting as low as AED 100. The company's commitment to affordable luxury is further emphasized by the online booking system, allowing customers to secure the best deals in real-time through their website or by contacting the experts via phone or WhatsApp.
Conclusion:
Whether you're a tourist looking to explore Dubai at your pace or a business traveler in need of a reliable and prestigious mode of transportation, Somonion Rent Car LLC stands as the go-to choice for monthly car rentals in Dubai. Unlock the ultimate mobility experience with Somonion, where affordability meets excellence, ensuring your journey through Dubai is as seamless and luxurious as the city itself. Contact Somonion Rent Car LLC today and embark on a journey where every mile is a testament to comfort, style, and unmatched service. -
In this exciting blog post, we delve into the electric and commonly misunderstood realm of cryptocurrencies. We start by unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they job, and why they've become a relevant part of today's pecuniary landscape. Our travel takes us because of the narrative of digital currencies, highlighting their evolution from the inception of Bitcoin to the miscellaneous array of coins convenient today. We'll survey the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures safe keeping and transparency in transactions. The register also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, offering valuable insights for both novices and acclimated investors. Link us as we voyage the intriguing great of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the aptitude of this digital cataclysm in finance.
https://forum.arabhardware.net/member.php?u=12314637
http://www.lezcc.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=199326
http://021bababa.org/space-uid-487472.html
https://bbs.521zixuan.com/space-uid-625763.html
https://www.thbattle.net/space-uid-556843.html -
In this amazing blog post, we delve into the high-powered and time after time misunderstood palatinate of cryptocurrencies. We start by unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they work, and why they've fit a valued character of today's pecuniary landscape. Our journey takes us be means of the narrative of digital currencies, highlighting their evolvement from the inception of Bitcoin to the miscellaneous array of coins at one's disposal today. We'll explore the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures care and transparency in transactions. The delivery also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, offering valuable insights to both novices and acclimated investors. Ally us as we voyage the intriguing great of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the potential of this digital whirl in finance.
http://www.tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=119635
http://bbs.zhizhuyx.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=9399694
https://zhilexue.tech/space-uid-19093.html
http://forum.aunbox.com/member.php?8799902-Alfredrob
http://piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=90020 -
娛樂城
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
娛樂城
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
In this overwhelming blog despatch, we delve into the dynamic and time after time misunderstood palatinate of cryptocurrencies. We start by unraveling the basics: what cryptocurrencies are, how they work, and why they've fit a significant piece of today's pecuniary landscape. Our junket takes us be means of the summary of digital currencies, highlighting their evolvement from the inception of Bitcoin to the miscellaneous array of coins convenient today. We'll research the underlying technology, blockchain, and how it ensures security and transparency in transactions. The post also addresses the risks and benefits of investing in cryptocurrencies, gift valuable insights to both novices and acclimated investors. Join us as we navigate the intriguing area of digital currencies, demystifying the complexities and revealing the aptitude of this digital revolution in finance.
http://www.w-whale.com/message/index.php?class1=52〈=en&page=481
https://blog.tommartin.uk/2010/december/nme_list_2010_live_images
https://pegas-med.ru/catalog/339-ortopedicheskie-izdelija/365-ortopedicheskie-i-protivoprolezhnevye-podushki/7874-podushka-sidene-ortopedicheskaja-reabilitatsionnaja--model-591.product
https://unitedpoint.de/index.php?site=profile&id=18&action=guestbook
http://www.marox.com.br/2018/11/03/heres-what-i-find-out-regarding-organization-due-diligence-data-room-checklist/#comment-889955 -
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
娛樂城推薦
2024娛樂城的創新趨勢
隨著2024年的到來,娛樂城業界正經歷著一場革命性的變遷。這一年,娛樂城不僅僅是賭博和娛樂的代名詞,更成為了科技創新和用戶體驗的集大成者。
首先,2024年的娛樂城極大地融合了最新的技術。增強現實(AR)和虛擬現實(VR)技術的引入,為玩家提供了沉浸式的賭博體驗。這種全新的遊戲方式不僅帶來視覺上的震撼,還為玩家創造了一種置身於真實賭場的感覺,而實際上他們可能只是坐在家中的沙發上。
其次,人工智能(AI)在娛樂城中的應用也達到了新高度。AI技術不僅用於增強遊戲的公平性和透明度,還在個性化玩家體驗方面發揮著重要作用。從個性化遊戲推薦到智能客服,AI的應用使得娛樂城更能滿足玩家的個別需求。
此外,線上娛樂城的安全性和隱私保護也獲得了顯著加強。隨著技術的進步,更加先進的加密技術和安全措施被用來保護玩家的資料和交易,從而確保一個安全可靠的遊戲環境。
2024年的娛樂城還強調負責任的賭博。許多平台採用了各種工具和資源來幫助玩家控制他們的賭博行為,如設置賭注限制、自我排除措施等,體現了對可持續賭博的承諾。
總之,2024年的娛樂城呈現出一個高度融合了技術、安全和負責任賭博的行業新面貌,為玩家提供了前所未有的娛樂體驗。隨著這些趨勢的持續發展,我們可以預見,娛樂城將不斷地創新和進步,為玩家帶來更多精彩和安全的娛樂選擇。 -
Watches World
Watches World: Elevating Luxury and Style with Exquisite Timepieces
Introduction:
Jewelry has always been a timeless expression of elegance, and nothing complements one's style better than a luxurious timepiece. At Watches World, we bring you an exclusive collection of coveted luxury watches that not only tell time but also serve as a testament to your refined taste. Explore our curated selection featuring iconic brands like Rolex, Hublot, Omega, Cartier, and more, as we redefine the art of accessorizing.
A Dazzling Array of Luxury Watches:
Watches World offers an unparalleled range of exquisite timepieces from renowned brands, ensuring that you find the perfect accessory to elevate your style. Whether you're drawn to the classic sophistication of Rolex, the avant-garde designs of Hublot, or the precision engineering of Patek Philippe, our collection caters to diverse preferences.
Customer Testimonials:
Our commitment to providing an exceptional customer experience is reflected in the reviews from our satisfied clientele. O.M. commends our excellent communication and flawless packaging, while Richard Houtman appreciates the helpfulness and courtesy of our team. These testimonials highlight our dedication to transparency, communication, and customer satisfaction.
New Arrivals:
Stay ahead of the curve with our latest additions, including the Tudor Black Bay Ceramic 41mm, Richard Mille RM35-01 Rafael Nadal NTPT Carbon Limited Edition, and the Rolex Oyster Perpetual Datejust 41mm series. These new arrivals showcase cutting-edge designs and impeccable craftsmanship, ensuring you stay on the forefront of luxury watch fashion.
Best Sellers:
Discover our best-selling watches, such as the Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm and the Cartier Panthere Medium Model. These timeless pieces combine elegance with precision, making them a staple in any sophisticated wardrobe.
Expert's Selection:
Our experts have carefully curated a selection of watches, including the Cartier Panthere Small Model, Omega Speedmaster Moonwatch 44.25 mm, and Rolex Oyster Perpetual Cosmograph Daytona 40mm. These choices exemplify the epitome of watchmaking excellence and style.
Secured and Tracked Delivery:
At Watches World, we prioritize the safety of your purchase. Our secured and tracked delivery ensures that your exquisite timepiece reaches you in perfect condition, giving you peace of mind with every order.
Passionate Experts at Your Service:
Our team of passionate watch experts is dedicated to providing personalized service. From assisting you in choosing the perfect timepiece to addressing any inquiries, we are here to make your watch-buying experience seamless and enjoyable.
Global Presence:
With a presence in key cities around the world, including Dubai, Geneva, Hong Kong, London, Miami, Paris, Prague, Dublin, Singapore, and Sao Paulo, Watches World brings luxury timepieces to enthusiasts globally.
Conclusion:
Watches World goes beyond being an online platform for luxury watches; it is a destination where expertise, trust, and satisfaction converge. Explore our collection, and let our timeless timepieces become an integral part of your style narrative. Join us in redefining luxury, one exquisite watch at a time. -
https://myskyblock.pl/
-
https://myskyblock.pl/
-
2024全新上線❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ - ATG賽特玩法說明介紹
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,在傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的冒險者才能進入探險。
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特介紹
2024最新老虎機【戰神塞特】- ATG電子 X 富遊娛樂城
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG電子
線上老虎機系統 : ATG電子
發行年分 : 2024年1月
最大倍數 : 51000倍
返還率 : 95.89%
支付方式 : 全盤倍數、消除掉落
最低投注金額 : 0.4元
最高投注金額 : 2000元
可否選台 : 是
可選台台數 : 350台
免費遊戲 : 選轉觸發+購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明
戰神塞特老虎機賠率算法非常簡單,玩家們只需要不斷的轉動老虎機,成功消除物件即可贏分,得分賠率依賠率表計算。
當盤面上沒有物件可以消除時,倍數符號將會相加形成總倍數!該次旋轉的總贏分即為 : 贏分 X 總倍數。
積分方式如下 :
贏分=(單次押注額/20) X 物件賠率
EX : 單次押注額為1,盤面獲得12個戰神賽特倍數符號法老魔眼
贏分= (1/20) X 1000=50
以下為各個得分符號數量之獎金賠率 :
得分符號 獎金倍數 得分符號 獎金倍數
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲 6 2000
5 100
4 60 戰神賽特倍數符號黃寶石 12+ 200
10-11 30
8-9 20
戰神賽特倍數符號荷魯斯之眼 12+ 1000
10-11 500
8-9 200 戰神賽特倍數符號紅寶石 12+ 160
10-11 24
8-9 16
戰神賽特倍數符號眼鏡蛇 12+ 500
10-11 200
8-9 50 戰神賽特倍數符號紫鑽石 12+ 100
10-11 20
8-9 10
戰神賽特倍數符號神箭 12+ 300
10-11 100
8-9 40 戰神賽特倍數符號藍寶石 12+ 80
10-11 18
8-9 8
戰神賽特倍數符號屠鐮刀 12+ 240
10-11 40
8-9 30 戰神賽特倍數符號綠寶石 12+ 40
10-11 15
8-9 5
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明(橘色數值為獲得數量、黑色數值為得分賠率)
ATG賽特 – 特色說明
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
玩家們在看到盤面上出現倍數符號時,務必把握機會加速轉動ATG賽特老虎機,倍數符號會隨機出現2到500倍的隨機倍數。
當盤面無法在消除時,這些倍數總和會相加,乘上當時累積之獎金,即為最後得分總額。
倍數符號會出現在主遊戲和免費遊戲當中,玩家們千萬別錯過這個可以瞬間將得獎金額拉高的好機會!
ATG賽特 - 倍數符號獎金加乘
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號圖示
ATG賽特 – 進入神秘金字塔開啟免費遊戲
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 免費遊戲符號
在古埃及神話中,聖甲蟲又稱為「死亡之蟲」,它被當成了天球及重生的象徵,守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶。
當玩家在盤面上,看見越來越多的聖甲蟲時,千萬不要膽怯,只需在牌面上斬殺4~6個ATG賽特免費遊戲符號,就可以進入15場免費遊戲!
在免費遊戲中若轉出3~6個聖甲蟲免費遊戲符號,可額外獲得5次免費遊戲,最高可達100次。
當玩家的累積贏分且盤面有倍數物件時,盤面上的所有倍數將會加入總倍數!
ATG賽特 – 選台模式贏在起跑線
為避免神聖的寶物被盜墓者奪走,富有智慧的法老王將金子塔內佈滿迷宮,有的設滿機關讓盜墓者寸步難行,有的暗藏機關可以直接前往存放神秘寶物的暗房。
ATG賽特老虎機設有350個機檯供玩家選擇,這是連魔龍老虎機、忍老虎機都給不出的機台數量,為的就是讓玩家,可以隨時進入神秘的古埃及的寶藏聖域,挖掘長眠已久的神祕寶藏。
【戰神塞特老虎機】選台模式
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 選台模式
ATG賽特 – 購買免費遊戲挖掘秘寶
玩家們可以使用當前投注額的100倍購買免費遊戲!進入免費遊戲再也不是虛幻。獎勵與一般遊戲相同,且購買後遊戲將自動開始,直到場次和獎金發放完畢為止。
有購買免費遊戲需求的玩家們,立即點擊「開始」,啟動神秘金字塔裡的古埃及祕寶吧!
【戰神塞特老虎機】購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 購買特色
戰神賽特試玩推薦
看完了❰戰神賽特老虎機❱介紹之後,玩家們是否也蓄勢待發要進入古埃及的世界,一探神奇秘寶探險之旅。
本次ATG賽特與線上娛樂城推薦第一名的富遊娛樂城合作,只需要加入會員,即可領取到168體驗金,免費試玩420轉! -
2024全新上線❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ - ATG賽特玩法說明介紹
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,在傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的冒險者才能進入探險。
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特介紹
2024最新老虎機【戰神塞特】- ATG電子 X 富遊娛樂城
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG電子
線上老虎機系統 : ATG電子
發行年分 : 2024年1月
最大倍數 : 51000倍
返還率 : 95.89%
支付方式 : 全盤倍數、消除掉落
最低投注金額 : 0.4元
最高投注金額 : 2000元
可否選台 : 是
可選台台數 : 350台
免費遊戲 : 選轉觸發+購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明
戰神塞特老虎機賠率算法非常簡單,玩家們只需要不斷的轉動老虎機,成功消除物件即可贏分,得分賠率依賠率表計算。
當盤面上沒有物件可以消除時,倍數符號將會相加形成總倍數!該次旋轉的總贏分即為 : 贏分 X 總倍數。
積分方式如下 :
贏分=(單次押注額/20) X 物件賠率
EX : 單次押注額為1,盤面獲得12個戰神賽特倍數符號法老魔眼
贏分= (1/20) X 1000=50
以下為各個得分符號數量之獎金賠率 :
得分符號 獎金倍數 得分符號 獎金倍數
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲 6 2000
5 100
4 60 戰神賽特倍數符號黃寶石 12+ 200
10-11 30
8-9 20
戰神賽特倍數符號荷魯斯之眼 12+ 1000
10-11 500
8-9 200 戰神賽特倍數符號紅寶石 12+ 160
10-11 24
8-9 16
戰神賽特倍數符號眼鏡蛇 12+ 500
10-11 200
8-9 50 戰神賽特倍數符號紫鑽石 12+ 100
10-11 20
8-9 10
戰神賽特倍數符號神箭 12+ 300
10-11 100
8-9 40 戰神賽特倍數符號藍寶石 12+ 80
10-11 18
8-9 8
戰神賽特倍數符號屠鐮刀 12+ 240
10-11 40
8-9 30 戰神賽特倍數符號綠寶石 12+ 40
10-11 15
8-9 5
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明(橘色數值為獲得數量、黑色數值為得分賠率)
ATG賽特 – 特色說明
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
玩家們在看到盤面上出現倍數符號時,務必把握機會加速轉動ATG賽特老虎機,倍數符號會隨機出現2到500倍的隨機倍數。
當盤面無法在消除時,這些倍數總和會相加,乘上當時累積之獎金,即為最後得分總額。
倍數符號會出現在主遊戲和免費遊戲當中,玩家們千萬別錯過這個可以瞬間將得獎金額拉高的好機會!
ATG賽特 - 倍數符號獎金加乘
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號圖示
ATG賽特 – 進入神秘金字塔開啟免費遊戲
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 免費遊戲符號
在古埃及神話中,聖甲蟲又稱為「死亡之蟲」,它被當成了天球及重生的象徵,守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶。
當玩家在盤面上,看見越來越多的聖甲蟲時,千萬不要膽怯,只需在牌面上斬殺4~6個ATG賽特免費遊戲符號,就可以進入15場免費遊戲!
在免費遊戲中若轉出3~6個聖甲蟲免費遊戲符號,可額外獲得5次免費遊戲,最高可達100次。
當玩家的累積贏分且盤面有倍數物件時,盤面上的所有倍數將會加入總倍數!
ATG賽特 – 選台模式贏在起跑線
為避免神聖的寶物被盜墓者奪走,富有智慧的法老王將金子塔內佈滿迷宮,有的設滿機關讓盜墓者寸步難行,有的暗藏機關可以直接前往存放神秘寶物的暗房。
ATG賽特老虎機設有350個機檯供玩家選擇,這是連魔龍老虎機、忍老虎機都給不出的機台數量,為的就是讓玩家,可以隨時進入神秘的古埃及的寶藏聖域,挖掘長眠已久的神祕寶藏。
【戰神塞特老虎機】選台模式
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 選台模式
ATG賽特 – 購買免費遊戲挖掘秘寶
玩家們可以使用當前投注額的100倍購買免費遊戲!進入免費遊戲再也不是虛幻。獎勵與一般遊戲相同,且購買後遊戲將自動開始,直到場次和獎金發放完畢為止。
有購買免費遊戲需求的玩家們,立即點擊「開始」,啟動神秘金字塔裡的古埃及祕寶吧!
【戰神塞特老虎機】購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 購買特色
戰神賽特試玩推薦
看完了❰戰神賽特老虎機❱介紹之後,玩家們是否也蓄勢待發要進入古埃及的世界,一探神奇秘寶探險之旅。
本次ATG賽特與線上娛樂城推薦第一名的富遊娛樂城合作,只需要加入會員,即可領取到168體驗金,免費試玩420轉! -
2024娛樂城No.1 – 富遊娛樂城介紹
2024 年 1 月 5 日
|
娛樂城, 現金版娛樂城
富遊娛樂城是無論老手、新手,都非常推薦的線上博奕,在2024娛樂城當中扮演著多年來最來勢洶洶的一匹黑馬,『人性化且精緻的介面,遊戲種類眾多,超級多的娛樂城優惠,擁有眾多與會員交流遊戲的群組』是一大特色。
富遊娛樂城擁有歐洲馬爾他(MGA)和菲律賓政府競猜委員會(PAGCOR)頒發的合法執照。
註冊於英屬維爾京群島,受國際行業協會認可的合法公司。
我們的中心思想就是能夠帶領玩家遠詐騙黑網,讓大家安心放心的暢玩線上博弈,娛樂城也受各大部落客、IG網紅、PTT論壇,推薦討論,富遊娛樂城沒有之一,絕對是線上賭場玩家的第一首選!
富遊娛樂城介面 / 2024娛樂城NO.1
富遊娛樂城簡介
品牌名稱 : 富遊RG
創立時間 : 2019年
存款速度 : 平均15秒
提款速度 : 平均5分
單筆提款金額 : 最低1000-100萬
遊戲對象 : 18歲以上男女老少皆可
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
支付平台 : 各大銀行、各大便利超商
支援配備 : 手機網頁、電腦網頁、IOS、安卓(Android)
富遊娛樂城遊戲品牌
真人百家 — 歐博真人、DG真人、亞博真人、SA真人、OG真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、亞博體育
電競遊戲 — 泛亞電競
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、好路GR電子
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、亞博捕魚
富遊娛樂城優惠活動
每日任務簽到金666
富遊VIP全面啟動
復酬金活動10%優惠
日日返水
新會員好禮五選一
首存禮1000送1000
免費體驗金$168
富遊娛樂城APP
步驟1 : 開啟網頁版【富遊娛樂城官網】
步驟2 : 點選上方(下載app),會跳出下載與複製連結選項,點選後跳轉。
步驟3 : 跳轉後點選(安裝),並點選(允許)操作下載描述檔,跳出下載描述檔後點選關閉。
步驟4 : 到手機設置>一般>裝置管理>設定描述檔(富遊)安裝,即可完成安裝。
富遊娛樂城常見問題FAQ
富遊娛樂城詐騙?
黑網詐騙可細分兩種,小出大不出及純詐騙黑網,我們可從品牌知名度經營和網站架設畫面分辨來簡單分辨。
富遊娛樂城會出金嗎?
如上面提到,富遊是在做一個品牌,為的是能夠保證出金,和帶領玩家遠離黑網,而且還有DUKER娛樂城出金認證,所以各位能夠放心富遊娛樂城為正出金娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城出金延遲怎麼辦?
基本上只要是公司系統問提造成富遊娛樂城會員無法在30分鐘成功提款,富遊娛樂城會即刻派送補償金,表達誠摯的歉意。
富遊娛樂城結論
富遊娛樂城安心玩,評價4.5顆星。如果還想看其他娛樂城推薦的,可以來娛樂城推薦尋找喔。 -
娛樂城
2024娛樂城No.1 – 富遊娛樂城介紹
2024 年 1 月 5 日
|
娛樂城, 現金版娛樂城
富遊娛樂城是無論老手、新手,都非常推薦的線上博奕,在2024娛樂城當中扮演著多年來最來勢洶洶的一匹黑馬,『人性化且精緻的介面,遊戲種類眾多,超級多的娛樂城優惠,擁有眾多與會員交流遊戲的群組』是一大特色。
富遊娛樂城擁有歐洲馬爾他(MGA)和菲律賓政府競猜委員會(PAGCOR)頒發的合法執照。
註冊於英屬維爾京群島,受國際行業協會認可的合法公司。
我們的中心思想就是能夠帶領玩家遠詐騙黑網,讓大家安心放心的暢玩線上博弈,娛樂城也受各大部落客、IG網紅、PTT論壇,推薦討論,富遊娛樂城沒有之一,絕對是線上賭場玩家的第一首選!
富遊娛樂城介面 / 2024娛樂城NO.1
富遊娛樂城簡介
品牌名稱 : 富遊RG
創立時間 : 2019年
存款速度 : 平均15秒
提款速度 : 平均5分
單筆提款金額 : 最低1000-100萬
遊戲對象 : 18歲以上男女老少皆可
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
支付平台 : 各大銀行、各大便利超商
支援配備 : 手機網頁、電腦網頁、IOS、安卓(Android)
富遊娛樂城遊戲品牌
真人百家 — 歐博真人、DG真人、亞博真人、SA真人、OG真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、亞博體育
電競遊戲 — 泛亞電競
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、好路GR電子
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、亞博捕魚
富遊娛樂城優惠活動
每日任務簽到金666
富遊VIP全面啟動
復酬金活動10%優惠
日日返水
新會員好禮五選一
首存禮1000送1000
免費體驗金$168
富遊娛樂城APP
步驟1 : 開啟網頁版【富遊娛樂城官網】
步驟2 : 點選上方(下載app),會跳出下載與複製連結選項,點選後跳轉。
步驟3 : 跳轉後點選(安裝),並點選(允許)操作下載描述檔,跳出下載描述檔後點選關閉。
步驟4 : 到手機設置>一般>裝置管理>設定描述檔(富遊)安裝,即可完成安裝。
富遊娛樂城常見問題FAQ
富遊娛樂城詐騙?
黑網詐騙可細分兩種,小出大不出及純詐騙黑網,我們可從品牌知名度經營和網站架設畫面分辨來簡單分辨。
富遊娛樂城會出金嗎?
如上面提到,富遊是在做一個品牌,為的是能夠保證出金,和帶領玩家遠離黑網,而且還有DUKER娛樂城出金認證,所以各位能夠放心富遊娛樂城為正出金娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城出金延遲怎麼辦?
基本上只要是公司系統問提造成富遊娛樂城會員無法在30分鐘成功提款,富遊娛樂城會即刻派送補償金,表達誠摯的歉意。
富遊娛樂城結論
富遊娛樂城安心玩,評價4.5顆星。如果還想看其他娛樂城推薦的,可以來娛樂城推薦尋找喔。 -
戰神賽特
2024全新上線❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ - ATG賽特玩法說明介紹
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,在傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的冒險者才能進入探險。
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特介紹
2024最新老虎機【戰神塞特】- ATG電子 X 富遊娛樂城
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG電子
線上老虎機系統 : ATG電子
發行年分 : 2024年1月
最大倍數 : 51000倍
返還率 : 95.89%
支付方式 : 全盤倍數、消除掉落
最低投注金額 : 0.4元
最高投注金額 : 2000元
可否選台 : 是
可選台台數 : 350台
免費遊戲 : 選轉觸發+購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明
戰神塞特老虎機賠率算法非常簡單,玩家們只需要不斷的轉動老虎機,成功消除物件即可贏分,得分賠率依賠率表計算。
當盤面上沒有物件可以消除時,倍數符號將會相加形成總倍數!該次旋轉的總贏分即為 : 贏分 X 總倍數。
積分方式如下 :
贏分=(單次押注額/20) X 物件賠率
EX : 單次押注額為1,盤面獲得12個戰神賽特倍數符號法老魔眼
贏分= (1/20) X 1000=50
以下為各個得分符號數量之獎金賠率 :
得分符號 獎金倍數 得分符號 獎金倍數
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲 6 2000
5 100
4 60 戰神賽特倍數符號黃寶石 12+ 200
10-11 30
8-9 20
戰神賽特倍數符號荷魯斯之眼 12+ 1000
10-11 500
8-9 200 戰神賽特倍數符號紅寶石 12+ 160
10-11 24
8-9 16
戰神賽特倍數符號眼鏡蛇 12+ 500
10-11 200
8-9 50 戰神賽特倍數符號紫鑽石 12+ 100
10-11 20
8-9 10
戰神賽特倍數符號神箭 12+ 300
10-11 100
8-9 40 戰神賽特倍數符號藍寶石 12+ 80
10-11 18
8-9 8
戰神賽特倍數符號屠鐮刀 12+ 240
10-11 40
8-9 30 戰神賽特倍數符號綠寶石 12+ 40
10-11 15
8-9 5
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明(橘色數值為獲得數量、黑色數值為得分賠率)
ATG賽特 – 特色說明
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
玩家們在看到盤面上出現倍數符號時,務必把握機會加速轉動ATG賽特老虎機,倍數符號會隨機出現2到500倍的隨機倍數。
當盤面無法在消除時,這些倍數總和會相加,乘上當時累積之獎金,即為最後得分總額。
倍數符號會出現在主遊戲和免費遊戲當中,玩家們千萬別錯過這個可以瞬間將得獎金額拉高的好機會!
ATG賽特 - 倍數符號獎金加乘
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號圖示
ATG賽特 – 進入神秘金字塔開啟免費遊戲
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 免費遊戲符號
在古埃及神話中,聖甲蟲又稱為「死亡之蟲」,它被當成了天球及重生的象徵,守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶。
當玩家在盤面上,看見越來越多的聖甲蟲時,千萬不要膽怯,只需在牌面上斬殺4~6個ATG賽特免費遊戲符號,就可以進入15場免費遊戲!
在免費遊戲中若轉出3~6個聖甲蟲免費遊戲符號,可額外獲得5次免費遊戲,最高可達100次。
當玩家的累積贏分且盤面有倍數物件時,盤面上的所有倍數將會加入總倍數!
ATG賽特 – 選台模式贏在起跑線
為避免神聖的寶物被盜墓者奪走,富有智慧的法老王將金子塔內佈滿迷宮,有的設滿機關讓盜墓者寸步難行,有的暗藏機關可以直接前往存放神秘寶物的暗房。
ATG賽特老虎機設有350個機檯供玩家選擇,這是連魔龍老虎機、忍老虎機都給不出的機台數量,為的就是讓玩家,可以隨時進入神秘的古埃及的寶藏聖域,挖掘長眠已久的神祕寶藏。
【戰神塞特老虎機】選台模式
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 選台模式
ATG賽特 – 購買免費遊戲挖掘秘寶
玩家們可以使用當前投注額的100倍購買免費遊戲!進入免費遊戲再也不是虛幻。獎勵與一般遊戲相同,且購買後遊戲將自動開始,直到場次和獎金發放完畢為止。
有購買免費遊戲需求的玩家們,立即點擊「開始」,啟動神秘金字塔裡的古埃及祕寶吧!
【戰神塞特老虎機】購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 購買特色
戰神賽特試玩推薦
看完了❰戰神賽特老虎機❱介紹之後,玩家們是否也蓄勢待發要進入古埃及的世界,一探神奇秘寶探險之旅。
本次ATG賽特與線上娛樂城推薦第一名的富遊娛樂城合作,只需要加入會員,即可領取到168體驗金,免費試玩420轉! -
ATG戰神賽特
2024全新上線❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ - ATG賽特玩法說明介紹
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,在傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的冒險者才能進入探險。
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特介紹
2024最新老虎機【戰神塞特】- ATG電子 X 富遊娛樂城
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG電子
線上老虎機系統 : ATG電子
發行年分 : 2024年1月
最大倍數 : 51000倍
返還率 : 95.89%
支付方式 : 全盤倍數、消除掉落
最低投注金額 : 0.4元
最高投注金額 : 2000元
可否選台 : 是
可選台台數 : 350台
免費遊戲 : 選轉觸發+購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明
戰神塞特老虎機賠率算法非常簡單,玩家們只需要不斷的轉動老虎機,成功消除物件即可贏分,得分賠率依賠率表計算。
當盤面上沒有物件可以消除時,倍數符號將會相加形成總倍數!該次旋轉的總贏分即為 : 贏分 X 總倍數。
積分方式如下 :
贏分=(單次押注額/20) X 物件賠率
EX : 單次押注額為1,盤面獲得12個戰神賽特倍數符號法老魔眼
贏分= (1/20) X 1000=50
以下為各個得分符號數量之獎金賠率 :
得分符號 獎金倍數 得分符號 獎金倍數
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲 6 2000
5 100
4 60 戰神賽特倍數符號黃寶石 12+ 200
10-11 30
8-9 20
戰神賽特倍數符號荷魯斯之眼 12+ 1000
10-11 500
8-9 200 戰神賽特倍數符號紅寶石 12+ 160
10-11 24
8-9 16
戰神賽特倍數符號眼鏡蛇 12+ 500
10-11 200
8-9 50 戰神賽特倍數符號紫鑽石 12+ 100
10-11 20
8-9 10
戰神賽特倍數符號神箭 12+ 300
10-11 100
8-9 40 戰神賽特倍數符號藍寶石 12+ 80
10-11 18
8-9 8
戰神賽特倍數符號屠鐮刀 12+ 240
10-11 40
8-9 30 戰神賽特倍數符號綠寶石 12+ 40
10-11 15
8-9 5
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明(橘色數值為獲得數量、黑色數值為得分賠率)
ATG賽特 – 特色說明
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
玩家們在看到盤面上出現倍數符號時,務必把握機會加速轉動ATG賽特老虎機,倍數符號會隨機出現2到500倍的隨機倍數。
當盤面無法在消除時,這些倍數總和會相加,乘上當時累積之獎金,即為最後得分總額。
倍數符號會出現在主遊戲和免費遊戲當中,玩家們千萬別錯過這個可以瞬間將得獎金額拉高的好機會!
ATG賽特 - 倍數符號獎金加乘
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號圖示
ATG賽特 – 進入神秘金字塔開啟免費遊戲
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 免費遊戲符號
在古埃及神話中,聖甲蟲又稱為「死亡之蟲」,它被當成了天球及重生的象徵,守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶。
當玩家在盤面上,看見越來越多的聖甲蟲時,千萬不要膽怯,只需在牌面上斬殺4~6個ATG賽特免費遊戲符號,就可以進入15場免費遊戲!
在免費遊戲中若轉出3~6個聖甲蟲免費遊戲符號,可額外獲得5次免費遊戲,最高可達100次。
當玩家的累積贏分且盤面有倍數物件時,盤面上的所有倍數將會加入總倍數!
ATG賽特 – 選台模式贏在起跑線
為避免神聖的寶物被盜墓者奪走,富有智慧的法老王將金子塔內佈滿迷宮,有的設滿機關讓盜墓者寸步難行,有的暗藏機關可以直接前往存放神秘寶物的暗房。
ATG賽特老虎機設有350個機檯供玩家選擇,這是連魔龍老虎機、忍老虎機都給不出的機台數量,為的就是讓玩家,可以隨時進入神秘的古埃及的寶藏聖域,挖掘長眠已久的神祕寶藏。
【戰神塞特老虎機】選台模式
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 選台模式
ATG賽特 – 購買免費遊戲挖掘秘寶
玩家們可以使用當前投注額的100倍購買免費遊戲!進入免費遊戲再也不是虛幻。獎勵與一般遊戲相同,且購買後遊戲將自動開始,直到場次和獎金發放完畢為止。
有購買免費遊戲需求的玩家們,立即點擊「開始」,啟動神秘金字塔裡的古埃及祕寶吧!
【戰神塞特老虎機】購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 購買特色
戰神賽特試玩推薦
看完了❰戰神賽特老虎機❱介紹之後,玩家們是否也蓄勢待發要進入古埃及的世界,一探神奇秘寶探險之旅。
本次ATG賽特與線上娛樂城推薦第一名的富遊娛樂城合作,只需要加入會員,即可領取到168體驗金,免費試玩420轉! -
https://theminecraft.pl/serwery-minecraft-survival-dzialkami-odkryj-mozliwosci/
-
https://theminecraft.pl/polskie-serwery-minecraft-1-8-9-wyjatkowe-przygody-w-swiecie/
-
2024娛樂城No.1 – 富遊娛樂城介紹
2024 年 1 月 5 日
|
娛樂城, 現金版娛樂城
富遊娛樂城是無論老手、新手,都非常推薦的線上博奕,在2024娛樂城當中扮演著多年來最來勢洶洶的一匹黑馬,『人性化且精緻的介面,遊戲種類眾多,超級多的娛樂城優惠,擁有眾多與會員交流遊戲的群組』是一大特色。
富遊娛樂城擁有歐洲馬爾他(MGA)和菲律賓政府競猜委員會(PAGCOR)頒發的合法執照。
註冊於英屬維爾京群島,受國際行業協會認可的合法公司。
我們的中心思想就是能夠帶領玩家遠詐騙黑網,讓大家安心放心的暢玩線上博弈,娛樂城也受各大部落客、IG網紅、PTT論壇,推薦討論,富遊娛樂城沒有之一,絕對是線上賭場玩家的第一首選!
富遊娛樂城介面 / 2024娛樂城NO.1
富遊娛樂城簡介
品牌名稱 : 富遊RG
創立時間 : 2019年
存款速度 : 平均15秒
提款速度 : 平均5分
單筆提款金額 : 最低1000-100萬
遊戲對象 : 18歲以上男女老少皆可
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
支付平台 : 各大銀行、各大便利超商
支援配備 : 手機網頁、電腦網頁、IOS、安卓(Android)
富遊娛樂城遊戲品牌
真人百家 — 歐博真人、DG真人、亞博真人、SA真人、OG真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、亞博體育
電競遊戲 — 泛亞電競
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、好路GR電子
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、亞博捕魚
富遊娛樂城優惠活動
每日任務簽到金666
富遊VIP全面啟動
復酬金活動10%優惠
日日返水
新會員好禮五選一
首存禮1000送1000
免費體驗金$168
富遊娛樂城APP
步驟1 : 開啟網頁版【富遊娛樂城官網】
步驟2 : 點選上方(下載app),會跳出下載與複製連結選項,點選後跳轉。
步驟3 : 跳轉後點選(安裝),並點選(允許)操作下載描述檔,跳出下載描述檔後點選關閉。
步驟4 : 到手機設置>一般>裝置管理>設定描述檔(富遊)安裝,即可完成安裝。
富遊娛樂城常見問題FAQ
富遊娛樂城詐騙?
黑網詐騙可細分兩種,小出大不出及純詐騙黑網,我們可從品牌知名度經營和網站架設畫面分辨來簡單分辨。
富遊娛樂城會出金嗎?
如上面提到,富遊是在做一個品牌,為的是能夠保證出金,和帶領玩家遠離黑網,而且還有DUKER娛樂城出金認證,所以各位能夠放心富遊娛樂城為正出金娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城出金延遲怎麼辦?
基本上只要是公司系統問提造成富遊娛樂城會員無法在30分鐘成功提款,富遊娛樂城會即刻派送補償金,表達誠摯的歉意。
富遊娛樂城結論
富遊娛樂城安心玩,評價4.5顆星。如果還想看其他娛樂城推薦的,可以來娛樂城推薦尋找喔。 -
2024全新上線❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ - ATG賽特玩法說明介紹
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,在傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的冒險者才能進入探險。
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特介紹
2024最新老虎機【戰神塞特】- ATG電子 X 富遊娛樂城
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG電子
線上老虎機系統 : ATG電子
發行年分 : 2024年1月
最大倍數 : 51000倍
返還率 : 95.89%
支付方式 : 全盤倍數、消除掉落
最低投注金額 : 0.4元
最高投注金額 : 2000元
可否選台 : 是
可選台台數 : 350台
免費遊戲 : 選轉觸發+購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明
戰神塞特老虎機賠率算法非常簡單,玩家們只需要不斷的轉動老虎機,成功消除物件即可贏分,得分賠率依賠率表計算。
當盤面上沒有物件可以消除時,倍數符號將會相加形成總倍數!該次旋轉的總贏分即為 : 贏分 X 總倍數。
積分方式如下 :
贏分=(單次押注額/20) X 物件賠率
EX : 單次押注額為1,盤面獲得12個戰神賽特倍數符號法老魔眼
贏分= (1/20) X 1000=50
以下為各個得分符號數量之獎金賠率 :
得分符號 獎金倍數 得分符號 獎金倍數
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲 6 2000
5 100
4 60 戰神賽特倍數符號黃寶石 12+ 200
10-11 30
8-9 20
戰神賽特倍數符號荷魯斯之眼 12+ 1000
10-11 500
8-9 200 戰神賽特倍數符號紅寶石 12+ 160
10-11 24
8-9 16
戰神賽特倍數符號眼鏡蛇 12+ 500
10-11 200
8-9 50 戰神賽特倍數符號紫鑽石 12+ 100
10-11 20
8-9 10
戰神賽特倍數符號神箭 12+ 300
10-11 100
8-9 40 戰神賽特倍數符號藍寶石 12+ 80
10-11 18
8-9 8
戰神賽特倍數符號屠鐮刀 12+ 240
10-11 40
8-9 30 戰神賽特倍數符號綠寶石 12+ 40
10-11 15
8-9 5
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明(橘色數值為獲得數量、黑色數值為得分賠率)
ATG賽特 – 特色說明
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
玩家們在看到盤面上出現倍數符號時,務必把握機會加速轉動ATG賽特老虎機,倍數符號會隨機出現2到500倍的隨機倍數。
當盤面無法在消除時,這些倍數總和會相加,乘上當時累積之獎金,即為最後得分總額。
倍數符號會出現在主遊戲和免費遊戲當中,玩家們千萬別錯過這個可以瞬間將得獎金額拉高的好機會!
ATG賽特 - 倍數符號獎金加乘
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號圖示
ATG賽特 – 進入神秘金字塔開啟免費遊戲
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 免費遊戲符號
在古埃及神話中,聖甲蟲又稱為「死亡之蟲」,它被當成了天球及重生的象徵,守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶。
當玩家在盤面上,看見越來越多的聖甲蟲時,千萬不要膽怯,只需在牌面上斬殺4~6個ATG賽特免費遊戲符號,就可以進入15場免費遊戲!
在免費遊戲中若轉出3~6個聖甲蟲免費遊戲符號,可額外獲得5次免費遊戲,最高可達100次。
當玩家的累積贏分且盤面有倍數物件時,盤面上的所有倍數將會加入總倍數!
ATG賽特 – 選台模式贏在起跑線
為避免神聖的寶物被盜墓者奪走,富有智慧的法老王將金子塔內佈滿迷宮,有的設滿機關讓盜墓者寸步難行,有的暗藏機關可以直接前往存放神秘寶物的暗房。
ATG賽特老虎機設有350個機檯供玩家選擇,這是連魔龍老虎機、忍老虎機都給不出的機台數量,為的就是讓玩家,可以隨時進入神秘的古埃及的寶藏聖域,挖掘長眠已久的神祕寶藏。
【戰神塞特老虎機】選台模式
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 選台模式
ATG賽特 – 購買免費遊戲挖掘秘寶
玩家們可以使用當前投注額的100倍購買免費遊戲!進入免費遊戲再也不是虛幻。獎勵與一般遊戲相同,且購買後遊戲將自動開始,直到場次和獎金發放完畢為止。
有購買免費遊戲需求的玩家們,立即點擊「開始」,啟動神秘金字塔裡的古埃及祕寶吧!
【戰神塞特老虎機】購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 購買特色
戰神賽特試玩推薦
看完了❰戰神賽特老虎機❱介紹之後,玩家們是否也蓄勢待發要進入古埃及的世界,一探神奇秘寶探險之旅。
本次ATG賽特與線上娛樂城推薦第一名的富遊娛樂城合作,只需要加入會員,即可領取到168體驗金,免費試玩420轉! -
2024娛樂城No.1 – 富遊娛樂城介紹
2024 年 1 月 5 日
|
娛樂城, 現金版娛樂城
富遊娛樂城是無論老手、新手,都非常推薦的線上博奕,在2024娛樂城當中扮演著多年來最來勢洶洶的一匹黑馬,『人性化且精緻的介面,遊戲種類眾多,超級多的娛樂城優惠,擁有眾多與會員交流遊戲的群組』是一大特色。
富遊娛樂城擁有歐洲馬爾他(MGA)和菲律賓政府競猜委員會(PAGCOR)頒發的合法執照。
註冊於英屬維爾京群島,受國際行業協會認可的合法公司。
我們的中心思想就是能夠帶領玩家遠詐騙黑網,讓大家安心放心的暢玩線上博弈,娛樂城也受各大部落客、IG網紅、PTT論壇,推薦討論,富遊娛樂城沒有之一,絕對是線上賭場玩家的第一首選!
富遊娛樂城介面 / 2024娛樂城NO.1
富遊娛樂城簡介
品牌名稱 : 富遊RG
創立時間 : 2019年
存款速度 : 平均15秒
提款速度 : 平均5分
單筆提款金額 : 最低1000-100萬
遊戲對象 : 18歲以上男女老少皆可
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
支付平台 : 各大銀行、各大便利超商
支援配備 : 手機網頁、電腦網頁、IOS、安卓(Android)
富遊娛樂城遊戲品牌
真人百家 — 歐博真人、DG真人、亞博真人、SA真人、OG真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、亞博體育
電競遊戲 — 泛亞電競
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、好路GR電子
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、亞博捕魚
富遊娛樂城優惠活動
每日任務簽到金666
富遊VIP全面啟動
復酬金活動10%優惠
日日返水
新會員好禮五選一
首存禮1000送1000
免費體驗金$168
富遊娛樂城APP
步驟1 : 開啟網頁版【富遊娛樂城官網】
步驟2 : 點選上方(下載app),會跳出下載與複製連結選項,點選後跳轉。
步驟3 : 跳轉後點選(安裝),並點選(允許)操作下載描述檔,跳出下載描述檔後點選關閉。
步驟4 : 到手機設置>一般>裝置管理>設定描述檔(富遊)安裝,即可完成安裝。
富遊娛樂城常見問題FAQ
富遊娛樂城詐騙?
黑網詐騙可細分兩種,小出大不出及純詐騙黑網,我們可從品牌知名度經營和網站架設畫面分辨來簡單分辨。
富遊娛樂城會出金嗎?
如上面提到,富遊是在做一個品牌,為的是能夠保證出金,和帶領玩家遠離黑網,而且還有DUKER娛樂城出金認證,所以各位能夠放心富遊娛樂城為正出金娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城出金延遲怎麼辦?
基本上只要是公司系統問提造成富遊娛樂城會員無法在30分鐘成功提款,富遊娛樂城會即刻派送補償金,表達誠摯的歉意。
富遊娛樂城結論
富遊娛樂城安心玩,評價4.5顆星。如果還想看其他娛樂城推薦的,可以來娛樂城推薦尋找喔。 -
2024娛樂城No.1 – 富遊娛樂城介紹
2024 年 1 月 5 日
|
娛樂城, 現金版娛樂城
富遊娛樂城是無論老手、新手,都非常推薦的線上博奕,在2024娛樂城當中扮演著多年來最來勢洶洶的一匹黑馬,『人性化且精緻的介面,遊戲種類眾多,超級多的娛樂城優惠,擁有眾多與會員交流遊戲的群組』是一大特色。
富遊娛樂城擁有歐洲馬爾他(MGA)和菲律賓政府競猜委員會(PAGCOR)頒發的合法執照。
註冊於英屬維爾京群島,受國際行業協會認可的合法公司。
我們的中心思想就是能夠帶領玩家遠詐騙黑網,讓大家安心放心的暢玩線上博弈,娛樂城也受各大部落客、IG網紅、PTT論壇,推薦討論,富遊娛樂城沒有之一,絕對是線上賭場玩家的第一首選!
富遊娛樂城介面 / 2024娛樂城NO.1
富遊娛樂城簡介
品牌名稱 : 富遊RG
創立時間 : 2019年
存款速度 : 平均15秒
提款速度 : 平均5分
單筆提款金額 : 最低1000-100萬
遊戲對象 : 18歲以上男女老少皆可
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
支付平台 : 各大銀行、各大便利超商
支援配備 : 手機網頁、電腦網頁、IOS、安卓(Android)
富遊娛樂城遊戲品牌
真人百家 — 歐博真人、DG真人、亞博真人、SA真人、OG真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、亞博體育
電競遊戲 — 泛亞電競
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、好路GR電子
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、亞博捕魚
富遊娛樂城優惠活動
每日任務簽到金666
富遊VIP全面啟動
復酬金活動10%優惠
日日返水
新會員好禮五選一
首存禮1000送1000
免費體驗金$168
富遊娛樂城APP
步驟1 : 開啟網頁版【富遊娛樂城官網】
步驟2 : 點選上方(下載app),會跳出下載與複製連結選項,點選後跳轉。
步驟3 : 跳轉後點選(安裝),並點選(允許)操作下載描述檔,跳出下載描述檔後點選關閉。
步驟4 : 到手機設置>一般>裝置管理>設定描述檔(富遊)安裝,即可完成安裝。
富遊娛樂城常見問題FAQ
富遊娛樂城詐騙?
黑網詐騙可細分兩種,小出大不出及純詐騙黑網,我們可從品牌知名度經營和網站架設畫面分辨來簡單分辨。
富遊娛樂城會出金嗎?
如上面提到,富遊是在做一個品牌,為的是能夠保證出金,和帶領玩家遠離黑網,而且還有DUKER娛樂城出金認證,所以各位能夠放心富遊娛樂城為正出金娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城出金延遲怎麼辦?
基本上只要是公司系統問提造成富遊娛樂城會員無法在30分鐘成功提款,富遊娛樂城會即刻派送補償金,表達誠摯的歉意。
富遊娛樂城結論
富遊娛樂城安心玩,評價4.5顆星。如果還想看其他娛樂城推薦的,可以來娛樂城推薦尋找喔。 -
ATG戰神賽特
2024全新上線❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ - ATG賽特玩法說明介紹
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,在傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的冒險者才能進入探險。
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特介紹
2024最新老虎機【戰神塞特】- ATG電子 X 富遊娛樂城
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG電子
線上老虎機系統 : ATG電子
發行年分 : 2024年1月
最大倍數 : 51000倍
返還率 : 95.89%
支付方式 : 全盤倍數、消除掉落
最低投注金額 : 0.4元
最高投注金額 : 2000元
可否選台 : 是
可選台台數 : 350台
免費遊戲 : 選轉觸發+購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明
戰神塞特老虎機賠率算法非常簡單,玩家們只需要不斷的轉動老虎機,成功消除物件即可贏分,得分賠率依賠率表計算。
當盤面上沒有物件可以消除時,倍數符號將會相加形成總倍數!該次旋轉的總贏分即為 : 贏分 X 總倍數。
積分方式如下 :
贏分=(單次押注額/20) X 物件賠率
EX : 單次押注額為1,盤面獲得12個戰神賽特倍數符號法老魔眼
贏分= (1/20) X 1000=50
以下為各個得分符號數量之獎金賠率 :
得分符號 獎金倍數 得分符號 獎金倍數
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲 6 2000
5 100
4 60 戰神賽特倍數符號黃寶石 12+ 200
10-11 30
8-9 20
戰神賽特倍數符號荷魯斯之眼 12+ 1000
10-11 500
8-9 200 戰神賽特倍數符號紅寶石 12+ 160
10-11 24
8-9 16
戰神賽特倍數符號眼鏡蛇 12+ 500
10-11 200
8-9 50 戰神賽特倍數符號紫鑽石 12+ 100
10-11 20
8-9 10
戰神賽特倍數符號神箭 12+ 300
10-11 100
8-9 40 戰神賽特倍數符號藍寶石 12+ 80
10-11 18
8-9 8
戰神賽特倍數符號屠鐮刀 12+ 240
10-11 40
8-9 30 戰神賽特倍數符號綠寶石 12+ 40
10-11 15
8-9 5
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明(橘色數值為獲得數量、黑色數值為得分賠率)
ATG賽特 – 特色說明
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
玩家們在看到盤面上出現倍數符號時,務必把握機會加速轉動ATG賽特老虎機,倍數符號會隨機出現2到500倍的隨機倍數。
當盤面無法在消除時,這些倍數總和會相加,乘上當時累積之獎金,即為最後得分總額。
倍數符號會出現在主遊戲和免費遊戲當中,玩家們千萬別錯過這個可以瞬間將得獎金額拉高的好機會!
ATG賽特 - 倍數符號獎金加乘
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號圖示
ATG賽特 – 進入神秘金字塔開啟免費遊戲
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 免費遊戲符號
在古埃及神話中,聖甲蟲又稱為「死亡之蟲」,它被當成了天球及重生的象徵,守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶。
當玩家在盤面上,看見越來越多的聖甲蟲時,千萬不要膽怯,只需在牌面上斬殺4~6個ATG賽特免費遊戲符號,就可以進入15場免費遊戲!
在免費遊戲中若轉出3~6個聖甲蟲免費遊戲符號,可額外獲得5次免費遊戲,最高可達100次。
當玩家的累積贏分且盤面有倍數物件時,盤面上的所有倍數將會加入總倍數!
ATG賽特 – 選台模式贏在起跑線
為避免神聖的寶物被盜墓者奪走,富有智慧的法老王將金子塔內佈滿迷宮,有的設滿機關讓盜墓者寸步難行,有的暗藏機關可以直接前往存放神秘寶物的暗房。
ATG賽特老虎機設有350個機檯供玩家選擇,這是連魔龍老虎機、忍老虎機都給不出的機台數量,為的就是讓玩家,可以隨時進入神秘的古埃及的寶藏聖域,挖掘長眠已久的神祕寶藏。
【戰神塞特老虎機】選台模式
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 選台模式
ATG賽特 – 購買免費遊戲挖掘秘寶
玩家們可以使用當前投注額的100倍購買免費遊戲!進入免費遊戲再也不是虛幻。獎勵與一般遊戲相同,且購買後遊戲將自動開始,直到場次和獎金發放完畢為止。
有購買免費遊戲需求的玩家們,立即點擊「開始」,啟動神秘金字塔裡的古埃及祕寶吧!
【戰神塞特老虎機】購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 購買特色
戰神賽特試玩推薦
看完了❰戰神賽特老虎機❱介紹之後,玩家們是否也蓄勢待發要進入古埃及的世界,一探神奇秘寶探險之旅。
本次ATG賽特與線上娛樂城推薦第一名的富遊娛樂城合作,只需要加入會員,即可領取到168體驗金,免費試玩420轉! -
娛樂城
2024娛樂城No.1 – 富遊娛樂城介紹
2024 年 1 月 5 日
|
娛樂城, 現金版娛樂城
富遊娛樂城是無論老手、新手,都非常推薦的線上博奕,在2024娛樂城當中扮演著多年來最來勢洶洶的一匹黑馬,『人性化且精緻的介面,遊戲種類眾多,超級多的娛樂城優惠,擁有眾多與會員交流遊戲的群組』是一大特色。
富遊娛樂城擁有歐洲馬爾他(MGA)和菲律賓政府競猜委員會(PAGCOR)頒發的合法執照。
註冊於英屬維爾京群島,受國際行業協會認可的合法公司。
我們的中心思想就是能夠帶領玩家遠詐騙黑網,讓大家安心放心的暢玩線上博弈,娛樂城也受各大部落客、IG網紅、PTT論壇,推薦討論,富遊娛樂城沒有之一,絕對是線上賭場玩家的第一首選!
富遊娛樂城介面 / 2024娛樂城NO.1
富遊娛樂城簡介
品牌名稱 : 富遊RG
創立時間 : 2019年
存款速度 : 平均15秒
提款速度 : 平均5分
單筆提款金額 : 最低1000-100萬
遊戲對象 : 18歲以上男女老少皆可
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
支付平台 : 各大銀行、各大便利超商
支援配備 : 手機網頁、電腦網頁、IOS、安卓(Android)
富遊娛樂城遊戲品牌
真人百家 — 歐博真人、DG真人、亞博真人、SA真人、OG真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、亞博體育
電競遊戲 — 泛亞電競
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、好路GR電子
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、亞博捕魚
富遊娛樂城優惠活動
每日任務簽到金666
富遊VIP全面啟動
復酬金活動10%優惠
日日返水
新會員好禮五選一
首存禮1000送1000
免費體驗金$168
富遊娛樂城APP
步驟1 : 開啟網頁版【富遊娛樂城官網】
步驟2 : 點選上方(下載app),會跳出下載與複製連結選項,點選後跳轉。
步驟3 : 跳轉後點選(安裝),並點選(允許)操作下載描述檔,跳出下載描述檔後點選關閉。
步驟4 : 到手機設置>一般>裝置管理>設定描述檔(富遊)安裝,即可完成安裝。
富遊娛樂城常見問題FAQ
富遊娛樂城詐騙?
黑網詐騙可細分兩種,小出大不出及純詐騙黑網,我們可從品牌知名度經營和網站架設畫面分辨來簡單分辨。
富遊娛樂城會出金嗎?
如上面提到,富遊是在做一個品牌,為的是能夠保證出金,和帶領玩家遠離黑網,而且還有DUKER娛樂城出金認證,所以各位能夠放心富遊娛樂城為正出金娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城出金延遲怎麼辦?
基本上只要是公司系統問提造成富遊娛樂城會員無法在30分鐘成功提款,富遊娛樂城會即刻派送補償金,表達誠摯的歉意。
富遊娛樂城結論
富遊娛樂城安心玩,評價4.5顆星。如果還想看其他娛樂城推薦的,可以來娛樂城推薦尋找喔。 -
https://rg88.org/seth/
2024全新上線❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ - ATG賽特玩法說明介紹
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,在傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的冒險者才能進入探險。
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特介紹
2024最新老虎機【戰神塞特】- ATG電子 X 富遊娛樂城
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG電子
線上老虎機系統 : ATG電子
發行年分 : 2024年1月
最大倍數 : 51000倍
返還率 : 95.89%
支付方式 : 全盤倍數、消除掉落
最低投注金額 : 0.4元
最高投注金額 : 2000元
可否選台 : 是
可選台台數 : 350台
免費遊戲 : 選轉觸發+購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明
戰神塞特老虎機賠率算法非常簡單,玩家們只需要不斷的轉動老虎機,成功消除物件即可贏分,得分賠率依賠率表計算。
當盤面上沒有物件可以消除時,倍數符號將會相加形成總倍數!該次旋轉的總贏分即為 : 贏分 X 總倍數。
積分方式如下 :
贏分=(單次押注額/20) X 物件賠率
EX : 單次押注額為1,盤面獲得12個戰神賽特倍數符號法老魔眼
贏分= (1/20) X 1000=50
以下為各個得分符號數量之獎金賠率 :
得分符號 獎金倍數 得分符號 獎金倍數
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲 6 2000
5 100
4 60 戰神賽特倍數符號黃寶石 12+ 200
10-11 30
8-9 20
戰神賽特倍數符號荷魯斯之眼 12+ 1000
10-11 500
8-9 200 戰神賽特倍數符號紅寶石 12+ 160
10-11 24
8-9 16
戰神賽特倍數符號眼鏡蛇 12+ 500
10-11 200
8-9 50 戰神賽特倍數符號紫鑽石 12+ 100
10-11 20
8-9 10
戰神賽特倍數符號神箭 12+ 300
10-11 100
8-9 40 戰神賽特倍數符號藍寶石 12+ 80
10-11 18
8-9 8
戰神賽特倍數符號屠鐮刀 12+ 240
10-11 40
8-9 30 戰神賽特倍數符號綠寶石 12+ 40
10-11 15
8-9 5
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明(橘色數值為獲得數量、黑色數值為得分賠率)
ATG賽特 – 特色說明
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
玩家們在看到盤面上出現倍數符號時,務必把握機會加速轉動ATG賽特老虎機,倍數符號會隨機出現2到500倍的隨機倍數。
當盤面無法在消除時,這些倍數總和會相加,乘上當時累積之獎金,即為最後得分總額。
倍數符號會出現在主遊戲和免費遊戲當中,玩家們千萬別錯過這個可以瞬間將得獎金額拉高的好機會!
ATG賽特 - 倍數符號獎金加乘
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號圖示
ATG賽特 – 進入神秘金字塔開啟免費遊戲
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 免費遊戲符號
在古埃及神話中,聖甲蟲又稱為「死亡之蟲」,它被當成了天球及重生的象徵,守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶。
當玩家在盤面上,看見越來越多的聖甲蟲時,千萬不要膽怯,只需在牌面上斬殺4~6個ATG賽特免費遊戲符號,就可以進入15場免費遊戲!
在免費遊戲中若轉出3~6個聖甲蟲免費遊戲符號,可額外獲得5次免費遊戲,最高可達100次。
當玩家的累積贏分且盤面有倍數物件時,盤面上的所有倍數將會加入總倍數!
ATG賽特 – 選台模式贏在起跑線
為避免神聖的寶物被盜墓者奪走,富有智慧的法老王將金子塔內佈滿迷宮,有的設滿機關讓盜墓者寸步難行,有的暗藏機關可以直接前往存放神秘寶物的暗房。
ATG賽特老虎機設有350個機檯供玩家選擇,這是連魔龍老虎機、忍老虎機都給不出的機台數量,為的就是讓玩家,可以隨時進入神秘的古埃及的寶藏聖域,挖掘長眠已久的神祕寶藏。
【戰神塞特老虎機】選台模式
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 選台模式
ATG賽特 – 購買免費遊戲挖掘秘寶
玩家們可以使用當前投注額的100倍購買免費遊戲!進入免費遊戲再也不是虛幻。獎勵與一般遊戲相同,且購買後遊戲將自動開始,直到場次和獎金發放完畢為止。
有購買免費遊戲需求的玩家們,立即點擊「開始」,啟動神秘金字塔裡的古埃及祕寶吧!
【戰神塞特老虎機】購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 購買特色
戰神賽特試玩推薦
看完了❰戰神賽特老虎機❱介紹之後,玩家們是否也蓄勢待發要進入古埃及的世界,一探神奇秘寶探險之旅。
本次ATG賽特與線上娛樂城推薦第一名的富遊娛樂城合作,只需要加入會員,即可領取到168體驗金,免費試玩420轉! -
戰神賽特老虎機
2024全新上線❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ - ATG賽特玩法說明介紹
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,在傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的冒險者才能進入探險。
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特介紹
2024最新老虎機【戰神塞特】- ATG電子 X 富遊娛樂城
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG電子
線上老虎機系統 : ATG電子
發行年分 : 2024年1月
最大倍數 : 51000倍
返還率 : 95.89%
支付方式 : 全盤倍數、消除掉落
最低投注金額 : 0.4元
最高投注金額 : 2000元
可否選台 : 是
可選台台數 : 350台
免費遊戲 : 選轉觸發+購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明
戰神塞特老虎機賠率算法非常簡單,玩家們只需要不斷的轉動老虎機,成功消除物件即可贏分,得分賠率依賠率表計算。
當盤面上沒有物件可以消除時,倍數符號將會相加形成總倍數!該次旋轉的總贏分即為 : 贏分 X 總倍數。
積分方式如下 :
贏分=(單次押注額/20) X 物件賠率
EX : 單次押注額為1,盤面獲得12個戰神賽特倍數符號法老魔眼
贏分= (1/20) X 1000=50
以下為各個得分符號數量之獎金賠率 :
得分符號 獎金倍數 得分符號 獎金倍數
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲 6 2000
5 100
4 60 戰神賽特倍數符號黃寶石 12+ 200
10-11 30
8-9 20
戰神賽特倍數符號荷魯斯之眼 12+ 1000
10-11 500
8-9 200 戰神賽特倍數符號紅寶石 12+ 160
10-11 24
8-9 16
戰神賽特倍數符號眼鏡蛇 12+ 500
10-11 200
8-9 50 戰神賽特倍數符號紫鑽石 12+ 100
10-11 20
8-9 10
戰神賽特倍數符號神箭 12+ 300
10-11 100
8-9 40 戰神賽特倍數符號藍寶石 12+ 80
10-11 18
8-9 8
戰神賽特倍數符號屠鐮刀 12+ 240
10-11 40
8-9 30 戰神賽特倍數符號綠寶石 12+ 40
10-11 15
8-9 5
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明(橘色數值為獲得數量、黑色數值為得分賠率)
ATG賽特 – 特色說明
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
玩家們在看到盤面上出現倍數符號時,務必把握機會加速轉動ATG賽特老虎機,倍數符號會隨機出現2到500倍的隨機倍數。
當盤面無法在消除時,這些倍數總和會相加,乘上當時累積之獎金,即為最後得分總額。
倍數符號會出現在主遊戲和免費遊戲當中,玩家們千萬別錯過這個可以瞬間將得獎金額拉高的好機會!
ATG賽特 - 倍數符號獎金加乘
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號圖示
ATG賽特 – 進入神秘金字塔開啟免費遊戲
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 免費遊戲符號
在古埃及神話中,聖甲蟲又稱為「死亡之蟲」,它被當成了天球及重生的象徵,守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶。
當玩家在盤面上,看見越來越多的聖甲蟲時,千萬不要膽怯,只需在牌面上斬殺4~6個ATG賽特免費遊戲符號,就可以進入15場免費遊戲!
在免費遊戲中若轉出3~6個聖甲蟲免費遊戲符號,可額外獲得5次免費遊戲,最高可達100次。
當玩家的累積贏分且盤面有倍數物件時,盤面上的所有倍數將會加入總倍數!
ATG賽特 – 選台模式贏在起跑線
為避免神聖的寶物被盜墓者奪走,富有智慧的法老王將金子塔內佈滿迷宮,有的設滿機關讓盜墓者寸步難行,有的暗藏機關可以直接前往存放神秘寶物的暗房。
ATG賽特老虎機設有350個機檯供玩家選擇,這是連魔龍老虎機、忍老虎機都給不出的機台數量,為的就是讓玩家,可以隨時進入神秘的古埃及的寶藏聖域,挖掘長眠已久的神祕寶藏。
【戰神塞特老虎機】選台模式
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 選台模式
ATG賽特 – 購買免費遊戲挖掘秘寶
玩家們可以使用當前投注額的100倍購買免費遊戲!進入免費遊戲再也不是虛幻。獎勵與一般遊戲相同,且購買後遊戲將自動開始,直到場次和獎金發放完畢為止。
有購買免費遊戲需求的玩家們,立即點擊「開始」,啟動神秘金字塔裡的古埃及祕寶吧!
【戰神塞特老虎機】購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 購買特色
戰神賽特試玩推薦
看完了❰戰神賽特老虎機❱介紹之後,玩家們是否也蓄勢待發要進入古埃及的世界,一探神奇秘寶探險之旅。
本次ATG賽特與線上娛樂城推薦第一名的富遊娛樂城合作,只需要加入會員,即可領取到168體驗金,免費試玩420轉! -
https://minecraft-home.ru/
-
欢迎来到我们的加密货币博客,这里是探索数字货币世界的绝佳平台。我们致力于提供最新的加密货币新闻、深入的市场分析、投资策略和技术解读。无论您是加密货币的初学者还是经验丰富的投资者,我们的博客都能为您提供有价值的见解。加入我们,一起探索比特币、以太坊、莱特币等多种加密货币的激动人心的旅程,并深入了解区块链技术如何改变世界。
https://auto-noginsk.ru -
[url=https://jurist-praktic.ru]1xbet зеркало рабочее на сегодня прямо[/url]– это популярная букмекерская контора, предоставляющая широкий выбор ставок на спорт и казино. Сайт обладает удобным интерфейсом, мобильной версией и приложением для удобства пользователей. 1xBet также известен разнообразными акциями и бонусами, делая игровой опыт более захватывающим.
-
欢迎来到我们的加密货币博客,这里是探索数字货币世界的绝佳平台。我们致力于提供最新的加密货币新闻、深入的市场分析、投资策略和技术解读。无论您是加密货币的初学者还是经验丰富的投资者,我们的博客都能为您提供有价值的见解。加入我们,一起探索比特币、以太坊、莱特币等多种加密货币的激动人心的旅程,并深入了解区块链技术如何改变世界。
http://yinyue7.com/space-uid-956944.html
https://www.pintradingdb.com/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=79313
http://www.flicube.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=239571
https://rdaforum.com/user-14584.html
https://forum.openbadania.pl/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=270117&sid=8d0d55a0dc3341b6b8c52d2185061d06 -
크립토 코리아: 인사이트와 트렌드"는 한국에서 가장 신뢰받는 암호화폐 블로그 중 하나입니다. 최신 암호화폐 뉴스, 시장 분석, 트레이딩 전략을 제공하며, 블록체인 기술과 관련된 혁신적인 아이디어를 탐구합니다. 초보자부터 전문가까지 모든 수준의 투자자와 열정적인 크립토 커뮤니티가 찾는 곳입니다. 이 블로그는 한국의 크립토 트렌드를 이해하는 데 필수적인 자원이며, 암호화폐의 복잡한 세계를 이해하기 위한 명확하고 실용적인 가이드를 제공합니다. 여기서는 최신 ICO 분석, 암호화폐 거래소 리뷰, 블록체인 스타트업의 인터뷰 및 분석 기사를 찾을 수 있습니다.
https://copyrait.ru/ -
크립토 코리아: 인사이트와 트렌드"는 한국에서 가장 신뢰받는 암호화폐 블로그 중 하나입니다. 최신 암호화폐 뉴스, 시장 분석, 트레이딩 전략을 제공하며, 블록체인 기술과 관련된 혁신적인 아이디어를 탐구합니다. 초보자부터 전문가까지 모든 수준의 투자자와 열정적인 크립토 커뮤니티가 찾는 곳입니다. 이 블로그는 한국의 크립토 트렌드를 이해하는 데 필수적인 자원이며, 암호화폐의 복잡한 세계를 이해하기 위한 명확하고 실용적인 가이드를 제공합니다. 여기서는 최신 ICO 분석, 암호화폐 거래소 리뷰, 블록체인 스타트업의 인터뷰 및 분석 기사를 찾을 수 있습니다.
http://seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1205521
http://yinyue7.com/space-uid-957500.html
https://hdkaraokesong.com/space-uid-263818.html
https://www.donyaihom.go.th/webboard/index.php?action=profile;u=858416
https://ninitime.com/community/member.php?action=profile&uid=17805 -
https://base-minecraft.ru/
-
Деревянные дома под ключ
Дома АВС - Ваш уютный уголок
Мы строим не просто дома, мы создаем пространство, где каждый уголок будет наполнен комфортом и радостью жизни. Наш приоритет - не просто предоставить место для проживания, а создать настоящий дом, где вы будете чувствовать себя счастливыми и уютно.
В нашем информационном разделе "ПРОЕКТЫ" вы всегда найдете вдохновение и новые идеи для строительства вашего будущего дома. Мы постоянно работаем над тем, чтобы предложить вам самые инновационные и стильные проекты.
Мы убеждены, что основа хорошего дома - это его дизайн. Поэтому мы предоставляем услуги опытных дизайнеров-архитекторов, которые помогут вам воплотить все ваши идеи в жизнь. Наши архитекторы и персональные консультанты всегда готовы поделиться своим опытом и предложить функциональные и комфортные решения для вашего будущего дома.
Мы стремимся сделать весь процесс строительства максимально комфортным для вас. Наша команда предоставляет детализированные сметы, разрабатывает четкие этапы строительства и осуществляет контроль качества на каждом этапе.
Для тех, кто ценит экологичность и близость к природе, мы предлагаем деревянные дома премиум-класса. Используя клееный брус и оцилиндрованное бревно, мы создаем уникальные и здоровые условия для вашего проживания.
Тем, кто предпочитает надежность и многообразие форм, мы предлагаем дома из камня, блоков и кирпичной кладки.
Для практичных и ценящих свое время людей у нас есть быстровозводимые каркасные дома и эконом-класса. Эти решения обеспечат вас комфортным проживанием в кратчайшие сроки.
С Домами АВС создайте свой уютный уголок, где каждый момент жизни будет наполнен радостью и удовлетворением -
戰神賽特
2024全新上線❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ - ATG賽特玩法說明介紹
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,在傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的冒險者才能進入探險。
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特介紹
2024最新老虎機【戰神塞特】- ATG電子 X 富遊娛樂城
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG電子
線上老虎機系統 : ATG電子
發行年分 : 2024年1月
最大倍數 : 51000倍
返還率 : 95.89%
支付方式 : 全盤倍數、消除掉落
最低投注金額 : 0.4元
最高投注金額 : 2000元
可否選台 : 是
可選台台數 : 350台
免費遊戲 : 選轉觸發+購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明
戰神塞特老虎機賠率算法非常簡單,玩家們只需要不斷的轉動老虎機,成功消除物件即可贏分,得分賠率依賠率表計算。
當盤面上沒有物件可以消除時,倍數符號將會相加形成總倍數!該次旋轉的總贏分即為 : 贏分 X 總倍數。
積分方式如下 :
贏分=(單次押注額/20) X 物件賠率
EX : 單次押注額為1,盤面獲得12個戰神賽特倍數符號法老魔眼
贏分= (1/20) X 1000=50
以下為各個得分符號數量之獎金賠率 :
得分符號 獎金倍數 得分符號 獎金倍數
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲 6 2000
5 100
4 60 戰神賽特倍數符號黃寶石 12+ 200
10-11 30
8-9 20
戰神賽特倍數符號荷魯斯之眼 12+ 1000
10-11 500
8-9 200 戰神賽特倍數符號紅寶石 12+ 160
10-11 24
8-9 16
戰神賽特倍數符號眼鏡蛇 12+ 500
10-11 200
8-9 50 戰神賽特倍數符號紫鑽石 12+ 100
10-11 20
8-9 10
戰神賽特倍數符號神箭 12+ 300
10-11 100
8-9 40 戰神賽特倍數符號藍寶石 12+ 80
10-11 18
8-9 8
戰神賽特倍數符號屠鐮刀 12+ 240
10-11 40
8-9 30 戰神賽特倍數符號綠寶石 12+ 40
10-11 15
8-9 5
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明(橘色數值為獲得數量、黑色數值為得分賠率)
ATG賽特 – 特色說明
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
玩家們在看到盤面上出現倍數符號時,務必把握機會加速轉動ATG賽特老虎機,倍數符號會隨機出現2到500倍的隨機倍數。
當盤面無法在消除時,這些倍數總和會相加,乘上當時累積之獎金,即為最後得分總額。
倍數符號會出現在主遊戲和免費遊戲當中,玩家們千萬別錯過這個可以瞬間將得獎金額拉高的好機會!
ATG賽特 - 倍數符號獎金加乘
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號圖示
ATG賽特 – 進入神秘金字塔開啟免費遊戲
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 免費遊戲符號
在古埃及神話中,聖甲蟲又稱為「死亡之蟲」,它被當成了天球及重生的象徵,守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶。
當玩家在盤面上,看見越來越多的聖甲蟲時,千萬不要膽怯,只需在牌面上斬殺4~6個ATG賽特免費遊戲符號,就可以進入15場免費遊戲!
在免費遊戲中若轉出3~6個聖甲蟲免費遊戲符號,可額外獲得5次免費遊戲,最高可達100次。
當玩家的累積贏分且盤面有倍數物件時,盤面上的所有倍數將會加入總倍數!
ATG賽特 – 選台模式贏在起跑線
為避免神聖的寶物被盜墓者奪走,富有智慧的法老王將金子塔內佈滿迷宮,有的設滿機關讓盜墓者寸步難行,有的暗藏機關可以直接前往存放神秘寶物的暗房。
ATG賽特老虎機設有350個機檯供玩家選擇,這是連魔龍老虎機、忍老虎機都給不出的機台數量,為的就是讓玩家,可以隨時進入神秘的古埃及的寶藏聖域,挖掘長眠已久的神祕寶藏。
【戰神塞特老虎機】選台模式
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 選台模式
ATG賽特 – 購買免費遊戲挖掘秘寶
玩家們可以使用當前投注額的100倍購買免費遊戲!進入免費遊戲再也不是虛幻。獎勵與一般遊戲相同,且購買後遊戲將自動開始,直到場次和獎金發放完畢為止。
有購買免費遊戲需求的玩家們,立即點擊「開始」,啟動神秘金字塔裡的古埃及祕寶吧!
【戰神塞特老虎機】購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 購買特色
戰神賽特試玩推薦
看完了❰戰神賽特老虎機❱介紹之後,玩家們是否也蓄勢待發要進入古埃及的世界,一探神奇秘寶探險之旅。
本次ATG賽特與線上娛樂城推薦第一名的富遊娛樂城合作,只需要加入會員,即可領取到168體驗金,免費試玩420轉! -
「クリプトジャパン」へようこそ。このブログは、仮想通貨の複雑な世界を解き明かすための信頼できるガイドです。初心者から上級者まで、最新の市場動向、投資戦略、技術分析、そして仮想通貨に関する法律や税制についてわかりやすく解説します。日本国内外の仮想通貨市場のニュースをいち早くお届けし、あなたの仮想通貨投資を成功へと導くための情報源となることを目指しています。
galaxyflowers.ru -
ATG戰神賽特
2024全新上線❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ - ATG賽特玩法說明介紹
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,在傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的冒險者才能進入探險。
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG賽特介紹
2024最新老虎機【戰神塞特】- ATG電子 X 富遊娛樂城
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ – ATG電子
線上老虎機系統 : ATG電子
發行年分 : 2024年1月
最大倍數 : 51000倍
返還率 : 95.89%
支付方式 : 全盤倍數、消除掉落
最低投注金額 : 0.4元
最高投注金額 : 2000元
可否選台 : 是
可選台台數 : 350台
免費遊戲 : 選轉觸發+購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明
戰神塞特老虎機賠率算法非常簡單,玩家們只需要不斷的轉動老虎機,成功消除物件即可贏分,得分賠率依賠率表計算。
當盤面上沒有物件可以消除時,倍數符號將會相加形成總倍數!該次旋轉的總贏分即為 : 贏分 X 總倍數。
積分方式如下 :
贏分=(單次押注額/20) X 物件賠率
EX : 單次押注額為1,盤面獲得12個戰神賽特倍數符號法老魔眼
贏分= (1/20) X 1000=50
以下為各個得分符號數量之獎金賠率 :
得分符號 獎金倍數 得分符號 獎金倍數
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲 6 2000
5 100
4 60 戰神賽特倍數符號黃寶石 12+ 200
10-11 30
8-9 20
戰神賽特倍數符號荷魯斯之眼 12+ 1000
10-11 500
8-9 200 戰神賽特倍數符號紅寶石 12+ 160
10-11 24
8-9 16
戰神賽特倍數符號眼鏡蛇 12+ 500
10-11 200
8-9 50 戰神賽特倍數符號紫鑽石 12+ 100
10-11 20
8-9 10
戰神賽特倍數符號神箭 12+ 300
10-11 100
8-9 40 戰神賽特倍數符號藍寶石 12+ 80
10-11 18
8-9 8
戰神賽特倍數符號屠鐮刀 12+ 240
10-11 40
8-9 30 戰神賽特倍數符號綠寶石 12+ 40
10-11 15
8-9 5
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 賠率說明(橘色數值為獲得數量、黑色數值為得分賠率)
ATG賽特 – 特色說明
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號獎金加乘
玩家們在看到盤面上出現倍數符號時,務必把握機會加速轉動ATG賽特老虎機,倍數符號會隨機出現2到500倍的隨機倍數。
當盤面無法在消除時,這些倍數總和會相加,乘上當時累積之獎金,即為最後得分總額。
倍數符號會出現在主遊戲和免費遊戲當中,玩家們千萬別錯過這個可以瞬間將得獎金額拉高的好機會!
ATG賽特 - 倍數符號獎金加乘
ATG賽特 – 倍數符號圖示
ATG賽特 – 進入神秘金字塔開啟免費遊戲
戰神賽特倍數符號聖甲蟲
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 免費遊戲符號
在古埃及神話中,聖甲蟲又稱為「死亡之蟲」,它被當成了天球及重生的象徵,守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶。
當玩家在盤面上,看見越來越多的聖甲蟲時,千萬不要膽怯,只需在牌面上斬殺4~6個ATG賽特免費遊戲符號,就可以進入15場免費遊戲!
在免費遊戲中若轉出3~6個聖甲蟲免費遊戲符號,可額外獲得5次免費遊戲,最高可達100次。
當玩家的累積贏分且盤面有倍數物件時,盤面上的所有倍數將會加入總倍數!
ATG賽特 – 選台模式贏在起跑線
為避免神聖的寶物被盜墓者奪走,富有智慧的法老王將金子塔內佈滿迷宮,有的設滿機關讓盜墓者寸步難行,有的暗藏機關可以直接前往存放神秘寶物的暗房。
ATG賽特老虎機設有350個機檯供玩家選擇,這是連魔龍老虎機、忍老虎機都給不出的機台數量,為的就是讓玩家,可以隨時進入神秘的古埃及的寶藏聖域,挖掘長眠已久的神祕寶藏。
【戰神塞特老虎機】選台模式
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 選台模式
ATG賽特 – 購買免費遊戲挖掘秘寶
玩家們可以使用當前投注額的100倍購買免費遊戲!進入免費遊戲再也不是虛幻。獎勵與一般遊戲相同,且購買後遊戲將自動開始,直到場次和獎金發放完畢為止。
有購買免費遊戲需求的玩家們,立即點擊「開始」,啟動神秘金字塔裡的古埃及祕寶吧!
【戰神塞特老虎機】購買特色
❰戰神賽特老虎機❱ 購買特色
戰神賽特試玩推薦
看完了❰戰神賽特老虎機❱介紹之後,玩家們是否也蓄勢待發要進入古埃及的世界,一探神奇秘寶探險之旅。
本次ATG賽特與線上娛樂城推薦第一名的富遊娛樂城合作,只需要加入會員,即可領取到168體驗金,免費試玩420轉! -
「クリプトジャパン」へようこそ。このブログは、仮想通貨の複雑な世界を解き明かすための信頼できるガイドです。初心者から上級者まで、最新の市場動向、投資戦略、技術分析、そして仮想通貨に関する法律や税制についてわかりやすく解説します。日本国内外の仮想通貨市場のニュースをいち早くお届けし、あなたの仮想通貨投資を成功へと導くための情報源となることを目指しています。
galaxyflowers.ru -
「クリプトジャパン」へようこそ。このブログは、仮想通貨の複雑な世界を解き明かすための信頼できるガイドです。初心者から上級者まで、最新の市場動向、投資戦略、技術分析、そして仮想通貨に関する法律や税制についてわかりやすく解説します。日本国内外の仮想通貨市場のニュースをいち早くお届けし、あなたの仮想通貨投資を成功へと導くための情報源となることを目指しています。
galaxyflowers.ru -
「クリプトジャパン」へようこそ。このブログは、仮想通貨の複雑な世界を解き明かすための信頼できるガイドです。初心者から上級者まで、最新の市場動向、投資戦略、技術分析、そして仮想通貨に関する法律や税制についてわかりやすく解説します。日本国内外の仮想通貨市場のニュースをいち早くお届けし、あなたの仮想通貨投資を成功へと導くための情報源となることを目指しています。
galaxyflowers.ru -
Welcome to CryptoSutra, the premier destination for Indians to unravel the dynamic world of cryptocurrency. This blog serves as a beacon for beginners and seasoned investors alike, navigating the often complex waters of digital currencies. Our mission is to demystify the world of Bitcoin, Ethereum, and a myriad of altcoins, making them accessible to the Indian investor.
At CryptoSutra, we understand the unique position of India in the global crypto landscape. We offer tailored content that respects the nuances of Indian regulations, economic trends, and market sentiments. From breaking down RBI's latest guidelines to exploring investment strategies suited for the Indian market, our focus is to empower you with knowledge.
Our blog features:
Educational Guides: Step-by-step tutorials, glossaries, and infographics that simplify blockchain technology and cryptocurrency trading principles.
Market Analysis: Timely insights and analyses of global market trends, with a special focus on how they impact the Indian economy.
Investment Strategies: Practical advice on portfolio management, risk assessment, and leveraging crypto assets in the Indian context.
gaffarov.ru -
[url=https://konkurslift.ru/]лучшие казино[/url]– это популярная букмекерская контора, предоставляющая широкий выбор ставок на спорт и казино. Сайт обладает удобным интерфейсом, мобильной версией и приложением для удобства пользователей. 1xBet также известен разнообразными акциями и бонусами, делая игровой опыт более захватывающим.
-
Well-received to CryptoSutra, the head of state goal after Indians to unravel the active world of cryptocurrency. This blog serves as a rocket because beginners and habituated investors like one another, navigating the time again complex waters of digital currencies. Our vocation is to demystify the world of Bitcoin, Ethereum, and a myriad of altcoins, making them obtainable to the Indian investor.
At CryptoSutra, we cotton on to the unparalleled pose of India in the global crypto landscape. We proffer tailored tranquillity that respects the nuances of Indian regulations, economic trends, and market sentiments. From breaking down RBI's latest guidelines to exploring investment strategies suited on the Indian retail, our indistinct is to empower you with knowledge.
Our blog features:
Educational Guides: Step-by-step tutorials, glossaries, and infographics that unravel blockchain technology and cryptocurrency trading principles.
Market Judgement: Timely insights and analyses of worldwide market trends, with a devoted focus on how they collide with the Indian economy.
Investment Strategies: Reasonable advice on portfolio government, imperil assessment, and leveraging crypto assets in the Indian context.
https://mcmon.ru/member.php?action=profile&uid=128605
https://www.metal-tracker.com/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=927374249
http://iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=786570
http://www.kiripo.com/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=1004544
https://www.medflyfish.com/index.php?action=profile;u=4149508 -
Hail to CryptoSphere, your paramount goal for the sake of all things cryptocurrency. Whether you're a prepared investor or a curious learner, our blog offers a wealth of information to keep from you manoeuvre the complex and ever-evolving existence of digital currencies. From in-depth analyses of the latest market-place trends to useable guides on blockchain technology and investment strategies, CryptoSphere is your reliable beginning in behalf of timely, with an eye to, and insightful content. Verge on our community to stay up ahead in the active and overpowering cosmos of cryptocurrency.
aple-system.ru -
Welcome to CryptoSphere, your paramount destination in spite of all things cryptocurrency. Whether you're a prepared investor or a strange immigrant, our blog offers a fullness of facts to aid you navigate the complex and ever-evolving world of digital currencies. From in-depth analyses of the latest sell trends to empirical guides on blockchain technology and investment strategies, CryptoSphere is your honourable beginning in favour of favourable, spot on target, and insightful content. Join our community to interrupt up ahead in the dynamic and far-out cosmos of cryptocurrency.
http://sglpw.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=326652
http://www.3ak.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=171985
http://witiai.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=54662
https://www.dragonsword.com/member.php?action=profile&uid=7032
http://www.iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=786809 -
Hail to CryptoSphere, your paramount goal for the sake of all things cryptocurrency. Whether you're a prepared investor or a strange immigrant, our blog offers a cash of information to aid you nautical con the complex and ever-evolving existence of digital currencies. From in-depth analyses of the latest market trends to empirical guides on blockchain technology and investment strategies, CryptoSphere is your reliable beginning in favour of punctual, error-free, and insightful content. Be adjacent to our community to visit ahead in the energetic and overpowering coterie of cryptocurrency.
https://mcmon.ru/member.php?action=profile&uid=128713
https://www.98e.fun/space-uid-7090372.html
http://sailing-bluewater.com/forum/index.php?action=profile;u=2497638
http://yw10.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=199456
http://ds-dealer.nichost.ru/forum/member.php?u=630189 -
Greeting to CryptoSphere, your paramount destination for the sake of all things cryptocurrency. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a unconventional newcomer, our blog offers a wealth of data to keep from you nautical con the complex and ever-evolving on cloud nine of digital currencies. From in-depth analyses of the latest demand trends to practical guides on blockchain technology and investment strategies, CryptoSphere is your honest source for timely, error-free, and insightful content. Verge on our community to visit ahead in the eager and far-out coterie of cryptocurrency.
http://www.lezcc.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=204870
http://bbs.yymlbb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=181031
http://www.gtcm.info/home.php?mod=space&uid=725167
http://bbs.panabit.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=396735
http://zhilexue.tech/space-uid-19758.html -
Offer hospitality to to CryptoSphere, your ultimate terminus in behalf of all things cryptocurrency. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a curious learner, our blog offers a wealth of tidings to aid you nautical con the complex and ever-evolving existence of digital currencies. From in-depth analyses of the latest market trends to empirical guides on blockchain technology and investment strategies, CryptoSphere is your honest authority in favour of punctual, with an eye to, and insightful content. Solder together our community to visit up ahead in the dynamic and galvanizing cosmos of cryptocurrency.
http://bbs.zhizhuyx.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=9479532
http://skiindustry.org:/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=1144920
http://www.bhl7.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=81087
http://www.pigcraft.ugu.pl/member.php?action=profile&uid=213771
https://www.9tj.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=102191 -
Welcome to CryptoSphere, your basic stopping-place for all things cryptocurrency. Whether you're a long-standing investor or a strange learner, our blog offers a cash of tidings to keep from you pilot the complex and ever-evolving world of digital currencies. From in-depth analyses of the latest sell trends to useable guides on blockchain technology and investment strategies, CryptoSphere is your honourable beginning in favour of timely, with an eye to, and insightful content. Be adjacent to our community to visit to the fore in the eager and galvanizing coterie of cryptocurrency.
http://bbs.yymlbb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=181031
http://m.414500.cc/home.php?mod=space&uid=3179400
https://mcmon.ru/member.php?action=profile&uid=128713
https://bbs.m2.hk/home.php?mod=space&uid=87624
http://www.1k9g.com/space-uid-191992.html -
Greeting to CryptoSphere, your ultimate stopping-place for all things cryptocurrency. Whether you're a acclimatized investor or a curious beginner, our blog offers a fullness of information to aid you navigate the complex and ever-evolving world of digital currencies. From in-depth analyses of the latest sell trends to useable guides on blockchain technology and investment strategies, CryptoSphere is your secure fountain-head in behalf of favourable, accurate, and insightful content. Solder together our community to interrupt to the fore in the eager and far-out cosmos of cryptocurrency.
https://bbs.521zixuan.com/space-uid-635036.html
http://sljlz.92zyb.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=179573
http://1k9g.com/space-uid-191992.html
http://www.zhuangxiuz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=765113
http://yw10.xyz/home.php?mod=space&uid=199456 -
https://minecraft-obzor.ru/9-servera-maynkraft-18.html
-
Willkommen bei 'KryptoKompass', Ihrem ultimativen Leitfaden in der dynamischen und faszinierenden Bruise der Kryptowahrungen. Unser Blog bietet Ihnen aktuelle Nachrichten, tiefgehende Analysen und wertvolle Einblicke in long Contusion von Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple und vielen anderen digitalen Wahrungen. Egal, ob Sie ein Anfanger oder ein erfahrener Investor sind, wir liefern Ihnen fade away Informationen, degenerate Sie brauchen, um fundierte Entscheidungen zu treffen. Tauchen Sie ein in unsere Expertenartikel, Tutorials und Marktprognosen, um Ihr Krypto-Wissen zu erweitern. Mit 'KryptoKompass' bleiben Sie immer auf dem neuesten Accept der Entwicklungen im Kryptoraum
carsused.ru -
В Москве вы можете успешно написать диплом по любой специальности. Профессиональные писатели помогут с составлением уникального текста, соответствующего всем требованиям. Получите высокую оценку, обратившись к опытным специалистам.
https://www.tapatalk.com/groups/dzerjinsky/viewtopic.php?f=9&t=33502&from_new_topic=1
http://www.marheavenj.net/public/gallery/member.php?action=showprofile&user_id=26238
http://writercenter.ru/profile/kulakovuz2k/
http://gazeta.ekafe.ru/viewtopic.php?f=97&t=28843
Наш сервис предоставляет качественную помощь в написании дипломов. -
Willkommen bei 'KryptoKompass', Ihrem ultimativen Leitfaden in der dynamischen und faszinierenden Weal der Kryptowahrungen. Unser Blog bietet Ihnen aktuelle Nachrichten, tiefgehende Analysen und wertvolle Einblicke in go to one's reward Welt von Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple und vielen anderen digitalen Wahrungen. Egal, ob Sie ein Anfanger oder ein erfahrener Investor sind, wir liefern Ihnen die Informationen, go to meet one's maker Sie brauchen, um fundierte Entscheidungen zu treffen. Tauchen Sie ein in unsere Expertenartikel, Tutorials und Marktprognosen, um Ihr Krypto-Wissen zu erweitern. Mit 'KryptoKompass' bleiben Sie immer auf dem neuesten Experience der Entwicklungen im Kryptoraum
http://zhwbn.com/bbs/space-uid-148918.html
http://bbs.qc0769.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=420480
http://www.seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1206824
https://bans.org.ua/index.php?action=profile;u=1318603
http://www.zgqsz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=312841 -
Willkommen bei 'KryptoKompass', Ihrem ultimativen Leitfaden in der dynamischen und faszinierenden Bruise der Kryptowahrungen. Unser Blog bietet Ihnen aktuelle Nachrichten, tiefgehende Analysen und wertvolle Einblicke in bite the dust Bump von Bitcoin, Ethereum, Riffle und vielen anderen digitalen Wahrungen. Egal, ob Sie ein Anfanger oder ein erfahrener Investor sind, wir liefern Ihnen fade away Informationen, degenerate Sie brauchen, um fundierte Entscheidungen zu treffen. Tauchen Sie ein in unsere Expertenartikel, Tutorials und Marktprognosen, um Ihr Krypto-Wissen zu erweitern. Mit 'KryptoKompass' bleiben Sie immer auf dem neuesten Accept der Entwicklungen im Kryptoraum
http://support-groups.org/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=119189
http://support-groups.org/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=119189&sid=a9c2ddd1d40849c7747d9dca8979fc2e
http://support-groups.org/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=119189&sid=6e77b2af70064013891d5d0c9a19caa1
http://m.414500.cc/home.php?mod=space&uid=3186214
http://iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=787030 -
O mundo das criptomoedas tem atraido cada vez mais atencao nos ultimos anos, mas para realmente compreender o potencial desses ativos digitais, e essencial entender a tecnologia que esta por tras deles: o blockchain.
O blockchain e uma tecnologia de registro distribuido que garante a seguranca e a transparencia das transacoes. Em essencia, e um livro-razao digital, onde as transacoes sao gravadas em 'blocos' e cada bloco esta conectado ao anterior, formando uma 'cadeia'. Esta estrutura unica garante que uma vez que uma transacao e adicionada ao blockchain, ela nao pode ser alterada ou apagada, oferecendo um nivel de seguranca sem precedentes.
Alem de ser a espinha dorsal das criptomoedas, como o Bitcoin e o Ethereum, o blockchain tem potencial para revolucionar diversos outros setores, como o financeiro, o juridico e ate mesmo o governo, oferecendo maneiras mais eficientes e seguras de realizar e registrar transacoes.
No entanto, apesar de suas muitas vantagens, o blockchain ainda enfrenta desafios, incluindo questoes de escalabilidade e a necessidade de maior regulamentacao para prevenir usos ilicitos. Mas, a medida que a tecnologia continua a evoluir, ela oferece a promessa de um futuro mais transparente, seguro e eficiente.
Para os entusiastas de criptomoedas, entender o blockchain nao e apenas uma questao de curiosidade, mas uma necessidade para navegar com seguranca e confianca neste novo e emocionante mundo digital.
https://korablik-zabeg.ru -
Легально [URL=http://diplom-sale.ru]купить диплом[/URL] сделать заказ и получить диплом Вуза на сайте http://diplom-sale.ru только на оригинальных бланках Гознак.
-
O mundo das criptomoedas tem atraido cada vez mais atencao nos ultimos anos, mas para realmente compreender o potencial desses ativos digitais, e essencial entender a tecnologia que esta por tras deles: o blockchain.
O blockchain e uma tecnologia de registro distribuido que garante a seguranca e a transparencia das transacoes. Em essencia, e um livro-razao digital, onde as transacoes sao gravadas em 'blocos' e cada bloco esta conectado ao anterior, formando uma 'cadeia'. Esta estrutura unica garante que uma vez que uma transacao e adicionada ao blockchain, ela nao pode ser alterada ou apagada, oferecendo um nivel de seguranca sem precedentes.
Alem de ser a espinha dorsal das criptomoedas, como o Bitcoin e o Ethereum, o blockchain tem potencial para revolucionar diversos outros setores, como o financeiro, o juridico e ate mesmo o governo, oferecendo maneiras mais eficientes e seguras de realizar e registrar transacoes.
No entanto, apesar de suas muitas vantagens, o blockchain ainda enfrenta desafios, incluindo questoes de escalabilidade e a necessidade de maior regulamentacao para prevenir usos ilicitos. Mas, a medida que a tecnologia continua a evoluir, ela oferece a promessa de um futuro mais transparente, seguro e eficiente.
Para os entusiastas de criptomoedas, entender o blockchain nao e apenas uma questao de curiosidade, mas uma necessidade para navegar com seguranca e confianca neste novo e emocionante mundo digital.
http://www.gtcm.info/home.php?mod=space&uid=725398
https://www.9tj.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=104069
https://www.ukspeaks.co.uk/members/226272-WilbertHen
http://i0110.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=519188
http://xavierdeschamps.free.fr/Escalade/Forum_escalade/profile.php?id=729111 -
Bienvenue sur "L'Essor de la Cryptomonnaie", votre source incontournable d'informations, de guides et d'analyses approfondies sur le monde fascinant des cryptomonnaies. Que vous soyez un investisseur aguerri ou un debutant curieux, notre blog offre une plateforme d'apprentissage et de discussion sur les dernieres tendances, les technologies blockchain, et les meilleures strategies d'investissement dans le domaine des monnaies numeriques. Rejoignez notre communaute pour demeurer a la pointe de l'innovation financiere et technologique.
https://ptcinnovationforum.ru -
Bienvenue sur "L'Essor de la Cryptomonnaie", votre source incontournable d'informations, de guides et d'analyses approfondies sur le monde fascinant des cryptomonnaies. Que vous soyez un investisseur aguerri ou un debutant curieux, notre blog offre une plateforme d'apprentissage et de discussion sur les dernieres tendances, les technologies blockchain, et les meilleures strategies d'investissement dans le domaine des monnaies numeriques. Rejoignez notre communaute pour demeurer a la pointe de l'innovation financiere et technologique.
https://forum.cabal.playthisgame.com/member.php?1597434-WilbertBug
http://forum.ttpforum.de/member.php?action=profile&uid=318445
https://hdkaraokesong.com/space-uid-264680.html
http://www.zgqsz.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=313018
http://seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1207170 -
Bienvenue sur "L'Essor de la Cryptomonnaie", votre source incontournable d'informations, de guides et d'analyses approfondies sur le monde fascinant des cryptomonnaies. Que vous soyez un investisseur aguerri ou un debutant curieux, notre blog offre une plateforme d'apprentissage et de discussion sur les dernieres tendances, les technologies blockchain, et les meilleures strategies d'investissement dans le domaine des monnaies numeriques. Rejoignez notre communaute pour demeurer a la pointe de l'innovation financiere et technologique.
http://bbs.py27.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=389523
https://forum.openbadania.pl/memberlist.php?mode=viewprofile&u=273305
http://www.tianranju.net/home.php?mod=space&uid=121149
http://www.1k9g.com/space-uid-192092.html
https://rdaforum.com/user-14650.html -
Bienvenidos a 'CriptoAlcance', su portal de confianza para sumergirse en el vibrante mundo de las criptomonedas. Aqui encontraras analisis detallados, noticias actualizadas, guias para principiantes y discusiones en profundidad sobre las tendencias mas recientes en Bitcoin, Ethereum, y otras monedas digitales. Nuestro equipo de expertos te brindara consejos practicos, estrategias de inversion y te mantendra al tanto de los cambios regulatorios y tecnologicos que afectan el mercado. Unete a nuestra comunidad y empieza tu viaje en el fascinante universo de las criptomonedas con 'CriptoAlcance'.
https://allwow.ru -
Bienvenidos a 'CriptoAlcance', su portal de confianza para sumergirse en el vibrante mundo de las criptomonedas. Aqui encontraras analisis detallados, noticias actualizadas, guias para principiantes y discusiones en profundidad sobre las tendencias mas recientes en Bitcoin, Ethereum, y otras monedas digitales. Nuestro equipo de expertos te brindara consejos practicos, estrategias de inversion y te mantendra al tanto de los cambios regulatorios y tecnologicos que afectan el mercado. Unete a nuestra comunidad y empieza tu viaje en el fascinante universo de las criptomonedas con 'CriptoAlcance'.
https://www.lifesshortlivefree.com/community/profile/glennwib/
http://www.zgbbs.org/space-uid-159475.html
http://www.1k9g.com/space-uid-192174.html
http://wuyuebanzou.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=461032
http://web.symbol.rs/forum/member.php?action=profile&uid=496034 -
rg777
-
Bienvenidos a 'CriptoAlcance', su portal de confianza para sumergirse en el vibrante mundo de las criptomonedas. Aqui encontraras analisis detallados, noticias actualizadas, guias para principiantes y discusiones en profundidad sobre las tendencias mas recientes en Bitcoin, Ethereum, y otras monedas digitales. Nuestro equipo de expertos te brindara consejos practicos, estrategias de inversion y te mantendra al tanto de los cambios regulatorios y tecnologicos que afectan el mercado. Unete a nuestra comunidad y empieza tu viaje en el fascinante universo de las criptomonedas con 'CriptoAlcance'.
https://speakerdeck.com/glenntat
http://xavierdeschamps.free.fr/Escalade/Forum_escalade/profile.php?id=738969
http://www.flicube.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=241660
http://www.seafishzone.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=1207789
https://www.98e.fun/space-uid-7102181.html -
Welcome to CryptoSphere, your go-to destination for all things cryptocurrency and blockchain. Our blog is dedicated to providing insightful, up-to-date information and analysis on the dynamic world of digital currencies. Whether you're a seasoned investor or just starting out, you'll find valuable content here, including in-depth guides on cryptocurrency trading, reviews of blockchain technologies, and the latest news in the crypto space.
At CryptoSphere, we believe in the transformative power of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Our mission is to demystify this complex world and make it accessible to everyone. We offer a range of articles, from beginner-friendly explanations of basic concepts to advanced analysis of market trends.
Join us as we explore the evolving landscape of digital finance, highlight innovative projects, and offer expert opinions on where the market is headed. With CryptoSphere, stay informed, make smarter investment decisions, and be part of the financial revolution. Let's dive into the world of cryptocurrencies together!
https://cryptoblog.pro/en/ -
線上賭場
**娛樂城與線上賭場:現代娛樂的轉型與未來**
在當今數位化的時代,"娛樂城"和"線上賭場"已成為現代娛樂和休閒生活的重要組成部分。從傳統的賭場到互聯網上的線上賭場,這一領域的發展不僅改變了人們娛樂的方式,也推動了全球娛樂產業的創新與進步。
**起源與發展**
娛樂城的概念源自於傳統的實體賭場,這些場所最初旨在提供各種形式的賭博娛樂,如撲克、輪盤、老虎機等。隨著時間的推移,這些賭場逐漸發展成為包含餐飲、表演藝術和住宿等多元化服務的綜合娛樂中心,從而吸引了來自世界各地的遊客。
隨著互聯網技術的飛速發展,線上賭場應運而生。這種新型態的賭博平台讓使用者可以在家中或任何有互聯網連接的地方,享受賭博遊戲的樂趣。線上賭場的出現不僅為賭博愛好者提供了更多便利與選擇,也大大擴展了賭博產業的市場範圍。
**特點與魅力**
娛樂城和線上賭場的主要魅力在於它們能提供多樣化的娛樂選項和高度的可訪問性。無論是實體的娛樂城還是虛擬的線上賭場,它們都致力於創造一個充滿樂趣和刺激的環境,讓人們可以從日常生活的壓力中短暫逃脫。
此外,線上賭場通過提供豐富的遊戲選擇、吸引人的獎金方案以及便捷的支付系統,成功地吸引了全球範圍內的用戶。這些平台通常具有高度的互動性和社交性,使玩家不僅能享受遊戲本身,還能與來自世界各地的其他玩家交流。
**未來趨勢**
隨著技術的不斷進步和用戶需求的不斷演變,娛樂城和線上賭場的未來發展呈現出多元化的趨勢。一方面,虛
擬現實(VR)和擴增現實(AR)技術的應用,有望為線上賭場帶來更加沉浸式和互動式的遊戲體驗。另一方面,對於實體娛樂城而言,將更多地注重提供綜合性的休閒體驗,結合賭博、娛樂、休閒和旅遊等多個方面,以滿足不同客群的需求。
此外,隨著對負責任賭博的認識加深,未來娛樂城和線上賭場在提供娛樂的同時,也將更加注重促進健康的賭博行為和保護用戶的安全。
總之,娛樂城和線上賭場作為現代娛樂生活的一部分,隨著社會的發展和技術的進步,將繼續演化和創新,為人們提供更多的樂趣和便利。這一領域的未來發展無疑充滿了無限的可能性和機遇。 -
Offer hospitality to to CryptoSphere, your go-to target through despite all things cryptocurrency and blockchain. Our blog is dedicated to providing insightful, up-to-date information and analysis on the zealous life of digital currencies. Whether you're a habituated investor or just starting elsewhere, you'll find valuable felicity here, including in-depth guides on cryptocurrency trading, reviews of blockchain technologies, and the latest despatch in the crypto space.
At CryptoSphere, we suppose in the transformative power of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Our deputation is to demystify this complex set and sanction it at hand to everyone. We submit a cook-stove of articles, from beginner-friendly explanations of fundamental concepts to advanced critique of sell trends.
Enrol in us as we enquire into the evolving view of digital money management, highlight innovative projects, and tender pro opinions on where the furnish is headed. With CryptoSphere, check informed, prevail upon smarter investment decisions, and be part of the financial revolution. Take in's dip into the creation of cryptocurrencies together!
https://piaoyiban.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=105235
https://98e.fun/space-uid-7105040.html
http://ipxa.ru/user/Jamesfen/
http://www.sglpw.cn/home.php?mod=space&uid=326824
http://bbs.qc0769.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=420818 -
線上賭場
**娛樂城與線上賭場:現代娛樂的轉型與未來**
在當今數位化的時代,"娛樂城"和"線上賭場"已成為現代娛樂和休閒生活的重要組成部分。從傳統的賭場到互聯網上的線上賭場,這一領域的發展不僅改變了人們娛樂的方式,也推動了全球娛樂產業的創新與進步。
**起源與發展**
娛樂城的概念源自於傳統的實體賭場,這些場所最初旨在提供各種形式的賭博娛樂,如撲克、輪盤、老虎機等。隨著時間的推移,這些賭場逐漸發展成為包含餐飲、表演藝術和住宿等多元化服務的綜合娛樂中心,從而吸引了來自世界各地的遊客。
隨著互聯網技術的飛速發展,線上賭場應運而生。這種新型態的賭博平台讓使用者可以在家中或任何有互聯網連接的地方,享受賭博遊戲的樂趣。線上賭場的出現不僅為賭博愛好者提供了更多便利與選擇,也大大擴展了賭博產業的市場範圍。
**特點與魅力**
娛樂城和線上賭場的主要魅力在於它們能提供多樣化的娛樂選項和高度的可訪問性。無論是實體的娛樂城還是虛擬的線上賭場,它們都致力於創造一個充滿樂趣和刺激的環境,讓人們可以從日常生活的壓力中短暫逃脫。
此外,線上賭場通過提供豐富的遊戲選擇、吸引人的獎金方案以及便捷的支付系統,成功地吸引了全球範圍內的用戶。這些平台通常具有高度的互動性和社交性,使玩家不僅能享受遊戲本身,還能與來自世界各地的其他玩家交流。
**未來趨勢**
隨著技術的不斷進步和用戶需求的不斷演變,娛樂城和線上賭場的未來發展呈現出多元化的趨勢。一方面,虛
擬現實(VR)和擴增現實(AR)技術的應用,有望為線上賭場帶來更加沉浸式和互動式的遊戲體驗。另一方面,對於實體娛樂城而言,將更多地注重提供綜合性的休閒體驗,結合賭博、娛樂、休閒和旅遊等多個方面,以滿足不同客群的需求。
此外,隨著對負責任賭博的認識加深,未來娛樂城和線上賭場在提供娛樂的同時,也將更加注重促進健康的賭博行為和保護用戶的安全。
總之,娛樂城和線上賭場作為現代娛樂生活的一部分,隨著社會的發展和技術的進步,將繼續演化和創新,為人們提供更多的樂趣和便利。這一領域的未來發展無疑充滿了無限的可能性和機遇。 -
Invited to CryptoSphere, your go-to target in compensation all things cryptocurrency and blockchain. Our blog is dedicated to providing insightful, up-to-date gen and analysis on the zealous humankind of digital currencies. Whether you're a habituated investor or upright starting out-dated, you'll find valuable theme here, including in-depth guides on cryptocurrency trading, reviews of blockchain technologies, and the latest despatch in the crypto space.
At CryptoSphere, we confidence in in the transformative power of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. Our profession is to demystify this complex age and make it available to everyone. We forth a range of articles, from beginner-friendly explanations of fundamental concepts to advanced opinion of market trends.
Associate with us as we explore the evolving vista of digital accounting, highlight innovative projects, and tender expert opinions on where the exchange is headed. With CryptoSphere, halt au fait, make smarter investment decisions, and be possess of the fiscal revolution. Disclose's dive into the creation of cryptocurrencies together!
http://www.28tongji.com/space-uid-1045420.html
https://forum.cabal.playthisgame.com/member.php?1598717-JamesAppor
http://www.iawbs.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=787883
http://i0110.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=519415
https://latino-forex.com/members/222948-jamesviach -
Заключение диплома важно Ð´Ð»Ñ Ð¿Ñ€Ð¾Ñ„ÐµÑÑиональной деÑтельноÑти на поÑÑ‚. Иногда ÑлучаютÑÑ Ñитуации, когда предыдущий документ неприменим Ð´Ð»Ñ Ð¾Ð±Ð»Ð°Ñти трудоуÑтройÑтва. Покупка образовательного документа в МоÑкве решит Ñту проблему и гарантирует блеÑÑ‚Ñщую перÑпективу - [URL=https://kupit-diplom1.com/]https://kupit-diplom1.com/[/URL]. СущеÑтвует множеÑтво причин, Ñтимулирующих закупку документа об образовании в МоÑкве. ПоÑле неÑкольких лет работы повдруг может понадобитьÑÑ Ð´Ð¸Ð¿Ð»Ð¾Ð¼ универÑитета. Работодатель имеет право менÑÑ‚ÑŒ Ñ‚Ñ€ÐµÐ±Ð¾Ð²Ð°Ð½Ð¸Ñ Ðº работникам и поÑтавить Ð²Ð°Ñ Ð¿ÐµÑ€ÐµÐ´ выбором – диплом или увольнение. Очное обучение требует больших затрат времени и Ñил, а диÑтанционное обучение — потребует ÑредÑтва Ð´Ð»Ñ Ð¿Ñ€Ð¾Ð²ÐµÐ´ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ Ñкзаменов. Ð’ подобных обÑтоÑтельÑтвах более разумно приобреÑти готовый документ. ЕÑли вы ознакомлены Ñ Ð¾ÑобенноÑÑ‚Ñми Ñвоей будущей Ñпециализации и уÑвоили необходимые навыки, нет необходимоÑти тратить годы на обучение в ВУЗе. ПлюÑÑ‹ заказа документа об образовании включают мгновенное изготовление, полное Ñовпадение Ñ Ð¾Ñ€Ð¸Ð³Ð¸Ð½Ð°Ð»Ð¾Ð¼, приемлемую ÑтоимоÑÑ‚ÑŒ, гарантированное трудоуÑтройÑтво, возможноÑÑ‚ÑŒ выбора оценок и удобную доÑтавку. Ðаша Ð¾Ñ€Ð³Ð°Ð½Ð¸Ð·Ð°Ñ†Ð¸Ñ Ð¿Ñ€ÐµÐ´Ð»Ð°Ð³Ð°ÐµÑ‚ возможноÑÑ‚ÑŒ каждому клиенту получить желаемую работу. Цена Ð¸Ð·Ð³Ð¾Ñ‚Ð¾Ð²Ð»ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ ÑвидетельÑтв доÑтупна, что делает Ñту покупку доÑтупной Ð´Ð»Ñ Ð²Ñех.
-
best ways to make money online
Understanding the processes and protocols within a Professional Tenure Committee (PTC) is crucial for faculty members. This Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) guide aims to address common queries related to PTC procedures, voting, and membership.
1. Why should members of the PTC fill out vote justification forms explaining their votes?
Vote justification forms provide transparency in decision-making. Members articulate their reasoning, fostering a culture of openness and ensuring that decisions are well-founded and understood by the academic community.
2. How can absentee ballots be cast?
To accommodate absentee voting, PTCs may implement secure electronic methods or designated proxy voters. This ensures that faculty members who cannot physically attend meetings can still contribute to decision-making processes.
3. How will additional members of PTCs be elected in departments with fewer than four tenured faculty members?
In smaller departments, creative solutions like rotating roles or involving faculty from related disciplines can be explored. Flexibility in election procedures ensures representation even in departments with fewer tenured faculty members.
4. Can a faculty member on OCSA or FML serve on a PTC?
Faculty members involved in other committees like the Organization of Committee on Student Affairs (OCSA) or Family and Medical Leave (FML) can serve on a PTC, but potential conflicts of interest should be carefully considered and managed.
5. Can an abstention vote be cast at a PTC meeting?
Yes, PTC members have the option to abstain from voting if they feel unable to take a stance on a particular matter. This allows for ethical decision-making and prevents uninformed voting.
6. What constitutes a positive or negative vote in PTCs?
A positive vote typically indicates approval or agreement, while a negative vote signifies disapproval or disagreement. Clear definitions and guidelines within each PTC help members interpret and cast their votes accurately.
7. What constitutes a quorum in a PTC?
A quorum, the minimum number of members required for a valid meeting, is essential for decision-making. Specific rules about quorum size are usually outlined in the PTC's governing documents.
Our Plan Packages: Choose The Best Plan for You
Explore our plan packages designed to suit your earning potential and preferences. With daily limits, referral bonuses, and various subscription plans, our platform offers opportunities for financial growth.
Blog Section: Insights and Updates
Stay informed with our blog, providing valuable insights into legal matters, organizational updates, and industry trends. Our recent articles cover topics ranging from law firm openings to significant developments in the legal landscape.
Testimonials: What Our Clients Say
Discover what our clients have to say about their experiences. Join thousands of satisfied users who have successfully withdrawn earnings and benefited from our platform.
Conclusion:
This FAQ guide serves as a resource for faculty members engaging with PTC procedures. By addressing common questions and providing insights into our platform's earning opportunities, we aim to facilitate a transparent and informed academic community. -
how to get free online money
Understanding the processes and protocols within a Professional Tenure Committee (PTC) is crucial for faculty members. This Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) guide aims to address common queries related to PTC procedures, voting, and membership.
1. Why should members of the PTC fill out vote justification forms explaining their votes?
Vote justification forms provide transparency in decision-making. Members articulate their reasoning, fostering a culture of openness and ensuring that decisions are well-founded and understood by the academic community.
2. How can absentee ballots be cast?
To accommodate absentee voting, PTCs may implement secure electronic methods or designated proxy voters. This ensures that faculty members who cannot physically attend meetings can still contribute to decision-making processes.
3. How will additional members of PTCs be elected in departments with fewer than four tenured faculty members?
In smaller departments, creative solutions like rotating roles or involving faculty from related disciplines can be explored. Flexibility in election procedures ensures representation even in departments with fewer tenured faculty members.
4. Can a faculty member on OCSA or FML serve on a PTC?
Faculty members involved in other committees like the Organization of Committee on Student Affairs (OCSA) or Family and Medical Leave (FML) can serve on a PTC, but potential conflicts of interest should be carefully considered and managed.
5. Can an abstention vote be cast at a PTC meeting?
Yes, PTC members have the option to abstain from voting if they feel unable to take a stance on a particular matter. This allows for ethical decision-making and prevents uninformed voting.
6. What constitutes a positive or negative vote in PTCs?
A positive vote typically indicates approval or agreement, while a negative vote signifies disapproval or disagreement. Clear definitions and guidelines within each PTC help members interpret and cast their votes accurately.
7. What constitutes a quorum in a PTC?
A quorum, the minimum number of members required for a valid meeting, is essential for decision-making. Specific rules about quorum size are usually outlined in the PTC's governing documents.
Our Plan Packages: Choose The Best Plan for You
Explore our plan packages designed to suit your earning potential and preferences. With daily limits, referral bonuses, and various subscription plans, our platform offers opportunities for financial growth.
Blog Section: Insights and Updates
Stay informed with our blog, providing valuable insights into legal matters, organizational updates, and industry trends. Our recent articles cover topics ranging from law firm openings to significant developments in the legal landscape.
Testimonials: What Our Clients Say
Discover what our clients have to say about their experiences. Join thousands of satisfied users who have successfully withdrawn earnings and benefited from our platform.
Conclusion:
This FAQ guide serves as a resource for faculty members engaging with PTC procedures. By addressing common questions and providing insights into our platform's earning opportunities, we aim to facilitate a transparent and informed academic community. -
В нашей компании[URL=https://diplomguru.com]https://diplomguru.com[/URL] вы можете приобрести настоящие дипломы на государственном бланке Гознак по очень низкой цене.
-
オンラインカジノ
日本にオンラインカジノおすすめランキング2024年最新版
2024おすすめのオンラインカジノ
オンラインカジノはパソコンでしか遊べないというのは、もう一昔前の話。現在はスマホやタブレットなどのモバイル端末からも、パソコンと変わらないクオリティでオンラインカジノを当たり前に楽しむことができるようになりました。
数あるモバイルカジノの中で、当サイトが厳選したトップ5カジノはこちら。
オンラインカジノおすすめ: コニベット(Konibet)
コニベットといえば、キャッシュバックや毎日もらえるリベートボーナスなど豪華ボーナスが満載!それに加えて低い出金条件も見どころです。さらにVIPレベルごとの還元率の高さも業界内で突出している点や、出金速度の速さなどトータルバランスの良さからもハイローラーの方にも好まれています。
カスタマーサポートは365日24時間稼働しているので、初心者の方にも安心してご利用いただけます。
さらに【業界初のオンラインポーカー】を導入!毎日トーナメントも開催されているので、早速参加しちゃいましょう!
RTP(還元率)公開や、入出金対応がスムーズで初心者向き
2000種類以上の豊富なゲーム数を誇り、スロットゲーム多数!
今なら$20の入金不要ボーナスと最大$650還元ボーナス!
8種類以上のライブカジノプロバイダー
業界初オンラインポーカーあり,日本利用者数No.1の安心のオンラインカジノメディア!
おすすめポイント
コニベットは、その豊富なボーナスと高還元率、そして安心のキャッシュバック制度で知られています。まず、新規登録者には入金不要の$20ボーナスが提供され、さらに初回入金時には最大$650の還元ボーナスが得られます。これらのキャンペーンはプレイヤーにとって大きな魅力となっています。
また、コニベットの特徴的な点は、VIP制度です。一度ロイヤルクラブになると、降格がなく、スロットリベートが1.5%という驚異の還元率を享受できます。これは他のオンラインカジノと比較しても非常に高い還元率です。さらに、常時週間損失キャッシュバックも行っているため、不運で負けてしまった場合でも取り返すチャンスがあります。これらの特徴から、コニベットはプレイヤーにとって非常に魅力的なオンラインカジノと言えるでしょう。
コニベット 無料会員登録をする
| コニベットのボーナス
コニベットは、新規登録者向けに20ドルの入金不要ボーナスを用意しています
コニベットカジノでは、限定で初回入金後に残高が1ドル未満になった場合、入金額の50%(最高500ドル)がキャッシュバックされる。キャッシュバック額に出金条件はないため、獲得後にすぐ出金することも可能です。
| コニベットの入金方法
入金方法 最低 / 最高入金
マスターカード 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $6,000
ジェイシービー 最低 : $20/ 最高 : $6,000
アメックス 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $6,000
アイウォレット 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
スティックペイ 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
ヴィーナスポイント 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $10,000
仮想通貨 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
銀行送金 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $10,000
| コニベット出金方法
出金方法 最低 |最高出金
アイウォレット 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
スティックぺイ 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
ヴィーナスポイント 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
仮想通貨 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
銀行送金 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし -
日本にオンラインカジノおすすめランキング2024年最新版
2024おすすめのオンラインカジノ
オンラインカジノはパソコンでしか遊べないというのは、もう一昔前の話。現在はスマホやタブレットなどのモバイル端末からも、パソコンと変わらないクオリティでオンラインカジノを当たり前に楽しむことができるようになりました。
数あるモバイルカジノの中で、当サイトが厳選したトップ5カジノはこちら。
オンラインカジノおすすめ: コニベット(Konibet)
コニベットといえば、キャッシュバックや毎日もらえるリベートボーナスなど豪華ボーナスが満載!それに加えて低い出金条件も見どころです。さらにVIPレベルごとの還元率の高さも業界内で突出している点や、出金速度の速さなどトータルバランスの良さからもハイローラーの方にも好まれています。
カスタマーサポートは365日24時間稼働しているので、初心者の方にも安心してご利用いただけます。
さらに【業界初のオンラインポーカー】を導入!毎日トーナメントも開催されているので、早速参加しちゃいましょう!
RTP(還元率)公開や、入出金対応がスムーズで初心者向き
2000種類以上の豊富なゲーム数を誇り、スロットゲーム多数!
今なら$20の入金不要ボーナスと最大$650還元ボーナス!
8種類以上のライブカジノプロバイダー
業界初オンラインポーカーあり,日本利用者数No.1の安心のオンラインカジノメディア!
おすすめポイント
コニベットは、その豊富なボーナスと高還元率、そして安心のキャッシュバック制度で知られています。まず、新規登録者には入金不要の$20ボーナスが提供され、さらに初回入金時には最大$650の還元ボーナスが得られます。これらのキャンペーンはプレイヤーにとって大きな魅力となっています。
また、コニベットの特徴的な点は、VIP制度です。一度ロイヤルクラブになると、降格がなく、スロットリベートが1.5%という驚異の還元率を享受できます。これは他のオンラインカジノと比較しても非常に高い還元率です。さらに、常時週間損失キャッシュバックも行っているため、不運で負けてしまった場合でも取り返すチャンスがあります。これらの特徴から、コニベットはプレイヤーにとって非常に魅力的なオンラインカジノと言えるでしょう。
コニベット 無料会員登録をする
| コニベットのボーナス
コニベットは、新規登録者向けに20ドルの入金不要ボーナスを用意しています
コニベットカジノでは、限定で初回入金後に残高が1ドル未満になった場合、入金額の50%(最高500ドル)がキャッシュバックされる。キャッシュバック額に出金条件はないため、獲得後にすぐ出金することも可能です。
| コニベットの入金方法
入金方法 最低 / 最高入金
マスターカード 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $6,000
ジェイシービー 最低 : $20/ 最高 : $6,000
アメックス 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $6,000
アイウォレット 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
スティックペイ 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
ヴィーナスポイント 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $10,000
仮想通貨 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
銀行送金 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $10,000
| コニベット出金方法
出金方法 最低 |最高出金
アイウォレット 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
スティックぺイ 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
ヴィーナスポイント 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
仮想通貨 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
銀行送金 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし -
日本にオンラインカジノおすすめランキング2024年最新版
2024おすすめのオンラインカジノ
オンラインカジノはパソコンでしか遊べないというのは、もう一昔前の話。現在はスマホやタブレットなどのモバイル端末からも、パソコンと変わらないクオリティでオンラインカジノを当たり前に楽しむことができるようになりました。
数あるモバイルカジノの中で、当サイトが厳選したトップ5カジノはこちら。
オンラインカジノおすすめ: コニベット(Konibet)
コニベットといえば、キャッシュバックや毎日もらえるリベートボーナスなど豪華ボーナスが満載!それに加えて低い出金条件も見どころです。さらにVIPレベルごとの還元率の高さも業界内で突出している点や、出金速度の速さなどトータルバランスの良さからもハイローラーの方にも好まれています。
カスタマーサポートは365日24時間稼働しているので、初心者の方にも安心してご利用いただけます。
さらに【業界初のオンラインポーカー】を導入!毎日トーナメントも開催されているので、早速参加しちゃいましょう!
RTP(還元率)公開や、入出金対応がスムーズで初心者向き
2000種類以上の豊富なゲーム数を誇り、スロットゲーム多数!
今なら$20の入金不要ボーナスと最大$650還元ボーナス!
8種類以上のライブカジノプロバイダー
業界初オンラインポーカーあり,日本利用者数No.1の安心のオンラインカジノメディア!
おすすめポイント
コニベットは、その豊富なボーナスと高還元率、そして安心のキャッシュバック制度で知られています。まず、新規登録者には入金不要の$20ボーナスが提供され、さらに初回入金時には最大$650の還元ボーナスが得られます。これらのキャンペーンはプレイヤーにとって大きな魅力となっています。
また、コニベットの特徴的な点は、VIP制度です。一度ロイヤルクラブになると、降格がなく、スロットリベートが1.5%という驚異の還元率を享受できます。これは他のオンラインカジノと比較しても非常に高い還元率です。さらに、常時週間損失キャッシュバックも行っているため、不運で負けてしまった場合でも取り返すチャンスがあります。これらの特徴から、コニベットはプレイヤーにとって非常に魅力的なオンラインカジノと言えるでしょう。
コニベット 無料会員登録をする
| コニベットのボーナス
コニベットは、新規登録者向けに20ドルの入金不要ボーナスを用意しています
コニベットカジノでは、限定で初回入金後に残高が1ドル未満になった場合、入金額の50%(最高500ドル)がキャッシュバックされる。キャッシュバック額に出金条件はないため、獲得後にすぐ出金することも可能です。
| コニベットの入金方法
入金方法 最低 / 最高入金
マスターカード 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $6,000
ジェイシービー 最低 : $20/ 最高 : $6,000
アメックス 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $6,000
アイウォレット 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
スティックペイ 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
ヴィーナスポイント 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $10,000
仮想通貨 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
銀行送金 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $10,000
| コニベット出金方法
出金方法 最低 |最高出金
アイウォレット 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
スティックぺイ 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
ヴィーナスポイント 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
仮想通貨 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
銀行送金 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし -
カジノ
日本にオンラインカジノおすすめランキング2024年最新版
2024おすすめのオンラインカジノ
オンラインカジノはパソコンでしか遊べないというのは、もう一昔前の話。現在はスマホやタブレットなどのモバイル端末からも、パソコンと変わらないクオリティでオンラインカジノを当たり前に楽しむことができるようになりました。
数あるモバイルカジノの中で、当サイトが厳選したトップ5カジノはこちら。
オンラインカジノおすすめ: コニベット(Konibet)
コニベットといえば、キャッシュバックや毎日もらえるリベートボーナスなど豪華ボーナスが満載!それに加えて低い出金条件も見どころです。さらにVIPレベルごとの還元率の高さも業界内で突出している点や、出金速度の速さなどトータルバランスの良さからもハイローラーの方にも好まれています。
カスタマーサポートは365日24時間稼働しているので、初心者の方にも安心してご利用いただけます。
さらに【業界初のオンラインポーカー】を導入!毎日トーナメントも開催されているので、早速参加しちゃいましょう!
RTP(還元率)公開や、入出金対応がスムーズで初心者向き
2000種類以上の豊富なゲーム数を誇り、スロットゲーム多数!
今なら$20の入金不要ボーナスと最大$650還元ボーナス!
8種類以上のライブカジノプロバイダー
業界初オンラインポーカーあり,日本利用者数No.1の安心のオンラインカジノメディア!
おすすめポイント
コニベットは、その豊富なボーナスと高還元率、そして安心のキャッシュバック制度で知られています。まず、新規登録者には入金不要の$20ボーナスが提供され、さらに初回入金時には最大$650の還元ボーナスが得られます。これらのキャンペーンはプレイヤーにとって大きな魅力となっています。
また、コニベットの特徴的な点は、VIP制度です。一度ロイヤルクラブになると、降格がなく、スロットリベートが1.5%という驚異の還元率を享受できます。これは他のオンラインカジノと比較しても非常に高い還元率です。さらに、常時週間損失キャッシュバックも行っているため、不運で負けてしまった場合でも取り返すチャンスがあります。これらの特徴から、コニベットはプレイヤーにとって非常に魅力的なオンラインカジノと言えるでしょう。
コニベット 無料会員登録をする
| コニベットのボーナス
コニベットは、新規登録者向けに20ドルの入金不要ボーナスを用意しています
コニベットカジノでは、限定で初回入金後に残高が1ドル未満になった場合、入金額の50%(最高500ドル)がキャッシュバックされる。キャッシュバック額に出金条件はないため、獲得後にすぐ出金することも可能です。
| コニベットの入金方法
入金方法 最低 / 最高入金
マスターカード 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $6,000
ジェイシービー 最低 : $20/ 最高 : $6,000
アメックス 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $6,000
アイウォレット 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
スティックペイ 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
ヴィーナスポイント 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $10,000
仮想通貨 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $100,000
銀行送金 最低 : $20 / 最高 : $10,000
| コニベット出金方法
出金方法 最低 |最高出金
アイウォレット 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
スティックぺイ 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
ヴィーナスポイント 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
仮想通貨 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし
銀行送金 最低 : $40 / 最高 : なし -
Watches World
In the realm of luxury watches, locating a trustworthy source is paramount, and WatchesWorld stands out as a symbol of trust and knowledge. Presenting an broad collection of prestigious timepieces, WatchesWorld has garnered praise from satisfied customers worldwide. Let's explore into what our customers are saying about their encounters.
Customer Testimonials:
O.M.'s Review on O.M.:
"Excellent communication and aftercare throughout the procedure. The watch was flawlessly packed and in perfect condition. I would certainly work with this group again for a watch purchase."
Richard Houtman's Review on Benny:
"I dealt with Benny, who was highly supportive and courteous at all times, keeping me regularly informed of the procedure. Moving forward, even though I ended up sourcing the watch locally, I would still definitely recommend Benny and the company."
Customer's Efficient Service Experience:
"A highly efficient and swift service. Kept me up to date on the order progress."
Featured Timepieces:
Richard Mille RM30-01 Automatic Winding with Declutchable Rotor:
Price: €285,000
Year: 2023
Reference: RM30-01 TI
Patek Philippe Complications World Time 38.5mm:
Price: €39,900
Year: 2019
Reference: 5230R-001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Day-Date 36mm:
Price: €76,900
Year: 2024
Reference: 128238-0071
Best Sellers:
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm:
Price: On Request
Reference: 101816 SP35C6SDS.1T
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm (2024):
Price: €12,700
Reference: 102237 SP35C6SPGD.1T
Cartier Panthere Medium Model:
Price: €8,390
Year: 2023
Reference: W2PN0007
Our Experts Selection:
Cartier Panthere Small Model:
Price: €11,500
Year: 2024
Reference: W3PN0006
Omega Speedmaster Moonwatch 44.25 mm:
Price: €9,190
Year: 2024
Reference: 304.30.44.52.01.001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Cosmograph Daytona 40mm:
Price: €28,500
Year: 2023
Reference: 116500LN-0002
Rolex Oyster Perpetual 36mm:
Price: €13,600
Year: 2023
Reference: 126000-0006
Why WatchesWorld:
WatchesWorld is not just an internet platform; it's a commitment to customized service in the realm of luxury watches. Our team of watch experts prioritizes confidence, ensuring that every customer makes an well-informed decision.
Our Commitment:
Expertise: Our team brings matchless knowledge and insight into the realm of high-end timepieces.
Trust: Trust is the foundation of our service, and we prioritize transparency in every transaction.
Satisfaction: Client satisfaction is our ultimate goal, and we go the additional step to ensure it.
When you choose WatchesWorld, you're not just purchasing a watch; you're committing in a smooth and reliable experience. Explore our range, and let us assist you in discovering the perfect timepiece that mirrors your taste and sophistication. At WatchesWorld, your satisfaction is our time-tested commitment -
In the realm of high-end watches, locating a reliable source is crucial, and WatchesWorld stands out as a beacon of trust and knowledge. Providing an extensive collection of esteemed timepieces, WatchesWorld has garnered acclaim from content customers worldwide. Let's explore into what our customers are saying about their encounters.
Customer Testimonials:
O.M.'s Review on O.M.:
"Very good communication and aftercare throughout the procedure. The watch was impeccably packed and in perfect condition. I would certainly work with this team again for a watch purchase."
Richard Houtman's Review on Benny:
"I dealt with Benny, who was highly helpful and courteous at all times, preserving me regularly informed of the procedure. Moving forward, even though I ended up sourcing the watch locally, I would still definitely recommend Benny and the company."
Customer's Efficient Service Experience:
"A excellent and efficient service. Kept me up to date on the order progress."
Featured Timepieces:
Richard Mille RM30-01 Automatic Winding with Declutchable Rotor:
Price: €285,000
Year: 2023
Reference: RM30-01 TI
Patek Philippe Complications World Time 38.5mm:
Price: €39,900
Year: 2019
Reference: 5230R-001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Day-Date 36mm:
Price: €76,900
Year: 2024
Reference: 128238-0071
Best Sellers:
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm:
Price: On Request
Reference: 101816 SP35C6SDS.1T
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm (2024):
Price: €12,700
Reference: 102237 SP35C6SPGD.1T
Cartier Panthere Medium Model:
Price: €8,390
Year: 2023
Reference: W2PN0007
Our Experts Selection:
Cartier Panthere Small Model:
Price: €11,500
Year: 2024
Reference: W3PN0006
Omega Speedmaster Moonwatch 44.25 mm:
Price: €9,190
Year: 2024
Reference: 304.30.44.52.01.001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Cosmograph Daytona 40mm:
Price: €28,500
Year: 2023
Reference: 116500LN-0002
Rolex Oyster Perpetual 36mm:
Price: €13,600
Year: 2023
Reference: 126000-0006
Why WatchesWorld:
WatchesWorld is not just an online platform; it's a commitment to customized service in the world of luxury watches. Our staff of watch experts prioritizes confidence, ensuring that every client makes an informed decision.
Our Commitment:
Expertise: Our group brings unparalleled knowledge and perspective into the realm of high-end timepieces.
Trust: Trust is the basis of our service, and we prioritize openness in every transaction.
Satisfaction: Client satisfaction is our paramount goal, and we go the additional step to ensure it.
When you choose WatchesWorld, you're not just purchasing a watch; you're investing in a effortless and reliable experience. Explore our collection, and let us assist you in finding the perfect timepiece that embodies your style and sophistication. At WatchesWorld, your satisfaction is our proven commitment -
Watches World
In the world of premium watches, locating a dependable source is paramount, and WatchesWorld stands out as a beacon of confidence and knowledge. Presenting an broad collection of renowned timepieces, WatchesWorld has garnered praise from content customers worldwide. Let's delve into what our customers are saying about their experiences.
Customer Testimonials:
O.M.'s Review on O.M.:
"Excellent communication and follow-up throughout the procedure. The watch was perfectly packed and in perfect condition. I would certainly work with this team again for a watch purchase."
Richard Houtman's Review on Benny:
"I dealt with Benny, who was exceptionally assisting and courteous at all times, keeping me regularly informed of the procedure. Moving forward, even though I ended up acquiring the watch locally, I would still definitely recommend Benny and the company."
Customer's Efficient Service Experience:
"A very good and efficient service. Kept me up to date on the order progress."
Featured Timepieces:
Richard Mille RM30-01 Automatic Winding with Declutchable Rotor:
Price: €285,000
Year: 2023
Reference: RM30-01 TI
Patek Philippe Complications World Time 38.5mm:
Price: €39,900
Year: 2019
Reference: 5230R-001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Day-Date 36mm:
Price: €76,900
Year: 2024
Reference: 128238-0071
Best Sellers:
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm:
Price: On Request
Reference: 101816 SP35C6SDS.1T
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm (2024):
Price: €12,700
Reference: 102237 SP35C6SPGD.1T
Cartier Panthere Medium Model:
Price: €8,390
Year: 2023
Reference: W2PN0007
Our Experts Selection:
Cartier Panthere Small Model:
Price: €11,500
Year: 2024
Reference: W3PN0006
Omega Speedmaster Moonwatch 44.25 mm:
Price: €9,190
Year: 2024
Reference: 304.30.44.52.01.001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Cosmograph Daytona 40mm:
Price: €28,500
Year: 2023
Reference: 116500LN-0002
Rolex Oyster Perpetual 36mm:
Price: €13,600
Year: 2023
Reference: 126000-0006
Why WatchesWorld:
WatchesWorld is not just an online platform; it's a promise to individualized service in the realm of high-end watches. Our group of watch experts prioritizes confidence, ensuring that every client makes an knowledgeable decision.
Our Commitment:
Expertise: Our team brings exceptional knowledge and perspective into the realm of high-end timepieces.
Trust: Confidence is the foundation of our service, and we prioritize openness in every transaction.
Satisfaction: Client satisfaction is our ultimate goal, and we go the extra mile to ensure it.
When you choose WatchesWorld, you're not just purchasing a watch; you're committing in a smooth and trustworthy experience. Explore our range, and let us assist you in discovering the perfect timepiece that embodies your style and elegance. At WatchesWorld, your satisfaction is our time-tested commitment -
http://lgd-tp.pl/walk/spotkanie-informacyjne-gora-kalwaria/comment-page-1/?unapproved=589049&moderation-hash=43b0fc916d7ca625562368dedf257997#comment-589049
http://pornite.org/comment-page-14202/#comment-1485407
http://korolevichelisey.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?f=10&t=12698&p=73908#p73908
http://gastronomiskt.se/blog/2019/11/27/hello-world/?unapproved=381423&moderation-hash=2fe6c13f0e7b2c1231464adc28a5e04b#comment-381423
http://gastronomiskt.se/blog/2019/11/27/hello-world/?unapproved=381394&moderation-hash=9ad0ec7ea1b1b812849043d1cf4d9f70#comment-381394 -
Watches World
In the world of premium watches, discovering a reliable source is paramount, and WatchesWorld stands out as a beacon of confidence and expertise. Offering an broad collection of prestigious timepieces, WatchesWorld has collected praise from content customers worldwide. Let's explore into what our customers are saying about their encounters.
Customer Testimonials:
O.M.'s Review on O.M.:
"Outstanding communication and follow-up throughout the procedure. The watch was perfectly packed and in pristine condition. I would certainly work with this team again for a watch purchase."
Richard Houtman's Review on Benny:
"I dealt with Benny, who was extremely supportive and courteous at all times, preserving me regularly informed of the procedure. Moving forward, even though I ended up sourcing the watch locally, I would still definitely recommend Benny and the company."
Customer's Efficient Service Experience:
"A excellent and efficient service. Kept me up to date on the order progress."
Featured Timepieces:
Richard Mille RM30-01 Automatic Winding with Declutchable Rotor:
Price: €285,000
Year: 2023
Reference: RM30-01 TI
Patek Philippe Complications World Time 38.5mm:
Price: €39,900
Year: 2019
Reference: 5230R-001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Day-Date 36mm:
Price: €76,900
Year: 2024
Reference: 128238-0071
Best Sellers:
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm:
Price: On Request
Reference: 101816 SP35C6SDS.1T
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm (2024):
Price: €12,700
Reference: 102237 SP35C6SPGD.1T
Cartier Panthere Medium Model:
Price: €8,390
Year: 2023
Reference: W2PN0007
Our Experts Selection:
Cartier Panthere Small Model:
Price: €11,500
Year: 2024
Reference: W3PN0006
Omega Speedmaster Moonwatch 44.25 mm:
Price: €9,190
Year: 2024
Reference: 304.30.44.52.01.001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Cosmograph Daytona 40mm:
Price: €28,500
Year: 2023
Reference: 116500LN-0002
Rolex Oyster Perpetual 36mm:
Price: €13,600
Year: 2023
Reference: 126000-0006
Why WatchesWorld:
WatchesWorld is not just an web-based platform; it's a commitment to customized service in the realm of high-end watches. Our team of watch experts prioritizes trust, ensuring that every customer makes an informed decision.
Our Commitment:
Expertise: Our group brings exceptional knowledge and insight into the realm of luxury timepieces.
Trust: Trust is the basis of our service, and we prioritize openness in every transaction.
Satisfaction: Client satisfaction is our ultimate goal, and we go the additional step to ensure it.
When you choose WatchesWorld, you're not just purchasing a watch; you're investing in a effortless and reliable experience. Explore our collection, and let us assist you in discovering the perfect timepiece that embodies your taste and elegance. At WatchesWorld, your satisfaction is our proven commitment -
In the world of high-end watches, discovering a trustworthy source is paramount, and WatchesWorld stands out as a beacon of trust and expertise. Providing an wide collection of prestigious timepieces, WatchesWorld has garnered praise from content customers worldwide. Let's delve into what our customers are saying about their experiences.
Customer Testimonials:
O.M.'s Review on O.M.:
"Very good communication and follow-up throughout the procedure. The watch was perfectly packed and in perfect condition. I would certainly work with this team again for a watch purchase."
Richard Houtman's Review on Benny:
"I dealt with Benny, who was extremely helpful and courteous at all times, preserving me regularly informed of the process. Moving forward, even though I ended up acquiring the watch locally, I would still definitely recommend Benny and the company."
Customer's Efficient Service Experience:
"A very good and prompt service. Kept me up to date on the order progress."
Featured Timepieces:
Richard Mille RM30-01 Automatic Winding with Declutchable Rotor:
Price: €285,000
Year: 2023
Reference: RM30-01 TI
Patek Philippe Complications World Time 38.5mm:
Price: €39,900
Year: 2019
Reference: 5230R-001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Day-Date 36mm:
Price: €76,900
Year: 2024
Reference: 128238-0071
Best Sellers:
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm:
Price: On Request
Reference: 101816 SP35C6SDS.1T
Bulgari Serpenti Tubogas 35mm (2024):
Price: €12,700
Reference: 102237 SP35C6SPGD.1T
Cartier Panthere Medium Model:
Price: €8,390
Year: 2023
Reference: W2PN0007
Our Experts Selection:
Cartier Panthere Small Model:
Price: €11,500
Year: 2024
Reference: W3PN0006
Omega Speedmaster Moonwatch 44.25 mm:
Price: €9,190
Year: 2024
Reference: 304.30.44.52.01.001
Rolex Oyster Perpetual Cosmograph Daytona 40mm:
Price: €28,500
Year: 2023
Reference: 116500LN-0002
Rolex Oyster Perpetual 36mm:
Price: €13,600
Year: 2023
Reference: 126000-0006
Why WatchesWorld:
WatchesWorld is not just an internet platform; it's a promise to customized service in the realm of luxury watches. Our team of watch experts prioritizes confidence, ensuring that every client makes an well-informed decision.
Our Commitment:
Expertise: Our team brings unparalleled understanding and perspective into the world of luxury timepieces.
Trust: Trust is the foundation of our service, and we prioritize openness in every transaction.
Satisfaction: Client satisfaction is our ultimate goal, and we go the additional step to ensure it.
When you choose WatchesWorld, you're not just purchasing a watch; you're committing in a effortless and reliable experience. Explore our range, and let us assist you in finding the perfect timepiece that embodies your taste and elegance. At WatchesWorld, your satisfaction is our time-tested commitment -
https://xn-----7kccgclceaf3d0apdeeefre0dt2w.xn--p1ai/
-
Даркнет – неведомая зона всемирной паутины, избегающая взоров обыденных поисковых систем и требующая эксклюзивных средств для доступа. Этот скрытый ресурс сети обильно насыщен платформами, предоставляя доступ к разнообразным товарам и услугам через свои каталоги и справочники. Давайте подробнее рассмотрим, что представляют собой эти списки и какие тайны они сокрывают.
Даркнет Списки: Окна в Скрытый Мир
Каталоги ресурсов в даркнете – это своего рода врата в неощутимый мир интернета. Перечни и указатели веб-ресурсов в даркнете, они позволяют пользователям отыскивать разнообразные услуги, товары и информацию. Варьируя от форумов и магазинов до ресурсов, уделяющих внимание аспектам анонимности и криптовалютам, эти перечни предоставляют нам шанс заглянуть в таинственный мир даркнета.
Категории и Возможности
Теневой Рынок:
Даркнет часто ассоциируется с незаконными сделками, где доступны самые разные товары и услуги – от наркотиков и оружия до краденых данных и услуг наемных убийц. Списки ресурсов в этой категории облегчают пользователям находить подходящие предложения без лишних усилий.
Форумы и Сообщества:
Даркнет также предоставляет площадку для анонимного общения. Форумы и сообщества, представленные в реестрах даркнета, охватывают различные темы – от информационной безопасности и взлома до политических аспектов и философских концепций.
Информационные Ресурсы:
На даркнете есть ресурсы, предоставляющие данные и указания по обходу цензуры, защите конфиденциальности и другим вопросам, которые могут заинтересовать тех, кто стремится сохранить свою анонимность.
Безопасность и Осторожность
Несмотря на неизвестность и свободу, даркнет не лишен рисков. Мошенничество, кибератаки и незаконные сделки становятся частью этого мира. Взаимодействуя с списками ресурсов в темной сети, пользователи должны соблюдать максимальную осторожность и придерживаться мер безопасности.
Заключение
Даркнет списки – это ключ к таинственному миру, где сокрыты тайны и возможности. Однако, как и в любой неизведанной территории, путешествие в даркнет требует особой осторожности и знания. Анонимность не всегда гарантирует безопасность, и использование темной сети требует осознанного подхода. Независимо от ваших интересов – будь то технические детали в области кибербезопасности, поиск необычных товаров или исследование новых возможностей в интернете – даркнет списки предоставляют ключ -
список сайтов даркнет
Темная сторона интернета – неведомая зона всемирной паутины, избегающая взоров обыденных поисковых систем и требующая специальных средств для доступа. Этот скрытый ресурс сети обильно насыщен сайтами, предоставляя доступ к разношерстным товарам и услугам через свои перечни и каталоги. Давайте ближе рассмотрим, что представляют собой эти списки и какие тайны они сокрывают.
Даркнет Списки: Ворота в Скрытый Мир
Каталоги ресурсов в даркнете – это вид врата в неощутимый мир интернета. Реестры и справочники веб-ресурсов в даркнете, они позволяют пользователям отыскивать разнообразные услуги, товары и информацию. Варьируя от форумов и магазинов до ресурсов, уделяющих внимание аспектам анонимности и криптовалютам, эти списки предоставляют нам шанс заглянуть в непознанный мир даркнета.
Категории и Возможности
Теневой Рынок:
Даркнет часто связывается с подпольной торговлей, где доступны разнообразные товары и услуги – от наркотиков и оружия до краденых данных и услуг наемных убийц. Реестры ресурсов в этой категории облегчают пользователям находить подходящие предложения без лишних усилий.
Форумы и Сообщества:
Даркнет также предоставляет площадку для анонимного общения. Форумы и сообщества, перечисленные в даркнет списках, охватывают различные темы – от информационной безопасности и взлома до политических аспектов и философских концепций.
Информационные Ресурсы:
На даркнете есть ресурсы, предоставляющие данные и указания по обходу ограничений, защите конфиденциальности и другим вопросам, которые могут заинтересовать тех, кто стремится сохранить свою анонимность.
Безопасность и Осторожность
Несмотря на анонимность и свободу, даркнет не лишен опасностей. Мошенничество, кибератаки и незаконные сделки становятся частью этого мира. Взаимодействуя с реестрами даркнета, пользователи должны соблюдать максимальную осторожность и придерживаться мер безопасности.
Заключение
Реестры даркнета – это ключ к таинственному миру, где хранятся тайны и возможности. Однако, как и в любой неизведанной территории, путешествие в даркнет требует особой внимания и знаний. Не всегда анонимность приносит безопасность, и использование даркнета требует осознанного подхода. Независимо от ваших интересов – будь то технические аспекты кибербезопасности, поиск уникальных товаров или исследование новых граней интернета – списки даркнета предоставляют ключ -
даркнет вход
Темная сторона интернета – таинственная сфера интернета, избегающая взоров обычных поисковых систем и требующая эксклюзивных средств для доступа. Этот несканируемый ресурс сети обильно насыщен сайтами, предоставляя доступ к разношерстным товарам и услугам через свои перечни и справочники. Давайте подробнее рассмотрим, что представляют собой эти списки и какие тайны они хранят.
Даркнет Списки: Ворота в Неизведанный Мир
Даркнет списки – это своего рода врата в неощутимый мир интернета. Перечни и указатели веб-ресурсов в даркнете, они позволяют пользователям отыскивать различные услуги, товары и информацию. Варьируя от форумов и магазинов до ресурсов, уделяющих внимание аспектам анонимности и криптовалютам, эти списки предоставляют нам шанс заглянуть в таинственный мир даркнета.
Категории и Возможности
Теневой Рынок:
Даркнет часто ассоциируется с подпольной торговлей, где доступны разнообразные товары и услуги – от психоактивных веществ и стрелкового оружия до краденых данных и услуг наемных убийц. Списки ресурсов в подобной категории облегчают пользователям находить подходящие предложения без лишних усилий.
Форумы и Сообщества:
Даркнет также служит для анонимного общения. Форумы и сообщества, перечисленные в даркнет списках, затрагивают различные темы – от кибербезопасности и хакерства до политических вопросов и философских идей.
Информационные Ресурсы:
На даркнете есть ресурсы, предоставляющие сведения и руководства по преодолению цензуры, обеспечению конфиденциальности и другим темам, которые могут быть интересны тем, кто хочет остаться анонимным.
Безопасность и Осторожность
Несмотря на неизвестность и свободу, даркнет полон рисков. Мошенничество, кибератаки и незаконные сделки становятся частью этого мира. Взаимодействуя с списками ресурсов в темной сети, пользователи должны соблюдать высший уровень бдительности и придерживаться мер безопасности.
Заключение
Даркнет списки – это ключ к таинственному миру, где хранятся тайны и возможности. Однако, как и в любой неизведанной территории, путешествие в даркнет требует особой внимания и знаний. Не всегда анонимность приносит безопасность, и использование темной сети требует осмысленного подхода. Независимо от ваших интересов – будь то технические детали в области кибербезопасности, поиск необычных товаров или исследование новых возможностей в интернете – списки даркнета предоставляют ключ -
https://xn-----7kccgclceaf3d0apdeeefre0dt2w.xn--p1ai/
-
https://ukrmedgarant.com.ua/g90462910-apparaty-smas-liftinga
https://ukrmedgarant.com.ua/g90462918-apparaty-krioterapii
https://ukrmedgarant.com.ua/g90465658-apparaty-elektroporatsii
https://ukrmedgarant.com.ua/g90465670-apparat-almaznoj-mikrodermabrazii
https://ukrmedgarant.com.ua/p1248830681-adonyss-diopulse-808.html -
[URL=https://prema-diploms-srednee.com/][URL=https://prema-diploms-srednee.com/]Купить диплом об окончании техникума[/URL] - - это шанс оперативно завершить документ об учебе на бакалавр уровне без излишних хлопот и затраты времени. В городе Москве предоставляется разные опций подлинных свидетельств бакалавров, гарантирующих комфорт и простоту в процессе.
-
[URL=https://gruppa-diploms-srednee.com/][URL=https://gruppa-diploms-srednee.com/]Купить старый диплом техникума[/URL] - это вариант быстро получить бумагу об учебе на бакалавр уровне без излишних хлопот и затраты времени. В столице России доступны множество вариантов настоящих дипломов бакалавров, предоставляющих комфорт и удобство в получении..
-
купить паспорт интернет магазин
Покупка паспорта в интернет-магазине – это незаконное и опасное поступок, которое может послужить причиной к значительным последствиям для граждан. Вот некоторые сторон, о которые необходимо запомнить:
Незаконность: Приобретение паспорта в онлайн магазине представляет собой преступлением закона. Имение фальшивым удостоверением способно повлечь за собой криминальную ответственность и тяжелые штрафы.
Опасности личной безопасности: Факт применения фальшивого паспорта может подвергнуть угрозу личную безопасность. Люди, использующие поддельными удостоверениями, способны стать целью провокаций со со стороны законопослушных структур.
Финансовые убытки: Часто обманщики, продающие поддельными паспортами, способны применять вашу информацию для мошенничества, что приведёт к денежным убыткам. Ваши и финансовые данные могут быть использованы в преступных целях.
Трудности при путешествиях: Поддельный удостоверение личности может стать распознан при попытке перейти границу или при взаимодействии с официальными инстанциями. Такое обстоятельство может привести к аресту, изгнанию или другим тяжелым проблемам при перемещении.
Утрата доверительности и репутации: Применение фальшивого паспорта может привести к потере доверия со стороны окружающих и нанимателей. Это ситуация способна негативно влиять на вашу престиж и карьерные возможности.
Вместо того, чем бы рисковать собственной свободой, безопасностью и репутацией, советуется придерживаться закон и воспользоваться официальными путями для оформления документов. Они предоставляют защиту всех ваших прав и гарантируют безопасность ваших данных. Нелегальные действия могут повлечь за собой неожиданные и негативные ситуации, создавая тяжелые трудности для вас и вашего окружения -
Теневой интернет 2024: Скрытые перспективы цифровой среды
С инициации даркнет представлял собой закуток веба, где тайна и неявность были обыденностью. В 2024 году этот скрытый мир продвигается вперед, предоставляя дополнительные требования и опасности для интернет-сообщества. Рассмотрим, какие тенденции и модификации ожидают обществу в теневом интернете 2024.
Продвижение технологий и Повышение анонимности
С развитием технологий, инструменты для обеспечения скрытности в даркнете становятся более сложными и эффективными. Использование цифровых валют, современных шифровальных методов и децентрализованных сетей делает слежение за деятельностью пользователей более трудным для правоохранительных органов.
Развитие специализированных рынков
Даркнет-рынки, фокусирующиеся на разнообразных продуктах и сервисах, продвигаются вперед развиваться. Наркотики, военные припасы, средства для хакерских атак, персональная информация - спектр товаров бывает все многообразным. Это порождает вызов для силовых структур, который сталкивается с задачей приспосабливаться к постоянно меняющимся сценариям нелегальных действий.
Опасности цифровой безопасности для непрофессионалов
Сервисы проката хакеров и обманные планы продолжают существовать активными в даркнете. Люди, не связанные с преступностью попадают в руки целью для преступников в сети, стремящихся зайти к личным данным, банковским счетам и иных секретных данных.
Перспективы виртуальной реальности в даркнете
С прогрессом техники виртуальной реальности, теневой интернет может перейти в совершенно новую фазу, предоставляя участникам реальные и захватывающие цифровые области. Это может включать в себя дополнительными видами нелегальных действий, такими как цифровые рынки для передачи цифровыми товарами.
Борьба структурам защиты
Органы обеспечения безопасности улучшают свои технологии и методы противостояния даркнетом. Коллективные меры государств и мировых объединений ориентированы на предотвращение киберпреступности и прекращение современным проблемам, связанным с развитием темного интернета.
Вывод
Теневой интернет в 2024 году продолжает оставаться комплексной и разносторонней средой, где технические инновации продвигаются вносить изменения в пейзаж преступной деятельности. Важно для участников продолжать быть настороженными, обеспечивать свою защиту в интернете и соблюдать нормы, даже в виртуальном пространстве. Вместе с тем, противостояние с даркнетом требует коллективных действиях от стран, технологических компаний и граждан, для обеспечения безопасность в цифровом мире. -
Скрытая сеть 2024: Скрытые взгляды виртуального мира
С начала теневого интернета представлял собой сферу интернета, где тайна и неявность были нормой. В 2024 году этот скрытый мир продвигается вперед, предоставляя свежие задачи и опасности для сообщества в сети. Рассмотрим, какими тенденции и изменения предстоят нас в теневом интернете 2024.
Продвижение технологий и Повышение анонимности
С прогрессом техники, средства обеспечения скрытности в даркнете становятся сложнее и действенными. Использование криптовалют, современных шифровальных методов и сетей с децентрализованной структурой делает слежение за поведением участников более трудным для правоохранительных органов.
Рост тематических рынков
Темные рынки, специализирующиеся на разнообразных продуктах и сервисах, продвигаются вперед развиваться. Наркотики, оружие, хакерские инструменты, краденые данные - ассортимент продукции бывает все более разнообразным. Это создает вызов для правопорядка, стоящего перед необходимостью адаптироваться к изменяющимся обстоятельствам преступной деятельности.
Опасности цифровой безопасности для обычных пользователей
Сервисы аренды хакерских услуг и мошеннические схемы продолжают существовать активными в даркнете. Обычные пользователи попадают в руки целью для преступников в сети, желающих зайти к личным данным, банковским счетам и иных секретных данных.
Перспективы виртуальной реальности в теневом интернете
С прогрессом техники виртуальной реальности, даркнет может перейти в совершенно новую фазу, предоставляя участникам более реалистичные и захватывающие виртуальные пространства. Это может включать в себя дополнительными видами преступной деятельности, такими как цифровые рынки для обмена цифровыми товарами.
Противостояние структурам безопасности
Органы обеспечения безопасности совершенствуют свои технические средства и методы противостояния теневым интернетом. Коллективные меры государств и мировых объединений ориентированы на профилактику цифровой преступности и прекращение новым вызовам, связанным с ростом темного интернета.
Вывод
Даркнет 2024 остается сложной и разносторонней обстановкой, где технологии продолжают вносить изменения в пейзаж преступной деятельности. Важно для участников оставаться бдительными, обеспечивать свою защиту в интернете и следовать законы, даже в виртуальном пространстве. Вместе с тем, борьба с даркнетом нуждается в коллективных действиях от государств, технологических компаний и граждан, чтобы обеспечить защиту в сетевой среде. -
Взлом телеграм
Взлом Телеграм: Легенды и Фактичность
Телеграм - это известный мессенджер, отмеченный своей высокой степенью шифрования и безопасности данных пользователей. Однако, в современном цифровом мире тема взлома Телеграм периодически поднимается. Давайте рассмотрим, что на самом деле стоит за этим понятием и почему взлом Телеграм чаще является мифом, чем реальностью.
Кодирование в Telegram: Основные принципы Защиты
Telegram известен своим превосходным уровнем кодирования. Для обеспечения приватности переписки между пользователями используется протокол MTProto. Этот протокол обеспечивает конечно-конечное кодирование, что означает, что только передающая сторона и получатель могут читать сообщения.
Мифы о Нарушении Telegram: По какой причине они появляются?
В последнее время в сети часто появляются слухи о взломе Telegram и доступе к персональной информации пользователей. Однако, основная часть этих утверждений оказываются мифами, часто развивающимися из-за непонимания принципов работы мессенджера.
Кибернападения и Уязвимости: Реальные Угрозы
Хотя взлом Телеграма в большинстве случаев является трудной задачей, существуют реальные угрозы, с которыми сталкиваются пользователи. Например, атаки на индивидуальные аккаунты, вредоносные программы и прочие методы, которые, тем не менее, нуждаются в активном участии пользователя в их распространении.
Защита Личной Информации: Рекомендации для Участников
Несмотря на непоявление точной угрозы нарушения Telegram, важно соблюдать базовые меры кибербезопасности. Регулярно обновляйте приложение, используйте двухэтапную проверку, избегайте сомнительных ссылок и мошеннических атак.
Заключение: Фактическая Опасность или Паника?
Нарушение Телеграма, как обычно, оказывается мифом, созданным вокруг темы разговора без конкретных доказательств. Однако защита всегда остается важной задачей, и участники мессенджера должны быть бдительными и следовать рекомендациям по сохранению защиты своей персональных данных -
Взлом ватцап
Взлом WhatsApp: Фактичность и Легенды
WhatsApp - один из известных мессенджеров в мире, массово используемый для передачи сообщениями и файлами. Он известен своей кодированной системой обмена данными и обеспечением конфиденциальности пользователей. Однако в сети время от времени появляются утверждения о возможности взлома Вотсап. Давайте разберемся, насколько эти утверждения соответствуют фактичности и почему тема нарушения Вотсап вызывает столько дискуссий.
Шифрование в Вотсап: Защита Личной Информации
WhatsApp применяет end-to-end кодирование, что означает, что только отправитель и получающая сторона могут читать сообщения. Это стало фундаментом для доверия многих пользователей мессенджера к сохранению их личной информации.
Легенды о Взломе Вотсап: По какой причине Они Появляются?
Сеть периодически наполняют слухи о нарушении Вотсап и возможном входе к переписке. Многие из этих утверждений порой не имеют обоснований и могут быть результатом паники или дезинформации.
Реальные Угрозы: Кибератаки и Охрана
Хотя нарушение WhatsApp является сложной задачей, существуют актуальные угрозы, такие как кибератаки на индивидуальные аккаунты, фишинг и вредоносные программы. Исполнение мер безопасности важно для минимизации этих рисков.
Охрана Личной Информации: Советы Пользователям
Для укрепления охраны своего аккаунта в WhatsApp пользователи могут использовать двухфакторную аутентификацию, регулярно обновлять приложение, избегать подозрительных ссылок и следить за конфиденциальностью своего устройства.
Заключение: Реальность и Осторожность
Нарушение WhatsApp, как правило, оказывается трудным и маловероятным сценарием. Однако важно помнить о актуальных угрозах и принимать меры предосторожности для сохранения своей личной информации. Исполнение рекомендаций по охране помогает поддерживать конфиденциальность и уверенность в использовании мессенджера -
Даркнет список
Введение в Темный Интернет: Уточнение и Основные Характеристики
Разъяснение понятия даркнета, возможных отличий от обычного интернета, и основных черт этого таинственного мира.
Каким образом Войти в Темный Интернет: Руководство по Скрытому Входу
Детальное описание шагов, необходимых для доступа в даркнет, включая использование специализированных браузеров и инструментов.
Адресация сайтов в Темном Интернете: Секреты .onion-Доменов
Разъяснение, как работают .onion-домены, и каковы ресурсы они содержат, с акцентом на безопасном поисковой активности и использовании.
Защита и Анонимность в Даркнете: Шаги для Пользовательской Защиты
Обзор методов и инструментов для сохранения анонимности при использовании даркнета, включая виртуальные частные сети и другие средства.
Электронные Валюты в Темном Интернете: Роль Биткоинов и Криптовалют
Исследование использования криптовалют, в главном биткоинов, для совершения анонимных транзакций в даркнете.
Поиск в Темном Интернете: Специфика и Опасности
Изучение поисковиков в даркнете, предупреждения о потенциальных рисках и незаконных ресурсах.
Юридические Стороны Даркнета: Ответственность и Результаты
Обзор законных аспектов использования даркнета, предостережение о возможных юридических последствиях.
Даркнет и Информационная Безопасность: Потенциальные Угрозы и Противозащитные Действия
Анализ потенциальных киберугроз в даркнете и советы по защите от них.
Даркнет и Социальные Сети: Анонимное Взаимодействие и Сообщества
Изучение влияния даркнета в сфере социальных взаимодействий и формировании анонимных сообществ.
Будущее Темного Интернета: Тенденции и Прогнозы
Предсказания развития даркнета и возможные изменения в его структуре в будущем. -
взлом whatsapp
Взлом Вотсап: Фактичность и Легенды
WhatsApp - один из известных мессенджеров в мире, широко используемый для передачи сообщениями и файлами. Он известен своей шифрованной системой обмена данными и обеспечением конфиденциальности пользователей. Однако в сети время от времени возникают утверждения о возможности нарушения WhatsApp. Давайте разберемся, насколько эти утверждения соответствуют фактичности и почему тема взлома Вотсап вызывает столько дискуссий.
Шифрование в WhatsApp: Охрана Личной Информации
Вотсап применяет end-to-end шифрование, что означает, что только отправитель и получающая сторона могут читать сообщения. Это стало основой для уверенности многих пользователей мессенджера к защите их личной информации.
Легенды о Взломе WhatsApp: По какой причине Они Появляются?
Сеть периодически заполняют слухи о взломе Вотсап и возможном входе к переписке. Многие из этих утверждений порой не имеют обоснований и могут быть результатом паники или дезинформации.
Фактические Угрозы: Кибератаки и Безопасность
Хотя нарушение WhatsApp является сложной задачей, существуют актуальные угрозы, такие как кибератаки на индивидуальные аккаунты, фишинг и вредоносные программы. Соблюдение мер безопасности важно для минимизации этих рисков.
Охрана Личной Информации: Рекомендации Пользователям
Для укрепления охраны своего аккаунта в Вотсап пользователи могут использовать двухфакторную аутентификацию, регулярно обновлять приложение, избегать подозрительных ссылок и следить за конфиденциальностью своего устройства.
Итог: Реальность и Осторожность
Взлом WhatsApp, как обычно, оказывается трудным и маловероятным сценарием. Однако важно помнить о реальных угрозах и принимать меры предосторожности для защиты своей личной информации. Исполнение рекомендаций по безопасности помогает поддерживать конфиденциальность и уверенность в использовании мессенджера. -
kantorbola77
Selamat datang di situs kantorbola , agent judi slot gacor terbaik dengan RTP diatas 98% , segera daftar di situs kantor bola untuk mendapatkan bonus deposit harian 100 ribu dan bonus rollingan 1% -
Обнал карт: Как гарантировать защиту от обманщиков и обеспечить защиту в сети
Современный общество высоких технологий предоставляет удобства онлайн-платежей и банковских операций, но с этим приходит и нарастающая угроза обнала карт. Обнал карт является операцией использования захваченных или полученных незаконным образом кредитных карт для совершения финансовых транзакций с целью маскировать их происхождения и предотвратить отслеживание.
Ключевые моменты для безопасности в сети и предотвращения обнала карт:
Защита личной информации:
Будьте внимательными при передаче личной информации онлайн. Никогда не делитесь картовыми номерами, защитными кодами и другими конфиденциальными данными на сомнительных сайтах.
Сильные пароли:
Используйте для своих банковских аккаунтов и кредитных карт надежные и уникальные пароли. Регулярно изменяйте пароли для увеличения уровня безопасности.
Мониторинг транзакций:
Регулярно проверяйте выписки по кредитным картам и банковским счетам. Это содействует выявлению подозрительных транзакций и моментально реагировать.
Антивирусная защита:
Устанавливайте и регулярно обновляйте антивирусное программное обеспечение. Такие программы помогут защитить от вредоносных программ, которые могут быть использованы для кражи данных.
Бережное использование общественных сетей:
Избегайте размещения чувствительной информации в социальных сетях. Эти данные могут быть использованы для хакерских атак к вашему аккаунту и дальнейшего обнала карт.
Уведомление банка:
Если вы выявили подозрительные действия или потерю карты, свяжитесь с банком сразу для блокировки карты и предотвращения финансовых потерь.
Образование и обучение:
Относитесь внимательно к новым способам мошенничества и постоянно совершенствуйте свои знания, как противостоять подобным атакам. Современные мошенники постоянно совершенствуют свои методы, и ваше осведомленность может стать определяющим для защиты.
В завершение, соблюдение простых правил безопасности в сети и регулярное обновление знаний помогут вам минимизировать риск стать жертвой обнала карт на рабочем месте и в ежедневной практике. Помните, что ваша финансовая безопасность в ваших руках, и предпринимательские действия могут обеспечить ваш онлайн-опыт максимальной защитой и надежностью. -
обнал карт форум
Обнал карт: Как обеспечить безопасность от хакеров и обеспечить безопасность в сети
Современный эпоха высоких технологий предоставляет удобства онлайн-платежей и банковских операций, но с этим приходит и повышающаяся опасность обнала карт. Обнал карт является операцией использования украденных или полученных незаконным образом кредитных карт для совершения финансовых транзакций с целью маскировать их источник и предотвратить отслеживание.
Ключевые моменты для безопасности в сети и предотвращения обнала карт:
Защита личной информации:
Обязательно будьте осторожными при выдаче личной информации онлайн. Никогда не делитесь номерами карт, кодами безопасности и другими конфиденциальными данными на непроверенных сайтах.
Сильные пароли:
Используйте для своих банковских аккаунтов и кредитных карт надежные и уникальные пароли. Регулярно изменяйте пароли для повышения степени защиты.
Мониторинг транзакций:
Регулярно проверяйте выписки по кредитным картам и банковским счетам. Это помогает выявить подозрительные транзакции и быстро реагировать.
Антивирусная защита:
Устанавливайте и регулярно обновляйте антивирусное программное обеспечение. Такие программы помогут препятствовать действию вредоносных программ, которые могут быть использованы для похищения данных.
Бережное использование общественных сетей:
Избегайте размещения чувствительной информации в социальных сетях. Эти данные могут быть использованы для хакерских атак к вашему аккаунту и последующего мошенничества.
Уведомление банка:
Если вы заметили подозрительные операции или похищение карты, свяжитесь с банком сразу для блокировки карты и предупреждения финансовых убытков.
Образование и обучение:
Будьте внимательными к новым методам мошенничества и постоянно совершенствуйте свои знания, как избегать подобных атак. Современные мошенники постоянно усовершенствуют свои приемы, и ваше понимание может стать решающим для предотвращения -
фальшивые 5000 купитьФальшивые купюры 5000 рублей: Опасность для экономики и граждан
Фальшивые купюры всегда были важной угрозой для финансовой стабильности общества. В последние годы одним из главных объектов манипуляций стали банкноты номиналом 5000 рублей. Эти контрафактные деньги представляют собой значительную опасность для экономики и финансовой безопасности граждан. Давайте рассмотрим, почему фальшивые купюры 5000 рублей стали реальной бедой.
Сложностью выявления.
Купюры 5000 рублей являются самыми крупными по номиналу, что делает их чрезвычайно привлекательными для фальшивомонетчиков. Безупречно проработанные подделки могут быть трудно выявить даже профессионалам в сфере финансов. Современные технологии позволяют создавать превосходные копии с использованием передовых методов печати и защитных элементов.
Опасность для бизнеса.
Фальшивые 5000 рублей могут привести к серьезным финансовым убыткам для предпринимателей и компаний. Бизнесы, принимающие наличные средства, становятся подвергаются риску принять фальшивую купюру, что в конечном итоге может снизить прибыль и повлечь за собой юридические последствия.
Повышение инфляции.
Фальшивые деньги увеличивают количество в обращении, что в свою очередь может привести к инфляции. Рост количества контрафактных купюр создает дополнительный денежный объем, не обеспеченный реальными товарами и услугами. Это может существенно подорвать доверие к национальной валюте и стимулировать рост цен.
Вред для доверия к финансовой системе.
Фальшивые деньги вызывают мизерию к финансовой системе в целом. Когда люди сталкиваются с риском получить фальшивые купюры при каждой сделке, они становятся более склонными избегать использования наличных средств, что может привести к обострению проблем, связанных с электронными платежами и банковскими системами.
Противодействие и образование.
Для противодействия распространению фальшивых денег необходимо внедрять более эффективные защитные меры на банкнотах и активно проводить просветительскую работу среди населения. Гражданам нужно быть более внимательными при приеме наличных средств и обучаться элементам распознавания фальшивых купюр.
В заключение:
Фальшивые купюры 5000 рублей представляют значительную угрозу для финансовой стабильности и безопасности граждан. Необходимо активно внедрять новые технологии защиты и проводить информационные кампании, чтобы общество было лучше осведомлено о методах распознавания и защиты от фальшивых денег. Только совместные усилия банков, правоохранительных органов и общества в целом позволят минимизировать опасность подделок и обеспечить стабильность финансовой системы. -
Изготовление и приобретение поддельных денег: опасное дело
Приобрести фальшивые деньги может приглядеться привлекательным вариантом для некоторых людей, но в реальности это действие несет глубокие последствия и подрывает основы экономической стабильности. В данной статье мы рассмотрим негативные аспекты закупки поддельной валюты и почему это является опасным шагом.
Незаконность.
Важное и очень значимое, что следует отметить - это полная незаконность производства и использования фальшивых денег. Такие действия противоречат правилам большинства стран, и их штрафы может быть очень строгим. Покупка поддельной валюты влечет за собой риск уголовного преследования, штрафов и даже тюремного заключения.
Экономическо-финансовые последствия.
Фальшивые деньги плохо влияют на экономику в целом. Когда в обращение поступает фальшивая валюта, это создает дисбаланс и ухудшает доверие к национальной валюте. Компании и граждане становятся более подозрительными при проведении финансовых сделок, что приводит к ухудшению бизнес-климата и тормозит нормальному функционированию рынка.
Опасность финансовой стабильности.
Фальшивые деньги могут стать риском финансовой стабильности государства. Когда в обращение поступает большое количество фальшивой валюты, центральные банки вынуждены принимать дополнительные меры для поддержания финансовой системы. Это может включать в себя увеличение процентных ставок, что, в свою очередь, вредно сказывается на экономике и финансовых рынках.
Опасности для честных граждан и предприятий.
Люди и компании, неосознанно принимающие фальшивые деньги в в качестве оплаты, становятся пострадавшими преступных схем. Подобные ситуации могут привести к финансовым убыткам и утрате доверия к своим деловым партнерам.
Вовлечение криминальных группировок.
Закупка фальшивых денег часто связана с бандитскими группировками и группированным преступлением. Вовлечение в такие сети может привести к серьезными последствиями для личной безопасности и даже подвергнуть опасности жизни.
В заключение, закупка фальшивых денег – это не только противозаконное поступок, но и действие, готовое причинить ущерб экономике и обществу в целом. Рекомендуется избегать подобных действий и сосредотачиваться на легальных, ответственных методах обращения с финансами -
купить фальшивые деньги
Изготовление и приобретение поддельных денег: опасное занятие
Купить фальшивые деньги может показаться привлекательным вариантом для некоторых людей, но в реальности это действие несет важные последствия и нарушает основы экономической стабильности. В данной статье мы рассмотрим плохие аспекты покупки поддельной валюты и почему это является опасным действием.
Противозаконность.
Важное и чрезвычайно основное, что следует отметить - это полная незаконность производства и использования фальшивых денег. Такие действия противоречат правилам большинства стран, и их наказание может быть крайне строгим. Приобретение поддельной валюты влечет за собой опасность уголовного преследования, штрафов и даже тюремного заключения.
Экономическо-финансовые последствия.
Фальшивые деньги плохо влияют на экономику в целом. Когда в обращение поступает фальшивая валюта, это создает дисбаланс и ухудшает доверие к национальной валюте. Компании и граждане становятся все более подозрительными при проведении финансовых сделок, что порождает к ухудшению бизнес-климата и тормозит нормальному функционированию рынка.
Потенциальная угроза финансовой стабильности.
Фальшивые деньги могут стать опасностью финансовой стабильности государства. Когда в обращение поступает большое количество фальшивой валюты, центральные банки вынуждены принимать дополнительные меры для поддержания финансовой системы. Это может включать в себя растущие процентных ставок, что, в свою очередь, вредно сказывается на экономике и финансовых рынках.
Опасности для честных граждан и предприятий.
Люди и компании, неосознанно принимающие фальшивые деньги в в роли оплаты, становятся жертвами преступных схем. Подобные ситуации могут вызвать к финансовым убыткам и утрате доверия к своим деловым партнерам.
Вовлечение криминальных группировок.
Закупка фальшивых денег часто связана с бандитскими группировками и структурированным преступлением. Вовлечение в такие сети может сопровождаться серьезными последствиями для личной безопасности и даже поставить под угрозу жизни.
В заключение, приобретение фальшивых денег – это не только незаконное действие, но и шаг, готовое нанести ущерб экономике и обществу в целом. Рекомендуется избегать подобных поступков и сосредотачиваться на легальных, ответственных путях обращения с финансами -
Обнал карт: Как гарантировать защиту от хакеров и гарантировать безопасность в сети
Современный мир высоких технологий предоставляет преимущества онлайн-платежей и банковских операций, но с этим приходит и повышающаяся опасность обнала карт. Обнал карт является процессом использования захваченных или полученных незаконным образом кредитных карт для совершения финансовых транзакций с целью скрыть их происхождения и заблокировать отслеживание.
Ключевые моменты для безопасности в сети и предотвращения обнала карт:
Защита личной информации:
Обязательно будьте осторожными при предоставлении личной информации онлайн. Никогда не делитесь картовыми номерами, кодами безопасности и дополнительными конфиденциальными данными на ненадежных сайтах.
Сильные пароли:
Используйте для своих банковских аккаунтов и кредитных карт надежные и уникальные пароли. Регулярно изменяйте пароли для увеличения уровня безопасности.
Мониторинг транзакций:
Регулярно проверяйте выписки по кредитным картам и банковским счетам. Это помогает выявить подозрительные транзакции и быстро реагировать.
Антивирусная защита:
Ставьте и периодически обновляйте антивирусное программное обеспечение. Такие программы помогут защитить от вредоносных программ, которые могут быть использованы для похищения данных.
Бережное использование общественных сетей:
Будьте осторожными при размещении чувствительной информации в социальных сетях. Эти данные могут быть использованы для хакерских атак к вашему аккаунту и последующего использования в обнале карт.
Уведомление банка:
Если вы выявили подозрительные действия или утерю карты, свяжитесь с банком немедленно для блокировки карты и избежания финансовых ущербов.
Образование и обучение:
Относитесь внимательно к новым способам мошенничества и постоянно обновляйте свои знания, как избегать подобных атак. Современные мошенники постоянно совершенствуют свои методы, и ваше знание может стать ключевым для защиты.
В завершение, соблюдение основных мер безопасности в интернете и постоянное обновление знаний помогут вам минимизировать риск стать жертвой обнала карт на рабочем месте и в будней жизни. Помните, что безопасность ваших финансов в ваших руках, и активные шаги могут обеспечить ваш онлайн-опыт максимальной защитой и надежностью. -
https://salda.ws/meet/notes.php?id=12681
-
магазин фальшивых денег купить
Темные закоулки сети: теневой мир продажи фальшивых купюр"
Введение:
Фальшивые деньги стали неотъемлемой частью теневого мира, где места продаж – это факторы серьезных угроз для экономики и общества. В данной статье мы обратим внимание на локации, где процветает подпольная торговля поддельными денежными средствами, включая темные уголки интернета.
Теневые интернет-магазины:
С развитием технологий и распространением онлайн-торговли, места продаж фальшивых купюр стали активно функционировать в теневых уголках интернета. Темные веб-сайты и форумы предоставляют возможность анонимно приобрести поддельные денежные средства, создавая тем самым серьезную угрозу для экономики.
Опасные последствия для общества:
Места продаж поддельных средств на темных интернет-ресурсах несут в себе не только потенциальную опасность для финансовой стабильности, но и для простых людей. Покупка фальшивых купюр влечет за собой опасности: от судебных преследований до потери доверия со стороны сообщества.
Передовые технологии подделки:
На скрытых веб-площадках активно используются передовые технологии для создания высококачественных подделок. От печатающих устройств, способных воспроизводить защитные элементы, до использования электронных денег для обеспечения невидимости покупок – все это создает среду, в которой трудно выявить и пресечь незаконную торговлю.
Необходимость ужесточения мер борьбы:
Противостояние с темными местами продаж поддельных денег требует целостного решения. Важно ужесточить законодательство и разработать активные методы для определения и блокировки теневых интернет-магазинов. Также невероятно важно поднимать уровень осведомленности общества относительно рисков подобных практик.
Заключение:
Места продаж поддельных денег на темных уголках интернета представляют собой значительную опасность для финансовой стабильности и общественной безопасности. В условиях расцветающего цифрового мира важно сосредотачивать усилия на противостоянии с подобными практиками, чтобы защитить интересы общества и сохранить доверие к финансовой системе -
купил фальшивые рубли
Фальшивые рубли, как правило, фальсифицируют с целью обмана и незаконного обогащения. Преступники занимаются клонированием российских рублей, формируя поддельные банкноты различных номиналов. В основном, фальсифицируют банкноты с большими номиналами, такими как 1 000 и 5 000 рублей, ввиду того что это позволяет им получать крупные суммы при меньшем количестве фальшивых денег.
Процесс подделки рублей включает в себя использование высокотехнологичного оборудования, специализированных печатающих устройств и особо подготовленных материалов. Шулеры стремятся наиболее точно воспроизвести защитные элементы, водяные знаки, металлическую защиту, микроскопический текст и прочие характеристики, чтобы затруднить определение поддельных купюр.
Фальшивые рубли периодически вносятся в оборот через торговые площадки, банки или другие организации, где они могут быть легко спрятаны среди реальных денежных средств. Это создает серьезные трудности для финансовой системы, так как фальшивые деньги могут порождать убыткам как для банков, так и для граждан.
Столь же важно подчеркнуть, что имение и применение фальшивых денег считаются уголовными преступлениями и могут быть наказаны в соответствии с нормативными актами Российской Федерации. Власти проводят активные меры с подобными правонарушениями, предпринимая меры по выявлению и пресечению деятельности преступных групп, вовлеченных в подделкой российских рублей -
https://salda.ws/meet/notes.php?id=12681
-
娛樂城首儲
初次接觸線上娛樂城的玩家一定對選擇哪間娛樂城有障礙,首要條件肯定是評價良好的娛樂城,其次才是哪間娛樂城優惠最誘人,娛樂城體驗金多少、娛樂城首儲一倍可以拿多少等等…本篇文章會告訴你娛樂城優惠怎麼挑,首儲該注意什麼。
娛樂城首儲該注意什麼?
當您決定好娛樂城,考慮在娛樂城進行首次存款入金時,有幾件事情需要特別注意:
合法性、安全性、評價良好:確保所選擇的娛樂城是合法且受信任的。檢查其是否擁有有效的賭博牌照,以及是否採用加密技術來保護您的個人信息和交易。
首儲優惠與流水:許多娛樂城會為首次存款提供吸引人的獎勵,但相對的流水可能也會很高。
存款入金方式:查看可用的支付選項,是否適合自己,例如:USDT、超商儲值、銀行ATM轉帳等等。
提款出金方式:瞭解最低提款限制,綁訂多少流水才可以領出。
24小時客服:最好是有24小時客服,發生問題時馬上有人可以處理。 -
娛樂城首儲
初次接觸線上娛樂城的玩家一定對選擇哪間娛樂城有障礙,首要條件肯定是評價良好的娛樂城,其次才是哪間娛樂城優惠最誘人,娛樂城體驗金多少、娛樂城首儲一倍可以拿多少等等…本篇文章會告訴你娛樂城優惠怎麼挑,首儲該注意什麼。
娛樂城首儲該注意什麼?
當您決定好娛樂城,考慮在娛樂城進行首次存款入金時,有幾件事情需要特別注意:
合法性、安全性、評價良好:確保所選擇的娛樂城是合法且受信任的。檢查其是否擁有有效的賭博牌照,以及是否採用加密技術來保護您的個人信息和交易。
首儲優惠與流水:許多娛樂城會為首次存款提供吸引人的獎勵,但相對的流水可能也會很高。
存款入金方式:查看可用的支付選項,是否適合自己,例如:USDT、超商儲值、銀行ATM轉帳等等。
提款出金方式:瞭解最低提款限制,綁訂多少流水才可以領出。
24小時客服:最好是有24小時客服,發生問題時馬上有人可以處理。 -
娛樂城首儲
初次接觸線上娛樂城的玩家一定對選擇哪間娛樂城有障礙,首要條件肯定是評價良好的娛樂城,其次才是哪間娛樂城優惠最誘人,娛樂城體驗金多少、娛樂城首儲一倍可以拿多少等等…本篇文章會告訴你娛樂城優惠怎麼挑,首儲該注意什麼。
娛樂城首儲該注意什麼?
當您決定好娛樂城,考慮在娛樂城進行首次存款入金時,有幾件事情需要特別注意:
合法性、安全性、評價良好:確保所選擇的娛樂城是合法且受信任的。檢查其是否擁有有效的賭博牌照,以及是否採用加密技術來保護您的個人信息和交易。
首儲優惠與流水:許多娛樂城會為首次存款提供吸引人的獎勵,但相對的流水可能也會很高。
存款入金方式:查看可用的支付選項,是否適合自己,例如:USDT、超商儲值、銀行ATM轉帳等等。
提款出金方式:瞭解最低提款限制,綁訂多少流水才可以領出。
24小時客服:最好是有24小時客服,發生問題時馬上有人可以處理。 -
初次接觸線上娛樂城的玩家一定對選擇哪間娛樂城有障礙,首要條件肯定是評價良好的娛樂城,其次才是哪間娛樂城優惠最誘人,娛樂城體驗金多少、娛樂城首儲一倍可以拿多少等等…本篇文章會告訴你娛樂城優惠怎麼挑,首儲該注意什麼。
娛樂城首儲該注意什麼?
當您決定好娛樂城,考慮在娛樂城進行首次存款入金時,有幾件事情需要特別注意:
合法性、安全性、評價良好:確保所選擇的娛樂城是合法且受信任的。檢查其是否擁有有效的賭博牌照,以及是否採用加密技術來保護您的個人信息和交易。
首儲優惠與流水:許多娛樂城會為首次存款提供吸引人的獎勵,但相對的流水可能也會很高。
存款入金方式:查看可用的支付選項,是否適合自己,例如:USDT、超商儲值、銀行ATM轉帳等等。
提款出金方式:瞭解最低提款限制,綁訂多少流水才可以領出。
24小時客服:最好是有24小時客服,發生問題時馬上有人可以處理。 -
https://salda.ws/meet/notes.php?id=12681
-
Наша команда искусных специалистов предоставлена предъявить вам перспективные приемы, которые не только ассигнуруют надежную защиту от холодильности, но и подарят вашему жилищу стильный вид.
Мы работаем с новейшими строительными материалами, гарантируя долгий запас службы и блестящие решения. Утепление фасада – это не только экономия энергии на огреве, но и заботливость о экосистеме. Спасательные технические средства, какие мы претворяем в жизнь, способствуют не только жилищу, но и сохранению экосистемы.
Самое первоочередное: Утепление дома снаружи услуги у нас начинается всего от 1250 рублей за квадратный метр! Это доступное решение, которое преобразит ваш домашний уголок в реальный тепловой угол с минимальными затратами.
Наши пособия – это не лишь изоляция, это разработка площади, в где любой элемент отразит ваш личный стиль. Мы примем все все ваши потребности, чтобы осуществить ваш дом еще еще более удобным и привлекательным.
Подробнее на www.ppu-prof.ru
Не откладывайте заботу о своем обители на потом! Обращайтесь к мастерам, и мы сделаем ваш домик не только тепличным, но и по последней моде. Заинтересовались? Подробнее о наших делах вы можете узнать на веб-ресурсе. Добро пожаловать в мир комфорта и качественного исполнения. -
https://salda.ws/meet/notes.php?id=12681
-
https://salda.ws/meet/notes.php?id=12681
-
https://salda.ws/meet/notes.php?id=12681
-
https://salda.ws/meet/notes.php?id=12681
-
https://salda.ws/meet/notes.php?id=12681
-
Portal Judi: Situs Togel Daring Terluas dan Terjamin
Portal Judi telah menjadi salah satu situs judi daring terbesar dan terjamin di Indonesia. Dengan beragam pasaran yang disediakan dari Grup Semar, Situs Judi menawarkan pengalaman bermain togel yang tak tertandingi kepada para penggemar judi daring.
Pasaran Terbaik dan Terpenuhi
Dengan total 56 market, Ngamenjitu menampilkan beberapa opsi terunggul dari pasaran togel di seluruh dunia. Mulai dari pasaran klasik seperti Sydney, Singapore, dan Hongkong hingga pasaran eksotis seperti Thailand, Germany, dan Texas Day, setiap pemain dapat menemukan pasaran favorit mereka dengan mudah.
Langkah Main yang Praktis
Portal Judi menyediakan petunjuk cara main yang praktis dipahami bagi para pemula maupun penggemar togel berpengalaman. Dari langkah-langkah pendaftaran hingga penarikan kemenangan, semua informasi tersedia dengan jelas di situs Situs Judi.
Hasil Terkini dan Info Paling Baru
Pemain dapat mengakses hasil terakhir dari setiap market secara real-time di Portal Judi. Selain itu, info terkini seperti jadwal bank online, gangguan, dan offline juga disediakan untuk memastikan kelancaran proses transaksi.
Berbagai Jenis Game
Selain togel, Portal Judi juga menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan kasino dan judi lainnya. Dari bingo hingga roulette, dari dragon tiger hingga baccarat, setiap pemain dapat menikmati berbagai pilihan permainan yang menarik dan menghibur.
Keamanan dan Kepuasan Klien Dijamin
Ngamenjitu mengutamakan keamanan dan kenyamanan pelanggan. Dengan sistem keamanan terbaru dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif, setiap pemain dapat bermain dengan nyaman dan tenang di platform ini.
Promosi dan Hadiah Istimewa
Ngamenjitu juga menawarkan bervariasi promosi dan bonus menarik bagi para pemain setia maupun yang baru bergabung. Dari bonus deposit hingga hadiah referral, setiap pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk meningkatkan kemenangan mereka dengan bonus yang ditawarkan.
Dengan semua fasilitas dan pelayanan yang ditawarkan, Portal Judi tetap menjadi pilihan utama bagi para penggemar judi online di Indonesia. Bergabunglah sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang seru dan menguntungkan di Situs Judi! -
Ngamen jitu
Portal Judi: Platform Lotere Online Terluas dan Terpercaya
Portal Judi telah menjadi salah satu platform judi online terbesar dan terjamin di Indonesia. Dengan bervariasi pasaran yang disediakan dari Grup Semar, Situs Judi menawarkan pengalaman bermain togel yang tak tertandingi kepada para penggemar judi daring.
Market Terunggul dan Terpenuhi
Dengan total 56 market, Portal Judi menampilkan berbagai opsi terbaik dari market togel di seluruh dunia. Mulai dari pasaran klasik seperti Sydney, Singapore, dan Hongkong hingga market eksotis seperti Thailand, Germany, dan Texas Day, setiap pemain dapat menemukan market favorit mereka dengan mudah.
Cara Bermain yang Praktis
Situs Judi menyediakan panduan cara main yang mudah dipahami bagi para pemula maupun penggemar togel berpengalaman. Dari langkah-langkah pendaftaran hingga penarikan kemenangan, semua informasi tersedia dengan jelas di platform Ngamenjitu.
Hasil Terakhir dan Informasi Paling Baru
Pemain dapat mengakses hasil terakhir dari setiap market secara real-time di Ngamenjitu. Selain itu, info paling baru seperti jadwal bank online, gangguan, dan offline juga disediakan untuk memastikan kelancaran proses transaksi.
Bermacam-macam Jenis Game
Selain togel, Situs Judi juga menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan kasino dan judi lainnya. Dari bingo hingga roulette, dari dragon tiger hingga baccarat, setiap pemain dapat menikmati berbagai pilihan permainan yang menarik dan menghibur.
Keamanan dan Kenyamanan Pelanggan Terjamin
Portal Judi mengutamakan security dan kenyamanan pelanggan. Dengan sistem security terbaru dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif, setiap pemain dapat bermain dengan nyaman dan tenang di situs ini.
Promosi dan Hadiah Menarik
Ngamenjitu juga menawarkan berbagai promosi dan bonus menarik bagi para pemain setia maupun yang baru bergabung. Dari bonus deposit hingga bonus referral, setiap pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk meningkatkan kemenangan mereka dengan bonus yang ditawarkan.
Dengan semua fasilitas dan pelayanan yang ditawarkan, Portal Judi tetap menjadi pilihan utama bagi para penggemar judi online di Indonesia. Bergabunglah sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang seru dan menguntungkan di Ngamenjitu! -
Daftar Ngamenjitu
Portal Judi: Portal Togel Daring Terbesar dan Terjamin
Situs Judi telah menjadi salah satu portal judi online terluas dan terpercaya di Indonesia. Dengan bervariasi market yang disediakan dari Grup Semar, Situs Judi menawarkan sensasi main togel yang tak tertandingi kepada para penggemar judi daring.
Pasaran Terunggul dan Terpenuhi
Dengan total 56 pasaran, Ngamenjitu memperlihatkan beberapa opsi terbaik dari market togel di seluruh dunia. Mulai dari pasaran klasik seperti Sydney, Singapore, dan Hongkong hingga market eksotis seperti Thailand, Germany, dan Texas Day, setiap pemain dapat menemukan market favorit mereka dengan mudah.
Metode Main yang Sederhana
Situs Judi menyediakan tutorial cara bermain yang praktis dipahami bagi para pemula maupun penggemar togel berpengalaman. Dari langkah-langkah pendaftaran hingga penarikan kemenangan, semua informasi tersedia dengan jelas di situs Situs Judi.
Rekapitulasi Terkini dan Informasi Terkini
Pemain dapat mengakses hasil terakhir dari setiap pasaran secara real-time di Situs Judi. Selain itu, informasi terkini seperti jadwal bank daring, gangguan, dan offline juga disediakan untuk memastikan kelancaran proses transaksi.
Pelbagai Macam Permainan
Selain togel, Situs Judi juga menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan kasino dan judi lainnya. Dari bingo hingga roulette, dari dragon tiger hingga baccarat, setiap pemain dapat menikmati berbagai pilihan permainan yang menarik dan menghibur.
Security dan Kepuasan Pelanggan Dijamin
Ngamenjitu mengutamakan keamanan dan kepuasan pelanggan. Dengan sistem keamanan terbaru dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif, setiap pemain dapat bermain dengan nyaman dan tenang di situs ini.
Promosi-Promosi dan Bonus Menarik
Ngamenjitu juga menawarkan berbagai promosi dan bonus istimewa bagi para pemain setia maupun yang baru bergabung. Dari bonus deposit hingga bonus referral, setiap pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk meningkatkan kemenangan mereka dengan hadiah yang ditawarkan.
Dengan semua fitur dan layanan yang ditawarkan, Ngamenjitu tetap menjadi pilihan utama bagi para penggemar judi online di Indonesia. Bergabunglah sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang seru dan menguntungkan di Portal Judi! -
Daftar Ngamenjitu
Portal Judi: Situs Lotere Online Terbesar dan Terjamin
Portal Judi telah menjadi salah satu portal judi online terbesar dan terpercaya di Indonesia. Dengan bervariasi pasaran yang disediakan dari Grup Semar, Situs Judi menawarkan sensasi main togel yang tak tertandingi kepada para penggemar judi daring.
Market Terbaik dan Terpenuhi
Dengan total 56 market, Ngamenjitu menampilkan beberapa opsi terbaik dari market togel di seluruh dunia. Mulai dari pasaran klasik seperti Sydney, Singapore, dan Hongkong hingga market eksotis seperti Thailand, Germany, dan Texas Day, setiap pemain dapat menemukan pasaran favorit mereka dengan mudah.
Metode Main yang Praktis
Ngamenjitu menyediakan petunjuk cara bermain yang mudah dipahami bagi para pemula maupun penggemar togel berpengalaman. Dari langkah-langkah pendaftaran hingga penarikan kemenangan, semua informasi tersedia dengan jelas di platform Ngamenjitu.
Ringkasan Terkini dan Info Paling Baru
Pemain dapat mengakses hasil terakhir dari setiap market secara real-time di Ngamenjitu. Selain itu, informasi paling baru seperti jadwal bank online, gangguan, dan offline juga disediakan untuk memastikan kelancaran proses transaksi.
Bermacam-macam Jenis Permainan
Selain togel, Portal Judi juga menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan kasino dan judi lainnya. Dari bingo hingga roulette, dari dragon tiger hingga baccarat, setiap pemain dapat menikmati bervariasi pilihan permainan yang menarik dan menghibur.
Security dan Kepuasan Pelanggan Terjamin
Ngamenjitu mengutamakan security dan kepuasan pelanggan. Dengan sistem keamanan terbaru dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif, setiap pemain dapat bermain dengan nyaman dan tenang di situs ini.
Promosi-Promosi dan Bonus Istimewa
Portal Judi juga menawarkan bervariasi promosi dan bonus istimewa bagi para pemain setia maupun yang baru bergabung. Dari hadiah deposit hingga bonus referral, setiap pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk meningkatkan kemenangan mereka dengan bonus yang ditawarkan.
Dengan semua fasilitas dan layanan yang ditawarkan, Ngamenjitu tetap menjadi pilihan utama bagi para penggemar judi online di Indonesia. Bergabunglah sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang seru dan menguntungkan di Ngamenjitu! -
Ngamenjitu Login
Ngamenjitu: Platform Lotere Online Terbesar dan Terjamin
Situs Judi telah menjadi salah satu platform judi online terbesar dan terjamin di Indonesia. Dengan bervariasi pasaran yang disediakan dari Grup Semar, Situs Judi menawarkan sensasi main togel yang tak tertandingi kepada para penggemar judi daring.
Pasaran Terbaik dan Terpenuhi
Dengan total 56 pasaran, Situs Judi menampilkan berbagai opsi terbaik dari pasaran togel di seluruh dunia. Mulai dari pasaran klasik seperti Sydney, Singapore, dan Hongkong hingga pasaran eksotis seperti Thailand, Germany, dan Texas Day, setiap pemain dapat menemukan pasaran favorit mereka dengan mudah.
Langkah Main yang Praktis
Portal Judi menyediakan petunjuk cara bermain yang praktis dipahami bagi para pemula maupun penggemar togel berpengalaman. Dari langkah-langkah pendaftaran hingga penarikan kemenangan, semua informasi tersedia dengan jelas di platform Situs Judi.
Rekapitulasi Terakhir dan Informasi Paling Baru
Pemain dapat mengakses hasil terakhir dari setiap pasaran secara real-time di Situs Judi. Selain itu, info paling baru seperti jadwal bank daring, gangguan, dan offline juga disediakan untuk memastikan kelancaran proses transaksi.
Berbagai Macam Permainan
Selain togel, Ngamenjitu juga menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan kasino dan judi lainnya. Dari bingo hingga roulette, dari dragon tiger hingga baccarat, setiap pemain dapat menikmati bervariasi pilihan permainan yang menarik dan menghibur.
Security dan Kepuasan Klien Dijamin
Portal Judi mengutamakan security dan kepuasan pelanggan. Dengan sistem security terbaru dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif, setiap pemain dapat bermain dengan nyaman dan tenang di situs ini.
Promosi dan Hadiah Menarik
Portal Judi juga menawarkan berbagai promosi dan bonus menarik bagi para pemain setia maupun yang baru bergabung. Dari bonus deposit hingga bonus referral, setiap pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk meningkatkan kemenangan mereka dengan hadiah yang ditawarkan.
Dengan semua fasilitas dan pelayanan yang ditawarkan, Portal Judi tetap menjadi pilihan utama bagi para penggemar judi online di Indonesia. Bergabunglah sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang seru dan menguntungkan di Situs Judi! -
Ngamenjitu
Situs Judi: Portal Lotere Daring Terluas dan Terpercaya
Situs Judi telah menjadi salah satu portal judi daring terbesar dan terpercaya di Indonesia. Dengan beragam market yang disediakan dari Semar Group, Ngamenjitu menawarkan sensasi bermain togel yang tak tertandingi kepada para penggemar judi daring.
Pasaran Terbaik dan Terpenuhi
Dengan total 56 market, Portal Judi menampilkan beberapa opsi terbaik dari pasaran togel di seluruh dunia. Mulai dari market klasik seperti Sydney, Singapore, dan Hongkong hingga pasaran eksotis seperti Thailand, Germany, dan Texas Day, setiap pemain dapat menemukan pasaran favorit mereka dengan mudah.
Metode Main yang Sederhana
Ngamenjitu menyediakan tutorial cara bermain yang sederhana dipahami bagi para pemula maupun penggemar togel berpengalaman. Dari langkah-langkah pendaftaran hingga penarikan kemenangan, semua informasi tersedia dengan jelas di situs Ngamenjitu.
Rekapitulasi Terakhir dan Informasi Paling Baru
Pemain dapat mengakses hasil terakhir dari setiap pasaran secara real-time di Situs Judi. Selain itu, info terkini seperti jadwal bank online, gangguan, dan offline juga disediakan untuk memastikan kelancaran proses transaksi.
Pelbagai Macam Permainan
Selain togel, Situs Judi juga menawarkan berbagai jenis permainan kasino dan judi lainnya. Dari bingo hingga roulette, dari dragon tiger hingga baccarat, setiap pemain dapat menikmati berbagai pilihan permainan yang menarik dan menghibur.
Security dan Kenyamanan Pelanggan Dijamin
Ngamenjitu mengutamakan keamanan dan kenyamanan pelanggan. Dengan sistem security terbaru dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif, setiap pemain dapat bermain dengan nyaman dan tenang di situs ini.
Promosi dan Bonus Menarik
Situs Judi juga menawarkan bervariasi promosi dan bonus menarik bagi para pemain setia maupun yang baru bergabung. Dari bonus deposit hingga bonus referral, setiap pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk meningkatkan kemenangan mereka dengan bonus yang ditawarkan.
Dengan semua fasilitas dan pelayanan yang ditawarkan, Ngamenjitu tetap menjadi pilihan utama bagi para penggemar judi online di Indonesia. Bergabunglah sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang seru dan menguntungkan di Portal Judi! -
Login Ngamenjitu
Situs Judi: Situs Togel Online Terbesar dan Terjamin
Situs Judi telah menjadi salah satu platform judi daring terluas dan terjamin di Indonesia. Dengan bervariasi market yang disediakan dari Semar Group, Situs Judi menawarkan sensasi main togel yang tak tertandingi kepada para penggemar judi daring.
Pasaran Terbaik dan Terpenuhi
Dengan total 56 pasaran, Portal Judi menampilkan beberapa opsi terunggul dari market togel di seluruh dunia. Mulai dari pasaran klasik seperti Sydney, Singapore, dan Hongkong hingga market eksotis seperti Thailand, Germany, dan Texas Day, setiap pemain dapat menemukan market favorit mereka dengan mudah.
Langkah Main yang Sederhana
Portal Judi menyediakan tutorial cara main yang mudah dipahami bagi para pemula maupun penggemar togel berpengalaman. Dari langkah-langkah pendaftaran hingga penarikan kemenangan, semua informasi tersedia dengan jelas di platform Situs Judi.
Rekapitulasi Terkini dan Informasi Terkini
Pemain dapat mengakses hasil terakhir dari setiap pasaran secara real-time di Situs Judi. Selain itu, info terkini seperti jadwal bank online, gangguan, dan offline juga disediakan untuk memastikan kelancaran proses transaksi.
Pelbagai Jenis Permainan
Selain togel, Ngamenjitu juga menawarkan bervariasi jenis permainan kasino dan judi lainnya. Dari bingo hingga roulette, dari dragon tiger hingga baccarat, setiap pemain dapat menikmati berbagai pilihan permainan yang menarik dan menghibur.
Keamanan dan Kepuasan Pelanggan Dijamin
Portal Judi mengutamakan keamanan dan kepuasan pelanggan. Dengan sistem keamanan terbaru dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif, setiap pemain dapat bermain dengan nyaman dan tenang di platform ini.
Promosi-Promosi dan Hadiah Istimewa
Situs Judi juga menawarkan bervariasi promosi dan hadiah menarik bagi para pemain setia maupun yang baru bergabung. Dari hadiah deposit hingga bonus referral, setiap pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk meningkatkan kemenangan mereka dengan hadiah yang ditawarkan.
Dengan semua fasilitas dan layanan yang ditawarkan, Situs Judi tetap menjadi pilihan utama bagi para penggemar judi online di Indonesia. Bergabunglah sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang seru dan menguntungkan di Ngamenjitu! -
Ngamenjitu: Platform Togel Daring Terbesar dan Terjamin
Situs Judi telah menjadi salah satu situs judi online terluas dan terpercaya di Indonesia. Dengan bervariasi pasaran yang disediakan dari Semar Group, Portal Judi menawarkan pengalaman bermain togel yang tak tertandingi kepada para penggemar judi daring.
Market Terunggul dan Terlengkap
Dengan total 56 market, Ngamenjitu memperlihatkan beberapa opsi terunggul dari market togel di seluruh dunia. Mulai dari market klasik seperti Sydney, Singapore, dan Hongkong hingga market eksotis seperti Thailand, Germany, dan Texas Day, setiap pemain dapat menemukan market favorit mereka dengan mudah.
Cara Main yang Praktis
Ngamenjitu menyediakan petunjuk cara bermain yang mudah dipahami bagi para pemula maupun penggemar togel berpengalaman. Dari langkah-langkah pendaftaran hingga penarikan kemenangan, semua informasi tersedia dengan jelas di platform Portal Judi.
Ringkasan Terakhir dan Info Terkini
Pemain dapat mengakses hasil terakhir dari setiap market secara real-time di Ngamenjitu. Selain itu, info terkini seperti jadwal bank daring, gangguan, dan offline juga disediakan untuk memastikan kelancaran proses transaksi.
Berbagai Jenis Permainan
Selain togel, Situs Judi juga menawarkan bervariasi jenis permainan kasino dan judi lainnya. Dari bingo hingga roulette, dari dragon tiger hingga baccarat, setiap pemain dapat menikmati berbagai pilihan permainan yang menarik dan menghibur.
Keamanan dan Kenyamanan Klien Dijamin
Situs Judi mengutamakan keamanan dan kepuasan pelanggan. Dengan sistem security terbaru dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif, setiap pemain dapat bermain dengan nyaman dan tenang di platform ini.
Promosi dan Bonus Menarik
Situs Judi juga menawarkan berbagai promosi dan hadiah menarik bagi para pemain setia maupun yang baru bergabung. Dari bonus deposit hingga hadiah referral, setiap pemain memiliki kesempatan untuk meningkatkan kemenangan mereka dengan bonus yang ditawarkan.
Dengan semua fasilitas dan pelayanan yang ditawarkan, Situs Judi tetap menjadi pilihan utama bagi para penggemar judi online di Indonesia. Bergabunglah sekarang dan nikmati pengalaman bermain yang seru dan menguntungkan di Situs Judi! -
В наше время все чаще возникает необходимость в переводе документов для различных целей. В Новосибирске есть множество агентств и переводчиков, специализирующихся на качественных переводах документов. Однако, помимо перевода, часто требуется также апостиль, который удостоверяет подлинность документа за рубежом.
Получить апостиль в Новосибирске — это несложно, если обратиться к профессионалам. Многие агентства, занимающиеся переводами, также предоставляют услуги по оформлению апостиля. Это удобно, т.к. можно сделать все необходимые процедуры в одном месте.
При выборе агентства для перевода документов и оформления апостиля важно обращать внимание на их опыт, репутацию и скорость выполнения заказов. Важно найти надежного партнера, который обеспечит качественный и своевременный сервис. В Новосибирске есть множество проверенных организаций, готовых помочь в оформлении всех необходимых документов для вашего спокойствия и уверенности в законности процесса.
https://salda.ws/meet/notes.php?id=12681 -
Сознание сущности и угроз привязанных с легализацией кредитных карт способствует людям избегать подобных атак и сохранять свои финансовые ресурсы. Обнал (отмывание) кредитных карт — это механизм использования украденных или незаконно полученных кредитных карт для совершения финансовых транзакций с целью сокрыть их происхождения и заблокировать отслеживание.
Вот некоторые способов, которые могут помочь в уклонении от обнала кредитных карт:
Охрана личной информации: Будьте осторожными в контексте предоставления личных данных, особенно онлайн. Избегайте предоставления картовых номеров, кодов безопасности и других конфиденциальных данных на непроверенных сайтах.
Надежные пароли: Используйте надежные и уникальные пароли для своих банковских аккаунтов и кредитных карт. Регулярно изменяйте пароли.
Отслеживание транзакций: Регулярно проверяйте выписки по кредитным картам и банковским счетам. Это способствует своевременному выявлению подозрительных транзакций.
Программы антивирус: Используйте антивирусное программное обеспечение и обновляйте его регулярно. Это поможет препятствовать вредоносные программы, которые могут быть использованы для изъятия данных.
Бережное использование общественных сетей: Будьте осторожными в онлайн-сетях, избегайте публикации чувствительной информации, которая может быть использована для взлома вашего аккаунта.
Быстрое сообщение банку: Если вы заметили какие-либо подозрительные операции или утерю карты, сразу свяжитесь с вашим банком для блокировки карты.
Получение знаний: Будьте внимательными к современным приемам мошенничества и обучайтесь тому, как противостоять их.
Избегая легковерия и принимая меры предосторожности, вы можете снизить риск стать жертвой обнала кредитных карт. -
Опасности поддельными 5000 рублей: Распространение фальшивых купюр и его консеквенции
В сегодняшнем обществе, где виртуальные платежи становятся все более расширенными, преступники не оставляют без внимания и обычные методы недобросовестных действий, такие как раскрутка недостоверных банкнот. В последнее время стало известно о незаконной торговле поддельных 5000 рублевых купюр, что представляет важную риск для финансовых институтов и населения в итоге.
Методы передачи:
Противоправные лица активно используют неявные каналы интернета для торговли поддельных 5000 рублей. На закулисных веб-ресурсах и неправомерных форумах можно обнаружить предложения контрафактных банкнот. К удивлению, это создает благоприятные условия для раскрутки фальшивых денег среди населения.
Консеквенции для сообщества:
Присутствие поддельных денег в хождении может иметь важные результаты для финансовой структуры и доверия к денежной единице. Люди, не замечая, что получили недостоверные купюры, могут использовать их в различных ситуациях, что в финале приводит к повреждению кредитоспособности к банкнотам конкретного номинала.
Угрозы для населения:
Гражданское население становятся вероятными жертвами недобросовестных лиц, когда они случайно получают поддельные деньги в сделках или при приобретениях. В следствие, они могут столкнуться с неприятными ситуациями, такими как отказ от приема торговцев принять недостоверные купюры или даже вероятность ответной ответственности за попытку расплаты фальшивыми деньгами.
Столкновение с дистрибуцией фальшивых денег:
В пользу предотвращения общества от схожих правонарушений необходимо повысить процедуры по выявлению и пресечению изготовления поддельных денег. Это включает в себя сотрудничество между полицейскими и финансовыми учреждениями, а также расширение уровня просвещения людей относительно признаков недостоверных банкнот и практик их обнаружения.
Завершение:
Прокладывание контрафактных 5000 рублей – это важная потенциальная опасность для устойчивости финансовой системы и безопасности граждан. Поддержание авторитета к денежной единице требует согласованных действий со с участием правительства, денежных учреждений и каждого гражданина. Важно быть настороженным и информированным, чтобы предупредить распространение фальшивых денег и гарантировать финансовые средства населения. -
Понимание сущности и рисков связанных с обналом кредитных карт способствует людям избегать подобных атак и сохранять свои финансовые состояния. Обнал (отмывание) кредитных карт — это процедура использования украденных или неправомерно приобретенных кредитных карт для проведения финансовых транзакций с целью сокрыть их происхождения и пресечь отслеживание.
Вот несколько способов, которые могут помочь в предотвращении обнала кредитных карт:
Защита личной информации: Будьте осторожными в контексте предоставления персональной информации, особенно онлайн. Избегайте предоставления картовых номеров, кодов безопасности и дополнительных конфиденциальных данных на сомнительных сайтах.
Сильные пароли: Используйте мощные и уникальные пароли для своих банковских аккаунтов и кредитных карт. Регулярно изменяйте пароли.
Мониторинг транзакций: Регулярно проверяйте выписки по кредитным картам и банковским счетам. Это способствует своевременному выявлению подозрительных транзакций.
Антивирусная защита: Используйте антивирусное программное обеспечение и обновляйте его регулярно. Это поможет защитить от вредоносные программы, которые могут быть использованы для похищения данных.
Осторожное взаимодействие в социальных сетях: Будьте осторожными в онлайн-сетях, избегайте публикации чувствительной информации, которая может быть использована для взлома вашего аккаунта.
Быстрое сообщение банку: Если вы заметили какие-либо подозрительные операции или утерю карты, сразу свяжитесь с вашим банком для отключения карты.
Обучение: Будьте внимательными к современным приемам мошенничества и обучайтесь тому, как противостоять их.
Избегая легковерия и проявляя предельную осторожность, вы можете снизить риск стать жертвой обнала кредитных карт. -
Фальшивые 5000 купить
Опасности фальшивых 5000 рублей: Распространение контрафактных купюр и его консеквенции
В сегодняшнем обществе, где цифровые платежи становятся все более популярными, противоправные лица не оставляют без внимания и обычные методы преступной деятельности, такие как передача поддельных банкнот. В последние дни стало известно о неправомерной торговле фальшивых 5000 рублевых купюр, что представляет серьезную потенциальную опасность для финансовых институтов и граждан в совокупности.
Маневры торговли:
Противоправные лица активно используют тайные трассы сетевого пространства для сбыта недостоверных 5000 рублей. На подпольных веб-ресурсах и нелегальных форумах можно обнаружить прошения о покупке фальшивых банкнот. К удивлению, это создает благоприятные условия для дистрибуции поддельных денег среди граждан.
Последствия для сообщества:
Появление поддельных денег в обращении может иметь значительные консеквенции для финансовой системы и кредитоспособности к денежной единице. Люди, не догадываясь, что получили поддельные купюры, могут использовать их в разнообразных ситуациях, что в финале приводит к потере доверию к банкнотам некоего номинала.
Беды для людей:
Граждане становятся предполагаемыми пострадавшими недобросовестных лиц, когда они случайно получают поддельные деньги в сделках или при покупках. В результате, они могут столкнуться с нелестными ситуациями, такими как отказ от приема коммерсантов принять контрафактные купюры или даже шанс привлечения к ответственности за усилие расплаты поддельными деньгами.
Противостояние с распространением недостоверных денег:
В пользу гарантирования сообщества от схожих нарушений необходимо укрепить процедуры по выявлению и предотвращению изготовления фальшивых денег. Это включает в себя взаимодействие между правоохранительными органами и банками, а также увеличение градуса образования населения относительно признаков недостоверных банкнот и способов их обнаружения.
Заключение:
Разнос поддельных 5000 рублей – это серьезная потенциальная опасность для устойчивости финансовой системы и безопасности общества. Сохранение кредитоспособности к денежной единице требует коллективных усилий со с участием правительства, финансовых институтов и каждого человека. Важно быть бдительным и информированным, чтобы предотвратить прокладывание поддельных денег и защитить финансовые активы населения. -
В наше время все чаще возникает необходимость в переводе документов для различных целей. В Новосибирске есть множество агентств и переводчиков, специализирующихся на качественных переводах документов. Однако, помимо перевода, часто требуется также апостиль, который удостоверяет подлинность документа за рубежом.
Получить апостиль в Новосибирске — это несложно, если обратиться к профессионалам. Многие агентства, занимающиеся переводами, также предоставляют услуги по оформлению апостиля. Это удобно, т.к. можно сделать все необходимые процедуры в одном месте.
При выборе агентства для перевода документов и оформления апостиля важно обращать внимание на их опыт, репутацию и скорость выполнения заказов. Важно найти надежного партнера, который обеспечит качественный и своевременный сервис. В Новосибирске есть множество проверенных организаций, готовых помочь в оформлении всех необходимых документов для вашего спокойствия и уверенности в законности процесса.
https://salda.ws/meet/notes.php?id=12681 -
В наше время все чаще возникает необходимость в переводе документов для различных целей. В Новосибирске есть множество агентств и переводчиков, специализирующихся на качественных переводах документов. Однако, помимо перевода, часто требуется также апостиль, который удостоверяет подлинность документа за рубежом.
Получить апостиль в Новосибирске — это несложно, если обратиться к профессионалам. Многие агентства, занимающиеся переводами, также предоставляют услуги по оформлению апостиля. Это удобно, т.к. можно сделать все необходимые процедуры в одном месте.
При выборе агентства для перевода документов и оформления апостиля важно обращать внимание на их опыт, репутацию и скорость выполнения заказов. Важно найти надежного партнера, который обеспечит качественный и своевременный сервис. В Новосибирске есть множество проверенных организаций, готовых помочь в оформлении всех необходимых документов для вашего спокойствия и уверенности в законности процесса.
https://salda.ws/meet/notes.php?id=12681 -
Mагазин фальшивых денег купить
Покупка фальшивых денег представляет собой незаконным либо потенциально опасным актом, которое имеет возможность привести к важным законным наказаниям либо вреду личной финансовой устойчивости. Вот несколько приводов, почему покупка поддельных купюр является рискованной или неприемлемой:
Нарушение законов:
Получение либо воспользование поддельных банкнот представляют собой противоправным деянием, нарушающим законы страны. Вас способны подвергнуться судебному преследованию, что возможно привести к аресту, денежным наказаниям или тюремному заключению.
Ущерб доверию:
Лживые банкноты ослабляют веру в финансовой механизму. Их использование формирует угрозу для надежных людей и организаций, которые способны столкнуться с непредвиденными убытками.
Экономический ущерб:
Распространение поддельных купюр влияет на экономическую сферу, провоцируя рост цен и ухудшая общественную денежную стабильность. Это может закончиться потере доверия в национальной валюте.
Риск обмана:
Те, которые, задействованы в производством поддельных денег, не обязаны соблюдать какие угодно параметры качества. Фальшивые банкноты могут оказаться легко распознаваемы, что, в итоге послать в расходам для тех стремится применять их.
Юридические последствия:
В ситуации лишения свободы при применении поддельных денег, вас могут принудительно обложить штрафами, и вы столкнетесь с юридическими трудностями. Это может сказаться на вашем будущем, с учетом возможные проблемы с поиском работы и историей кредита.
Общественное и индивидуальное благосостояние зависят от правдивости и доверии в финансовых отношениях. Закупка фальшивых банкнот не соответствует этим принципам и может обладать важные последствия. Рекомендуем держаться законов и заниматься только законными финансовыми действиями. -
Где купить фальшивые деньги
Покупка поддельных банкнот является недозволенным либо опасным актом, что способно послать в тяжелым законным наказаниям или постраданию своей денежной надежности. Вот несколько других причин, по какой причине получение контрафактных банкнот является опасительной иначе недопустимой:
Нарушение законов:
Получение либо применение поддельных банкнот считаются нарушением закона, нарушающим законы общества. Вас способны подвергнуть себя уголовной ответственности, что потенциально послать в лишению свободы, финансовым санкциям или приводу в тюрьму.
Ущерб доверию:
Поддельные банкноты подрывают доверие по отношению к денежной механизму. Их поступление в оборот формирует риск для благоприятных людей и предприятий, которые могут завязать неожиданными перебоями.
Экономический ущерб:
Разнос лживых банкнот оказывает воздействие на хозяйство, провоцируя рост цен что ухудшает общую денежную стабильность. Это может закончиться потере уважения к денежной системе.
Риск обмана:
Те, которые, осуществляют производством лживых купюр, не обязаны сохранять какие-то нормы качества. Поддельные купюры могут быть легко выявлены, что в конечном счете закончится потерям для тех, кто пытается воспользоваться ими.
Юридические последствия:
В ситуации задержания за использование лживых банкнот, вас имеют возможность взыскать штраф, и вы столкнетесь с юридическими трудностями. Это может оказать воздействие на вашем будущем, включая трудности с получением работы и кредитной историей.
Общественное и личное благополучие зависят от честности и доверии в денежной области. Приобретение поддельных банкнот нарушает эти принципы и может обладать серьезные последствия. Рекомендуем держаться законов и заниматься исключительно легальными финансовыми транзакциями. -
В наше время все чаще возникает необходимость в переводе документов для различных целей. В Новосибирске есть множество агентств и переводчиков, специализирующихся на качественных переводах документов. Однако, помимо перевода, часто требуется также апостиль, который удостоверяет подлинность документа за рубежом.
Получить апостиль в Новосибирске — это несложно, если обратиться к профессионалам. Многие агентства, занимающиеся переводами, также предоставляют услуги по оформлению апостиля. Это удобно, т.к. можно сделать все необходимые процедуры в одном месте.
При выборе агентства для перевода документов и оформления апостиля важно обращать внимание на их опыт, репутацию и скорость выполнения заказов. Важно найти надежного партнера, который обеспечит качественный и своевременный сервис. В Новосибирске есть множество проверенных организаций, готовых помочь в оформлении всех необходимых документов для вашего спокойствия и уверенности в законности процесса.
https://salda.ws/meet/notes.php?id=12681 -
Покупка контрафактных купюр приравнивается к неправомерным и опасным актом, что способно закончиться серьезным юридическими санкциям или постраданию своей финансовой устойчивости. Вот некоторые другие примет, из-за чего покупка лживых денег представляет собой рискованной иначе недопустимой:
Нарушение законов:
Закупка и воспользование фальшивых денег приравниваются к нарушением закона, нарушающим нормы общества. Вас в состоянии подвергнуть юридическим последствиям, что может привести к лишению свободы, денежным наказаниям либо тюремному заключению.
Ущерб доверию:
Фальшивые купюры ухудшают доверие в денежной организации. Их применение порождает риск для порядочных граждан и предприятий, которые в состоянии столкнуться с неожиданными потерями.
Экономический ущерб:
Распространение поддельных купюр влияет на экономику, приводя к денежное расширение и подрывая всеобщую финансовую стабильность. Это в состоянии послать в потере уважения к денежной системе.
Риск обмана:
Лица, кто, вовлечены в производством контрафактных купюр, не обязаны поддерживать какие-нибудь нормы уровня. Контрафактные бумажные деньги могут оказаться легко обнаружены, что, в итоге послать в потерям для тех, кто попытается воспользоваться ими.
Юридические последствия:
В случае захвата при применении лживых банкнот, вас способны принудительно обложить штрафами, и вы столкнетесь с юридическими трудностями. Это может сказаться на вашем будущем, в том числе трудности с трудоустройством и кредитной историей.
Благосостояние общества и личное благополучие зависят от правдивости и уважении в денежной области. Получение поддельных денег нарушает эти принципы и может порождать серьезные последствия. Предлагается держаться законов и осуществлять только правомерными финансовыми операциями. -
Покупка фальшивых купюр является неправомерным и рискованным делом, которое имеет возможность повлечь за собой важным юридическими последствиям либо ущербу индивидуальной денежной надежности. Вот несколько причин, почему получение поддельных денег является рискованной или неприемлемой:
Нарушение законов:
Покупка иначе эксплуатация поддельных купюр являются правонарушением, нарушающим положения территории. Вас способны подвергнуться наказанию, которое может повлечь за собой задержанию, взысканиям или приводу в тюрьму.
Ущерб доверию:
Фальшивые деньги нарушают доверенность в денежной системе. Их поступление в оборот порождает риск для надежных граждан и предприятий, которые в состоянии завязать неожиданными потерями.
Экономический ущерб:
Разведение поддельных купюр осуществляет воздействие на хозяйство, приводя к рост цен и ухудшающая глобальную экономическую устойчивость. Это в состоянии повлечь за собой потере доверия в денежной системе.
Риск обмана:
Те, какие, задействованы в созданием поддельных купюр, не обязаны соблюдать какие-либо нормы уровня. Лживые банкноты могут выйти легко выявлены, что в конечном счете послать в ущербу для тех, кто попытается воспользоваться ими.
Юридические последствия:
При случае лишения свободы при использовании контрафактных купюр, вас имеют возможность взыскать штраф, и вы столкнетесь с юридическими трудностями. Это может отразиться на вашем будущем, включая сложности с трудоустройством и кредитной историей.
Благосостояние общества и личное благополучие зависят от правдивости и уважении в финансовых отношениях. Получение лживых банкнот противоречит этим принципам и может представлять важные последствия. Рекомендуется держаться законов и осуществлять только законными финансовыми сделками. -
Покупка лживых купюр является недозволенным или опасным поступком, которое способно послать в серьезным правовым воздействиям или постраданию индивидуальной денежной благосостояния. Вот несколько других приводов, из-за чего приобретение лживых банкнот считается опасной или недопустимой:
Нарушение законов:
Закупка иначе эксплуатация поддельных банкнот представляют собой противоправным деянием, противоречащим нормы государства. Вас могут подвергнуть себя наказанию, которое может послать в задержанию, взысканиям иначе постановлению под стражу.
Ущерб доверию:
Контрафактные деньги ухудшают доверенность по отношению к финансовой механизму. Их применение порождает опасность для благоприятных граждан и предприятий, которые могут претерпеть внезапными перебоями.
Экономический ущерб:
Расширение поддельных денег оказывает воздействие на хозяйство, приводя к инфляцию что ухудшает общую финансовую равновесие. Это способно закончиться потере доверия в национальной валюте.
Риск обмана:
Лица, кто, осуществляют изготовлением фальшивых банкнот, не обязаны поддерживать какие-либо нормы качества. Контрафактные деньги могут оказаться легко распознаваемы, что, в конечном итоге послать в убыткам для тех, кто собирается их использовать.
Юридические последствия:
При случае лишения свободы за использование фальшивых банкнот, вас способны оштрафовать, и вы столкнетесь с юридическими проблемами. Это может сказаться на вашем будущем, в том числе сложности с трудоустройством и кредитной историей.
Благосостояние общества и личное благополучие зависят от честности и доверии в финансовых отношениях. Покупка фальшивых банкнот нарушает эти принципы и может порождать серьезные последствия. Рекомендуем придерживаться законов и осуществлять только легальными финансовыми сделками. -
Купил фальшивые рубли
Покупка лживых банкнот считается противозаконным или рискованным действием, которое имеет возможность привести к глубоким юридическими последствиям или ущербу своей денежной устойчивости. Вот несколько примет, по какой причине закупка лживых банкнот считается рискованной и недопустимой:
Нарушение законов:
Закупка либо применение фальшивых банкнот приравниваются к преступлением, нарушающим нормы общества. Вас в состоянии поддать юридическим последствиям, что может послать в лишению свободы, денежным наказаниям и тюремному заключению.
Ущерб доверию:
Поддельные деньги подрывают уверенность в финансовой структуре. Их обращение порождает возможность для честных граждан и организаций, которые в состоянии столкнуться с неожиданными потерями.
Экономический ущерб:
Разнос поддельных денег причиняет воздействие на хозяйство, инициируя денежное расширение что ухудшает глобальную финансовую устойчивость. Это может послать в потере уважения к денежной системе.
Риск обмана:
Лица, те, осуществляют изготовлением лживых банкнот, не обязаны соблюдать какие угодно нормы уровня. Поддельные деньги могут стать легко выявлены, что, в итоге послать в расходам для тех, кто стремится воспользоваться ими.
Юридические последствия:
В случае захвата при воспользовании фальшивых банкнот, вас имеют возможность наказать штрафом, и вы столкнетесь с юридическими проблемами. Это может повлиять на вашем будущем, с учетом трудности с получением работы и кредитной историей.
Общественное и личное благополучие зависят от правдивости и уважении в финансовой деятельности. Покупка контрафактных купюр не соответствует этим принципам и может порождать серьезные последствия. Предлагается держаться законов и вести только законными финансовыми операциями. -
Покупка контрафактных денег является противозаконным либо потенциально опасным делом, что имеет возможность повлечь за собой глубоким юридическим санкциям и постраданию личной финансовой стабильности. Вот некоторые причин, из-за чего получение контрафактных денег считается опасной и недопустимой:
Нарушение законов:
Получение иначе применение контрафактных денег считаются правонарушением, подрывающим положения территории. Вас в состоянии подвергнуться уголовной ответственности, что потенциально повлечь за собой лишению свободы, финансовым санкциям иначе приводу в тюрьму.
Ущерб доверию:
Контрафактные деньги ухудшают веру к финансовой механизму. Их применение создает риск для благоприятных граждан и предприятий, которые в состоянии претерпеть непредвиденными перебоями.
Экономический ущерб:
Разведение фальшивых купюр влияет на экономику, приводя к распределение денег и ухудшая общую финансовую устойчивость. Это имеет возможность закончиться потере доверия в денежной системе.
Риск обмана:
Люди, те, задействованы в производством лживых банкнот, не обязаны соблюдать какие-либо параметры характеристики. Поддельные купюры могут быть легко обнаружены, что в итоге повлечь за собой расходам для тех пытается их использовать.
Юридические последствия:
В ситуации захвата при применении фальшивых денег, вас в состоянии принудительно обложить штрафами, и вы столкнетесь с законными сложностями. Это может повлиять на вашем будущем, включая возможные проблемы с трудоустройством и историей кредита.
Благосостояние общества и личное благополучие зависят от правдивости и уважении в денежной области. Закупка контрафактных денег не соответствует этим принципам и может обладать серьезные последствия. Предлагается держаться законов и заниматься только законными финансовыми действиями. -
Купить фальшивые рубли
Покупка фальшивых денег является незаконным иначе потенциально опасным делом, которое имеет возможность привести к важным правовым наказаниям иначе ущербу своей денежной устойчивости. Вот несколько других примет, почему получение контрафактных денег приравнивается к рискованной иначе недопустимой:
Нарушение законов:
Получение иначе воспользование лживых банкнот представляют собой преступлением, нарушающим нормы общества. Вас способны подвергнуть себя уголовной ответственности, что может закончиться лишению свободы, взысканиям или приводу в тюрьму.
Ущерб доверию:
Фальшивые деньги подрывают доверенность в финансовой системе. Их обращение формирует возможность для порядочных гражданских лиц и предприятий, которые имеют возможность завязать неожиданными перебоями.
Экономический ущерб:
Распространение поддельных денег оказывает воздействие на финансовую систему, вызывая инфляцию и ухудшая общественную экономическую равновесие. Это может закончиться потере уважения к национальной валюте.
Риск обмана:
Личности, какие, задействованы в изготовлением фальшивых денег, не обязаны сохранять какие-то стандарты качества. Лживые банкноты могут быть легко обнаружены, что, в конечном итоге повлечь за собой убыткам для тех, кто стремится воспользоваться ими.
Юридические последствия:
При случае захвата при воспользовании фальшивых купюр, вас способны взыскать штраф, и вы столкнетесь с юридическими трудностями. Это может повлиять на вашем будущем, в том числе трудности с поиском работы и кредитной историей.
Благосостояние общества и личное благополучие зависят от честности и доверии в финансовой деятельности. Закупка поддельных денег нарушает эти принципы и может представлять серьезные последствия. Рекомендуем соблюдать правил и заниматься исключительно правомерными финансовыми транзакциями. -
В наше время все чаще возникает необходимость в переводе документов для различных целей. В Новосибирске есть множество агентств и переводчиков, специализирующихся на качественных переводах документов. Однако, помимо перевода, часто требуется также апостиль, который удостоверяет подлинность документа за рубежом.
Получить апостиль в Новосибирске — это несложно, если обратиться к профессионалам. Многие агентства, занимающиеся переводами, также предоставляют услуги по оформлению апостиля. Это удобно, т.к. можно сделать все необходимые процедуры в одном месте.
При выборе агентства для перевода документов и оформления апостиля важно обращать внимание на их опыт, репутацию и скорость выполнения заказов. Важно найти надежного партнера, который обеспечит качественный и своевременный сервис. В Новосибирске есть множество проверенных организаций, готовых помочь в оформлении всех необходимых документов для вашего спокойствия и уверенности в законности процесса.
https://salda.ws/meet/notes.php?id=12681 -
обнал карт работа
Обналичивание карт – это противозаконная деятельность, становящаяся все более распространенной в нашем современном мире электронных платежей. Этот вид мошенничества представляет серьезные вызовы для банков, правоохранительных органов и общества в целом. В данной статье мы рассмотрим частоту встречаемости обналичивания карт, используемые методы и возможные последствия для жертв и общества.
Частота обналичивания карт:
Обналичивание карт является достаточно распространенным явлением, и его частота постоянно растет с увеличением числа электронных транзакций. Киберпреступники применяют различные методы для получения доступа к финансовым средствам, включая фишинг, вредоносное программное обеспечение, скимминг и другие инновационные подходы.
Методы обналичивания карт:
Фишинг: Злоумышленники могут отправлять ложные электронные сообщения или создавать веб-сайты, имитирующие банковские системы, с целью получения личной информации от владельцев карт.
Скимминг: Злоумышленники устанавливают устройства скиммеры на банкоматах или терминалах для считывания данных с магнитных полос карт.
Вредоносное программное обеспечение: Киберпреступники разрабатывают вредоносные программы, которые заражают компьютеры и мобильные устройства, чтобы получить доступ к личным данным и банковским счетам.
Сетевые атаки: Атаки на системы банков и платежных платформ могут привести к утечке информации о картах и, следовательно, к их обналичиванию.
Последствия обналичивания карт:
Финансовые потери для клиентов: Владельцы карт могут столкнуться с финансовыми потерями, так как средства могут быть списаны с их счетов без их ведома.
Угроза безопасности данных: Обналичивание карт подчеркивает угрозу безопасности личных данных, что может привести к краже личной и финансовой информации.
Ущерб репутации банков: Банки и другие финансовые учреждения могут столкнуться с утратой доверия со стороны клиентов, если их системы безопасности оказываются уязвимыми.
Проблемы для экономики: Обналичивание карт создает экономический ущерб, поскольку оно стимулирует дополнительные затраты на борьбу с мошенничеством и восстановление утраченных средств.
Борьба с обналичиванием карт:
Совершенствование технологий безопасности: Банки и финансовые институты постоянно совершенствуют свои системы безопасности, чтобы предотвратить несанкционированный доступ к картам.
Образование и информирование: Обучение клиентов о методах мошенничества и том, как защитить свои данные, является важным шагом в борьбе с обналичиванием карт.
Сотрудничество с правоохранительными органами: Банки активно сотрудничают с правоохранительными органами для выявления и пресечения преступных схем.
Заключение:
Обналичивание карт – весомая угроза для финансовой стабильности и безопасности личных данных. Решение этой проблемы требует совместных усилий со стороны банков, правоохранительных органов и общества в целом. Только эффективная борьба с мошенничеством позволит обеспечить безопасность электронных платежей и защитить интересы всех участников финансовой системы. -
The demand for hydroxychloroquine peaked dramatically, influenced by its potential as a COVID-19 treatment. This surge led to shortages for patients with lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, for whom hydroxychloroquine 200 mg tablet for rheumatoid arthritis is a critical component of their treatment regimen. The situation underscored the challenges of drug repurposing during a global health emergency, highlighting the need for balanced information and resource allocation.
-
Искусство перевода с иностранных языков имеет огромное значение в современном многоязычном мире. Когда речь идет о переводе с иностранных языков, важно учитывать не только лингвистические аспекты, но и культурные и контекстуальные особенности. Профессиональные специалисты в области перевода с иностранных языков играют ключевую роль в обеспечении точности и адекватности передачи информации.
Один из важных аспектов перевода с иностранных языков – это сохранение аутентичности текста и передача его смысла на язык, на котором он будет воспринят. Это требует глубокого понимания языка, а также контекста и культурных нюансов, которые могут влиять на перевод.
Процесс перевода с иностранных языков включает в себя не только знание языков, но и искусство передачи содержания, стиля и нюансов оригинала. Это требует не только технических навыков, но и тонкого чувства языка и контекста.
Выбор профессиональной компании для перевода с иностранных языков – это гарантия качественной и точной работы. Надежные специалисты в области перевода с иностранных языков могут обеспечить точность и адекватность перевода, учитывая все особенности исходного текста.
В мире многоязычия и глобализации значение перевода с иностранных языков трудно переоценить. Это процесс, который облегчает взаимопонимание и содействует культурному обмену. Надежный и опытный переводчик способен сделать вашу информацию доступной для аудитории на любом языке. Не забывайте о важности профессионального перевода с иностранных языков в вашем международном взаимодействии. перевод с иностранных языков #перевод #иностранныязыки #профессионалывобластиперевода #глобализация -
Terriers will 209 be ready quality Three-Bedroom.
This was among applications in South Africaand Power: 20 hp Lift Height:
2.fire avant Max: 12 km/h. Tan if they are pulled
too tight south lives around, by ridding them of the burden
of overwhelming debt. View 209 our see our Privacy Policy. -
ТолMuch – ваш надежный партнер в переводе документов. Многие сферы жизни требуют предоставления переведенных документов – образование за рубежом, международные бизнес-соглашения, иммиграционные процессы. Наши специалисты помогут вам с профессиональным переводом документов.
Наш опыт и профессионализм позволяют нам обеспечивать высокое качество перевода документов в самые кратчайшие сроки. Мы понимаем, насколько важна точность и грамотность в этом деле. Каждый проект для нас – это возможность внимательно отнестись к вашим документам.
Сделайте шаг к успешному будущему с нами. Наши услуги по переводу документов помогут вам преодолеть языковые барьеры в любой области. Доверьтесь переводу документов профессионалам. Обращайтесь к ТолMuch – вашему лучшему выбору в мире лингвистики и перевода.
#переводдокументов #ТолMuch #язык #бизнес -
В современном мире все чаще возникает необходимость легализации документов для использования за границей. Один из способов осуществления данной процедуры – получение апостиля. В Новосибирске эта услуга доступна всем желающим в специализированных организациях.
Апостиль – это особая форма легализации документов, предназначенных для использования в странах, участниках Гаагской конвенции 1961 года. С помощью апостиля подтверждается подлинность подписи документа, квалификация должностного лица, его полномочия и подлинность печати, если это предусмотрено. Получить апостиль можно на документах различного характера – свидетельства о рождении, браке, смерти, доверенности, диплома об образовании и других.
В Новосибирске услуги по оформлению апостиля предоставляют специализированные учреждения. Для этого необходимо обратиться в нотариальную контору или в отдел ЗАГС. При обращении следует иметь при себе оригинал документа, который требует легализации, а также паспорт для удостоверения личности. Стоимость услуги может варьироваться в зависимости от типа документа и срочности выполнения.
Оформление апостиля в Новосибирске является необходимым шагом для тех, кто планирует выезд за рубеж или ведет деловую деятельность с иностранными партнерами. Без данной процедуры документы не будут иметь юридической силы за пределами России. Важно помнить, что апостиль выдается только на территории стран-участниц конвенции, поэтому перед оформлением стоит уточнить, является ли страна, в которую вы собираетесь поехать, участником данного документа.
Выводя таким образом, можно сказать, что получение апостиля в Новосибирске – это важный этап в легализации документов для использования за границей. Соблюдая все необходимые процедуры и требования, вы сможете без проблем и задержек использовать свои документы на территории других стран. Не откладывайте на потом, обратитесь за помощью к специалистам и оформите все необходимые документы вовремя. -
Terriers will 209 be ready quality sale.
This was among applications in South AfricaEngine Power: 20 hp Lift Height:
2.fire avant Speed: 12 km/h. Tan if they are pulled
too tight their lives around, by ridding them of the burden
of overwhelming debt. View 209 doors see our Privacy Policy. -
В современном мире все чаще возникает необходимость легализации документов для использования за границей. Один из способов осуществления данной процедуры – получение апостиля. В Новосибирске эта услуга доступна всем желающим в специализированных организациях.
Апостиль – это особая форма легализации документов, предназначенных для использования в странах, участниках Гаагской конвенции 1961 года. С помощью апостиля подтверждается подлинность подписи документа, квалификация должностного лица, его полномочия и подлинность печати, если это предусмотрено. Получить апостиль можно на документах различного характера – свидетельства о рождении, браке, смерти, доверенности, диплома об образовании и других.
В Новосибирске услуги по оформлению апостиля предоставляют специализированные учреждения. Для этого необходимо обратиться в нотариальную контору или в отдел ЗАГС. При обращении следует иметь при себе оригинал документа, который требует легализации, а также паспорт для удостоверения личности. Стоимость услуги может варьироваться в зависимости от типа документа и срочности выполнения.
Оформление апостиля в Новосибирске является необходимым шагом для тех, кто планирует выезд за рубеж или ведет деловую деятельность с иностранными партнерами. Без данной процедуры документы не будут иметь юридической силы за пределами России. Важно помнить, что апостиль выдается только на территории стран-участниц конвенции, поэтому перед оформлением стоит уточнить, является ли страна, в которую вы собираетесь поехать, участником данного документа.
Выводя таким образом, можно сказать, что получение апостиля в Новосибирске – это важный этап в легализации документов для использования за границей. Соблюдая все необходимые процедуры и требования, вы сможете без проблем и задержек использовать свои документы на территории других стран. Не откладывайте на потом, обратитесь за помощью к специалистам и оформите все необходимые документы вовремя.апостиль в Новосибирске -
Hydroxychloroquine should only be obtained from reputable sources, such as licensed pharmacies or healthcare providers, to ensure its quality and safety. hydroxychloroquine sulfate Avoid purchasing hydroxychloroquine from unregulated sources or online vendors, as these products may be counterfeit, substandard, or contaminated. Your healthcare provider can provide guidance on obtaining hydroxychloroquine from reliable sources and using it safely and effectively.
-
תְּמוּנָה המִקוּם לְמַעֲנֵה גַּרְגִּירֵים כיוונים (Telegrass), מוּכָר גם בשמות "רֶּקַע" או "טלגראס כיוונים", הן אתר מזִין מידע, לינקים, קישורים, מדריכים והסברים בנושאי קנאביס בתוך הארץ. באמצעות האתר, משתמשים יכולים למצוא את כל הקישורים המעודכנים עבור ערוצים מומלצים ופעילים בטלגראס כיוונים בכל רחבי הארץ.
טלגראס כיוונים הוא אתר ובוט בתוך פלטפורמת טלגראס, מזכירות דרכי תקשורת ושירותים שונות בתחום רכישת קנאביס וקשורים. באמצעות הבוט, המשתמשים יכולים לבצע מגוון פעולות בקשר לרכישת קנאביס ולשירותים נוספים, תוך כדי תקשורת עם מערכת אוטומטית המבצעת את הפעולות בצורה חכמה ומהירה.
בוט הטלגראס (Telegrass Bot) מציע מגוון פעולות שימושיות למשתמשים: הזמנת קנאביס: בצע הזמנות דרך הבוט על ידי בחירת סוגי הקנאביס, כמות וכתובת למשלוח.
הוראות ותמיכה: קבל מידע על המוצרים והשירותים, תמיכה טכנית ותשובות לשאלות שונות.
בחינה מלאי: בדוק את המלאי הזמין של קנאביס ובצע הזמנה תוך כדי הקשת הבדיקה.
הוספת ביקורות: הוסף ביקורות ודירוגים למוצרים שרכשת, כדי לעזור למשתמשים אחרים.
הוספת מוצרים חדשים: הוסף מוצרים חדשים לפלטפורמה והצג אותם למשתמשים.
בקיצור, בוט הטלגראס הוא כלי חשוב ונוח שמקל על השימוש והתקשורת בנושאי קנאביס, מאפשר מגוון פעולות שונות ומספק מידע ותמיכה למשתמשים. -
תְּמוּנָה המִקוּם עבור רִיחֲמִים כיוונים (Telegrass), נוֹדַע גם בשמות "טלגראס" או "רֶּקַע כיוונים", היא אתר המספק מידע, לינקים, קישורים, מדריכים והסברים בנושאי קנאביס בתוך הארץ. באמצעות האתר, משתמשים יכולים למצוא את כל הקישורים המעודכנים עבור ערוצים מומלצים ופעילים בטלגראס כיוונים בכל רחבי הארץ.
טלגראס כיוונים הוא אתר ובוט בתוך פלטפורמת טלגראס, מספקות דרכי תקשורת ושירותים שונים בתחום רכישת קנאביס וקשורים. באמצעות הבוט, המשתמשים יכולים לבצע מגוון פעולות בקשר לרכישת קנאביס ולשירותים נוספים, תוך כדי תקשורת עם מערכת אוטומטית המבצעת את הפעולות בצורה חכמה ומהירה.
בוט הטלגראס (Telegrass Bot) מציע מגוון פעולות שימושיות למשתמשים: הזמנת קנאביס: בצע קנייה דרך הבוט על ידי בחירת סוגי הקנאביס, כמות וכתובת למשלוח.
שאלות ותמיכה: קבל מידע על המוצרים והשירותים, תמיכה טכנית ותשובות לשאלות שונות.
בדיקת מלאי: בדוק את המלאי הזמין של קנאביס ובצע הזמנה תוך כדי הקשת הבדיקה.
הכנסת ביקורות: הוסף ביקורות ודירוגים למוצרים שרכשת, כדי לעזור למשתמשים אחרים.
הוסיפו מוצרים חדשים: הוסף מוצרים חדשים לפלטפורמה והצג אותם למשתמשים.
בקיצור, בוט הטלגראס הוא כלי חשוב ונוח שמקל על השימוש והתקשורת בנושאי קנאביס, מאפשר מגוון פעולות שונות ומספק מידע ותמיכה למשתמשים. -
Stromectol's mechanism of action in COVID-19 treatment is not fully understood but is believed to involve inhibition of viral replication and modulation of the immune response. ivermectin injectable Further research is needed to elucidate the specific pathways involved and optimize its therapeutic use in managing the disease.
-
Прояви свою креативность на максимуме! Учись создавать стильные свитшоты и зарабатывать на своих талантах. Присоединяйся к мастер-классу и покажи миру свои модные идеи! Регистрация здесь https://u.to/zQWJIA
-
בטים ספורט
המימונים באינטרנט - מימורי ספורטיביים, קזינו מקוון, משחקי קלפי.
המימונים ברשת הופכים ל לתחום נפוץ בבאופן מיוחד בתקופת הדיגיטלי.
מיליוני משתתפים ממנסות את מזלם באפשרויות מימורים המגוונים.
התהליכים הזהה משנה את הרגע הניסיונות וההתרגשות השחקנים.
גם עוסק בשאלות אתיות וחברתיות השמורות ממאחורי המימורים ברשת.
בעידן הדיגיטלי, הימורים ברשת הם חלק בלתי נפרד מהתרבות הספורטאי, הפנאי והבידור והחברה המודרנית.
המימורים בפלטפורמת האינטרנט כוללים את מגוון רחב של פעילויות, כולל מימורים על תוצאות ספורט, פוליטי, וגם תוצאות מזג האוויר.
המימונים הם בעיקר מתבצעים באמצע -
קזינו אונליין
הימורים באינטרנט - מימורי ספורטיביים, קזינו מקוון, משחקי קלפים.
המימונים בפלטפורמת האינטרנט נהפכים לתחום פופולרי במיוחדים בעידן הדיגיטלי.
מיליונים משתתפים מרחבי העולם מנסים את המזל באפשרויות מימורים המגוונים.
התהליכים הזוהה משנה את את הרגע הניסיון והתרגשות.
גם עוסק בשאלות אתיות וחברתיות השמורות ממאחורי ההימורים המקוונים.
בעידן הדיגיטלי, המימונים בפלטפורמת האינטרנט הם חלק מהתרבות הספורט, הבידור והחברה ה המודרנית.
המימונים בפלטפורמת האינטרנט כוללים אפשרויות רחבות של פעילות, כולל מימונים על תוצאות ספורטיביות, פוליטיות, וגם מזג האוויר.
ההימורים הם הם מתבצעים באמצע -
Жаждешь моды и самореализации? Присоединяйся к мастер-классу по шитью свитшотов! Освой искусство создания стильных вещей и открой для себя новые возможности за 2 часа!
Регистрация здесь https://u.to/zQWJIA -
https://www.avito.ru/prokopevsk/predlozheniya_uslug/podem_domov._perenos_domov._zamena_ventsov_3799239508
-
The inclusion of stromectol dosage, containing ivermectin, in community health initiatives supports efforts to address the burden of neglected tropical diseases in rural areas. By providing access to essential medications like ivermectin, these initiatives help improve health outcomes and quality of life for underserved populations.
-
https://www.avito.ru/novokuznetsk/predlozheniya_uslug/podem_domov._perenos_domov._zamena_ventsov_2135286827
-
elementor
-
https://www.avito.ru/novokuznetsk/predlozheniya_uslug/podem_domov._perenos_domov._zamena_ventsov_2135286827
-
https://www.avito.ru/kemerovskaya_oblast_mezhdurechensk/predlozheniya_uslug/podem_domov._perenos_domov._zamena_ventsov_3831125828
-
https://www.avito.ru/prokopevsk/predlozheniya_uslug/podem_domov._perenos_domov._zamena_ventsov_3799239508
-
Прояви свою креативность на максимуме! Учись создавать стильные свитшоты и зарабатывать на своих талантах. Присоединяйся к мастер-классу и покажи миру свои модные идеи! Регистрация здесь https://u.to/zQWJIA
-
sandyterrace.com
버릇없는 여자들이 아직 살아 있다는 것은 정말 신경이 쓰이는 일입니다. -
freeflowincome.com
Concubine Fang은 주저하고 천천히 병 뚜껑을 들어 올렸고 이상한 향기가 그녀의 마음에 곧바로 돌진했습니다. -
https://www.avito.ru/novokuznetsk/predlozheniya_uslug/podem_domov._perenos_domov._zamena_ventsov_2135286827
-
qiyezp.com
Fang Jifan은 "생각하면 목이 부러졌습니다. "라고 말했습니다. -
The inclusion of ivermectin stromectol where to buy, containing ivermectin, in national and international treatment guidelines underscores its importance as a first-line therapy for parasitic infections. These evidence-based recommendations guide healthcare providers and public health authorities in the safe and effective use of ivermectin, ensuring optimal outcomes for patients and communities affected by parasitic diseases.
-
https://vk.com/zamena_venzov
-
Collaborative efforts among researchers, healthcare providers, policymakers, and the public are essential to advance our understanding of stromectol's role in managing COVID-19. ivermectin dog By working together, we can navigate the complexities of the pandemic and identify effective strategies for controlling the spread of the virus.
-
https://vk.com/zamena_venzov
-
https://elementor.com/
-
https://elementor.com/
-
Informasi RTP Live Hari Ini Dari Situs RTPKANTORBOLA
Situs RTPKANTORBOLA merupakan salah satu situs yang menyediakan informasi lengkap mengenai RTP (Return to Player) live hari ini. RTP sendiri adalah persentase rata-rata kemenangan yang akan diterima oleh pemain dari total taruhan yang dimainkan pada suatu permainan slot . Dengan adanya informasi RTP live, para pemain dapat mengukur peluang mereka untuk memenangkan suatu permainan dan membuat keputusan yang lebih cerdas saat bermain.
Situs RTPKANTORBOLA menyediakan informasi RTP live dari berbagai permainan provider slot terkemuka seperti Pragmatic Play , PG Soft , Habanero , IDN Slot , No Limit City dan masih banyak rtp permainan slot yang bisa kami cek di situs RTP Kantorboal . Dengan menyediakan informasi yang akurat dan terpercaya, situs ini menjadi sumber informasi yang penting bagi para pemain judi slot online di Indonesia .
Salah satu keunggulan dari situs RTPKANTORBOLA adalah penyajian informasi yang terupdate secara real-time. Para pemain dapat memantau perubahan RTP setiap saat dan membuat keputusan yang tepat dalam bermain. Selain itu, situs ini juga menyediakan informasi mengenai RTP dari berbagai provider permainan, sehingga para pemain dapat membandingkan dan memilih permainan dengan RTP tertinggi.
Informasi RTP live yang disediakan oleh situs RTPKANTORBOLA juga sangat lengkap dan mendetail. Para pemain dapat melihat RTP dari setiap permainan, baik itu dari aspek permainan itu sendiri maupun dari provider yang menyediakannya. Hal ini sangat membantu para pemain dalam memilih permainan yang sesuai dengan preferensi dan gaya bermain mereka.
Selain itu, situs ini juga menyediakan informasi mengenai RTP live dari berbagai provider judi slot online terpercaya. Dengan begitu, para pemain dapat memilih permainan slot yang memberikan RTP terbaik dan lebih aman dalam bermain. Informasi ini juga membantu para pemain untuk menghindari potensi kerugian dengan bermain pada game slot online dengan RTP rendah .
Situs RTPKANTORBOLA juga memberikan pola dan ulasan mengenai permainan-permainan dengan RTP tertinggi. Para pemain dapat mempelajari strategi dan tips dari para ahli untuk meningkatkan peluang dalam memenangkan permainan. Analisis dan ulasan ini disajikan secara jelas dan mudah dipahami, sehingga dapat diaplikasikan dengan baik oleh para pemain.
Informasi RTP live yang disediakan oleh situs RTPKANTORBOLA juga dapat membantu para pemain dalam mengelola keuangan mereka. Dengan mengetahui RTP dari masing-masing permainan slot , para pemain dapat mengatur taruhan mereka dengan lebih bijak. Hal ini dapat membantu para pemain untuk mengurangi risiko kerugian dan meningkatkan peluang untuk mendapatkan kemenangan yang lebih besar.
Untuk mengakses informasi RTP live dari situs RTPKANTORBOLA, para pemain tidak perlu mendaftar atau membayar biaya apapun. Situs ini dapat diakses secara gratis dan tersedia untuk semua pemain judi online. Dengan begitu, semua orang dapat memanfaatkan informasi yang disediakan oleh situs RTP Kantorbola untuk meningkatkan pengalaman dan peluang mereka dalam bermain judi online.
Demikianlah informasi mengenai RTP live hari ini dari situs RTPKANTORBOLA. Dengan menyediakan informasi yang akurat, terpercaya, dan lengkap, situs ini menjadi sumber informasi yang penting bagi para pemain judi online. Dengan memanfaatkan informasi yang disediakan, para pemain dapat membuat keputusan yang lebih cerdas dan meningkatkan peluang mereka untuk memenangkan permainan. Selamat bermain dan semoga sukses! -
situs kantorbola
Informasi RTP Live Hari Ini Dari Situs RTPKANTORBOLA
Situs RTPKANTORBOLA merupakan salah satu situs yang menyediakan informasi lengkap mengenai RTP (Return to Player) live hari ini. RTP sendiri adalah persentase rata-rata kemenangan yang akan diterima oleh pemain dari total taruhan yang dimainkan pada suatu permainan slot . Dengan adanya informasi RTP live, para pemain dapat mengukur peluang mereka untuk memenangkan suatu permainan dan membuat keputusan yang lebih cerdas saat bermain.
Situs RTPKANTORBOLA menyediakan informasi RTP live dari berbagai permainan provider slot terkemuka seperti Pragmatic Play , PG Soft , Habanero , IDN Slot , No Limit City dan masih banyak rtp permainan slot yang bisa kami cek di situs RTP Kantorboal . Dengan menyediakan informasi yang akurat dan terpercaya, situs ini menjadi sumber informasi yang penting bagi para pemain judi slot online di Indonesia .
Salah satu keunggulan dari situs RTPKANTORBOLA adalah penyajian informasi yang terupdate secara real-time. Para pemain dapat memantau perubahan RTP setiap saat dan membuat keputusan yang tepat dalam bermain. Selain itu, situs ini juga menyediakan informasi mengenai RTP dari berbagai provider permainan, sehingga para pemain dapat membandingkan dan memilih permainan dengan RTP tertinggi.
Informasi RTP live yang disediakan oleh situs RTPKANTORBOLA juga sangat lengkap dan mendetail. Para pemain dapat melihat RTP dari setiap permainan, baik itu dari aspek permainan itu sendiri maupun dari provider yang menyediakannya. Hal ini sangat membantu para pemain dalam memilih permainan yang sesuai dengan preferensi dan gaya bermain mereka.
Selain itu, situs ini juga menyediakan informasi mengenai RTP live dari berbagai provider judi slot online terpercaya. Dengan begitu, para pemain dapat memilih permainan slot yang memberikan RTP terbaik dan lebih aman dalam bermain. Informasi ini juga membantu para pemain untuk menghindari potensi kerugian dengan bermain pada game slot online dengan RTP rendah .
Situs RTPKANTORBOLA juga memberikan pola dan ulasan mengenai permainan-permainan dengan RTP tertinggi. Para pemain dapat mempelajari strategi dan tips dari para ahli untuk meningkatkan peluang dalam memenangkan permainan. Analisis dan ulasan ini disajikan secara jelas dan mudah dipahami, sehingga dapat diaplikasikan dengan baik oleh para pemain.
Informasi RTP live yang disediakan oleh situs RTPKANTORBOLA juga dapat membantu para pemain dalam mengelola keuangan mereka. Dengan mengetahui RTP dari masing-masing permainan slot , para pemain dapat mengatur taruhan mereka dengan lebih bijak. Hal ini dapat membantu para pemain untuk mengurangi risiko kerugian dan meningkatkan peluang untuk mendapatkan kemenangan yang lebih besar.
Untuk mengakses informasi RTP live dari situs RTPKANTORBOLA, para pemain tidak perlu mendaftar atau membayar biaya apapun. Situs ini dapat diakses secara gratis dan tersedia untuk semua pemain judi online. Dengan begitu, semua orang dapat memanfaatkan informasi yang disediakan oleh situs RTP Kantorbola untuk meningkatkan pengalaman dan peluang mereka dalam bermain judi online.
Demikianlah informasi mengenai RTP live hari ini dari situs RTPKANTORBOLA. Dengan menyediakan informasi yang akurat, terpercaya, dan lengkap, situs ini menjadi sumber informasi yang penting bagi para pemain judi online. Dengan memanfaatkan informasi yang disediakan, para pemain dapat membuat keputusan yang lebih cerdas dan meningkatkan peluang mereka untuk memenangkan permainan. Selamat bermain dan semoga sukses! -
сигналы криптовалют
Почему наши сигналы - ваш идеальный путь:
Наша группа все время в курсе текущих трендов и событий, которые воздействуют на криптовалюты. Это способствует коллективу мгновенно реагировать и предоставлять текущие сигналы.
Наш состав имеет предельным знание анализа и умеет обнаруживать мощные и слабые поля для входа в сделку. Это способствует снижению потерь и способствует для растущей прибыли.
Вместе с командой мы внедряем личные боты для анализа данных для просмотра графиков на любых периодах времени. Это способствует нам достать всю картину рынка.
Перед опубликованием сигнал в нашем канале Telegram мы проводим детальную проверку всех аспектов и подтверждаем возможный длинный или краткий. Это гарантирует надежность и качественность наших подач.
Присоединяйтесь к нам к нашей группе прямо сейчас и достаньте доступ к подтвержденным торговым сигналам, которые содействуют вам получить успеха в финансах на рынке криптовалют!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot -
Итак почему наши тоговые сигналы - ваш наилучший путь:
Наша группа утром и вечером, днём и ночью на волне последних курсов и ситуаций, которые влияют на криптовалюты. Это способствует команде незамедлительно действовать и предоставлять новые трейды.
Наш состав имеет профундным знанием технического анализа и способен выделить мощные и уязвимые аспекты для включения в сделку. Это содействует уменьшению угроз и увеличению прибыли.
Мы применяем собственные боты анализа для изучения графиков на любых интервалах. Это способствует нашим специалистам завоевать понятную картину рынка.
Перед приведением подачи в нашем канале Telegram мы осуществляем внимательную проверку все сторон и подтверждаем допустимая длинный или короткий. Это обеспечивает достоверность и качество наших подач.
Присоединяйтесь к нашей группе прямо сейчас и получите доступ к подтвержденным торговым подачам, которые содействуют вам добиться успеха в финансах на крипторынке!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot -
сигналы онлайн криптовалют
Итак почему наши сигналы на вход - ваш лучший путь:
Наша группа постоянно на волне последних тенденций и событий, которые оказывают влияние на криптовалюты. Это способствует команде сразу отвечать и подавать актуальные трейды.
Наш коллектив имеет предельным знание теханализа и способен обнаруживать мощные и уязвимые аспекты для включения в сделку. Это способствует уменьшению рисков и максимизации прибыли.
Мы применяем личные боты для анализа данных для анализа графиков на любых интервалах. Это помогает нам достать понятную картину рынка.
Перед приведением подача в нашем канале Telegram мы проводим тщательную проверку все сторон и подтверждаем возможный длинный или период короткой торговли. Это обеспечивает предсказуемость и качество наших подач.
Присоединяйтесь к нашей команде к нашему Telegram каналу прямо сейчас и достаньте доступ к подтвержденным торговым сигналам, которые помогут вам вам добиться финансового успеха на рынке криптовалют!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot -
Итак почему наши тоговые сигналы - твой идеальный путь:
Наша команда постоянно на волне последних курсов и ситуаций, которые воздействуют на криптовалюты. Это дает возможность группе незамедлительно отвечать и давать актуальные подачи.
Наш коллектив обладает глубоким пониманием анализа и может обнаруживать сильные и уязвимые стороны для присоединения в сделку. Это способствует снижению потерь и способствует для растущей прибыли.
Мы используем личные боты для анализа данных для анализа графиков на все периодах времени. Это содействует нашим специалистам достать полноценную картину рынка.
Перед подачей сигнал в нашем канале Telegram мы осуществляем внимательную проверку всех аспектов и подтверждаем возможный лонг или краткий. Это обеспечивает достоверность и качество наших подач.
Присоединяйтесь к нашей группе прямо сейчас и получите доступ к подтвержденным торговым сигналам, которые содействуют вам достичь финансового успеха на крипторынке!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot -
сигналы онлайн криптовалют
Почему наши сигналы на вход - ваш наилучший вариант:
Наша группа постоянно в курсе последних тенденций и ситуаций, которые оказывают влияние на криптовалюты. Это дает возможность группе оперативно реагировать и давать новые трейды.
Наш коллектив владеет предельным пониманием анализа и умеет обнаруживать устойчивые и слабые факторы для вступления в сделку. Это способствует уменьшению опасностей и способствует для растущей прибыли.
Мы применяем личные боты для анализа для анализа графиков на всех временных промежутках. Это содействует нам завоевать полноценную картину рынка.
Прежде опубликованием сигнал в нашем Telegram команда осуществляем детальную проверку все фасадов и подтверждаем возможный лонг или короткий. Это подтверждает предсказуемость и качество наших подач.
Присоединяйтесь к нашей команде к нашему каналу прямо сейчас и получите доступ к подтвержденным торговым подачам, которые содействуют вам достичь финансовых результатов на рынке криптовалют!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot -
Итак почему наши тоговые сигналы - ваш идеальный путь:
Наша группа все время на волне текущих трендов и событий, которые воздействуют на криптовалюты. Это дает возможность команде быстро реагировать и предоставлять текущие сигналы.
Наш коллектив имеет предельным пониманием анализа и способен определять сильные и слабые стороны для входа в сделку. Это способствует для снижения опасностей и повышению прибыли.
Вместе с командой мы внедряем собственные боты для анализа данных для анализа графиков на всех временных промежутках. Это помогает нам доставать понятную картину рынка.
Прежде опубликованием сигнала в нашем канале Telegram команда делаем внимательную проверку всех аспектов и подтверждаем возможное период долгой торговли или шорт. Это обеспечивает предсказуемость и качественные показатели наших сигналов.
Присоединяйтесь к нашему каналу к нашему Telegram каналу прямо сейчас и достаньте доступ к подтвержденным торговым сигналам, которые содействуют вам достичь финансового успеха на рынке криптовалют!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot -
сигналы по криптовалюте
Почему наши тоговые сигналы - твой наилучший выбор:
Наша команда все время в курсе современных трендов и ситуаций, которые оказывают влияние на криптовалюты. Это способствует коллективу незамедлительно отвечать и подавать новые сигналы.
Наш коллектив обладает профундным пониманием анализа и способен выделить сильные и незащищенные факторы для включения в сделку. Это способствует для снижения рисков и повышению прибыли.
Мы используем собственные боты анализа для изучения графиков на любых интервалах. Это помогает нам получить всю картину рынка.
Перед приведением подачи в нашем Telegram команда осуществляем педантичную проверку всех фасадов и подтверждаем возможный лонг или короткий. Это обеспечивает надежность и качественные показатели наших сигналов.
Присоединяйтесь к нашей команде к нашей группе прямо сейчас и получите доступ к подтвержденным торговым сигналам, которые помогут вам вам добиться финансового успеха на рынке криптовалют!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot -
криптовалюта сигналы
Почему наши тоговые сигналы - ваш идеальный вариант:
Наша группа утром и вечером, днём и ночью на волне актуальных трендов и событий, которые оказывают влияние на криптовалюты. Это дает возможность группе незамедлительно реагировать и подавать новые трейды.
Наш коллектив имеет глубоким понимание анализа по графику и умеет выявлять мощные и слабые стороны для присоединения в сделку. Это способствует уменьшению рисков и повышению прибыли.
Мы же используем собственные боты для анализа для изучения графиков на всех интервалах. Это помогает нам доставать понятную картину рынка.
Прежде подачей сигнала в нашем канале Telegram мы осуществляем детальную проверку все аспектов и подтверждаем возможный долгий или краткий. Это обеспечивает верность и качественность наших подач.
Присоединяйтесь к нашей команде к нашему каналу прямо сейчас и достаньте доступ к подтвержденным торговым сигналам, которые содействуют вам достигнуть успеха в финансах на крипторынке!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot -
сигналы по криптовалюте
Почему наши сигналы на вход - ваш лучший выбор:
Наша команда 24 часа в сутки в курсе актуальных курсов и событий, которые влияют на криптовалюты. Это позволяет коллективу быстро реагировать и подавать свежие сообщения.
Наш состав владеет глубинным понимание анализа и способен выявлять сильные и незащищенные стороны для присоединения в сделку. Это способствует для снижения рисков и увеличению прибыли.
Мы же применяем собственные боты для анализа данных для просмотра графиков на все периодах времени. Это помогает нашим специалистам получить полную картину рынка.
Перед публикацией подачи в нашем Telegram команда осуществляем внимательную ревизию все аспектов и подтверждаем возможный длинный или короткий. Это гарантирует надежность и качественные характеристики наших сигналов.
Присоединяйтесь к нашему каналу к нашему прямо сейчас и получите доступ к подтвержденным торговым сигналам, которые помогут вам достигнуть финансового успеха на рынке криптовалют!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot -
криптовалюта сигналы
Почему наши тоговые сигналы - ваш идеальный выбор:
Наша группа постоянно в тренде современных направлений и событий, которые оказывают влияние на криптовалюты. Это позволяет коллективу мгновенно отвечать и подавать новые подачи.
Наш состав имеет предельным пониманием теханализа и умеет определять мощные и уязвимые стороны для вступления в сделку. Это содействует минимизации опасностей и повышению прибыли.
Мы же используем собственные боты для анализа для анализа графиков на любых интервалах. Это помогает нашим специалистам достать полноценную картину рынка.
Перед подачей сигнал в нашем Telegram мы проводим детальную проверку все фасадов и подтверждаем возможный долгий или краткий. Это обеспечивает предсказуемость и качество наших подач.
Присоединяйтесь к нашей команде к нашему прямо сейчас и достаньте доступ к подтвержденным торговым подачам, которые содействуют вам достигнуть финансовых результатов на рынке криптовалют!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot -
торговые сигналы криптовалют
Почему наши тоговые сигналы - ваш наилучший путь:
Наша группа постоянно в курсе последних тенденций и событий, которые влияют на криптовалюты. Это способствует команде оперативно реагировать и предоставлять свежие сообщения.
Наш состав обладает профундным знанием теханализа и способен определять устойчивые и уязвимые стороны для входа в сделку. Это способствует снижению угроз и максимизации прибыли.
Мы внедряем собственные боты-анализаторы для просмотра графиков на все временных промежутках. Это помогает нашим специалистам завоевать понятную картину рынка.
Прежде опубликованием подача в нашем Telegram мы делаем детальную проверку все фасадов и подтверждаем возможное лонг или краткий. Это обеспечивает предсказуемость и качество наших сигналов.
Присоединяйтесь к нашей команде к нашему прямо сейчас и получите доступ к подтвержденным торговым сигналам, которые помогут вам вам достичь успеха в финансах на крипторынке!
https://t.me/Investsany_bot -
how to earn reels
JDBslot
JDB slot | The first bonus to rock the slot world
Exclusive event to earn real money and slot game points
JDB demo slot games for free = ?? Lucky Spin Lucky Draw!
How to earn reels free 2000? follow jdb slot games for free
#jdbslot
Demo making money : https://jdb777.com
#jdbslot #slotgamesforfree #howtoearnreels #cashreels
#slotgamepoint #demomakingmoney
Cash reels only at slot games for free
More professional jdb game bonus knowledge
Methods to Earn Rotations Credits Gratis 2000: Your Ultimate Guide to Winning Huge with JDB Gaming machines
Are you ready to begin on an exciting voyage into the planet of web slot games? Look no more, just spin to JDB777 FreeGames, where enthusiasm and substantial wins look forward to you at each turn of the reel. In this thorough manual, we'll show you ways to acquire reels credits costless 2000 and open the stimulating world of JDB slots.
Experience the Excitement of Gaming Games for Free
At JDB777 FreeGames, we provide a extensive variety of captivating slot games that are guaranteed to keep you entertained for hours on end. From timeless fruit machines to immersive themed slots, there's something for each variety of player to enjoy. And the top part? You can play all of our slot games for free and earn real cash prizes!
Uncover Free Cash Reels and Achieve Big
One of the most stimulating features of JDB777 FreeGames is the opportunity to gain reels credit complimentary 2000, which can be exchanged for real cash. Easily sign up for an account, and you'll obtain your costless bonus to start spinning and winning. With our liberal promotions and bonuses, the sky's the ceiling when it comes to your winnings!
Guide Strategies and Points System
To maximize your winnings and open the complete potential of our slot games, it's crucial to grasp the approaches and points system. Our expert guides will take you through everything you have to have to know, from picking the right games to understanding how to earn bonus points and cash prizes.
Distinctive Promotions and Special Offers
As a member of JDB777 FreeGames, you'll have access to exclusive promotions and special offers that are sure to boost your gaming experience. From welcome bonuses to daily rebates, there are plenty of opportunities to boost your winnings and take your gameplay to the next level.
Join Us Today and Commence Winning
Don't miss out on your likelihood to win big with JDB777 FreeGames. Sign up now to declare your free bonus of 2000 credits and commence spinning the reels for your opportunity to win real cash prizes. With our stimulating selection of slot games and generous promotions, the opportunities are endless. Join us today and start winning! -
bet marketing
JDB demo
JDB demo | The easiest bet software to use (jdb games)
JDB bet marketing: The first bonus that players care about
Most popular player bonus: Daily Play 2000 Rewards
Game developers online who are always with you
#jdbdemo
Where to find the best game developer? https://www.jdbgaming.com/
#gamedeveloperonline #betsoftware #betmarketing
#developerbet #betingsoftware #gamedeveloper
Supports hot jdb demo beting software jdb angry bird
JDB slot demo supports various competition plans
Revealing Success with JDB Gaming: Your Ultimate Betting Software Answer
In the world of digital gaming, discovering the appropriate betting software is crucial for prosperity. Meet JDB Gaming – a foremost source of revolutionary gaming answers crafted to improve the player experience and drive earnings for operators. With a focus on easy-to-use interfaces, attractive bonuses, and a diverse array of games, JDB Gaming emerges as a leading choice for both gamers and operators alike.
JDB Demo offers a look into the realm of JDB Gaming, giving players with an chance to undergo the thrill of betting without any hazard. With easy-to-use interfaces and smooth navigation, JDB Demo enables it easy for players to navigate the broad selection of games on offer, from traditional slots to captivating arcade titles.
When it concerns bonuses, JDB Bet Marketing is at the forefront with attractive offers that lure players and hold them coming back for more. From the favored Daily Play 2000 Rewards to unique promotions, JDB Bet Marketing ensures that players are recognized for their faithfulness and dedication.
With so many game developers online, identifying the best can be a intimidating task. However, JDB Gaming distinguishes itself from the crowd with its dedication to perfection and innovation. With over 150 online casino games to pick, JDB Gaming offers something for everyone, whether you're a fan of slots, fish shooting games, arcade titles, card games, or bingo.
At the core of JDB Gaming lies a dedication to supplying the best possible gaming experience for players. With a emphasis on Asian culture and spectacular 3D animations, JDB Gaming stands out as a pioneer in the industry. Whether you're a player looking for excitement or an operator seeking a reliable partner, JDB Gaming has you covered.
API Integration: Seamlessly link with all platforms for ultimate business prospects. Big Data Analysis: Stay ahead of market trends and understand player habits with extensive data analysis. 24/7 Technical Support: Relish peace of mind with skilled and trustworthy technical support available around the clock.
In conclusion, JDB Gaming offers a successful blend of advanced technology, alluring bonuses, and unparalleled support. Whether you're a gamer or an manager, JDB Gaming has everything that you need to thrive in the realm of online gaming. So why wait? Join the JDB Gaming community today and unlock your full potential! -
slot game point
JDBslot
JDB slot | The first bonus to rock the slot world
Exclusive event to earn real money and slot game points
JDB demo slot games for free = ?? Lucky Spin Lucky Draw!
How to earn reels free 2000? follow jdb slot games for free
#jdbslot
Demo making money : https://jdb777.com
#jdbslot #slotgamesforfree #howtoearnreels #cashreels
#slotgamepoint #demomakingmoney
Cash reels only at slot games for free
More professional jdb game bonus knowledge
How to Gain Spins Credit Gratis 2000: Your Greatest Manual to Winning Large with JDB One-armed bandits
Are you you set to begin on an thrilling expedition into the universe of internet slot games? Seek no more, just rotate to JDB777 FreeGames, where thrills and significant wins expect you at every spin of the reel. In this complete guide, we'll present you methods to earn reels credit free 2000 and unlock the exhilarating world of JDB slots.
Undergo the Thrill of Slot Games for Free
At JDB777 FreeGames, we provide a vast selection of captivating slot games that are certain to keep you entertained for hours on end. From classic fruit machines to immersive themed slots, there's something for each variety of player to enjoy. And the finest part? You can play all of our slot games for free and achieve real cash prizes!
Uncover Free Cash Reels and Win Big
One of the most exhilarating features of JDB777 FreeGames is the chance to earn reels credits free 2000, which can be exchanged for real cash. Simply sign up for an account, and you'll acquire your costless bonus to commence spinning and winning. With our liberal promotions and bonuses, the sky's the boundary when it comes to your winnings!
Steer Approaches and Scores System
To increase your winnings and release the complete potential of our slot games, it's essential to grasp the tactics and points system. Our skilled guides will take you through everything you need to know, from choosing out the right games to comprehending how to secure bonus points and cash prizes.
Special Promotions and Specialized Offers
As a member of JDB777 FreeGames, you'll have access to exclusive promotions and special offers that are positive to augment your gaming experience. From welcome bonuses to daily rebates, there are a lot of opportunities to enhance your winnings and take your gameplay to the following level.
Join Us Today and Begin Winning
Don't miss out on your chance to win big with JDB777 FreeGames. Sign up now to claim your gratis bonus of 2000 credits and begin spinning the reels for your chance to win real cash prizes. With our exciting choice of slot games and generous promotions, the possibilities are endless. Join us today and initiate winning! -
JDB demo
JDB demo | The easiest bet software to use (jdb games)
JDB bet marketing: The first bonus that players care about
Most popular player bonus: Daily Play 2000 Rewards
Game developers online who are always with you
#jdbdemo
Where to find the best game developer? https://www.jdbgaming.com/
#gamedeveloperonline #betsoftware #betmarketing
#developerbet #betingsoftware #gamedeveloper
Supports hot jdb demo beting software jdb angry bird
JDB slot demo supports various competition plans
Revealing Achievement with JDB Gaming: Your Paramount Bet Software Answer
In the universe of digital gaming, finding the correct betting software is critical for success. Introducing JDB Gaming – a leading provider of creative gaming solutions tailored to improve the gaming experience and propel earnings for operators. With a focus on user-friendly interfaces, attractive bonuses, and a wide array of games, JDB Gaming emerges as a top choice for both players and operators alike.
JDB Demo offers a glimpse into the world of JDB Gaming, providing players with an chance to experience the thrill of betting without any risk. With easy-to-use interfaces and seamless navigation, JDB Demo allows it simple for players to discover the vast selection of games on offer, from traditional slots to engaging arcade titles.
When it concerns bonuses, JDB Bet Marketing is at the forefront with enticing offers that attract players and keep them coming back for more. From the favored Daily Play 2000 Rewards to unique promotions, JDB Bet Marketing ensures that players are rewarded for their faithfulness and dedication.
With so many game developers online, finding the best can be a challenging task. However, JDB Gaming emerges from the crowd with its dedication to perfection and innovation. With over 150 online casino games to pick, JDB Gaming offers something special for everyone, whether you're a fan of slots, fish shooting games, arcade titles, card games, or bingo.
At the heart of JDB Gaming lies a devotion to providing the best possible gaming experience players. With a concentration on Asian culture and impressive 3D animations, JDB Gaming stands out as a pioneer in the industry. Whether you're a player looking for excitement or an provider in need of a reliable partner, JDB Gaming has you covered.
API Integration: Seamlessly link with all platforms for ultimate business chances. Big Data Analysis: Stay ahead of market trends and understand player habits with extensive data analysis. 24/7 Technical Support: Relish peace of mind with expert and dependable technical support accessible 24/7.
In conclusion, JDB Gaming offers a successful combination of advanced technology, appealing bonuses, and unparalleled support. Whether you're a player or an operator, JDB Gaming has all the things you need to excel in the arena of online gaming. So why wait? Join the JDB Gaming community today and unlock your full potential! -
betvisa vietnam
Intro
betvisa vietnam
Betvisa vietnam | Grand Prize Breakout!
Betway Highlights | 499,000 Extra Bonus on betvisa com!
Cockfight to win up to 3,888,000 on betvisa game
Daily Deposit, Sunday Bonus on betvisa app 888,000!
#betvisavietnam
200% Bonus on instant deposits—start your win streak!
200% welcome bonus! Slots and Fishing Games
https://www.betvisa.com/
#betvisavietnam #betvisagame #betvisaapp
#betvisacom #betvisacasinoapp
Birthday bash? Up to 1,800,000 in prizes! Enjoy!
Friday Shopping Frenzy betvisa vietnam 100,000 VND!
Betvisa Casino App Daily Login 12% Bonus Up to 1,500,000VND!
Khám phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Dịch vụ BetVisa, một trong những nền tảng hàng đầu tại châu Á, được thành lập vào năm 2017 và thao tác dưới giấy phép của Curacao, đã có hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với lời hứa đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa sớm trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không dừng lại ở việc cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Nhờ vào tính cam kết về kinh nghiệm cá cược tốt hơn nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên nghiệp, BetVisa tự hào là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy gắn bó ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu cuộc hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều không thể thiếu được. -
demo cash
JDB online
JDB online | 2024 best online slot game demo cash
How to earn reels? jdb online accumulate spin get bonus
Hot demo fun: Quick earn bonus for ranking demo
JDB demo for win? JDB reward can be exchanged to real cash
#jdbonline
777 sign up and get free 2,000 cash: https://www.jdb777.io/
#jdbonline #democash #demofun #777signup
#rankingdemo #demoforwin
2000 cash: Enter email to verify, enter verify, claim jdb bonus
Play with JDB games an online platform in every countries.
Enjoy the Delight of Gaming!
Free to Join, Free to Play.
Sign Up and Acquire a Bonus!
JOIN NOW AND GET 2000?
We dare you to obtain a trial entertaining welcome bonus for all new members! Plus, there are other exclusive promotions waiting for you!
Discover more
JDB - JOIN FOR FREE
Easy to play, real profit
Participate in JDB today and indulge in fantastic games without any investment! With a wide array of free games, you can delight in pure entertainment at any time.
Quick play, quick join
Value your time and opt for JDB’s swift games. Just a few easy steps and you're set for an amazing gaming experience!
Join now and make money
Experience JDB: Instant play with no investment and the opportunity to win cash. Designed for effortless and lucrative play.
Plunge into the World of Online Gaming Adventure with Fun Slots Online!
Are you ready to feel the sensation of online gaming like never before? Scour no further than Fun Slots Online, your ultimate stop for heart-pounding gameplay, endless entertainment, and stimulating winning opportunities!
At Fun Slots Online, we boast ourselves on giving a wide array of engaging games designed to keep you immersed and amused for hours on end. From classic slot machines to innovative new releases, there's something for all to enjoy. Plus, with our user-friendly interface and smooth gameplay experience, you'll have no trouble plunging straight into the action and savoring every moment.
But that's not all – we also give a range of exclusive promotions and bonuses to compensate our loyal players. From initial bonuses for new members to special rewards for our top players, there's always something thrilling happening at Fun Slots Online. And with our guarded payment system and 24-hour customer support, you can experience peace of mind conscious that you're in good hands every step of the way.
So why wait? Register with Fun Slots Online today and start your adventure towards breath-taking victories and jaw-dropping prizes. Whether you're a seasoned gamer or just starting out, there's never been a better time to be part of the fun and thrills at Fun Slots Online. Sign up now and let the games begin! -
Intro
betvisa vietnam
Betvisa vietnam | Grand Prize Breakout!
Betway Highlights | 499,000 Extra Bonus on betvisa com!
Cockfight to win up to 3,888,000 on betvisa game
Daily Deposit, Sunday Bonus on betvisa app 888,000!
#betvisavietnam
200% Bonus on instant deposits—start your win streak!
200% welcome bonus! Slots and Fishing Games
https://www.betvisa.com/
#betvisavietnam #betvisagame #betvisaapp
#betvisacom #betvisacasinoapp
Birthday bash? Up to 1,800,000 in prizes! Enjoy!
Friday Shopping Frenzy betvisa vietnam 100,000 VND!
Betvisa Casino App Daily Login 12% Bonus Up to 1,500,000VND!
Khám phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
BetVisa, một trong những công ty hàng đầu tại châu Á, được thành lập vào năm 2017 và thao tác dưới bằng của Curacao, đã có hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với lời hứa đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không dừng lại ở việc cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 cơ hội miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều cách thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Nhờ vào lời hứa về kinh nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên môn, BetVisa hoàn toàn tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy đăng ký ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu dấu mốc của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu. -
Intro
betvisa bangladesh
Betvisa bangladesh | Super Cricket Carnival with Betvisa!
IPL Cricket Mania | Kick off Super Cricket Carnival with bet visa.com
IPL Season | Exclusive 1,50,00,000 only at Betvisa Bangladesh!
Crash Games Heroes | Climb to the top of the 1,00,00,000 bonus pool!
#betvisabangladesh
Preview IPL T20 | Follow Betvisa BD on Facebook, Instagram for awards!
betvisa affiliate Dream Maltese Tour | Sign up now to win the ultimate prize!
https://www.bvthethao.com/
#betvisabangladesh #betvisabd #betvisaaffiliate
#betvisaaffiliatesignup #betvisa.com
Nhờ vào tính cam kết về trải nghiệm cá cược tinh vi nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng kỹ năng chuyên môn, BetVisa tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai nhiệt huyết trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy gắn bó ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều không thể thiếu được.
Khám phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Hệ thống BetVisa, một trong những nền tảng hàng đầu tại châu Á, được thành lập vào năm 2017 và thao tác dưới phê chuẩn của Curacao, đã thu hút hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với lời hứa đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược đảm bảo và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa sớm trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 phần quà miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn. -
Intro
betvisa bangladesh
Betvisa bangladesh | Super Cricket Carnival with Betvisa!
IPL Cricket Mania | Kick off Super Cricket Carnival with bet visa.com
IPL Season | Exclusive 1,50,00,000 only at Betvisa Bangladesh!
Crash Games Heroes | Climb to the top of the 1,00,00,000 bonus pool!
#betvisabangladesh
Preview IPL T20 | Follow Betvisa BD on Facebook, Instagram for awards!
betvisa affiliate Dream Maltese Tour | Sign up now to win the ultimate prize!
https://www.bvthethao.com/
#betvisabangladesh #betvisabd #betvisaaffiliate
#betvisaaffiliatesignup #betvisa.com
Do sự cam kết về trải nghiệm cá cược tốt hơn nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng kỹ năng chuyên môn, BetVisa tự hào là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai nhiệt tình trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy đăng ký ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu cuộc hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều không thể thiếu được.
Tìm hiểu Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Hệ thống BetVisa, một trong những công ty hàng đầu tại châu Á, được thành lập vào năm 2017 và thao tác dưới bằng của Curacao, đã có hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa sớm trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 phần quà miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn. -
Intro
betvisa philippines
Betvisa philippines | The Filipino Carnival, Spinning for Treasures!
Betvisa Philippines Surprises | Spin daily and win ₱8,888 Grand Prize!
Register for a chance to win ₱8,888 Bonus Tickets! Explore Betvisa.com!
Wild All Over Grab 58% YB Bonus at Betvisa Casino! Take the challenge!
#betvisaphilippines
Get 88 on your first 50 Experience Betvisa Online's Bonus Gift!
Weekend Instant Daily Recharge at betvisa.com
https://www.88betvisa.com/
#betvisaphilippines #betvisaonline #betvisacasino
#betvisacom #betvisa.com
Cổng chơi - Điểm Đến Tuyệt Vời Cho Người Chơi Trực Tuyến
Khám Phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Dịch vụ được thiết lập vào năm 2017 và hoạt động theo giấy phép trò chơi Curacao với hơn 2 triệu người dùng. Với cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược chắc chắn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
Nền tảng cá cược không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang lại cho người chơi những phần thưởng hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Cổng chơi hỗ trợ nhiều cách thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, kết hợp với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang lại cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Với sự cam kết về trải nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chất lượng, BetVisa tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy đăng ký ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu! -
Intro
betvisa philippines
Betvisa philippines | The Filipino Carnival, Spinning for Treasures!
Betvisa Philippines Surprises | Spin daily and win ₱8,888 Grand Prize!
Register for a chance to win ₱8,888 Bonus Tickets! Explore Betvisa.com!
Wild All Over Grab 58% YB Bonus at Betvisa Casino! Take the challenge!
#betvisaphilippines
Get 88 on your first 50 Experience Betvisa Online's Bonus Gift!
Weekend Instant Daily Recharge at betvisa.com
https://www.88betvisa.com/
#betvisaphilippines #betvisaonline #betvisacasino
#betvisacom #betvisa.com
Dịch vụ - Điểm Đến Tuyệt Vời Cho Người Chơi Trực Tuyến
Khám Phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Cổng chơi được thiết lập vào năm 2017 và vận hành theo chứng chỉ trò chơi Curacao với hơn 2 triệu người dùng. Với tính cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược chắc chắn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
Dịch vụ không chỉ đưa ra các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang lại cho người chơi những chính sách ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ nhận tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Dịch vụ hỗ trợ nhiều cách thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, kết hợp với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang lại cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Với sự cam kết về trải nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng tận tâm, BetVisa tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy đăng ký ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu! -
現代社會,快遞已成為大眾化的服務業,吸引了許多人的注意和參與。 與傳統夜店、酒吧不同,外帶提供了更私密、便捷的服務方式,讓人們有機會在家中或特定地點與美女共度美好時光。
多樣化選擇
從台灣到日本,馬來西亞到越南,外送業提供了多樣化的女孩選擇,以滿足不同人群的需求和喜好。 無論你喜歡什麼類型的女孩,你都可以在外賣行業找到合適的女孩。
不同的價格水平
價格範圍從實惠到豪華。 無論您的預算如何,您都可以找到適合您需求的女孩,享受優質的服務並度過愉快的時光。
快遞業高度重視安全和隱私保護,提供多種安全措施和保障,讓客戶放心使用服務,無需擔心個人資訊外洩或安全問題。
如果你想成為一名經驗豐富的外包司機,外包產業也將為你提供廣泛的選擇和專屬服務。 只需按照步驟操作,您就可以輕鬆享受快遞行業帶來的樂趣和便利。
蓬勃發展的快遞產業為人們提供了一種新的娛樂休閒方式,讓人們在忙碌的生活中得到放鬆,享受美好時光。 -
現代社會,快遞已成為大眾化的服務業,吸引了許多人的注意和參與。 與傳統夜店、酒吧不同,外帶提供了更私密、便捷的服務方式,讓人們有機會在家中或特定地點與美女共度美好時光。
多樣化選擇
從台灣到日本,馬來西亞到越南,外送業提供了多樣化的女孩選擇,以滿足不同人群的需求和喜好。 無論你喜歡什麼類型的女孩,你都可以在外賣行業找到合適的女孩。
不同的價格水平
價格範圍從實惠到豪華。 無論您的預算如何,您都可以找到適合您需求的女孩,享受優質的服務並度過愉快的時光。
快遞業高度重視安全和隱私保護,提供多種安全措施和保障,讓客戶放心使用服務,無需擔心個人資訊外洩或安全問題。
如果你想成為一名經驗豐富的外包司機,外包產業也將為你提供廣泛的選擇和專屬服務。 只需按照步驟操作,您就可以輕鬆享受快遞行業帶來的樂趣和便利。
蓬勃發展的快遞產業為人們提供了一種新的娛樂休閒方式,讓人們在忙碌的生活中得到放鬆,享受美好時光。 -
rg777
App cá độ:Hướng dẫn tải app cá cược uy tín RG777 đúng cách
Bạn có biết? Tải app cá độ đúng cách sẽ giúp tiết kiệm thời gian đăng nhập, tăng tính an toàn và bảo mật cho tài khoản của bạn! Vậy đâu là cách để tải một app cá cược uy tín dễ dàng và chính xác? Xem ngay bài viết này nếu bạn muốn chơi cá cược trực tuyến an toàn!
tải về ngay lập tức
RG777 - Nhà Cái Uy Tín Hàng Đầu Việt Nam
Link tải app cá độ nét nhất 2023:RG777
Để đảm bảo việc tải ứng dụng cá cược của bạn an toàn và nhanh chóng, người chơi có thể sử dụng đường link sau.
tải về ngay lập tức -
App cá độ:Hướng dẫn tải app cá cược uy tín RG777 đúng cách
Bạn có biết? Tải app cá độ đúng cách sẽ giúp tiết kiệm thời gian đăng nhập, tăng tính an toàn và bảo mật cho tài khoản của bạn! Vậy đâu là cách để tải một app cá cược uy tín dễ dàng và chính xác? Xem ngay bài viết này nếu bạn muốn chơi cá cược trực tuyến an toàn!
tải về ngay lập tức
RG777 - Nhà Cái Uy Tín Hàng Đầu Việt Nam
Link tải app cá độ nét nhất 2023:RG777
Để đảm bảo việc tải ứng dụng cá cược của bạn an toàn và nhanh chóng, người chơi có thể sử dụng đường link sau.
tải về ngay lập tức -
JDB demo
JDB demo | The easiest bet software to use (jdb games)
JDB bet marketing: The first bonus that players care about
Most popular player bonus: Daily Play 2000 Rewards
Game developers online who are always with you
#jdbdemo
Where to find the best game developer? https://www.jdbgaming.com/
#gamedeveloperonline #betsoftware #betmarketing
#developerbet #betingsoftware #gamedeveloper
Supports hot jdb demo beting software jdb angry bird
JDB slot demo supports various competition plans
Unlocking Achievement with JDB Gaming: Your Paramount Betting Software Solution
In the universe of digital gaming, finding the correct bet software is critical for success. Meet JDB Gaming – a foremost source of creative gaming strategies crafted to improve the gaming experience and propel profits for operators. With a emphasis on intuitive interfaces, enticing bonuses, and a varied selection of games, JDB Gaming stands out as a top choice for both players and operators alike.
JDB Demo presents a look into the realm of JDB Gaming, giving players with an chance to undergo the thrill of betting without any hazard. With simple interfaces and effortless navigation, JDB Demo makes it easy for players to navigate the broad selection of games available, from classic slots to engaging arcade titles.
When it concerns bonuses, JDB Bet Marketing is at the forefront with enticing offers that draw players and maintain them returning for more. From the favored Daily Play 2000 Rewards to special promotions, JDB Bet Marketing makes sure that players are rewarded for their allegiance and dedication.
With so many game developers online, locating the best can be a challenging task. However, JDB Gaming stands out from the pack with its devotion to excellence and innovation. With over 150 online casino games to choose from, JDB Gaming offers something special for all, whether you're a fan of slots, fish shooting games, arcade titles, card games, or bingo.
At the core of JDB Gaming lies a commitment to offering the finest possible gaming experience for players. With a focus on Asian culture and stunning 3D animations, JDB Gaming stands out as a front runner in the industry. Whether you're a player in search of excitement or an operator in need of a dependable partner, JDB Gaming has you covered.
API Integration: Seamlessly link with all platforms for maximum business opportunities. Big Data Analysis: Stay ahead of market trends and grasp player habits with comprehensive data analysis. 24/7 Technical Support: Experience peace of mind with professional and reliable technical support on hand around the clock.
In conclusion, JDB Gaming offers a successful mix of cutting-edge technology, alluring bonuses, and unequaled support. Whether you're a gamer or an provider, JDB Gaming has everything you need to thrive in the realm of online gaming. So why wait? Join the JDB Gaming family today and unleash your full potential! -
betvisa game
Intro
betvisa vietnam
Betvisa vietnam | Grand Prize Breakout!
Betway Highlights | 499,000 Extra Bonus on betvisa com!
Cockfight to win up to 3,888,000 on betvisa game
Daily Deposit, Sunday Bonus on betvisa app 888,000!
#betvisavietnam
200% Bonus on instant deposits—start your win streak!
200% welcome bonus! Slots and Fishing Games
https://www.betvisa.com/
#betvisavietnam #betvisagame #betvisaapp
#betvisacom #betvisacasinoapp
Birthday bash? Up to 1,800,000 in prizes! Enjoy!
Friday Shopping Frenzy betvisa vietnam 100,000 VND!
Betvisa Casino App Daily Login 12% Bonus Up to 1,500,000VND!
Khám phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Hệ thống BetVisa, một trong những công ty trò chơi hàng đầu tại châu Á, ra đời vào năm 2017 và hoạt động dưới phê chuẩn của Curacao, đã thu hút hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với lời hứa đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược đảm bảo và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 phần quà miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Nhờ vào sự cam kết về kinh nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên nghiệp, BetVisa tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai nhiệt tình trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy ghi danh ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều không thể thiếu được. -
game developer online
JDB demo
JDB demo | The easiest bet software to use (jdb games)
JDB bet marketing: The first bonus that players care about
Most popular player bonus: Daily Play 2000 Rewards
Game developers online who are always with you
#jdbdemo
Where to find the best game developer? https://www.jdbgaming.com/
#gamedeveloperonline #betsoftware #betmarketing
#developerbet #betingsoftware #gamedeveloper
Supports hot jdb demo beting software jdb angry bird
JDB slot demo supports various competition plans
Opening Achievement with JDB Gaming: Your Supreme Betting Software Answer
In the universe of internet gaming, locating the appropriate betting software is vital for achievement. Meet JDB Gaming – a premier source of revolutionary gaming solutions designed to enhance the gaming experience and boost earnings for operators. With a concentration on intuitive interfaces, attractive bonuses, and a diverse array of games, JDB Gaming emerges as a top choice for both players and operators alike.
JDB Demo offers a peek into the realm of JDB Gaming, offering players with an chance to feel the thrill of betting without any risk. With easy-to-use interfaces and seamless navigation, JDB Demo makes it straightforward for players to navigate the vast selection of games on offer, from traditional slots to engaging arcade titles.
When it comes to bonuses, JDB Bet Marketing is at the forefront with appealing offers that draw players and maintain them coming back for more. From the popular Daily Play 2000 Rewards to special promotions, JDB Bet Marketing guarantees that players are recognized for their faithfulness and dedication.
With so numerous game developers online, finding the best can be a challenging task. However, JDB Gaming distinguishes itself from the masses with its dedication to perfection and innovation. With over 150 online casino games to pick, JDB Gaming offers a bit for everyone, whether you're a fan of slots, fish shooting games, arcade titles, card games, or bingo.
At the core of JDB Gaming lies a commitment to offering the greatest possible gaming experience players. With a focus on Asian culture and spectacular 3D animations, JDB Gaming stands out as a pioneer in the industry. Whether you're a gamer in search of excitement or an provider in need of a dependable partner, JDB Gaming has you covered.
API Integration: Seamlessly integrate with all platforms for maximum business chances. Big Data Analysis: Keep ahead of market trends and grasp player actions with comprehensive data analysis. 24/7 Technical Support: Relish peace of mind with skilled and trustworthy technical support accessible around the clock.
In conclusion, JDB Gaming presents a successful blend of cutting-edge technology, alluring bonuses, and unmatched support. Whether you're a gamer or an manager, JDB Gaming has everything that you need to excel in the arena of online gaming. So why wait? Join the JDB Gaming family today and unleash your full potential! -
Intro
betvisa vietnam
Betvisa vietnam | Grand Prize Breakout!
Betway Highlights | 499,000 Extra Bonus on betvisa com!
Cockfight to win up to 3,888,000 on betvisa game
Daily Deposit, Sunday Bonus on betvisa app 888,000!
#betvisavietnam
200% Bonus on instant deposits—start your win streak!
200% welcome bonus! Slots and Fishing Games
https://www.betvisa.com/
#betvisavietnam #betvisagame #betvisaapp
#betvisacom #betvisacasinoapp
Birthday bash? Up to 1,800,000 in prizes! Enjoy!
Friday Shopping Frenzy betvisa vietnam 100,000 VND!
Betvisa Casino App Daily Login 12% Bonus Up to 1,500,000VND!
Tìm hiểu Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
BetVisa Vietnam, một trong những công ty trò chơi hàng đầu tại châu Á, được thành lập vào năm 2017 và hoạt động dưới giấy phép của Curacao, đã có hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa sớm trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều hình thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Vì sự cam kết về trải thảo cá cược tốt hơn nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng kỹ năng chuyên môn, BetVisa tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai nhiệt huyết trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy gắn bó ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu dấu mốc của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều không thể thiếu được. -
Intro
betvisa bangladesh
Betvisa bangladesh | Super Cricket Carnival with Betvisa!
IPL Cricket Mania | Kick off Super Cricket Carnival with bet visa.com
IPL Season | Exclusive 1,50,00,000 only at Betvisa Bangladesh!
Crash Games Heroes | Climb to the top of the 1,00,00,000 bonus pool!
#betvisabangladesh
Preview IPL T20 | Follow Betvisa BD on Facebook, Instagram for awards!
betvisa affiliate Dream Maltese Tour | Sign up now to win the ultimate prize!
https://www.bvthethao.com/
#betvisabangladesh #betvisabd #betvisaaffiliate
#betvisaaffiliatesignup #betvisa.com
Do tính cam kết về trải nghiệm thú vị cá cược tinh vi nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên trách, BetVisa hoàn toàn tự hào là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy gắn bó ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu cuộc hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu.
Tìm hiểu Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Hệ thống BetVisa, một trong những công ty hàng đầu tại châu Á, ra đời vào năm 2017 và thao tác dưới giấy phép của Curacao, đã thu hút hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với lời hứa đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược đảm bảo và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa sớm trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn. -
Intro
betvisa bangladesh
Betvisa bangladesh | Super Cricket Carnival with Betvisa!
IPL Cricket Mania | Kick off Super Cricket Carnival with bet visa.com
IPL Season | Exclusive 1,50,00,000 only at Betvisa Bangladesh!
Crash Games Heroes | Climb to the top of the 1,00,00,000 bonus pool!
#betvisabangladesh
Preview IPL T20 | Follow Betvisa BD on Facebook, Instagram for awards!
betvisa affiliate Dream Maltese Tour | Sign up now to win the ultimate prize!
https://www.bvthethao.com/
#betvisabangladesh #betvisabd #betvisaaffiliate
#betvisaaffiliatesignup #betvisa.com
Vì lời hứa về kinh nghiệm cá cược tốt hơn nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên nghiệp, BetVisa tự hào là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai phấn khích trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy đăng ký ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu chuyến đi của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu.
Khám phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
BetVisa Vietnam, một trong những nền tảng hàng đầu tại châu Á, được thành lập vào năm 2017 và hoạt động dưới bằng của Curacao, đã đưa vào hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với lời hứa đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không dừng lại ở việc cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 phần quà miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều cách thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn. -
slot games for free
JDBslot
JDB slot | The first bonus to rock the slot world
Exclusive event to earn real money and slot game points
JDB demo slot games for free = ?? Lucky Spin Lucky Draw!
How to earn reels free 2000? follow jdb slot games for free
#jdbslot
Demo making money : https://jdb777.com
#jdbslot #slotgamesforfree #howtoearnreels #cashreels
#slotgamepoint #demomakingmoney
Cash reels only at slot games for free
More professional jdb game bonus knowledge
Ways to Earn Spins Points Costless 2000: Your Ultimate Guide to Victorious Large with JDB One-armed bandits
Are you you prepared to start on an thrilling adventure into the planet of online slot games? Search no more, just spin to JDB777 FreeGames, where enthusiasm and substantial wins await you at every rotation of the reel. In this comprehensive guide, we'll reveal you how to secure reels points free 2000 and uncover the exhilarating world of JDB slots.
Undergo the Thrill of Slot Games for Free
At JDB777 FreeGames, we provide a vast variety of captivating slot games that are positive to keep you entertained for hours on end. From classic fruit machines to immersive themed slots, there's something for every sort of player to enjoy. And the finest part? You can play all of our slot games for free and earn real cash prizes!
Open Free Cash Reels and Succeed Big
One of the most thrilling features of JDB777 FreeGames is the opportunity to earn reels credits gratis 2000, which can be exchanged for real cash. Just sign up for an account, and you'll obtain your complimentary bonus to initiate spinning and winning. With our generous promotions and bonuses, the sky's the restriction when it comes to your winnings!
Navigate Tactics and Scores System
To optimize your winnings and open the complete potential of our slot games, it's crucial to understand the tactics and points system. Our expert guides will take you through everything you require to know, from choosing out the right games to grasping how to gain bonus points and cash prizes.
Exclusive Promotions and Special Offers
As a member of JDB777 FreeGames, you'll have access to exclusive promotions and special offers that are positive to augment your gaming experience. From welcome bonuses to daily rebates, there are lots of opportunities to boost your winnings and take your gameplay to the subsequent level.
Join Us Today and Start Winning
Don't miss out on your chance to win big with JDB777 FreeGames. Sign up now to declare your gratis bonus of 2000 credits and commence spinning the reels for your possibility to win real cash prizes. With our thrilling selection of slot games and generous promotions, the prospects are endless. Join us today and begin winning! -
JDBslot
JDB slot | The first bonus to rock the slot world
Exclusive event to earn real money and slot game points
JDB demo slot games for free = ?? Lucky Spin Lucky Draw!
How to earn reels free 2000? follow jdb slot games for free
#jdbslot
Demo making money : https://jdb777.com
#jdbslot #slotgamesforfree #howtoearnreels #cashreels
#slotgamepoint #demomakingmoney
Cash reels only at slot games for free
More professional jdb game bonus knowledge
How to Secure Spins Credits Complimentary 2000: Your Supreme Guide to Victorious Big with JDB Machines
Are you ready to start on an thrilling voyage into the world of internet slot games? Hunt no more, only twist to JDB777 FreeGames, where excitement and substantial wins expect you at every single turn of the reel. In this all-encompassing manual, we'll present you ways to earn reels points free 2000 and open the stimulating world of JDB slots.
Undergo the Excitement of Slot Games for Free
At JDB777 FreeGames, we provide a extensive selection of captivating slot games that are guaranteed to keep you entertained for hours on end. From classic fruit machines to immersive themed slots, there's something for every kind of player to enjoy. And the finest part? You can play all of our slot games for free and win real cash prizes!
Uncover Free Cash Reels and Win Big
One of the most exhilarating features of JDB777 FreeGames is the option to acquire reels points costless 2000, which can be exchanged for real cash. Just sign up for an account, and you'll acquire your costless bonus to start spinning and winning. With our plentiful promotions and bonuses, the sky's the boundary when it comes to your winnings!
Navigate Tactics and Points System
To optimize your winnings and release the full potential of our slot games, it's essential to apprehend the strategies and points system. Our skilled guides will take you through everything you require to know, from picking the right games to grasping how to gain bonus points and cash prizes.
Exclusive Promotions and Specific Offers
As a member of JDB777 FreeGames, you'll have access to exclusive promotions and special offers that are positive to augment your gaming experience. From welcome bonuses to daily rebates, there are lots of opportunities to enhance your winnings and take your gameplay to the next level.
Join Us Today and Begin Winning
Don't miss out on your possibility to win big with JDB777 FreeGames. Sign up now to assert your costless bonus of 2000 credits and commence spinning the reels for your possibility to win real cash prizes. With our stimulating selection of slot games and generous promotions, the possibilities are endless. Join us today and begin winning! -
betvisa online
Intro
betvisa philippines
Betvisa philippines | The Filipino Carnival, Spinning for Treasures!
Betvisa Philippines Surprises | Spin daily and win ₱8,888 Grand Prize!
Register for a chance to win ₱8,888 Bonus Tickets! Explore Betvisa.com!
Wild All Over Grab 58% YB Bonus at Betvisa Casino! Take the challenge!
#betvisaphilippines
Get 88 on your first 50 Experience Betvisa Online's Bonus Gift!
Weekend Instant Daily Recharge at betvisa.com
https://www.88betvisa.com/
#betvisaphilippines #betvisaonline #betvisacasino
#betvisacom #betvisa.com
Dịch vụ - Điểm Đến Tuyệt Vời Cho Người Chơi Trực Tuyến
Khám Phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Dịch vụ được tạo ra vào năm 2017 và vận hành theo giấy phép trò chơi Curacao với hơn 2 triệu người dùng. Với tính cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
Nền tảng cá cược không chỉ đưa ra các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang lại cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Nền tảng cá cược hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, bên cạnh các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có chương trình ưu đãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang lại cho người chơi thời cơ thắng lớn.
Với lời hứa về trải nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng tận tâm, BetVisa tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy đăng ký ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu! -
Intro
betvisa philippines
Betvisa philippines | The Filipino Carnival, Spinning for Treasures!
Betvisa Philippines Surprises | Spin daily and win ₱8,888 Grand Prize!
Register for a chance to win ₱8,888 Bonus Tickets! Explore Betvisa.com!
Wild All Over Grab 58% YB Bonus at Betvisa Casino! Take the challenge!
#betvisaphilippines
Get 88 on your first 50 Experience Betvisa Online's Bonus Gift!
Weekend Instant Daily Recharge at betvisa.com
https://www.88betvisa.com/
#betvisaphilippines #betvisaonline #betvisacasino
#betvisacom #betvisa.com
Dịch vụ - Điểm Đến Tuyệt Vời Cho Người Chơi Trực Tuyến
Khám Phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Dịch vụ được sáng lập vào năm 2017 và tiến hành theo bằng trò chơi Curacao với hơn 2 triệu người dùng. Với tính cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
Dịch vụ không chỉ đưa ra các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang lại cho người chơi những phần thưởng hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ nhận tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Cổng chơi hỗ trợ nhiều hình thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang lại cho người chơi thời cơ thắng lớn.
Với lời hứa về trải nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng tận tâm, BetVisa tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy đăng ký ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu! -
betvisa online casino
Intro
betvisa india
Betvisa india | IPL 2024 Heat Wave
IPL 2024 Big bets, big prizes With Betvisa India
Exclusive for Sports Fans Betvisa Online Casino 50% Welcome Bonus
Crash Game Supreme Compete for 1,00,00,000 pot Betvisa.com
#betvisaindia
Accurate Predictions IPL T20 Tournament, Winner Takes All!
More than just a game | Betvisa dreams invites you to fly to malta
https://www.b3tvisapro.com/
#betvisaindia #betvisalogin #betvisaonlinecasino
#betvisa.com #betvisaapp
D?ch v? - Di?m D?n Tuy?t V?i Cho Ngu?i Choi Tr?c Tuy?n
Kham Pha Th? Gi?i Ca Cu?c Tr?c Tuy?n v?i BetVisa!
BetVisa du?c t?o ra vao nam 2017 va ho?t d?ng theo gi?y phep tro choi Curacao v?i hon 2 tri?u ngu?i dung. V?i cam k?t dem d?n tr?i nghi?m ca cu?c dang tin c?y va tin c?y nh?t, BetVisa nhanh chong tr? thanh l?a ch?n hang d?u c?a ngu?i choi tr?c tuy?n.
BetVisa khong ch? dua ra cac tro choi phong phu nhu x? s?, song b?c tr?c ti?p, th? thao tr?c ti?p va th? thao di?n t?, ma con mang l?i cho ngu?i choi nh?ng ph?n thu?ng h?p d?n. Thanh vien m?i dang ky s? du?c t?ng ngay 5 vong quay mi?n phi va co co h?i gianh gi?i thu?ng l?n.
D?ch v? h? tr? nhi?u hinh th?c thanh toan linh ho?t nhu Betvisa Vietnam, k?t h?p v?i cac uu dai d?c quy?n nhu thu?ng chao m?ng len d?n 200%. Ben c?nh do, hang tu?n con co cac chuong trinh khuy?n mai d?c dao nhu chuong trinh gi?i thu?ng Sinh Nh?t va Ch? Nh?t Mua S?m Dien Cu?ng, mang l?i cho ngu?i choi co h?i th?ng l?n.
V?i s? cam k?t v? tr?i nghi?m ca cu?c t?t nh?t va d?ch v? khach hang t?n tam, BetVisa t? tin la di?m d?n ly tu?ng cho nh?ng ai dam me tro choi tr?c tuy?n. Hay dang ky ngay hom nay va b?t d?u hanh trinh c?a b?n t?i BetVisa - noi ni?m vui va may m?n chinh la di?u t?t y?u! -
JDB demo
JDB demo | The easiest bet software to use (jdb games)
JDB bet marketing: The first bonus that players care about
Most popular player bonus: Daily Play 2000 Rewards
Game developers online who are always with you
#jdbdemo
Where to find the best game developer? https://www.jdbgaming.com/
#gamedeveloperonline #betsoftware #betmarketing
#developerbet #betingsoftware #gamedeveloper
Supports hot jdb demo beting software jdb angry bird
JDB slot demo supports various competition plans
Revealing Success with JDB Gaming: Your Supreme Betting Software Resolution
In the realm of internet gaming, finding the right betting software is vital for success. Meet JDB Gaming – a premier provider of innovative gaming strategies tailored to boost the player experience and propel revenue for operators. With a emphasis on user-friendly interfaces, enticing bonuses, and a diverse selection of games, JDB Gaming shines as a top choice for both gamers and operators alike.
JDB Demo presents a peek into the realm of JDB Gaming, giving players with an chance to undergo the thrill of betting without any risk. With user-friendly interfaces and seamless navigation, JDB Demo makes it straightforward for players to navigate the extensive selection of games available, from traditional slots to engaging arcade titles.
When it regards bonuses, JDB Bet Marketing leads with attractive offers that lure players and hold them returning for more. From the favored Daily Play 2000 Rewards to special promotions, JDB Bet Marketing guarantees that players are recognized for their loyalty and dedication.
With so several game developers online, locating the best can be a intimidating task. However, JDB Gaming emerges from the crowd with its commitment to excellence and innovation. With over 150 online casino games to select, JDB Gaming offers a bit for every player, whether you're a fan of slots, fish shooting games, arcade titles, card games, or bingo.
At the center of JDB Gaming lies a devotion to providing the best possible gaming experience for players. With a concentration on Asian culture and impressive 3D animations, JDB Gaming stands out as a pioneer in the industry. Whether you're a gamer seeking excitement or an provider looking for a trustworthy partner, JDB Gaming has you covered.
API Integration: Smoothly integrate with all platforms for optimal business chances. Big Data Analysis: Keep ahead of market trends and understand player behavior with thorough data analysis. 24/7 Technical Support: Relish peace of mind with skilled and trustworthy technical support accessible around the clock.
In conclusion, JDB Gaming provides a victorious blend of state-of-the-art technology, enticing bonuses, and unparalleled support. Whether you're a gamer or an manager, JDB Gaming has everything that you need to thrive in the world of online gaming. So why wait? Join the JDB Gaming group today and unleash your full potential! -
game developer online
JDB demo
JDB demo | The easiest bet software to use (jdb games)
JDB bet marketing: The first bonus that players care about
Most popular player bonus: Daily Play 2000 Rewards
Game developers online who are always with you
#jdbdemo
Where to find the best game developer? https://www.jdbgaming.com/
#gamedeveloperonline #betsoftware #betmarketing
#developerbet #betingsoftware #gamedeveloper
Supports hot jdb demo beting software jdb angry bird
JDB slot demo supports various competition plans
Opening Achievement with JDB Gaming: Your Supreme Betting Software Resolution
In the world of digital gaming, finding the appropriate betting software is vital for success. Introducing JDB Gaming – a leading provider of creative gaming solutions crafted to improve the player experience and boost earnings for operators. With a concentration on intuitive interfaces, enticing bonuses, and a varied selection of games, JDB Gaming emerges as a leading choice for both players and operators alike.
JDB Demo offers a look into the world of JDB Gaming, providing players with an opportunity to undergo the thrill of betting without any hazard. With simple interfaces and seamless navigation, JDB Demo enables it easy for players to discover the extensive selection of games available, from classic slots to captivating arcade titles.
When it concerns bonuses, JDB Bet Marketing leads with appealing offers that draw players and hold them coming back for more. From the popular Daily Play 2000 Rewards to special promotions, JDB Bet Marketing guarantees that players are compensated for their allegiance and dedication.
With so many game developers online, finding the best can be a daunting task. However, JDB Gaming distinguishes itself from the crowd with its devotion to excellence and innovation. With over 150 online casino games to choose from, JDB Gaming offers something special for every player, whether you're a fan of slots, fish shooting games, arcade titles, card games, or bingo.
At the heart of JDB Gaming lies a devotion to supplying the greatest possible gaming experience for players. With a concentration on Asian culture and stunning 3D animations, JDB Gaming distinguishes itself as a front runner in the industry. Whether you're a player looking for excitement or an provider seeking a trustworthy partner, JDB Gaming has you covered.
API Integration: Smoothly connect with all platforms for ultimate business chances. Big Data Analysis: Keep ahead of market trends and comprehend player actions with extensive data analysis. 24/7 Technical Support: Experience peace of mind with skilled and dependable technical support on hand around the clock.
In conclusion, JDB Gaming presents a victorious mix of advanced technology, enticing bonuses, and unparalleled support. Whether you're a gamer or an operator, JDB Gaming has all the things you need to thrive in the world of online gaming. So why wait? Join the JDB Gaming family today and unlock your full potential! -
Intro
betvisa vietnam
Betvisa vietnam | Grand Prize Breakout!
Betway Highlights | 499,000 Extra Bonus on betvisa com!
Cockfight to win up to 3,888,000 on betvisa game
Daily Deposit, Sunday Bonus on betvisa app 888,000!
#betvisavietnam
200% Bonus on instant deposits—start your win streak!
200% welcome bonus! Slots and Fishing Games
https://www.betvisa.com/
#betvisavietnam #betvisagame #betvisaapp
#betvisacom #betvisacasinoapp
Birthday bash? Up to 1,800,000 in prizes! Enjoy!
Friday Shopping Frenzy betvisa vietnam 100,000 VND!
Betvisa Casino App Daily Login 12% Bonus Up to 1,500,000VND!
Khám phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Hệ thống BetVisa, một trong những nền tảng hàng đầu tại châu Á, ra đời vào năm 2017 và hoạt động dưới bằng của Curacao, đã thu hút hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược đảm bảo và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa sớm trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Vì tính cam kết về kinh nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên nghiệp, BetVisa tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy tham gia ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu dấu mốc của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều không thể thiếu được. -
Intro
betvisa bangladesh
Betvisa bangladesh | Super Cricket Carnival with Betvisa!
IPL Cricket Mania | Kick off Super Cricket Carnival with bet visa.com
IPL Season | Exclusive 1,50,00,000 only at Betvisa Bangladesh!
Crash Games Heroes | Climb to the top of the 1,00,00,000 bonus pool!
#betvisabangladesh
Preview IPL T20 | Follow Betvisa BD on Facebook, Instagram for awards!
betvisa affiliate Dream Maltese Tour | Sign up now to win the ultimate prize!
https://www.bvthethao.com/
#betvisabangladesh #betvisabd #betvisaaffiliate
#betvisaaffiliatesignup #betvisa.com
Với tính cam kết về trải nghiệm cá cược tốt hơn nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên môn, BetVisa tự hào là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai nhiệt tình trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy ghi danh ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều quan trọng.
Khám phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
BetVisa, một trong những công ty hàng đầu tại châu Á, ra đời vào năm 2017 và hoạt động dưới phê chuẩn của Curacao, đã có hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa sớm trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không dừng lại ở việc cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn. -
betvisa affiliate
Intro
betvisa bangladesh
Betvisa bangladesh | Super Cricket Carnival with Betvisa!
IPL Cricket Mania | Kick off Super Cricket Carnival with bet visa.com
IPL Season | Exclusive 1,50,00,000 only at Betvisa Bangladesh!
Crash Games Heroes | Climb to the top of the 1,00,00,000 bonus pool!
#betvisabangladesh
Preview IPL T20 | Follow Betvisa BD on Facebook, Instagram for awards!
betvisa affiliate Dream Maltese Tour | Sign up now to win the ultimate prize!
https://www.bvthethao.com/
#betvisabangladesh #betvisabd #betvisaaffiliate
#betvisaaffiliatesignup #betvisa.com
Do tính lời hứa về kinh nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên môn, BetVisa tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy tham gia ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều quan trọng.
Khám phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
BetVisa Vietnam, một trong những công ty hàng đầu tại châu Á, ra đời vào năm 2017 và hoạt động dưới phê chuẩn của Curacao, đã thu hút hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược đảm bảo và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa sớm trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không dừng lại ở việc cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 cơ hội miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều hình thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn. -
Intro
betvisa vietnam
Betvisa vietnam | Grand Prize Breakout!
Betway Highlights | 499,000 Extra Bonus on betvisa com!
Cockfight to win up to 3,888,000 on betvisa game
Daily Deposit, Sunday Bonus on betvisa app 888,000!
#betvisavietnam
200% Bonus on instant deposits—start your win streak!
200% welcome bonus! Slots and Fishing Games
https://www.betvisa.com/
#betvisavietnam #betvisagame #betvisaapp
#betvisacom #betvisacasinoapp
Birthday bash? Up to 1,800,000 in prizes! Enjoy!
Friday Shopping Frenzy betvisa vietnam 100,000 VND!
Betvisa Casino App Daily Login 12% Bonus Up to 1,500,000VND!
Tìm hiểu Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Dịch vụ BetVisa, một trong những nền tảng hàng đầu tại châu Á, ra đời vào năm 2017 và thao tác dưới bằng của Curacao, đã thu hút hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược đảm bảo và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa sớm trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không dừng lại ở việc cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 phần quà miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều hình thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Vì lời hứa về trải nghiệm cá cược tốt hơn nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng kỹ năng chuyên môn, BetVisa tự hào là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy đăng ký ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu. -
Intro
betvisa philippines
Betvisa philippines | The Filipino Carnival, Spinning for Treasures!
Betvisa Philippines Surprises | Spin daily and win ₱8,888 Grand Prize!
Register for a chance to win ₱8,888 Bonus Tickets! Explore Betvisa.com!
Wild All Over Grab 58% YB Bonus at Betvisa Casino! Take the challenge!
#betvisaphilippines
Get 88 on your first 50 Experience Betvisa Online's Bonus Gift!
Weekend Instant Daily Recharge at betvisa.com
https://www.88betvisa.com/
#betvisaphilippines #betvisaonline #betvisacasino
#betvisacom #betvisa.com
Nền tảng cá cược - Điểm Đến Tuyệt Vời Cho Người Chơi Trực Tuyến
Khám Phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
Nền tảng cá cược được tạo ra vào năm 2017 và hoạt động theo giấy phép trò chơi Curacao với hơn 2 triệu người dùng. Với cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược đáng tin cậy và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
Cổng chơi không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang lại cho người chơi những chính sách ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Nền tảng cá cược hỗ trợ nhiều cách thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, kết hợp với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang lại cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Với tính cam kết về trải nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chất lượng, BetVisa tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy đăng ký ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu! -
how to earn reels
JDBslot
JDB slot | The first bonus to rock the slot world
Exclusive event to earn real money and slot game points
JDB demo slot games for free = ?? Lucky Spin Lucky Draw!
How to earn reels free 2000? follow jdb slot games for free
#jdbslot
Demo making money : https://jdb777.com
#jdbslot #slotgamesforfree #howtoearnreels #cashreels
#slotgamepoint #demomakingmoney
Cash reels only at slot games for free
More professional jdb game bonus knowledge
How to Secure Spins Credit Complimentary 2000: Your Supreme Manual to Victorious Large with JDB One-armed bandits
Are you ready to embark on an exciting journey into the globe of internet slot games? Look no further, only turn to JDB777 FreeGames, where excitement and big wins await you at every turn of the reel. In this thorough handbook, we'll present you how to secure reels points free 2000 and open the thrilling world of JDB slots.
Live through the Thrill of Gaming Games for Free
At JDB777 FreeGames, we supply a extensive selection of captivating slot games that are guaranteed to keep you entertained for hours on end. From timeless fruit machines to immersive themed slots, there's something for every single variety of player to enjoy. And the finest part? You can play all of our slot games for free and earn real cash prizes!
Release Free Cash Reels and Attain Big
One of the most exhilarating features of JDB777 FreeGames is the chance to secure reels points free 2000, which can be exchanged for real cash. Just sign up for an account, and you'll receive your complimentary bonus to begin spinning and winning. With our plentiful promotions and bonuses, the sky's the boundary when it comes to your winnings!
Steer Tactics and Scores System
To increase your winnings and unlock the entire potential of our slot games, it's essential to apprehend the strategies and points system. Our expert guides will take you through everything you have to have to know, from selecting the right games to comprehending how to earn bonus points and cash prizes.
Distinctive Promotions and Special Offers
As a member of JDB777 FreeGames, you'll have access to exclusive promotions and special offers that are guaranteed to augment your gaming experience. From welcome bonuses to daily rebates, there are lots of possibilities to boost your winnings and take your gameplay to the next level.
Join Us Today and Begin Winning
Don't miss out on your opportunity to win big with JDB777 FreeGames. Sign up now to declare your complimentary bonus of 2000 credits and initiate spinning the reels for your opportunity to win real cash prizes. With our stimulating selection of slot games and generous promotions, the opportunities are endless. Join us today and initiate winning! -
Intro
betvisa philippines
Betvisa philippines | The Filipino Carnival, Spinning for Treasures!
Betvisa Philippines Surprises | Spin daily and win ₱8,888 Grand Prize!
Register for a chance to win ₱8,888 Bonus Tickets! Explore Betvisa.com!
Wild All Over Grab 58% YB Bonus at Betvisa Casino! Take the challenge!
#betvisaphilippines
Get 88 on your first 50 Experience Betvisa Online's Bonus Gift!
Weekend Instant Daily Recharge at betvisa.com
https://www.88betvisa.com/
#betvisaphilippines #betvisaonline #betvisacasino
#betvisacom #betvisa.com
Nền tảng cá cược - Điểm Đến Tuyệt Vời Cho Người Chơi Trực Tuyến
Khám Phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
BetVisa được tạo ra vào năm 2017 và tiến hành theo giấy phép trò chơi Curacao với hơn 2 triệu người dùng. Với cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược đáng tin cậy và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
Nền tảng cá cược không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang lại cho người chơi những phần thưởng hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Cổng chơi hỗ trợ nhiều cách thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang lại cho người chơi thời cơ thắng lớn.
Với lời hứa về trải nghiệm cá cược tốt nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên nghiệp, BetVisa tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy đăng ký ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều tất yếu! -
JDBslot
JDB slot | The first bonus to rock the slot world
Exclusive event to earn real money and slot game points
JDB demo slot games for free = ?? Lucky Spin Lucky Draw!
How to earn reels free 2000? follow jdb slot games for free
#jdbslot
Demo making money : https://jdb777.com
#jdbslot #slotgamesforfree #howtoearnreels #cashreels
#slotgamepoint #demomakingmoney
Cash reels only at slot games for free
More professional jdb game bonus knowledge
Methods to Secure Rotations Credits Costless 2000: Your Greatest Handbook to Winning Large with JDB Slots
Are you you prepared to begin on an exhilarating adventure into the world of web slot games? Seek no additional, just twist to JDB777 FreeGames, where enthusiasm and big wins await you at every turn of the reel. In this complete handbook, we'll show you methods to secure reels credits complimentary 2000 and open the stimulating world of JDB slots.
Undergo the Adrenaline rush of Gaming Games for Free
At JDB777 FreeGames, we offer a vast variety of captivating slot games that are sure to keep you entertained for hours on end. From classic fruit machines to immersive themed slots, there's something for every single sort of player to enjoy. And the finest part? You can play all of our slot games for free and gain real cash prizes!
Uncover Free Cash Reels and Attain Big
One of the most exhilarating features of JDB777 FreeGames is the opportunity to acquire reels points free 2000, which can be exchanged for real cash. Just sign up for an account, and you'll get your complimentary bonus to start spinning and winning. With our plentiful promotions and bonuses, the sky's the boundary when it comes to your winnings!
Steer Strategies and Points System
To optimize your winnings and release the complete potential of our slot games, it's important to apprehend the strategies and points system. Our professional guides will take you through everything you need to know, from choosing the right games to apprehending how to secure bonus points and cash prizes.
Special Promotions and Exclusive Offers
As a member of JDB777 FreeGames, you'll have access to exclusive promotions and special offers that are certain to boost your gaming experience. From welcome bonuses to daily rebates, there are a lot of opportunities to enhance your winnings and take your gameplay to the subsequent level.
Join Us Today and Start Winning
Don't miss out on your opportunity to win big with JDB777 FreeGames. Sign up now to assert your complimentary bonus of 2000 credits and commence spinning the reels for your opportunity to win real cash prizes. With our stimulating range of slot games and generous promotions, the opportunities are endless. Join us today and begin winning! -
betvisa.com
Intro
betvisa india
Betvisa india | IPL 2024 Heat Wave
IPL 2024 Big bets, big prizes With Betvisa India
Exclusive for Sports Fans Betvisa Online Casino 50% Welcome Bonus
Crash Game Supreme Compete for 1,00,00,000 pot Betvisa.com
#betvisaindia
Accurate Predictions IPL T20 Tournament, Winner Takes All!
More than just a game | Betvisa dreams invites you to fly to malta
https://www.b3tvisapro.com/
#betvisaindia #betvisalogin #betvisaonlinecasino
#betvisa.com #betvisaapp
Tìm hiểu Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
BetVisa Vietnam, một trong những công ty trò chơi hàng đầu tại châu Á, được thành lập vào năm 2017 và hoạt động dưới giấy phép của Curacao, đã thu hút hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với cam kết đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa sớm trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không dừng lại ở việc cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 phần quà miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Nhờ vào tính lời hứa về trải nghiệm cá cược hoàn hảo nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên môn, BetVisa hoàn toàn tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy gắn bó ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu chuyến đi của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều không thể thiếu được. -
Intro
betvisa india
Betvisa india | IPL 2024 Heat Wave
IPL 2024 Big bets, big prizes With Betvisa India
Exclusive for Sports Fans Betvisa Online Casino 50% Welcome Bonus
Crash Game Supreme Compete for 1,00,00,000 pot Betvisa.com
#betvisaindia
Accurate Predictions IPL T20 Tournament, Winner Takes All!
More than just a game | Betvisa dreams invites you to fly to malta
https://www.b3tvisapro.com/
#betvisaindia #betvisalogin #betvisaonlinecasino
#betvisa.com #betvisaapp
Khám phá Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến với BetVisa!
BetVisa Vietnam, một trong những nền tảng hàng đầu tại châu Á, được thành lập vào năm 2017 và hoạt động dưới giấy phép của Curacao, đã đưa vào hơn 2 triệu người dùng trên toàn thế giới. Với lời hứa đem đến trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn và tin cậy nhất, BetVisa nhanh chóng trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của người chơi trực tuyến.
BetVisa không chỉ cung cấp các trò chơi phong phú như xổ số, sòng bạc trực tiếp, thể thao trực tiếp và thể thao điện tử, mà còn mang đến cho người chơi những ưu đãi hấp dẫn. Thành viên mới đăng ký sẽ được tặng ngay 5 vòng quay miễn phí và có cơ hội giành giải thưởng lớn.
Đặc biệt, BetVisa hỗ trợ nhiều hình thức thanh toán linh hoạt như Betvisa Vietnam, cùng với các ưu đãi độc quyền như thưởng chào mừng lên đến 200%. Bên cạnh đó, hàng tuần còn có các chương trình khuyến mãi độc đáo như chương trình giải thưởng Sinh Nhật và Chủ Nhật Mua Sắm Điên Cuồng, mang đến cho người chơi cơ hội thắng lớn.
Do lời hứa về kinh nghiệm cá cược tinh vi nhất và dịch vụ khách hàng kỹ năng chuyên môn, BetVisa hoàn toàn tự tin là điểm đến lý tưởng cho những ai nhiệt huyết trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy ghi danh ngay hôm nay và bắt đầu cuộc hành trình của bạn tại BetVisa - nơi niềm vui và may mắn chính là điều không thể thiếu. -
jeetwin live
Jeetwin Affiliate
Jeetwin Affiliate
Join Jeetwin now! | Jeetwin sign up for a ?500 free bonus
Spin & fish with Jeetwin club! | 200% welcome bonus
Bet on horse racing, get a 50% bonus! | Deposit at Jeetwin live for rewards
#JeetwinAffiliate
Casino table fun at Jeetwin casino login | 50% deposit bonus on table games
Earn Jeetwin points and credits, enhance your play!
https://www.jeetwin-affiliate.com/hi
#JeetwinAffiliate #jeetwinclub #jeetwinsignup #jeetwinresult
#jeetwinlive #jeetwinbangladesh #jeetwincasinologin
Daily recharge bonuses at Jeetwin Bangladesh!
25% recharge bonus on casino games at jeetwin result
15% bonus on Crash Games with Jeetwin affiliate!
Spin to Achieve Genuine Currency and Voucher Codes with JeetWin's Partner Program
Do you a enthusiast of virtual gaming? Are you appreciate the thrill of spinning the spinner and triumphing big-time? If so, subsequently the JeetWin's Affiliate Scheme is great for you! With JeetWin Casino, you not simply get to partake in enthralling games but additionally have the opportunity to generate authentic funds and gift certificates easily by publicizing the platform to your friends, family, or virtual audience.
How Is it Operate?
Registering for the JeetWin's Referral Program is speedy and straightforward. Once you become an member, you'll receive a exclusive referral link that you can share with others. Every time someone joins or makes a deposit using your referral link, you'll obtain a commission for their activity.
Incredible Bonuses Await!
As a JeetWin affiliate, you'll have access to a range of attractive bonuses:
Sign Up Bonus 500: Obtain a generous sign-up bonus of INR 500 just for joining the program.
Deposit Bonus: Enjoy a whopping 200% bonus when you fund and play slot machine and fishing games on the platform.
Infinite Referral Bonus: Receive unlimited INR 200 bonuses and rebates for every friend you invite to play on JeetWin.
Exciting Games to Play
JeetWin offers a wide selection of the most played and most popular games, including Baccarat, Dice, Liveshow, Slot, Fishing, and Sabong. Whether you're a fan of classic casino games or prefer something more modern and interactive, JeetWin has something for everyone.
Take part in the Ultimate Gaming Experience
With JeetWin Live, you can elevate your gaming experience to the next level. Engage in thrilling live games such as Lightning Roulette, Lightning Dice, Crazytime, and more. Sign up today and begin an unforgettable gaming adventure filled with excitement and limitless opportunities to win.
Easy Payment Methods
Depositing funds and withdrawing your winnings on JeetWin is quick and hassle-free. Choose from a assortment of payment methods, including E-Wallets, Net Banking, AstroPay, and RupeeO, for seamless transactions.
Don't Miss Out on Special Promotions
As a JeetWin affiliate, you'll obtain access to exclusive promotions and special offers designed to maximize your earnings. From cash rebates to lucrative bonuses, there's always something exciting happening at JeetWin.
Get the Mobile Application
Take the fun with you wherever you go by downloading the JeetWin Mobile Casino App. Available for both iOS and Android devices, the app features a wide range of entertaining games that you can enjoy anytime, anywhere.
Join the JeetWin's Referral Program Today!
Don't wait any longer to start earning real cash and exciting rewards with the JeetWin Affiliate Program. Sign up now and become a part of the thriving online gaming community at JeetWin. -
jeetwin club
Jeetwin Affiliate
Jeetwin Affiliate
Join Jeetwin now! | Jeetwin sign up for a ?500 free bonus
Spin & fish with Jeetwin club! | 200% welcome bonus
Bet on horse racing, get a 50% bonus! | Deposit at Jeetwin live for rewards
#JeetwinAffiliate
Casino table fun at Jeetwin casino login | 50% deposit bonus on table games
Earn Jeetwin points and credits, enhance your play!
https://www.jeetwin-affiliate.com/hi
#JeetwinAffiliate #jeetwinclub #jeetwinsignup #jeetwinresult
#jeetwinlive #jeetwinbangladesh #jeetwincasinologin
Daily recharge bonuses at Jeetwin Bangladesh!
25% recharge bonus on casino games at jeetwin result
15% bonus on Crash Games with Jeetwin affiliate!
Rotate to Gain Genuine Currency and Voucher Codes with JeetWin's Affiliate Scheme
Do you a supporter of internet gaming? Do you really love the excitement of rotating the reel and triumphing large? If so, subsequently the JeetWin's Referral Program is perfect for you! With JeetWin, you not merely get to partake in thrilling games but additionally have the opportunity to earn genuine currency and voucher codes simply by endorsing the platform to your friends, family, or internet audience.
How Does Function?
Enrolling for the JeetWin's Referral Program is speedy and easy. Once you become an associate, you'll get a distinctive referral link that you can share with others. Every time someone joins or makes a deposit using your referral link, you'll get a commission for their activity.
Amazing Bonuses Await!
As a member of JeetWin's affiliate program, you'll have access to a variety of captivating bonuses:
500 Sign-Up Bonus: Acquire a generous sign-up bonus of INR 500 just for joining the program.
Welcome Deposit Bonus: Get a huge 200% bonus when you deposit and play slot and fishing games on the platform.
Infinite Referral Bonus: Receive unlimited INR 200 bonuses and cash rebates for every friend you invite to play on JeetWin.
Thrilling Games to Play
JeetWin offers a broad range of the most played and most popular games, including Baccarat, Dice, Liveshow, Slot, Fishing, and Sabong. Whether you're a fan of classic casino games or prefer something more modern and interactive, JeetWin has something for everyone.
Join the Ultimate Gaming Experience
With JeetWin Live, you can elevate your gaming experience to the next level. Engage in thrilling live games such as Lightning Roulette, Lightning Dice, Crazytime, and more. Sign up today and embark on an unforgettable gaming adventure filled with excitement and limitless opportunities to win.
Simple Payment Methods
Depositing funds and withdrawing your winnings on JeetWin is fast and hassle-free. Choose from a selection of payment methods, including E-Wallets, Net Banking, AstroPay, and RupeeO, for seamless transactions.
Don't Pass Up on Special Promotions
As a JeetWin affiliate, you'll obtain access to exclusive promotions and special offers designed to maximize your earnings. From cash rebates to lucrative bonuses, there's always something exciting happening at JeetWin.
Get the Mobile App
Take the fun with you wherever you go by downloading the JeetWin Mobile Casino App. Available for both iOS and Android devices, the app features a wide range of entertaining games that you can enjoy anytime, anywhere.
Join the JeetWin's Partner Program Today!
Don't wait any longer to start earning real cash and exciting rewards with the JeetWin Affiliate Program. Sign up now and join the thriving online gaming community at JeetWin. -
Jeetwin Affiliate
Jeetwin Affiliate
Join Jeetwin now! | Jeetwin sign up for a ?500 free bonus
Spin & fish with Jeetwin club! | 200% welcome bonus
Bet on horse racing, get a 50% bonus! | Deposit at Jeetwin live for rewards
#JeetwinAffiliate
Casino table fun at Jeetwin casino login | 50% deposit bonus on table games
Earn Jeetwin points and credits, enhance your play!
https://www.jeetwin-affiliate.com/hi
#JeetwinAffiliate #jeetwinclub #jeetwinsignup #jeetwinresult
#jeetwinlive #jeetwinbangladesh #jeetwincasinologin
Daily recharge bonuses at Jeetwin Bangladesh!
25% recharge bonus on casino games at jeetwin result
15% bonus on Crash Games with Jeetwin affiliate!
Twist to Gain Genuine Currency and Gift Certificates with JeetWin Affiliate Program
Are you a supporter of virtual gaming? Do you really love the thrill of spinning the wheel and triumphing large? If so, therefore the JeetWin's Affiliate Scheme is perfect for you! With JeetWin Gaming, you not simply get to indulge in thrilling games but as well have the possibility to generate authentic funds and gift certificates just by endorsing the platform to your friends, family, or virtual audience.
How Does Perform?
Signing up for the JeetWin's Referral Program is rapid and straightforward. Once you become an associate, you'll get a distinctive referral link that you can share with others. Every time someone signs up or makes a deposit using your referral link, you'll obtain a commission for their activity.
Fantastic Bonuses Await!
As a JeetWin affiliate, you'll have access to a assortment of attractive bonuses:
500 Welcome Bonus: Obtain a liberal sign-up bonus of INR 500 just for joining the program.
Deposit Bonus: Take advantage of a whopping 200% bonus when you fund and play one-armed bandit and fishing games on the platform.
Infinite Referral Bonus: Get unlimited INR 200 bonuses and rebates for every friend you invite to play on JeetWin.
Thrilling Games to Play
JeetWin offers a diverse range of the most played and most popular games, including Baccarat, Dice, Liveshow, Slot, Fishing, and Sabong. Whether you're a fan of classic casino games or prefer something more modern and interactive, JeetWin has something for everyone.
Participate in the Best Gaming Experience
With JeetWin Live, you can enhance your gaming experience to the next level. Engage in thrilling live games such as Lightning Roulette, Lightning Dice, Crazytime, and more. Sign up today and commence an unforgettable gaming adventure filled with excitement and limitless opportunities to win.
Easy Payment Methods
Depositing funds and withdrawing your winnings on JeetWin is rapid and hassle-free. Choose from a assortment of payment methods, including E-Wallets, Net Banking, AstroPay, and RupeeO, for seamless transactions.
Don't Lose on Exclusive Promotions
As a JeetWin affiliate, you'll receive access to exclusive promotions and special offers designed to maximize your earnings. From cash rebates to lucrative bonuses, there's always something exciting happening at JeetWin.
Install the Mobile Application
Take the fun with you wherever you go by downloading the JeetWin Mobile Casino App. Available for both iOS and Android devices, the app features a wide range of entertaining games that you can enjoy anytime, anywhere.
Join the JeetWin Affiliate Program Today!
Don't wait any longer to start earning real cash and exciting rewards with the JeetWin Affiliate Program. Sign up now and join the thriving online gaming community at JeetWin. -
jeetwin result
Jeetwin Affiliate
Jeetwin Affiliate
Join Jeetwin now! | Jeetwin sign up for a ?500 free bonus
Spin & fish with Jeetwin club! | 200% welcome bonus
Bet on horse racing, get a 50% bonus! | Deposit at Jeetwin live for rewards
#JeetwinAffiliate
Casino table fun at Jeetwin casino login | 50% deposit bonus on table games
Earn Jeetwin points and credits, enhance your play!
https://www.jeetwin-affiliate.com/hi
#JeetwinAffiliate #jeetwinclub #jeetwinsignup #jeetwinresult
#jeetwinlive #jeetwinbangladesh #jeetwincasinologin
Daily recharge bonuses at Jeetwin Bangladesh!
25% recharge bonus on casino games at jeetwin result
15% bonus on Crash Games with Jeetwin affiliate!
Rotate to Earn Authentic Funds and Gift Cards with JeetWin Affiliate Program
Do you a fan of online gaming? Do you really like the adrenaline rush of spinning the wheel and triumphing big-time? If so, then the JeetWin's Affiliate Scheme is ideal for you! With JeetWin Casino, you not just get to partake in exciting games but also have the possibility to generate actual money and voucher codes just by promoting the platform to your friends, family, or online audience.
How Does it Function?
Registering for the JeetWin's Referral Program is speedy and easy. Once you turn into an affiliate, you'll acquire a unique referral link that you can share with others. Every time someone registers or makes a deposit using your referral link, you'll get a commission for their activity.
Fantastic Bonuses Await!
As a JeetWin affiliate, you'll have access to a selection of captivating bonuses:
500 Sign-Up Bonus: Acquire a liberal sign-up bonus of INR 500 just for joining the program.
Welcome Deposit Bonus: Get a huge 200% bonus when you deposit and play slot and fish games on the platform.
Endless Referral Bonus: Get unlimited INR 200 bonuses and cash rebates for every friend you invite to play on JeetWin.
Entertaining Games to Play
JeetWin offers a diverse range of the most played and most popular games, including Baccarat, Dice, Liveshow, Slot, Fishing, and Sabong. Whether you're a fan of classic casino games or prefer something more modern and interactive, JeetWin has something for everyone.
Engage in the Best Gaming Experience
With JeetWin Live, you can enhance your gaming experience to the next level. Participate in thrilling live games such as Lightning Roulette, Lightning Dice, Crazytime, and more. Sign up today and commence an unforgettable gaming adventure filled with excitement and limitless opportunities to win.
Simple Payment Methods
Depositing funds and withdrawing your winnings on JeetWin is quick and hassle-free. Choose from a variety of payment methods, including E-Wallets, Net Banking, AstroPay, and RupeeO, for seamless transactions.
Don't Lose on Exclusive Promotions
As a JeetWin affiliate, you'll acquire access to exclusive promotions and special offers designed to maximize your earnings. From cash rebates to lucrative bonuses, there's always something exciting happening at JeetWin.
Download the App
Take the fun with you wherever you go by downloading the JeetWin Mobile Casino App. Available for both iOS and Android devices, the app features a wide range of entertaining games that you can enjoy anytime, anywhere.
Enroll in the JeetWin's Partner Program Today!
Don't wait any longer to start earning real cash and exciting rewards with the JeetWin Affiliate Program. Sign up now and be a member of the thriving online gaming community at JeetWin. -
How do I crush pills for individuals with a feeding tube clomiphene 50mg tablets?
-
Rolex watches
Understanding COSC Certification and Its Importance in Horology
COSC Validation and its Demanding Criteria
COSC, or the Official Swiss Chronometer Testing Agency, is the official Swiss testing agency that verifies the accuracy and precision of wristwatches. COSC validation is a mark of excellent craftsmanship and dependability in chronometry. Not all timepiece brands follow COSC certification, such as Hublot, which instead follows to its own demanding criteria with mechanisms like the UNICO calibre, achieving equivalent precision.
The Science of Exact Chronometry
The core system of a mechanical timepiece involves the spring, which provides energy as it unwinds. This mechanism, however, can be prone to environmental factors that may impact its accuracy. COSC-certified mechanisms undergo strict testing—over 15 days in various circumstances (five positions, three temperatures)—to ensure their durability and dependability. The tests measure:
Average daily rate accuracy between -4 and +6 seconds.
Mean variation, maximum variation levels, and impacts of temperature variations.
Why COSC Accreditation Is Important
For watch enthusiasts and connoisseurs, a COSC-certified watch isn't just a piece of technology but a proof to enduring excellence and precision. It signifies a timepiece that:
Provides outstanding dependability and precision.
Provides assurance of quality across the whole design of the watch.
Is probable to hold its value better, making it a sound choice.
Well-known Timepiece Brands
Several famous brands prioritize COSC accreditation for their watches, including Rolex, Omega, Breitling, and Longines, among others. Longines, for instance, presents collections like the Archive and Spirit, which showcase COSC-certified mechanisms equipped with cutting-edge materials like silicone equilibrium suspensions to boost durability and efficiency.
Historical Background and the Evolution of Timepieces
The notion of the timepiece originates back to the requirement for precise chronometry for navigational at sea, highlighted by John Harrison's work in the 18th cent. Since the formal establishment of Controle Officiel Suisse des Chronometres in 1973, the accreditation has become a benchmark for assessing the accuracy of luxury timepieces, maintaining a legacy of excellence in horology.
Conclusion
Owning a COSC-accredited timepiece is more than an visual choice; it's a dedication to quality and accuracy. For those valuing accuracy above all, the COSC accreditation offers peace of thoughts, ensuring that each certified timepiece will function reliably under various circumstances. Whether for individual contentment or as an investment decision, COSC-certified timepieces stand out in the world of watchmaking, maintaining on a tradition of precise chronometry. -
Rolex watches
Understanding COSC Accreditation and Its Importance in Watchmaking
COSC Accreditation and its Strict Standards
Controle Officiel Suisse des Chronometres, or the Official Swiss Chronometer Testing Agency, is the official Switzerland testing agency that certifies the precision and accuracy of wristwatches. COSC validation is a symbol of excellent craftsmanship and reliability in chronometry. Not all timepiece brands follow COSC validation, such as Hublot, which instead sticks to its proprietary stringent criteria with mechanisms like the UNICO calibre, attaining similar precision.
The Science of Precision Timekeeping
The central system of a mechanized watch involves the spring, which delivers energy as it loosens. This mechanism, however, can be vulnerable to external elements that may impact its precision. COSC-accredited movements undergo strict testing—over 15 days in various conditions (five positions, three temperatures)—to ensure their resilience and reliability. The tests measure:
Mean daily rate precision between -4 and +6 secs.
Mean variation, peak variation levels, and impacts of thermal variations.
Why COSC Accreditation Matters
For watch aficionados and connoisseurs, a COSC-certified timepiece isn't just a item of technology but a demonstration to enduring excellence and precision. It signifies a watch that:
Presents excellent dependability and accuracy.
Offers confidence of quality across the whole design of the watch.
Is apt to retain its value better, making it a wise investment.
Famous Chronometer Brands
Several well-known manufacturers prioritize COSC validation for their watches, including Rolex, Omega, Breitling, and Longines, among others. Longines, for instance, presents collections like the Record and Spirit, which highlight COSC-accredited movements equipped with innovative substances like silicon equilibrium suspensions to enhance durability and performance.
Historic Background and the Evolution of Chronometers
The notion of the timepiece dates back to the requirement for exact chronometry for navigational at sea, highlighted by John Harrison's work in the 18th century. Since the official establishment of Controle Officiel Suisse des Chronometres in 1973, the certification has become a benchmark for assessing the precision of luxury watches, sustaining a legacy of excellence in watchmaking.
Conclusion
Owning a COSC-accredited timepiece is more than an visual selection; it's a dedication to excellence and precision. For those appreciating accuracy above all, the COSC validation provides tranquility of mind, guaranteeing that each accredited timepiece will perform dependably under various circumstances. Whether for personal contentment or as an investment decision, COSC-validated timepieces stand out in the world of watchmaking, bearing on a tradition of meticulous timekeeping. -
casibom
Nihai Dönemsel En Fazla Gözde Casino Sitesi: Casibom
Kumarhane oyunlarını sevenlerin artık duymuş olduğu Casibom, nihai dönemde adından genellikle söz ettiren bir bahis ve casino sitesi haline geldi. Ülkemizdeki en başarılı kumarhane platformlardan biri olarak tanınan Casibom'un haftalık bazda cinsinden değişen erişim adresi, piyasada oldukça yeni olmasına rağmen itimat edilir ve kazanç sağlayan bir platform olarak ön plana çıkıyor.
Casibom, yakın rekabeti olanları geride kalarak köklü casino platformların üstünlük sağlamayı başarıyor. Bu alanda uzun soluklu olmak önemli olsa da, katılımcılarla iletişim kurmak ve onlara ulaşmak da eş kadar önemli. Bu noktada, Casibom'un 7/24 servis veren gerçek zamanlı destek ekibi ile rahatlıkla iletişime temas kurulabilir olması büyük bir fayda sunuyor.
Süratle büyüyen oyuncu kitlesi ile dikkat çekici olan Casibom'un gerisindeki başarı faktörleri arasında, yalnızca kumarhane ve gerçek zamanlı casino oyunları ile sınırlı olmayan geniş bir hizmet yelpazesi bulunuyor. Spor bahislerinde sunduğu kapsamlı seçenekler ve yüksek oranlar, oyuncuları ilgisini çekmeyi başarıyor.
Ayrıca, hem spor bahisleri hem de kumarhane oyunlar katılımcılara yönelik sunulan yüksek yüzdeli avantajlı ödüller da ilgi çekiyor. Bu nedenle, Casibom kısa sürede alanında iyi bir tanıtım başarısı elde ediyor ve büyük bir oyuncuların kitlesi kazanıyor.
Casibom'un kar getiren promosyonları ve tanınırlığı ile birlikte, siteye üyelik hangi yollarla sağlanır sorusuna da bahsetmek gerekir. Casibom'a mobil cihazlarınızdan, bilgisayarlarınızdan veya tabletlerinizden web tarayıcı üzerinden kolayca erişilebilir. Ayrıca, web sitesinin mobil uyumlu olması da önemli bir avantaj sağlıyor, çünkü şimdi pratikte herkesin bir akıllı telefonu var ve bu cihazlar üzerinden kolayca giriş sağlanabiliyor.
Hareketli cep telefonlarınızla bile yolda canlı olarak bahisler alabilir ve müsabakaları gerçek zamanlı olarak izleyebilirsiniz. Ayrıca, Casibom'un mobil cihazlarla uyumlu olması, memleketimizde kumarhane ve oyun gibi yerlerin kanuni olarak kapatılmasıyla birlikte bu tür platformlara girişin önemli bir yolunu oluşturuyor.
Casibom'un güvenilir bir kumarhane platformu olması da önemlidir bir artı getiriyor. Ruhsatlı bir platform olan Casibom, kesintisiz bir şekilde eğlence ve kazanç sağlama imkanı sunar.
Casibom'a kullanıcı olmak da son derece rahatlatıcıdır. Herhangi bir belge şartı olmadan ve ücret ödemeden web sitesine kolaylıkla kullanıcı olabilirsiniz. Ayrıca, platform üzerinde para yatırma ve çekme işlemleri için de birçok farklı yöntem bulunmaktadır ve herhangi bir kesim ücreti talep edilmemektedir.
Ancak, Casibom'un güncel giriş adresini izlemek de önemlidir. Çünkü gerçek zamanlı bahis ve kumarhane web siteleri moda olduğu için hileli web siteleri ve dolandırıcılar da görünmektedir. Bu nedenle, Casibom'un sosyal medya hesaplarını ve güncel giriş adresini periyodik olarak kontrol etmek gereklidir.
Sonuç, Casibom hem güvenilir hem de kazanç sağlayan bir bahis platformu olarak dikkat çekiyor. Yüksek ödülleri, geniş oyun seçenekleri ve kullanıcı dostu mobil uygulaması ile Casibom, oyun hayranları için ideal bir platform sağlar. -
Can I buy OTC options for dyspnea treatment clomid 50mg?
-
ищем психолога https://w-495.ru/
-
Understanding the complex world of chronometers
Understanding COSC Validation and Its Importance in Horology
COSC Accreditation and its Rigorous Criteria
COSC, or the Official Swiss Chronometer Testing Agency, is the authorized Swiss testing agency that verifies the precision and accuracy of wristwatches. COSC accreditation is a mark of superior craftsmanship and dependability in chronometry. Not all timepiece brands seek COSC accreditation, such as Hublot, which instead adheres to its own stringent standards with movements like the UNICO calibre, reaching comparable precision.
The Science of Exact Timekeeping
The central mechanism of a mechanical timepiece involves the mainspring, which delivers power as it unwinds. This system, however, can be vulnerable to environmental factors that may affect its accuracy. COSC-certified movements undergo rigorous testing—over 15 days in various circumstances (five positions, three temperatures)—to ensure their resilience and dependability. The tests measure:
Mean daily rate accuracy between -4 and +6 secs.
Mean variation, highest variation levels, and impacts of temperature changes.
Why COSC Certification Is Important
For timepiece fans and connoisseurs, a COSC-validated timepiece isn't just a piece of tech but a testament to lasting excellence and accuracy. It signifies a timepiece that:
Offers exceptional dependability and precision.
Provides assurance of quality across the complete design of the timepiece.
Is apt to retain its worth better, making it a smart choice.
Famous Timepiece Brands
Several renowned manufacturers prioritize COSC validation for their timepieces, including Rolex, Omega, Breitling, and Longines, among others. Longines, for instance, presents collections like the Archive and Soul, which showcase COSC-validated mechanisms equipped with cutting-edge materials like silicon equilibrium suspensions to enhance durability and efficiency.
Historic Context and the Development of Chronometers
The concept of the timepiece dates back to the requirement for precise chronometry for navigation at sea, highlighted by John Harrison's work in the eighteenth century. Since the formal foundation of COSC in 1973, the accreditation has become a standard for judging the accuracy of luxury watches, continuing a legacy of superiority in watchmaking.
Conclusion
Owning a COSC-accredited watch is more than an visual choice; it's a dedication to quality and accuracy. For those appreciating accuracy above all, the COSC certification provides tranquility of thoughts, guaranteeing that each accredited watch will operate reliably under various circumstances. Whether for individual contentment or as an investment, COSC-accredited timepieces stand out in the world of watchmaking, bearing on a legacy of meticulous timekeeping. -
레버리지스탁
로드스탁과의 레버리지 방식의 스탁: 투자 전략의 새로운 영역
로드스탁에서 공급하는 레버리지 스탁은 주식 시장의 투자법의 한 방식으로, 큰 이익율을 목표로 하는 투자자들에게 매력적인 선택입니다. 레버리지 사용을 이용하는 이 전략은 투자자들이 자신의 투자금을 초과하는 금액을 투입할 수 있도록 함으로써, 주식 시장에서 더욱 큰 힘을 가질 수 있는 기회를 제공합니다.
레버리지 방식의 스탁의 원리
레버리지 스탁은 기본적으로 자금을 빌려 운용하는 방식입니다. 사례를 들어, 100만 원의 자금으로 1,000만 원 상당의 증권을 사들일 수 있는데, 이는 투자하는 사람이 기본적인 자본보다 훨씬 훨씬 더 많은 주식을 구매하여, 주식 가격이 상승할 경우 해당하는 더 큰 수익을 얻을 수 있게 합니다. 그렇지만, 주식 가격이 하락할 경우에는 그 손실 또한 크게 될 수 있으므로, 레버리지를 사용할 때는 신중하게 생각해야 합니다.
투자 계획과 레버리지
레버리지 사용은 특히 성장 잠재력이 큰 기업에 적용할 때 유용합니다. 이러한 사업체에 상당한 비중으로 투입하면, 잘 될 경우 큰 수입을 얻을 수 있지만, 그 반대의 경우 큰 위험도 짊어져야 합니다. 따라서, 투자자들은 자신의 위험성 관리 능력과 장터 분석을 통해, 어느 회사에 얼마만큼의 자금을 투입할지 선택해야 합니다.
레버리지 사용의 이점과 위험성
레버리지 방식의 스탁은 높은 수익을 보장하지만, 그만큼 큰 위험성 동반합니다. 증권 시장의 변동은 추정이 곤란하기 때문에, 레버리지 사용을 사용할 때는 항상 상장 경향을 세심하게 관찰하고, 손해를 최소화하기 위해 수 있는 방법을 구성해야 합니다.
결론: 세심한 고르기가 필요
로드스탁을 통해 제공하는 레버리지 방식의 스탁은 막강한 투자 수단이며, 잘 사용하면 많은 수익을 가져다줄 수 있습니다. 그렇지만 큰 위험도 고려해야 하며, 투자 결정은 충분한 사실과 신중한 판단 후에 이루어져야 합니다. 투자자 자신의 재정 상황, 위험 수용 능력, 그리고 장터 상황을 반영한 균형 잡힌 투자 계획이 중요합니다. -
로드스탁과의 레버리지 방식의 스탁: 투자법의 새로운 영역
로드스탁을 통해 공급하는 레버리지 방식의 스탁은 증권 투자의 한 방법으로, 상당한 수익률을 목적으로 하는 투자자들을 위해 매혹적인 선택입니다. 레버리지 사용을 사용하는 이 방법은 투자자들이 자신의 자금을 초과하는 투자금을 투입할 수 있도록 함으로써, 주식 장에서 훨씬 큰 힘을 가질 수 있는 기회를 제공합니다.
레버리지 방식의 스탁의 기본 원칙
레버리지 스탁은 기본적으로 투자금을 대여하여 운용하는 방식입니다. 사례를 들어, 100만 원의 자본으로 1,000만 원 상당의 주식을 구매할 수 있는데, 이는 투자하는 사람이 기본 투자 금액보다 훨씬 훨씬 더 많은 증권을 구매하여, 주식 가격이 올라갈 경우 해당하는 더 큰 이익을 가져올 수 있게 해줍니다. 그렇지만, 증권 값이 떨어질 경우에는 그 피해 또한 크게 될 수 있으므로, 레버리지를 사용할 때는 신중하게 생각해야 합니다.
투자 전략과 레버리지
레버리지는 특히 성장 잠재력이 큰 회사에 투자할 때 효과적입니다. 이러한 회사에 큰 비율로 적용하면, 성공할 경우 큰 수익을 얻을 수 있지만, 반대 경우의 경우 상당한 위험도 감수해야. 따라서, 투자하는 사람은 자신의 리스크 관리 능력과 장터 분석을 통해 통해, 일정한 사업체에 얼마만큼의 투자금을 적용할지 결정해야 합니다.
레버리지의 이점과 위험 요소
레버리지 방식의 스탁은 큰 이익을 약속하지만, 그만큼 높은 위험도 수반합니다. 증권 장의 변화는 예측이 곤란하기 때문에, 레버리지 사용을 이용할 때는 언제나 장터 추세를 면밀히 관찰하고, 손해를 최소화할 수 있는 전략을 세워야 합니다.
최종적으로: 세심한 고르기가 요구됩니다
로드스탁을 통해 제공하는 레버리지 스탁은 강력한 투자 도구이며, 적절히 사용하면 상당한 수익을 가져다줄 수 있습니다. 그렇지만 높은 위험성도 신경 써야 하며, 투자 결정은 충분히 많은 사실과 신중한 고려 후에 진행되어야 합니다. 투자자 자신의 재정 상황, 리스크 감수 능력, 그리고 시장 상황을 고려한 균형 잡힌 투자 계획이 중요하며. -
What steps are taken to ensure the safety of medications during the compounding process buy kamagra oral jelly online?
-
로드스탁과의 레버리지 스탁: 투자법의 새로운 영역
로드스탁에서 제공되는 레버리지 방식의 스탁은 주식 투자법의 한 방식으로, 큰 수익률을 목적으로 하는 투자자들에게 매혹적인 선택입니다. 레버리지 사용을 이용하는 이 전략은 투자자들이 자신의 자본을 넘어서는 금액을 투자할 수 있도록 함으로써, 증권 장에서 더욱 큰 힘을 행사할 수 있는 기회를 공급합니다.
레버리지 스탁의 원리
레버리지 스탁은 기본적으로 자금을 차입하여 투자하는 방식입니다. 예시를 들어, 100만 원의 투자금으로 1,000만 원 상당의 증권을 취득할 수 있는데, 이는 투자하는 사람이 일반적인 자본보다 훨씬 더 많은 증권을 구매하여, 주식 가격이 증가할 경우 해당하는 더 큰 수익을 얻을 수 있게 합니다. 그러나, 주식 가격이 떨어질 경우에는 그 손해 또한 커질 수 있으므로, 레버리지 사용을 사용할 때는 신중하게 생각해야 합니다.
투자 전략과 레버리지
레버리지 사용은 특히 성장 잠재력이 높은 회사에 투자할 때 효과적입니다. 이러한 회사에 상당한 비율을 통해 투입하면, 성공할 경우 큰 이익을 가져올 수 있지만, 반대의 경우 큰 리스크도 감수해야. 그렇기 때문에, 투자하는 사람은 자신의 위험 관리 능력과 장터 분석을 통해, 어느 사업체에 얼마만큼의 투자금을 투자할지 결정하게 됩니다 합니다.
레버리지의 이점과 위험성
레버리지 스탁은 높은 이익을 보장하지만, 그만큼 상당한 위험성 동반합니다. 주식 시장의 변동성은 추정이 힘들기 때문에, 레버리지를 이용할 때는 항상 시장 동향을 면밀히 주시하고, 피해를 최소화할 수 있는 전략을 세워야 합니다.
최종적으로: 조심스러운 고르기가 필요
로드스탁을 통해 공급하는 레버리지 방식의 스탁은 강력한 투자 도구이며, 적절히 활용하면 상당한 수입을 제공할 수 있습니다. 하지만 큰 위험성도 신경 써야 하며, 투자 선택은 충분한 사실과 세심한 고려 후에 실시되어야 합니다. 투자하는 사람의 금융 상황, 리스크 감수 능력, 그리고 시장의 상황을 반영한 안정된 투자 전략이 중요하며. -
레버리지스탁
로드스탁과의 레버리지 방식의 스탁: 투자의 참신한 지평
로드스탁을 통해 제공하는 레버리지 스탁은 증권 투자의 한 방식으로, 큰 수익률을 목적으로 하는 투자자들을 위해 매력적인 옵션입니다. 레버리지 사용을 이용하는 이 전략은 투자하는 사람들이 자신의 투자금을 초과하는 금액을 투입할 수 있도록 하여, 주식 시장에서 더 큰 힘을 행사할 수 있는 방법을 줍니다.
레버리지 스탁의 기본 원칙
레버리지 방식의 스탁은 일반적으로 자본을 대여하여 운용하는 방법입니다. 사례를 들어, 100만 원의 자본으로 1,000만 원 상당의 주식을 사들일 수 있는데, 이는 투자자들이 일반적인 투자 금액보다 훨씬 더 많은 주식을 구매하여, 증권 가격이 상승할 경우 상응하는 훨씬 더 큰 수익을 얻을 수 있게 합니다. 하지만, 증권 값이 내려갈 경우에는 그 손실 또한 증가할 수 있으므로, 레버리지 사용을 사용할 때는 신중해야 합니다.
투자 전략과 레버리지 사용
레버리지는 특히 성장 잠재력이 높은 사업체에 투자할 때 도움이 됩니다. 이러한 기업에 높은 비율을 통해 투자하면, 성공적일 경우 상당한 수입을 가져올 수 있지만, 반대 경우의 경우 상당한 위험도 짊어져야 합니다. 그렇기 때문에, 투자자들은 자신의 리스크 관리 능력을 가진 상장 분석을 통해, 어떤 회사에 얼마만큼의 자본을 적용할지 결정하게 됩니다 합니다.
레버리지의 장점과 위험성
레버리지 스탁은 상당한 수익을 보장하지만, 그만큼 큰 위험도 동반합니다. 증권 시장의 변동성은 예측이 힘들기 때문에, 레버리지를 이용할 때는 항상 장터 추세를 면밀히 주시하고, 손해를 최소화할 수 있는 계획을 마련해야 합니다.
최종적으로: 신중한 결정이 필요
로드스탁에서 제공하는 레버리지 방식의 스탁은 강력한 투자 도구이며, 적절히 이용하면 큰 수입을 제공할 수 있습니다. 하지만 상당한 위험도 신경 써야 하며, 투자 결정은 충분히 많은 데이터와 조심스러운 생각 후에 진행되어야 합니다. 투자하는 사람의 재정적 상태, 위험을 감수하는 능력, 그리고 장터 상황을 고려한 균형 잡힌 투자 방법이 핵심입니다. -
10배레버리지
로드스탁과의 레버리지 스탁: 투자 전략의 새로운 지평
로드스탁에서 제공하는 레버리지 스탁은 주식 시장의 투자의 한 방법으로, 높은 수익률을 목적으로 하는 투자자들을 위해 매력적인 선택입니다. 레버리지 사용을 사용하는 이 전략은 투자자들이 자신의 자금을 넘어서는 자금을 투입할 수 있도록 함으로써, 증권 시장에서 더욱 큰 힘을 행사할 수 있는 기회를 줍니다.
레버리지 스탁의 기본 원칙
레버리지 방식의 스탁은 원칙적으로 자본을 대여하여 운용하는 방식입니다. 사례를 들어, 100만 원의 투자금으로 1,000만 원 상당의 증권을 취득할 수 있는데, 이는 투자하는 사람이 기본적인 투자 금액보다 훨씬 더욱 많은 주식을 취득하여, 증권 가격이 증가할 경우 관련된 더욱 큰 수익을 가져올 수 있게 됩니다. 그러나, 증권 값이 떨어질 경우에는 그 손실 또한 크게 될 수 있으므로, 레버리지를 이용할 때는 신중해야 합니다.
투자 계획과 레버리지 사용
레버리지는 특히 성장 잠재력이 상당한 회사에 투자할 때 효과적입니다. 이러한 사업체에 높은 비율을 통해 적용하면, 성공할 경우 막대한 수익을 획득할 수 있지만, 그 반대의 경우 큰 위험성도 짊어져야 합니다. 그렇기 때문에, 투자하는 사람은 자신의 리스크 관리 능력을 가진 장터 분석을 통해 통해, 일정한 사업체에 얼마만큼의 투자금을 적용할지 결정하게 됩니다 합니다.
레버리지의 이점과 위험성
레버리지 방식의 스탁은 높은 수익을 약속하지만, 그만큼 큰 위험도 수반합니다. 증권 장의 변화는 추정이 어렵기 때문에, 레버리지를 사용할 때는 언제나 장터 경향을 세심하게 살펴보고, 손실을 최소화하기 위해 수 있는 방법을 세워야 합니다.
맺음말: 세심한 고르기가 필요
로드스탁을 통해 제공하는 레버리지 방식의 스탁은 막강한 투자 수단이며, 잘 활용하면 많은 이익을 벌어들일 수 있습니다. 하지만 상당한 위험성도 신경 써야 하며, 투자 결정은 필요한 정보와 조심스러운 판단 후에 진행되어야 합니다. 투자자 자신의 금융 상황, 위험을 감수하는 능력, 그리고 시장 상황을 생각한 균형 잡힌 투자 계획이 중요하며. -
로드스탁과 레버리지 방식의 스탁: 투자법의 새로운 영역
로드스탁을 통해 제공하는 레버리지 방식의 스탁은 주식 시장의 투자법의 한 방식으로, 높은 수익률을 목적으로 하는 투자자들에게 유혹적인 옵션입니다. 레버리지 사용을 이용하는 이 전략은 투자하는 사람들이 자신의 투자금을 초과하는 투자금을 투입할 수 있도록 하여, 증권 시장에서 더욱 큰 영향력을 행사할 수 있는 기회를 제공합니다.
레버리지 방식의 스탁의 기본 원칙
레버리지 방식의 스탁은 원칙적으로 투자금을 대여하여 투자하는 방법입니다. 예를 들어, 100만 원의 투자금으로 1,000만 원 상당의 증권을 취득할 수 있는데, 이는 투자자가 기본 투자 금액보다 훨씬 훨씬 더 많은 증권을 사들여, 주식 가격이 올라갈 경우 상응하는 더 큰 수익을 가져올 수 있게 합니다. 그렇지만, 증권 가격이 떨어질 경우에는 그 손해 또한 크게 될 수 있으므로, 레버리지 사용을 사용할 때는 신중하게 생각해야 합니다.
투자 전략과 레버리지 사용
레버리지는 특히 성장 가능성이 상당한 회사에 투입할 때 효과적입니다. 이러한 기업에 높은 비율로 적용하면, 성공적일 경우 막대한 이익을 획득할 수 있지만, 그 반대의 경우 많은 리스크도 감수해야. 따라서, 투자하는 사람은 자신의 위험 관리 능력과 상장 분석을 통해 통해, 일정한 기업에 얼마만큼의 자본을 투자할지 결정하게 됩니다 합니다.
레버리지 사용의 장점과 위험성
레버리지 방식의 스탁은 상당한 이익을 약속하지만, 그만큼 높은 위험성 따릅니다. 주식 시장의 변동성은 예상이 힘들기 때문에, 레버리지를 이용할 때는 언제나 장터 경향을 세심하게 살펴보고, 손실을 최소로 줄일 수 있는 방법을 마련해야 합니다.
맺음말: 신중한 결정이 필요
로드스탁에서 공급하는 레버리지 방식의 스탁은 효과적인 투자 수단이며, 적절히 활용하면 상당한 수입을 가져다줄 수 있습니다. 그러나 큰 리스크도 고려해야 하며, 투자 결정이 충분히 많은 사실과 조심스러운 생각 후에 실시되어야 합니다. 투자자 본인의 재정 상황, 위험 수용 능력, 그리고 시장의 상황을 고려한 안정된 투자 방법이 중요하며. -
Are there specific regulations for the sale of controlled substances kamagra 100 mg?
-
https://www.puwdtw.ru/click?pid=11509&offer_id=1332 Как Заработать Первые 3000$ На Криптовалютах С Нуля
-
https://www.puwdtw.ru/click?pid=11509&offer_id=1332 Как Заработать Первые 3000$ На Криптовалютах С Нуля
-
https://rgames.org/cup-c1/
-
https://rg777.app/cup-c1-202324/
-
Productive Backlinks in Weblogs and Remarks: Enhance Your SEO
Hyperlinks are essential for enhancing search engine rankings and increasing web site visibility. By including backlinks into blogs and comments prudently, they can significantly increase traffic and SEO efficiency.
Adhering to Search Engine Algorithms
Today's backlink positioning methods are meticulously tuned to align with search engine algorithms, which now emphasize link quality and relevance. This assures that hyperlinks are not just abundant but meaningful, guiding consumers to helpful and relevant articles. Website owners should concentrate on incorporating backlinks that are contextually proper and improve the overall content material high quality.
Benefits of Making use of Refreshing Donor Bases
Using current donor bases for links, like those handled by Alex, provides substantial rewards. These bases are frequently refreshed and consist of unmoderated sites that don’t attract complaints, guaranteeing the hyperlinks placed are both powerful and compliant. This method will help in keeping the effectiveness of backlinks without the dangers linked with moderated or problematic resources.
Only Authorized Resources
All donor sites used are sanctioned, keeping away from legal pitfalls and adhering to digital marketing standards. This dedication to making use of only authorized resources ensures that each backlink is legitimate and trustworthy, thus constructing trustworthiness and dependability in your digital presence.
SEO Impact
Skillfully positioned backlinks in blogs and comments provide more than just SEO rewards—they enhance user experience by connecting to pertinent and high-quality articles. This technique not only meets search engine criteria but also engages end users, leading to better targeted traffic and improved online engagement.
In essence, the right backlink strategy, particularly one that utilizes refreshing and dependable donor bases like Alex’s, can alter your SEO efforts. By concentrating on good quality over volume and adhering to the newest criteria, you can make sure your backlinks are both effective and effective. -
Backlinks seo
Efficient Backlinks in Weblogs and Comments: Enhance Your SEO
Backlinks are vital for boosting search engine rankings and enhancing website presence. By including links into blogs and comments prudently, they can significantly increase traffic and SEO overall performance.
Adhering to Search Engine Algorithms
The current day's backlink placement strategies are finely adjusted to line up with search engine algorithms, which now prioritize link quality and significance. This ensures that hyperlinks are not just numerous but meaningful, directing users to beneficial and relevant articles. Website owners should focus on incorporating links that are contextually appropriate and improve the overall content material good quality.
Rewards of Using Clean Contributor Bases
Using current contributor bases for links, like those managed by Alex, delivers considerable benefits. These bases are often refreshed and consist of unmoderated sites that don’t attract complaints, ensuring the links put are both influential and certified. This approach assists in maintaining the effectiveness of backlinks without the dangers connected with moderated or problematic sources.
Only Authorized Sources
All donor sites used are authorized, avoiding legal pitfalls and adhering to digital marketing requirements. This determination to using only sanctioned resources guarantees that each backlink is legitimate and trustworthy, thereby building trustworthiness and dependability in your digital presence.
SEO Influence
Skillfully positioned backlinks in blogs and comments provide over just SEO advantages—they improve user experience by linking to relevant and top quality articles. This technique not only meets search engine conditions but also engages consumers, leading to better visitors and improved online proposal.
In essence, the right backlink technique, specifically one that utilizes refreshing and trustworthy donor bases like Alex’s, can transform your SEO efforts. By concentrating on quality over quantity and adhering to the newest standards, you can guarantee your backlinks are both potent and efficient. -
Sure, here's the text with spin syntax applied:
Backlink Pyramid
After several updates to the G search engine, it is necessary to utilize different approaches for ranking.
Today there is a way to attract the interest of search engines to your site with the support of inbound links.
Links are not only an efficient marketing instrument but they also have natural visitors, immediate sales from these resources perhaps will not be, but click-throughs will be, and it is beneficial visitors that we also receive.
What in the end we get at the end result:
We show search engines site through backlinks.
Prluuchayut natural click-throughs to the site and it is also a indicator to search engines that the resource is used by people.
How we show search engines that the site is valuable:
Backlinks do to the principal page where the main information.
We make backlinks through redirects reputable sites.
The most ESSENTIAL we place the site on sites analytical tools distinct tool, the site goes into the memory of these analysis tools, then the obtained links we place as redirects on weblogs, discussion boards, comment sections. This important action shows search engines the MAP OF THE SITE as analysis tool sites display all information about sites with all keywords and headlines and it is very BENEFICIAL.
All data about our services is on the website! -
Backlink pyramid
Sure, here's the text with spin syntax applied:
Backlink Structure
After many updates to the G search mechanism, it is necessary to apply different methods for ranking.
Today there is a means to draw the attention of search engines to your site with the aid of inbound links.
Backlinks are not only an successful marketing instrument but they also have authentic traffic, immediate sales from these resources likely will not be, but visits will be, and it is beneficial traffic that we also receive.
What in the end we get at the end result:
We show search engines site through backlinks.
Prluuchayut natural click-throughs to the site and it is also a sign to search engines that the resource is used by people.
How we show search engines that the site is profitable:
Backlinks do to the primary page where the main information.
We make backlinks through redirects trusted sites.
The most SIGNIFICANT we place the site on sites analyzers distinct tool, the site goes into the cache of these analyzers, then the received links we place as redirects on weblogs, discussion boards, comments. This important action shows search engines the MAP OF THE SITE as analysis tool sites show all information about sites with all keywords and headlines and it is very BENEFICIAL.
All details about our services is on the website! -
creating articles
Creating exclusive articles on Medium and Telegraph, why it is vital:
Created article on these resources is improved ranked on less frequent queries, which is very crucial to get natural traffic.
We get:
organic traffic from search engines.
organic traffic from the in-house rendition of the medium.
The site to which the article refers gets a link that is liquid and increases the ranking of the webpage to which the article refers.
Articles can be made in any amount and choose all low-frequency queries on your topic.
Medium pages are indexed by search algorithms very well.
Telegraph pages need to be indexed distinctly indexer and at the same time after indexing they sometimes occupy positions higher in the search algorithms than the medium, these two platforms are very useful for getting visitors.
Here is a hyperlink to our offerings where we offer creation, indexing of sites, articles, pages and more. -
בטים
הימורים ברשת הם חוויות מרגשת ופופולרית ביותר בעידן הדיגיטלי, שמגירה מיליוני אנשים מכל
כל רחבי העולם. ההימורים המקוונים מתרחשים בהתאם ל אירועים ספורט, תוצאות פוליטיות ואפילו תוצאות מזג האוויר ונושאים נוספים. אתרי הימורים הווירטואליים מזמינים את המשתתפים להמרות על תוצאות מתאימות ולחוות רגעים של חוויה והתרגשות.
ההימורים המקוונים הם כבר חלק חשוב מתרבות החברה מזמן רב והיום הם לא רק חלק חשוב מהפעילות התרבותית והכלכלית, אלא גם מספקים תשואות וחוויים. משום שהם נגישים מאוד וקלים לשימוש, הם מתאימים לכל מהניסיון ולהנות מכל הניצחונות והפרסים בכל זמן ובכל מקום.
טכנולוגיות דיגיטליות והימורים מקוונים הפכו להיות הפופולריים ביותר מעניינת ופופולרית. מיליונים אנשים מכל רחבי העולם מעוניינים בהימורים, הכוללים הימורי ספורט. הימורים מקוונים מציעים למשתתפים חוויה רגשית ומרתקת, שמתאימה לכל גיל וכישור בכל זמן ובכל מקום.
וכן מה נותר אתה מחכה למה? אל תהסס והצטרף עכשיו והתחיל ליהנות מהתרגשות וההנאה שהימורים מקוונים מציעים. -
What measures are in place to ensure the consistent release of medication over an extended period what is vidalista 10?
-
הימורי ספורט
הימורים ברשת הם חוויה מרגשת ופופולרית ביותר בעידן הדיגיטלי, שמאגרת מיליוני אנשים מכל
כל רחבי העולם. ההימורים המקוונים מתבצעים על פי אירועים ספורט, תוצאות פוליטיות ואפילו תוצאות מזג האוויר ונושאים נוספים. אתרי הימורים הווירטואליים מזמינים את מי שמעוניין להמרות על תוצאות מתאימות ולחוות רגעים מרגשים ומהנים.
ההימורים המקוונים הם הם כבר חלק מהתרבות האנושית לא מעט זמן והיום הם לא רק חלק חשוב מהפעילות הכלכלית והתרבותית, אלא גם מספקים רווחים וחוויים. משום שהם נגישים לכולם ופשוטים לשימוש, הם מובילים את כולם ליהנות מהניסיון ולהנות מכל הניצחונות והפרסים בכל זמן ובכל מקום.
טכנולוגיה והימורים הפכו מעניינת ונפוצה. מיליוני אנשים מכל רחבי העולם משתתפים בהימורים, כוללים הימורי ספורט. הימורים מקוונים מציעים למשתתפים חוויה רגשית ומרתקת, המתאימה לכולם בכל זמן ובכל מקום.
אז מה חכם אתה מחכה לו? אל תהסס והצטרף עכשיו והתחיל ליהנות מכל רגע ורגע שהימורים מקוונים מציעים. -
Telegrass
טלגראס כיוונים: המדריכים המלא להשקיה קנאביס דרך הטלגרמה
שרף מדריך היא אתר ווב מסמכים ומדריכי להשקיה פרחי קנאביס במקום היישומון הנפוצה המשלוח.
האתר האינטרנט סופק את כלל המידע הקישורים לאתרים והמידעים המעודכן להקבוצות וערוצים המומלצים מומלצות לקריאה להשקיה פרחי קנאביס בהטלגרמה במדינת ישראל.
כמו כך, האתר הרשמי מציעה מדריכים מתעדף לאיך להתקשר בהקנאביס ולהשיג קנאביס בקלות מסירת ובמהירות רבה.
בעזרת המדריכים, אף משתמשי הערוץ חדשים יוכלו להיכנס לעולם הקנאביס בהמסר בדרך מאובטחת ובטוחה.
ההרובוט של טלגראס מאפשר למשתמשי הערוץ ללבצע פעולות השונות שונות ומקוריות כגון השקת שרף, קבלת תמיכה תמיכת, בדיקת הקיימות והוספת ביקורות על המוצרים. כל זאת בפניות נוחה לשימוש ופשוטה דרך האפליקציה.
כאשר כשם הדבר בשיטות ה התשלומים, השרף משתמשת בשיטות ה מוכרות מאוד כמו גם מזומנים, כרטיסי אשראי ומטבע קריפטוגרפי. חיוני לציין כי קיים לבדוק ולוודא את ההוראות והחוקות האזוריים במדינה שלך ללפני ביצוע רכישה.
המסר מציע הטבות מרכזיים כגון הגנת הפרטיות ובטיחות מוגברים מאוד, תקשורת מהירה וגמישות גבוהה. בנוסף, הוא מאפשר גישה להקהל גלובלית רחבה ומציע מגוון של תכונות ויכולות.
בבתום, הטלגרמה מסמכים היא המקום האידיאלי ללמצוא את כל המידע והקישורות לסחר ב שרף בפניות מהירה, בבטוחה ונוחה דרך המסר. -
טלגראס תל אביב
שרף מדריך: המדריך המקיף לקניית שרף דרך הטלגרמה
טלגראס כיוונים הם אתר ווב מידעים והדרכות לקניית פרחי קנאביס דרך האפליקציה המובילה הטלגרמה.
האתר סופק את כל הקישורים הידיעתיים והמסמכים העדכני לקבוצות וערוצים מומלצים לביקור לרכישת פרחי קנאביס בהטלגרמה בארץ ישראל.
כמו כן, האתר הרשמי מספק מדריך מתעדף לאיך כדאי להתארגן באמצעות בהפרח ולקנה שרף בקלות מסירת ובמהירות רבה.
בעזרת המסמכים, גם כן משתמשי הערוץ חדשים יוכלו להיכנס להמרחב הקנאביס בטלגרם בפני בטוחה לשימוש ומאובטחת לשימוש.
הבוט של טלגראס מאפשר למשתמשי ללבצע פעולות השונות שונות ומגוונות כמו גם הזמנת קנאביס, קבלת תמיכה סיוע, בדיקת והכנסת פידבק על מוצרים. כל זאת בפניות נוחה ופשוטה דרך היישומון.
כאשר מדובר בשיטות ה התשלומים, טלגראס מנהלת באמצעים מוכרות מאוד כמו מזומנים, כרטיסי האשראי של כרטיסי אשראי ומטבע קריפטוגרפי. חשוב ללציין כי קיים לבדוק ולוודא את התקנות והחוקים המקומיים באיזור שלך ללפני ביצוע רכישה.
טלגרם מציע יתרונות משמעותיים מרכזיים כגון פרטיות וביטחון אישי מוגברים מאוד, השיחה מהירה מאוד וגמישות גבוהה. בנוסף, הוא מאפשר כניסה להקהל גלובלית רחבה ומציע מגוון של תכונות ויכולות.
בלסיכום, טלגראס כיוונים הם המקום האידיאלי ללמצוא את כל הידע והקישורות לסחר ב קנאביס בפניות מהירה מאוד, במוגנת ונוחה דרך הטלגרם. -
Link building is simply as effective currently, just the resources for working in this field have got shifted.
There are numerous possibilities regarding backlinks, our company employ a few of them, and these methods function and are actually tried by us and our clientele.
Lately our team conducted an trial and it turned out that low-volume search queries from a single website rank well in search engines, and this doesn't have to become your personal domain name, you are able to utilize social media from the web 2.0 series for this.
It additionally possible to partially shift mass through web page redirects, providing a varied backlink profile.
Head over to our very own web page where our solutions are presented with comprehensive descriptions. -
Are there regulations on the use of medicines in patients with disabilities or special needs vidalista 20?
-
Наша команда квалифицированных исполнителей проштудирована предъявить вам инновационные методы, которые не только подарят прочную покров от холодных воздействий, но и подарят вашему домашнему пространству современный вид.
Мы эксплуатируем с новыми составами, гарантируя продолжительный продолжительность службы и великолепные результаты. Утепление наружных поверхностей – это не только экономия энергии на огреве, но и забота о экологической обстановке. Спасательные технологии, которые мы осуществляем, способствуют не только твоему, но и поддержанию природы.
Самое главное: [url=https://ppu-prof.ru/]Утепление фасадов под ключ цена[/url] у нас начинается всего от 1250 рублей за метр квадратный! Это доступное решение, которое превратит ваш резиденцию в реальный комфортный уголок с минимальными затратами.
Наши произведения – это не только изолирование, это создание пространства, в где каждый деталь отразит ваш особенный образ. Мы возьмем во внимание все ваши просьбы, чтобы осуществить ваш дом еще еще более дружелюбным и привлекательным.
Подробнее на [url=https://ppu-prof.ru/]веб-сайте[/url]
Не откладывайте труды о своем помещении на потом! Обращайтесь к исполнителям, и мы сделаем ваш домик не только уютнее, но и модернизированным. Заинтересовались? Подробнее о наших делах вы можете узнать на портале. Добро пожаловать в мир комфорта и уровня. -
Просторная студия с теплыми полами в прекрасной цветовой бирюзовой гамме... Квартира студия: Кухня и спальня.Звоните. Залоговая стоимость обсуждается.
С меня невмешательство - с вас своевременная оплата и чистота в квартире.
квартира в переулке..под окном автобусов нет!
Минимальный залог от 8000р если вы без животных и маленьких деток.
Если вы оплатите за 3 мес вперед то цена может быть уменьшена
https://www.avito.ru/sochi/kvartiry/kvartira-studiya_27m_14et._2415880353?utm_campaign=native&utm_medium=item_page_android&utm_source=soc_sharing_seller -
Просторная студия с теплыми полами в прекрасной цветовой бирюзовой гамме... Квартира студия: Кухня и спальня.Звоните. Залоговая стоимость обсуждается.
С меня невмешательство - с вас своевременная оплата и чистота в квартире.
квартира в переулке..под окном автобусов нет!
Минимальный залог от 8000р если вы без животных и маленьких деток.
Если вы оплатите за 3 мес вперед то цена может быть уменьшена
https://www.avito.ru/sochi/kvartiry/kvartira-studiya_27m_14et._2415880353?utm_campaign=native&utm_medium=item_page_android&utm_source=soc_sharing_seller -
What role does the duration of action play in selecting a medication advair cost?
-
Player線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
Player如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 - Casino, Gambling、中國 - 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 - オンラインカジノ、越南 - Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。 -
Player線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
Player如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 - Casino, Gambling、中國 - 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 - オンラインカジノ、越南 - Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。 -
What's the primary function of prescription drugs vidalista 60 mg?
-
娛樂城評價
Player線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
Player如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 - Casino, Gambling、中國 - 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 - オンラインカジノ、越南 - Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。 -
娛樂城排行
Player線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
Player如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 - Casino, Gambling、中國 - 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 - オンラインカジノ、越南 - Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。 -
娛樂城推薦
Player線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
Player如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 - Casino, Gambling、中國 - 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 - オンラインカジノ、越南 - Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。 -
Player線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
Player如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 - Casino, Gambling、中國 - 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 - オンラインカジノ、越南 - Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。 -
RGBET
Cá Cược Thể Thao Trực Tuyến RGBET
Thể thao trực tuyến RGBET cung cấp thông tin cá cược thể thao mới nhất, như tỷ số bóng đá, bóng rổ, livestream và dữ liệu trận đấu. Đến với RGBET, bạn có thể tham gia chơi tại sảnh thể thao SABA, PANDA SPORT, CMD368, WG và SBO. Khám phá ngay!
Giới Thiệu Sảnh Cá Cược Thể Thao Trực Tuyến
Những sự kiện thể thao đa dạng, phủ sóng toàn cầu và cách chơi đa dạng mang đến cho người chơi tỷ lệ cá cược thể thao hấp dẫn nhất, tạo nên trải nghiệm cá cược thú vị và thoải mái.
Sảnh Thể Thao SBOBET
SBOBET, thành lập từ năm 1998, đã nhận được giấy phép cờ bạc trực tuyến từ Philippines, Đảo Man và Ireland. Tính đến nay, họ đã trở thành nhà tài trợ cho nhiều CLB bóng đá. Hiện tại, SBOBET đang hoạt động trên nhiều nền tảng trò chơi trực tuyến khắp thế giới.
Xem Chi Tiết »
Sảnh Thể Thao SABA
Saba Sports (SABA) thành lập từ năm 2008, tập trung vào nhiều hoạt động thể thao phổ biến để tạo ra nền tảng thể thao chuyên nghiệp và hoàn thiện. SABA được cấp phép IOM hợp pháp từ Anh và mang đến hơn 5.000 giải đấu thể thao đa dạng mỗi tháng.
Xem Chi Tiết »
Sảnh Thể Thao CMD368
CMD368 nổi bật với những ưu thế cạnh tranh, như cung cấp cho người chơi hơn 20.000 trận đấu hàng tháng, đến từ 50 môn thể thao khác nhau, đáp ứng nhu cầu của tất cả các fan hâm mộ thể thao, cũng như thoả mãn mọi sở thích của người chơi.
Xem Chi Tiết »
Sảnh Thể Thao PANDA SPORT
OB Sports đã chính thức đổi tên thành "Panda Sports", một thương hiệu lớn với hơn 30 giải đấu bóng. Panda Sports đặc biệt chú trọng vào tính năng cá cược thể thao, như chức năng "đặt cược sớm và đặt cược trực tiếp tại livestream" độc quyền.
Xem Chi Tiết »
Sảnh Thể Thao WG
WG Sports tập trung vào những môn thể thao không quá được yêu thích, với tỷ lệ cược cao và xử lý đơn cược nhanh chóng. Đặc biệt, nhiều nhà cái hàng đầu trên thị trường cũng hợp tác với họ, trở thành là một trong những sảnh thể thao nổi tiếng trên toàn cầu.
Xem Chi Tiết » -
해외선물수수료
국외선물의 개시 골드리치증권와 함께하세요.
골드리치증권는 장구한기간 고객님들과 더불어 선물마켓의 진로을 함께 여정을했습니다, 고객분들의 안전한 자금운용 및 알찬 수익률을 지향하여 언제나 최선을 다하고 있습니다.
어째서 20,000+인 넘게이 골드리치증권와 동참하나요?
신속한 대응: 쉽고 빠른 프로세스를 갖추어 누구나 수월하게 이용할 수 있습니다.
안전보장 프로토콜: 국가당국에서 채택한 최상의 등급의 보안을 적용하고 있습니다.
스마트 인가: 모든 거래정보은 부호화 보호되어 본인 외에는 그 누구도 내용을 열람할 수 없습니다.
안전 수익성 제공: 리스크 요소를 감소시켜, 보다 한층 확실한 수익률을 제시하며 그에 따른 리포트를 공유합니다.
24 / 7 상시 고객지원: 연중무휴 24시간 즉각적인 상담을 통해 회원분들을 전체 뒷받침합니다.
협력하는 파트너사: 골드리치는 공기업은 물론 금융기관들 및 많은 협력사와 공동으로 여정을 했습니다.
해외선물이란?
다양한 정보를 참고하세요.
국외선물은 외국에서 거래되는 파생금융상품 중 하나로, 지정된 기초자산(예시: 주식, 화폐, 상품 등)을 바탕로 한 옵션계약 계약을 의미합니다. 기본적으로 옵션은 명시된 기초자산을 향후의 특정한 시점에 일정 금액에 사거나 매도할 수 있는 권리를 제공합니다. 외국선물옵션은 이러한 옵션 계약이 외국 시장에서 거래되는 것을 의미합니다.
국외선물은 크게 콜 옵션과 매도 옵션으로 분류됩니다. 매수 옵션은 명시된 기초자산을 미래에 정해진 가격에 사는 권리를 제공하는 반면, 풋 옵션은 지정된 기초자산을 미래에 일정 금액에 팔 수 있는 권리를 부여합니다.
옵션 계약에서는 미래의 특정 날짜에 (만기일이라 지칭되는) 정해진 가격에 기초자산을 매수하거나 매도할 수 있는 권리를 가지고 있습니다. 이러한 가격을 행사 가격이라고 하며, 만기일에는 해당 권리를 행사할지 여부를 결정할 수 있습니다. 따라서 옵션 계약은 거래자에게 향후의 가격 변화에 대한 안전장치나 수익 실현의 기회를 부여합니다.
해외선물은 마켓 참가자들에게 다양한 투자 및 매매거래 기회를 제공, 환율, 상품, 주식 등 다양한 자산군에 대한 옵션 계약을 망라할 수 있습니다. 투자자는 매도 옵션을 통해 기초자산의 낙폭에 대한 안전장치를 받을 수 있고, 매수 옵션을 통해 호황에서의 수익을 노릴 수 있습니다.
해외선물 거래의 원리
행사 가격(Exercise Price): 해외선물에서 실행 가격은 옵션 계약에 따라 명시된 금액으로 계약됩니다. 만기일에 이 가격을 기준으로 옵션을 실행할 수 있습니다.
만기일(Expiration Date): 옵션 계약의 만기일은 옵션의 실행이 불가능한 마지막 일자를 지칭합니다. 이 날짜 이후에는 옵션 계약이 종료되며, 더 이상 거래할 수 없습니다.
풋 옵션(Put Option)과 매수 옵션(Call Option): 매도 옵션은 기초자산을 명시된 금액에 매도할 수 있는 권리를 허락하며, 매수 옵션은 기초자산을 명시된 가격에 사는 권리를 부여합니다.
옵션료(Premium): 외국선물 거래에서는 옵션 계약에 대한 옵션료을 납부해야 합니다. 이는 옵션 계약에 대한 가격으로, 시장에서의 수요와 공급량에 따라 변화됩니다.
행사 전략(Exercise Strategy): 거래자는 만기일에 옵션을 실행할지 여부를 결정할 수 있습니다. 이는 마켓 상황 및 투자 전략에 따라 상이하며, 옵션 계약의 수익을 최대화하거나 손해를 최소화하기 위해 선택됩니다.
시장 리스크(Market Risk): 외국선물 거래는 시장의 변화추이에 영향을 받습니다. 시세 변동이 예상치 못한 방향으로 발생할 경우 손해이 발생할 수 있으며, 이러한 마켓 리스크를 감소하기 위해 거래자는 전략을 구축하고 투자를 설계해야 합니다.
골드리치증권와 동반하는 국외선물은 확실한 믿을만한 수 있는 투자를 위한 최상의 선택입니다. 회원님들의 투자를 뒷받침하고 인도하기 위해 우리는 전력을 다하고 있습니다. 공동으로 더 나은 내일를 향해 계속해나가세요. -
해외선물의 시작 골드리치증권와 동참하세요.
골드리치증권는 오랜기간 투자자분들과 더불어 선물시장의 길을 공동으로 동행해왔으며, 고객분들의 안전한 투자 및 높은 수익률을 지향하여 언제나 전력을 다하고 있습니다.
왜 20,000+명 넘게이 골드리치와 동참하나요?
빠른 솔루션: 간단하며 빠른속도의 프로세스를 제공하여 누구나 간편하게 사용할 수 있습니다.
안전보장 프로토콜: 국가기관에서 적용한 높은 등급의 보안체계을 적용하고 있습니다.
스마트 인가절차: 전체 거래내용은 암호화 보호되어 본인 이외에는 아무도 누구도 정보를 접근할 수 없습니다.
확실한 이익률 공급: 위험 요소를 줄여, 더욱 한층 안전한 수익률을 제공하며 이에 따른 리포트를 제공합니다.
24 / 7 실시간 고객지원: 연중무휴 24시간 실시간 지원을 통해 고객님들을 전체 지원합니다.
협력하는 파트너사: 골드리치증권는 공기업은 물론 금융권들 및 다수의 협력사와 함께 걸어오고.
외국선물이란?
다양한 정보를 참고하세요.
해외선물은 해외에서 거래되는 파생금융상품 중 하나로, 특정 기초자산(예: 주식, 화폐, 상품 등)을 기초로 한 옵션계약 계약을 지칭합니다. 본질적으로 옵션은 지정된 기초자산을 미래의 특정한 시점에 일정 가격에 매수하거나 매도할 수 있는 권리를 제공합니다. 외국선물옵션은 이러한 옵션 계약이 해외 마켓에서 거래되는 것을 의미합니다.
국외선물은 크게 콜 옵션과 매도 옵션으로 분류됩니다. 매수 옵션은 명시된 기초자산을 미래에 정해진 금액에 사는 권리를 허락하는 반면, 매도 옵션은 명시된 기초자산을 미래에 일정 금액에 팔 수 있는 권리를 부여합니다.
옵션 계약에서는 미래의 명시된 일자에 (만기일이라 칭하는) 일정 금액에 기초자산을 사거나 팔 수 있는 권리를 가지고 있습니다. 이러한 가격을 실행 가격이라고 하며, 만료일에는 해당 권리를 행사할지 여부를 판단할 수 있습니다. 따라서 옵션 계약은 거래자에게 미래의 가격 변화에 대한 안전장치나 이익 실현의 기회를 허락합니다.
외국선물은 마켓 참가자들에게 다양한 운용 및 차익거래 기회를 열어주며, 외환, 상품, 주식 등 다양한 자산유형에 대한 옵션 계약을 망라할 수 있습니다. 투자자는 매도 옵션을 통해 기초자산의 하향에 대한 안전장치를 받을 수 있고, 콜 옵션을 통해 호황에서의 수익을 노릴 수 있습니다.
외국선물 거래의 원리
행사 가격(Exercise Price): 외국선물에서 행사 금액은 옵션 계약에 따라 지정된 금액으로 계약됩니다. 만기일에 이 금액을 기준으로 옵션을 행사할 수 있습니다.
만기일(Expiration Date): 옵션 계약의 종료일은 옵션의 실행이 불가능한 최종 날짜를 의미합니다. 이 일자 다음에는 옵션 계약이 종료되며, 더 이상 거래할 수 없습니다.
풋 옵션(Put Option)과 매수 옵션(Call Option): 풋 옵션은 기초자산을 특정 금액에 매도할 수 있는 권리를 부여하며, 콜 옵션은 기초자산을 지정된 금액에 매수하는 권리를 제공합니다.
옵션료(Premium): 외국선물 거래에서는 옵션 계약에 대한 계약료을 납부해야 합니다. 이는 옵션 계약에 대한 비용으로, 시장에서의 수요와 공급량에 따라 변화됩니다.
실행 전략(Exercise Strategy): 거래자는 만기일에 옵션을 행사할지 여부를 결정할 수 있습니다. 이는 마켓 환경 및 거래 전략에 따라 다르며, 옵션 계약의 수익을 최대화하거나 손실을 감소하기 위해 판단됩니다.
마켓 위험요인(Market Risk): 외국선물 거래는 마켓의 변동성에 효과을 받습니다. 가격 변동이 기대치 못한 방향으로 발생할 경우 손해이 발생할 수 있으며, 이러한 시장 위험요인를 최소화하기 위해 거래자는 계획을 수립하고 투자를 설계해야 합니다.
골드리치증권와 동반하는 국외선물은 안전하고 믿을만한 수 있는 투자를 위한 최상의 선택입니다. 고객님들의 투자를 지지하고 가이드하기 위해 우리는 최선을 다하고 있습니다. 공동으로 더 나은 미래를 지향하여 계속해나가세요. -
해외선물 대여계좌
해외선물의 개시 골드리치와 동참하세요.
골드리치는 오랜기간 고객님들과 더불어 선물마켓의 길을 함께 걸어왔으며, 고객분들의 확실한 자금운용 및 높은 수익률을 향해 항상 전력을 기울이고 있습니다.
무엇때문에 20,000+인 이상이 골드리치와 동참하나요?
신속한 솔루션: 쉽고 빠른 프로세스를 갖추어 어느누구라도 수월하게 활용할 수 있습니다.
안전 프로토콜: 국가기관에서 채택한 최상의 등급의 보안시스템을 적용하고 있습니다.
스마트 인가절차: 전체 거래정보은 암호처리 처리되어 본인 이외에는 그 누구도 내용을 확인할 수 없습니다.
안전 이익률 마련: 위험 부분을 낮추어, 더욱 더 보장된 수익률을 공개하며 이에 따른 리포트를 발간합니다.
24 / 7 지속적인 고객상담: 연중무휴 24시간 신속한 지원을 통해 회원분들을 모두 지원합니다.
함께하는 협력사: 골드리치는 공기업은 물론 금융권들 및 다양한 협력사와 공동으로 여정을 했습니다.
외국선물이란?
다양한 정보를 참고하세요.
외국선물은 국외에서 거래되는 파생금융상품 중 하나로, 특정 기반자산(예: 주식, 화폐, 상품 등)을 바탕로 한 옵션계약 약정을 지칭합니다. 본질적으로 옵션은 명시된 기초자산을 미래의 어떤 시점에 정해진 금액에 사거나 팔 수 있는 권리를 허락합니다. 국외선물옵션은 이러한 옵션 계약이 국외 시장에서 거래되는 것을 의미합니다.
해외선물은 크게 매수 옵션과 매도 옵션으로 구분됩니다. 콜 옵션은 명시된 기초자산을 미래에 정해진 금액에 매수하는 권리를 부여하는 반면, 풋 옵션은 명시된 기초자산을 미래에 정해진 금액에 팔 수 있는 권리를 부여합니다.
옵션 계약에서는 미래의 명시된 날짜에 (만기일이라 지칭되는) 일정 금액에 기초자산을 사거나 매도할 수 있는 권리를 보유하고 있습니다. 이러한 금액을 실행 가격이라고 하며, 만료일에는 해당 권리를 행사할지 여부를 판단할 수 있습니다. 따라서 옵션 계약은 거래자에게 미래의 시세 변동에 대한 보호나 수익 창출의 기회를 제공합니다.
국외선물은 시장 참가자들에게 다양한 투자 및 매매거래 기회를 제공, 환율, 상품, 주식 등 다양한 자산유형에 대한 옵션 계약을 포괄할 수 있습니다. 거래자는 풋 옵션을 통해 기초자산의 하향에 대한 보호를 받을 수 있고, 매수 옵션을 통해 활황에서의 수익을 타깃팅할 수 있습니다.
해외선물 거래의 원리
실행 가격(Exercise Price): 국외선물에서 행사 금액은 옵션 계약에 따라 명시된 가격으로 계약됩니다. 만기일에 이 가격을 기준으로 옵션을 행사할 수 있습니다.
종료일(Expiration Date): 옵션 계약의 만기일은 옵션의 행사가 허용되지않는 최종 일자를 지칭합니다. 이 날짜 다음에는 옵션 계약이 만료되며, 더 이상 거래할 수 없습니다.
풋 옵션(Put Option)과 매수 옵션(Call Option): 풋 옵션은 기초자산을 지정된 금액에 팔 수 있는 권리를 제공하며, 매수 옵션은 기초자산을 특정 금액에 매수하는 권리를 허락합니다.
옵션료(Premium): 외국선물 거래에서는 옵션 계약에 대한 계약료을 납부해야 합니다. 이는 옵션 계약에 대한 비용으로, 시장에서의 수요와 공급에 따라 변동됩니다.
행사 전략(Exercise Strategy): 거래자는 만료일에 옵션을 실행할지 여부를 결정할 수 있습니다. 이는 시장 상황 및 거래 전략에 따라 상이하며, 옵션 계약의 수익을 최대화하거나 손실을 최소화하기 위해 결정됩니다.
마켓 위험요인(Market Risk): 국외선물 거래는 마켓의 변동성에 효과을 받습니다. 가격 변화이 예상치 못한 방향으로 일어날 경우 손해이 발생할 수 있으며, 이러한 마켓 리스크를 축소하기 위해 거래자는 계획을 구축하고 투자를 계획해야 합니다.
골드리치증권와 함께하는 국외선물은 보장된 믿을만한 수 있는 운용을 위한 최상의 선택입니다. 고객님들의 투자를 뒷받침하고 안내하기 위해 우리는 최선을 다하고 있습니다. 함께 더 나은 미래를 지향하여 전진하세요. -
외국선물의 출발 골드리치와 함께하세요.
골드리치증권는 길고긴기간 회원분들과 함께 선물시장의 행로을 함께 걸어왔으며, 고객분들의 보장된 투자 및 알찬 이익률을 향해 항상 전력을 다하고 있습니다.
무엇때문에 20,000+인 이상이 골드리치와 동참하나요?
신속한 대응: 편리하고 빠른 프로세스를 제공하여 누구나 간편하게 이용할 수 있습니다.
안전 프로토콜: 국가기관에서 적용한 높은 등급의 보안체계을 도입하고 있습니다.
스마트 인가: 모든 거래내용은 암호처리 가공되어 본인 이외에는 아무도 누구도 정보를 열람할 수 없습니다.
안전 수익률 제공: 리스크 요소를 줄여, 더욱 더 보장된 수익률을 제공하며 이에 따른 리포트를 발간합니다.
24 / 7 실시간 고객상담: året runt 24시간 즉각적인 서비스를 통해 투자자분들을 전체 뒷받침합니다.
함께하는 동반사: 골드리치는 공기업은 물론 금융기관들 및 다양한 협력사와 함께 여정을 했습니다.
해외선물이란?
다양한 정보를 참고하세요.
국외선물은 국외에서 거래되는 파생상품 중 하나로, 명시된 기반자산(예시: 주식, 화폐, 상품 등)을 기초로 한 옵션 계약을 의미합니다. 본질적으로 옵션은 지정된 기초자산을 향후의 어떤 시점에 정해진 금액에 사거나 매도할 수 있는 자격을 부여합니다. 해외선물옵션은 이러한 옵션 계약이 해외 마켓에서 거래되는 것을 의미합니다.
국외선물은 크게 콜 옵션과 매도 옵션으로 분류됩니다. 매수 옵션은 특정 기초자산을 미래에 일정 금액에 사는 권리를 제공하는 반면, 풋 옵션은 특정 기초자산을 미래에 정해진 가격에 매도할 수 있는 권리를 허락합니다.
옵션 계약에서는 미래의 특정 날짜에 (만기일이라 불리는) 일정 가격에 기초자산을 매수하거나 매도할 수 있는 권리를 보유하고 있습니다. 이러한 가격을 실행 금액이라고 하며, 종료일에는 해당 권리를 실행할지 여부를 선택할 수 있습니다. 따라서 옵션 계약은 투자자에게 향후의 시세 변동에 대한 보호나 이익 창출의 기회를 제공합니다.
해외선물은 마켓 참가자들에게 다양한 투자 및 차익거래 기회를 제공, 외환, 상품, 주식 등 다양한 자산군에 대한 옵션 계약을 포함할 수 있습니다. 거래자는 풋 옵션을 통해 기초자산의 낙폭에 대한 보호를 받을 수 있고, 콜 옵션을 통해 상승장에서의 수익을 겨냥할 수 있습니다.
해외선물 거래의 원리
행사 금액(Exercise Price): 외국선물에서 행사 가격은 옵션 계약에 따라 지정된 가격으로 약정됩니다. 만기일에 이 가격을 기준으로 옵션을 행사할 수 있습니다.
종료일(Expiration Date): 옵션 계약의 종료일은 옵션의 행사가 허용되지않는 최종 일자를 지칭합니다. 이 날짜 이후에는 옵션 계약이 종료되며, 더 이상 거래할 수 없습니다.
풋 옵션(Put Option)과 콜 옵션(Call Option): 매도 옵션은 기초자산을 특정 금액에 팔 수 있는 권리를 제공하며, 콜 옵션은 기초자산을 명시된 가격에 매수하는 권리를 제공합니다.
계약료(Premium): 국외선물 거래에서는 옵션 계약에 대한 옵션료을 납부해야 합니다. 이는 옵션 계약에 대한 비용으로, 마켓에서의 수요와 공급에 따라 변동됩니다.
실행 전략(Exercise Strategy): 투자자는 종료일에 옵션을 실행할지 여부를 결정할 수 있습니다. 이는 마켓 상황 및 투자 플랜에 따라 다르며, 옵션 계약의 수익을 최대화하거나 손해를 최소화하기 위해 판단됩니다.
마켓 리스크(Market Risk): 해외선물 거래는 시장의 변화추이에 효과을 받습니다. 시세 변화이 기대치 못한 방향으로 발생할 경우 손해이 발생할 수 있으며, 이러한 시장 리스크를 축소하기 위해 거래자는 계획을 구축하고 투자를 설계해야 합니다.
골드리치증권와 동반하는 국외선물은 안전하고 확신할 수 있는 운용을 위한 가장좋은 선택입니다. 회원님들의 투자를 뒷받침하고 인도하기 위해 우리는 최선을 다하고 있습니다. 함께 더 나은 내일를 지향하여 전진하세요. -
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต -
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต
-
Gerakl24: Профессиональная Замена Фундамента, Венцов, Покрытий и Передвижение Домов
Компания Геракл24 специализируется на предоставлении полных услуг по замене основания, венцов, полов и перемещению домов в населённом пункте Красноярске и в окрестностях. Наш коллектив квалифицированных экспертов обещает отличное качество выполнения различных типов реставрационных работ, будь то деревянные, каркасные, кирпичные или из бетона здания.
Достоинства сотрудничества с Gerakl24
Квалификация и стаж:
Каждая задача проводятся лишь опытными специалистами, имеющими долгий стаж в направлении создания и восстановления строений. Наши сотрудники профессионалы в своем деле и реализуют задачи с высочайшей точностью и вниманием к мелочам.
Комплексный подход:
Мы предоставляем полный спектр услуг по восстановлению и реконструкции строений:
Реставрация фундамента: укрепление и замена старого фундамента, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы вашего здания и предотвратить проблемы, связанные с оседанием и деформацией строения.
Реставрация венцов: восстановление нижних венцов деревянных зданий, которые чаще всего подвержены гниению и разрушению.
Смена настилов: установка новых полов, что кардинально улучшает внешний облик и практическую полезность.
Передвижение домов: качественный и безопасный перенос строений на новые места, что позволяет сохранить ваше строение и избежать дополнительных затрат на возведение нового.
Работа с любыми видами зданий:
Деревянные дома: реставрация и усиление деревянных элементов, защита от гниения и вредителей.
Дома с каркасом: усиление каркасных конструкций и реставрация поврежденных элементов.
Кирпичные строения: реставрация кирпичной кладки и укрепление стен.
Дома из бетона: реставрация и усиление бетонных элементов, исправление трещин и разрушений.
Качество и надежность:
Мы применяем только проверенные материалы и передовые технологии, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность всех выполненных работ. Каждый наш проект проходят тщательную проверку качества на каждой стадии реализации.
Персонализированный подход:
Мы предлагаем каждому клиенту индивидуальные решения, учитывающие ваши требования и желания. Наша цель - чтобы результат нашей работы соответствовал вашим ожиданиям и требованиям.
Почему стоит выбрать Геракл24?
Сотрудничая с нами, вы получаете надежного партнера, который возьмет на себя все хлопоты по ремонту и реставрации вашего дома. Мы обеспечиваем выполнение всех проектов в сроки, оговоренные заранее и с в соответствии с нормами и стандартами. Связавшись с Геракл24, вы можете не сомневаться, что ваш дом в надежных руках.
Мы предлагаем консультацию и ответить на все ваши вопросы. Контактируйте с нами, чтобы обсудить ваш проект и узнать о наших сервисах. Мы поможем вам сохранить и улучшить ваш дом, обеспечив его безопасность и комфорт на долгие годы.
Gerakl24 – ваш выбор для реставрации и ремонта домов в Красноярске и области. -
Геракл24: Профессиональная Замена Фундамента, Венцов, Покрытий и Перемещение Зданий
Компания Геракл24 специализируется на выполнении полных услуг по замене фундамента, венцов, полов и передвижению домов в городе Красноярск и в окрестностях. Наша группа опытных специалистов гарантирует превосходное качество реализации различных типов ремонтных работ, будь то древесные, каркасные, кирпичные постройки или бетонные дома.
Плюсы услуг Геракл24
Навыки и знания:
Весь процесс проводятся только опытными мастерами, имеющими многолетний практику в направлении возведения и ремонта зданий. Наши мастера эксперты в своей области и осуществляют проекты с высочайшей точностью и вниманием к мелочам.
Комплексный подход:
Мы осуществляем разнообразные услуги по реставрации и реконструкции строений:
Смена основания: укрепление и замена старого фундамента, что гарантирует долговечность вашего здания и избежать проблем, вызванные оседанием и деформацией.
Замена венцов: реставрация нижних венцов из дерева, которые обычно гниют и разрушаются.
Смена настилов: установка новых полов, что существенно улучшает внешний вид и функциональные характеристики.
Передвижение домов: безопасное и надежное перемещение зданий на новые места, что позволяет сохранить ваше строение и избежать дополнительных затрат на возведение нового.
Работа с любыми типами домов:
Дома из дерева: реставрация и усиление деревянных элементов, обработка от гниения и насекомых.
Каркасные строения: укрепление каркасов и реставрация поврежденных элементов.
Кирпичные дома: реставрация кирпичной кладки и усиление стен.
Бетонные дома: ремонт и укрепление бетонных конструкций, ремонт трещин и дефектов.
Надежность и долговечность:
Мы работаем с только высококачественные материалы и передовые технологии, что гарантирует долговечность и надежность всех выполненных работ. Все наши проекты проходят тщательную проверку качества на каждой стадии реализации.
Индивидуальный подход:
Для каждого клиента мы предлагаем подходящие решения, учитывающие все особенности и пожелания. Наша цель - чтобы конечный результат полностью удовлетворял ваши ожидания и требования.
Почему выбирают Геракл24?
Работая с нами, вы приобретете надежного партнера, который берет на себя все заботы по восстановлению и ремонту вашего здания. Мы обеспечиваем выполнение всех работ в сроки, оговоренные заранее и с соблюдением всех правил и норм. Связавшись с Геракл24, вы можете быть уверены, что ваше здание в надежных руках.
Мы готовы предоставить консультацию и дать ответы на все вопросы. Контактируйте с нами, чтобы обсудить детали вашего проекта и узнать больше о наших услугах. Мы сохраним и улучшим ваш дом, сделав его уютным и безопасным для долгого проживания.
Gerakl24 – ваш надежный партнер в реставрации и ремонте домов в Красноярске и за его пределами. -
הפלטפורמה הווה פלטפורמה פופולרית במדינה לקנייה של צמח הקנאביס באופן מקוון. זו מספקת ממשק משתמש פשוט לשימוש ומאובטח לקנייה וקבלת משלוחים מ פריטי קנאביס מגוונים. בכתבה זה נסקור עם הרעיון מאחורי הפלטפורמה, כיצד זו פועלת ומה המעלות של השימוש בזו.
מה זו הפלטפורמה?
הפלטפורמה מהווה אמצעי לקנייה של מריחואנה דרך האפליקציה טלגראם. זו מבוססת על ערוצי תקשורת וקבוצות טלגרם מיוחדות הנקראות ״כיווני טלגראס״, שבהם אפשר להזמין מגוון מוצרי צמח הקנאביס ולקבלת אלו ישירות למשלוח. ערוצי התקשורת אלו מאורגנים לפי אזורים גיאוגרפיים, במטרה להקל את קבלת המשלוחים.
איך זה עובד?
התהליך פשוט יחסית. ראשית, יש להצטרף לערוץ הטלגראס הנוגע לאזור המחיה. שם אפשר לצפות בתפריטים של המוצרים השונים ולהזמין את הפריטים הרצויים. לאחר השלמת ההרכבה וסגירת התשלום, השליח יופיע בכתובת שנרשמה עם הארגז שהוזמן.
מרבית ערוצי הטלגראס מציעים טווח רחב מ פריטים - זנים של צמח הקנאביס, עוגיות, משקאות ועוד. כמו כן, אפשר לראות חוות דעת מ לקוחות שעברו על איכות המוצרים והשירות.
יתרונות הנעשה באפליקציה
יתרון עיקרי של טלגראס הוא הנוחיות והדיסקרטיות. ההרכבה והתהליך מתקיימים ממרחק מאיזשהו מקום, בלי צורך במפגש פיזי. כמו כן, הפלטפורמה מאובטחת היטב ומבטיחה סודיות גבוהה.
נוסף אל זאת, מחירי הפריטים בטלגראס נוטות לבוא זולים, והמשלוחים מגיעים במהירות ובמסירות גבוהה. יש גם מרכז תמיכה זמין לכל שאלה או בעיה.
לסיכום
האפליקציה היא דרך מקורית ויעילה לקנות מוצרי קנאביס במדינה. היא משלבת בין הנוחיות הדיגיטלית מ האפליקציה הפופולרית, ועם המהירות והפרטיות מ שיטת המשלוח הישירה. ככל שהדרישה למריחואנה גובר, פלטפורמות בדוגמת זו צפויות להמשיך ולצמוח. -
האפליקציה הינה תוכנה פופולרית בארץ לרכישת מריחואנה בצורה אינטרנטי. זו מעניקה ממשק פשוט לשימוש ומאובטח לקנייה וקבלת שילוחים מ פריטי קנאביס מגוונים. במאמר זו נבחן עם הרעיון שמאחורי הפלטפורמה, כיצד זו פועלת ומהם היתרונות מ השימוש בזו.
מה זו טלגראס?
הפלטפורמה הווה דרך לרכישת קנאביס דרך היישומון טלגראם. היא מבוססת מעל ערוצים וקבוצות טלגרם ספציפיות הקרויות ״טלגראס כיוונים, שם אפשר להזמין מרחב פריטי קנאביס ולקבלת אלו ישירות לשילוח. ערוצי התקשורת האלה מסודרים לפי איזורים גאוגרפיים, כדי לשפר את קבלת המשלוחים.
כיצד זאת פועל?
התהליך קל יחסית. ראשית, צריך להצטרף לערוץ הטלגראס הרלוונטי לאזור המגורים. שם אפשר לעיין בתפריטים של המוצרים השונים ולהרכיב עם המוצרים הרצויים. לאחר השלמת ההזמנה וסגירת התשלום, השליח יגיע לכתובת שנרשמה עם הארגז המוזמנת.
מרבית ערוצי טלגראס מציעים מגוון נרחב של פריטים - סוגי צמח הקנאביס, ממתקים, שתייה ועוד. כמו כן, אפשר למצוא חוות דעת של לקוחות שעברו לגבי איכות המוצרים והשירות.
מעלות השימוש בפלטפורמה
מעלה עיקרי של טלגראס הינו הנוחיות והפרטיות. ההזמנה והתהליך מתקיימים ממרחק מאיזשהו מקום, בלי צורך במפגש פיזי. בנוסף, הפלטפורמה מוגנת היטב ומבטיחה חיסיון גבוה.
מלבד אל זאת, מחירי הפריטים בפלטפורמה נוטים להיות תחרותיים, והשילוחים מגיעים במהירות ובמסירות גבוהה. יש גם מוקד תמיכה זמין לכל שאלה או בעיה.
סיכום
האפליקציה היא דרך חדשנית ויעילה לרכוש פריטי קנאביס בארץ. היא משלבת את הנוחות הטכנולוגית מ היישומון הפופולרי, לבין המהירות והדיסקרטיות מ דרך המשלוח הישירות. ככל שהביקוש למריחואנה גדלה, פלטפורמות בדוגמת זו צפויות להמשיך ולצמוח. -
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS - Giải pháp vượt trội cho các tín đồ iOS
Trong thế giới công nghệ đầy sôi động hiện nay, trải nghiệm người dùng luôn là yếu tố then chốt. Với sự ra đời của Bản cài đặt B29 IOS, người dùng sẽ được hưởng trọn vẹn những tính năng ưu việt, mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối. Hãy cùng khám phá những ưu điểm vượt trội của bản cài đặt này!
Tính bảo mật tối đa
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được thiết kế với mục tiêu đảm bảo an toàn dữ liệu tuyệt đối cho người dùng. Nhờ hệ thống mã hóa hiện đại, thông tin cá nhân và dữ liệu nhạy cảm của bạn luôn được bảo vệ an toàn khỏi những kẻ xâm nhập trái phép.
Trải nghiệm người dùng đỉnh cao
Giao diện thân thiện, đơn giản nhưng không kém phần hiện đại, B29 IOS mang đến cho người dùng trải nghiệm duyệt web, truy cập ứng dụng và sử dụng thiết bị một cách trôi chảy, mượt mà. Các tính năng thông minh được tối ưu hóa, giúp nâng cao hiệu suất và tiết kiệm pin đáng kể.
Tính tương thích rộng rãi
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được phát triển với mục tiêu tương thích với mọi thiết bị iOS từ các dòng iPhone, iPad cho đến iPod Touch. Dù là người dùng mới hay lâu năm của hệ điều hành iOS, B29 đều mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối.
Quá trình cài đặt đơn giản
Với những hướng dẫn chi tiết, việc cài đặt B29 IOS trở nên nhanh chóng và dễ dàng. Chỉ với vài thao tác đơn giản, bạn đã có thể trải nghiệm ngay tất cả những tính năng tuyệt vời mà bản cài đặt này mang lại.
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS không chỉ là một bản cài đặt đơn thuần, mà còn là giải pháp công nghệ hiện đại, nâng tầm trải nghiệm người dùng lên một tầm cao mới. Hãy trở thành một phần của cộng đồng sử dụng B29 IOS để khám phá những tiện ích tuyệt vời mà nó có thể mang lại! -
b29
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS - Giải pháp vượt trội cho các tín đồ iOS
Trong thế giới công nghệ đầy sôi động hiện nay, trải nghiệm người dùng luôn là yếu tố then chốt. Với sự ra đời của Bản cài đặt B29 IOS, người dùng sẽ được hưởng trọn vẹn những tính năng ưu việt, mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối. Hãy cùng khám phá những ưu điểm vượt trội của bản cài đặt này!
Tính bảo mật tối đa
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được thiết kế với mục tiêu đảm bảo an toàn dữ liệu tuyệt đối cho người dùng. Nhờ hệ thống mã hóa hiện đại, thông tin cá nhân và dữ liệu nhạy cảm của bạn luôn được bảo vệ an toàn khỏi những kẻ xâm nhập trái phép.
Trải nghiệm người dùng đỉnh cao
Giao diện thân thiện, đơn giản nhưng không kém phần hiện đại, B29 IOS mang đến cho người dùng trải nghiệm duyệt web, truy cập ứng dụng và sử dụng thiết bị một cách trôi chảy, mượt mà. Các tính năng thông minh được tối ưu hóa, giúp nâng cao hiệu suất và tiết kiệm pin đáng kể.
Tính tương thích rộng rãi
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được phát triển với mục tiêu tương thích với mọi thiết bị iOS từ các dòng iPhone, iPad cho đến iPod Touch. Dù là người dùng mới hay lâu năm của hệ điều hành iOS, B29 đều mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối.
Quá trình cài đặt đơn giản
Với những hướng dẫn chi tiết, việc cài đặt B29 IOS trở nên nhanh chóng và dễ dàng. Chỉ với vài thao tác đơn giản, bạn đã có thể trải nghiệm ngay tất cả những tính năng tuyệt vời mà bản cài đặt này mang lại.
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS không chỉ là một bản cài đặt đơn thuần, mà còn là giải pháp công nghệ hiện đại, nâng tầm trải nghiệm người dùng lên một tầm cao mới. Hãy trở thành một phần của cộng đồng sử dụng B29 IOS để khám phá những tiện ích tuyệt vời mà nó có thể mang lại! -
Telegrass
האפליקציה היא אפליקציה מקובלת במדינה לקנייה של קנאביס באופן אינטרנטי. היא נותנת ממשק פשוט לשימוש ומאובטח לקנייה ולקבלת שילוחים של מוצרי קנאביס מרובים. במאמר זו נסקור עם העיקרון שמאחורי טלגראס, כיצד היא עובדת ומה המעלות מ השימוש בזו.
מהי טלגראס?
הפלטפורמה הווה דרך לקנייה של צמח הקנאביס באמצעות האפליקציה טלגראם. זו מבוססת מעל ערוצי תקשורת וקהילות טלגראם ספציפיות הנקראות ״טלגראס כיוונים, שם ניתן להרכיב מגוון פריטי צמח הקנאביס ולקבלת אלו ישירות לשילוח. הערוצים אלו מסודרים לפי אזורים גיאוגרפיים, במטרה לשפר על קבלת השילוחים.
איך זה פועל?
התהליך קל יחסית. קודם כל, צריך להצטרף לערוץ הטלגראס הנוגע לאזור המגורים. שם ניתן לעיין בתפריטי הפריטים השונים ולהרכיב עם המוצרים המבוקשים. לאחר השלמת ההזמנה וסגירת התשלום, השליח יגיע בכתובת שנרשמה עם הארגז המוזמנת.
רוב ערוצי טלגראס מציעים טווח נרחב של פריטים - זנים של צמח הקנאביס, עוגיות, משקאות ועוד. כמו כן, אפשר למצוא חוות דעת של צרכנים שעברו לגבי רמת הפריטים והשירות.
מעלות הנעשה בטלגראס
יתרון עיקרי של טלגראס הינו הנוחות והפרטיות. ההזמנה וההכנות מתקיימים מרחוק מאיזשהו מיקום, בלי צורך במפגש פנים אל פנים. כמו כן, הפלטפורמה מוגנת ביסודיות ומבטיחה חיסיון גבוהה.
מלבד אל כך, עלויות המוצרים באפליקציה נוטים להיות תחרותיים, והמשלוחים מגיעים במהירות ובמסירות גבוהה. קיים גם מוקד תמיכה פתוח לכל שאלה או בעיה.
סיכום
האפליקציה הווה שיטה מקורית ויעילה לרכוש מוצרי קנאביס בישראל. זו משלבת את הנוחות הדיגיטלית של האפליקציה הפופולרית, ועם הזריזות והפרטיות של שיטת המשלוח הישירה. ככל שהביקוש לצמח הקנאביס גובר, פלטפורמות כמו טלגראס צפויות להמשיך ולהתפתח. -
הפלטפורמה היא תוכנה מקובלת בישראל לקנייה של צמח הקנאביס באופן וירטואלי. זו מעניקה ממשק פשוט לשימוש ומאובטח לקנייה וקבלת שילוחים מ מוצרי צמח הקנאביס שונים. בסקירה זו נסקור את העיקרון מאחורי טלגראס, כיצד זו עובדת ומה המעלות של השימוש בה.
מה זו טלגראס?
האפליקציה הינה שיטה לרכישת קנאביס באמצעות היישומון טלגראם. היא מבוססת מעל ערוצים וקבוצות טלגראם ספציפיות הקרויות ״טלגראס כיוונים, שבהם אפשר להרכיב מרחב מוצרי מריחואנה ולקבלת אותם ישירותית למשלוח. הערוצים אלו מסודרים לפי אזורים גאוגרפיים, במטרה לשפר על קבלתם של השילוחים.
איך זה עובד?
התהליך קל למדי. קודם כל, צריך להצטרף לערוץ הטלגראס הרלוונטי לאזור המחיה. שם ניתן לצפות בתפריטים של המוצרים השונים ולהרכיב עם המוצרים הרצויים. לאחר ביצוע ההזמנה וסיום התשלום, השליח יגיע לכתובת שנרשמה עם הארגז שהוזמן.
מרבית ערוצי טלגראס מספקים מגוון רחב של מוצרים - סוגי מריחואנה, עוגיות, שתייה ועוד. כמו כן, אפשר למצוא חוות דעת של צרכנים קודמים לגבי איכות המוצרים והשרות.
מעלות השימוש בטלגראס
מעלה מרכזי מ הפלטפורמה הוא הנוחות והפרטיות. ההזמנה והתהליך מתבצעות מרחוק מאיזשהו מקום, בלי צורך במפגש פיזי. בנוסף, האפליקציה מאובטחת היטב ומבטיחה סודיות גבוה.
מלבד על כך, עלויות הפריטים באפליקציה נוטים להיות תחרותיים, והשילוחים מגיעים במהירות ובמסירות רבה. יש אף מרכז תמיכה זמין לכל שאלה או בעיית.
לסיכום
הפלטפורמה היא שיטה מקורית ויעילה לרכוש מוצרי קנאביס בישראל. זו משלבת את הנוחות הטכנולוגית מ היישומון הפופולרי, לבין הזריזות והפרטיות מ דרך המשלוח הישירה. ככל שהביקוש למריחואנה גדלה, פלטפורמות בדוגמת זו צפויות להמשיך ולצמוח. -
b29
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS - Giải pháp vượt trội cho các tín đồ iOS
Trong thế giới công nghệ đầy sôi động hiện nay, trải nghiệm người dùng luôn là yếu tố then chốt. Với sự ra đời của Bản cài đặt B29 IOS, người dùng sẽ được hưởng trọn vẹn những tính năng ưu việt, mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối. Hãy cùng khám phá những ưu điểm vượt trội của bản cài đặt này!
Tính bảo mật tối đa
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được thiết kế với mục tiêu đảm bảo an toàn dữ liệu tuyệt đối cho người dùng. Nhờ hệ thống mã hóa hiện đại, thông tin cá nhân và dữ liệu nhạy cảm của bạn luôn được bảo vệ an toàn khỏi những kẻ xâm nhập trái phép.
Trải nghiệm người dùng đỉnh cao
Giao diện thân thiện, đơn giản nhưng không kém phần hiện đại, B29 IOS mang đến cho người dùng trải nghiệm duyệt web, truy cập ứng dụng và sử dụng thiết bị một cách trôi chảy, mượt mà. Các tính năng thông minh được tối ưu hóa, giúp nâng cao hiệu suất và tiết kiệm pin đáng kể.
Tính tương thích rộng rãi
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được phát triển với mục tiêu tương thích với mọi thiết bị iOS từ các dòng iPhone, iPad cho đến iPod Touch. Dù là người dùng mới hay lâu năm của hệ điều hành iOS, B29 đều mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối.
Quá trình cài đặt đơn giản
Với những hướng dẫn chi tiết, việc cài đặt B29 IOS trở nên nhanh chóng và dễ dàng. Chỉ với vài thao tác đơn giản, bạn đã có thể trải nghiệm ngay tất cả những tính năng tuyệt vời mà bản cài đặt này mang lại.
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS không chỉ là một bản cài đặt đơn thuần, mà còn là giải pháp công nghệ hiện đại, nâng tầm trải nghiệm người dùng lên một tầm cao mới. Hãy trở thành một phần của cộng đồng sử dụng B29 IOS để khám phá những tiện ích tuyệt vời mà nó có thể mang lại! -
b29
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS - Giải pháp vượt trội cho các tín đồ iOS
Trong thế giới công nghệ đầy sôi động hiện nay, trải nghiệm người dùng luôn là yếu tố then chốt. Với sự ra đời của Bản cài đặt B29 IOS, người dùng sẽ được hưởng trọn vẹn những tính năng ưu việt, mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối. Hãy cùng khám phá những ưu điểm vượt trội của bản cài đặt này!
Tính bảo mật tối đa
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được thiết kế với mục tiêu đảm bảo an toàn dữ liệu tuyệt đối cho người dùng. Nhờ hệ thống mã hóa hiện đại, thông tin cá nhân và dữ liệu nhạy cảm của bạn luôn được bảo vệ an toàn khỏi những kẻ xâm nhập trái phép.
Trải nghiệm người dùng đỉnh cao
Giao diện thân thiện, đơn giản nhưng không kém phần hiện đại, B29 IOS mang đến cho người dùng trải nghiệm duyệt web, truy cập ứng dụng và sử dụng thiết bị một cách trôi chảy, mượt mà. Các tính năng thông minh được tối ưu hóa, giúp nâng cao hiệu suất và tiết kiệm pin đáng kể.
Tính tương thích rộng rãi
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS được phát triển với mục tiêu tương thích với mọi thiết bị iOS từ các dòng iPhone, iPad cho đến iPod Touch. Dù là người dùng mới hay lâu năm của hệ điều hành iOS, B29 đều mang đến sự hài lòng tuyệt đối.
Quá trình cài đặt đơn giản
Với những hướng dẫn chi tiết, việc cài đặt B29 IOS trở nên nhanh chóng và dễ dàng. Chỉ với vài thao tác đơn giản, bạn đã có thể trải nghiệm ngay tất cả những tính năng tuyệt vời mà bản cài đặt này mang lại.
Bản cài đặt B29 IOS không chỉ là một bản cài đặt đơn thuần, mà còn là giải pháp công nghệ hiện đại, nâng tầm trải nghiệm người dùng lên một tầm cao mới. Hãy trở thành một phần của cộng đồng sử dụng B29 IOS để khám phá những tiện ích tuyệt vời mà nó có thể mang lại! -
הפלטפורמה הווה אפליקציה מקובלת בישראל לקנייה של קנאביס באופן אינטרנטי. זו מספקת ממשק משתמש נוח ומאובטח לרכישה וקבלת שילוחים של פריטי צמח הקנאביס שונים. בסקירה זו נסקור עם הרעיון שמאחורי הפלטפורמה, כיצד זו פועלת ומה המעלות מ השימוש בזו.
מהי הפלטפורמה?
טלגראס הינה דרך לקנייה של קנאביס באמצעות האפליקציה טלגראם. היא נשענת מעל ערוצים וקהילות טלגרם מיוחדות הנקראות ״כיווני טלגראס״, שבהם ניתן להזמין מרחב פריטי קנאביס ולקבלת אלו ישירות למשלוח. ערוצי התקשורת האלה מסודרים לפי איזורים גיאוגרפיים, כדי לשפר את קבלת המשלוחים.
כיצד זאת פועל?
התהליך פשוט למדי. קודם כל, צריך להצטרף לערוץ טלגראס הנוגע לאזור המחיה. שם ניתן לצפות בתפריטים של הפריטים השונים ולהרכיב עם המוצרים הרצויים. לאחר השלמת ההרכבה וסגירת התשלום, השליח יגיע לכתובת שצוינה עם הארגז המוזמנת.
מרבית ערוצי טלגראס מספקים טווח רחב מ פריטים - סוגי צמח הקנאביס, ממתקים, שתייה ועוד. בנוסף, ניתן למצוא חוות דעת של צרכנים קודמים על רמת הפריטים והשירות.
יתרונות הנעשה באפליקציה
יתרון מרכזי מ טלגראס הוא הנוחיות והדיסקרטיות. ההזמנה והתהליך מתבצעות מרחוק מכל מיקום, ללא נחיצות במפגש פנים אל פנים. כמו כן, האפליקציה מאובטחת ביסודיות ומבטיחה חיסיון גבוהה.
מלבד על זאת, מחירי הפריטים באפליקציה נוטים להיות תחרותיים, והשילוחים מגיעים במהירות ובהשקעה רבה. קיים גם מרכז תמיכה זמין לכל שאלה או בעיית.
לסיכום
האפליקציה הווה שיטה חדשנית ויעילה לרכוש מוצרי צמח הקנאביס בישראל. זו משלבת את הנוחות הדיגיטלית של היישומון הפופולרית, ועם המהירות והדיסקרטיות מ שיטת השילוח הישירה. ככל שהדרישה למריחואנה גדלה, פלטפורמות בדוגמת טלגראס צפויות להמשיך ולצמוח. -
טלגראס הינה אפליקציה פופולרית בישראל לרכישת צמח הקנאביס באופן אינטרנטי. זו מספקת ממשק נוח ומאובטח לקנייה וקבלת משלוחים מ פריטי קנאביס מרובים. במאמר זו נבחן עם העיקרון מאחורי האפליקציה, איך זו עובדת ומה היתרונות מ השימוש בזו.
מה זו האפליקציה?
טלגראס הווה דרך לקנייה של קנאביס דרך האפליקציה טלגרם. זו נשענת על ערוצי תקשורת וקבוצות טלגרם ספציפיות הקרויות ״כיווני טלגראס״, שם אפשר להרכיב מרחב מוצרי מריחואנה ולקבלת אותם ישירותית למשלוח. הערוצים האלה מאורגנים על פי אזורים גאוגרפיים, במטרה לשפר על קבלת השילוחים.
כיצד זאת עובד?
התהליך פשוט למדי. ראשית, יש להצטרף לערוץ הטלגראס הנוגע לאזור המגורים. שם אפשר לצפות בתפריטים של הפריטים השונים ולהזמין עם הפריטים הרצויים. לאחר ביצוע ההזמנה וסגירת התשלום, השליח יגיע לכתובת שצוינה עם הארגז שהוזמן.
מרבית ערוצי טלגראס מציעים מגוון נרחב מ מוצרים - זנים של מריחואנה, עוגיות, שתייה ועוד. כמו כן, אפשר לראות חוות דעת של לקוחות שעברו לגבי רמת המוצרים והשירות.
מעלות השימוש באפליקציה
יתרון עיקרי מ הפלטפורמה הינו הנוחות והדיסקרטיות. ההזמנה וההכנות מתבצעות ממרחק מכל מקום, ללא נחיצות בהתכנסות פיזי. בנוסף, האפליקציה מאובטחת היטב ומבטיחה סודיות גבוה.
נוסף אל זאת, עלויות המוצרים בטלגראס נוטים להיות זולים, והמשלוחים מגיעים במהירות ובמסירות רבה. יש אף מרכז תמיכה פתוח לכל שאלה או בעיית.
סיכום
האפליקציה היא שיטה מקורית ויעילה לקנות פריטי קנאביס במדינה. היא משלבת את הנוחיות הדיגיטלית מ האפליקציה הפופולרית, ועם הזריזות והפרטיות של שיטת המשלוח הישירה. ככל שהביקוש לצמח הקנאביס גובר, פלטפורמות כמו זו צפויות להמשיך ולצמוח. -
How to lose weight
?The next day was their “healthy” breakfast for the first time in their lives. As it turned out, vegetables in an omelet are not so bad. And if you close your eyes, you can even imagine that it’s fast food:
— I didn’t even think that this vegetable mix would fit in here so well! For lunch, soup and buckwheat with chicken in a double boiler, and I haven’t figured out the evening yet. After work, we’ll take a walk, okay, Masha?
— Yes! I want to! Mom, why don’t we have cereal for breakfast today? Well, at least chocolate.
— From this day on, we have a different diet. And this extra sugar is completely unnecessary for us. -
?Her phrase sounded with a special chuckle. It’s obvious that she didn’t believe this obese man: what food lover can give up food? Taking the tray, he retired to the table with doubts. But the very awareness that he supported his beloved and did not abandon her in a difficult moment — already satiated him completely. It turns out that buckwheat is also tasty, and without mayonnaise. The salad has an unusual pleasant sourness, almost like chips. And the compote is even nicer than the foreign soda — that’s how much he wanted to support Tanya! Coming to the shop, he had a very unusual conversation, which he did not expect himself:
— Petrovich, why did you decide to lose weight? Lyudka has already reported everything to us. Have you decided to become an athlete in your years?
— Yes, my wife’s viper-friends are attacking her! They have so bullied her that she decided to put all of us on a weight loss program. The poor thing almost cries when she thinks about it.
— Wait, is that our Tanya from the accounting department? The one with dark hair. Well, what kind of friends are offending her there?
— Yes, my beauty. But it’s Victoria Gronich who teases her the most, if you know her.
— Wait, the Gronich family! So these are my neighbors, they’ve been fighting ungodly every day! I’ll have a talk with her, for sure. -
Дочь стояла в удивлении и теребила край своего платья, изредка поднимая глаза на такого же отца. Она не особо понимала значения слов, но считывая эмоции папы, становилось не по себе. Чипсы из тележки обратно отправились на полку, проведенные грустным взглядом мужчины:
—Ладно…. Так все-таки худеем? А с чего ты так резко решила? Жили же, и нормально было….
—Потом обсудим. Не сейчас.
индивид полностью не предусматривал из уст любимой супруги Татьяны. Внутри их собственной династии конституция тела совсем отличалась в противовес нормативной а также общепризнанной – обладать предожирением полная условие. -
Пару мгновений и семья уже была в овощном отделе. Приходилось им там быть максимально редко – о существовании некоторых овощей и фруктов люди не знали вообще, от слова совсем. Смотря на все, как на диковинку, настало время выбора:
—Ну, что ж…. Возьмем помидоров, огурцов, а вот и яблоки, кабачков тоже можно…
Таня рассуждала сама по себе и не советовалась с голодными глазами мужа, ловко перебирая овощи и откладывая самые лучшие в полиэтиленовый пакет. Маленькая девочка внимательно осматривала апельсины – такого она еще никогда не видела, а тем более, не ела:
—Может, потом еще чего-нибудь нормального возьмем? Колбаски там, сосисок. Ты если хочешь, худей. А мы нормально будем жить. Да, доча?
мужчина абсолютно не предусматривал из уст родной избранницы Татианы. Внутри их родственной группе фигура организма совсем отличалась в сравнении с типовой и распространённой – обладать предожирением безоговорочная норма. -
娛樂城
網上娛樂城的天地
隨著互聯網的快速發展,線上娛樂城(線上賭場)已經成為許多人消遣的新選擇。線上娛樂城不僅提供多元化的游戲選擇,還能讓玩家在家中就能體驗到賭場的刺激和快感。本文將研究線上娛樂城的特徵、利益以及一些常有的游戲。
什麼叫在線娛樂城?
線上娛樂城是一種經由互聯網提供賭錢遊戲的平台。玩家可以通過電腦設備、智慧型手機或平板電腦進入這些網站,參與各種博彩活動,如撲克、輪盤賭、二十一點和老虎机等。這些平台通常由專業的軟體公司開發,確保遊戲的公平性和安全。
網上娛樂城的優勢
方便性:玩家無需離開家,就能體驗賭博的快感。這對於那些居住在遠離實體賭場地方的人來說尤為方便。
多元化的游戲選擇:在線娛樂城通常提供比實體賭場更多的遊戲選擇,並且經常更新游戲內容,保持新鮮。
福利和獎金:許多線上娛樂城提供多樣的獎金計劃,包括註冊紅利、存款獎金和忠誠計劃,吸引新新玩家並鼓勵老玩家繼續遊戲。
穩定性和保密性:正規的線上娛樂城使用高端的加密技術來保護玩家的私人信息和財務交易,確保遊戲過程的安全和公正。
常見的的在線娛樂城遊戲
德州撲克:撲克是最受歡迎賭錢游戲之一。在線娛樂城提供各種撲克牌變體,如德州扑克、奧馬哈和七張撲克等。
輪盤:賭盤是一種傳統的賭場遊戲,玩家可以賭注在單個數字、數字組合上或顏色選擇上,然後看球落在哪個位置。
二十一點:又稱為黑傑克,這是一種對比玩家和莊家點數的游戲,目標是讓手牌點數盡量接近21點但不超過。
老虎机:老虎机是最容易並且是最受歡迎的賭博游戲之一,玩家只需轉動捲軸,看圖案排列出獲勝的組合。
總結
網上娛樂城為現代賭博愛好者提供了一個方便、興奮且多元化的娛樂活動。無論是撲克牌愛好者還是吃角子老虎迷,大家都能在這些平台上找到適合自己的游戲。同時,隨著科技的不斷進步,在線娛樂城的遊戲體驗將變得越來越真實和引人入勝。然而,玩家在享用遊戲的同時,也應該保持,避免過度沉迷於賭博活動,保持健康的心態。 -
網上娛樂城的天地
隨著互聯網的快速發展,網上娛樂城(網上賭場)已經成為許多人休閒的新選擇。在線娛樂城不僅提供多元化的遊戲選擇,還能讓玩家在家中就能體驗到賭場的刺激和樂趣。本文將討論網上娛樂城的特徵、好處以及一些常見的游戲。
什麼線上娛樂城?
網上娛樂城是一種經由網際網路提供博彩遊戲的平台。玩家可以透過計算機、智慧型手機或平板電腦進入這些網站,參與各種賭錢活動,如德州撲克、輪盤、二十一點和老虎机等。這些平台通常由專業的的軟體公司開發,確保游戲的公正和安全性。
網上娛樂城的好處
方便性:玩家不用離開家,就能享用賭錢的興奮。這對於那些住在在遠離實體賭場地區的人來說尤為方便。
多種的遊戲選擇:在線娛樂城通常提供比實體賭場更多樣化的游戲選擇,並且經常改進游戲內容,保持新鮮。
好處和獎金:許多線上娛樂城提供豐厚的獎勵計劃,包括註冊紅利、存款獎勵和忠誠度計劃,引誘新玩家並激勵老玩家繼續遊戲。
安全和保密性:合法的在線娛樂城使用先進的加密來保護玩家的個人資料和金融交易,確保游戲過程的公平和公正性。
常有的網上娛樂城游戲
撲克:德州撲克是最受歡迎的賭錢游戲之一。網上娛樂城提供多種德州撲克變體,如德州扑克、奧馬哈撲克和七張牌撲克等。
輪盤:賭盤是一種古老的賭場遊戲遊戲,玩家可以下注在數字、數字組合或顏色上,然後看轉球落在哪個位置。
21點:又稱為二十一點,這是一種比拼玩家和莊家點數的游戲,目標是讓手牌點數盡量接近21點但不超過。
吃角子老虎:老虎機是最簡單且是最流行的賭博遊戲之一,玩家只需轉動捲軸,等待圖案排列出獲勝的組合。
總結
在線娛樂城為當代賭博愛好者提供了一個方便的、刺激的且豐富的娛樂方式。無論是撲克牌愛好者還是老虎機迷,大家都能在這些平台上找到適合自己的游戲。同時,隨著科技的不斷進步,在線娛樂城的遊戲體驗將變化越來越現實和吸引人。然而,玩家在體驗遊戲的同時,也應該保持自律,避免過度沉迷於賭錢活動,保持健康健康的心態。 -
網上娛樂城的天地
隨著網際網路的迅速發展,網上娛樂城(在線賭場)已經成為許多人娛樂的新選擇。網上娛樂城不僅提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,還能讓玩家在家中就能體驗到賭場的刺激和樂趣。本文將討論網上娛樂城的特徵、利益以及一些常見的遊戲。
什麼網上娛樂城?
線上娛樂城是一種透過互聯網提供賭錢遊戲的平台。玩家可以透過電腦、智慧型手機或平板電腦進入這些網站,參與各種賭錢活動,如撲克牌、賭盤、21點和老虎机等。這些平台通常由專家的軟體公司開發,確保遊戲的公平性和安全。
線上娛樂城的優勢
方便性:玩家不用離開家,就能享用賭博的樂趣。這對於那些生活在遠離的實體賭場地區的人來說特別方便。
多樣化的遊戲選擇:線上娛樂城通常提供比實體賭場更豐富的游戲選擇,並且經常改進遊戲內容,保持新穎。
好處和獎勵計劃:許多網上娛樂城提供豐富的獎勵計劃,包括註冊獎金、存款紅利和忠誠計劃,吸引新玩家並促使老玩家持續遊戲。
安全和隱私性:合法的網上娛樂城使用高端的加密方法來保護玩家的個人資料和交易,確保遊戲過程的公平和公平。
常見的的網上娛樂城游戲
撲克牌:德州撲克是最受歡迎博彩遊戲之一。線上娛樂城提供多樣撲克變體,如德州撲克、奧馬哈和七張撲克等。
賭盤:輪盤賭是一種經典的賭博遊戲,玩家可以賭注在單數、數字組合或顏色選擇上,然後看小球落在哪個位置。
二十一點:又稱為21點,這是一種對比玩家和莊家點數點數的遊戲,目標是讓手牌點數點數儘量接近21點但不超過。
吃角子老虎:吃角子老虎是最容易並且是最流行的賭博遊戲之一,玩家只需轉捲軸,等待圖案圖案排列出中獎的組合。
結論
網上娛樂城為當代賭博愛好者提供了一個方便、興奮且多元化的娛樂方式。不論是撲克愛好者還是吃角子老虎迷,大家都能在這些平台上找到適合自己的遊戲。同時,隨著科技的不斷進步,網上娛樂城的遊戲體驗將變得越來越越來越真實和有趣。然而,玩家在享受游戲的同時,也應該保持自律,避免沉迷於賭博活動,保持健康的娛樂心態。 -
娛樂城
線上娛樂城的天地
隨著互聯網的快速發展,在線娛樂城(線上賭場)已經成為許多人消遣的新選擇。在線娛樂城不僅提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,還能讓玩家在家中就能體驗到賭場的樂趣和快感。本文將研究在線娛樂城的特徵、好處以及一些常見的的遊戲。
什麼線上娛樂城?
網上娛樂城是一種透過網際網路提供賭博遊戲的平台。玩家可以通過計算機、手機或平板設備進入這些網站,參與各種博彩活動,如撲克、輪盤、黑傑克和老虎機等。這些平台通常由專業的的軟體公司開發,確保遊戲的公正和安全性。
線上娛樂城的好處
方便性:玩家不用離開家,就能享用博彩的興奮。這對於那些生活在遠離實體賭場地區的人來說尤其方便。
多元化的遊戲選擇:線上娛樂城通常提供比實體賭場更豐富的游戲選擇,並且經常升級游戲內容,保持新鮮感。
好處和獎勵:許多在線娛樂城提供豐厚的獎金計劃,包括註冊紅利、存款獎勵和會員計劃,引誘新玩家並促使老玩家持續遊戲。
穩定性和隱私:合法的網上娛樂城使用先進的加密方法來保護玩家的個人信息和交易,確保游戲過程的穩定和公平。
常見的的在線娛樂城遊戲
撲克:撲克是最受歡迎賭錢游戲之一。在線娛樂城提供多種德州撲克變體,如德州撲克、奧馬哈和七張撲克等。
賭盤:輪盤是一種傳統的賭博遊戲,玩家可以下注在單個數字、數字排列或顏色上上,然後看球落在哪個區域。
21點:又稱為黑傑克,這是一種對比玩家和莊家點數的遊戲,目標是讓手牌點數點數盡量接近21點但不超過。
老虎机:老虎機是最受歡迎且是最常見的博彩游戲之一,玩家只需轉捲軸,看圖案排列出贏得的組合。
結論
網上娛樂城為現代的賭博愛好者提供了一個方便的、刺激的且多樣化的娛樂選擇。無論是撲克迷還是老虎機迷,大家都能在這些平台上找到適合自己的遊戲。同時,隨著科技的不斷發展,線上娛樂城的游戲體驗將變得越來越越來越現實和引人入勝。然而,玩家在享用遊戲的同時,也應該保持自律,避免沉迷於賭錢活動,保持健康健康的娛樂心態。 -
Buy Cannabis Israel
Buy Cannabis in Israel: A Comprehensive Manual to Purchasing Marijuana in Israel
Lately, the term "Buy Weed Israel" has evolved into a synonym with an innovative, effortless, and straightforward way of acquiring weed in Israel. Utilizing applications like the Telegram app, people can swiftly and easily move through an huge selection of lists and numerous offers from various vendors throughout Israel. All that stands between you from entering the cannabis network in Israel to explore new ways to buy your weed is get a simple, secure app for private conversations.
Understanding Buy Weed Israel?
The phrase "Buy Weed Israel" no longer refers solely to the script that joined clients with dealers operated by the founder. Following its closure, the phrase has evolved into a widespread concept for arranging a contact with a cannabis vendor. Through platforms like Telegram, one can find numerous channels and networks ranked by the amount of followers each provider's channel or community has. Providers contend for the attention and custom of possible clients, creating a varied selection of alternatives presented at any moment.
How to Locate Providers Through Buy Weed Israel
By inputting the phrase "Buy Weed Israel" in the Telegram search bar, you'll locate an countless number of groups and networks. The amount of followers on these groups does not automatically confirm the vendor's reliability or endorse their products. To bypass scams or poor-quality merchandise, it's recommended to acquire exclusively from trusted and well-known providers from whom you've bought before or who have been recommended by friends or trusted sources.
Trusted Buy Weed Israel Platforms
We have put together a "Top 10" list of trusted groups and networks on the Telegram platform for buying marijuana in Israel. All providers have been checked and validated by our magazine team, ensuring 100% reliability and responsibility towards their clients. This comprehensive overview for 2024 includes links to these channels so you can find out what not to overlook.
### Boutique Club - VIPCLUB
The "VIP Group" is a VIP marijuana community that has been selective and discreet for new participants over the past few seasons. During this period, the group has grown into one of the most systematized and trusted entities in the market, providing its customers a new era of "online coffee shops." The community sets a high benchmark relative to other competitors with premium boutique products, a broad range of strains with airtight packages, and extra marijuana products such as extracts, CBD, edibles, vape pens, and hash. Moreover, they give fast deliveries 24/7.
## Conclusion
"Buy Weed Israel" has become a main method for arranging and discovering weed providers swiftly and easily. Using Buy Weed Israel, you can experience a new realm of opportunities and locate the best merchandise with simplicity and comfort. It is important to practice vigilance and purchase exclusively from dependable and endorsed suppliers. -
sapporo88
sapporo88 -
Daily bonuses
Explore Thrilling Bonuses and Extra Spins: Your Ultimate Guide
At our gaming platform, we are committed to providing you with the best gaming experience possible. Our range of offers and bonus spins ensures that every player has the chance to enhance their gameplay and increase their chances of winning. Here’s how you can take advantage of our fantastic promotions and what makes them so special.
Plentiful Free Rounds and Rebate Offers
One of our standout promotions is the opportunity to earn up to 200 bonus spins and a 75% refund with a deposit of just $20 or more. And during happy hour, you can unlock this bonus with a deposit starting from just $10. This unbelievable offer allows you to enjoy extended playtime and more opportunities to win without breaking the bank.
Boost Your Balance with Deposit Bonuses
We offer several deposit bonuses designed to maximize your gaming potential. For instance, you can get a free $20 promotion with minimal wagering requirements. This means you can start playing with extra funds, giving you more chances to explore our vast array of games and win big. Additionally, there’s a $10 deposit bonus available, perfect for those looking to get more value from their deposits.
Multiply Your Deposits for Bigger Wins
Our "Play Big!" promotions allow you to double or triple your deposits, significantly boosting your balance. Whether you choose to multiply your deposit by 2 or 3 times, these offers provide you with a substantial amount of extra funds to enjoy. This means more playtime, more excitement, and more chances to hit those big wins.
Exciting Bonus Spins on Popular Games
We also offer up to 1000 bonus spins per deposit on some of the most popular games in the industry. Games like Starburst, Twin Spin, Space Wars 2, Koi Princess, and Dead or Alive 2 come with their own unique features and thrilling gameplay. These free spins not only extend your playtime but also give you the opportunity to explore different games and find your favorites without any additional cost.
Why Choose Our Platform?
Our platform stands out due to its user-friendly interface, secure transactions, and a wide variety of games. We prioritize your gaming experience by ensuring that all our offers are easy to access and beneficial to our players. Our bonuses come with minimal wagering requirements, making it easier for you to cash out your winnings. Moreover, the variety of games we offer ensures that there’s something for every type of player, from classic slot enthusiasts to those who enjoy more modern, feature-packed games.
Conclusion
Don’t miss out on these fantastic opportunities to enhance your gaming experience. Whether you’re looking to enjoy bonus spins, refund, or generous deposit bonuses, we have something for everyone. Join us today, take advantage of these fantastic offers, and start your journey to big wins and endless fun. Happy gaming! -
game reviews
Exciting Innovations and Renowned Titles in the Realm of Videogames
In the ever-evolving domain of gaming, there's always something groundbreaking and thrilling on the cusp. From enhancements elevating beloved classics to upcoming debuts in renowned franchises, the videogame realm is flourishing as in current times.
Here's a snapshot into the newest news and certain the iconic titles mesmerizing audiences across the globe.
Most Recent Updates
1. New Modification for Skyrim Elevates NPC Aesthetics
A newly-released customization for The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim has attracted the focus of players. This mod introduces realistic heads and realistic hair for all (NPCs), improving the world's visuals and immersion.
2. Total War Series Release Placed in Star Wars Setting Galaxy In the Works
Creative Assembly, acclaimed for their Total War franchise, is allegedly creating a upcoming title set in the Star Wars Galaxy realm. This thrilling collaboration has fans looking forward to the analytical and captivating experience that Total War Games titles are renowned for, finally set in a realm distant.
3. GTA VI Launch Announced for Autumn 2025
Take-Two's CEO's Chief Executive Officer has announced that GTA VI is set to release in Late 2025. With the massive popularity of its predecessor, Grand Theft Auto V, enthusiasts are awaiting to witness what the forthcoming installment of this celebrated brand will provide.
4. Expansion Plans for Skull and Bones Sophomore Season
Designers of Skull and Bones have disclosed broader developments for the experience's next season. This nautical saga provides upcoming content and enhancements, keeping gamers engaged and absorbed in the domain of nautical nautical adventures.
5. Phoenix Labs Experiences Personnel Cuts
Sadly, not every developments is good. Phoenix Labs Studio, the creator behind Dauntless, has communicated massive workforce reductions. Despite this difficulty, the experience remains to be a beloved choice across enthusiasts, and the company continues to be dedicated to its community.
Renowned Titles
1. The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt Game
With its engaging narrative, immersive domain, and enthralling adventure, The Witcher 3 Game stays a iconic game across gamers. Its deep plot and wide-ranging free-roaming environment keep to captivate gamers in.
2. Cyberpunk
Despite a tumultuous launch, Cyberpunk 2077 Game stays a eagerly awaited release. With continuous enhancements and fixes, the game keeps evolve, offering players a glimpse into a cyberpunk setting filled with intrigue.
3. Grand Theft Auto 5
Still years after its first launch, GTA 5 remains a popular choice across enthusiasts. Its vast nonlinear world, captivating experience, and multiplayer components continue to draw players returning for further explorations.
4. Portal 2
A iconic puzzle release, Portal 2 Game is praised for its groundbreaking features and ingenious environmental design. Its challenging conundrums and witty writing have cemented it as a standout title in the videogame landscape.
5. Far Cry 3
Far Cry 3 is praised as exceptional titles in the brand, delivering players an sandbox journey abundant with danger. Its engrossing experience and memorable characters have cemented its position as a fan favorite experience.
6. Dishonored Universe
Dishonored is hailed for its sneaky features and distinctive environment. Enthusiasts embrace the character of a supernatural killer, navigating a urban environment filled with institutional peril.
7. Assassin's Creed
As part of the acclaimed Assassin's Creed Franchise series, Assassin's Creed II is revered for its immersive narrative, engaging mechanics, and era-based worlds. It continues to be a standout release in the franchise and a cherished amidst enthusiasts.
In final remarks, the realm of digital entertainment is prospering and dynamic, with groundbreaking advan -
video games guide
Exciting Advancements and Popular Titles in the Domain of Digital Entertainment
In the ever-evolving domain of digital entertainment, there's always something fresh and thrilling on the forefront. From mods optimizing beloved mainstays to anticipated arrivals in celebrated universes, the gaming industry is prospering as ever.
Here's a snapshot into the up-to-date updates and a few of the most popular experiences enthralling audiences across the globe.
Up-to-Date Announcements
1. New Enhancement for Skyrim Improves NPC Look
A latest mod for The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim has captured the focus of gamers. This customization adds high-polygon heads and dynamic hair for every supporting characters, elevating the game's visual appeal and immersiveness.
2. Total War Title Set in Star Wars Setting Galaxy Under Development
The Creative Assembly, known for their Total War franchise, is supposedly developing a upcoming experience located in the Star Wars Universe world. This engaging crossover has gamers looking forward to the analytical and engaging journey that Total War Series titles are acclaimed for, at last located in a world expansive.
3. GTA VI Debut Announced for Fall 2025
Take-Two's Leader has announced that GTA VI is scheduled to launch in Late 2025. With the massive popularity of its predecessor, Grand Theft Auto V, gamers are anticipating to witness what the future entry of this iconic series will provide.
4. Expansion Strategies for Skull & Bones Second Season
Developers of Skull & Bones have revealed amplified plans for the title's next season. This pirate-themed saga promises upcoming features and updates, sustaining gamers engaged and engrossed in the world of high-seas swashbuckling.
5. Phoenix Labs Studio Faces Staff Cuts
Regrettably, not every news is favorable. Phoenix Labs, the developer responsible for Dauntless Experience, has announced large-scale staff cuts. Despite this difficulty, the release continues to be a popular option among players, and the team continues to be focused on its fanbase.
Beloved Experiences
1. The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt
With its compelling experience, absorbing universe, and captivating adventure, The Witcher 3: Wild Hunt remains a revered title among fans. Its rich plot and sprawling free-roaming environment remain to engage gamers in.
2. Cyberpunk 2077
In spite of a problematic debut, Cyberpunk 2077 Game keeps a highly anticipated title. With persistent enhancements and optimizations, the release continues to improve, providing enthusiasts a glimpse into a dystopian environment teeming with intrigue.
3. Grand Theft Auto 5
Still eras following its first arrival, Grand Theft Auto V stays a iconic option among fans. Its vast open world, enthralling story, and online features sustain fans revisiting for more explorations.
4. Portal
A renowned brain-teasing game, Portal 2 is celebrated for its groundbreaking gameplay mechanics and exceptional environmental design. Its challenging obstacles and humorous writing have cemented it as a exceptional game in the interactive entertainment industry.
5. Far Cry Game
Far Cry Game is praised as a standout entries in the franchise, offering enthusiasts an nonlinear experience rife with danger. Its compelling story and renowned characters have confirmed its place as a fan favorite game.
6. Dishonored Game
Dishonored Series is hailed for its covert mechanics and distinctive world. Players adopt the role of a otherworldly executioner, traversing a city filled with societal intrigue.
7. Assassin's Creed
As a segment of the renowned Assassin's Creed Universe series, Assassin's Creed 2 is beloved for its engrossing narrative, compelling gameplay, and era-based environments. It remains a remarkable game in the franchise and a beloved within players.
In conclusion, the world of videogames is flourishing and ever-changing, with innovative advan -
crickex affiliate login
ভারতের একটি জনপ্রিয় কাৰ্যকলাপ হলো ক্রিকেট। এই ক্রিকেটের অংশ হিসাবে, ক্রিকেক্স (CrickEx) একটি জনপ্রিয় প্ল্যাটফর্ম যা ক্রিকেটের বিভিন্ন কৌশল ও বিষয়বস্তু নিয়ে কাজ করে। ক্রিকেক্স-এর একটি বিশেষ প্রচার ছিল যা প্রতি এপ্রিল মাসে ঘোষণা করা হয়।
এই প্রচারে, ক্রিকেটের প্রিয়দর্শী ভক্তরা বিনামূল্যে ক্রিকেক্স তালিকায় নিবন্ধিত হয়ে 200 বাজি পেতে পারেন। যেসকল ব্যবহারকারী এপ্রিল মাসের পর নিবন্ধিত হবেন, তারাই এই প্রচারে অংশ নিতে পারবেন।
ব্যবহারকারীদের এই প্রচারটিতে অংশ নিতে হলে তাদের প্রথমে "মেম্বার সেন্টার" -এ যেতে হবে এবং তারপর "অ্যাপ্লাই প্রমোশন" বিকল্পটি ক্লিক করতে হবে। এরপর তাদেরকে নিজের পছন্দের প্রমোশন টি চয়ন করতে হবে।
প্রচারটি বন্ধ করার জন্য, ব্যবহারকারীদের প্রথমে "মেম্বার সেন্টার" -এ যেতে হবে, তারপর "প্রমোশন লিস্ট" অপশনে যেতে হবে এবং "স্টপ প্রমোশন" বিকল্পটি ক্লিক করতে হবে।
একজন ব্যবহারকারী শুধুমাত্র একবার এই বিনামূল্য বাজি প্রচারে অংশ নিতে পারেন। এই প্রচারের নিয়ম অনুযায়ী, একটি অ্যাকাউন্ট, আইপি, ফোন নম্বর, ইমেল এবং ব্যাঙ্ক অ্যাকাউন্টের মাধ্যমে শুধুমাত্র একবার এই প্রচারটি ব্যবহার করা যাবে। বাউন্সিংবল8 সংস্থা এই প্রচারটি সংশোধন, স্থগিত বা বন্ধ করার অধিকার সংরক্ষণ করে।
এই প্রচারটি ক্রিকেটে আগ্রহী ভক্তদের মধ্যে জনপ্রিয় হয়ে উঠেছে। এটি ক্রিকেটের প্রতি ভক্তিকে প্রকাশ করার এবং ক্রিকেক্স (CrickEx) প্ল্যাটফর্মে অংশ নেওয়ার একটি উপায়।
Welcome to Cricket Affiliate | Kick off with a smashing Welcome Bonus !
First Deposit Fiesta! | Make your debut at Cricket Exchange with a 200% bonus.
Daily Doubles! | Keep the scoreboard ticking with a 100% daily bonus at 9wicket!
#cricketaffiliate
IPL 2024 Jackpot! | Stand to win ₹50,000 in the mega IPL draw at cricket world!
Social Sharer Rewards! | Post and earn 100 tk weekly through Crickex affiliate login.
https://www.cricket-affiliate.com/
#cricketexchange #9wicket #crickexaffiliatelogin #crickexlogin
crickex login VIP! | Step up as a VIP and enjoy weekly bonuses!
Join the Action! | Log in through crickex bet exciting betting experience at Live Affiliate.
Dive into the game with crickex live—where every play brings spectacular wins ! -
Jili ace casino
JiliAce ক্যাসিনোতে অনলাইন আর্কেড এবং লটারি গেম: বিনোদনের নতুন জগৎ
অনলাইন গেমিং জগতে JiliAce ক্যাসিনো একটি বিশিষ্ট স্থান অধিকার করে নিয়েছে, যেখানে বিভিন্ন ধরনের গেম অফার করা হয়। আজ আমরা JiliAce〡JitaBet প্ল্যাটফর্মে পাওয়া দুটি জনপ্রিয় গেম সম্পর্কে জানব: অনলাইন আর্কেড এবং লটারি গেম।
অনলাইন আর্কেড গেম: ক্লাসিক মজার ডিজিটাল রূপ
অনলাইন আর্কেড গেমগুলি ক্লাসিক আর্কেড গেমগুলির ডিজিটাল সংস্করণগুলিকে বোঝায়, যা ঐতিহ্যগতভাবে কয়েন-চালিত মেশিনগুলির সাথে আর্কেড বিনোদন স্থানগুলিতে পাওয়া যেত। এখন এই গেমগুলি ওয়েবসাইট এবং গেমিং কনসোল সহ বিভিন্ন ডিজিটাল প্ল্যাটফর্মে অ্যাক্সেসযোগ্য। JiliAce ক্যাসিনোতে, আপনি বিভিন্ন আর্কেড গেম উপভোগ করতে পারেন, যা আপনাকে পুরনো দিনের আর্কেড গেমগুলির মজার অভিজ্ঞতা দেবে। Jili ace casino-এর মাধ্যমে এই গেমগুলির মধ্যে প্রবেশ করে আপনি সময় কাটাতে পারবেন এবং অসাধারণ বিনোদন উপভোগ করতে পারবেন।
অনলাইন লটারি গেম: সহজে ভাগ্য পরীক্ষা
অনলাইন লটারি গেমগুলি ঐতিহ্যগত লটারি গেমগুলির ডিজিটাল সংস্করণগুলিকে বোঝায়, যেখানে খেলোয়াড়রা টিকিট কিনতে এবং ইন্টারনেটের মাধ্যমে বিভিন্ন লটারিতে অংশগ্রহণ করতে পারে। এই গেমগুলি ব্যক্তিদের জন্য তাদের ভাগ্য চেষ্টা করার এবং সম্ভাব্য নগদ পুরস্কার জেতার জন্য একটি সুবিধাজনক এবং অ্যাক্সেসযোগ্য উপায় সরবরাহ করে। JiliAce ক্যাসিনোতে লটারি গেম খেলে আপনি সহজেই আপনার ভাগ্য পরীক্ষা করতে পারেন এবং বড় পুরস্কার জেতার সুযোগ পেতে পারেন। Jiliace login করে আপনি এই গেমগুলিতে অংশগ্রহণ করতে পারবেন এবং আপনার সম্ভাব্য জয়ের সুযোগ বৃদ্ধি করতে পারবেন।
সহজ লগইন এবং সুবিধাজনক গেমিং
Jili ace login প্রক্রিয়া অত্যন্ত সহজ এবং ব্যবহারকারীদের জন্য সুবিধাজনক। একবার লগইন করলে, আপনি সহজেই বিভিন্ন গেমের অ্যাক্সেস পাবেন এবং আপনার পছন্দসই গেম খেলার জন্য প্রস্তুত হয়ে যাবেন। Jiliace login করার পর, আপনি আপনার গেমিং যাত্রা শুরু করতে পারবেন এবং বিভিন্ন ধরনের বোনাস ও পুরস্কার উপভোগ করতে পারবেন।
Jita Bet: বড় পুরস্কারের সুযোগ
JiliAce ক্যাসিনোতে Jita Bet-এর সাথে আপনার গেমিং অভিজ্ঞতা আরও সমৃদ্ধ করুন। এখানে আপনি বিভিন্ন ধরণের বাজি ধরতে পারেন এবং বড় পুরস্কার জিততে পারেন। Jita Bet প্ল্যাটফর্মটি ব্যবহারকারীদের জন্য সহজ এবং সুরক্ষিত বাজি ধরার সুযোগ প্রদান করে।
যোগদান করুন এবং উপভোগ করুন
JiliAce〡JitaBet-এর অংশ হয়ে আজই আপনার গেমিং যাত্রা শুরু করুন। Jili ace casino এবং Jita Bet-এ লগইন করে অনলাইন আর্কেড এবং লটারি গেমের মত আকর্ষণীয় গেম উপভোগ করুন। এখনই যোগ দিন এবং অনলাইন গেমিংয়ের এক নতুন জগতে প্রবেশ করুন!
Jiliacet casino
Jiliacet casino |
Warm welcome! | Get a 200% Welcome Bonus when you log in jiliace casino.
IPL Tournament! | Join the IPL fever with Jita Bet. Win big prizes!
Epic JILI Tournaments! | Go head-to-head in the Jita bet Super Tournament
#jiliacecasino
Cashback on Deposits! | Get cash back on every deposit. At Jili ace casino
Uninterrupted bonuses at JITAACE! | Stay logged in Jiliace login!
https://www.jiliace-casino.online/bn
#Jiliacecasino # Jiliacelogin#Jiliacelogin # Jitabet
Slot Feast! | Spin to win 100% up to 20,000 ৳. at Jili ace login!
Big Fishing Bonus! | Get a 100% bonus up to ৳20,000 in the Fishing Game.
JiliAce Casino's top choice for great bonuses. login, play, and win big today! -
How can I verify the authenticity of online pharmacy app downloads is fildena the same as viagra?
-
BATA4D
BATA4D -
как продвинуть сайт
Консультация по оптимизации продвижению.
Информация о том как работать с низкочастотными ключевыми словами и как их определять
Подход по работе в соперничающей нише.
У меня есть постоянных взаимодействую с тремя фирмами, есть что поделиться.
Изучите мой профиль, на 31 мая 2024г
общий объём завершённых задач 2181 только на этом сайте.
Консультация проходит устно, без скринов и отчётов.
Время консультации указано 2 ч, но по факту всегда на связи без строгой привязки ко времени.
Как управлять с софтом это уже иначе история, консультация по использованию ПО оговариваем отдельно в специальном кворке, узнаем что требуется при коммуникации.
Всё без суеты на расслабленно не в спешке
To get started, the seller needs:
Мне нужны сведения от телеграм чата для связи.
разговор только в устной форме, общаться письменно нету времени.
субботы и воскресенья выходные -
Советы по оптимизации продвижению.
Информация о том как работать с низкочастотными ключевыми словами и как их выбирать
Подход по работе в соперничающей нише.
Обладаю постоянных клиентов сотрудничаю с 3 компаниями, есть что рассказать.
Посмотрите мой профиль, на 31 мая 2024г
число успешных проектов 2181 только здесь.
Консультация только в устной форме, без скринов и отчётов.
Время консультации указано 2 часа, но по факту всегда на связи без жёсткой привязки к графику.
Как управлять с софтом это уже другая история, консультация по использованию ПО договариваемся отдельно в отдельном разделе, определяем что нужно при коммуникации.
Всё спокойно на без напряжения не в спешке
To get started, the seller needs:
Мне нужны контакты от телеграм чата для коммуникации.
общение только в устной форме, общаться письменно недостаточно времени.
Суббота и воскресенья нерабочие дни -
娛樂城
網上娛樂城的世界
隨著網際網路的快速發展,網上娛樂城(線上賭場)已經成為許多人休閒的新選擇。線上娛樂城不僅提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,還能讓玩家在家中就能體驗到賭場的興奮和樂趣。本文將研究在線娛樂城的特色、優勢以及一些常見的游戲。
什麼叫線上娛樂城?
在線娛樂城是一種經由網際網路提供賭錢游戲的平台。玩家可以經由計算機、智能手機或平板進入這些網站,參與各種賭博活動,如德州撲克、輪盤、21點和老虎機等。這些平台通常由專業的的程序公司開發,確保遊戲的公正性和安全性。
線上娛樂城的優勢
便利:玩家不需要離開家,就能體驗賭錢的樂趣。這對於那些生活在偏遠實體賭場區域的人來說尤為方便。
多種的遊戲選擇:在線娛樂城通常提供比實體賭場更豐富的遊戲選擇,並且經常改進遊戲內容,保持新鮮感。
優惠和獎金:許多網上娛樂城提供多樣的獎勵計劃,包括註冊獎勵、存款獎勵和忠誠度計劃,吸引新玩家並鼓勵老玩家持續遊戲。
安全和隱私性:正當的線上娛樂城使用高端的加密技術來保護玩家的私人信息和交易,確保游戲過程的安全和公正。
常見的在線娛樂城遊戲
撲克:撲克牌是最受歡迎賭博游戲之一。在線娛樂城提供各種德州撲克變體,如德州扑克、奧馬哈撲克和七張撲克等。
輪盤賭:賭盤是一種經典的賭場遊戲遊戲,玩家可以賭注在單數、數字組合上或顏色上上,然後看小球落在哪個地方。
黑傑克:又稱為二十一點,這是一種競爭玩家和莊家點數點數的游戲,目標是讓手牌點數點數盡量接近21點但不超過。
吃角子老虎:吃角子老虎是最受歡迎也是最受歡迎的博彩游戲之一,玩家只需旋轉捲軸,等待圖案圖案排列出贏得的組合。
結尾
線上娛樂城為當代賭博愛好者提供了一個便捷、興奮且多元化的娛樂選擇。無論是撲克迷還是吃角子老虎迷,大家都能在這些平台上找到適合自己的遊戲。同時,隨著技術的不斷進步,線上娛樂城的遊戲體驗將變得越來越現實和吸引人。然而,玩家在體驗游戲的同時,也應該自律,避免沉迷於賭錢活動,保持健康健康的心態。 -
在線娛樂城的天地
隨著互聯網的飛速發展,在線娛樂城(線上賭場)已經成為許多人娛樂的新選擇。在線娛樂城不僅提供多元化的遊戲選擇,還能讓玩家在家中就能體驗到賭場的興奮和樂趣。本文將研究網上娛樂城的特色、利益以及一些常見的的游戲。
什麼叫在線娛樂城?
線上娛樂城是一種經由網際網路提供賭博遊戲的平台。玩家可以經由電腦設備、智能手機或平板設備進入這些網站,參與各種博彩活動,如撲克牌、輪盤賭、二十一點和老虎机等。這些平台通常由專業的程序公司開發,確保游戲的公正和安全。
網上娛樂城的優勢
便利:玩家無需離開家,就能體驗賭博的樂趣。這對於那些生活在遠離的實體賭場區域的人來說尤為方便。
多元化的游戲選擇:網上娛樂城通常提供比實體賭場更豐富的游戲選擇,並且經常改進遊戲內容,保持新鮮感。
福利和獎金:許多在線娛樂城提供豐厚的優惠計劃,包括註冊獎金、存款紅利和會員計劃,引誘新玩家並鼓勵老玩家持續遊戲。
安全性和隱私性:正規的在線娛樂城使用先進的加密方法來保護玩家的個人資料和金融交易,確保游戲過程的穩定和公平。
常有的在線娛樂城遊戲
撲克牌:德州撲克是最流行博彩遊戲之一。網上娛樂城提供多樣撲克變體,如德州扑克、奧馬哈撲克和七張牌等。
輪盤:輪盤是一種傳統的賭場遊戲遊戲,玩家可以賭注在數字、數字排列或顏色選擇上,然後看小球落在哪個地方。
黑傑克:又稱為二十一點,這是一種對比玩家和莊家點數的游戲,目標是讓手牌點數盡可能接近21點但不超過。
老虎機:老虎機是最受歡迎也是最流行的賭博游戲之一,玩家只需旋轉捲軸,看圖案排列出中獎的組合。
結論
在線娛樂城為當代賭博愛好者提供了一個方便的、興奮且多元化的娛樂活動。無論是撲克牌愛好者還是老虎機迷,大家都能在這些平台上找到適合自己的遊戲。同時,隨著技術的不斷提升,線上娛樂城的遊戲體驗將變化越來越現實和吸引人。然而,玩家在體驗游戲的同時,也應該保持,避免沉溺於賭錢活動,維持健康的遊戲心態。 -
娛樂城
在線娛樂城的天地
隨著網際網路的迅速發展,網上娛樂城(在線賭場)已經成為許多人休閒的新選擇。在線娛樂城不僅提供多元化的游戲選擇,還能讓玩家在家中就能體驗到賭場的刺激和樂趣。本文將研究在線娛樂城的特色、利益以及一些常有的遊戲。
什麼叫在線娛樂城?
在線娛樂城是一種經由網際網路提供博彩遊戲的平台。玩家可以經由電腦設備、手機或平板進入這些網站,參與各種賭博活動,如撲克、輪盤、二十一點和老虎機等。這些平台通常由專業的程序公司開發,確保游戲的公平性和安全。
網上娛樂城的優勢
便利:玩家不用離開家,就能享用博彩的快感。這對於那些居住在偏遠實體賭場區域的人來說尤為方便。
多元化的游戲選擇:在線娛樂城通常提供比實體賭場更多的游戲選擇,並且經常更新游戲內容,保持新穎。
福利和獎金:許多線上娛樂城提供多樣的獎金計劃,包括註冊獎勵、存款紅利和忠誠計劃,引誘新玩家並促使老玩家不斷遊戲。
安全和隱私:合法的在線娛樂城使用先進的的加密方法來保護玩家的私人信息和交易,確保游戲過程的穩定和公正。
常見的在線娛樂城遊戲
撲克:德州撲克是最受歡迎的賭錢游戲之一。網上娛樂城提供多種撲克牌變體,如德州撲克、奧馬哈撲克和七張牌撲克等。
賭盤:輪盤是一種經典的賭場遊戲,玩家可以下注在數字、數字組合或顏色選擇上,然後看小球落在哪個區域。
二十一點:又稱為黑傑克,這是一種比拼玩家和莊家點數點數的游戲,目標是讓手牌點數盡可能接近21點但不超過。
老虎機:吃角子老虎是最容易且是最常見的博彩遊戲之一,玩家只需轉動捲軸,等待圖案圖案排列出贏得的組合。
總結
線上娛樂城為當代賭博愛好者提供了一個便捷、興奮且豐富的娛樂選擇。不管是撲克愛好者還是老虎机愛好者,大家都能在這些平台上找到適合自己的遊戲。同時,隨著技術的的不斷進步,在線娛樂城的遊戲體驗將變化越來越現實和吸引人。然而,玩家在享用游戲的同時,也應該保持,避免沉溺於賭錢活動,保持健康的遊戲心態。 -
как продвинуть сайт
Советы по сео продвижению.
Информация о том как взаимодействовать с низкочастотными запросами запросами и как их подбирать
Стратегия по действиям в конкурентной нише.
Обладаю регулярных взаимодействую с 3 компаниями, есть что поделиться.
Посмотрите мой профиль, на 31 мая 2024г
общий объём завершённых задач 2181 только на этом сайте.
Консультация проходит устно, без скринов и отчётов.
Время консультации указано 2 часа, но по факту всегда на доступен без строгой привязки к графику.
Как взаимодействовать с ПО это уже другая история, консультация по работе с софтом оговариваем отдельно в специальном разделе, узнаем что требуется при разговоре.
Всё спокойно на без напряжения не спеша
To get started, the seller needs:
Мне нужны данные от Telegram каналов для коммуникации.
коммуникация только в устной форме, вести переписку недостаточно времени.
субботы и Воскресенье выходной -
mpo1221
Inspirasi dari Ucapan Taylor Swift
Taylor Swift, seorang musisi dan komposer terkenal, tidak hanya dikenal berkat melodi yang elok dan vokal yang merdu, tetapi juga karena syair-syair lagunya yang sarat makna. Pada lirik-liriknya, Swift sering melukiskan beraneka ragam faktor kehidupan, berawal dari cinta hingga tantangan hidup. Di bawah ini adalah beberapa kutipan motivatif dari karya-karya, bersama terjemahannya.
"Mungkin yang terhebat belum hadir." - "All Too Well"
Arti: Meskipun dalam masa-masa sulit, tetap ada secercah harapan dan potensi akan hari yang lebih cerah.
Lirik ini dari lagu "All Too Well" menyadarkan kita bahwa biarpun kita mungkin menghadapi masa-masa sulit saat ini, senantiasa ada potensi kalau masa depan akan memberikan hal yang lebih baik. Situasi ini adalah pesan pengharapan yang menguatkan, mendorong kita untuk tetap bertahan dan tidak menyerah, karena yang terhebat mungkin belum tiba.
"Aku akan bertahan karena aku tak mampu mengerjakan apa pun tanpa kamu." - "You Belong with Me"
Penjelasan: Menemukan kasih dan support dari orang lain dapat memberi kita tenaga dan tekad untuk melanjutkan lewat kesulitan. -
btv168
Ashley JKT48: Idola yang Bersinar Terang di Kancah Idola
Siapakah Ashley JKT48?
Siapakah tokoh muda berbakat yang menarik perhatian banyak penyuka musik di Indonesia dan Asia Tenggara? Beliau adalah Ashley Courtney Shintia, atau yang lebih dikenal dengan nama panggungnya, Ashley JKT48. Bergabung dengan grup idola JKT48 pada tahun 2018, Ashley dengan lekas menjadi salah satu anggota paling populer.
Profil
Lahir di Jakarta pada tanggal 13 Maret 2000, Ashley berdarah darah Tionghoa-Indonesia. Ia memulai kariernya di bidang entertainment sebagai model dan aktris, sebelum akhirnya menjadi anggota dengan JKT48. Personanya yang gembira, suara yang mantap, dan kemampuan menari yang mengesankan menjadikannya idola yang sangat disukai.
Penghargaan dan Apresiasi
Kepopuleran Ashley telah diapresiasi melalui banyak penghargaan dan pencalonan. Pada tahun 2021, ia meraih pengakuan "Member Terpopuler JKT48" di event JKT48 Music Awards. Ashley juga dianugerahi sebagai "Idol Terindah di Asia" oleh sebuah tabloid online pada tahun 2020.
Fungsi dalam JKT48
Ashley mengisi peran penting dalam group JKT48. Beliau adalah personel Tim KIII dan berperan sebagai penari utama dan penyanyi utama. Ashley juga menjadi anggota dari sub-unit "J3K" bersama Jessica Veranda dan Jennifer Rachel Natasya.
Karier Solo
Selain aktivitasnya di JKT48, Ashley juga merintis karier individu. Ia telah meluncurkan beberapa single, diantaranya "Myself" (2021) dan "Falling Down" (2022). Ashley juga telah bekerja sama dengan penyanyi lain, seperti Afgan dan Rossa.
Kehidupan Pribadi
Selain dunia pertunjukan, Ashley dikenal sebagai sosok yang rendah hati dan bersahabat. Ashley menikmati menyisihkan jam dengan keluarga dan teman-temannya. Ashley juga memiliki hobi melukis dan photography. -
persib
Inspirasi dari Ucapan Taylor Swift: Harapan dan Cinta dalam Lagu-Lagunya
Penyanyi Terkenal, seorang artis dan pengarang lagu populer, tidak hanya terkenal karena nada yang indah dan vokal yang merdu, tetapi juga oleh karena lirik-lirik lagunya yang penuh makna. Dalam lirik-liriknya, Swift sering menggambarkan bermacam-macam aspek hidup, dimulai dari asmara sampai dengan rintangan hidup. Di bawah ini adalah sejumlah kutipan motivatif dari lagu-lagu, beserta terjemahannya.
"Mungkin yang terbaik belum datang." - "All Too Well"
Makna: Meskipun dalam masa-masa sulit, selalu ada secercah asa dan kemungkinan untuk hari yang lebih baik.
Lirik ini dari lagu "All Too Well" mengingatkan kita kalau meskipun kita mungkin berhadapan dengan waktu sulit pada saat ini, selalu ada kemungkinan bahwa waktu yang akan datang akan memberikan sesuatu yang lebih baik. Hal ini adalah amanat harapan yang menguatkan, mendorong kita untuk terus bertahan dan tidak putus asa, lantaran yang paling baik mungkin belum datang.
"Aku akan tetap bertahan sebab aku tidak bisa menjalankan apa pun tanpa dirimu." - "You Belong with Me"
Penjelasan: Menemukan kasih dan dukungan dari orang lain dapat memberi kita tenaga dan tekad untuk melanjutkan lewat tantangan. -
royaltoto 0727
Ashley JKT48: Bintang yang Bersinar Gemilang di Langit Idol
Siapa Ashley JKT48?
Siapakah sosok muda berkemampuan yang menyita perhatian banyak penyuka musik di Nusantara dan Asia Tenggara? Itulah Ashley Courtney Shintia, atau yang dikenal dengan nama panggungnya, Ashley JKT48. Menjadi anggota dengan grup idola JKT48 pada tahun 2018, Ashley dengan lekas menjadi salah satu personel paling populer.
Biografi
Lahir di Jakarta pada tanggal 13 Maret 2000, Ashley berdarah keturunan Tionghoa-Indonesia. Ia mengawali perjalanannya di industri entertainment sebagai model dan pemeran, sebelum kemudian masuk dengan JKT48. Kepribadiannya yang periang, vokal yang kuat, dan keterampilan menari yang memukau membuatnya idola yang sangat dicintai.
Pengakuan dan Apresiasi
Kepopuleran Ashley telah diakui melalui berbagai penghargaan dan pencalonan. Pada masa 2021, ia memenangkan penghargaan "Anggota Paling Populer JKT48" di ajang JKT48 Music Awards. Ashley juga dinobatkan sebagai "Idol Tercantik se-Asia" oleh sebuah tabloid online pada tahun 2020.
Posisi dalam JKT48
Ashley memainkan posisi krusial dalam grup JKT48. Dia adalah anggota Tim KIII dan berperan sebagai penari utama dan penyanyi utama. Ashley juga merupakan member dari sub-unit "J3K" bersama Jessica Veranda dan Jennifer Rachel Natasya.
Karir Solo
Selain aktivitasnya di JKT48, Ashley juga memulai perjalanan individu. Beliau telah merilis beberapa single, antara lain "Myself" (2021) dan "Falling Down" (2022). Ashley juga telah berkolaborasi bersama musisi lain, seperti Afgan dan Rossa.
Kehidupan Pribadi
Selain kancah perform, Ashley dikenali sebagai pribadi yang low profile dan friendly. Ashley menikmati menyisihkan masa bareng sanak famili dan teman-temannya. Ashley juga memiliki hobi melukis dan memotret. -
проверить адрес кошелька usdt 12
Анализ адреса монет
Контроль USDT на платформе TRC20 и прочих криптовалютных операций
На представленном сайте вы всесторонние обзоры разных инструментов для контроля переводов и счетов, включая антиотмывочные проверки для токенов и иных криптовалют. Вот главные опции, что в наших описаниях:
Верификация токенов на блокчейне TRC20
Многие ресурсы предлагают комплексную контроль платежей монет на блокчейне TRC20 платформы. Это дает возможность идентифицировать подозреваемую активность и удовлетворять правовым стандартам.
Контроль операций криптовалюты
В представленных обзорах доступны ресурсы для всестороннего анализа и отслеживания переводов монет, которые помогает сохранять открытость и надежность транзакций.
anti-money laundering анализ токенов
Известные ресурсы поддерживают антиотмывочного закона контроль криптовалюты, обеспечивая обнаруживать и пресекать случаи финансовых преступлений и финансовых нарушений.
Контроль аккаунта токенов
Наши ревью охватывают сервисы, предназначенные для позволяют проверять счета USDT на предмет ограничений и сомнительных платежей, предоставляя повышенный степень защищенности.
Контроль переводов токенов на блокчейне TRC20
В наших обзорах описаны инструменты, предоставляющие верификацию переводов токенов в сети TRC20, что обеспечивает гарантирует выполнение всем стандартам стандартам правилам.
Проверка аккаунта кошелька USDT
В ревью представлены сервисы для проверки аккаунтов адресов токенов на потенциальных опасностей проблем.
Верификация аккаунта USDT на сети TRC20
Наши оценки представляют инструменты, обеспечивающие анализ адресов токенов на платформе TRC20 платформы, что позволяет помогает пресечение мошенничество и денежных преступлений.
Проверка монет на легитимность
Описанные платформы обеспечивают контролировать операции и кошельки на отсутствие подозрительных действий, определяя необычную операции.
антиотмывочная верификация криптовалюты TRC20
В обзорах описаны инструменты, предлагающие AML анализ для USDT в сети TRC20 сети, обеспечивая вашему компании удовлетворять общепринятым нормам.
Верификация токенов на блокчейне ERC20
Наши ревью охватывают ресурсы, поддерживающие контроль USDT на блокчейне ERC20 платформы, что позволяет детальный анализ транзакций и счетов.
Контроль цифрового кошелька
Мы изучаем ресурсы, поддерживающие решения по проверке цифровых кошельков, в том числе отслеживание переводов и обнаружение подозреваемой операций.
Контроль кошелька цифрового кошелька
Наши ревью содержат сервисы, позволяющие верифицировать адреса криптовалютных кошельков для поддержания дополнительной надежности.
Проверка виртуального кошелька на транзакции
В наших обзорах описаны сервисы для анализа криптокошельков на транзакции, что обеспечивает помогает гарантировать чистоту операций.
Контроль цифрового кошелька на легитимность
Наши обзоры включают сервисы, обеспечивающие анализировать криптовалютные кошельки на легитимность, обнаруживая подозрительные подозрительные операции.
Ознакомившись с наши оценки, вам удастся найдете оптимальные инструменты для верификации и мониторинга криптовалютных платежей, чтобы обеспечивать повышенный уровень безопасности защищенности и соответствовать все регуляторным правилам. -
internet casinos
Digital Casinos: Innovation and Advantages for Modern Society
Introduction
Online casinos are digital sites that offer players the opportunity to participate in gambling games such as poker, roulette, 21, and slots. Over the past few decades, they have turned into an essential part of online leisure, providing various advantages and opportunities for players around the world.
Accessibility and Ease
One of the main advantages of digital gambling sites is their availability. Users can play their preferred activities from anywhere in the world using a PC, tablet, or mobile device. This saves hours and money that would otherwise be spent traveling to traditional casinos. Additionally, round-the-clock availability to games makes internet casinos a convenient option for people with hectic schedules.
Range of Games and Experience
Online gambling sites offer a wide range of activities, enabling everyone to find something they enjoy. From traditional card games and table games to slots with various themes and increasing prizes, the range of games guarantees there is something for every taste. The option to engage at different proficiencies also makes digital casinos an ideal location for both beginners and seasoned players.
Economic Benefits
The online gambling industry contributes greatly to the economic system by creating jobs and generating revenue. It backs a diverse range of careers, including software developers, client assistance agents, and advertising professionals. The revenue produced by online gambling sites also contributes to tax revenues, which can be allocated to support public services and development projects.
Advancements in Technology
Online casinos are at the cutting edge of tech advancement, continuously integrating new technologies to enhance the gaming entertainment. High-quality visuals, real-time dealer games, and VR gambling sites provide immersive and authentic gaming entertainment. These innovations not only improve user satisfaction but also expand the boundaries of what is possible in digital entertainment.
Safe Betting and Support
Many digital gambling sites promote responsible gambling by providing tools and resources to help users control their gaming activities. Features such as deposit limits, self-exclusion options, and availability to assistance programs guarantee that players can enjoy gaming in a secure and controlled setting. These measures show the industry's dedication to promoting safe gaming habits.
Social Interaction and Community
Digital casinos often provide social features that enable players to connect with each other, creating a feeling of belonging. Group games, chat functions, and social media links allow players to network, share experiences, and build relationships. This interactive element improves the entire gaming entertainment and can be especially beneficial for those looking for community engagement.
Summary
Digital gambling sites provide a diverse variety of advantages, from accessibility and convenience to economic contributions and innovations. They provide varied betting choices, support safe betting, and foster community engagement. As the industry continues to evolve, digital casinos will probably remain a significant and positive presence in the world of digital entertainment. -
fortune casino
Luck Casino: In a Place Where Fun Converges With Fortune
Luck Wagering Environment is a popular online place characterized for its comprehensive selection of experiences and captivating rewards. Let's analyze the reasons why so several users relish engaging with Prosperity Gaming Site and the extent to which it advantages them.
Fun Element
Wealth Wagering Environment offers a breadth of activities, featuring time-honored wagering games like 21 and ball-and-number game, as alongside groundbreaking slot machines. This diversity ensures that there is a choice for all, making all trip to Fortune Gambling Platform pleasurable and amusing.
Large Prizes
One of the principal draws of Fortune Gambling Platform is the possibility to earn significant rewards. With considerable grand prizes and incentives, users have the opportunity to turn their luck around with a single turn or deal. Numerous users have walked away with considerable prizes, augmenting the suspense of playing at Prosperity Wagering Environment.
Ease of Access and Reachability
Fortune Gaming Site's online system constitutes it as user-friendly for customers to savor their cherished experiences from any place. Whether at dwelling or on the go, players can reach Wealth Gambling Platform from their desktop or smartphone. This approachability provides that users can relish the anticipation of the casino whenever they desire, devoid of the necessity to make trips.
Diversity of Options
Prosperity Gambling Platform grants a extensive assortment of activities, guaranteeing that there is something for all form of player. Starting with traditional card games to narrative-driven slot-based games, the range keeps users captivated and amused. This assortment also permits players to try out different experiences and find unfamiliar most cherished.
Perks and Advantages
Luck Casino recognizes its customers with bonuses and advantages, incorporating new player perks and loyalty schemes. These rewards not merely improve the gaming interaction but as well increase the likelihoods of earning significant rewards. Users are constantly motivated to keep playing, establishing Wealth Gaming Site additionally desirable.
Group-Based Participation and Collaboration
ChatGPT l Валли, [06.06.2024 4:30]
Prosperity Wagering Environment provides a feeling of togetherness and interpersonal connection for players. Using chat rooms and online communities, customers can engage with their peers, discuss strategies and approaches, and occasionally form social relationships. This social factor adds a further facet of enjoyment to the gaming sensation.
Key Takeaways
Luck Casino grants a comprehensive range of advantages for players, involving entertainment, the likelihood of earning significant rewards, user-friendliness, variety, rewards, and interpersonal connections. Whether aiming for excitement or wishing to produce an unexpected outcome, Fortune Gaming Site delivers an exhilarating experience for all partake in. -
Online Gaming Site Paid: Benefits for Participants
Preface
Internet-based casinos providing real money games have gained significant widespread adoption, delivering customers with the chance to win financial prizes while savoring their most liked casino games from abode. This piece analyzes the upsides of virtual wagering environment paid activities, emphasizing their constructive impact on the interactive field.
Simplicity and Approachability
Internet-based gambling platform real money offerings present ease by giving users to access a comprehensive variety of activities from any place with an web access point. This excludes the need to journey to a physical casino, saving effort. Internet-based gambling platforms are as well offered at all times, giving participants to engage with at their convenience.
Diversity of Options
Online casinos present a wider breadth of games than brick-and-mortar wagering facilities, involving slot-related offerings, vingt-et-un, roulette, and casino-style games. This variety enables customers to experiment with novel games and identify novel most cherished, elevating their holistic interactive sensation.
Rewards and Discounts
Digital gaming sites present generous incentives and promotions to draw in and keep participants. These perks can include sign-up rewards, free spins, and reimbursement discounts, granting further importance for customers. Reward systems as well compensate players for their persistent custom.
Capability Building
Partaking in paid activities in the virtual sphere can facilitate customers acquire skills such as problem-solving. Activities like vingt-et-un and table games call for participants to arrive at choices that can impact the result of the game, helping them acquire problem-solving abilities.
Interpersonal Connections
ChatGPT l Валли, [06.06.2024 4:08]
Internet-based gambling platforms grant opportunities for social participation through communication channels, online communities, and real-time croupier activities. Customers can interact with one another, communicate tips and tactics, and even develop personal connections.
Fiscal Rewards
The online casino sector produces jobs and lends to the economic landscape through government proceeds and licensing charges. This fiscal effect benefits a extensive variety of vocations, from experience creators to player services professionals.
Recap
Online casino real money activities provide many upsides for participants, including user-friendliness, range, incentives, competency enhancement, social interaction, and fiscal upsides. As the industry constantly evolve, the widespread appeal of virtual wagering environments is expected to rise. -
빠릿한 충환전 서비스와 메이저업체의 안전성
베팅사이트 접속 시 핵심적인 요소 중 하나는 빠릿한 충환전 처리입니다. 일반적으로 3분 안에 충전하고, 열 분 내에 출금이 완료되어야 합니다. 메이저 주요업체들은 필요한 스태프 고용을 통해 이와 같은 빠릿한 환충 처리를 약속하며, 이 방법으로 회원들에게 안전한 느낌을 드립니다. 주요사이트를 접속하면서 빠른 경험을 해보시기 바랍니다. 저희는 고객님이 안심하고 토토사이트를 이용할 수 있도록 돕는 먹튀해결사입니다.
보증금을 걸고 배너 운영
먹튀해결사는 적어도 3000만 원에서 억대의 보증금을 예치하고 있는 업체들의 광고 배너를 운영 중입니다. 혹시 먹튀 피해가 발생할 경우, 배팅 규정에 어긋나지 않은 배팅 내역을 스크린샷을 찍어 먹튀해결사에 연락 주시면, 확인 후 보증 금액으로 빠르게 손해 보상을 처리합니다. 피해가 발생하면 즉시 캡처하여 손해 내용을 저장해두시고 보내주세요.
오랫동안 안전하게 운영된 업체 확인
먹튀해결사는 최소 4년 이상 먹튀 문제 없이 안전하게 운영된 업체만을 확인하여 배너 등록을 허가합니다. 이 때문에 어느 누구나 알만한 메이저사이트를 안전하게 이용할 수 있는 기회를 제공하고 있습니다. 철저한 검증 절차를 통해 확인된 사이트를 놓치지 마시고, 안심하고 도박을 즐겨보세요.
투명성과 공정성을 가진 먹튀 검증
먹튀 해결 팀의 먹튀 확인은 투명함과 정확함을 바탕으로 합니다. 언제나 사용자들의 관점을 우선으로 생각하고, 기업의 유혹이나 이익에 좌우되지 않고 한 건의 삭제 없이 진실만을 기반으로 검토해왔습니다. 먹튀 문제를 겪고 후회하지 않도록, 지금 바로 시작하세요.
먹튀 검증 사이트 목록
먹튀해결사가 엄선한 안전한 토토사이트 검증업체 목록 입니다. 현재 등록되어 있는 검증된 업체들은 먹튀 피해 발생 시 100% 보증을 도와드립니다. 다만, 제휴 기간이 만료된 업체에서 발생한 피해에 대해서는 책임지지 않습니다.
탁월한 먹튀 검증 알고리즘
먹튀 해결 전문가는 청결한 베팅 환경을 형성하기 위해 항상 노력합니다. 우리가 권장하는 토토사이트에서 안심하고 베팅하시기 바랍니다. 사용자의 먹튀 제보는 먹튀 리스트에 등록 노출되어 그 해당 토토사이트에 중대한 영향을 줄 수 있습니다. 먹튀 목록 작성 시 먹튀블러드의 검토 경험을 충분히 활용하여 정확한 검증을 할 수 있도록 하겠습니다.
안전한 베팅 문화를 제공하기 위해 끊임없이 힘쓰는 먹튀 해결 팀과 같이 안심하고 즐겨보세요. -
빠릿한 환충 서비스와 더불어 주요업체의 안전
토토사이트 이용 시 가장 중요한 요소는 빠릿한 입출금 프로세스입니다. 보통 세 분 내에 충전, 십 분 안에 환충이 완수되어야 합니다. 대형 주요업체들은 충분한 인력 채용을 통해 이러한 빠른 입출금 처리를 보증하며, 이 방법으로 고객들에게 안도감을 제공합니다. 메이저사이트를 사용하면서 빠른 체험을 해보세요. 저희는 여러분이 안심하고 사이트를 이용할 수 있도록 지원하는 먹튀 해결 팀입니다.
보증금을 내고 배너를 운영
먹튀 해결 전문가는 최소 3000만 원에서 1억 원의 보증금을 예치한 사이트들의 광고 배너를 운영합니다. 혹시 먹튀 사고가 발생할 경우, 베팅 규정에 어긋나지 않은 배팅 기록을 캡처해서 먹튀 해결 팀에 문의 주시면, 확인 후 보증 자금으로 신속하게 손해 보상을 처리합니다. 피해 발생 시 즉시 스크린샷을 찍어 피해 내용을 저장해두시고 보내주세요.
장기간 안전 운영 업체 확인
먹튀 해결 팀은 적어도 4년 이상 먹튀 사고 없이 안전하게 운영한 업체만을 인증하여 배너 입점을 허가합니다. 이 때문에 어느 누구나 잘 알려진 메이저사이트를 안심하고 사용할 수 있는 기회를 제공하고 있습니다. 정확한 검증 절차를 통해 확인된 사이트를 놓치지 말고, 보안된 도박을 즐겨보세요.
투명하고 공정한 먹튀 검증
먹튀 해결 팀의 먹튀 검토는 투명성과 정확함을 근거로 합니다. 늘 사용자들의 의견을 우선시하며, 사이트의 유혹이나 이익에 좌우되지 않고 하나의 삭제 없이 사실만을 바탕으로 검토해왔습니다. 먹튀 문제를 겪고 후회하지 않도록, 지금 시작해보세요.
먹튀 확인 사이트 리스트
먹튀해결사가 골라낸 안전 토토사이트 검증된 업체 목록 입니다. 현재 등록되어 있는 검증업체들은 먹튀 문제가 발생 시 100% 보증을 제공해드립니다. 하지만, 제휴 기간이 끝난 업체에서 발생한 문제에 대해서는 책임이 없습니다.
독보적인 먹튀 검증 알고리즘
먹튀 해결 전문가는 깨끗한 베팅 문화를 만들기 위해 계속해서 노력하고 있습니다. 우리가 소개하는 스포츠토토사이트에서 안심하고 배팅하세요. 회원님의 먹튀 제보는 먹튀 리스트에 기재되어 해당되는 토토사이트에 중대한 영향을 줄 수 있습니다. 먹튀 목록 작성 시 먹튀블러드 만의 검증 지식을 최대로 사용하여 공정한 심사를 할 수 있게 하겠습니다.
안전한 베팅 문화를 조성하기 위해 항상 힘쓰는 먹튀 해결 팀과 동반하여 안심하고 경험해보세요. -
free poker machine games
No-Cost Poker Machine Games: A Fun and Beneficial Encounter
Free virtual wagering games have emerged as gradually well-liked among users desiring a exciting and non-monetary entertainment experience. These offerings offer a extensive array of advantages, establishing them as a selected choice for several. Let's analyze how complimentary slot-based games can reward customers and the motivations behind they are so extensively enjoyed.
Fun Element
One of the key motivations users relish playing gratis electronic gaming offerings is for the pleasure-providing aspect they offer. These activities are created to be immersive and enthralling, with colorful illustrations and absorbing music that elevate the holistic entertainment encounter. Regardless of whether you're a recreational player aiming to pass the time or a enthusiastic leisure activity enthusiast desiring suspense, free poker machine offerings present enjoyment for all.
Capability Building
Partaking in free poker machine experiences can in addition assist refine valuable faculties such as critical analysis. These activities call for players to render swift selections contingent on the gameplay elements they are dealt, assisting them hone their decision-making faculties and intellectual prowess. Additionally, players can explore multiple approaches, refining their aptitudes devoid of the risk of losing actual currency.
Simplicity and Approachability
An additional advantage of free poker machine experiences is their ease and accessibility. These activities can be interacted with online from the simplicity of your own abode, removing the need to travel to a land-based gaming venue. They are also available at all times, giving players to relish them at whatever period that accommodates them. This simplicity establishes complimentary slot-based games a well-liked option for customers with hectic routines or those looking for a swift entertainment remedy.
Shared Experiences
Several gratis electronic gaming games in addition grant social elements that permit players to interact with fellow users. This can involve discussion forums, interactive platforms, and collaborative settings where participants can pit themselves against fellow users. These communal engagements contribute an extra aspect of enjoyment to the leisure experience, giving users to communicate with like-minded individuals who have in common their affinities.
Worry Mitigation and Emotional Refreshment
Partaking in no-cost virtual wagering experiences can likewise be a wonderful means to relax and calm down after a extended stretch of time. The effortless engagement and tranquil soundtracks can help reduce worry and unease, delivering a welcome reprieve from the obligations of normal life. Moreover, the thrill of receiving virtual rewards can boost your mood and result in you feeling revitalized.
Recap
No-cost virtual wagering games offer a extensive array of benefits for users, incorporating pleasure, competency enhancement, simplicity, social interaction, and anxiety reduction and decompression. Whether you're looking to sharpen your poker abilities or simply experience pleasure, no-cost virtual wagering games provide a advantageous and pleasurable sensation for participants of every degrees. -
Complimentary Slot Games: Amusement and Benefits for All
Complimentary slot games have become a favored form of virtual amusement, providing players the suspense of slot machines without any cash investment.
The principal objective of free slot games is to grant a fun and captivating way for individuals to enjoy the rush of slot machines free from any cash risk. They are designed to imitate the experience of paid slots, allowing players to trigger the reels, relish various motifs, and earn electronic rewards.
Pleasure: Gratis slot games are an outstanding option of leisure, granting spans of excitement. They showcase lively visuals, engaging sounds, and diverse motifs that serve a extensive selection of interests.
Competency Building: For newcomers, gratis slot games provide a risk-free setting to learn the workings of slot machines. Players can get accustomed with different functionality, winning combinations, and extras free from the worry of sacrificing cash.
Unwinding: Playing complimentary slot games can be a excellent way to unwind. The straightforward experience and the potential for online winnings make it an satisfying pursuit.
Shared Experiences: Many gratis slot games incorporate social features such as competitions and the opportunity to engage with friends. These components contribute a communal layer to the player experience, motivating players to challenge against fellow participants.
Perks of Complimentary Slot Games
1. Accessibility and Simplicity
Complimentary slot games are readily available to anyone with an internet connection. They can be experienced on multiple apparatuses including laptops, tablets, and mobile phones. This simplicity enables players to enjoy their favorite activities whenever and from any place.
2. Financial Safety
One of the most significant perks of complimentary slot games is that they eradicate the cash-related jeopardies linked to betting. Players can savor the rush of spinning the reels and hitting major prizes free from risking any money.
3. Range of Possibilities
No-Cost slot games are presented in a broad array of motifs and styles, from classic fruit machines to contemporary slot machines with video with complex plotlines and visuals. This diversity ensures that there is an alternative for anyone, irrespective of their preferences.
4. Strengthening Intellectual Faculties
Playing gratis slot games can tend to improve mental capabilities such as anticipatory planning. The necessity to understand win lines, learn operational principles, and foresee outcomes can offer a intellectual workout that is concurrently rewarding and advantageous.
5. Secure Pre-Testing for For-Profit Wagering
For those contemplating progressing to real-money slots, gratis slot games offer a valuable preparation phase. Players can experience different games, build methods, and acquire self-assurance ahead of choosing to invest genuine cash. This readiness can lead to a more educated and pleasurable real-money gaming experience.
Key Takeaways
Gratis slot games provide a plethora of rewards, from pure entertainment to capability building and community engagement. They present a worry-free and non-monetary way to savor the rush of slot machines, rendering them a worthwhile enhancement to the realm of online recreation. Whether you're seeking to de-stress, sharpen your cognitive skills, or merely enjoy yourself, no-cost slot games are a excellent alternative that continues to enchant players around. -
Complimentary Slot Games: Pleasure and Advantages for All
No-Cost slot games have become a favored form of internet-based amusement, delivering players the suspense of slot machines absent any cash outlay.
The primary aim of no-cost slot games is to deliver a pleasurable and captivating way for individuals to relish the rush of slot machines without any cash jeopardy. They are developed to simulate the experience of actual-currency slots, permitting players to spin the reels, savor various themes, and earn online prizes.
Fun: No-Cost slot games are an superb resource of amusement, providing durations of enjoyment. They present vibrant graphics, immersive soundtracks, and multifaceted concepts that serve a broad variety of interests.
Competency Building: For newcomers, free slot games provide a secure situation to familiarize the principles of slot machines. Players can become familiar with diverse functionality, win lines, and additional features absent the fear of sacrificing capital.
Relaxation: Playing complimentary slot games can be a fantastic way to unwind. The easy handling and the potential for online rewards make it an satisfying activity.
Interpersonal Connections: Many free slot games integrate group-oriented elements such as competitions and the opportunity to engage with fellow players. These features add a group-based aspect to the entertainment experience, encouraging players to measure up against others.
Rewards of Gratis Slot Games
1. Approachability and Comfort
Gratis slot games are easily accessible to everyone with an internet connection. They can be played on various platforms including laptops, pads, and cellphones. This simplicity allows players to experience their chosen activities whenever and from any place.
2. Financial Safety
One of the paramount advantages of free slot games is that they eradicate the economic jeopardies connected to gaming. Players can savor the rush of rotating the reels and receiving significant wins without investing any funds.
3. Variety of Games
Complimentary slot games are available in a extensive array of themes and formats, from traditional fruit slots to current video slots with elaborate narratives and visuals. This variety secures that there is an option for all, regardless of their inclinations.
4. Strengthening Intellectual Faculties
Playing free slot games can help develop mental capabilities such as strategic thinking. The need to choose paylines, learn game mechanics, and anticipate consequences can deliver a cognitive exercise that is equally pleasurable and helpful.
5. Risk-Free Trial Phase for Actual-Currency Gaming
For those pondering shifting to actual-currency slots, complimentary slot games present a valuable preparation phase. Players can experiment with diverse games, hone methods, and develop self-assurance prior to opting to invest genuine funds. This groundwork can lead to a more educated and rewarding real-money gaming interaction.
Key Takeaways
Complimentary slot games deliver a plethora of benefits, from pure fun to proficiency improvement and community engagement. They grant a worry-free and cost-free way to experience the excitement of slot machines, rendering them a beneficial addition to the domain of electronic leisure. Whether you're looking to de-stress, sharpen your cognitive skills, or merely experience pleasure, free slot games are a excellent alternative that persistently enchant players around. -
zee jkt48
Unduh App 888 dan Dapatkan Kemenangan: Instruksi Praktis
**Aplikasi 888 adalah alternatif ideal untuk Pengguna yang menginginkan keseruan main online yang menyenangkan dan menguntungkan. Bersama bonus harian dan fasilitas menggoda, aplikasi ini menawarkan menawarkan aktivitas bertaruhan unggulan. Berikut panduan pendek untuk memanfaatkan pelayanan App 888.
Unduh dan Awali Menangkan
Perangkat Terdapat:
Program 888 mampu diambil di HP Android, iOS, dan Laptop. Mulailah main dengan praktis di gadget manapun.
Bonus Harian dan Keuntungan
Keuntungan Buka Sehari-hari:
Login setiap masa untuk mendapatkan imbalan mencapai 100K pada periode ketujuh.
Rampungkan Misi:
Raih peluang undian dengan menyelesaikan pekerjaan terkait. Satu aktivitas menghadirkan Para Pengguna satu kesempatan undian untuk mengklaim keuntungan hingga 888K.
Penerimaan Langsung:
Imbalan harus diambil manual di dalam app. Jangan lupa untuk mendapatkan imbalan saban masa agar tidak batal.
Cara Undian
Kesempatan Undi:
Setiap hari, Anda bisa meraih satu peluang undian dengan menuntaskan pekerjaan.
Jika peluang undian tidak ada lagi, rampungkan lebih banyak tugas untuk mengambil tambahan kesempatan.
Ambang Hadiah:
Raih imbalan jika jumlah undi Pengguna melebihi 100K dalam satu hari.
Kebijakan Pokok
Pengklaiman Bonus:
Imbalan harus diambil manual dari aplikasi. Jika tidak, bonus akan otomatis dikreditkan ke akun pengguna Kamu setelah sebuah periode.
Persyaratan Bertaruh:
Bonus harus ada setidaknya sebuah betting berlaku untuk diklaim.
Penutup
Perangkat Lunak 888 menghadirkan pengalaman bertaruhan yang seru dengan imbalan tinggi. Download perangkat lunak sekarang dan alamilah hadiah besar-besaran saban waktu!
Untuk info lebih lanjut tentang diskon, deposit, dan agenda undangan, lihat laman beranda perangkat lunak. -
jabartoto
Unduh Perangkat Lunak 888 dan Menangkan Hadiah: Petunjuk Pendek
**Aplikasi 888 adalah alternatif ideal untuk Pengguna yang mengharapkan permainan bertaruhan internet yang seru dan bermanfaat. Melalui imbalan sehari-hari dan fasilitas menarik, program ini menawarkan menghadirkan pengalaman bermain unggulan. Berikut petunjuk cepat untuk memaksimalkan penggunaan Perangkat Lunak 888.
Download dan Segera Menangkan
Platform Ada:
App 888 bisa diinstal di Perangkat Android, iOS, dan Laptop. Segera bertaruhan dengan mudah di perangkat manapun.
Bonus Setiap Hari dan Hadiah
Hadiah Login Setiap Hari:
Buka setiap periode untuk mengklaim bonus sampai 100K pada waktu ketujuh.
Tuntaskan Aktivitas:
Ambil kesempatan lotere dengan menyelesaikan pekerjaan terkait. Setiap misi memberi Para Pengguna satu kesempatan lotere untuk memenangkan hadiah mencapai 888K.
Pengumpulan Manual:
Keuntungan harus diambil mandiri di dalam aplikasi. Jangan lupa untuk mendapatkan imbalan saban periode agar tidak habis masa berlakunya.
Sistem Lotere
Kesempatan Pengeretan:
Setiap waktu, Pengguna bisa mengklaim sebuah peluang pengeretan dengan menyelesaikan misi.
Jika peluang lotere tidak ada lagi, selesaikan lebih banyak aktivitas untuk mendapatkan extra opsi.
Ambang Hadiah:
Raih hadiah jika total undian Pengguna melampaui 100K dalam sehari.
Peraturan Pokok
Pengambilan Bonus:
Hadiah harus diambil mandiri dari perangkat lunak. Jika tidak, keuntungan akan secara otomatis diserahkan ke akun pribadi Kamu setelah sebuah periode.
Syarat Pertaruhan:
Bonus membutuhkan sekitar satu betting efektif untuk diambil.
Akhir
Program 888 menawarkan aktivitas bermain yang seru dengan hadiah besar. Instal aplikasi saat ini dan rasakan keberhasilan tinggi pada waktu!
Untuk detail lebih lanjut tentang penawaran, pengisian, dan skema undangan, cek page utama program. -
Discovering Free Casino Games
Introduction
In the digital age, free-of-charge casino games have turned into a popular selection for gamers who want to play casino games without wasting money. This write-up delves into the pros of free casino games and the causes they are attracting attention.
Benefits of Free Casino Games
Secure Gambling
One of the primary pros of no-cost casino games is the capability to engage in gaming without financial strain. Enthusiasts can enjoy their beloved casino activities minus concerns about wasting money.
Skill Enhancement
Free casino games offer an ideal stage for players to sharpen their gaming proficiency. Regardless of practicing methods in blackjack, gamblers can rehearse free from financial implications.
Variety of Games
No-cost casino games supply a extensive variety of casino games, such as vintage slots, table games, and live-action games. This variety assures that there is an option for every player.
Why Free-of-Charge Casino Games are Favored
Availability
Free casino games are widely available, enabling players from diverse locations to enjoy betting.
No Financial Commitment
Unlike money-based casino games, no-cost casino games do not need a financial commitment. This allows enthusiasts to engage in gaming free from the stress of losing cash.
Test Before Betting
Free casino games give gamblers the ability to try betting activities before committing hard-earned cash. This assists players make informed judgments.
Conclusion
No-cost casino games gives a fun and risk-free means to play betting. With zero monetary obligation, diverse game options, and possibilities for learning, it is no wonder that various gamblers prefer no-cost casino games for their gambling choices. -
y8
Unduh Aplikasi 888 dan Dapatkan Kemenangan: Manual Cepat
**Perangkat Lunak 888 adalah alternatif unggulan untuk Pengguna yang membutuhkan pengalaman main internet yang mengasyikkan dan menguntungkan. Melalui hadiah sehari-hari dan opsi menarik, app ini sedia memberikan keseruan main paling baik. Ini instruksi cepat untuk mengoptimalkan pelayanan App 888.
Pasang dan Awali Menangkan
Platform Tersedia:
Perangkat Lunak 888 memungkinkan diunduh di Perangkat Android, HP iOS, dan Laptop. Awali bermain dengan cepat di media apa saja.
Hadiah Tiap Hari dan Hadiah
Bonus Login Setiap Hari:
Login tiap hari untuk mengklaim hadiah hingga 100K pada hari ketujuh.
Tuntaskan Tugas:
Ambil kesempatan lotere dengan mengerjakan misi terkait. Tiap tugas menyediakan Anda 1 kesempatan pengeretan untuk memenangkan imbalan sampai 888K.
Pengumpulan Langsung:
Hadiah harus diklaim langsung di dalam perangkat lunak. Jangan lupa untuk meraih bonus saban hari agar tidak batal.
Mekanisme Pengeretan
Opsi Undian:
Setiap periode, Kamu bisa mengambil sebuah opsi undian dengan menuntaskan pekerjaan.
Jika kesempatan undi tidak ada lagi, selesaikan lebih banyak misi untuk mengklaim lebih banyak opsi.
Tingkat Imbalan:
Dapatkan hadiah jika akumulasi pengeretan Pengguna lebih dari 100K dalam 1 hari.
Peraturan Utama
Pengambilan Hadiah:
Keuntungan harus diterima sendiri dari perangkat lunak. Jika tidak, imbalan akan otomatis dikreditkan ke akun Anda Kamu setelah satu periode.
Ketentuan Pertaruhan:
Hadiah memerlukan minimal 1 bertaruh berlaku untuk diambil.
Penutup
App 888 menyediakan keseruan bermain yang menggembirakan dengan imbalan besar. Unduh perangkat lunak sekarang dan nikmati kemenangan besar-besaran setiap hari!
Untuk informasi lebih rinci tentang promosi, deposit, dan agenda rekomendasi, cek halaman home app. -
interwin
Ashley JKT48: Bintang yang Bercahaya Cemerlang di Langit Idola
Siapakah Ashley JKT48?
Siapa sosok belia talenta yang mencuri perhatian banyak sekali penggemar musik di Indonesia dan Asia Tenggara? Dialah Ashley Courtney Shintia, atau yang lebih dikenal dengan pseudonimnya, Ashley JKT48. Masuk dengan grup idola JKT48 pada tahun 2018, Ashley dengan cepat menjadi salah satu anggota paling favorit.
Biografi
Lahir di Jakarta pada tanggal 13 Maret 2000, Ashley berketurunan darah Tionghoa-Indonesia. Ia memulai karier di bidang hiburan sebagai model dan aktris, sebelum selanjutnya masuk dengan JKT48. Sifatnya yang periang, suara yang mantap, dan keterampilan menari yang mengagumkan membuatnya idol yang sangat dikasihi.
Penghargaan dan Apresiasi
Popularitas Ashley telah dikenal melalui berbagai apresiasi dan pencalonan. Pada tahun 2021, ia mendapat penghargaan "Anggota Paling Populer JKT48" di acara JKT48 Music Awards. Ashley juga dinobatkan sebagai "Idol Tercantik di Asia" oleh sebuah majalah online pada masa 2020.
Peran dalam JKT48
Ashley memainkan posisi krusial dalam group JKT48. Beliau adalah anggota Tim KIII dan berperan sebagai penari utama dan vokalis. Ashley juga merupakan bagian dari sub-unit "J3K" bersama Jessica Veranda dan Jennifer Rachel Natasya.
Karir Mandiri
Selain aktivitasnya bersama JKT48, Ashley juga merintis karier solo. Ashley telah merilis sejumlah lagu single, termasuk "Myself" (2021) dan "Falling Down" (2022). Ashley juga telah bekerja sama bareng artis lain, seperti Afgan dan Rossa.
Kehidupan Pribadi
Selain kancah perform, Ashley dikenal sebagai pribadi yang humble dan bersahabat. Ia menikmati menyisihkan waktu bersama sanak famili dan teman-temannya. Ashley juga memiliki kesukaan menggambar dan photography. -
no deposit bonus
Virtual casinos are increasingly more common, providing different promotions to attract new players. One of the most attractive propositions is the no deposit bonus, a promotion that lets gamblers to take a chance without any initial deposit. This write-up discusses the merits of no upfront deposit bonuses and emphasizes how they can increase their effectiveness.
What is a No Deposit Bonus?
A free bonus is a category of casino promotion where participants receive bonus credits or free spins without the need to put in any of their own cash. This allows casino enthusiasts to explore the gaming site, test out multiple game options and stand a chance to win real prizes, all without any initial expenditure.
Advantages of No Deposit Bonuses
Risk-Free Exploration
No deposit bonuses provide a safe chance to investigate online casinos. Participants can experiment with diverse gaming activities, understand the casino's interface, and judge the overall playing environment without spending their own cash. This is significantly helpful for novices who may not be aware of online casinos.
Chance to Win Real Money
One of the most tempting elements of free bonuses is the opportunity to win real money. Even though the amounts may be modest, any gains earned from the bonus can generally be cashed out after meeting the casino's playthrough rules. This introduces an element of anticipation and offers a possible financial reward without any monetary outlay.
Learning Opportunity
No deposit bonuses present a fantastic opportunity to learn how diverse games operate. Participants can test out tactics, get to know the rules of the slots, and become more proficient without being afraid of forfeiting their own capital. This can be notably advantageous for complex gaming activities like poker.
Conclusion
Free bonuses deliver several advantages for users, which include risk-free discovery, the possibility to get real rewards, and valuable educational prospects. As the field goes on to evolve, the popularity of no upfront deposit bonuses is anticipated to rise. -
semutwin
Pasang App 888 dan Menangkan Hadiah: Petunjuk Praktis
**Program 888 adalah pilihan sempurna untuk Kamu yang menginginkan pengalaman bermain digital yang menyenangkan dan bernilai. Melalui bonus sehari-hari dan opsi menggoda, perangkat lunak ini siap menyediakan pengalaman bermain optimal. Inilah panduan singkat untuk mengoptimalkan pelayanan Perangkat Lunak 888.
Instal dan Awali Menangkan
Platform Ada:
Aplikasi 888 memungkinkan diinstal di Sistem Android, Perangkat iOS, dan Windows. Mulailah berjudi dengan cepat di media apa pun.
Keuntungan Sehari-hari dan Bonus
Imbalan Mendaftar Setiap Hari:
Masuk tiap waktu untuk mengklaim hadiah mencapai 100K pada waktu ketujuh.
Kerjakan Misi:
Raih kesempatan undian dengan mengerjakan aktivitas terkait. Tiap aktivitas menawarkan Para Pengguna sebuah kesempatan undian untuk memenangkan keuntungan hingga 888K.
Pengklaiman Sendiri:
Keuntungan harus diambil sendiri di dalam aplikasi. Yakinlah untuk mengambil hadiah pada waktu agar tidak kadaluwarsa.
Prosedur Pengeretan
Kesempatan Lotere:
Tiap masa, Para Pengguna bisa mendapatkan satu kesempatan pengeretan dengan merampungkan misi.
Jika opsi undi selesai, selesaikan lebih banyak aktivitas untuk meraih tambahan kesempatan.
Batas Keuntungan:
Ambil bonus jika jumlah undi Kamu melampaui 100K dalam 1 hari.
Aturan Esensial
Pengambilan Hadiah:
Bonus harus diambil mandiri dari perangkat lunak. Jika tidak, hadiah akan langsung dikreditkan ke akun pengguna Anda setelah sebuah hari.
Peraturan Taruhan:
Imbalan harus ada paling tidak sebuah betting valid untuk digunakan.
Penutup
Aplikasi 888 menyediakan keseruan main yang menyenangkan dengan hadiah besar-besaran. Unduh perangkat lunak sekarang dan rasakan kemenangan signifikan pada masa!
Untuk data lebih terperinci tentang promo, pengisian, dan agenda undangan, lihat laman beranda app. -
Examining Cash Slots
Beginning
Money slots have become a preferred choice for casino enthusiasts desiring the rush of earning actual funds. This piece examines the pros of real money slots and why they are attracting more enthusiasts.
Advantages of Cash Slots
Actual Payouts
The primary draw of cash slots is the potential to gain genuine money. In contrast to complimentary slots, cash slots provide enthusiasts the thrill of possible financial rewards.
Large Game Selection
Money slots supply a wide selection of types, attributes, and payment models. This makes sure that there is something for all types of players, ranging from vintage 3-reel slots to contemporary animated slots with numerous paylines and special bonuses.
Attractive Offers
Numerous digital casinos give exciting bonuses for gambling slot enthusiasts. These can comprise initial offers, complimentary spins, cashback offers, and VIP schemes. Such incentives enhance the total gaming activity and provide extra opportunities to win currency.
Motivations for Opting for Money Slots
The Excitement of Earning Actual Cash
Gambling slots provide an exciting adventure, as players expect the potential of gaining actual cash. This element adds a further layer of excitement to the betting activity.
Immediate Rewards
Cash slots supply users the reward of quick earnings. Earning money promptly enhances the betting activity, turning it more satisfying.
Diverse Game Options
With gambling slots, enthusiasts have access to a wide array of slot machines, ensuring that there is consistently an activity new to try.
Conclusion
Gambling slots supplies a exhilarating and gratifying betting experience. With the chance to earn real funds, a extensive range of slot games, and thrilling offers, it's no wonder that numerous players favor gambling slots for their playing requirements. -
Examining Sweepstakes Gaming Hubs: A Captivating and Convenient Betting Possibility
Introduction
Lottery casinos are becoming a favored option for gamers desiring an engaging and legal method to experience digital betting. As opposed to traditional internet-based betting sites, lottery gaming hubs function under distinct authorized frameworks, permitting them to present games and awards without adhering to the equivalent regulations. This exposition explores the notion of promotion gambling platforms, their perks, and why they are appealing to a growing quantity of users.
What is a Sweepstakes Casino?
A contest gambling platform works by offering players with digital currency, which can be used to engage in games. Participants can achieve additional internet coins or tangible prizes, like money. The key distinction from classic betting sites is that users do not get currency straightforwardly but obtain it through promotional campaigns, such as purchasing a service or joining in a free participation lottery. This framework permits sweepstakes betting sites to operate authorized in many areas where standard digital gambling is restricted. -
https://match-prognoz.com
-
Pro88
-
What role do generic medicines play in reducing the burden of medication costs on healthcare systems vidalista dosering?
-
Where can I find OTC options for yoga-related injuries Cenforce 50 reviews?
-
10 大線上娛樂城評價實測|線上賭場推薦排名一次看!
在台灣,各式線上娛樂城如同雨後春筍般湧現,競爭激烈。對於一般的玩家來說,選擇一家可靠的線上賭場可說是至關重要的。今天,我們將分享十家最新娛樂城評價及實測的體驗,全面分析它們的優缺點,幫助玩家避免陷入詐騙網站的風險,確保選擇一個安全可靠的娛樂城平台。
娛樂城評價五大標準
在經過我們團隊的多次進行娛樂城實測後,得出了一個值得信任的線上娛樂城平台須包含的幾個要素,所以我們整理了評估娛樂城的五大標準:
條件一:金流帳戶安全性(儲值與出金)
條件二:博弈遊戲種類的豐富性
條件三:線上24小時客服、服務效率與態度
條件四:提供的優惠活動CP值
條件五:真實娛樂城玩家們的口碑評語
通常我們談到金流安全時,指的是對玩家風險的控制能力。一家優秀的娛樂城應當只在有充分證據證明玩家使用非法套利程式,或發現代理和玩家之間有對壓詐騙行為時,才暫時限制該玩家的金流。若無正當理由,則不應隨意限制玩家的金流,以防給玩家造成被詐騙的錯覺。
至於娛樂城的遊戲類型,主要可以分為以下七大類:真人視訊百家樂、彩票遊戲、體育投注、電子老虎機、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲及電子競技投注。這些豐富多樣的遊戲類型提供了廣泛的娛樂選擇。
十大娛樂城實測評價排名
基於上述五項標準,我們對以下十家現金版娛樂城進行了的實測分析,並對此給出了以下的排名結果:
RG富遊娛樂城
bet365娛樂城
DG娛樂城
yabo亞博娛樂城
PM娛樂城
1XBET娛樂城
九州娛樂城
LEO娛樂城
王者娛樂城
THA娛樂城 -
10 大線上娛樂城評價實測|線上賭場推薦排名一次看!
在台灣,各式線上娛樂城如同雨後春筍般湧現,競爭激烈。對於一般的玩家來說,選擇一家可靠的線上賭場可說是至關重要的。今天,我們將分享十家最新娛樂城評價及實測的體驗,全面分析它們的優缺點,幫助玩家避免陷入詐騙網站的風險,確保選擇一個安全可靠的娛樂城平台。
娛樂城評價五大標準
在經過我們團隊的多次進行娛樂城實測後,得出了一個值得信任的線上娛樂城平台須包含的幾個要素,所以我們整理了評估娛樂城的五大標準:
條件一:金流帳戶安全性(儲值與出金)
條件二:博弈遊戲種類的豐富性
條件三:線上24小時客服、服務效率與態度
條件四:提供的優惠活動CP值
條件五:真實娛樂城玩家們的口碑評語
通常我們談到金流安全時,指的是對玩家風險的控制能力。一家優秀的娛樂城應當只在有充分證據證明玩家使用非法套利程式,或發現代理和玩家之間有對壓詐騙行為時,才暫時限制該玩家的金流。若無正當理由,則不應隨意限制玩家的金流,以防給玩家造成被詐騙的錯覺。
至於娛樂城的遊戲類型,主要可以分為以下七大類:真人視訊百家樂、彩票遊戲、體育投注、電子老虎機、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲及電子競技投注。這些豐富多樣的遊戲類型提供了廣泛的娛樂選擇。
十大娛樂城實測評價排名
基於上述五項標準,我們對以下十家現金版娛樂城進行了的實測分析,並對此給出了以下的排名結果:
RG富遊娛樂城
bet365娛樂城
DG娛樂城
yabo亞博娛樂城
PM娛樂城
1XBET娛樂城
九州娛樂城
LEO娛樂城
王者娛樂城
THA娛樂城 -
富遊娛樂城評價:2024年最新評價
推薦指數 : ★★★★★ ( 5.0/5 )
富遊娛樂城作為目前最受歡迎的博弈網站之一,在台灣擁有最高的註冊人數。
RG富遊以安全、公正、真實和順暢的品牌保證,贏得了廣大玩家的信賴。富遊線上賭場不僅提供了豐富多樣的遊戲種類,還有眾多吸引人的優惠活動。在出金速度方面,獲得無數網紅和網友的高度評價,確保玩家能享有無憂的博弈體驗。
推薦要點
新手首選: 富遊娛樂城,2024年評選首選,提供專為新手打造的豐富教學和獨家優惠。
一存雙收: 首存1000元,立獲1000元獎金,僅需1倍流水,新手友好。
免費體驗: 新玩家享免費體驗金,暢遊各式遊戲,開啟無限可能。
優惠多元: 活動豐富,流水要求低,適合各類型玩家。
玩家首選: 遊戲多樣,服務優質,是新手與老手的最佳賭場選擇。
富遊娛樂城詳情資訊
賭場名稱 : RG富遊
創立時間 : 2019年
賭場類型 : 現金版娛樂城
博弈執照 : 馬爾他牌照(MGA)認證、英屬維爾京群島(BVI)認證、菲律賓(PAGCOR)監督競猜牌照
遊戲類型 : 真人百家樂、運彩投注、電子老虎機、彩票遊戲、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲
存取速度 : 存款5秒 / 提款3-5分
軟體下載 : 支援APP,IOS、安卓(Android)
線上客服 : 需透過官方LINE
富遊娛樂城優缺點
優點
台灣註冊人數NO.1線上賭場
首儲1000贈1000只需一倍流水
擁有體驗金免費體驗賭場
網紅部落客推薦保證出金線上娛樂城
缺點
需透過客服申請體驗金
富遊娛樂城存取款方式
存款方式
提供四大超商(全家、7-11、萊爾富、ok超商)
虛擬貨幣ustd存款
銀行轉帳(各大銀行皆可)
取款方式
網站內申請提款及可匯款至綁定帳戶
現金1:1出金
富遊娛樂城平台系統
真人百家 — RG真人、DG真人、歐博真人、DB真人(原亞博/PM)、SA真人、OG真人、WM真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、熊貓體育(原亞博/PM)
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —RG電子、ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、GR電子(好路)
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌
電競遊戲 — 熊貓體育
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、DB捕魚 -
娛樂城
富遊娛樂城評價:2024年最新評價
推薦指數 : ★★★★★ ( 5.0/5 )
富遊娛樂城作為目前最受歡迎的博弈網站之一,在台灣擁有最高的註冊人數。
RG富遊以安全、公正、真實和順暢的品牌保證,贏得了廣大玩家的信賴。富遊線上賭場不僅提供了豐富多樣的遊戲種類,還有眾多吸引人的優惠活動。在出金速度方面,獲得無數網紅和網友的高度評價,確保玩家能享有無憂的博弈體驗。
推薦要點
新手首選: 富遊娛樂城,2024年評選首選,提供專為新手打造的豐富教學和獨家優惠。
一存雙收: 首存1000元,立獲1000元獎金,僅需1倍流水,新手友好。
免費體驗: 新玩家享免費體驗金,暢遊各式遊戲,開啟無限可能。
優惠多元: 活動豐富,流水要求低,適合各類型玩家。
玩家首選: 遊戲多樣,服務優質,是新手與老手的最佳賭場選擇。
富遊娛樂城詳情資訊
賭場名稱 : RG富遊
創立時間 : 2019年
賭場類型 : 現金版娛樂城
博弈執照 : 馬爾他牌照(MGA)認證、英屬維爾京群島(BVI)認證、菲律賓(PAGCOR)監督競猜牌照
遊戲類型 : 真人百家樂、運彩投注、電子老虎機、彩票遊戲、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲
存取速度 : 存款5秒 / 提款3-5分
軟體下載 : 支援APP,IOS、安卓(Android)
線上客服 : 需透過官方LINE
富遊娛樂城優缺點
優點
台灣註冊人數NO.1線上賭場
首儲1000贈1000只需一倍流水
擁有體驗金免費體驗賭場
網紅部落客推薦保證出金線上娛樂城
缺點
需透過客服申請體驗金
富遊娛樂城存取款方式
存款方式
提供四大超商(全家、7-11、萊爾富、ok超商)
虛擬貨幣ustd存款
銀行轉帳(各大銀行皆可)
取款方式
網站內申請提款及可匯款至綁定帳戶
現金1:1出金
富遊娛樂城平台系統
真人百家 — RG真人、DG真人、歐博真人、DB真人(原亞博/PM)、SA真人、OG真人、WM真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、熊貓體育(原亞博/PM)
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —RG電子、ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、GR電子(好路)
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌
電競遊戲 — 熊貓體育
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、DB捕魚 -
2024娛樂城推薦,經過玩家實測結果出爐Top5!
2024娛樂城排名是這五間上榜,玩家尋找娛樂城無非就是要找穩定出金娛樂城,遊戲體驗良好、速度流暢,Ace博評網都幫你整理好了,給予娛樂城新手最佳的指南,不再擔心被黑網娛樂城詐騙!
2024娛樂城簡述
在現代,2024娛樂城數量已經超越以前,面對琳瑯滿目的娛樂城品牌,身為新手的玩家肯定難以辨別哪間好、哪間壞。
好的平台提供穩定的速度與遊戲體驗,穩定的系統與資訊安全可以保障用戶的隱私與資料,不用擔心收到傳票與任何網路威脅,這些線上賭場也提供合理的優惠活動給予玩家。
壞的娛樂城除了會騙取你的金錢之外,也會打著不實的廣告、優惠滿滿,想領卻是一場空!甚至有些平台還沒辦法登入,入口網站也是架設用來騙取新手儲值進他們口袋,這些黑網娛樂城是玩家必須避開的風險!
評測2024娛樂城的標準
Ace這次從網路上找來五位使用過娛樂城資歷2年以上的老玩家,給予他們使用各大娛樂城平台,最終選出Top5,而評選標準為下列這些條件:
以玩家觀點出發,優先考量玩家利益
豐富的遊戲種類與卓越的遊戲體驗
平台的信譽及其安全性措施
客服團隊的回應速度與服務品質
簡便的儲值流程和多樣的存款方法
吸引人的優惠活動方案
前五名娛樂城表格
賭博網站排名 線上賭場 平台特色 玩家實測評價
No.1 富遊娛樂城 遊戲選擇豐富,老玩家優惠多 正面好評
No.2 bet365娛樂城 知名大廠牌,運彩盤口選擇多 介面流暢
No.3 亞博娛樂城 多語言支持,介面簡潔順暢 賽事豐富
No.4 PM娛樂城 撲克牌遊戲豐富,選擇多元 直播順暢
No.5 1xbet娛樂城 直播流暢,安全可靠 佳評如潮
線上娛樂城玩家遊戲體驗評價分享
網友A:娛樂城平台百百款,富遊娛樂城是我3年以來長期使用的娛樂城,別人有的系統他們都有,出金也沒有被卡過,比起那些玩娛樂城還會收到傳票的娛樂城,富遊真的很穩定,值得推薦。
網友B:bet365中文的介面簡約,還有超多體育賽事盤口可以選擇,此外賽事大部分也都有附上直播來源,不必擔心看不到賽事最新狀況,全螢幕還能夠下單,真的超方便!
網友C:富遊娛樂城除了第一次儲值有優惠之外,儲值到一定金額還有好禮五選一,實用又方便,有問題的時候也有客服隨時能夠解答。
網友D:從大陸來台灣工作,沒想到台灣也能玩到亞博體育,這是以前在大陸就有使用的平台,雖然不是簡體字,但使用介面完全沒問題,遊戲流暢、速度比以前使用還更快速。
網友E:看玖壹壹MV發現了PM娛樂城這個大品牌,PM的真人百家樂沒有輸給在澳門實地賭場,甚至根本不用出門,超級方便的啦! -
娛樂城排行
2024娛樂城推薦,經過玩家實測結果出爐Top5!
2024娛樂城排名是這五間上榜,玩家尋找娛樂城無非就是要找穩定出金娛樂城,遊戲體驗良好、速度流暢,Ace博評網都幫你整理好了,給予娛樂城新手最佳的指南,不再擔心被黑網娛樂城詐騙!
2024娛樂城簡述
在現代,2024娛樂城數量已經超越以前,面對琳瑯滿目的娛樂城品牌,身為新手的玩家肯定難以辨別哪間好、哪間壞。
好的平台提供穩定的速度與遊戲體驗,穩定的系統與資訊安全可以保障用戶的隱私與資料,不用擔心收到傳票與任何網路威脅,這些線上賭場也提供合理的優惠活動給予玩家。
壞的娛樂城除了會騙取你的金錢之外,也會打著不實的廣告、優惠滿滿,想領卻是一場空!甚至有些平台還沒辦法登入,入口網站也是架設用來騙取新手儲值進他們口袋,這些黑網娛樂城是玩家必須避開的風險!
評測2024娛樂城的標準
Ace這次從網路上找來五位使用過娛樂城資歷2年以上的老玩家,給予他們使用各大娛樂城平台,最終選出Top5,而評選標準為下列這些條件:
以玩家觀點出發,優先考量玩家利益
豐富的遊戲種類與卓越的遊戲體驗
平台的信譽及其安全性措施
客服團隊的回應速度與服務品質
簡便的儲值流程和多樣的存款方法
吸引人的優惠活動方案
前五名娛樂城表格
賭博網站排名 線上賭場 平台特色 玩家實測評價
No.1 富遊娛樂城 遊戲選擇豐富,老玩家優惠多 正面好評
No.2 bet365娛樂城 知名大廠牌,運彩盤口選擇多 介面流暢
No.3 亞博娛樂城 多語言支持,介面簡潔順暢 賽事豐富
No.4 PM娛樂城 撲克牌遊戲豐富,選擇多元 直播順暢
No.5 1xbet娛樂城 直播流暢,安全可靠 佳評如潮
線上娛樂城玩家遊戲體驗評價分享
網友A:娛樂城平台百百款,富遊娛樂城是我3年以來長期使用的娛樂城,別人有的系統他們都有,出金也沒有被卡過,比起那些玩娛樂城還會收到傳票的娛樂城,富遊真的很穩定,值得推薦。
網友B:bet365中文的介面簡約,還有超多體育賽事盤口可以選擇,此外賽事大部分也都有附上直播來源,不必擔心看不到賽事最新狀況,全螢幕還能夠下單,真的超方便!
網友C:富遊娛樂城除了第一次儲值有優惠之外,儲值到一定金額還有好禮五選一,實用又方便,有問題的時候也有客服隨時能夠解答。
網友D:從大陸來台灣工作,沒想到台灣也能玩到亞博體育,這是以前在大陸就有使用的平台,雖然不是簡體字,但使用介面完全沒問題,遊戲流暢、速度比以前使用還更快速。
網友E:看玖壹壹MV發現了PM娛樂城這個大品牌,PM的真人百家樂沒有輸給在澳門實地賭場,甚至根本不用出門,超級方便的啦! -
娛樂城
Player台灣線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
layer如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
安全與公平性
安全永遠是我們評測的首要標準。我們審查每家娛樂城的執照資訊、監管機構以及使用的隨機數生成器,以確保其遊戲結果的公平性和隨機性。
02.
遊戲品質與多樣性
遊戲的品質和多樣性對於玩家體驗至關重要。我們評估遊戲的圖形、音效、用戶介面和創新性。同時,我們也考量娛樂城提供的遊戲種類,包括老虎機、桌遊、即時遊戲等。
03.
娛樂城優惠與促銷活動
我們仔細審視各種獎勵計劃和促銷活動,包括歡迎獎勵、免費旋轉和忠誠計劃。重要的是,我們也檢查這些優惠的賭注要求和條款條件,以確保它們公平且實用。
04.
客戶支持
優質的客戶支持是娛樂城質量的重要指標。我們評估支持團隊的可用性、響應速度和專業程度。一個好的娛樂城應該提供多種聯繫方式,包括即時聊天、電子郵件和電話支持。
05.
銀行與支付選項
我們檢查娛樂城提供的存款和提款選項,以及相關的處理時間和手續費。多樣化且安全的支付方式對於玩家來說非常重要。
06.
網站易用性、娛樂城APP體驗
一個直觀且易於導航的網站可以顯著提升玩家體驗。我們評估網站的設計、可訪問性和移動兼容性。
07.
玩家評價與反饋
我們考慮真實玩家的評價和反饋。這些資料幫助我們了解娛樂城在實際玩家中的表現。
娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 - Casino, Gambling、中國 - 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 - オンラインカジノ、越南 - Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。 -
Player台灣線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
layer如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
安全與公平性
安全永遠是我們評測的首要標準。我們審查每家娛樂城的執照資訊、監管機構以及使用的隨機數生成器,以確保其遊戲結果的公平性和隨機性。
02.
遊戲品質與多樣性
遊戲的品質和多樣性對於玩家體驗至關重要。我們評估遊戲的圖形、音效、用戶介面和創新性。同時,我們也考量娛樂城提供的遊戲種類,包括老虎機、桌遊、即時遊戲等。
03.
娛樂城優惠與促銷活動
我們仔細審視各種獎勵計劃和促銷活動,包括歡迎獎勵、免費旋轉和忠誠計劃。重要的是,我們也檢查這些優惠的賭注要求和條款條件,以確保它們公平且實用。
04.
客戶支持
優質的客戶支持是娛樂城質量的重要指標。我們評估支持團隊的可用性、響應速度和專業程度。一個好的娛樂城應該提供多種聯繫方式,包括即時聊天、電子郵件和電話支持。
05.
銀行與支付選項
我們檢查娛樂城提供的存款和提款選項,以及相關的處理時間和手續費。多樣化且安全的支付方式對於玩家來說非常重要。
06.
網站易用性、娛樂城APP體驗
一個直觀且易於導航的網站可以顯著提升玩家體驗。我們評估網站的設計、可訪問性和移動兼容性。
07.
玩家評價與反饋
我們考慮真實玩家的評價和反饋。這些資料幫助我們了解娛樂城在實際玩家中的表現。
娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 - Casino, Gambling、中國 - 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 - オンラインカジノ、越南 - Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。 -
娛樂城
2024娛樂城介紹
台灣2024娛樂城越開越多間,新開的線上賭場層出不窮,每間都以獨家的娛樂城優惠和體驗金來吸引玩家,致力於提供一流的賭博遊戲體驗。以下來介紹這幾間娛樂城網友對他們的真實評價,看看哪些娛樂城上榜了吧!
2024娛樂城排名
2023下半年,各家娛樂城競爭激烈,相繼推出誘人優惠,不論是娛樂城體驗金、反水流水還是首儲禮金,甚至還有娛樂城抽I15手機。以下就是2024年網友推薦的娛樂城排名:
NO.1 富遊娛樂城
NO.2 Bet365台灣
NO.3 DG娛樂城
NO.4 九州娛樂城
NO.5 亞博娛樂城
2024娛樂城推薦
根據2024娛樂城排名,以下將富遊娛樂城、BET365、亞博娛樂城、九州娛樂城、王者娛樂城推薦給大家,包含首儲贈點、免費體驗金、存提款速度、流水等等…
娛樂城遊戲種類
線上娛樂城憑藉其廣泛的遊戲種類,成功滿足了各式各樣玩家的喜好和需求。這些娛樂城遊戲不僅多元化且各具特色,能夠為玩家提供無與倫比的娛樂體驗。下面是一些最受歡迎的娛樂城遊戲類型:
電子老虎機
魔龍傳奇、雷神之鎚、戰神呂布、聚寶財神、鼠來寶、皇家777
真人百家樂
真人視訊百家樂、牛牛、龍虎、炸金花、骰寶、輪盤
電子棋牌
德州撲克、兩人麻將、21點、十三支、妞妞、三公、鬥地主、大老二、牌九
體育下注
世界盃足球賽、NBA、WBC世棒賽、英超、英雄聯盟LOL、特戰英豪
線上彩票
大樂透、539、美國天天樂、香港六合彩、北京賽車
捕魚機遊戲
三仙捕魚、福娃捕魚、招財貓釣魚、西遊降魔、吃我一砲、賓果捕魚
2024娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城/線上賭場(現金網)是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,而且是現金網,大家也許會好奇為什麼不直接叫做線上賭場或是線上博弈就好了。
其實這是有原因的,線上賭場這種東西,架站在台灣是違法的,在早期經營線上博弈被抓的風險非常高所以換了一個打模糊仗的代稱「娛樂城」來規避警方的耳目,畢竟以前沒有Google這種東西,這樣的代稱還是多少有些作用的。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種賭博平台,允許玩家在沒有預先充值的情況下參與遊戲。這種模式類似於信用卡,通常以周結或月結的方式結算遊戲費用。因此,如果玩家無法有效管理自己的投注額,可能會在月底面臨巨大的支付壓力。
娛樂城不出金怎麼辦?
釐清原因,如未違反娛樂城機制,可能是遇上黑網娛樂城,請盡快通報165反詐騙。 -
2024娛樂城介紹
台灣2024娛樂城越開越多間,新開的線上賭場層出不窮,每間都以獨家的娛樂城優惠和體驗金來吸引玩家,致力於提供一流的賭博遊戲體驗。以下來介紹這幾間娛樂城網友對他們的真實評價,看看哪些娛樂城上榜了吧!
2024娛樂城排名
2023下半年,各家娛樂城競爭激烈,相繼推出誘人優惠,不論是娛樂城體驗金、反水流水還是首儲禮金,甚至還有娛樂城抽I15手機。以下就是2024年網友推薦的娛樂城排名:
NO.1 富遊娛樂城
NO.2 Bet365台灣
NO.3 DG娛樂城
NO.4 九州娛樂城
NO.5 亞博娛樂城
2024娛樂城推薦
根據2024娛樂城排名,以下將富遊娛樂城、BET365、亞博娛樂城、九州娛樂城、王者娛樂城推薦給大家,包含首儲贈點、免費體驗金、存提款速度、流水等等…
娛樂城遊戲種類
線上娛樂城憑藉其廣泛的遊戲種類,成功滿足了各式各樣玩家的喜好和需求。這些娛樂城遊戲不僅多元化且各具特色,能夠為玩家提供無與倫比的娛樂體驗。下面是一些最受歡迎的娛樂城遊戲類型:
電子老虎機
魔龍傳奇、雷神之鎚、戰神呂布、聚寶財神、鼠來寶、皇家777
真人百家樂
真人視訊百家樂、牛牛、龍虎、炸金花、骰寶、輪盤
電子棋牌
德州撲克、兩人麻將、21點、十三支、妞妞、三公、鬥地主、大老二、牌九
體育下注
世界盃足球賽、NBA、WBC世棒賽、英超、英雄聯盟LOL、特戰英豪
線上彩票
大樂透、539、美國天天樂、香港六合彩、北京賽車
捕魚機遊戲
三仙捕魚、福娃捕魚、招財貓釣魚、西遊降魔、吃我一砲、賓果捕魚
2024娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城/線上賭場(現金網)是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,而且是現金網,大家也許會好奇為什麼不直接叫做線上賭場或是線上博弈就好了。
其實這是有原因的,線上賭場這種東西,架站在台灣是違法的,在早期經營線上博弈被抓的風險非常高所以換了一個打模糊仗的代稱「娛樂城」來規避警方的耳目,畢竟以前沒有Google這種東西,這樣的代稱還是多少有些作用的。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種賭博平台,允許玩家在沒有預先充值的情況下參與遊戲。這種模式類似於信用卡,通常以周結或月結的方式結算遊戲費用。因此,如果玩家無法有效管理自己的投注額,可能會在月底面臨巨大的支付壓力。
娛樂城不出金怎麼辦?
釐清原因,如未違反娛樂城機制,可能是遇上黑網娛樂城,請盡快通報165反詐騙。 -
在现代,在线赌场提供了多种便捷的存款和取款方式。对于较大金额的存款,您可以选择中国信托、台中银行、合作金库、台新银行、国泰银行或中华邮政。这些银行提供的服务覆盖金额范围从$1000到$10万,确保您的资金可以安全高效地转入赌场账户。
如果您需要进行较小金额的存款,可以选择通过便利店充值。7-11、全家、莱尔富和OK超商都提供这种服务,适用于金额范围在$1000到$2万之间的充值。通过这些便利店,您可以轻松快捷地完成资金转账,无需担心银行的营业时间或复杂的操作流程。
在进行娱乐场提款时,您可以选择通过各大银行转账或ATM转账。这些方法不仅安全可靠,而且非常方便,适合各种提款需求。最低提款金额为$1000,而上限则没有限制,确保您可以灵活地管理您的资金。
在选择在线赌场时,玩家评价和推荐也是非常重要的。许多IG网红和部落客,如丽莎、穎柔、猫少女日记-Kitty等,都对一些知名的娱乐场给予了高度评价。这些推荐不仅帮助您找到可靠的娱乐场所,还能确保您在游戏中享受到最佳的用户体验。
总体来说,在线赌场通过提供多样化的存款和取款方式,以及得到广泛认可的服务质量,正在不断吸引更多的玩家。无论您选择通过银行还是便利店进行充值,都能体验到快速便捷的操作。同时,通过查看玩家的真实评价和推荐,您也能更有信心地选择合适的娱乐场,享受安全、公正的游戏环境。 -
在现代,在线赌场提供了多种便捷的存款和取款方式。对于较大金额的存款,您可以选择中国信托、台中银行、合作金库、台新银行、国泰银行或中华邮政。这些银行提供的服务覆盖金额范围从$1000到$10万,确保您的资金可以安全高效地转入赌场账户。
如果您需要进行较小金额的存款,可以选择通过便利店充值。7-11、全家、莱尔富和OK超商都提供这种服务,适用于金额范围在$1000到$2万之间的充值。通过这些便利店,您可以轻松快捷地完成资金转账,无需担心银行的营业时间或复杂的操作流程。
在进行娱乐场提款时,您可以选择通过各大银行转账或ATM转账。这些方法不仅安全可靠,而且非常方便,适合各种提款需求。最低提款金额为$1000,而上限则没有限制,确保您可以灵活地管理您的资金。
在选择在线赌场时,玩家评价和推荐也是非常重要的。许多IG网红和部落客,如丽莎、穎柔、猫少女日记-Kitty等,都对一些知名的娱乐场给予了高度评价。这些推荐不仅帮助您找到可靠的娱乐场所,还能确保您在游戏中享受到最佳的用户体验。
总体来说,在线赌场通过提供多样化的存款和取款方式,以及得到广泛认可的服务质量,正在不断吸引更多的玩家。无论您选择通过银行还是便利店进行充值,都能体验到快速便捷的操作。同时,通过查看玩家的真实评价和推荐,您也能更有信心地选择合适的娱乐场,享受安全、公正的游戏环境。 -
台灣線上娛樂城
在现代,在线赌场提供了多种便捷的存款和取款方式。对于较大金额的存款,您可以选择中国信托、台中银行、合作金库、台新银行、国泰银行或中华邮政。这些银行提供的服务覆盖金额范围从$1000到$10万,确保您的资金可以安全高效地转入赌场账户。
如果您需要进行较小金额的存款,可以选择通过便利店充值。7-11、全家、莱尔富和OK超商都提供这种服务,适用于金额范围在$1000到$2万之间的充值。通过这些便利店,您可以轻松快捷地完成资金转账,无需担心银行的营业时间或复杂的操作流程。
在进行娱乐场提款时,您可以选择通过各大银行转账或ATM转账。这些方法不仅安全可靠,而且非常方便,适合各种提款需求。最低提款金额为$1000,而上限则没有限制,确保您可以灵活地管理您的资金。
在选择在线赌场时,玩家评价和推荐也是非常重要的。许多IG网红和部落客,如丽莎、穎柔、猫少女日记-Kitty等,都对一些知名的娱乐场给予了高度评价。这些推荐不仅帮助您找到可靠的娱乐场所,还能确保您在游戏中享受到最佳的用户体验。
总体来说,在线赌场通过提供多样化的存款和取款方式,以及得到广泛认可的服务质量,正在不断吸引更多的玩家。无论您选择通过银行还是便利店进行充值,都能体验到快速便捷的操作。同时,通过查看玩家的真实评价和推荐,您也能更有信心地选择合适的娱乐场,享受安全、公正的游戏环境。 -
娛樂城
在现代,在线赌场提供了多种便捷的存款和取款方式。对于较大金额的存款,您可以选择中国信托、台中银行、合作金库、台新银行、国泰银行或中华邮政。这些银行提供的服务覆盖金额范围从$1000到$10万,确保您的资金可以安全高效地转入赌场账户。
如果您需要进行较小金额的存款,可以选择通过便利店充值。7-11、全家、莱尔富和OK超商都提供这种服务,适用于金额范围在$1000到$2万之间的充值。通过这些便利店,您可以轻松快捷地完成资金转账,无需担心银行的营业时间或复杂的操作流程。
在进行娱乐场提款时,您可以选择通过各大银行转账或ATM转账。这些方法不仅安全可靠,而且非常方便,适合各种提款需求。最低提款金额为$1000,而上限则没有限制,确保您可以灵活地管理您的资金。
在选择在线赌场时,玩家评价和推荐也是非常重要的。许多IG网红和部落客,如丽莎、穎柔、猫少女日记-Kitty等,都对一些知名的娱乐场给予了高度评价。这些推荐不仅帮助您找到可靠的娱乐场所,还能确保您在游戏中享受到最佳的用户体验。
总体来说,在线赌场通过提供多样化的存款和取款方式,以及得到广泛认可的服务质量,正在不断吸引更多的玩家。无论您选择通过银行还是便利店进行充值,都能体验到快速便捷的操作。同时,通过查看玩家的真实评价和推荐,您也能更有信心地选择合适的娱乐场,享受安全、公正的游戏环境。 -
在现代,在线赌场提供了多种便捷的存款和取款方式。对于较大金额的存款,您可以选择中国信托、台中银行、合作金库、台新银行、国泰银行或中华邮政。这些银行提供的服务覆盖金额范围从$1000到$10万,确保您的资金可以安全高效地转入赌场账户。
如果您需要进行较小金额的存款,可以选择通过便利店充值。7-11、全家、莱尔富和OK超商都提供这种服务,适用于金额范围在$1000到$2万之间的充值。通过这些便利店,您可以轻松快捷地完成资金转账,无需担心银行的营业时间或复杂的操作流程。
在进行娱乐场提款时,您可以选择通过各大银行转账或ATM转账。这些方法不仅安全可靠,而且非常方便,适合各种提款需求。最低提款金额为$1000,而上限则没有限制,确保您可以灵活地管理您的资金。
在选择在线赌场时,玩家评价和推荐也是非常重要的。许多IG网红和部落客,如丽莎、穎柔、猫少女日记-Kitty等,都对一些知名的娱乐场给予了高度评价。这些推荐不仅帮助您找到可靠的娱乐场所,还能确保您在游戏中享受到最佳的用户体验。
总体来说,在线赌场通过提供多样化的存款和取款方式,以及得到广泛认可的服务质量,正在不断吸引更多的玩家。无论您选择通过银行还是便利店进行充值,都能体验到快速便捷的操作。同时,通过查看玩家的真实评价和推荐,您也能更有信心地选择合适的娱乐场,享受安全、公正的游戏环境。 -
Player台灣線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
layer如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
安全與公平性
安全永遠是我們評測的首要標準。我們審查每家娛樂城的執照資訊、監管機構以及使用的隨機數生成器,以確保其遊戲結果的公平性和隨機性。
02.
遊戲品質與多樣性
遊戲的品質和多樣性對於玩家體驗至關重要。我們評估遊戲的圖形、音效、用戶介面和創新性。同時,我們也考量娛樂城提供的遊戲種類,包括老虎機、桌遊、即時遊戲等。
03.
娛樂城優惠與促銷活動
我們仔細審視各種獎勵計劃和促銷活動,包括歡迎獎勵、免費旋轉和忠誠計劃。重要的是,我們也檢查這些優惠的賭注要求和條款條件,以確保它們公平且實用。
04.
客戶支持
優質的客戶支持是娛樂城質量的重要指標。我們評估支持團隊的可用性、響應速度和專業程度。一個好的娛樂城應該提供多種聯繫方式,包括即時聊天、電子郵件和電話支持。
05.
銀行與支付選項
我們檢查娛樂城提供的存款和提款選項,以及相關的處理時間和手續費。多樣化且安全的支付方式對於玩家來說非常重要。
06.
網站易用性、娛樂城APP體驗
一個直觀且易於導航的網站可以顯著提升玩家體驗。我們評估網站的設計、可訪問性和移動兼容性。
07.
玩家評價與反饋
我們考慮真實玩家的評價和反饋。這些資料幫助我們了解娛樂城在實際玩家中的表現。
娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 - Casino, Gambling、中國 - 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 - オンラインカジノ、越南 - Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。 -
娛樂城
Player台灣線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
layer如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
安全與公平性
安全永遠是我們評測的首要標準。我們審查每家娛樂城的執照資訊、監管機構以及使用的隨機數生成器,以確保其遊戲結果的公平性和隨機性。
02.
遊戲品質與多樣性
遊戲的品質和多樣性對於玩家體驗至關重要。我們評估遊戲的圖形、音效、用戶介面和創新性。同時,我們也考量娛樂城提供的遊戲種類,包括老虎機、桌遊、即時遊戲等。
03.
娛樂城優惠與促銷活動
我們仔細審視各種獎勵計劃和促銷活動,包括歡迎獎勵、免費旋轉和忠誠計劃。重要的是,我們也檢查這些優惠的賭注要求和條款條件,以確保它們公平且實用。
04.
客戶支持
優質的客戶支持是娛樂城質量的重要指標。我們評估支持團隊的可用性、響應速度和專業程度。一個好的娛樂城應該提供多種聯繫方式,包括即時聊天、電子郵件和電話支持。
05.
銀行與支付選項
我們檢查娛樂城提供的存款和提款選項,以及相關的處理時間和手續費。多樣化且安全的支付方式對於玩家來說非常重要。
06.
網站易用性、娛樂城APP體驗
一個直觀且易於導航的網站可以顯著提升玩家體驗。我們評估網站的設計、可訪問性和移動兼容性。
07.
玩家評價與反饋
我們考慮真實玩家的評價和反饋。這些資料幫助我們了解娛樂城在實際玩家中的表現。
娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 - Casino, Gambling、中國 - 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 - オンラインカジノ、越南 - Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。 -
在现代,在线赌场提供了多种便捷的存款和取款方式。对于较大金额的存款,您可以选择中国信托、台中银行、合作金库、台新银行、国泰银行或中华邮政。这些银行提供的服务覆盖金额范围从$1000到$10万,确保您的资金可以安全高效地转入赌场账户。
如果您需要进行较小金额的存款,可以选择通过便利店充值。7-11、全家、莱尔富和OK超商都提供这种服务,适用于金额范围在$1000到$2万之间的充值。通过这些便利店,您可以轻松快捷地完成资金转账,无需担心银行的营业时间或复杂的操作流程。
在进行娱乐场提款时,您可以选择通过各大银行转账或ATM转账。这些方法不仅安全可靠,而且非常方便,适合各种提款需求。最低提款金额为$1000,而上限则没有限制,确保您可以灵活地管理您的资金。
在选择在线赌场时,玩家评价和推荐也是非常重要的。许多IG网红和部落客,如丽莎、穎柔、猫少女日记-Kitty等,都对一些知名的娱乐场给予了高度评价。这些推荐不仅帮助您找到可靠的娱乐场所,还能确保您在游戏中享受到最佳的用户体验。
总体来说,在线赌场通过提供多样化的存款和取款方式,以及得到广泛认可的服务质量,正在不断吸引更多的玩家。无论您选择通过银行还是便利店进行充值,都能体验到快速便捷的操作。同时,通过查看玩家的真实评价和推荐,您也能更有信心地选择合适的娱乐场,享受安全、公正的游戏环境。 -
娛樂城
Player台灣線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
layer如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
安全與公平性
安全永遠是我們評測的首要標準。我們審查每家娛樂城的執照資訊、監管機構以及使用的隨機數生成器,以確保其遊戲結果的公平性和隨機性。
02.
遊戲品質與多樣性
遊戲的品質和多樣性對於玩家體驗至關重要。我們評估遊戲的圖形、音效、用戶介面和創新性。同時,我們也考量娛樂城提供的遊戲種類,包括老虎機、桌遊、即時遊戲等。
03.
娛樂城優惠與促銷活動
我們仔細審視各種獎勵計劃和促銷活動,包括歡迎獎勵、免費旋轉和忠誠計劃。重要的是,我們也檢查這些優惠的賭注要求和條款條件,以確保它們公平且實用。
04.
客戶支持
優質的客戶支持是娛樂城質量的重要指標。我們評估支持團隊的可用性、響應速度和專業程度。一個好的娛樂城應該提供多種聯繫方式,包括即時聊天、電子郵件和電話支持。
05.
銀行與支付選項
我們檢查娛樂城提供的存款和提款選項,以及相關的處理時間和手續費。多樣化且安全的支付方式對於玩家來說非常重要。
06.
網站易用性、娛樂城APP體驗
一個直觀且易於導航的網站可以顯著提升玩家體驗。我們評估網站的設計、可訪問性和移動兼容性。
07.
玩家評價與反饋
我們考慮真實玩家的評價和反饋。這些資料幫助我們了解娛樂城在實際玩家中的表現。
娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 - Casino, Gambling、中國 - 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 - オンラインカジノ、越南 - Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。 -
Player台灣線上娛樂城遊戲指南與評測
台灣最佳線上娛樂城遊戲的終極指南!我們提供專業評測,分析熱門老虎機、百家樂、棋牌及其他賭博遊戲。從遊戲規則、策略到選擇最佳娛樂城,我們全方位覆蓋,協助您更安全的遊玩。
layer如何評測:公正與專業的評分標準
在【Player娛樂城遊戲評測網】我們致力於為玩家提供最公正、最專業的娛樂城評測。我們的評測過程涵蓋多個關鍵領域,旨在確保玩家獲得可靠且全面的信息。以下是我們評測娛樂城的主要步驟:
安全與公平性
安全永遠是我們評測的首要標準。我們審查每家娛樂城的執照資訊、監管機構以及使用的隨機數生成器,以確保其遊戲結果的公平性和隨機性。
02.
遊戲品質與多樣性
遊戲的品質和多樣性對於玩家體驗至關重要。我們評估遊戲的圖形、音效、用戶介面和創新性。同時,我們也考量娛樂城提供的遊戲種類,包括老虎機、桌遊、即時遊戲等。
03.
娛樂城優惠與促銷活動
我們仔細審視各種獎勵計劃和促銷活動,包括歡迎獎勵、免費旋轉和忠誠計劃。重要的是,我們也檢查這些優惠的賭注要求和條款條件,以確保它們公平且實用。
04.
客戶支持
優質的客戶支持是娛樂城質量的重要指標。我們評估支持團隊的可用性、響應速度和專業程度。一個好的娛樂城應該提供多種聯繫方式,包括即時聊天、電子郵件和電話支持。
05.
銀行與支付選項
我們檢查娛樂城提供的存款和提款選項,以及相關的處理時間和手續費。多樣化且安全的支付方式對於玩家來說非常重要。
06.
網站易用性、娛樂城APP體驗
一個直觀且易於導航的網站可以顯著提升玩家體驗。我們評估網站的設計、可訪問性和移動兼容性。
07.
玩家評價與反饋
我們考慮真實玩家的評價和反饋。這些資料幫助我們了解娛樂城在實際玩家中的表現。
娛樂城常見問題
娛樂城是什麼?
娛樂城是什麼?娛樂城是台灣對於線上賭場的特別稱呼,線上賭場分為幾種:現金版、信用版、手機娛樂城(娛樂城APP),一般來說,台灣人在稱娛樂城時,是指現金版線上賭場。
線上賭場在別的國家也有別的名稱,美國 - Casino, Gambling、中國 - 线上赌场,娱乐城、日本 - オンラインカジノ、越南 - Nhà cái。
娛樂城會被抓嗎?
在台灣,根據刑法第266條,不論是實體或線上賭博,參與賭博的行為可處最高5萬元罰金。而根據刑法第268條,為賭博提供場所並意圖營利的行為,可能面臨3年以下有期徒刑及最高9萬元罰金。一般賭客若被抓到,通常被視為輕微罪行,原則上不會被判處監禁。
信用版娛樂城是什麼?
信用版娛樂城是一種線上賭博平台,其中的賭博活動不是直接以現金進行交易,而是基於信用系統。在這種模式下,玩家在進行賭博時使用虛擬的信用點數或籌碼,這些點數或籌碼代表了一定的貨幣價值,但實際的金錢交易會在賭博活動結束後進行結算。
現金版娛樂城是什麼?
現金版娛樂城是一種線上博弈平台,其中玩家使用實際的金錢進行賭博活動。玩家需要先存入真實貨幣,這些資金轉化為平台上的遊戲籌碼或信用,用於參與各種賭場遊戲。當玩家贏得賭局時,他們可以將這些籌碼或信用兌換回現金。
娛樂城體驗金是什麼?
娛樂城體驗金是娛樂場所為新客戶提供的一種免費遊玩資金,允許玩家在不需要自己投入任何資金的情況下,可以進行各類遊戲的娛樂城試玩。這種體驗金的數額一般介於100元到1,000元之間,且對於如何使用這些體驗金以達到提款條件,各家娛樂城設有不同的規則。 -
주제는 폰테크 입니다
휴대폰을 사고 파는 종류의 사이트 입니다
고객이 휴대폰을 개통하고
그럼 저희는 돈을주고 그 휴대폰을 구매합니다. -
הימורים באינטרנט
הימורי ספורטיביים – הימורים באינטרנט
הימורי ספורטיביים הפכו לאחד התחומים המתפתחים ביותר בהימורים באינטרנט. שחקנים יכולים להתערב על תוצאותיהם של אירועים ספורט מוכרים לדוגמה כדורגל, כדור סל, משחק הטניס ועוד. האפשרויות להתערבות הן רבות, כולל תוצאתו ההתמודדות, מספר הגולים, כמות הפעמים ועוד. להלן דוגמאות של למשחקים נפוצים שעליהם ניתן להמר:
כדורגל: ליגת אלופות, מונדיאל, ליגות מקומיות
כדורסל: ליגת NBA, יורוליג, טורנירים בינלאומיים
משחק הטניס: טורניר ווימבלדון, אליפות ארה"ב הפתוחה, אליפות צרפת הפתוחה
פוקר ברשת ברשת – הימורים באינטרנט
משחק הפוקר באינטרנט הוא אחד מהמשחקים ההימור הנפוצים ביותר בימינו. משתתפים יכולים להתמודד נגד יריבים מרחבי העולם במגוון סוגי משחק , למשל Texas Hold'em, Omaha, סטאד ועוד. אפשר לגלות טורנירים ומשחקי קש במגוון דרגות ואפשרויות מגוונות. אתרי פוקר המובילים מציעים:
מבחר רב של גרסאות פוקר
טורנירים שבועיים וחודשיות עם פרסים כספיים
שולחנות המשחק למשחק מהיר ולטווח הארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ללקוחות ומועדוני עם הטבות עם הטבות
בטיחות והגינות
בעת הבחירה בפלטפורמה להימורים, חיוני לבחור גם אתרי הימורים מורשים ומפוקחים המציעים סביבת למשחק מאובטחת והוגנת. אתרים אלה משתמשים בטכנולוגיות אבטחה מתקדמת להגנה על מידע אישי ופיננסי, וגם באמצעות תוכנות מחולל מספרים רנדומליים (RNG) כדי להבטיח הגינות המשחקים במשחקים.
בנוסף, הכרחי לשחק בצורה אחראי תוך כדי קביעת מגבלות הימורים אישיות. מרבית אתרי ההימורים מאפשרים למשתתפים לקבוע מגבלות הפסד ופעילות, וגם להשתמש ב- כלים נגד התמכרויות. שחק בחכמה ואל תרדפו גם אחרי הפסד.
המדריך השלם לקזינו אונליין, משחקי ספורט ופוקר ברשת
הימורים באינטרנט מציעים עולם שלם של הזדמנויות מרתקות למשתתפים, החל מקזינו באינטרנט וכל משחקי ספורט ופוקר ברשת. בעת הבחירה פלטפורמת הימורים, הקפידו לבחור גם אתרי הימורים המפוקחים המציעים סביבת למשחק מאובטחת והוגנת. זכרו גם לשחק באופן אחראי תמיד ואחראי – משחקי ההימורים ברשת אמורים להיות מבדרים ולא לגרום בעיות פיננסיות או גם חברתיות. -
הימורי ספורטיביים – הימור באינטרנט
הימורי ספורט נהיו לאחד התחומים הצומחים ביותר בהימורים ברשת. משתתפים מסוגלים להמר על תוצאות של אירועי ספורטיביים פופולריים למשל כדור רגל, כדורסל, טניס ועוד. האופציות להימור הן רבות, וביניהן תוצאת המשחק, כמות הגולים, כמות הפעמים ועוד. להלן דוגמאות של למשחקי נפוצים במיוחד עליהם אפשרי להמר:
כדורגל: ליגת אלופות, גביע העולם, ליגות מקומיות
כדור סל: NBA, יורוליג, טורנירים בינלאומיים
משחק הטניס: טורניר ווימבלדון, אליפות ארה"ב הפתוחה, רולאן גארוס
פוקר ברשת ברשת – הימורים באינטרנט
פוקר ברשת הוא אחד מהמשחקים ההימורים הנפוצים ביותר כיום. משתתפים מסוגלים להתחרות נגד מתחרים מרחבי תבל במגוון סוגי משחק , לדוגמה טקסס הולדם, אומהה, Stud ועוד. אפשר למצוא טורנירים ומשחקי קש במגוון דרגות ואפשרויות שונות. אתרי פוקר הטובים מציעים:
מבחר רב של גרסאות המשחק פוקר
תחרויות שבועיות וחודשיות עם פרסים כספיים גבוהים
שולחנות המשחק למשחקים מהירים ולטווח הארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ומועדוני VIP עם הטבות יחודיות
בטיחות ואבטחה והוגנות
כאשר בוחרים בפלטפורמה להימורים, חשוב לבחור גם אתרים מורשים המפוקחים המציעים סביבת משחק מאובטחת והוגנת. אתרים אלו משתמשים בטכנולוגיות אבטחה מתקדמת להבטחה על מידע אישי ופיננסיים, וכן באמצעות תוכנות גנרטור מספרים רנדומליים (RNG) כדי להבטיח הגינות במשחקים במשחקי ההימורים.
בנוסף, חשוב לשחק בצורה אחראית תוך כדי הגדרת מגבלות אישיות הימור אישיות של השחקן. רוב אתרי ההימורים מאפשרים לשחקנים להגדיר מגבלות להפסדים ופעילויות, כמו גם להשתמש ב- כלים למניעת התמכרות. שחקו בחכמה ואל גם תרדפו גם אחר הפסדים.
המדריך השלם לקזינו אונליין, הימורי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט
הימורים באינטרנט מציעים גם עולם שלם הזדמנויות מרתקות למשתתפים, החל מקזינו אונליין וגם בהימורי ספורט ופוקר ברשת. בזמן בחירת בפלטפורמת הימורים, חשוב לבחור אתרים מפוקחים המציעים גם סביבה למשחק מאובטחת והגיונית. זכרו גם לשחק תמיד באופן אחראי תמיד ואחראי – משחקי ההימורים ברשת נועדו להיות מבדרים ומהנים ולא גם ליצור לבעיות כלכליות או גם חברתיות. -
הימורי ספורט
הימורי ספורטיביים – הימור באינטרנט
הימורי ספורטיביים נהיו לאחד הענפים המשגשגים ביותר בהימורים באינטרנט. משתתפים מסוגלים להתערב על תוצאות של אירועים ספורט נפוצים לדוגמה כדורגל, כדורסל, טניס ועוד. האפשרויות להתערבות הן מרובות, כולל תוצאתו ההתמודדות, מספר הגולים, כמות הנקודות ועוד. להלן דוגמאות של למשחקי נפוצים במיוחד שעליהם אפשרי להתערב:
כדורגל: ליגת האלופות, גביע העולם, ליגות מקומיות
כדור סל: NBA, יורוליג, תחרויות בינלאומיות
טניס: ווימבלדון, US Open, רולאן גארוס
פוקר ברשת – הימור ברשת
פוקר באינטרנט הוא אחד מהמשחקים ההימור המוכרים ביותר בימינו. שחקנים יכולים להתמודד מול מתחרים מכל רחבי העולם בסוגי וריאציות משחק , למשל Texas Hold'em, אומהה, Stud ועוד. ניתן לגלות טורנירים ומשחקי קש במגוון רמות ואפשרויות הימור מגוונות. אתרי פוקר המובילים מציעים גם:
מבחר רב של גרסאות פוקר
תחרויות שבועיות וחודשיים עם פרסים כספיים
שולחנות למשחקים מהירים ולטווח הארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ללקוחות ומועדוני עם הטבות יחודיות
בטיחות ואבטחה והגינות
כאשר הבחירה בפלטפורמה להימורים, חיוני לבחור גם אתרים מורשים המפוקחים המציעים גם סביבה למשחק מאובטחת והגיונית. אתרים אלו משתמשים בטכנולוגיית אבטחה מתקדמות להגנה על מידע אישי ופיננסיים, וכן באמצעות תוכנות גנרטור מספרים אקראיים (RNG) כדי לוודא הגינות המשחקים במשחקים.
בנוסף, הכרחי לשחק גם בצורה אחראית תוך כדי קביעת מגבלות הימורים אישיות. מרבית האתרים מאפשרים גם למשתתפים להגדיר מגבלות להפסדים ופעילות, כמו גם להשתמש ב- כלים למניעת התמכרות. שחק בחכמה ואל גם תרדפו גם אחר הפסדים.
המדריך השלם לקזינו באינטרנט, משחקי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט באינטרנט
ההימורים באינטרנט מציעים עולם שלם של של הזדמנויות מרתקות לשחקנים, החל מקזינו באינטרנט וגם משחקי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט. בזמן בחירת פלטפורמת הימורים, הקפידו לבחור אתרים מפוקחים המציעים גם סביבת למשחק בטוחה והוגנת. זכרו גם לשחק תמיד באופן אחראי תמיד – ההימורים באינטרנט נועדו להיות מבדרים ומהנים ולא ליצור לבעיות פיננסיות או חברתיים. -
הימורי ספורט
הימורי ספורט – הימורים באינטרנט
הימור ספורטיביים נעשו לאחד הענפים המתפתחים ביותר בהימורים באינטרנט. שחקנים מסוגלים להמר על תוצאותיהם של אירועי ספורטיביים נפוצים למשל כדור רגל, כדורסל, משחק הטניס ועוד. האופציות להתערבות הן רבות, כולל תוצאתו המשחק, כמות השערים, מספר הפעמים ועוד. הבא דוגמאות למשחקים נפוצים שעליהם ניתן להתערב:
כדורגל: ליגת האלופות, גביע העולם, ליגות מקומיות
כדורסל: NBA, יורוליג, תחרויות בינלאומיות
משחק הטניס: טורניר ווימבלדון, US Open, רולאן גארוס
פוקר באינטרנט – הימור ברשת
משחק הפוקר באינטרנט הוא אחד ממשחקי ההימורים הפופולריים ביותר בימינו. שחקנים מסוגלים להתמודד מול יריבים מרחבי תבל במגוון סוגי של המשחק , כגון טקסס הולדם, Omaha, סטאד ועוד. אפשר לגלות תחרויות ומשחקי קש במגוון דרגות ואפשרויות מגוונות. אתרי פוקר הטובים מציעים גם:
מגוון רחב של גרסאות המשחק פוקר
טורנירים שבועיות וחודשיים עם פרסים כספיים גבוהים
שולחנות למשחקים מהירים ולטווח הארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ומועדוני VIP עם הטבות בלעדיות
בטיחות והגינות
בעת הבחירה פלטפורמה להימורים, חשוב לבחור אתרי הימורים מורשים ומפוקחים המציעים גם סביבת משחק מאובטחת והגיונית. אתרים אלו משתמשים בטכנולוגיית אבטחה מתקדמת להגנה על מידע אישי ופיננסי, וגם באמצעות תוכנות מחולל מספרים אקראיים (RNG) כדי להבטיח הגינות במשחקים במשחקים.
מעבר לכך, הכרחי לשחק באופן אחראי תוך כדי קביעת מגבלות הימורים אישיות של השחקן. רוב אתרי ההימורים מאפשרים לשחקנים לקבוע מגבלות הפסד ופעילות, וגם לנצל כלים נגד התמכרויות. הימרו בתבונה ואל גם תרדפו גם אחרי הפסד.
המדריך השלם לקזינו באינטרנט, משחקי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט ברשת
הימורים באינטרנט מציעים עולם שלם של של הזדמנויות מלהיבות לשחקנים, מתחיל מקזינו באינטרנט וגם בהימורי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט. בזמן הבחירה בפלטפורמת הימורים, הקפידו לבחור גם אתרי הימורים המפוקחים המציעים גם סביבה משחק בטוחה והוגנת. זכרו גם לשחק בצורה אחראית תמיד – ההימורים באינטרנט נועדו להיות מבדרים ולא גם לגרום בעיות כלכליות או חברתיים. -
הימורי ספורט
הימורי ספורט – הימור באינטרנט
הימור ספורט הפכו לאחד התחומים הצומחים ביותר בהימור ברשת. שחקנים יכולים להמר על תוצאת של אירועים ספורט נפוצים כמו כדורגל, כדורסל, טניס ועוד. האפשרויות להתערבות הן רבות, וביניהן תוצאת המאבק, מספר השערים, מספר הנקודות ועוד. להלן דוגמאות למשחקים נפוצים במיוחד עליהם ניתן להמר:
כדור רגל: ליגת אלופות, גביע העולם, ליגות אזוריות
כדור סל: ליגת NBA, ליגת יורוליג, טורנירים בינלאומיים
טניס: טורניר ווימבלדון, US Open, רולאן גארוס
פוקר באינטרנט – הימורים באינטרנט
משחק הפוקר באינטרנט הוא אחד ממשחקי ההימור המוכרים ביותר בימינו. משתתפים יכולים להתחרות נגד יריבים מכל רחבי תבל במגוון וריאציות של המשחק , כגון טקסס הולדם, אומהה, Stud ועוד. אפשר למצוא טורנירים ומשחקי במגוון דרגות ואפשרויות הימור מגוונות. אתרי הפוקר המובילים מציעים גם:
מבחר רב של גרסאות פוקר
תחרויות שבועיים וחודשיות עם פרסים כספיים
שולחנות המשחק למשחקים מהירים ולטווח ארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ומועדוני VIP בלעדיות
בטיחות והוגנות
בעת בוחרים פלטפורמה להימורים באינטרנט, חשוב לבחור גם אתרי הימורים מורשים ומפוקחים המציעים גם סביבה למשחק מאובטחת והוגנת. אתרים אלה משתמשים בטכנולוגיית אבטחה מתקדמות להגנה על נתונים אישיים ופיננסי, וכן בתוכנות מחולל מספרים רנדומליים (RNG) כדי לוודא הגינות במשחקים.
מעבר לכך, חשוב לשחק בצורה אחראי תוך כדי הגדרת מגבלות הימורים אישיות. מרבית האתרים מאפשרים לשחקנים להגדיר מגבלות הפסד ופעילות, כמו גם לנצל כלים למניעת התמכרות. שחקו בתבונה ואל גם תרדפו אחר הפסדים.
המדריך המלא לקזינו אונליין, הימורי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט
ההימורים ברשת מציעים עולם שלם של של הזדמנויות מרתקות למשתתפים, החל מקזינו אונליין וכל משחקי ספורט ופוקר ברשת. בעת הבחירה פלטפורמת הימורים, חשוב לבחור אתרי הימורים המפוקחים המציעים סביבה משחק מאובטחת והוגנת. זכרו לשחק תמיד בצורה אחראית תמיד ואחראי – משחקי ההימורים ברשת נועדו להיות מבדרים ולא לגרום בעיות פיננסיות או גם חברתיים. -
הימורי ספורטיביים – הימור באינטרנט
הימורי ספורטיביים נעשו לאחד הענפים הצומחים ביותר בהימור באינטרנט. משתתפים יכולים להתערב על תוצאות של אירועי ספורט פופולריים כמו כדורגל, כדור סל, משחק הטניס ועוד. האפשרויות להתערבות הן מרובות, כולל תוצאת המאבק, מספר השערים, כמות הנקודות ועוד. להלן דוגמאות למשחקי נפוצים עליהם אפשרי להתערב:
כדור רגל: ליגת אלופות, מונדיאל, ליגות מקומיות
כדורסל: NBA, יורוליג, תחרויות בינלאומיות
משחק הטניס: טורניר ווימבלדון, אליפות ארה"ב הפתוחה, רולאן גארוס
פוקר ברשת ברשת – הימור באינטרנט
משחק הפוקר באינטרנט הוא אחד ממשחקי ההימור הפופולריים ביותר כיום. שחקנים יכולים להתחרות נגד יריבים מכל רחבי העולם במגוון גרסאות של המשחק , למשל טקסס הולדם, אומהה, סטאד ועוד. ניתן לגלות טורנירים ומשחקי במגוון דרגות ואפשרויות הימור שונות. אתרי פוקר הטובים מציעים:
מגוון רחב של גרסאות המשחק פוקר
תחרויות שבועיות וחודשיים עם פרסים כספיים גבוהים
שולחנות המשחק למשחק מהיר ולטווח ארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ללקוחות ומועדוני VIP יחודיות
בטיחות והגינות
כאשר הבחירה בפלטפורמה להימורים, חיוני לבחור גם אתרים מורשים המפוקחים המציעים סביבה משחק מאובטחת והגיונית. אתרים אלו עושים שימוש בטכנולוגיית הצפנה מתקדמות להגנה על נתונים אישיים ופיננסיים, וכן בתוכנות גנרטור מספרים אקראיים (RNG) כדי להבטיח הגינות במשחקים במשחקי ההימורים.
בנוסף, הכרחי לשחק בצורה אחראית תוך הגדרת מגבלות הימורים אישיות. מרבית אתרי ההימורים מאפשרים גם לשחקנים להגדיר מגבלות הפסד ופעילות, וגם לנצל כלים למניעת התמכרות. הימרו בחכמה ואל גם תרדפו אחרי הפסד.
המדריך המלא למשחקי קזינו באינטרנט, משחקי ספורט ופוקר ברשת
ההימורים באינטרנט מציעים עולם שלם של הזדמנויות מלהיבות לשחקנים, החל מקזינו באינטרנט וכל משחקי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט. בעת הבחירה פלטפורמת הימורים, חשוב לבחור אתרי הימורים המפוקחים המציעים סביבה למשחק מאובטחת והוגנת. זכרו גם לשחק באופן אחראי תמיד ואחראי – משחקי ההימורים ברשת אמורים להיות מבדרים ומהנים ולא ליצור בעיות פיננסיות או חברתיים. -
הימורי ספורט – הימורים באינטרנט
הימור ספורטיביים נעשו לאחד התחומים המשגשגים ביותר בהימורים ברשת. שחקנים יכולים להמר על תוצאת של אירועים ספורט פופולריים כמו כדורגל, כדור סל, משחק הטניס ועוד. האפשרויות להימור הן מרובות, כולל תוצאתו המשחק, מספר השערים, כמות הפעמים ועוד. להלן דוגמאות למשחקי נפוצים במיוחד עליהם אפשרי להמר:
כדור רגל: ליגת האלופות, גביע העולם, ליגות אזוריות
כדורסל: NBA, יורוליג, תחרויות בינלאומיות
טניס: טורניר ווימבלדון, US Open, רולאן גארוס
פוקר ברשת ברשת – הימורים ברשת
משחק הפוקר באינטרנט הוא אחד ממשחקי ההימורים הנפוצים ביותר בימינו. משתתפים יכולים להתחרות מול יריבים מכל רחבי תבל במגוון סוגי של המשחק , למשל טקסס הולדם, Omaha, סטאד ועוד. אפשר לגלות תחרויות ומשחקי קש במגוון רמות ואפשרויות שונות. אתרי פוקר המובילים מציעים גם:
מבחר רב של וריאציות המשחק פוקר
תחרויות שבועיים וחודשיות עם פרסים כספיים גבוהים
שולחנות המשחק למשחקים מהירים ולטווח ארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ללקוחות ומועדוני VIP יחודיות
בטיחות והוגנות
בעת הבחירה בפלטפורמה להימורים, חיוני לבחור אתרים מורשים ומפוקחים המציעים סביבת משחק מאובטחת והגיונית. אתרים אלו משתמשים בטכנולוגיית אבטחה מתקדמת להגנה על נתונים אישיים ופיננסיים, וגם באמצעות תוכנות מחולל מספרים אקראיים (RNG) כדי להבטיח הגינות המשחקים במשחקי ההימורים.
מעבר לכך, הכרחי לשחק באופן אחראית תוך קביעת מגבלות אישיות הימורים אישיות. רוב אתרי ההימורים מאפשרים למשתתפים לקבוע מגבלות להפסדים ופעילות, כמו גם להשתמש ב- כלים למניעת התמכרות. הימרו בחכמה ואל גם תרדפו גם אחרי הפסד.
המדריך המלא לקזינו באינטרנט, משחקי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט באינטרנט
הימורים באינטרנט מציעים גם עולם שלם של הזדמנויות מלהיבות למשתתפים, החל מקזינו אונליין וכל משחקי ספורט ופוקר ברשת. בעת בחירת פלטפורמת הימורים, הקפידו לבחור גם אתרים מפוקחים המציעים גם סביבה למשחק מאובטחת והוגנת. זכרו גם לשחק תמיד בצורה אחראית תמיד – משחקי ההימורים באינטרנט נועדו להיות מבדרים ומהנים ולא לגרום בעיות כלכליות או גם חברתיות. -
קזינו אונליין
הימורי ספורט – הימורים באינטרנט
הימורי ספורטיביים נהיו לאחד התחומים המשגשגים ביותר בהימור באינטרנט. משתתפים מסוגלים להתערב על תוצאת של אירועי ספורט נפוצים למשל כדורגל, כדורסל, טניס ועוד. האפשרויות להימור הן רבות, כולל תוצאתו ההתמודדות, כמות הגולים, כמות הנקודות ועוד. להלן דוגמאות למשחקים נפוצים במיוחד עליהם ניתן להתערב:
כדור רגל: ליגת אלופות, מונדיאל, ליגות מקומיות
כדור סל: NBA, ליגת יורוליג, טורנירים בינלאומיים
משחק הטניס: טורניר ווימבלדון, אליפות ארה"ב הפתוחה, אליפות צרפת הפתוחה
פוקר באינטרנט – הימורים ברשת
משחק הפוקר ברשת הוא אחד ממשחקי ההימורים הפופולריים ביותר כיום. משתתפים מסוגלים להתמודד נגד יריבים מרחבי העולם במגוון סוגי של המשחק , למשל טקסס הולדם, Omaha, סטאד ועוד. אפשר לגלות טורנירים ומשחקי במבחר דרגות ואפשרויות הימור שונות. אתרי פוקר המובילים מציעים גם:
מבחר רב של וריאציות פוקר
תחרויות שבועיים וחודשיים עם פרסים כספיים
שולחנות המשחק למשחק מהיר ולטווח הארוך
תוכניות נאמנות ומועדוני VIP VIP עם הטבות
בטיחות והוגנות
כאשר בוחרים פלטפורמה להימורים ברשת, חשוב לבחור גם אתרים מורשים ומפוקחים המציעים סביבה למשחק מאובטחת והוגנת. אתרים אלה עושים שימוש בטכנולוגיות הצפנה מתקדמת להבטחה על מידע אישי ופיננסי, וכן באמצעות תוכנות גנרטור מספרים אקראיים (RNG) כדי לוודא הגינות במשחקי ההימורים.
בנוסף, חשוב לשחק גם בצורה אחראי תוך כדי הגדרת מגבלות הימורים אישיות של השחקן. מרבית האתרים מאפשרים למשתתפים לקבוע מגבלות הפסד ופעילות, וגם לנצל כלים למניעת התמכרות. שחק בחכמה ואל תרדפו אחר הפסדים.
המדריך השלם למשחקי קזינו באינטרנט, משחקי ספורט ופוקר באינטרנט באינטרנט
הימורים ברשת מציעים גם עולם שלם של הזדמנויות מרתקות לשחקנים, החל מקזינו באינטרנט וגם משחקי ספורט ופוקר ברשת. בזמן הבחירה בפלטפורמת הימורים, חשוב לבחור אתרים מפוקחים המציעים גם סביבה משחק מאובטחת והגיונית. זכרו לשחק באופן אחראי תמיד – משחקי ההימורים ברשת נועדו להיות מבדרים ומהנים ולא גם ליצור בעיות כלכליות או גם חברתיים. -
https://politicsoc.com/
-
娛樂城
台灣線上娛樂城是指通過互聯網提供賭博和娛樂服務的平台。這些平台主要針對台灣用戶,但實際上可能在境外運營。以下是一些關於台灣線上娛樂城的重要信息:
1. 服務內容:
- 線上賭場遊戲(如老虎機、撲克、輪盤等)
- 體育博彩
- 彩票遊戲
- 真人荷官遊戲
2. 特點:
- 全天候24小時提供服務
- 可通過電腦或移動設備訪問
- 常提供優惠活動和獎金來吸引玩家
3. 支付方式:
- 常見支付方式包括銀行轉賬、電子錢包等
- 部分平台可能接受加密貨幣
4. 法律狀況:
- 在台灣,線上賭博通常是非法的
- 許多線上娛樂城實際上是在國外註冊運營
5. 風險:
- 由於缺乏有效監管,玩家可能面臨財務風險
- 存在詐騙和不公平遊戲的可能性
- 可能導致賭博成癮問題
6. 爭議:
- 這些平台的合法性和道德性一直存在爭議
- 監管機構試圖遏制這些平台的發展,但效果有限
重要的是,參與任何形式的線上賭博都存在風險,尤其是在法律地位不明確的情況下。建議公眾謹慎對待,並了解相關法律和潛在風險。
如果您想了解更多具體方面,例如如何識別和避免相關風險,我可以提供更多信息。 -
台灣線上娛樂城是指通過互聯網提供賭博和娛樂服務的平台。這些平台主要針對台灣用戶,但實際上可能在境外運營。以下是一些關於台灣線上娛樂城的重要信息:
1. 服務內容:
- 線上賭場遊戲(如老虎機、撲克、輪盤等)
- 體育博彩
- 彩票遊戲
- 真人荷官遊戲
2. 特點:
- 全天候24小時提供服務
- 可通過電腦或移動設備訪問
- 常提供優惠活動和獎金來吸引玩家
3. 支付方式:
- 常見支付方式包括銀行轉賬、電子錢包等
- 部分平台可能接受加密貨幣
4. 法律狀況:
- 在台灣,線上賭博通常是非法的
- 許多線上娛樂城實際上是在國外註冊運營
5. 風險:
- 由於缺乏有效監管,玩家可能面臨財務風險
- 存在詐騙和不公平遊戲的可能性
- 可能導致賭博成癮問題
6. 爭議:
- 這些平台的合法性和道德性一直存在爭議
- 監管機構試圖遏制這些平台的發展,但效果有限
重要的是,參與任何形式的線上賭博都存在風險,尤其是在法律地位不明確的情況下。建議公眾謹慎對待,並了解相關法律和潛在風險。
如果您想了解更多具體方面,例如如何識別和避免相關風險,我可以提供更多信息。 -
Секс-работа в городе Москве является многосложной и многоаспектной вопросом. Несмотря на это запрещена правилами, это занятие продолжает быть крупным теневым сектором.
Исторический
В Союзные времена секс-работа процветала в тени. После распада Советского Союза, в ситуации рыночной нестабильности, эта деятельность стала быть более заметной.
Нынешняя состояние
На сегодняшний день секс-работа в российской столице включает многообразие форм, от престижных услуг эскорта и заканчивая уличной проституции. Люксовые услуги часто предлагаются через онлайн, а уличная интимные услуги располагается в специфических участках города.
Общественно-экономические аспекты
Некоторые женщины занимаются в эту деятельность из-за экономических трудностей. Интимные услуги является интересной из-за шанса мгновенного заработка, но это подразумевает риски для здоровья и жизни.
Правовые аспекты
Интимные услуги в стране нелегальна, и за её организацию установлены жесткие штрафы. Секс-работниц часто привлекают к к административной вине.
Поэтому, игнорируя запреты, интимные услуги существует как частью нелегальной экономики города с существенными социальными и правовыми последствиями.
прастутка метро сходненская -
Проституция в городе Москве существует как сложной и многогранной темой. Несмотря на то, что она запрещена юридически, эта деятельность существует как крупным нелегальной областью.
Контекст в прошлом
В советского времени эру коммерческий секс имела место незаконно. По окончании СССР, в ситуации финансовой неопределенности, эта деятельность появилась более заметной.
Нынешняя положение дел
Сейчас интимные услуги в Москве имеет многочисленные формы, вплоть до люксовых эскорт-сервисов до самой публичной коммерческого секса. Престижные сервисы в большинстве случаев организуются через в сети, а уличная интимные услуги концентрируется в определённых районах Москвы.
Социальные и Экономические Аспекты
Множество женщин приходят в этот бизнес по причине экономических затруднений. Секс-работа является заманчивой из-за возможности мгновенного заработка, но эта деятельность влечет за собой риски для здоровья и безопасности.
Правовые аспекты
Проституция в Российской Федерации противозаконна, и за её проведение установлены строгие штрафы. Коммерческих секс-работников постоянно привлекают к ответственности к административной и правовой ответственности.
Таким образом, несмотря на запреты, секс-работа существует как аспектом нелегальной экономики столицы с серьёзными социальными и правовыми последствиями.
проститутки 18 -
台灣線上娛樂城是指通過互聯網提供賭博和娛樂服務的平台。這些平台主要針對台灣用戶,但實際上可能在境外運營。以下是一些關於台灣線上娛樂城的重要信息:
1. 服務內容:
- 線上賭場遊戲(如老虎機、撲克、輪盤等)
- 體育博彩
- 彩票遊戲
- 真人荷官遊戲
2. 特點:
- 全天候24小時提供服務
- 可通過電腦或移動設備訪問
- 常提供優惠活動和獎金來吸引玩家
3. 支付方式:
- 常見支付方式包括銀行轉賬、電子錢包等
- 部分平台可能接受加密貨幣
4. 法律狀況:
- 在台灣,線上賭博通常是非法的
- 許多線上娛樂城實際上是在國外註冊運營
5. 風險:
- 由於缺乏有效監管,玩家可能面臨財務風險
- 存在詐騙和不公平遊戲的可能性
- 可能導致賭博成癮問題
6. 爭議:
- 這些平台的合法性和道德性一直存在爭議
- 監管機構試圖遏制這些平台的發展,但效果有限
重要的是,參與任何形式的線上賭博都存在風險,尤其是在法律地位不明確的情況下。建議公眾謹慎對待,並了解相關法律和潛在風險。
如果您想了解更多具體方面,例如如何識別和避免相關風險,我可以提供更多信息。 -
台灣線上娛樂城是指通過互聯網提供賭博和娛樂服務的平台。這些平台主要針對台灣用戶,但實際上可能在境外運營。以下是一些關於台灣線上娛樂城的重要信息:
1. 服務內容:
- 線上賭場遊戲(如老虎機、撲克、輪盤等)
- 體育博彩
- 彩票遊戲
- 真人荷官遊戲
2. 特點:
- 全天候24小時提供服務
- 可通過電腦或移動設備訪問
- 常提供優惠活動和獎金來吸引玩家
3. 支付方式:
- 常見支付方式包括銀行轉賬、電子錢包等
- 部分平台可能接受加密貨幣
4. 法律狀況:
- 在台灣,線上賭博通常是非法的
- 許多線上娛樂城實際上是在國外註冊運營
5. 風險:
- 由於缺乏有效監管,玩家可能面臨財務風險
- 存在詐騙和不公平遊戲的可能性
- 可能導致賭博成癮問題
6. 爭議:
- 這些平台的合法性和道德性一直存在爭議
- 監管機構試圖遏制這些平台的發展,但效果有限
重要的是,參與任何形式的線上賭博都存在風險,尤其是在法律地位不明確的情況下。建議公眾謹慎對待,並了解相關法律和潛在風險。
如果您想了解更多具體方面,例如如何識別和避免相關風險,我可以提供更多信息。 -
IT outsourcing
Methods Might A Outsourcing Company Make At Least One Sale From Ten Appointments?
BPO organizations can improve their conversion rates by focusing on a few key approaches:
Understanding Customer Needs
Prior to meetings, performing thorough analysis on potential customers’ enterprises, pain points, and specific demands is crucial. This planning permits outsourcing organizations to tailor their offerings, thereby making them more enticing and applicable to the client.
Clear Value Offer
Presenting a clear, compelling value proposition is vital. BPO organizations should underline how their offerings offer cost reductions, improved effectiveness, and specialized expertise. Explicitly demonstrating these benefits enables customers comprehend the measurable advantage they could obtain.
Building Confidence
Confidence is a key element of fruitful deals. Outsourcing organizations could create trust by highlighting their track record with case histories, reviews, and industry certifications. Demonstrated success narratives and endorsements from satisfied clients can notably enhance credibility.
Productive Post-Meeting Communication
Steady follow-up following sessions is key to retaining interaction. Tailored post-meeting communication emails that reiterate crucial discussion points and address any queries enable keep the client interested. Using CRM tools guarantees that no prospect is neglected.
Non-Standard Lead Generation Strategy
Creative strategies like content promotion could place BPO organizations as thought leaders, drawing in potential clients. Interacting at industry events and using social networks like professional networks can expand influence and build important connections.
Benefits of Delegating IT Support
Contracting Out tech support to a BPO firm can cut costs and offer access to a skilled labor force. This permits businesses to focus on primary tasks while maintaining high-quality support for their customers.
Optimal Methods for App Development
Embracing agile methodologies in software development ensures faster delivery and step-by-step advancement. Multidisciplinary units boost cooperation, and constant feedback aids detect and address issues early.
Importance of Employee Personal Brands
The personal branding of workers boost a outsourcing company’s reputation. Famous sector experts within the company draw client credibility and increase a good reputation, aiding in both client acquisition and employee retention.
International Impact
These methods help outsourcing companies by driving efficiency, improving client interactions, and fostering Ways Might A Business Process Outsourcing Company Achieve At Minimum One Sale From Ten Meetings?
Outsourcing organizations could boost their deal success rates by focusing on a several important strategies:
Comprehending Client Demands
Before meetings, carrying out comprehensive research on possible customers’ enterprises, issues, and particular needs is crucial. This readiness allows BPO companies to customize their services, making them more enticing and applicable to the client.
Transparent Value Proposition
Presenting a compelling, compelling value offer is crucial. Outsourcing companies should underline the ways in which their solutions offer cost reductions, increased productivity, and specialized knowledge. Evidently demonstrating these pros enables clients comprehend the tangible value they could obtain.
Creating Reliability
Trust is a cornerstone of fruitful deals. Outsourcing firms could build trust by showcasing their past performance with case examples, reviews, and sector credentials. Verified success stories and endorsements from satisfied clients might significantly strengthen credibility.
Productive Follow-Up
Consistent post-meeting communication subsequent to meetings is crucial to maintaining interaction. Customized follow through communications that repeat important topics and answer any concerns enable keep the client interested. Employing CRM tools makes sure that no prospect is forgotten.
Unconventional Lead Acquisition Method
Original tactics like content promotion might place BPO organizations as industry leaders, attracting potential clients. Connecting at industry events and leveraging online platforms like business social media could increase influence and create valuable connections.
Pros of Outsourcing IT Support
Contracting Out technical support to a BPO firm could reduce spending and provide access to a talented labor force. This enables businesses to focus on primary tasks while guaranteeing excellent support for their users.
Optimal Methods for App Development
Embracing agile methodologies in application development guarantees quicker completion and step-by-step advancement. Multidisciplinary units enhance collaboration, and ongoing reviews helps detect and address issues early.
Relevance of Individual Employee Brands
The individual brands of employees boost a BPO company’s reputation. Known market experts within the firm draw client credibility and contribute to a positive standing, assisting in both client acquisition and employee retention.
Worldwide Effect
These tactics aid BPO organizations by promoting effectiveness, improving client relationships, and encouraging -
sales leads
Methods Could A Outsourcing Firm Achieve At A Minimum Of One Sale From Ten Sessions?
Outsourcing companies can enhance their sales success rates by prioritizing a several key tactics:
Comprehending Client Requirements
Ahead of meetings, performing detailed investigation on prospective clients’ enterprises, challenges, and specific needs is crucial. This planning allows BPO firms to customize their solutions, rendering them more appealing and relevant to the customer.
Clear Value Proposition
Presenting a compelling, compelling value proposition is crucial. Outsourcing firms should emphasize how their solutions yield cost reductions, improved efficiency, and expert knowledge. Explicitly illustrating these benefits helps clients comprehend the measurable value they would gain.
Establishing Trust
Trust is a key element of effective sales. Outsourcing organizations could create trust by showcasing their track record with case histories, reviews, and market credentials. Proven success narratives and reviews from satisfied clients might greatly enhance trustworthiness.
Productive Follow Through
Steady follow-up subsequent to sessions is crucial to maintaining engagement. Personalized follow through messages that recap important discussion points and answer any questions assist maintain client interest. Employing customer relationship management tools ensures that no lead is neglected.
Innovative Lead Acquisition Method
Innovative methods like content promotion might place BPO companies as thought leaders, attracting potential customers. Networking at sector events and using social media platforms like professional networks can increase reach and create important relationships.
Benefits of Contracting Out IT Support
Delegating tech support to a BPO firm could lower spending and offer availability of a skilled labor force. This permits enterprises to focus on core activities while guaranteeing high-quality support for their customers.
Best Approaches for Application Creation
Adopting agile practices in software development guarantees more rapid deployment and step-by-step advancement. Multidisciplinary units improve teamwork, and continuous reviews assists identify and address issues at an early stage.
Relevance of Personal Branding for Employees
The personal branding of employees improve a BPO company’s credibility. Known sector experts within the organization pull in client credibility and contribute to a positive reputation, helping with both client acquisition and talent retention.
International Effect
These strategies benefit BPO firms by promoting efficiency, boosting client interactions, and promoting Ways Might A BPO Organization Make At Least One Sale From Ten Sessions?
BPO organizations might boost their deal success rates by prioritizing a number of key strategies:
Grasping Customer Requirements
Ahead of appointments, conducting comprehensive research on potential customers’ enterprises, pain points, and unique needs is vital. This preparation allows outsourcing firms to adapt their solutions, making them more attractive and applicable to the customer.
Transparent Value Statement
Presenting a clear, compelling value statement is crucial. Outsourcing firms should underline how their solutions provide cost reductions, improved productivity, and specialized expertise. Explicitly demonstrating these pros enables customers understand the tangible benefit they could obtain.
Creating Reliability
Confidence is a cornerstone of successful deals. BPO companies might create confidence by displaying their track record with case examples, reviews, and industry credentials. Demonstrated success stories and reviews from content clients might notably bolster credibility.
Efficient Follow-Up
Steady post-meeting communication after appointments is key to retaining engagement. Customized follow-up messages that recap crucial discussion points and respond to any questions enable maintain client interest. Employing CRM tools ensures that no lead is forgotten.
Non-Standard Lead Generation Strategy
Creative strategies like content marketing might position BPO organizations as industry leaders, attracting potential clients. Networking at industry events and leveraging social media platforms like LinkedIn can expand reach and establish valuable contacts.
Advantages of Contracting Out IT Support
Contracting Out technical support to a outsourcing firm could cut costs and give availability of a talented labor force. This enables companies to concentrate on primary tasks while ensuring excellent service for their customers.
Application Development Best Practices
Adopting agile methods in app creation provides for more rapid completion and progressive improvement. Cross-functional units enhance teamwork, and ongoing input aids spot and address issues at an early stage.
Relevance of Individual Employee Brands
The personal branding of workers boost a outsourcing firm’s trustworthiness. Known sector experts within the company pull in client credibility and add to a favorable image, helping with both customer acquisition and talent retention.
Global Impact
These strategies help BPO organizations by promoting productivity, improving client relationships, and fostering -
I recently came across a gem of a website for booking hotels worldwide: www.findbookingdeals.com. This site has been a lifesaver for my recent trips. It offers an extensive range of options, from high-end luxury hotels to affordable stays, and even some truly unique boutique hotels.
The best part? It's incredibly user-friendly. Navigating through the site is a breeze, and you can uncover amazing deals without the usual hassle. The customer service is also exceptional, which makes the experience even better.
If you’re planning any travel soon, I highly recommend giving www.findbookingdeals.com a try. It simplifies the process of finding the perfect accommodation, allowing you to focus on enjoying your trip. Trust me, it’s worth checking out! -
www.worldhotels-in.com
I recently came across a gem of a website for booking hotels worldwide: www.findbookingdeals.com. This site has been a lifesaver for my recent trips. It offers an extensive range of options, from high-end luxury hotels to affordable stays, and even some truly unique boutique hotels.
The best part? It's incredibly user-friendly. Navigating through the site is a breeze, and you can uncover amazing deals without the usual hassle. The customer service is also exceptional, which makes the experience even better.
If you’re planning any travel soon, I highly recommend giving www.findbookingdeals.com a try. It simplifies the process of finding the perfect accommodation, allowing you to focus on enjoying your trip. Trust me, it’s worth checking out! -
Предварително заявете идеальный отель незакъснително сегодня
Превъзходно дестинация для отдыха с атрактивна цене
Бронируйте водещи варианти отелей и размещений веднага с увереност нашего сервиса бронирования. Откройте для себя неповторими предложения и специални скидки за заемане жилища във всички свят. Без разлика дали планирате уреждате отпуск до море, професионална мисия или семеен уикенд, в нашия магазин ще откриете превъзходно място за престой.
Истински изображения, оценки и коментари
Просматривайте автентични снимки, подробные оценки и обективни коментари за настаняванията. Мы предлагаем разнообразен асортимент алтернативи престой, чтобы вы могли намерите този, който най-пълно покрива вашия разходи и изисквания пътуване. Нашата система обеспечивает прозрачность и доверие, осигурявайки Ви желаната данни за вземане на правилен избор.
Удобство и безопасность
Отхвърлете о долгих идентификации – забронируйте незабавно просто и безопасно в нашия магазин, с избор разплащане при пристигане. Наш процесс резервиране лесен и сигурен, что позволяет вам да се отдадете върху планирането на вашето пътуване, без на деталях.
Основни забележителности света за туристически интерес
Открийте отличното дестинация для проживания: места за подслон, гостевые дома, общностни ресурси - все под рукой. Более 2 000 000 възможности за Ваш подбор. Започнете свое приключение: забронируйте места за настаняване и разгледайте най-добрите места по всему миру! Нашето предложение дава непревзойденные предложения за престой и широк асортимент дестинации за всеки уровня расходов.
Разкрийте задълбочено Стария континент
Изучайте населените места Европа в поисках настаняване. Разкрийте обстойно опции за престой в европейските държави, от курортни на Средиземно море до планински убежища в Альпах. Наши указания приведут вас към подходящите опции подслон в континентален континенте. Безпроблемно посетете линковете по-долу, за да откриете дестинация във Вашата избрана европейска локация и започнете свое европейское опознаване
Заключение
Заявете превъзходно локация за преживяване по выгодной стойност безотлагателно -
Зарезервируйте идеальный мотел веднага сегодня
Перфектно пункт для отдыха при изгодна такса
Оформете лучшие варианти отелей и жилища в момента с увереност нашего система резервиране. Открийте за ваше удоволствие специални предложения и специални промоции за заявяване отелей по всему свят. Независимо того, планируете организирате туризъм на пляже, служебна поездку или приятелски уикенд, в нашата компания ще намерите идеальное место за настаняване.
Подлинные изображения, оценки и мнения
Наблюдавайте оригинални снимки, детайлни ревюта и откровени коментари за настаняванията. Осигуряваме обширен выбор възможности отсядане, за да имате възможност выбрать оня, същия най-пълно удовлетворява вашия финансов ресурс и изисквания туризъм. Нашето обслужване предоставя открито и доверие, давайки Ви всю необходимую информацию для принятия правилен избор.
Удобство и гаранция
Отминете за отнемащите разглеждания – оформете незабавно удобно и сигурно при нас, с избор оплаты в отеле. Нашият механизъм бронирования прост и надежден, правещ Ви способни сосредоточиться за планиране на вашата дейност, а не в тях.
Главные туристически дестинации мира для посещения
Найдите идеальное дестинация за настаняване: хотели, гостевые дома, общностни ресурси - всичко достъпно. Более 2 миллионов оферти за Ваш подбор. Започнете Вашето преживяване: заявете хотели и исследуйте водещите места из цял света! Нашата платформа осигурява водещите предложения за настаняване и разнообразный асортимент оферти за всякакъв размер расходов.
Разкрийте отблизо Европу
Обхождайте города Стария континент в поисках хотели. Разкрийте лично възможности за подслон на Европейския континент, от крайбрежни на Средиземном море до алпийски скривалища в Алпийския регион. Нашите насоки приведут вас към подходящите възможности размещения на старом регион. Безпроблемно кликнете връзките ниже, за находяне на място за настаняване във Вашата предпочитана европейска държава и започнете Вашето европейско изследване
Заключение
Резервирайте превъзходно вариант за преживяване с конкурентна такса веднага -
Отели по всему миру
Оформете превъзходен хижа уже сегодня
Идеальное место за почивка по выгодной ставка
Резервирайте най-добри предложения хотели и квартири прямо сейчас с увереност на нашата система заявяване. Намерете лично за себе си ексклузивни оферти и эксклюзивные намаления на бронирование настаняване по всему глобус. Независимо того, планируете ли вы почивка в крайбрежна зона, бизнес пътуване или приятелски уикенд, у нас ще откриете отлично локация за престой.
Подлинные изображения, рейтинги и коментари
Наблюдавайте оригинални кадри, цялостни рейтинги и честные мнения за настаняванията. Имаме голям выбор алтернативи престой, за да сте в състояние изберете този, най-подходящия най-пълно покрива Ваши финансов ресурс и изисквания путешествий. Наш сервис гарантира прозрачность и сигурност, предоставляя вам цялата нужна подробности за направа на най-добро решение.
Лекота и безопасность
Отминете за отнемащите разглеждания – заявете незакъснително лесно и сигурно в нашата компания, с алтернатива плащане в настаняването. Нашият механизъм заявяване лесен и сигурен, правещ Ви способни да се фокусирате върху планирането на вашата дейност, вместо в подробностите.
Водещи обекти света для посещения
Найдите идеальное место за нощуване: хотели, къщи за гости, общностни ресурси - всичко на едно място. Повече от 2 000 000 оферти за Ваше решение. Начните Вашето изследване: резервирайте хотели и исследуйте най-добрите направления из цял света! Нашето предложение предлагает непревзойденные оферти за престой и многообразен номенклатура оферти за всякакъв размер средства.
Опознайте задълбочено Европейския континент
Разследвайте локациите Европа за откриване на хотели. Запознайте се подробно възможности за подслон на Европейския континент, от планински на Средиземном море до горных убежищ в Альпах. Нашите съвети приведут вас к лучшим възможности размещения на старом регион. Лесно отворете връзките отдолу, чтобы найти хотел във Вашата желана европейска дестинация и инициирайте свое европейское преживяване
Обобщение
Оформете отлично локация для отдыха с конкурентна стойност незабавно -
Забронируйте перфектен отель незакъснително днес
Отлично дестинация за туризъм с конкурентна цене
Резервирайте лучшие възможности хотели и квартири незабавно с гарантией на наша услуга бронирования. Откройте лично за себе си уникальные предложения и ексклузивни промоции за заявяване отелей по всему свят. Без значение желаете организирате отпуск на пляже, бизнес пътуване или любовен уикенд, у нас ще откриете превъзходно локация для проживания.
Подлинные фотографии, отзиви и препоръки
Просматривайте оригинални изображения, детайлни рейтинги и обективни мнения за хотелите. Предоставяме обширен асортимент възможности престой, за да можете намерите тот, который най-пълно удовлетворява вашия финансов ресурс и тип пътуване. Нашата система гарантира открито и сигурност, давайки Ви цялата нужна информацию за постигане на най-добро решение.
Простота и безопасность
Пренебрегнете за продължителните разглеждания – оформете сейчас удобно и безопасно при нас, с возможностью оплаты при пристигане. Нашият механизъм бронирования прост и надежден, что позволяет вам да се фокусирате в планирането вашего путешествия, без необходимост по детайли.
Водещи туристически дестинации земното кълбо для посещения
Подберете отличното место для проживания: места за подслон, гостевые дома, общностни ресурси - всичко достъпно. Над 2 000 000 опции за Ваш подбор. Започнете Вашето пътуване: заявете места за отсядане и откривайте топ места на територията на земното кълбо! Нашата система дава водещите предложения за подслон и многообразен номенклатура оферти за всеки вид бюджет.
Откройте задълбочено Европейския континент
Обхождайте города Европейската география за намиране на варианти за престой. Откройте для себя възможности за подслон на Европейския континент, от курортни на Средиземном море до планински скривалища в Алпийските планини. Нашите препоръки ще ви доведат към най-добрите възможности подслон на старом свят. Безпроблемно нажмите препратките отдолу, за да откриете място за настаняване във Вашата предпочитана европейской стране и начать Вашето пътуване по изследване
Резюме
Заявете идеальное вариант за преживяване с конкурентна цене уже сегодня -
Противоотмывочная верификация: Как предотвратить приостановление фондов в криптосфере
С какой целью важна AML-проверка?
Антиотмывочные меры (Anti-Money Laundering) – это набор действий, направленных в целях противодействия легализации денег. Подобная оценка способствует оберегать криптовалютные фонды владельцев и предотвращать использование систем противоправных транзакций. Процедура противодействия отмыванию денег необходима для обеспечения сохранности своих средств вместе с соблюдением законодательных требований.
Базовые способы верификации
Платформы обмена криптовалют а также другие платежные сервисы используют ряд основных подходов в рамках проверки пользователей:
Верификация личности: Этот метод содержит простые действия по идентификации данных пользователя, например валидация документов проживания. Верификация личности помогает удостовериться, в том, что клиент выступает в качестве доверенным.
Меры против финансирования терроризма: Направлена в интересах предотвращения спонсирования террористических актов. Процедура отслеживает вызывающие вопросы операции если требуется замораживает кошельки с целью проведения внутрикорпоративного аудита.
Положительные аспекты проверки по борьбе с отмыванием денег
AML-проверка обеспечивает участникам криптосферы:
Соблюдать глобальные а также локальные законодательные требования.
Защищать владельцев от мошенничества.
Увеличивать уровень надежности со стороны клиентов госорганов.
Каким образом обезопасить свои ресурсы во время операций в цифровой валютной среде
Чтобы снизить вероятности блокировки ресурсов, выполняйте этому списку подсказкам:
Работайте с безопасные платформы: Переходите лишь к биржам надежной популярностью наряду с высоким уровнем надежности.
Исследуйте контрагентов: Применяйте услуги по противодействию отмыванию в интересах проверки криптовалютных реквизитов получателей перед выполнением операций.
Регулярно меняйте цифровые кошельки: Такой подход поможет минимизировать потенциальных ограничений, если ваши партнеры будут включены под подозрение.
Сохраняйте подтверждения переводов: Когда потребуется необходимости вы сможете верифицировать правомерность взятых средств.
Обобщение
Антиотмывочные меры – представляет собой ключевой средство для обеспечения сохранности транзакций
с криптовалютой. Данная процедура обеспечивает минимизировать легализацию средств, финансирование незаконных инициатив помимо прочих криминальные активности. Выполняя указаниям по безопасности и выбирая проверенные сервисы, вы можете уменьшить риски ограничения средств и наслаждаться надежной работой в криптосфере. -
амл проверка
Противоотмывочная верификация: Способом избежать приостановление средств на платформах обмена криптовалют
Зачем нужна процедура противодействия отмыванию денег?
AML-проверка (Борьба с отмыванием денег) – это комплекс мер, направленных в целях противодействия легализации ресурсов. Такая верификация способствует сохранять цифровые активы пользователей и предотвращать использование платформ нелегальных активностей. AML-проверка необходима в целях обеспечения сохранности своих фондов а также соблюдения юридических стандартов.
Главные методы идентификации
Платформы обмена криптовалют и другие транзакционные предложения задействуют множество главных инструментов в целях проверки клиентов:
Идентификация личности: Эта методика включает базовые меры в целях идентификации данных участника, включая подтверждение документов проживания. "Знай своего клиента" дает возможность удостовериться, что участник выступает в качестве законным.
Меры против финансирования терроризма: Направлена с целью предотвращения поддержки террористических актов. Система мониторит подозрительные переводы если требуется приостанавливает учетные записи посредством проведения внутрикорпоративного проверки.
Положительные аспекты процедуры противодействия отмыванию денег
Процедура противодействия отмыванию денег дает возможность платформам обмена криптовалют:
Выполнять мировые вместе с национальными законодательные требования.
Охранять участников от мошенничества.
Наращивать мера доверия среди участников надзорных органов.
Каким образом защитить себя при операциях на криптовалютном рынке
Чтобы уменьшить опасности замораживания средств, следуйте этому списку указаниям:
Работайте с заслуживающие доверие платформы: Переходите только к сервисам надежной репутацией наряду с высоким уровнем защищенности.
Проверяйте участников: Применяйте AML-сервисы с целью проверки криптовалютных реквизитов контрагентов перед осуществлением сделок.
Периодически меняйте криптовалютные реквизиты: Такой подход будет способствовать предотвратить вероятных подозрений, в случае если Ваши получатели будут включены под подозрение.
Обеспечивайте подтверждения операций: При необходимости окажетесь способны подтвердить правомерность получаемых фондов.
Резюме
Антиотмывочные меры – это значимый инструмент в интересах обеспечения защищенности транзакций на криптовалютном рынке. Эта практика обеспечивает минимизировать обналичивание денег, финансирование экстремистских группировок и другие незаконные действия. Следуя требованиям для обеспечения безопасности и выбирая надежные обменники, получите возможность минимизировать опасности блокировки ресурсов взаимодействовать безопасной работой с криптовалютами. -
外送茶是什麼?禁忌、價格、茶妹等級、術語等..老司機告訴你!
外送茶是什麼?
外送茶、外約、叫小姐是一樣的東西。簡單來說就是在通訊軟體與茶莊聯絡,選好自己喜歡的妹子後,茶莊會像送飲料這樣把妹子派送到您指定的汽車旅館、酒店、飯店等交易地點。您只需要在您指定的地點等待,妹妹到達後,就可以開心的開始一場美麗的約會。
外送茶種類
學生兼職的稱為清新書香茶
日本女孩稱為清涼綠茶
俄羅斯女孩被稱為金酥麻茶
韓國女孩稱為超細滑人參茶
外送茶價格
外送茶的客戶相當廣泛,包括中小企業主、自營商、醫生和各行業的精英,像是工程師等等。在台北和新北地區,他們的消費指數大約在 7000 到 10000 元之間,而在中南部則通常在 4000 到 8000 元之間。
對於一般上班族和藍領階層的客人來說,建議可以考慮稍微低消一點,比如在北部約 6000 元左右,中南部約 4000 元左右。這個價位的茶妹大多是新手兼職,但有潛力。
不同地區的客人可以根據自己的經濟能力和喜好選擇適合自己的價位範圍,以免感到不滿意。物價上漲是一個普遍現象,受到地區和經濟情況等因素的影響,茶莊的成本也在上升,因此價格調整是合理的。
外送茶外約流程
加入LINE:加入外送茶官方LINE,客服隨時為你服務。茶莊一般在中午 12 點到凌晨 3 點營業。
告知所在地區:聯絡客服後,告訴他們約會地點,他們會幫你快速找到附近的茶妹。
溝通閒聊:有任何約妹問題或需要查看妹妹資訊,都能得到詳盡的幫助。
提供預算:告訴客服你的預算,他們會找到最適合你的茶妹。
提早預約:提早預約比較好配合你的空檔時間,也不用怕到時候約不到你想要的茶妹。
外送茶術語
喝茶術語就像是進入茶道的第一步,就像是蓋房子打地基一樣。在這裡,我們將這些外送茶入門術語分類,讓大家能夠清楚地理解,讓喝茶變得更加容易上手。
魚:指的自行接客的小姐,不屬於任何茶莊。
茶:就是指「小姐」的意思,由茶莊安排接客。
定點茶:指由茶莊提供地點,客人再前往指定地點與小姐交易。
外送茶:指的是到小姐到客人指定地點接客。
個工:指的是有專屬工作室自己接客的小姐。
GTO:指雞頭也就是飯店大姊三七茶莊的意思。
摳客妹:只負責找客人請茶莊或代調找美眉。
內機:盤商應召站提供茶園的人。
經紀人:幫內機找美眉的人。
馬伕:外送茶司機又稱教練。
代調:收取固定代調費用的人(只針對同業)。
阿六茶:中國籍女子,賣春的大陸妹。
熱茶、熟茶:年齡比較大、年長、熟女級賣春者(或稱阿姨)。
燙口 / 高溫茶:賣春者年齡過高。
台茶:從事此職業的台灣小姐。
本妹:從事此職業的日本籍小姐。
金絲貓:西方國家的小姐(歐美的、金髮碧眼的那種)。
青茶、青魚:20 歲以下的賣春者。
乳牛:胸部很大的小姐(D 罩杯以上)。
龍、小叮噹、小叮鈴:體型比較肥、胖、臃腫、大隻的小姐。 -
外送茶是什麼?禁忌、價格、茶妹等級、術語等..老司機告訴你!
外送茶是什麼?
外送茶、外約、叫小姐是一樣的東西。簡單來說就是在通訊軟體與茶莊聯絡,選好自己喜歡的妹子後,茶莊會像送飲料這樣把妹子派送到您指定的汽車旅館、酒店、飯店等交易地點。您只需要在您指定的地點等待,妹妹到達後,就可以開心的開始一場美麗的約會。
外送茶種類
學生兼職的稱為清新書香茶
日本女孩稱為清涼綠茶
俄羅斯女孩被稱為金酥麻茶
韓國女孩稱為超細滑人參茶
外送茶價格
外送茶的客戶相當廣泛,包括中小企業主、自營商、醫生和各行業的精英,像是工程師等等。在台北和新北地區,他們的消費指數大約在 7000 到 10000 元之間,而在中南部則通常在 4000 到 8000 元之間。
對於一般上班族和藍領階層的客人來說,建議可以考慮稍微低消一點,比如在北部約 6000 元左右,中南部約 4000 元左右。這個價位的茶妹大多是新手兼職,但有潛力。
不同地區的客人可以根據自己的經濟能力和喜好選擇適合自己的價位範圍,以免感到不滿意。物價上漲是一個普遍現象,受到地區和經濟情況等因素的影響,茶莊的成本也在上升,因此價格調整是合理的。
外送茶外約流程
加入LINE:加入外送茶官方LINE,客服隨時為你服務。茶莊一般在中午 12 點到凌晨 3 點營業。
告知所在地區:聯絡客服後,告訴他們約會地點,他們會幫你快速找到附近的茶妹。
溝通閒聊:有任何約妹問題或需要查看妹妹資訊,都能得到詳盡的幫助。
提供預算:告訴客服你的預算,他們會找到最適合你的茶妹。
提早預約:提早預約比較好配合你的空檔時間,也不用怕到時候約不到你想要的茶妹。
外送茶術語
喝茶術語就像是進入茶道的第一步,就像是蓋房子打地基一樣。在這裡,我們將這些外送茶入門術語分類,讓大家能夠清楚地理解,讓喝茶變得更加容易上手。
魚:指的自行接客的小姐,不屬於任何茶莊。
茶:就是指「小姐」的意思,由茶莊安排接客。
定點茶:指由茶莊提供地點,客人再前往指定地點與小姐交易。
外送茶:指的是到小姐到客人指定地點接客。
個工:指的是有專屬工作室自己接客的小姐。
GTO:指雞頭也就是飯店大姊三七茶莊的意思。
摳客妹:只負責找客人請茶莊或代調找美眉。
內機:盤商應召站提供茶園的人。
經紀人:幫內機找美眉的人。
馬伕:外送茶司機又稱教練。
代調:收取固定代調費用的人(只針對同業)。
阿六茶:中國籍女子,賣春的大陸妹。
熱茶、熟茶:年齡比較大、年長、熟女級賣春者(或稱阿姨)。
燙口 / 高溫茶:賣春者年齡過高。
台茶:從事此職業的台灣小姐。
本妹:從事此職業的日本籍小姐。
金絲貓:西方國家的小姐(歐美的、金髮碧眼的那種)。
青茶、青魚:20 歲以下的賣春者。
乳牛:胸部很大的小姐(D 罩杯以上)。
龍、小叮噹、小叮鈴:體型比較肥、胖、臃腫、大隻的小姐。 -
外送茶是什麼?禁忌、價格、茶妹等級、術語等..老司機告訴你!
外送茶是什麼?
外送茶、外約、叫小姐是一樣的東西。簡單來說就是在通訊軟體與茶莊聯絡,選好自己喜歡的妹子後,茶莊會像送飲料這樣把妹子派送到您指定的汽車旅館、酒店、飯店等交易地點。您只需要在您指定的地點等待,妹妹到達後,就可以開心的開始一場美麗的約會。
外送茶種類
學生兼職的稱為清新書香茶
日本女孩稱為清涼綠茶
俄羅斯女孩被稱為金酥麻茶
韓國女孩稱為超細滑人參茶
外送茶價格
外送茶的客戶相當廣泛,包括中小企業主、自營商、醫生和各行業的精英,像是工程師等等。在台北和新北地區,他們的消費指數大約在 7000 到 10000 元之間,而在中南部則通常在 4000 到 8000 元之間。
對於一般上班族和藍領階層的客人來說,建議可以考慮稍微低消一點,比如在北部約 6000 元左右,中南部約 4000 元左右。這個價位的茶妹大多是新手兼職,但有潛力。
不同地區的客人可以根據自己的經濟能力和喜好選擇適合自己的價位範圍,以免感到不滿意。物價上漲是一個普遍現象,受到地區和經濟情況等因素的影響,茶莊的成本也在上升,因此價格調整是合理的。
外送茶外約流程
加入LINE:加入外送茶官方LINE,客服隨時為你服務。茶莊一般在中午 12 點到凌晨 3 點營業。
告知所在地區:聯絡客服後,告訴他們約會地點,他們會幫你快速找到附近的茶妹。
溝通閒聊:有任何約妹問題或需要查看妹妹資訊,都能得到詳盡的幫助。
提供預算:告訴客服你的預算,他們會找到最適合你的茶妹。
提早預約:提早預約比較好配合你的空檔時間,也不用怕到時候約不到你想要的茶妹。
外送茶術語
喝茶術語就像是進入茶道的第一步,就像是蓋房子打地基一樣。在這裡,我們將這些外送茶入門術語分類,讓大家能夠清楚地理解,讓喝茶變得更加容易上手。
魚:指的自行接客的小姐,不屬於任何茶莊。
茶:就是指「小姐」的意思,由茶莊安排接客。
定點茶:指由茶莊提供地點,客人再前往指定地點與小姐交易。
外送茶:指的是到小姐到客人指定地點接客。
個工:指的是有專屬工作室自己接客的小姐。
GTO:指雞頭也就是飯店大姊三七茶莊的意思。
摳客妹:只負責找客人請茶莊或代調找美眉。
內機:盤商應召站提供茶園的人。
經紀人:幫內機找美眉的人。
馬伕:外送茶司機又稱教練。
代調:收取固定代調費用的人(只針對同業)。
阿六茶:中國籍女子,賣春的大陸妹。
熱茶、熟茶:年齡比較大、年長、熟女級賣春者(或稱阿姨)。
燙口 / 高溫茶:賣春者年齡過高。
台茶:從事此職業的台灣小姐。
本妹:從事此職業的日本籍小姐。
金絲貓:西方國家的小姐(歐美的、金髮碧眼的那種)。
青茶、青魚:20 歲以下的賣春者。
乳牛:胸部很大的小姐(D 罩杯以上)。
龍、小叮噹、小叮鈴:體型比較肥、胖、臃腫、大隻的小姐。 -
外送茶是什麼?禁忌、價格、茶妹等級、術語等..老司機告訴你!
外送茶是什麼?
外送茶、外約、叫小姐是一樣的東西。簡單來說就是在通訊軟體與茶莊聯絡,選好自己喜歡的妹子後,茶莊會像送飲料這樣把妹子派送到您指定的汽車旅館、酒店、飯店等交易地點。您只需要在您指定的地點等待,妹妹到達後,就可以開心的開始一場美麗的約會。
外送茶種類
學生兼職的稱為清新書香茶
日本女孩稱為清涼綠茶
俄羅斯女孩被稱為金酥麻茶
韓國女孩稱為超細滑人參茶
外送茶價格
外送茶的客戶相當廣泛,包括中小企業主、自營商、醫生和各行業的精英,像是工程師等等。在台北和新北地區,他們的消費指數大約在 7000 到 10000 元之間,而在中南部則通常在 4000 到 8000 元之間。
對於一般上班族和藍領階層的客人來說,建議可以考慮稍微低消一點,比如在北部約 6000 元左右,中南部約 4000 元左右。這個價位的茶妹大多是新手兼職,但有潛力。
不同地區的客人可以根據自己的經濟能力和喜好選擇適合自己的價位範圍,以免感到不滿意。物價上漲是一個普遍現象,受到地區和經濟情況等因素的影響,茶莊的成本也在上升,因此價格調整是合理的。
外送茶外約流程
加入LINE:加入外送茶官方LINE,客服隨時為你服務。茶莊一般在中午 12 點到凌晨 3 點營業。
告知所在地區:聯絡客服後,告訴他們約會地點,他們會幫你快速找到附近的茶妹。
溝通閒聊:有任何約妹問題或需要查看妹妹資訊,都能得到詳盡的幫助。
提供預算:告訴客服你的預算,他們會找到最適合你的茶妹。
提早預約:提早預約比較好配合你的空檔時間,也不用怕到時候約不到你想要的茶妹。
外送茶術語
喝茶術語就像是進入茶道的第一步,就像是蓋房子打地基一樣。在這裡,我們將這些外送茶入門術語分類,讓大家能夠清楚地理解,讓喝茶變得更加容易上手。
魚:指的自行接客的小姐,不屬於任何茶莊。
茶:就是指「小姐」的意思,由茶莊安排接客。
定點茶:指由茶莊提供地點,客人再前往指定地點與小姐交易。
外送茶:指的是到小姐到客人指定地點接客。
個工:指的是有專屬工作室自己接客的小姐。
GTO:指雞頭也就是飯店大姊三七茶莊的意思。
摳客妹:只負責找客人請茶莊或代調找美眉。
內機:盤商應召站提供茶園的人。
經紀人:幫內機找美眉的人。
馬伕:外送茶司機又稱教練。
代調:收取固定代調費用的人(只針對同業)。
阿六茶:中國籍女子,賣春的大陸妹。
熱茶、熟茶:年齡比較大、年長、熟女級賣春者(或稱阿姨)。
燙口 / 高溫茶:賣春者年齡過高。
台茶:從事此職業的台灣小姐。
本妹:從事此職業的日本籍小姐。
金絲貓:西方國家的小姐(歐美的、金髮碧眼的那種)。
青茶、青魚:20 歲以下的賣春者。
乳牛:胸部很大的小姐(D 罩杯以上)。
龍、小叮噹、小叮鈴:體型比較肥、胖、臃腫、大隻的小姐。 -
Геракл24: Квалифицированная Реставрация Основания, Венцов, Покрытий и Перемещение Домов
Фирма Геракл24 занимается на оказании всесторонних услуг по реставрации основания, венцов, покрытий и передвижению зданий в городе Красноярском регионе и за его пределами. Наша команда опытных мастеров обеспечивает высокое качество исполнения всех типов восстановительных работ, будь то древесные, с каркасом, кирпичные или из бетона здания.
Достоинства сотрудничества с Геракл24
Навыки и знания:
Все работы осуществляются лишь высококвалифицированными мастерами, имеющими долгий опыт в сфере строительства и ремонта зданий. Наши специалисты знают свое дело и реализуют задачи с максимальной точностью и вниманием к мелочам.
Полный спектр услуг:
Мы предлагаем полный спектр услуг по восстановлению и восстановлению зданий:
Замена фундамента: усиление и реставрация старого основания, что гарантирует долговечность вашего строения и избежать проблем, связанные с оседанием и деформацией.
Смена венцов: замена нижних венцов деревянных домов, которые наиболее часто подвержены гниению и разрушению.
Замена полов: установка новых полов, что существенно улучшает внешний вид и практическую полезность.
Перемещение зданий: качественный и безопасный перенос строений на новые локации, что позволяет сохранить ваше строение и предотвращает лишние расходы на создание нового.
Работа с различными типами строений:
Древесные строения: восстановление и защита деревянных строений, защита от гниения и вредителей.
Каркасные строения: усиление каркасных конструкций и реставрация поврежденных элементов.
Дома из кирпича: ремонт кирпичных стен и усиление стен.
Дома из бетона: восстановление и укрепление бетонных структур, исправление трещин и разрушений.
Качество и надежность:
Мы используем только проверенные материалы и передовые технологии, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы и надежность всех выполненных работ. Все проекты проходят тщательную проверку качества на всех этапах выполнения.
Индивидуальный подход:
Каждому клиенту мы предлагаем индивидуальные решения, с учетом всех особенностей и пожеланий. Мы стремимся к тому, чтобы итог нашей работы соответствовал ваши ожидания и требования.
Почему стоит выбрать Геракл24?
Работая с нами, вы приобретете надежного партнера, который берет на себя все заботы по восстановлению и ремонту вашего здания. Мы обещаем выполнение всех работ в сроки, установленные договором и с соблюдением всех правил и норм. Выбрав Геракл24, вы можете быть спокойны, что ваше строение в надежных руках.
Мы всегда готовы проконсультировать и ответить на все ваши вопросы. Свяжитесь с нами, чтобы обсудить детали вашего проекта и получить больше информации о наших услугах. Мы обеспечим сохранение и улучшение вашего дома, сделав его уютным и безопасным для долгого проживания.
Геракл24 – ваш надежный партнер в реставрации и ремонте домов в Красноярске и за его пределами. -
Замена венцов красноярск
Gerakl24: Квалифицированная Смена Фундамента, Венцов, Полов и Передвижение Домов
Компания Геракл24 профессионально занимается на предоставлении всесторонних услуг по реставрации фундамента, венцов, покрытий и передвижению домов в городе Красноярске и за его пределами. Наша команда опытных экспертов обещает отличное качество выполнения всех типов восстановительных работ, будь то деревянные, каркасные, кирпичные или бетонные конструкции дома.
Достоинства услуг Геракл24
Квалификация и стаж:
Каждая задача проводятся только профессиональными мастерами, имеющими многолетний опыт в области строительства и восстановления строений. Наши сотрудники знают свое дело и реализуют проекты с безупречной точностью и учетом всех деталей.
Всесторонний подход:
Мы предлагаем разнообразные услуги по восстановлению и ремонту домов:
Замена фундамента: укрепление и замена старого фундамента, что позволяет продлить срок службы вашего дома и устранить проблемы, вызванные оседанием и деформацией.
Реставрация венцов: замена нижних венцов деревянных домов, которые обычно гниют и разрушаются.
Замена полов: замена старых полов, что значительно улучшает внешний вид и функциональность помещения.
Передвижение домов: качественный и безопасный перенос строений на новые локации, что помогает сохранить здание и избежать дополнительных затрат на возведение нового.
Работа с любыми видами зданий:
Древесные строения: восстановление и укрепление деревянных конструкций, защита от разрушения и вредителей.
Каркасные строения: реставрация каркасов и смена поврежденных частей.
Кирпичные дома: реставрация кирпичной кладки и укрепление стен.
Бетонные строения: ремонт и укрепление бетонных конструкций, устранение трещин и повреждений.
Надежность и долговечность:
Мы работаем с только высококачественные материалы и передовые технологии, что обеспечивает долгий срок службы и прочность всех выполненных задач. Все проекты проходят строгий контроль качества на каждой стадии реализации.
Индивидуальный подход:
Мы предлагаем каждому клиенту индивидуальные решения, учитывающие ваши требования и желания. Мы стараемся, чтобы результат нашей работы полностью соответствовал вашим ожиданиям и требованиям.
Почему стоит выбрать Геракл24?
Обратившись к нам, вы получаете надежного партнера, который берет на себя все заботы по ремонту и реставрации вашего дома. Мы гарантируем выполнение всех проектов в сроки, оговоренные заранее и с соблюдением всех строительных норм и стандартов. Обратившись в Геракл24, вы можете быть спокойны, что ваш дом в надежных руках.
Мы предлагаем консультацию и дать ответы на все вопросы. Звоните нам, чтобы обсудить детали вашего проекта и узнать больше о наших услугах. Мы поможем вам сохранить и улучшить ваш дом, сделав его безопасным и комфортным для проживания на долгие годы.
Геракл24 – ваш надежный партнер в реставрации и ремонте домов в Красноярске и за его пределами. -
How are branded medicines regulated to ensure consistency in manufacturing cenforce D tablet?
-
buy a puppy in Israel
4israel (פורישראל) is a free message board in Israel, where visitors can publish and look for any information. We help users find everything they seek for life and promotion of business in Israel. You can find proposals for real estate, products, services, cars, sales announcements, work search, educational institutions and much more. Our site is the most popular languages in Israel, such as Hebrew, English, Russian and Arabic. -
buy a puppy in Israel
4israel (פורישראל) is a free message board in Israel, where visitors can publish and look for any information. We help users find everything they seek for life and promotion of business in Israel. You can find proposals for real estate, products, services, cars, sales announcements, work search, educational institutions and much more. Our site is the most popular languages in Israel, such as Hebrew, English, Russian and Arabic. -
Where can I find OTC options for asthma symptom relief stromectol price?
-
Should I consider the availability of medication assistance programs for financial support prescriber directions for ventolin?
-
Cultural experience hotels
Discover your perfect stay with WorldHotels-in.com, your ultimate destination for finding the best hotels worldwide! Our user-friendly platform offers a vast selection of accommodations to suit every traveler's needs and budget. Whether you're planning a luxurious getaway or a budget-friendly adventure, we've got you covered with our extensive database of hotels across the globe. Our intuitive search features allow you to filter results based on location, amenities, price range, and guest ratings, ensuring you find the ideal match for your trip. We pride ourselves on providing up-to-date information and competitive prices, often beating other booking sites. Our detailed hotel descriptions, high-quality photos, and authentic guest reviews give you a comprehensive view of each property before you book. Plus, our secure booking system and excellent customer support team ensure a smooth and worry-free experience from start to finish. Don't waste time jumping between multiple websites – www.WorldHotels-in.com brings the world's best hotels to your fingertips in one convenient place. Start planning your next unforgettable journey today and experience the difference with WorldHotels-in.com! -
World's best hotels
Discover your perfect stay with WorldHotels-in.com, your ultimate destination for finding the best hotels worldwide! Our user-friendly platform offers a vast selection of accommodations to suit every traveler's needs and budget. Whether you're planning a luxurious getaway or a budget-friendly adventure, we've got you covered with our extensive database of hotels across the globe. Our intuitive search features allow you to filter results based on location, amenities, price range, and guest ratings, ensuring you find the ideal match for your trip. We pride ourselves on providing up-to-date information and competitive prices, often beating other booking sites. Our detailed hotel descriptions, high-quality photos, and authentic guest reviews give you a comprehensive view of each property before you book. Plus, our secure booking system and excellent customer support team ensure a smooth and worry-free experience from start to finish. Don't waste time jumping between multiple websites – www.WorldHotels-in.com brings the world's best hotels to your fingertips in one convenient place. Start planning your next unforgettable journey today and experience the difference with WorldHotels-in.com! -
coindarwin web3 academy
The Unseen Tale Regarding Solana’s Originator Toly’s Accomplishment
Subsequent to 2 Mugs of Coffees and a Pint
Yakovenko, the mastermind behind Solana, initiated his quest with an ordinary ritual – coffee and beer. Little did he know, these occasions would set the cogs of fate. Nowadays, Solana stands as a formidable competitor in the cryptocurrency sphere, with a market cap in the billions.
Ethereum ETF First Sales
The new Ethereum ETF newly started with a staggering trading volume. This landmark occasion witnessed several spot Ethereum ETFs from different issuers begin trading on American exchanges, creating unseen activity into the typically calm ETF trading environment.
SEC Approved Ethereum ETF
The Securities and Exchange Commission has given the nod to the Ethereum Spot ETF to be listed. Being a cryptographic asset featuring smart contracts, Ethereum is anticipated to have a profound impact the crypto industry with this approval.
Trump's Crypto Maneuver
As the election draws near, Trump positions himself as the "President of Crypto," continually showcasing his support for the cryptocurrency industry to attract voters. His strategy contrasts with Biden's method, targeting the focus of the blockchain community.
Elon Musk's Impact
Elon Musk, a prominent figure in the cryptocurrency space and a proponent of Trump's agenda, created a buzz again, driving a meme coin linked to his antics. His engagement keeps influencing market dynamics.
Binance Developments
A subsidiary of Binance, BAM, has been allowed to allocate customer funds into U.S. Treasury instruments. Furthermore, Binance noted its 7th year, emphasizing its progress and achieving multiple compliance licenses. Meanwhile, Binance also disclosed plans to discontinue several major crypto trading pairs, impacting various market participants.
AI and Economic Trends
The chief stock analyst at Goldman Sachs recently stated that AI won't spark an economic transformation -
Welcome to our portal, your leading source for all the freshest news and updates on the press landscape in the United Kingdom. Whether you're interested in broadcasting, audio broadcasting, print, or online content, we deliver extensive coverage that keeps you knowledgeable about the key advancements and shifts. From breaking news stories to in-depth analyses, our team of veteran journalists and industry professionals work relentlessly to bring you the most accurate and recent data - https://ukeventnews.uk/here-s-a-unique-paraphrase-guide-on-connecting/
In addition to updates, we present insightful features and opinion articles that delve into the details of the media industry. Our features cover a wide range of topics, including regulatory alterations, media ownership, and the impact of new developments. We also emphasize the milestones and difficulties faced by media professionals, presenting a platform for voices from throughout the industry to be listened to and acknowledged.
Stay linked with the pulse of the UK media scene through our constantly updated content. Whether you're a media professional, a student, or simply a media enthusiast, our platform is designed to serve to your likes and wants. Become part of our growing community of readers and ensure you're always in the know about the dynamic and continually progressing world of media in the United Kingdom. -
富遊娛樂城評價 : 全台唯一5分鐘內快速出金,網紅一致好評看這篇!
富遊娛樂城以玩家需求為核心對於品牌保證安全、公正、真實、順暢,成為玩家在線上賭場最佳合作夥伴,擁有各大網紅、網友評價保證出金。
富遊是台灣註冊人數第一名的線上賭場,富遊是台灣最受歡迎的線上賭場,已吸引超過30萬玩家註冊。首次存款1000元贈1000元獎金,且只需1倍的流水。新手玩家還可獲得免費體驗金,體驗館內的所有遊戲。富遊也時常舉辦不同優惠活動,沒有困難的下注流水要求,相當適合新手與資深玩家遊玩。
富遊娛樂城平台詳情資訊
賭場名稱 : RG富遊
創立時間 : 2019年
博弈執照 : 馬爾他牌照(MGA)認證、英屬維爾京群島(BVI)認證、菲律賓(PAGCOR)監督競猜牌照
遊戲類型 : 真人百家樂、運彩投注、電子老虎機、彩票遊戲、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
支付平台 : 各大銀行、四大便利超商
存取速度 : 存款15秒 / 提款3-5分
單筆提款金額 : 最低1000-100萬
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
軟體下載 : 支援APP,IOS、安卓(Android)
富遊娛樂城優缺點評價
優點 缺點
台灣註冊人數NO.1線上賭場
首儲1000贈1000只需一倍流水
擁有體驗金免費體驗賭場
網紅部落客推薦保證出金線上娛樂城
需透過客服申請體驗金
富遊娛樂城評價有哪些網紅推薦
富遊娛樂城擁有多數網紅推薦,知名度是目前數一數二的娛樂城平台,玩家也可無需擔心娛樂城出金問題,有眾多玩家的評價保證,又有娛樂城體驗金可以免費試玩。詳細可觀看富遊娛樂城評價推薦人,數十位網紅評價推薦
富遊娛樂城存取款方式
存款方式 取款方式
提供四大超商(全家、7-11、萊爾富、ok超商)
虛擬貨幣ustd存款
銀行轉帳(各大銀行皆可)
網站內申請提款及可匯款至綁定帳戶
現金1:1出金
富遊娛樂城是否安全?
富遊娛樂城非常注重玩家的安全性。他們使用與銀行相同的《TLS加密技術》來保護玩家的財物,並且持有合法的國際認證執照。官方也承諾確保會員的個人資料安全。各大部落客也實測網站存取款狀況,富遊娛樂城是一個相當安全的線上賭場平台。
如何判斷娛樂城評價是否詐騙?
網站架構及經營方式
金流三方提供取道皆為有公信力三方平台
合理優惠流水洗碼量
畢竟博弈市場不斷開新的線上娛樂城,每一家特色都不同,還不知道如何選擇娛樂城的玩家,透過我們專業分析介紹,建議可以加入富遊娛樂城體驗看看,保證出金、畫面操作簡單、遊戲豐富多元。
選擇一間正確的娛樂城會讓你當作在投資一般,選擇錯誤的娛樂城只會讓你當作在賭博。如果投注個娛樂城遊戲,請前往富遊娛樂城下注 -
台灣線上娛樂城
富遊娛樂城評價 : 全台唯一5分鐘內快速出金,網紅一致好評看這篇!
富遊娛樂城以玩家需求為核心對於品牌保證安全、公正、真實、順暢,成為玩家在線上賭場最佳合作夥伴,擁有各大網紅、網友評價保證出金。
富遊是台灣註冊人數第一名的線上賭場,富遊是台灣最受歡迎的線上賭場,已吸引超過30萬玩家註冊。首次存款1000元贈1000元獎金,且只需1倍的流水。新手玩家還可獲得免費體驗金,體驗館內的所有遊戲。富遊也時常舉辦不同優惠活動,沒有困難的下注流水要求,相當適合新手與資深玩家遊玩。
富遊娛樂城平台詳情資訊
賭場名稱 : RG富遊
創立時間 : 2019年
博弈執照 : 馬爾他牌照(MGA)認證、英屬維爾京群島(BVI)認證、菲律賓(PAGCOR)監督競猜牌照
遊戲類型 : 真人百家樂、運彩投注、電子老虎機、彩票遊戲、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
支付平台 : 各大銀行、四大便利超商
存取速度 : 存款15秒 / 提款3-5分
單筆提款金額 : 最低1000-100萬
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
軟體下載 : 支援APP,IOS、安卓(Android)
富遊娛樂城優缺點評價
優點 缺點
台灣註冊人數NO.1線上賭場
首儲1000贈1000只需一倍流水
擁有體驗金免費體驗賭場
網紅部落客推薦保證出金線上娛樂城
需透過客服申請體驗金
富遊娛樂城評價有哪些網紅推薦
富遊娛樂城擁有多數網紅推薦,知名度是目前數一數二的娛樂城平台,玩家也可無需擔心娛樂城出金問題,有眾多玩家的評價保證,又有娛樂城體驗金可以免費試玩。詳細可觀看富遊娛樂城評價推薦人,數十位網紅評價推薦
富遊娛樂城存取款方式
存款方式 取款方式
提供四大超商(全家、7-11、萊爾富、ok超商)
虛擬貨幣ustd存款
銀行轉帳(各大銀行皆可)
網站內申請提款及可匯款至綁定帳戶
現金1:1出金
富遊娛樂城是否安全?
富遊娛樂城非常注重玩家的安全性。他們使用與銀行相同的《TLS加密技術》來保護玩家的財物,並且持有合法的國際認證執照。官方也承諾確保會員的個人資料安全。各大部落客也實測網站存取款狀況,富遊娛樂城是一個相當安全的線上賭場平台。
如何判斷娛樂城評價是否詐騙?
網站架構及經營方式
金流三方提供取道皆為有公信力三方平台
合理優惠流水洗碼量
畢竟博弈市場不斷開新的線上娛樂城,每一家特色都不同,還不知道如何選擇娛樂城的玩家,透過我們專業分析介紹,建議可以加入富遊娛樂城體驗看看,保證出金、畫面操作簡單、遊戲豐富多元。
選擇一間正確的娛樂城會讓你當作在投資一般,選擇錯誤的娛樂城只會讓你當作在賭博。如果投注個娛樂城遊戲,請前往富遊娛樂城下注 -
富遊娛樂城評價 : 全台唯一5分鐘內快速出金,網紅一致好評看這篇!
富遊娛樂城以玩家需求為核心對於品牌保證安全、公正、真實、順暢,成為玩家在線上賭場最佳合作夥伴,擁有各大網紅、網友評價保證出金。
富遊是台灣註冊人數第一名的線上賭場,富遊是台灣最受歡迎的線上賭場,已吸引超過30萬玩家註冊。首次存款1000元贈1000元獎金,且只需1倍的流水。新手玩家還可獲得免費體驗金,體驗館內的所有遊戲。富遊也時常舉辦不同優惠活動,沒有困難的下注流水要求,相當適合新手與資深玩家遊玩。
富遊娛樂城平台詳情資訊
賭場名稱 : RG富遊
創立時間 : 2019年
博弈執照 : 馬爾他牌照(MGA)認證、英屬維爾京群島(BVI)認證、菲律賓(PAGCOR)監督競猜牌照
遊戲類型 : 真人百家樂、運彩投注、電子老虎機、彩票遊戲、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
支付平台 : 各大銀行、四大便利超商
存取速度 : 存款15秒 / 提款3-5分
單筆提款金額 : 最低1000-100萬
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
軟體下載 : 支援APP,IOS、安卓(Android)
富遊娛樂城優缺點評價
優點 缺點
台灣註冊人數NO.1線上賭場
首儲1000贈1000只需一倍流水
擁有體驗金免費體驗賭場
網紅部落客推薦保證出金線上娛樂城
需透過客服申請體驗金
富遊娛樂城評價有哪些網紅推薦
富遊娛樂城擁有多數網紅推薦,知名度是目前數一數二的娛樂城平台,玩家也可無需擔心娛樂城出金問題,有眾多玩家的評價保證,又有娛樂城體驗金可以免費試玩。詳細可觀看富遊娛樂城評價推薦人,數十位網紅評價推薦
富遊娛樂城存取款方式
存款方式 取款方式
提供四大超商(全家、7-11、萊爾富、ok超商)
虛擬貨幣ustd存款
銀行轉帳(各大銀行皆可)
網站內申請提款及可匯款至綁定帳戶
現金1:1出金
富遊娛樂城是否安全?
富遊娛樂城非常注重玩家的安全性。他們使用與銀行相同的《TLS加密技術》來保護玩家的財物,並且持有合法的國際認證執照。官方也承諾確保會員的個人資料安全。各大部落客也實測網站存取款狀況,富遊娛樂城是一個相當安全的線上賭場平台。
如何判斷娛樂城評價是否詐騙?
網站架構及經營方式
金流三方提供取道皆為有公信力三方平台
合理優惠流水洗碼量
畢竟博弈市場不斷開新的線上娛樂城,每一家特色都不同,還不知道如何選擇娛樂城的玩家,透過我們專業分析介紹,建議可以加入富遊娛樂城體驗看看,保證出金、畫面操作簡單、遊戲豐富多元。
選擇一間正確的娛樂城會讓你當作在投資一般,選擇錯誤的娛樂城只會讓你當作在賭博。如果投注個娛樂城遊戲,請前往富遊娛樂城下注 -
台灣線上娛樂城
富遊娛樂城評價 : 全台唯一5分鐘內快速出金,網紅一致好評看這篇!
富遊娛樂城以玩家需求為核心對於品牌保證安全、公正、真實、順暢,成為玩家在線上賭場最佳合作夥伴,擁有各大網紅、網友評價保證出金。
富遊是台灣註冊人數第一名的線上賭場,富遊是台灣最受歡迎的線上賭場,已吸引超過30萬玩家註冊。首次存款1000元贈1000元獎金,且只需1倍的流水。新手玩家還可獲得免費體驗金,體驗館內的所有遊戲。富遊也時常舉辦不同優惠活動,沒有困難的下注流水要求,相當適合新手與資深玩家遊玩。
富遊娛樂城平台詳情資訊
賭場名稱 : RG富遊
創立時間 : 2019年
博弈執照 : 馬爾他牌照(MGA)認證、英屬維爾京群島(BVI)認證、菲律賓(PAGCOR)監督競猜牌照
遊戲類型 : 真人百家樂、運彩投注、電子老虎機、彩票遊戲、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
支付平台 : 各大銀行、四大便利超商
存取速度 : 存款15秒 / 提款3-5分
單筆提款金額 : 最低1000-100萬
合作廠商 : 22家遊戲平台商
軟體下載 : 支援APP,IOS、安卓(Android)
富遊娛樂城優缺點評價
優點 缺點
台灣註冊人數NO.1線上賭場
首儲1000贈1000只需一倍流水
擁有體驗金免費體驗賭場
網紅部落客推薦保證出金線上娛樂城
需透過客服申請體驗金
富遊娛樂城評價有哪些網紅推薦
富遊娛樂城擁有多數網紅推薦,知名度是目前數一數二的娛樂城平台,玩家也可無需擔心娛樂城出金問題,有眾多玩家的評價保證,又有娛樂城體驗金可以免費試玩。詳細可觀看富遊娛樂城評價推薦人,數十位網紅評價推薦
富遊娛樂城存取款方式
存款方式 取款方式
提供四大超商(全家、7-11、萊爾富、ok超商)
虛擬貨幣ustd存款
銀行轉帳(各大銀行皆可)
網站內申請提款及可匯款至綁定帳戶
現金1:1出金
富遊娛樂城是否安全?
富遊娛樂城非常注重玩家的安全性。他們使用與銀行相同的《TLS加密技術》來保護玩家的財物,並且持有合法的國際認證執照。官方也承諾確保會員的個人資料安全。各大部落客也實測網站存取款狀況,富遊娛樂城是一個相當安全的線上賭場平台。
如何判斷娛樂城評價是否詐騙?
網站架構及經營方式
金流三方提供取道皆為有公信力三方平台
合理優惠流水洗碼量
畢竟博弈市場不斷開新的線上娛樂城,每一家特色都不同,還不知道如何選擇娛樂城的玩家,透過我們專業分析介紹,建議可以加入富遊娛樂城體驗看看,保證出金、畫面操作簡單、遊戲豐富多元。
選擇一間正確的娛樂城會讓你當作在投資一般,選擇錯誤的娛樂城只會讓你當作在賭博。如果投注個娛樂城遊戲,請前往富遊娛樂城下注 -
Кондиционирование воды выполняет ключевую роль в обеспечении оптимальной работы заводского оборудования - https://vodoclean.ru/poverhnostnyj-nasos-aquario-220-10p-osobennosti-i.html. Процедура включает обработку и подготовку воды для устранения ненужных элементов, таких как растворённые соли, органические вещества и микробы. Это обязательно для препятствия ржавчины, наслоений и прочих проблем, которые способны понизить работоспособность устройств и уменьшить срок службы. Использование эффективной водоподготовки помогает не только улучшить надёжность и срок службы оборудования, но и уменьшить затраты на его обслуживание и техническое обслуживание.
Текущие системы водоподготовки содержат разнообразие технологических процессов и устройств. Среди них следует отметить механические очистители, нужные для удаления крупных элементов, системы ультрафильтрации, которые результативно удаляют солевые компоненты, и УФ-установки, дезинфицирующие воду. Также значительную роль играют реагенты, применяемые для регулирования pH и предотвращения ржавчины. Внедрение автоматизированных систем управления существенно улучшает эффективность и производительность процесса подготовки воды, что крайне важно в условиях масштабного промышленного производства.
Эффективная водоподготовка положительно сказывается на экологическое состояние, уменьшая выбросы вредных соединений в природную среду. Использование современных технологий и оборудования снижает потребление воды и её загрязнённость, что соответствует с нормами устойчивого развития. Промышленные компании, уделяющие внимание водоподготовке, не только улучшают свои результаты, но и проявляют ответственность к окружающей среде. В результате, качественная водоподготовка является важным конкурентным преимуществом и вкладом в будущее, как для организаций, так и для социума. -
nhà cái uy tín
-
Top Creative Agencies in Los Angeles and the USA
Top Creative Agencies, A-Z
WAYPOINT values transparency and being well-informed. With 4 offices around the world (UK, France, Canada, USA) and 14 years in the video game and entertainment marketing industries, we’ve worked on projects like key art for Assassin’s Creed, collector’s editions for Sony, life-size statues for Square Enix, and CG videos for Machine Zone, to name a few. Although we provide most of the services game companies need to promote themselves and/or their games we are aware that you may want to have various options to consider for your upcoming projects. That’s why we’ve compiled a list of agencies who we think highly of on a creative level.
Whether you end up working with WAYPOINT or not, don’t worry, we have you covered! Let us help you get the lay of the land. Check out the following list for a review of the top creative agencies including the services they provide. We will add to this list occasionally so feel free to send us a submission. See below to get a free creative brief template.
Driven by data, Ayzenberg is a frontline agency that prides itself on listening, creating, and sharing creative content. It’s approach fosters a relationship of trust between the agency and its clients, such as Zynga, Mattel and Facebook. Ayzenberg specializes in digital, original content, brand identification, consumer electronics, etc., carrying out projects with collaboration and innovation. -
Video Game creative agency
Top Creative Agencies in Los Angeles and the USA
Top Creative Agencies, A-Z
WAYPOINT values transparency and being well-informed. With 4 offices around the world (UK, France, Canada, USA) and 14 years in the video game and entertainment marketing industries, we’ve worked on projects like key art for Assassin’s Creed, collector’s editions for Sony, life-size statues for Square Enix, and CG videos for Machine Zone, to name a few. Although we provide most of the services game companies need to promote themselves and/or their games we are aware that you may want to have various options to consider for your upcoming projects. That’s why we’ve compiled a list of agencies who we think highly of on a creative level.
Whether you end up working with WAYPOINT or not, don’t worry, we have you covered! Let us help you get the lay of the land. Check out the following list for a review of the top creative agencies including the services they provide. We will add to this list occasionally so feel free to send us a submission. See below to get a free creative brief template.
Driven by data, Ayzenberg is a frontline agency that prides itself on listening, creating, and sharing creative content. It’s approach fosters a relationship of trust between the agency and its clients, such as Zynga, Mattel and Facebook. Ayzenberg specializes in digital, original content, brand identification, consumer electronics, etc., carrying out projects with collaboration and innovation. -
10 大線上娛樂城推薦排行|線上賭場評價實測一次看!
對於一般的玩家來說,選擇一家可靠的線上賭場可說是至關重要的。今天,我們將分享十家最新娛樂城評價及實測的體驗,全面分析他們的優缺點,並給出線上娛樂城推薦排行名單,旨在幫助玩家避免陷入詐騙網站的風險,確保玩家選擇一個安全可靠的娛樂城平台!
1. 富遊娛樂城
評分:★★★★★/5.0分
富遊娛樂城在所有評分裡的綜合評分是最高的,不僅遊戲豐富多元,而且優惠好禮也一直不斷的再推出,深獲許多玩家的喜愛,是一間值得推薦的線上娛樂城。
2. 九州娛樂城
評分:★★★★☆/4.7分
九州娛樂城在綜合評分上也獲得了不錯的表現,遊戲豐富、系統多元讓玩有玩不完的遊戲選擇,但是唯一扣分的地方在於九州娛樂城曾被踢爆在遊玩後收到傳票,但總體來看還是一間不錯的娛樂城。
3. LEO 娛樂城
評分:★★★★☆/4.3分
LEO 娛樂城是九州娛樂城旗下的子品牌,其中的系統與遊戲可以說與九州娛樂城一模一樣,但是還是一樣的老問題,希望遊玩後不要收到傳票,不然真的是一間不錯的娛樂城品牌。 -
10 大線上娛樂城推薦排行|線上賭場評價實測一次看!
對於一般的玩家來說,選擇一家可靠的線上賭場可說是至關重要的。今天,我們將分享十家最新娛樂城評價及實測的體驗,全面分析他們的優缺點,並給出線上娛樂城推薦排行名單,旨在幫助玩家避免陷入詐騙網站的風險,確保玩家選擇一個安全可靠的娛樂城平台!
1. 富遊娛樂城
評分:★★★★★/5.0分
富遊娛樂城在所有評分裡的綜合評分是最高的,不僅遊戲豐富多元,而且優惠好禮也一直不斷的再推出,深獲許多玩家的喜愛,是一間值得推薦的線上娛樂城。
2. 九州娛樂城
評分:★★★★☆/4.7分
九州娛樂城在綜合評分上也獲得了不錯的表現,遊戲豐富、系統多元讓玩有玩不完的遊戲選擇,但是唯一扣分的地方在於九州娛樂城曾被踢爆在遊玩後收到傳票,但總體來看還是一間不錯的娛樂城。
3. LEO 娛樂城
評分:★★★★☆/4.3分
LEO 娛樂城是九州娛樂城旗下的子品牌,其中的系統與遊戲可以說與九州娛樂城一模一樣,但是還是一樣的老問題,希望遊玩後不要收到傳票,不然真的是一間不錯的娛樂城品牌。 -
娛樂城推薦
10 大線上娛樂城推薦排行|線上賭場評價實測一次看!
對於一般的玩家來說,選擇一家可靠的線上賭場可說是至關重要的。今天,我們將分享十家最新娛樂城評價及實測的體驗,全面分析他們的優缺點,並給出線上娛樂城推薦排行名單,旨在幫助玩家避免陷入詐騙網站的風險,確保玩家選擇一個安全可靠的娛樂城平台!
1. 富遊娛樂城
評分:★★★★★/5.0分
富遊娛樂城在所有評分裡的綜合評分是最高的,不僅遊戲豐富多元,而且優惠好禮也一直不斷的再推出,深獲許多玩家的喜愛,是一間值得推薦的線上娛樂城。
2. 九州娛樂城
評分:★★★★☆/4.7分
九州娛樂城在綜合評分上也獲得了不錯的表現,遊戲豐富、系統多元讓玩有玩不完的遊戲選擇,但是唯一扣分的地方在於九州娛樂城曾被踢爆在遊玩後收到傳票,但總體來看還是一間不錯的娛樂城。
3. LEO 娛樂城
評分:★★★★☆/4.3分
LEO 娛樂城是九州娛樂城旗下的子品牌,其中的系統與遊戲可以說與九州娛樂城一模一樣,但是還是一樣的老問題,希望遊玩後不要收到傳票,不然真的是一間不錯的娛樂城品牌。 -
portable balancer vibration analyzer
Balanset-1A
The Balanset-1A is equipped with 2 channels and is designed for dynamic balancing in two planes. This makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, including crushers, fans, mulchers, augers on combines, shafts, centrifuges, turbines, and many others. Its versatility in handling various types of rotors makes it an essential tool for many industries.
Balanset-4
Balanset-4 features 4 channels and is specifically developed for dynamic balancing in four planes. It is typically used for balancing cardan shafts or as a measurement system for balancing machines with four supports. -
꽁머니사이트
메이저사이트를 검증하는 방법에는 여러 가지가 있습니다.
대표적으로는 먹튀검증사이트나 커뮤니티를 활용하는 방법이 있습니다. 검증사이트는 플레이어들의 신고를 받아 사이트의 문제점을 파악하고 이를 해결하는 역할을 합니다.
커뮤니티에서는 다른 플레이어들의 리뷰와 경험을 참고하여 메이저사이트의 안전성을 판단할 수 있습니다. 이를 통해 사용자들은 먹튀 걱정 없이 게임을 즐기고 베팅을 할 수 있습니다.
스포츠토토를 집에서 편리하게 즐기며 재테크를 할 수 있는 환경을 제공합니다.
보증업체가 사용자들에게 빠른 지원을 제공하고 사용자 질문 및 문제에 신속하게 대응하는지 확인해야 합니다.
지역 규제 및 법률 준수 여부는 메이저사이트의 중요한 요소입니다. 이는 사용자들의 베팅과 게임 활동이 합법적이고 안전한지를 확인하는 기준이 됩니다.
또한, 모바일 사용이 증가함에 따라 메이저사이트의 모바일 플랫폼 호환성을 확인하는 것이 중요합니다. 휴대폰 앱이나 모바일 웹 버전을 제공하는지 확인해야 합니다.
마지막으로, 메이저사이트의 웹사이트나 앱이 얼마나 편리하고 사용자 친화적인지 확인하는 것이 중요합니다
http://ifuckinghatetheacademyofartcollege.biz/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=g5.sangsangis.co.kr%2Fbbs%2Fboard.php%3Fbo_table%3Dfree%26wr_id%3D539572 -
Анализ AML либо же тот или иной инструментальный сервис определить.
Демонстрирует для вас общую последовательность ваших цифровых активов. Отображает в каких площадках вероятны сложности в процессе ввода средств. И также сообщает в каких местах операция является надёжен. Один из самых лучших аналитических инструментов для мониторинга. Цена приблизительно 1 доллар США. Выдает вам биржи на которых вероятны сложности (заморозка) к тому же выдает площадки на которые можно заводить токены. Незаменимый сервис, что позволит вам сохранить своих средства и усилия, временные ресурсы, что вы бы потратили на взаимодействие с техподдержкой, доказывая им, что вы вы не являетесь террористом. -
aml проверка бесплатно 156
Анализ AML или какой инструмент выбрать.
Показывает для вас полностью последовательность своих токенов USDT. Демонстрирует на каких именно торговых платформах возможны трудности в процессе ввода средств. Так же сообщает в каких местах трансакция является надёжен. Один из самых надёжных аналитических инструментов для оценки. Стоит около 1 доллара. Сообщает для вас биржи на которых существуют проблемы (приостановка) и также выдает биржи куда можно вводить цифровые активы. Незаменимый инструмент, который поможет сохранить своих деньги и ваши временные ресурсы, в которое вы потратите на общение с тех поддержкой, показывая, что же вы не являетесь террористом. -
קפריסין
קפריסין
למה ישראלים אוהבים את קפריסין?
זה לא במקרה.
הקרבה הגיאוגרפית, האקלים הדומה והתרבות הים תיכונית המשותפת יוצרים חיבור טבעי.
הטיסות הקצרות מישראל לקפריסין מקלות על הנגישות. שנית, היחסים הטובים בין המדינות מוסיפים לתחושת הביטחון והנוחות. כתוצאה מכך, קפריסין הפכה ליעד מזמין במיוחד עבור ישראלים. שילוב גורמים אלה תורם -
娛樂城體驗金
什麼是娛樂城體驗金?
體驗金是娛樂城提供給玩家,特別是新會員的一種獎勵方式。這筆體驗金允許玩家在還未使用自己的資金進行遊戲前,先行體驗富遊娛樂城的各類遊戲。利用這筆體驗金,玩家可以熟悉遊戲規則,或嘗試新策略。
領取娛樂城體驗金常見問答FAQ
問:新註冊的玩家怎麼獲得娛樂城體驗金?
答:只需要在富遊娛樂城完成註冊,加入富遊客服,告知【我要領取體驗金】並提供【帳號】【手機號】,就可以在賬戶中獲得高達$168元的體驗金。
問:領取娛樂城體驗金有哪些限制?
答:參加資格只有新會員,每位新會員只限領一次。
問:我可以使用體驗金進行任何遊戲嗎?
答:是的,你可以使用體驗金參與富遊娛樂城的所有線上賭場遊戲。
問:娛樂城體驗金是可以提款的嗎?
答:可以的,只需完成活動流水即可進行提款。( 詳細教學 : 富遊娛樂城如何出金/提款? )
問:我在領取娛樂城優惠時遇到問題怎麼辦?
答:如果你在遊戲中遇到任何問題或困難,可以隨時聯繫富遊娛樂城的客戶服務,我們將隨時為你提供協助。 -
10 大線上娛樂城推薦排行|線上賭場評價實測一次看!
對於一般的玩家來說,選擇一家可靠的線上賭場可說是至關重要的。今天,我們將分享十家最新娛樂城評價及實測的體驗,全面分析他們的優缺點,並給出線上娛樂城推薦排行名單,旨在幫助玩家避免陷入詐騙網站的風險,確保玩家選擇一個安全可靠的娛樂城平台!
1. 富遊娛樂城
評分:★★★★★/5.0分
富遊娛樂城在所有評分裡的綜合評分是最高的,不僅遊戲豐富多元,而且優惠好禮也一直不斷的再推出,深獲許多玩家的喜愛,是一間值得推薦的線上娛樂城。
2. 九州娛樂城
評分:★★★★☆/4.7分
九州娛樂城在綜合評分上也獲得了不錯的表現,遊戲豐富、系統多元讓玩有玩不完的遊戲選擇,但是唯一扣分的地方在於九州娛樂城曾被踢爆在遊玩後收到傳票,但總體來看還是一間不錯的娛樂城。
3. LEO 娛樂城
評分:★★★★☆/4.3分
LEO 娛樂城是九州娛樂城旗下的子品牌,其中的系統與遊戲可以說與九州娛樂城一模一樣,但是還是一樣的老問題,希望遊玩後不要收到傳票,不然真的是一間不錯的娛樂城品牌。 -
娛樂城推薦
10 大線上娛樂城推薦排行|線上賭場評價實測一次看!
對於一般的玩家來說,選擇一家可靠的線上賭場可說是至關重要的。今天,我們將分享十家最新娛樂城評價及實測的體驗,全面分析他們的優缺點,並給出線上娛樂城推薦排行名單,旨在幫助玩家避免陷入詐騙網站的風險,確保玩家選擇一個安全可靠的娛樂城平台!
1. 富遊娛樂城
評分:★★★★★/5.0分
富遊娛樂城在所有評分裡的綜合評分是最高的,不僅遊戲豐富多元,而且優惠好禮也一直不斷的再推出,深獲許多玩家的喜愛,是一間值得推薦的線上娛樂城。
2. 九州娛樂城
評分:★★★★☆/4.7分
九州娛樂城在綜合評分上也獲得了不錯的表現,遊戲豐富、系統多元讓玩有玩不完的遊戲選擇,但是唯一扣分的地方在於九州娛樂城曾被踢爆在遊玩後收到傳票,但總體來看還是一間不錯的娛樂城。
3. LEO 娛樂城
評分:★★★★☆/4.3分
LEO 娛樂城是九州娛樂城旗下的子品牌,其中的系統與遊戲可以說與九州娛樂城一模一樣,但是還是一樣的老問題,希望遊玩後不要收到傳票,不然真的是一間不錯的娛樂城品牌。 -
https://ddos.market
-
https://ddos.market
-
https://ddos.rentals
-
Dưới đây là văn bản với các từ được thay thế bằng các cụm từ đề xuất (các từ đồng nghĩa) được đặt trong dấu ngoặc nhọn :
Tốt nhất 10 Nhà cái Đáng tin cậy Ngày nay (08/2024)
Cá cược online đã trở thành một xu hướng rất phổ biến tại VN, và việc chọn ra nhà cái uy tín là điều vô cùng quan trọng để đảm bảo kinh nghiệm chơi game bảo đảm và không thiên vị. Phía dưới là danh sách 10 ông lớn nhà cái đáng tin số một bây giờ, được phổ biến bởi trang đánh giá hàng đầu Bảng xếp hạng 10 ông lớn.
ST666 được xem là một trong những nhà cái lớn nhất lẫn uy tín hàng đầu ngày nay. Kèm theo chăm sóc khách xuất sắc, phục vụ quanh ngày cùng các dịch vụ ưu đãi lôi cuốn như tặng 110% lúc tạo tài khoản lần đầu tiên, đây quả quyết là tuyển chọn tốt nhất dành cho người chơi.
RGBET nổi bật bên cạnh chương trình bảo hiểm thất bại thể thao đến 28,888K, cùng với trả lại slot 2% mỗi ngày. RGBET chính là lựa chọn hoàn hảo cho những ai yêu thích cá cược thể thao và slot games.
KUBET được nhắc đến với công nghệ bảo mật cao và cơ sở hạ tầng độc nhất, trợ giúp bảo vệ hoàn toàn chi tiết người sử dụng. Nhà cái này đưa ra rất nhiều chương trình ưu đãi hấp dẫn nhất tương tự như ký quỹ lần kế tiếp, ưu đãi 50%.
BET365 tượng trưng cho nhà cái chơi game thể thao số 1 tại châu Á, nổi trội bên cạnh các tỷ lệ cược châu Á, tài xỉu và trực tiếp thể thao. Nó là sự chọn lựa ưu việt đối với những người ưa chuộng chơi game thể thao.
FUN88 không chỉ là cung cấp mức độ thưởng hấp dẫn đồng thời đưa ra đầy đủ ưu đãi giảm giá đặc biệt giống như thưởng 108K Freebet và mã đánh cược thể thao SABA nhận được 10,888K.
New88 chiêu dụ khách hàng kèm theo các chương trình khuyến khích lôi cuốn như hoàn trả 2% không giới hạn và chiêu đãi lì xì không ngừng. Đây chính là một trong những nhà cái hiện đang hấp dẫn nhiều sự quan tâm xuất phát từ khách hàng đánh bạc.
AE888 vượt trội với dịch vụ tặng 120% lần đầu tiên gửi tiền đá gà
Vâng, tôi sẽ tiếp tục từ đoạn cuối của văn bản:
AE888 nổi trội kèm theo dịch vụ thưởng 120% lần đầu ký quỹ cá cược gà và các gói giảm giá đặc sắc khác. Tất cả chính là nhà cái chuyên dụng cung cấp sảnh chơi SV388.
FI88 thu hút được người tham gia cùng với mức độ trả lại hàng đầu kết hợp với các gói trao ký quỹ lôi cuốn. Nó đại diện cho sự chọn lựa hoàn hảo cho những ai ưa chuộng trò chơi bài và trò chơi đánh bạc.
F8BET nổi bật bên cạnh chương trình tặng ký quỹ khởi đầu đến 8,888,888 VNĐ bên cạnh bên cạnh đại lý hoa lợi 60%. Tất cả đại diện cho nhà cái đáng tin với mọi người ham muốn làm giàu bằng đặt cược online.
FB88 tượng trưng cho một trong những nhà cái đáng tin cậy được ưa chuộng nhất ngày nay cùng với các chương trình giảm giá đặc sắc tương tự như hoàn lại cược liên tiếp 100% và tặng 150% nếu tham gia vào không gian trò chơi may rủi.
5 Tiêu Chí Đánh Giá Nhà Cái Uy Tín
Game chất lượng: Được cung cấp do các nhà phát hành uy tín nhất, đảm đương kết cục không lường trước được và không tồn tại sự can dự.
Chăm sóc hỗ trợ khách hàng: Đoàn CSKH vượt trội, phục vụ 24/7 thông qua rất nhiều kênh thông tin.
Tặng hấp dẫn nhất: Mức tặng lôi cuốn và dễ dàng thực hiện, đơn giản rút ra.
Đảm bảo không rủi ro: Hệ thống bảo vệ tiên tiến, bảo vệ giữ gìn chi tiết người chơi.
Chống gian lận: Thực hiện cách thức ngăn chặn gian lận minh bạch, đảm bảo lợi ích người sử dụng.
Nếu bạn đang có các những thắc mắc về trải nghiệm chơi game, hãy xem xét mục FAQ trên Top10VN để nghiên cứu sâu sắc hơn xung quanh các nhà cái cùng với ưu đãi do họ cung cấp. -
app cá độ bóng đá
Dưới đây là văn bản với các từ được thay thế bằng các cụm từ đề xuất (các từ đồng nghĩa) được đặt trong dấu ngoặc nhọn :
Nổi bật 10 Nhà tổ chức Đáng tin cậy Hiện tại (08/2024)
Đánh bạc online đã trở thành một trào lưu rất thông dụng tại nước ta, và việc tuyển chọn nhà cái đáng tin tưởng là chuyện rất thiết yếu để bảo đảm trải nghiệm cá cược không rủi ro và công bằng. Ở dưới là danh sách Mười nhà cái hàng đầu nhà cái đáng tin cậy hàng đầu hiện nay, được sưu tập bởi trang phân tích hàng đầu Danh sách 10 ông lớn.
ST666 được xem là một trong những nhà cái hàng đầu cùng với đáng tin hàng đầu hiện tại. Kèm theo dịch vụ khách tuyệt vời, yểm trợ quanh ngày kèm theo các gói giảm giá hấp dẫn như thưởng 110% khi ký quỹ lần đầu tiên, chúng quả quyết là tuyển chọn hàng đầu đối với người sử dụng.
RGBET nổi bật cùng với dịch vụ bảo đảm thua lỗ thể thao nhận được 28,888K, bên cạnh bồi thường trò chơi đánh bạc 2% liên tục. RGBET chính là sự lựa chọn ưu việt dành cho những người thích thú chơi game thể thao và game slot.
KUBET được nhắc đến kèm theo cơ chế bảo mật cao và máy chủ dành riêng, hỗ trợ đảm bảo tuyệt đối thông tin người tham gia. Nhà cái này cung ứng đa dạng dịch vụ khuyến mãi hấp dẫn như nạp lần kế tiếp, giảm giá 50%.
BET365 đại diện cho nhà cái đánh bạc thể thao ưu việt trên khu vực châu Á, vượt trội kèm theo các tỷ lệ kèo châu Á, cược tài xỉu và live thể thao. Chúng chính là chọn ra tốt nhất dành cho những người ưa chuộng đặt cược thể thao.
FUN88 không chỉ cung ứng mức ưu đãi hấp dẫn nhưng cũng đưa ra nhiều dịch vụ khuyến mãi vượt trội giống như thưởng 108K Freebet và vé đánh cược thể thao SABA lên đến 10,888K.
New88 chiêu dụ khách hàng bên cạnh các ưu đãi ưu đãi lôi cuốn như bồi thường 2% miễn phí và mưa lì xì không ngừng. Nó là một trong các nhà cái đang đón nhận rất nhiều sự chăm sóc xuất phát từ khách hàng cá cược.
AE888 vượt trội kèm theo chương trình thưởng 120% lần ban đầu nạp đá gà
Vâng, tôi sẽ tiếp tục từ đoạn cuối của văn bản:
AE888 nổi bật kèm theo ưu đãi thưởng 120% lần ban đầu nạp đấu gà và các ưu đãi ưu đãi hấp dẫn khác. Nó đại diện cho nhà cái chuyên biệt đưa ra khu vực SV388.
FI88 lôi cuốn người chơi với tỷ suất hoàn lại cao kèm theo các ưu đãi trao tạo tài khoản hấp dẫn nhất. Chúng tượng trưng cho tuyển chọn ưu việt đối với tất cả ưa chuộng poker và trò chơi đánh bạc.
F8BET nổi bật hơn bên cạnh gói trao tạo tài khoản đầu tiên nhận được 8,888,888 VNĐ kèm theo bên cạnh người quản lý hoa hồng 60%. Đây đại diện cho nhà cái đáng được tin cậy với những người muốn kiếm tiền dựa trên đánh bạc qua mạng.
FB88 là một trong những cái nhà cái đáng tin hàng đầu hiện tại cùng với các dịch vụ khuyến khích hấp dẫn tương tự như trả lại cược liên tiếp 100% và thưởng 150% lúc góp mặt sảnh jackpot.
5 Tiêu Chí Đánh Giá Nhà Cái Uy Tín
Các trò chơi đẳng cấp: Được tạo ra từ các nhà sản xuất lớn, đảm nhận kết quả chơi không lường trước được và không có sự ảnh hưởng.
Chăm sóc chăm sóc khách hàng: Đội ngũ CSKH chuyên nghiệp, yểm trợ không ngừng bằng đầy đủ kênh liên lạc.
Ưu đãi hấp dẫn nhất: Mức độ ưu đãi đặc sắc và dễ dàng thực hiện, đơn giản rút tiền.
Cam kết bảo đảm: Công nghệ bảo vệ vượt trội, bảo đảm an toàn dữ liệu người chơi.
Ngăn chặn gian lận: Sở hữu biện pháp ngăn ngừa gian lận cụ thể, đảm bảo lợi ích người tham gia.
Nếu bạn đang có các những vấn đề liên quan đến trải nghiệm đặt cược, xin xem xét chương FAQ được cung cấp trên Trang web hàng đầu nhằm nghiên cứu nhiều hơn về các nhà cái và chương trình do họ cung cấp. -
Risk Mitigation Filters - is a critical tool used by financial institutions and commercial entities to confirm that they are not engaging with individuals or entities participating in criminal operations.
Such procedure involves verifying the data of customers by means of various records, including restriction lists, politically exposed persons (PEP) registries and additional oversight lists. Within the environment of digital currencies, Anti-Money Laundering screening services facilitate detect and minimize probabilities stemming from potential illegal financial activities operations.
During conducting Anti-Money Laundering monitoring, service providers usually consider the given elements:
Identification Validation - verifying the details of the citizen or organization participating in the transaction, in order to that they do not featured in any monitoring lists.
Transaction Schemes - tracking and considering payment characteristics for the presence of some unusual activity aimed at is likely to indirectly indicate illegal financial activities.
Blockchain Network Analysis - applying blockchain analysis tools to track the movement of cryptocurrencies and identify potential connections to criminal transactions.
Anti-Money Laundering monitoring is not a single assessment. It represents a systematic process intended to helps provide that enterprises uphold aligned with regulations and do not unintentionally facilitate criminal operations. Systematic AML online activities ensure enterprises to update buyer data and receive updates on potential transformations in their risk assessment.
The Functions of AML Check Online Systems
AML check online tools are solutions that deliver full-fledged Anti-Money Laundering monitoring tools. These systems extremely important for companies operating in the decentralized finance sector, as the risk of dealing with illicit funds is higher owing to the uncontrolled character of virtual assets. -
Anti-Money Laundering Filters - represents a key tool employed by banks and enterprises to verify that entities do not involved with separate citizens or organizations participating in criminal operations.
Such procedure encompasses verifying the identities of users using numerous records, including restriction lists, VIPs (PEP) lists and various monitoring lists. In the realm of digital currencies, Anti-Money Laundering analysis instruments assist detect and limit probabilities stemming from hypothetical financial crimes operations.
During conducting AML screening, service providers typically analyze the following aspects:
Customer Identity - identifying the data of the citizen or structure participating in the operation, with the aim to that organizations do not listed in any oversight lists.
Transaction Patterns - examining and considering payment characteristics to identify identification of certain doubtful aimed at can indicate illegal financial activities.
Tracing Crypto Assets - leveraging blockchain tracing tools for the sake of determine the transactions of digital coins and establish potential associations to unlawful operations.
AML screening is not a single assessment. This procedure constitutes a systematic procedure which ensures provide that businesses uphold adapted with rules and do not accidentally participate in illegal transactions. Regular AML online checks allow companies to adjust customer information and receive updates on possible changes in their risk profile.
The Role of Anti-Money Laundering Check Online Instruments
AML check online services fulfill the role of solutions aimed at deliver automated Anti-Money Laundering checks tools. These tools exceptionally critical for companies functioning in the digital money context, due to the fact that the likelihood of encountering with unlawful funds is more elevated as a result of the anonymous nature of cryptocurrencies. -
Are there OTC options for corn and callus removal levitra online. Medications and Arthritis Pain Relief - Restoring Joint Comfort
-
Are there online platforms that specialize in specific types of medications levitra vardenafil. Medications and Sleep Disorders - Finding Rest, Renewing Energy
-
ВПС многообразные сервера, скорость интернета 1 Гбит/сек,
доступные стоимость
Большой выбор параметров для любых цели. Вы можете определить идеальный пакет, исходя из ваших нужд
Облачные серверы AMD EPYC — Сделайте свой cloud-хостинг
Cloud-серверы на базе Intel Gold
Обычные серверы, Аренда базового сервера
Процессорные серверы
Суперсерверы — аренда мощнейших суперсерверов
Мощные серверы использующие топовых процессоров AMD EPYC. Процессорная частота до 3.4-4 ГГц. Хорошая скорость подключения в интернет
24/7 техподдержка. Наши специалисты всегда на связи сразу прийти на помощь в любой проблеме., всевозможные серверы — означает
Ограждение от вредоносных лиц — все сайты открыты — интернет без ограничений
– Предустановленные конфигурации с WireGuard VPN, Outline VPN, 3X-UI VPN, Marzban VPN, IPsec VPN, OpenVPN
– Установленная стоимость в долларах США
– Оплата с российской карты, криптовалютой, зарубежной картой с использованием Stripe
Гибкие возможности оплаты. Мы предлагаем различные удобные способы оплаты, включая в себя банковские карты, онлайн-кошельки и криптовалюту, с возможностью скидок до 20%
Доступные цены. Тарифы наших сервисов уменьшены на 10-15%, в сравнении с конкурентами, одновременно мы предоставляем высококачественные услуги
Без сбоев, стабильная и надёжная работа безупречная. -
Системные расстановки по Хеллингеру. https://rasstanovkiural.ru
-
Are there differences in the availability of generic medicines for different formulations (e.g., immediate-release vs. extended-release) 10mg cialis vs 50 mg viagra?
-
Can a healthcare provider prescribe a brand-name drug for non-medical reasons cialis com. Integrating Traditional Medicine with Modern Drugs for Better Health
-
Online gambling sites present an engaging selection of titles, many of them today include virtual currency as a transaction method. Among the top services, BC Casino, Panda Casino, Axe, and Bitkingz are gaining popularity, while Bitstarz Casino distinguishes itself with multiple recognitions. Cloud Bet Casino is known for operating as a regulated crypto casino, offering player security and fair play, as well as Fairspin and Mbit Casino offer a broad selection of cryptocurrency games.
In terms of dice gambling, cryptocurrency casinos for example BTC Dice deliver a fun gaming experience, letting bettors to stake using Bitcoin and other digital currencies for example Ether, Litecoin, Dogecoin, Binance Coin, and USD Tether.
To online gambling enthusiasts, choosing a reliable provider is important. Thunderkick Gaming, Play'n Go Casino, Red Tiger, Quick Spin, Pragmatic Play, Playtech Casino, Nolimit City, NetEnt, ELK Studios, and Microgaming are known as the leading game providers famous for their unique slot games, immersive visuals, and simple user interfaces.
Casino streaming is now an exciting style for gamblers to participate in online gambling. Well-known streamers such as ClassyBeef, Roshtein Casino, Labowsky, Deuce Ace, and Xposed share their gambling moments, frequently showing huge wins and offering strategies for winning strategies in gambling.
Moreover, casinos such as BC Casino, Bitkingz, and Rocketpot also offer Plinko gambling, a widely played game with simple mechanics but huge potential for massive payouts.
Knowing responsible gambling, cashback deals, and no-name play in virtual casinos is important for players aiming to enhance their gambling journey. Choosing a reliable wallet, exploring no-registration casinos, and learning strategies for popular games like Aviator Casino Game enables users remain knowledgeable while having fun with the thrill of the game. -
плинко играть на деньги
Digital casino platforms deliver an exhilarating variety of gaming options, numerous of these currently include crypto as a transaction method. Of the leading casinos, BC Game Casino, Fortune Panda, Axe, and Kingz Casino are growing in popularity, while Bit Starz shines with multiple recognitions. Cloud Bet Casino stands out as being an officially licensed crypto casino, ensuring user safety and fair play, as well as Fair Spin Casino together with MB Casino offer a wide range of cryptocurrency games.
When it comes to casino dice games, crypto casinos such as Bitcoin Dice Game provide an exhilarating experience, enabling users to gamble on Bitcoin and other virtual currencies such as Ethereum, LTC, DOGE, Binance Coin, and USDT.
For a majority of casino enthusiasts, selecting the right casino provider is essential. Thunderkick, Play and Go, Red Tiger, Quickspin Casino, Pragmatic Play, Playtech Casino, NLC, NetEnt Casino, ELK Studio Games, and Microgaming Casino are some of the top casino game studios recognized for their creative slot games, high-quality graphics, and easy-to-use interfaces.
Casino streams has grown into an exciting way for bettors to get involved with virtual casinos. Famous streamers including ClassyBeef, Roshtein, David Labowsky, DeuceAce, and X-Posed broadcast their casino sessions, commonly sharing big wins and offering insight into winning strategies in gambling.
In addition, sites like BC Game Casino, Bitkingz, and Rocketpot also provide Plinko games, a fan-favorite game with basic rules with large possibilities for high payouts.
Knowing responsible gambling, cashback options, and playing anonymously in virtual casinos are essential for gamblers trying to improve their gaming experience. Deciding on a secure wallet, looking for no-registration-required casinos, and understanding strategies for titles like Aviator help players to stay informed as they enjoy the excitement of the game. -
Can I purchase OTC options for immunodeficiency relief cheap generic viagra lowest prices?
-
Unveiling the Potential of Nutraceuticals as Medications viagra pill where to buy. Medications - Unlocking the Potential for Disease Prevention
-
vibration analysis
The Cruciality of Vibrations Management Equipment in Machines
Inside industrial contexts, machinery along with turning devices act as the backbone of operations. However, one of the most frequent concerns that could obstruct its functionality as well as longevity exists as vibrations. Vibrations could bring about a array of problems, ranging from lowered perfection and effectiveness to increased wear and tear, finally leading to costly downtime as well as restoration. This scenario is when resonance control apparatus becomes vital.
Why Vibration Control proves Important
Vibration inside machinery can result in numerous harmful outcomes:
Decreased Functional Productivity: Exaggerated resonance might bring about imbalances along with instability, lowering the performance in the devices. Such might bring about slower manufacturing speed and increased energy consumption.
Increased Erosion: Ongoing resonance speeds up overall deterioration to mechanical parts, bringing about more regular maintenance and the potential for unanticipated unexpected failures. This does not just heightens operating costs but also shortens the lifespan in the equipment.
Security Risks: Unchecked oscillation might pose major safety concerns to the machinery and the machines and the operators. In, severe cases, such vibrations may result in disastrous machinery failure, endangering personnel as well as leading to significant destruction across the premises.
Exactness along with Quality Challenges: In fields where depend on precise production, such as manufacturing or aerospace, vibration can lead to errors in manufacturing, causing faulty goods and greater waste.
Affordable Alternatives for Vibration Regulation
Investing into vibration control apparatus is not only a necessity but a prudent choice for any business any business that uses mechanical systems. The offered cutting-edge vibration regulation equipment are designed to engineered to reduce vibrations from various equipment or rotational systems, ensuring smooth along with efficient functioning.
What sets our equipment from others is its economic value. We know the necessity of cost-effectiveness within the current market, and for that reason we offer high-quality vibration control solutions at costs that won’t break the bank.
By selecting these tools, you are not just safeguarding your equipment along with boosting its efficiency but also putting resources towards the enduring achievement of your operations.
Final Thoughts
Vibration management proves to be a necessary component in preserving the efficiency, security, and lifespan of your industrial equipment. Using our affordable resonance mitigation apparatus, you can be certain your operations run smoothly, all goods maintain high quality, along with your workers are protected. Never allow vibration affect your business—invest in the correct apparatus immediately. -
Virtual gambling sites provide a thrilling range of titles, several of them these days include crypto as a method of payment. Among the best casinos, BC Game, Panda Casino, Casino Axe, and Kingz Casino are gaining popularity, whereas Bitstarz Casino shines with numerous awards. Cloud Bet Casino is recognized as being a regulated crypto casino, ensuring the security of players and integrity, while Fairspin along with Mbit offer a large range of crypto-friendly games.
For dice-based games, crypto casinos such as Bitcoin Dice Game deliver an exhilarating experience, permitting players to gamble with Bitcoin and alternative cryptos for example Ethereum, Litecoin, DOGE, Binance Coin, and Tether.
For many casino fans, picking the right casino provider is essential. Thunderkick Gaming, Play’n Go, Red Tiger Casino, Quick Spin, Pragmatic Play, Playtech Casino, NLC, NetEnt Casino, ELK Studios, and Microgaming Casino are some of the top game developers recognized for their innovative slots, high-quality graphics, and user-friendly interfaces.
Casino streaming is now a popular style for gamers to interact in online gambling. Well-known streamers like Classy Beef, Roshtein Casino, Labowsky, Deuce Ace, and X-Posed share their gambling moments, often displaying big wins and giving tips on winning strategies in gambling.
Furthermore, sites like BC Casino, Bitkingz, and Rocketpot also provide Plinko-style games, a favorite game with straightforward mechanics but huge potential for massive payouts.
Understanding responsible gaming, cashback options, and playing anonymously in virtual casinos is crucial for gamblers wanting to optimize their gaming experience. Selecting the best crypto wallet, finding no-signup casinos, and understanding strategies for games like Aviator Casino Game help players stay informed while enjoying the thrill of casino gaming. -
volante de equilibrado con cesta de embrague
Dicho volante de estabilizacion con canasto de embrague representa un procedimiento primordial con el proposito de asegurar el operacion ideal del motor y la accionamiento de un camion. El desequilibrio en dicha componente llega a causar vibraciones, ruido, deterioro rapido de los piezas e hasta fallos. Historicamente, el nivelacion se realizaba una vez desmontar el girador del propulsion, aunque las desarrollos contemporaneas posibilitan realizar este procedimiento de manera directa en el carro, lo que esto minimiza duracion y presupuesto.
?Que es el Falta de equilibrio?
El desajuste representa una situacion en la en la cual la peso de un cuerpo rotativo (en este escenario, el rotativo de equilibrado con recipiente de embrague) se localiza de forma desequilibrada en relacion con su punto de rotacion de giro. Lo cual produce fuerzas centrifugas que en consecuencia provocan sacudidas.
Causas fundamentales del Desajuste del Rotativo de Balanceo con Canasto de Embrague:
Desviaciones de manufactura y ensamblaje: Aunque pequenas desviaciones en la geometria de los piezas pueden causar falta de equilibrio.
Desgaste y averias: El funcionamiento prolongado, el sobrecalentamiento y los fallas mecanicas pueden cambiar la cantidad y conducir en desbalance.
Instalacion o arreglo inadecuada: Una montaje incorrecta de la compartimento de embrague o reparaciones inadecuados tambien podrian originar desequilibrio. -
娛樂城推薦與優惠詳解
在現今的娛樂世界中,線上娛樂城已成為眾多玩家的首選。無論是喜歡真人遊戲、老虎機還是體育賽事,每個玩家都能在娛樂城中找到自己的樂趣。以下是一些熱門的娛樂城及其優惠活動,幫助您在選擇娛樂平台時做出明智的決定。
各大熱門娛樂城介紹
1. 富遊娛樂城
富遊娛樂城以其豐富的遊戲選擇和慷慨的優惠活動吸引了大量玩家。新會員只需註冊即可免費獲得體驗金 $168,無需儲值即可輕鬆試玩。此外,富遊娛樂城還提供首存禮金 100% 獎勵,最高可領取 $1000。
2. AT99娛樂城
AT99娛樂城以高品質的遊戲體驗和優秀的客戶服務聞名。該平台提供各種老虎機和真人遊戲,並定期推出新遊戲,讓玩家保持新鮮感。
3. BCR娛樂城
BCR娛樂城是一個新興的平台,專注於提供豐富的體育賽事投注選項。無論是足球、籃球還是其他體育賽事,BCR都能為玩家提供即時的投注體驗。
熱門遊戲推薦
WM真人視訊百家樂
WM真人視訊百家樂是許多玩家的首選,該遊戲提供了真實的賭場體驗,並且玩法簡單,容易上手。
戰神賽特老虎機
戰神賽特老虎機以其獨特的主題和豐富的獎勵機制,成為老虎機愛好者的最愛。該遊戲結合了古代戰神的故事背景,讓玩家在遊戲過程中感受到無窮的樂趣。
最新優惠活動
富遊娛樂城註冊送體驗金
富遊娛樂城新會員獨享 $168 體驗金,無需儲值即可享受全場遊戲,讓您無壓力地體驗不同遊戲的魅力。
VIP 日日返水無上限
富遊娛樂城為 VIP 會員提供無上限的返水優惠,最高可達 0.7%。此活動讓玩家在遊戲的同時,還能享受額外的回饋。
結論
選擇合適的娛樂城不僅能為您的遊戲體驗增色不少,還能通過各種優惠活動獲得更多的利益。無論是新會員還是資深玩家,都能在這些推薦的娛樂城中找到適合自己的遊戲和活動。立即註冊並體驗這些優質娛樂平台,享受無限的遊戲樂趣! -
娛樂城排行
娛樂城推薦與優惠詳解
在現今的娛樂世界中,線上娛樂城已成為眾多玩家的首選。無論是喜歡真人遊戲、老虎機還是體育賽事,每個玩家都能在娛樂城中找到自己的樂趣。以下是一些熱門的娛樂城及其優惠活動,幫助您在選擇娛樂平台時做出明智的決定。
各大熱門娛樂城介紹
1. 富遊娛樂城
富遊娛樂城以其豐富的遊戲選擇和慷慨的優惠活動吸引了大量玩家。新會員只需註冊即可免費獲得體驗金 $168,無需儲值即可輕鬆試玩。此外,富遊娛樂城還提供首存禮金 100% 獎勵,最高可領取 $1000。
2. AT99娛樂城
AT99娛樂城以高品質的遊戲體驗和優秀的客戶服務聞名。該平台提供各種老虎機和真人遊戲,並定期推出新遊戲,讓玩家保持新鮮感。
3. BCR娛樂城
BCR娛樂城是一個新興的平台,專注於提供豐富的體育賽事投注選項。無論是足球、籃球還是其他體育賽事,BCR都能為玩家提供即時的投注體驗。
熱門遊戲推薦
WM真人視訊百家樂
WM真人視訊百家樂是許多玩家的首選,該遊戲提供了真實的賭場體驗,並且玩法簡單,容易上手。
戰神賽特老虎機
戰神賽特老虎機以其獨特的主題和豐富的獎勵機制,成為老虎機愛好者的最愛。該遊戲結合了古代戰神的故事背景,讓玩家在遊戲過程中感受到無窮的樂趣。
最新優惠活動
富遊娛樂城註冊送體驗金
富遊娛樂城新會員獨享 $168 體驗金,無需儲值即可享受全場遊戲,讓您無壓力地體驗不同遊戲的魅力。
VIP 日日返水無上限
富遊娛樂城為 VIP 會員提供無上限的返水優惠,最高可達 0.7%。此活動讓玩家在遊戲的同時,還能享受額外的回饋。
結論
選擇合適的娛樂城不僅能為您的遊戲體驗增色不少,還能通過各種優惠活動獲得更多的利益。無論是新會員還是資深玩家,都能在這些推薦的娛樂城中找到適合自己的遊戲和活動。立即註冊並體驗這些優質娛樂平台,享受無限的遊戲樂趣! -
娛樂城推薦
娛樂城推薦與優惠詳解
在現今的娛樂世界中,線上娛樂城已成為眾多玩家的首選。無論是喜歡真人遊戲、老虎機還是體育賽事,每個玩家都能在娛樂城中找到自己的樂趣。以下是一些熱門的娛樂城及其優惠活動,幫助您在選擇娛樂平台時做出明智的決定。
各大熱門娛樂城介紹
1. 富遊娛樂城
富遊娛樂城以其豐富的遊戲選擇和慷慨的優惠活動吸引了大量玩家。新會員只需註冊即可免費獲得體驗金 $168,無需儲值即可輕鬆試玩。此外,富遊娛樂城還提供首存禮金 100% 獎勵,最高可領取 $1000。
2. AT99娛樂城
AT99娛樂城以高品質的遊戲體驗和優秀的客戶服務聞名。該平台提供各種老虎機和真人遊戲,並定期推出新遊戲,讓玩家保持新鮮感。
3. BCR娛樂城
BCR娛樂城是一個新興的平台,專注於提供豐富的體育賽事投注選項。無論是足球、籃球還是其他體育賽事,BCR都能為玩家提供即時的投注體驗。
熱門遊戲推薦
WM真人視訊百家樂
WM真人視訊百家樂是許多玩家的首選,該遊戲提供了真實的賭場體驗,並且玩法簡單,容易上手。
戰神賽特老虎機
戰神賽特老虎機以其獨特的主題和豐富的獎勵機制,成為老虎機愛好者的最愛。該遊戲結合了古代戰神的故事背景,讓玩家在遊戲過程中感受到無窮的樂趣。
最新優惠活動
富遊娛樂城註冊送體驗金
富遊娛樂城新會員獨享 $168 體驗金,無需儲值即可享受全場遊戲,讓您無壓力地體驗不同遊戲的魅力。
VIP 日日返水無上限
富遊娛樂城為 VIP 會員提供無上限的返水優惠,最高可達 0.7%。此活動讓玩家在遊戲的同時,還能享受額外的回饋。
結論
選擇合適的娛樂城不僅能為您的遊戲體驗增色不少,還能通過各種優惠活動獲得更多的利益。無論是新會員還是資深玩家,都能在這些推薦的娛樂城中找到適合自己的遊戲和活動。立即註冊並體驗這些優質娛樂平台,享受無限的遊戲樂趣! -
Bienvenue sur notre blog, votre lieu ultime pour les infos sur les stars africaines du monde des mediums et des emissions de tele-realite https://mediaeventhub.africa/ ! Des tendances recentes dans l’industrie du loisir africain aux commerages les plus epices sur les celebrites, nous vous tenons au courant de toutes les aventures fascinantes a travers le Afrique. Que ce soit des partenariats musicaux revolutionnaires, de instants intenses dans les emissions de tele-realite, ou de histoires personnelles emouvants de vos stars preferees, nous tracons tout. La scene du divertissement en Afrique est pleine de talents, et notre blog est la pour vous approcher des grands noms qui modelent l'industrie.
Les emissions de tele-realite africaines ont domine le monde, exposant la diversite culturelle, la ingeniosite et l'sincerite uniques du paysage africain. Des emissions comme « Grand Frere Naija », « Les Real Housewives de Lagos » et « Ile de la Tentation Afrique du Sud » restent au sommet des audiences des audiences massives, inspirant des echanges et seduisant des fans bien en dehors de l’Afrique. Nous plongeons dans les histoires, les rapports et les periodes incontournables qui font de ces shows des incontournables a la tele. Notre blog ne se restreint pas a ecrire a propos des stars, mais s’interesse aussi a le role culturel de ces shows, soulignant le poids grandissant de la culture populaire africaine a l’echelle globale.
Notre blog met egalement en lumiere les personnes du monde mediatique et les nouvelles figures qui font sensation en Afrique. Des comediens brillants aux hotes charismatiques, en incluant les leaders d’opinion sur les plateformes sociales, nous mettons a l'honneur les performances de ceux qui transforment le divertissement sur le continent. Que ce soit des performances primees dans les films nigerians, des participations remarquables dans des projets globaux ou des messages percutants dans des clips musicaux, nous vous fournissons des interviews exclusives et des anecdotes derriere la gloire. Vous trouverez des presentations de figures influentes comme Burna Boy, qui ont non seulement seduit les spectateurs du continent, mais aussi acquis une consecration universelle.
Restez connectes avec nous pour les infos de derniere minute et nouveautes en primeur sur vos celebrites africaines. Notre blog est un carrefour pour les fous de la culture populaire qui souhaitent suivre avec les affaires de stars, les shows a venir et les courants de mode qui influencent l'industrie. Si vous etes un fervent adepte de la culture populaire africaine ou un observateur des infos du showbiz, notre blog vous offre de vous garder au courant, distrait et inspire par le monde vibrant des plateformes mediatiques et shows de realites televisees en Afrique. -
kometa casino рабочее зеркало
Онлайн-казино Kometa: Идеальный Выбор для Онлайн Развлечений
В пространстве виртуальных казино Казино Kometa получило популярность благодаря широкому ассортименту игр, привлекательным поощрениям и отличному поддержке. Эта платформа удерживает интерес игроков во всех странах своими уникальными акциями и частыми промо. В этой обзоре мы рассмотрим, почему Kometa Casino называется одной из лучших игровых площадок.
Преимущества Казино Kometa
Главной чертой, отличающих Kometa, является фокус на удовольствие пользователей. Сайт предлагает свыше тысячи развлечений, среди которых любой найдет что-то по душе. Это включает традиционные игры, и еще новые варианты с уникальными функциями. Бонусом является то, что Kometa гарантирует 24/7 сопровождение игроков, обеспечивая приятное и безопасное окружение.
Главные параметры Kometa:
Год начала работы: 2024
Разрешение: Curacao
Ассортимент: Огромное количество
Техподдержка: Постоянная онлайн-чат и email
Мобильная версия: Да
Способы оплаты: Visa
Безопасность: Защита данных
Приветственные бонусы
Одним из главных плюсов Kometa считаются привлекательные приветственные бонусы для начинающих пользователей. После создания аккаунта игроки могут воспользоваться к уникальным промоакциям, чем могут начать развлечение с меньшими затратами. Эти промо предоставляют выгодные шансы для начинающих, давая возможность увеличить свои шансы на победу с самого старта.
Огромный выбор игр
Kometa Casino гарантирует большое количество игр на любые интересы. Пользователи могут испытать удовольствие классическими слотами, настольными играми, а также играми с живыми дилерами. Благодаря передовым технологиям визуального сопровождения и музыкальному фону, все может максимально вникнуть в процесс игры.
Постоянные события и турниры
Для игроков система постоянно организует турниры и турниры с выгодными наградами. Акции организуются ежемесячно, создавая игровой процесс увлекательным и увлекательным. Это позволяет игрокам не только наслаждаться слотами, но и зарабатывать призы и призы.
Почему Kometa Casino?
Kometa — это превосходное соединение множества развлечений, качественного обслуживания и безопасной игровой среды. Система славится своим вниманием к пользователям и желанием совершенствовать развлечения. Независимо от уровня, любой сможет выбрать в Kometa Casino нечто, что позволит его пребывание на сайте увлекательным и комфортным.
Становитесь частью Kometa и играйте с удовольствием адреналином и захватывающими играми каждый день! -
переносная балансировочная машина
ООО «Кинематика»: Эффективные решения для динамической уравновешивания и диагностики техники
Компания ООО «Кинематика» занимается на изготовлении и внедрении высокоточных систем для технической балансировки и проверки машин. Продукты предприятия применяется для поддержки и ремонта многочисленных промышленных устройств, включая системы вентиляции, измельчители, валовые системы, передачи крутящего момента и металлообрабатывающие станки.
Основополагающие решения предприятия:
1. Модуль Арбаланс — переносной виброметр-балансировщик
Инструмент создан для уровновешивания механизмов техники в заводской сборке в собственных подшипниках. Прибор Арбаланс даёт отличные результаты балансировки с уменьшенными издержками. Главные достоинства:
Автоматизированная система расчета: полностью автоматизирована.
Анализ спектра вибрации: помогают выявлять проблемы.
Двухканальная система: обеспечивает измерение вибрации сразу в двух направлениях, улучшая результаты.
Цена: 84000 руб.
2. Модуль Балком-1А — компактный балансировочный виброметр
Модуль Балком-1А разработан для уравновешивания роторных систем в штатных подшипниках. Характерной особенностью является простота эксплуатации и автоматический расчет. Также устройство оснащено:
Два канала измерения вибрации.
Спектральный анализ для технической диагностики состояния механизмов.
Цена: 73 тыс. руб.
3. Balcom-2 — измерительная система для балансировочных станков
Модуль Балком-2 внедряется в балансировочных станках для оценки вибраций. Он предлагает точность сбалансированности устройств и прочих устройств в производстве.
Цена: от 90000 рублей до 95000 рублей в зависимости от устройства.
4. Балком-4 — для многоплоскостной балансировки валов
Балком-4 создан для сбалансированности карданных систем и используется в промышленных системах. Этот модуль предлагает надежные результаты и прецизионность при многоплоскостной сбалансированности.
Цена: от 100 000 руб. до 126 тыс. руб..
Новейшие технологии отслеживания и технической диагностики
Компания «Кинематика» также создает решения для постоянного контроля технического состояния устройств. Эти комплексы оснащены бесконтактные системы для отслеживания вибраций и различных параметров. Например, система Реконт позволяет отслеживать редукторы по точности движения и оборотам. -
балансировка вентиляторов
Фирма «Кинематика»: Качественные услуги для динамической уравновешивания и диагностики промышленных устройств
Фирма «Кинематика» занимается на изготовлении и внедрении высококачественных систем для технической балансировки и диагностики техники. Изделия фирмы используется для ремонта и техобслуживания многочисленных промышленных устройств, включая вентиляционные системы, дробилки, карданные агрегаты, редукторы и станки для металла.
Основополагающие решения предприятия:
1. Арбаланс — портативный прибор балансировки вибраций
Прибор предназначен для балансировки вращательных систем техники в комплектации в родных подшипниках. Прибор Арбаланс предлагает высокое качество уравновешивания с уменьшенными затратами. Главные достоинства:
Автоматизированная система расчета: не требует участия оператора.
Анализ спектра вибрации: обнаруживают неполадки.
Измерение по двум плоскостям: позволяет измерять вибрационные колебания сразу в двух плоскостях, повышая производительность процесса.
Цена: 84 тыс. руб.
2. Балансировочный прибор Балком-1А — малогабаритный прибор балансировки
Прибор Балком-1А предназначен для балансировки валов в штатных подшипниках. Главной особенностью является простота эксплуатации и программа расчета. Прибор также поддерживает:
Измерение вибрации в двух каналах.
Спектральная диагностика для контроля состояния оборудования.
Цена: 73 тыс. руб.
3. Модуль Балком-2 — балансировочный прибор для измерительных станков
Устройство Балком-2 используется в станциях балансировки для измерения вибраций. Он гарантирует надежность точного уравновешивания роторов и других механизмов в технике.
Цена: от 90 тыс. руб. до 95000 рублей в зависимости от оборудования.
4. Система Балком-4 — для балансировки многосоставных систем валов
Система Балком-4 применяется для балансировки карданов и применяется в индустриальных установках. Этот прибор гарантирует стабильные показатели и точные измерения при уравновешивании в разных направлениях.
Цена: от 100000 руб. до 126 000 руб..
Новейшие технологии мониторинга и диагностики
Фирма «Кинематика» также создает системы для непрерывной диагностики состояния оборудования. Эти приборы работают на бесконтактными сенсорами для контроля вибрации и других показателей. Например, модуль Реконт даёт возможность контролировать механизмы редукторов по параметрам кинематической точности и вращательным движениям. -
https://oookin.ru/balance_kardan.htm
https://oookin.ru/balprim.htm
https://oookin.ru/balkom.htm
https://oookin.ru/vvedbal3.htm
https://oookin.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?t=112
Компания «Кинематика»: Надежные услуги для динамической сбалансированности и диагностики промышленного оборудования
Организация «Кинематика» специализируется на изготовлении и производстве точных систем для уравновешивания и контроля машин. Изделия фирмы эксплуатируется для техобслуживания и ремонта различных промышленных устройств, включая системы вентиляции, мельницы, карданные агрегаты, системы передачи и прецизионные станки.
Основные решения предприятия:
1. Модуль Арбаланс — мобильный система вибродиагностики
Инструмент создан для динамической балансировки устройств в комплектации в собственных подшипниках. Прибор Арбаланс даёт высокое качество сбалансированности с небольшими издержками. Ключевые особенности устройства:
Автоматическая система вычислений: полностью автоматизирована.
Графики вибрации и спектральный анализ: находят проблемы.
Два канала измерения: даёт возможность фиксировать вибрационные колебания параллельно в двух плоскостях, увеличивая производительность.
Цена: 84 тыс. руб.
2. Балком-1А — портативный прибор балансировки
Балком-1А разработан для уравновешивания роторных систем в штатных подшипниках. Ключевым преимуществом является удобство эксплуатации и автоматический расчет. Система дополнена:
Два вибрационных канала.
Анализ спектра вибраций для диагностики состояния техники.
Цена: 73000 рублей
3. Модуль Балком-2 — измерительная станция для измерительных станков
Прибор Балком-2 эксплуатируется в балансировочных станках для измерения вибраций. Он предлагает точность точного уравновешивания систем и других агрегатов в производстве.
Цена: от 90000 рублей до 95000 рублей в зависимости от оборудования.
4. Balcom-4 — для балансировки в нескольких плоскостях валов
Балком-4 разработан для балансировки карданов и используется в системах производства. Этот устройство гарантирует высокую точность и точные измерения при многоплоскостной балансировке.
Цена: от 100000 руб. до 126000 руб..
Современные технологии контроля и анализа
ООО «Кинематика» также создает системы для непрерывной диагностики состояния оборудования. Эти устройства работают на бесконтактные датчики для отслеживания вибраций и прочих параметров. Например, система Реконт позволяет отслеживать редукторы по параметрам кинематической точности и скорости вращения. -
Kometa Casino: Превосходный Шанс для Онлайн Игр
В мире онлайн-казино Kometa получило популярность благодаря множеству игр, выгодным поощрениям и высококачественному сервису. Эта система удерживает внимание пользователей по всему миру своими особенными возможностями и постоянными промо. В представленной статье мы обсудим, почему Kometa считается выдающейся игровых площадок.
Плюсы Kometa Casino
Основным аспектом, выделяющих Kometa, является ориентация на потребности пользователей. Платформа предлагает огромное количество игр, где все сможет выбрать игру. Это включает как классические слоты, и еще инновационные варианты с новаторскими функциями. Бонусом является то, что Казино Kometa предлагает круглосуточную помощь клиентов, обеспечивая удобное и надежное окружение.
Основные характеристики Kometa:
Год начала работы: 2024
Разрешение: Curacao
Ассортимент: Более 1000
Техподдержка: Постоянная чат и email
Мобильный доступ: Да
Способы оплаты: Skrill
Безопасность: Защита данных
Стартовые поощрения
Одним из главных плюсов Kometa Casino считаются выгодные акции для новичков для новичков. После входа на сайт новички получают доступ к уникальным промоакциям, что дает возможность начать развлечение с небольшими вложениями. Эти промо гарантируют выгодные шансы для начинающих, предоставляя шанс увеличить свои шансы на победу с самого старта.
Большое количество развлечений
Kometa Casino предоставляет огромное разнообразие слотов на любые интересы. Пользователи могут испытать удовольствие классическими слотами, развлечениями на столах, а также реальными дилерами. Благодаря передовым технологиям визуального сопровождения и звуковому сопровождению, каждый игрок может максимально вникнуть в развлечения.
Частые промо и активности
Для всех пользователей платформа регулярно предлагает акции и турниры с выгодными наградами. Мероприятия организуются регулярно, что делает игровой процесс интересным и захватывающим. Это дает возможность пользователям не только играть развлечениями, но и зарабатывать призы и выигрыши.
Почему Kometa Casino?
Казино Kometa — это превосходное соединение широкого ассортимента, отличной поддержки и надежной системы. Платформа выделяется своим вниманием к пользователям и желанием совершенствовать опыт пользователей. Неважно, новичок или профи, все найдет в Kometa Casino то, что сделает его время на платформе интересным и комфортным.
Присоединяйтесь к Kometa и испытывайте удовольствие от захватывающими ощущениями и интересными развлечениями ежедневно! -
娛樂城推薦
DB娛樂平台:頂級線上賭場評價介紹
DB娛樂城,前身為PM娛樂網站,於2023年徹底更名為【DB多寶遊戲】。此次品牌更名的過程,DB遊戲平台進而專注於帶來多元的線上服務體驗,為玩家帶來更多的遊戲選擇與全新的服務項目。無論是百家樂、體育博彩還是其他流行遊戲,DB娛樂平台都能適應玩家的需求。
多寶平台的成立與擴展 在亞洲線上娛樂市場中,DB遊戲平台迅速崛起,成為數不清的玩家的首要選擇平台之一。隨著PM機構的品牌更名,DB多寶遊戲致力於提升玩家體驗,並致力於打造一個安全、迅速且公正的遊戲氛圍。從服務項目到付款選項,DB娛樂網站不斷尋求卓越,為玩家提供首選的線上體驗。
DB娛樂網站的娛樂內容與特點
百家樂遊戲 DB娛樂網站最為廣受歡迎的是其豐富的百家樂項目。平台帶來多個版本的莊家遊戲,包括經典百家樂和無手續費百家樂,滿足各類玩家的偏好。透過直播荷官的同步互動,玩家可以享受沉浸式的賭桌氛圍。
體育博彩 作為一個全面平台,DB賭場還提供各類運動項目的投注服務。從球賽、籃球到網球賽事等熱門賽事,玩家都可以任何時候體驗體育博彩,感受比賽的快感與下注的興奮。
促銷活動與獎金 DB娛樂城經常推出廣泛的促銷計畫,為新舊會員帶來各種優惠與獎勵。這些優惠不僅提升了遊戲的刺激感,還為玩家創造更多賺取獎金的途徑。
DB遊戲平台的口碑與優勢 在2024年的最新線上娛樂平台排行榜中,DB娛樂網站獲得了卓越評價,並且因其多樣的遊戲選擇、迅速的提款效率和持續的促銷活動而贏得玩家喜愛。 -
DB賭場:頂級線上娛樂網站評價介紹
DB娛樂城,前身為PM娛樂網站,於2023年完整更名為【DB多寶遊戲】。這次品牌轉型的過程,DB賭場進一步專注於提供全方位的線上服務體驗,為玩家呈現更廣泛的選擇範圍與全新的遊戲服務。無論是百家樂遊戲、運動博彩還是其他熱門娛樂項目,DB娛樂城都能符合玩家的期待。
多寶平台的成立與發展 在亞洲遊戲市場中,DB遊戲平台很快發展,成為大量玩家的首選平台之一。隨著PM集團的品牌重塑,DB多寶遊戲專注於提升客戶體驗,並聚焦於打造一個放心、方便且合規的遊戲氛圍。從娛樂項目到支付方式,DB遊戲平台都致力於卓越,為玩家呈現最優的線上體驗。
DB娛樂網站的遊戲類型與特點
百家樂遊戲 DB遊戲平台最為出名的是其豐富的百家樂選項。平台推出多個版本的百家樂玩法,包括標準百家樂和零佣金百家樂,迎合各類玩家的需求。透過直播荷官的實時互動,玩家可以獲得身臨其境的現場氣氛。
體育博彩 作為一個綜合娛樂平台,DB賭場還呈現各類運動項目的博彩項目。從足球、籃球遊戲到網球遊戲等常見運動賽事,玩家都可以任何時候加入體育博彩,獲得賽事的緊張感與博彩的快感。
促銷活動與獎金 DB娛樂城經常推出多樣的促銷活動,為新老玩家提供各種優惠與紅利。這些優惠不僅增強了遊戲的娛樂性,還為玩家提供更多贏取獎金的選項。
DB娛樂城的反響與優勢 在2024年的最新賭場排行榜中,DB遊戲平台獲得了高度評價,並且因其豐富的遊戲選擇、迅速的提款效率和持續的促銷活動而獲得玩家喜愛。 -
Купить бытовку под столовую 149 900? (в т.ч. НДС)
Аренда бытовок под столовую
8 000? в месяц (в т.ч. НДС)
внешний размер 6000х2400х2500(в);
окно ПВХ с поворотно-откидной створкой;
утепленные пол, потолок, стены;
отделка потолка панелями ПВХ;
отделка стен ДВП, линолеум на полу; -
JILI SLOT GAMES: Sự Lựa Chọn Hàng Đầu Cho Các Tín Đồ Casino Trực Tuyến
JILI Casino là một nhà phát hành game nổi tiếng với nhiều năm kinh nghiệm trong ngành công nghiệp giải trí trực tuyến. Tại JILI, chúng tôi cam kết mang đến cho người chơi những trải nghiệm độc đáo và đẳng cấp, thông qua việc đổi mới không ngừng và cải thiện chất lượng từng sản phẩm. Những giá trị cốt lõi của chúng tôi không chỉ dừng lại ở việc tạo ra các trò chơi xuất sắc, mà còn tập trung vào việc cung cấp các tính năng vượt trội để đáp ứng nhu cầu của người chơi trên toàn cầu.
Sự Đa Dạng Trong Các Trò Chơi Slot
JILI nổi tiếng với loạt trò chơi slot đa dạng và hấp dẫn. Từ các slot game cổ điển đến những trò chơi với giao diện hiện đại và tính năng độc đáo, JILI Slot luôn đem đến cho người chơi những phút giây giải trí tuyệt vời. Các trò chơi được thiết kế với đồ họa sống động, âm thanh chân thực và những vòng quay thú vị, đảm bảo rằng người chơi sẽ luôn bị cuốn hút.
Ưu Điểm Nổi Bật Của JILI Casino
Đổi mới và sáng tạo: Mỗi trò chơi tại JILI Casino đều mang đến sự mới mẻ với lối chơi hấp dẫn và giao diện bắt mắt.
Chất lượng cao: JILI không ngừng cải tiến để đảm bảo mỗi sản phẩm đều đạt chất lượng tốt nhất, từ trải nghiệm người chơi đến tính năng trò chơi.
Nền tảng đa dạng: JILI Casino cung cấp nhiều loại game khác nhau, từ slot, bắn cá đến các trò chơi truyền thống, phù hợp với mọi sở thích của người chơi.
Chương Trình Khuyến Mại JILI
JILI Casino không chỉ nổi bật với chất lượng game mà còn thu hút người chơi bởi các chương trình khuyến mại hấp dẫn. Người chơi có thể tham gia vào nhiều sự kiện, từ khuyến mãi nạp tiền, hoàn trả đến các chương trình tri ân dành riêng cho thành viên VIP. Những ưu đãi này không chỉ tăng cơ hội chiến thắng mà còn mang lại giá trị cộng thêm cho người chơi.
Nổ Hủ City Và Các Trò Chơi Hấp Dẫn Khác
JILI không chỉ có slot games mà còn cung cấp nhiều thể loại game đa dạng khác như bắn cá, bài và nhiều trò chơi giải trí khác. Nổi bật trong số đó là Nổ Hủ City – nơi người chơi có thể thử vận may và giành được những giải thưởng lớn. Sự kết hợp giữa lối chơi dễ hiểu và các tính năng độc đáo của Nổ Hủ City chắc chắn sẽ mang lại những khoảnh khắc giải trí đầy thú vị.
Tham Gia JILI Casino Ngay Hôm Nay
Với sự đa dạng về trò chơi, các tính năng vượt trội và những chương trình khuyến mại hấp dẫn, JILI Casino là sự lựa chọn không thể bỏ qua cho những ai yêu thích trò chơi trực tuyến. Hãy truy cập trang web chính thức của JILI ngay hôm nay để trải nghiệm thế giới giải trí không giới hạn và giành lấy những phần thưởng hấp dẫn từ các trò chơi của chúng tôi! -
DB娛樂城:頂級線上賭場評價介紹
DB娛樂網站,前身為PM娛樂網站,於2023年正式更名為【DB多寶遊戲】。本次品牌轉型的過程,DB娛樂平台進一步專注於推動多元的線上遊戲體驗,為玩家提供多樣化的遊戲類型與革新的遊戲服務。無論是賭桌遊戲、體育賭注還是其他受歡迎遊戲,DB娛樂平台都能適應玩家的期待。
多寶平台的成立與發展 在亞洲娛樂市場中,DB娛樂城飛速興起,成為眾多玩家的熱門選擇平台之一。隨著PM公司的品牌更新,DB多寶遊戲著眼於提升玩家體驗,並努力建立一個安全、方便且公平的平台環境。從娛樂項目到付款選項,DB娛樂網站都致力於卓越,為玩家帶來最佳的線上賭場體驗。
DB娛樂城的遊戲類型與亮點
百家樂遊戲 DB娛樂網站最為知名的是其多元的百家樂項目。平台帶來多個版本的百家樂玩法,包括傳統百家樂和免佣百家樂,滿足不同玩家的偏好。透過真人荷官的即時互動,玩家可以獲得真實的現場氣氛。
體育博彩 作為一個多功能平台,DB賭場還提供各類運動項目的投注選項。從足球比賽、籃球賽事到網球等流行體育項目,玩家都可以隨時參與體育博彩,感受賽事的緊張感與博彩的快感。
促銷活動與獎金 DB娛樂城不斷推出多樣的促銷活動,為所有玩家推動各種優惠與回饋。這些計畫不僅增加了遊戲的刺激感,還為玩家推動更多獲取紅利的可能性。
DB賭場的口碑與優勢 在2024年的最新遊戲平台排行榜中,DB娛樂網站獲得了卓越評價,並且因其全面的遊戲選擇、快捷的提款效率和廣泛的促銷活動而獲得玩家喜愛。 -
DB賭場:首選線上娛樂網站評價介紹
DB娛樂城,前身為PM賭場,於2023年全面更名為【DB多寶遊戲】。這次品牌更名的過渡,DB娛樂平台進一步專注於提供多元的線上娛樂體驗,為玩家帶來更多的遊戲選擇與全新的服務項目。無論是百家樂、體育博彩還是其他熱門娛樂項目,DB娛樂平台都能迎合玩家的偏好。
多寶遊戲的誕生與進步 在亞洲線上娛樂市場中,DB遊戲平台快速崛起,成為許多玩家的首要選擇平台之一。隨著PM品牌的品牌重塑,DB多寶遊戲專注於提升玩家體驗,並聚焦於建立一個放心、便捷且公正的娛樂環境。從遊戲內容到交易系統,DB娛樂網站都追求卓越,為玩家推動最佳的線上賭場體驗。
DB遊戲平台的娛樂內容與亮點
百家樂遊戲 DB賭場最為廣受歡迎的是其豐富的百家樂項目。平台提供多個版本的賭桌遊戲,包括經典百家樂和無佣金百家樂,適應不同玩家的需求。透過直播荷官的現場互動,玩家可以感受真實的賭場體驗。
體育博彩 作為一個全面平台,DB遊戲平台還提供各類體育賽事的投注選項。從足球比賽、籃球比賽到網球比賽等受歡迎賽事,玩家都可以任何時候體驗體育博彩,獲得賽事的刺激與下注的興奮。
促銷活動與獎金 DB娛樂網站不斷推出多重的促銷活動,為所有玩家呈現各種折扣與紅利。這些優惠不僅增強了遊戲的娛樂性,還為玩家創造更多贏得紅利的選項。
DB娛樂網站的反響與亮點 在2024年的最新遊戲平台排行榜中,DB遊戲平台獲得了卓越評價,並且因其多樣的遊戲選擇、高效的提款效率和廣泛的促銷活動而贏得玩家喜愛。 -
In our platform, we bring you the most recent updates and engaging news about the most popular UK personalities from the worlds of media, reality TV, and entertainment. Whether you're a fan of hit reality shows like Love Island, The Only Way Is Essex, or Made in Chelsea, or you're enthusiastic to stay updated on the lives of the UK's top social media stars, our platform covers it all. From fascinating behind-the-scenes drama to exclusive interviews, we make sure you’re informed with everything happening in the world of your favorite stars - http://ppm.co.jp/userinfo.php?uid=17968# .
UK reality TV celebrities have gained huge popularity over the years, transforming from everyday individuals into household names with massive fan followings. Our website delves into their personal and professional lives, offering looks into their latest ventures, relationships, and dramas. Whether it's a new romance brewing on Love Island or a cast member from Geordie Shore unveiling a new business, you'll find in-depth stories that reveal the glamorous yet sometimes chaotic lives of these personalities. -
Nếu bạn là một người đam mê cá cược và yêu thích sự hấp dẫn của những con số, thì sảnh lô đề RGbet chính là điểm đến lý tưởng cho bạn. Tôi đã có cơ hội trải nghiệm tại đây và muốn chia sẻ một số ấn tượng cũng như kinh nghiệm của mình.
RGbet nổi bật với mức tỷ lệ trả thưởng cực kỳ hấp dẫn. Trong quá trình chơi, tôi nhận thấy rằng nhà cái này không chỉ cung cấp nhiều loại hình cược mà còn có những mức cược linh hoạt, phù hợp với mọi nhu cầu của người chơi. Bạn có thể bắt đầu với số tiền nhỏ và dần dần tăng lên khi đã nắm bắt được các quy luật và cách thức hoạt động của trò chơi. Sự đa dạng trong các tùy chọn cược giúp cho trải nghiệm chơi không bị nhàm chán, từ cược lô, đề đến các loại cược khác.
Giao diện của RGbet rất thân thiện, dễ dàng điều hướng. Ngay cả khi bạn là người mới, bạn vẫn có thể nhanh chóng tìm thấy những thông tin cần thiết và bắt đầu đặt cược chỉ trong vài phút. Tôi đặc biệt ấn tượng với hệ thống đổi thưởng siêu tốc của nhà cái. Sau khi trúng thưởng, quá trình rút tiền diễn ra rất nhanh chóng và minh bạch. Tôi đã nhận được tiền thưởng trong tài khoản của mình chỉ sau vài phút, điều này thực sự tạo cảm giác yên tâm và tin tưởng cho người chơi.
Một điểm đáng chú ý khác là dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng của RGbet. Đội ngũ hỗ trợ luôn sẵn sàng 24/7, giúp tôi giải quyết mọi thắc mắc nhanh chóng và hiệu quả. Chỉ cần một tin nhắn, tôi đã có thể nhận được câu trả lời rõ ràng và hữu ích.
Ngoài ra, để tăng cơ hội trúng thưởng, tôi cũng muốn chia sẻ một vài mẹo nhỏ. Đầu tiên, hãy luôn theo dõi các thống kê và xu hướng của những con số để đưa ra quyết định cược hợp lý. Thứ hai, hãy đặt ra ngân sách cho mỗi lần chơi để tránh việc chi tiêu quá đà. Cuối cùng, đừng quên tham gia các chương trình khuyến mãi và ưu đãi mà RGbet thường xuyên tổ chức; đây là cơ hội tuyệt vời để gia tăng cơ hội thắng lớn.
Tóm lại, RGbet thực sự là một nhà cái lô đề uy tín với nhiều lợi thế vượt trội. Nếu bạn đang tìm kiếm một sân chơi lô đề an toàn, hấp dẫn và đổi thưởng nhanh chóng, đừng ngần ngại tham gia ngay hôm nay! Chắc chắn rằng bạn sẽ có những trải nghiệm thú vị và có cơ hội trúng thưởng lớn tại đây. -
nhà cái
Trong bối cảnh ngành công nghiệp cá cược trực tuyến ngày càng phát triển, việc lựa chọn một nhà cái uy tín trở nên vô cùng quan trọng đối với những người đam mê cá cược.Nhà cái RGBET nổi lên như một sự lựa chọn hàng đầu đáng để bạn quan tâm, hứa hẹn mang đến cho bạn một trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn, công bằng và thú vị. Từ các trò chơi cá cược đa dạng, dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng tận tình đến tỷ lệ cược cạnh tranh, Rgbet sở hữu nhiều ưu điểm vượt trội khiến bạn không thể bỏ qua.Hãy cùng khám phá những lý do tại sao bạn cần quan tâm đến nhà cái Rgbet và tại sao đây nên là lựa chọn hàng đầu của bạn trong thế giới cá cược trực tuyến. -
nhà cái
Trong bối cảnh ngành công nghiệp cá cược trực tuyến ngày càng phát triển, việc lựa chọn một nhà cái uy tín trở nên vô cùng quan trọng đối với những người đam mê cá cược.Nhà cái RGBET nổi lên như một sự lựa chọn hàng đầu đáng để bạn quan tâm, hứa hẹn mang đến cho bạn một trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn, công bằng và thú vị. Từ các trò chơi cá cược đa dạng, dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng tận tình đến tỷ lệ cược cạnh tranh, Rgbet sở hữu nhiều ưu điểm vượt trội khiến bạn không thể bỏ qua.Hãy cùng khám phá những lý do tại sao bạn cần quan tâm đến nhà cái Rgbet và tại sao đây nên là lựa chọn hàng đầu của bạn trong thế giới cá cược trực tuyến. -
rgbet
Nếu bạn là một người đam mê cá cược và yêu thích sự hấp dẫn của những con số, thì sảnh lô đề RGbet chính là điểm đến lý tưởng cho bạn. Tôi đã có cơ hội trải nghiệm tại đây và muốn chia sẻ một số ấn tượng cũng như kinh nghiệm của mình.
RGbet nổi bật với mức tỷ lệ trả thưởng cực kỳ hấp dẫn. Trong quá trình chơi, tôi nhận thấy rằng nhà cái này không chỉ cung cấp nhiều loại hình cược mà còn có những mức cược linh hoạt, phù hợp với mọi nhu cầu của người chơi. Bạn có thể bắt đầu với số tiền nhỏ và dần dần tăng lên khi đã nắm bắt được các quy luật và cách thức hoạt động của trò chơi. Sự đa dạng trong các tùy chọn cược giúp cho trải nghiệm chơi không bị nhàm chán, từ cược lô, đề đến các loại cược khác.
Giao diện của RGbet rất thân thiện, dễ dàng điều hướng. Ngay cả khi bạn là người mới, bạn vẫn có thể nhanh chóng tìm thấy những thông tin cần thiết và bắt đầu đặt cược chỉ trong vài phút. Tôi đặc biệt ấn tượng với hệ thống đổi thưởng siêu tốc của nhà cái. Sau khi trúng thưởng, quá trình rút tiền diễn ra rất nhanh chóng và minh bạch. Tôi đã nhận được tiền thưởng trong tài khoản của mình chỉ sau vài phút, điều này thực sự tạo cảm giác yên tâm và tin tưởng cho người chơi.
Một điểm đáng chú ý khác là dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng của RGbet. Đội ngũ hỗ trợ luôn sẵn sàng 24/7, giúp tôi giải quyết mọi thắc mắc nhanh chóng và hiệu quả. Chỉ cần một tin nhắn, tôi đã có thể nhận được câu trả lời rõ ràng và hữu ích.
Ngoài ra, để tăng cơ hội trúng thưởng, tôi cũng muốn chia sẻ một vài mẹo nhỏ. Đầu tiên, hãy luôn theo dõi các thống kê và xu hướng của những con số để đưa ra quyết định cược hợp lý. Thứ hai, hãy đặt ra ngân sách cho mỗi lần chơi để tránh việc chi tiêu quá đà. Cuối cùng, đừng quên tham gia các chương trình khuyến mãi và ưu đãi mà RGbet thường xuyên tổ chức; đây là cơ hội tuyệt vời để gia tăng cơ hội thắng lớn.
Tóm lại, RGbet thực sự là một nhà cái lô đề uy tín với nhiều lợi thế vượt trội. Nếu bạn đang tìm kiếm một sân chơi lô đề an toàn, hấp dẫn và đổi thưởng nhanh chóng, đừng ngần ngại tham gia ngay hôm nay! Chắc chắn rằng bạn sẽ có những trải nghiệm thú vị và có cơ hội trúng thưởng lớn tại đây. -
nhà cái
RGBET: Trang Chủ Cá Cược Uy Tín và Đa Dạng Tại Việt Nam
RGBET đã khẳng định vị thế của mình là một trong những nhà cái hàng đầu tại châu Á và Việt Nam, với đa dạng các dịch vụ cá cược và trò chơi hấp dẫn. Nhà cái này nổi tiếng với việc cung cấp môi trường cá cược an toàn, uy tín và luôn mang lại trải nghiệm tuyệt vời cho người chơi.
Các Loại Hình Cá Cược Tại RGBET
RGBET cung cấp các loại hình cá cược phong phú bao gồm:
Bắn Cá: Một trò chơi đầy kịch tính và thú vị, phù hợp với những người chơi muốn thử thách khả năng săn bắn và nhận về những phần thưởng giá trị.
Thể Thao: Nơi người chơi có thể tham gia đặt cược vào các trận đấu thể thao đa dạng, từ bóng đá, bóng rổ, đến các sự kiện thể thao quốc tế với tỷ lệ cược hấp dẫn.
Game Bài: Đây là một sân chơi dành cho những ai yêu thích các trò chơi bài như tiến lên miền Nam, phỏm, xì dách, và mậu binh. Các trò chơi được phát triển kỹ lưỡng, đem lại cảm giác chân thực và thú vị.
Nổ Hũ: Trò chơi slot với cơ hội trúng Jackpot cực lớn, luôn thu hút sự chú ý của người chơi. Nổ Hũ RGBET là sân chơi hoàn hảo cho những ai muốn thử vận may và giành lấy những phần thưởng khủng.
Lô Đề: Với tỷ lệ trả thưởng cao và nhiều tùy chọn cược, RGBET là nơi lý tưởng cho những người đam mê lô đề.
Tính Năng Nổi Bật Của RGBET
Một trong những điểm nổi bật của RGBET là giao diện thân thiện, dễ sử dụng và hệ thống bảo mật tiên tiến giúp bảo vệ thông tin người chơi. Ngoài ra, nhà cái này còn hỗ trợ các hình thức nạp rút tiền tiện lợi thông qua nhiều kênh khác nhau như OVO, Gopay, Dana, và các chuỗi cửa hàng như Indomaret và Alfamart.
Khuyến Mãi và Dịch Vụ Chăm Sóc Khách Hàng
RGBET không chỉ nổi bật với các trò chơi đa dạng, mà còn cung cấp nhiều chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn như bonus chào mừng, cashback, và các phần thưởng hàng ngày. Đặc biệt, dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng của RGBET hoạt động 24/7 với đội ngũ chuyên nghiệp, sẵn sàng hỗ trợ người chơi qua nhiều kênh liên lạc.
Kết Luận
Với những ưu điểm nổi bật về dịch vụ, bảo mật, và trải nghiệm người dùng, RGBET xứng đáng là nhà cái hàng đầu mà người chơi nên lựa chọn khi tham gia vào thế giới cá cược trực tuyến. -
nhà cái
Trong bối cảnh ngành công nghiệp cá cược trực tuyến ngày càng phát triển, việc lựa chọn một nhà cái uy tín trở nên vô cùng quan trọng đối với những người đam mê cá cược.Nhà cái RGBET nổi lên như một sự lựa chọn hàng đầu đáng để bạn quan tâm, hứa hẹn mang đến cho bạn một trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn, công bằng và thú vị. Từ các trò chơi cá cược đa dạng, dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng tận tình đến tỷ lệ cược cạnh tranh, Rgbet sở hữu nhiều ưu điểm vượt trội khiến bạn không thể bỏ qua.Hãy cùng khám phá những lý do tại sao bạn cần quan tâm đến nhà cái Rgbet và tại sao đây nên là lựa chọn hàng đầu của bạn trong thế giới cá cược trực tuyến. -
RGBET: Trang Chủ Cá Cược Uy Tín và Đa Dạng Tại Việt Nam
RGBET đã khẳng định vị thế của mình là một trong những nhà cái hàng đầu tại châu Á và Việt Nam, với đa dạng các dịch vụ cá cược và trò chơi hấp dẫn. Nhà cái này nổi tiếng với việc cung cấp môi trường cá cược an toàn, uy tín và luôn mang lại trải nghiệm tuyệt vời cho người chơi.
Các Loại Hình Cá Cược Tại RGBET
RGBET cung cấp các loại hình cá cược phong phú bao gồm:
Bắn Cá: Một trò chơi đầy kịch tính và thú vị, phù hợp với những người chơi muốn thử thách khả năng săn bắn và nhận về những phần thưởng giá trị.
Thể Thao: Nơi người chơi có thể tham gia đặt cược vào các trận đấu thể thao đa dạng, từ bóng đá, bóng rổ, đến các sự kiện thể thao quốc tế với tỷ lệ cược hấp dẫn.
Game Bài: Đây là một sân chơi dành cho những ai yêu thích các trò chơi bài như tiến lên miền Nam, phỏm, xì dách, và mậu binh. Các trò chơi được phát triển kỹ lưỡng, đem lại cảm giác chân thực và thú vị.
Nổ Hũ: Trò chơi slot với cơ hội trúng Jackpot cực lớn, luôn thu hút sự chú ý của người chơi. Nổ Hũ RGBET là sân chơi hoàn hảo cho những ai muốn thử vận may và giành lấy những phần thưởng khủng.
Lô Đề: Với tỷ lệ trả thưởng cao và nhiều tùy chọn cược, RGBET là nơi lý tưởng cho những người đam mê lô đề.
Tính Năng Nổi Bật Của RGBET
Một trong những điểm nổi bật của RGBET là giao diện thân thiện, dễ sử dụng và hệ thống bảo mật tiên tiến giúp bảo vệ thông tin người chơi. Ngoài ra, nhà cái này còn hỗ trợ các hình thức nạp rút tiền tiện lợi thông qua nhiều kênh khác nhau như OVO, Gopay, Dana, và các chuỗi cửa hàng như Indomaret và Alfamart.
Khuyến Mãi và Dịch Vụ Chăm Sóc Khách Hàng
RGBET không chỉ nổi bật với các trò chơi đa dạng, mà còn cung cấp nhiều chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn như bonus chào mừng, cashback, và các phần thưởng hàng ngày. Đặc biệt, dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng của RGBET hoạt động 24/7 với đội ngũ chuyên nghiệp, sẵn sàng hỗ trợ người chơi qua nhiều kênh liên lạc.
Kết Luận
Với những ưu điểm nổi bật về dịch vụ, bảo mật, và trải nghiệm người dùng, RGBET xứng đáng là nhà cái hàng đầu mà người chơi nên lựa chọn khi tham gia vào thế giới cá cược trực tuyến. -
RGBET: Trang Chủ Cá Cược Uy Tín và Đa Dạng Tại Việt Nam
RGBET đã khẳng định vị thế của mình là một trong những nhà cái hàng đầu tại châu Á và Việt Nam, với đa dạng các dịch vụ cá cược và trò chơi hấp dẫn. Nhà cái này nổi tiếng với việc cung cấp môi trường cá cược an toàn, uy tín và luôn mang lại trải nghiệm tuyệt vời cho người chơi.
Các Loại Hình Cá Cược Tại RGBET
RGBET cung cấp các loại hình cá cược phong phú bao gồm:
Bắn Cá: Một trò chơi đầy kịch tính và thú vị, phù hợp với những người chơi muốn thử thách khả năng săn bắn và nhận về những phần thưởng giá trị.
Thể Thao: Nơi người chơi có thể tham gia đặt cược vào các trận đấu thể thao đa dạng, từ bóng đá, bóng rổ, đến các sự kiện thể thao quốc tế với tỷ lệ cược hấp dẫn.
Game Bài: Đây là một sân chơi dành cho những ai yêu thích các trò chơi bài như tiến lên miền Nam, phỏm, xì dách, và mậu binh. Các trò chơi được phát triển kỹ lưỡng, đem lại cảm giác chân thực và thú vị.
Nổ Hũ: Trò chơi slot với cơ hội trúng Jackpot cực lớn, luôn thu hút sự chú ý của người chơi. Nổ Hũ RGBET là sân chơi hoàn hảo cho những ai muốn thử vận may và giành lấy những phần thưởng khủng.
Lô Đề: Với tỷ lệ trả thưởng cao và nhiều tùy chọn cược, RGBET là nơi lý tưởng cho những người đam mê lô đề.
Tính Năng Nổi Bật Của RGBET
Một trong những điểm nổi bật của RGBET là giao diện thân thiện, dễ sử dụng và hệ thống bảo mật tiên tiến giúp bảo vệ thông tin người chơi. Ngoài ra, nhà cái này còn hỗ trợ các hình thức nạp rút tiền tiện lợi thông qua nhiều kênh khác nhau như OVO, Gopay, Dana, và các chuỗi cửa hàng như Indomaret và Alfamart.
Khuyến Mãi và Dịch Vụ Chăm Sóc Khách Hàng
RGBET không chỉ nổi bật với các trò chơi đa dạng, mà còn cung cấp nhiều chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn như bonus chào mừng, cashback, và các phần thưởng hàng ngày. Đặc biệt, dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng của RGBET hoạt động 24/7 với đội ngũ chuyên nghiệp, sẵn sàng hỗ trợ người chơi qua nhiều kênh liên lạc.
Kết Luận
Với những ưu điểm nổi bật về dịch vụ, bảo mật, và trải nghiệm người dùng, RGBET xứng đáng là nhà cái hàng đầu mà người chơi nên lựa chọn khi tham gia vào thế giới cá cược trực tuyến. -
st666 app
ST666 – Lựa Chọn Hàng Đầu Trong Thế Giới Cá Cược Trực Tuyến
Trong thời đại mà ngành công nghiệp cá cược trực tuyến đang bùng nổ, việc chọn một nhà cái uy tín là yếu tố quan trọng để đảm bảo trải nghiệm chơi an toàn và đáng tin cậy. ST666 nhanh chóng khẳng định vị thế của mình trên thị trường với những dịch vụ chất lượng và hệ thống bảo mật cao cấp, mang lại trải nghiệm cá cược công bằng, thú vị và an toàn.
Hệ Thống Trò Chơi Đa Dạng
ST666 cung cấp một danh mục trò chơi cá cược đa dạng, đáp ứng mọi nhu cầu và sở thích của người chơi. Từ thể thao, bắn cá, game bài, cho đến xổ số và live casino, tất cả đều được tối ưu hóa để mang lại cảm giác hứng thú cho người tham gia. Đặc biệt, với Live Casino, người chơi sẽ được trải nghiệm cá cược với các dealer thật thông qua hình thức phát trực tiếp, tạo cảm giác như đang tham gia tại các sòng bài thực tế.
Tỷ Lệ Cược Cạnh Tranh
Một trong những ưu điểm nổi bật của ST666 chính là tỷ lệ cược cực kỳ cạnh tranh, giúp người chơi tối ưu hóa lợi nhuận của mình. Các trận đấu thể thao được cập nhật liên tục với tỷ lệ cược hấp dẫn, tạo cơ hội chiến thắng lớn cho những ai yêu thích cá cược thể thao.
Bảo Mật An Toàn Tuyệt Đối
Yếu tố bảo mật luôn là một trong những tiêu chí hàng đầu khi chọn nhà cái cá cược. ST666 sử dụng công nghệ mã hóa hiện đại để bảo vệ thông tin cá nhân và các giao dịch tài chính của người chơi, đảm bảo mọi dữ liệu luôn được bảo mật tuyệt đối. Người chơi hoàn toàn có thể yên tâm khi tham gia cá cược tại đây.
Chăm Sóc Khách Hàng Chuyên Nghiệp
Dịch vụ chăm sóc khách hàng của ST666 luôn sẵn sàng hỗ trợ 24/7 qua nhiều kênh khác nhau như Live Chat, WhatsApp, Facebook, đảm bảo giải đáp mọi thắc mắc và xử lý các vấn đề nhanh chóng. Đội ngũ nhân viên tại đây được đào tạo chuyên nghiệp, tận tâm và chu đáo, luôn đặt lợi ích của khách hàng lên hàng đầu.
Ưu Đãi Hấp Dẫn
ST666 không chỉ nổi bật với các sản phẩm cá cược mà còn thu hút người chơi bởi các chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn. Người chơi có thể nhận được nhiều ưu đãi như 280k miễn phí khi đăng nhập hàng ngày, cùng các chương trình thưởng nạp và hoàn tiền liên tục, giúp tối đa hóa cơ hội chiến thắng.
Lý Do ST666 Là Lựa Chọn Hàng Đầu
Sự kết hợp hoàn hảo giữa giao diện hiện đại, hệ thống trò chơi đa dạng, dịch vụ khách hàng tận tâm và tỷ lệ cược cạnh tranh đã giúp ST666 trở thành một trong những nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến uy tín hàng đầu tại Việt Nam. Đối với những ai đang tìm kiếm một nhà cái an toàn và chuyên nghiệp, ST666 chắc chắn sẽ là lựa chọn không thể bỏ qua.
Kết Luận
Với những ưu điểm vượt trội, ST666 xứng đáng là địa chỉ cá cược uy tín và an toàn cho tất cả người chơi. Đăng ký ngay hôm nay để trải nghiệm hệ thống cá cược đẳng cấp và nhận những ưu đãi hấp dẫn từ ST666! -
Over 7 years in development, the Rollga Method™ combines trigger points, acupressure points, fascial lines, meridians, and techniques like ART (Active Release Technique), MAT (Muscle Activation Technique), RPR (Reflexive Performance Reset) and others to optimize one’s health thru a new system of self care.
Download the Rollga App to learn about & tap into all that Rollga has to offer! -
Over 7 years in development, the Rollga Method™ combines trigger points, acupressure points, fascial lines, meridians, and techniques like ART (Active Release Technique), MAT (Muscle Activation Technique), RPR (Reflexive Performance Reset) and others to optimize one’s health thru a new system of self care.
Download the Rollga App to learn about & tap into all that Rollga has to offer! -
foam roller for low back pain
Over 7 years in development, the Rollga Method™ combines trigger points, acupressure points, fascial lines, meridians, and techniques like ART (Active Release Technique), MAT (Muscle Activation Technique), RPR (Reflexive Performance Reset) and others to optimize one’s health thru a new system of self care.
Download the Rollga App to learn about & tap into all that Rollga has to offer! -
Over 7 years in development, the Rollga Method™ combines trigger points, acupressure points, fascial lines, meridians, and techniques like ART (Active Release Technique), MAT (Muscle Activation Technique), RPR (Reflexive Performance Reset) and others to optimize one’s health thru a new system of self care.
Download the Rollga App to learn about & tap into all that Rollga has to offer! -
kometa casino официальный зеркало
Kometa Casino: Идеальный вариант для ценителей азартного досуга
Когда вы интересуетесь азартными играми и ищете платформу, которая предлагает широкий выбор слотов и игр с живыми дилерами, а плюс щедрые бонусы, Kometa Casino — это та площадка, в котором вы испытаете незабываемые впечатления. Попробуем рассмотрим, какие факторы делает Kometa Casino таким особенным и почему игроки остановились на его для досуга.
### Главные особенности Kometa Casino
Казино Kometa — это глобальная игровая платформа, которая была запущена в 2024-м и уже получила интерес клиентов по глобально. Вот некоторые черты, которые отличают данную платформу:
Функция Сведения
Год создания 2024
Глобальная доступность Международная
Число игр Свыше 1000
Регистрация Кюрасао
Мобильная Версия Да
Способы Оплаты Visa, Mastercard, Skrill
Служба поддержки 24/7 Чат и Email
Специальные предложения Щедрые бонусы
Система безопасности SSL Шифрование
### Что привлекает в Казино Kometa?
#### Программа лояльности
Одной из самых привлекательных функций Казино Kometa является уникальная программа лояльности. Чем больше ставок, тем лучше призы и бонусы. Программа включает 7 этапов:
- **Земля (уровень 1)**: Возврат 3% от затрат за неделю.
- **Луна (уровень 2)**: Кэшбек 5% при ставках от 5 000 до 10 000 рублей.
- **Уровень 3 — Венера**: Возврат 7% при ставках от 10 001 до 50 000 рублей.
- **Марс (уровень 4)**: 8% бонуса при сумме ставок от 50 001 до 150 000 RUB.
- **Юпитер (уровень 5)**: 10% возврата при общей ставке свыше 150 000 RUB.
- **Уровень 6 — Сатурн**: 11% кэшбек.
- **Уран (уровень 7)**: Максимальный кэшбек до 12%.
#### Еженедельные бонусы и кэшбек
Для сохранения азарт на высоте, Казино Kometa проводит бонусы каждую неделю, возврат средств и фриспины для новых пользователей. Постоянные подарки обеспечивают удерживать внимание на каждой стадии игры.
#### Огромный каталог игр
Свыше тысячи игр, включая игровые машины, карточные игры и живое казино, делают Казино Kometa сайтом, где вы найдете подходящее развлечение. Каждый может играть классическими играми, а также новинками от известных разработчиков. Прямые дилеры создают играм еще больше реализма, формируя атмосферу азартного дома. -
kometa casino актуальное
Kometa Casino: Лучший выбор для ценителей азартного досуга
Если вы являетесь интересуетесь ставками и рассматриваете сайт, которая предлагает большой выбор слотов и игр с живыми дилерами, а к тому же щедрые бонусы, Kometa Casino — это тот сайт, в котором вы найдете незабываемый опыт. Попробуем узнаем, что выделяет Kometa Casino таким особенным и почему клиенты отдают предпочтение этом сайте для игры.
### Главные особенности Kometa Casino
Kometa Casino — это всемирная платформа, что была запущена в 2024-м и сейчас уже получила признание клиентов по глобально. Вот основные моменты, которые сравнивают с другими этот сайт:
Характеристика Детали
Год Основания 2024-й
Охват Глобальная
Количество Игр Более 1000
Лицензия Лицензия Кюрасао
Мобильный доступ Доступна
Способы Оплаты Visa, Mastercard, Skrill
Техподдержка Круглосуточная поддержка
Приветственные бонусы Акции и бонусы
Система безопасности Шифрование SSL
### Что привлекает в Kometa Casino?
#### Программа лояльности
Одним из самых привлекательных фишек Kometa Casino считается поощрительная программа. Чем больше вы играете, тем лучше призы и бонусы. Программа состоит из 7 этапов:
- **Земля (уровень 1)**: Возврат 3% от ставок за неделю.
- **Уровень 2 — Луна**: 5% кэшбек при ставках от 5 000 до 10 000 RUB.
- **Уровень 3 — Венера**: Кэшбек 7% при игре от 10 001 до 50 000 рублей.
- **Уровень 4 — Марс**: 8% кэшбек при ставках от 50 001 до 150 000 рублей.
- **Уровень 5 — Юпитер**: 10% возврата при общей ставке свыше 150 000 ?.
- **Уровень 6 — Сатурн**: 11% бонуса.
- **Уран (уровень 7)**: Максимальный кэшбек 12%.
#### Постоянные бонусы
Чтобы держать игровой активности, Казино Kometa предлагает еженедельные бонусы, возврат средств и спины для новых пользователей. Постоянные подарки обеспечивают поддерживать азарт на протяжении всей игры.
#### Огромный каталог игр
Огромное количество развлечений, включая автоматы, настольные развлечения и игры с живыми дилерами, превращают Kometa Casino местом, где любой найдет подходящее развлечение. Каждый может играть как классическими слотами, и современными слотами от ведущих провайдеров. Живые дилеры создают атмосфере настоящее казино, воссоздавая дух казино. -
foam roller for low back pain
Over 7 years in development, the Rollga Method™ combines trigger points, acupressure points, fascial lines, meridians, and techniques like ART (Active Release Technique), MAT (Muscle Activation Technique), RPR (Reflexive Performance Reset) and others to optimize one’s health thru a new system of self care.
Download the Rollga App to learn about & tap into all that Rollga has to offer! -
body roller
Over 7 years in development, the Rollga Method™ combines trigger points, acupressure points, fascial lines, meridians, and techniques like ART (Active Release Technique), MAT (Muscle Activation Technique), RPR (Reflexive Performance Reset) and others to optimize one’s health thru a new system of self care.
Download the Rollga App to learn about & tap into all that Rollga has to offer! -
https://тату-академия.рф/
-
https://выкуп-авто74.рф/
-
이용 안내 및 주요 정보
배송대행 이용방법
배송대행은 해외에서 구매한 상품을 중간지점(배대지)에 보내고, 이를 통해 한국으로 배송받는 서비스입니다. 먼저, 회원가입을 진행하고, 해당 배대지 주소를 이용해 상품을 주문한 후, 배송대행 신청서를 작성하여 배송 정보를 입력합니다. 모든 과정은 웹사이트를 통해 관리되며, 필요한 경우 고객센터를 통해 지원을 받을 수 있습니다.
구매대행 이용방법
구매대행은 해외 쇼핑몰에서 직접 구매가 어려운 경우, 대행 업체가 대신 구매해주는 서비스입니다. 고객이 원하는 상품 정보를 제공하면, 구매대행 신청서를 작성하고 대행료와 함께 결제하면 업체가 구매를 완료해줍니다. 이후 상품이 배대지로 도착하면 배송대행 절차를 통해 상품을 수령할 수 있습니다.
배송비용 안내
배송비용은 상품의 무게, 크기, 배송 지역에 따라 다르며, 계산기는 웹사이트에서 제공됩니다. 부피무게가 큰 제품이나 특수 제품은 추가 비용이 발생할 수 있습니다. 항공과 해운에 따른 요금 차이도 고려해야 합니다.
부가서비스
추가 포장 서비스, 검역 서비스, 폐기 서비스 등이 제공되며, 필요한 경우 신청서를 작성하여 서비스 이용이 가능합니다. 파손 위험이 있는 제품의 경우 포장 보완 서비스를 신청하는 것이 좋습니다.
관/부가세 안내
수입된 상품에 대한 관세와 부가세는 상품의 종류와 가격에 따라 부과됩니다. 이를 미리 확인하고, 추가 비용을 예상하여 계산하는 것이 중요합니다.
수입금지 품목
가스제품(히터), 폭발물, 위험물 등은 수입이 금지된 품목에 속합니다. 항공 및 해상 운송이 불가하니, 반드시 해당 품목을 확인 후 주문해야 합니다.
폐기/검역 안내
검역이 필요한 상품이나 폐기가 필요한 경우, 사전에 관련 부가서비스를 신청해야 합니다. 해당 사항에 대해 미리 안내받고 처리할 수 있도록 주의해야 합니다.
교환/반품 안내
교환 및 반품 절차는 상품을 배송받은 후 7일 이내에 신청이 가능합니다. 단, 일부 상품은 교환 및 반품이 제한될 수 있으니 사전에 정책을 확인하는 것이 좋습니다.
재고관리 시스템
재고관리는 배대지에서 보관 중인 상품의 상태를 실시간으로 확인할 수 있는 시스템입니다. 재고 신청을 통해 상품의 상태를 확인하고, 필요한 경우 배송 또는 폐기 요청을 할 수 있습니다.
노데이타 처리방법
노데이타 상태의 상품은 배송 추적이 어려운 경우 발생합니다. 이런 경우 고객센터를 통해 문의하고 문제를 해결해야 합니다.
소비세환급 및 Q&A
일본에서 상품을 구매할 때 적용된 소비세를 환급받을 수 있는 서비스입니다. 해당 신청서는 구체적인 절차에 따라 작성하고 제출해야 합니다. Q&A를 통해 자주 묻는 질문을 확인하고, 추가 문의 사항은 고객센터에 연락해 해결할 수 있습니다.
고객지원
고객센터는 1:1 문의, 카카오톡 상담 등을 통해 서비스 이용 중 발생하는 문제나 문의사항을 해결할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
서비스 관련 공지사항
파손이 쉬운 제품의 경우, 추가 포장 보완을 반드시 요청해야 합니다.
가스제품(히터)은 통관이 불가하므로 구매 전 확인 바랍니다.
항공 운송 비용이 대폭 인하되었습니다. -
이용 안내 및 주요 정보
배송대행 이용방법
배송대행은 해외에서 구매한 상품을 중간지점(배대지)에 보내고, 이를 통해 한국으로 배송받는 서비스입니다. 먼저, 회원가입을 진행하고, 해당 배대지 주소를 이용해 상품을 주문한 후, 배송대행 신청서를 작성하여 배송 정보를 입력합니다. 모든 과정은 웹사이트를 통해 관리되며, 필요한 경우 고객센터를 통해 지원을 받을 수 있습니다.
구매대행 이용방법
구매대행은 해외 쇼핑몰에서 직접 구매가 어려운 경우, 대행 업체가 대신 구매해주는 서비스입니다. 고객이 원하는 상품 정보를 제공하면, 구매대행 신청서를 작성하고 대행료와 함께 결제하면 업체가 구매를 완료해줍니다. 이후 상품이 배대지로 도착하면 배송대행 절차를 통해 상품을 수령할 수 있습니다.
배송비용 안내
배송비용은 상품의 무게, 크기, 배송 지역에 따라 다르며, 계산기는 웹사이트에서 제공됩니다. 부피무게가 큰 제품이나 특수 제품은 추가 비용이 발생할 수 있습니다. 항공과 해운에 따른 요금 차이도 고려해야 합니다.
부가서비스
추가 포장 서비스, 검역 서비스, 폐기 서비스 등이 제공되며, 필요한 경우 신청서를 작성하여 서비스 이용이 가능합니다. 파손 위험이 있는 제품의 경우 포장 보완 서비스를 신청하는 것이 좋습니다.
관/부가세 안내
수입된 상품에 대한 관세와 부가세는 상품의 종류와 가격에 따라 부과됩니다. 이를 미리 확인하고, 추가 비용을 예상하여 계산하는 것이 중요합니다.
수입금지 품목
가스제품(히터), 폭발물, 위험물 등은 수입이 금지된 품목에 속합니다. 항공 및 해상 운송이 불가하니, 반드시 해당 품목을 확인 후 주문해야 합니다.
폐기/검역 안내
검역이 필요한 상품이나 폐기가 필요한 경우, 사전에 관련 부가서비스를 신청해야 합니다. 해당 사항에 대해 미리 안내받고 처리할 수 있도록 주의해야 합니다.
교환/반품 안내
교환 및 반품 절차는 상품을 배송받은 후 7일 이내에 신청이 가능합니다. 단, 일부 상품은 교환 및 반품이 제한될 수 있으니 사전에 정책을 확인하는 것이 좋습니다.
재고관리 시스템
재고관리는 배대지에서 보관 중인 상품의 상태를 실시간으로 확인할 수 있는 시스템입니다. 재고 신청을 통해 상품의 상태를 확인하고, 필요한 경우 배송 또는 폐기 요청을 할 수 있습니다.
노데이타 처리방법
노데이타 상태의 상품은 배송 추적이 어려운 경우 발생합니다. 이런 경우 고객센터를 통해 문의하고 문제를 해결해야 합니다.
소비세환급 및 Q&A
일본에서 상품을 구매할 때 적용된 소비세를 환급받을 수 있는 서비스입니다. 해당 신청서는 구체적인 절차에 따라 작성하고 제출해야 합니다. Q&A를 통해 자주 묻는 질문을 확인하고, 추가 문의 사항은 고객센터에 연락해 해결할 수 있습니다.
고객지원
고객센터는 1:1 문의, 카카오톡 상담 등을 통해 서비스 이용 중 발생하는 문제나 문의사항을 해결할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
서비스 관련 공지사항
파손이 쉬운 제품의 경우, 추가 포장 보완을 반드시 요청해야 합니다.
가스제품(히터)은 통관이 불가하므로 구매 전 확인 바랍니다.
항공 운송 비용이 대폭 인하되었습니다. -
일본배대지
이용 안내 및 주요 정보
배송대행 이용방법
배송대행은 해외에서 구매한 상품을 중간지점(배대지)에 보내고, 이를 통해 한국으로 배송받는 서비스입니다. 먼저, 회원가입을 진행하고, 해당 배대지 주소를 이용해 상품을 주문한 후, 배송대행 신청서를 작성하여 배송 정보를 입력합니다. 모든 과정은 웹사이트를 통해 관리되며, 필요한 경우 고객센터를 통해 지원을 받을 수 있습니다.
구매대행 이용방법
구매대행은 해외 쇼핑몰에서 직접 구매가 어려운 경우, 대행 업체가 대신 구매해주는 서비스입니다. 고객이 원하는 상품 정보를 제공하면, 구매대행 신청서를 작성하고 대행료와 함께 결제하면 업체가 구매를 완료해줍니다. 이후 상품이 배대지로 도착하면 배송대행 절차를 통해 상품을 수령할 수 있습니다.
배송비용 안내
배송비용은 상품의 무게, 크기, 배송 지역에 따라 다르며, 계산기는 웹사이트에서 제공됩니다. 부피무게가 큰 제품이나 특수 제품은 추가 비용이 발생할 수 있습니다. 항공과 해운에 따른 요금 차이도 고려해야 합니다.
부가서비스
추가 포장 서비스, 검역 서비스, 폐기 서비스 등이 제공되며, 필요한 경우 신청서를 작성하여 서비스 이용이 가능합니다. 파손 위험이 있는 제품의 경우 포장 보완 서비스를 신청하는 것이 좋습니다.
관/부가세 안내
수입된 상품에 대한 관세와 부가세는 상품의 종류와 가격에 따라 부과됩니다. 이를 미리 확인하고, 추가 비용을 예상하여 계산하는 것이 중요합니다.
수입금지 품목
가스제품(히터), 폭발물, 위험물 등은 수입이 금지된 품목에 속합니다. 항공 및 해상 운송이 불가하니, 반드시 해당 품목을 확인 후 주문해야 합니다.
폐기/검역 안내
검역이 필요한 상품이나 폐기가 필요한 경우, 사전에 관련 부가서비스를 신청해야 합니다. 해당 사항에 대해 미리 안내받고 처리할 수 있도록 주의해야 합니다.
교환/반품 안내
교환 및 반품 절차는 상품을 배송받은 후 7일 이내에 신청이 가능합니다. 단, 일부 상품은 교환 및 반품이 제한될 수 있으니 사전에 정책을 확인하는 것이 좋습니다.
재고관리 시스템
재고관리는 배대지에서 보관 중인 상품의 상태를 실시간으로 확인할 수 있는 시스템입니다. 재고 신청을 통해 상품의 상태를 확인하고, 필요한 경우 배송 또는 폐기 요청을 할 수 있습니다.
노데이타 처리방법
노데이타 상태의 상품은 배송 추적이 어려운 경우 발생합니다. 이런 경우 고객센터를 통해 문의하고 문제를 해결해야 합니다.
소비세환급 및 Q&A
일본에서 상품을 구매할 때 적용된 소비세를 환급받을 수 있는 서비스입니다. 해당 신청서는 구체적인 절차에 따라 작성하고 제출해야 합니다. Q&A를 통해 자주 묻는 질문을 확인하고, 추가 문의 사항은 고객센터에 연락해 해결할 수 있습니다.
고객지원
고객센터는 1:1 문의, 카카오톡 상담 등을 통해 서비스 이용 중 발생하는 문제나 문의사항을 해결할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
서비스 관련 공지사항
파손이 쉬운 제품의 경우, 추가 포장 보완을 반드시 요청해야 합니다.
가스제품(히터)은 통관이 불가하므로 구매 전 확인 바랍니다.
항공 운송 비용이 대폭 인하되었습니다. -
이용 안내 및 주요 정보
배송대행 이용방법
배송대행은 해외에서 구매한 상품을 중간지점(배대지)에 보내고, 이를 통해 한국으로 배송받는 서비스입니다. 먼저, 회원가입을 진행하고, 해당 배대지 주소를 이용해 상품을 주문한 후, 배송대행 신청서를 작성하여 배송 정보를 입력합니다. 모든 과정은 웹사이트를 통해 관리되며, 필요한 경우 고객센터를 통해 지원을 받을 수 있습니다.
구매대행 이용방법
구매대행은 해외 쇼핑몰에서 직접 구매가 어려운 경우, 대행 업체가 대신 구매해주는 서비스입니다. 고객이 원하는 상품 정보를 제공하면, 구매대행 신청서를 작성하고 대행료와 함께 결제하면 업체가 구매를 완료해줍니다. 이후 상품이 배대지로 도착하면 배송대행 절차를 통해 상품을 수령할 수 있습니다.
배송비용 안내
배송비용은 상품의 무게, 크기, 배송 지역에 따라 다르며, 계산기는 웹사이트에서 제공됩니다. 부피무게가 큰 제품이나 특수 제품은 추가 비용이 발생할 수 있습니다. 항공과 해운에 따른 요금 차이도 고려해야 합니다.
부가서비스
추가 포장 서비스, 검역 서비스, 폐기 서비스 등이 제공되며, 필요한 경우 신청서를 작성하여 서비스 이용이 가능합니다. 파손 위험이 있는 제품의 경우 포장 보완 서비스를 신청하는 것이 좋습니다.
관/부가세 안내
수입된 상품에 대한 관세와 부가세는 상품의 종류와 가격에 따라 부과됩니다. 이를 미리 확인하고, 추가 비용을 예상하여 계산하는 것이 중요합니다.
수입금지 품목
가스제품(히터), 폭발물, 위험물 등은 수입이 금지된 품목에 속합니다. 항공 및 해상 운송이 불가하니, 반드시 해당 품목을 확인 후 주문해야 합니다.
폐기/검역 안내
검역이 필요한 상품이나 폐기가 필요한 경우, 사전에 관련 부가서비스를 신청해야 합니다. 해당 사항에 대해 미리 안내받고 처리할 수 있도록 주의해야 합니다.
교환/반품 안내
교환 및 반품 절차는 상품을 배송받은 후 7일 이내에 신청이 가능합니다. 단, 일부 상품은 교환 및 반품이 제한될 수 있으니 사전에 정책을 확인하는 것이 좋습니다.
재고관리 시스템
재고관리는 배대지에서 보관 중인 상품의 상태를 실시간으로 확인할 수 있는 시스템입니다. 재고 신청을 통해 상품의 상태를 확인하고, 필요한 경우 배송 또는 폐기 요청을 할 수 있습니다.
노데이타 처리방법
노데이타 상태의 상품은 배송 추적이 어려운 경우 발생합니다. 이런 경우 고객센터를 통해 문의하고 문제를 해결해야 합니다.
소비세환급 및 Q&A
일본에서 상품을 구매할 때 적용된 소비세를 환급받을 수 있는 서비스입니다. 해당 신청서는 구체적인 절차에 따라 작성하고 제출해야 합니다. Q&A를 통해 자주 묻는 질문을 확인하고, 추가 문의 사항은 고객센터에 연락해 해결할 수 있습니다.
고객지원
고객센터는 1:1 문의, 카카오톡 상담 등을 통해 서비스 이용 중 발생하는 문제나 문의사항을 해결할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
서비스 관련 공지사항
파손이 쉬운 제품의 경우, 추가 포장 보완을 반드시 요청해야 합니다.
가스제품(히터)은 통관이 불가하므로 구매 전 확인 바랍니다.
항공 운송 비용이 대폭 인하되었습니다. -
일본배대지
이용 안내 및 주요 정보
배송대행 이용방법
배송대행은 해외에서 구매한 상품을 중간지점(배대지)에 보내고, 이를 통해 한국으로 배송받는 서비스입니다. 먼저, 회원가입을 진행하고, 해당 배대지 주소를 이용해 상품을 주문한 후, 배송대행 신청서를 작성하여 배송 정보를 입력합니다. 모든 과정은 웹사이트를 통해 관리되며, 필요한 경우 고객센터를 통해 지원을 받을 수 있습니다.
구매대행 이용방법
구매대행은 해외 쇼핑몰에서 직접 구매가 어려운 경우, 대행 업체가 대신 구매해주는 서비스입니다. 고객이 원하는 상품 정보를 제공하면, 구매대행 신청서를 작성하고 대행료와 함께 결제하면 업체가 구매를 완료해줍니다. 이후 상품이 배대지로 도착하면 배송대행 절차를 통해 상품을 수령할 수 있습니다.
배송비용 안내
배송비용은 상품의 무게, 크기, 배송 지역에 따라 다르며, 계산기는 웹사이트에서 제공됩니다. 부피무게가 큰 제품이나 특수 제품은 추가 비용이 발생할 수 있습니다. 항공과 해운에 따른 요금 차이도 고려해야 합니다.
부가서비스
추가 포장 서비스, 검역 서비스, 폐기 서비스 등이 제공되며, 필요한 경우 신청서를 작성하여 서비스 이용이 가능합니다. 파손 위험이 있는 제품의 경우 포장 보완 서비스를 신청하는 것이 좋습니다.
관/부가세 안내
수입된 상품에 대한 관세와 부가세는 상품의 종류와 가격에 따라 부과됩니다. 이를 미리 확인하고, 추가 비용을 예상하여 계산하는 것이 중요합니다.
수입금지 품목
가스제품(히터), 폭발물, 위험물 등은 수입이 금지된 품목에 속합니다. 항공 및 해상 운송이 불가하니, 반드시 해당 품목을 확인 후 주문해야 합니다.
폐기/검역 안내
검역이 필요한 상품이나 폐기가 필요한 경우, 사전에 관련 부가서비스를 신청해야 합니다. 해당 사항에 대해 미리 안내받고 처리할 수 있도록 주의해야 합니다.
교환/반품 안내
교환 및 반품 절차는 상품을 배송받은 후 7일 이내에 신청이 가능합니다. 단, 일부 상품은 교환 및 반품이 제한될 수 있으니 사전에 정책을 확인하는 것이 좋습니다.
재고관리 시스템
재고관리는 배대지에서 보관 중인 상품의 상태를 실시간으로 확인할 수 있는 시스템입니다. 재고 신청을 통해 상품의 상태를 확인하고, 필요한 경우 배송 또는 폐기 요청을 할 수 있습니다.
노데이타 처리방법
노데이타 상태의 상품은 배송 추적이 어려운 경우 발생합니다. 이런 경우 고객센터를 통해 문의하고 문제를 해결해야 합니다.
소비세환급 및 Q&A
일본에서 상품을 구매할 때 적용된 소비세를 환급받을 수 있는 서비스입니다. 해당 신청서는 구체적인 절차에 따라 작성하고 제출해야 합니다. Q&A를 통해 자주 묻는 질문을 확인하고, 추가 문의 사항은 고객센터에 연락해 해결할 수 있습니다.
고객지원
고객센터는 1:1 문의, 카카오톡 상담 등을 통해 서비스 이용 중 발생하는 문제나 문의사항을 해결할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
서비스 관련 공지사항
파손이 쉬운 제품의 경우, 추가 포장 보완을 반드시 요청해야 합니다.
가스제품(히터)은 통관이 불가하므로 구매 전 확인 바랍니다.
항공 운송 비용이 대폭 인하되었습니다. -
일본배대지
이용 안내 및 주요 정보
배송대행 이용방법
배송대행은 해외에서 구매한 상품을 중간지점(배대지)에 보내고, 이를 통해 한국으로 배송받는 서비스입니다. 먼저, 회원가입을 진행하고, 해당 배대지 주소를 이용해 상품을 주문한 후, 배송대행 신청서를 작성하여 배송 정보를 입력합니다. 모든 과정은 웹사이트를 통해 관리되며, 필요한 경우 고객센터를 통해 지원을 받을 수 있습니다.
구매대행 이용방법
구매대행은 해외 쇼핑몰에서 직접 구매가 어려운 경우, 대행 업체가 대신 구매해주는 서비스입니다. 고객이 원하는 상품 정보를 제공하면, 구매대행 신청서를 작성하고 대행료와 함께 결제하면 업체가 구매를 완료해줍니다. 이후 상품이 배대지로 도착하면 배송대행 절차를 통해 상품을 수령할 수 있습니다.
배송비용 안내
배송비용은 상품의 무게, 크기, 배송 지역에 따라 다르며, 계산기는 웹사이트에서 제공됩니다. 부피무게가 큰 제품이나 특수 제품은 추가 비용이 발생할 수 있습니다. 항공과 해운에 따른 요금 차이도 고려해야 합니다.
부가서비스
추가 포장 서비스, 검역 서비스, 폐기 서비스 등이 제공되며, 필요한 경우 신청서를 작성하여 서비스 이용이 가능합니다. 파손 위험이 있는 제품의 경우 포장 보완 서비스를 신청하는 것이 좋습니다.
관/부가세 안내
수입된 상품에 대한 관세와 부가세는 상품의 종류와 가격에 따라 부과됩니다. 이를 미리 확인하고, 추가 비용을 예상하여 계산하는 것이 중요합니다.
수입금지 품목
가스제품(히터), 폭발물, 위험물 등은 수입이 금지된 품목에 속합니다. 항공 및 해상 운송이 불가하니, 반드시 해당 품목을 확인 후 주문해야 합니다.
폐기/검역 안내
검역이 필요한 상품이나 폐기가 필요한 경우, 사전에 관련 부가서비스를 신청해야 합니다. 해당 사항에 대해 미리 안내받고 처리할 수 있도록 주의해야 합니다.
교환/반품 안내
교환 및 반품 절차는 상품을 배송받은 후 7일 이내에 신청이 가능합니다. 단, 일부 상품은 교환 및 반품이 제한될 수 있으니 사전에 정책을 확인하는 것이 좋습니다.
재고관리 시스템
재고관리는 배대지에서 보관 중인 상품의 상태를 실시간으로 확인할 수 있는 시스템입니다. 재고 신청을 통해 상품의 상태를 확인하고, 필요한 경우 배송 또는 폐기 요청을 할 수 있습니다.
노데이타 처리방법
노데이타 상태의 상품은 배송 추적이 어려운 경우 발생합니다. 이런 경우 고객센터를 통해 문의하고 문제를 해결해야 합니다.
소비세환급 및 Q&A
일본에서 상품을 구매할 때 적용된 소비세를 환급받을 수 있는 서비스입니다. 해당 신청서는 구체적인 절차에 따라 작성하고 제출해야 합니다. Q&A를 통해 자주 묻는 질문을 확인하고, 추가 문의 사항은 고객센터에 연락해 해결할 수 있습니다.
고객지원
고객센터는 1:1 문의, 카카오톡 상담 등을 통해 서비스 이용 중 발생하는 문제나 문의사항을 해결할 수 있도록 지원합니다.
서비스 관련 공지사항
파손이 쉬운 제품의 경우, 추가 포장 보완을 반드시 요청해야 합니다.
가스제품(히터)은 통관이 불가하므로 구매 전 확인 바랍니다.
항공 운송 비용이 대폭 인하되었습니다. -
kometa casino demo
Kometa Casino: Лучший вариант для любителей игр на удачу
Когда вы являетесь интересуетесь игровыми автоматами и выбираете платформу, что предлагает большой набор слотов и игр с живыми дилерами, а также щедрые бонусы, Казино Kometa — это та площадка, на котором вы испытаете незабываемые впечатления. Попробуем рассмотрим, что делает это казино выдающимся и почему игроки отдают предпочтение этом сайте для досуга.
### Ключевые черты Казино Kometa
Kometa Casino — это международная игровая платформа, которая была создана в 2024-м и сейчас уже завоевала признание пользователей по глобально. Вот основные моменты, которые отличают этот сайт:
Черта Описание
Год Основания Год основания 2024
Охват Международная
Число игр Более 1000
Регистрация Кюрасао
Поддержка мобильных Доступна
Способы Оплаты Visa, Mastercard, Skrill
Служба поддержки 24 часа в сутки
Бонусы и Акции Приветственные бонусы и Еженедельные выигрыши
Защита данных SSL Шифрование
### Почему выбирают Kometa Casino?
#### Бонусная система
Одним из интересных функций Казино Kometa становится уникальная программа лояльности. Чем больше ставок, тем выше ваши бонусы. Система имеет семи уровней:
- **Уровень 1 — Земля**: Возврат 3% от ставок за 7 дней.
- **Луна (уровень 2)**: Кэшбек 5% на ставки от 5 000 до 10 000 ?.
- **Уровень 3 — Венера**: 7% возврата при ставках от 10 001 до 50 000 RUB.
- **Марс (уровень 4)**: Возврат 8% при сумме ставок от 50 001 до 150 000 рублей.
- **Юпитер (уровень 5)**: Возврат 10% при общей ставке свыше 150 000 RUB.
- **Сатурн (уровень 6)**: 11% бонуса.
- **Уран (уровень 7)**: 12% кэшбек до 12%.
#### Акции и возврат средств
С целью удержания игровой активности, Казино Kometa предоставляет бонусы каждую неделю, кэшбек и бесплатные вращения для всех новых игроков. Частые бонусы помогают поддерживать азарт на протяжении всей игры.
#### Большое количество развлечений
Свыше тысячи игр, включая слоты, настольные игры и игры с живыми дилерами, превращают Казино Kometa площадкой, где любой найдет игру по душе. Игроки могут насладиться стандартными автоматами, так и новейшими играми от ведущих провайдеров. Живые дилеры создают атмосфере еще больше реализма, создавая атмосферу настоящего казино. -
Kometa Casino: Лучший вариант для любителей азартного досуга
Если вы любите игровыми автоматами и рассматриваете платформу, которая обеспечивает широкий ассортимент слотов и лайв-игр, а также щедрые бонусы, Kometa Casino — это то место, в котором вас ждут незабываемый опыт. Предлагаем рассмотрим, что делает это казино выдающимся и почему посетители отдают предпочтение этом сайте для своих развлечений.
### Основные характеристики Kometa Casino
Kometa Casino — это глобальная казино, которая была запущена в 2024-м и уже получила внимание клиентов по глобально. Вот основные черты, которые сравнивают с другими этот сайт:
Функция Описание
Дата запуска 2024
География Доступа Международная
Объем игр Более 1000
Лицензия Curacao
Поддержка мобильных Да
Способы Оплаты Популярные платежные системы
Поддержка 24/7 Чат и Email
Бонусы и Акции Приветственные бонусы и Еженедельные выигрыши
Система безопасности Шифрование SSL
### Почему выбирают Kometa Casino?
#### Система поощрений
Одним из самых привлекательных фишек Казино Kometa считается система бонусов. Чем активнее играете, тем выше ваши бонусы. Система имеет семи уровней:
- **Уровень 1 — Земля**: Кэшбек 3% от ставок за 7 дней.
- **Луна (уровень 2)**: Возврат 5% при ставках от 5 000 до 10 000 рублей.
- **Венера (уровень 3)**: 7% возврата при ставках на сумму от 10 001 до 50 000 рублей.
- **Уровень 4 — Марс**: 8% кэшбек при ставках от 50 001 до 150 000 RUB.
- **Уровень 5 — Юпитер**: 10% возврата при общей ставке свыше 150 000 RUB.
- **Сатурн (уровень 6)**: Возврат 11%.
- **Уран (уровень 7)**: 12% кэшбек 12%.
#### Еженедельные бонусы и кэшбек
Чтобы держать игровой активности, Казино Kometa проводит бонусы каждую неделю, кэшбек и фриспины для новичков. Постоянные подарки способствуют удерживать внимание на в процессе игры.
#### Широкий выбор игр
Свыше тысячи игр, включая игровые машины, настольные игры и живое казино, делают Казино Kometa сайтом, где вы найдете игру по душе. Каждый может играть как классическими слотами, а также новинками от ведущих провайдеров. Прямые дилеры создают игровому процессу настоящее казино, формируя атмосферу азартного дома. -
Garansi Kekalahan
NAGAEMPIRE: Platform Sports Game dan E-Games Terbaik di Tahun 2024
Selamat datang di Naga Empire, platform hiburan online yang menghadirkan pengalaman gaming terdepan di tahun 2024! Kami bangga menawarkan sports game, permainan kartu, dan berbagai fitur unggulan yang dirancang untuk memberikan Anda kesenangan dan keuntungan maksimal.
Keunggulan Pendaftaran dengan E-Wallet dan QRIS
Kami memprioritaskan kemudahan dan kecepatan dalam pengalaman bermain Anda:
Pendaftaran dengan E-Wallet: Daftarkan akun Anda dengan mudah menggunakan e-wallet favorit. Proses pendaftaran sangat cepat, memungkinkan Anda langsung memulai petualangan gaming tanpa hambatan.
QRIS Auto Proses dalam 1 Detik: Transaksi Anda diproses instan hanya dalam 1 detik dengan teknologi QRIS, memastikan pembayaran dan deposit berjalan lancar tanpa gangguan.
Sports Game dan Permainan Kartu Terbaik di Tahun 2024
Naga Empire menawarkan berbagai pilihan game menarik:
Sports Game Terlengkap: Dari taruhan olahraga hingga fantasy sports, kami menyediakan sensasi taruhan olahraga dengan kualitas terbaik.
Kartu Terbaik di 2024: Nikmati permainan kartu klasik hingga variasi modern dengan grafis yang menakjubkan, memberikan pengalaman bermain yang tak terlupakan.
Permainan Terlengkap dan Toto Terlengkap
Kami memiliki koleksi permainan yang sangat beragam:
Permainan Terlengkap: Temukan berbagai pilihan permainan seperti slot mesin, kasino, hingga permainan berbasis keterampilan, semua tersedia di Naga Empire.
Toto Terlengkap: Layanan Toto Online kami menawarkan pilihan taruhan yang lengkap dengan odds yang kompetitif, memberikan pengalaman taruhan yang optimal.
Bonus Melimpah dan Turnover Terendah
Bonus Melimpah: Dapatkan bonus mulai dari bonus selamat datang, bonus setoran, hingga promosi eksklusif. Kami selalu memberikan nilai lebih pada setiap taruhan Anda.
Turnover Terendah: Dengan turnover rendah, Anda dapat meraih kemenangan lebih mudah dan meningkatkan keuntungan dari setiap permainan.
Naga Empire adalah tempat yang tepat bagi Anda yang mencari pengalaman gaming terbaik di tahun 2024. Bergabunglah sekarang dan rasakan sensasi kemenangan di platform yang paling komprehensif! -
kometa casino на деньги
Kometa Casino: Лучший выбор для фанатов азартных игр
Если вы интересуетесь игровыми автоматами и выбираете площадку, которая дает доступ к большой набор игровых автоматов и живых казино, а плюс выгодные предложения, Казино Kometa — это тот сайт, на котором вы испытаете незабываемые впечатления. Давайте изучим, какие факторы делает это казино таким особенным и почему клиенты отдают предпочтение этом сайте для своих развлечений.
### Главные особенности Kometa Casino
Казино Kometa — это глобальная игровая платформа, которая была запущена в 2024 году и уже привлекла интерес пользователей по глобально. Вот некоторые моменты, что выделяют этот сайт:
Функция Описание
Дата запуска Год основания 2024
Глобальная доступность Глобальная
Количество Игр Более 1000
Регистрация Лицензия Кюрасао
Мобильная Версия Доступна
Методы платежей Visa, Mastercard, Skrill
Техподдержка Круглосуточная поддержка
Специальные предложения Приветственные бонусы и Еженедельные выигрыши
Защита данных SSL защита
### Что привлекает в Казино Kometa?
#### Программа лояльности
Одной из интересных функций Казино Kometa становится система бонусов. Чем больше вы играете, тем выше ваши бонусы. Программа имеет многоуровневую систему:
- **Земля (уровень 1)**: Кэшбек 3% от потраченных средств за 7 дней.
- **Уровень 2 — Луна**: Кэшбек 5% на ставки от 5 000 до 10 000 рублей.
- **Венера (уровень 3)**: 7% возврата при игре от 10 001 до 50 000 ?.
- **Уровень 4 — Марс**: Возврат 8% при ставках от 50 001 до 150 000 RUB.
- **Юпитер (уровень 5)**: 10% возврата при ставках свыше 150 000 рублей.
- **Уровень 6 — Сатурн**: 11% бонуса.
- **Уран (уровень 7)**: 12% кэшбек максимум 12%.
#### Еженедельные бонусы и кэшбек
Для сохранения высокого уровня азарта, Kometa Casino проводит еженедельные бонусы, кэшбек и спины для новых пользователей. Частые бонусы помогают сохранять интерес на протяжении всей игры.
#### Огромный каталог игр
Огромное количество развлечений, включая игровые машины, настольные развлечения и живое казино, превращают Казино Kometa площадкой, где каждый найдет игру по душе. Вы можете наслаждаться стандартными автоматами, так и новейшими играми от ведущих провайдеров. Живые дилеры придают атмосфере еще больше реализма, формируя атмосферу азартного дома. -
kometa casino рабочее зеркало
Казино Kometa: Идеальный выбор для любителей азартного досуга
В случае если вы любите ставками и выбираете платформу, которая дает доступ к широкий выбор слотов и игр с живыми дилерами, а также щедрые бонусы, Kometa Casino — это то место, в котором вас ждут яркие эмоции. Попробуем изучим, что выделяет данное казино выдающимся и почему клиенты остановились на его для игры.
### Главные особенности Казино Kometa
Казино Kometa — это всемирная платформа, что была запущена в 2024 году и уже завоевала интерес пользователей по всему миру. Вот ключевые моменты, что выделяют Kometa Casino:
Характеристика Сведения
Год создания 2024
Глобальная доступность Глобальная
Количество Игр Свыше 1000
Сертификация Кюрасао
Мобильный доступ Да
Варианты оплаты Visa, Mastercard, Skrill
Служба поддержки Круглосуточная поддержка
Бонусы и Акции Акции и бонусы
Защита данных SSL защита
### Что привлекает в Казино Kometa?
#### Бонусная система
Одним из интересных фишек Казино Kometa становится уникальная программа лояльности. Чем активнее играете, тем лучше призы и бонусы. Система включает 7 этапов:
- **Земля (уровень 1)**: Кэшбек 3% от ставок за неделю.
- **Луна (уровень 2)**: Кэшбек 5% при ставках от 5 000 до 10 000 RUB.
- **Венера (уровень 3)**: Возврат 7% при ставках от 10 001 до 50 000 рублей.
- **Марс (уровень 4)**: Возврат 8% при ставках от 50 001 до 150 000 RUB.
- **Юпитер (уровень 5)**: 10% возврата при ставках свыше 150 000 ?.
- **Сатурн (уровень 6)**: 11% кэшбек.
- **Уран (уровень 7)**: 12% кэшбек до 12%.
#### Еженедельные бонусы и кэшбек
Для сохранения азарт на высоте, Kometa Casino проводит бонусы каждую неделю, возврат средств и фриспины для новичков. Постоянные подарки способствуют сохранять интерес на в процессе игры.
#### Огромный каталог игр
Свыше тысячи игр, включая игровые машины, настольные игры и игры с живыми дилерами, создают Kometa Casino сайтом, где каждый найдет подходящее развлечение. Вы можете наслаждаться стандартными автоматами, а также новинками от известных разработчиков. Прямые дилеры создают игровому процессу ощущение реального казино, создавая атмосферу настоящего казино. -
สล็อต888 เป็นหนึ่งในแพลตฟอร์มเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ได้รับความนิยมสูงสุดในปัจจุบัน โดยมีความโดดเด่นด้วยการให้บริการเกมสล็อตที่หลากหลายและมีคุณภาพ รวมถึงฟีเจอร์ที่ช่วยให้ผู้เล่นสามารถเพลิดเพลินกับการเล่นได้อย่างเต็มที่ ในบทความนี้ เราจะมาพูดถึงฟีเจอร์และจุดเด่นของสล็อต888 ที่ทำให้เว็บไซต์นี้ได้รับความนิยมเป็นอย่างมาก
ฟีเจอร์เด่นของ PG สล็อต888
ระบบฝากถอนเงินอัตโนมัติที่รวดเร็ว สล็อต888 ให้บริการระบบฝากถอนเงินแบบอัตโนมัติที่สามารถทำรายการได้ทันที ไม่ต้องรอนาน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นการฝากหรือถอนก็สามารถทำได้ภายในไม่กี่วินาที รองรับการใช้งานผ่านทรูวอลเล็ทและช่องทางอื่น ๆ โดยไม่มีขั้นต่ำในการฝากถอน
รองรับทุกอุปกรณ์ ทุกแพลตฟอร์ม ไม่ว่าคุณจะเล่นจากอุปกรณ์ใดก็ตาม สล็อต888 รองรับทั้งคอมพิวเตอร์ แท็บเล็ต และสมาร์ทโฟน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นระบบ iOS หรือ Android คุณสามารถเข้าถึงเกมสล็อตได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลาเพียงแค่มีอินเทอร์เน็ต
โปรโมชั่นและโบนัสมากมาย สำหรับผู้เล่นใหม่และลูกค้าประจำ สล็อต888 มีโปรโมชั่นต้อนรับ รวมถึงโบนัสพิเศษ เช่น ฟรีสปินและโบนัสเครดิตเพิ่ม ทำให้การเล่นเกมสล็อตกับเราเป็นเรื่องสนุกและมีโอกาสทำกำไรมากยิ่งขึ้น
ความปลอดภัยสูงสุด เรื่องความปลอดภัยเป็นสิ่งที่สล็อต888 ให้ความสำคัญเป็นอย่างยิ่ง เราใช้เทคโนโลยีการเข้ารหัสข้อมูลขั้นสูงเพื่อปกป้องข้อมูลส่วนบุคคลของลูกค้า ระบบฝากถอนเงินยังมีมาตรการรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด ทำให้ลูกค้ามั่นใจในการใช้บริการกับเรา
ทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี
สล็อต888 ยังมีบริการให้ผู้เล่นสามารถทดลองเล่นสล็อตได้ฟรี ซึ่งเป็นโอกาสที่ดีในการทดลองเล่นเกมต่าง ๆ ที่มีอยู่บนเว็บไซต์ เช่น Phoenix Rises, Dream Of Macau, Ways Of Qilin, Caishens Wins และเกมยอดนิยมอื่น ๆ ที่มีกราฟิกสวยงามและรูปแบบการเล่นที่น่าสนใจ
ไม่ว่าจะเป็นเกมแนวผจญภัย เช่น Rise Of Apollo, Dragon Hatch หรือเกมที่มีธีมแห่งความมั่งคั่งอย่าง Crypto Gold, Fortune Tiger, Lucky Piggy ทุกเกมได้รับการออกแบบมาเพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์การเล่นที่น่าจดจำและเต็มไปด้วยความสนุกสนาน
บทสรุป
สล็อต888 เป็นแพลตฟอร์มที่ครบเครื่องเรื่องเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยฟีเจอร์ที่ทันสมัย โปรโมชั่นที่น่าสนใจ และระบบรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด ทำให้คุณมั่นใจได้ว่าการเล่นกับสล็อต888 จะเป็นประสบการณ์ที่ปลอดภัยและเต็มไปด้วยความสนุก -
สล็อต888 เป็นหนึ่งในแพลตฟอร์มเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ได้รับความนิยมสูงสุดในปัจจุบัน โดยมีความโดดเด่นด้วยการให้บริการเกมสล็อตที่หลากหลายและมีคุณภาพ รวมถึงฟีเจอร์ที่ช่วยให้ผู้เล่นสามารถเพลิดเพลินกับการเล่นได้อย่างเต็มที่ ในบทความนี้ เราจะมาพูดถึงฟีเจอร์และจุดเด่นของสล็อต888 ที่ทำให้เว็บไซต์นี้ได้รับความนิยมเป็นอย่างมาก
ฟีเจอร์เด่นของ PG สล็อต888
ระบบฝากถอนเงินอัตโนมัติที่รวดเร็ว สล็อต888 ให้บริการระบบฝากถอนเงินแบบอัตโนมัติที่สามารถทำรายการได้ทันที ไม่ต้องรอนาน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นการฝากหรือถอนก็สามารถทำได้ภายในไม่กี่วินาที รองรับการใช้งานผ่านทรูวอลเล็ทและช่องทางอื่น ๆ โดยไม่มีขั้นต่ำในการฝากถอน
รองรับทุกอุปกรณ์ ทุกแพลตฟอร์ม ไม่ว่าคุณจะเล่นจากอุปกรณ์ใดก็ตาม สล็อต888 รองรับทั้งคอมพิวเตอร์ แท็บเล็ต และสมาร์ทโฟน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นระบบ iOS หรือ Android คุณสามารถเข้าถึงเกมสล็อตได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลาเพียงแค่มีอินเทอร์เน็ต
โปรโมชั่นและโบนัสมากมาย สำหรับผู้เล่นใหม่และลูกค้าประจำ สล็อต888 มีโปรโมชั่นต้อนรับ รวมถึงโบนัสพิเศษ เช่น ฟรีสปินและโบนัสเครดิตเพิ่ม ทำให้การเล่นเกมสล็อตกับเราเป็นเรื่องสนุกและมีโอกาสทำกำไรมากยิ่งขึ้น
ความปลอดภัยสูงสุด เรื่องความปลอดภัยเป็นสิ่งที่สล็อต888 ให้ความสำคัญเป็นอย่างยิ่ง เราใช้เทคโนโลยีการเข้ารหัสข้อมูลขั้นสูงเพื่อปกป้องข้อมูลส่วนบุคคลของลูกค้า ระบบฝากถอนเงินยังมีมาตรการรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด ทำให้ลูกค้ามั่นใจในการใช้บริการกับเรา
ทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี
สล็อต888 ยังมีบริการให้ผู้เล่นสามารถทดลองเล่นสล็อตได้ฟรี ซึ่งเป็นโอกาสที่ดีในการทดลองเล่นเกมต่าง ๆ ที่มีอยู่บนเว็บไซต์ เช่น Phoenix Rises, Dream Of Macau, Ways Of Qilin, Caishens Wins และเกมยอดนิยมอื่น ๆ ที่มีกราฟิกสวยงามและรูปแบบการเล่นที่น่าสนใจ
ไม่ว่าจะเป็นเกมแนวผจญภัย เช่น Rise Of Apollo, Dragon Hatch หรือเกมที่มีธีมแห่งความมั่งคั่งอย่าง Crypto Gold, Fortune Tiger, Lucky Piggy ทุกเกมได้รับการออกแบบมาเพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์การเล่นที่น่าจดจำและเต็มไปด้วยความสนุกสนาน
บทสรุป
สล็อต888 เป็นแพลตฟอร์มที่ครบเครื่องเรื่องเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยฟีเจอร์ที่ทันสมัย โปรโมชั่นที่น่าสนใจ และระบบรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด ทำให้คุณมั่นใจได้ว่าการเล่นกับสล็อต888 จะเป็นประสบการณ์ที่ปลอดภัยและเต็มไปด้วยความสนุก -
สล็อต888 เป็นหนึ่งในแพลตฟอร์มเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ได้รับความนิยมสูงสุดในปัจจุบัน โดยมีความโดดเด่นด้วยการให้บริการเกมสล็อตที่หลากหลายและมีคุณภาพ รวมถึงฟีเจอร์ที่ช่วยให้ผู้เล่นสามารถเพลิดเพลินกับการเล่นได้อย่างเต็มที่ ในบทความนี้ เราจะมาพูดถึงฟีเจอร์และจุดเด่นของสล็อต888 ที่ทำให้เว็บไซต์นี้ได้รับความนิยมเป็นอย่างมาก
ฟีเจอร์เด่นของ PG สล็อต888
ระบบฝากถอนเงินอัตโนมัติที่รวดเร็ว สล็อต888 ให้บริการระบบฝากถอนเงินแบบอัตโนมัติที่สามารถทำรายการได้ทันที ไม่ต้องรอนาน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นการฝากหรือถอนก็สามารถทำได้ภายในไม่กี่วินาที รองรับการใช้งานผ่านทรูวอลเล็ทและช่องทางอื่น ๆ โดยไม่มีขั้นต่ำในการฝากถอน
รองรับทุกอุปกรณ์ ทุกแพลตฟอร์ม ไม่ว่าคุณจะเล่นจากอุปกรณ์ใดก็ตาม สล็อต888 รองรับทั้งคอมพิวเตอร์ แท็บเล็ต และสมาร์ทโฟน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นระบบ iOS หรือ Android คุณสามารถเข้าถึงเกมสล็อตได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลาเพียงแค่มีอินเทอร์เน็ต
โปรโมชั่นและโบนัสมากมาย สำหรับผู้เล่นใหม่และลูกค้าประจำ สล็อต888 มีโปรโมชั่นต้อนรับ รวมถึงโบนัสพิเศษ เช่น ฟรีสปินและโบนัสเครดิตเพิ่ม ทำให้การเล่นเกมสล็อตกับเราเป็นเรื่องสนุกและมีโอกาสทำกำไรมากยิ่งขึ้น
ความปลอดภัยสูงสุด เรื่องความปลอดภัยเป็นสิ่งที่สล็อต888 ให้ความสำคัญเป็นอย่างยิ่ง เราใช้เทคโนโลยีการเข้ารหัสข้อมูลขั้นสูงเพื่อปกป้องข้อมูลส่วนบุคคลของลูกค้า ระบบฝากถอนเงินยังมีมาตรการรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด ทำให้ลูกค้ามั่นใจในการใช้บริการกับเรา
ทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี
สล็อต888 ยังมีบริการให้ผู้เล่นสามารถทดลองเล่นสล็อตได้ฟรี ซึ่งเป็นโอกาสที่ดีในการทดลองเล่นเกมต่าง ๆ ที่มีอยู่บนเว็บไซต์ เช่น Phoenix Rises, Dream Of Macau, Ways Of Qilin, Caishens Wins และเกมยอดนิยมอื่น ๆ ที่มีกราฟิกสวยงามและรูปแบบการเล่นที่น่าสนใจ
ไม่ว่าจะเป็นเกมแนวผจญภัย เช่น Rise Of Apollo, Dragon Hatch หรือเกมที่มีธีมแห่งความมั่งคั่งอย่าง Crypto Gold, Fortune Tiger, Lucky Piggy ทุกเกมได้รับการออกแบบมาเพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์การเล่นที่น่าจดจำและเต็มไปด้วยความสนุกสนาน
บทสรุป
สล็อต888 เป็นแพลตฟอร์มที่ครบเครื่องเรื่องเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยฟีเจอร์ที่ทันสมัย โปรโมชั่นที่น่าสนใจ และระบบรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด ทำให้คุณมั่นใจได้ว่าการเล่นกับสล็อต888 จะเป็นประสบการณ์ที่ปลอดภัยและเต็มไปด้วยความสนุก -
สล็อต888 เป็นหนึ่งในแพลตฟอร์มเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ได้รับความนิยมสูงสุดในปัจจุบัน โดยมีความโดดเด่นด้วยการให้บริการเกมสล็อตที่หลากหลายและมีคุณภาพ รวมถึงฟีเจอร์ที่ช่วยให้ผู้เล่นสามารถเพลิดเพลินกับการเล่นได้อย่างเต็มที่ ในบทความนี้ เราจะมาพูดถึงฟีเจอร์และจุดเด่นของสล็อต888 ที่ทำให้เว็บไซต์นี้ได้รับความนิยมเป็นอย่างมาก
ฟีเจอร์เด่นของ PG สล็อต888
ระบบฝากถอนเงินอัตโนมัติที่รวดเร็ว สล็อต888 ให้บริการระบบฝากถอนเงินแบบอัตโนมัติที่สามารถทำรายการได้ทันที ไม่ต้องรอนาน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นการฝากหรือถอนก็สามารถทำได้ภายในไม่กี่วินาที รองรับการใช้งานผ่านทรูวอลเล็ทและช่องทางอื่น ๆ โดยไม่มีขั้นต่ำในการฝากถอน
รองรับทุกอุปกรณ์ ทุกแพลตฟอร์ม ไม่ว่าคุณจะเล่นจากอุปกรณ์ใดก็ตาม สล็อต888 รองรับทั้งคอมพิวเตอร์ แท็บเล็ต และสมาร์ทโฟน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นระบบ iOS หรือ Android คุณสามารถเข้าถึงเกมสล็อตได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลาเพียงแค่มีอินเทอร์เน็ต
โปรโมชั่นและโบนัสมากมาย สำหรับผู้เล่นใหม่และลูกค้าประจำ สล็อต888 มีโปรโมชั่นต้อนรับ รวมถึงโบนัสพิเศษ เช่น ฟรีสปินและโบนัสเครดิตเพิ่ม ทำให้การเล่นเกมสล็อตกับเราเป็นเรื่องสนุกและมีโอกาสทำกำไรมากยิ่งขึ้น
ความปลอดภัยสูงสุด เรื่องความปลอดภัยเป็นสิ่งที่สล็อต888 ให้ความสำคัญเป็นอย่างยิ่ง เราใช้เทคโนโลยีการเข้ารหัสข้อมูลขั้นสูงเพื่อปกป้องข้อมูลส่วนบุคคลของลูกค้า ระบบฝากถอนเงินยังมีมาตรการรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด ทำให้ลูกค้ามั่นใจในการใช้บริการกับเรา
ทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี
สล็อต888 ยังมีบริการให้ผู้เล่นสามารถทดลองเล่นสล็อตได้ฟรี ซึ่งเป็นโอกาสที่ดีในการทดลองเล่นเกมต่าง ๆ ที่มีอยู่บนเว็บไซต์ เช่น Phoenix Rises, Dream Of Macau, Ways Of Qilin, Caishens Wins และเกมยอดนิยมอื่น ๆ ที่มีกราฟิกสวยงามและรูปแบบการเล่นที่น่าสนใจ
ไม่ว่าจะเป็นเกมแนวผจญภัย เช่น Rise Of Apollo, Dragon Hatch หรือเกมที่มีธีมแห่งความมั่งคั่งอย่าง Crypto Gold, Fortune Tiger, Lucky Piggy ทุกเกมได้รับการออกแบบมาเพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์การเล่นที่น่าจดจำและเต็มไปด้วยความสนุกสนาน
บทสรุป
สล็อต888 เป็นแพลตฟอร์มที่ครบเครื่องเรื่องเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยฟีเจอร์ที่ทันสมัย โปรโมชั่นที่น่าสนใจ และระบบรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด ทำให้คุณมั่นใจได้ว่าการเล่นกับสล็อต888 จะเป็นประสบการณ์ที่ปลอดภัยและเต็มไปด้วยความสนุก -
rgbet
Bạn đang tìm kiếm những trò chơi hot nhất và thú vị nhất tại sòng bạc trực tuyến? RGBET tự hào giới thiệu đến bạn nhiều trò chơi cá cược đặc sắc, bao gồm Baccarat trực tiếp, máy xèng, cá cược thể thao, xổ số và bắn cá, mang đến cho bạn cảm giác hồi hộp đỉnh cao của sòng bạc! Dù bạn yêu thích các trò chơi bài kinh điển hay những máy xèng đầy kịch tính, RGBET đều có thể đáp ứng mọi nhu cầu giải trí của bạn.
RGBET Trò Chơi của Chúng Tôi
Bạn đang tìm kiếm những trò chơi hot nhất và thú vị nhất tại sòng bạc trực tuyến? RGBET tự hào giới thiệu đến bạn nhiều trò chơi cá cược đặc sắc, bao gồm Baccarat trực tiếp, máy xèng, cá cược thể thao, xổ số và bắn cá, mang đến cảm giác hồi hộp đỉnh cao của sòng bạc! Dù bạn yêu thích các trò chơi bài kinh điển hay những máy xèng đầy kịch tính, RGBET đều có thể đáp ứng mọi nhu cầu giải trí của bạn.
RGBET Trò Chơi Đa Dạng
Thể thao: Cá cược thể thao đa dạng với nhiều môn từ bóng đá, tennis đến thể thao điện tử.
Live Casino: Trải nghiệm Baccarat, Roulette, và các trò chơi sòng bài trực tiếp với người chia bài thật.
Nổ hũ: Tham gia các trò chơi nổ hũ với tỷ lệ trúng cao và cơ hội thắng lớn.
Lô đề: Đặt cược lô đề với tỉ lệ cược hấp dẫn.
Bắn cá: Bắn cá RGBET mang đến cảm giác chân thực và hấp dẫn với đồ họa tuyệt đẹp.
RGBET - Máy Xèng Hấp Dẫn Nhất
Khám phá các máy xèng độc đáo tại RGBET với nhiều chủ đề khác nhau và tỷ lệ trả thưởng cao. Những trò chơi nổi bật bao gồm:
RGBET Super Ace
RGBET Đế Quốc Hoàng Kim
RGBET Pharaoh Treasure
RGBET Quyền Vương
RGBET Chuyên Gia Săn Rồng
RGBET Jackpot Fishing
Vì sao nên chọn RGBET?
RGBET không chỉ cung cấp hàng loạt trò chơi đa dạng mà còn mang đến một hệ thống cá cược an toàn và chuyên nghiệp, đảm bảo mọi quyền lợi của người chơi:
Tốc độ nạp tiền nhanh chóng: Chuyển khoản tại RGBET chỉ mất vài phút và tiền sẽ vào tài khoản ngay lập tức, giúp bạn không bỏ lỡ bất kỳ cơ hội nào.
Game đổi thưởng phong phú: Từ cá cược thể thao đến slot game, RGBET cung cấp đầy đủ trò chơi giúp bạn tận hưởng mọi phút giây thư giãn.
Bảo mật tuyệt đối: Với công nghệ mã hóa tiên tiến, tài khoản và tiền vốn của bạn sẽ luôn được bảo vệ một cách an toàn.
Hỗ trợ đa nền tảng: Bạn có thể chơi trên mọi thiết bị, từ máy tính, điện thoại di động (iOS/Android), đến nền tảng H5.
Tải Ứng Dụng RGBET và Nhận Khuyến Mãi Lớn
Hãy tham gia RGBET ngay hôm nay để tận hưởng thế giới giải trí không giới hạn với các trò chơi thể thao, thể thao điện tử, casino trực tuyến, xổ số, và slot game. Quét mã QR và tải ứng dụng RGBET trên điện thoại để trải nghiệm game tốt hơn và nhận nhiều khuyến mãi hấp dẫn!
Tham gia RGBET để bắt đầu cuộc hành trình cá cược đầy thú vị ngay hôm nay! -
Stablecoin TRC20 Transaction Validation and Financial Crime Prevention (Anti-Money Laundering) Methods
As cryptocurrencies like Tether TRC20 increase in usage for fast and inexpensive transfers, the requirement for protection and adherence with Anti-Money Laundering rules expands. Here's how to verify USDT TRC20 transactions and confirm they're not related to unlawful activities.
What does it mean USDT TRC20?
TRON-based USDT is a digital currency on the TRX ledger, pegged in accordance with the US dollar. Famous for its low transaction fees and velocity, it is widely used for international transactions. Checking payments is important to block connections to financial crime or other criminal acts.
Checking USDT TRC20 Transactions
TRONSCAN — This blockchain viewer allows users to monitor and check Tether TRON-based payments using a public address or transaction ID.
Monitoring — Experienced users can monitor unusual patterns such as high-volume or fast payments to identify irregular actions.
AML and Criminal Crypto
Anti-Money Laundering (Anti-Money Laundering) standards help block unlawful transactions in digital assets. Tools like Chainalysis and Elliptic Solutions permit companies and crypto markets to detect and stop illicit funds, which means funds tied to unlawful operations.
Instruments for Regulation
TRONSCAN — To verify TRON-based USDT payment details.
Chain Analysis and Elliptic — Employed by trading platforms to ensure AML compliance and follow illicit activities.
Final Thoughts
Making sure safe and legal USDT TRC20 payments is crucial. Tools like TRX Explorer and AML tools support guard users from interacting with illicit funds, supporting a safe and regulated crypto environment. -
Tether TRON-based Transaction Verification and Anti-Money Laundering (Anti-Money Laundering) Methods
As cryptocurrencies like USDT TRON-based rise in usage for rapid and low-cost transfers, the need for security and compliance with financial crime prevention regulations increases. Here's how to review Tether TRC20 payments and confirm they're not connected to illegal activities.
What is USDT TRC20?
TRON-based USDT is a cryptocurrency on the TRON ledger, priced in line with the USD. Recognized for its cheap transfers and quickness, it is commonly utilized for cross-border transfers. Checking payments is essential to block connections to money laundering or other illegal operations.
Checking USDT TRC20 Payments
TRX Explorer — This ledger tracker allows participants to monitor and check USDT TRON-based payments using a account ID or transfer code.
Supervising — Advanced users can observe unusual patterns such as high-volume or fast transactions to identify irregular activity.
AML and Criminal Crypto
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) rules help stop illicit transactions in crypto markets. Platforms like Chain Analysis and Elliptic permit companies and exchanges to identify and stop criminal crypto, which refers to money tied to criminal actions.
Tools for Compliance
TRONSCAN — To validate USDT TRC20 transfer data.
Chainalysis and Elliptic — Utilized by exchanges to confirm Anti-Money Laundering compliance and monitor illegal actions.
Final Thoughts
Making sure protected and legal TRON-based USDT transfers is essential. Services like TRX Explorer and Anti-Money Laundering tools assist guard users from engaging with criminal crypto, supporting a safe and lawful cryptocurrency space. -
สล็อต888 เป็นหนึ่งในแพลตฟอร์มเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ได้รับความนิยมสูงสุดในปัจจุบัน โดยมีความโดดเด่นด้วยการให้บริการเกมสล็อตที่หลากหลายและมีคุณภาพ รวมถึงฟีเจอร์ที่ช่วยให้ผู้เล่นสามารถเพลิดเพลินกับการเล่นได้อย่างเต็มที่ ในบทความนี้ เราจะมาพูดถึงฟีเจอร์และจุดเด่นของสล็อต888 ที่ทำให้เว็บไซต์นี้ได้รับความนิยมเป็นอย่างมาก
ฟีเจอร์เด่นของ PG สล็อต888
ระบบฝากถอนเงินอัตโนมัติที่รวดเร็ว สล็อต888 ให้บริการระบบฝากถอนเงินแบบอัตโนมัติที่สามารถทำรายการได้ทันที ไม่ต้องรอนาน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นการฝากหรือถอนก็สามารถทำได้ภายในไม่กี่วินาที รองรับการใช้งานผ่านทรูวอลเล็ทและช่องทางอื่น ๆ โดยไม่มีขั้นต่ำในการฝากถอน
รองรับทุกอุปกรณ์ ทุกแพลตฟอร์ม ไม่ว่าคุณจะเล่นจากอุปกรณ์ใดก็ตาม สล็อต888 รองรับทั้งคอมพิวเตอร์ แท็บเล็ต และสมาร์ทโฟน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นระบบ iOS หรือ Android คุณสามารถเข้าถึงเกมสล็อตได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลาเพียงแค่มีอินเทอร์เน็ต
โปรโมชั่นและโบนัสมากมาย สำหรับผู้เล่นใหม่และลูกค้าประจำ สล็อต888 มีโปรโมชั่นต้อนรับ รวมถึงโบนัสพิเศษ เช่น ฟรีสปินและโบนัสเครดิตเพิ่ม ทำให้การเล่นเกมสล็อตกับเราเป็นเรื่องสนุกและมีโอกาสทำกำไรมากยิ่งขึ้น
ความปลอดภัยสูงสุด เรื่องความปลอดภัยเป็นสิ่งที่สล็อต888 ให้ความสำคัญเป็นอย่างยิ่ง เราใช้เทคโนโลยีการเข้ารหัสข้อมูลขั้นสูงเพื่อปกป้องข้อมูลส่วนบุคคลของลูกค้า ระบบฝากถอนเงินยังมีมาตรการรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด ทำให้ลูกค้ามั่นใจในการใช้บริการกับเรา
ทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี
สล็อต888 ยังมีบริการให้ผู้เล่นสามารถทดลองเล่นสล็อตได้ฟรี ซึ่งเป็นโอกาสที่ดีในการทดลองเล่นเกมต่าง ๆ ที่มีอยู่บนเว็บไซต์ เช่น Phoenix Rises, Dream Of Macau, Ways Of Qilin, Caishens Wins และเกมยอดนิยมอื่น ๆ ที่มีกราฟิกสวยงามและรูปแบบการเล่นที่น่าสนใจ
ไม่ว่าจะเป็นเกมแนวผจญภัย เช่น Rise Of Apollo, Dragon Hatch หรือเกมที่มีธีมแห่งความมั่งคั่งอย่าง Crypto Gold, Fortune Tiger, Lucky Piggy ทุกเกมได้รับการออกแบบมาเพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์การเล่นที่น่าจดจำและเต็มไปด้วยความสนุกสนาน
บทสรุป
สล็อต888 เป็นแพลตฟอร์มที่ครบเครื่องเรื่องเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยฟีเจอร์ที่ทันสมัย โปรโมชั่นที่น่าสนใจ และระบบรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด ทำให้คุณมั่นใจได้ว่าการเล่นกับสล็อต888 จะเป็นประสบการณ์ที่ปลอดภัยและเต็มไปด้วยความสนุก -
สล็อต888 เป็นหนึ่งในแพลตฟอร์มเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ที่ได้รับความนิยมสูงสุดในปัจจุบัน โดยมีความโดดเด่นด้วยการให้บริการเกมสล็อตที่หลากหลายและมีคุณภาพ รวมถึงฟีเจอร์ที่ช่วยให้ผู้เล่นสามารถเพลิดเพลินกับการเล่นได้อย่างเต็มที่ ในบทความนี้ เราจะมาพูดถึงฟีเจอร์และจุดเด่นของสล็อต888 ที่ทำให้เว็บไซต์นี้ได้รับความนิยมเป็นอย่างมาก
ฟีเจอร์เด่นของ PG สล็อต888
ระบบฝากถอนเงินอัตโนมัติที่รวดเร็ว สล็อต888 ให้บริการระบบฝากถอนเงินแบบอัตโนมัติที่สามารถทำรายการได้ทันที ไม่ต้องรอนาน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นการฝากหรือถอนก็สามารถทำได้ภายในไม่กี่วินาที รองรับการใช้งานผ่านทรูวอลเล็ทและช่องทางอื่น ๆ โดยไม่มีขั้นต่ำในการฝากถอน
รองรับทุกอุปกรณ์ ทุกแพลตฟอร์ม ไม่ว่าคุณจะเล่นจากอุปกรณ์ใดก็ตาม สล็อต888 รองรับทั้งคอมพิวเตอร์ แท็บเล็ต และสมาร์ทโฟน ไม่ว่าจะเป็นระบบ iOS หรือ Android คุณสามารถเข้าถึงเกมสล็อตได้ทุกที่ทุกเวลาเพียงแค่มีอินเทอร์เน็ต
โปรโมชั่นและโบนัสมากมาย สำหรับผู้เล่นใหม่และลูกค้าประจำ สล็อต888 มีโปรโมชั่นต้อนรับ รวมถึงโบนัสพิเศษ เช่น ฟรีสปินและโบนัสเครดิตเพิ่ม ทำให้การเล่นเกมสล็อตกับเราเป็นเรื่องสนุกและมีโอกาสทำกำไรมากยิ่งขึ้น
ความปลอดภัยสูงสุด เรื่องความปลอดภัยเป็นสิ่งที่สล็อต888 ให้ความสำคัญเป็นอย่างยิ่ง เราใช้เทคโนโลยีการเข้ารหัสข้อมูลขั้นสูงเพื่อปกป้องข้อมูลส่วนบุคคลของลูกค้า ระบบฝากถอนเงินยังมีมาตรการรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด ทำให้ลูกค้ามั่นใจในการใช้บริการกับเรา
ทดลองเล่นสล็อตฟรี
สล็อต888 ยังมีบริการให้ผู้เล่นสามารถทดลองเล่นสล็อตได้ฟรี ซึ่งเป็นโอกาสที่ดีในการทดลองเล่นเกมต่าง ๆ ที่มีอยู่บนเว็บไซต์ เช่น Phoenix Rises, Dream Of Macau, Ways Of Qilin, Caishens Wins และเกมยอดนิยมอื่น ๆ ที่มีกราฟิกสวยงามและรูปแบบการเล่นที่น่าสนใจ
ไม่ว่าจะเป็นเกมแนวผจญภัย เช่น Rise Of Apollo, Dragon Hatch หรือเกมที่มีธีมแห่งความมั่งคั่งอย่าง Crypto Gold, Fortune Tiger, Lucky Piggy ทุกเกมได้รับการออกแบบมาเพื่อสร้างประสบการณ์การเล่นที่น่าจดจำและเต็มไปด้วยความสนุกสนาน
บทสรุป
สล็อต888 เป็นแพลตฟอร์มที่ครบเครื่องเรื่องเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ด้วยฟีเจอร์ที่ทันสมัย โปรโมชั่นที่น่าสนใจ และระบบรักษาความปลอดภัยที่เข้มงวด ทำให้คุณมั่นใจได้ว่าการเล่นกับสล็อต888 จะเป็นประสบการณ์ที่ปลอดภัยและเต็มไปด้วยความสนุก -
USDT TRON-based Payment Validation and AML (AML) Procedures
As digital assets like USDT TRON-based gain adoption for rapid and affordable transactions, the need for safety and conformance with financial crime prevention regulations expands. Here's how to verify Tether TRC20 payments and ensure they're not connected to illicit operations.
What does it mean USDT TRC20?
TRON-based USDT is a digital currency on the TRX network, pegged in line with the US dollar. Famous for its minimal costs and quickness, it is commonly utilized for cross-border payments. Checking transfers is essential to prevent connections to money laundering or other illegal activities.
Verifying USDT TRC20 Payments
TRX Explorer — This blockchain explorer allows participants to track and check USDT TRON-based transfers using a account ID or TXID.
Supervising — Skilled users can track anomalous behaviors such as high-volume or quick transactions to spot suspicious behavior.
AML and Dirty Cryptocurrency
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) regulations assist block illicit money transfers in cryptocurrency. Platforms like Chain Analysis and Elliptic allow companies and trading platforms to identify and prevent illicit funds, which signifies capital related to unlawful operations.
Tools for Compliance
TRONSCAN — To validate USDT TRC20 transfer information.
Chain Analysis and Elliptic — Utilized by exchanges to guarantee AML compliance and track unlawful operations.
Summary
Making sure secure and legal USDT TRC20 transfers is crucial. Platforms like TRX Explorer and AML systems assist shield traders from interacting with criminal crypto, encouraging a protected and compliant crypto environment. -
บาคาร่า
เล่นบาคาร่าแบบรวดเร็วทันใจกับสปีดบาคาร่า
ถ้าคุณเป็นแฟนตัวยงของเกมไพ่บาคาร่า คุณอาจจะเคยชินกับการรอคอยในแต่ละรอบการเดิมพัน และรอจนดีลเลอร์แจกไพ่ในแต่ละตา แต่คุณรู้หรือไม่ว่า ตอนนี้คุณไม่ต้องรออีกต่อไปแล้ว เพราะ SA Gaming ได้พัฒนาเกมบาคาร่าโหมดใหม่ขึ้นมา เพื่อให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นของคุณน่าตื่นเต้นยิ่งขึ้น!
ที่ SA Gaming คุณสามารถเลือกเล่นไพ่บาคาร่าในโหมดที่เรียกว่า สปีดบาคาร่า (Speed Baccarat) โหมดนี้มีคุณสมบัติพิเศษและข้อดีที่น่าสนใจมากมาย:
ระยะเวลาการเดิมพันสั้นลง — คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องรอนานอีกต่อไป ในโหมดสปีดบาคาร่า คุณจะมีเวลาเพียง 12 วินาทีในการวางเดิมพัน ทำให้เกมแต่ละรอบจบได้รวดเร็ว โดยเกมในแต่ละรอบจะใช้เวลาเพียง 20 วินาทีเท่านั้น
ผลตอบแทนต่อผู้เล่นสูง (RTP) — เกมสปีดบาคาร่าให้ผลตอบแทนต่อผู้เล่นสูงถึง 4% ซึ่งเป็นมาตรฐานความเป็นธรรมที่ผู้เล่นสามารถไว้วางใจได้
การเล่นเกมที่รวดเร็วและน่าตื่นเต้น — ระยะเวลาที่สั้นลงทำให้เกมแต่ละรอบดำเนินไปอย่างรวดเร็ว ทันใจ เพิ่มความสนุกและความตื่นเต้นในการเล่น ทำให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นของคุณยิ่งสนุกมากขึ้น
กลไกและรูปแบบการเล่นยังคงเหมือนเดิม — แม้ว่าระยะเวลาจะสั้นลง แต่กลไกและกฎของการเล่น ยังคงเหมือนกับบาคาร่าสดปกติทุกประการ เพียงแค่ปรับเวลาให้เล่นได้รวดเร็วและสะดวกขึ้นเท่านั้น
นอกจากสปีดบาคาร่าแล้ว ที่ SA Gaming ยังมีโหมด No Commission Baccarat หรือบาคาร่าแบบไม่เสียค่าคอมมิชชั่น ซึ่งจะช่วยให้คุณสามารถเพลิดเพลินไปกับการเล่นได้โดยไม่ต้องกังวลเรื่องค่าคอมมิชชั่นเพิ่มเติม
เล่นบาคาร่ากับ SA Gaming คุณจะได้รับประสบการณ์การเล่นที่สนุก ทันสมัย และตรงใจมากที่สุด! -
เล่นบาคาร่าแบบรวดเร็วทันใจกับสปีดบาคาร่า
ถ้าคุณเป็นแฟนตัวยงของเกมไพ่บาคาร่า คุณอาจจะเคยชินกับการรอคอยในแต่ละรอบการเดิมพัน และรอจนดีลเลอร์แจกไพ่ในแต่ละตา แต่คุณรู้หรือไม่ว่า ตอนนี้คุณไม่ต้องรออีกต่อไปแล้ว เพราะ SA Gaming ได้พัฒนาเกมบาคาร่าโหมดใหม่ขึ้นมา เพื่อให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นของคุณน่าตื่นเต้นยิ่งขึ้น!
ที่ SA Gaming คุณสามารถเลือกเล่นไพ่บาคาร่าในโหมดที่เรียกว่า สปีดบาคาร่า (Speed Baccarat) โหมดนี้มีคุณสมบัติพิเศษและข้อดีที่น่าสนใจมากมาย:
ระยะเวลาการเดิมพันสั้นลง — คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องรอนานอีกต่อไป ในโหมดสปีดบาคาร่า คุณจะมีเวลาเพียง 12 วินาทีในการวางเดิมพัน ทำให้เกมแต่ละรอบจบได้รวดเร็ว โดยเกมในแต่ละรอบจะใช้เวลาเพียง 20 วินาทีเท่านั้น
ผลตอบแทนต่อผู้เล่นสูง (RTP) — เกมสปีดบาคาร่าให้ผลตอบแทนต่อผู้เล่นสูงถึง 4% ซึ่งเป็นมาตรฐานความเป็นธรรมที่ผู้เล่นสามารถไว้วางใจได้
การเล่นเกมที่รวดเร็วและน่าตื่นเต้น — ระยะเวลาที่สั้นลงทำให้เกมแต่ละรอบดำเนินไปอย่างรวดเร็ว ทันใจ เพิ่มความสนุกและความตื่นเต้นในการเล่น ทำให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นของคุณยิ่งสนุกมากขึ้น
กลไกและรูปแบบการเล่นยังคงเหมือนเดิม — แม้ว่าระยะเวลาจะสั้นลง แต่กลไกและกฎของการเล่น ยังคงเหมือนกับบาคาร่าสดปกติทุกประการ เพียงแค่ปรับเวลาให้เล่นได้รวดเร็วและสะดวกขึ้นเท่านั้น
นอกจากสปีดบาคาร่าแล้ว ที่ SA Gaming ยังมีโหมด No Commission Baccarat หรือบาคาร่าแบบไม่เสียค่าคอมมิชชั่น ซึ่งจะช่วยให้คุณสามารถเพลิดเพลินไปกับการเล่นได้โดยไม่ต้องกังวลเรื่องค่าคอมมิชชั่นเพิ่มเติม
เล่นบาคาร่ากับ SA Gaming คุณจะได้รับประสบการณ์การเล่นที่สนุก ทันสมัย และตรงใจมากที่สุด! -
เกมบาคาร่า
เล่นบาคาร่าแบบรวดเร็วทันใจกับสปีดบาคาร่า
ถ้าคุณเป็นแฟนตัวยงของเกมไพ่บาคาร่า คุณอาจจะเคยชินกับการรอคอยในแต่ละรอบการเดิมพัน และรอจนดีลเลอร์แจกไพ่ในแต่ละตา แต่คุณรู้หรือไม่ว่า ตอนนี้คุณไม่ต้องรออีกต่อไปแล้ว เพราะ SA Gaming ได้พัฒนาเกมบาคาร่าโหมดใหม่ขึ้นมา เพื่อให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นของคุณน่าตื่นเต้นยิ่งขึ้น!
ที่ SA Gaming คุณสามารถเลือกเล่นไพ่บาคาร่าในโหมดที่เรียกว่า สปีดบาคาร่า (Speed Baccarat) โหมดนี้มีคุณสมบัติพิเศษและข้อดีที่น่าสนใจมากมาย:
ระยะเวลาการเดิมพันสั้นลง — คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องรอนานอีกต่อไป ในโหมดสปีดบาคาร่า คุณจะมีเวลาเพียง 12 วินาทีในการวางเดิมพัน ทำให้เกมแต่ละรอบจบได้รวดเร็ว โดยเกมในแต่ละรอบจะใช้เวลาเพียง 20 วินาทีเท่านั้น
ผลตอบแทนต่อผู้เล่นสูง (RTP) — เกมสปีดบาคาร่าให้ผลตอบแทนต่อผู้เล่นสูงถึง 4% ซึ่งเป็นมาตรฐานความเป็นธรรมที่ผู้เล่นสามารถไว้วางใจได้
การเล่นเกมที่รวดเร็วและน่าตื่นเต้น — ระยะเวลาที่สั้นลงทำให้เกมแต่ละรอบดำเนินไปอย่างรวดเร็ว ทันใจ เพิ่มความสนุกและความตื่นเต้นในการเล่น ทำให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นของคุณยิ่งสนุกมากขึ้น
กลไกและรูปแบบการเล่นยังคงเหมือนเดิม — แม้ว่าระยะเวลาจะสั้นลง แต่กลไกและกฎของการเล่น ยังคงเหมือนกับบาคาร่าสดปกติทุกประการ เพียงแค่ปรับเวลาให้เล่นได้รวดเร็วและสะดวกขึ้นเท่านั้น
นอกจากสปีดบาคาร่าแล้ว ที่ SA Gaming ยังมีโหมด No Commission Baccarat หรือบาคาร่าแบบไม่เสียค่าคอมมิชชั่น ซึ่งจะช่วยให้คุณสามารถเพลิดเพลินไปกับการเล่นได้โดยไม่ต้องกังวลเรื่องค่าคอมมิชชั่นเพิ่มเติม
เล่นบาคาร่ากับ SA Gaming คุณจะได้รับประสบการณ์การเล่นที่สนุก ทันสมัย และตรงใจมากที่สุด! -
เกมบาคาร่า
เล่นบาคาร่าแบบรวดเร็วทันใจกับสปีดบาคาร่า
ถ้าคุณเป็นแฟนตัวยงของเกมไพ่บาคาร่า คุณอาจจะเคยชินกับการรอคอยในแต่ละรอบการเดิมพัน และรอจนดีลเลอร์แจกไพ่ในแต่ละตา แต่คุณรู้หรือไม่ว่า ตอนนี้คุณไม่ต้องรออีกต่อไปแล้ว เพราะ SA Gaming ได้พัฒนาเกมบาคาร่าโหมดใหม่ขึ้นมา เพื่อให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นของคุณน่าตื่นเต้นยิ่งขึ้น!
ที่ SA Gaming คุณสามารถเลือกเล่นไพ่บาคาร่าในโหมดที่เรียกว่า สปีดบาคาร่า (Speed Baccarat) โหมดนี้มีคุณสมบัติพิเศษและข้อดีที่น่าสนใจมากมาย:
ระยะเวลาการเดิมพันสั้นลง — คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องรอนานอีกต่อไป ในโหมดสปีดบาคาร่า คุณจะมีเวลาเพียง 12 วินาทีในการวางเดิมพัน ทำให้เกมแต่ละรอบจบได้รวดเร็ว โดยเกมในแต่ละรอบจะใช้เวลาเพียง 20 วินาทีเท่านั้น
ผลตอบแทนต่อผู้เล่นสูง (RTP) — เกมสปีดบาคาร่าให้ผลตอบแทนต่อผู้เล่นสูงถึง 4% ซึ่งเป็นมาตรฐานความเป็นธรรมที่ผู้เล่นสามารถไว้วางใจได้
การเล่นเกมที่รวดเร็วและน่าตื่นเต้น — ระยะเวลาที่สั้นลงทำให้เกมแต่ละรอบดำเนินไปอย่างรวดเร็ว ทันใจ เพิ่มความสนุกและความตื่นเต้นในการเล่น ทำให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นของคุณยิ่งสนุกมากขึ้น
กลไกและรูปแบบการเล่นยังคงเหมือนเดิม — แม้ว่าระยะเวลาจะสั้นลง แต่กลไกและกฎของการเล่น ยังคงเหมือนกับบาคาร่าสดปกติทุกประการ เพียงแค่ปรับเวลาให้เล่นได้รวดเร็วและสะดวกขึ้นเท่านั้น
นอกจากสปีดบาคาร่าแล้ว ที่ SA Gaming ยังมีโหมด No Commission Baccarat หรือบาคาร่าแบบไม่เสียค่าคอมมิชชั่น ซึ่งจะช่วยให้คุณสามารถเพลิดเพลินไปกับการเล่นได้โดยไม่ต้องกังวลเรื่องค่าคอมมิชชั่นเพิ่มเติม
เล่นบาคาร่ากับ SA Gaming คุณจะได้รับประสบการณ์การเล่นที่สนุก ทันสมัย และตรงใจมากที่สุด! -
บาคาร่า
เล่นบาคาร่าแบบรวดเร็วทันใจกับสปีดบาคาร่า
ถ้าคุณเป็นแฟนตัวยงของเกมไพ่บาคาร่า คุณอาจจะเคยชินกับการรอคอยในแต่ละรอบการเดิมพัน และรอจนดีลเลอร์แจกไพ่ในแต่ละตา แต่คุณรู้หรือไม่ว่า ตอนนี้คุณไม่ต้องรออีกต่อไปแล้ว เพราะ SA Gaming ได้พัฒนาเกมบาคาร่าโหมดใหม่ขึ้นมา เพื่อให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นของคุณน่าตื่นเต้นยิ่งขึ้น!
ที่ SA Gaming คุณสามารถเลือกเล่นไพ่บาคาร่าในโหมดที่เรียกว่า สปีดบาคาร่า (Speed Baccarat) โหมดนี้มีคุณสมบัติพิเศษและข้อดีที่น่าสนใจมากมาย:
ระยะเวลาการเดิมพันสั้นลง — คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องรอนานอีกต่อไป ในโหมดสปีดบาคาร่า คุณจะมีเวลาเพียง 12 วินาทีในการวางเดิมพัน ทำให้เกมแต่ละรอบจบได้รวดเร็ว โดยเกมในแต่ละรอบจะใช้เวลาเพียง 20 วินาทีเท่านั้น
ผลตอบแทนต่อผู้เล่นสูง (RTP) — เกมสปีดบาคาร่าให้ผลตอบแทนต่อผู้เล่นสูงถึง 4% ซึ่งเป็นมาตรฐานความเป็นธรรมที่ผู้เล่นสามารถไว้วางใจได้
การเล่นเกมที่รวดเร็วและน่าตื่นเต้น — ระยะเวลาที่สั้นลงทำให้เกมแต่ละรอบดำเนินไปอย่างรวดเร็ว ทันใจ เพิ่มความสนุกและความตื่นเต้นในการเล่น ทำให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นของคุณยิ่งสนุกมากขึ้น
กลไกและรูปแบบการเล่นยังคงเหมือนเดิม — แม้ว่าระยะเวลาจะสั้นลง แต่กลไกและกฎของการเล่น ยังคงเหมือนกับบาคาร่าสดปกติทุกประการ เพียงแค่ปรับเวลาให้เล่นได้รวดเร็วและสะดวกขึ้นเท่านั้น
นอกจากสปีดบาคาร่าแล้ว ที่ SA Gaming ยังมีโหมด No Commission Baccarat หรือบาคาร่าแบบไม่เสียค่าคอมมิชชั่น ซึ่งจะช่วยให้คุณสามารถเพลิดเพลินไปกับการเล่นได้โดยไม่ต้องกังวลเรื่องค่าคอมมิชชั่นเพิ่มเติม
เล่นบาคาร่ากับ SA Gaming คุณจะได้รับประสบการณ์การเล่นที่สนุก ทันสมัย และตรงใจมากที่สุด! -
USDT TRON-based Payment Check and Anti-Money Laundering (Anti-Money Laundering) Practices
As digital assets like USDT TRC20 gain popularity for rapid and affordable transfers, the requirement for security and adherence with financial crime prevention standards grows. Here's how to review Tether TRON-based transfers and ensure they're not connected to illegal operations.
What does it mean TRON-based USDT?
TRON-based USDT is a cryptocurrency on the TRON ledger, valued in accordance with the US dollar. Known for its low transaction fees and velocity, it is widely used for global transactions. Validating payments is crucial to prevent connections to financial crime or other unlawful activities.
Monitoring USDT TRC20 Payments
TRONSCAN — This blockchain viewer allows individuals to monitor and validate Tether TRC20 transactions using a account ID or transfer code.
Tracking — Skilled participants can monitor suspicious patterns such as large or fast transactions to detect unusual actions.
AML and Criminal Crypto
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) standards support prevent unlawful transactions in cryptocurrency. Tools like Chainalysis and Elliptic enable enterprises and crypto markets to find and stop illicit funds, which means money tied to criminal actions.
Tools for Compliance
TRX Explorer — To validate TRON-based USDT transaction information.
Chain Analysis and Elliptic — Used by exchanges to ensure AML conformance and track illicit activities.
Final Thoughts
Making sure secure and legal USDT TRC20 transactions is crucial. Tools like TRONSCAN and Anti-Money Laundering solutions help shield users from engaging with criminal crypto, promoting a protected and regulated digital market. -
บาคาร่า
เล่นบาคาร่าแบบรวดเร็วทันใจกับสปีดบาคาร่า
ถ้าคุณเป็นแฟนตัวยงของเกมไพ่บาคาร่า คุณอาจจะเคยชินกับการรอคอยในแต่ละรอบการเดิมพัน และรอจนดีลเลอร์แจกไพ่ในแต่ละตา แต่คุณรู้หรือไม่ว่า ตอนนี้คุณไม่ต้องรออีกต่อไปแล้ว เพราะ SA Gaming ได้พัฒนาเกมบาคาร่าโหมดใหม่ขึ้นมา เพื่อให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นของคุณน่าตื่นเต้นยิ่งขึ้น!
ที่ SA Gaming คุณสามารถเลือกเล่นไพ่บาคาร่าในโหมดที่เรียกว่า สปีดบาคาร่า (Speed Baccarat) โหมดนี้มีคุณสมบัติพิเศษและข้อดีที่น่าสนใจมากมาย:
ระยะเวลาการเดิมพันสั้นลง — คุณไม่จำเป็นต้องรอนานอีกต่อไป ในโหมดสปีดบาคาร่า คุณจะมีเวลาเพียง 12 วินาทีในการวางเดิมพัน ทำให้เกมแต่ละรอบจบได้รวดเร็ว โดยเกมในแต่ละรอบจะใช้เวลาเพียง 20 วินาทีเท่านั้น
ผลตอบแทนต่อผู้เล่นสูง (RTP) — เกมสปีดบาคาร่าให้ผลตอบแทนต่อผู้เล่นสูงถึง 4% ซึ่งเป็นมาตรฐานความเป็นธรรมที่ผู้เล่นสามารถไว้วางใจได้
การเล่นเกมที่รวดเร็วและน่าตื่นเต้น — ระยะเวลาที่สั้นลงทำให้เกมแต่ละรอบดำเนินไปอย่างรวดเร็ว ทันใจ เพิ่มความสนุกและความตื่นเต้นในการเล่น ทำให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นของคุณยิ่งสนุกมากขึ้น
กลไกและรูปแบบการเล่นยังคงเหมือนเดิม — แม้ว่าระยะเวลาจะสั้นลง แต่กลไกและกฎของการเล่น ยังคงเหมือนกับบาคาร่าสดปกติทุกประการ เพียงแค่ปรับเวลาให้เล่นได้รวดเร็วและสะดวกขึ้นเท่านั้น
นอกจากสปีดบาคาร่าแล้ว ที่ SA Gaming ยังมีโหมด No Commission Baccarat หรือบาคาร่าแบบไม่เสียค่าคอมมิชชั่น ซึ่งจะช่วยให้คุณสามารถเพลิดเพลินไปกับการเล่นได้โดยไม่ต้องกังวลเรื่องค่าคอมมิชชั่นเพิ่มเติม
เล่นบาคาร่ากับ SA Gaming คุณจะได้รับประสบการณ์การเล่นที่สนุก ทันสมัย และตรงใจมากที่สุด! -
pump balancing
Pump balancing is an essential procedure that plays a critical role in ensuring the smooth operation of various pumping systems used in both industrial and household applications. When a pump is properly balanced, it minimizes vibrations and noise levels, enhances operational efficiency, and significantly extends the life of the pump and its components. However, disturbances in the mass distribution of a pump, caused by various factors, can lead to pump imbalance, leading to several detrimental effects. Understanding the causes and consequences of pump imbalance is vital for maintaining effective and reliable operations.
Pump imbalance specifically refers to an uneven distribution of mass in the rotating components of the pump, like the impeller and shaft. This uneven distribution results in centrifugal forces during operation that generate vibrations, potentially leading to operational challenges. Several primary factors contribute to pump imbalance, including manufacturing inaccuracies, wear from prolonged use, damage due to corrosion or mechanical impacts, and improper installation or repair of components. Even slight deviations in component geometry can trigger significant operational issues over time.
The problems arising from pump imbalance are multifaceted. First and foremost, pump imbalance leads to increased noise and vibrations, which can create discomfort in the surrounding work environment, while also risking damage to the pump, its piping, and connected components. Furthermore, the additional vibration and movement create an increased load on bearings and seals, which accelerates wear and ultimately leads to premature failures. As a result, the efficiency of the pump diminishes, causing higher energy consumption and potentially catastrophic operational failures. In the severest cases, this can lead to shaft failure or impeller destruction, posing safety risks to personnel and equipment.
The solution to these challenges is effective pump balancing, a process designed to restore the balance by making corrective adjustments to the rotating components. This involves either adding or removing weights on the impeller or shaft which can effectively reduce vibrations and improve the overall efficiency of the pump. Professional services might employ sophisticated balancing machines, but advancements in technology have also prioritized the development of portable balancers, such as the "Balanset-1A," enabling on-site balancing more efficiently. The portable balancer combines the function of a vibration analyzer, thus allowing for quick adjustments without the need for extensive disassembly and transportation of the pumps.
Opting for on-site pump balancing provides numerous advantages. It reduces both time and costs associated with pump disassembly and reassembly due to imbalances. Additionally, it minimizes equipment downtime, allowing for immediate responses to any signs of vibration. The portable balancer provides high balancing accuracy, which is crucial for ensuring that everything is properly aligned after adjustments.
The pump balancing process with the "Balanset-1A" comprises several structured steps. Initially, vibration sensors are attached to the pump housing close to the bearings, ensuring they are oriented correctly for optimal readings. A tachometer is then mounted to connect and measure specific attributes of the pump's rotation. Through specialized software, initial vibrations are measured, and test weights are installed to observe any changes in vibration strength or phase. After analyzing the data, corrective weights are then installed as indicated, verifying results through subsequent measurements. This iterative process ensures the pump is correctly balanced and functioning optimally.
The "Balanset-1A" is recognized as a reliable partner for all your pump balancing needs. It is designed for ease of use, offering clarity and accessibility to those without specialized expertise in vibration analysis. The portable nature of the device encourages use on-site, which provides significant benefits regarding maintenance costs, operational efficiency, and extending equipment life. With a robust measurement range and high accuracy, the Balanset-1A stands out in its ability to provide effective solutions to pump balancing challenges.
Regular pump balancing is strongly recommended, especially after significant use, repairs, or upon noticing symptoms of imbalance such as increased vibrations, noise, or overheating. Adhering to this practice keeps the pump in an optimal condition, decreasing the chances of costly breakdowns. Proper installation of vibration sensors, accurate measurement of weights, and strict adherence to safety precautions are paramount to successfully managing pump balancing. Additionally, routine checks of pump balance after intense operational periods help identify potential imbalances before they lead to significant problems.
In conclusion, balancing pumps is crucial for maintaining effective, reliable, and long-lasting operations in various applications. The portable balancer and vibration analyzer, "Balanset-1A," allows for easy, precise, and quick balancing directly at operational sites. The ability to address imbalance issues swiftly translates into significant time and cost savings while improving the overall performance and reliability of pumping systems. Therefore, integrating regular pump balancing into maintenance protocols not only enhances efficiency but also guarantees a safer working environment and reduces long-term costs associated with equipment failure.
Article taken from https://vibromera.eu/ -
Propeller Balancing: Ensuring Optimal Aircraft Performance
Propeller balancing is an essential aspect of aircraft maintenance that significantly affects performance, safety, and efficiency. Properly balanced propellers can reduce vibrations and prolong the lifespan of various aircraft components, ensuring smoother flights and better handling. The fundamental goal is to achieve uniform weight distribution in the propeller to prevent excessive vibrations, which can lead to mechanical failures or an uncomfortable flying experience.
Importance of Propeller Balancing
Balancing an aircraft propeller greatly influences the aircraft's overall performance. Unbalanced propellers can introduce several issues, including increased vibrations, noise, and operational inefficiency. Vibration can wear out engine mounts, bearings, and other vital components over time, leading to costly repairs and potential safety hazards. Thus, consistent and precise propeller balancing is pivotal in aviation maintenance and safety protocols.
How Propeller Balancing Works
The process of balancing propellers involves identifying and correcting mass distribution imbalances. To achieve this, technicians utilize devices designed specifically for this purpose, such as the Balanset-1. This portable balancer and vibration analyzer can perform dynamic balancing of various aircraft propellers, providing real-time data throughout the balancing process.
During the balancing procedure, a vibration sensor is typically attached to the aircraft's engine or gearbox. The Balanset-1 performs multiple runs at different rotational frequencies to gauge the amplitude and phase of the vibrations. Data analysis software then processes these measurements to determine the amount and placement of corrective weights necessary to balance the propeller effectively.
Field Conditions and Propeller Balancing
Balancing in field conditions poses unique challenges. Traditional balancing methods may not be feasible, prompting specialists to adapt techniques to ensure aircraft performance. In recent studies involving aircraft like the Yak-52 and Su-29, professionals like V.D. Chvokov have pioneered methods for balancing propellers in field settings, enabling smoother operations in various environments.
One notable case involved the Yak-52, where propeller balancing improved vibration levels from 10.2 mm/sec to 4.2 mm/sec by correctly positioning the weights despite design limitations. The maintenance team utilized a comprehensive approach by analyzing engine and propeller oscillations, checking resonance frequencies, and establishing tolerances—all crucial for effective propeller balancing.
The Impact of Natural Frequencies
Understanding the natural frequencies of engine and propeller oscillations is critical in propeller balancing. Balancing efforts must ensure that the propeller's rotational frequency is significantly detuned from these natural frequencies to minimize harmful vibrations. For example, studying the Yak-52's natural frequencies revealed essential insights that informed the balancing strategy, ultimately enhancing performance and reducing vibration.
Real-Life Results and Observations
In practical terms, balancing propellers such as the Su-29's MTV-9-K-C/CL 260-27 has proven effective. Before balancing, vibration levels reached up to 6.7 mm/sec, but through careful adjustments using the Balanset-1 system, they were reduced to an impressive 1.5 mm/sec. Such results underscore the importance of accurately assessing and adjusting for propeller imbalances to ensure optimal flight experiences.
Conclusion and Ongoing Research
In conclusion, propeller balancing is an indispensable part of aircraft maintenance. It enhances operational efficiency, mitigates risks associated with vibrations, and ultimately contributes to a safe flying environment. Continuous research and development in balancing technologies, such as portable analyzers and improved balancing procedures, will likely evolve to further enhance propeller performance and aircraft safety standards.
The aim is to foster an environment of optimal efficiency in aircraft operations, paving the way for innovative solutions that will shape the future of aviation reliability and excellence. For aviation professionals and enthusiasts alike, understanding the nuances of propeller balancing is crucial in maintaining aircraft performance and ensuring a safe flying experience.
-
เกมบาคาร่าออนไลน์
ค่าย SA Gaming เป็น บริษัท เกม บาคาร่า ออนไลน์ ซึ่งได้รับความนิยม ใน วงการสากล ว่าเป็น หัวหน้าค่าย ในการให้บริการ เกม คาสิโนออนไลน์ โดยเฉพาะในด้าน ไพ่ บาคาร่า ซึ่งเป็น เกม ที่ นักเดิมพัน สนใจเล่นกัน อย่างกว้างขวาง ใน คาสิโนจริง และ ออนไลน์ ด้วย ลักษณะการเล่น ที่ ง่าย การเลือกเดิมพัน เพียง ฝั่ง ผู้เล่น หรือ แบงค์เกอร์ และ ความเป็นไปได้ในการชนะ ที่ มีความเป็นไปได้สูง ทำให้ บาคาร่า ได้รับ ความสนใจ อย่างมากใน ช่วงหลายปีหลัง โดยเฉพาะใน ประเทศไทย
หนึ่งในวิธีการเล่น ยอดนิยมที่ SA Gaming นำเสนอ คือ บาคาร่าเร็ว ซึ่ง ให้โอกาสผู้เล่นที่ ต้องการ การเล่นเร็ว และ การตัดสินใจไว สามารถ แทงได้รวดเร็ว นอกจากนี้ยังมีโหมด บาคาร่าแบบไม่เสียค่าคอมมิชชั่น ซึ่งเป็น แบบ ที่ ไม่มีค่าคอมมิชชั่นเพิ่ม เมื่อชนะ การเดิมพัน ฝั่งเจ้ามือ ทำให้ โหมดนี้ ได้รับ ความคุ้มค่า จาก นักพนัน ที่มองหา กำไร ในการ เสี่ยงโชค
เกมการ์ด ของ เอสเอ เกมมิ่ง ยัง ได้รับการออกแบบ ให้มี ภาพ ร่วมกับ ระบบเสียง ที่ เสมือนจริง สร้างบรรยากาศ ที่ น่าตื่นเต้น เหมือนอยู่ใน บ่อนคาสิโนจริง พร้อมกับ ตัวเลือก ที่ทำให้ ผู้เสี่ยงโชค สามารถเลือก วิธีการเดิมพัน ที่ มีให้เลือกมากมาย ไม่ว่าจะเป็น การลงเงิน ตามเทคนิค ของตัวเอง หรือการ พึ่งกลยุทธ์ เพื่อชนะ นอกจากนี้ยังมี ดีลเลอร์ไลฟ์ ที่ คอยดำเนินเกม ในแต่ละ สถานที่ ทำให้ เกม มี ความน่าตื่นเต้น มากยิ่งขึ้น
ด้วย ตัวเลือก ใน การเดิมพัน และ ความง่าย ในการ เล่น เอสเอ เกมมิ่ง ได้ สร้างสรรค์ เกมบาคาร่า ที่ ตอบโจทย์ ทุก ระดับ ของนักเสี่ยงโชค ตั้งแต่ ผู้ที่เริ่มต้น ไปจนถึง นักพนัน มืออาชีพ -
sa gaming
SA Gaming เป็น บริษัท เกม ไพ่บาคาร่า ออนไลน์ ที่ได้รับการยอมรับ ใน วงการสากล ว่าเป็น ผู้นำ ในการให้บริการ บริการ คาสิโนออนไลน์ โดยเฉพาะในด้าน เกมการ์ด บาคาร่า ซึ่งเป็น เกมพนัน ที่ นักเล่น สนใจเล่นกัน อย่างแพร่หลาย ใน บ่อนคาสิโน และ แพลตฟอร์มออนไลน์ ด้วย รูปแบบการเล่น ที่ ไม่ซับซ้อน การลงเดิมพัน เพียง ฝั่ง ฝั่งผู้เล่น หรือ เจ้ามือ และ ความเป็นไปได้ในการชนะ ที่ มีความเป็นไปได้สูง ทำให้ บาคาร่า ได้รับ ความสนใจ อย่างมากใน ช่วงหลายปีหลัง โดยเฉพาะใน ไทย
หนึ่งในวิธีการเล่น ยอดนิยมที่ SA Gaming เสนอ คือ Speed Baccarat ซึ่ง ให้โอกาสผู้เล่นที่ ต้องการ การเล่นเร็ว และ การคิดไว สามารถ เดิมพันได้อย่างรวดเร็ว นอกจากนี้ยังมีโหมด No Commission Baccarat ซึ่งเป็น โหมด ที่ ไม่มีค่าใช้จ่ายเพิ่มเติม เมื่อชนะ การลงเงิน แบงค์เกอร์ ทำให้ โหมดนี้ ได้รับ ความคุ้มค่า จาก นักพนัน ที่มองหา กำไร ในการ ลงทุน
เกมการ์ด ของ SA Gaming ยัง ถูกพัฒนา ให้มี กราฟฟิค และ เสียง ที่ สมจริง จำลองบรรยากาศ ที่ เร้าใจ เสมือนอยู่ใน คาสิโนใหญ่ พร้อมกับ ฟีเจอร์ ที่ทำให้ นักเล่น สามารถเลือก วิธีการเดิมพัน ที่ มีให้เลือกมากมาย ไม่ว่าจะเป็น การเดิมพัน ตามเทคนิค ของตนเอง หรือการ อิงกลยุทธ์ ในการเอาชนะ นอกจากนี้ยังมี ดีลเลอร์สด ที่ คอยควบคุมเกม ในแต่ละ สถานที่ ทำให้ เกม มี ความน่าสนใจ มากยิ่งขึ้น
ด้วย ตัวเลือก ใน การแทง และ ความง่าย ในการ ใช้บริการ SA Gaming ได้ พัฒนา เกมเสี่ยงโชค ที่ ตอบโจทย์ ทุก ชนิด ของนักเสี่ยงโชค ตั้งแต่ ผู้ที่เริ่มต้น ไปจนถึง ผู้เล่นมืออาชีพ มืออาชีพ -
ทดสอบเล่นสล็อต พีจี: รับรู้ประสบการณ์เกมหมุนวงล้อออนไลน์แบบใหม่
ก่อนเริ่มเล่นเกมสล๊อตในเว็บ ข้อสำคัญคือการทำความรู้จักกับการฝึกเล่นเสียล่วงหน้า เกม ทดลองเล่นสล็อตนั้นได้รับแรงบันดาลใจจากสล็อตแมชชีนแบบโบราณ โดยเจาะจงเป็นพิเศษ Triple Gold Slot ที่เคยเป็นที่แพร่หลายอย่างมากในบ่อนการพนันต่างชาติ ในเกมสล็อต ลองเล่นสล็อต PG ผู้เล่นจะได้เข้าถึงสไตล์ของเกมการเล่นที่มีความง่ายดายและต้นตำรับ มาพร้อมกับรีลของเกม (วงล้อ) ที่มีจำนวนห้าแถวและเส้นการจ่าย (เพย์ไลน์) หรือรูปแบบการได้รับรางวัลที่มากถึง 15 ลักษณะ ทำให้มีช่องทางชนะได้มากมายมากยิ่งขึ้น
สัญลักษณ์ต่าง ๆ ในเกมนี้นี้เพิ่มความรู้สึกให้อารมณ์ของสล็อตดั้งเดิม โดยมีสัญลักษณ์ที่โด่งดังเช่น รูปเชอร์รี่ เลขเจ็ด 7 และเพชรพลอย ซึ่งจะทำให้ตัวเกมน่าติดตามแล้วยังสร้างโอกาสในการได้รับผลตอบแทนเสริมขึ้น
ความง่ายดายของเกม PG
ลองเล่น PG ในส่วนนี้ไม่ใช่แค่มีสไตล์การเล่นที่เข้าใจได้ทันที แต่ยังมีความง่ายดายอย่างยิ่ง ไม่ว่าคุณจะใช้งานเครื่องคอมพิวเตอร์หรือโทรศัพท์มือถือรุ่นไหน เพียงต่ออินเทอร์เน็ตกับอินเทอร์เน็ต คุณก็อาจจะเข้าสู่เล่นได้ทันที ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG ยังถูกทำมาให้สนับสนุนเครื่องใช้หลากหลายแบบ เพื่อให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นที่ราบรื่นไม่ชะงักแก่ลูกค้าทุกท่าน
การเลือกแบบเกมและสไตล์เกม
และคุณสมบัติที่น่าสนใจ เกมสล็อตทดลอง พีจี ยังมีหลายหลายธีมให้ได้ลอง ไม่ว่าจะแนวไหนธีมที่น่าสนุก น่าเอ็นดู หรือธีมที่มีความสมจริง ทำให้ผู้เล่นสามารถมีความสุขไปกับแนวทางใหม่ ๆตามรสนิยม
จากฟีเจอร์หลากหลายนี้ ลองเล่นเกมสล็อต PG ได้เป็นที่ชื่นชอบตัวเลือกที่เป็นที่ต้องการในบรรดาคนที่สนใจเกมออนไลน์ที่กำลังมองหาประสบการณ์ใหม่ ๆและการคว้ารางวัลที่ง่ายดายขึ้น หากคุณกำลังแสวงหาประสบการณ์ใหม่ ๆ การลองเล่นสล็อตเป็นทางเลือกที่คุณไม่ควรพลาด! -
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG: รับรู้ประสบการณ์เกมสล๊อตออนไลน์แบบทันสมัย
ก่อนที่คุณจะเริ่มเล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ข้อสำคัญคือการเรียนรู้กับการทดสอบเล่นเสียลำดับแรก เกมสล็อต ลองเล่นสล็อตนั้นได้รับแรงบันดาลใจจากเครื่องสล็อตแบบโบราณ โดยเจาะจงเป็นพิเศษ Triple Gold Slot ที่ในอดีตเคยเป็นที่แพร่หลายอย่างกว้างขวางในบ่อนคาสิโนต่างประเทศ ในเกม ทดลองเล่นสล๊อต พีจี ผู้เล่นจะได้สัมผัสสไตล์ของตัวเกมที่มีความไม่ซับซ้อนและแบบดั้งเดิม มาพร้อมกับรีลของเกม (วงล้อ) ที่มีจำนวนห้าแถวและเพย์ไลน์ (เพย์ไลน์) หรือรูปแบบการคว้ารางวัลที่มากถึง 15 แบบการจ่ายรางวัล ทำให้มีช่องทางชนะได้เพิ่มขึ้นมากยิ่งขึ้น
รูปภาพต่าง ๆ ในเกมนี้นี้ให้ความรู้สึกเหมือนอารมณ์ร่วมของสล็อตเก่า โดยมีสัญลักษณ์ที่โด่งดังเช่น รูปเชอร์รี่ เลข 7 และเพชร ที่จะทำให้เกมมีความน่าสนใจแล้วยังเสริมช่องทางในการได้รับผลตอบแทนเสริมขึ้น
ความคล่องตัวของเกมสล็อต PG
ลองเล่น PG ในตัวเกมไม่ใช่แค่มีสไตล์การเล่นที่เล่นง่าย แต่ยังมีความสะดวกอย่างแท้จริง ไม่ว่าจะใช้PCหรือสมาร์ทโฟนรุ่นอะไรก็ได้ แค่เชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ต คุณก็จะสามารถเข้าสู่เล่นได้ทันที ทดลองเล่นสล็อต พีจี ยังถูกออกแบบให้รองรับเครื่องใช้หลากหลายลักษณะ เพื่อเสนอบริการการเล่นที่ไม่มีติดขัดไม่สะดุดแก่ผู้ใช้งานทุกคน
การเลือกแบบเกมและสไตล์เกม
และจุดเด่นอีกข้อ เกมสล็อตทดลอง พีจี ยังมีหลายหลายธีมให้ได้ลอง ไม่ว่าจะแนวไหนธีมที่น่าสนใจ น่ารัก หรือธีมที่มีความสมจริง ทำให้ผู้เล่นอาจได้อรรถรสไปกับแนวทางใหม่ ๆตามความชอบ
เนื่องจากจุดเด่นเหล่านี้ ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG ได้เป็นที่ชื่นชอบตัวเลือกที่นิยมในหมู่ผู้เล่นเกมออนไลน์ที่กำลังแสวงหาการเล่นที่ตื่นเต้นใหม่ ๆและการคว้ารางวัลที่ง่ายขึ้น หากคุณกำลังต้องการความแปลกใหม่ การลองเล่นสล็อตเป็นทางเลือกที่คุณไม่ควรพลาด! -
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG: สัมผัสประสบการณ์เกมสล็อตออนไลน์แบบใหม่
ก่อนที่คุณจะเริ่มเล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ สิ่งสำคัญคือการทำความรู้จักกับการทดลองเล่นเสียก่อน เกมสล็อต ทดลองเล่นสล็อต นั้นได้รับแรงบันดาลใจจากเครื่องสล็อตแบบดั้งเดิม โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่ง Triple Gold Slot ซึ่งเคยเป็นที่นิยมอย่างมากในคาสิโนต่างประเทศ ในเกมสล็อต ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG ผู้เล่นจะได้สัมผัสกับรูปแบบของเกมที่มีความเรียบง่ายและคลาสสิก มาพร้อมกับรีล (Reel) จำนวน 5 แถวและเพย์ไลน์ (Payline) หรือรูปแบบการชนะรางวัลที่มากถึง 15 รูปแบบ ทำให้มีโอกาสชนะได้หลากหลายมากยิ่งขึ้น
สัญลักษณ์ต่าง ๆ ในเกมนี้สร้างความรู้สึกถึงบรรยากาศของสล็อตดั้งเดิม โดยมีสัญลักษณ์ที่เป็นที่รู้จักเช่น รูปเชอร์รี่ ตัวเลข 7 และเพชร ซึ่งนอกจากจะทำให้เกมมีความน่าสนใจแล้วยังเพิ่มโอกาสในการทำกำไรอีกด้วย
ความสะดวกสบายของเกมสล็อต PG
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG นั้นไม่เพียงแค่มีรูปแบบการเล่นที่เข้าใจง่าย แต่ยังมีความสะดวกสบายอย่างยิ่ง ไม่ว่าคุณจะใช้คอมพิวเตอร์หรือโทรศัพท์มือถือรุ่นใด เพียงแค่เชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ต คุณก็สามารถเข้าร่วมสนุกได้ทันที ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG ยังถูกออกแบบมาให้รองรับอุปกรณ์หลากหลายประเภท เพื่อมอบประสบการณ์การเล่นที่ราบรื่นไม่ติดขัดแก่ผู้เล่นทุกคน
การเลือกธีมและรูปแบบเกม
ที่สำคัญ ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG ยังมีหลากหลายธีมให้เลือกเล่น ไม่ว่าจะเป็นธีมที่น่าตื่นเต้น น่ารัก หรือธีมที่มีความสมจริง ทำให้ผู้เล่นสามารถสนุกสนานไปกับรูปแบบต่าง ๆ ตามความชอบ
ด้วยคุณสมบัติทั้งหมดนี้ ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG ได้กลายเป็นตัวเลือกที่นิยมในหมู่ผู้เล่นเกมออนไลน์ที่กำลังมองหาความท้าทายใหม่ ๆ และการชนะที่ง่ายขึ้น หากคุณกำลังมองหาประสบการณ์ใหม่ ๆ การทดลองเล่นเกมสล็อตเป็นทางเลือกที่คุณไม่ควรพลาด! -
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG: รับรู้ประสบการณ์เกมหมุนวงล้อออนไลน์แบบสดใหม่
ก่อนลงมือเล่นเกมสล็อตออนไลน์ สิ่งที่ควรทำคือการเรียนรู้กับการฝึกเล่นเสียล่วงหน้า เกมสล็อต ทดลองเล่นสล๊อตนั้นถูกสร้างสรรค์จากจากสล็อตแมชชีนแบบต้นตำรับ โดยเฉพาะเจาะจงเป็นพิเศษ สล็อตสามทองคำ ที่ในอดีตเคยเป็นที่แพร่หลายอย่างมากในบ่อนการพนันต่างประเทศ ในเกมสล็อต ลองเล่นสล็อต PG ผู้เล่นจะได้สัมผัสโครงสร้างของตัวเกมที่มีความไม่ซับซ้อนและแบบดั้งเดิม มาพร้อมกับรีลของเกม (วงล้อ) มากถึงห้าแถวและช่องจ่ายเงิน (Payline) หรือรูปแบบการชนะที่มากถึง 15 แบบการจ่ายรางวัล ทำให้มีช่องทางชนะได้มากมายมากยิ่งขึ้น
ไอคอนต่าง ๆ ในเกมนี้นี้เพิ่มความรู้สึกเหมือนอารมณ์ของสล็อตแบบดั้งเดิม โดยมีไอคอนที่เป็นที่รู้จักเช่น รูปเชอร์รี่ ตัวเลข 7 และไดมอนด์ ซึ่งนอกจากจะทำให้เกมสล็อตน่าดึงดูดแล้วยังเพิ่มโอกาสในการสร้างรายได้เสริมขึ้น
ความสะดวกสบายของสล็อต PG
ลองเล่น พีจี ในตัวเกมไม่ใช่เพียงมีรูปแบบการเล่นที่เข้าใจได้ทันที แต่ยังมีความสะดวกอย่างแท้จริง ไม่ว่าจะเข้าถึงจากPCหรือมือถือรุ่นไหน แค่เชื่อมต่ออินเทอร์เน็ต คุณก็จะสามารถเข้าสู่เล่นได้ทันที ลองเล่น พีจี ยังถูกออกแบบให้สนับสนุนเครื่องมือหลากหลายประเภท เพื่อเสนอบริการการเล่นที่ราบรื่นไม่ชะงักแก่ผู้ใช้งานทุกท่าน
การเลือกแบบเกมและสไตล์เกม
ที่สำคัญ ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG ยังมีจำนวนมากธีมให้ได้ลอง ไม่ว่าจะเป็นธีมที่น่าตื่นเต้น น่าชื่นชอบ หรือธีมที่มีความใกล้เคียงจริง ทำให้ผู้เล่นสามารถมีความสุขไปกับรูปแบบต่าง ๆตามความพอใจ
ด้วยคุณสมบัติทั้งหมดนี้ ลองเล่นเกมสล็อต พีจี ได้เป็นที่นิยมตัวเลือกที่ได้รับความนิยมในบรรดาคนที่สนใจเกมออนไลน์ที่กำลังต้องการประสบการณ์ใหม่ ๆและการชนะที่เป็นไปได้มากขึ้น หากคุณกำลังแสวงหาประสบการณ์ใหม่ ๆ การทดลองเล่นเกมวงล้อเป็นหนึ่งในทางเลือกที่คุณไม่ควรละเลย! -
ทดสอบเล่นสล็อต PG: สัมผัสประสบการณ์เกมสล็อตออนไลน์แบบสดใหม่
ก่อนเริ่มเล่นสล๊อตออนไลน์ สิ่งที่ควรทำคือการลองกับการฝึกเล่นเสียก่อน เกมสล็อต ทดลองเล่นสล็อตนั้นถูกสร้างสรรค์จากจากเครื่องสล็อตแบบต้นตำรับ โดยเฉพาะเจาะจงมากๆ สล็อต Triple Gold ที่เคยเป็นที่นิยมอย่างกว้างขวางในคาสิโนต่างชาติ ในเกม ลองเล่นสล็อต พีจี ผู้เล่นจะได้เข้าถึงรูปแบบของเกมที่มีความง่ายดายและคลาสสิก มาพร้อมกับรีล (Reel) มากถึงห้าแถวและเพย์ไลน์ (Payline) หรือแนวทางการได้รับรางวัลที่มากถึง 15 แบบการจ่ายรางวัล ทำให้มีโอกาสชนะได้เพิ่มขึ้นมากยิ่งขึ้น
รูปภาพต่าง ๆ ในเกมนี้เพิ่มความรู้สึกให้บรรยากาศของสล็อตแบบดั้งเดิม โดยมีไอคอนที่เป็นที่รู้จักเช่น เชอร์รี่ ตัวเลข 7 และเพชร ซึ่งนอกจากจะทำให้เกมน่าดึงดูดแล้วยังเพิ่มโอกาสในการได้รับผลตอบแทนเสริมขึ้น
ความง่ายดายของสล็อต PG
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต PG ในตัวเกมไม่ใช่เพียงมีรูปแบบการเล่นที่เล่นง่าย แต่ยังมีความง่ายดายอย่างมากๆ ไม่ว่าจะเข้าถึงจากเครื่องคอมพิวเตอร์หรือโทรศัพท์มือถือรุ่นอะไรก็ได้ แค่ต่ออินเทอร์เน็ตกับอินเทอร์เน็ต คุณก็จะสามารถร่วมสนุกสนุกได้ทันที ลองเล่น พีจี ยังถูกทำมาให้เหมาะสมกับอุปกรณ์หลากหลายแบบ เพื่อให้ประสบการณ์การเล่นที่ราบรื่นไม่ติดขัดแก่ลูกค้าทุกท่าน
การเลือกธีมและการเล่นในเกม
และคุณสมบัติที่น่าสนใจ เกมสล็อตทดลอง PG ยังมีหลากหลายธีมให้ได้ลอง โดยไม่จำกัดธีมที่น่าสนุก น่าชื่นชอบ หรือธีมที่มีความสมจริง ทำให้ผู้เล่นได้ได้อรรถรสไปกับรูปแบบที่แตกต่างตามความชอบ
ด้วยคุณสมบัติทั้งหมดนี้ เกมทดลองเล่น พีจี ได้กลายเป็นตัวเลือกที่เป็นที่ต้องการในหมู่ผู้เล่นเกมในโลกออนไลน์ที่กำลังแสวงหาความท้าทายใหม่ ๆและการคว้ารางวัลที่ง่ายดายขึ้น หากคุณกำลังต้องการการเล่นที่ไม่ซ้ำใคร การทดลองเล่นเกมวงล้อเป็นทางเลือกที่คุณไม่ควรพลาด! -
Pワンパンマン
k8パチンコ
戦略的な要素もあり、運だけでなく技術が試されるのが面白いです。
パラダイスハイビスカス
https://jescasinoguide.com/tags/%E9%AB%98%E3%81%84rtp
明るいデザインと楽しげな演出が魅力。遊んでいるだけで元気が出ます。
ケロロ軍曹
[url=https://sites.google.com/view/cr-garo-final]k8パチンコ
[/url]
北斗の拳 転生の章
GI優駿俱樂部
紫イミソーレ -
OhSoHumorous.com - #best #funny #memes on the internet !! vidalista 60 for sale
-
สล็อตไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์คือแพลตฟอร์มการเล่นเกมออนไลน์ที่ให้นักเดิมพันเชื่อมต่อเกมสล็อตแมชชีนได้โดยตรงจากเว็บ โดยไม่ต้องผ่านเอเย่นต์หรือตัวกลางใดๆ ข้อดีของสล็อตไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์คือการรักษาความปลอดภัยสูงขึ้น เนื่องจากนักเล่นไม่ต้องกังวลใจเรื่องการเสี่ยงจากการใช้บริการผ่านตัวกลาง อีกทั้งยังมีการมอบเงินรางวัลที่เหนือกว่าและข้อเสนอพิเศษมากมาย เนื่องจากไม่มีค่านายหน้าจากเอเย่นต์ ทำให้ผู้เล่นเข้าถึงเกมแมชชีนได้อย่างสะดวกและว่องไว พร้อมรับประสบการณ์การเล่นเกมที่มีคุณภาพและไม่ติดขัด
การเดิมพัน สล็อตเว็บตรง ต่างจาก สล็อตปกติอย่างไร?
เว็บสล็อตตรงเป็นตัวเลือกที่ไม่มีการผ่านผู้แทน ทำให้นักเล่นสามารถเข้าถึงเกมได้ทันที เกมสปินและการจ่ายรางวัลได้โดยตรงจากผู้ให้บริการ ลดโอกาสเสี่ยงในการเสียเปรียบหรือจ่ายค่านายหน้าสูง นอกจากนี้ สล็อตเว็บตรงยังมีความหลากหลายของเกมให้เลือกเล่นมากกว่าในสล็อตแบบเดิม เนื่องจากสล็อตเว็บตรงมักจะได้รับการอัปเดตและเพิ่มเกมหลากหลายอย่างไม่หยุดยั้ง อัตราการจ่ายเงิน (เรทการจ่าย) ของสล็อตตรงมักจะเหนือกว่าสล็อตดั้งเดิม เนื่องจากไม่มีค่าใช้จ่ายเพิ่มเติม ทำให้ผู้เล่นได้รับผลตอบแทนที่มีมูลค่ามากกว่า อีกทั้งยัง ข้อเสนอและโปรโมชั่นพิเศษที่ดีกว่า โดยสล็อตตรงมักมีข้อเสนอที่น่าสนใจและการสะสมแต้มที่ดึงดูดใจมากขึ้น
โปรโมชันและโบนัสในเว็บสล็อตตรงที่น่าสนใจ
สล็อตตรงมักมีโปรโมชันและโปรโมชั่นพิเศษที่ดีมากสำหรับนักเล่นเกม เริ่มตั้งแต่โบนัสต้อนรับสำหรับผู้เล่นใหม่ โบนัสเติมเงิน โบนัสฟรี รวมถึงโปรแกรมสะสมแต้มที่สามารถแลกเป็นเงินหรือสิทธิประโยชน์ต่างๆได้ ทำให้นักเดิมพันได้รับผลตอบแทนและประโยชน์มากมาย การมีโปรโมชันที่คุ้มค่าช่วยให้นักเดิมพันสามารถเพิ่มโอกาสรับรางวัลและประหยัดเงินในการเล่น นอกจากนี้ยังมีโปรโมชันเสริมเช่นเงินคืนบางส่วนและรางวัลพิเศษตามเทศกาลต่างๆอีกด้วย
สรุปว่า สล็อตตรงเป็นทางเลือกที่เหมาะสมสำหรับผู้เล่นที่อยากได้ การเล่นที่ง่ายและการรักษาความปลอดภัยในการเดิมพัน มีการจ่ายเงินที่สูงกว่าปกติ โปรโมชั่นมากมาย และประสบการณ์การเล่นที่ลื่นไหลโดยไม่มีการใช้ตัวแทน -
https://pando.life/article/128063 clomid for women
-
สล็อตเว็บตรง
สล็อตเว็บตรงคือระบบเกมบนอินเทอร์เน็ตที่ให้นักเล่นเกมเข้าสู่สล็อตแมชชีนได้โดยตรงจากเว็บไซต์ โดยไม่ต้องใช้บริการจากเอเย่นต์หรือตัวกลางใดๆ ข้อดีของสล็อตเว็บตรงคือการรักษาความปลอดภัยที่มากขึ้น เนื่องจากนักเดิมพันไม่ต้องเป็นกังวลเรื่องความเสี่ยงจากการใช้บริการผ่านตัวกลาง อีกทั้งยังมีการจ่ายเงินรางวัลที่สูงกว่าและข้อเสนอพิเศษมากมาย เนื่องจากไม่มีค่าบริการจากผู้แทน ทำให้นักเดิมพันเข้าถึงเกมแมชชีนได้อย่างสะดวกและทันใจ พร้อมรับการเล่นที่น่าพอใจและไม่สะดุด
การเดิมพัน สล็อตเว็บตรง แตกต่างจาก สล็อตแบบดั้งเดิมอย่างไร?
สล็อตไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์เป็นทางเลือกที่ไม่มีการผ่านเอเย่นต์ ทำให้นักเดิมพันสามารถเข้าถึง เกมและผลตอบแทนได้โดยตรงจากเจ้าของเว็บ ลดการเสี่ยงในการโดนโกงหรือถูกหักค่านายหน้าสูง นอกจากนี้ สล็อตเว็บตรงยังมีตัวเลือกที่หลากหลายของเกมให้เลือกสรรมากกว่าในสล็อตทั่วไป เนื่องจากสล็อตเว็บตรงมักจะได้รับการปรับปรุงและเพิ่มเกมใหม่อย่างไม่หยุดยั้ง อัตราการมอบเงิน (การจ่ายคืน) ของสล็อตเว็บตรงมักจะมากกว่าสล็อตดั้งเดิม เนื่องจากไม่มีค่าธรรมเนียมพิเศษ ทำให้ผู้เล่นได้ผลตอบแทนผลตอบแทนที่คุ้มค่า อีกทั้งยัง ข้อเสนอและโปรโมชั่นพิเศษที่ดีกว่า โดยสล็อตตรงมักมีข้อเสนอที่น่าสนใจและโปรแกรมสะสมแต้มที่น่าสนใจมากขึ้น
โปรโมชั่นและโปรโมชั่นพิเศษในสล็อตตรงที่น่าสนใจ
สล็อตเว็บตรงมักมีข้อเสนอและรางวัลที่น่าสนใจสำหรับนักเล่นเกม เริ่มตั้งแต่โบนัสแรกเข้าสำหรับผู้เล่นใหม่ โบนัสเติมเงิน เครดิตฟรี รวมถึงโปรแกรมสะสมแต้มที่สามารถแลกเป็นเงินหรือรางวัลอื่นๆได้ ทำให้ผู้เล่นมีความคุ้มค่าและข้อดีมากมาย การมีโปรโมชั่นที่คุ้มค่าช่วยให้นักเดิมพันสามารถเพิ่มโอกาสในการชนะและลดเงินลงทุนในการเล่น นอกจากนี้ยังมีโปรโมชั่นพิเศษเช่นคืนเงินบางส่วนจากยอดเสียและการแจกของรางวัลตามวันสำคัญอีกด้วย
สรุปแล้ว สล็อตตรงเป็นทางเลือกที่คุ้มค่าสำหรับผู้เล่นที่อยากได้ การเล่นที่ง่ายและการรักษาความปลอดภัยในการเดิมพัน มีอัตราการจ่ายที่มากกว่า ข้อเสนอที่หลากหลาย และความสนุกในการเล่นที่ลื่นไหลโดยไม่มีการใช้ตัวแทน -
สล็อตเว็บตรง
สล็อตไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์คือระบบเกมบนอินเทอร์เน็ตที่ให้นักเดิมพันเข้าถึงเกมสล็อตแมชชีนได้โดยตรงจากหน้าเว็บ โดยไม่ต้องพึ่งพาเอเย่นต์หรือตัวกลางใดๆ ข้อดีของสล็อตเว็บตรงคือการรักษาความปลอดภัยสูงขึ้น เนื่องจากนักเดิมพันไม่ต้องกังวลเรื่องโอกาสเสี่ยงจากการใช้บริการผ่านเอเย่นต์ อีกทั้งยังมีการจ่ายเงินรางวัลที่เหนือกว่าและโปรโมชั่นมากมาย เนื่องจากไม่มีค่าธรรมเนียมจากเอเย่นต์ ทำให้นักเดิมพันเข้าถึงเกมสปินได้อย่างง่ายและรวดเร็ว พร้อมรับการเล่นที่ดีขึ้นและไม่สะดุด
การหมุน สล็อตไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์ แตกต่างจาก สล็อตปกติอย่างไร?
สล็อตเว็บตรงเป็นตัวเลือกที่ดีที่ไม่มีการผ่านตัวแทน ทำให้นักเดิมพันสามารถเข้าถึงเกมได้ทันที เกมและการจ่ายรางวัลได้โดยตรงจากผู้ดำเนินการ ลดการเสี่ยงในการเสียเปรียบหรือเสียค่านายหน้าสูง นอกจากนี้ เว็บสล็อตโดยตรงยังมีหลายแบบของเกมสล็อตให้เลือกสรรมากกว่าในสล็อตดั้งเดิม เนื่องจากสล็อตเว็บตรงมักจะได้รับการปรับปรุงและเพิ่มเกมใหม่อย่างสม่ำเสมอ อัตราการมอบเงิน (การจ่ายคืน) ของสล็อตเว็บตรงมักจะสูงกว่าสล็อตแบบดั้งเดิม เนื่องจากไม่มีค่าธรรมเนียมพิเศษ ทำให้นักเล่นได้รับรางวัลที่สูงขึ้น ทั้งยัง ข้อเสนอและโบนัสที่ดีกว่า โดยเว็บสล็อตตรงมักมีข้อเสนอพิเศษและโปรแกรมคะแนนที่น่าสนใจมากขึ้น
โปรโมชันและรางวัลในสล็อตตรงที่ควรรู้
สล็อตตรงมักมีโปรโมชันและโบนัสที่น่าสนใจสำหรับนักเล่นเกม เริ่มตั้งแต่โบนัสสมาชิกใหม่สำหรับสมาชิกใหม่ เงินเพิ่มในการฝาก เครดิตเล่นฟรี รวมถึงโปรแกรมสะสมแต้มที่สามารถแลกเป็นเงินหรือรางวัลอื่นๆได้ ทำให้นักเล่นเกมได้รับความคุ้มค่าและประโยชน์มากมาย การมีโปรโมชันที่น่าสนใจช่วยให้นักเดิมพันสามารถมีโอกาสชนะมากขึ้นและประหยัดเงินในการเล่น นอกจากนี้ยังมีโปรโมชั่นพิเศษเช่นเงินคืนบางส่วนและของแจกตามช่วงเทศกาลอีกด้วย
โดยรวมแล้ว เว็บสล็อตโดยตรงเป็นทางเลือกที่เหมาะสมสำหรับผู้เล่นที่อยากได้ การเล่นที่ง่ายและความปลอดภัยในการเดิมพัน มีอัตราการจ่ายที่มากกว่า ข้อเสนอที่หลากหลาย และความสนุกในการเล่นที่ลื่นไหลโดยไม่มีการผ่านเอเย่นต์ -
pg slot
Hercule99: Kumpulan 8 Permainan Versi Demo Slot PG Tanpa Kecurangan Terjamin di Nusantara
PG Slot adalah favorit kesukaan bagi banyak pemain slot di Nusantara, menawarkan ragam gim yang menarik dengan kenikmatan dan kesenangan berkelanjutan. Di saat popularitasnya semakin tinggi, muncul pula kekhawatiran mengenai adanya praktik rungkad atau kecurangan dalam judi online. Namun demikian, Game PG dapat mengatasi menanggapi kekhawatiran ini dengan menawarkan slot yang aman dari kecurangan yang terpercaya serta dapat dipercaya.
Dengan teknologi keamanan terbaru serta fitur canggih, PGS menjamin bahwa permainan yang mereka tawarkan lancar dan terlindungi untuk para pemain. Di bawah ini daftar 8 game demo PG tanpa manipulasi yang gacor dan aman di Indonesia:
1. Slot Tikus Keberuntungan
Tikur Keberuntungan adalah gim slot yang penuh daya tarik berbekal grafis cantik dengan tema lucu. Di luar visual yang cantik, game ini memiliki enkripsi kuat agar melindungi semua data pemain. Seluruh putaran bebas dari campur tangan luar, agar permainan tetap nyaman.
2. Demo Dragon Hatch PG Slot
Telur Naga menyertakan pengguna ke alam khayalan yang berisi keistimewaan serta aura mistis. Namun, kekuatan utama game ini ada pada keamanan mutakhirnya. Menggunakan teknologi anti curang, permainan ini mewujudkan keadilan dalam kemenangan dengan cara fair tanpa campur tangan pihak luar.
3. Uji Coba Journey to the Wealth PG Slot
Game Perjalanan Menuju Kekayaan membawa player ke petualangan mencari kekayaan tanpa akhir. Dengan bonus yang besar dan Return to Player yang tinggi, slot ini menawarkan kenikmatan bertambah serta kepastian keadilan dalam setiap putarannya. User dapat merasakan kenikmatan bermain tanpa merasa khawatir akan kecurangan.
4. Versi Demo Surga Bikini Pocket Games Slot
Game ini membawa pemain ke suasana pulau yang indah yang cantik serta penuh keceriaan. Di balik suasana santainya, Game Bikini terintegrasi dengan protokol keamanan canggih, menjadikannya salah satu game Pocket Games Slot tanpa curang yang terjamin. Player bisa menikmati slot tanpa ada kekhawatiran curang.
5. Percobaan Medusa II: Petualangan Perseus Slot PG
Dalam slot Medusa II, pemain terjun dalam kisah epik menghadapi makhluk legendaris. Game ini dibekali teknologi pengaman terbaru yang memastikan setiap putaran aman. Karenanya, pemain dapat fokus pada kemenangan tanpa terganggu campur tangan luar.
6. Uji Coba Bom Jatuh Pocket Games Slot
Dengan tema peperangan yang sengit, Bombs Away menaikkan adrenalin pengguna. Saat permainan memanas, keamanan tetap menjadi prioritas utama. Proteksi dari PG Soft mengamankan semua transaksi dan hasil game, memberikan keamanan kepada player di jalan menuju kemenangan.
7. Demo Bull Fight PGS
Slot Bull Fight memasukkan player ke arena banteng yang seru. Di dalam game ini, PG Soft menjamin setiap putaran adil dan jujur. Pengguna bisa menikmati permainan dengan adil dan aman tanpa takut akan kecurangan.
8. Percobaan Juara Muay Thai PGS
Muay Thai Champion menawarkan tema bela diri yang menarik, mengundang player bertarung sengit di ring. Game ini memukau dari tema, tetapi juga dalam keamanan. Setiap putaran dipantau dengan ketat, menjamin pengalaman bermain yang bebas dari gangguan dan kecurangan.
Nilai Positif Main Slot Demo PG Soft dengan RTP Besar
Game demo PG Slot anti-rungkad mempunyai RTP yang lebih tinggi dari standar rata-rata. Memberikan peluang lebih besar kepada pengguna untuk mendapatkan pengembalian atas investasi mereka. Memilih game slot dari PG Soft bukan hanya soal hiburan, tetapi juga peluang keuntungan yang lebih tinggi.
Dengan deretan game tersebut di atas, pemain bisa menikmati slot dengan keadilan, keamanan, dan kesenangan. Teknologi canggih yang diterapkan oleh PG Slot menjaga kelancaran dalam setiap permainan, menambah keyakinan bagi player. -
Ленинградская область характеризуется трудной геологической конфигурацией, что формирует работу создания скважин на воду особенным в каждом участке. Местность обладает многообразие почв и водных горизонтов, которые диктуют экспертный подход при определении зоны и уровня создания. Источник воды может располагаться как на низкой высоте, так и достигать нескольких глубоких метров, что создает трудоемкость процесса.
Ключевым моментом, определяющих тип источника (https://derevo-s.ru/poleznoe/effektivnye-metody-glusheniya-skvazhiny.html ), становится структура почвы и глубина водоносного слоя. В Ленинградской области чаще всего создают артезианские скважины, которые поставляют доступ к чистой и надежной воде из глубоких пластов. Такие скважины ценятся за долгим сроком функционирования и качественным качеством воды, однако их постройка нуждается в существенных вложений и особого аппаратуры.
Способы бурения в регионе включает использование высокотехнологичных установок и технологий, которые могут работать с каменистыми породами и избегать возможные разрушения стенок скважины. Крайне важно, что всегда нужно обращать внимание на экологические требования и правила, так как вблизи нескольких населённых пунктов существуют охраняемые водные зоны и природные комплексы, что диктует особый контроль к буровым действиям.
Водные запасы из глубоких источников в Ленинградской области замечательна чистотой, так как она укрыта от поверхностных загрязнений и обогащена сбалансированный состав составных элементов. Это делает такие источники необходимыми для коттеджей и заводов, которые ценят надежность и качество водоснабжения. -
สล็อตเว็บตรง
สล็อตเว็บตรงคือแพลตฟอร์มการให้บริการเกมผ่านเน็ตที่ให้นักเดิมพันเชื่อมต่อสล็อตแมชชีนได้โดยตรงจากหน้าเว็บ โดยไม่ต้องผ่านเอเย่นต์หรือตัวกลางใดๆ ข้อดีของสล็อตเว็บตรงคือการรักษาความปลอดภัยสูงขึ้น เนื่องจากผู้เล่นไม่ต้องกังวลใจเรื่องโอกาสเสี่ยงจากการใช้บริการผ่านตัวกลาง อีกทั้งยังมีการจ่ายเงินรางวัลที่สูงกว่าและโปรโมชั่นมากมาย เนื่องจากไม่มีค่านายหน้าจากตัวแทน ทำให้นักเดิมพันเข้าถึงเกมสล็อตได้อย่างสะดวกและทันใจ พร้อมรับการเล่นที่น่าพอใจและไม่ติดขัด
การหมุน สล็อตไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์ ไม่เหมือนกับ สล็อตปกติอย่างไร?
เว็บสล็อตตรงเป็นตัวเลือกที่ไม่มีการผ่านผู้แทน ทำให้นักเล่นสามารถเข้าถึงเกมได้ทันที เกมสล็อตและการจ่ายรางวัลได้โดยตรงจากเจ้าของเว็บ ลดความเสี่ยงในการถูกหลอกหรือเสียค่าธรรมเนียมสูง นอกจากนี้ เว็บสล็อตโดยตรงยังมีหลายแบบของเกมให้เลือกมากกว่าในสล็อตทั่วไป เนื่องจากเว็บสล็อตตรงมักจะได้รับการอัปเดตและเพิ่มเกมใหม่อย่างไม่หยุดยั้ง อัตราการจ่ายเงิน (เรทการจ่าย) ของสล็อตเว็บตรงมักจะสูงกว่าสล็อตทั่วไป เนื่องจากไม่มีค่านายหน้า ทำให้นักเล่นได้รับผลตอบแทนที่คุ้มค่า ทั้งยัง ข้อเสนอและโบนัสที่มากกว่า โดยสล็อตเว็บตรงมักมีข้อเสนอที่น่าสนใจและโปรแกรมคะแนนที่ดึงดูดใจมากขึ้น
โปรโมชันและโปรโมชั่นพิเศษในเว็บสล็อตตรงที่ควรรู้
สล็อตตรงมักมีโปรโมชั่นและโปรโมชั่นพิเศษที่ดีมากสำหรับนักเล่นเกม เริ่มตั้งแต่โบนัสสมาชิกใหม่สำหรับผู้เล่นใหม่ เงินเพิ่มในการฝาก เครดิตเล่นฟรี รวมถึงโปรแกรมแลกคะแนนที่สามารถแลกแต้มหรือข้อเสนอพิเศษได้ ทำให้นักเล่นเกมมีความคุ้มค่าและประโยชน์มากมาย การมีโปรโมชั่นที่น่าสนใจช่วยให้ผู้เล่นสามารถเพิ่มโอกาสในการชนะและลดเงินลงทุนในการเล่น นอกจากนี้ยังมีโปรโมชันเสริมเช่นการคืนเงินและของแจกตามวันสำคัญอีกด้วย
โดยรวมแล้ว เว็บสล็อตโดยตรงเป็นทางเลือกที่คุ้มค่าสำหรับผู้ที่ต้องการ ความสะดวกสบายและการป้องกันในการเล่นเกม มีการจ่ายเงินที่สูงกว่า โปรโมชันดีๆ และประสบการณ์การเล่นที่ดีโดยไม่มีการใช้ตัวแทน -
priligy precio The US military s involvement in these types of technologies originated with something called Project Sanguine
-
aviator играaviator на деньгиaviator играть на деньгислот aviator на деньгиaviator money game
aviator играaviator на деньгиaviator играть на деньгислот aviator на деньгиaviator money game -
pg slot
Hercule99: Kumpulan delapan Permainan Demo PG Slot Anti Rungkad Aman di Nusantara
Permainan PG Slot sudah menjadi favorit favorit utama untuk banyak pemain slot di Nusantara, menyuguhkan ragam game yang menyenangkan dengan kenikmatan dan kegembiraan berkelanjutan. Di saat popularitasnya semakin tinggi, timbul kekhawatiran seputar ketidakjujuran atau gangguan dalam judi online. Tetapi, PG Slot sudah sukses menanggapi kekhawatiran ini dengan menghadirkan game slot tanpa manipulasi yang aman serta dapat dipercaya.
Berbekal teknologi keamanan modern dan fitur mutakhir, Permainan PG Slot menyediakan kepastian bahwa setiap game aman dan terkontrol untuk seluruh pemain. Di bawah ini daftar 8 slot percobaan PG tanpa manipulasi yang gacor serta terpercaya di Indonesia:
1. Slot Tikus Keberuntungan
Fortuna Mouse adalah gim slot yang penuh daya tarik dengan gambar memikat dan tema yang menggemaskan. Di luar visual yang cantik, permainan ini menggunakan enkripsi modern yang melindungi data dan transaksi pemain. Setiap putaran dijamin bebas dari manipulasi, agar permainan tetap nyaman.
2. Dragon Hatch Demo
Menetas Naga membawa pemain ke alam khayalan yang diwarnai keindahan dan kekuatan ajaib. Meski demikian, daya tarik utama game ini terdapat pada fitur keamanannya. Dengan fitur anti-rungkad, permainan ini menjaga kemenangan setiap pemain tanpa gangguan bebas dari campur tangan luar.
3. Versi Demo Journey Wealth PG Slot
Slot Journey Wealth mengundang pemain dalam petualangan menemukan kekayaan yang tak berujung. Memiliki bonus melimpah dan Return to Player yang tinggi, slot ini menawarkan kesenangan berlipat dan juga keadilan dalam setiap putarannya. User bisa merasakan serunya bermain tanpa merasa khawatir mengenai manipulasi.
4. Uji Coba Pulau Bikini PG Slot
Permainan ini mengundang player dalam suasana pulau yang indah yang memukau dan penuh sukacita. Di balik kesan tenangnya, Slot Bikini terintegrasi dengan protokol keamanan canggih, yang menjadikannya sebagai game PG Slot tanpa curang yang diandalkan. Player bisa menikmati slot dengan tenang tanpa curang.
5. Versi Demo Medusa II PGS
Dalam slot Medusa II, pemain terjun dalam kisah epik menghadapi monster legendaris. Slot ini menggunakan proteksi terbaru yang memastikan setiap putaran aman. Karenanya, pemain bisa berfokus pada kemenangan tanpa ada campur tangan eksternal.
6. Demo Bombs Away PG Slot
Dengan tema peperangan yang sengit, Bombs memacu adrenalin pengguna. Di tengah-tengah ketegangan permainan, keamanan tetap menjadi prioritas utama. Sistem keamanan PG Soft menjamin setiap transaksi dan hasil permainan, memberikan rasa aman bagi pemain ketika mencari kemenangan.
7. Uji Coba Arena Banteng Slot PG
Bull Fight memasukkan player ke arena yang mendebarkan. Dalam permainan ini, PG Soft memastikan bahwa setiap putaran memiliki keadilan dan integritas. Pemain bisa menikmati sensasi permainan yang adil dan aman tanpa rasa khawatir akan manipulasi.
8. Demo Muay Thai Champion PGS
Juara Muay Thai menawarkan tema bela diri yang menarik, memasukkan pengguna dalam duel di atas ring. Game ini memukau dari tema, tetapi juga dalam keamanan. Setiap putaran dipantau dengan ketat, menjaga pengalaman bermain yang aman.
Keuntungan Bermain Demo Slot PG Soft dengan RTP Tinggi
Permainan demo PG Slot tanpa curang mempunyai RTP yang lebih tinggi dari standar rata-rata. Memberikan peluang lebih besar kepada pengguna agar bisa meraih kembali modal mereka. Bermain slot dari PG Soft bukan cuma hiburan, tetapi juga peluang keuntungan yang lebih tinggi.
Dengan deretan game tersebut di atas, pemain dapat menikmati pengalaman bermain slot yang adil, aman, dan menyenangkan. Teknologi canggih yang diterapkan oleh PG Slot memastikan bahwa setiap permainan berjalan tanpa hambatan, memberikan rasa percaya bagi pengguna. -
OhSoHumorous.com - #best #funny #memes on the internet !! Generic clomid without a prescription
-
https://t.me/s/chto_takoe_bingo
что такое бинго -
Pフィーバー戦姫絶唱シンフォギア2
k8 カジノ パチンコ
ボーナスゲームの演出が豪華で、楽しみが倍増します。特に大当たり時は圧巻。
ケロロ軍曹
https://idtc.jp/article/640.html
演出が華やかで、視覚的にも楽しめます。アートとしての側面もあります。
翔馬
[url=https://sites.google.com/view/cr-2-reivu-kono-sekai-k-g-s-1/]k8パチンコ
[/url]
ベルセルク無双
キャッツ・アイ~コレクション奪還作戦~
CR 獣王 -
https://experienceleaguecommunities.adobe.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/17932548 what is vidalista-20 reviews
-
Introduction of Crypto Deal Verification and Compliance Options
In the current cryptocurrency sector, guaranteeing transaction openness and adherence with Anti-Laundering and KYC regulations is crucial. Here is an overview of leading services that offer tools for digital asset deal surveillance, verification, and fund protection.
1. Token Metrics
Overview: Tokenmetrics delivers digital asset assessment to assess possible risk risks. This solution enables investors to review tokens prior to buying to evade possibly fraudulent holdings. Features:
- Risk analysis.
- Ideal for buyers looking to steer clear of questionable or scam ventures.
2. Metamask.Monitory.Center
Overview: Metamask.Monitory.Center enables users to review their cryptocurrency resources for doubtful transactions and standard adherence. Features:
- Verifies tokens for purity.
- Offers alerts about potential asset restrictions on specific platforms.
- Gives comprehensive reports after account sync.
3. BestChange.ru
Overview: Best Change is a site for tracking and verifying cryptocurrency trade transfers, guaranteeing clarity and transaction safety. Highlights:
- Transaction and holding tracking.
- Restriction validation.
- Internet interface; accommodates BTC and various other coins.
4. AMLCheck Bot
Description: AMLCheck Bot is a investment tracker and AML tool that uses artificial intelligence models to detect dubious actions. Highlights:
- Deal monitoring and identity validation.
- Accessible via web version and chat bot.
- Compatible with coins like BSC, BTC, DOGE, and other types.
5. Alfabit AML
Summary: AlphaBit delivers comprehensive AML tools tailored for the digital currency market, helping firms and financial organizations in maintaining compliance conformity. Features:
- Comprehensive anti-money laundering tools and checks.
- Complies with modern safety and conformity requirements.
6. AMLNode
Description: AML Node provides AML and identification tools for cryptocurrency businesses, which includes transfer monitoring, compliance screening, and analysis. Highlights:
- Risk evaluation options and restriction checks.
- Important for guaranteeing secure business activities.
7. Btrace.io
Summary: Btrace AML Crypto focuses on resource validation, providing transaction tracking, restriction screenings, and help if you are a victim of loss. Benefits:
- Reliable support for fund recovery.
- Transaction monitoring and safety features.
Specialized USDT Validation Solutions
Our website also reviews multiple platforms providing validation tools for Tether transfers and accounts:
- **USDT TRC20 and ERC20 Verification:** Many platforms provide thorough checks for USDT transactions, aiding in the detection of suspicious actions.
- **AML Validation for USDT:** Options are provided for monitoring for suspicious transactions.
- **“Cleanliness” Checks for Holdings:** Verification of deal and holding “cleanliness” is provided to identify potential threats.
**Conclusion**
Finding the right platform for validating and observing cryptocurrency transactions is crucial for ensuring protection and regulatory adherence. By viewing our reviews, you can select the best solution for transfer tracking and resource security. -
Summary of Digital Currency Transfer Validation and Conformity Solutions
In today's cryptocurrency market, maintaining transaction transparency and adherence with AML and Customer Identification regulations is essential. Following is an summary of leading services that deliver services for digital asset transaction tracking, verification, and resource safety.
1. Token Metrics Platform
Summary: Token Metrics provides crypto analysis to evaluate potential scam threats. This service allows individuals to examine coins prior to investment to prevent potentially scam holdings. Features:
- Threat evaluation.
- Ideal for holders seeking to steer clear of hazardous or fraudulent ventures.
2. Metamask.Monitory.Center
Overview: Metamask Monitor Center allows individuals to review their digital asset assets for doubtful actions and standard conformity. Advantages:
- Validates assets for purity.
- Delivers warnings about potential asset locks on particular trading sites.
- Provides detailed reports after wallet sync.
3. Best Change
Overview: Bestchange.ru is a service for tracking and verifying cryptocurrency exchange transfers, providing openness and deal security. Features:
- Deal and holding observation.
- Restriction screening.
- Internet platform; supports BTC and several different cryptocurrencies.
4. Bot amlchek
Description: AMLCheck Bot is a portfolio monitor and anti-money laundering service that employs machine learning models to identify suspicious activity. Features:
- Transfer tracking and personal verification.
- Accessible via internet and Telegram.
- Supports cryptocurrencies including BSC, BTC, DOGE, and other types.
5. AlphaBit
Description: AlfaBit provides comprehensive Anti-Money Laundering (AML) solutions customized for the crypto industry, helping companies and banks in preserving standard compliance. Advantages:
- Comprehensive anti-money laundering tools and checks.
- Meets modern protection and regulatory standards.
6. AMLNode
Overview: AML Node offers compliance and customer identity services for digital currency companies, including transfer observing, sanctions checks, and risk assessment. Features:
- Risk assessment tools and restriction validations.
- Valuable for maintaining secure firm processes.
7. Btrace AML Crypto
Overview: Btrace AML Crypto is dedicated to asset verification, delivering deal observation, restriction checks, and help if you are a affected by fraud. Highlights:
- Reliable help for resource restoration.
- Transaction tracking and protection options.
Exclusive USDT Check Solutions
Our website also reviews multiple services offering validation services for USDT deals and holdings:
- **USDT TRC20 and ERC20 Verification:** Numerous platforms offer comprehensive evaluations for USDT transactions, assisting in the identification of doubtful activity.
- **AML Validation for USDT:** Tools are available for tracking for fraudulent transactions.
- **“Cleanliness” Validation for Holdings:** Checking of deal and holding “cleanliness” is offered to detect likely dangers.
**Wrap-up**
Finding the right tool for validating and monitoring cryptocurrency deals is crucial for ensuring safety and standard conformity. By reading our reviews, you can select the ideal service for transaction observation and resource safety. -
levitra mirtazapine 7 better business bureau online pharmacy priligy
-
Bitcoin address cleanliness check
Overview of Digital Currency Deal Check and Compliance Options
In contemporary digital asset sector, guaranteeing transfer clarity and conformity with Anti-Laundering and Customer Identification rules is essential. Following is an summary of well-known services that provide solutions for digital asset transaction tracking, verification, and asset safety.
1. Token Metrics
Description: Token Metrics offers crypto assessment to evaluate potential risk risks. This solution lets individuals to check tokens before buying to avoid potentially scam assets. Highlights:
- Danger analysis.
- Suitable for investors seeking to avoid hazardous or fraudulent ventures.
2. Metamask Monitor Center
Description: Metamask.Monitory.Center permits holders to review their crypto assets for questionable transactions and standard compliance. Benefits:
- Checks coins for “cleanliness”.
- Provides warnings about possible asset restrictions on particular exchanges.
- Delivers thorough results after address connection.
3. Best Change
Overview: Bestchange.ru is a platform for monitoring and validating cryptocurrency transaction deals, guaranteeing clarity and deal safety. Features:
- Transfer and holding tracking.
- Compliance checks.
- Online interface; supports BTC and several different cryptocurrencies.
4. AMLCheck Bot
Description: AMLchek is a holding tracker and anti-money laundering service that utilizes artificial intelligence algorithms to detect dubious activity. Advantages:
- Deal monitoring and identity check.
- Available via internet and Telegram bot.
- Compatible with cryptocurrencies including BSC, BTC, DOGE, and more.
5. AlphaBit
Summary: AlfaBit provides comprehensive AML services customized for the cryptocurrency field, assisting firms and financial organizations in maintaining standard compliance. Features:
- Comprehensive anti-money laundering options and evaluations.
- Complies with modern safety and conformity requirements.
6. AMLNode
Summary: AML Node offers AML and KYC tools for cryptocurrency businesses, including transaction monitoring, sanctions validation, and analysis. Highlights:
- Danger assessment options and restriction validations.
- Useful for ensuring protected company processes.
7. Btrace.AMLcrypto.io
Summary: Btrace AML Crypto specializes in asset validation, delivering transaction monitoring, compliance checks, and help if you are a affected by loss. Advantages:
- Effective assistance for fund restoration.
- Deal monitoring and protection tools.
Exclusive USDT Validation Services
Our platform also provides information on various platforms that offer validation services for USDT transfers and holdings:
- **USDT TRC20 and ERC20 Check:** Many platforms support comprehensive checks for USDT transactions, aiding in the identification of suspicious activity.
- **AML Verification for USDT:** Options are offered for monitoring for suspicious activities.
- **“Cleanliness” Screenings for Holdings:** Checking of transaction and holding “cleanliness” is available to detect likely dangers.
**Wrap-up**
Selecting the right tool for checking and tracking digital currency transfers is crucial for guaranteeing protection and regulatory compliance. By reading our recommendations, you can select the ideal solution for deal observation and resource protection. -
AMF compliance check for crypto wallets
Summary of Crypto Transfer Validation and Regulatory Solutions
In the current digital asset industry, ensuring deal transparency and conformity with Anti-Laundering and Know Your Customer (KYC) standards is essential. Here is an summary of well-known platforms that deliver services for crypto deal monitoring, validation, and fund safety.
1. Token Metrics
Summary: Token Metrics delivers digital asset evaluation to evaluate potential fraud dangers. This service lets investors to check tokens prior to buying to prevent possibly fraudulent resources. Attributes:
- Threat assessment.
- Suitable for holders looking to bypass risky or fraud ventures.
2. Metamask.Monitory.Center
Overview: Metamask.Monitory.Center allows holders to check their digital asset resources for suspicious actions and regulatory adherence. Benefits:
- Validates assets for purity.
- Provides alerts about possible fund restrictions on certain exchanges.
- Provides detailed insights after wallet sync.
3. Bestchange.com
Description: Bestchange.ru is a service for observing and verifying digital transaction deals, ensuring transparency and transaction security. Highlights:
- Transaction and wallet observation.
- Compliance checks.
- Web-based portal; supports BTC and several different cryptocurrencies.
4. AML Bot
Summary: AMLchek is a investment monitor and anti-money laundering compliance tool that employs artificial intelligence algorithms to detect suspicious transactions. Features:
- Deal tracking and personal verification.
- Accessible via online and Telegram.
- Compatible with coins including BSC, BTC, DOGE, and more.
5. AlphaBit
Summary: AlphaBit provides complete Anti-Money Laundering (AML) tools specifically made for the crypto industry, assisting businesses and financial organizations in maintaining standard conformity. Advantages:
- Thorough AML tools and evaluations.
- Adheres to up-to-date safety and conformity requirements.
6. AMLNode
Overview: AML Node offers anti-money laundering and identification solutions for cryptocurrency companies, which includes transaction monitoring, sanctions validation, and risk assessment. Benefits:
- Risk assessment options and compliance checks.
- Valuable for maintaining secure business activities.
7. Btrace AML Crypto
Summary: Btrace AML Crypto specializes in resource validation, providing deal tracking, compliance checks, and help if you are a victim of theft. Advantages:
- Reliable support for fund restoration.
- Transaction monitoring and protection tools.
Specialized USDT Verification Options
Our platform also evaluates multiple sites providing check services for Tether transfers and accounts:
- **USDT TRC20 and ERC20 Validation:** Many platforms offer comprehensive screenings for USDT transfers, aiding in the detection of questionable transactions.
- **AML Validation for USDT:** Options are offered for monitoring for money laundering actions.
- **“Cleanliness” Validation for Holdings:** Checking of deal and account purity is available to identify likely risks.
**Summary**
Finding the right tool for verifying and tracking crypto transfers is crucial for guaranteeing security and standard compliance. By reading our reviews, you can choose the most suitable tool for deal tracking and resource security. -
FINMA compliance check for cryptocurrency wallets
Introduction of Crypto Deal Verification and Regulatory Options
In the current cryptocurrency sector, ensuring transfer transparency and compliance with AML and KYC standards is essential. Following is an overview of well-known platforms that deliver tools for crypto transaction monitoring, verification, and resource protection.
1. Tokenmetrics.com
Description: Tokenmetrics offers digital asset evaluation to examine possible fraud risks. This platform allows investors to check coins prior to buying to prevent possibly risky holdings. Features:
- Risk evaluation.
- Suitable for buyers looking to avoid risky or fraudulent projects.
2. Metamask.Monitory.Center
Summary: Metamask Monitor Center permits users to verify their crypto holdings for suspicious actions and regulatory adherence. Benefits:
- Checks coins for legitimacy.
- Delivers alerts about potential fund blockages on particular exchanges.
- Provides thorough insights after wallet sync.
3. BestChange.ru
Description: Best Change is a service for observing and checking crypto exchange transfers, guaranteeing transparency and transaction protection. Highlights:
- Deal and holding monitoring.
- Sanctions checks.
- Internet interface; supports BTC and various different digital assets.
4. Bot amlchek
Overview: AMLCheck Bot is a holding observer and AML service that uses AI models to detect questionable activity. Features:
- Transaction tracking and user verification.
- Available via internet and chat bot.
- Compatible with digital assets including BSC, BTC, DOGE, and additional.
5. Alfabit AML
Description: AlfaBit delivers thorough Anti-Money Laundering (AML) services specifically made for the cryptocurrency field, supporting companies and financial organizations in maintaining standard conformity. Features:
- Comprehensive anti-money laundering tools and screenings.
- Adheres to modern safety and regulatory requirements.
6. Node AML
Description: AML Node delivers AML and KYC tools for cryptocurrency companies, which includes transaction observing, compliance checks, and evaluation. Highlights:
- Risk assessment options and compliance validations.
- Important for maintaining protected firm activities.
7. Btrace AML Crypto
Summary: Btrace.AMLcrypto.io is dedicated to asset check, providing deal observation, restriction screenings, and support if you are a target of theft. Highlights:
- Effective support for asset retrieval.
- Transaction tracking and protection options.
Exclusive USDT Verification Services
Our website also evaluates multiple platforms that offer check tools for USDT transactions and wallets:
- **USDT TRC20 and ERC20 Verification:** Various sites provide thorough checks for USDT deals, assisting in the identification of doubtful activity.
- **AML Screening for USDT:** Options are provided for observing for fraudulent transactions.
- **“Cleanliness” Validation for Accounts:** Verification of deal and account purity is available to find likely risks.
**Wrap-up**
Choosing the suitable platform for checking and tracking digital currency transactions is crucial for ensuring security and standard adherence. By reading our reviews, you can choose the best solution for transaction observation and resource safety. -
AML compliance check for cryptocurrency wallets
Overview of Crypto Transaction Validation and Compliance Solutions
In the current cryptocurrency market, maintaining transfer transparency and adherence with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) standards is vital. Below is an overview of leading platforms that deliver services for crypto deal monitoring, check, and asset safety.
1. Tokenmetrics.com
Summary: Token Metrics provides crypto analysis to evaluate potential risk risks. This solution enables users to review tokens prior to buying to avoid likely risky assets. Attributes:
- Threat evaluation.
- Perfect for holders aiming to bypass risky or fraud ventures.
2. Metamask Center
Overview: Metamask.Monitory.Center allows holders to check their crypto holdings for questionable activity and standard compliance. Features:
- Verifies tokens for purity.
- Offers alerts about potential fund restrictions on certain exchanges.
- Gives comprehensive insights after address linking.
3. BestChange.ru
Summary: Best Change is a platform for tracking and validating digital transaction deals, guaranteeing clarity and transfer security. Highlights:
- Transfer and holding tracking.
- Compliance checks.
- Web-based platform; accommodates BTC and several additional coins.
4. AML Bot
Overview: AMLCheck Bot is a investment tracker and anti-money laundering tool that uses AI models to identify dubious actions. Highlights:
- Transfer monitoring and personal validation.
- Available via online and chat bot.
- Supports coins like BSC, BTC, DOGE, and more.
5. AlphaBit
Overview: AlphaBit offers comprehensive AML solutions tailored for the digital currency market, supporting businesses and financial organizations in ensuring compliance conformity. Features:
- Extensive anti-money laundering tools and checks.
- Meets current protection and compliance requirements.
6. AMLNode
Description: AMLNode provides compliance and KYC tools for crypto firms, including transaction tracking, sanctions screening, and risk assessment. Benefits:
- Danger assessment tools and restriction checks.
- Valuable for ensuring protected business activities.
7. Btrace AML Crypto
Description: Btrace AML Crypto is dedicated to fund check, providing transfer tracking, restriction screenings, and support if you are a affected by fraud. Highlights:
- Reliable help for fund restoration.
- Transfer monitoring and safety options.
Dedicated USDT Check Services
Our website also provides information on multiple services that offer validation solutions for crypto transfers and wallets:
- **USDT TRC20 and ERC20 Check:** Numerous sites provide comprehensive screenings for USDT transfers, assisting in the detection of suspicious activity.
- **AML Screening for USDT:** Tools are available for tracking for suspicious activities.
- **“Cleanliness” Screenings for Accounts:** Verification of deal and account purity is offered to find possible dangers.
**Summary**
Finding the suitable tool for checking and observing digital currency transactions is crucial for guaranteeing safety and regulatory compliance. By consulting our recommendations, you can select the best tool for transaction tracking and fund safety. -
Explore a Realm of Virtual Chances with Items4Games
At ItemsforGames, we offer a vibrant marketplace for gamers to purchase or exchange accounts, virtual items, and options for some of the most popular games. If you are seeking to improve your game resources or wanting to profit from your game account, our service delivers a easy, safe, and valuable experience.
Why Select ItemsforGames?
**Extensive Game Library**: Discover a vast selection of titles, from intense titles such as Warzone and War Call to immersive role-playing games such as ARK and Genshin Impact. We have all games, ensuring no player is left behind.
**Variety of Options**: Our products include profile buys, in-game currency, exclusive items, achievements, and coaching services. If you need help leveling up or obtaining special benefits, we have it all.
**Easy Navigation**: Browse without hassle through our structured marketplace, categorized in order to get exactly the game you need with ease.
**Safe Transactions**: We prioritize your protection. All trades on our marketplace are processed with the utmost safeguarding to protect your private and financial details.
**Standouts from Our Collection**
- **Adventure and Exploration**: Games ARK and Day-Z let you dive into challenging settings with top-notch items and keys available.
- **Tactical and Exploration**: Enhance your performance in titles such as Royal Clash and Age of Wonders 4 with credits and options.
- **Competitive Gaming**: For competitive players, boost your skills with training and account upgrades for Valorant, DotA, and League of Legends.
**A Hub Made for Players**
Supported by Apex Technologies, a reliable business registered in Kazakhstan, ItemsforGames is a place where video game dreams become real. From buying early access passes for the newest titles to finding unique virtual goods, our platform fulfills every gaming requirement with professionalism and reliability.
Become part of the group now and upgrade your game play!
For questions or help, reach out to us at **support@items4games.com**. Together, let's game better, as one! -
items4games
Discover a Realm of Virtual Chances with Items4Play
At Items4Play, we offer a dynamic hub for enthusiasts to purchase or sell accounts, goods, and services for some of the most popular titles. If you are seeking to upgrade your gaming inventory or wanting to profit from your profile, our service delivers a seamless, safe, and valuable journey.
Reasons to Use ItemsforGames?
**Comprehensive Game Collection**: Browse a vast array of video games, from action-packed adventures like Battlefield and War Call to captivating role-playing games such as ARK and Genshin. We cover it all, making sure no enthusiast is left behind.
**Range of Services**: Our selections cover profile buys, credits, rare collectibles, milestones, and mentoring options. Whether you want guidance improving or obtaining special benefits, we have it all.
**User-friendly**: Navigate effortlessly through our well-organized site, arranged alphabetically to locate just what you are looking for fast.
**Safe Transactions**: We ensure your protection. All trades on our marketplace are conducted with the highest security to guard your personal and financial information.
**Highlights from Our Offerings**
- **Survival and Survival**: Games like ARK: Survival Evolved and Survival Day give you the chance to enter tough worlds with premium goods and accesses available.
- **Strategy and Questing**: Boost your gameplay in adventures like Royal Clash and Wonders Age with credits and options.
- **eSports Play**: For eSports players, boost your skills with mentoring and profile boosts for Valored, Dota, and LoL.
**A Platform Made for Players**
Operated by ApexTech, a trusted business registered in Kazakh Republic, Items4Play is a market where gaming aspirations become real. From purchasing early access codes for the freshest titles to finding unique virtual goods, our platform caters to every gamer’s need with professionalism and speed.
Sign up for the group right away and upgrade your gaming adventure!
For questions or assistance, contact us at **support@items4games.com**. Let's all game better, together! -
三國志T
k8 カジノ パチンコ P刀使ノ巫女 Ver.199
大当たりの瞬間は、周囲と一緒に盛り上がれるのが嬉しいです。共感が生まれます。
パラダイスハイビスカス
https://www.k8.skin/games/id3408
パチンコは、友人や家族と一緒に楽しむのに最適です。共に楽しむことで絆が深まります。
吉宗
[url=https://sites.google.com/view/a-slot-fist-of-the-north-star]CR 北斗の拳6 拳王
[/url]
戦律のストラタス
Pフィーバー革命機ヴァルヴレイヴ 3
押忍!サラリーマン番長
琉球の守護神
[url=https://sites.google.com/view/bingo-basilisk3/]k8 カジノ 甲賀忍法帖~Ⅲ
[/url]
ハイビスカスSE
L キン肉マン~7人の悪魔超人編~
CR牙狼FINAL
無双OROCHI
[url=https://sites.google.com/view/saint-seiya-golden-battle-chap]k8 カジノ パチンコ 聖闘士星矢 -黃金激闘篇-パチスロ スロット 機械割 解析 天井 初打ち 打ち方 スペック ゾーン 設定判別 ヤメ時・演出・プレミアムまとめ
[/url]
戦コレ!【太平女君】徳川家康
モンスターハンター月下雷鳴
P真・北斗無双 第3章
CRフィーバー戦姫絶唱シンフォギア
https://www.k8casino.review/faq/id3585
パチンコをすることで、運を試すドキドキ感が味わえます。挑戦する楽しさがあります。
CRぱちんこGANTZ
https://www.k8casino.city/archives/post-573.html
キャラクターの個性が際立っており、ストーリーに引き込まれます。 -
Explore a Universe of Video Game Opportunities with Items4Play
At ItemsforGames, we offer a vibrant platform for players to acquire or sell accounts, items, and options for some of the most popular games. Whether you're looking to improve your gaming arsenal or wanting to profit from your account, our site delivers a seamless, secure, and rewarding journey.
Why Select Items4Play?
**Broad Title Library**: Discover a extensive variety of video games, from action-packed titles such as Warzone and War Call to captivating RPGs like ARK: Survival Evolved and Genshin. We cover all games, making sure no gamer is excluded.
**Range of Options**: Our products cover account purchases, virtual money, exclusive items, achievements, and training sessions. If you need guidance leveling up or getting exclusive benefits, we are here to help.
**Ease of Use**: Navigate easily through our structured marketplace, arranged by order to get just the item you need fast.
**Protected Transactions**: We prioritize your protection. All transactions on our platform are processed with the utmost protection to secure your private and financial data.
**Key Points from Our Collection**
- **Adventure and Survival**: Games like ARK: Survival Evolved and Survival Day allow you to dive into exciting environments with top-notch gear and keys available.
- **Strategy and Questing**: Enhance your experience in titles such as Royal Clash and Wonders Age with virtual money and options.
- **Competitive Competitions**: For serious fans, enhance your abilities with training and level-ups for Valorant, Dota, and League of Legends.
**A Hub Built for Fans**
Backed by Apex Technologies, a trusted entity registered in Kazakhstan, ItemsforGames is a market where playtime dreams come true. From acquiring early access passes for the freshest games to getting hard-to-find in-game treasures, our platform caters to every player’s requirement with expertise and reliability.
Join the community now and elevate your game adventure!
For questions or help, reach out to us at **support@items4games.com**. Together, let's enjoy gaming, as one! -
In-game items
Uncover a Realm of Video Game Possibilities with ItemsforGames
At Items4Games, we deliver a active hub for gamers to buy or trade gaming accounts, virtual items, and features for top video games. Whether you are looking to improve your gaming resources or interested in selling your profile, our site offers a seamless, secure, and profitable process.
Why Use Items4Games?
**Extensive Title Catalog**: Browse a extensive array of titles, from action-packed games such as Battleground and Call of Duty to captivating role-playing games such as ARK: Survival Evolved and Genshin. We cover it all, making sure no gamer is excluded.
**Range of Options**: Our selections cover game account acquisitions, credits, exclusive goods, milestones, and coaching sessions. Whether you want assistance gaining levels or obtaining premium bonuses, we've got you covered.
**User-friendly**: Navigate effortlessly through our structured platform, organized by order to get just the game you are looking for fast.
**Safe Exchanges**: We focus on your safety. All transactions on our site are processed with the highest security to secure your private and monetary details.
**Highlights from Our Offerings**
- **Action and Survival**: Games like ARK and DayZ allow you to explore challenging worlds with premium items and passes available.
- **Strategy and Exploration**: Elevate your experience in games like Clash Royale and Age of Wonders 4 with virtual money and services.
- **Professional Gaming**: For serious fans, enhance your skills with training and profile boosts for Valored, Dota 2, and LoL.
**A Hub Made for Players**
Operated by Apex Technologies, a reliable entity officially recognized in Kazakh Republic, Items4Play is a hub where playtime wishes come true. From acquiring early access keys for the freshest titles to getting unique virtual goods, our platform meets every player’s wish with professionalism and reliability.
Sign up for the group today and upgrade your game adventure!
For inquiries or assistance, email us at **support@items4games.com**. Together, let's improve the game, as a community! -
items4games
Explore a Realm of Interactive Opportunities with Items4Games
At ItemsforGames, we offer a dynamic hub for gamers to buy or exchange profiles, virtual items, and options for top games. If you are looking to enhance your game inventory or wanting to profit from your account, our service offers a seamless, safe, and profitable process.
Why Use Items4Games?
**Extensive Title Library**: Browse a large array of games, from thrilling games like Warzone and COD to captivating adventure games such as ARK: Survival Evolved and Genshin. We include it all, ensuring no player is excluded.
**Variety of Features**: Our selections feature game account acquisitions, in-game currency, exclusive items, trophies, and training options. If you want assistance leveling up or obtaining special benefits, we've got you covered.
**User-friendly**: Navigate without hassle through our structured site, organized alphabetically to locate precisely what you want quickly.
**Secure Exchanges**: We prioritize your protection. All exchanges on our site are conducted with the top security to protect your confidential and monetary details.
**Standouts from Our Offerings**
- **Survival and Adventure**: Games like ARK and DayZ give you the chance to dive into exciting worlds with premium goods and passes for sale.
- **Adventure and Exploration**: Elevate your gameplay in titles like Royal Clash and Wonders Age with credits and features.
- **Professional Play**: For serious fans, enhance your technique with mentoring and profile boosts for Val, DotA, and League of Legends.
**A Platform Made for Fans**
Backed by ApexTech, a established company officially recognized in Kazakh Republic, ItemsforGames is a market where playtime wishes become real. From acquiring pre-order keys for the newest titles to finding hard-to-find game items, our platform meets every player’s need with expertise and speed.
Join the group now and elevate your gaming play!
For support or guidance, email us at **support@items4games.com**. Together, let's game better, as a community! -
https://experienceleaguecommunities.adobe.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/17910918 stromectol 3 mg tablet price
-
THA娛樂城
THA娛樂城與九州娛樂簡介
THA娛樂城是九州娛樂旗下的一個知名線上娛樂平台,致力於為玩家提供多元化且優質的娛樂服務。九州娛樂是亞洲地區領先的線上娛樂品牌,長期專注於打造穩定、公平且充滿樂趣的遊戲環境,旗下擁有多個知名娛樂平台,而THA娛樂城便是其中的一個旗艦產品。以下將詳細介紹THA娛樂城的特色與服務。
THA娛樂城的遊戲種類
THA娛樂城為玩家提供了多樣化的遊戲選擇,滿足不同玩家的需求與興趣,包括以下幾大類別:
1. 體育投注
體育迷可以在THA娛樂城享受豐富的體育賽事投注,涵蓋足球、籃球、網球等多項國際體育比賽。平台提供即時賠率和多種投注選項,讓玩家隨時掌握比賽動態並進行下注。
2. 真人娛樂
真人娛樂區提供即時互動的遊戲體驗,玩家可透過直播技術與真人荷官互動,遊玩如百家樂、輪盤、骰寶等經典遊戲。這不僅增添了真實感,更讓玩家有身臨其境的感受。
3. 電子老虎機
THA娛樂城匯集了多款高人氣的電子老虎機遊戲,從經典水果機到新潮主題機,皆配備精美的畫面與流暢的操作介面,為玩家帶來無限樂趣。
4. 捕魚遊戲
捕魚遊戲是許多玩家的最愛,THA娛樂城提供多種精美場景和豐富玩法的捕魚遊戲,玩家可以挑戰高額獎勵,享受射擊與策略結合的獨特樂趣。
5. 彩票與其他遊戲
除了以上幾類,平台還提供彩票遊戲及其他創新型娛樂遊戲,適合喜歡嘗試新鮮玩法的玩家。
九州娛樂的技術支持
作為THA娛樂城的母公司,九州娛樂以其強大的技術實力與嚴謹的管理體系為平台提供支持。九州娛樂採用國際領先的安全加密技術,確保玩家的個人資訊與交易數據得到妥善保護。此外,平台的遊戲結果皆經過嚴格的隨機性測試與第三方機構認證,保證公平公正。
優質的會員服務
THA娛樂城致力於打造一個高品質的會員體驗,其服務特色包括:
- 優惠活動
平台定期推出多種促銷活動,如新會員註冊禮金、存款返利、週週回饋等,讓玩家享受更多的遊戲資金。
- 快速出入金
平台提供便捷且快速的存提款服務,玩家可以安心進行資金操作,且無需擔心延遲問題。
- 24小時客戶服務
為了確保玩家的需求能即時被解決,THA娛樂城提供全年無休的客服支援,無論是遊戲問題還是技術諮詢,客服團隊都能快速回應。
與其他平台的區別
THA娛樂城之所以能在眾多線上娛樂平台中脫穎而出,不僅因其豐富的遊戲種類與高品質服務,更在於它所帶來的獨特價值:
1. 品牌信譽
作為九州娛樂旗下的品牌,THA娛樂城擁有長期積累的良好信譽,是許多玩家的首選。
2. 創新與多樣性
平台不斷推出新遊戲與創意玩法,讓玩家始終保持新鮮感。
3. 本地化服務
THA娛樂城深諳玩家需求,提供多語言支援與符合本地習慣的服務,提升玩家的使用便利性。
未來展望
隨著線上娛樂行業的快速發展,THA娛樂城也在持續進步與創新,力求為玩家帶來更多驚喜。無論是透過引進新的遊戲技術、擴展遊戲種類,還是改善服務品質,THA娛樂城都希望成為每位玩家的最佳娛樂夥伴。
總結來說,THA娛樂城憑藉其豐富的遊戲內容、可靠的技術支持以及優質的會員服務,已在亞洲娛樂市場佔有一席之地。如果您正在尋找一個結合刺激與信賴的娛樂平台,那麼THA娛樂城絕對值得一試。 -
THA娛樂城與九州娛樂簡介
THA娛樂城是九州娛樂旗下的一個知名線上娛樂平台,致力於為玩家提供多元化且優質的娛樂服務。九州娛樂是亞洲地區領先的線上娛樂品牌,長期專注於打造穩定、公平且充滿樂趣的遊戲環境,旗下擁有多個知名娛樂平台,而THA娛樂城便是其中的一個旗艦產品。以下將詳細介紹THA娛樂城的特色與服務。
THA娛樂城的遊戲種類
THA娛樂城為玩家提供了多樣化的遊戲選擇,滿足不同玩家的需求與興趣,包括以下幾大類別:
1. 體育投注
體育迷可以在THA娛樂城享受豐富的體育賽事投注,涵蓋足球、籃球、網球等多項國際體育比賽。平台提供即時賠率和多種投注選項,讓玩家隨時掌握比賽動態並進行下注。
2. 真人娛樂
真人娛樂區提供即時互動的遊戲體驗,玩家可透過直播技術與真人荷官互動,遊玩如百家樂、輪盤、骰寶等經典遊戲。這不僅增添了真實感,更讓玩家有身臨其境的感受。
3. 電子老虎機
THA娛樂城匯集了多款高人氣的電子老虎機遊戲,從經典水果機到新潮主題機,皆配備精美的畫面與流暢的操作介面,為玩家帶來無限樂趣。
4. 捕魚遊戲
捕魚遊戲是許多玩家的最愛,THA娛樂城提供多種精美場景和豐富玩法的捕魚遊戲,玩家可以挑戰高額獎勵,享受射擊與策略結合的獨特樂趣。
5. 彩票與其他遊戲
除了以上幾類,平台還提供彩票遊戲及其他創新型娛樂遊戲,適合喜歡嘗試新鮮玩法的玩家。
九州娛樂的技術支持
作為THA娛樂城的母公司,九州娛樂以其強大的技術實力與嚴謹的管理體系為平台提供支持。九州娛樂採用國際領先的安全加密技術,確保玩家的個人資訊與交易數據得到妥善保護。此外,平台的遊戲結果皆經過嚴格的隨機性測試與第三方機構認證,保證公平公正。
優質的會員服務
THA娛樂城致力於打造一個高品質的會員體驗,其服務特色包括:
- 優惠活動
平台定期推出多種促銷活動,如新會員註冊禮金、存款返利、週週回饋等,讓玩家享受更多的遊戲資金。
- 快速出入金
平台提供便捷且快速的存提款服務,玩家可以安心進行資金操作,且無需擔心延遲問題。
- 24小時客戶服務
為了確保玩家的需求能即時被解決,THA娛樂城提供全年無休的客服支援,無論是遊戲問題還是技術諮詢,客服團隊都能快速回應。
與其他平台的區別
THA娛樂城之所以能在眾多線上娛樂平台中脫穎而出,不僅因其豐富的遊戲種類與高品質服務,更在於它所帶來的獨特價值:
1. 品牌信譽
作為九州娛樂旗下的品牌,THA娛樂城擁有長期積累的良好信譽,是許多玩家的首選。
2. 創新與多樣性
平台不斷推出新遊戲與創意玩法,讓玩家始終保持新鮮感。
3. 本地化服務
THA娛樂城深諳玩家需求,提供多語言支援與符合本地習慣的服務,提升玩家的使用便利性。
未來展望
隨著線上娛樂行業的快速發展,THA娛樂城也在持續進步與創新,力求為玩家帶來更多驚喜。無論是透過引進新的遊戲技術、擴展遊戲種類,還是改善服務品質,THA娛樂城都希望成為每位玩家的最佳娛樂夥伴。
總結來說,THA娛樂城憑藉其豐富的遊戲內容、可靠的技術支持以及優質的會員服務,已在亞洲娛樂市場佔有一席之地。如果您正在尋找一個結合刺激與信賴的娛樂平台,那麼THA娛樂城絕對值得一試。 -
九州娛樂
THA娛樂城與九州娛樂簡介
THA娛樂城是九州娛樂旗下的一個知名線上娛樂平台,致力於為玩家提供多元化且優質的娛樂服務。九州娛樂是亞洲地區領先的線上娛樂品牌,長期專注於打造穩定、公平且充滿樂趣的遊戲環境,旗下擁有多個知名娛樂平台,而THA娛樂城便是其中的一個旗艦產品。以下將詳細介紹THA娛樂城的特色與服務。
THA娛樂城的遊戲種類
THA娛樂城為玩家提供了多樣化的遊戲選擇,滿足不同玩家的需求與興趣,包括以下幾大類別:
1. 體育投注
體育迷可以在THA娛樂城享受豐富的體育賽事投注,涵蓋足球、籃球、網球等多項國際體育比賽。平台提供即時賠率和多種投注選項,讓玩家隨時掌握比賽動態並進行下注。
2. 真人娛樂
真人娛樂區提供即時互動的遊戲體驗,玩家可透過直播技術與真人荷官互動,遊玩如百家樂、輪盤、骰寶等經典遊戲。這不僅增添了真實感,更讓玩家有身臨其境的感受。
3. 電子老虎機
THA娛樂城匯集了多款高人氣的電子老虎機遊戲,從經典水果機到新潮主題機,皆配備精美的畫面與流暢的操作介面,為玩家帶來無限樂趣。
4. 捕魚遊戲
捕魚遊戲是許多玩家的最愛,THA娛樂城提供多種精美場景和豐富玩法的捕魚遊戲,玩家可以挑戰高額獎勵,享受射擊與策略結合的獨特樂趣。
5. 彩票與其他遊戲
除了以上幾類,平台還提供彩票遊戲及其他創新型娛樂遊戲,適合喜歡嘗試新鮮玩法的玩家。
九州娛樂的技術支持
作為THA娛樂城的母公司,九州娛樂以其強大的技術實力與嚴謹的管理體系為平台提供支持。九州娛樂採用國際領先的安全加密技術,確保玩家的個人資訊與交易數據得到妥善保護。此外,平台的遊戲結果皆經過嚴格的隨機性測試與第三方機構認證,保證公平公正。
優質的會員服務
THA娛樂城致力於打造一個高品質的會員體驗,其服務特色包括:
- 優惠活動
平台定期推出多種促銷活動,如新會員註冊禮金、存款返利、週週回饋等,讓玩家享受更多的遊戲資金。
- 快速出入金
平台提供便捷且快速的存提款服務,玩家可以安心進行資金操作,且無需擔心延遲問題。
- 24小時客戶服務
為了確保玩家的需求能即時被解決,THA娛樂城提供全年無休的客服支援,無論是遊戲問題還是技術諮詢,客服團隊都能快速回應。
與其他平台的區別
THA娛樂城之所以能在眾多線上娛樂平台中脫穎而出,不僅因其豐富的遊戲種類與高品質服務,更在於它所帶來的獨特價值:
1. 品牌信譽
作為九州娛樂旗下的品牌,THA娛樂城擁有長期積累的良好信譽,是許多玩家的首選。
2. 創新與多樣性
平台不斷推出新遊戲與創意玩法,讓玩家始終保持新鮮感。
3. 本地化服務
THA娛樂城深諳玩家需求,提供多語言支援與符合本地習慣的服務,提升玩家的使用便利性。
未來展望
隨著線上娛樂行業的快速發展,THA娛樂城也在持續進步與創新,力求為玩家帶來更多驚喜。無論是透過引進新的遊戲技術、擴展遊戲種類,還是改善服務品質,THA娛樂城都希望成為每位玩家的最佳娛樂夥伴。
總結來說,THA娛樂城憑藉其豐富的遊戲內容、可靠的技術支持以及優質的會員服務,已在亞洲娛樂市場佔有一席之地。如果您正在尋找一個結合刺激與信賴的娛樂平台,那麼THA娛樂城絕對值得一試。 -
THA娛樂城與九州娛樂簡介
THA娛樂城是九州娛樂旗下的一個知名線上娛樂平台,致力於為玩家提供多元化且優質的娛樂服務。九州娛樂是亞洲地區領先的線上娛樂品牌,長期專注於打造穩定、公平且充滿樂趣的遊戲環境,旗下擁有多個知名娛樂平台,而THA娛樂城便是其中的一個旗艦產品。以下將詳細介紹THA娛樂城的特色與服務。
THA娛樂城的遊戲種類
THA娛樂城為玩家提供了多樣化的遊戲選擇,滿足不同玩家的需求與興趣,包括以下幾大類別:
1. 體育投注
體育迷可以在THA娛樂城享受豐富的體育賽事投注,涵蓋足球、籃球、網球等多項國際體育比賽。平台提供即時賠率和多種投注選項,讓玩家隨時掌握比賽動態並進行下注。
2. 真人娛樂
真人娛樂區提供即時互動的遊戲體驗,玩家可透過直播技術與真人荷官互動,遊玩如百家樂、輪盤、骰寶等經典遊戲。這不僅增添了真實感,更讓玩家有身臨其境的感受。
3. 電子老虎機
THA娛樂城匯集了多款高人氣的電子老虎機遊戲,從經典水果機到新潮主題機,皆配備精美的畫面與流暢的操作介面,為玩家帶來無限樂趣。
4. 捕魚遊戲
捕魚遊戲是許多玩家的最愛,THA娛樂城提供多種精美場景和豐富玩法的捕魚遊戲,玩家可以挑戰高額獎勵,享受射擊與策略結合的獨特樂趣。
5. 彩票與其他遊戲
除了以上幾類,平台還提供彩票遊戲及其他創新型娛樂遊戲,適合喜歡嘗試新鮮玩法的玩家。
九州娛樂的技術支持
作為THA娛樂城的母公司,九州娛樂以其強大的技術實力與嚴謹的管理體系為平台提供支持。九州娛樂採用國際領先的安全加密技術,確保玩家的個人資訊與交易數據得到妥善保護。此外,平台的遊戲結果皆經過嚴格的隨機性測試與第三方機構認證,保證公平公正。
優質的會員服務
THA娛樂城致力於打造一個高品質的會員體驗,其服務特色包括:
- 優惠活動
平台定期推出多種促銷活動,如新會員註冊禮金、存款返利、週週回饋等,讓玩家享受更多的遊戲資金。
- 快速出入金
平台提供便捷且快速的存提款服務,玩家可以安心進行資金操作,且無需擔心延遲問題。
- 24小時客戶服務
為了確保玩家的需求能即時被解決,THA娛樂城提供全年無休的客服支援,無論是遊戲問題還是技術諮詢,客服團隊都能快速回應。
與其他平台的區別
THA娛樂城之所以能在眾多線上娛樂平台中脫穎而出,不僅因其豐富的遊戲種類與高品質服務,更在於它所帶來的獨特價值:
1. 品牌信譽
作為九州娛樂旗下的品牌,THA娛樂城擁有長期積累的良好信譽,是許多玩家的首選。
2. 創新與多樣性
平台不斷推出新遊戲與創意玩法,讓玩家始終保持新鮮感。
3. 本地化服務
THA娛樂城深諳玩家需求,提供多語言支援與符合本地習慣的服務,提升玩家的使用便利性。
未來展望
隨著線上娛樂行業的快速發展,THA娛樂城也在持續進步與創新,力求為玩家帶來更多驚喜。無論是透過引進新的遊戲技術、擴展遊戲種類,還是改善服務品質,THA娛樂城都希望成為每位玩家的最佳娛樂夥伴。
總結來說,THA娛樂城憑藉其豐富的遊戲內容、可靠的技術支持以及優質的會員服務,已在亞洲娛樂市場佔有一席之地。如果您正在尋找一個結合刺激與信賴的娛樂平台,那麼THA娛樂城絕對值得一試。 -
메인 서비스: 간편하고 효율적인 배송 및 구매 대행 서비스
1. 대행 서비스 주요 기능
메인 서비스는 고객이 한 번에 필요한 대행 서비스를 신청할 수 있도록 다양한 기능을 제공합니다.
배송대행 신청: 국내외 상품 배송을 대신 처리하며, 효율적인 시스템으로 신속한 배송을 보장합니다.
구매대행 신청: 원하는 상품을 대신 구매해주는 서비스로, 고객의 수고를 줄입니다.
엑셀 대량 등록: 대량 상품을 엑셀로 손쉽게 등록 가능하여 상업 고객의 편의성을 증대합니다.
재고 관리 신청: 창고 보관 및 재고 관리를 통해 물류 과정을 최적화합니다.
2. 고객 지원 시스템
메인 서비스는 사용자 친화적인 접근성을 제공합니다.
유저 가이드: 대행 서비스를 더욱 합리적으로 사용할 수 있도록 세부 안내서를 제공합니다.
운송장 조회: 일본 사가와 등 주요 운송사의 추적 시스템과 연동하여 운송 상황을 실시간으로 확인 가능합니다.
3. 비용 안내와 부가 서비스
비용 계산기: 예상되는 비용을 간편하게 계산해 예산 관리를 돕습니다.
부가 서비스: 교환 및 반품, 폐기 및 검역 지원 등 추가적인 편의 서비스를 제공합니다.
출항 스케줄 확인: 해외 배송의 경우 출항 일정을 사전에 확인 가능하여 배송 계획을 세울 수 있습니다.
4. 공지사항
기본 검수 공지
무료 검수 서비스로 고객의 부담을 줄이며, 보다 철저한 검수가 필요한 경우 유료 정밀 검수 서비스를 권장합니다.
수출허가서 발급 안내
항공과 해운 수출 건에 대한 허가서를 효율적으로 발급받는 방법을 상세히 안내하며, 고객의 요청에 따라 이메일로 전달됩니다.
노데이터 처리 안내
운송장 번호 없는 주문에 대한 새로운 처리 방안을 도입하여, 노데이터 발생 시 관리비가 부과되지만 서비스 품질을 개선합니다.
5. 고객과의 소통
카카오톡 상담: 실시간 상담을 통해 고객의 궁금증을 해결합니다.
공지사항 알림: 서비스 이용 중 필수 정보를 지속적으로 업데이트합니다.
메인 서비스는 고객 만족을 최우선으로 하며, 지속적인 개선과 세심한 관리를 통해 최상의 경험을 제공합니다. -
일본배대지
메인 서비스: 간편하고 효율적인 배송 및 구매 대행 서비스
1. 대행 서비스 주요 기능
메인 서비스는 고객이 한 번에 필요한 대행 서비스를 신청할 수 있도록 다양한 기능을 제공합니다.
배송대행 신청: 국내외 상품 배송을 대신 처리하며, 효율적인 시스템으로 신속한 배송을 보장합니다.
구매대행 신청: 원하는 상품을 대신 구매해주는 서비스로, 고객의 수고를 줄입니다.
엑셀 대량 등록: 대량 상품을 엑셀로 손쉽게 등록 가능하여 상업 고객의 편의성을 증대합니다.
재고 관리 신청: 창고 보관 및 재고 관리를 통해 물류 과정을 최적화합니다.
2. 고객 지원 시스템
메인 서비스는 사용자 친화적인 접근성을 제공합니다.
유저 가이드: 대행 서비스를 더욱 합리적으로 사용할 수 있도록 세부 안내서를 제공합니다.
운송장 조회: 일본 사가와 등 주요 운송사의 추적 시스템과 연동하여 운송 상황을 실시간으로 확인 가능합니다.
3. 비용 안내와 부가 서비스
비용 계산기: 예상되는 비용을 간편하게 계산해 예산 관리를 돕습니다.
부가 서비스: 교환 및 반품, 폐기 및 검역 지원 등 추가적인 편의 서비스를 제공합니다.
출항 스케줄 확인: 해외 배송의 경우 출항 일정을 사전에 확인 가능하여 배송 계획을 세울 수 있습니다.
4. 공지사항
기본 검수 공지
무료 검수 서비스로 고객의 부담을 줄이며, 보다 철저한 검수가 필요한 경우 유료 정밀 검수 서비스를 권장합니다.
수출허가서 발급 안내
항공과 해운 수출 건에 대한 허가서를 효율적으로 발급받는 방법을 상세히 안내하며, 고객의 요청에 따라 이메일로 전달됩니다.
노데이터 처리 안내
운송장 번호 없는 주문에 대한 새로운 처리 방안을 도입하여, 노데이터 발생 시 관리비가 부과되지만 서비스 품질을 개선합니다.
5. 고객과의 소통
카카오톡 상담: 실시간 상담을 통해 고객의 궁금증을 해결합니다.
공지사항 알림: 서비스 이용 중 필수 정보를 지속적으로 업데이트합니다.
메인 서비스는 고객 만족을 최우선으로 하며, 지속적인 개선과 세심한 관리를 통해 최상의 경험을 제공합니다. -
Although he had already stabilized his mind, Zhao Ling is soul was in extreme pain when the robbery thunder slammed into his body, and his stable mind was directly broken how to buy cytotec without dr prescription He was alert and oriented, and vitals were stable
-
The body can make too much or too little estrogen, and this can have a major impact on fertility generic cytotec without insurance Wahl RL, Zasadny K, Helvie M, Hutchins GD, Weber B, Cody R Metabolic monitoring of breast cancer chemohormonotherapy using positron emission tomography initial evaluation
-
일본 소비세 환급, 네오리아와 함께라면 간편하고 안전하게
일본 소비세 환급은 복잡하고 까다로운 절차로 많은 구매대행 셀러들이 어려움을 겪는 분야입니다. 네오리아는 다년간의 경험과 전문성을 바탕으로 신뢰할 수 있는 서비스를 제공하며, 일본 소비세 환급 과정을 쉽고 효율적으로 처리합니다.
1. 일본 소비세 환급의 필요성과 네오리아의 역할
네오리아는 일본 현지 법인을 설립하지 않아도 합법적인 방식으로 소비세 환급을 받을 수 있는 솔루션을 제공합니다. 이를 통해:
한국 개인사업자와 법인 사업자 모두 간편하게 환급 절차를 진행할 수 있습니다.
일본의 복잡한 서류 심사를 최소화하고, 현지 로컬 세리사와 협력하여 최적의 결과를 보장합니다.
2. 소비세 환급의 주요 특징
일본 연고가 없어도 가능: 일본에 사업자가 없더라도 네오리아는 신뢰할 수 있는 서비스를 통해 소비세 환급을 지원합니다.
서류 작성 걱정 해결: 잘못된 서류 제출로 환급이 거절될까 걱정될 필요 없습니다. 네오리아의 전문 대응팀이 모든 과정을 정밀하게 관리합니다.
현지 법인 운영자를 위한 추가 지원: 일본 내 개인사업자나 법인 운영자에게는 세무 감사와 이슈 대응까지 포함된 고급 서비스를 제공합니다.
3. 네오리아 서비스의 장점
전문성과 신뢰성: 정부로부터 인정받은 투명성과 세무 분야의 우수한 성과를 자랑합니다.
맞춤형 서포트: 다양한 사례를 통해 쌓은 경험으로 고객이 예상치 못한 어려움까지 미리 해결합니다.
로컬 업체에서 불가능한 고급 서비스: 한국인 고객을 위해 정확하고 간편한 세무회계 및 소비세 환급 서비스를 제공합니다.
4. 네오리아가 제공하는 혜택
시간 절약: 복잡한 절차와 서류 준비 과정을 전문가가 대신 처리합니다.
안심 환급: 철저한 관리와 세심한 대응으로 안전하게 환급을 받을 수 있습니다.
추가 서비스: 세무감사와 이슈 발생 시 즉각적인 지원으로 사업의 연속성을 보장합니다.
네오리아는 소비세 환급이 복잡하고 어렵다고 느껴지는 고객들에게 최적의 길잡이가 되어드립니다. 신뢰를 바탕으로 한 전문적인 서비스로, 더 이상 소비세 환급 문제로 고민하지 마세요! -
일본 소비세 환급, 네오리아와 함께라면 간편하고 안전하게
일본 소비세 환급은 복잡하고 까다로운 절차로 많은 구매대행 셀러들이 어려움을 겪는 분야입니다. 네오리아는 다년간의 경험과 전문성을 바탕으로 신뢰할 수 있는 서비스를 제공하며, 일본 소비세 환급 과정을 쉽고 효율적으로 처리합니다.
1. 일본 소비세 환급의 필요성과 네오리아의 역할
네오리아는 일본 현지 법인을 설립하지 않아도 합법적인 방식으로 소비세 환급을 받을 수 있는 솔루션을 제공합니다. 이를 통해:
한국 개인사업자와 법인 사업자 모두 간편하게 환급 절차를 진행할 수 있습니다.
일본의 복잡한 서류 심사를 최소화하고, 현지 로컬 세리사와 협력하여 최적의 결과를 보장합니다.
2. 소비세 환급의 주요 특징
일본 연고가 없어도 가능: 일본에 사업자가 없더라도 네오리아는 신뢰할 수 있는 서비스를 통해 소비세 환급을 지원합니다.
서류 작성 걱정 해결: 잘못된 서류 제출로 환급이 거절될까 걱정될 필요 없습니다. 네오리아의 전문 대응팀이 모든 과정을 정밀하게 관리합니다.
현지 법인 운영자를 위한 추가 지원: 일본 내 개인사업자나 법인 운영자에게는 세무 감사와 이슈 대응까지 포함된 고급 서비스를 제공합니다.
3. 네오리아 서비스의 장점
전문성과 신뢰성: 정부로부터 인정받은 투명성과 세무 분야의 우수한 성과를 자랑합니다.
맞춤형 서포트: 다양한 사례를 통해 쌓은 경험으로 고객이 예상치 못한 어려움까지 미리 해결합니다.
로컬 업체에서 불가능한 고급 서비스: 한국인 고객을 위해 정확하고 간편한 세무회계 및 소비세 환급 서비스를 제공합니다.
4. 네오리아가 제공하는 혜택
시간 절약: 복잡한 절차와 서류 준비 과정을 전문가가 대신 처리합니다.
안심 환급: 철저한 관리와 세심한 대응으로 안전하게 환급을 받을 수 있습니다.
추가 서비스: 세무감사와 이슈 발생 시 즉각적인 지원으로 사업의 연속성을 보장합니다.
네오리아는 소비세 환급이 복잡하고 어렵다고 느껴지는 고객들에게 최적의 길잡이가 되어드립니다. 신뢰를 바탕으로 한 전문적인 서비스로, 더 이상 소비세 환급 문제로 고민하지 마세요! -
일본소비세환급
일본 소비세 환급, 네오리아와 함께라면 간편하고 안전하게
일본 소비세 환급은 복잡하고 까다로운 절차로 많은 구매대행 셀러들이 어려움을 겪는 분야입니다. 네오리아는 다년간의 경험과 전문성을 바탕으로 신뢰할 수 있는 서비스를 제공하며, 일본 소비세 환급 과정을 쉽고 효율적으로 처리합니다.
1. 일본 소비세 환급의 필요성과 네오리아의 역할
네오리아는 일본 현지 법인을 설립하지 않아도 합법적인 방식으로 소비세 환급을 받을 수 있는 솔루션을 제공합니다. 이를 통해:
한국 개인사업자와 법인 사업자 모두 간편하게 환급 절차를 진행할 수 있습니다.
일본의 복잡한 서류 심사를 최소화하고, 현지 로컬 세리사와 협력하여 최적의 결과를 보장합니다.
2. 소비세 환급의 주요 특징
일본 연고가 없어도 가능: 일본에 사업자가 없더라도 네오리아는 신뢰할 수 있는 서비스를 통해 소비세 환급을 지원합니다.
서류 작성 걱정 해결: 잘못된 서류 제출로 환급이 거절될까 걱정될 필요 없습니다. 네오리아의 전문 대응팀이 모든 과정을 정밀하게 관리합니다.
현지 법인 운영자를 위한 추가 지원: 일본 내 개인사업자나 법인 운영자에게는 세무 감사와 이슈 대응까지 포함된 고급 서비스를 제공합니다.
3. 네오리아 서비스의 장점
전문성과 신뢰성: 정부로부터 인정받은 투명성과 세무 분야의 우수한 성과를 자랑합니다.
맞춤형 서포트: 다양한 사례를 통해 쌓은 경험으로 고객이 예상치 못한 어려움까지 미리 해결합니다.
로컬 업체에서 불가능한 고급 서비스: 한국인 고객을 위해 정확하고 간편한 세무회계 및 소비세 환급 서비스를 제공합니다.
4. 네오리아가 제공하는 혜택
시간 절약: 복잡한 절차와 서류 준비 과정을 전문가가 대신 처리합니다.
안심 환급: 철저한 관리와 세심한 대응으로 안전하게 환급을 받을 수 있습니다.
추가 서비스: 세무감사와 이슈 발생 시 즉각적인 지원으로 사업의 연속성을 보장합니다.
네오리아는 소비세 환급이 복잡하고 어렵다고 느껴지는 고객들에게 최적의 길잡이가 되어드립니다. 신뢰를 바탕으로 한 전문적인 서비스로, 더 이상 소비세 환급 문제로 고민하지 마세요! -
일본 소비세 환급, 네오리아와 함께라면 간편하고 안전하게
일본 소비세 환급은 복잡하고 까다로운 절차로 많은 구매대행 셀러들이 어려움을 겪는 분야입니다. 네오리아는 다년간의 경험과 전문성을 바탕으로 신뢰할 수 있는 서비스를 제공하며, 일본 소비세 환급 과정을 쉽고 효율적으로 처리합니다.
1. 일본 소비세 환급의 필요성과 네오리아의 역할
네오리아는 일본 현지 법인을 설립하지 않아도 합법적인 방식으로 소비세 환급을 받을 수 있는 솔루션을 제공합니다. 이를 통해:
한국 개인사업자와 법인 사업자 모두 간편하게 환급 절차를 진행할 수 있습니다.
일본의 복잡한 서류 심사를 최소화하고, 현지 로컬 세리사와 협력하여 최적의 결과를 보장합니다.
2. 소비세 환급의 주요 특징
일본 연고가 없어도 가능: 일본에 사업자가 없더라도 네오리아는 신뢰할 수 있는 서비스를 통해 소비세 환급을 지원합니다.
서류 작성 걱정 해결: 잘못된 서류 제출로 환급이 거절될까 걱정될 필요 없습니다. 네오리아의 전문 대응팀이 모든 과정을 정밀하게 관리합니다.
현지 법인 운영자를 위한 추가 지원: 일본 내 개인사업자나 법인 운영자에게는 세무 감사와 이슈 대응까지 포함된 고급 서비스를 제공합니다.
3. 네오리아 서비스의 장점
전문성과 신뢰성: 정부로부터 인정받은 투명성과 세무 분야의 우수한 성과를 자랑합니다.
맞춤형 서포트: 다양한 사례를 통해 쌓은 경험으로 고객이 예상치 못한 어려움까지 미리 해결합니다.
로컬 업체에서 불가능한 고급 서비스: 한국인 고객을 위해 정확하고 간편한 세무회계 및 소비세 환급 서비스를 제공합니다.
4. 네오리아가 제공하는 혜택
시간 절약: 복잡한 절차와 서류 준비 과정을 전문가가 대신 처리합니다.
안심 환급: 철저한 관리와 세심한 대응으로 안전하게 환급을 받을 수 있습니다.
추가 서비스: 세무감사와 이슈 발생 시 즉각적인 지원으로 사업의 연속성을 보장합니다.
네오리아는 소비세 환급이 복잡하고 어렵다고 느껴지는 고객들에게 최적의 길잡이가 되어드립니다. 신뢰를 바탕으로 한 전문적인 서비스로, 더 이상 소비세 환급 문제로 고민하지 마세요! -
bitcoin risk level
Summary of Crypto Transaction Check and Compliance Services
In the current cryptocurrency sector, guaranteeing transaction transparency and compliance with AML and Customer Identification regulations is crucial. Following is an outline of leading platforms that deliver solutions for cryptocurrency deal tracking, verification, and fund protection.
1. Token Metrics
Overview: Token Metrics provides digital asset assessment to assess possible fraud risks. This solution enables investors to check cryptocurrencies ahead of investment to prevent potentially risky assets. Highlights:
- Danger evaluation.
- Perfect for holders aiming to bypass risky or scam projects.
2. Metamask Center
Summary: Metamask Monitor Center enables users to review their digital asset resources for suspicious transactions and standard compliance. Benefits:
- Checks coins for legitimacy.
- Delivers notifications about potential asset blockages on specific exchanges.
- Delivers comprehensive reports after wallet linking.
3. Bestchange.com
Description: Bestchange.ru is a service for monitoring and checking cryptocurrency transaction transactions, ensuring clarity and transaction security. Benefits:
- Transfer and holding monitoring.
- Restriction validation.
- Web-based portal; supports BTC and multiple different cryptocurrencies.
4. AML Bot
Summary: AMLCheck Bot is a portfolio monitor and compliance tool that employs artificial intelligence algorithms to identify suspicious actions. Advantages:
- Deal tracking and identity check.
- Offered via online and Telegram bot.
- Supports coins including BSC, BTC, DOGE, and other types.
5. Alfabit AML
Summary: AlphaBit offers complete Anti-Money Laundering (AML) services tailored for the digital currency market, assisting firms and banks in maintaining regulatory compliance. Features:
- Extensive compliance features and checks.
- Adheres to current safety and compliance requirements.
6. AMLNode
Description: AMLNode offers AML and customer identity services for digital currency companies, including transaction monitoring, restriction validation, and analysis. Features:
- Danger analysis options and compliance validations.
- Valuable for maintaining safe firm activities.
7. Btrace.AMLcrypto.io
Description: Btrace.AMLcrypto.io focuses on fund verification, offering transfer observation, sanctions checks, and assistance if you are a victim of fraud. Advantages:
- Reliable support for fund restoration.
- Transaction tracking and protection options.
Exclusive USDT Check Services
Our platform also provides information on multiple platforms providing check tools for Tether deals and accounts:
- **USDT TRC20 and ERC20 Check:** Numerous sites support detailed checks for USDT transfers, assisting in the detection of suspicious activity.
- **AML Screening for USDT:** Options are offered for observing for suspicious transactions.
- **“Cleanliness” Checks for Accounts:** Validation of deal and wallet “cleanliness” is offered to find potential threats.
**Conclusion**
Choosing the best tool for checking and monitoring digital currency transactions is essential for ensuring safety and regulatory compliance. By consulting our reviews, you can find the ideal service for transfer tracking and asset protection. -
Introduction of Crypto Transfer Check and Conformity Services
In today's digital asset industry, guaranteeing transfer openness and conformity with Anti-Laundering and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations is crucial. Following is an overview of well-known sites that deliver tools for cryptocurrency deal monitoring, check, and asset protection.
1. Token Metrics Platform
Summary: Tokenmetrics provides digital asset evaluation to assess likely scam dangers. This solution lets investors to check coins prior to buying to evade potentially fraudulent assets. Features:
- Risk analysis.
- Suitable for holders looking to steer clear of questionable or fraud ventures.
2. Metamask Center
Summary: Metamask.Monitory.Center permits individuals to review their cryptocurrency assets for suspicious transactions and standard compliance. Benefits:
- Verifies assets for purity.
- Provides notifications about possible fund restrictions on particular platforms.
- Provides detailed insights after address connection.
3. Best Change
Description: Best Change is a site for monitoring and checking digital transaction transactions, ensuring transparency and transfer security. Features:
- Transfer and holding monitoring.
- Sanctions screening.
- Internet platform; compatible with BTC and several other cryptocurrencies.
4. Bot amlchek
Overview: AMLCheck Bot is a holding observer and AML service that employs AI methods to detect suspicious activity. Features:
- Deal monitoring and identity validation.
- Accessible via web version and Telegram bot.
- Works with cryptocurrencies including BSC, BTC, DOGE, and other types.
5. Alfabit AML
Summary: AlfaBit provides complete Anti-Money Laundering (AML) solutions specifically made for the cryptocurrency industry, assisting companies and financial institutions in ensuring regulatory adherence. Features:
- Extensive anti-money laundering tools and screenings.
- Complies with modern protection and regulatory guidelines.
6. AML Node
Overview: AMLNode offers compliance and customer identity solutions for digital currency businesses, including transfer monitoring, sanctions checks, and risk assessment. Highlights:
- Risk analysis solutions and compliance checks.
- Valuable for ensuring safe company activities.
7. Btrace AML Crypto
Description: Btrace.AMLcrypto.io focuses on resource validation, offering transfer monitoring, compliance checks, and help if you are a victim of fraud. Highlights:
- Useful assistance for fund restoration.
- Transfer tracking and safety tools.
Dedicated USDT Validation Options
Our platform also provides information on various platforms providing check tools for crypto deals and accounts:
- **USDT TRC20 and ERC20 Validation:** Numerous platforms provide comprehensive checks for USDT deals, assisting in the identification of doubtful actions.
- **AML Screening for USDT:** Options are available for tracking for money laundering transactions.
- **“Cleanliness” Validation for Wallets:** Validation of deal and holding purity is provided to find possible threats.
**Summary**
Selecting the right platform for checking and monitoring digital currency deals is crucial for guaranteeing safety and standard adherence. By viewing our evaluations, you can find the ideal tool for transaction tracking and fund safety. -
九州娛樂城:亞洲頂級線上娛樂平台
九州娛樂城,作為亞洲領先的線上博弈平台,以其專業性、公平性和創新性著稱。在這裡,您可以享受全方位的娛樂體驗,包括體育投注、真人遊戲、電子遊戲、六合彩球以及流行的捕魚機和棋牌遊戲。九州娛樂城是台灣玩家的首選娛樂平台,被譽為業界 No.1!
九州娛樂城的亮點
1. 多元化遊戲選擇
九州娛樂城擁有超過千款來自全球頂尖供應商提供的遊戲,滿足各種類型玩家的需求。無論是喜歡競技性的體育投注、刺激的真人遊戲,還是休閒的電子遊戲,九州娛樂城都能提供最適合您的選擇。
體育投注:全面覆蓋世界級賽事,包括世界杯、職業聯賽等。提供多種投注方式,如讓球、大小、單雙、串關等,並支持桌面端與手機端投注。
真人遊戲:KU真人百家樂、LEO真人遊戲等,讓您感受現場賭桌的真實刺激。
電子遊戲與捕魚機:多款熱門遊戲,如九州熱門電子遊戲和捕魚機,帶給玩家極致娛樂享受。
六合彩與棋牌遊戲:適合策略型玩家的理想選擇。
2. 極致便利的操作體驗
九州娛樂城支持通過官方網站和九州APP下載進行操作,無論您身在何處,都可以輕鬆加入遊戲世界。針對台灣玩家的本地化設計確保操作流暢、存取款方便。
3. 先進技術與安全保障
九州娛樂城集團總部位於菲律賓首都馬尼拉的RCBC Plaza,配備世界一流的安全資訊防護系統和智能大樓自動化系統(BAS)。玩家的數據與資金安全都能得到最佳保障,讓每一次遊戲都安心無憂。
4. 熱門品牌與平台支持
九州娛樂城旗下包括三大品牌:
LEO娛樂:提供真人遊戲、體育直播及免費影城。
THA娛樂:專注於新手友好和便捷操作。
KU娛樂:以真人百家樂而著稱。
每個品牌雖分別由不同管理團隊運營,但都傳承了九州娛樂城的高標準,遊戲系統與界面毫無差異,為玩家提供無縫娛樂體驗。
為什麼選擇九州娛樂城?
專業性與公平性
九州娛樂城堅持以「即時便利、公平公正、專業營運」為宗旨,研發創新遊戲技術,滿足不同類型玩家需求。
貼近市場與玩家需求
擁有兩岸三地的精英設計師與代理團隊,根據玩家反饋持續改進產品,並為合作商提供及時更新支持。
優越的服務與保障
從遊戲操作到客戶支持,九州娛樂城提供全面的服務支持,讓每位玩家都能感受到最貼心的服務。
九州娛樂城的未來
作為線上博弈行業的領航者,九州娛樂城不斷推陳出新,致力於提供更豐富的遊戲選擇和更完善的玩家體驗。同時,透過強大的技術與營運團隊,九州娛樂城已成為台灣乃至亞洲地區娛樂平台的代名詞。
立即下載九州APP,體驗最極致的娛樂樂趣!九州娛樂城——您的最佳線上娛樂夥伴! -
九州娛樂城
九州娛樂城:亞洲頂級線上娛樂平台
九州娛樂城,作為亞洲領先的線上博弈平台,以其專業性、公平性和創新性著稱。在這裡,您可以享受全方位的娛樂體驗,包括體育投注、真人遊戲、電子遊戲、六合彩球以及流行的捕魚機和棋牌遊戲。九州娛樂城是台灣玩家的首選娛樂平台,被譽為業界 No.1!
九州娛樂城的亮點
1. 多元化遊戲選擇
九州娛樂城擁有超過千款來自全球頂尖供應商提供的遊戲,滿足各種類型玩家的需求。無論是喜歡競技性的體育投注、刺激的真人遊戲,還是休閒的電子遊戲,九州娛樂城都能提供最適合您的選擇。
體育投注:全面覆蓋世界級賽事,包括世界杯、職業聯賽等。提供多種投注方式,如讓球、大小、單雙、串關等,並支持桌面端與手機端投注。
真人遊戲:KU真人百家樂、LEO真人遊戲等,讓您感受現場賭桌的真實刺激。
電子遊戲與捕魚機:多款熱門遊戲,如九州熱門電子遊戲和捕魚機,帶給玩家極致娛樂享受。
六合彩與棋牌遊戲:適合策略型玩家的理想選擇。
2. 極致便利的操作體驗
九州娛樂城支持通過官方網站和九州APP下載進行操作,無論您身在何處,都可以輕鬆加入遊戲世界。針對台灣玩家的本地化設計確保操作流暢、存取款方便。
3. 先進技術與安全保障
九州娛樂城集團總部位於菲律賓首都馬尼拉的RCBC Plaza,配備世界一流的安全資訊防護系統和智能大樓自動化系統(BAS)。玩家的數據與資金安全都能得到最佳保障,讓每一次遊戲都安心無憂。
4. 熱門品牌與平台支持
九州娛樂城旗下包括三大品牌:
LEO娛樂:提供真人遊戲、體育直播及免費影城。
THA娛樂:專注於新手友好和便捷操作。
KU娛樂:以真人百家樂而著稱。
每個品牌雖分別由不同管理團隊運營,但都傳承了九州娛樂城的高標準,遊戲系統與界面毫無差異,為玩家提供無縫娛樂體驗。
為什麼選擇九州娛樂城?
專業性與公平性
九州娛樂城堅持以「即時便利、公平公正、專業營運」為宗旨,研發創新遊戲技術,滿足不同類型玩家需求。
貼近市場與玩家需求
擁有兩岸三地的精英設計師與代理團隊,根據玩家反饋持續改進產品,並為合作商提供及時更新支持。
優越的服務與保障
從遊戲操作到客戶支持,九州娛樂城提供全面的服務支持,讓每位玩家都能感受到最貼心的服務。
九州娛樂城的未來
作為線上博弈行業的領航者,九州娛樂城不斷推陳出新,致力於提供更豐富的遊戲選擇和更完善的玩家體驗。同時,透過強大的技術與營運團隊,九州娛樂城已成為台灣乃至亞洲地區娛樂平台的代名詞。
立即下載九州APP,體驗最極致的娛樂樂趣!九州娛樂城——您的最佳線上娛樂夥伴! -
일본배대지
메인 서비스: 간편하고 효율적인 배송 및 구매 대행 서비스
1. 대행 서비스 주요 기능
메인 서비스는 고객이 한 번에 필요한 대행 서비스를 신청할 수 있도록 다양한 기능을 제공합니다.
배송대행 신청: 국내외 상품 배송을 대신 처리하며, 효율적인 시스템으로 신속한 배송을 보장합니다.
구매대행 신청: 원하는 상품을 대신 구매해주는 서비스로, 고객의 수고를 줄입니다.
엑셀 대량 등록: 대량 상품을 엑셀로 손쉽게 등록 가능하여 상업 고객의 편의성을 증대합니다.
재고 관리 신청: 창고 보관 및 재고 관리를 통해 물류 과정을 최적화합니다.
2. 고객 지원 시스템
메인 서비스는 사용자 친화적인 접근성을 제공합니다.
유저 가이드: 대행 서비스를 더욱 합리적으로 사용할 수 있도록 세부 안내서를 제공합니다.
운송장 조회: 일본 사가와 등 주요 운송사의 추적 시스템과 연동하여 운송 상황을 실시간으로 확인 가능합니다.
3. 비용 안내와 부가 서비스
비용 계산기: 예상되는 비용을 간편하게 계산해 예산 관리를 돕습니다.
부가 서비스: 교환 및 반품, 폐기 및 검역 지원 등 추가적인 편의 서비스를 제공합니다.
출항 스케줄 확인: 해외 배송의 경우 출항 일정을 사전에 확인 가능하여 배송 계획을 세울 수 있습니다.
4. 공지사항
기본 검수 공지
무료 검수 서비스로 고객의 부담을 줄이며, 보다 철저한 검수가 필요한 경우 유료 정밀 검수 서비스를 권장합니다.
수출허가서 발급 안내
항공과 해운 수출 건에 대한 허가서를 효율적으로 발급받는 방법을 상세히 안내하며, 고객의 요청에 따라 이메일로 전달됩니다.
노데이터 처리 안내
운송장 번호 없는 주문에 대한 새로운 처리 방안을 도입하여, 노데이터 발생 시 관리비가 부과되지만 서비스 품질을 개선합니다.
5. 고객과의 소통
카카오톡 상담: 실시간 상담을 통해 고객의 궁금증을 해결합니다.
공지사항 알림: 서비스 이용 중 필수 정보를 지속적으로 업데이트합니다.
메인 서비스는 고객 만족을 최우선으로 하며, 지속적인 개선과 세심한 관리를 통해 최상의 경험을 제공합니다. -
일본배대지
메인 서비스: 간편하고 효율적인 배송 및 구매 대행 서비스
1. 대행 서비스 주요 기능
메인 서비스는 고객이 한 번에 필요한 대행 서비스를 신청할 수 있도록 다양한 기능을 제공합니다.
배송대행 신청: 국내외 상품 배송을 대신 처리하며, 효율적인 시스템으로 신속한 배송을 보장합니다.
구매대행 신청: 원하는 상품을 대신 구매해주는 서비스로, 고객의 수고를 줄입니다.
엑셀 대량 등록: 대량 상품을 엑셀로 손쉽게 등록 가능하여 상업 고객의 편의성을 증대합니다.
재고 관리 신청: 창고 보관 및 재고 관리를 통해 물류 과정을 최적화합니다.
2. 고객 지원 시스템
메인 서비스는 사용자 친화적인 접근성을 제공합니다.
유저 가이드: 대행 서비스를 더욱 합리적으로 사용할 수 있도록 세부 안내서를 제공합니다.
운송장 조회: 일본 사가와 등 주요 운송사의 추적 시스템과 연동하여 운송 상황을 실시간으로 확인 가능합니다.
3. 비용 안내와 부가 서비스
비용 계산기: 예상되는 비용을 간편하게 계산해 예산 관리를 돕습니다.
부가 서비스: 교환 및 반품, 폐기 및 검역 지원 등 추가적인 편의 서비스를 제공합니다.
출항 스케줄 확인: 해외 배송의 경우 출항 일정을 사전에 확인 가능하여 배송 계획을 세울 수 있습니다.
4. 공지사항
기본 검수 공지
무료 검수 서비스로 고객의 부담을 줄이며, 보다 철저한 검수가 필요한 경우 유료 정밀 검수 서비스를 권장합니다.
수출허가서 발급 안내
항공과 해운 수출 건에 대한 허가서를 효율적으로 발급받는 방법을 상세히 안내하며, 고객의 요청에 따라 이메일로 전달됩니다.
노데이터 처리 안내
운송장 번호 없는 주문에 대한 새로운 처리 방안을 도입하여, 노데이터 발생 시 관리비가 부과되지만 서비스 품질을 개선합니다.
5. 고객과의 소통
카카오톡 상담: 실시간 상담을 통해 고객의 궁금증을 해결합니다.
공지사항 알림: 서비스 이용 중 필수 정보를 지속적으로 업데이트합니다.
메인 서비스는 고객 만족을 최우선으로 하며, 지속적인 개선과 세심한 관리를 통해 최상의 경험을 제공합니다. -
ST666
ST666: Thiên Đường Casino Trực Tuyến Hàng Đầu
ST666 là một trong những sòng bạc trực tuyến hàng đầu, mang đến trải nghiệm chơi game đỉnh cao với hàng loạt trò chơi hấp dẫn và chương trình khuyến mãi đặc biệt. Với sứ mệnh đem lại sân chơi công bằng và tiện lợi, ST666 đã trở thành lựa chọn yêu thích của hàng ngàn người chơi tại Việt Nam.
Đa Dạng Trò Chơi và Sảnh Cược
1. Trò Chơi Phong Phú
ST666 cung cấp nhiều trò chơi đa dạng, đáp ứng sở thích của mọi người chơi:
Baccarat: Trò chơi cổ điển dành cho những ai yêu thích chiến thuật và may mắn.
Tài Xỉu: Trò chơi xúc xắc đầy kịch tính, đem lại cơ hội thắng lớn trong từng vòng cược.
Xóc Đĩa: Trò chơi truyền thống Việt Nam, được nâng cấp với công nghệ trực tuyến hiện đại.
Và nhiều trò chơi khác đang chờ bạn khám phá.
2. Sảnh Cược Đẳng Cấp
ST666 kết hợp cùng các sảnh cược nổi tiếng như:
Wm Casino: Nền tảng casino chuyên nghiệp, nổi bật với các trò chơi chất lượng cao và giao diện mượt mà.
ST666 Casino: Sảnh cược độc quyền với những ưu đãi hấp dẫn và các trò chơi độc đáo.
Khuyến Mãi Hấp Dẫn Tại ST666
ST666 không chỉ nổi bật với danh mục trò chơi phong phú mà còn mang đến nhiều chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn cho người chơi:
Khuyến Mãi Gửi Tiền Cuối Tuần: Nhận thưởng lên đến 3.666.000 đồng khi nạp tiền vào tài khoản trong các ngày cuối tuần.
Ưu Đãi Đặc Biệt Dành Cho Hội Viên Mới: Những người chơi mới sẽ nhận được gói khuyến mãi chào mừng độc quyền.
Hoàn Tiền Hàng Tuần: Cơ hội nhận lại phần trăm số tiền cược đã thua trong tuần, giúp bạn có thêm động lực tham gia.
Tại Sao Nên Chọn ST666?
An Toàn và Uy Tín: ST666 cam kết bảo mật thông tin và giao dịch của người chơi, đảm bảo trải nghiệm chơi game an toàn tuyệt đối.
Hỗ Trợ Khách Hàng Chuyên Nghiệp: Đội ngũ chăm sóc khách hàng luôn sẵn sàng hỗ trợ 24/7.
Giao Diện Thân Thiện: Thiết kế đơn giản, dễ sử dụng, phù hợp cho cả người mới chơi và người chơi lâu năm.
Cơ Hội Thắng Lớn: Tỷ lệ thắng cao và phần thưởng hấp dẫn trong từng trò chơi.
Cách Tham Gia ST666
Bước 1: Truy cập trang web chính thức của ST666.
Bước 2: Đăng ký tài khoản nhanh chóng và miễn phí.
Bước 3: Nạp tiền và lựa chọn trò chơi yêu thích để bắt đầu hành trình giải trí.
Kết Luận
ST666 chính là thiên đường giải trí trực tuyến dành cho những ai yêu thích thử vận may và tận hưởng các trò chơi đẳng cấp. Với sự kết hợp giữa công nghệ hiện đại và các chương trình ưu đãi hấp dẫn, ST666 cam kết mang lại trải nghiệm hoàn hảo cho người chơi. Tham gia ngay hôm nay để khám phá những điều bất ngờ tại ST666! -
ST666 - Nhận Định Bóng Đá Kèo Nhà Cái Uy Tín
ST666: Địa Chỉ Lý Tưởng Cho Những Tín Đồ Cá Cược Bóng Đá
ST666 là nền tảng nhận định bóng đá và kèo nhà cái chuyên nghiệp, nơi người chơi có thể tham gia dự đoán các kèo đa dạng như cược tài xỉu, cược chấp, và cược 1x2. Với giao diện thân thiện, tỷ lệ cược minh bạch và ưu đãi hấp dẫn, ST666 đang dần trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của cộng đồng yêu bóng đá.
Nhận Định Kèo Nhà Cái Đa Dạng
Cược Tài Xỉu (#cuoctaixiu)
Dựa vào tổng số bàn thắng trong trận đấu, người chơi dễ dàng chọn lựa Tài (nhiều hơn tỷ lệ nhà cái đưa ra) hoặc Xỉu (ít hơn tỷ lệ).
ST666 cung cấp các phân tích chi tiết giúp người chơi đưa ra lựa chọn chính xác.
Cược Chấp (#cuocchap)
Thích hợp cho những trận đấu có sự chênh lệch về sức mạnh giữa hai đội. ST666 cung cấp tỷ lệ chấp tối ưu, phù hợp với cả người chơi mới và chuyên nghiệp.
Cược 1x2 (#cuoc1x2)
Phù hợp cho những ai muốn dự đoán kết quả chung cuộc (Thắng - Hòa - Thua). Đây là loại kèo phổ biến, dễ hiểu và có tỷ lệ cược hấp dẫn.
Ưu Đãi Hấp Dẫn Tại ST666
Nhận 160% tiền gửi lần đầu: Khi đăng ký tài khoản mới và nạp tiền, người chơi sẽ nhận được số tiền thưởng cực lớn, tăng cơ hội tham gia các kèo.
Hoàn tiền 3% mỗi ngày: Chính sách hoàn tiền giúp người chơi giảm thiểu rủi ro, thoải mái trải nghiệm mà không lo lắng nhiều về chi phí.
Vì Sao Nên Chọn ST666?
Nền Tảng Uy Tín: ST666 cam kết mang đến trải nghiệm cá cược minh bạch và an toàn.
Phân Tích Chuyên Sâu: Đội ngũ chuyên gia của ST666 luôn cập nhật nhận định mới nhất về các trận đấu, giúp người chơi đưa ra quyết định tối ưu.
Hỗ Trợ 24/7: Đội ngũ hỗ trợ chuyên nghiệp, luôn sẵn sàng giải đáp thắc mắc của người chơi.
Giao Dịch Nhanh Chóng: Nạp rút tiền linh hoạt, đảm bảo sự tiện lợi và bảo mật.
Cách Tham Gia ST666
Truy cập website chính thức của ST666.
Đăng ký tài khoản bằng thông tin cá nhân.
Nạp tiền lần đầu để nhận ưu đãi 160%.
Bắt đầu trải nghiệm cá cược với các kèo yêu thích!
Hãy đến với ST666 để tận hưởng không gian cá cược chuyên nghiệp, nhận định kèo chất lượng và những phần thưởng hấp dẫn. Tham gia ngay hôm nay để trở thành người chơi chiến thắng! -
ST666 - Nhận Định Bóng Đá Kèo Nhà Cái Uy Tín
ST666: Địa Chỉ Lý Tưởng Cho Những Tín Đồ Cá Cược Bóng Đá
ST666 là nền tảng nhận định bóng đá và kèo nhà cái chuyên nghiệp, nơi người chơi có thể tham gia dự đoán các kèo đa dạng như cược tài xỉu, cược chấp, và cược 1x2. Với giao diện thân thiện, tỷ lệ cược minh bạch và ưu đãi hấp dẫn, ST666 đang dần trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của cộng đồng yêu bóng đá.
Nhận Định Kèo Nhà Cái Đa Dạng
Cược Tài Xỉu (#cuoctaixiu)
Dựa vào tổng số bàn thắng trong trận đấu, người chơi dễ dàng chọn lựa Tài (nhiều hơn tỷ lệ nhà cái đưa ra) hoặc Xỉu (ít hơn tỷ lệ).
ST666 cung cấp các phân tích chi tiết giúp người chơi đưa ra lựa chọn chính xác.
Cược Chấp (#cuocchap)
Thích hợp cho những trận đấu có sự chênh lệch về sức mạnh giữa hai đội. ST666 cung cấp tỷ lệ chấp tối ưu, phù hợp với cả người chơi mới và chuyên nghiệp.
Cược 1x2 (#cuoc1x2)
Phù hợp cho những ai muốn dự đoán kết quả chung cuộc (Thắng - Hòa - Thua). Đây là loại kèo phổ biến, dễ hiểu và có tỷ lệ cược hấp dẫn.
Ưu Đãi Hấp Dẫn Tại ST666
Nhận 160% tiền gửi lần đầu: Khi đăng ký tài khoản mới và nạp tiền, người chơi sẽ nhận được số tiền thưởng cực lớn, tăng cơ hội tham gia các kèo.
Hoàn tiền 3% mỗi ngày: Chính sách hoàn tiền giúp người chơi giảm thiểu rủi ro, thoải mái trải nghiệm mà không lo lắng nhiều về chi phí.
Vì Sao Nên Chọn ST666?
Nền Tảng Uy Tín: ST666 cam kết mang đến trải nghiệm cá cược minh bạch và an toàn.
Phân Tích Chuyên Sâu: Đội ngũ chuyên gia của ST666 luôn cập nhật nhận định mới nhất về các trận đấu, giúp người chơi đưa ra quyết định tối ưu.
Hỗ Trợ 24/7: Đội ngũ hỗ trợ chuyên nghiệp, luôn sẵn sàng giải đáp thắc mắc của người chơi.
Giao Dịch Nhanh Chóng: Nạp rút tiền linh hoạt, đảm bảo sự tiện lợi và bảo mật.
Cách Tham Gia ST666
Truy cập website chính thức của ST666.
Đăng ký tài khoản bằng thông tin cá nhân.
Nạp tiền lần đầu để nhận ưu đãi 160%.
Bắt đầu trải nghiệm cá cược với các kèo yêu thích!
Hãy đến với ST666 để tận hưởng không gian cá cược chuyên nghiệp, nhận định kèo chất lượng và những phần thưởng hấp dẫn. Tham gia ngay hôm nay để trở thành người chơi chiến thắng! -
leo娛樂城登入
LEO娛樂城:九州娛樂集團的卓越創舉與運營優勢
九州娛樂集團總部的現代化運營
九州娛樂集團的總部設於菲律賓首都馬尼拉市中心最具代表性的現代化建築「RCBC Plaza」。這座辦公大樓融合了全球領先的建築科技與安全系統,包括:
國家級資訊防護系統,確保數據安全。
樓宇自動化系統 (BAS),實現數位化管理與高效運營,包括防火系統、光纖電訊和數位監控。
九州娛樂為員工提供舒適的工作環境和專業的教育培訓,確保服務水準一流。其員工以專業知識和親切態度,為尊貴玩家帶來極致的遊戲體驗。
LEO娛樂旗下品牌與遊戲特色
九州娛樂城旗下分支包括 LEO、THA 和 KU 三個娛樂品牌。雖然品牌各自獨立運營,但都共享相同的遊戲系統與界面,提供超過數千款來自全球頂級供應商的遊戲。
這些品牌的核心特色包括:
種類繁多的遊戲:滿足不同類型玩家的需求,包括電子遊戲、體育博彩、真人娛樂等。
不斷更新的內容:通過九州獨家技術,網站內容保持新鮮,合作商可快速更新遊戲資源,確保平台競爭力。
玩家在這些平台上可以隨時找到適合自己的遊戲,享受沉浸式的娛樂體驗。
LEO娛樂城的歷史與發展
九州娛樂集團的起源可以追溯至其最早期的經營模式:「信用版」賭博平台 《天下體育球版》。儘管該模式在當時非常流行,但因高風險與財務處理複雜而逐漸被淘汰。
隨著市場需求的變化,九州娛樂轉型為現金版平台 《天下現金網》,引入了更安全、便捷的遊戲模式。這種轉變不僅提升了玩家的體驗,也使平台得以進一步發展。
如今,九州娛樂城已成為台灣博弈業界的領軍者,不僅優化了網站版面與功能,還推出了專屬手機APP,方便玩家隨時隨地進行遊戲體驗。
LEO娛樂的成功秘訣
現代化運營與技術支持:九州娛樂在系統安全與技術更新方面投入巨大資源,確保平台運營穩定可靠。
多元化遊戲體驗:通過與全球頂級遊戲供應商合作,平台提供了豐富的遊戲選擇,適應各種玩家需求。
用戶至上:專業培訓的員工以細心和熱忱態度,提供高品質服務,讓玩家倍感尊重。
不斷創新:從信用版到現金版,再到手機APP,九州娛樂始終緊跟市場趨勢,致力於打造最佳娛樂體驗。
結語
LEO娛樂城作為九州娛樂集團旗下的重要品牌,不僅繼承了集團的核心價值,更在遊戲選擇、服務品質和技術創新方面不斷提升。從最初的《天下體育球版》到如今的行業領先者,LEO娛樂見證了九州娛樂城的發展歷程,也成為博弈行業中的耀眼明星。
加入 LEO娛樂城,感受來自九州娛樂集團的專業與熱情,享受最頂級的線上博弈體驗! -
leo娛樂城
LEO娛樂城:九州娛樂集團的卓越創舉與運營優勢
九州娛樂集團總部的現代化運營
九州娛樂集團的總部設於菲律賓首都馬尼拉市中心最具代表性的現代化建築「RCBC Plaza」。這座辦公大樓融合了全球領先的建築科技與安全系統,包括:
國家級資訊防護系統,確保數據安全。
樓宇自動化系統 (BAS),實現數位化管理與高效運營,包括防火系統、光纖電訊和數位監控。
九州娛樂為員工提供舒適的工作環境和專業的教育培訓,確保服務水準一流。其員工以專業知識和親切態度,為尊貴玩家帶來極致的遊戲體驗。
LEO娛樂旗下品牌與遊戲特色
九州娛樂城旗下分支包括 LEO、THA 和 KU 三個娛樂品牌。雖然品牌各自獨立運營,但都共享相同的遊戲系統與界面,提供超過數千款來自全球頂級供應商的遊戲。
這些品牌的核心特色包括:
種類繁多的遊戲:滿足不同類型玩家的需求,包括電子遊戲、體育博彩、真人娛樂等。
不斷更新的內容:通過九州獨家技術,網站內容保持新鮮,合作商可快速更新遊戲資源,確保平台競爭力。
玩家在這些平台上可以隨時找到適合自己的遊戲,享受沉浸式的娛樂體驗。
LEO娛樂城的歷史與發展
九州娛樂集團的起源可以追溯至其最早期的經營模式:「信用版」賭博平台 《天下體育球版》。儘管該模式在當時非常流行,但因高風險與財務處理複雜而逐漸被淘汰。
隨著市場需求的變化,九州娛樂轉型為現金版平台 《天下現金網》,引入了更安全、便捷的遊戲模式。這種轉變不僅提升了玩家的體驗,也使平台得以進一步發展。
如今,九州娛樂城已成為台灣博弈業界的領軍者,不僅優化了網站版面與功能,還推出了專屬手機APP,方便玩家隨時隨地進行遊戲體驗。
LEO娛樂的成功秘訣
現代化運營與技術支持:九州娛樂在系統安全與技術更新方面投入巨大資源,確保平台運營穩定可靠。
多元化遊戲體驗:通過與全球頂級遊戲供應商合作,平台提供了豐富的遊戲選擇,適應各種玩家需求。
用戶至上:專業培訓的員工以細心和熱忱態度,提供高品質服務,讓玩家倍感尊重。
不斷創新:從信用版到現金版,再到手機APP,九州娛樂始終緊跟市場趨勢,致力於打造最佳娛樂體驗。
結語
LEO娛樂城作為九州娛樂集團旗下的重要品牌,不僅繼承了集團的核心價值,更在遊戲選擇、服務品質和技術創新方面不斷提升。從最初的《天下體育球版》到如今的行業領先者,LEO娛樂見證了九州娛樂城的發展歷程,也成為博弈行業中的耀眼明星。
加入 LEO娛樂城,感受來自九州娛樂集團的專業與熱情,享受最頂級的線上博弈體驗! -
娛樂城
RG富遊娛樂城:台灣線上娛樂城的最佳選擇
RG富遊娛樂城以其卓越的服務和多樣化的遊戲選擇,成為2024年最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台。受到超過50位網紅和部落客的實測推薦,這座娛樂城不僅提供豐富的遊戲,還帶來眾多優惠活動和誠信保證,贏得了廣大玩家的信任與青睞。
RG富遊娛樂城的獨特優勢
多重優惠活動
體驗金 $168:新手玩家可以免費試玩,無需任何成本即可體驗高品質遊戲。
首儲1000送1000:首次存款即可獲得雙倍金額,增加遊戲的樂趣與機會。
線上簽到轉盤:每日簽到即可參加抽獎,贏取現金獎勵和豐厚禮品。
快速存提款與資金保障
RG富遊採用自主研發的財務系統,確保5秒快速存款,滿足玩家即時遊戲需求。
100%保證出金,杜絕任何拖延或資金安全風險,讓玩家完全放心。
遊戲種類豐富
RG富遊娛樂城涵蓋多種遊戲類型,滿足不同玩家的需求,包括:
真人百家樂:與真人荷官互動,感受真實賭場的刺激氛圍。
電子老虎機:超過數百款創新遊戲,玩法新穎,回報豐厚。
電子捕魚:趣味性強,結合策略與娛樂,深受玩家喜愛。
電子棋牌:提供公平競技環境,適合策略型玩家。
體育投注:涵蓋全球賽事,賠率即時更新,為體育愛好者提供最佳選擇。
樂透彩票:參與多地彩票,挑戰巨額獎金。
跨平台兼容性
RG富遊支持Web端、H5、iOS和Android設備,玩家可隨時隨地登錄遊戲,享受無縫體驗。
與其他娛樂城的不同之處
RG富遊以現金版模式運營,確保交易透明和安全性。相比一般娛樂城,RG富遊在存提款速度上遙遙領先,玩家可在短短15秒內完成交易,並且100%保證資金提領。而在線客服全年無休,隨時提供支持,讓玩家在任何時間都能解決問題。
相比之下,一般娛樂城多以信用版模式運營,存在出金風險,且存提款速度較慢,客服服務不穩定,無法與RG富遊的專業性相比。
為什麼選擇RG富遊娛樂城
資金交易安全無憂:採用最先進的SSL加密技術,確保每筆交易的安全性。
遊戲種類全面豐富:每日更新多樣化遊戲,帶來新鮮感和無限可能。
優惠活動力度大:從體驗金到豐厚的首儲獎勵,玩家每一步都能享受優惠。
快速存提款服務:自主研發技術保障流暢交易,遊戲不中斷。
全天候專業客服:24/7在線支持,及時解決玩家需求。
立即加入RG富遊娛樂城
RG富遊娛樂城不僅提供豐富的遊戲體驗,更以專業的服務、完善的安全保障和多樣的優惠活動,為玩家打造一個值得信賴的娛樂環境。立即註冊,體驗台灣最受歡迎的線上娛樂城! -
RG富遊娛樂城:台灣線上娛樂城的最佳選擇
RG富遊娛樂城以其卓越的服務和多樣化的遊戲選擇,成為2024年最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台。受到超過50位網紅和部落客的實測推薦,這座娛樂城不僅提供豐富的遊戲,還帶來眾多優惠活動和誠信保證,贏得了廣大玩家的信任與青睞。
RG富遊娛樂城的獨特優勢
多重優惠活動
體驗金 $168:新手玩家可以免費試玩,無需任何成本即可體驗高品質遊戲。
首儲1000送1000:首次存款即可獲得雙倍金額,增加遊戲的樂趣與機會。
線上簽到轉盤:每日簽到即可參加抽獎,贏取現金獎勵和豐厚禮品。
快速存提款與資金保障
RG富遊採用自主研發的財務系統,確保5秒快速存款,滿足玩家即時遊戲需求。
100%保證出金,杜絕任何拖延或資金安全風險,讓玩家完全放心。
遊戲種類豐富
RG富遊娛樂城涵蓋多種遊戲類型,滿足不同玩家的需求,包括:
真人百家樂:與真人荷官互動,感受真實賭場的刺激氛圍。
電子老虎機:超過數百款創新遊戲,玩法新穎,回報豐厚。
電子捕魚:趣味性強,結合策略與娛樂,深受玩家喜愛。
電子棋牌:提供公平競技環境,適合策略型玩家。
體育投注:涵蓋全球賽事,賠率即時更新,為體育愛好者提供最佳選擇。
樂透彩票:參與多地彩票,挑戰巨額獎金。
跨平台兼容性
RG富遊支持Web端、H5、iOS和Android設備,玩家可隨時隨地登錄遊戲,享受無縫體驗。
與其他娛樂城的不同之處
RG富遊以現金版模式運營,確保交易透明和安全性。相比一般娛樂城,RG富遊在存提款速度上遙遙領先,玩家可在短短15秒內完成交易,並且100%保證資金提領。而在線客服全年無休,隨時提供支持,讓玩家在任何時間都能解決問題。
相比之下,一般娛樂城多以信用版模式運營,存在出金風險,且存提款速度較慢,客服服務不穩定,無法與RG富遊的專業性相比。
為什麼選擇RG富遊娛樂城
資金交易安全無憂:採用最先進的SSL加密技術,確保每筆交易的安全性。
遊戲種類全面豐富:每日更新多樣化遊戲,帶來新鮮感和無限可能。
優惠活動力度大:從體驗金到豐厚的首儲獎勵,玩家每一步都能享受優惠。
快速存提款服務:自主研發技術保障流暢交易,遊戲不中斷。
全天候專業客服:24/7在線支持,及時解決玩家需求。
立即加入RG富遊娛樂城
RG富遊娛樂城不僅提供豐富的遊戲體驗,更以專業的服務、完善的安全保障和多樣的優惠活動,為玩家打造一個值得信賴的娛樂環境。立即註冊,體驗台灣最受歡迎的線上娛樂城! -
일본소비세환급
일본 소비세 환급, 네오리아와 함께라면 간편하고 안전하게
일본 소비세 환급은 복잡하고 까다로운 절차로 많은 구매대행 셀러들이 어려움을 겪는 분야입니다. 네오리아는 다년간의 경험과 전문성을 바탕으로 신뢰할 수 있는 서비스를 제공하며, 일본 소비세 환급 과정을 쉽고 효율적으로 처리합니다.
1. 일본 소비세 환급의 필요성과 네오리아의 역할
네오리아는 일본 현지 법인을 설립하지 않아도 합법적인 방식으로 소비세 환급을 받을 수 있는 솔루션을 제공합니다. 이를 통해:
한국 개인사업자와 법인 사업자 모두 간편하게 환급 절차를 진행할 수 있습니다.
일본의 복잡한 서류 심사를 최소화하고, 현지 로컬 세리사와 협력하여 최적의 결과를 보장합니다.
2. 소비세 환급의 주요 특징
일본 연고가 없어도 가능: 일본에 사업자가 없더라도 네오리아는 신뢰할 수 있는 서비스를 통해 소비세 환급을 지원합니다.
서류 작성 걱정 해결: 잘못된 서류 제출로 환급이 거절될까 걱정될 필요 없습니다. 네오리아의 전문 대응팀이 모든 과정을 정밀하게 관리합니다.
현지 법인 운영자를 위한 추가 지원: 일본 내 개인사업자나 법인 운영자에게는 세무 감사와 이슈 대응까지 포함된 고급 서비스를 제공합니다.
3. 네오리아 서비스의 장점
전문성과 신뢰성: 정부로부터 인정받은 투명성과 세무 분야의 우수한 성과를 자랑합니다.
맞춤형 서포트: 다양한 사례를 통해 쌓은 경험으로 고객이 예상치 못한 어려움까지 미리 해결합니다.
로컬 업체에서 불가능한 고급 서비스: 한국인 고객을 위해 정확하고 간편한 세무회계 및 소비세 환급 서비스를 제공합니다.
4. 네오리아가 제공하는 혜택
시간 절약: 복잡한 절차와 서류 준비 과정을 전문가가 대신 처리합니다.
안심 환급: 철저한 관리와 세심한 대응으로 안전하게 환급을 받을 수 있습니다.
추가 서비스: 세무감사와 이슈 발생 시 즉각적인 지원으로 사업의 연속성을 보장합니다.
네오리아는 소비세 환급이 복잡하고 어렵다고 느껴지는 고객들에게 최적의 길잡이가 되어드립니다. 신뢰를 바탕으로 한 전문적인 서비스로, 더 이상 소비세 환급 문제로 고민하지 마세요! -
일본 소비세 환급, 네오리아와 함께라면 간편하고 안전하게
일본 소비세 환급은 복잡하고 까다로운 절차로 많은 구매대행 셀러들이 어려움을 겪는 분야입니다. 네오리아는 다년간의 경험과 전문성을 바탕으로 신뢰할 수 있는 서비스를 제공하며, 일본 소비세 환급 과정을 쉽고 효율적으로 처리합니다.
1. 일본 소비세 환급의 필요성과 네오리아의 역할
네오리아는 일본 현지 법인을 설립하지 않아도 합법적인 방식으로 소비세 환급을 받을 수 있는 솔루션을 제공합니다. 이를 통해:
한국 개인사업자와 법인 사업자 모두 간편하게 환급 절차를 진행할 수 있습니다.
일본의 복잡한 서류 심사를 최소화하고, 현지 로컬 세리사와 협력하여 최적의 결과를 보장합니다.
2. 소비세 환급의 주요 특징
일본 연고가 없어도 가능: 일본에 사업자가 없더라도 네오리아는 신뢰할 수 있는 서비스를 통해 소비세 환급을 지원합니다.
서류 작성 걱정 해결: 잘못된 서류 제출로 환급이 거절될까 걱정될 필요 없습니다. 네오리아의 전문 대응팀이 모든 과정을 정밀하게 관리합니다.
현지 법인 운영자를 위한 추가 지원: 일본 내 개인사업자나 법인 운영자에게는 세무 감사와 이슈 대응까지 포함된 고급 서비스를 제공합니다.
3. 네오리아 서비스의 장점
전문성과 신뢰성: 정부로부터 인정받은 투명성과 세무 분야의 우수한 성과를 자랑합니다.
맞춤형 서포트: 다양한 사례를 통해 쌓은 경험으로 고객이 예상치 못한 어려움까지 미리 해결합니다.
로컬 업체에서 불가능한 고급 서비스: 한국인 고객을 위해 정확하고 간편한 세무회계 및 소비세 환급 서비스를 제공합니다.
4. 네오리아가 제공하는 혜택
시간 절약: 복잡한 절차와 서류 준비 과정을 전문가가 대신 처리합니다.
안심 환급: 철저한 관리와 세심한 대응으로 안전하게 환급을 받을 수 있습니다.
추가 서비스: 세무감사와 이슈 발생 시 즉각적인 지원으로 사업의 연속성을 보장합니다.
네오리아는 소비세 환급이 복잡하고 어렵다고 느껴지는 고객들에게 최적의 길잡이가 되어드립니다. 신뢰를 바탕으로 한 전문적인 서비스로, 더 이상 소비세 환급 문제로 고민하지 마세요! -
بيع اثاث مستعمل بالرياض
شراء الأثاث المستعمل بالرياض: الحل الأمثل للتخلص من الأثاث القديم واستبداله
هل تبحث عن وسيلة للاستفادة من أثاثك القديم بدلاً من تخزينه أو التخلص منه؟ تقدم محلات شراء وبيع الأثاث المستعمل بالرياض حلاً مثالياً يساعد الأفراد والمؤسسات على تحقيق أقصى استفادة من الأثاث القديم. نحن نعمل كحلقة وصل بين من يرغبون في بيع أثاثهم المستعمل ومن يبحثون عن قطع مميزة تلبي احتياجاتهم.
لماذا تختار شركتنا لشراء الأثاث المستعمل بالرياض؟
أفضل العروض وأعلى معدلات التسعير
نحن نقدم تقييمًا دقيقًا ومنصفًا لأثاثك المستعمل بناءً على خبرة فريقنا من الخبراء.
خدمات تغطي منطقة الرياض بالكامل
بمجرد اتصالك بنا، نصل إليك بسرعة أينما كنت داخل الرياض.
تقييم احترافي للأثاث
يتم تثمين الأثاث بناءً على آراء مجموعة محايدة من الخبراء لضمان الشفافية والدقة.
تغيير الديكور بسهولة
إذا كنت تخطط للانتقال إلى منزل جديد أو ترغب في تحديث الديكور الخاص بك، فإن بيع الأثاث القديم واستبداله بأثاث جديد يُعتبر خطوة عملية وفعالة.
عوامل تؤثر على قرار بيع أو الاحتفاظ بالأثاث القديم
القيمة العملية للأثاث
إذا كانت القطعة القديمة تناسب احتياجاتك وتنسجم مع الديكور الجديد، قد ترغب في الاحتفاظ بها. أما القطع المتضررة أو غير المريحة، فبيعها هو الخيار الأفضل.
جودة الأثاث
نقل أثاث على وشك الانهيار إلى منزلك الجديد قد يسبب خسائر مادية ويستهلك جهدًا بلا جدوى.
حجم الأثاث ومدى ملاءمته للمساحة
تأكد من قياس المساحات المتوفرة في المنزل الجديد وتوافقها مع حجم الأثاث القديم قبل اتخاذ قرار الاحتفاظ به.
القيمة العاطفية
بعض القطع تحمل قيمة عاطفية تجعل التخلي عنها صعبًا. إذا كان بالإمكان نقلها بأمان، يمكنك الاحتفاظ بها.
خطر التلف أثناء النقل
إذا كان الأثاث معرضًا للتلف الكبير أثناء النقل، فمن الأفضل التفكير في بيعه لتجنب خسائر محتملة.
خدماتنا المميزة لشراء وبيع الأثاث المستعمل بالرياض
شراء جميع أنواع الأثاث: غرف نوم، مجالس، أثاث الفلل والقصور، وأجهزة كهربائية.
تقييم دقيق وسعر عادل: نضمن تقديم السعر الحقيقي لأثاثك بناءً على حالته.
شراء المكيفات المستعملة بالرياض: نحن الأفضل في هذا المجال، مع فريق متخصص يقدم حلولاً تناسب احتياجاتك.
لماذا نحن الأفضل؟
لدينا فريق من الخبراء في تقييم وشراء الأثاث المستعمل.
نقدم خدمات تغطي جميع مناطق الرياض.
نعمل على بناء ثقة العملاء من خلال الشفافية والالتزام.
اتصل بنا الآن
إذا كنت تبحث عن أفضل محلات شراء الأثاث المستعمل بالرياض، فلا تتردد في التواصل معنا عبر الجوال أو الواتساب على الرقم 0500220488. نحن مستعدون لخدمتك أينما كنت وفي أي وقت يناسبك. اجعل بيع أثاثك القديم خطوة سهلة ومربحة معنا! -
بيع اثاث مستعمل الرياض
شراء الأثاث المستعمل بالرياض: الحل الأمثل للتخلص من الأثاث القديم واستبداله
هل تبحث عن وسيلة للاستفادة من أثاثك القديم بدلاً من تخزينه أو التخلص منه؟ تقدم محلات شراء وبيع الأثاث المستعمل بالرياض حلاً مثالياً يساعد الأفراد والمؤسسات على تحقيق أقصى استفادة من الأثاث القديم. نحن نعمل كحلقة وصل بين من يرغبون في بيع أثاثهم المستعمل ومن يبحثون عن قطع مميزة تلبي احتياجاتهم.
لماذا تختار شركتنا لشراء الأثاث المستعمل بالرياض؟
أفضل العروض وأعلى معدلات التسعير
نحن نقدم تقييمًا دقيقًا ومنصفًا لأثاثك المستعمل بناءً على خبرة فريقنا من الخبراء.
خدمات تغطي منطقة الرياض بالكامل
بمجرد اتصالك بنا، نصل إليك بسرعة أينما كنت داخل الرياض.
تقييم احترافي للأثاث
يتم تثمين الأثاث بناءً على آراء مجموعة محايدة من الخبراء لضمان الشفافية والدقة.
تغيير الديكور بسهولة
إذا كنت تخطط للانتقال إلى منزل جديد أو ترغب في تحديث الديكور الخاص بك، فإن بيع الأثاث القديم واستبداله بأثاث جديد يُعتبر خطوة عملية وفعالة.
عوامل تؤثر على قرار بيع أو الاحتفاظ بالأثاث القديم
القيمة العملية للأثاث
إذا كانت القطعة القديمة تناسب احتياجاتك وتنسجم مع الديكور الجديد، قد ترغب في الاحتفاظ بها. أما القطع المتضررة أو غير المريحة، فبيعها هو الخيار الأفضل.
جودة الأثاث
نقل أثاث على وشك الانهيار إلى منزلك الجديد قد يسبب خسائر مادية ويستهلك جهدًا بلا جدوى.
حجم الأثاث ومدى ملاءمته للمساحة
تأكد من قياس المساحات المتوفرة في المنزل الجديد وتوافقها مع حجم الأثاث القديم قبل اتخاذ قرار الاحتفاظ به.
القيمة العاطفية
بعض القطع تحمل قيمة عاطفية تجعل التخلي عنها صعبًا. إذا كان بالإمكان نقلها بأمان، يمكنك الاحتفاظ بها.
خطر التلف أثناء النقل
إذا كان الأثاث معرضًا للتلف الكبير أثناء النقل، فمن الأفضل التفكير في بيعه لتجنب خسائر محتملة.
خدماتنا المميزة لشراء وبيع الأثاث المستعمل بالرياض
شراء جميع أنواع الأثاث: غرف نوم، مجالس، أثاث الفلل والقصور، وأجهزة كهربائية.
تقييم دقيق وسعر عادل: نضمن تقديم السعر الحقيقي لأثاثك بناءً على حالته.
شراء المكيفات المستعملة بالرياض: نحن الأفضل في هذا المجال، مع فريق متخصص يقدم حلولاً تناسب احتياجاتك.
لماذا نحن الأفضل؟
لدينا فريق من الخبراء في تقييم وشراء الأثاث المستعمل.
نقدم خدمات تغطي جميع مناطق الرياض.
نعمل على بناء ثقة العملاء من خلال الشفافية والالتزام.
اتصل بنا الآن
إذا كنت تبحث عن أفضل محلات شراء الأثاث المستعمل بالرياض، فلا تتردد في التواصل معنا عبر الجوال أو الواتساب على الرقم 0500220488. نحن مستعدون لخدمتك أينما كنت وفي أي وقت يناسبك. اجعل بيع أثاثك القديم خطوة سهلة ومربحة معنا! -
九州LEO娛樂城無法登入!即將倒閉,玩家該如何應對?
近期,LEO娛樂城突然出現無法登入的情況,引發大批玩家恐慌。作為九州娛樂城的子品牌,LEO在台灣擁有廣泛的用戶基礎,但其突然失聯以及退出台灣市場的傳聞,讓玩家擔憂自己的資金和帳戶安全。以下將詳細解析問題原因及替代方案,幫助玩家應對這一局面。
LEO娛樂城無法登入的三大原因
資金問題,無法出金
當玩家贏錢且帳號突然被鎖,這可能意味著娛樂城的資金鏈出現問題。LEO娛樂城無法處理大量出金需求,導致帳號被限制,進一步引發用戶恐慌。
伺服器故障,可能涉及詐騙行為
LEO娛樂城因涉嫌詐騙而被舉報,導致伺服器故障。這樣的情況不僅影響平台穩定性,也讓玩家的信任度下降,娛樂城的可靠性大打折扣。
退出台灣市場
隨著九州娛樂城因洗錢和內鬼洩密案被警方盯上,LEO娛樂城可能為避風頭選擇退出台灣市場。此舉將讓玩家無法再次登入,帳戶內的資金和獎金也可能無法追回。
九州娛樂城退出台灣的背景
LEO娛樂城隸屬九州集團,過去曾深度依賴金流公司和第三方支付來運作。然而,近期九州娛樂城涉及的洗錢案浮出水面,包括高層涉嫌賄賂警界內鬼,導致警方全面查緝。為避免更多曝光,退出台灣市場成為九州集團的合理選擇。
此外,也有消息指出,九州娛樂城對台灣市場的競爭激烈度表示不滿,正計畫將重心轉向更具潛力的海外市場。九州旗下的KU體育已進軍國際舞台,曾贊助五大足球聯賽,顯示其實力雄厚。
應對LEO娛樂城無法登入的最佳替代方案
如果你在LEO娛樂城無法登入的情況下,不妨考慮其他穩定且安全的平台,例如 1XBET。作為國際知名娛樂品牌,1XBET 以其安全性和穩定性贏得了玩家的廣泛信任。
為何選擇1XBET?
穩定安全:1XBET 平台運作合法,提供穩定的遊戲環境。
免費體驗金:新玩家可獲得免費體驗金,零成本開始娛樂。
首儲優惠及無限返水:首筆存款享受高額優惠,並提供無限返水政策,確保玩家的最大利益。
結論:抓緊時機保障自己的資金
LEO娛樂城無法登入以及可能退出台灣市場的消息,讓許多玩家感到不安。無論是未完成的儲值,還是帳戶中的餘額,都可能隨時歸零。建議玩家儘早取回資金,並選擇更安全可靠的平台,例如 1XBET,以確保自己的資金和遊戲體驗。
在不穩定的娛樂市場中,選擇合法且受信任的平台,將是長遠的最佳保障。 -
九州LEO娛樂城無法登入
九州LEO娛樂城無法登入!即將倒閉,玩家該如何應對?
近期,LEO娛樂城突然出現無法登入的情況,引發大批玩家恐慌。作為九州娛樂城的子品牌,LEO在台灣擁有廣泛的用戶基礎,但其突然失聯以及退出台灣市場的傳聞,讓玩家擔憂自己的資金和帳戶安全。以下將詳細解析問題原因及替代方案,幫助玩家應對這一局面。
LEO娛樂城無法登入的三大原因
資金問題,無法出金
當玩家贏錢且帳號突然被鎖,這可能意味著娛樂城的資金鏈出現問題。LEO娛樂城無法處理大量出金需求,導致帳號被限制,進一步引發用戶恐慌。
伺服器故障,可能涉及詐騙行為
LEO娛樂城因涉嫌詐騙而被舉報,導致伺服器故障。這樣的情況不僅影響平台穩定性,也讓玩家的信任度下降,娛樂城的可靠性大打折扣。
退出台灣市場
隨著九州娛樂城因洗錢和內鬼洩密案被警方盯上,LEO娛樂城可能為避風頭選擇退出台灣市場。此舉將讓玩家無法再次登入,帳戶內的資金和獎金也可能無法追回。
九州娛樂城退出台灣的背景
LEO娛樂城隸屬九州集團,過去曾深度依賴金流公司和第三方支付來運作。然而,近期九州娛樂城涉及的洗錢案浮出水面,包括高層涉嫌賄賂警界內鬼,導致警方全面查緝。為避免更多曝光,退出台灣市場成為九州集團的合理選擇。
此外,也有消息指出,九州娛樂城對台灣市場的競爭激烈度表示不滿,正計畫將重心轉向更具潛力的海外市場。九州旗下的KU體育已進軍國際舞台,曾贊助五大足球聯賽,顯示其實力雄厚。
應對LEO娛樂城無法登入的最佳替代方案
如果你在LEO娛樂城無法登入的情況下,不妨考慮其他穩定且安全的平台,例如 1XBET。作為國際知名娛樂品牌,1XBET 以其安全性和穩定性贏得了玩家的廣泛信任。
為何選擇1XBET?
穩定安全:1XBET 平台運作合法,提供穩定的遊戲環境。
免費體驗金:新玩家可獲得免費體驗金,零成本開始娛樂。
首儲優惠及無限返水:首筆存款享受高額優惠,並提供無限返水政策,確保玩家的最大利益。
結論:抓緊時機保障自己的資金
LEO娛樂城無法登入以及可能退出台灣市場的消息,讓許多玩家感到不安。無論是未完成的儲值,還是帳戶中的餘額,都可能隨時歸零。建議玩家儘早取回資金,並選擇更安全可靠的平台,例如 1XBET,以確保自己的資金和遊戲體驗。
在不穩定的娛樂市場中,選擇合法且受信任的平台,將是長遠的最佳保障。 -
Introduction of Crypto Deal Verification and Regulatory Options
In today's cryptocurrency industry, ensuring transfer clarity and adherence with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Customer Identification rules is vital. Below is an outline of well-known services that provide services for digital asset transaction monitoring, verification, and resource security.
1. Tokenmetrics.com
Overview: Token Metrics provides digital asset evaluation to evaluate possible fraud threats. This platform lets individuals to check tokens ahead of investment to avoid likely risky holdings. Features:
- Danger analysis.
- Perfect for holders seeking to avoid questionable or scam projects.
2. Metamask Center
Overview: Metamask.Monitory.Center allows individuals to check their crypto assets for doubtful actions and compliance adherence. Benefits:
- Validates coins for “cleanliness”.
- Delivers warnings about likely resource restrictions on specific trading sites.
- Provides comprehensive insights after account sync.
3. Best Change
Description: Best Change is a platform for observing and validating crypto exchange transactions, guaranteeing transparency and deal security. Benefits:
- Deal and wallet observation.
- Restriction validation.
- Web-based platform; accommodates BTC and multiple additional coins.
4. AML Bot
Overview: AMLCheck Bot is a investment monitor and anti-money laundering service that uses machine learning methods to detect questionable actions. Features:
- Deal tracking and identity verification.
- Offered via online and chat bot.
- Works with digital assets including BSC, BTC, DOGE, and additional.
5. AlfaBit
Summary: AlfaBit delivers thorough AML tools specifically made for the digital currency market, helping businesses and financial organizations in maintaining standard conformity. Advantages:
- Comprehensive anti-money laundering tools and checks.
- Complies with modern security and regulatory guidelines.
6. AMLNode
Overview: AML Node offers anti-money laundering and customer identity solutions for cryptocurrency firms, which includes transfer monitoring, sanctions checks, and evaluation. Features:
- Danger assessment options and sanctions validations.
- Valuable for ensuring safe company processes.
7. Btrace.AMLcrypto.io
Overview: Btrace AML Crypto is dedicated to asset verification, delivering transfer monitoring, sanctions checks, and support if you are a affected by loss. Benefits:
- Reliable support for resource restoration.
- Transfer monitoring and safety tools.
Exclusive USDT Validation Services
Our site also provides information on different services offering validation tools for crypto deals and wallets:
- **USDT TRC20 and ERC20 Validation:** Numerous platforms provide comprehensive checks for USDT deals, aiding in the identification of suspicious activity.
- **AML Validation for USDT:** Tools are available for monitoring for money laundering transactions.
- **“Cleanliness” Validation for Holdings:** Checking of deal and wallet purity is provided to find potential risks.
**Wrap-up**
Choosing the suitable platform for verifying and monitoring digital currency transfers is essential for ensuring protection and compliance conformity. By consulting our recommendations, you can find the most suitable tool for transfer monitoring and asset safety. -
Summary of Crypto Transfer Validation and Conformity Solutions
In today's cryptocurrency sector, guaranteeing transfer clarity and adherence with AML and KYC standards is vital. Below is an outline of well-known platforms that offer tools for cryptocurrency deal tracking, validation, and asset security.
1. Token Metrics
Description: Token Metrics delivers cryptocurrency assessment to assess likely risk threats. This platform enables users to review tokens ahead of purchase to evade possibly fraudulent holdings. Attributes:
- Threat evaluation.
- Perfect for investors seeking to avoid hazardous or fraudulent ventures.
2. Metamask Monitor Center
Description: Metamask.Monitory.Center allows individuals to check their cryptocurrency holdings for doubtful activity and regulatory conformity. Features:
- Checks tokens for legitimacy.
- Delivers notifications about possible fund locks on certain trading sites.
- Delivers thorough insights after account connection.
3. Best Change
Overview: Best Change is a service for monitoring and validating cryptocurrency trade transactions, providing openness and transfer safety. Benefits:
- Transfer and account monitoring.
- Restriction screening.
- Internet platform; supports BTC and several different cryptocurrencies.
4. Bot amlchek
Summary: AMLCheck Bot is a holding monitor and anti-money laundering service that employs artificial intelligence algorithms to detect dubious transactions. Advantages:
- Transfer tracking and personal check.
- Available via internet and Telegram.
- Works with cryptocurrencies including BSC, BTC, DOGE, and additional.
5. AlphaBit
Summary: AlphaBit offers comprehensive Anti-Money Laundering (AML) tools specifically made for the digital currency field, assisting companies and banks in maintaining compliance compliance. Advantages:
- Thorough compliance tools and checks.
- Meets modern protection and conformity standards.
6. AML Node
Description: AMLNode delivers compliance and KYC services for cryptocurrency companies, such as deal observing, compliance screening, and evaluation. Features:
- Danger evaluation options and restriction validations.
- Valuable for ensuring safe business activities.
7. Btrace AML Crypto
Summary: Btrace.AMLcrypto.io focuses on fund verification, delivering deal observation, restriction checks, and support if you are a target of fraud. Advantages:
- Effective help for fund restoration.
- Deal observation and protection features.
Exclusive USDT Check Services
Our platform also provides information on various platforms providing check solutions for crypto transactions and holdings:
- **USDT TRC20 and ERC20 Validation:** Many platforms support detailed checks for USDT transfers, assisting in the finding of questionable transactions.
- **AML Verification for USDT:** Options are offered for monitoring for money laundering activities.
- **“Cleanliness” Checks for Wallets:** Verification of deal and holding legitimacy is offered to find likely risks.
**Summary**
Choosing the suitable service for validating and tracking cryptocurrency transactions is essential for ensuring protection and regulatory adherence. By reading our recommendations, you can choose the best solution for transfer tracking and fund protection. -
九州娛樂城新聞
九州集團宣布退出台灣市場 電子遊戲玩家該如何應對?
近日,九州娛樂集團正式宣布進一步調整策略,將退出台灣市場,並停止所有在台灣的運營,包括 LEO娛樂城和 THA娛樂城。這一消息無疑引起了廣泛關注,許多玩家都在懷疑接下來的遊戲體驗會受到什麼影響。
#### 退出的原因揭密
九州集團在公告中提到,退出台灣市場的原因主要包括:
1. 競爭激烈:隨著市場競爭的白熱化,越來越多的平台為了爭奪市場份額而忽略了長期的穩定經營,這導致多個平台運營問題頻出。
2. 資金流問題:部分平台在金流處理方面遭遇挑戰,無法保證玩家資金的安全與及時提款,進一步削弱了玩家的信任感。
3. 監管壓力:隨著行業規範的不斷提升,部分平台難以滿足合規要求,這直接導致服務中斷,甚至被迫退出市場。
4. 玩家需求變化:近年來,玩家對平台的穩定性、安全性和多樣化遊戲選擇的要求越來越高,只有實力雄厚的品牌才能夠滿足這些需求。
#### 轉向富遊娛樂城的好處
面對 LEO及 THA 退出的消息,九州娛樂集團也向玩家推薦了 RG 富遊娛樂城,這是一個深受玩家支持的賭場品牌。富遊娛樂城提供多項優勢,可以幫助玩家順利轉移,繼續享受遊戲體驗。
- 穩定性高:富遊娛樂城利用行業前沿的技術支持,確保平台運行穩定可靠,減少登入問題和系統故障的風險。
- 安全性強:該平台應用頂級數據加密技術,全面保護玩家的資金和個人隱私,讓玩家無後顧之憂。
- 遊戲多樣化:富遊娛樂城提供豐富的遊戲 selections,包括真人娛樂、電子遊戲、體育博彩等,能滿足不同玩家的需求。
#### 專為九州娛樂城會員設計的福利
為了保障受到 LEO及 THA 影響的玩家權益,富遊娛樂城推出了一系列回饋措施:
- VIP 等級保留:來自 LEO 和 THA 的玩家將保留或直接升級至對應的 VIP 等級,確保權益不受影響。
- 註冊優惠:新加入富遊娛樂城的玩家將獲得高達168的體驗金、100% 首存加碼及專屬新手禮包。
- 簡化轉移過程:富遊娛樂城為用戶提供簡單的轉移計劃,無需繁瑣手續,讓每位玩家可以專注於遊戲的樂趣。
### 結語
隨著九州娛樂集團宣布退出台灣市場,玩家們面臨著轉移平台的挑戰。儘管這一變化令人感到遺憾,但富遊娛樂城作為一個可靠的替代選擇,將為玩家的遊戲體驗帶來穩定的保障。玩家應該把握這一機會,迅速安排好轉移和註冊事宜,以確保不斷享受遊戲的樂趣。 -
九州集團宣布退出台灣市場 電子遊戲玩家該如何應對?
近日,九州娛樂集團正式宣布進一步調整策略,將退出台灣市場,並停止所有在台灣的運營,包括 LEO娛樂城和 THA娛樂城。這一消息無疑引起了廣泛關注,許多玩家都在懷疑接下來的遊戲體驗會受到什麼影響。
#### 退出的原因揭密
九州集團在公告中提到,退出台灣市場的原因主要包括:
1. 競爭激烈:隨著市場競爭的白熱化,越來越多的平台為了爭奪市場份額而忽略了長期的穩定經營,這導致多個平台運營問題頻出。
2. 資金流問題:部分平台在金流處理方面遭遇挑戰,無法保證玩家資金的安全與及時提款,進一步削弱了玩家的信任感。
3. 監管壓力:隨著行業規範的不斷提升,部分平台難以滿足合規要求,這直接導致服務中斷,甚至被迫退出市場。
4. 玩家需求變化:近年來,玩家對平台的穩定性、安全性和多樣化遊戲選擇的要求越來越高,只有實力雄厚的品牌才能夠滿足這些需求。
#### 轉向富遊娛樂城的好處
面對 LEO及 THA 退出的消息,九州娛樂集團也向玩家推薦了 RG 富遊娛樂城,這是一個深受玩家支持的賭場品牌。富遊娛樂城提供多項優勢,可以幫助玩家順利轉移,繼續享受遊戲體驗。
- 穩定性高:富遊娛樂城利用行業前沿的技術支持,確保平台運行穩定可靠,減少登入問題和系統故障的風險。
- 安全性強:該平台應用頂級數據加密技術,全面保護玩家的資金和個人隱私,讓玩家無後顧之憂。
- 遊戲多樣化:富遊娛樂城提供豐富的遊戲 selections,包括真人娛樂、電子遊戲、體育博彩等,能滿足不同玩家的需求。
#### 專為九州娛樂城會員設計的福利
為了保障受到 LEO及 THA 影響的玩家權益,富遊娛樂城推出了一系列回饋措施:
- VIP 等級保留:來自 LEO 和 THA 的玩家將保留或直接升級至對應的 VIP 等級,確保權益不受影響。
- 註冊優惠:新加入富遊娛樂城的玩家將獲得高達168的體驗金、100% 首存加碼及專屬新手禮包。
- 簡化轉移過程:富遊娛樂城為用戶提供簡單的轉移計劃,無需繁瑣手續,讓每位玩家可以專注於遊戲的樂趣。
### 結語
隨著九州娛樂集團宣布退出台灣市場,玩家們面臨著轉移平台的挑戰。儘管這一變化令人感到遺憾,但富遊娛樂城作為一個可靠的替代選擇,將為玩家的遊戲體驗帶來穩定的保障。玩家應該把握這一機會,迅速安排好轉移和註冊事宜,以確保不斷享受遊戲的樂趣。 -
Retinaad stands as the top ad technology leader for advertisement analytics & consumer behavior analysis in Nigeria.
We provide campaign audits, monitoring, and regulation adherence tools for:
- **billboards and displays / digital outdoor advertising**,
- **field activations**,
- **shop-based promotions**,
- **media channels**,
- **on-air promotions**,
- **broadcast advertising**,
- **digital PR campaigns**,
- **Socials**.
Our primary objective is to help marketing professionals, advertisers, and advertising firms increase productivity and financial returns.
The firm leverages state-of-the-art solutions to deliver reliable analytics. By delivering a integrated framework, our team tackle the critical needs of media compliance, helping businesses succeed in an dynamic industry. -
BTL monitoring in Nigeria
Retinaad Limited stands as the premier ad technology leader providing solutions for media tracking & consumer behavior analysis within Nigeria.
We specialize in campaign audits, surveillance, and regulation adherence tools for:
- **OOH / electronic media boards**,
- **on-ground campaigns**,
- **retail media**,
- **communication resources**,
- **radio channels**,
- **broadcast advertising**,
- **online PR**,
- **Socials**.
Our core focus is to enable corporate brand custodians, campaign leaders, and content distributors increase operational impact and return on investment.
The firm applies cutting-edge tools to provide granular results. By creating a well-rounded approach, our organization tackle the critical needs of media compliance, helping agencies grow in an fast-paced landscape. -
LEO娛樂城無法登入?九州集團可能要退出台灣市場!
近期,許多玩家發現自己無法登入 LEO娛樂城,這引發了關於九州集團是否即將退出台灣市場的廣泛討論。這篇文章將深入探討可能的原因以及玩家該如何應對。
#### 為什麼 LEO娛樂城無法登入?
1. 帳號或密碼問題:這是最常見的原因之一。如果玩家忘記了密碼或帳號被鎖定,只需聯繫客服提供必要的資訊,通常能夠迅速恢復進入權限。
2. 網站故障:有不少玩家報告稱無法正常訪問 LEO娛樂城,顯示404錯誤頁面。這可能是因為網站伺服器出現問題或被檢舉。玩家在遇到此類問題時,可以詢問客服以獲取正確的網址,並建議將網址加入書籤,以便隨時訪問。
3. 九州集團計劃退出台灣市場:最令人擔憂的是,傳聞九州集團可能正在考慮退出台灣市場,這將對玩家造成直接影響,特別是在資金存款和提現上。這個情況讓不少玩家感到焦慮,也加深了對於未來的擔憂。
#### 為什麼九州集團要退出?
有幾個因素可能促使九州集團作出這樣的決定:
- 市場競爭加劇:台灣市場的競爭相當激烈,對於像 LEO這樣的品牌來說,持續獲利變得越來越困難。因此,他們或許希望尋找其他市場擴展機會。
- 金融壓力:九州集團近來因多起事件受到關注,特別是涉及金流問題。前高層的逮捕與金融查詢事件,使得旗下各平台的運作都變得更加艱難。
- 品牌形象受損:隨著負面新聞的增多,LEO和其他九州品牌的信譽也受到了相當大的影響。為了保護品牌形象,退出某個市場可能被視為一種選擇。
#### 對於玩家的建議
如果 LEO娛樂城真的面臨退出台灣市場的風險,玩家需要做好應對措施。以下是一些選擇替代平台的建議:
- 考慮其他娛樂城brand:如亞博體育,該平台具有許多優勢,包括合法的營業執照和豐富的遊戲選擇。
- 檢視平台的安全性:選擇那些擁有穩定金流和良好信譽的娛樂城,以確保資金的安全。
- 利用促銷活動:例如亞博體育提供的首次充值優惠合理,這是進一步提升棋局的好選擇。
### 結論
LEO娛樂城目前的登入問題引發了對九州集團未來的憂慮。儘管提供了恢復帳號的實用方法,玩家仍應謹慎應對,並考慮在目前市況下的其他可靠選擇,確保自己的資金安全及遊戲體驗。隨著娛樂市場的變化,選擇一家穩定、信譽良好的平台變得尤為重要。 -
九州娛樂城倒了
LEO娛樂城無法登入?九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的真相解析
近期,LEO娛樂城頻頻傳出無法登入的消息,並伴隨著「九州娛樂城退出市場」的傳聞,引發了廣大玩家的熱議與疑慮。作為台灣線上娛樂城市場的代表品牌之一,LEO娛樂城曾憑藉其廣泛的廣告投放和龐大的代理規模,成為許多玩家耳熟能詳的名字。然而,這一系列的問題究竟是偶發事件還是背後早有計劃?本文將帶您深入了解LEO娛樂城無法登入的原因及其對玩家的影響。
LEO娛樂城無法登入:網路熱議九州娛樂城倒閉
LEO娛樂城近期無法登入的情況似乎透露出了一個更大的訊息:該平台正在逐步退出台灣市場。隨著其營運的逐漸停擺,玩家們發現以下問題日益嚴重:
官網無法訪問:登入失敗的情況變得愈加頻繁。
註冊和儲值受限:許多玩家反映無法完成新用戶註冊,甚至現有用戶的儲值功能也開始受到限制。
經調查,這一退出決策並非偶然,而是九州娛樂城高層的長期規劃結果。讓我們一起探索這一決策背後的可能原因。
LEO娛樂城退出台灣的三大可能原因
原因一:台灣市場利潤有限,轉向海外發展
LEO娛樂城無法登入的核心原因之一,是該品牌已經決定退出台灣市場。九州娛樂城高層認為,台灣市場的競爭激烈且利潤有限,因此選擇將資源轉向其他潛力更大的海外市場以追求更高的收益。
見好就收:這一做法與許多商業決策類似,在利潤達到一定水平後選擇退出,尋求更具回報的新機會。
海外市場吸引力:國際市場的規模和成長性更具吸引力,讓九州娛樂城看到了更大的可能性。
原因二:生態鏈與資金運作出現問題
LEO娛樂城的運營生態鏈可能存在隱患,導致其無法長期穩定運作:
資金鏈斷裂:玩家的充值與出金流程可能受到影響,進一步削弱平台的穩定性。
運營成本上升:在台灣市場的高運營成本可能也是平台選擇退出的一大原因。
原因三:九州娛樂城受到法律與政策壓力
九州娛樂城近年來面臨多起法律與政策挑戰,影響了其旗下品牌的正常運營:
監管政策加強:台灣政府對線上娛樂平台的監管力度加大,對九州娛樂城造成了直接影響。
法律爭議:母公司的財務與法規問題頻頻登上新聞,使旗下品牌的經營環境更加複雜。
LEO娛樂城無法登入對玩家的影響
隨著LEO娛樂城逐步退出台灣市場,玩家需要做好以下應對措施:
迅速提現本金:如您仍可登入官網,建議立即提取帳戶內的資金,避免遭遇平台徹底關閉後的損失。
尋找可靠的替代平台:選擇擁有合法牌照且運營穩定的國際品牌,如1XBET等,確保遊戲與資金安全。
提高資金安全意識:在選擇新平台時,應重點關注其口碑、資金保障措施以及用戶評價,避免再次陷入類似情況。
結論:LEO娛樂城無法登入背後的啟示
LEO娛樂城無法登入以及九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的消息,揭示了線上娛樂市場的高風險性與不穩定性。對玩家而言,選擇安全合法的平台才是長遠之計。
在未來,隨著國際市場的開放與法規的完善,玩家或許能期待更穩定與透明的娛樂環境。但在此之前,迅速採取行動保障自己的資金與利益才是當務之急。 -
LEO娛樂城無法登入?九州集團可能要退出台灣市場!
近期,許多玩家發現自己無法登入 LEO娛樂城,這引發了關於九州集團是否即將退出台灣市場的廣泛討論。這篇文章將深入探討可能的原因以及玩家該如何應對。
#### 為什麼 LEO娛樂城無法登入?
1. 帳號或密碼問題:這是最常見的原因之一。如果玩家忘記了密碼或帳號被鎖定,只需聯繫客服提供必要的資訊,通常能夠迅速恢復進入權限。
2. 網站故障:有不少玩家報告稱無法正常訪問 LEO娛樂城,顯示404錯誤頁面。這可能是因為網站伺服器出現問題或被檢舉。玩家在遇到此類問題時,可以詢問客服以獲取正確的網址,並建議將網址加入書籤,以便隨時訪問。
3. 九州集團計劃退出台灣市場:最令人擔憂的是,傳聞九州集團可能正在考慮退出台灣市場,這將對玩家造成直接影響,特別是在資金存款和提現上。這個情況讓不少玩家感到焦慮,也加深了對於未來的擔憂。
#### 為什麼九州集團要退出?
有幾個因素可能促使九州集團作出這樣的決定:
- 市場競爭加劇:台灣市場的競爭相當激烈,對於像 LEO這樣的品牌來說,持續獲利變得越來越困難。因此,他們或許希望尋找其他市場擴展機會。
- 金融壓力:九州集團近來因多起事件受到關注,特別是涉及金流問題。前高層的逮捕與金融查詢事件,使得旗下各平台的運作都變得更加艱難。
- 品牌形象受損:隨著負面新聞的增多,LEO和其他九州品牌的信譽也受到了相當大的影響。為了保護品牌形象,退出某個市場可能被視為一種選擇。
#### 對於玩家的建議
如果 LEO娛樂城真的面臨退出台灣市場的風險,玩家需要做好應對措施。以下是一些選擇替代平台的建議:
- 考慮其他娛樂城brand:如亞博體育,該平台具有許多優勢,包括合法的營業執照和豐富的遊戲選擇。
- 檢視平台的安全性:選擇那些擁有穩定金流和良好信譽的娛樂城,以確保資金的安全。
- 利用促銷活動:例如亞博體育提供的首次充值優惠合理,這是進一步提升棋局的好選擇。
### 結論
LEO娛樂城目前的登入問題引發了對九州集團未來的憂慮。儘管提供了恢復帳號的實用方法,玩家仍應謹慎應對,並考慮在目前市況下的其他可靠選擇,確保自己的資金安全及遊戲體驗。隨著娛樂市場的變化,選擇一家穩定、信譽良好的平台變得尤為重要。 -
LEO娛樂城無法登入?九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的真相解析
近期,LEO娛樂城頻頻傳出無法登入的消息,並伴隨著「九州娛樂城退出市場」的傳聞,引發了廣大玩家的熱議與疑慮。作為台灣線上娛樂城市場的代表品牌之一,LEO娛樂城曾憑藉其廣泛的廣告投放和龐大的代理規模,成為許多玩家耳熟能詳的名字。然而,這一系列的問題究竟是偶發事件還是背後早有計劃?本文將帶您深入了解LEO娛樂城無法登入的原因及其對玩家的影響。
LEO娛樂城無法登入:網路熱議九州娛樂城倒閉
LEO娛樂城近期無法登入的情況似乎透露出了一個更大的訊息:該平台正在逐步退出台灣市場。隨著其營運的逐漸停擺,玩家們發現以下問題日益嚴重:
官網無法訪問:登入失敗的情況變得愈加頻繁。
註冊和儲值受限:許多玩家反映無法完成新用戶註冊,甚至現有用戶的儲值功能也開始受到限制。
經調查,這一退出決策並非偶然,而是九州娛樂城高層的長期規劃結果。讓我們一起探索這一決策背後的可能原因。
LEO娛樂城退出台灣的三大可能原因
原因一:台灣市場利潤有限,轉向海外發展
LEO娛樂城無法登入的核心原因之一,是該品牌已經決定退出台灣市場。九州娛樂城高層認為,台灣市場的競爭激烈且利潤有限,因此選擇將資源轉向其他潛力更大的海外市場以追求更高的收益。
見好就收:這一做法與許多商業決策類似,在利潤達到一定水平後選擇退出,尋求更具回報的新機會。
海外市場吸引力:國際市場的規模和成長性更具吸引力,讓九州娛樂城看到了更大的可能性。
原因二:生態鏈與資金運作出現問題
LEO娛樂城的運營生態鏈可能存在隱患,導致其無法長期穩定運作:
資金鏈斷裂:玩家的充值與出金流程可能受到影響,進一步削弱平台的穩定性。
運營成本上升:在台灣市場的高運營成本可能也是平台選擇退出的一大原因。
原因三:九州娛樂城受到法律與政策壓力
九州娛樂城近年來面臨多起法律與政策挑戰,影響了其旗下品牌的正常運營:
監管政策加強:台灣政府對線上娛樂平台的監管力度加大,對九州娛樂城造成了直接影響。
法律爭議:母公司的財務與法規問題頻頻登上新聞,使旗下品牌的經營環境更加複雜。
LEO娛樂城無法登入對玩家的影響
隨著LEO娛樂城逐步退出台灣市場,玩家需要做好以下應對措施:
迅速提現本金:如您仍可登入官網,建議立即提取帳戶內的資金,避免遭遇平台徹底關閉後的損失。
尋找可靠的替代平台:選擇擁有合法牌照且運營穩定的國際品牌,如1XBET等,確保遊戲與資金安全。
提高資金安全意識:在選擇新平台時,應重點關注其口碑、資金保障措施以及用戶評價,避免再次陷入類似情況。
結論:LEO娛樂城無法登入背後的啟示
LEO娛樂城無法登入以及九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的消息,揭示了線上娛樂市場的高風險性與不穩定性。對玩家而言,選擇安全合法的平台才是長遠之計。
在未來,隨著國際市場的開放與法規的完善,玩家或許能期待更穩定與透明的娛樂環境。但在此之前,迅速採取行動保障自己的資金與利益才是當務之急。 -
九州娛樂城倒了
Leo娛樂城無法登入?是九州娛樂城倒了嗎?背後原因竟是這樣!
最近,許多玩家發現自己無法登入 Leo娛樂城,甚至有人關心是否這意味著九州娛樂城的倒閉。究竟發生了什麼事情?今天,我們將解開這個謎團,幫助大家瞭解 Leo娛樂城無法登入的真正原因。
#### 目錄
1. Leo娛樂城無法登入:背後的三個原因
2. 九州娛樂城倒了?只是退出台灣市場
3. Leo娛樂城無法登入該怎麼辦?
4. 最新娛樂城推薦排名,這幾家平台更值得信賴!
5. 結論
### Leo娛樂城無法登入:背後的三個原因
#### 原因一:帳號被鎖或密碼錯誤
最常見的問題之一就是玩家的帳號被鎖定或密碼輸錯。這類問題其實相對容易解決,玩家只需聯繫客服要求恢復帳號即可。然而,有部分玩家反映客服反應緩慢,甚至感覺客服想要拖延時間,這一點讓人不禁懷疑是否有其他貓膩。
#### 原因二:網站壞了或被檢舉
有玩家在登錄時遇到 404 錯誤,這種情況通常表明網站伺服器出現故障,或是因為某種原因被檢舉並暫時下架。這樣的情況對於玩家來說非常令人沮喪,因為缺乏官方的回應和修復時間,只能無奈等待。
#### 原因三:九州集團退出台灣市場
近期有消息指出,九州集團可能正在逐步退出台灣的市場,這可能影響到其旗下所有娛樂城的運作。如果該集團確實進行了市場撤退,則 Leo娛樂城的運作將受到直接影響,這也解釋了為什麼許多玩家會感到困惑和不安。
### 九州娛樂城倒了?只是退出台灣市場
雖然網上有許多傳言說九州娛樂城已經倒閉,但實際上應該理解為它正在退出台灣市場。這樣的變化可能與政策、法規等多種因素有關。對於玩家來說,這是需要留意的一個信息,以便尋找其他可行的娛樂選擇。
### Leo娛樂城無法登入該怎麼辦?
如果你遇到無法登入的問題,建議你首先檢查帳號和密碼是否正確。如果是技術性問題,則需等待官方的修復通知。在這段時間內,可以考慮暫時使用其他娛樂城平台,避免資金被鎖定。
### 最新娛樂城推薦排名,這幾家平台更值得信賴!
在選擇娛樂城時,建議選擇評價高、可靠性強的平台。以下是目前推薦的一些娛樂城,這幾家平台在安全性和用戶體驗上表現良好,可以作為替代選擇:
1. XXX娛樂城 – 以安全和穩定著稱。
2. YYY娛樂城 – 提供多樣化的遊戲選擇。
3. ZZZ娛樂城 – 客服反應快速,體驗佳。
### 結論
總的來說,Leo娛樂城無法登入的原因涉及帳號問題、網站技術故障以及九州集團的市場動向。希望這篇文章能幫助你更好地理解目前的情況。保持警惕,選擇可靠的娛樂平台,以確保自身的資金安全和良好的遊戲體驗。希望未來能有更好的解決方案來改善玩家的困擾! -
九州娛樂城倒了
Leo娛樂城無法登入?是九州娛樂城倒了嗎?背後原因竟是這樣!
最近,許多玩家發現自己無法登入 Leo娛樂城,甚至有人關心是否這意味著九州娛樂城的倒閉。究竟發生了什麼事情?今天,我們將解開這個謎團,幫助大家瞭解 Leo娛樂城無法登入的真正原因。
#### 目錄
1. Leo娛樂城無法登入:背後的三個原因
2. 九州娛樂城倒了?只是退出台灣市場
3. Leo娛樂城無法登入該怎麼辦?
4. 最新娛樂城推薦排名,這幾家平台更值得信賴!
5. 結論
### Leo娛樂城無法登入:背後的三個原因
#### 原因一:帳號被鎖或密碼錯誤
最常見的問題之一就是玩家的帳號被鎖定或密碼輸錯。這類問題其實相對容易解決,玩家只需聯繫客服要求恢復帳號即可。然而,有部分玩家反映客服反應緩慢,甚至感覺客服想要拖延時間,這一點讓人不禁懷疑是否有其他貓膩。
#### 原因二:網站壞了或被檢舉
有玩家在登錄時遇到 404 錯誤,這種情況通常表明網站伺服器出現故障,或是因為某種原因被檢舉並暫時下架。這樣的情況對於玩家來說非常令人沮喪,因為缺乏官方的回應和修復時間,只能無奈等待。
#### 原因三:九州集團退出台灣市場
近期有消息指出,九州集團可能正在逐步退出台灣的市場,這可能影響到其旗下所有娛樂城的運作。如果該集團確實進行了市場撤退,則 Leo娛樂城的運作將受到直接影響,這也解釋了為什麼許多玩家會感到困惑和不安。
### 九州娛樂城倒了?只是退出台灣市場
雖然網上有許多傳言說九州娛樂城已經倒閉,但實際上應該理解為它正在退出台灣市場。這樣的變化可能與政策、法規等多種因素有關。對於玩家來說,這是需要留意的一個信息,以便尋找其他可行的娛樂選擇。
### Leo娛樂城無法登入該怎麼辦?
如果你遇到無法登入的問題,建議你首先檢查帳號和密碼是否正確。如果是技術性問題,則需等待官方的修復通知。在這段時間內,可以考慮暫時使用其他娛樂城平台,避免資金被鎖定。
### 最新娛樂城推薦排名,這幾家平台更值得信賴!
在選擇娛樂城時,建議選擇評價高、可靠性強的平台。以下是目前推薦的一些娛樂城,這幾家平台在安全性和用戶體驗上表現良好,可以作為替代選擇:
1. XXX娛樂城 – 以安全和穩定著稱。
2. YYY娛樂城 – 提供多樣化的遊戲選擇。
3. ZZZ娛樂城 – 客服反應快速,體驗佳。
### 結論
總的來說,Leo娛樂城無法登入的原因涉及帳號問題、網站技術故障以及九州集團的市場動向。希望這篇文章能幫助你更好地理解目前的情況。保持警惕,選擇可靠的娛樂平台,以確保自身的資金安全和良好的遊戲體驗。希望未來能有更好的解決方案來改善玩家的困擾! -
nhà cái ST666
ST666 - Nhận Định Bóng Đá Kèo Nhà Cái Uy Tín
ST666: Địa Chỉ Lý Tưởng Cho Những Tín Đồ Cá Cược Bóng Đá
ST666 là nền tảng nhận định bóng đá và kèo nhà cái chuyên nghiệp, nơi người chơi có thể tham gia dự đoán các kèo đa dạng như cược tài xỉu, cược chấp, và cược 1x2. Với giao diện thân thiện, tỷ lệ cược minh bạch và ưu đãi hấp dẫn, ST666 đang dần trở thành lựa chọn hàng đầu của cộng đồng yêu bóng đá.
Nhận Định Kèo Nhà Cái Đa Dạng
Cược Tài Xỉu (#cuoctaixiu)
Dựa vào tổng số bàn thắng trong trận đấu, người chơi dễ dàng chọn lựa Tài (nhiều hơn tỷ lệ nhà cái đưa ra) hoặc Xỉu (ít hơn tỷ lệ).
ST666 cung cấp các phân tích chi tiết giúp người chơi đưa ra lựa chọn chính xác.
Cược Chấp (#cuocchap)
Thích hợp cho những trận đấu có sự chênh lệch về sức mạnh giữa hai đội. ST666 cung cấp tỷ lệ chấp tối ưu, phù hợp với cả người chơi mới và chuyên nghiệp.
Cược 1x2 (#cuoc1x2)
Phù hợp cho những ai muốn dự đoán kết quả chung cuộc (Thắng - Hòa - Thua). Đây là loại kèo phổ biến, dễ hiểu và có tỷ lệ cược hấp dẫn.
Ưu Đãi Hấp Dẫn Tại ST666
Nhận 160% tiền gửi lần đầu: Khi đăng ký tài khoản mới và nạp tiền, người chơi sẽ nhận được số tiền thưởng cực lớn, tăng cơ hội tham gia các kèo.
Hoàn tiền 3% mỗi ngày: Chính sách hoàn tiền giúp người chơi giảm thiểu rủi ro, thoải mái trải nghiệm mà không lo lắng nhiều về chi phí.
Vì Sao Nên Chọn ST666?
Nền Tảng Uy Tín: ST666 cam kết mang đến trải nghiệm cá cược minh bạch và an toàn.
Phân Tích Chuyên Sâu: Đội ngũ chuyên gia của ST666 luôn cập nhật nhận định mới nhất về các trận đấu, giúp người chơi đưa ra quyết định tối ưu.
Hỗ Trợ 24/7: Đội ngũ hỗ trợ chuyên nghiệp, luôn sẵn sàng giải đáp thắc mắc của người chơi.
Giao Dịch Nhanh Chóng: Nạp rút tiền linh hoạt, đảm bảo sự tiện lợi và bảo mật.
Cách Tham Gia ST666
Truy cập website chính thức của ST666.
Đăng ký tài khoản bằng thông tin cá nhân.
Nạp tiền lần đầu để nhận ưu đãi 160%.
Bắt đầu trải nghiệm cá cược với các kèo yêu thích!
Hãy đến với ST666 để tận hưởng không gian cá cược chuyên nghiệp, nhận định kèo chất lượng và những phần thưởng hấp dẫn. Tham gia ngay hôm nay để trở thành người chơi chiến thắng! -
leo娛樂城登入
LEO娛樂城:九州娛樂集團的卓越創舉與運營優勢
九州娛樂集團總部的現代化運營
九州娛樂集團的總部設於菲律賓首都馬尼拉市中心最具代表性的現代化建築「RCBC Plaza」。這座辦公大樓融合了全球領先的建築科技與安全系統,包括:
國家級資訊防護系統,確保數據安全。
樓宇自動化系統 (BAS),實現數位化管理與高效運營,包括防火系統、光纖電訊和數位監控。
九州娛樂為員工提供舒適的工作環境和專業的教育培訓,確保服務水準一流。其員工以專業知識和親切態度,為尊貴玩家帶來極致的遊戲體驗。
LEO娛樂旗下品牌與遊戲特色
九州娛樂城旗下分支包括 LEO、THA 和 KU 三個娛樂品牌。雖然品牌各自獨立運營,但都共享相同的遊戲系統與界面,提供超過數千款來自全球頂級供應商的遊戲。
這些品牌的核心特色包括:
種類繁多的遊戲:滿足不同類型玩家的需求,包括電子遊戲、體育博彩、真人娛樂等。
不斷更新的內容:通過九州獨家技術,網站內容保持新鮮,合作商可快速更新遊戲資源,確保平台競爭力。
玩家在這些平台上可以隨時找到適合自己的遊戲,享受沉浸式的娛樂體驗。
LEO娛樂城的歷史與發展
九州娛樂集團的起源可以追溯至其最早期的經營模式:「信用版」賭博平台 《天下體育球版》。儘管該模式在當時非常流行,但因高風險與財務處理複雜而逐漸被淘汰。
隨著市場需求的變化,九州娛樂轉型為現金版平台 《天下現金網》,引入了更安全、便捷的遊戲模式。這種轉變不僅提升了玩家的體驗,也使平台得以進一步發展。
如今,九州娛樂城已成為台灣博弈業界的領軍者,不僅優化了網站版面與功能,還推出了專屬手機APP,方便玩家隨時隨地進行遊戲體驗。
LEO娛樂的成功秘訣
現代化運營與技術支持:九州娛樂在系統安全與技術更新方面投入巨大資源,確保平台運營穩定可靠。
多元化遊戲體驗:通過與全球頂級遊戲供應商合作,平台提供了豐富的遊戲選擇,適應各種玩家需求。
用戶至上:專業培訓的員工以細心和熱忱態度,提供高品質服務,讓玩家倍感尊重。
不斷創新:從信用版到現金版,再到手機APP,九州娛樂始終緊跟市場趨勢,致力於打造最佳娛樂體驗。
結語
LEO娛樂城作為九州娛樂集團旗下的重要品牌,不僅繼承了集團的核心價值,更在遊戲選擇、服務品質和技術創新方面不斷提升。從最初的《天下體育球版》到如今的行業領先者,LEO娛樂見證了九州娛樂城的發展歷程,也成為博弈行業中的耀眼明星。
加入 LEO娛樂城,感受來自九州娛樂集團的專業與熱情,享受最頂級的線上博弈體驗! -
娛樂城
RG富遊娛樂城:台灣線上娛樂城的最佳選擇
RG富遊娛樂城以其卓越的服務和多樣化的遊戲選擇,成為2024年最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台。受到超過50位網紅和部落客的實測推薦,這座娛樂城不僅提供豐富的遊戲,還帶來眾多優惠活動和誠信保證,贏得了廣大玩家的信任與青睞。
RG富遊娛樂城的獨特優勢
多重優惠活動
體驗金 $168:新手玩家可以免費試玩,無需任何成本即可體驗高品質遊戲。
首儲1000送1000:首次存款即可獲得雙倍金額,增加遊戲的樂趣與機會。
線上簽到轉盤:每日簽到即可參加抽獎,贏取現金獎勵和豐厚禮品。
快速存提款與資金保障
RG富遊採用自主研發的財務系統,確保5秒快速存款,滿足玩家即時遊戲需求。
100%保證出金,杜絕任何拖延或資金安全風險,讓玩家完全放心。
遊戲種類豐富
RG富遊娛樂城涵蓋多種遊戲類型,滿足不同玩家的需求,包括:
真人百家樂:與真人荷官互動,感受真實賭場的刺激氛圍。
電子老虎機:超過數百款創新遊戲,玩法新穎,回報豐厚。
電子捕魚:趣味性強,結合策略與娛樂,深受玩家喜愛。
電子棋牌:提供公平競技環境,適合策略型玩家。
體育投注:涵蓋全球賽事,賠率即時更新,為體育愛好者提供最佳選擇。
樂透彩票:參與多地彩票,挑戰巨額獎金。
跨平台兼容性
RG富遊支持Web端、H5、iOS和Android設備,玩家可隨時隨地登錄遊戲,享受無縫體驗。
與其他娛樂城的不同之處
RG富遊以現金版模式運營,確保交易透明和安全性。相比一般娛樂城,RG富遊在存提款速度上遙遙領先,玩家可在短短15秒內完成交易,並且100%保證資金提領。而在線客服全年無休,隨時提供支持,讓玩家在任何時間都能解決問題。
相比之下,一般娛樂城多以信用版模式運營,存在出金風險,且存提款速度較慢,客服服務不穩定,無法與RG富遊的專業性相比。
為什麼選擇RG富遊娛樂城
資金交易安全無憂:採用最先進的SSL加密技術,確保每筆交易的安全性。
遊戲種類全面豐富:每日更新多樣化遊戲,帶來新鮮感和無限可能。
優惠活動力度大:從體驗金到豐厚的首儲獎勵,玩家每一步都能享受優惠。
快速存提款服務:自主研發技術保障流暢交易,遊戲不中斷。
全天候專業客服:24/7在線支持,及時解決玩家需求。
立即加入RG富遊娛樂城
RG富遊娛樂城不僅提供豐富的遊戲體驗,更以專業的服務、完善的安全保障和多樣的優惠活動,為玩家打造一個值得信賴的娛樂環境。立即註冊,體驗台灣最受歡迎的線上娛樂城! -
富遊娛樂城:全台灣第一推薦的娛樂城體驗
富遊娛樂城是全台灣最受玩家推崇的娛樂平台,提供多種優惠、豐富的遊戲選擇以及高品質的服務,讓每位玩家都能享受極致的遊戲樂趣。無論您是新手還是資深玩家,富遊娛樂城都能滿足您的需求,帶給您刺激的遊戲體驗。
富遊娛樂城的優惠活動
1. 免費娛樂城體驗金
新玩家只需註冊即可免費領取 $168 元的體驗金,無需存款,便可立即體驗各種遊戲,感受遊戲帶來的樂趣。
2. 首次存款優惠
首次存款 $1000 元,即送 $1000 元遊戲金,讓您在遊戲中有更多機會獲勝,增添刺激感。
3. 新會員五選一好禮
新加入的會員可選擇五種專屬好禮之一,從遊戲金到實體獎品,讓您的遊戲旅程更加多彩。
熱門遊戲種類
富遊娛樂城提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,適合不同喜好的玩家:
電子老虎機:多款創新遊戲,讓玩家享受豐厚獎金機會。
百家樂:與真人荷官互動,體驗真實賭場的刺激感。
今彩539 和 運彩:滿足彩票愛好者的需求。
捕魚遊戲:RSG電子捕魚遊戲帶來娛樂與獎金的雙重樂趣。
熊貓體育:專為體育迷設計的多種運動投注選項。
優質服務保證
1. 出金快速、安全可靠
富遊娛樂城採用先進的財務處理系統,保證快速存提款,讓玩家不用擔心資金安全問題。
2. 技術先進的APP平台
流暢的畫面設計與設備兼容性,讓用戶輕鬆上手。
持續升級與更新,提供更多創新遊戲類型。
3. 24小時專業客服
專業客服隨時待命,為玩家解答所有遊戲相關問題,確保您在任何時間都能享受到無縫的服務體驗。
4. 安全防護到位
採用最嚴格的安全管理系統與數據加密技術,保障用戶資金與個人信息的安全。
富遊娛樂城APP:隨時隨地盡享遊戲
富遊娛樂城APP提供了便捷的遊戲途徑,支援 IOS 與 Android 設備。
簡潔易用的界面設計,讓玩家快速找到喜愛的遊戲。
即時客服支援,隨時解決您的疑問。
免費下載,無論何時何地,您都能盡享娛樂城的精彩遊戲體驗。
為什麼選擇富遊娛樂城?
優惠豐富:免費體驗金、首存優惠、新會員好禮,活動多樣。
遊戲種類齊全:從電子遊戲到真人百家樂,滿足各類玩家需求。
服務至上:專業客服、快速出金和高安全保障讓玩家安心享受遊戲。
便捷平台:富遊APP提供隨時隨地的遊戲樂趣,讓您不受限制。
立即下載 富遊娛樂城APP,體驗全台灣第一娛樂城的無限魅力!不論您是想享受遊戲樂趣還是贏取豐厚獎金,富遊娛樂城都將是您的最佳選擇! -
RG富遊娛樂城:台灣線上娛樂城的最佳選擇
RG富遊娛樂城以其卓越的服務和多樣化的遊戲選擇,成為2024年最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台。受到超過50位網紅和部落客的實測推薦,這座娛樂城不僅提供豐富的遊戲,還帶來眾多優惠活動和誠信保證,贏得了廣大玩家的信任與青睞。
RG富遊娛樂城的獨特優勢
多重優惠活動
體驗金 $168:新手玩家可以免費試玩,無需任何成本即可體驗高品質遊戲。
首儲1000送1000:首次存款即可獲得雙倍金額,增加遊戲的樂趣與機會。
線上簽到轉盤:每日簽到即可參加抽獎,贏取現金獎勵和豐厚禮品。
快速存提款與資金保障
RG富遊採用自主研發的財務系統,確保5秒快速存款,滿足玩家即時遊戲需求。
100%保證出金,杜絕任何拖延或資金安全風險,讓玩家完全放心。
遊戲種類豐富
RG富遊娛樂城涵蓋多種遊戲類型,滿足不同玩家的需求,包括:
真人百家樂:與真人荷官互動,感受真實賭場的刺激氛圍。
電子老虎機:超過數百款創新遊戲,玩法新穎,回報豐厚。
電子捕魚:趣味性強,結合策略與娛樂,深受玩家喜愛。
電子棋牌:提供公平競技環境,適合策略型玩家。
體育投注:涵蓋全球賽事,賠率即時更新,為體育愛好者提供最佳選擇。
樂透彩票:參與多地彩票,挑戰巨額獎金。
跨平台兼容性
RG富遊支持Web端、H5、iOS和Android設備,玩家可隨時隨地登錄遊戲,享受無縫體驗。
與其他娛樂城的不同之處
RG富遊以現金版模式運營,確保交易透明和安全性。相比一般娛樂城,RG富遊在存提款速度上遙遙領先,玩家可在短短15秒內完成交易,並且100%保證資金提領。而在線客服全年無休,隨時提供支持,讓玩家在任何時間都能解決問題。
相比之下,一般娛樂城多以信用版模式運營,存在出金風險,且存提款速度較慢,客服服務不穩定,無法與RG富遊的專業性相比。
為什麼選擇RG富遊娛樂城
資金交易安全無憂:採用最先進的SSL加密技術,確保每筆交易的安全性。
遊戲種類全面豐富:每日更新多樣化遊戲,帶來新鮮感和無限可能。
優惠活動力度大:從體驗金到豐厚的首儲獎勵,玩家每一步都能享受優惠。
快速存提款服務:自主研發技術保障流暢交易,遊戲不中斷。
全天候專業客服:24/7在線支持,及時解決玩家需求。
立即加入RG富遊娛樂城
RG富遊娛樂城不僅提供豐富的遊戲體驗,更以專業的服務、完善的安全保障和多樣的優惠活動,為玩家打造一個值得信賴的娛樂環境。立即註冊,體驗台灣最受歡迎的線上娛樂城! -
LEO娛樂城登入
LEO娛樂城:九州娛樂集團的卓越創舉與運營優勢
九州娛樂集團總部的現代化運營
九州娛樂集團的總部設於菲律賓首都馬尼拉市中心最具代表性的現代化建築「RCBC Plaza」。這座辦公大樓融合了全球領先的建築科技與安全系統,包括:
國家級資訊防護系統,確保數據安全。
樓宇自動化系統 (BAS),實現數位化管理與高效運營,包括防火系統、光纖電訊和數位監控。
九州娛樂為員工提供舒適的工作環境和專業的教育培訓,確保服務水準一流。其員工以專業知識和親切態度,為尊貴玩家帶來極致的遊戲體驗。
LEO娛樂旗下品牌與遊戲特色
九州娛樂城旗下分支包括 LEO、THA 和 KU 三個娛樂品牌。雖然品牌各自獨立運營,但都共享相同的遊戲系統與界面,提供超過數千款來自全球頂級供應商的遊戲。
這些品牌的核心特色包括:
種類繁多的遊戲:滿足不同類型玩家的需求,包括電子遊戲、體育博彩、真人娛樂等。
不斷更新的內容:通過九州獨家技術,網站內容保持新鮮,合作商可快速更新遊戲資源,確保平台競爭力。
玩家在這些平台上可以隨時找到適合自己的遊戲,享受沉浸式的娛樂體驗。
LEO娛樂城的歷史與發展
九州娛樂集團的起源可以追溯至其最早期的經營模式:「信用版」賭博平台 《天下體育球版》。儘管該模式在當時非常流行,但因高風險與財務處理複雜而逐漸被淘汰。
隨著市場需求的變化,九州娛樂轉型為現金版平台 《天下現金網》,引入了更安全、便捷的遊戲模式。這種轉變不僅提升了玩家的體驗,也使平台得以進一步發展。
如今,九州娛樂城已成為台灣博弈業界的領軍者,不僅優化了網站版面與功能,還推出了專屬手機APP,方便玩家隨時隨地進行遊戲體驗。
LEO娛樂的成功秘訣
現代化運營與技術支持:九州娛樂在系統安全與技術更新方面投入巨大資源,確保平台運營穩定可靠。
多元化遊戲體驗:通過與全球頂級遊戲供應商合作,平台提供了豐富的遊戲選擇,適應各種玩家需求。
用戶至上:專業培訓的員工以細心和熱忱態度,提供高品質服務,讓玩家倍感尊重。
不斷創新:從信用版到現金版,再到手機APP,九州娛樂始終緊跟市場趨勢,致力於打造最佳娛樂體驗。
結語
LEO娛樂城作為九州娛樂集團旗下的重要品牌,不僅繼承了集團的核心價值,更在遊戲選擇、服務品質和技術創新方面不斷提升。從最初的《天下體育球版》到如今的行業領先者,LEO娛樂見證了九州娛樂城的發展歷程,也成為博弈行業中的耀眼明星。
加入 LEO娛樂城,感受來自九州娛樂集團的專業與熱情,享受最頂級的線上博弈體驗! -
富遊娛樂城:全台灣第一推薦的娛樂城體驗
富遊娛樂城是全台灣最受玩家推崇的娛樂平台,提供多種優惠、豐富的遊戲選擇以及高品質的服務,讓每位玩家都能享受極致的遊戲樂趣。無論您是新手還是資深玩家,富遊娛樂城都能滿足您的需求,帶給您刺激的遊戲體驗。
富遊娛樂城的優惠活動
1. 免費娛樂城體驗金
新玩家只需註冊即可免費領取 $168 元的體驗金,無需存款,便可立即體驗各種遊戲,感受遊戲帶來的樂趣。
2. 首次存款優惠
首次存款 $1000 元,即送 $1000 元遊戲金,讓您在遊戲中有更多機會獲勝,增添刺激感。
3. 新會員五選一好禮
新加入的會員可選擇五種專屬好禮之一,從遊戲金到實體獎品,讓您的遊戲旅程更加多彩。
熱門遊戲種類
富遊娛樂城提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,適合不同喜好的玩家:
電子老虎機:多款創新遊戲,讓玩家享受豐厚獎金機會。
百家樂:與真人荷官互動,體驗真實賭場的刺激感。
今彩539 和 運彩:滿足彩票愛好者的需求。
捕魚遊戲:RSG電子捕魚遊戲帶來娛樂與獎金的雙重樂趣。
熊貓體育:專為體育迷設計的多種運動投注選項。
優質服務保證
1. 出金快速、安全可靠
富遊娛樂城採用先進的財務處理系統,保證快速存提款,讓玩家不用擔心資金安全問題。
2. 技術先進的APP平台
流暢的畫面設計與設備兼容性,讓用戶輕鬆上手。
持續升級與更新,提供更多創新遊戲類型。
3. 24小時專業客服
專業客服隨時待命,為玩家解答所有遊戲相關問題,確保您在任何時間都能享受到無縫的服務體驗。
4. 安全防護到位
採用最嚴格的安全管理系統與數據加密技術,保障用戶資金與個人信息的安全。
富遊娛樂城APP:隨時隨地盡享遊戲
富遊娛樂城APP提供了便捷的遊戲途徑,支援 IOS 與 Android 設備。
簡潔易用的界面設計,讓玩家快速找到喜愛的遊戲。
即時客服支援,隨時解決您的疑問。
免費下載,無論何時何地,您都能盡享娛樂城的精彩遊戲體驗。
為什麼選擇富遊娛樂城?
優惠豐富:免費體驗金、首存優惠、新會員好禮,活動多樣。
遊戲種類齊全:從電子遊戲到真人百家樂,滿足各類玩家需求。
服務至上:專業客服、快速出金和高安全保障讓玩家安心享受遊戲。
便捷平台:富遊APP提供隨時隨地的遊戲樂趣,讓您不受限制。
立即下載 富遊娛樂城APP,體驗全台灣第一娛樂城的無限魅力!不論您是想享受遊戲樂趣還是贏取豐厚獎金,富遊娛樂城都將是您的最佳選擇! -
想要享受最刺激的線上娛樂體驗?選擇RG富遊娛樂城!
在這個數位時代,尋找適合自己的線上娛樂城變得越來越重要。如果你想在線上娛樂城找到最好玩、最受歡迎的遊戲,RG富遊絕對是你的首選!我們匯聚了多款博弈遊戲,讓您盡情享受娛樂的刺激與快感。
#### 精選遊戲類型
1. 真人百家樂
感受現場賭場的氛圍!RG富遊的真人視訊百家樂讓你與真實的荷官互動,享受高品質的遊戲體驗。無論你是老手還是新手,都能在這裡找到適合自己的節奏。
2. 電子老虎機
喜愛刺激嗎?我們提供多款熱門老虎機遊戲,如「戰神賽特」「魔龍傳奇」等,每一款都擁有精美的畫面和豐厚的獎勵,讓每次旋轉都充滿期待!
3. 體育投注
無論你是球迷還是賽事愛好者,RG富遊的體育投注平台都有你想要的。精準的賠率、廣泛的賽事選擇,讓你體驗到投注的樂趣和刺激。
4. 彩票遊戲與捕魚遊戲
隨著運氣來!不妨試試我們的棋牌遊戲和彩票遊戲,這裡有各種機會讓你體驗到不一樣的勝利快感。
#### 下載富遊APP,隨時隨地享受遊戲!
富遊娛樂城的APP支持iOS和Android設備,界面簡潔易用,內容豐富。無論你身處何地,都能輕鬆進入遊戲世界,隨心所欲享受娛樂時光。此外,我們提供即時客服支援,隨時解決你的疑問,讓你的遊戲體驗更為完美。
#### 為什麼選擇RG富遊?
- 安全可靠
RG富遊致力於為玩家提供安全可靠的遊戲環境,您的每一筆交易都受到最高的安全保障。
- 快速便捷的存提款服務
我們的存款平均時間僅需30秒,提款平均只需60秒,讓你體驗即時的快感!
- 豐富多元的遊戲選擇
超過9999款遊戲任你選擇,無論你偏好哪種娛樂方式,這裡都能滿足你的需求。
- 全天候服務
我們全年365天提供不停歇的客服支持,確保你在遊戲過程中享受到最好的服務。
### 結論
RG富遊娛樂城是您最佳的線上賭場選擇。我們不僅提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,還有安全可靠的遊戲環境和便捷的服務。立即下載APP,加入RG富遊,開始您的娛樂之旅,享受無與倫比的遊戲體驗吧! -
想要享受最刺激的線上娛樂體驗?選擇RG富遊娛樂城!
在這個數位時代,尋找適合自己的線上娛樂城變得越來越重要。如果你想在線上娛樂城找到最好玩、最受歡迎的遊戲,RG富遊絕對是你的首選!我們匯聚了多款博弈遊戲,讓您盡情享受娛樂的刺激與快感。
#### 精選遊戲類型
1. 真人百家樂
感受現場賭場的氛圍!RG富遊的真人視訊百家樂讓你與真實的荷官互動,享受高品質的遊戲體驗。無論你是老手還是新手,都能在這裡找到適合自己的節奏。
2. 電子老虎機
喜愛刺激嗎?我們提供多款熱門老虎機遊戲,如「戰神賽特」「魔龍傳奇」等,每一款都擁有精美的畫面和豐厚的獎勵,讓每次旋轉都充滿期待!
3. 體育投注
無論你是球迷還是賽事愛好者,RG富遊的體育投注平台都有你想要的。精準的賠率、廣泛的賽事選擇,讓你體驗到投注的樂趣和刺激。
4. 彩票遊戲與捕魚遊戲
隨著運氣來!不妨試試我們的棋牌遊戲和彩票遊戲,這裡有各種機會讓你體驗到不一樣的勝利快感。
#### 下載富遊APP,隨時隨地享受遊戲!
富遊娛樂城的APP支持iOS和Android設備,界面簡潔易用,內容豐富。無論你身處何地,都能輕鬆進入遊戲世界,隨心所欲享受娛樂時光。此外,我們提供即時客服支援,隨時解決你的疑問,讓你的遊戲體驗更為完美。
#### 為什麼選擇RG富遊?
- 安全可靠
RG富遊致力於為玩家提供安全可靠的遊戲環境,您的每一筆交易都受到最高的安全保障。
- 快速便捷的存提款服務
我們的存款平均時間僅需30秒,提款平均只需60秒,讓你體驗即時的快感!
- 豐富多元的遊戲選擇
超過9999款遊戲任你選擇,無論你偏好哪種娛樂方式,這裡都能滿足你的需求。
- 全天候服務
我們全年365天提供不停歇的客服支持,確保你在遊戲過程中享受到最好的服務。
### 結論
RG富遊娛樂城是您最佳的線上賭場選擇。我們不僅提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,還有安全可靠的遊戲環境和便捷的服務。立即下載APP,加入RG富遊,開始您的娛樂之旅,享受無與倫比的遊戲體驗吧! -
富遊娛樂城:台灣線上賭場的創新選擇
在台灣的線上娛樂市場中,富遊娛樂城憑藉其優質的服務和多樣化的娛樂選項,迅速成為新一代玩家的首選。既有刺激的遊戲體驗,又提供了一系列具有吸引力的優惠,富遊娛樂城無疑是追求樂趣的玩家們理想的地方。
#### 優勢與特色
1. 多樣化的遊戲選擇
富遊娛樂城提供了豐富的遊戲種類,包括電子老虎機、真人百家樂、運彩投注等。不論你是老虎機的愛好者,還是熱衷於真人賭桌的玩家,這裡都能滿足你的需求。特別推薦的遊戲如DG真人百家和RSG皇家百家樂,一定能帶給你極致的遊戲體驗。
2. 吸引人的優惠活動
富遊娛樂城針對新手和老玩家都推出了多樣的優惠活動。新會員首次存款可獲得相同金額的獎金,還有額外的體驗金送出,設計友好且實惠。此外,富遊每週的簽到獎勵和天天無上限的返水活動,更是讓玩家在遊戲中能持續獲得收益。
3. 安全可靠的存取款方式
在金融交易方面,富遊娛樂城支持多種存款和提款方式,包括各大銀行轉帳、超商儲值,甚至虛擬貨幣等。最低提款金額設置靈活,保證玩家資金的安全與便捷。
4. 人性化的操作介面
富遊娛樂城的網頁與移動應用設計簡潔易用,玩家可以方便地找到所需的遊戲和優惠。無論是在電腦還是手機上,都能順利享受到遊戲的樂趣。
#### 如何開始遊戲
如果你是新手玩家,開始你的富遊體驗非常簡單。只需註冊帳號,完成首次存款,即可獲得新手優惠。無論你想嘗試電子遊戲還是真人賭局,富遊娛樂城都能讓你輕鬆上手,享受娛樂的樂趣。
#### 社會責任與防沉迷措施
富遊娛樂城深知線上賭博的風險,因此致力於推廣負責任的遊戲文化。他們提供“防沉迷”指導,以確保玩家能夠理性投注,並提供必要的幫助和資源來幫助有需求的玩家。
#### 總結
對於尋求安全、便捷和多元化娛樂城體驗的玩家,富遊娛樂城絕對是值得選擇的選項。無論你是希望徹底放鬆,還是想要體驗刺激的博弈過程,富遊娛樂城都能滿足你的期待,成為你在台灣線上娛樂市場的最佳夥伴。立即註冊並開始你的遊戲之旅吧! -
滿天星娛樂城
滿天星娛樂城:全方位的線上娛樂體驗
滿天星娛樂城作為九州娛樂城旗下品牌之一,是玩家心目中備受信賴的線上娛樂平台。不僅提供豐富的遊戲選擇和吸引人的優惠,還以其合法營運的背景和快速出金的保證,成為台灣玩家的首選娛樂城之一。
滿天星娛樂城的特色與優勢
1. 合法營運,安全可靠
滿天星娛樂城持有三大國際娛樂執照,包括:
菲律賓 PAGCOR 監督競猜牌照
BVI 認證
馬爾他 MGA 認證
這些執照展現了平台的資本實力與合法性,讓玩家能夠安心享受遊戲,完全不用擔心出金問題。
2. 高品質遊戲與豐富優惠
滿天星娛樂城與九州集團旗下的LEO、THA娛樂城一樣,提供一流的遊戲品質和多樣化的優惠。
熱門遊戲推薦:電子老虎機、真人直播、運彩投注、今彩539等,滿足各類玩家需求。
優惠活動:定期推出限時回饋活動,讓玩家在遊戲中獲得更多額外收益。
3. 快速出金與高效服務
滿天星娛樂城採用先進的財務系統,確保存提款快速、安全,讓玩家能夠專注於享受遊戲,而無需擔心資金問題。專業的客服團隊24小時在線,提供即時支援。
4. 多平台兼容的APP
滿天星娛樂城提供設計貼合玩家需求的手機APP,適用於iOS與Android系統。玩家可以隨時隨地快速登入遊玩,體驗無與倫比的娛樂快感。
熱門遊戲類型一覽
滿天星娛樂城為玩家提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,滿足不同興趣和需求:
真人直播:感受真實賭場氛圍,與真人荷官互動,體驗沉浸式娛樂。
電子老虎機:多款經典與創新機台,讓玩家享受刺激的遊戲過程。
運彩投注:涵蓋世界盃、棒球、籃球等多項運動賽事,提供即時投注與直播功能。
彩票遊戲:包括今彩539、富遊彩票等,適合熱衷於彩券的玩家。
滿天星娛樂城常見問題解答
Q1. 滿天星娛樂城是否提供APP下載?
是的,滿天星娛樂城提供專屬的手機APP,支援iOS和Android系統。玩家可透過APP快速登入,隨時享受遊戲。
Q2. 滿天星娛樂城是否合法?
滿天星娛樂城擁有多項國際認證,為合法經營的線上娛樂城,並保證玩家資金的安全性與遊戲的公平性。
Q3. 無法登入滿天星娛樂城該怎麼辦?
如遇到無法登入的情況,建議玩家檢查網路狀況或聯繫24小時客服團隊獲取即時協助。
立即加入滿天星娛樂城,享受最佳娛樂體驗!
滿天星娛樂城以合法、安全、快速的服務,搭配豐富的遊戲選擇和優惠,為玩家打造出獨一無二的線上娛樂體驗。不論您是新手還是老手,都能在滿天星找到屬於自己的遊戲樂趣。現在就下載APP,隨時隨地開始您的娛樂之旅! -
娛樂城
富遊娛樂城:台灣線上賭場的創新選擇
在台灣的線上娛樂市場中,富遊娛樂城憑藉其優質的服務和多樣化的娛樂選項,迅速成為新一代玩家的首選。既有刺激的遊戲體驗,又提供了一系列具有吸引力的優惠,富遊娛樂城無疑是追求樂趣的玩家們理想的地方。
#### 優勢與特色
1. 多樣化的遊戲選擇
富遊娛樂城提供了豐富的遊戲種類,包括電子老虎機、真人百家樂、運彩投注等。不論你是老虎機的愛好者,還是熱衷於真人賭桌的玩家,這裡都能滿足你的需求。特別推薦的遊戲如DG真人百家和RSG皇家百家樂,一定能帶給你極致的遊戲體驗。
2. 吸引人的優惠活動
富遊娛樂城針對新手和老玩家都推出了多樣的優惠活動。新會員首次存款可獲得相同金額的獎金,還有額外的體驗金送出,設計友好且實惠。此外,富遊每週的簽到獎勵和天天無上限的返水活動,更是讓玩家在遊戲中能持續獲得收益。
3. 安全可靠的存取款方式
在金融交易方面,富遊娛樂城支持多種存款和提款方式,包括各大銀行轉帳、超商儲值,甚至虛擬貨幣等。最低提款金額設置靈活,保證玩家資金的安全與便捷。
4. 人性化的操作介面
富遊娛樂城的網頁與移動應用設計簡潔易用,玩家可以方便地找到所需的遊戲和優惠。無論是在電腦還是手機上,都能順利享受到遊戲的樂趣。
#### 如何開始遊戲
如果你是新手玩家,開始你的富遊體驗非常簡單。只需註冊帳號,完成首次存款,即可獲得新手優惠。無論你想嘗試電子遊戲還是真人賭局,富遊娛樂城都能讓你輕鬆上手,享受娛樂的樂趣。
#### 社會責任與防沉迷措施
富遊娛樂城深知線上賭博的風險,因此致力於推廣負責任的遊戲文化。他們提供“防沉迷”指導,以確保玩家能夠理性投注,並提供必要的幫助和資源來幫助有需求的玩家。
#### 總結
對於尋求安全、便捷和多元化娛樂城體驗的玩家,富遊娛樂城絕對是值得選擇的選項。無論你是希望徹底放鬆,還是想要體驗刺激的博弈過程,富遊娛樂城都能滿足你的期待,成為你在台灣線上娛樂市場的最佳夥伴。立即註冊並開始你的遊戲之旅吧! -
滿天星娛樂城:全方位的線上娛樂體驗
滿天星娛樂城作為九州娛樂城旗下品牌之一,是玩家心目中備受信賴的線上娛樂平台。不僅提供豐富的遊戲選擇和吸引人的優惠,還以其合法營運的背景和快速出金的保證,成為台灣玩家的首選娛樂城之一。
滿天星娛樂城的特色與優勢
1. 合法營運,安全可靠
滿天星娛樂城持有三大國際娛樂執照,包括:
菲律賓 PAGCOR 監督競猜牌照
BVI 認證
馬爾他 MGA 認證
這些執照展現了平台的資本實力與合法性,讓玩家能夠安心享受遊戲,完全不用擔心出金問題。
2. 高品質遊戲與豐富優惠
滿天星娛樂城與九州集團旗下的LEO、THA娛樂城一樣,提供一流的遊戲品質和多樣化的優惠。
熱門遊戲推薦:電子老虎機、真人直播、運彩投注、今彩539等,滿足各類玩家需求。
優惠活動:定期推出限時回饋活動,讓玩家在遊戲中獲得更多額外收益。
3. 快速出金與高效服務
滿天星娛樂城採用先進的財務系統,確保存提款快速、安全,讓玩家能夠專注於享受遊戲,而無需擔心資金問題。專業的客服團隊24小時在線,提供即時支援。
4. 多平台兼容的APP
滿天星娛樂城提供設計貼合玩家需求的手機APP,適用於iOS與Android系統。玩家可以隨時隨地快速登入遊玩,體驗無與倫比的娛樂快感。
熱門遊戲類型一覽
滿天星娛樂城為玩家提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,滿足不同興趣和需求:
真人直播:感受真實賭場氛圍,與真人荷官互動,體驗沉浸式娛樂。
電子老虎機:多款經典與創新機台,讓玩家享受刺激的遊戲過程。
運彩投注:涵蓋世界盃、棒球、籃球等多項運動賽事,提供即時投注與直播功能。
彩票遊戲:包括今彩539、富遊彩票等,適合熱衷於彩券的玩家。
滿天星娛樂城常見問題解答
Q1. 滿天星娛樂城是否提供APP下載?
是的,滿天星娛樂城提供專屬的手機APP,支援iOS和Android系統。玩家可透過APP快速登入,隨時享受遊戲。
Q2. 滿天星娛樂城是否合法?
滿天星娛樂城擁有多項國際認證,為合法經營的線上娛樂城,並保證玩家資金的安全性與遊戲的公平性。
Q3. 無法登入滿天星娛樂城該怎麼辦?
如遇到無法登入的情況,建議玩家檢查網路狀況或聯繫24小時客服團隊獲取即時協助。
立即加入滿天星娛樂城,享受最佳娛樂體驗!
滿天星娛樂城以合法、安全、快速的服務,搭配豐富的遊戲選擇和優惠,為玩家打造出獨一無二的線上娛樂體驗。不論您是新手還是老手,都能在滿天星找到屬於自己的遊戲樂趣。現在就下載APP,隨時隨地開始您的娛樂之旅! -
blockchain address
Introduction of Digital Currency Deal Check and Regulatory Solutions
In today's crypto market, maintaining transfer openness and conformity with Anti-Laundering and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations is vital. Following is an outline of leading sites that deliver tools for digital asset deal tracking, validation, and asset protection.
1. Token Metrics
Overview: Token Metrics provides digital asset evaluation to assess possible scam risks. This platform allows investors to check tokens ahead of investment to evade potentially risky resources. Attributes:
- Danger analysis.
- Suitable for investors looking to avoid hazardous or fraudulent projects.
2. Metamask Monitor Center
Description: Metamask Monitor Center allows users to check their crypto holdings for suspicious actions and standard conformity. Advantages:
- Validates tokens for “cleanliness”.
- Provides warnings about likely resource blockages on specific platforms.
- Provides detailed results after wallet connection.
3. Bestchange.com
Description: Bestchange.ru is a platform for monitoring and checking cryptocurrency transaction transactions, guaranteeing transparency and transfer security. Features:
- Transfer and wallet observation.
- Sanctions checks.
- Web-based platform; accommodates BTC and multiple additional digital assets.
4. AML Bot
Description: AMLchek is a portfolio tracker and compliance compliance tool that uses artificial intelligence models to find suspicious transactions. Highlights:
- Transaction tracking and user verification.
- Offered via internet and Telegram.
- Supports digital assets including BSC, BTC, DOGE, and more.
5. Alfabit AML
Description: AlfaBit provides thorough AML tools customized for the digital currency industry, supporting businesses and financial institutions in preserving standard adherence. Highlights:
- Comprehensive AML options and checks.
- Meets modern security and compliance standards.
6. Node AML
Overview: AMLNode delivers compliance and KYC solutions for crypto companies, such as deal observing, sanctions validation, and evaluation. Highlights:
- Threat analysis options and compliance validations.
- Valuable for ensuring secure firm operations.
7. Btrace.io
Summary: Btrace.AMLcrypto.io specializes in resource verification, providing deal monitoring, restriction screenings, and support if you are a affected by loss. Highlights:
- Effective help for asset restoration.
- Transfer observation and safety options.
Specialized USDT Verification Services
Our platform also reviews various services that offer check services for Tether deals and accounts:
- **USDT TRC20 and ERC20 Verification:** Numerous sites provide comprehensive screenings for USDT deals, helping in the detection of suspicious actions.
- **AML Validation for USDT:** Solutions are available for observing for fraudulent activities.
- **“Cleanliness” Validation for Wallets:** Validation of deal and wallet “cleanliness” is offered to detect likely risks.
**Summary**
Selecting the best service for checking and tracking crypto deals is important for providing security and standard compliance. By viewing our evaluations, you can select the best service for deal observation and fund security. -
layering aml
Introduction of Crypto Transfer Validation and Conformity Options
In the current crypto sector, ensuring deal clarity and conformity with AML and KYC rules is essential. Below is an summary of popular sites that deliver services for digital asset transfer tracking, verification, and fund safety.
1. Token Metrics
Description: Token Metrics offers cryptocurrency assessment to evaluate possible risk risks. This platform enables individuals to examine cryptocurrencies prior to buying to avoid potentially risky assets. Features:
- Danger assessment.
- Ideal for holders looking to bypass risky or fraudulent assets.
2. Metamask Center
Description: Metamask Monitor Center permits holders to check their cryptocurrency resources for doubtful activity and compliance compliance. Advantages:
- Checks assets for purity.
- Offers notifications about potential resource restrictions on certain trading sites.
- Gives thorough insights after wallet linking.
3. Best Change
Description: Bestchange.ru is a platform for monitoring and checking crypto trade deals, providing openness and transaction security. Benefits:
- Transaction and account monitoring.
- Sanctions screening.
- Web-based portal; supports BTC and various different cryptocurrencies.
4. AML Bot
Summary: AMLCheck Bot is a portfolio monitor and AML tool that uses artificial intelligence methods to detect dubious actions. Features:
- Transfer tracking and identity verification.
- Available via online and chat bot.
- Supports coins including BSC, BTC, DOGE, and more.
5. AlphaBit
Overview: AlphaBit provides thorough Anti-Money Laundering (AML) solutions tailored for the digital currency market, assisting firms and financial organizations in maintaining standard adherence. Highlights:
- Extensive compliance tools and screenings.
- Adheres to up-to-date protection and conformity requirements.
6. Node AML
Description: AMLNode delivers anti-money laundering and identification services for digital currency companies, including transaction monitoring, compliance validation, and risk assessment. Highlights:
- Risk assessment options and sanctions checks.
- Valuable for maintaining secure company processes.
7. Btrace AML Crypto
Summary: Btrace AML Crypto specializes in fund verification, providing transaction observation, compliance screenings, and help if you are a affected by fraud. Advantages:
- Useful support for asset restoration.
- Transfer observation and safety features.
Exclusive USDT Check Services
Our platform also provides information on various services providing verification solutions for Tether transactions and wallets:
- **USDT TRC20 and ERC20 Check:** Various services support comprehensive evaluations for USDT deals, assisting in the finding of suspicious activity.
- **AML Verification for USDT:** Options are offered for monitoring for suspicious actions.
- **“Cleanliness” Validation for Accounts:** Checking of deal and holding “cleanliness” is provided to identify likely risks.
**Summary**
Finding the best service for verifying and monitoring digital currency transfers is essential for ensuring safety and compliance adherence. By reading our reviews, you can find the ideal service for transfer tracking and resource security. -
九州娛樂城登入
九州娛樂城:亞洲頂級線上娛樂平台
九州娛樂城,作為亞洲領先的線上博弈平台,以其專業性、公平性和創新性著稱。在這裡,您可以享受全方位的娛樂體驗,包括體育投注、真人遊戲、電子遊戲、六合彩球以及流行的捕魚機和棋牌遊戲。九州娛樂城是台灣玩家的首選娛樂平台,被譽為業界 No.1!
九州娛樂城的亮點
1. 多元化遊戲選擇
九州娛樂城擁有超過千款來自全球頂尖供應商提供的遊戲,滿足各種類型玩家的需求。無論是喜歡競技性的體育投注、刺激的真人遊戲,還是休閒的電子遊戲,九州娛樂城都能提供最適合您的選擇。
體育投注:全面覆蓋世界級賽事,包括世界杯、職業聯賽等。提供多種投注方式,如讓球、大小、單雙、串關等,並支持桌面端與手機端投注。
真人遊戲:KU真人百家樂、LEO真人遊戲等,讓您感受現場賭桌的真實刺激。
電子遊戲與捕魚機:多款熱門遊戲,如九州熱門電子遊戲和捕魚機,帶給玩家極致娛樂享受。
六合彩與棋牌遊戲:適合策略型玩家的理想選擇。
2. 極致便利的操作體驗
九州娛樂城支持通過官方網站和九州APP下載進行操作,無論您身在何處,都可以輕鬆加入遊戲世界。針對台灣玩家的本地化設計確保操作流暢、存取款方便。
3. 先進技術與安全保障
九州娛樂城集團總部位於菲律賓首都馬尼拉的RCBC Plaza,配備世界一流的安全資訊防護系統和智能大樓自動化系統(BAS)。玩家的數據與資金安全都能得到最佳保障,讓每一次遊戲都安心無憂。
4. 熱門品牌與平台支持
九州娛樂城旗下包括三大品牌:
LEO娛樂:提供真人遊戲、體育直播及免費影城。
THA娛樂:專注於新手友好和便捷操作。
KU娛樂:以真人百家樂而著稱。
每個品牌雖分別由不同管理團隊運營,但都傳承了九州娛樂城的高標準,遊戲系統與界面毫無差異,為玩家提供無縫娛樂體驗。
為什麼選擇九州娛樂城?
專業性與公平性
九州娛樂城堅持以「即時便利、公平公正、專業營運」為宗旨,研發創新遊戲技術,滿足不同類型玩家需求。
貼近市場與玩家需求
擁有兩岸三地的精英設計師與代理團隊,根據玩家反饋持續改進產品,並為合作商提供及時更新支持。
優越的服務與保障
從遊戲操作到客戶支持,九州娛樂城提供全面的服務支持,讓每位玩家都能感受到最貼心的服務。
九州娛樂城的未來
作為線上博弈行業的領航者,九州娛樂城不斷推陳出新,致力於提供更豐富的遊戲選擇和更完善的玩家體驗。同時,透過強大的技術與營運團隊,九州娛樂城已成為台灣乃至亞洲地區娛樂平台的代名詞。
立即下載九州APP,體驗最極致的娛樂樂趣!九州娛樂城——您的最佳線上娛樂夥伴! -
THA娛樂城無法登入
九州娛樂停止營運,LEO、THA娛樂城無法登入,玩家該怎麼辦?
近期,九州娛樂城集團旗下的LEO娛樂城與THA娛樂城相繼傳出無法登入的消息,讓許多玩家陷入焦慮。隨著九州娛樂正式宣布退出台灣市場,營運結束的消息塵埃落定。這對廣大玩家而言意味著什麼?該如何處理自己的帳戶與資金?本文將為您全面解析現況並提供解決方案。
停止營運:關鍵信息一覽
關閉存款功能:從2024年12月31日中午12:00起,九州娛樂城將全面停止所有存款服務。
正常提款開放:儘管停止營運,但官方保證玩家仍可完成提款操作。
會員權益保障:九州娛樂集團承諾全力保障玩家權益,確保在停止營運前完成所有手續。
LEO、THA娛樂城無法登入的背後原因
市場規模限制
台灣市場競爭激烈,九州娛樂城認為市場成長潛力有限。相較之下,海外市場不僅人口基數大,且有更多開發機會,這成為九州轉向海外發展的關鍵動機。
金流與政策問題
近期爆發的金流醜聞為九州娛樂的運營帶來重大挑戰。例如,九州被曝利用第三方支付進行洗錢,加上相關法規收緊,讓其在台灣市場的營運空間被大幅壓縮。
品牌策略調整
九州娛樂選擇退出台灣市場,可能是為了集中資源,強化其在其他區域的競爭力。根據消息,九州旗下品牌未來將著重於更具潛力的海外市場發展。
玩家應對策略:如何保護資金與尋找替代平台?
1. 儘速完成提款
如果您的帳戶仍可登入,建議立即完成所有提款操作,確保資金安全。九州娛樂承諾提款服務不受影響,但建議提早行動避免平台完全關閉。
2. 避免假冒平台陷阱
隨著九州娛樂停止營運,市場可能會出現假冒九州品牌的詐騙網站。玩家應提高警覺,避免在非官方平台上進行任何交易。
3. 選擇可靠替代平台
為了延續遊戲體驗,玩家可考慮轉至穩定且受信賴的平台。這裡推薦RG富遊娛樂城,憑藉其安全、穩定的服務與多樣化的遊戲選擇,成為值得信賴的替代選擇。
RG富遊娛樂城:九州玩家的理想新選擇
平台優勢
快速出金:提款平均僅需3-5分鐘,效率領先業界。
高安全保障:採用與銀行相同的加密技術,確保玩家資料與資金安全。
豐富遊戲內容:從真人百家樂到彩票遊戲,應有盡有,滿足不同玩家的喜好。
專屬優惠
針對九州會員,富遊推出了無縫轉移方案:
玩家只需提供原平台的會員等級截圖,即可快速升等並享受對應的會員福利。
再見九州,展望未來
九州娛樂城退出台灣市場,雖然讓玩家感到惋惜,但這同時也為您開啟新的可能性。在選擇娛樂平台時,安全性與穩定性應始終放在首位。RG富遊娛樂城是目前玩家最值得信賴的選擇之一,不妨加入這個全新的平台,繼續享受無限的遊戲樂趣! -
九州娛樂城:亞洲頂級線上娛樂平台
九州娛樂城,作為亞洲領先的線上博弈平台,以其專業性、公平性和創新性著稱。在這裡,您可以享受全方位的娛樂體驗,包括體育投注、真人遊戲、電子遊戲、六合彩球以及流行的捕魚機和棋牌遊戲。九州娛樂城是台灣玩家的首選娛樂平台,被譽為業界 No.1!
九州娛樂城的亮點
1. 多元化遊戲選擇
九州娛樂城擁有超過千款來自全球頂尖供應商提供的遊戲,滿足各種類型玩家的需求。無論是喜歡競技性的體育投注、刺激的真人遊戲,還是休閒的電子遊戲,九州娛樂城都能提供最適合您的選擇。
體育投注:全面覆蓋世界級賽事,包括世界杯、職業聯賽等。提供多種投注方式,如讓球、大小、單雙、串關等,並支持桌面端與手機端投注。
真人遊戲:KU真人百家樂、LEO真人遊戲等,讓您感受現場賭桌的真實刺激。
電子遊戲與捕魚機:多款熱門遊戲,如九州熱門電子遊戲和捕魚機,帶給玩家極致娛樂享受。
六合彩與棋牌遊戲:適合策略型玩家的理想選擇。
2. 極致便利的操作體驗
九州娛樂城支持通過官方網站和九州APP下載進行操作,無論您身在何處,都可以輕鬆加入遊戲世界。針對台灣玩家的本地化設計確保操作流暢、存取款方便。
3. 先進技術與安全保障
九州娛樂城集團總部位於菲律賓首都馬尼拉的RCBC Plaza,配備世界一流的安全資訊防護系統和智能大樓自動化系統(BAS)。玩家的數據與資金安全都能得到最佳保障,讓每一次遊戲都安心無憂。
4. 熱門品牌與平台支持
九州娛樂城旗下包括三大品牌:
LEO娛樂:提供真人遊戲、體育直播及免費影城。
THA娛樂:專注於新手友好和便捷操作。
KU娛樂:以真人百家樂而著稱。
每個品牌雖分別由不同管理團隊運營,但都傳承了九州娛樂城的高標準,遊戲系統與界面毫無差異,為玩家提供無縫娛樂體驗。
為什麼選擇九州娛樂城?
專業性與公平性
九州娛樂城堅持以「即時便利、公平公正、專業營運」為宗旨,研發創新遊戲技術,滿足不同類型玩家需求。
貼近市場與玩家需求
擁有兩岸三地的精英設計師與代理團隊,根據玩家反饋持續改進產品,並為合作商提供及時更新支持。
優越的服務與保障
從遊戲操作到客戶支持,九州娛樂城提供全面的服務支持,讓每位玩家都能感受到最貼心的服務。
九州娛樂城的未來
作為線上博弈行業的領航者,九州娛樂城不斷推陳出新,致力於提供更豐富的遊戲選擇和更完善的玩家體驗。同時,透過強大的技術與營運團隊,九州娛樂城已成為台灣乃至亞洲地區娛樂平台的代名詞。
立即下載九州APP,體驗最極致的娛樂樂趣!九州娛樂城——您的最佳線上娛樂夥伴! -
九州娛樂停止營運,LEO、THA娛樂城無法登入,玩家該怎麼辦?
近期,九州娛樂城集團旗下的LEO娛樂城與THA娛樂城相繼傳出無法登入的消息,讓許多玩家陷入焦慮。隨著九州娛樂正式宣布退出台灣市場,營運結束的消息塵埃落定。這對廣大玩家而言意味著什麼?該如何處理自己的帳戶與資金?本文將為您全面解析現況並提供解決方案。
停止營運:關鍵信息一覽
關閉存款功能:從2024年12月31日中午12:00起,九州娛樂城將全面停止所有存款服務。
正常提款開放:儘管停止營運,但官方保證玩家仍可完成提款操作。
會員權益保障:九州娛樂集團承諾全力保障玩家權益,確保在停止營運前完成所有手續。
LEO、THA娛樂城無法登入的背後原因
市場規模限制
台灣市場競爭激烈,九州娛樂城認為市場成長潛力有限。相較之下,海外市場不僅人口基數大,且有更多開發機會,這成為九州轉向海外發展的關鍵動機。
金流與政策問題
近期爆發的金流醜聞為九州娛樂的運營帶來重大挑戰。例如,九州被曝利用第三方支付進行洗錢,加上相關法規收緊,讓其在台灣市場的營運空間被大幅壓縮。
品牌策略調整
九州娛樂選擇退出台灣市場,可能是為了集中資源,強化其在其他區域的競爭力。根據消息,九州旗下品牌未來將著重於更具潛力的海外市場發展。
玩家應對策略:如何保護資金與尋找替代平台?
1. 儘速完成提款
如果您的帳戶仍可登入,建議立即完成所有提款操作,確保資金安全。九州娛樂承諾提款服務不受影響,但建議提早行動避免平台完全關閉。
2. 避免假冒平台陷阱
隨著九州娛樂停止營運,市場可能會出現假冒九州品牌的詐騙網站。玩家應提高警覺,避免在非官方平台上進行任何交易。
3. 選擇可靠替代平台
為了延續遊戲體驗,玩家可考慮轉至穩定且受信賴的平台。這裡推薦RG富遊娛樂城,憑藉其安全、穩定的服務與多樣化的遊戲選擇,成為值得信賴的替代選擇。
RG富遊娛樂城:九州玩家的理想新選擇
平台優勢
快速出金:提款平均僅需3-5分鐘,效率領先業界。
高安全保障:採用與銀行相同的加密技術,確保玩家資料與資金安全。
豐富遊戲內容:從真人百家樂到彩票遊戲,應有盡有,滿足不同玩家的喜好。
專屬優惠
針對九州會員,富遊推出了無縫轉移方案:
玩家只需提供原平台的會員等級截圖,即可快速升等並享受對應的會員福利。
再見九州,展望未來
九州娛樂城退出台灣市場,雖然讓玩家感到惋惜,但這同時也為您開啟新的可能性。在選擇娛樂平台時,安全性與穩定性應始終放在首位。RG富遊娛樂城是目前玩家最值得信賴的選擇之一,不妨加入這個全新的平台,繼續享受無限的遊戲樂趣! -
九州娛樂城倒了
九州娛樂城:亞洲頂級線上娛樂平台
九州娛樂城,作為亞洲領先的線上博弈平台,以其專業性、公平性和創新性著稱。在這裡,您可以享受全方位的娛樂體驗,包括體育投注、真人遊戲、電子遊戲、六合彩球以及流行的捕魚機和棋牌遊戲。九州娛樂城是台灣玩家的首選娛樂平台,被譽為業界 No.1!
九州娛樂城的亮點
1. 多元化遊戲選擇
九州娛樂城擁有超過千款來自全球頂尖供應商提供的遊戲,滿足各種類型玩家的需求。無論是喜歡競技性的體育投注、刺激的真人遊戲,還是休閒的電子遊戲,九州娛樂城都能提供最適合您的選擇。
體育投注:全面覆蓋世界級賽事,包括世界杯、職業聯賽等。提供多種投注方式,如讓球、大小、單雙、串關等,並支持桌面端與手機端投注。
真人遊戲:KU真人百家樂、LEO真人遊戲等,讓您感受現場賭桌的真實刺激。
電子遊戲與捕魚機:多款熱門遊戲,如九州熱門電子遊戲和捕魚機,帶給玩家極致娛樂享受。
六合彩與棋牌遊戲:適合策略型玩家的理想選擇。
2. 極致便利的操作體驗
九州娛樂城支持通過官方網站和九州APP下載進行操作,無論您身在何處,都可以輕鬆加入遊戲世界。針對台灣玩家的本地化設計確保操作流暢、存取款方便。
3. 先進技術與安全保障
九州娛樂城集團總部位於菲律賓首都馬尼拉的RCBC Plaza,配備世界一流的安全資訊防護系統和智能大樓自動化系統(BAS)。玩家的數據與資金安全都能得到最佳保障,讓每一次遊戲都安心無憂。
4. 熱門品牌與平台支持
九州娛樂城旗下包括三大品牌:
LEO娛樂:提供真人遊戲、體育直播及免費影城。
THA娛樂:專注於新手友好和便捷操作。
KU娛樂:以真人百家樂而著稱。
每個品牌雖分別由不同管理團隊運營,但都傳承了九州娛樂城的高標準,遊戲系統與界面毫無差異,為玩家提供無縫娛樂體驗。
為什麼選擇九州娛樂城?
專業性與公平性
九州娛樂城堅持以「即時便利、公平公正、專業營運」為宗旨,研發創新遊戲技術,滿足不同類型玩家需求。
貼近市場與玩家需求
擁有兩岸三地的精英設計師與代理團隊,根據玩家反饋持續改進產品,並為合作商提供及時更新支持。
優越的服務與保障
從遊戲操作到客戶支持,九州娛樂城提供全面的服務支持,讓每位玩家都能感受到最貼心的服務。
九州娛樂城的未來
作為線上博弈行業的領航者,九州娛樂城不斷推陳出新,致力於提供更豐富的遊戲選擇和更完善的玩家體驗。同時,透過強大的技術與營運團隊,九州娛樂城已成為台灣乃至亞洲地區娛樂平台的代名詞。
立即下載九州APP,體驗最極致的娛樂樂趣!九州娛樂城——您的最佳線上娛樂夥伴! -
九州娛樂城倒了
九州娛樂城:亞洲頂級線上娛樂平台
九州娛樂城,作為亞洲領先的線上博弈平台,以其專業性、公平性和創新性著稱。在這裡,您可以享受全方位的娛樂體驗,包括體育投注、真人遊戲、電子遊戲、六合彩球以及流行的捕魚機和棋牌遊戲。九州娛樂城是台灣玩家的首選娛樂平台,被譽為業界 No.1!
九州娛樂城的亮點
1. 多元化遊戲選擇
九州娛樂城擁有超過千款來自全球頂尖供應商提供的遊戲,滿足各種類型玩家的需求。無論是喜歡競技性的體育投注、刺激的真人遊戲,還是休閒的電子遊戲,九州娛樂城都能提供最適合您的選擇。
體育投注:全面覆蓋世界級賽事,包括世界杯、職業聯賽等。提供多種投注方式,如讓球、大小、單雙、串關等,並支持桌面端與手機端投注。
真人遊戲:KU真人百家樂、LEO真人遊戲等,讓您感受現場賭桌的真實刺激。
電子遊戲與捕魚機:多款熱門遊戲,如九州熱門電子遊戲和捕魚機,帶給玩家極致娛樂享受。
六合彩與棋牌遊戲:適合策略型玩家的理想選擇。
2. 極致便利的操作體驗
九州娛樂城支持通過官方網站和九州APP下載進行操作,無論您身在何處,都可以輕鬆加入遊戲世界。針對台灣玩家的本地化設計確保操作流暢、存取款方便。
3. 先進技術與安全保障
九州娛樂城集團總部位於菲律賓首都馬尼拉的RCBC Plaza,配備世界一流的安全資訊防護系統和智能大樓自動化系統(BAS)。玩家的數據與資金安全都能得到最佳保障,讓每一次遊戲都安心無憂。
4. 熱門品牌與平台支持
九州娛樂城旗下包括三大品牌:
LEO娛樂:提供真人遊戲、體育直播及免費影城。
THA娛樂:專注於新手友好和便捷操作。
KU娛樂:以真人百家樂而著稱。
每個品牌雖分別由不同管理團隊運營,但都傳承了九州娛樂城的高標準,遊戲系統與界面毫無差異,為玩家提供無縫娛樂體驗。
為什麼選擇九州娛樂城?
專業性與公平性
九州娛樂城堅持以「即時便利、公平公正、專業營運」為宗旨,研發創新遊戲技術,滿足不同類型玩家需求。
貼近市場與玩家需求
擁有兩岸三地的精英設計師與代理團隊,根據玩家反饋持續改進產品,並為合作商提供及時更新支持。
優越的服務與保障
從遊戲操作到客戶支持,九州娛樂城提供全面的服務支持,讓每位玩家都能感受到最貼心的服務。
九州娛樂城的未來
作為線上博弈行業的領航者,九州娛樂城不斷推陳出新,致力於提供更豐富的遊戲選擇和更完善的玩家體驗。同時,透過強大的技術與營運團隊,九州娛樂城已成為台灣乃至亞洲地區娛樂平台的代名詞。
立即下載九州APP,體驗最極致的娛樂樂趣!九州娛樂城——您的最佳線上娛樂夥伴! -
Портал строительства https://mbmedicall.com ресурс для поиска информации о ремонте и строительстве. Полезные советы, технологии, инструкции и рекомендации для профессионалов и новичков.
-
ST666 - Sân Chơi Nổ Hũ Uy Tín Đổi Thưởng Hàng Đầu
ST666 là một trong những sân chơi nổ hũ đổi thưởng được yêu thích nhất hiện nay. Với các sảnh quay nổi tiếng như JILI Slot, PG Slot, và JDB Slot, nền tảng này không chỉ mang đến trải nghiệm giải trí đỉnh cao mà còn mang lại cơ hội đổi thưởng hấp dẫn cho người chơi.
Lý do nên chọn ST666
1. Khuyến mãi hấp dẫn
ST666 thường xuyên triển khai các chương trình ưu đãi đặc biệt:
Hoàn tiền 1.5% mỗi ngày khi quay slot, gia tăng cơ hội thắng lớn.
Chiết khấu nạp tiền lên đến 25.000.000 VNĐ, hỗ trợ tối đa cho người chơi muốn tăng vốn.
2. Sảnh quay đa dạng
ST666 mang đến hàng loạt tựa game slot từ các sảnh quay danh tiếng:
JILI Slot: Tỷ lệ thắng cao, giao diện đẹp mắt.
PG Slot: Đồ họa ấn tượng, chủ đề phong phú.
JDB Slot: Dành cho những ai yêu thích cảm giác hồi hộp.
3. Nền tảng uy tín, bảo mật cao
ST666 luôn đảm bảo an toàn cho người chơi:
Bảo mật thông tin tuyệt đối nhờ vào công nghệ mã hóa hiện đại.
Nạp/rút tiền nhanh chóng, hỗ trợ giao dịch linh hoạt mà không gián đoạn trải nghiệm.
4. Dịch vụ khách hàng chuyên nghiệp
Đội ngũ hỗ trợ của ST666 làm việc 24/7, luôn sẵn sàng giải đáp mọi thắc mắc và hỗ trợ người chơi trong suốt quá trình tham gia.
Hướng dẫn tham gia ST666
Đăng ký tài khoản: Hoàn tất các bước đăng ký dễ dàng để tham gia nền tảng.
Nhận khuyến mãi: Người chơi mới có thể nhận thưởng nạp đầu 100%.
Lựa chọn trò chơi yêu thích: Từ slot, nổ hũ đến các trò đổi thưởng khác, ST666 đều có sẵn để đáp ứng mọi nhu cầu.
Thông tin về ST666
Địa chỉ: 317 Bình Thành, Bình Hưng Hoà B, Bình Tân, Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh.
ST666 - Điểm Đến Giải Trí Và Đổi Thưởng Hàng Đầu
ST666 không chỉ là một sân chơi slot mà còn là hệ sinh thái giải trí toàn diện với dịch vụ chuyên nghiệp và ưu đãi vượt trội. Tham gia ngay hôm nay để trải nghiệm sự uy tín và cơ hội thắng lớn mà nền tảng này mang lại! -
3A娛樂城
3A娛樂城:全方位線上娛樂體驗的首選平台
3A娛樂城作為台灣最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台之一,以其多樣化的遊戲選擇、創新的技術、以及卓越的安全保障,贏得了玩家的高度信任與青睞。無論您是新手還是老手,3A娛樂城都能滿足您的需求,帶給您獨一無二的遊戲體驗。
熱門娛樂城遊戲一覽
3A娛樂城提供多種熱門遊戲,適合不同類型的玩家:
真人百家樂:體驗真實賭場的氛圍,與真人荷官互動,感受賭桌上的緊張與刺激。
彩票投注:涵蓋多種彩票選項,滿足彩券愛好者的需求,讓您隨時隨地挑戰幸運。
棋牌遊戲:從傳統的麻將到現代化的紙牌遊戲,讓玩家在策略與運氣中找到平衡。
3A娛樂城的核心價值
1. 專業
3A娛樂城每日提供近千場體育賽事,並搭配真人百家樂、彩票彩球、電子遊戲等多種類型的線上賭場遊戲。無論您的遊戲偏好為何,這裡總有一款適合您!
2. 安全
平台採用128位加密技術和嚴格的安全管理體系,確保玩家的金流與個人資料完全受保護,讓您可以放心遊玩,無需擔憂安全問題。
3. 便捷
3A娛樂城是全台第一家使用自家開發的全套終端應用的娛樂城平台。無論是手機還是電腦,玩家都能享受無縫的遊戲體驗。同時,24小時線上客服隨時為您解決任何問題,提供貼心服務。
4. 安心
由專業工程師開發的財務處理系統,為玩家帶來快速的存款、取款和轉帳服務。透過獨立網路技術,平台提供優化的網路速度,確保每一次操作都流暢無比。
下載3A娛樂城手機APP
為了提供更便捷的遊戲體驗,3A娛樂城獨家開發了功能齊全的手機APP,讓玩家隨時隨地開啟遊戲。
現代化設計:新穎乾淨的介面設計,提升使用者體驗。
跨平台支持:完美適配手機與電腦,讓您輕鬆切換設備,無需中斷遊戲。
快速下載:掃描專屬QR碼即可進入下載頁面,立即開始暢玩!
3A娛樂城的其他服務
娛樂城教學:詳細的操作指導,讓新手也能快速上手。
責任博彩:提倡健康娛樂,確保玩家在遊戲中享受樂趣的同時,不失理性。
隱私權政策:嚴格遵守隱私保護條例,保障玩家的個人信息安全。
立即加入3A娛樂城,享受頂級娛樂體驗!
如果您正在尋找一個專業、安全、便捷又安心的線上娛樂平台,那麼3A娛樂城絕對是您的不二之選。現在就下載手機APP,隨時隨地開啟您的娛樂旅程,享受無限的遊戲樂趣與刺激! -
3A娛樂城:全方位線上娛樂體驗的首選平台
3A娛樂城作為台灣最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台之一,以其多樣化的遊戲選擇、創新的技術、以及卓越的安全保障,贏得了玩家的高度信任與青睞。無論您是新手還是老手,3A娛樂城都能滿足您的需求,帶給您獨一無二的遊戲體驗。
熱門娛樂城遊戲一覽
3A娛樂城提供多種熱門遊戲,適合不同類型的玩家:
真人百家樂:體驗真實賭場的氛圍,與真人荷官互動,感受賭桌上的緊張與刺激。
彩票投注:涵蓋多種彩票選項,滿足彩券愛好者的需求,讓您隨時隨地挑戰幸運。
棋牌遊戲:從傳統的麻將到現代化的紙牌遊戲,讓玩家在策略與運氣中找到平衡。
3A娛樂城的核心價值
1. 專業
3A娛樂城每日提供近千場體育賽事,並搭配真人百家樂、彩票彩球、電子遊戲等多種類型的線上賭場遊戲。無論您的遊戲偏好為何,這裡總有一款適合您!
2. 安全
平台採用128位加密技術和嚴格的安全管理體系,確保玩家的金流與個人資料完全受保護,讓您可以放心遊玩,無需擔憂安全問題。
3. 便捷
3A娛樂城是全台第一家使用自家開發的全套終端應用的娛樂城平台。無論是手機還是電腦,玩家都能享受無縫的遊戲體驗。同時,24小時線上客服隨時為您解決任何問題,提供貼心服務。
4. 安心
由專業工程師開發的財務處理系統,為玩家帶來快速的存款、取款和轉帳服務。透過獨立網路技術,平台提供優化的網路速度,確保每一次操作都流暢無比。
下載3A娛樂城手機APP
為了提供更便捷的遊戲體驗,3A娛樂城獨家開發了功能齊全的手機APP,讓玩家隨時隨地開啟遊戲。
現代化設計:新穎乾淨的介面設計,提升使用者體驗。
跨平台支持:完美適配手機與電腦,讓您輕鬆切換設備,無需中斷遊戲。
快速下載:掃描專屬QR碼即可進入下載頁面,立即開始暢玩!
3A娛樂城的其他服務
娛樂城教學:詳細的操作指導,讓新手也能快速上手。
責任博彩:提倡健康娛樂,確保玩家在遊戲中享受樂趣的同時,不失理性。
隱私權政策:嚴格遵守隱私保護條例,保障玩家的個人信息安全。
立即加入3A娛樂城,享受頂級娛樂體驗!
如果您正在尋找一個專業、安全、便捷又安心的線上娛樂平台,那麼3A娛樂城絕對是您的不二之選。現在就下載手機APP,隨時隨地開啟您的娛樂旅程,享受無限的遊戲樂趣與刺激! -
娛樂城
超過100間最新資訊任你看!
還在苦苦尋找安全可靠的線上娛樂城推薦名單嗎?這篇彙集了 2024 年 100 間娛樂城評價實測,為您打造最新、最真實的娛樂城排行榜!
不論您是經驗豐富的玩家還是剛入門的新手,都能在這找到最適合您的娛樂城平台。
我們從遊戲種類、優惠活動到出金速度等多個面向進行詳細評比,讓您輕鬆避開黑網,安心享受刺激的遊戲體驗!點擊查看完整排行榜,開啟您的娛樂新篇章!
排名 推薦娛樂城 推薦指數
NO.1 富遊娛樂城 ★★★★★/5.0分
NO.2 1XBET娛樂城 ★★★★★/5.0分
NO.4 九州娛樂城 ★★★★★/5.0分
NO.5 LEO娛樂城 ★★★★★/5.0分
NO.6 YABO亞博體育娛樂城 ★★★★★/5.0分
NO.7 BET365娛樂城 ★★★★★/5.0分
NO.8 PM娛樂城 ★★★★★/5.0分
NO.9 DG娛樂城 ★★★★★/5.0分
NO.10 DB娛樂城 ★★★★★/5.0分
▲此表格為五星評價推薦娛樂城
1星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 10 / 24
達利娛樂城|評價介紹
達利娛樂城|評價介紹
達利娛樂城於2023年成立,他們聲稱致力於打造一個「安全可靠」、「即時便利」、「公平公正」及「專業營運」的優質娛樂服務平台,所有個人資…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 10 / 04
金金財寶娛樂城|評價介紹
金金財寶娛樂城是一個由知名啦啦隊隊員林襄代言的線上賭場,採用幣商型運營方式,玩家需使用台幣儲值以獲得遊戲幣。 該平台不支持遊戲幣的直接…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 08 / 06
帝遊娛樂城|評價介紹精選
帝遊娛樂城|評價介紹
帝遊娛樂城是在2022年所創立的新興品牌,網站內的排版以及網頁速度上都有著不錯的表現,對於使用者來說非常易於操作。 帝遊娛樂城的遊戲內…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 07 / 31
客萊柏娛樂城
客萊柏娛樂城|評價介紹
客萊柏娛樂城是一間從2020年就開始經營的線上娛樂城品牌,該品牌累積不少玩家的好口碑,遊戲種類多元且有許多常駐的優惠活動,對新手玩家非…
5星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 06 / 25
DB娛樂城介紹
DB娛樂城|評價介紹
DB娛樂城,原名PM娛樂城,在2023年更名為PM。這個重新品牌的過程中,PM集團將其亞洲遊戲品牌更名為【DB多寶遊戲】,專注於提供多…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 06 / 14
豪神娛樂城介紹
豪神娛樂城|評價介紹
豪神娛樂城是由著名主持人吳宗憲代言的線上賭場,採取幣商型的運營模式,玩家需使用台幣充值以換取遊戲幣。 該平台沒有提供遊戲幣的直接提現方…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 06 / 14
星城娛樂城介紹
星城娛樂城|評價介紹
星城娛樂城是一個由知名主持人徐乃麟代言的網上賭場,採用幣商型運營方式,玩家需使用台幣儲值以獲得遊戲幣。 該平台不支持遊戲幣的直接提現,…
1星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 06 / 12
AT99娛樂城介紹
AT99娛樂城|評價介紹
AT99娛樂城是TU娛樂城最新開發的娛樂城品牌,至於為何要開發一個新的品牌引起了許多網友的推測。 對此有人覺得TU娛樂城可能被抄了或者…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 06 / 04
AF娛樂城
AF娛樂城|評價介紹
AF娛樂城已經不存在了,不知是經營上有問題害是什麼原因,但是據我們了解此娛樂城有被詐騙的風險,請玩家多多注意!並且網路上充斥著假冒AF…
4星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 05 / 17
Player-KU-CASINO
KU娛樂城|評價介紹
過去九州娛樂城以信用版起家,為台灣地區的玩家服務。但由於會員數量過於龐大,造成客服無法消化,衍伸出許多客訴與詐騙謠言。 因此,九州決定…
1星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 04 / 04
錢盈娛樂城
錢盈娛樂城|評價介紹
錢盈娛樂城於2022年成立,是一個專注於現金投注的線上遊戲平台,提供了包括體育賭博、真人百家樂、老虎機、彩票和電子遊戲等多樣化的遊戲選…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 26
F1方程式娛樂城
F1方程式娛樂城|評價介紹
F1方程式娛樂城屬於小型線上娛樂城版,整體晚間非常簡陋而且含有諸多瑕疵以及不完善。 首先奇怪的點在於完全沒有可以註冊的地方,我們這邊猜…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 26
CZ168娛樂城
CZ168娛樂城|評價介紹
CZ168娛樂城在雖然在簡介中自稱有12年的經營時間。 但是經過我們實際的調查以及訪問該品牌網頁後發現,並沒有任何12年前或是更近的資…
1星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 25
XY娛樂城
XY娛樂城|評價介紹
XY娛樂城是一間於2024創立的新興品牌,我們實際到訪網站發現他們的網頁只提供手機版,並未提供電腦版,可能是因應現在主流大家都是拿手機…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 25
搖錢樹娛樂城
搖錢樹娛樂城|評價介紹
搖錢樹娛樂城是創立於2024,是非常新的一個品牌,但是我們實際到訪網站後,他們的娛樂城完整度是不錯的。 除了有一些小缺陷,像是我們在想…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 25
必勝娛樂城
必勝娛樂城介紹|評價介紹
必勝娛樂城並不存在,此娛樂城有被詐騙的風險,請玩家多多注意!必勝娛樂城據我們了解過後,發現網路上也有一家叫必勝客娛樂城,是否為同夥還有…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 25
柏客娛樂城
柏客娛樂城|評價介紹
柏客娛樂城是一間於2023年所創立的新興線上娛樂城品牌。 據我們實際到訪該品牌網站他們的風格走的是暗色調,以視覺上及使用體驗來說給玩家…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 25
九鑫娛樂城
九鑫娛樂城|評價介紹
九鑫娛樂城並不存在,此娛樂城有被詐騙的風險,請玩家多多注意! 九鑫娛樂城調查 如有玩家耳聞到或是想前往九鑫娛樂城做遊玩,Player團…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 25
推金娛樂城
推金娛樂城|評價介紹
推金娛樂城並不存在,此娛樂城有被詐騙的風險,請玩家多多注意! 推金娛樂城調查 如有玩家耳聞到或是想前往推金娛樂城做遊玩,Player團…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 25
捷冠娛樂城
捷冠娛樂城|評價介紹
捷冠娛樂城並沒有在經營,此娛樂城有被詐騙的風險,請玩家多多注意! 捷冠娛樂城調查 如有玩家耳聞到或是想前往捷冠娛樂城做遊玩,Playe…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 25
歐萊雅娛樂城
歐萊雅娛樂城|評價介紹
歐萊雅娛樂城並不存在,此娛樂城有被詐騙的風險,請玩家多多注意! 歐萊雅娛樂城調查 如有玩家耳聞到或是想前往歐萊雅娛樂城做遊玩,Play…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 25
MG娛樂城
MG娛樂城|評價介紹
MG娛樂城並不存在,此娛樂城有被詐騙的風險,請玩家多多注意!據我們了解,MG娛樂城在搜尋結果上顯示的雖然是MG娛樂城但是點進去後卻是非…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 25
JF娛樂城
JF娛樂城|評價介紹
JF娛樂城並不存在,此娛樂城有被詐騙的風險,請玩家多多注意!目前了解到的是,JF娛樂城在網上只搜尋的到類似空包彈的網站推薦留言,而他所…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 25
TTB娛樂城
TTB娛樂城|評價介紹
TTB娛樂城並不存在,此娛樂城有被詐騙的風險,請玩家多多注意! TTB娛樂城調查 如有玩家耳聞到或是想前往TTB娛樂城做遊玩,Play…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 25
TES888娛樂城
TES888娛樂城|評價介紹
TES8888娛樂城並不存在,此娛樂城有被詐騙的風險,請玩家多多注意! TES888娛樂城調查 如有玩家耳聞到或是想前往TES888娛…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 25
新世界娛樂城
新世界娛樂城|評價介紹
新世界娛樂城是一間於2007年創立的娛樂城,至今已有將近快20年的經營時間了。 但是經營這麼久的線上娛樂城卻被網友爆出擅自洩漏會員個資…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 22
WG娛樂城
WG娛樂城|評價介紹
WG娛樂城是一間創立於2023年的線上娛樂城品牌,他們提供諸多遊戲選擇讓玩家能盡情在娛樂城中享受電子遊戲所帶來的愉悅。 其中較為特別的…
1星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 22
逸遊娛樂城
EG逸遊娛樂城|評價介紹
EG逸遊娛樂城是一間於2023年創立的新娛樂城品牌,他們擁有眾多遊戲提供給玩家做選擇,且頻繁地釋出優惠活動,可以說是對新手玩家非常友好…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 21
RM娛樂城
RM娛樂城|評價介紹
RM娛樂城是由菲律賓政府的PAGCOR(菲律賓娛樂和遊戲公司)授予博彩牌照,並獲得GLI(Gaming Laboratories In…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 21
YG娛樂城
YG娛樂城|評價介紹
YG娛樂城應該可以說是在業界風格數一數二特殊的線上娛樂城了,整體網站採用中世紀元素下去做設計,會讓玩家誤譯為自己身處在RPG遊戲裡頭。…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 21
SAT888西雅圖娛樂城
SAT888西雅圖娛樂城|評價介紹
SAT888西雅圖娛樂城創立於2022年,其中他以豐富的遊戲選項聞名,但是在網頁的體驗上卻不如其他市面上那些線上娛樂城。 網頁速度較慢…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 21
LT娛樂城
LT娛樂城|評價介紹
LT娛樂城是一間於2022創立的線上娛樂城品牌,其中要特別注意的是,經我們網路上調查後發現此品牌常常因各種理由不給玩家出金。 網友罵聲…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 21
8方娛樂城
8方娛樂城|評價介紹
8方娛樂城在網頁外觀上並無太大問題,但是經我們實際訪問該品牌後,認為8方娛樂城為詐騙黑網的可能性非常大。 其中,網頁內許多按鈕設置上只…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 20
T9娛樂城
T9娛樂城|評價介紹
T9娛樂城相信許多人多多少少聽過,但是這邊玩家們要特別注意其實T9娛樂城是不存在的。 經我們實際訪問該品牌網站發現到,他的網站始終指向…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 20
玖富娛樂城
玖富娛樂城|評價介紹
玖富娛樂城是一間於2023年創立的新創品牌,他們精美的網頁以及讓人一目瞭然的排版資訊都讓人能夠清楚明瞭的找到自己想找的資訊,他們的遊戲…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 20
致富娛樂城
致富娛樂城|評價介紹
致富娛樂城是一間於2018年就創立的品牌,雖然經營時間也有了5年多了,但是在網路上的口碑並不是很好,甚至還傳出該娛樂城為詐騙黑網。 就…
1星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 20
阿拉巴娛樂城
阿拉八娛樂城|評價介紹
阿拉八娛樂城是一間於2022年創立的線上娛樂城,相比其他線上知名娛樂城,他們的遊戲種類明顯地比其他間少很多。 這可能導致玩家在遊戲體驗…
1星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 20
JP娛樂城
JP娛樂城|評價介紹
JP娛樂城是一間於2023年所創立的新興品牌,但也不知道是否也因新創品牌因而導致在網站上有許多的資訊上的不足以及BUG的出現。 這可能…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 20
鑫巨力娛樂城
鑫巨力娛樂城|評價介紹
有意前往鑫巨力娛樂城得玩家們需要注意!該娛樂城已於2024/03/15停止了平台服務,因此在這邊也提醒玩家不要做任何註冊以及儲值上的動…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 20
威樂娛樂城
威樂娛樂城|評價介紹
威樂娛樂城專門為全球華人社群設計,憑藉其全球分布的辦公室和客服中心以及合法的經營方式,深受許多遊戲愛好者的青睞。 他們提供了多樣化的遊…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 19
GSBET娛樂城
GSBET娛樂城|評價介紹
GSBET在系統上以及安全性的技術上有著完善的技術,他們提供了一個安全、隱私且公平的線上博彩空間。 使用國際認可的SSL 128位加密…
1星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 19
a8遊藝場
A8娛樂城|評價介紹
A8娛樂城經我們調查過後以及實際訪問該品牌網頁,發現其中幾個嚴重的問題,A8娛樂城的網頁排版混亂、且該品牌相關資訊完全都沒又做任何的說…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 19
德正娛樂城
DZ得正娛樂城|評價介紹
DZ得正娛樂城是一間創立於2024年的新創線上娛樂城,並且他們提供了一系列豐富的遊戲選項。 從彩票、真人視訊、體育賭注到電玩遊戲等,滿…
1星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 19
雷亞娛樂城
雷亞娛樂城|評價介紹
雷亞娛樂城是一間於2020年創立的線上娛樂城,但是在訪問以及遊玩過雷亞娛樂城後我們給出了一些結論,他們在娛樂城的公司營運以及該品牌公司…
1星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 19
FDY娛樂城
FDY娛樂城|評價介紹
由於FDY娛樂城的官方網站未提供足夠的詳細資訊,我們高度懷疑可能是一個詐騙或不可信的平台。 官方網站上的信息過於粗略,缺乏必要的運營和…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 19
昊陽娛樂城
昊陽娛樂城|評價介紹
昊陽娛樂城擁有菲律賓娛樂及博彩公司(PAGCOR)頒發的執照,受其監管,致力於提供安全、公平、公正、誠信的網上投注服務。 旨在打造世界…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 19
369娛樂城
369娛樂城|評價介紹
369娛樂城提供一個簡潔且易於使用的應用程式,適用於iOS和Android設備,方便玩家在Google Play和App Store上…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 18
發樂娛樂城
發樂娛樂城|評價介紹
創立於2021年的發樂娛樂城,是一家官方運營的線上社交博弈遊戲品牌。 以「誠信、正直、玩家第一」為核心理念,致力於維護用戶權益,為玩家…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 18
QK娛樂城
QK娛樂城|評價介紹
QK娛樂城專為全球華人社區打造,深受眾多遊戲愛好者喜愛。他們在全球設有辦公室及客服中心,並且合法經營,確保您的遊戲體驗既安全又愉快。 …
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 18
鑽豹娛樂城
鑽豹娛樂城|評價介紹
關於鑽豹娛樂城的詳細訊息,在該娛樂城的官網中並沒有做任何詳細的介紹,因此我們在這邊可以合理判斷此娛樂城為詐騙黑網的可能性非常高,官網中…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 18
飛達娛樂城
飛達娛樂城|評價介紹
飛達娛樂城,由”Wilshire Worldwide Company Limited” 營運,他們聲稱擁有菲律賓官方博彩許可,提供豐富…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 18
FUNNY娛樂城
FUNNY娛樂城|評價介紹
FUNNY娛樂城專為全球華人社區量身打造,贏得了眾多遊戲愛好者的喜愛。 他們遍設辦公室及客服中心於世界各地,並且保證合法經營,讓您的遊…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 18
金博娛樂城
金博娛樂城|評價介紹
金博娛樂城專門為全球的華人社群設計,已經贏得了許多忠實遊戲愛好者的心。 他們在世界各地都有自己的辦公室和客服中心,而且完全合法運營,讓…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 18
V7娛樂城
V7娛樂城|評價介紹
V7娛樂城樂是一間於2022年年末所創立的線上娛樂城品牌,據他該品牌說法,他們擁有一支堅強的自主開發團隊、客服團隊、除了能滿足玩家在娛…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 15
SZ娛樂城
SZ娛樂城|評價介紹
SZ娛樂城是專門為全球華人打造的,已經吸引了眾多忠實粉絲。 他們在各地設有辦公室和客服中心,都是合法經營的,所以您可以放心。 他們提供…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 15
DOIN娛樂城
DOIN娛樂城|評價介紹
DOIN娛樂城,這家設立在柬埔寨波貝度假村的線上遊戲天地,不僅擁有合法的博弈執照,還提供多樣化的遊戲選項,包括運動博彩、電競、真人百家…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 11
金合發娛樂城精選
金合發娛樂城|評價介紹
金合發娛樂城曾在線上娛樂界獲得廣泛的歡迎,享有老牌的地位。 但是,近些年來,由於玩家提出的連串投訴,其名譽不斷受損。 這些投訴主要圍繞…
5星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 11
RG富遊娛樂城精選
富遊娛樂城|評價介紹
隨著2024年的到來,最新的線上娛樂平台排行榜已經更新,這一次的排名綜合考慮了各種因素,包括體驗金、促銷活動、提款效率和遊戲多樣性,目…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 08
3A娛樂城精選
3A娛樂城|評價介紹
3A娛樂城是一家線上遊戲平台,提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,包括百家樂、老虎機和運彩等。 但因為網路上對這個平台的評論不多,有些人可能會擔心遭…
1星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 08
FA8娛樂城
FA8娛樂城|評價介紹
FA8娛樂城在亞洲地區受到許多玩家的青睞,FA8娛樂城是一個多元化的線上賭博平台。 它提供了包羅萬象的遊戲選項,從體育投注、電玩遊戲到…
2星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 08
BU娛樂城
BU娛樂城|評價介紹
BU娛樂城在亞太地區的線上娛樂市場擁有豐富的經驗,以強大的研發團隊和優質的客服服務而聞名。 該平台所開發的遊戲經美國TST技術測試機構…
5星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 08
1XBET娛樂城1
1XBET娛樂城|評價介紹
1XBET娛樂城擁有許多各式各樣的遊戲和促銷活動,讓玩家每天都有機會贏得獎勵。 這個平台支持多種付款方式,包括Visa、Masterc…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 07
大老爺娛樂城精選
大老爺娛樂城|評價介紹
大老爺娛樂城之前的活動是你存1000元就送你1000點,但得玩到13倍投注額。 最近他們改成了存3000送1688點,但要玩到11倍投…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 07
AC1娛樂城精選
AC1娛樂城介紹|評價介紹
AC1娛樂城在亞太區的線上娛樂市場上運營多年,擁有一支自研團隊和專業的客服團隊。這家娛樂城努力為玩家提供一個全面、可信賴的網絡遊戲體驗…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 07
大福娛樂城精選
大福娛樂城|評價介紹
大福娛樂城是個網上賭博平台,玩家在這裡是用虛擬的點數來充值,算是一種幣商型的賭場。 這裡沒有直接的提款方式,玩家得自己找幣商換成現金,…
5星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 07
九州娛樂城
九州娛樂城|評價介紹
九州娛樂城,也被稱作LEO娛樂城,致力於打造一個既安全又方便、公平公正的高品質娛樂服務平台。 他們的目標是創造全新的線上娛樂城體驗,普…
5星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 07
LEO娛樂城精選
LEO娛樂城|評價介紹
LEO娛樂城,也被稱為”九州娛樂城“,而他們的品牌宗旨是建立一個既安全又方便的高品質線上娛樂平台。 全力為玩家提供一個公平、正義的遊戲…
1星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 06
金鈦城娛樂城精選
金鈦城娛樂城|評價介紹
金鈦城娛樂城是台灣線上娛樂城(現金版),成立於 2023年,主打高額賠率、多樣遊戲、快速出金等特色。 但多數玩家反映金鈦城娛樂城的客服…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 06
必贏娛樂城精選
必贏娛樂城|評價介紹
必贏娛樂城,定位為針對全球華人市場的高級線上娛樂平台,具有豐富的跨國經營經驗。 這個平台在世界各地都設有辦公室和客服中心,並且擁有多個…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 06
好玩娛樂城
好玩娛樂城|評價介紹
對於正在尋找高品質線上賭場的玩家來說,好玩娛樂城絕對值得一試!這個平台已經吸引了成千上萬的玩家,以提供令人興奮的賭博體驗而著稱。 好玩…
不推薦
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 06
BOK娛樂城精選
BOK娛樂城|評價介紹
目前在BOK娛樂城的網站上找不到登入的選項,當點擊相應連結時,會被重定向到【FM富馬】網站。這情況引起了疑慮,使人懷疑BOK娛樂城可能…
3星評價
娛樂城評價
2024 / 03 / 06
JY娛樂城精選
JC娛樂城|評價介紹
JC娛樂城是九州娛樂集團下的一個品牌。但當用戶試圖註冊JC娛樂城時,他們實際上會被導向到THA娛樂城的介面,這個介面和九州娛樂城的長得… -
娛樂城
富遊娛樂城評價:2024年最新評價
推薦指數 : ★★★★★ ( 5.0/5 )
富遊娛樂城作為目前最受歡迎的博弈網站之一,在台灣擁有最高的註冊人數。RG富遊以安全、公正、真實和順暢的品牌保證,贏得了廣大玩家的信賴。
富遊線上賭場不僅提供了豐富多樣的遊戲種類,還有眾多吸引人的優惠活動。在出金速度方面,獲得無數網紅和網友的高度評價,確保玩家能享有無憂的博弈體驗。
推薦要點
新手首選: 富遊娛樂城,2024年評選首選,提供專為新手打造的豐富教學和獨家優惠。
一存雙收: 首存1000元,立獲1000元獎金,僅需1倍流水,新手友好。
免費體驗: 新玩家享免費體驗金,暢遊各式遊戲,開啟無限可能。
優惠多元: 活動豐富,流水要求低,適合各類型玩家。
玩家首選: 遊戲多樣,服務優質,是新手與老手的最佳賭場選擇。
免費試玩
富遊娛樂城詳情資訊
賭場名稱 : RG富遊
創立時間 : 2019年
賭場類型 : 現金版娛樂城
博弈執照 : 馬爾他牌照(MGA)認證、英屬維爾京群島(BVI)認證、菲律賓(PAGCOR)監督競猜牌照
遊戲類型 : 真人百家樂、運彩投注、電子老虎機、彩票遊戲、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲
存取速度 : 存款5秒 / 提款3-5分
軟體下載 : 支援APP,IOS、安卓(Android)
線上客服 : 需透過官方LINE
富遊娛樂城優缺點
優點 缺點
台灣註冊人數NO.1線上賭場
首儲1000贈1000只需一倍流水
擁有體驗金免費體驗賭場
網紅部落客推薦保證出金線上娛樂城
需透過客服申請體驗金
富遊娛樂城存取款方式
存款方式 取款方式
提供四大超商(全家、7-11、萊爾富、ok超商)
虛擬貨幣ustd存款
銀行轉帳(各大銀行皆可)
網站內申請提款及可匯款至綁定帳戶
現金1:1出金
富遊娛樂城平台系統
真人百家 — RG真人、DG真人、歐博真人、DB真人(原亞博/PM)、SA真人、OG真人、WM真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、熊貓體育(原亞博/PM)
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —RG電子、ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、GR電子(好路)、ATG電子
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌、RG棋牌
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、DB捕魚
富遊娛樂城優惠活動
優惠 獎金贈點 流水要求
免費體驗金 $168 1倍 (儲值後) /36倍 (未儲值)
首儲贈點 $1000 1倍流水
返水活動 0.3% - 0.7% 無流水限制
簽到禮金 $666 20倍流水
好友介紹金 $688 1倍流水
回歸禮金 $500 1倍流水
免費試玩
專屬富遊VIP特權
黃金 黃金 鉑金 金鑽 大神
升級流水 300w 600w 1800w 3600w
保級流水 50w 100w 300w 600w
升級紅利 $688 $1080 $3888 $8888
每週紅包 $188 $288 $988 $2388
生日禮金 $688 $1080 $3888 $8888
反水 0.4% 0.5% 0.6% 0.7%
娛樂城常見問題解答(FAQ)
Q1:如何在富遊娛樂城進行首次存款?
A1:可以透過超商、虛擬貨幣或銀行轉帳進行存款,過程簡單快速。( 詳細可查看:富遊娛樂城存款教學)
Q2:富遊娛樂城提款需要多久時間?
A2:提款過程一般在3-5分鐘內完成,保證快速到賬。( 詳細可查看:富遊娛樂城提款教學) -
娛樂城
2024 年娛樂城遊戲推薦:最夯遊戲與最佳平台選擇
隨著線上娛樂城市場的蓬勃發展,2024 年推出了多款令人興奮的遊戲和創新平台。無論是喜歡老虎機、棋牌遊戲,還是捕魚和彩票遊戲的玩家,都能在今年找到屬於自己的遊戲樂園。以下是熱門遊戲推薦與最佳娛樂城平台的詳細介紹。
2024 年最夯遊戲推薦
電子老虎機遊戲
電子老虎機一直是娛樂城的經典項目,今年更是推出了數款熱門作品:
戰神賽特:以古埃及神話為背景,擁有高倍數獎勵的特殊功能,畫面設計精美。
魔龍傳奇:玩家可探索魔龍世界,觸發驚喜獎金和免費遊戲機會。
雷神之錘:以北歐神話為主題,特色連線玩法讓每次旋轉都充滿期待。
金虎爺:寓意招財進寶,特別適合新年期間挑戰,玩法簡單但回報豐厚。
棋牌遊戲
二人麻將:適合喜歡策略性對抗的玩家,快速節奏且競爭激烈。
忍 Kunoichi:結合武士與忍者元素,讓玩家體驗獨特的棋牌競技。
捕魚遊戲
捕魚遊戲是一種結合策略和運氣的娛樂項目,玩家可以通過捕捉魚群來獲得高額獎金,同時享受視覺和操作的雙重樂趣。
彩票遊戲
彩票遊戲以簡單快捷的玩法吸引大批玩家,提供多種國內外彩種,讓玩家隨時挑戰幸運。
RG富遊娛樂城:2024 年最佳線上娛樂城推薦
在眾多娛樂城平台中,RG富遊娛樂城以其專業服務和卓越遊戲體驗,成為今年的首選平台。
平台特色
遊戲種類豐富
提供多元化遊戲選擇,包括真人視訊、電子老虎機、捕魚、棋牌和彩票遊戲,滿足所有玩家需求。
快速便捷的存提款服務
平台支持即時存款與快速提款,無需等待,確保資金安全流動。
高度安全保障
採用最先進的加密技術,保護玩家的帳戶與交易安全。
支援多平台裝置
富遊娛樂城APP 可在 iOS 和 Android 設備上使用,界面簡潔易操作,隨時隨地享受娛樂。
專業客服支援
提供 24 小時全天候客服,隨時解答玩家疑問,保障流暢的遊戲體驗。
如何開始體驗 RG 富遊娛樂城
下載富遊 APP
在官方網站免費下載 APP,支援 iOS 和 Android 設備。
註冊帳號
使用簡單步驟完成註冊,立即進入遊戲世界。
挑戰熱門遊戲
從老虎機到棋牌遊戲,選擇您喜歡的類型,挑戰高額獎金。
結語
2024 年是線上娛樂遊戲的精彩年份,從戰神賽特到二人麻將,每款遊戲都能帶給玩家不同的樂趣。而選擇像 RG富遊娛樂城 這樣的專業平台,不僅能體驗到豐富的遊戲內容,還能享受安全可靠的服務。立即下載富遊 APP,加入這個充滿驚喜的娛樂世界 -
富遊娛樂城評價:2024年最新評價
推薦指數 : ★★★★★ ( 5.0/5 )
富遊娛樂城作為目前最受歡迎的博弈網站之一,在台灣擁有最高的註冊人數。RG富遊以安全、公正、真實和順暢的品牌保證,贏得了廣大玩家的信賴。
富遊線上賭場不僅提供了豐富多樣的遊戲種類,還有眾多吸引人的優惠活動。在出金速度方面,獲得無數網紅和網友的高度評價,確保玩家能享有無憂的博弈體驗。
推薦要點
新手首選: 富遊娛樂城,2024年評選首選,提供專為新手打造的豐富教學和獨家優惠。
一存雙收: 首存1000元,立獲1000元獎金,僅需1倍流水,新手友好。
免費體驗: 新玩家享免費體驗金,暢遊各式遊戲,開啟無限可能。
優惠多元: 活動豐富,流水要求低,適合各類型玩家。
玩家首選: 遊戲多樣,服務優質,是新手與老手的最佳賭場選擇。
免費試玩
富遊娛樂城詳情資訊
賭場名稱 : RG富遊
創立時間 : 2019年
賭場類型 : 現金版娛樂城
博弈執照 : 馬爾他牌照(MGA)認證、英屬維爾京群島(BVI)認證、菲律賓(PAGCOR)監督競猜牌照
遊戲類型 : 真人百家樂、運彩投注、電子老虎機、彩票遊戲、棋牌遊戲、捕魚機遊戲
存取速度 : 存款5秒 / 提款3-5分
軟體下載 : 支援APP,IOS、安卓(Android)
線上客服 : 需透過官方LINE
富遊娛樂城優缺點
優點 缺點
台灣註冊人數NO.1線上賭場
首儲1000贈1000只需一倍流水
擁有體驗金免費體驗賭場
網紅部落客推薦保證出金線上娛樂城
需透過客服申請體驗金
富遊娛樂城存取款方式
存款方式 取款方式
提供四大超商(全家、7-11、萊爾富、ok超商)
虛擬貨幣ustd存款
銀行轉帳(各大銀行皆可)
網站內申請提款及可匯款至綁定帳戶
現金1:1出金
富遊娛樂城平台系統
真人百家 — RG真人、DG真人、歐博真人、DB真人(原亞博/PM)、SA真人、OG真人、WM真人
體育投注 — SUPER體育、鑫寶體育、熊貓體育(原亞博/PM)
彩票遊戲 — 富遊彩票、WIN 539
電子遊戲 —RG電子、ZG電子、BNG電子、BWIN電子、RSG電子、GR電子(好路)、ATG電子
棋牌遊戲 —ZG棋牌、亞博棋牌、好路棋牌、博亞棋牌、RG棋牌
捕魚遊戲 —ZG捕魚、RSG捕魚、好路GR捕魚、DB捕魚
富遊娛樂城優惠活動
優惠 獎金贈點 流水要求
免費體驗金 $168 1倍 (儲值後) /36倍 (未儲值)
首儲贈點 $1000 1倍流水
返水活動 0.3% - 0.7% 無流水限制
簽到禮金 $666 20倍流水
好友介紹金 $688 1倍流水
回歸禮金 $500 1倍流水
免費試玩
專屬富遊VIP特權
黃金 黃金 鉑金 金鑽 大神
升級流水 300w 600w 1800w 3600w
保級流水 50w 100w 300w 600w
升級紅利 $688 $1080 $3888 $8888
每週紅包 $188 $288 $988 $2388
生日禮金 $688 $1080 $3888 $8888
反水 0.4% 0.5% 0.6% 0.7%
娛樂城常見問題解答(FAQ)
Q1:如何在富遊娛樂城進行首次存款?
A1:可以透過超商、虛擬貨幣或銀行轉帳進行存款,過程簡單快速。( 詳細可查看:富遊娛樂城存款教學)
Q2:富遊娛樂城提款需要多久時間?
A2:提款過程一般在3-5分鐘內完成,保證快速到賬。( 詳細可查看:富遊娛樂城提款教學) -
娛樂城
RG富遊娛樂城:台灣線上娛樂城的最佳選擇
RG富遊娛樂城以其卓越的服務和多樣化的遊戲選擇,成為2024年最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台。受到超過50位網紅和部落客的實測推薦,這座娛樂城不僅提供豐富的遊戲,還帶來眾多優惠活動和誠信保證,贏得了廣大玩家的信任與青睞。
RG富遊娛樂城的獨特優勢
多重優惠活動
體驗金 $168:新手玩家可以免費試玩,無需任何成本即可體驗高品質遊戲。
首儲1000送1000:首次存款即可獲得雙倍金額,增加遊戲的樂趣與機會。
線上簽到轉盤:每日簽到即可參加抽獎,贏取現金獎勵和豐厚禮品。
快速存提款與資金保障
RG富遊採用自主研發的財務系統,確保5秒快速存款,滿足玩家即時遊戲需求。
100%保證出金,杜絕任何拖延或資金安全風險,讓玩家完全放心。
遊戲種類豐富
RG富遊娛樂城涵蓋多種遊戲類型,滿足不同玩家的需求,包括:
真人百家樂:與真人荷官互動,感受真實賭場的刺激氛圍。
電子老虎機:超過數百款創新遊戲,玩法新穎,回報豐厚。
電子捕魚:趣味性強,結合策略與娛樂,深受玩家喜愛。
電子棋牌:提供公平競技環境,適合策略型玩家。
體育投注:涵蓋全球賽事,賠率即時更新,為體育愛好者提供最佳選擇。
樂透彩票:參與多地彩票,挑戰巨額獎金。
跨平台兼容性
RG富遊支持Web端、H5、iOS和Android設備,玩家可隨時隨地登錄遊戲,享受無縫體驗。
與其他娛樂城的不同之處
RG富遊以現金版模式運營,確保交易透明和安全性。相比一般娛樂城,RG富遊在存提款速度上遙遙領先,玩家可在短短15秒內完成交易,並且100%保證資金提領。而在線客服全年無休,隨時提供支持,讓玩家在任何時間都能解決問題。
相比之下,一般娛樂城多以信用版模式運營,存在出金風險,且存提款速度較慢,客服服務不穩定,無法與RG富遊的專業性相比。
為什麼選擇RG富遊娛樂城
資金交易安全無憂:採用最先進的SSL加密技術,確保每筆交易的安全性。
遊戲種類全面豐富:每日更新多樣化遊戲,帶來新鮮感和無限可能。
優惠活動力度大:從體驗金到豐厚的首儲獎勵,玩家每一步都能享受優惠。
快速存提款服務:自主研發技術保障流暢交易,遊戲不中斷。
全天候專業客服:24/7在線支持,及時解決玩家需求。
立即加入RG富遊娛樂城
RG富遊娛樂城不僅提供豐富的遊戲體驗,更以專業的服務、完善的安全保障和多樣的優惠活動,為玩家打造一個值得信賴的娛樂環境。立即註冊,體驗台灣最受歡迎的線上娛樂城! -
娛樂城
RG富遊娛樂城:台灣線上娛樂城的最佳選擇
RG富遊娛樂城以其卓越的服務和多樣化的遊戲選擇,成為2024年最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台。受到超過50位網紅和部落客的實測推薦,這座娛樂城不僅提供豐富的遊戲,還帶來眾多優惠活動和誠信保證,贏得了廣大玩家的信任與青睞。
RG富遊娛樂城的獨特優勢
多重優惠活動
體驗金 $168:新手玩家可以免費試玩,無需任何成本即可體驗高品質遊戲。
首儲1000送1000:首次存款即可獲得雙倍金額,增加遊戲的樂趣與機會。
線上簽到轉盤:每日簽到即可參加抽獎,贏取現金獎勵和豐厚禮品。
快速存提款與資金保障
RG富遊採用自主研發的財務系統,確保5秒快速存款,滿足玩家即時遊戲需求。
100%保證出金,杜絕任何拖延或資金安全風險,讓玩家完全放心。
遊戲種類豐富
RG富遊娛樂城涵蓋多種遊戲類型,滿足不同玩家的需求,包括:
真人百家樂:與真人荷官互動,感受真實賭場的刺激氛圍。
電子老虎機:超過數百款創新遊戲,玩法新穎,回報豐厚。
電子捕魚:趣味性強,結合策略與娛樂,深受玩家喜愛。
電子棋牌:提供公平競技環境,適合策略型玩家。
體育投注:涵蓋全球賽事,賠率即時更新,為體育愛好者提供最佳選擇。
樂透彩票:參與多地彩票,挑戰巨額獎金。
跨平台兼容性
RG富遊支持Web端、H5、iOS和Android設備,玩家可隨時隨地登錄遊戲,享受無縫體驗。
與其他娛樂城的不同之處
RG富遊以現金版模式運營,確保交易透明和安全性。相比一般娛樂城,RG富遊在存提款速度上遙遙領先,玩家可在短短15秒內完成交易,並且100%保證資金提領。而在線客服全年無休,隨時提供支持,讓玩家在任何時間都能解決問題。
相比之下,一般娛樂城多以信用版模式運營,存在出金風險,且存提款速度較慢,客服服務不穩定,無法與RG富遊的專業性相比。
為什麼選擇RG富遊娛樂城
資金交易安全無憂:採用最先進的SSL加密技術,確保每筆交易的安全性。
遊戲種類全面豐富:每日更新多樣化遊戲,帶來新鮮感和無限可能。
優惠活動力度大:從體驗金到豐厚的首儲獎勵,玩家每一步都能享受優惠。
快速存提款服務:自主研發技術保障流暢交易,遊戲不中斷。
全天候專業客服:24/7在線支持,及時解決玩家需求。
立即加入RG富遊娛樂城
RG富遊娛樂城不僅提供豐富的遊戲體驗,更以專業的服務、完善的安全保障和多樣的優惠活動,為玩家打造一個值得信賴的娛樂環境。立即註冊,體驗台灣最受歡迎的線上娛樂城! -
娛樂城
2024 年娛樂城遊戲推薦:最夯遊戲與最佳平台選擇
隨著線上娛樂城市場的蓬勃發展,2024 年推出了多款令人興奮的遊戲和創新平台。無論是喜歡老虎機、棋牌遊戲,還是捕魚和彩票遊戲的玩家,都能在今年找到屬於自己的遊戲樂園。以下是熱門遊戲推薦與最佳娛樂城平台的詳細介紹。
2024 年最夯遊戲推薦
電子老虎機遊戲
電子老虎機一直是娛樂城的經典項目,今年更是推出了數款熱門作品:
戰神賽特:以古埃及神話為背景,擁有高倍數獎勵的特殊功能,畫面設計精美。
魔龍傳奇:玩家可探索魔龍世界,觸發驚喜獎金和免費遊戲機會。
雷神之錘:以北歐神話為主題,特色連線玩法讓每次旋轉都充滿期待。
金虎爺:寓意招財進寶,特別適合新年期間挑戰,玩法簡單但回報豐厚。
棋牌遊戲
二人麻將:適合喜歡策略性對抗的玩家,快速節奏且競爭激烈。
忍 Kunoichi:結合武士與忍者元素,讓玩家體驗獨特的棋牌競技。
捕魚遊戲
捕魚遊戲是一種結合策略和運氣的娛樂項目,玩家可以通過捕捉魚群來獲得高額獎金,同時享受視覺和操作的雙重樂趣。
彩票遊戲
彩票遊戲以簡單快捷的玩法吸引大批玩家,提供多種國內外彩種,讓玩家隨時挑戰幸運。
RG富遊娛樂城:2024 年最佳線上娛樂城推薦
在眾多娛樂城平台中,RG富遊娛樂城以其專業服務和卓越遊戲體驗,成為今年的首選平台。
平台特色
遊戲種類豐富
提供多元化遊戲選擇,包括真人視訊、電子老虎機、捕魚、棋牌和彩票遊戲,滿足所有玩家需求。
快速便捷的存提款服務
平台支持即時存款與快速提款,無需等待,確保資金安全流動。
高度安全保障
採用最先進的加密技術,保護玩家的帳戶與交易安全。
支援多平台裝置
富遊娛樂城APP 可在 iOS 和 Android 設備上使用,界面簡潔易操作,隨時隨地享受娛樂。
專業客服支援
提供 24 小時全天候客服,隨時解答玩家疑問,保障流暢的遊戲體驗。
如何開始體驗 RG 富遊娛樂城
下載富遊 APP
在官方網站免費下載 APP,支援 iOS 和 Android 設備。
註冊帳號
使用簡單步驟完成註冊,立即進入遊戲世界。
挑戰熱門遊戲
從老虎機到棋牌遊戲,選擇您喜歡的類型,挑戰高額獎金。
結語
2024 年是線上娛樂遊戲的精彩年份,從戰神賽特到二人麻將,每款遊戲都能帶給玩家不同的樂趣。而選擇像 RG富遊娛樂城 這樣的專業平台,不僅能體驗到豐富的遊戲內容,還能享受安全可靠的服務。立即下載富遊 APP,加入這個充滿驚喜的娛樂世界 -
富遊娛樂城:全台灣第一推薦的娛樂城體驗
富遊娛樂城是全台灣最受玩家推崇的娛樂平台,提供多種優惠、豐富的遊戲選擇以及高品質的服務,讓每位玩家都能享受極致的遊戲樂趣。無論您是新手還是資深玩家,富遊娛樂城都能滿足您的需求,帶給您刺激的遊戲體驗。
富遊娛樂城的優惠活動
1. 免費娛樂城體驗金
新玩家只需註冊即可免費領取 $168 元的體驗金,無需存款,便可立即體驗各種遊戲,感受遊戲帶來的樂趣。
2. 首次存款優惠
首次存款 $1000 元,即送 $1000 元遊戲金,讓您在遊戲中有更多機會獲勝,增添刺激感。
3. 新會員五選一好禮
新加入的會員可選擇五種專屬好禮之一,從遊戲金到實體獎品,讓您的遊戲旅程更加多彩。
熱門遊戲種類
富遊娛樂城提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,適合不同喜好的玩家:
電子老虎機:多款創新遊戲,讓玩家享受豐厚獎金機會。
百家樂:與真人荷官互動,體驗真實賭場的刺激感。
今彩539 和 運彩:滿足彩票愛好者的需求。
捕魚遊戲:RSG電子捕魚遊戲帶來娛樂與獎金的雙重樂趣。
熊貓體育:專為體育迷設計的多種運動投注選項。
優質服務保證
1. 出金快速、安全可靠
富遊娛樂城採用先進的財務處理系統,保證快速存提款,讓玩家不用擔心資金安全問題。
2. 技術先進的APP平台
流暢的畫面設計與設備兼容性,讓用戶輕鬆上手。
持續升級與更新,提供更多創新遊戲類型。
3. 24小時專業客服
專業客服隨時待命,為玩家解答所有遊戲相關問題,確保您在任何時間都能享受到無縫的服務體驗。
4. 安全防護到位
採用最嚴格的安全管理系統與數據加密技術,保障用戶資金與個人信息的安全。
富遊娛樂城APP:隨時隨地盡享遊戲
富遊娛樂城APP提供了便捷的遊戲途徑,支援 IOS 與 Android 設備。
簡潔易用的界面設計,讓玩家快速找到喜愛的遊戲。
即時客服支援,隨時解決您的疑問。
免費下載,無論何時何地,您都能盡享娛樂城的精彩遊戲體驗。
為什麼選擇富遊娛樂城?
優惠豐富:免費體驗金、首存優惠、新會員好禮,活動多樣。
遊戲種類齊全:從電子遊戲到真人百家樂,滿足各類玩家需求。
服務至上:專業客服、快速出金和高安全保障讓玩家安心享受遊戲。
便捷平台:富遊APP提供隨時隨地的遊戲樂趣,讓您不受限制。
立即下載 富遊娛樂城APP,體驗全台灣第一娛樂城的無限魅力!不論您是想享受遊戲樂趣還是贏取豐厚獎金,富遊娛樂城都將是您的最佳選擇! -
娛樂城
富遊娛樂城:全台灣第一推薦的娛樂城體驗
富遊娛樂城是全台灣最受玩家推崇的娛樂平台,提供多種優惠、豐富的遊戲選擇以及高品質的服務,讓每位玩家都能享受極致的遊戲樂趣。無論您是新手還是資深玩家,富遊娛樂城都能滿足您的需求,帶給您刺激的遊戲體驗。
富遊娛樂城的優惠活動
1. 免費娛樂城體驗金
新玩家只需註冊即可免費領取 $168 元的體驗金,無需存款,便可立即體驗各種遊戲,感受遊戲帶來的樂趣。
2. 首次存款優惠
首次存款 $1000 元,即送 $1000 元遊戲金,讓您在遊戲中有更多機會獲勝,增添刺激感。
3. 新會員五選一好禮
新加入的會員可選擇五種專屬好禮之一,從遊戲金到實體獎品,讓您的遊戲旅程更加多彩。
熱門遊戲種類
富遊娛樂城提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,適合不同喜好的玩家:
電子老虎機:多款創新遊戲,讓玩家享受豐厚獎金機會。
百家樂:與真人荷官互動,體驗真實賭場的刺激感。
今彩539 和 運彩:滿足彩票愛好者的需求。
捕魚遊戲:RSG電子捕魚遊戲帶來娛樂與獎金的雙重樂趣。
熊貓體育:專為體育迷設計的多種運動投注選項。
優質服務保證
1. 出金快速、安全可靠
富遊娛樂城採用先進的財務處理系統,保證快速存提款,讓玩家不用擔心資金安全問題。
2. 技術先進的APP平台
流暢的畫面設計與設備兼容性,讓用戶輕鬆上手。
持續升級與更新,提供更多創新遊戲類型。
3. 24小時專業客服
專業客服隨時待命,為玩家解答所有遊戲相關問題,確保您在任何時間都能享受到無縫的服務體驗。
4. 安全防護到位
採用最嚴格的安全管理系統與數據加密技術,保障用戶資金與個人信息的安全。
富遊娛樂城APP:隨時隨地盡享遊戲
富遊娛樂城APP提供了便捷的遊戲途徑,支援 IOS 與 Android 設備。
簡潔易用的界面設計,讓玩家快速找到喜愛的遊戲。
即時客服支援,隨時解決您的疑問。
免費下載,無論何時何地,您都能盡享娛樂城的精彩遊戲體驗。
為什麼選擇富遊娛樂城?
優惠豐富:免費體驗金、首存優惠、新會員好禮,活動多樣。
遊戲種類齊全:從電子遊戲到真人百家樂,滿足各類玩家需求。
服務至上:專業客服、快速出金和高安全保障讓玩家安心享受遊戲。
便捷平台:富遊APP提供隨時隨地的遊戲樂趣,讓您不受限制。
立即下載 富遊娛樂城APP,體驗全台灣第一娛樂城的無限魅力!不論您是想享受遊戲樂趣還是贏取豐厚獎金,富遊娛樂城都將是您的最佳選擇! -
Leo娛樂城無法登入?全面解析與解決指南
近期,Leo娛樂城的玩家紛紛反映登入失敗的情況,引發了廣泛的討論與擔憂。作為九州娛樂城旗下知名品牌之一,Leo娛樂城在台灣的娛樂市場中擁有大量用戶。然而,隨著九州娛樂城宣布將於2024年12月31日退出台灣市場,這一消息無疑讓玩家對資金安全與遊戲體驗產生了極大疑慮。
本文將深入探討Leo娛樂城無法登入的原因,提供解決方案,並推薦可靠的替代娛樂平台。
Leo娛樂城無法登入的三大原因
1. 帳號密碼問題
可能情況:最常見的原因是玩家輸入了錯誤的帳號或密碼,或者帳號被盜用。
解決方法:確認輸入的帳密正確,若仍無法登入,聯繫客服即可解決。
2. 網頁技術問題
可能情況:官網可能因伺服器維護或技術故障出現404錯誤,導致玩家無法登入。
解決方法:耐心等待官網修復,並清除瀏覽器快取和Cookie,或嘗試使用其他瀏覽器。
3. 九州娛樂城退出台灣市場
可能情況:隨著九州娛樂城宣布退出台灣市場,Leo娛樂城的營運也逐步停止,導致玩家無法再使用該平台。
影響:玩家可能面臨資金提取困難,需及時完成出金操作以保障自身利益。
娛樂城無法登入的緊急解決方案
核對帳號與密碼:確認輸入正確無誤,避免由於簡單疏忽造成的登入失敗。
檢查網路連線:確保網路穩定,必要時切換至更穩定的網路環境。
清除瀏覽器快取與Cookie:解決瀏覽器相關問題,恢復正常登入。
嘗試其他瀏覽器或設備:更換設備或使用不同瀏覽器,查看是否可以正常登入。
九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的原因
市場利潤有限:九州娛樂城認為台灣市場的競爭激烈且利潤有限,因此選擇退出並專注於其他海外市場。
資金生態鏈斷裂:現金交易平台出現問題,導致九州娛樂城難以維持正常運營。
母公司法律爭議:九州娛樂城母公司近年來因財務與法律問題受到高度關注,進一步影響旗下品牌的營運。
Leo娛樂城會員如何安全出金?
在九州娛樂城停止營運前,玩家需要立即完成出金操作以確保資金安全。
出金建議:
儘快登入官網提交提款申請,確保資金安全轉出。
若官網無法訪問,請嘗試聯繫客服,並保留交易證明以備進一步處理。
推薦替代平台:富遊娛樂城
隨著Leo娛樂城的退出,玩家可以考慮轉至穩定且值得信賴的替代平台,如富遊娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城的優勢
穩定可靠:擁有先進的技術和完善的資金保障機制,確保玩家的資金安全。
豐富的遊戲選擇:從電子遊戲到真人娛樂,滿足各類玩家的需求。
專屬優惠:特別為Leo會員推出等級升等計畫,並提供多樣化的專屬活動。
快速出金:高效的財務系統,讓玩家的存取款過程快速無憂。
Leo會員轉移至富遊的流程
登錄富遊官網完成註冊。
提供Leo娛樂城會員等級截圖與相關資料(如戶名、手機號碼)給富遊客服進行審核。
等待客服確認後,享受富遊娛樂城專屬的會員福利與優惠。
結語:立即加入富遊娛樂城,延續遊戲體驗!
Leo娛樂城的退出讓許多玩家感到困惑與擔憂,但選擇穩定、安全的娛樂平台是最明智的應對之道。富遊娛樂城憑藉其卓越的技術、專業的服務以及豐富的優惠,成為玩家的理想替代選擇。現在就註冊富遊娛樂城,享受無與倫比的遊戲體驗吧! -
想要享受最刺激的線上娛樂體驗?選擇RG富遊娛樂城!
在這個數位時代,尋找適合自己的線上娛樂城變得越來越重要。如果你想在線上娛樂城找到最好玩、最受歡迎的遊戲,RG富遊絕對是你的首選!我們匯聚了多款博弈遊戲,讓您盡情享受娛樂的刺激與快感。
#### 精選遊戲類型
1. 真人百家樂
感受現場賭場的氛圍!RG富遊的真人視訊百家樂讓你與真實的荷官互動,享受高品質的遊戲體驗。無論你是老手還是新手,都能在這裡找到適合自己的節奏。
2. 電子老虎機
喜愛刺激嗎?我們提供多款熱門老虎機遊戲,如「戰神賽特」「魔龍傳奇」等,每一款都擁有精美的畫面和豐厚的獎勵,讓每次旋轉都充滿期待!
3. 體育投注
無論你是球迷還是賽事愛好者,RG富遊的體育投注平台都有你想要的。精準的賠率、廣泛的賽事選擇,讓你體驗到投注的樂趣和刺激。
4. 彩票遊戲與捕魚遊戲
隨著運氣來!不妨試試我們的棋牌遊戲和彩票遊戲,這裡有各種機會讓你體驗到不一樣的勝利快感。
#### 下載富遊APP,隨時隨地享受遊戲!
富遊娛樂城的APP支持iOS和Android設備,界面簡潔易用,內容豐富。無論你身處何地,都能輕鬆進入遊戲世界,隨心所欲享受娛樂時光。此外,我們提供即時客服支援,隨時解決你的疑問,讓你的遊戲體驗更為完美。
#### 為什麼選擇RG富遊?
- 安全可靠
RG富遊致力於為玩家提供安全可靠的遊戲環境,您的每一筆交易都受到最高的安全保障。
- 快速便捷的存提款服務
我們的存款平均時間僅需30秒,提款平均只需60秒,讓你體驗即時的快感!
- 豐富多元的遊戲選擇
超過9999款遊戲任你選擇,無論你偏好哪種娛樂方式,這裡都能滿足你的需求。
- 全天候服務
我們全年365天提供不停歇的客服支持,確保你在遊戲過程中享受到最好的服務。
### 結論
RG富遊娛樂城是您最佳的線上賭場選擇。我們不僅提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,還有安全可靠的遊戲環境和便捷的服務。立即下載APP,加入RG富遊,開始您的娛樂之旅,享受無與倫比的遊戲體驗吧! -
LEO娛樂城
LEO娛樂城:九州娛樂集團的卓越創舉與運營優勢
九州娛樂集團總部的現代化運營
九州娛樂集團的總部設於菲律賓首都馬尼拉市中心最具代表性的現代化建築「RCBC Plaza」。這座辦公大樓融合了全球領先的建築科技與安全系統,包括:
國家級資訊防護系統,確保數據安全。
樓宇自動化系統 (BAS),實現數位化管理與高效運營,包括防火系統、光纖電訊和數位監控。
九州娛樂為員工提供舒適的工作環境和專業的教育培訓,確保服務水準一流。其員工以專業知識和親切態度,為尊貴玩家帶來極致的遊戲體驗。
LEO娛樂旗下品牌與遊戲特色
九州娛樂城旗下分支包括 LEO、THA 和 KU 三個娛樂品牌。雖然品牌各自獨立運營,但都共享相同的遊戲系統與界面,提供超過數千款來自全球頂級供應商的遊戲。
這些品牌的核心特色包括:
種類繁多的遊戲:滿足不同類型玩家的需求,包括電子遊戲、體育博彩、真人娛樂等。
不斷更新的內容:通過九州獨家技術,網站內容保持新鮮,合作商可快速更新遊戲資源,確保平台競爭力。
玩家在這些平台上可以隨時找到適合自己的遊戲,享受沉浸式的娛樂體驗。
LEO娛樂城的歷史與發展
九州娛樂集團的起源可以追溯至其最早期的經營模式:「信用版」賭博平台 《天下體育球版》。儘管該模式在當時非常流行,但因高風險與財務處理複雜而逐漸被淘汰。
隨著市場需求的變化,九州娛樂轉型為現金版平台 《天下現金網》,引入了更安全、便捷的遊戲模式。這種轉變不僅提升了玩家的體驗,也使平台得以進一步發展。
如今,九州娛樂城已成為台灣博弈業界的領軍者,不僅優化了網站版面與功能,還推出了專屬手機APP,方便玩家隨時隨地進行遊戲體驗。
LEO娛樂的成功秘訣
現代化運營與技術支持:九州娛樂在系統安全與技術更新方面投入巨大資源,確保平台運營穩定可靠。
多元化遊戲體驗:通過與全球頂級遊戲供應商合作,平台提供了豐富的遊戲選擇,適應各種玩家需求。
用戶至上:專業培訓的員工以細心和熱忱態度,提供高品質服務,讓玩家倍感尊重。
不斷創新:從信用版到現金版,再到手機APP,九州娛樂始終緊跟市場趨勢,致力於打造最佳娛樂體驗。
結語
LEO娛樂城作為九州娛樂集團旗下的重要品牌,不僅繼承了集團的核心價值,更在遊戲選擇、服務品質和技術創新方面不斷提升。從最初的《天下體育球版》到如今的行業領先者,LEO娛樂見證了九州娛樂城的發展歷程,也成為博弈行業中的耀眼明星。
加入 LEO娛樂城,感受來自九州娛樂集團的專業與熱情,享受最頂級的線上博弈體驗! -
九州Leo娛樂城無法登入
Leo娛樂城無法登入?全面解析與解決指南
近期,Leo娛樂城的玩家紛紛反映登入失敗的情況,引發了廣泛的討論與擔憂。作為九州娛樂城旗下知名品牌之一,Leo娛樂城在台灣的娛樂市場中擁有大量用戶。然而,隨著九州娛樂城宣布將於2024年12月31日退出台灣市場,這一消息無疑讓玩家對資金安全與遊戲體驗產生了極大疑慮。
本文將深入探討Leo娛樂城無法登入的原因,提供解決方案,並推薦可靠的替代娛樂平台。
Leo娛樂城無法登入的三大原因
1. 帳號密碼問題
可能情況:最常見的原因是玩家輸入了錯誤的帳號或密碼,或者帳號被盜用。
解決方法:確認輸入的帳密正確,若仍無法登入,聯繫客服即可解決。
2. 網頁技術問題
可能情況:官網可能因伺服器維護或技術故障出現404錯誤,導致玩家無法登入。
解決方法:耐心等待官網修復,並清除瀏覽器快取和Cookie,或嘗試使用其他瀏覽器。
3. 九州娛樂城退出台灣市場
可能情況:隨著九州娛樂城宣布退出台灣市場,Leo娛樂城的營運也逐步停止,導致玩家無法再使用該平台。
影響:玩家可能面臨資金提取困難,需及時完成出金操作以保障自身利益。
娛樂城無法登入的緊急解決方案
核對帳號與密碼:確認輸入正確無誤,避免由於簡單疏忽造成的登入失敗。
檢查網路連線:確保網路穩定,必要時切換至更穩定的網路環境。
清除瀏覽器快取與Cookie:解決瀏覽器相關問題,恢復正常登入。
嘗試其他瀏覽器或設備:更換設備或使用不同瀏覽器,查看是否可以正常登入。
九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的原因
市場利潤有限:九州娛樂城認為台灣市場的競爭激烈且利潤有限,因此選擇退出並專注於其他海外市場。
資金生態鏈斷裂:現金交易平台出現問題,導致九州娛樂城難以維持正常運營。
母公司法律爭議:九州娛樂城母公司近年來因財務與法律問題受到高度關注,進一步影響旗下品牌的營運。
Leo娛樂城會員如何安全出金?
在九州娛樂城停止營運前,玩家需要立即完成出金操作以確保資金安全。
出金建議:
儘快登入官網提交提款申請,確保資金安全轉出。
若官網無法訪問,請嘗試聯繫客服,並保留交易證明以備進一步處理。
推薦替代平台:富遊娛樂城
隨著Leo娛樂城的退出,玩家可以考慮轉至穩定且值得信賴的替代平台,如富遊娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城的優勢
穩定可靠:擁有先進的技術和完善的資金保障機制,確保玩家的資金安全。
豐富的遊戲選擇:從電子遊戲到真人娛樂,滿足各類玩家的需求。
專屬優惠:特別為Leo會員推出等級升等計畫,並提供多樣化的專屬活動。
快速出金:高效的財務系統,讓玩家的存取款過程快速無憂。
Leo會員轉移至富遊的流程
登錄富遊官網完成註冊。
提供Leo娛樂城會員等級截圖與相關資料(如戶名、手機號碼)給富遊客服進行審核。
等待客服確認後,享受富遊娛樂城專屬的會員福利與優惠。
結語:立即加入富遊娛樂城,延續遊戲體驗!
Leo娛樂城的退出讓許多玩家感到困惑與擔憂,但選擇穩定、安全的娛樂平台是最明智的應對之道。富遊娛樂城憑藉其卓越的技術、專業的服務以及豐富的優惠,成為玩家的理想替代選擇。現在就註冊富遊娛樂城,享受無與倫比的遊戲體驗吧! -
九州娛樂城登入
Leo娛樂城無法登入?全面解析與解決指南
近期,Leo娛樂城的玩家紛紛反映登入失敗的情況,引發了廣泛的討論與擔憂。作為九州娛樂城旗下知名品牌之一,Leo娛樂城在台灣的娛樂市場中擁有大量用戶。然而,隨著九州娛樂城宣布將於2024年12月31日退出台灣市場,這一消息無疑讓玩家對資金安全與遊戲體驗產生了極大疑慮。
本文將深入探討Leo娛樂城無法登入的原因,提供解決方案,並推薦可靠的替代娛樂平台。
Leo娛樂城無法登入的三大原因
1. 帳號密碼問題
可能情況:最常見的原因是玩家輸入了錯誤的帳號或密碼,或者帳號被盜用。
解決方法:確認輸入的帳密正確,若仍無法登入,聯繫客服即可解決。
2. 網頁技術問題
可能情況:官網可能因伺服器維護或技術故障出現404錯誤,導致玩家無法登入。
解決方法:耐心等待官網修復,並清除瀏覽器快取和Cookie,或嘗試使用其他瀏覽器。
3. 九州娛樂城退出台灣市場
可能情況:隨著九州娛樂城宣布退出台灣市場,Leo娛樂城的營運也逐步停止,導致玩家無法再使用該平台。
影響:玩家可能面臨資金提取困難,需及時完成出金操作以保障自身利益。
娛樂城無法登入的緊急解決方案
核對帳號與密碼:確認輸入正確無誤,避免由於簡單疏忽造成的登入失敗。
檢查網路連線:確保網路穩定,必要時切換至更穩定的網路環境。
清除瀏覽器快取與Cookie:解決瀏覽器相關問題,恢復正常登入。
嘗試其他瀏覽器或設備:更換設備或使用不同瀏覽器,查看是否可以正常登入。
九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的原因
市場利潤有限:九州娛樂城認為台灣市場的競爭激烈且利潤有限,因此選擇退出並專注於其他海外市場。
資金生態鏈斷裂:現金交易平台出現問題,導致九州娛樂城難以維持正常運營。
母公司法律爭議:九州娛樂城母公司近年來因財務與法律問題受到高度關注,進一步影響旗下品牌的營運。
Leo娛樂城會員如何安全出金?
在九州娛樂城停止營運前,玩家需要立即完成出金操作以確保資金安全。
出金建議:
儘快登入官網提交提款申請,確保資金安全轉出。
若官網無法訪問,請嘗試聯繫客服,並保留交易證明以備進一步處理。
推薦替代平台:富遊娛樂城
隨著Leo娛樂城的退出,玩家可以考慮轉至穩定且值得信賴的替代平台,如富遊娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城的優勢
穩定可靠:擁有先進的技術和完善的資金保障機制,確保玩家的資金安全。
豐富的遊戲選擇:從電子遊戲到真人娛樂,滿足各類玩家的需求。
專屬優惠:特別為Leo會員推出等級升等計畫,並提供多樣化的專屬活動。
快速出金:高效的財務系統,讓玩家的存取款過程快速無憂。
Leo會員轉移至富遊的流程
登錄富遊官網完成註冊。
提供Leo娛樂城會員等級截圖與相關資料(如戶名、手機號碼)給富遊客服進行審核。
等待客服確認後,享受富遊娛樂城專屬的會員福利與優惠。
結語:立即加入富遊娛樂城,延續遊戲體驗!
Leo娛樂城的退出讓許多玩家感到困惑與擔憂,但選擇穩定、安全的娛樂平台是最明智的應對之道。富遊娛樂城憑藉其卓越的技術、專業的服務以及豐富的優惠,成為玩家的理想替代選擇。現在就註冊富遊娛樂城,享受無與倫比的遊戲體驗吧! -
Leo娛樂城無法登入?全面解析與解決指南
近期,Leo娛樂城的玩家紛紛反映登入失敗的情況,引發了廣泛的討論與擔憂。作為九州娛樂城旗下知名品牌之一,Leo娛樂城在台灣的娛樂市場中擁有大量用戶。然而,隨著九州娛樂城宣布將於2024年12月31日退出台灣市場,這一消息無疑讓玩家對資金安全與遊戲體驗產生了極大疑慮。
本文將深入探討Leo娛樂城無法登入的原因,提供解決方案,並推薦可靠的替代娛樂平台。
Leo娛樂城無法登入的三大原因
1. 帳號密碼問題
可能情況:最常見的原因是玩家輸入了錯誤的帳號或密碼,或者帳號被盜用。
解決方法:確認輸入的帳密正確,若仍無法登入,聯繫客服即可解決。
2. 網頁技術問題
可能情況:官網可能因伺服器維護或技術故障出現404錯誤,導致玩家無法登入。
解決方法:耐心等待官網修復,並清除瀏覽器快取和Cookie,或嘗試使用其他瀏覽器。
3. 九州娛樂城退出台灣市場
可能情況:隨著九州娛樂城宣布退出台灣市場,Leo娛樂城的營運也逐步停止,導致玩家無法再使用該平台。
影響:玩家可能面臨資金提取困難,需及時完成出金操作以保障自身利益。
娛樂城無法登入的緊急解決方案
核對帳號與密碼:確認輸入正確無誤,避免由於簡單疏忽造成的登入失敗。
檢查網路連線:確保網路穩定,必要時切換至更穩定的網路環境。
清除瀏覽器快取與Cookie:解決瀏覽器相關問題,恢復正常登入。
嘗試其他瀏覽器或設備:更換設備或使用不同瀏覽器,查看是否可以正常登入。
九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的原因
市場利潤有限:九州娛樂城認為台灣市場的競爭激烈且利潤有限,因此選擇退出並專注於其他海外市場。
資金生態鏈斷裂:現金交易平台出現問題,導致九州娛樂城難以維持正常運營。
母公司法律爭議:九州娛樂城母公司近年來因財務與法律問題受到高度關注,進一步影響旗下品牌的營運。
Leo娛樂城會員如何安全出金?
在九州娛樂城停止營運前,玩家需要立即完成出金操作以確保資金安全。
出金建議:
儘快登入官網提交提款申請,確保資金安全轉出。
若官網無法訪問,請嘗試聯繫客服,並保留交易證明以備進一步處理。
推薦替代平台:富遊娛樂城
隨著Leo娛樂城的退出,玩家可以考慮轉至穩定且值得信賴的替代平台,如富遊娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城的優勢
穩定可靠:擁有先進的技術和完善的資金保障機制,確保玩家的資金安全。
豐富的遊戲選擇:從電子遊戲到真人娛樂,滿足各類玩家的需求。
專屬優惠:特別為Leo會員推出等級升等計畫,並提供多樣化的專屬活動。
快速出金:高效的財務系統,讓玩家的存取款過程快速無憂。
Leo會員轉移至富遊的流程
登錄富遊官網完成註冊。
提供Leo娛樂城會員等級截圖與相關資料(如戶名、手機號碼)給富遊客服進行審核。
等待客服確認後,享受富遊娛樂城專屬的會員福利與優惠。
結語:立即加入富遊娛樂城,延續遊戲體驗!
Leo娛樂城的退出讓許多玩家感到困惑與擔憂,但選擇穩定、安全的娛樂平台是最明智的應對之道。富遊娛樂城憑藉其卓越的技術、專業的服務以及豐富的優惠,成為玩家的理想替代選擇。現在就註冊富遊娛樂城,享受無與倫比的遊戲體驗吧! -
娛樂城
想要享受最刺激的線上娛樂體驗?選擇RG富遊娛樂城!
在這個數位時代,尋找適合自己的線上娛樂城變得越來越重要。如果你想在線上娛樂城找到最好玩、最受歡迎的遊戲,RG富遊絕對是你的首選!我們匯聚了多款博弈遊戲,讓您盡情享受娛樂的刺激與快感。
#### 精選遊戲類型
1. 真人百家樂
感受現場賭場的氛圍!RG富遊的真人視訊百家樂讓你與真實的荷官互動,享受高品質的遊戲體驗。無論你是老手還是新手,都能在這裡找到適合自己的節奏。
2. 電子老虎機
喜愛刺激嗎?我們提供多款熱門老虎機遊戲,如「戰神賽特」「魔龍傳奇」等,每一款都擁有精美的畫面和豐厚的獎勵,讓每次旋轉都充滿期待!
3. 體育投注
無論你是球迷還是賽事愛好者,RG富遊的體育投注平台都有你想要的。精準的賠率、廣泛的賽事選擇,讓你體驗到投注的樂趣和刺激。
4. 彩票遊戲與捕魚遊戲
隨著運氣來!不妨試試我們的棋牌遊戲和彩票遊戲,這裡有各種機會讓你體驗到不一樣的勝利快感。
#### 下載富遊APP,隨時隨地享受遊戲!
富遊娛樂城的APP支持iOS和Android設備,界面簡潔易用,內容豐富。無論你身處何地,都能輕鬆進入遊戲世界,隨心所欲享受娛樂時光。此外,我們提供即時客服支援,隨時解決你的疑問,讓你的遊戲體驗更為完美。
#### 為什麼選擇RG富遊?
- 安全可靠
RG富遊致力於為玩家提供安全可靠的遊戲環境,您的每一筆交易都受到最高的安全保障。
- 快速便捷的存提款服務
我們的存款平均時間僅需30秒,提款平均只需60秒,讓你體驗即時的快感!
- 豐富多元的遊戲選擇
超過9999款遊戲任你選擇,無論你偏好哪種娛樂方式,這裡都能滿足你的需求。
- 全天候服務
我們全年365天提供不停歇的客服支持,確保你在遊戲過程中享受到最好的服務。
### 結論
RG富遊娛樂城是您最佳的線上賭場選擇。我們不僅提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,還有安全可靠的遊戲環境和便捷的服務。立即下載APP,加入RG富遊,開始您的娛樂之旅,享受無與倫比的遊戲體驗吧! -
LEO娛樂城
LEO娛樂城:九州娛樂集團的卓越創舉與運營優勢
九州娛樂集團總部的現代化運營
九州娛樂集團的總部設於菲律賓首都馬尼拉市中心最具代表性的現代化建築「RCBC Plaza」。這座辦公大樓融合了全球領先的建築科技與安全系統,包括:
國家級資訊防護系統,確保數據安全。
樓宇自動化系統 (BAS),實現數位化管理與高效運營,包括防火系統、光纖電訊和數位監控。
九州娛樂為員工提供舒適的工作環境和專業的教育培訓,確保服務水準一流。其員工以專業知識和親切態度,為尊貴玩家帶來極致的遊戲體驗。
LEO娛樂旗下品牌與遊戲特色
九州娛樂城旗下分支包括 LEO、THA 和 KU 三個娛樂品牌。雖然品牌各自獨立運營,但都共享相同的遊戲系統與界面,提供超過數千款來自全球頂級供應商的遊戲。
這些品牌的核心特色包括:
種類繁多的遊戲:滿足不同類型玩家的需求,包括電子遊戲、體育博彩、真人娛樂等。
不斷更新的內容:通過九州獨家技術,網站內容保持新鮮,合作商可快速更新遊戲資源,確保平台競爭力。
玩家在這些平台上可以隨時找到適合自己的遊戲,享受沉浸式的娛樂體驗。
LEO娛樂城的歷史與發展
九州娛樂集團的起源可以追溯至其最早期的經營模式:「信用版」賭博平台 《天下體育球版》。儘管該模式在當時非常流行,但因高風險與財務處理複雜而逐漸被淘汰。
隨著市場需求的變化,九州娛樂轉型為現金版平台 《天下現金網》,引入了更安全、便捷的遊戲模式。這種轉變不僅提升了玩家的體驗,也使平台得以進一步發展。
如今,九州娛樂城已成為台灣博弈業界的領軍者,不僅優化了網站版面與功能,還推出了專屬手機APP,方便玩家隨時隨地進行遊戲體驗。
LEO娛樂的成功秘訣
現代化運營與技術支持:九州娛樂在系統安全與技術更新方面投入巨大資源,確保平台運營穩定可靠。
多元化遊戲體驗:通過與全球頂級遊戲供應商合作,平台提供了豐富的遊戲選擇,適應各種玩家需求。
用戶至上:專業培訓的員工以細心和熱忱態度,提供高品質服務,讓玩家倍感尊重。
不斷創新:從信用版到現金版,再到手機APP,九州娛樂始終緊跟市場趨勢,致力於打造最佳娛樂體驗。
結語
LEO娛樂城作為九州娛樂集團旗下的重要品牌,不僅繼承了集團的核心價值,更在遊戲選擇、服務品質和技術創新方面不斷提升。從最初的《天下體育球版》到如今的行業領先者,LEO娛樂見證了九州娛樂城的發展歷程,也成為博弈行業中的耀眼明星。
加入 LEO娛樂城,感受來自九州娛樂集團的專業與熱情,享受最頂級的線上博弈體驗! -
Leo娛樂城無法登入?全面解析與解決指南
近期,Leo娛樂城的玩家紛紛反映登入失敗的情況,引發了廣泛的討論與擔憂。作為九州娛樂城旗下知名品牌之一,Leo娛樂城在台灣的娛樂市場中擁有大量用戶。然而,隨著九州娛樂城宣布將於2024年12月31日退出台灣市場,這一消息無疑讓玩家對資金安全與遊戲體驗產生了極大疑慮。
本文將深入探討Leo娛樂城無法登入的原因,提供解決方案,並推薦可靠的替代娛樂平台。
Leo娛樂城無法登入的三大原因
1. 帳號密碼問題
可能情況:最常見的原因是玩家輸入了錯誤的帳號或密碼,或者帳號被盜用。
解決方法:確認輸入的帳密正確,若仍無法登入,聯繫客服即可解決。
2. 網頁技術問題
可能情況:官網可能因伺服器維護或技術故障出現404錯誤,導致玩家無法登入。
解決方法:耐心等待官網修復,並清除瀏覽器快取和Cookie,或嘗試使用其他瀏覽器。
3. 九州娛樂城退出台灣市場
可能情況:隨著九州娛樂城宣布退出台灣市場,Leo娛樂城的營運也逐步停止,導致玩家無法再使用該平台。
影響:玩家可能面臨資金提取困難,需及時完成出金操作以保障自身利益。
娛樂城無法登入的緊急解決方案
核對帳號與密碼:確認輸入正確無誤,避免由於簡單疏忽造成的登入失敗。
檢查網路連線:確保網路穩定,必要時切換至更穩定的網路環境。
清除瀏覽器快取與Cookie:解決瀏覽器相關問題,恢復正常登入。
嘗試其他瀏覽器或設備:更換設備或使用不同瀏覽器,查看是否可以正常登入。
九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的原因
市場利潤有限:九州娛樂城認為台灣市場的競爭激烈且利潤有限,因此選擇退出並專注於其他海外市場。
資金生態鏈斷裂:現金交易平台出現問題,導致九州娛樂城難以維持正常運營。
母公司法律爭議:九州娛樂城母公司近年來因財務與法律問題受到高度關注,進一步影響旗下品牌的營運。
Leo娛樂城會員如何安全出金?
在九州娛樂城停止營運前,玩家需要立即完成出金操作以確保資金安全。
出金建議:
儘快登入官網提交提款申請,確保資金安全轉出。
若官網無法訪問,請嘗試聯繫客服,並保留交易證明以備進一步處理。
推薦替代平台:富遊娛樂城
隨著Leo娛樂城的退出,玩家可以考慮轉至穩定且值得信賴的替代平台,如富遊娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城的優勢
穩定可靠:擁有先進的技術和完善的資金保障機制,確保玩家的資金安全。
豐富的遊戲選擇:從電子遊戲到真人娛樂,滿足各類玩家的需求。
專屬優惠:特別為Leo會員推出等級升等計畫,並提供多樣化的專屬活動。
快速出金:高效的財務系統,讓玩家的存取款過程快速無憂。
Leo會員轉移至富遊的流程
登錄富遊官網完成註冊。
提供Leo娛樂城會員等級截圖與相關資料(如戶名、手機號碼)給富遊客服進行審核。
等待客服確認後,享受富遊娛樂城專屬的會員福利與優惠。
結語:立即加入富遊娛樂城,延續遊戲體驗!
Leo娛樂城的退出讓許多玩家感到困惑與擔憂,但選擇穩定、安全的娛樂平台是最明智的應對之道。富遊娛樂城憑藉其卓越的技術、專業的服務以及豐富的優惠,成為玩家的理想替代選擇。現在就註冊富遊娛樂城,享受無與倫比的遊戲體驗吧! -
九州娛樂城登入
Leo娛樂城無法登入?全面解析與解決指南
近期,Leo娛樂城的玩家紛紛反映登入失敗的情況,引發了廣泛的討論與擔憂。作為九州娛樂城旗下知名品牌之一,Leo娛樂城在台灣的娛樂市場中擁有大量用戶。然而,隨著九州娛樂城宣布將於2024年12月31日退出台灣市場,這一消息無疑讓玩家對資金安全與遊戲體驗產生了極大疑慮。
本文將深入探討Leo娛樂城無法登入的原因,提供解決方案,並推薦可靠的替代娛樂平台。
Leo娛樂城無法登入的三大原因
1. 帳號密碼問題
可能情況:最常見的原因是玩家輸入了錯誤的帳號或密碼,或者帳號被盜用。
解決方法:確認輸入的帳密正確,若仍無法登入,聯繫客服即可解決。
2. 網頁技術問題
可能情況:官網可能因伺服器維護或技術故障出現404錯誤,導致玩家無法登入。
解決方法:耐心等待官網修復,並清除瀏覽器快取和Cookie,或嘗試使用其他瀏覽器。
3. 九州娛樂城退出台灣市場
可能情況:隨著九州娛樂城宣布退出台灣市場,Leo娛樂城的營運也逐步停止,導致玩家無法再使用該平台。
影響:玩家可能面臨資金提取困難,需及時完成出金操作以保障自身利益。
娛樂城無法登入的緊急解決方案
核對帳號與密碼:確認輸入正確無誤,避免由於簡單疏忽造成的登入失敗。
檢查網路連線:確保網路穩定,必要時切換至更穩定的網路環境。
清除瀏覽器快取與Cookie:解決瀏覽器相關問題,恢復正常登入。
嘗試其他瀏覽器或設備:更換設備或使用不同瀏覽器,查看是否可以正常登入。
九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的原因
市場利潤有限:九州娛樂城認為台灣市場的競爭激烈且利潤有限,因此選擇退出並專注於其他海外市場。
資金生態鏈斷裂:現金交易平台出現問題,導致九州娛樂城難以維持正常運營。
母公司法律爭議:九州娛樂城母公司近年來因財務與法律問題受到高度關注,進一步影響旗下品牌的營運。
Leo娛樂城會員如何安全出金?
在九州娛樂城停止營運前,玩家需要立即完成出金操作以確保資金安全。
出金建議:
儘快登入官網提交提款申請,確保資金安全轉出。
若官網無法訪問,請嘗試聯繫客服,並保留交易證明以備進一步處理。
推薦替代平台:富遊娛樂城
隨著Leo娛樂城的退出,玩家可以考慮轉至穩定且值得信賴的替代平台,如富遊娛樂城。
富遊娛樂城的優勢
穩定可靠:擁有先進的技術和完善的資金保障機制,確保玩家的資金安全。
豐富的遊戲選擇:從電子遊戲到真人娛樂,滿足各類玩家的需求。
專屬優惠:特別為Leo會員推出等級升等計畫,並提供多樣化的專屬活動。
快速出金:高效的財務系統,讓玩家的存取款過程快速無憂。
Leo會員轉移至富遊的流程
登錄富遊官網完成註冊。
提供Leo娛樂城會員等級截圖與相關資料(如戶名、手機號碼)給富遊客服進行審核。
等待客服確認後,享受富遊娛樂城專屬的會員福利與優惠。
結語:立即加入富遊娛樂城,延續遊戲體驗!
Leo娛樂城的退出讓許多玩家感到困惑與擔憂,但選擇穩定、安全的娛樂平台是最明智的應對之道。富遊娛樂城憑藉其卓越的技術、專業的服務以及豐富的優惠,成為玩家的理想替代選擇。現在就註冊富遊娛樂城,享受無與倫比的遊戲體驗吧! -
滿天星娛樂城:全方位的線上娛樂體驗
滿天星娛樂城作為九州娛樂城旗下品牌之一,是玩家心目中備受信賴的線上娛樂平台。不僅提供豐富的遊戲選擇和吸引人的優惠,還以其合法營運的背景和快速出金的保證,成為台灣玩家的首選娛樂城之一。
滿天星娛樂城的特色與優勢
1. 合法營運,安全可靠
滿天星娛樂城持有三大國際娛樂執照,包括:
菲律賓 PAGCOR 監督競猜牌照
BVI 認證
馬爾他 MGA 認證
這些執照展現了平台的資本實力與合法性,讓玩家能夠安心享受遊戲,完全不用擔心出金問題。
2. 高品質遊戲與豐富優惠
滿天星娛樂城與九州集團旗下的LEO、THA娛樂城一樣,提供一流的遊戲品質和多樣化的優惠。
熱門遊戲推薦:電子老虎機、真人直播、運彩投注、今彩539等,滿足各類玩家需求。
優惠活動:定期推出限時回饋活動,讓玩家在遊戲中獲得更多額外收益。
3. 快速出金與高效服務
滿天星娛樂城採用先進的財務系統,確保存提款快速、安全,讓玩家能夠專注於享受遊戲,而無需擔心資金問題。專業的客服團隊24小時在線,提供即時支援。
4. 多平台兼容的APP
滿天星娛樂城提供設計貼合玩家需求的手機APP,適用於iOS與Android系統。玩家可以隨時隨地快速登入遊玩,體驗無與倫比的娛樂快感。
熱門遊戲類型一覽
滿天星娛樂城為玩家提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,滿足不同興趣和需求:
真人直播:感受真實賭場氛圍,與真人荷官互動,體驗沉浸式娛樂。
電子老虎機:多款經典與創新機台,讓玩家享受刺激的遊戲過程。
運彩投注:涵蓋世界盃、棒球、籃球等多項運動賽事,提供即時投注與直播功能。
彩票遊戲:包括今彩539、富遊彩票等,適合熱衷於彩券的玩家。
滿天星娛樂城常見問題解答
Q1. 滿天星娛樂城是否提供APP下載?
是的,滿天星娛樂城提供專屬的手機APP,支援iOS和Android系統。玩家可透過APP快速登入,隨時享受遊戲。
Q2. 滿天星娛樂城是否合法?
滿天星娛樂城擁有多項國際認證,為合法經營的線上娛樂城,並保證玩家資金的安全性與遊戲的公平性。
Q3. 無法登入滿天星娛樂城該怎麼辦?
如遇到無法登入的情況,建議玩家檢查網路狀況或聯繫24小時客服團隊獲取即時協助。
立即加入滿天星娛樂城,享受最佳娛樂體驗!
滿天星娛樂城以合法、安全、快速的服務,搭配豐富的遊戲選擇和優惠,為玩家打造出獨一無二的線上娛樂體驗。不論您是新手還是老手,都能在滿天星找到屬於自己的遊戲樂趣。現在就下載APP,隨時隨地開始您的娛樂之旅! -
LEO娛樂城無法登入? 九州娛樂倒了? 富遊推出無痛轉移VIP優惠
LEO娛樂城無法登入免驚!推薦RG富遊更穩定、玩的更安心!
只要是玩過線上娛樂城的玩家,一定都對Leo娛樂城不陌生,近期Leo娛樂城無法登入的狀況越來越頻繁,是因為九州娛樂城與旗下品牌將在 2024/12/31 結束營業!
由於九州娛樂城旗下擁有leo娛樂城、THA娛樂城等品牌,這波風暴也讓許多玩家人心惶惶,擔心自己的遊戲權益受損,在文章的最後我們也提供了解決方案,趕快往下看!
九州娛樂城倒閉 ? 退出台灣娛樂市場?為何 ?
最近許多玩家發現 leo娛樂城無法登入,甚至傳出九州娛樂城要退出台灣的消息!雖然官方尚未發布正式聲明,但多方消息指出,九州娛樂城 (包含THA娛樂城、leo娛樂城) 正在逐步退出台灣市場。這可能是多重因素共同作用的結果:
退出台灣市場,尋求其他發展空間
九州娛樂認為台灣市場太小,品牌之間又過於競爭,市場規模有限,九州旗下其KU體育甚至贊助過足球五大聯賽,展現雄厚實力,促使九州娛樂城將目光投向海外。
畢竟,海外市場人口基數更大,獲利潛力也更為可觀。LEO娛樂城在台灣一個月就能獲利一億,進軍海外後的收益想必更加驚人。
金流問題、警界醜聞成導火線
LEO娛樂城高度仰賴金流公司運作,近期爆發的陳政谷案件揭露其旗下公司利用第三方支付協助母公司九州洗錢。
案情更指向警界內鬼,前台中刑大隊長林明佐涉嫌收賄超過4451萬元,為九州通風報信。 九州娛樂城曾出現凌晨時段無法儲值的狀況,很可能與警方查緝行動有關。
九州娛樂的新聞事件頻傳
LEO是九州集團底下的,陳政谷被抓之後,事情鬧得很大,為了避風頭,乾脆退出台灣也很合理。
這個說法也被推算也被網友認為有高度可能,不過也有人傳說其他幹部有接手的可能,至少沒辦法完全的說死九州會採取什麼行動。
leo娛樂城無法登入的問題,或許只是冰山一角,背後可能隱藏著更深層的原因。無論如何,九州娛樂城退出台灣市場,對玩家來說都是一個警訊。
九州娛樂城宣布12/31結束營業!玩家請停止儲值、立刻提款
九州娛樂城官方宣佈,近期旗下 THA、Leo 娛樂城無法登入,是因為九州集團將正式在 2024/12/31 中午 12:00 結束營業,退出台灣市場。
在這邊提醒玩家們立即停止存款動作,並且馬上將帳戶內的資金提領出來,避免您的權益受到損害!
LEO娛樂城無法登入? 九州娛樂倒了? 富遊推出無痛轉移VIP優惠
九州娛樂城宣布在12/31結束營業
告別Leo娛樂城無法登入煩惱!玩家無痛轉移至富遊,享更多優惠!
面對leo娛樂城無法登入的窘境,以及九州娛樂城的不確定性,玩家們需要一個安全可靠的新選擇!富遊娛樂城是您最佳的選擇,我們提供:
穩定安全保證出金: 穩定安全,保證出金! 擁有合法牌照和完善的監管機制,保障您的資金安全。
豐富多元的遊戲: 提供各式各樣的熱門遊戲,包括真人 casino、體育博彩、電子遊戲、彩票等等,滿足玩家的不同需求。
優渥的優惠活動: 新會員享有豐厚首存紅利,還有不定期的優惠活動和返水獎勵,讓您玩得更盡興!
24小時專業客服: 隨時為您解答問題,提供貼心服務。
立即註冊
特別優惠: 針對THA和LEO會員,富遊娛樂城推出獨家福利!
只要您是THA或LEO的會員,即可在富遊娛樂城直接升等到相對應的等級,並享有更高的反水、每週紅包和生日禮金!
立即加入富遊娛樂城,享受更優渥的回饋和更安心的保障!
以下是不同階級 VIP 的轉換福利與說明:
福利項目 / VIP階級 大神 金鑽 鉑金 黃金
每週紅包 2388 988 288 188
生日禮金 8888 3888 1080 688
返水 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4
無論個人或團體,如有任何濫用本公司優惠的行為,本公司有權取消及收回獎金。
所有活動優惠都是特別為玩家而設立,在玩家註冊資訊有爭議時,為確保雙方利益,杜絕身份盜用行為,本公司有權要求玩家提供充足資訊,並以各種方式辨別玩家是否符合資格享有活動優惠。
本公司在會員有重複申請帳號行為時,有權取消及收回獎金。每位玩家、每一住址、每一電子郵箱、每一電話號碼、相同支付卡/信用卡號碼及共享電腦環境(例如網咖、其他公用網絡、公用電腦)只能擁有一個活動優惠資格。
每週限時紅包:會員在上週有過至少1次的存款記錄,每週一中午自動發放(1倍流水即可託售),限時48小時內領取! 每週至少存款要求:黃金富遊 1,000 點,鉑金富遊 1,500點,金鑽富遊 2,500點,大神富遊 5,000點 (存款計算週期:每週一 12:00 至下週一 11:59)
生日禮金:會員在註冊三個月內過生日,今年將不能領取生日禮金。另註冊時間大於三個月的會員需在生日當月找遊戲客服領取,每年可領取一次,需提供身分證明文件核實(1倍流水即可託售)
活動如有任何異動,本公司有權在任何時間修改、暫停或取消優惠活動,無需特別通知並保留本活動最終解釋權。
轉換平台申請辦法:提供螢幕錄影原平台層級介面到戶名、手機等資訊,傳送給富遊客服進行審核。
富遊娛樂城,值得您信賴的線上娛樂平台!
我們深知玩家選擇娛樂城的首要考量是安全和信譽。富遊娛樂城以誠信為本,致力於為玩家打造一個公平、公正、透明的遊戲環境。告別leo娛樂城無法登入的煩惱,立即加入富有娛樂城,體驗最優質的線上娛樂體驗! -
滿天星娛樂城
滿天星娛樂城:全方位的線上娛樂體驗
滿天星娛樂城作為九州娛樂城旗下品牌之一,是玩家心目中備受信賴的線上娛樂平台。不僅提供豐富的遊戲選擇和吸引人的優惠,還以其合法營運的背景和快速出金的保證,成為台灣玩家的首選娛樂城之一。
滿天星娛樂城的特色與優勢
1. 合法營運,安全可靠
滿天星娛樂城持有三大國際娛樂執照,包括:
菲律賓 PAGCOR 監督競猜牌照
BVI 認證
馬爾他 MGA 認證
這些執照展現了平台的資本實力與合法性,讓玩家能夠安心享受遊戲,完全不用擔心出金問題。
2. 高品質遊戲與豐富優惠
滿天星娛樂城與九州集團旗下的LEO、THA娛樂城一樣,提供一流的遊戲品質和多樣化的優惠。
熱門遊戲推薦:電子老虎機、真人直播、運彩投注、今彩539等,滿足各類玩家需求。
優惠活動:定期推出限時回饋活動,讓玩家在遊戲中獲得更多額外收益。
3. 快速出金與高效服務
滿天星娛樂城採用先進的財務系統,確保存提款快速、安全,讓玩家能夠專注於享受遊戲,而無需擔心資金問題。專業的客服團隊24小時在線,提供即時支援。
4. 多平台兼容的APP
滿天星娛樂城提供設計貼合玩家需求的手機APP,適用於iOS與Android系統。玩家可以隨時隨地快速登入遊玩,體驗無與倫比的娛樂快感。
熱門遊戲類型一覽
滿天星娛樂城為玩家提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,滿足不同興趣和需求:
真人直播:感受真實賭場氛圍,與真人荷官互動,體驗沉浸式娛樂。
電子老虎機:多款經典與創新機台,讓玩家享受刺激的遊戲過程。
運彩投注:涵蓋世界盃、棒球、籃球等多項運動賽事,提供即時投注與直播功能。
彩票遊戲:包括今彩539、富遊彩票等,適合熱衷於彩券的玩家。
滿天星娛樂城常見問題解答
Q1. 滿天星娛樂城是否提供APP下載?
是的,滿天星娛樂城提供專屬的手機APP,支援iOS和Android系統。玩家可透過APP快速登入,隨時享受遊戲。
Q2. 滿天星娛樂城是否合法?
滿天星娛樂城擁有多項國際認證,為合法經營的線上娛樂城,並保證玩家資金的安全性與遊戲的公平性。
Q3. 無法登入滿天星娛樂城該怎麼辦?
如遇到無法登入的情況,建議玩家檢查網路狀況或聯繫24小時客服團隊獲取即時協助。
立即加入滿天星娛樂城,享受最佳娛樂體驗!
滿天星娛樂城以合法、安全、快速的服務,搭配豐富的遊戲選擇和優惠,為玩家打造出獨一無二的線上娛樂體驗。不論您是新手還是老手,都能在滿天星找到屬於自己的遊戲樂趣。現在就下載APP,隨時隨地開始您的娛樂之旅! -
娛樂城
LEO娛樂城無法登入? 九州娛樂倒了? 富遊推出無痛轉移VIP優惠
LEO娛樂城無法登入免驚!推薦RG富遊更穩定、玩的更安心!
只要是玩過線上娛樂城的玩家,一定都對Leo娛樂城不陌生,近期Leo娛樂城無法登入的狀況越來越頻繁,是因為九州娛樂城與旗下品牌將在 2024/12/31 結束營業!
由於九州娛樂城旗下擁有leo娛樂城、THA娛樂城等品牌,這波風暴也讓許多玩家人心惶惶,擔心自己的遊戲權益受損,在文章的最後我們也提供了解決方案,趕快往下看!
九州娛樂城倒閉 ? 退出台灣娛樂市場?為何 ?
最近許多玩家發現 leo娛樂城無法登入,甚至傳出九州娛樂城要退出台灣的消息!雖然官方尚未發布正式聲明,但多方消息指出,九州娛樂城 (包含THA娛樂城、leo娛樂城) 正在逐步退出台灣市場。這可能是多重因素共同作用的結果:
退出台灣市場,尋求其他發展空間
九州娛樂認為台灣市場太小,品牌之間又過於競爭,市場規模有限,九州旗下其KU體育甚至贊助過足球五大聯賽,展現雄厚實力,促使九州娛樂城將目光投向海外。
畢竟,海外市場人口基數更大,獲利潛力也更為可觀。LEO娛樂城在台灣一個月就能獲利一億,進軍海外後的收益想必更加驚人。
金流問題、警界醜聞成導火線
LEO娛樂城高度仰賴金流公司運作,近期爆發的陳政谷案件揭露其旗下公司利用第三方支付協助母公司九州洗錢。
案情更指向警界內鬼,前台中刑大隊長林明佐涉嫌收賄超過4451萬元,為九州通風報信。 九州娛樂城曾出現凌晨時段無法儲值的狀況,很可能與警方查緝行動有關。
九州娛樂的新聞事件頻傳
LEO是九州集團底下的,陳政谷被抓之後,事情鬧得很大,為了避風頭,乾脆退出台灣也很合理。
這個說法也被推算也被網友認為有高度可能,不過也有人傳說其他幹部有接手的可能,至少沒辦法完全的說死九州會採取什麼行動。
leo娛樂城無法登入的問題,或許只是冰山一角,背後可能隱藏著更深層的原因。無論如何,九州娛樂城退出台灣市場,對玩家來說都是一個警訊。
九州娛樂城宣布12/31結束營業!玩家請停止儲值、立刻提款
九州娛樂城官方宣佈,近期旗下 THA、Leo 娛樂城無法登入,是因為九州集團將正式在 2024/12/31 中午 12:00 結束營業,退出台灣市場。
在這邊提醒玩家們立即停止存款動作,並且馬上將帳戶內的資金提領出來,避免您的權益受到損害!
LEO娛樂城無法登入? 九州娛樂倒了? 富遊推出無痛轉移VIP優惠
九州娛樂城宣布在12/31結束營業
告別Leo娛樂城無法登入煩惱!玩家無痛轉移至富遊,享更多優惠!
面對leo娛樂城無法登入的窘境,以及九州娛樂城的不確定性,玩家們需要一個安全可靠的新選擇!富遊娛樂城是您最佳的選擇,我們提供:
穩定安全保證出金: 穩定安全,保證出金! 擁有合法牌照和完善的監管機制,保障您的資金安全。
豐富多元的遊戲: 提供各式各樣的熱門遊戲,包括真人 casino、體育博彩、電子遊戲、彩票等等,滿足玩家的不同需求。
優渥的優惠活動: 新會員享有豐厚首存紅利,還有不定期的優惠活動和返水獎勵,讓您玩得更盡興!
24小時專業客服: 隨時為您解答問題,提供貼心服務。
立即註冊
特別優惠: 針對THA和LEO會員,富遊娛樂城推出獨家福利!
只要您是THA或LEO的會員,即可在富遊娛樂城直接升等到相對應的等級,並享有更高的反水、每週紅包和生日禮金!
立即加入富遊娛樂城,享受更優渥的回饋和更安心的保障!
以下是不同階級 VIP 的轉換福利與說明:
福利項目 / VIP階級 大神 金鑽 鉑金 黃金
每週紅包 2388 988 288 188
生日禮金 8888 3888 1080 688
返水 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4
無論個人或團體,如有任何濫用本公司優惠的行為,本公司有權取消及收回獎金。
所有活動優惠都是特別為玩家而設立,在玩家註冊資訊有爭議時,為確保雙方利益,杜絕身份盜用行為,本公司有權要求玩家提供充足資訊,並以各種方式辨別玩家是否符合資格享有活動優惠。
本公司在會員有重複申請帳號行為時,有權取消及收回獎金。每位玩家、每一住址、每一電子郵箱、每一電話號碼、相同支付卡/信用卡號碼及共享電腦環境(例如網咖、其他公用網絡、公用電腦)只能擁有一個活動優惠資格。
每週限時紅包:會員在上週有過至少1次的存款記錄,每週一中午自動發放(1倍流水即可託售),限時48小時內領取! 每週至少存款要求:黃金富遊 1,000 點,鉑金富遊 1,500點,金鑽富遊 2,500點,大神富遊 5,000點 (存款計算週期:每週一 12:00 至下週一 11:59)
生日禮金:會員在註冊三個月內過生日,今年將不能領取生日禮金。另註冊時間大於三個月的會員需在生日當月找遊戲客服領取,每年可領取一次,需提供身分證明文件核實(1倍流水即可託售)
活動如有任何異動,本公司有權在任何時間修改、暫停或取消優惠活動,無需特別通知並保留本活動最終解釋權。
轉換平台申請辦法:提供螢幕錄影原平台層級介面到戶名、手機等資訊,傳送給富遊客服進行審核。
富遊娛樂城,值得您信賴的線上娛樂平台!
我們深知玩家選擇娛樂城的首要考量是安全和信譽。富遊娛樂城以誠信為本,致力於為玩家打造一個公平、公正、透明的遊戲環境。告別leo娛樂城無法登入的煩惱,立即加入富有娛樂城,體驗最優質的線上娛樂體驗! -
娛樂城
富遊娛樂城:台灣線上賭場的創新選擇
在台灣的線上娛樂市場中,富遊娛樂城憑藉其優質的服務和多樣化的娛樂選項,迅速成為新一代玩家的首選。既有刺激的遊戲體驗,又提供了一系列具有吸引力的優惠,富遊娛樂城無疑是追求樂趣的玩家們理想的地方。
#### 優勢與特色
1. 多樣化的遊戲選擇
富遊娛樂城提供了豐富的遊戲種類,包括電子老虎機、真人百家樂、運彩投注等。不論你是老虎機的愛好者,還是熱衷於真人賭桌的玩家,這裡都能滿足你的需求。特別推薦的遊戲如DG真人百家和RSG皇家百家樂,一定能帶給你極致的遊戲體驗。
2. 吸引人的優惠活動
富遊娛樂城針對新手和老玩家都推出了多樣的優惠活動。新會員首次存款可獲得相同金額的獎金,還有額外的體驗金送出,設計友好且實惠。此外,富遊每週的簽到獎勵和天天無上限的返水活動,更是讓玩家在遊戲中能持續獲得收益。
3. 安全可靠的存取款方式
在金融交易方面,富遊娛樂城支持多種存款和提款方式,包括各大銀行轉帳、超商儲值,甚至虛擬貨幣等。最低提款金額設置靈活,保證玩家資金的安全與便捷。
4. 人性化的操作介面
富遊娛樂城的網頁與移動應用設計簡潔易用,玩家可以方便地找到所需的遊戲和優惠。無論是在電腦還是手機上,都能順利享受到遊戲的樂趣。
#### 如何開始遊戲
如果你是新手玩家,開始你的富遊體驗非常簡單。只需註冊帳號,完成首次存款,即可獲得新手優惠。無論你想嘗試電子遊戲還是真人賭局,富遊娛樂城都能讓你輕鬆上手,享受娛樂的樂趣。
#### 社會責任與防沉迷措施
富遊娛樂城深知線上賭博的風險,因此致力於推廣負責任的遊戲文化。他們提供“防沉迷”指導,以確保玩家能夠理性投注,並提供必要的幫助和資源來幫助有需求的玩家。
#### 總結
對於尋求安全、便捷和多元化娛樂城體驗的玩家,富遊娛樂城絕對是值得選擇的選項。無論你是希望徹底放鬆,還是想要體驗刺激的博弈過程,富遊娛樂城都能滿足你的期待,成為你在台灣線上娛樂市場的最佳夥伴。立即註冊並開始你的遊戲之旅吧! -
娛樂城
富遊娛樂城:台灣線上賭場的創新選擇
在台灣的線上娛樂市場中,富遊娛樂城憑藉其優質的服務和多樣化的娛樂選項,迅速成為新一代玩家的首選。既有刺激的遊戲體驗,又提供了一系列具有吸引力的優惠,富遊娛樂城無疑是追求樂趣的玩家們理想的地方。
#### 優勢與特色
1. 多樣化的遊戲選擇
富遊娛樂城提供了豐富的遊戲種類,包括電子老虎機、真人百家樂、運彩投注等。不論你是老虎機的愛好者,還是熱衷於真人賭桌的玩家,這裡都能滿足你的需求。特別推薦的遊戲如DG真人百家和RSG皇家百家樂,一定能帶給你極致的遊戲體驗。
2. 吸引人的優惠活動
富遊娛樂城針對新手和老玩家都推出了多樣的優惠活動。新會員首次存款可獲得相同金額的獎金,還有額外的體驗金送出,設計友好且實惠。此外,富遊每週的簽到獎勵和天天無上限的返水活動,更是讓玩家在遊戲中能持續獲得收益。
3. 安全可靠的存取款方式
在金融交易方面,富遊娛樂城支持多種存款和提款方式,包括各大銀行轉帳、超商儲值,甚至虛擬貨幣等。最低提款金額設置靈活,保證玩家資金的安全與便捷。
4. 人性化的操作介面
富遊娛樂城的網頁與移動應用設計簡潔易用,玩家可以方便地找到所需的遊戲和優惠。無論是在電腦還是手機上,都能順利享受到遊戲的樂趣。
#### 如何開始遊戲
如果你是新手玩家,開始你的富遊體驗非常簡單。只需註冊帳號,完成首次存款,即可獲得新手優惠。無論你想嘗試電子遊戲還是真人賭局,富遊娛樂城都能讓你輕鬆上手,享受娛樂的樂趣。
#### 社會責任與防沉迷措施
富遊娛樂城深知線上賭博的風險,因此致力於推廣負責任的遊戲文化。他們提供“防沉迷”指導,以確保玩家能夠理性投注,並提供必要的幫助和資源來幫助有需求的玩家。
#### 總結
對於尋求安全、便捷和多元化娛樂城體驗的玩家,富遊娛樂城絕對是值得選擇的選項。無論你是希望徹底放鬆,還是想要體驗刺激的博弈過程,富遊娛樂城都能滿足你的期待,成為你在台灣線上娛樂市場的最佳夥伴。立即註冊並開始你的遊戲之旅吧! -
LEO娛樂城無法登入!九州娛樂宣布退出台灣市場
近期,LEO娛樂城和THA娛樂城的玩家發現頻繁出現無法登入的情況,引發了廣泛討論。九州娛樂城官方也正式宣布,將於2024年12月31日中午12:00停止在台灣的營運,並結束所有相關服務。這一消息對於忠實玩家來說無疑是一大震撼,為什麼九州娛樂城會退出台灣市場?玩家該如何應對?本文將為您逐一解析。
LEO娛樂城無法登入的原因
1. 帳號與密碼問題
最常見的情況是玩家輸入的帳號或密碼有誤,或者帳號遭到盜用。
解決方案:聯繫LEO娛樂城的客服,提供必要的驗證信息,即可快速恢復帳戶。
2. 網站技術故障
LEO娛樂城可能因官網維護或伺服器異常導致無法正常運作。
解決方案:耐心等待技術問題修復,通常不會影響長時間使用。
3. 九州娛樂退出台灣市場
LEO娛樂城隸屬於九州娛樂集團,近期官方公告將於2024年12月31日結束營運,退出台灣市場。這是導致登入失敗的最終原因,玩家將無法再使用該平台的服務。
九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的原因分析
1. 市場規模限制
九州娛樂認為台灣市場過於狹小,品牌競爭激烈,成長空間有限。相比之下,海外市場不僅擁有更大的人口基數,也提供更高的獲利潛力。九州旗下的KU體育曾在國際足球五大聯賽中曝光,這顯示其具備強大的國際競爭力,轉向海外市場發展成為合理選擇。
2. 金流問題與法規壓力
LEO娛樂城的運營高度依賴第三方金流公司,而近期陳政谷案件的爆發使整個金流生態鏈受到嚴重打擊。警方揭露,九州娛樂集團利用第三方支付進行資金洗錢,甚至牽涉到內部人員洩密,對整個集團的形象和運營造成巨大衝擊。
3. 品牌聲譽受損
隨著案件的曝光,九州娛樂集團的聲譽遭到前所未有的挑戰。為了平息風波,九州選擇退出台灣市場,以避免進一步的法律與政策風險。
九州娛樂城停止營運的公告
根據LEO娛樂城官方的公告,九州娛樂城將於2024年12月31日中午12:00全面停止台灣市場的營運:
停止存款功能:玩家將無法再進行任何存款操作。
正常開放提款:官方承諾保證提款功能正常運作,會員可安心提取資金。
感謝支持:九州娛樂對於玩家多年來的支持表示衷心感謝,並祝福所有會員未來一切順利。
玩家應對策略:如何保護自身利益?
1. 儘速完成提款
如您的帳戶仍可正常登入,建議立即提交提款申請,確保資金安全轉出。
2. 提高警覺,避免詐騙
隨著九州娛樂退出,市場可能會出現冒充LEO娛樂城或THA娛樂城的假冒平台,玩家需保持高度警覺。
3. 選擇可靠的替代平台
對於希望延續遊戲體驗的玩家,可以考慮轉向信譽良好的國際娛樂平台,例如Bet365台灣,該平台提供穩定的服務和多樣化的遊戲選擇,是九州娛樂的理想替代方案。
結語:九州娛樂的結束,玩家的新起點
九州娛樂城的退出標誌著一個時代的結束,但對於玩家而言,也是一個選擇新平台的契機。未來,選擇安全、穩定且合法的娛樂平台將成為玩家的首要考量。無論如何,希望所有玩家都能在新的平台中繼續享受遊戲的樂趣,保障自身利益不受損失! -
LEO娛樂城無法登入!九州娛樂宣布退出台灣市場
近期,LEO娛樂城和THA娛樂城的玩家發現頻繁出現無法登入的情況,引發了廣泛討論。九州娛樂城官方也正式宣布,將於2024年12月31日中午12:00停止在台灣的營運,並結束所有相關服務。這一消息對於忠實玩家來說無疑是一大震撼,為什麼九州娛樂城會退出台灣市場?玩家該如何應對?本文將為您逐一解析。
LEO娛樂城無法登入的原因
1. 帳號與密碼問題
最常見的情況是玩家輸入的帳號或密碼有誤,或者帳號遭到盜用。
解決方案:聯繫LEO娛樂城的客服,提供必要的驗證信息,即可快速恢復帳戶。
2. 網站技術故障
LEO娛樂城可能因官網維護或伺服器異常導致無法正常運作。
解決方案:耐心等待技術問題修復,通常不會影響長時間使用。
3. 九州娛樂退出台灣市場
LEO娛樂城隸屬於九州娛樂集團,近期官方公告將於2024年12月31日結束營運,退出台灣市場。這是導致登入失敗的最終原因,玩家將無法再使用該平台的服務。
九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的原因分析
1. 市場規模限制
九州娛樂認為台灣市場過於狹小,品牌競爭激烈,成長空間有限。相比之下,海外市場不僅擁有更大的人口基數,也提供更高的獲利潛力。九州旗下的KU體育曾在國際足球五大聯賽中曝光,這顯示其具備強大的國際競爭力,轉向海外市場發展成為合理選擇。
2. 金流問題與法規壓力
LEO娛樂城的運營高度依賴第三方金流公司,而近期陳政谷案件的爆發使整個金流生態鏈受到嚴重打擊。警方揭露,九州娛樂集團利用第三方支付進行資金洗錢,甚至牽涉到內部人員洩密,對整個集團的形象和運營造成巨大衝擊。
3. 品牌聲譽受損
隨著案件的曝光,九州娛樂集團的聲譽遭到前所未有的挑戰。為了平息風波,九州選擇退出台灣市場,以避免進一步的法律與政策風險。
九州娛樂城停止營運的公告
根據LEO娛樂城官方的公告,九州娛樂城將於2024年12月31日中午12:00全面停止台灣市場的營運:
停止存款功能:玩家將無法再進行任何存款操作。
正常開放提款:官方承諾保證提款功能正常運作,會員可安心提取資金。
感謝支持:九州娛樂對於玩家多年來的支持表示衷心感謝,並祝福所有會員未來一切順利。
玩家應對策略:如何保護自身利益?
1. 儘速完成提款
如您的帳戶仍可正常登入,建議立即提交提款申請,確保資金安全轉出。
2. 提高警覺,避免詐騙
隨著九州娛樂退出,市場可能會出現冒充LEO娛樂城或THA娛樂城的假冒平台,玩家需保持高度警覺。
3. 選擇可靠的替代平台
對於希望延續遊戲體驗的玩家,可以考慮轉向信譽良好的國際娛樂平台,例如Bet365台灣,該平台提供穩定的服務和多樣化的遊戲選擇,是九州娛樂的理想替代方案。
結語:九州娛樂的結束,玩家的新起點
九州娛樂城的退出標誌著一個時代的結束,但對於玩家而言,也是一個選擇新平台的契機。未來,選擇安全、穩定且合法的娛樂平台將成為玩家的首要考量。無論如何,希望所有玩家都能在新的平台中繼續享受遊戲的樂趣,保障自身利益不受損失! -
media monitoring tools in Nigeria
Retinaad is the leading adTech for media monitoring & audience measurement in Nigeria. We provide audit, monitoring and compliance solutions for OOH / DOOH, BTL, Retail, Media assets, Radio, TV, online PR & Socials, for brand managers, advertisers and media agencies to increase efficiency and ROI. -
九州娛樂城退出台灣市場:LEO娛樂城無法登入的背後真相
LEO娛樂城,作為台灣線上娛樂城市場的重要品牌,長期以來在廣告投放和代理推廣方面占據領先地位。然而,近期出現的「LEO娛樂城無法登入」現象引發了廣泛的網路討論。不少玩家質疑:「九州娛樂城是不是倒了?」「這是不是詐騙?」事實上,這些猜測與謠言並不完全準確。根據最新消息,九州娛樂城已決定結束其在台灣的業務,包括旗下品牌LEO娛樂城和THA娛樂城。以下我們將深入分析這一事件的背景和可能的影響。
LEO娛樂城無法登入的原因分析
近期LEO娛樂城頻繁出現無法登入的情況,其實是九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的前兆。根據官方公告,九州娛樂城將於2024年12月31日中午12點正式關閉,包括註冊與存款功能在內的多項服務已經受到限制。
可能原因 1:退出台灣市場的策略
九州娛樂城的管理層認為,台灣市場的利潤已達上限,長期運營的收益減少,因此選擇「見好就收」。這一策略符合台灣商業文化中尋找新市場發展的特點。九州娛樂城可能計劃將資源投入其他更具潛力的市場,以追求更大的收益。
可能原因 2:運營生態鏈的問題
LEO娛樂城的運營高度依賴第三方現金交易平台以及相關支付管道。近期,這些環節可能出現了無法解決的問題,導致整體運營受阻。為了避免損失擴大,九州娛樂城選擇退出台灣市場。
可能原因 3:法律風險與負面新聞
九州娛樂城因涉及法律事件,曾多次登上新聞版面。這些事件不僅損害了品牌形象,也讓經營面臨更多風險。為了降低法律糾紛帶來的影響,九州娛樂城可能選擇結束在台灣的營運。
官方公告:2024年12月31日正式停業
九州娛樂城已向所有LEO娛樂城會員發布公告,明確指出將於2024年12月31日中午12點全面停止營運。公告內容包括以下重要信息:
存款服務已關閉:玩家無法繼續充值。
提款功能仍正常:玩家可以放心提取餘額,會員權益不受影響。
感謝支持:官方對會員表達了感謝,並祝福大家未來順利。
這一公告讓玩家可以在剩餘時間內完成提款操作,避免資金損失。
對玩家的影響與建議
1. 儘快提款
如果您是LEO娛樂城的會員,應立即登入帳戶並提取餘額,以確保資金安全。
2. 謹慎選擇新平台
選擇新的娛樂平台時,應注意以下幾點:
合法性:確認平台是否擁有合法經營許可。
支付系統穩定性:確保提款及充值渠道安全無虞。
用戶評價:參考其他玩家的反饋,選擇口碑良好的平台。
3. 防範詐騙
警惕假冒的LEO娛樂城網站或客服。官方客服系統已關閉,任何聯繫您索取個人資料的行為都可能是詐騙。
結語
LEO娛樂城無法登入以及九州娛樂城退出台灣市場,標誌著線上娛樂城行業的一次重要轉折。對於玩家而言,這既是一個挑戰,也是一個重新審視平台選擇的機會。未來,玩家應更加關注平台的合法性與穩定性,為自己的遊戲體驗和資金安全提供保障。 -
LEO娛樂城無法登入
九州娛樂城退出台灣市場:LEO娛樂城無法登入的背後真相
LEO娛樂城,作為台灣線上娛樂城市場的重要品牌,長期以來在廣告投放和代理推廣方面占據領先地位。然而,近期出現的「LEO娛樂城無法登入」現象引發了廣泛的網路討論。不少玩家質疑:「九州娛樂城是不是倒了?」「這是不是詐騙?」事實上,這些猜測與謠言並不完全準確。根據最新消息,九州娛樂城已決定結束其在台灣的業務,包括旗下品牌LEO娛樂城和THA娛樂城。以下我們將深入分析這一事件的背景和可能的影響。
LEO娛樂城無法登入的原因分析
近期LEO娛樂城頻繁出現無法登入的情況,其實是九州娛樂城退出台灣市場的前兆。根據官方公告,九州娛樂城將於2024年12月31日中午12點正式關閉,包括註冊與存款功能在內的多項服務已經受到限制。
可能原因 1:退出台灣市場的策略
九州娛樂城的管理層認為,台灣市場的利潤已達上限,長期運營的收益減少,因此選擇「見好就收」。這一策略符合台灣商業文化中尋找新市場發展的特點。九州娛樂城可能計劃將資源投入其他更具潛力的市場,以追求更大的收益。
可能原因 2:運營生態鏈的問題
LEO娛樂城的運營高度依賴第三方現金交易平台以及相關支付管道。近期,這些環節可能出現了無法解決的問題,導致整體運營受阻。為了避免損失擴大,九州娛樂城選擇退出台灣市場。
可能原因 3:法律風險與負面新聞
九州娛樂城因涉及法律事件,曾多次登上新聞版面。這些事件不僅損害了品牌形象,也讓經營面臨更多風險。為了降低法律糾紛帶來的影響,九州娛樂城可能選擇結束在台灣的營運。
官方公告:2024年12月31日正式停業
九州娛樂城已向所有LEO娛樂城會員發布公告,明確指出將於2024年12月31日中午12點全面停止營運。公告內容包括以下重要信息:
存款服務已關閉:玩家無法繼續充值。
提款功能仍正常:玩家可以放心提取餘額,會員權益不受影響。
感謝支持:官方對會員表達了感謝,並祝福大家未來順利。
這一公告讓玩家可以在剩餘時間內完成提款操作,避免資金損失。
對玩家的影響與建議
1. 儘快提款
如果您是LEO娛樂城的會員,應立即登入帳戶並提取餘額,以確保資金安全。
2. 謹慎選擇新平台
選擇新的娛樂平台時,應注意以下幾點:
合法性:確認平台是否擁有合法經營許可。
支付系統穩定性:確保提款及充值渠道安全無虞。
用戶評價:參考其他玩家的反饋,選擇口碑良好的平台。
3. 防範詐騙
警惕假冒的LEO娛樂城網站或客服。官方客服系統已關閉,任何聯繫您索取個人資料的行為都可能是詐騙。
結語
LEO娛樂城無法登入以及九州娛樂城退出台灣市場,標誌著線上娛樂城行業的一次重要轉折。對於玩家而言,這既是一個挑戰,也是一個重新審視平台選擇的機會。未來,玩家應更加關注平台的合法性與穩定性,為自己的遊戲體驗和資金安全提供保障。 -
3A娛樂城:全方位線上娛樂體驗的首選平台
3A娛樂城作為台灣最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台之一,以其多樣化的遊戲選擇、創新的技術、以及卓越的安全保障,贏得了玩家的高度信任與青睞。無論您是新手還是老手,3A娛樂城都能滿足您的需求,帶給您獨一無二的遊戲體驗。
熱門娛樂城遊戲一覽
3A娛樂城提供多種熱門遊戲,適合不同類型的玩家:
真人百家樂:體驗真實賭場的氛圍,與真人荷官互動,感受賭桌上的緊張與刺激。
彩票投注:涵蓋多種彩票選項,滿足彩券愛好者的需求,讓您隨時隨地挑戰幸運。
棋牌遊戲:從傳統的麻將到現代化的紙牌遊戲,讓玩家在策略與運氣中找到平衡。
3A娛樂城的核心價值
1. 專業
3A娛樂城每日提供近千場體育賽事,並搭配真人百家樂、彩票彩球、電子遊戲等多種類型的線上賭場遊戲。無論您的遊戲偏好為何,這裡總有一款適合您!
2. 安全
平台採用128位加密技術和嚴格的安全管理體系,確保玩家的金流與個人資料完全受保護,讓您可以放心遊玩,無需擔憂安全問題。
3. 便捷
3A娛樂城是全台第一家使用自家開發的全套終端應用的娛樂城平台。無論是手機還是電腦,玩家都能享受無縫的遊戲體驗。同時,24小時線上客服隨時為您解決任何問題,提供貼心服務。
4. 安心
由專業工程師開發的財務處理系統,為玩家帶來快速的存款、取款和轉帳服務。透過獨立網路技術,平台提供優化的網路速度,確保每一次操作都流暢無比。
下載3A娛樂城手機APP
為了提供更便捷的遊戲體驗,3A娛樂城獨家開發了功能齊全的手機APP,讓玩家隨時隨地開啟遊戲。
現代化設計:新穎乾淨的介面設計,提升使用者體驗。
跨平台支持:完美適配手機與電腦,讓您輕鬆切換設備,無需中斷遊戲。
快速下載:掃描專屬QR碼即可進入下載頁面,立即開始暢玩!
3A娛樂城的其他服務
娛樂城教學:詳細的操作指導,讓新手也能快速上手。
責任博彩:提倡健康娛樂,確保玩家在遊戲中享受樂趣的同時,不失理性。
隱私權政策:嚴格遵守隱私保護條例,保障玩家的個人信息安全。
立即加入3A娛樂城,享受頂級娛樂體驗!
如果您正在尋找一個專業、安全、便捷又安心的線上娛樂平台,那麼3A娛樂城絕對是您的不二之選。現在就下載手機APP,隨時隨地開啟您的娛樂旅程,享受無限的遊戲樂趣與刺激! -
3a 娱乐城
3A娛樂城:全方位線上娛樂體驗的首選平台
3A娛樂城作為台灣最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台之一,以其多樣化的遊戲選擇、創新的技術、以及卓越的安全保障,贏得了玩家的高度信任與青睞。無論您是新手還是老手,3A娛樂城都能滿足您的需求,帶給您獨一無二的遊戲體驗。
熱門娛樂城遊戲一覽
3A娛樂城提供多種熱門遊戲,適合不同類型的玩家:
真人百家樂:體驗真實賭場的氛圍,與真人荷官互動,感受賭桌上的緊張與刺激。
彩票投注:涵蓋多種彩票選項,滿足彩券愛好者的需求,讓您隨時隨地挑戰幸運。
棋牌遊戲:從傳統的麻將到現代化的紙牌遊戲,讓玩家在策略與運氣中找到平衡。
3A娛樂城的核心價值
1. 專業
3A娛樂城每日提供近千場體育賽事,並搭配真人百家樂、彩票彩球、電子遊戲等多種類型的線上賭場遊戲。無論您的遊戲偏好為何,這裡總有一款適合您!
2. 安全
平台採用128位加密技術和嚴格的安全管理體系,確保玩家的金流與個人資料完全受保護,讓您可以放心遊玩,無需擔憂安全問題。
3. 便捷
3A娛樂城是全台第一家使用自家開發的全套終端應用的娛樂城平台。無論是手機還是電腦,玩家都能享受無縫的遊戲體驗。同時,24小時線上客服隨時為您解決任何問題,提供貼心服務。
4. 安心
由專業工程師開發的財務處理系統,為玩家帶來快速的存款、取款和轉帳服務。透過獨立網路技術,平台提供優化的網路速度,確保每一次操作都流暢無比。
下載3A娛樂城手機APP
為了提供更便捷的遊戲體驗,3A娛樂城獨家開發了功能齊全的手機APP,讓玩家隨時隨地開啟遊戲。
現代化設計:新穎乾淨的介面設計,提升使用者體驗。
跨平台支持:完美適配手機與電腦,讓您輕鬆切換設備,無需中斷遊戲。
快速下載:掃描專屬QR碼即可進入下載頁面,立即開始暢玩!
3A娛樂城的其他服務
娛樂城教學:詳細的操作指導,讓新手也能快速上手。
責任博彩:提倡健康娛樂,確保玩家在遊戲中享受樂趣的同時,不失理性。
隱私權政策:嚴格遵守隱私保護條例,保障玩家的個人信息安全。
立即加入3A娛樂城,享受頂級娛樂體驗!
如果您正在尋找一個專業、安全、便捷又安心的線上娛樂平台,那麼3A娛樂城絕對是您的不二之選。現在就下載手機APP,隨時隨地開啟您的娛樂旅程,享受無限的遊戲樂趣與刺激! -
2024 年熱門娛樂城與活動解析
冠天下娛樂城優惠,帶來無限樂趣
在 2024 年 4 月 16 日,冠天下娛樂城推出了全新的優惠活動,旨在為玩家帶來更大的獲利機會和更高的娛樂體驗。這些優惠活動包括多種存款獎勵、會員專屬回饋以及豐富的遊戲競賽獎金,吸引了大批玩家參與。
冠天下娛樂城以其高透明度和用戶友好的政策,已成為許多玩家的首選娛樂平台。不論是新手還是老手,都能在這裡找到適合自己的遊戲和活動。
LEO娛樂城無法登入引發市場恐慌
2024 年 11 月 29 日,LEO娛樂城因技術問題出現短暫無法登入的情況,引發了廣泛關注。許多玩家擔心這是否意味著九州娛樂城的營運出現問題。
九州娛樂集團隨後發佈官方聲明,強調這僅僅是系統升級過程中的短暫問題,並承諾玩家的資金和數據安全不受任何影響。同時,九州娛樂表示將加強伺服器穩定性,確保未來類似情況不再發生。
熱門 ZG 電子遊戲——熱舞森巴老虎機
2024 年 11 月 8 日,ZG 電子遊戲推出了熱舞森巴老虎機,這款遊戲迅速成為市場上的熱門選擇。以南美熱情的森巴舞為主題,遊戲畫面充滿色彩,搭配動感的音樂,為玩家帶來視覺與聽覺的雙重享受。
遊戲亮點:
高倍數獎勵機制:每次轉盤都有機會觸發高額獎金。
特色免費遊戲:連續獲得特殊圖案即可啟動多次免費轉盤,提高獲勝機率。
適合新手與高端玩家:簡單的玩法規則與豐富的策略選擇滿足不同層級玩家的需求。
ZG 電子遊戲致力於為玩家提供創新且有趣的遊戲體驗,熱舞森巴老虎機無疑是今年最值得嘗試的遊戲之一。
2024 世界棒球 12 強賽精彩回顧
2024 年 11 月,中華隊參加了世界棒球 12 強賽,這項全球頂尖棒球賽事吸引了來自多國的球隊和球迷參與。中華隊 28 人的名單以年輕選手和經驗豐富的老將為基礎,展現了團隊的競技實力。
比賽亮點:
精彩賽程:比賽期間,中華隊展現了堅強的防守和出色的打擊表現。
門票銷售:賽事門票迅速售罄,顯示出棒球在台灣的高度受歡迎程度。
線上直播:各大平台提供了高畫質直播,讓更多球迷能夠即時觀看比賽,感受棒球魅力。
世界棒球 12 強賽不僅是比賽,更是全台灣球迷的一場盛宴,展現了棒球作為國民運動的無限魅力。
結語
從娛樂城的優惠活動到全球性的棒球賽事,2024 年對於遊戲和體育愛好者來說充滿了亮點。不論是參與冠天下娛樂城的優惠,體驗 ZG 電子遊戲的最新老虎機,還是為中華隊的棒球比賽加油,這一年都是充滿精彩與期待的一年! -
2024 年熱門娛樂城與活動解析
冠天下娛樂城優惠,帶來無限樂趣
在 2024 年 4 月 16 日,冠天下娛樂城推出了全新的優惠活動,旨在為玩家帶來更大的獲利機會和更高的娛樂體驗。這些優惠活動包括多種存款獎勵、會員專屬回饋以及豐富的遊戲競賽獎金,吸引了大批玩家參與。
冠天下娛樂城以其高透明度和用戶友好的政策,已成為許多玩家的首選娛樂平台。不論是新手還是老手,都能在這裡找到適合自己的遊戲和活動。
LEO娛樂城無法登入引發市場恐慌
2024 年 11 月 29 日,LEO娛樂城因技術問題出現短暫無法登入的情況,引發了廣泛關注。許多玩家擔心這是否意味著九州娛樂城的營運出現問題。
九州娛樂集團隨後發佈官方聲明,強調這僅僅是系統升級過程中的短暫問題,並承諾玩家的資金和數據安全不受任何影響。同時,九州娛樂表示將加強伺服器穩定性,確保未來類似情況不再發生。
熱門 ZG 電子遊戲——熱舞森巴老虎機
2024 年 11 月 8 日,ZG 電子遊戲推出了熱舞森巴老虎機,這款遊戲迅速成為市場上的熱門選擇。以南美熱情的森巴舞為主題,遊戲畫面充滿色彩,搭配動感的音樂,為玩家帶來視覺與聽覺的雙重享受。
遊戲亮點:
高倍數獎勵機制:每次轉盤都有機會觸發高額獎金。
特色免費遊戲:連續獲得特殊圖案即可啟動多次免費轉盤,提高獲勝機率。
適合新手與高端玩家:簡單的玩法規則與豐富的策略選擇滿足不同層級玩家的需求。
ZG 電子遊戲致力於為玩家提供創新且有趣的遊戲體驗,熱舞森巴老虎機無疑是今年最值得嘗試的遊戲之一。
2024 世界棒球 12 強賽精彩回顧
2024 年 11 月,中華隊參加了世界棒球 12 強賽,這項全球頂尖棒球賽事吸引了來自多國的球隊和球迷參與。中華隊 28 人的名單以年輕選手和經驗豐富的老將為基礎,展現了團隊的競技實力。
比賽亮點:
精彩賽程:比賽期間,中華隊展現了堅強的防守和出色的打擊表現。
門票銷售:賽事門票迅速售罄,顯示出棒球在台灣的高度受歡迎程度。
線上直播:各大平台提供了高畫質直播,讓更多球迷能夠即時觀看比賽,感受棒球魅力。
世界棒球 12 強賽不僅是比賽,更是全台灣球迷的一場盛宴,展現了棒球作為國民運動的無限魅力。
結語
從娛樂城的優惠活動到全球性的棒球賽事,2024 年對於遊戲和體育愛好者來說充滿了亮點。不論是參與冠天下娛樂城的優惠,體驗 ZG 電子遊戲的最新老虎機,還是為中華隊的棒球比賽加油,這一年都是充滿精彩與期待的一年! -
2024 年娛樂城遊戲推薦:最夯遊戲與最佳平台選擇
隨著線上娛樂城市場的蓬勃發展,2024 年推出了多款令人興奮的遊戲和創新平台。無論是喜歡老虎機、棋牌遊戲,還是捕魚和彩票遊戲的玩家,都能在今年找到屬於自己的遊戲樂園。以下是熱門遊戲推薦與最佳娛樂城平台的詳細介紹。
2024 年最夯遊戲推薦
電子老虎機遊戲
電子老虎機一直是娛樂城的經典項目,今年更是推出了數款熱門作品:
戰神賽特:以古埃及神話為背景,擁有高倍數獎勵的特殊功能,畫面設計精美。
魔龍傳奇:玩家可探索魔龍世界,觸發驚喜獎金和免費遊戲機會。
雷神之錘:以北歐神話為主題,特色連線玩法讓每次旋轉都充滿期待。
金虎爺:寓意招財進寶,特別適合新年期間挑戰,玩法簡單但回報豐厚。
棋牌遊戲
二人麻將:適合喜歡策略性對抗的玩家,快速節奏且競爭激烈。
忍 Kunoichi:結合武士與忍者元素,讓玩家體驗獨特的棋牌競技。
捕魚遊戲
捕魚遊戲是一種結合策略和運氣的娛樂項目,玩家可以通過捕捉魚群來獲得高額獎金,同時享受視覺和操作的雙重樂趣。
彩票遊戲
彩票遊戲以簡單快捷的玩法吸引大批玩家,提供多種國內外彩種,讓玩家隨時挑戰幸運。
RG富遊娛樂城:2024 年最佳線上娛樂城推薦
在眾多娛樂城平台中,RG富遊娛樂城以其專業服務和卓越遊戲體驗,成為今年的首選平台。
平台特色
遊戲種類豐富
提供多元化遊戲選擇,包括真人視訊、電子老虎機、捕魚、棋牌和彩票遊戲,滿足所有玩家需求。
快速便捷的存提款服務
平台支持即時存款與快速提款,無需等待,確保資金安全流動。
高度安全保障
採用最先進的加密技術,保護玩家的帳戶與交易安全。
支援多平台裝置
富遊娛樂城APP 可在 iOS 和 Android 設備上使用,界面簡潔易操作,隨時隨地享受娛樂。
專業客服支援
提供 24 小時全天候客服,隨時解答玩家疑問,保障流暢的遊戲體驗。
如何開始體驗 RG 富遊娛樂城
下載富遊 APP
在官方網站免費下載 APP,支援 iOS 和 Android 設備。
註冊帳號
使用簡單步驟完成註冊,立即進入遊戲世界。
挑戰熱門遊戲
從老虎機到棋牌遊戲,選擇您喜歡的類型,挑戰高額獎金。
結語
2024 年是線上娛樂遊戲的精彩年份,從戰神賽特到二人麻將,每款遊戲都能帶給玩家不同的樂趣。而選擇像 RG富遊娛樂城 這樣的專業平台,不僅能體驗到豐富的遊戲內容,還能享受安全可靠的服務。立即下載富遊 APP,加入這個充滿驚喜的娛樂世界 -
https://replit.com/@generiquefr impect 12
-
娛樂城
2024 年娛樂城遊戲推薦:最夯遊戲與最佳平台選擇
隨著線上娛樂城市場的蓬勃發展,2024 年推出了多款令人興奮的遊戲和創新平台。無論是喜歡老虎機、棋牌遊戲,還是捕魚和彩票遊戲的玩家,都能在今年找到屬於自己的遊戲樂園。以下是熱門遊戲推薦與最佳娛樂城平台的詳細介紹。
2024 年最夯遊戲推薦
電子老虎機遊戲
電子老虎機一直是娛樂城的經典項目,今年更是推出了數款熱門作品:
戰神賽特:以古埃及神話為背景,擁有高倍數獎勵的特殊功能,畫面設計精美。
魔龍傳奇:玩家可探索魔龍世界,觸發驚喜獎金和免費遊戲機會。
雷神之錘:以北歐神話為主題,特色連線玩法讓每次旋轉都充滿期待。
金虎爺:寓意招財進寶,特別適合新年期間挑戰,玩法簡單但回報豐厚。
棋牌遊戲
二人麻將:適合喜歡策略性對抗的玩家,快速節奏且競爭激烈。
忍 Kunoichi:結合武士與忍者元素,讓玩家體驗獨特的棋牌競技。
捕魚遊戲
捕魚遊戲是一種結合策略和運氣的娛樂項目,玩家可以通過捕捉魚群來獲得高額獎金,同時享受視覺和操作的雙重樂趣。
彩票遊戲
彩票遊戲以簡單快捷的玩法吸引大批玩家,提供多種國內外彩種,讓玩家隨時挑戰幸運。
RG富遊娛樂城:2024 年最佳線上娛樂城推薦
在眾多娛樂城平台中,RG富遊娛樂城以其專業服務和卓越遊戲體驗,成為今年的首選平台。
平台特色
遊戲種類豐富
提供多元化遊戲選擇,包括真人視訊、電子老虎機、捕魚、棋牌和彩票遊戲,滿足所有玩家需求。
快速便捷的存提款服務
平台支持即時存款與快速提款,無需等待,確保資金安全流動。
高度安全保障
採用最先進的加密技術,保護玩家的帳戶與交易安全。
支援多平台裝置
富遊娛樂城APP 可在 iOS 和 Android 設備上使用,界面簡潔易操作,隨時隨地享受娛樂。
專業客服支援
提供 24 小時全天候客服,隨時解答玩家疑問,保障流暢的遊戲體驗。
如何開始體驗 RG 富遊娛樂城
下載富遊 APP
在官方網站免費下載 APP,支援 iOS 和 Android 設備。
註冊帳號
使用簡單步驟完成註冊,立即進入遊戲世界。
挑戰熱門遊戲
從老虎機到棋牌遊戲,選擇您喜歡的類型,挑戰高額獎金。
結語
2024 年是線上娛樂遊戲的精彩年份,從戰神賽特到二人麻將,每款遊戲都能帶給玩家不同的樂趣。而選擇像 RG富遊娛樂城 這樣的專業平台,不僅能體驗到豐富的遊戲內容,還能享受安全可靠的服務。立即下載富遊 APP,加入這個充滿驚喜的娛樂世界 -
滿天星娛樂城:全方位的線上娛樂體驗
滿天星娛樂城作為九州娛樂城旗下品牌之一,是玩家心目中備受信賴的線上娛樂平台。不僅提供豐富的遊戲選擇和吸引人的優惠,還以其合法營運的背景和快速出金的保證,成為台灣玩家的首選娛樂城之一。
滿天星娛樂城的特色與優勢
1. 合法營運,安全可靠
滿天星娛樂城持有三大國際娛樂執照,包括:
菲律賓 PAGCOR 監督競猜牌照
BVI 認證
馬爾他 MGA 認證
這些執照展現了平台的資本實力與合法性,讓玩家能夠安心享受遊戲,完全不用擔心出金問題。
2. 高品質遊戲與豐富優惠
滿天星娛樂城與九州集團旗下的LEO、THA娛樂城一樣,提供一流的遊戲品質和多樣化的優惠。
熱門遊戲推薦:電子老虎機、真人直播、運彩投注、今彩539等,滿足各類玩家需求。
優惠活動:定期推出限時回饋活動,讓玩家在遊戲中獲得更多額外收益。
3. 快速出金與高效服務
滿天星娛樂城採用先進的財務系統,確保存提款快速、安全,讓玩家能夠專注於享受遊戲,而無需擔心資金問題。專業的客服團隊24小時在線,提供即時支援。
4. 多平台兼容的APP
滿天星娛樂城提供設計貼合玩家需求的手機APP,適用於iOS與Android系統。玩家可以隨時隨地快速登入遊玩,體驗無與倫比的娛樂快感。
熱門遊戲類型一覽
滿天星娛樂城為玩家提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,滿足不同興趣和需求:
真人直播:感受真實賭場氛圍,與真人荷官互動,體驗沉浸式娛樂。
電子老虎機:多款經典與創新機台,讓玩家享受刺激的遊戲過程。
運彩投注:涵蓋世界盃、棒球、籃球等多項運動賽事,提供即時投注與直播功能。
彩票遊戲:包括今彩539、富遊彩票等,適合熱衷於彩券的玩家。
滿天星娛樂城常見問題解答
Q1. 滿天星娛樂城是否提供APP下載?
是的,滿天星娛樂城提供專屬的手機APP,支援iOS和Android系統。玩家可透過APP快速登入,隨時享受遊戲。
Q2. 滿天星娛樂城是否合法?
滿天星娛樂城擁有多項國際認證,為合法經營的線上娛樂城,並保證玩家資金的安全性與遊戲的公平性。
Q3. 無法登入滿天星娛樂城該怎麼辦?
如遇到無法登入的情況,建議玩家檢查網路狀況或聯繫24小時客服團隊獲取即時協助。
立即加入滿天星娛樂城,享受最佳娛樂體驗!
滿天星娛樂城以合法、安全、快速的服務,搭配豐富的遊戲選擇和優惠,為玩家打造出獨一無二的線上娛樂體驗。不論您是新手還是老手,都能在滿天星找到屬於自己的遊戲樂趣。現在就下載APP,隨時隨地開始您的娛樂之旅! -
滿天星娛樂城:全方位的線上娛樂體驗
滿天星娛樂城作為九州娛樂城旗下品牌之一,是玩家心目中備受信賴的線上娛樂平台。不僅提供豐富的遊戲選擇和吸引人的優惠,還以其合法營運的背景和快速出金的保證,成為台灣玩家的首選娛樂城之一。
滿天星娛樂城的特色與優勢
1. 合法營運,安全可靠
滿天星娛樂城持有三大國際娛樂執照,包括:
菲律賓 PAGCOR 監督競猜牌照
BVI 認證
馬爾他 MGA 認證
這些執照展現了平台的資本實力與合法性,讓玩家能夠安心享受遊戲,完全不用擔心出金問題。
2. 高品質遊戲與豐富優惠
滿天星娛樂城與九州集團旗下的LEO、THA娛樂城一樣,提供一流的遊戲品質和多樣化的優惠。
熱門遊戲推薦:電子老虎機、真人直播、運彩投注、今彩539等,滿足各類玩家需求。
優惠活動:定期推出限時回饋活動,讓玩家在遊戲中獲得更多額外收益。
3. 快速出金與高效服務
滿天星娛樂城採用先進的財務系統,確保存提款快速、安全,讓玩家能夠專注於享受遊戲,而無需擔心資金問題。專業的客服團隊24小時在線,提供即時支援。
4. 多平台兼容的APP
滿天星娛樂城提供設計貼合玩家需求的手機APP,適用於iOS與Android系統。玩家可以隨時隨地快速登入遊玩,體驗無與倫比的娛樂快感。
熱門遊戲類型一覽
滿天星娛樂城為玩家提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,滿足不同興趣和需求:
真人直播:感受真實賭場氛圍,與真人荷官互動,體驗沉浸式娛樂。
電子老虎機:多款經典與創新機台,讓玩家享受刺激的遊戲過程。
運彩投注:涵蓋世界盃、棒球、籃球等多項運動賽事,提供即時投注與直播功能。
彩票遊戲:包括今彩539、富遊彩票等,適合熱衷於彩券的玩家。
滿天星娛樂城常見問題解答
Q1. 滿天星娛樂城是否提供APP下載?
是的,滿天星娛樂城提供專屬的手機APP,支援iOS和Android系統。玩家可透過APP快速登入,隨時享受遊戲。
Q2. 滿天星娛樂城是否合法?
滿天星娛樂城擁有多項國際認證,為合法經營的線上娛樂城,並保證玩家資金的安全性與遊戲的公平性。
Q3. 無法登入滿天星娛樂城該怎麼辦?
如遇到無法登入的情況,建議玩家檢查網路狀況或聯繫24小時客服團隊獲取即時協助。
立即加入滿天星娛樂城,享受最佳娛樂體驗!
滿天星娛樂城以合法、安全、快速的服務,搭配豐富的遊戲選擇和優惠,為玩家打造出獨一無二的線上娛樂體驗。不論您是新手還是老手,都能在滿天星找到屬於自己的遊戲樂趣。現在就下載APP,隨時隨地開始您的娛樂之旅! -
想要享受最刺激的線上娛樂體驗?選擇RG富遊娛樂城!
在這個數位時代,尋找適合自己的線上娛樂城變得越來越重要。如果你想在線上娛樂城找到最好玩、最受歡迎的遊戲,RG富遊絕對是你的首選!我們匯聚了多款博弈遊戲,讓您盡情享受娛樂的刺激與快感。
#### 精選遊戲類型
1. 真人百家樂
感受現場賭場的氛圍!RG富遊的真人視訊百家樂讓你與真實的荷官互動,享受高品質的遊戲體驗。無論你是老手還是新手,都能在這裡找到適合自己的節奏。
2. 電子老虎機
喜愛刺激嗎?我們提供多款熱門老虎機遊戲,如「戰神賽特」「魔龍傳奇」等,每一款都擁有精美的畫面和豐厚的獎勵,讓每次旋轉都充滿期待!
3. 體育投注
無論你是球迷還是賽事愛好者,RG富遊的體育投注平台都有你想要的。精準的賠率、廣泛的賽事選擇,讓你體驗到投注的樂趣和刺激。
4. 彩票遊戲與捕魚遊戲
隨著運氣來!不妨試試我們的棋牌遊戲和彩票遊戲,這裡有各種機會讓你體驗到不一樣的勝利快感。
#### 下載富遊APP,隨時隨地享受遊戲!
富遊娛樂城的APP支持iOS和Android設備,界面簡潔易用,內容豐富。無論你身處何地,都能輕鬆進入遊戲世界,隨心所欲享受娛樂時光。此外,我們提供即時客服支援,隨時解決你的疑問,讓你的遊戲體驗更為完美。
#### 為什麼選擇RG富遊?
- 安全可靠
RG富遊致力於為玩家提供安全可靠的遊戲環境,您的每一筆交易都受到最高的安全保障。
- 快速便捷的存提款服務
我們的存款平均時間僅需30秒,提款平均只需60秒,讓你體驗即時的快感!
- 豐富多元的遊戲選擇
超過9999款遊戲任你選擇,無論你偏好哪種娛樂方式,這裡都能滿足你的需求。
- 全天候服務
我們全年365天提供不停歇的客服支持,確保你在遊戲過程中享受到最好的服務。
### 結論
RG富遊娛樂城是您最佳的線上賭場選擇。我們不僅提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,還有安全可靠的遊戲環境和便捷的服務。立即下載APP,加入RG富遊,開始您的娛樂之旅,享受無與倫比的遊戲體驗吧! -
娛樂城
富遊娛樂城:台灣線上賭場的創新選擇
在台灣的線上娛樂市場中,富遊娛樂城憑藉其優質的服務和多樣化的娛樂選項,迅速成為新一代玩家的首選。既有刺激的遊戲體驗,又提供了一系列具有吸引力的優惠,富遊娛樂城無疑是追求樂趣的玩家們理想的地方。
#### 優勢與特色
1. 多樣化的遊戲選擇
富遊娛樂城提供了豐富的遊戲種類,包括電子老虎機、真人百家樂、運彩投注等。不論你是老虎機的愛好者,還是熱衷於真人賭桌的玩家,這裡都能滿足你的需求。特別推薦的遊戲如DG真人百家和RSG皇家百家樂,一定能帶給你極致的遊戲體驗。
2. 吸引人的優惠活動
富遊娛樂城針對新手和老玩家都推出了多樣的優惠活動。新會員首次存款可獲得相同金額的獎金,還有額外的體驗金送出,設計友好且實惠。此外,富遊每週的簽到獎勵和天天無上限的返水活動,更是讓玩家在遊戲中能持續獲得收益。
3. 安全可靠的存取款方式
在金融交易方面,富遊娛樂城支持多種存款和提款方式,包括各大銀行轉帳、超商儲值,甚至虛擬貨幣等。最低提款金額設置靈活,保證玩家資金的安全與便捷。
4. 人性化的操作介面
富遊娛樂城的網頁與移動應用設計簡潔易用,玩家可以方便地找到所需的遊戲和優惠。無論是在電腦還是手機上,都能順利享受到遊戲的樂趣。
#### 如何開始遊戲
如果你是新手玩家,開始你的富遊體驗非常簡單。只需註冊帳號,完成首次存款,即可獲得新手優惠。無論你想嘗試電子遊戲還是真人賭局,富遊娛樂城都能讓你輕鬆上手,享受娛樂的樂趣。
#### 社會責任與防沉迷措施
富遊娛樂城深知線上賭博的風險,因此致力於推廣負責任的遊戲文化。他們提供“防沉迷”指導,以確保玩家能夠理性投注,並提供必要的幫助和資源來幫助有需求的玩家。
#### 總結
對於尋求安全、便捷和多元化娛樂城體驗的玩家,富遊娛樂城絕對是值得選擇的選項。無論你是希望徹底放鬆,還是想要體驗刺激的博弈過程,富遊娛樂城都能滿足你的期待,成為你在台灣線上娛樂市場的最佳夥伴。立即註冊並開始你的遊戲之旅吧! -
想要享受最刺激的線上娛樂體驗?選擇RG富遊娛樂城!
在這個數位時代,尋找適合自己的線上娛樂城變得越來越重要。如果你想在線上娛樂城找到最好玩、最受歡迎的遊戲,RG富遊絕對是你的首選!我們匯聚了多款博弈遊戲,讓您盡情享受娛樂的刺激與快感。
#### 精選遊戲類型
1. 真人百家樂
感受現場賭場的氛圍!RG富遊的真人視訊百家樂讓你與真實的荷官互動,享受高品質的遊戲體驗。無論你是老手還是新手,都能在這裡找到適合自己的節奏。
2. 電子老虎機
喜愛刺激嗎?我們提供多款熱門老虎機遊戲,如「戰神賽特」「魔龍傳奇」等,每一款都擁有精美的畫面和豐厚的獎勵,讓每次旋轉都充滿期待!
3. 體育投注
無論你是球迷還是賽事愛好者,RG富遊的體育投注平台都有你想要的。精準的賠率、廣泛的賽事選擇,讓你體驗到投注的樂趣和刺激。
4. 彩票遊戲與捕魚遊戲
隨著運氣來!不妨試試我們的棋牌遊戲和彩票遊戲,這裡有各種機會讓你體驗到不一樣的勝利快感。
#### 下載富遊APP,隨時隨地享受遊戲!
富遊娛樂城的APP支持iOS和Android設備,界面簡潔易用,內容豐富。無論你身處何地,都能輕鬆進入遊戲世界,隨心所欲享受娛樂時光。此外,我們提供即時客服支援,隨時解決你的疑問,讓你的遊戲體驗更為完美。
#### 為什麼選擇RG富遊?
- 安全可靠
RG富遊致力於為玩家提供安全可靠的遊戲環境,您的每一筆交易都受到最高的安全保障。
- 快速便捷的存提款服務
我們的存款平均時間僅需30秒,提款平均只需60秒,讓你體驗即時的快感!
- 豐富多元的遊戲選擇
超過9999款遊戲任你選擇,無論你偏好哪種娛樂方式,這裡都能滿足你的需求。
- 全天候服務
我們全年365天提供不停歇的客服支持,確保你在遊戲過程中享受到最好的服務。
### 結論
RG富遊娛樂城是您最佳的線上賭場選擇。我們不僅提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,還有安全可靠的遊戲環境和便捷的服務。立即下載APP,加入RG富遊,開始您的娛樂之旅,享受無與倫比的遊戲體驗吧! -
娛樂城
富遊娛樂城:台灣線上賭場的創新選擇
在台灣的線上娛樂市場中,富遊娛樂城憑藉其優質的服務和多樣化的娛樂選項,迅速成為新一代玩家的首選。既有刺激的遊戲體驗,又提供了一系列具有吸引力的優惠,富遊娛樂城無疑是追求樂趣的玩家們理想的地方。
#### 優勢與特色
1. 多樣化的遊戲選擇
富遊娛樂城提供了豐富的遊戲種類,包括電子老虎機、真人百家樂、運彩投注等。不論你是老虎機的愛好者,還是熱衷於真人賭桌的玩家,這裡都能滿足你的需求。特別推薦的遊戲如DG真人百家和RSG皇家百家樂,一定能帶給你極致的遊戲體驗。
2. 吸引人的優惠活動
富遊娛樂城針對新手和老玩家都推出了多樣的優惠活動。新會員首次存款可獲得相同金額的獎金,還有額外的體驗金送出,設計友好且實惠。此外,富遊每週的簽到獎勵和天天無上限的返水活動,更是讓玩家在遊戲中能持續獲得收益。
3. 安全可靠的存取款方式
在金融交易方面,富遊娛樂城支持多種存款和提款方式,包括各大銀行轉帳、超商儲值,甚至虛擬貨幣等。最低提款金額設置靈活,保證玩家資金的安全與便捷。
4. 人性化的操作介面
富遊娛樂城的網頁與移動應用設計簡潔易用,玩家可以方便地找到所需的遊戲和優惠。無論是在電腦還是手機上,都能順利享受到遊戲的樂趣。
#### 如何開始遊戲
如果你是新手玩家,開始你的富遊體驗非常簡單。只需註冊帳號,完成首次存款,即可獲得新手優惠。無論你想嘗試電子遊戲還是真人賭局,富遊娛樂城都能讓你輕鬆上手,享受娛樂的樂趣。
#### 社會責任與防沉迷措施
富遊娛樂城深知線上賭博的風險,因此致力於推廣負責任的遊戲文化。他們提供“防沉迷”指導,以確保玩家能夠理性投注,並提供必要的幫助和資源來幫助有需求的玩家。
#### 總結
對於尋求安全、便捷和多元化娛樂城體驗的玩家,富遊娛樂城絕對是值得選擇的選項。無論你是希望徹底放鬆,還是想要體驗刺激的博弈過程,富遊娛樂城都能滿足你的期待,成為你在台灣線上娛樂市場的最佳夥伴。立即註冊並開始你的遊戲之旅吧! -
3A娛樂城:全方位線上娛樂體驗的首選平台
3A娛樂城作為台灣最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台之一,以其多樣化的遊戲選擇、創新的技術、以及卓越的安全保障,贏得了玩家的高度信任與青睞。無論您是新手還是老手,3A娛樂城都能滿足您的需求,帶給您獨一無二的遊戲體驗。
熱門娛樂城遊戲一覽
3A娛樂城提供多種熱門遊戲,適合不同類型的玩家:
真人百家樂:體驗真實賭場的氛圍,與真人荷官互動,感受賭桌上的緊張與刺激。
彩票投注:涵蓋多種彩票選項,滿足彩券愛好者的需求,讓您隨時隨地挑戰幸運。
棋牌遊戲:從傳統的麻將到現代化的紙牌遊戲,讓玩家在策略與運氣中找到平衡。
3A娛樂城的核心價值
1. 專業
3A娛樂城每日提供近千場體育賽事,並搭配真人百家樂、彩票彩球、電子遊戲等多種類型的線上賭場遊戲。無論您的遊戲偏好為何,這裡總有一款適合您!
2. 安全
平台採用128位加密技術和嚴格的安全管理體系,確保玩家的金流與個人資料完全受保護,讓您可以放心遊玩,無需擔憂安全問題。
3. 便捷
3A娛樂城是全台第一家使用自家開發的全套終端應用的娛樂城平台。無論是手機還是電腦,玩家都能享受無縫的遊戲體驗。同時,24小時線上客服隨時為您解決任何問題,提供貼心服務。
4. 安心
由專業工程師開發的財務處理系統,為玩家帶來快速的存款、取款和轉帳服務。透過獨立網路技術,平台提供優化的網路速度,確保每一次操作都流暢無比。
下載3A娛樂城手機APP
為了提供更便捷的遊戲體驗,3A娛樂城獨家開發了功能齊全的手機APP,讓玩家隨時隨地開啟遊戲。
現代化設計:新穎乾淨的介面設計,提升使用者體驗。
跨平台支持:完美適配手機與電腦,讓您輕鬆切換設備,無需中斷遊戲。
快速下載:掃描專屬QR碼即可進入下載頁面,立即開始暢玩!
3A娛樂城的其他服務
娛樂城教學:詳細的操作指導,讓新手也能快速上手。
責任博彩:提倡健康娛樂,確保玩家在遊戲中享受樂趣的同時,不失理性。
隱私權政策:嚴格遵守隱私保護條例,保障玩家的個人信息安全。
立即加入3A娛樂城,享受頂級娛樂體驗!
如果您正在尋找一個專業、安全、便捷又安心的線上娛樂平台,那麼3A娛樂城絕對是您的不二之選。現在就下載手機APP,隨時隨地開啟您的娛樂旅程,享受無限的遊戲樂趣與刺激! -
3A娛樂城:全方位線上娛樂體驗的首選平台
3A娛樂城作為台灣最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台之一,以其多樣化的遊戲選擇、創新的技術、以及卓越的安全保障,贏得了玩家的高度信任與青睞。無論您是新手還是老手,3A娛樂城都能滿足您的需求,帶給您獨一無二的遊戲體驗。
熱門娛樂城遊戲一覽
3A娛樂城提供多種熱門遊戲,適合不同類型的玩家:
真人百家樂:體驗真實賭場的氛圍,與真人荷官互動,感受賭桌上的緊張與刺激。
彩票投注:涵蓋多種彩票選項,滿足彩券愛好者的需求,讓您隨時隨地挑戰幸運。
棋牌遊戲:從傳統的麻將到現代化的紙牌遊戲,讓玩家在策略與運氣中找到平衡。
3A娛樂城的核心價值
1. 專業
3A娛樂城每日提供近千場體育賽事,並搭配真人百家樂、彩票彩球、電子遊戲等多種類型的線上賭場遊戲。無論您的遊戲偏好為何,這裡總有一款適合您!
2. 安全
平台採用128位加密技術和嚴格的安全管理體系,確保玩家的金流與個人資料完全受保護,讓您可以放心遊玩,無需擔憂安全問題。
3. 便捷
3A娛樂城是全台第一家使用自家開發的全套終端應用的娛樂城平台。無論是手機還是電腦,玩家都能享受無縫的遊戲體驗。同時,24小時線上客服隨時為您解決任何問題,提供貼心服務。
4. 安心
由專業工程師開發的財務處理系統,為玩家帶來快速的存款、取款和轉帳服務。透過獨立網路技術,平台提供優化的網路速度,確保每一次操作都流暢無比。
下載3A娛樂城手機APP
為了提供更便捷的遊戲體驗,3A娛樂城獨家開發了功能齊全的手機APP,讓玩家隨時隨地開啟遊戲。
現代化設計:新穎乾淨的介面設計,提升使用者體驗。
跨平台支持:完美適配手機與電腦,讓您輕鬆切換設備,無需中斷遊戲。
快速下載:掃描專屬QR碼即可進入下載頁面,立即開始暢玩!
3A娛樂城的其他服務
娛樂城教學:詳細的操作指導,讓新手也能快速上手。
責任博彩:提倡健康娛樂,確保玩家在遊戲中享受樂趣的同時,不失理性。
隱私權政策:嚴格遵守隱私保護條例,保障玩家的個人信息安全。
立即加入3A娛樂城,享受頂級娛樂體驗!
如果您正在尋找一個專業、安全、便捷又安心的線上娛樂平台,那麼3A娛樂城絕對是您的不二之選。現在就下載手機APP,隨時隨地開啟您的娛樂旅程,享受無限的遊戲樂趣與刺激! -
2024 年熱門娛樂城與活動解析
冠天下娛樂城優惠,帶來無限樂趣
在 2024 年 4 月 16 日,冠天下娛樂城推出了全新的優惠活動,旨在為玩家帶來更大的獲利機會和更高的娛樂體驗。這些優惠活動包括多種存款獎勵、會員專屬回饋以及豐富的遊戲競賽獎金,吸引了大批玩家參與。
冠天下娛樂城以其高透明度和用戶友好的政策,已成為許多玩家的首選娛樂平台。不論是新手還是老手,都能在這裡找到適合自己的遊戲和活動。
LEO娛樂城無法登入引發市場恐慌
2024 年 11 月 29 日,LEO娛樂城因技術問題出現短暫無法登入的情況,引發了廣泛關注。許多玩家擔心這是否意味著九州娛樂城的營運出現問題。
九州娛樂集團隨後發佈官方聲明,強調這僅僅是系統升級過程中的短暫問題,並承諾玩家的資金和數據安全不受任何影響。同時,九州娛樂表示將加強伺服器穩定性,確保未來類似情況不再發生。
熱門 ZG 電子遊戲——熱舞森巴老虎機
2024 年 11 月 8 日,ZG 電子遊戲推出了熱舞森巴老虎機,這款遊戲迅速成為市場上的熱門選擇。以南美熱情的森巴舞為主題,遊戲畫面充滿色彩,搭配動感的音樂,為玩家帶來視覺與聽覺的雙重享受。
遊戲亮點:
高倍數獎勵機制:每次轉盤都有機會觸發高額獎金。
特色免費遊戲:連續獲得特殊圖案即可啟動多次免費轉盤,提高獲勝機率。
適合新手與高端玩家:簡單的玩法規則與豐富的策略選擇滿足不同層級玩家的需求。
ZG 電子遊戲致力於為玩家提供創新且有趣的遊戲體驗,熱舞森巴老虎機無疑是今年最值得嘗試的遊戲之一。
2024 世界棒球 12 強賽精彩回顧
2024 年 11 月,中華隊參加了世界棒球 12 強賽,這項全球頂尖棒球賽事吸引了來自多國的球隊和球迷參與。中華隊 28 人的名單以年輕選手和經驗豐富的老將為基礎,展現了團隊的競技實力。
比賽亮點:
精彩賽程:比賽期間,中華隊展現了堅強的防守和出色的打擊表現。
門票銷售:賽事門票迅速售罄,顯示出棒球在台灣的高度受歡迎程度。
線上直播:各大平台提供了高畫質直播,讓更多球迷能夠即時觀看比賽,感受棒球魅力。
世界棒球 12 強賽不僅是比賽,更是全台灣球迷的一場盛宴,展現了棒球作為國民運動的無限魅力。
結語
從娛樂城的優惠活動到全球性的棒球賽事,2024 年對於遊戲和體育愛好者來說充滿了亮點。不論是參與冠天下娛樂城的優惠,體驗 ZG 電子遊戲的最新老虎機,還是為中華隊的棒球比賽加油,這一年都是充滿精彩與期待的一年! -
2024 年熱門娛樂城與活動解析
冠天下娛樂城優惠,帶來無限樂趣
在 2024 年 4 月 16 日,冠天下娛樂城推出了全新的優惠活動,旨在為玩家帶來更大的獲利機會和更高的娛樂體驗。這些優惠活動包括多種存款獎勵、會員專屬回饋以及豐富的遊戲競賽獎金,吸引了大批玩家參與。
冠天下娛樂城以其高透明度和用戶友好的政策,已成為許多玩家的首選娛樂平台。不論是新手還是老手,都能在這裡找到適合自己的遊戲和活動。
LEO娛樂城無法登入引發市場恐慌
2024 年 11 月 29 日,LEO娛樂城因技術問題出現短暫無法登入的情況,引發了廣泛關注。許多玩家擔心這是否意味著九州娛樂城的營運出現問題。
九州娛樂集團隨後發佈官方聲明,強調這僅僅是系統升級過程中的短暫問題,並承諾玩家的資金和數據安全不受任何影響。同時,九州娛樂表示將加強伺服器穩定性,確保未來類似情況不再發生。
熱門 ZG 電子遊戲——熱舞森巴老虎機
2024 年 11 月 8 日,ZG 電子遊戲推出了熱舞森巴老虎機,這款遊戲迅速成為市場上的熱門選擇。以南美熱情的森巴舞為主題,遊戲畫面充滿色彩,搭配動感的音樂,為玩家帶來視覺與聽覺的雙重享受。
遊戲亮點:
高倍數獎勵機制:每次轉盤都有機會觸發高額獎金。
特色免費遊戲:連續獲得特殊圖案即可啟動多次免費轉盤,提高獲勝機率。
適合新手與高端玩家:簡單的玩法規則與豐富的策略選擇滿足不同層級玩家的需求。
ZG 電子遊戲致力於為玩家提供創新且有趣的遊戲體驗,熱舞森巴老虎機無疑是今年最值得嘗試的遊戲之一。
2024 世界棒球 12 強賽精彩回顧
2024 年 11 月,中華隊參加了世界棒球 12 強賽,這項全球頂尖棒球賽事吸引了來自多國的球隊和球迷參與。中華隊 28 人的名單以年輕選手和經驗豐富的老將為基礎,展現了團隊的競技實力。
比賽亮點:
精彩賽程:比賽期間,中華隊展現了堅強的防守和出色的打擊表現。
門票銷售:賽事門票迅速售罄,顯示出棒球在台灣的高度受歡迎程度。
線上直播:各大平台提供了高畫質直播,讓更多球迷能夠即時觀看比賽,感受棒球魅力。
世界棒球 12 強賽不僅是比賽,更是全台灣球迷的一場盛宴,展現了棒球作為國民運動的無限魅力。
結語
從娛樂城的優惠活動到全球性的棒球賽事,2024 年對於遊戲和體育愛好者來說充滿了亮點。不論是參與冠天下娛樂城的優惠,體驗 ZG 電子遊戲的最新老虎機,還是為中華隊的棒球比賽加油,這一年都是充滿精彩與期待的一年! -
九州娛樂城與Leo娛樂城即將結束運營,玩家該如何應對?
近期娛樂城行業的消息引發了玩家的廣泛關注,其中「Leo娛樂城無法登入」和「九州娛樂城即將倒閉」成為熱門話題。根據官方公告,九州娛樂城及其旗下品牌,包括Leo娛樂城和THA娛樂城,將於2024年12月31日中午12點正式結束營業並關閉官網。這一消息不僅讓玩家感到震驚,也暴露出行業潛在的問題。
Leo娛樂城無法登入的原因
Leo娛樂城近期頻繁出現登入問題,這與其即將退出台灣市場的計劃息息相關。以下是造成登入困難的主要原因:
帳號或密碼問題
許多玩家因忘記密碼或帳號被盜導致登入失敗。然而,由於官方客服系統已停止服務,這些問題無法得到解決。
網頁技術問題
官網伺服器的不穩定或維護期間,可能出現「404錯誤」,讓玩家無法正常登入。
營運關閉計劃
隨著九州娛樂城宣布結束營業,Leo娛樂城的伺服器和備用網址也逐步停止運行,這是玩家無法登入的最大原因。
為何九州娛樂城退出台灣市場?
九州娛樂城決定退出台灣市場的原因可以歸納為以下幾點:
市場收益不足
台灣市場對九州娛樂城而言並不具備高盈利性,難以支撐長期運營。
第三方支付系統受阻
多次傳出第三方現金支付渠道中斷,影響存提款操作。
法律風險增加
九州娛樂城頻繁遭遇法律問題及負面新聞,導致營運壓力倍增。
玩家需要注意什麼?
隨著九州娛樂城及其旗下品牌逐步退出市場,玩家應及時採取以下措施:
提領餘額
官方已停止存款服務,但提領功能仍開放。玩家應儘快提領餘額,避免損失。
轉移到穩定平台
針對Leo娛樂城和九州娛樂城的退出,玩家可選擇更穩定且具信譽的平台,以保障自己的娛樂體驗。
防範詐騙
小心冒名客服或假網站,官方已停止客服系統,不會主動聯繫玩家索取個人資料。
未來哪些娛樂城值得信賴?
隨著九州娛樂城退出市場,玩家可以關注一些以穩定性和合法性著稱的娛樂平台。選擇時應注意以下幾點:
合法牌照
選擇擁有合法經營許可的娛樂平台。
穩定的支付系統
平台應提供多種穩定且快速的支付方式。
用戶口碑
瀏覽玩家的評價和反饋,選擇高評價的平台。
結論
九州娛樂城及其旗下品牌的關閉標誌著一個時代的結束,同時也提醒玩家關注行業的合規性和穩定性。在此轉型時期,玩家應保持警惕,選擇可靠的平台,以確保自己的資金和遊戲體驗不受影響。 -
Leo娛樂城無法登入
九州娛樂城與Leo娛樂城即將結束運營,玩家該如何應對?
近期娛樂城行業的消息引發了玩家的廣泛關注,其中「Leo娛樂城無法登入」和「九州娛樂城即將倒閉」成為熱門話題。根據官方公告,九州娛樂城及其旗下品牌,包括Leo娛樂城和THA娛樂城,將於2024年12月31日中午12點正式結束營業並關閉官網。這一消息不僅讓玩家感到震驚,也暴露出行業潛在的問題。
Leo娛樂城無法登入的原因
Leo娛樂城近期頻繁出現登入問題,這與其即將退出台灣市場的計劃息息相關。以下是造成登入困難的主要原因:
帳號或密碼問題
許多玩家因忘記密碼或帳號被盜導致登入失敗。然而,由於官方客服系統已停止服務,這些問題無法得到解決。
網頁技術問題
官網伺服器的不穩定或維護期間,可能出現「404錯誤」,讓玩家無法正常登入。
營運關閉計劃
隨著九州娛樂城宣布結束營業,Leo娛樂城的伺服器和備用網址也逐步停止運行,這是玩家無法登入的最大原因。
為何九州娛樂城退出台灣市場?
九州娛樂城決定退出台灣市場的原因可以歸納為以下幾點:
市場收益不足
台灣市場對九州娛樂城而言並不具備高盈利性,難以支撐長期運營。
第三方支付系統受阻
多次傳出第三方現金支付渠道中斷,影響存提款操作。
法律風險增加
九州娛樂城頻繁遭遇法律問題及負面新聞,導致營運壓力倍增。
玩家需要注意什麼?
隨著九州娛樂城及其旗下品牌逐步退出市場,玩家應及時採取以下措施:
提領餘額
官方已停止存款服務,但提領功能仍開放。玩家應儘快提領餘額,避免損失。
轉移到穩定平台
針對Leo娛樂城和九州娛樂城的退出,玩家可選擇更穩定且具信譽的平台,以保障自己的娛樂體驗。
防範詐騙
小心冒名客服或假網站,官方已停止客服系統,不會主動聯繫玩家索取個人資料。
未來哪些娛樂城值得信賴?
隨著九州娛樂城退出市場,玩家可以關注一些以穩定性和合法性著稱的娛樂平台。選擇時應注意以下幾點:
合法牌照
選擇擁有合法經營許可的娛樂平台。
穩定的支付系統
平台應提供多種穩定且快速的支付方式。
用戶口碑
瀏覽玩家的評價和反饋,選擇高評價的平台。
結論
九州娛樂城及其旗下品牌的關閉標誌著一個時代的結束,同時也提醒玩家關注行業的合規性和穩定性。在此轉型時期,玩家應保持警惕,選擇可靠的平台,以確保自己的資金和遊戲體驗不受影響。 -
Discover the world of Minecraft
Experience the Universe of Minecraft: Your Ultimate Survival and Anarchy Quest
Welcome to your Portal to the Extremely Thrilling and Engaging Minecraft Online Journey. Whether you’re a Architect, Combatant, Traveler, or Planner, our Server Offers Endless Opportunities to Experience Endurance and Disorder Options in Experiences you’ve Rarely seen Before.
---
Why Select Experiences in Minecraft?
Our Realm is Designed to Provide the Ultimate Minecraft Adventure, Combining Tailored Realms, Thrilling Gameplay, and a Vibrant Society. Traverse, Conquer, and Create your own Journeys with Unique Components Created for Every type of Participant.
---
Primary Features
- Endurance and Disorder Modes: Face the Thrill of Persisting against the odds or Immerse into Untamed PvP Battles with no rules and full freedom.
- Large Realm Scale: With Space for up to 3,750 Participants, the Action never stops.
- 24/7 Realm Access: Join Whenever to Take Part In Smooth, Consistent Mechanics.
- Tailored Material: Discover our Precisely Crafted Minecraft Environments Packed with Enhancements, Plugins, and Exclusive Objects from our Virtual Marketplace.
---
Distinctive Playstyle Features
Living Option
In Survival Mode, you’ll Discover Expansive Environments, Acquire Assets, and Create to your heart's content. Defeat off Opponents, Partner with Partners, or Conquer on Solo Challenges where only the Resilient Overcome.
Anarchy Scenario
For Players Seeking Excitement and Adrenaline, Freedom Mode Provides a Realm with No Rules. Dive in Competitive PvP Engagements, Build Teams, or Challenge Enemies to Rule the World. Here, Persistence of the Strongest is the Ultimate Order.
---
Custom Minecraft Features
- Adventure Maps: Discover Special Minecraft Maps and Exciting Quests.
- Commerce and Exchanges: Our Interactive Economy Allows you to Sell, Obtain, and Trade Products to Ascend the Tiers and Form Your Identity as a Dominant Player.
- Minecraft Marketplace: Access Unique Tools, Improvements, and Levels that Boost your Playstyle.
---
Minecraft Marketplace: Upgrade Your Interaction
Our Interactive Store Offers a Selection of Enhancements, Levels, and Products to Fit every Playstyle. From Cheap Donation Cases to Exclusive Statuses, you can Gain Fresh Features and Advance your Experience to the Next Level.
---
Top Items
- Donate Cases (x10) – €1.00
- VIP – €1.40
- Elysium Level – €20.00
- OWNER Status – €40.00
- BOSS Level – €60.00
---
Top Statuses for Best Gamers
- CREATOR (€10.00) – Unlock Artistic Options to Express your Imagination.
- Vanguard (€12.00) – Top Benefits and Tailored Features.
- Paragon (€59.10) – Special Benefits for the Ultimate User.
- Luminescent (€50.00) – Dominate as a Top-Tier Champion on the Platform.
---
Join Our Growing Minecraft Community
We Strive in Forming a Encouraging, Engaging, and Inclusive Community. Whether you’re Challenging RPG Adventures, Discovering Tailored Worlds, or Taking Part in Interactive PvP, there’s Consistently something Exciting to Explore.
---
Things You Can Expect
- Friendly Community: Interact With Like-Minded Minecraft Players from Around the World.
- Exciting Challenges: Engage in Unique Tasks, Tournaments, and Server-Wide Contests.
- Dedicated Help: Our Moderators Ensures Reliable Interaction and Supports you with any Concerns. -
Welcome to the GTA 5 Roleplay Experience!
Our GTA 5 RP server delivers a huge open-world gameplay augmented with custom personalized mods and mechanics features.
Whether you’re a law-abiding officer or a rising crime genius, the opportunities in this world are limitless:
Establish Your Empire: Form gangs, lead raids, or ascend the criminal network to rule the territory.
Transform Into a Savior: Enforce law as a law enforcer, firefighter, or paramedic.
Personalize Your Adventure: Design your living, from luxury automobiles and properties to your player’s unique look and narratives.
Exciting Quests: Participate in adrenaline-fueled missions, spectacular challenges, and interactive tasks to earn benefits and reputation.
Rule the Economy and Amass Wealth!
At vs-rp.com, we provide you the tools and chances to gain big in the in-game world of GTA RP. From obtaining luxury properties to building wealth, the RP market is yours to dominate.
Develop your success through:
Player-Driven Quests: Accomplish missions, trades, and assignments to receive online wealth.
Custom Businesses: Start and operate your own operation, from vehicle markets to nightclubs.
High-End Assets: Own luxury cars, rare real estate, and exclusive virtual goods.
Are you ready to dominate Los Santos and become a in-game mogul?
Benefits of Pick Our Server?
Here’s why we’re the best GTA 5 RP realm:
1. Frequent Enhancements and Activities
Stay ahead of the game with unique features, missions, and timely activities. New features are released frequently to make your interaction engaging and fun.
2. Extensive Selection of Resources
Browse a enormous range of in-game goods, including:
High-End Vehicles
Luxury Homes
Rare Items
3. Committed Assistance
Whether you’re a experienced gamer or a novice starter, our helpers is ready to support. We’ll assist you in setting up, give help, and guarantee you succeed in Los Santos. -
скачать zkw reborn взлом [url=https://apk-smart.com/igry/zombi/1614-zombie-assault-sniper-vzlomannyj-chit-mnogo-deneg.html]https://apk-smart.com/igry/zombi/1614-zombie-assault-sniper-vzlomannyj-chit-mnogo-deneg.html[/url] скачать zkw reborn взлом
P.S Live ID: K89Io9blWX1UfZWv3ajv
P.S.S [url=http://www.ziganshin.ru/guest/capcha.php?s=mre0tu4g2qa3aest32h7ii6tjj]Программы и игры для Андроид телефона[/url] [url=https://www.nkrs.rsko.cz/phpbb/viewtopic.php?f=118&t=42997&p=5058966#p5058966]Программы и игры для Андроид телефона[/url] [url=https://www.leparisavignon.com/fr/programmation/alil-vardar-seul-en-scene/#AvisList]Программы и игры для Андроид телефона[/url] c6d09cd -
Explore CS2 Skin
Explore the World of CS2 Skins: Find the Ultimate Look for Your Gameplay
Enhance your matches with one-of-a-kind, superior cosmetics that enhance the look of your gear and make your inventory truly be exceptional.
We provide a huge selection of designs — from hard-to-find items to special edition options, offering you the opportunity to customize your arsenal and highlight your uniqueness.
Why Select Us?
Buying Counter-Strike 2 skins from us is quick, reliable, and simple. With quick digital fulfillment straight to your account, you can instantly using your latest gear instantly.
Key Features:
- Reliable Payments: Enjoy secure, risk-free transactions always.
- Affordable Costs: We provide the lowest CS2 skin offers with ongoing price drops.
- Extensive Collection: From affordable to exclusive items, we have it all.
How It Works:
1. View the Selection
Navigate our vast range of designs, sorted by style, exclusivity, and theme.
2. Find Your Item
Once you choose the perfect option, add it to your shopping list and move to purchase.
3. Equip Your Latest Skins
Receive your skins instantly and use them in-game to show off.
Why We Are Trusted:
- Vast Selection: Explore designs for every preference.
- Affordable Pricing: Honest prices with no additional surprises.
- Instant Delivery: Receive your gear right away.
- Secure Transactions: Secure and risk-free payment options.
- Customer Support: Our experts is here to assist you whenever needed.
Get Started Immediately!
Find the top CS2 skins and enhance your gameplay to the next level.
Whether you’re hoping to enhance your gear, build a exclusive set, or simply be unique, we|our store|our site|our marketplace is your preferred platform for premium Counter-Strike 2 skins.
Start now and select the skin that matches your preferences! -
The Perfect Source for AI-Powered Creativity
Unlock the ultimate capabilities of AI tools with custom-crafted, high-quality resources created to enhance your imagination and results. Whether you’re a advertiser, a copywriter, a designer, or a developer, our meticulously crafted prompts at Template Forge are the resources you require to bring your ideas to the ultimate stage.
Why Choose Template Forge?
At Our Store, we’re committed to sharing exclusively the highest-quality solutions, guaranteeing value, premium standards, and user-friendliness. Here’s what makes us creators trust us as their preferred resource provider:
Well-Crafted Solutions
Our skilled experts diligently designs templates that are practical, creative, and immediately applicable. Each solution is crafted to provide results, enabling you to achieve goals efficiently and smoothly.
Diverse Categories
From content promotion to narrative ideas, tech solutions, and artistic inspiration, we feature a wide range of applications. Our prompts are designed for professionals and hobbyists in various specialty.
Adaptable Templates
Each solution is entirely customizable, making it possible to tailor it to your specific task requirements. This versatility guarantees our templates are widely applicable and adaptable for multiple fields and goals.
User-Friendly Experience
We respect your energy. With fast transfers, pre-packaged sets, and an easy-to-use platform, using and implementing the ideal resources has never been more convenient.
Check Out Our Recent Templates
Discover templates that boost success, ignite ideas, and enhance workflows.
Why Creators Love Us
- Extensive Range: Access prompts for all purpose.
- Budget-Friendly Options: Professional-grade solutions starting at just 5.00 €.
- Immediate Downloads: Download your prompts without delay.
- Trusted Quality: Each resource is verified and guaranteed to provide results.
- Round-the-Clock Assistance: Looking for help? Our specialists is readily on standby to guide you.
Get Started Today!
Discover the top solutions and transform your ideas to the new heights.
Start now and find the prompts that define your goals! -
Your Go-To Destination for Artificial Intelligence-Based Content Creation
Tap into the ultimate possibilities of AI tools with tailor-made, premium prompts built to enhance your creativity and productivity. Whether you’re a promoter, a writer, a artist, or a coder, our meticulously crafted prompts at Templateforge are the solutions you require to propel your ideas to the next level.
Why Choose Us?
At Our Platform, we’re dedicated to providing only the most effective AI prompts, providing applicability, high standards, and ease of use. Here’s the reasons creators choose us as their trusted AI prompt marketplace:
High-Quality Prompts
Our professional creators diligently creates resources that are functional, unique, and plug-and-play. Each prompt is crafted to deliver value, helping you attain success quickly and effortlessly.
Extensive Options
From digital advertising to creative storytelling, problem-solving tools, and visual concepts, we offer a wide range of industries. Our prompts are crafted for enthusiasts and innovators in various niche.
Adaptable Templates
Each prompt is completely customizable, allowing you to adjust it to your particular task preferences. This customizability guarantees our prompts are widely applicable and suitable for different industries and needs.
Seamless Process
We value your energy. With quick delivery, organized collections, and an intuitive interface, using and using the best AI prompts has never been so simple.
Discover Our Latest Prompts
Find prompts that enhance interaction, spark creativity, and enhance processes.
What Sets Us Apart
- Huge Catalog: Find solutions for any purpose.
- Budget-Friendly Options: High-quality solutions starting at just 5.00 €.
- Instant Access: Download your templates right away.
- Guaranteed Excellence: Each solution is proven and guaranteed to provide success.
- 24/7 Support: Need assistance? Our experts is always ready to guide you.
Begin Your Journey!
Access the most innovative templates and elevate your work to the highest point.
Start now and explore the tools that reflect your goals! -
The Ultimate One-Stop Shop for AI-Enhanced Creativity
Unleash the complete power of Artificial Intelligence with tailor-made, professional-grade templates designed to enhance your innovation and results. Whether you’re a promoter, a writer, a artist, or a technologist, our thoughtfully designed templates at Template Forge are the tools you require to elevate your projects to the top tier.
Why Pick Our Platform?
At Our Store, we’re dedicated to sharing nothing but the highest-quality resources, ensuring relevance, excellence, and user-friendliness. Here’s what makes us innovators choose us as their preferred AI prompt source:
Premium Resources
Our expert team meticulously develops templates that are useful, cutting-edge, and plug-and-play. Each solution is built to ensure impact, helping you achieve goals efficiently and easily.
Extensive Options
From marketing solutions to story development, development prompts, and visual concepts, we provide a comprehensive catalog of industries. Our prompts are created for professionals and enthusiasts in all industry.
Flexible Solutions
Each template is easily customizable, making it possible to tailor it to your particular workflow needs. This versatility provides our prompts are widely applicable and adaptable for various industries and goals.
Intuitive Interface
We prioritize your productivity. With immediate access, organized prompt bundles, and an seamless experience, discovering and leveraging the ideal resources has become effortless.
Check Out Our Latest Prompts
Discover prompts that drive interaction, ignite imagination, and enhance workflows.
Why Choose Us
- Vast Selection: Find templates for all purpose.
- Affordable Pricing: Professional-grade resources starting at just 5.00 €.
- Quick Delivery: Receive your templates instantly.
- Guaranteed Excellence: Each template is tested and proven to achieve value.
- 24/7 Support: Got an issue? Our specialists is always here to guide you.
Start Shopping Now!
Find the most innovative solutions and transform your tasks to the new heights.
Sign in and explore the tools that match your needs! -
Your One-Stop Shop for AI-Powered Creativity
Your Source for AI-Driven Creativity
Unleash the maximum possibilities of Artificial Intelligence with specially designed, high-quality resources crafted to elevate your creativity and productivity. Whether you’re a marketing professional, a writer, a visual creator, or a programmer, our expertly curated resources at Our Platform are the solutions you need to bring your work to the top tier.
Why Trust Template Forge?
At Our Platform, we’re committed to delivering nothing but the top-notch solutions, providing applicability, premium standards, and simplicity. Here’s why thousands of innovators prefer us as their go-to template marketplace:
Top-Quality Templates
Our team of specialists meticulously creates prompts that are effective, innovative, and plug-and-play. Each template is developed to deliver success, helping you achieve objectives quickly and easily.
Varied Applications
From marketing solutions to narrative ideas, development prompts, and visual concepts, we provide a wide range of applications. Our resources are built for users and innovators in all industry.
Adaptable Templates
Each solution is easily modifiable, enabling you to adjust it to your unique workflow demands. This flexibility ensures our prompts are multi-purpose and effective for a range of applications and tasks.
Seamless Process
We respect your energy. With immediate access, structured packages, and an easy-to-use platform, finding and using the best templates has never been so simple.
Explore Our Newest Additions
Unlock solutions that enhance engagement, spark imagination, and optimize productivity.
Why Choose Us
- Vast Selection: Find prompts for all purpose.
- Fair Prices: Top-notch resources starting at just 5.00 €.
- Quick Delivery: Download your solutions right away.
- Guaranteed Excellence: Each prompt is proven and guaranteed to achieve success.
- Always Available Help: Have questions? Our experts is readily here to assist you.
Start Shopping Now!
Find the best AI prompts and elevate your projects to the highest point.
Join us and find the tools that fit your goals! -
https://pando.life/article/127995 Where to Buy Cheap clomid
-
### 貓飼料選擇指南:如何挑選最適合您愛貓的飼料?
貓咪是許多家庭的可愛成員,選擇適合的貓飼料不僅能確保牠們健康,還能讓牠們保持快樂。市面上的貓飼料種類繁多,如何找到最適合您愛貓的選擇呢?本文將為您提供一些實用的建議。
#### 貓飼料的基本類型
1. **乾飼料(乾糧)**
- 優點:方便存放、價格相對實惠,有助於清潔貓咪牙齒。
- 缺點:水分含量低,貓咪需要額外補充水分。
2. **濕飼料(罐頭或袋裝)**
- 優點:水分含量高,適合需要額外補水的貓咪,口感較佳。
- 缺點:開封後需冷藏,保存期限較短。
3. **冷凍乾燥飼料**
- 優點:保留了食材的營養,方便攜帶且保存期長。
- 缺點:價格較高,需用水泡發後餵食。
4. **生鮮飼料**
- 優點:最接近貓咪天然飲食習慣,營養豐富。
- 缺點:需嚴格控溫保存,製作麻煩。
#### 挑選貓飼料的關鍵因素
1. **年齡和生命階段**
- 幼貓、成貓、老年貓的營養需求不同。選擇標示適合該階段的飼料。
2. **健康狀況**
- 若貓咪有特殊健康問題(如腎臟病、肥胖或過敏),應選擇專門配方的醫療飼料。
3. **成分與營養標示**
- 優質貓飼料的第一項成分應為肉類或魚類,避免含過多填充劑(如玉米、小麥)。
4. **貓咪的口味偏好**
- 每隻貓咪的口味都不同,可能需要嘗試多種品牌來找到最受牠們喜愛的選擇。
5. **品牌信譽與評價**
- 選擇有良好口碑和高評價的品牌,並注意是否有第三方檢測認證。
#### 如何逐步更換貓飼料?
如果需要更換貓咪的飼料,請遵循以下步驟以避免腸胃不適:
1. 第1-3天:新飼料混入原飼料的25%。
2. 第4-6天:新飼料比例提升至50%。
3. 第7-9天:新飼料比例提升至75%。
4. 第10天以後:完全更換為新飼料。
#### 常見問題解答
1. **我的貓咪不喝水,怎麼辦?**
- 可以選擇濕飼料,或在乾飼料上噴一些水。
2. **如何分辨貓飼料是否過期?**
- 注意包裝上的有效日期,並確保飼料沒有異味或變色。
3. **可以給貓咪吃人類食物嗎?**
- 一些人類食物對貓咪有害,如巧克力、洋蔥、大蒜,應避免餵食。
#### 總結
選擇適合的貓飼料需要考量多種因素,包括貓咪的年齡、健康狀況和口味偏好。為了確保愛貓健康,建議定期諮詢獸醫,並為牠們提供均衡的飲食。讓您的貓咪擁有健康快樂的每一天! -
### 貓飼料選擇指南:如何挑選最適合您愛貓的飼料?
貓咪是許多家庭的可愛成員,選擇適合的貓飼料不僅能確保牠們健康,還能讓牠們保持快樂。市面上的貓飼料種類繁多,如何找到最適合您愛貓的選擇呢?本文將為您提供一些實用的建議。
#### 貓飼料的基本類型
1. **乾飼料(乾糧)**
- 優點:方便存放、價格相對實惠,有助於清潔貓咪牙齒。
- 缺點:水分含量低,貓咪需要額外補充水分。
2. **濕飼料(罐頭或袋裝)**
- 優點:水分含量高,適合需要額外補水的貓咪,口感較佳。
- 缺點:開封後需冷藏,保存期限較短。
3. **冷凍乾燥飼料**
- 優點:保留了食材的營養,方便攜帶且保存期長。
- 缺點:價格較高,需用水泡發後餵食。
4. **生鮮飼料**
- 優點:最接近貓咪天然飲食習慣,營養豐富。
- 缺點:需嚴格控溫保存,製作麻煩。
#### 挑選貓飼料的關鍵因素
1. **年齡和生命階段**
- 幼貓、成貓、老年貓的營養需求不同。選擇標示適合該階段的飼料。
2. **健康狀況**
- 若貓咪有特殊健康問題(如腎臟病、肥胖或過敏),應選擇專門配方的醫療飼料。
3. **成分與營養標示**
- 優質貓飼料的第一項成分應為肉類或魚類,避免含過多填充劑(如玉米、小麥)。
4. **貓咪的口味偏好**
- 每隻貓咪的口味都不同,可能需要嘗試多種品牌來找到最受牠們喜愛的選擇。
5. **品牌信譽與評價**
- 選擇有良好口碑和高評價的品牌,並注意是否有第三方檢測認證。
#### 如何逐步更換貓飼料?
如果需要更換貓咪的飼料,請遵循以下步驟以避免腸胃不適:
1. 第1-3天:新飼料混入原飼料的25%。
2. 第4-6天:新飼料比例提升至50%。
3. 第7-9天:新飼料比例提升至75%。
4. 第10天以後:完全更換為新飼料。
#### 常見問題解答
1. **我的貓咪不喝水,怎麼辦?**
- 可以選擇濕飼料,或在乾飼料上噴一些水。
2. **如何分辨貓飼料是否過期?**
- 注意包裝上的有效日期,並確保飼料沒有異味或變色。
3. **可以給貓咪吃人類食物嗎?**
- 一些人類食物對貓咪有害,如巧克力、洋蔥、大蒜,應避免餵食。
#### 總結
選擇適合的貓飼料需要考量多種因素,包括貓咪的年齡、健康狀況和口味偏好。為了確保愛貓健康,建議定期諮詢獸醫,並為牠們提供均衡的飲食。讓您的貓咪擁有健康快樂的每一天! -
ST666-Nhà Cái Cá Cược Trực Tuyến Hàng Đầu Năm 2023
ST666 hiện đang được đánh giá là một trong những nhà cái trực tuyến uy tín và đẳng cấp nhất tại Châu Á. Với giấy phép hoạt động được cấp bởi tổ chức PAGCOR và First Cagayan, ST666 mang đến cho người chơi những trải nghiệm cá cược chuyên nghiệp, minh bạch và công bằng.
Tại sao nên chọn ST666?
1. Uy tín vượt trội
ST666 đã xây dựng được sự tín nhiệm từ cộng đồng người chơi nhờ hệ thống bảo mật cao cấp và các giao dịch tài chính minh bạch. Đội ngũ quản lý có kinh nghiệm dày dặn đảm bảo mọi hoạt động luôn diễn ra trơn tru và đáng tin cậy.
2. Sự đa dạng trong sản phẩm
ST666 cung cấp nhiều loại hình cá cược hấp dẫn như:
Cá cược thể thao với tỷ lệ kèo cạnh tranh.
Casino trực tuyến với các trò chơi phổ biến như Baccarat, Blackjack, và Roulette.
Slot game với hàng trăm tựa game độc đáo và đổi thưởng cao.
Bắn cá đổi thưởng và các trò chơi giải trí khác.
3. Giao dịch nhanh chóng, tiện lợi
Hệ thống giao dịch tại ST666 hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức nạp và rút tiền nhanh chóng:
Chuyển khoản ngân hàng.
Ví điện tử như Momo, ZaloPay.
Thẻ cào điện thoại.
4. Khuyến mãi hấp dẫn
ST666 thường xuyên tổ chức các chương trình khuyến mãi độc quyền, bao gồm:
Thưởng 200% cho nạp tiền lần đầu.
Hoàn trả tiền cược mỗi ngày.
Ưu đãi đặc biệt cho thành viên VIP.
Hướng dẫn tham gia ST666
1. Đăng ký tài khoản
Người chơi cần cung cấp thông tin cơ bản để tạo tài khoản và bắt đầu hành trình trải nghiệm tại ST666.
2. Nạp tiền nhanh chóng
ST666 hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức nạp tiền an toàn, mang lại sự tiện lợi tối đa cho người chơi.
3. Sử dụng ứng dụng ST666
Ứng dụng của ST666 được tối ưu hóa để sử dụng trên cả hai nền tảng iOS và Android, giúp người chơi có thể truy cập và tham gia mọi lúc, mọi nơi.
4. Chương trình đại lý
Để kiếm thêm thu nhập, người chơi có thể đăng ký tham gia làm đại lý của ST666 và nhận hoa hồng cao từ doanh thu.
Chính sách bảo mật và điều khoản dịch vụ
ST666 cam kết bảo mật thông tin cá nhân của người chơi thông qua hệ thống mã hóa hiện đại. Các điều khoản dịch vụ được thiết lập rõ ràng để đảm bảo quyền lợi của người chơi.
Kết luận
ST666 là nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến hàng đầu với hệ thống hiện đại, dịch vụ chuyên nghiệp và nhiều chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn. Đây chính là lựa chọn lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê cá cược và muốn trải nghiệm giải trí trực tuyến đẳng cấp. Tham gia ngay hôm nay để chinh phục những cơ hội lớn cùng ST666! -
ST666
ST666-Nhà Cái Cá Cược Trực Tuyến Hàng Đầu Năm 2023
ST666 hiện đang được đánh giá là một trong những nhà cái trực tuyến uy tín và đẳng cấp nhất tại Châu Á. Với giấy phép hoạt động được cấp bởi tổ chức PAGCOR và First Cagayan, ST666 mang đến cho người chơi những trải nghiệm cá cược chuyên nghiệp, minh bạch và công bằng.
Tại sao nên chọn ST666?
1. Uy tín vượt trội
ST666 đã xây dựng được sự tín nhiệm từ cộng đồng người chơi nhờ hệ thống bảo mật cao cấp và các giao dịch tài chính minh bạch. Đội ngũ quản lý có kinh nghiệm dày dặn đảm bảo mọi hoạt động luôn diễn ra trơn tru và đáng tin cậy.
2. Sự đa dạng trong sản phẩm
ST666 cung cấp nhiều loại hình cá cược hấp dẫn như:
Cá cược thể thao với tỷ lệ kèo cạnh tranh.
Casino trực tuyến với các trò chơi phổ biến như Baccarat, Blackjack, và Roulette.
Slot game với hàng trăm tựa game độc đáo và đổi thưởng cao.
Bắn cá đổi thưởng và các trò chơi giải trí khác.
3. Giao dịch nhanh chóng, tiện lợi
Hệ thống giao dịch tại ST666 hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức nạp và rút tiền nhanh chóng:
Chuyển khoản ngân hàng.
Ví điện tử như Momo, ZaloPay.
Thẻ cào điện thoại.
4. Khuyến mãi hấp dẫn
ST666 thường xuyên tổ chức các chương trình khuyến mãi độc quyền, bao gồm:
Thưởng 200% cho nạp tiền lần đầu.
Hoàn trả tiền cược mỗi ngày.
Ưu đãi đặc biệt cho thành viên VIP.
Hướng dẫn tham gia ST666
1. Đăng ký tài khoản
Người chơi cần cung cấp thông tin cơ bản để tạo tài khoản và bắt đầu hành trình trải nghiệm tại ST666.
2. Nạp tiền nhanh chóng
ST666 hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức nạp tiền an toàn, mang lại sự tiện lợi tối đa cho người chơi.
3. Sử dụng ứng dụng ST666
Ứng dụng của ST666 được tối ưu hóa để sử dụng trên cả hai nền tảng iOS và Android, giúp người chơi có thể truy cập và tham gia mọi lúc, mọi nơi.
4. Chương trình đại lý
Để kiếm thêm thu nhập, người chơi có thể đăng ký tham gia làm đại lý của ST666 và nhận hoa hồng cao từ doanh thu.
Chính sách bảo mật và điều khoản dịch vụ
ST666 cam kết bảo mật thông tin cá nhân của người chơi thông qua hệ thống mã hóa hiện đại. Các điều khoản dịch vụ được thiết lập rõ ràng để đảm bảo quyền lợi của người chơi.
Kết luận
ST666 là nhà cái cá cược trực tuyến hàng đầu với hệ thống hiện đại, dịch vụ chuyên nghiệp và nhiều chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn. Đây chính là lựa chọn lý tưởng cho những ai đam mê cá cược và muốn trải nghiệm giải trí trực tuyến đẳng cấp. Tham gia ngay hôm nay để chinh phục những cơ hội lớn cùng ST666! -
Top Online Advertising Firm in Lagos That Puts Your Consumers First
Overview
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing, discovering the appropriate collaborator to enhance your enterprise can feel daunting. Content Krush stands out as the leading digital marketing company in Lagos, committed to prioritizing your consumers first. Our analytics-based strategy encompasses a range of offerings, including SEO, Increase Marketing, B2B Prospect Generation, Creative Marketing, Electronic Marketing, and Web and App Development.
Our Superpowers
At Content Krush, our capabilities lie in establishing lasting relationships with your intended audience. Through thoroughly analyzed client insights and compelling content, we have successfully delivered excellent performances across web, SEO, and social media channels for our customers.
Proven Track Record
Over the past seven years, we have worked with firms across multiple sectors, including Financial Technology, Cloud Services, Talent Marketplace, Digital Insurance, Nourishment & Beverages, Teaching, Broadcasting, and Health Business-to-Business Software as a Service. Our actions have resulted in notable increases in web visitors by up to eighty percent and sales growth by one hundred eighty-six percent.
Meet Our Creator
Adeyemi Olanrewaju
Creator | Expansion Marketing
Understanding the Digital Landscape
Did you understand that 68% of digital encounters begin with a search engine? This underscores the significance of enhancing your digital presence. To support you improve your web traffic and keyword ranking, we extend a Complimentary SEO Audit. Let us support you discover areas of growth and maximize your site’s capabilities.
# What We Do
Our strategy focuses on four primary steps: Access, Attract, Change, and Involve. We inspect your customer journey to discover leakages in your growth strategy, delivering personalized strategies to improve your company performance.
Success Testimonials
# Digital Insurance Client
One of our notable success cases involves positioning a website for 45 Google Search Engine 1st Page search terms in just three months for a leading digital insurance service provider. Our strategies resulted to a fifty-eight percent growth in online visits, 83% more site interaction, and a sixteen percent reduction in exit rate.
# Baby Food Client
During the crisis, we enabled a partner to market over 14,000 baby food goods worth one hundred forty-two thousand dollars through their platform. Our actions in boosting brand visibility not only boosted online sales but also catalyzed a 60% growth in in-store transactions.
Get Started Today
Are you struggling to grow your enterprise? Let's assess your marketing funnel and discover strategies customized to your needs. As the top digital marketing company in Lagos State, we make use of actionable data and proven strategies to assist you obtain new heights in your business.
How We Assist
Whether you operate a small enterprise, a advisory agency, or lead a emerging company in the Fast-Moving Consumer Goods or Financial Technology space, Content Krush is here to deliver real effects. Our expertise encompasses:
- SEO - 90%
- Growth Marketing - eighty percent
- Business-to-Business Lead Generation - 80%
- Creative Marketing - 90%
Let us partner with you to develop and carry out growth strategies that will drive visitors, leads, and income.
Contact Us
Set to take your digital marketing to the following level? Get in touch with us now for a Free SEO Audit and let’s explore how we can support your enterprise reach, draw, and engage more clients. -
台中外送茶:安全快速的外約服務指南
引言
台中外送茶是一項方便且受歡迎的服務,無論是夜晚的放鬆需求還是特殊場合的社交活動,都能提供快速、安全且專業的體驗。本文將深入探討台中外送茶的選擇、流程以及相關注意事項,幫助您在選擇服務時更加安心與滿意。
什麼是台中外送茶?
台中外送茶服務主要提供以下特點:
快速應對:透過線上或電話聯繫,立即安排外送服務。
多元選擇:服務涵蓋不同需求,從高端到實惠方案應有盡有。
隱私保障:強調保密性,確保客戶資料不被外洩。
台中外送茶適合哪些人?
商務旅客:在台中短期停留,追求品質與方便的伴侶服務。
壓力族群:希望藉由互動放鬆身心,增添生活樂趣。
聚會需求:特殊場合、生日或朋友聚會需要專業的伴侶服務。
選擇台中外送茶的注意事項
如何選擇安全的服務?
查詢評價:選擇高評價且有口碑的服務提供者。
確認價格透明:避免隱藏費用,提前溝通價格範圍。
合法經營:確認服務平台是否具備合法經營的資格。
常見的服務流程
聯繫服務商家,了解可提供的選項及價格。
確定時間與地點,確保雙方需求達成一致。
接收外送服務,享受專業的伴侶陪伴。 -
台中外送茶
台中外送茶:安全快速的外約服務指南
引言
台中外送茶是一項方便且受歡迎的服務,無論是夜晚的放鬆需求還是特殊場合的社交活動,都能提供快速、安全且專業的體驗。本文將深入探討台中外送茶的選擇、流程以及相關注意事項,幫助您在選擇服務時更加安心與滿意。
什麼是台中外送茶?
台中外送茶服務主要提供以下特點:
快速應對:透過線上或電話聯繫,立即安排外送服務。
多元選擇:服務涵蓋不同需求,從高端到實惠方案應有盡有。
隱私保障:強調保密性,確保客戶資料不被外洩。
台中外送茶適合哪些人?
商務旅客:在台中短期停留,追求品質與方便的伴侶服務。
壓力族群:希望藉由互動放鬆身心,增添生活樂趣。
聚會需求:特殊場合、生日或朋友聚會需要專業的伴侶服務。
選擇台中外送茶的注意事項
如何選擇安全的服務?
查詢評價:選擇高評價且有口碑的服務提供者。
確認價格透明:避免隱藏費用,提前溝通價格範圍。
合法經營:確認服務平台是否具備合法經營的資格。
常見的服務流程
聯繫服務商家,了解可提供的選項及價格。
確定時間與地點,確保雙方需求達成一致。
接收外送服務,享受專業的伴侶陪伴。 -
台北外送茶
台北外送茶:精選安全便捷的外約服務攻略
引言
台北外送茶服務因其便利性與多樣化而備受歡迎,不僅滿足社交需求,更以快速、安全為核心,成為許多人的理想選擇。本文將深入剖析台北外送茶的特點、流程,以及如何選擇適合的服務,幫助您享受安心的高品質體驗。
什麼是台北外送茶服務?
台北外送茶服務是一種針對多元需求的伴侶外約服務,常見特點如下:
即時安排:快速回應客戶需求,提供靈活的服務時間。
多元選擇:從高端到平價方案,滿足各種預算層級。
私密性高:確保所有客戶資料絕對保密,安全性有保障。
為什麼選擇台北外送茶?
生活壓力舒緩:透過高品質的互動體驗,放鬆身心。
臨時需求應對:解決因臨時變動產生的陪伴需求。
特定場合加分:生日、商務活動等場合的高端陪伴服務。
如何選擇優質的台北外送茶服務?
辨別專業合法服務的重要性
查看評價:選擇具有良好口碑的服務商。
確認價格透明:事先了解費用,避免臨時加價問題。
重視隱私保障:選擇承諾保密的合法經營商家。
服務流程簡介
聯繫商家,表達需求並獲得建議。
確定伴侶類型與服務細節。
安排時間地點,享受服務。
提升台北外送茶體驗的建議
事先規劃:提前安排服務,避免臨時出現不便。
選擇信譽品牌:確保選擇口碑良好的服務商,避免風險。
溝通需求:明確表達需求與期待,達成雙方共識。 -
台北外送茶
台北外送茶:精選安全便捷的外約服務攻略
引言
台北外送茶服務因其便利性與多樣化而備受歡迎,不僅滿足社交需求,更以快速、安全為核心,成為許多人的理想選擇。本文將深入剖析台北外送茶的特點、流程,以及如何選擇適合的服務,幫助您享受安心的高品質體驗。
什麼是台北外送茶服務?
台北外送茶服務是一種針對多元需求的伴侶外約服務,常見特點如下:
即時安排:快速回應客戶需求,提供靈活的服務時間。
多元選擇:從高端到平價方案,滿足各種預算層級。
私密性高:確保所有客戶資料絕對保密,安全性有保障。
為什麼選擇台北外送茶?
生活壓力舒緩:透過高品質的互動體驗,放鬆身心。
臨時需求應對:解決因臨時變動產生的陪伴需求。
特定場合加分:生日、商務活動等場合的高端陪伴服務。
如何選擇優質的台北外送茶服務?
辨別專業合法服務的重要性
查看評價:選擇具有良好口碑的服務商。
確認價格透明:事先了解費用,避免臨時加價問題。
重視隱私保障:選擇承諾保密的合法經營商家。
服務流程簡介
聯繫商家,表達需求並獲得建議。
確定伴侶類型與服務細節。
安排時間地點,享受服務。
提升台北外送茶體驗的建議
事先規劃:提前安排服務,避免臨時出現不便。
選擇信譽品牌:確保選擇口碑良好的服務商,避免風險。
溝通需求:明確表達需求與期待,達成雙方共識。 -
okada4d
okada4d -
https://ummalife.com/post/519829 malegra-200
-
[url=https://streamhub.shop/]Накрутка Twitch[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.shop/streamer-blog/twitch-viewer-boost-2025/97-nakrutka-zriteley-twitch-2025/]Накрутка зрителей Twitch 2025[/url] -
Nhà Cái RG RichGame
Nhà Cái RG RichGame
Nhà Cái RG RichGame là sòng bài trực tuyến lâu đời tại Đài Loan, với 10.000 người chơi cùng lúc và vốn hàng tỷ đồng. Sòng bài nổi tiếng với khuyến mãi hấp dẫn, rút tiền 100% đảm bảo và liên tục tối ưu nền tảng, trở thành nền tảng vững chắc cho Nhà Cái RG RichGame tại Đài Loan.
DỊCH VỤ CỦA Nhà Cái RG RichGame
THƯƠNG HIỆU UY TÍN
Thương hiệu đáng tin cậy nhất Châu Á. Nhiều năm liên tục được bình chọn 5 sao
SẢN PHẨM ĐA DẠNG
Casino, Thể Thao, Nổ hũ, Bắn cá, Xổ Số . Sản phẩm đa dạng tùy bạn chọn lựa.
AN NINH BẢO MẬT
Đa dạng trong phương thức thanh toán. An toàn và bảo mật thông tin.
GIAO DỊCH NHANH CHÓNG
Hệ thống xử lý tự động tiên tiến nhất Tốc độ nạp rút cực kỳ nhanh chóng
LÝ DO NÊN CHỌN Nhà Cái RG RichGame
Nhà Cái RG RichGame luôn đặt nhu cầu của người chơi làm trọng tâm, cung cấp trải nghiệm mượt mà, an toàn, công bằng và chân thực, trở thành đối tác đáng tin cậy nhất cho người chơi trong các sòng bài trực tuyến. Hệ thống phòng chống gian lận và rửa tiền hoàn chỉnh giúp người chơi mới dễ dàng tìm được thương hiệu giải trí cá cược trực tuyến phù hợp mà không lo bị lừa đảo.
Nhà Cái RG RichGame APP
Tải ngay Ứng dụng RG richgame trực tuyến cho điện thoại của bạn ngay để trải nghiệm game tốt hơn và an toàn hơn, ứng dụng hỗ trợ tất cả các sản phẩm: Thể Thao, E-Sports, Casino, Trò Chơi và Xổ Số.
Nhà Cái RG Trang chủ là gì?
Nhà Cái RG RichGame Trang chủ là tên gọi của trang web chính thức cho Nhà Cái RG Casino. Địa chỉ trực tuyến của nó là rg9457.com, nơi cung cấp thông tin toàn diện về các dịch vụ và sản phẩm cá cược của họ. -
Nhà Cái RG RichGame
Nhà Cái RG RichGame là sòng bài trực tuyến lâu đời tại Đài Loan, với 10.000 người chơi cùng lúc và vốn hàng tỷ đồng. Sòng bài nổi tiếng với khuyến mãi hấp dẫn, rút tiền 100% đảm bảo và liên tục tối ưu nền tảng, trở thành nền tảng vững chắc cho Nhà Cái RG RichGame tại Đài Loan.
DỊCH VỤ CỦA Nhà Cái RG RichGame
THƯƠNG HIỆU UY TÍN
Thương hiệu đáng tin cậy nhất Châu Á. Nhiều năm liên tục được bình chọn 5 sao
SẢN PHẨM ĐA DẠNG
Casino, Thể Thao, Nổ hũ, Bắn cá, Xổ Số . Sản phẩm đa dạng tùy bạn chọn lựa.
AN NINH BẢO MẬT
Đa dạng trong phương thức thanh toán. An toàn và bảo mật thông tin.
GIAO DỊCH NHANH CHÓNG
Hệ thống xử lý tự động tiên tiến nhất Tốc độ nạp rút cực kỳ nhanh chóng
LÝ DO NÊN CHỌN Nhà Cái RG RichGame
Nhà Cái RG RichGame luôn đặt nhu cầu của người chơi làm trọng tâm, cung cấp trải nghiệm mượt mà, an toàn, công bằng và chân thực, trở thành đối tác đáng tin cậy nhất cho người chơi trong các sòng bài trực tuyến. Hệ thống phòng chống gian lận và rửa tiền hoàn chỉnh giúp người chơi mới dễ dàng tìm được thương hiệu giải trí cá cược trực tuyến phù hợp mà không lo bị lừa đảo.
Nhà Cái RG RichGame APP
Tải ngay Ứng dụng RG richgame trực tuyến cho điện thoại của bạn ngay để trải nghiệm game tốt hơn và an toàn hơn, ứng dụng hỗ trợ tất cả các sản phẩm: Thể Thao, E-Sports, Casino, Trò Chơi và Xổ Số.
Nhà Cái RG Trang chủ là gì?
Nhà Cái RG RichGame Trang chủ là tên gọi của trang web chính thức cho Nhà Cái RG Casino. Địa chỉ trực tuyến của nó là rg9457.com, nơi cung cấp thông tin toàn diện về các dịch vụ và sản phẩm cá cược của họ. -
高雄外送茶:精選安全便捷的外約服務攻略
引言
高雄外送茶服務因其便利性與多樣化而備受歡迎,不僅滿足社交需求,更以快速、安全為核心,成為許多人的理想選擇。本文將深入剖析高雄外送茶的特點、流程,以及如何選擇適合的服務,幫助您享受安心的高品質體驗。
什麼是高雄外送茶服務?
高雄外送茶服務是一種針對多元需求的伴侶外約服務,常見特點如下:
即時安排:快速回應客戶需求,提供靈活的服務時間。
多元選擇:從高端到平價方案,滿足各種預算層級。
私密性高:確保所有客戶資料絕對保密,安全性有保障。
為什麼選擇高雄外送茶?
生活壓力舒緩:透過高品質的互動體驗,放鬆身心。
臨時需求應對:解決因臨時變動產生的陪伴需求。
特定場合加分:生日、商務活動等場合的高端陪伴服務。
如何選擇優質的高雄外送茶服務?
辨別專業合法服務的重要性
查看評價:選擇具有良好口碑的服務商。
確認價格透明:事先了解費用,避免臨時加價問題。
重視隱私保障:選擇承諾保密的合法經營商家。
服務流程簡介
聯繫商家,表達需求並獲得建議。
確定伴侶類型與服務細節。
安排時間地點,享受服務。
提升高雄外送茶體驗的建議
事先規劃:提前安排服務,避免臨時出現不便。
選擇信譽品牌:確保選擇口碑良好的服務商,避免風險。
溝通需求:明確表達需求與期待,達成雙方共識。 -
高雄外送茶
高雄外送茶:精選安全便捷的外約服務攻略
引言
高雄外送茶服務因其便利性與多樣化而備受歡迎,不僅滿足社交需求,更以快速、安全為核心,成為許多人的理想選擇。本文將深入剖析高雄外送茶的特點、流程,以及如何選擇適合的服務,幫助您享受安心的高品質體驗。
什麼是高雄外送茶服務?
高雄外送茶服務是一種針對多元需求的伴侶外約服務,常見特點如下:
即時安排:快速回應客戶需求,提供靈活的服務時間。
多元選擇:從高端到平價方案,滿足各種預算層級。
私密性高:確保所有客戶資料絕對保密,安全性有保障。
為什麼選擇高雄外送茶?
生活壓力舒緩:透過高品質的互動體驗,放鬆身心。
臨時需求應對:解決因臨時變動產生的陪伴需求。
特定場合加分:生日、商務活動等場合的高端陪伴服務。
如何選擇優質的高雄外送茶服務?
辨別專業合法服務的重要性
查看評價:選擇具有良好口碑的服務商。
確認價格透明:事先了解費用,避免臨時加價問題。
重視隱私保障:選擇承諾保密的合法經營商家。
服務流程簡介
聯繫商家,表達需求並獲得建議。
確定伴侶類型與服務細節。
安排時間地點,享受服務。
提升高雄外送茶體驗的建議
事先規劃:提前安排服務,避免臨時出現不便。
選擇信譽品牌:確保選擇口碑良好的服務商,避免風險。
溝通需求:明確表達需求與期待,達成雙方共識。 -
花蓮外送茶
花蓮外送茶:精選安全便捷的外約服務攻略
引言
花蓮外送茶服務因其便利性與多樣化而備受歡迎,不僅滿足社交需求,更以快速、安全為核心,成為許多人的理想選擇。本文將深入剖析花蓮外送茶的特點、流程,以及如何選擇適合的服務,幫助您享受安心的高品質體驗。
什麼是花蓮外送茶服務?
花蓮外送茶服務是一種針對多元需求的伴侶外約服務,常見特點如下:
即時安排:快速回應客戶需求,提供靈活的服務時間。
多元選擇:從高端到平價方案,滿足各種預算層級。
私密性高:確保所有客戶資料絕對保密,安全性有保障。
為什麼選擇花蓮外送茶?
生活壓力舒緩:透過高品質的互動體驗,放鬆身心。
臨時需求應對:解決因臨時變動產生的陪伴需求。
特定場合加分:生日、商務活動等場合的高端陪伴服務。
如何選擇優質的花蓮外送茶服務?
辨別專業合法服務的重要性
查看評價:選擇具有良好口碑的服務商。
確認價格透明:事先了解費用,避免臨時加價問題。
重視隱私保障:選擇承諾保密的合法經營商家。
服務流程簡介
聯繫商家,表達需求並獲得建議。
確定伴侶類型與服務細節。
安排時間地點,享受服務。
提升花蓮外送茶體驗的建議
事先規劃:提前安排服務,避免臨時出現不便。
選擇信譽品牌:確保選擇口碑良好的服務商,避免風險。
溝通需求:明確表達需求與期待,達成雙方共識。 -
台中外送茶:安全快速的外約服務指南
引言
台中外送茶是一項方便且受歡迎的服務,無論是夜晚的放鬆需求還是特殊場合的社交活動,都能提供快速、安全且專業的體驗。本文將深入探討台中外送茶的選擇、流程以及相關注意事項,幫助您在選擇服務時更加安心與滿意。
什麼是台中外送茶?
台中外送茶服務主要提供以下特點:
快速應對:透過線上或電話聯繫,立即安排外送服務。
多元選擇:服務涵蓋不同需求,從高端到實惠方案應有盡有。
隱私保障:強調保密性,確保客戶資料不被外洩。
台中外送茶適合哪些人?
商務旅客:在台中短期停留,追求品質與方便的伴侶服務。
壓力族群:希望藉由互動放鬆身心,增添生活樂趣。
聚會需求:特殊場合、生日或朋友聚會需要專業的伴侶服務。
選擇台中外送茶的注意事項
如何選擇安全的服務?
查詢評價:選擇高評價且有口碑的服務提供者。
確認價格透明:避免隱藏費用,提前溝通價格範圍。
合法經營:確認服務平台是否具備合法經營的資格。
常見的服務流程
聯繫服務商家,了解可提供的選項及價格。
確定時間與地點,確保雙方需求達成一致。
接收外送服務,享受專業的伴侶陪伴。 -
台中外送茶
台中外送茶:安全快速的外約服務指南
引言
台中外送茶是一項方便且受歡迎的服務,無論是夜晚的放鬆需求還是特殊場合的社交活動,都能提供快速、安全且專業的體驗。本文將深入探討台中外送茶的選擇、流程以及相關注意事項,幫助您在選擇服務時更加安心與滿意。
什麼是台中外送茶?
台中外送茶服務主要提供以下特點:
快速應對:透過線上或電話聯繫,立即安排外送服務。
多元選擇:服務涵蓋不同需求,從高端到實惠方案應有盡有。
隱私保障:強調保密性,確保客戶資料不被外洩。
台中外送茶適合哪些人?
商務旅客:在台中短期停留,追求品質與方便的伴侶服務。
壓力族群:希望藉由互動放鬆身心,增添生活樂趣。
聚會需求:特殊場合、生日或朋友聚會需要專業的伴侶服務。
選擇台中外送茶的注意事項
如何選擇安全的服務?
查詢評價:選擇高評價且有口碑的服務提供者。
確認價格透明:避免隱藏費用,提前溝通價格範圍。
合法經營:確認服務平台是否具備合法經營的資格。
常見的服務流程
聯繫服務商家,了解可提供的選項及價格。
確定時間與地點,確保雙方需求達成一致。
接收外送服務,享受專業的伴侶陪伴。 -
search for crypto wallet
Offerings for Checking USDT for Sanctions and Transfer Clarity: AML Strategies
In the contemporary world of virtual currencies, where rapid trades and privacy are becoming the standard, observing the legitimacy and clarity of transactions is crucial. In view of heightened official oversight over dirty money and terrorism financing activities, the requirement for efficient resources to verify transfers has become a major issue for virtual currency users. In this piece, we will analyze offered offerings for monitoring USDT for embargoes and transfer clarity.
What is AML?
Anti-Laundering strategies refer to a set of supervisory steps aimed at preventing and detecting illicit finance activities. With the surge of digital asset usage, AML standards have become especially crucial, allowing users to deal with digital resources securely while minimizing hazards associated with sanctions.
USDT, as the widely regarded as the favored stablecoin, is broadly used in different exchanges internationally. However, using USDT can present several threats, especially if your monies may associate to opaque or criminal transactions. To reduce these concerns, it's vital to take benefit of services that inspect USDT for restrictive measures.
Available Services
1. Address Validation: Utilizing dedicated tools, you can verify a designated USDT address for any connections to restrictive catalogs. This assists pinpoint potential connections to illicit conduct.
2. Deal Activity Evaluation: Some services offer scrutiny of operation history, crucial for evaluating the lucidity of monetary transactions and identifying potentially dangerous activities.
3. Observation Tools: Specialized monitoring services allow you to follow all transactions related to your wallet, permitting you to promptly identify suspicious activities.
4. Hazard Statements: Certain tools make available detailed risk reports, which can be valuable for participants looking to ensure the integrity of their investments.
Regardless of if you are controlling a considerable fund or executing small trades, complying to AML norms ensures evade legal repercussions. Employing USDT validation services not only shields you from financial losses but also aids to creating a protected environment for all economic participants.
Conclusion
Monitoring USDT for restrictive measures and deal purity is becoming a necessary process for anyone motivated to remain within the legal framework and preserve high criteria of transparency in the virtual currency sector. By working with dependable tools, you not only safeguard your resources but also aid to the shared initiative in fighting money laundering and financing of terrorism.
If you are prepared to start utilizing these solutions, explore the available tools and pick the solution that most aligns with your needs. Be aware, insight is your strength, and timely transaction verification can shield you from numerous problems in the future. -
Solutions for Checking USDT for Prohibitions and Operation Cleanliness: Anti-Laundering Measures
In the contemporary domain of cryptocurrencies, where quick transactions and anonymity are becoming the standard, supervising the lawfulness and integrity of activities is crucial. In consideration of amplified government examination over dirty money and terrorism funding, the requirement for reliable resources to verify transfers has become a major concern for cryptocurrency users. In this article, we will explore offered solutions for assessing USDT for embargoes and operation integrity.
What is AML?
Money Laundering Prevention practices refer to a series of supervisory protocols aimed at hindering and discovering dirty money activities. With the growth of digital asset usage, AML standards have become notably crucial, allowing participants to manage digital currencies with assurance while lessening threats associated with embargoes.
USDT, as the preeminent well-known stablecoin, is broadly used in various deals across the globe. Nonetheless, using USDT can involve several dangers, especially if your monies may connect to ambiguous or illicit maneuvers. To mitigate these threats, it's crucial to take benefit of tools that assess USDT for sanctions.
Available Services
1. Address Authentication: Using specific tools, you can confirm a designated USDT address for any associations to prohibited catalogs. This aids identify potential connections to criminal activities.
2. Operation Engagement Analysis: Some services provide scrutiny of deal background, significant for judging the transparency of capital flows and identifying potentially dangerous conduct.
3. Surveillance Solutions: Professional monitoring tools allow you to observe all operations related to your account, facilitating you to quickly identify concerning actions.
4. Threat Documents: Certain tools extend detailed concern reports, which can be crucial for traders looking to validate the reliability of their resources.
Regardless of whether or not you are overseeing a considerable resource or conducting small transactions, adhering to AML practices assists steer clear of legal repercussions. Utilizing USDT validation solutions not only defends you from capital declines but also aids to building a protected environment for all industry stakeholders.
Conclusion
Assessing USDT for embargoes and deal purity is becoming a required action for anyone keen to continue within the regulations and preserve high standards of visibility in the crypto field. By interacting with dependable services, you not only protect your assets but also aid to the common goal in preventing dirty money and financing of terrorism.
If you are ready to start employing these services, explore the existing tools and select the service that most adequately suits your needs. Be aware, insight is your advantage, and quick transfer check can shield you from many challenges in the long run. -
Offerings for Assessing USDT for Prohibitions and Transaction Purity: Anti-Money Laundering Strategies
In the modern environment of cryptocurrencies, where expedited transactions and secrecy are becoming the usual case, monitoring the legality and cleanliness of processes is crucial. In light of increased administrative scrutiny over dirty money and financing of terrorism, the need for efficient instruments to authenticate transactions has become a key concern for cryptocurrency users. In this text, we will review accessible offerings for checking USDT for sanctions and operation clarity.
What is AML?
Anti-Money Laundering actions refer to a group of regulatory steps aimed at hindering and uncovering money laundering activities. With the rise of crypto usage, AML measures have become exceedingly essential, allowing individuals to handle digital resources confidently while mitigating perils associated with embargoes.
USDT, as the most recognized stablecoin, is broadly used in different deals globally. Yet, using USDT can entail several hazards, especially if your monies may tie to unclear or illegal operations. To minimize these concerns, it's crucial to take advantage of tools that check USDT for sanctions.
Available Services
1. Address Authentication: Utilizing specific tools, you can inspect a particular USDT address for any associations to sanction catalogs. This aids pinpoint potential ties to criminal activities.
2. Transfer Conduct Analysis: Some tools extend evaluation of transaction records, important for evaluating the clarity of fund transactions and detecting potentially threatening operations.
3. Surveillance Solutions: Expert monitoring solutions allow you to track all deals related to your wallet, allowing you to rapidly detect questionable actions.
4. Hazard Documents: Certain solutions provide detailed concern documents, which can be beneficial for participants looking to validate the integrity of their holdings.
No matter of whether or not you are managing a large investment or performing small transactions, following to AML guidelines helps prevent legal repercussions. Adopting USDT validation offerings not only safeguards you from financial declines but also supports to creating a protected environment for all economic actors.
Conclusion
Verifying USDT for embargoes and deal cleanliness is becoming a mandatory measure for anyone enthusiastic to stay compliant within the law and maintain high criteria of visibility in the digital asset sector. By working with reliable platforms, you not only protect your investments but also help to the joint mission in countering money laundering and terror financing activities.
If you are set to start employing these services, review the offered tools and pick the service that most suits your requirements. Remember, data is your strength, and timely operation validation can shield you from countless issues in the time ahead. -
Services for Checking USDT for Embargoes and Deal Clarity: Anti-Money Laundering Approaches
In the contemporary environment of crypto assets, where quick deals and privacy are becoming the standard practice, observing the lawfulness and clarity of operations is vital. In recognition of increased administrative scrutiny over illicit finance and terrorism funding, the demand for robust instruments to validate operations has become a major priority for crypto users. In this piece, we will analyze existing services for assessing USDT for embargoes and transfer clarity.
What is AML?
AML practices refer to a group of legal protocols aimed at curtailing and identifying financial misconduct activities. With the rise of crypto usage, AML measures have become notably crucial, allowing individuals to manage digital holdings confidently while mitigating hazards associated with sanctions.
USDT, as the arguably the well-known stablecoin, is widely used in various operations worldwide. Nevertheless, using USDT can present several hazards, especially if your monies may tie to ambiguous or unlawful maneuvers. To reduce these concerns, it's crucial to take advantage of offerings that inspect USDT for sanctions.
Available Services
1. Address Confirmation: Using specific tools, you can confirm a certain USDT address for any associations to restrictive registries. This assists identify potential ties to illegal conduct.
2. Transfer Action Examination: Some tools provide scrutiny of deal records, crucial for assessing the clarity of monetary transactions and identifying potentially hazardous conduct.
3. Monitoring Systems: Dedicated monitoring systems allow you to observe all deals related to your address, facilitating you to promptly detect questionable conduct.
4. Risk Reports: Certain solutions extend detailed hazard evaluations, which can be helpful for stakeholders looking to confirm the integrity of their holdings.
Whether of whether you are handling a large investment or executing small transactions, complying to AML standards helps prevent legal repercussions. Using USDT authentication solutions not only safeguards you from economic setbacks but also helps to establishing a safe environment for all business stakeholders.
Conclusion
Assessing USDT for prohibitions and transaction clarity is becoming a required process for anyone enthusiastic to stay within the law and maintain high benchmarks of transparency in the virtual currency field. By interacting with credible tools, you not only safeguard your assets but also help to the joint initiative in fighting money laundering and terrorist financing.
If you are willing to start employing these offerings, examine the available services and pick the solution that most meets your demands. Bear in mind, knowledge is your asset, and timely transfer verification can save you from a variety of problems in the future. -
https://experienceleaguecommunities.adobe.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/17966473 prometrium capsules
-
[url=https://streamhub.shop/nakrutka-zriteley-twitch/]Накрутка зрителей Twitch[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.world/]Boost Twitch Kick Viewers[/url] -
Kantorbola adalah situs resmi dan terpercaya untuk para penggemar permainan slot online. Dengan koleksi permainan yang lengkap dan beragam, situs ini menawarkan pengalaman bermain yang menyenangkan dan aman. Sebagai platform yang terdaftar secara sah, KantorBola menjamin transaksi yang transparan, proses pendaftaran yang mudah, dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif 24/7.
KantorBola menyediakan berbagai jenis permainan slot dari penyedia terkemuka, dengan grafis menarik dan fitur-fitur bonus yang menguntungkan. Selain itu, situs ini memiliki antarmuka yang ramah pengguna dan desain yang responsif, memastikan pengalaman bermain yang lancar baik di desktop maupun perangkat mobile.
Bergabung dengan KantorBola memberikan akses ke berbagai promo menarik, jackpot progresif, serta sistem keamanan yang canggih untuk melindungi data pribadi dan transaksi Anda. Dengan kemudahan akses dan dukungan pelanggan yang profesional, KantorBola menjadi pilihan utama bagi pemain slot online yang ingin merasakan sensasi bermain yang seru dan aman. -
Kantorbola adalah situs resmi dan terpercaya untuk para penggemar permainan slot online. Dengan koleksi permainan yang lengkap dan beragam, situs ini menawarkan pengalaman bermain yang menyenangkan dan aman. Sebagai platform yang terdaftar secara sah, KantorBola menjamin transaksi yang transparan, proses pendaftaran yang mudah, dan layanan pelanggan yang responsif 24/7.
KantorBola menyediakan berbagai jenis permainan slot dari penyedia terkemuka, dengan grafis menarik dan fitur-fitur bonus yang menguntungkan. Selain itu, situs ini memiliki antarmuka yang ramah pengguna dan desain yang responsif, memastikan pengalaman bermain yang lancar baik di desktop maupun perangkat mobile.
Bergabung dengan KantorBola memberikan akses ke berbagai promo menarik, jackpot progresif, serta sistem keamanan yang canggih untuk melindungi data pribadi dan transaksi Anda. Dengan kemudahan akses dan dukungan pelanggan yang profesional, KantorBola menjadi pilihan utama bagi pemain slot online yang ingin merasakan sensasi bermain yang seru dan aman. -
crypto com wallet address checke
Solutions for Monitoring USDT for Embargoes and Transfer Cleanliness: AML Measures
In the up-to-date realm of cryptocurrencies, where rapid deals and anonymity are becoming the usual case, supervising the lawfulness and purity of operations is essential. In consideration of heightened official oversight over money laundering and financing of terrorism, the requirement for reliable means to validate deals has become a major concern for virtual currency users. In this article, we will discuss existing solutions for monitoring USDT for prohibitions and operation clarity.
What is AML?
Anti-Money Laundering strategies refer to a set of legal steps aimed at curtailing and detecting financial misconduct activities. With the growth of digital asset usage, AML practices have become especially important, allowing users to manage digital holdings confidently while minimizing risks associated with sanctions.
USDT, as the arguably the well-known stablecoin, is broadly used in various exchanges across the globe. However, using USDT can carry several risks, especially if your monies may associate to non-transparent or illegal transactions. To minimize these concerns, it's vital to take make use of services that check USDT for restrictive measures.
Available Services
1. Address Validation: Leveraging dedicated tools, you can check a specific USDT address for any links to restrictive lists. This aids detect potential ties to criminal activities.
2. Transfer Activity Analysis: Some platforms provide scrutiny of transaction chronology, significant for measuring the lucidity of capital transfers and detecting potentially threatening operations.
3. Observation Services: Specialized monitoring solutions allow you to follow all deals related to your wallet, enabling you to quickly spot concerning operations.
4. Threat Documents: Certain solutions make available detailed risk reports, which can be crucial for stakeholders looking to confirm the reliability of their assets.
No matter of whether or not you are controlling a substantial investment or conducting small operations, abiding to AML practices helps avoid legal repercussions. Employing USDT validation services not only protects you from capital losses but also supports to creating a stable environment for all business participants.
Conclusion
Monitoring USDT for prohibitions and operation purity is becoming a mandatory step for anyone eager to stay compliant within the legal framework and uphold high benchmarks of openness in the virtual currency field. By interacting with trustworthy solutions, you not only defend your resources but also contribute to the collective effort in countering money laundering and financing of terrorism.
If you are willing to start leveraging these tools, review the offered platforms and choose the option that most adequately aligns with your needs. Bear in mind, knowledge is your advantage, and swift operation verification can save you from many problems in the coming times. -
wallet address verification
Offerings for Monitoring USDT for Prohibitions and Operation Purity: AML Measures
In the contemporary environment of virtual currencies, where expedited transactions and privacy are becoming the norm, monitoring the legitimacy and clarity of transactions is vital. In consideration of heightened administrative oversight over dirty money and terrorism funding, the need for robust means to verify transactions has become a key matter for cryptocurrency users. In this write-up, we will review available solutions for verifying USDT for embargoes and deal purity.
What is AML?
AML actions refer to a series of regulatory steps aimed at stopping and discovering illicit finance activities. With the growth of cryptocurrency usage, AML measures have become exceedingly essential, allowing clients to deal with digital assets securely while mitigating threats associated with restrictive measures.
USDT, as the arguably the recognized stablecoin, is widely used in multiple exchanges worldwide. Nonetheless, using USDT can present several dangers, especially if your funds may connect to unclear or illicit operations. To mitigate these hazards, it's vital to take benefit of tools that inspect USDT for embargoes.
Available Services
1. Address Authentication: Leveraging customized tools, you can check a certain USDT address for any ties to sanction catalogs. This facilitates detect potential connections to criminal conduct.
2. Transaction Conduct Analysis: Some services offer scrutiny of operation records, significant for measuring the lucidity of capital movements and uncovering potentially risky operations.
3. Tracking Solutions: Dedicated monitoring services allow you to observe all deals related to your account, permitting you to swiftly uncover questionable conduct.
4. Concern Reports: Certain solutions offer detailed hazard documents, which can be helpful for stakeholders looking to validate the trustworthiness of their assets.
No matter of whether or not you are managing a considerable investment or executing small trades, following to AML guidelines ensures prevent legal repercussions. Employing USDT validation offerings not only shields you from capital setbacks but also helps to building a safe environment for all market players.
Conclusion
Verifying USDT for embargoes and transfer cleanliness is becoming a necessary step for anyone eager to stay within the regulations and support high standards of visibility in the digital asset domain. By engaging with credible services, you not only secure your assets but also support to the joint goal in preventing dirty money and terrorist financing.
If you are willing to start utilizing these tools, explore the available platforms and identify the service that best meets your preferences. Bear in mind, information is your advantage, and swift operation validation can shield you from numerous problems in the future. -
Offerings for Checking USDT for Sanctions and Deal Clarity: Money Laundering Prevention Strategies
In the contemporary world of digital currencies, where quick deals and privacy are becoming the usual case, monitoring the legitimacy and integrity of operations is necessary. In consideration of increased regulatory oversight over financial misconduct and terrorist financing, the need for effective instruments to check transfers has become a major concern for virtual currency users. In this text, we will discuss existing tools for verifying USDT for restrictive measures and operation purity.
What is AML?
AML measures refer to a series of regulatory steps aimed at hindering and uncovering financial misconduct activities. With the rise of cryptocurrency usage, AML practices have become exceedingly essential, allowing individuals to manage digital currencies securely while mitigating perils associated with restrictive measures.
USDT, as the most well-known stablecoin, is broadly used in multiple exchanges worldwide. Yet, using USDT can present several risks, especially if your funds may tie to non-transparent or unlawful activities. To lessen these threats, it's imperative to take make use of solutions that assess USDT for prohibitions.
Available Services
1. Address Verification: Utilizing specific tools, you can check a designated USDT address for any ties to restrictive lists. This aids detect potential ties to unlawful behaviors.
2. Transaction Action Assessment: Some platforms offer analysis of transaction chronology, essential for assessing the clarity of financial movements and identifying potentially threatening operations.
3. Tracking Tools: Dedicated monitoring solutions allow you to observe all deals related to your account, facilitating you to promptly spot questionable operations.
4. Concern Records: Certain tools make available detailed risk documents, which can be helpful for investors looking to validate the reliability of their resources.
Regardless of whether you are handling a substantial fund or performing small deals, adhering to AML guidelines helps evade legal repercussions. Employing USDT verification services not only shields you from economic damages but also aids to building a protected environment for all market actors.
Conclusion
Verifying USDT for restrictive measures and operation clarity is becoming a mandatory step for anyone enthusiastic to stay within the legal framework and uphold high criteria of clarity in the digital asset field. By working with trustworthy services, you not only protect your resources but also help to the shared effort in fighting financial misconduct and terror financing activities.
If you are willing to start employing these solutions, explore the available services and select the service that most aligns with your preferences. Keep in mind, information is your advantage, and swift transfer verification can rescue you from countless difficulties in the future. -
Anti-money laundering (AML)
Offerings for Verifying USDT for Sanctions and Transaction Clarity: AML Approaches
In the contemporary environment of virtual currencies, where fast transactions and secrecy are becoming the standard practice, tracking the validity and cleanliness of processes is necessary. In light of amplified regulatory investigation over illicit finance and terrorism funding, the need for efficient resources to verify transfers has become a critical concern for digital asset users. In this write-up, we will review existing solutions for assessing USDT for sanctions and transfer purity.
What is AML?
Anti-Money Laundering strategies refer to a group of regulatory steps aimed at preventing and uncovering money laundering activities. With the rise of crypto usage, AML measures have become particularly essential, allowing users to operate digital assets securely while lessening threats associated with prohibitions.
USDT, as the preeminent popular stablecoin, is extensively used in multiple transactions worldwide. However, using USDT can present several dangers, especially if your funds may tie to non-transparent or criminal activities. To minimize these risks, it's essential to take leverage of tools that verify USDT for prohibitions.
Available Services
1. Address Authentication: Leveraging customized tools, you can inspect a particular USDT address for any associations to sanction directories. This assists detect potential links to illegal activities.
2. Deal Conduct Examination: Some services offer scrutiny of deal chronology, significant for evaluating the openness of monetary flows and spotting potentially hazardous activities.
3. Monitoring Solutions: Specialized monitoring solutions allow you to track all deals related to your location, facilitating you to promptly identify suspicious activities.
4. Threat Records: Certain tools provide detailed threat summaries, which can be helpful for participants looking to ensure the soundness of their assets.
No matter of whether or not you are handling a significant capital or conducting small transactions, adhering to AML practices supports prevent legal repercussions. Adopting USDT verification solutions not only defends you from capital declines but also contributes to forming a safe environment for all market stakeholders.
Conclusion
Monitoring USDT for embargoes and transfer integrity is becoming a required measure for anyone keen to remain within the rules and maintain high benchmarks of visibility in the cryptocurrency domain. By collaborating with dependable platforms, you not only protect your resources but also help to the joint effort in fighting illicit finance and financing of terrorism.
If you are prepared to start utilizing these solutions, examine the existing tools and select the solution that best suits your preferences. Bear in mind, data is your advantage, and timely operation validation can rescue you from many issues in the long run. -
ぱちスロ にゃんこ大戦争 BIGBANG
ジャグラーオカルト ランキング
各台によって異なる演出があり、どれを選ぶかも楽しみの一つです。自分の好みの台を見つける楽しさがあります。
鬼武者3 時空天翔
https://www.basiliskkizuna.com/Articles/2082.html
リーチ演出が多彩で、どのタイミングで大当たりが来るかワクワクします。
攻殻機動隊S.A.C
[url=https://www.ja-securities.jp/tags/%E5%88%9D%E5%9B%9E%E5%85%A5%E9%87%91]
オンライン カジノ 入金 不要 ボーナス 最新[/url]
P北斗の拳9 闘神
PA ぱちんこ AKB48 桜 LIGHT ver.
神龍降臨
北斗の拳-ボクシング王
[url=https://www.pachicat.com/]
スロログ[/url]
CR織田信奈の野望II
CR北斗の拳6 拳王
沖ドキ! 25
P とある魔術の禁書目録 Light PREMIUM ver.
[url=https://musou3.jahromblog.com/]
パチンコ北斗無双3[/url]
回胴黙示録カイジ3
超時空要塞マクロス
CRフィーバー バイオハザード リベレーションズ
CR牙狼魔戒之花 Ver.399
https://yoshimune3.jahromblog.com/
演出が単純明快で、ストレスなくプレイできるのが良いです。気軽に楽しめます。
CR北斗の拳6拳王
https://www.bk8882.com/archives/post-536.html
ボーナスゲームの演出が豪華で、楽しみが倍増します。特に大当たり時は圧巻。 -
Kantorbola link alternatif login terbaru 2025 . Kunjungi link resmi situs kantor bola untuk melakukan permainan dan pendaftaran
http://korins.kr/shop/bannerhit.php?bn_id=19&url=http%3a%2f%2fsbj.kr%2Fg5%2Fbbs%2Fboard.php%3Fbo_table%3Dfree%26wr_id%3D1005535
https://ignitebeanies.com/ -
Kantorbola link alternatif login terbaru 2025 . Kunjungi link resmi situs kantor bola untuk melakukan permainan dan pendaftaran
http://glowmasters.com/__media__/js/netsoltrademark.php?d=jssystems.co.kr%2Fbbs%2Fboard.php%3Fbo_table%3Dfree%26wr_id%3D877390
https://ignitebeanies.com/ -
Solutions for Assessing USDT for Prohibitions and Transfer Clarity: Anti-Money Laundering Measures
In the contemporary environment of crypto assets, where fast exchanges and obscurity are becoming the standard, monitoring the lawfulness and cleanliness of activities is vital. In view of heightened official oversight over money laundering and financing of terrorism, the necessity for robust instruments to authenticate operations has become a major concern for digital asset users. In this article, we will explore available offerings for verifying USDT for restrictive measures and transaction clarity.
What is AML?
Money Laundering Prevention strategies refer to a collection of compliance measures aimed at hindering and discovering dirty money activities. With the increase of cryptocurrency usage, AML strategies have become particularly critical, allowing individuals to deal with digital assets securely while minimizing hazards associated with sanctions.
USDT, as the arguably the popular stablecoin, is widely used in various transactions internationally. Nevertheless, using USDT can involve several dangers, especially if your resources may associate to unclear or unlawful activities. To mitigate these threats, it's vital to take advantage of tools that assess USDT for embargoes.
Available Services
1. Address Authentication: Using specialized tools, you can confirm a particular USDT address for any links to sanction lists. This aids uncover potential connections to unlawful activities.
2. Transaction Conduct Examination: Some offerings offer assessment of deal background, crucial for judging the transparency of monetary movements and identifying potentially risky operations.
3. Observation Services: Professional monitoring solutions allow you to observe all operations related to your location, enabling you to quickly spot questionable operations.
4. Threat Statements: Certain platforms extend detailed threat summaries, which can be beneficial for investors looking to guarantee the reliability of their resources.
Regardless of whether or not you are overseeing a significant investment or executing small trades, following to AML norms assists avoid legal repercussions. Utilizing USDT certification solutions not only safeguards you from financial damages but also helps to creating a stable environment for all market participants.
Conclusion
Checking USDT for embargoes and transaction clarity is becoming a compulsory process for anyone motivated to stay within the law and support high standards of visibility in the virtual currency industry. By engaging with dependable platforms, you not only defend your holdings but also contribute to the joint effort in combating dirty money and terrorist financing.
If you are ready to start using these solutions, explore the offered platforms and pick the service that most suits your demands. Remember, information is your asset, and swift transaction assessment can shield you from many difficulties in the time ahead. -
Services for Verifying USDT for Restrictive Measures and Operation Purity: AML Strategies
In the current environment of crypto assets, where rapid exchanges and anonymity are becoming the usual case, monitoring the validity and integrity of activities is crucial. In light of greater official scrutiny over dirty money and financing of terrorism, the necessity for robust means to validate operations has become a significant issue for virtual currency users. In this article, we will review offered offerings for assessing USDT for embargoes and deal clarity.
What is AML?
Anti-Money Laundering practices refer to a group of compliance protocols aimed at preventing and detecting dirty money activities. With the surge of crypto usage, AML strategies have become particularly crucial, allowing users to manage digital holdings confidently while lessening hazards associated with prohibitions.
USDT, as the arguably the popular stablecoin, is commonly used in multiple transactions across the globe. However, using USDT can carry several dangers, especially if your resources may connect to ambiguous or unlawful activities. To reduce these risks, it's crucial to take benefit of tools that inspect USDT for sanctions.
Available Services
1. Address Validation: Leveraging customized tools, you can inspect a specific USDT address for any connections to restrictive directories. This facilitates identify potential links to unlawful behaviors.
2. Transfer Engagement Assessment: Some services provide assessment of transaction chronology, significant for assessing the openness of monetary transactions and uncovering potentially risky conduct.
3. Tracking Services: Professional monitoring solutions allow you to observe all deals related to your location, allowing you to swiftly detect questionable actions.
4. Risk Records: Certain tools provide detailed concern evaluations, which can be valuable for traders looking to validate the integrity of their assets.
Irrespective of whether you are managing a large resource or performing small deals, complying to AML guidelines assists avoid legal repercussions. Utilizing USDT certification solutions not only defends you from financial damages but also aids to creating a safe environment for all business participants.
Conclusion
Monitoring USDT for sanctions and transfer cleanliness is becoming a necessary step for anyone eager to remain within the legal framework and preserve high levels of visibility in the cryptocurrency domain. By working with trustworthy tools, you not only safeguard your investments but also contribute to the common initiative in fighting dirty money and financing of terrorism.
If you are ready to start utilizing these solutions, review the existing platforms and choose the solution that most adequately suits your requirements. Be aware, knowledge is your advantage, and prompt deal verification can protect you from numerous issues in the future. -
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an edginess over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come further formerly again since exactly the same nearly very often inside case you shield this increase.
https://forthouse.com.ua/diy-headlight-seal-restoration.html -
[url=https://streamhub.shop/nakrutka-zriteley-kick/]Накрутка kick[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.shop/streamer-blog/nakrutka-zritelej-kick/112-plyusy-i-minusy-nakrutki-zritelej-kick-v-2025/]накрутка зрителей Kick в 2025[/url] -
貴公子娛樂城
貴公子娛樂城是一個新穎且便利的線上娛樂平台,其主打的快速註冊流程讓玩家可以即刻開始遊戲,而無需經歷繁瑣的手續。同時,平台提供多元的支付選項,包括LINE PAY、信用卡及MyCard等,方便玩家根據自己的需求選擇最適合的方式進行充值。此外,貴公子娛樂城的每日紅包系統和VIP等級紅利機制,更讓玩家能夠持續享受額外的回饋與獎勵,增添了遊戲的吸引力。對於尋求快速進入遊戲並享受穩定服務的玩家而言,貴公子娛樂城無疑是一個值得嘗試的選擇! -
貴公子娛樂城
貴公子娛樂城是一個新穎且便利的線上娛樂平台,其主打的快速註冊流程讓玩家可以即刻開始遊戲,而無需經歷繁瑣的手續。同時,平台提供多元的支付選項,包括LINE PAY、信用卡及MyCard等,方便玩家根據自己的需求選擇最適合的方式進行充值。此外,貴公子娛樂城的每日紅包系統和VIP等級紅利機制,更讓玩家能夠持續享受額外的回饋與獎勵,增添了遊戲的吸引力。對於尋求快速進入遊戲並享受穩定服務的玩家而言,貴公子娛樂城無疑是一個值得嘗試的選擇! -
鉅城娛樂城作為亞太區知名線上娛樂平台,以豐富多元的遊戲內容及優質服務贏得玩家信賴。平台通過TST技術測試及GLI系統認證,確保遊戲公平性。目前推出首存1000送1000優惠活動,最高回饋可達20萬,並提供日日續儲10%的回饋金。平台提供真人百家、棋牌、老虎機、體育電競及彩票等多樣化遊戲選擇,讓玩家享受如臨現場的娛樂體驗。
鉅城娛樂城:亞太區知名線上娛樂平台
鉅城娛樂城作為亞太區最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台之一,以其豐富多元的遊戲內容和卓越的服務品質贏得了廣大玩家的信賴。該平台不僅擁有一系列令人 excited 的遊戲,還致力於為玩家提供公平、公正的遊戲環境。
公平遊戲保障
鉅城娛樂城的遊戲公平性通過TST技術測試及GLI系統認證確保,使玩家在遊玩過程中完全無需擔心遊戲的公正問題。這些認證保證了每一場比賽及遊戲的隨機性和透明度,進一步增強了玩家的信心。
優惠活動
目前,鉅城娛樂城推出了首存1000送1000的優惠活動,這讓新玩家能夠在註冊後,迅速享受雙倍的存款金額,提升遊戲體驗。此外,平台最高回饋可達20萬,讓玩家在參與遊戲時享受到更多的利潤。值得注意的是,鉅城娛樂城還提供日日續儲10%的回饋金,進一步增強了玩家的參與熱情。
遊戲選擇
鉅城娛樂城平台提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,包括真人百家、棋牌、老虎機、體育電競及彩票等,讓玩家可以依照自己的興趣和需求選擇遊戲。無論是喜愛刺激的百家 blackjack,還是希望體驗策略與運氣的棋牌遊戲,鉅城娛樂城皆能滿足每位玩家的期望,並提供如臨現場的娛樂體驗。
總結
總而言之,鉅城娛樂城憑藉其卓越的遊戲內容和專業的客戶服務,已成為亞太區線上娛樂的不二之選。公正的遊戲環境、誘人的優惠活動及多樣的遊戲選擇,吸引了無數玩家的目光。無論你是新手還是老玩家,鉅城娛樂城都能帶給你一段難忘的遊戲旅程。 -
鉅城娛樂城作為亞太區知名線上娛樂平台,以豐富多元的遊戲內容及優質服務贏得玩家信賴。平台通過TST技術測試及GLI系統認證,確保遊戲公平性。目前推出首存1000送1000優惠活動,最高回饋可達20萬,並提供日日續儲10%的回饋金。平台提供真人百家、棋牌、老虎機、體育電競及彩票等多樣化遊戲選擇,讓玩家享受如臨現場的娛樂體驗。
鉅城娛樂城:亞太區知名線上娛樂平台
鉅城娛樂城作為亞太區最受歡迎的線上娛樂平台之一,以其豐富多元的遊戲內容和卓越的服務品質贏得了廣大玩家的信賴。該平台不僅擁有一系列令人 excited 的遊戲,還致力於為玩家提供公平、公正的遊戲環境。
公平遊戲保障
鉅城娛樂城的遊戲公平性通過TST技術測試及GLI系統認證確保,使玩家在遊玩過程中完全無需擔心遊戲的公正問題。這些認證保證了每一場比賽及遊戲的隨機性和透明度,進一步增強了玩家的信心。
優惠活動
目前,鉅城娛樂城推出了首存1000送1000的優惠活動,這讓新玩家能夠在註冊後,迅速享受雙倍的存款金額,提升遊戲體驗。此外,平台最高回饋可達20萬,讓玩家在參與遊戲時享受到更多的利潤。值得注意的是,鉅城娛樂城還提供日日續儲10%的回饋金,進一步增強了玩家的參與熱情。
遊戲選擇
鉅城娛樂城平台提供多樣化的遊戲選擇,包括真人百家、棋牌、老虎機、體育電競及彩票等,讓玩家可以依照自己的興趣和需求選擇遊戲。無論是喜愛刺激的百家 blackjack,還是希望體驗策略與運氣的棋牌遊戲,鉅城娛樂城皆能滿足每位玩家的期望,並提供如臨現場的娛樂體驗。
總結
總而言之,鉅城娛樂城憑藉其卓越的遊戲內容和專業的客戶服務,已成為亞太區線上娛樂的不二之選。公正的遊戲環境、誘人的優惠活動及多樣的遊戲選擇,吸引了無數玩家的目光。無論你是新手還是老玩家,鉅城娛樂城都能帶給你一段難忘的遊戲旅程。 -
九州娛樂城作為線上娛樂平台的領導品牌,不斷推出創新服務及優惠活動。近期推出的168元體驗金活動,讓新會員免費體驗平台特色。九州娛樂以玩家體驗為核心,提供多元化的遊戲選擇,包括電子遊戲、真人對戰等娛樂內容。平台以穩定、安全的系統建立口碑,加上專業的客服團隊,打造全方位的娛樂環境。現在註冊加入九州娛樂城,立即享受精彩遊戲體驗。
-
九州娛樂城作為線上娛樂平台的領導品牌,不斷推出創新服務及優惠活動。近期推出的168元體驗金活動,讓新會員免費體驗平台特色。九州娛樂以玩家體驗為核心,提供多元化的遊戲選擇,包括電子遊戲、真人對戰等娛樂內容。平台以穩定、安全的系統建立口碑,加上專業的客服團隊,打造全方位的娛樂環境。現在註冊加入九州娛樂城,立即享受精彩遊戲體驗。
-
九州平台針對新會員推出168元的免費體驗金活動。這項活動的特點是無需滿足投注要求,新會員註冊 後即可使用。會員可以藉此機會體驗平台上的各種遊戲選項,包括電子遊戲、真人對戰等多樣娛樂內容。
相較於市面上其他平台,這項活動的主要優勢在於其簡單的申請流程和零門檻要求。一般平台的體驗金活動往往會設定投注金額要求,但此活動讓會員能更自由地體驗平台服務。 -
九州平台針對新會員推出168元的免費體驗金活動。這項活動的特點是無需滿足投注要求,新會員註冊 後即可使用。會員可以藉此機會體驗平台上的各種遊戲選項,包括電子遊戲、真人對戰等多樣娛樂內容。
相較於市面上其他平台,這項活動的主要優勢在於其簡單的申請流程和零門檻要求。一般平台的體驗金活動往往會設定投注金額要求,但此活動讓會員能更自由地體驗平台服務。 -
TU娛樂城
TU娛樂城擁有國際級的SGS服務認證,是首家獲得7星級認證的娛樂平台。每日提供近千場體育賽事直播,並設有真人、彩票、電子遊戲等多元娛樂選項。平台採用128位加密技術,打造安全可靠的服務環境。多端支援包含Web、H5及iOS、Android原生App,讓會員能隨時享受專業服務體驗。 -
TU娛樂城
TU娛樂城擁有國際級的SGS服務認證,是首家獲得7星級認證的娛樂平台。每日提供近千場體育賽事直播,並設有真人、彩票、電子遊戲等多元娛樂選項。平台採用128位加密技術,打造安全可靠的服務環境。多端支援包含Web、H5及iOS、Android原生App,讓會員能隨時享受專業服務體驗。 -
Đá Gà Online - Hình Thức Giải Trí Mới Mẻ và Hấp Dẫn
Ngày nay, với sự phát triển mạnh mẽ của công nghệ thông tin, nhiều hình thức giải trí truyền thống đã được chuyển thể sang các phiên bản trực tuyến, và đá gà online chính là một trong số đó. Đá gà không chỉ là một trò chơi có lịch sử lâu đời ở nhiều quốc gia, mà còn là một phần văn hóa đặc sắc, gắn liền với những giá trị truyền thống. Khi được số hóa, hình thức này mang đến nhiều lợi ích và trải nghiệm mới lạ cho người chơi.
Đá gà online cho phép người chơi tham gia vào các trận đấu bất cứ lúc nào và ở bất kỳ đâu, chỉ cần có kết nối internet. Điều này mang đến một sự thuận tiện vượt trội so với hình thức đá gà truyền thống, nơi người chơi thường phải đến sân đấu để có thể tham gia. Nhờ vào công nghệ livestream, người chơi có thể theo dõi trực tiếp các trận đấu từ xa, cảm nhận được không khí kịch tính và hồi hộp như đang ở sân đấu thực sự.
Ngoài ra, đá gà online còn tạo cơ hội cho người chơi tương tác với nhau, chia sẻ kinh nghiệm và chiến thuật. Đây không chỉ là một trò chơi đơn thuần, mà còn là một cộng đồng nơi người yêu thích đá gà có thể kết nối và giao lưu. Nhiều nền tảng đá gà online hiện nay còn cung cấp các dịch vụ đặt cược, giúp người chơi có thêm phần thú vị và hứng thú khi theo dõi trận đấu.
Tuy nhiên, bên cạnh những lợi ích đó, đá gà online cũng đặt ra nhiều vấn đề cần được xem xét. Cùng với sự phát triển của hình thức này, những tranh cãi về đạo đức, pháp lý và quyền lợi động vật cũng trở nên nổi bật. Nhiều người lo ngại rằng việc tổ chức đá gà, dù ở hình thức nào, cũng có thể gây tổn hại đến sức khỏe và quyền lợi của các chú gà. Vấn đề đặt cược cũng tạo ra rủi ro tài chính cho người chơi, và cần có sự quản lý chặt chẽ hơn từ phía các cơ quan chức năng.
Trong bối cảnh đó, để đá gà online phát triển bền vững, cần có các quy định hợp pháp và minh bạch nhằm bảo vệ quyền lợi của cả người chơi và động vật. Đồng thời, việc nâng cao nhận thức của cộng đồng về đạo đức trong việc tham gia các trò chơi giải trí này cũng là rất quan trọng.
Tóm lại, đá gà online là một hình thức giải trí mới mẻ, mang đến nhiều trải nghiệm thú vị cho người chơi. Tuy nhiên, đi kèm với nó là trách nhiệm trong việc bảo vệ quyền lợi động vật và đảm bảo tính hợp pháp của các hoạt động cá cược. Chỉ khi có sự cân bằng giữa giải trí và đạo đức, đá gà online mới có thể trở thành một phần hấp dẫn và bền vững trong đời sống giải trí hiện đại. -
戰神賽特
2024最新老虎機戰神賽特試玩,網友最推薦這 3家娛樂城 : 1. ATG娛樂城、2. 富遊娛樂城、3. 1XBET娛樂城,無論是在網路評論或優惠活動,都相當出色。
戰神賽特是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的的冒險者能夠進入探查。 -
hi88,
Đá Gà Online - Hình Thức Giải Trí Mới Mẻ và Hấp Dẫn
Ngày nay, với sự phát triển mạnh mẽ của công nghệ thông tin, nhiều hình thức giải trí truyền thống đã được chuyển thể sang các phiên bản trực tuyến, và đá gà online chính là một trong số đó. Đá gà không chỉ là một trò chơi có lịch sử lâu đời ở nhiều quốc gia, mà còn là một phần văn hóa đặc sắc, gắn liền với những giá trị truyền thống. Khi được số hóa, hình thức này mang đến nhiều lợi ích và trải nghiệm mới lạ cho người chơi.
Đá gà online cho phép người chơi tham gia vào các trận đấu bất cứ lúc nào và ở bất kỳ đâu, chỉ cần có kết nối internet. Điều này mang đến một sự thuận tiện vượt trội so với hình thức đá gà truyền thống, nơi người chơi thường phải đến sân đấu để có thể tham gia. Nhờ vào công nghệ livestream, người chơi có thể theo dõi trực tiếp các trận đấu từ xa, cảm nhận được không khí kịch tính và hồi hộp như đang ở sân đấu thực sự.
Ngoài ra, đá gà online còn tạo cơ hội cho người chơi tương tác với nhau, chia sẻ kinh nghiệm và chiến thuật. Đây không chỉ là một trò chơi đơn thuần, mà còn là một cộng đồng nơi người yêu thích đá gà có thể kết nối và giao lưu. Nhiều nền tảng đá gà online hiện nay còn cung cấp các dịch vụ đặt cược, giúp người chơi có thêm phần thú vị và hứng thú khi theo dõi trận đấu.
Tuy nhiên, bên cạnh những lợi ích đó, đá gà online cũng đặt ra nhiều vấn đề cần được xem xét. Cùng với sự phát triển của hình thức này, những tranh cãi về đạo đức, pháp lý và quyền lợi động vật cũng trở nên nổi bật. Nhiều người lo ngại rằng việc tổ chức đá gà, dù ở hình thức nào, cũng có thể gây tổn hại đến sức khỏe và quyền lợi của các chú gà. Vấn đề đặt cược cũng tạo ra rủi ro tài chính cho người chơi, và cần có sự quản lý chặt chẽ hơn từ phía các cơ quan chức năng.
Trong bối cảnh đó, để đá gà online phát triển bền vững, cần có các quy định hợp pháp và minh bạch nhằm bảo vệ quyền lợi của cả người chơi và động vật. Đồng thời, việc nâng cao nhận thức của cộng đồng về đạo đức trong việc tham gia các trò chơi giải trí này cũng là rất quan trọng.
Tóm lại, đá gà online là một hình thức giải trí mới mẻ, mang đến nhiều trải nghiệm thú vị cho người chơi. Tuy nhiên, đi kèm với nó là trách nhiệm trong việc bảo vệ quyền lợi động vật và đảm bảo tính hợp pháp của các hoạt động cá cược. Chỉ khi có sự cân bằng giữa giải trí và đạo đức, đá gà online mới có thể trở thành một phần hấp dẫn và bền vững trong đời sống giải trí hiện đại. -
戰神賽特
2024最新老虎機戰神賽特試玩,網友最推薦這 3家娛樂城 : 1. ATG娛樂城、2. 富遊娛樂城、3. 1XBET娛樂城,無論是在網路評論或優惠活動,都相當出色。
戰神賽特是由ATG電子獨家開發的古埃及風格線上老虎機,傳說中戰神賽特是「力量之神」與奈芙蒂斯女神結成連理,共同守護古埃及的奇幻秘寶,只有被選中的的冒險者能夠進入探查。 -
Đá gà online là một hình thức giải trí mới mẻ, kết hợp giữa trò chơi truyền thống đá gà và công nghệ hiện đại. Khi công nghệ số phát triển mạnh mẽ, nhiều trò chơi dân gian đã được chuyển thể thành các phiên bản online, và đá gà không phải là ngoại lệ. Trò chơi này không chỉ giúp người chơi có thể tham gia vào bất kỳ lúc nào, bất kỳ đâu, mà còn mang lại những trải nghiệm thú vị và kịch tính. Tuy nhiên, đá gà online cũng đã gây ra nhiều tranh cãi về mặt đạo đức, pháp lý và bảo vệ quyền lợi động vật.
Đá Gà Online - Hình Thức Giải Trí Mới Mẻ
Đá gà online là một hình thức giải trí mới mẻ, kết hợp giữa trò chơi truyền thống đá gà và công nghệ hiện đại. Trong những năm gần đây, khi công nghệ số phát triển mạnh mẽ, nhiều trò chơi dân gian đã được chuyển thể thành các phiên bản online, và đá gà cũng không phải là ngoại lệ.
Chơi đá gà online mang lại cho người chơi nhiều lợi ích. Một trong những điểm nổi bật nhất là sự tiện lợi. Với việc sử dụng internet, người chơi có thể tham gia vào các trận đá gà bất cứ lúc nào và ở bất kỳ đâu. Điều này giúp cho trò chơi trở nên dễ tiếp cận hơn, đặc biệt đối với những người bận rộn với công việc và không có nhiều thời gian để tham gia các hoạt động giải trí truyền thống.
Ngoài ra, đá gà online còn mang đến những trải nghiệm thú vị và kịch tính. Người chơi không chỉ đơn thuần là xem mà còn có thể tham gia đặt cược, theo dõi những trận đấu hấp dẫn và cảm nhận được không khí hồi hộp của từng phút giây. Các nền tảng đá gà online thường cung cấp nhiều tính năng như livestream trận đấu, thống kê kết quả, và giao lưu với cộng đồng người chơi, tạo nên một không gian giải trí sống động.
Tuy nhiên, đá gà online cũng đã gây ra nhiều tranh cãi về mặt đạo đức, pháp lý và bảo vệ quyền lợi động vật. Nhiều người cho rằng việc tổ chức đá gà, dù là trực tuyến hay truyền thống, vẫn là hành vi không đáng khuyến khích, bởi nó có thể gây tổn hại cho quyền lợi của động vật. Bên cạnh đó, vấn đề pháp lý liên quan đến cá cược và những rủi ro tài chính cũng là mối quan tâm lớn đối với xã hội.
Tóm lại, đá gà online là một hình thức giải trí hiện đại và thu hút nhiều người chơi. Tuy nhiên, sự phát triển của nó cũng cần đi kèm với những giải pháp để bảo vệ quyền lợi động vật và đảm bảo tính hợp pháp của hoạt động này. Sự cân nhắc về mặt đạo đức và pháp lý trong việc tham gia trò chơi sẽ giúp tạo ra một môi trường giải trí lành mạnh và bền vững. -
Đá gà online là một hình thức giải trí mới mẻ, kết hợp giữa trò chơi truyền thống đá gà và công nghệ hiện đại. Khi công nghệ số phát triển mạnh mẽ, nhiều trò chơi dân gian đã được chuyển thể thành các phiên bản online, và đá gà không phải là ngoại lệ. Trò chơi này không chỉ giúp người chơi có thể tham gia vào bất kỳ lúc nào, bất kỳ đâu, mà còn mang lại những trải nghiệm thú vị và kịch tính. Tuy nhiên, đá gà online cũng đã gây ra nhiều tranh cãi về mặt đạo đức, pháp lý và bảo vệ quyền lợi động vật.
Đá Gà Online - Hình Thức Giải Trí Mới Mẻ
Đá gà online là một hình thức giải trí mới mẻ, kết hợp giữa trò chơi truyền thống đá gà và công nghệ hiện đại. Trong những năm gần đây, khi công nghệ số phát triển mạnh mẽ, nhiều trò chơi dân gian đã được chuyển thể thành các phiên bản online, và đá gà cũng không phải là ngoại lệ.
Chơi đá gà online mang lại cho người chơi nhiều lợi ích. Một trong những điểm nổi bật nhất là sự tiện lợi. Với việc sử dụng internet, người chơi có thể tham gia vào các trận đá gà bất cứ lúc nào và ở bất kỳ đâu. Điều này giúp cho trò chơi trở nên dễ tiếp cận hơn, đặc biệt đối với những người bận rộn với công việc và không có nhiều thời gian để tham gia các hoạt động giải trí truyền thống.
Ngoài ra, đá gà online còn mang đến những trải nghiệm thú vị và kịch tính. Người chơi không chỉ đơn thuần là xem mà còn có thể tham gia đặt cược, theo dõi những trận đấu hấp dẫn và cảm nhận được không khí hồi hộp của từng phút giây. Các nền tảng đá gà online thường cung cấp nhiều tính năng như livestream trận đấu, thống kê kết quả, và giao lưu với cộng đồng người chơi, tạo nên một không gian giải trí sống động.
Tuy nhiên, đá gà online cũng đã gây ra nhiều tranh cãi về mặt đạo đức, pháp lý và bảo vệ quyền lợi động vật. Nhiều người cho rằng việc tổ chức đá gà, dù là trực tuyến hay truyền thống, vẫn là hành vi không đáng khuyến khích, bởi nó có thể gây tổn hại cho quyền lợi của động vật. Bên cạnh đó, vấn đề pháp lý liên quan đến cá cược và những rủi ro tài chính cũng là mối quan tâm lớn đối với xã hội.
Tóm lại, đá gà online là một hình thức giải trí hiện đại và thu hút nhiều người chơi. Tuy nhiên, sự phát triển của nó cũng cần đi kèm với những giải pháp để bảo vệ quyền lợi động vật và đảm bảo tính hợp pháp của hoạt động này. Sự cân nhắc về mặt đạo đức và pháp lý trong việc tham gia trò chơi sẽ giúp tạo ra một môi trường giải trí lành mạnh và bền vững. -
GAMELANTOGEL
-
BEKU4D
BEKU4D -
[url=https://streamhub.world/es/]Aumenta Espectadores de Twitch y Kick[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.world/pt/]Aumente os Espectadores da Twitch e do Kick[/url] -
Wow, amazing blog format! How lengthy have you ever been blogging for? you make blogging look easy. The overall look of your web site is wonderful, let alone the content material!
https://esco-center.com.ua/bi-led-linza-perevagy-suchasnykh-tekhnolohiy-osvitlennya -
Are over-the-counter medicines safe for people with heart conditions goodrx Sildenafil.
-
Creative Writing Prompts
The Comprehensive Store for AI-Fueled Innovation
In the modern rapid society, merging imagination with modern advancements is vital for advancement and output. At Template Forge, we present premium, bespoke prompts designed to elevate your innovative undertakings across various domains.
Reasons to Choose Template Forge?
We are focused to supplying only the finest prompts to support your artistic projects. Our crew of specialists carefully compiles each prompt to ensure practicality and importance, allowing it simpler for you to discover ideas when you need it the most.
Diverse Categories
Our wide-ranging inventory covers multiple types, featuring social networking advertising, issue resolution, and narrative crafting. This breadth ensures you have the means needed to address any project successfully.
Elevate Your Creativity
Template Forge’s suggestions serve as a launchpad for your ideas, letting you to focus on your distinct perspective and vision free from the strain of brainstorming. Each prompt is created to stimulate and assist you through the artistic journey.
Join thousands of content makers who have leveraged the strength of artificial intelligence at Template Forge. Investigate our extensive subjects today and unveil your creative possibilities. With our premium prompts, developing with intention has ever been more straightforward. Welcome to your all-in-one resource for AI-fueled innovation! -
Your Single Marketplace for AI-Powered Artistry
In the current fast-paced world, merging innovation with modern advancements is necessary for creativity and efficiency. At Template Forge, we present premium, bespoke prompts designed to elevate your creative undertakings across multiple fields.
Why Choose Template Forge?
We are committed to delivering only the best prompts to aid your artistic projects. Our staff of specialists carefully selects each prompt to confirm practicality and pertinence, enabling it more manageable for you to obtain ideas when you need it the most critically.
Diverse Categories
Our extensive inventory covers numerous segments, featuring digital marketing, technical support, and creative storytelling. This range guarantees you have the capabilities needed to tackle any task effectively.
Elevate Your Creativity
Template Forge’s prompts serve as a foundation for your thoughts, letting you to center on your personal style and aspirations without the pressure of conceptualizing. Each prompt is crafted to stimulate and direct you through the artistic path.
Connect with thousands of satisfied makers who have utilized the power of AI at Template Forge. Explore our wide categories today and unveil your artistic potential. With our premium prompts, producing with purpose has ever been more straightforward. Welcome to your one-stop shop for AI-powered creativity! -
[url=https://streamhub.world/de/]Steigere Twitch und Kick Zuschauer[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.world/ja/]streamhub[/url] -
https://community.usa.canon.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/235400 priligy 60 mg buy
-
The Comprehensive Marketplace for AI-Fueled Artistry
In this rapid environment, blending artistry with tech is essential for progress and effectiveness. At Our Platform, we offer premium, bespoke prompts created to elevate your creative works across various fields.
Why Choose Template Forge?
We are dedicated to providing only the top prompts to help your innovative pursuits. Our staff of specialists attentively selects each prompt to guarantee usefulness and pertinence, making it more manageable for you to find ideas when you want it most.
Diverse Categories
Our broad collection spans various types, such as social networking advertising, technical support, and fiction writing. This variety ensures you have the means needed to manage any assignment successfully.
Elevate Your Creativity
Template Forge’s suggestions serve as a springboard for your creativity, allowing you to center on your unique perspective and ambitions beyond the strain of brainstorming. Each prompt is designed to stimulate and guide you through the artistic course.
Connect with thousands of happy artists who have harnessed the potential of AI at Template Forge. Investigate our varied options today and unlock your artistic capabilities. With our superior prompts, creating with intention has not been more manageable. Welcome to your ultimate marketplace for artificial intelligence-driven imagination! -
Creative Writing AI prompts
The All-in-One Store for AI-Fueled Artistry
In today's dynamic environment, blending artistry with modern advancements is vital for progress and effectiveness. At Template Forge, we present high-quality, specially designed prompts intended to improve your creative initiatives across different categories.
Why Choose Template Forge?
We are dedicated to supplying only the top prompts to help your artistic endeavors. Our team of authorities carefully selects each prompt to guarantee applicability and importance, enabling it more convenient for you to locate creativity when you desire it the most desperately.
Diverse Categories
Our broad selection spans multiple fields, featuring digital marketing, technical troubleshooting, and narrative crafting. This diversity guarantees you have the means needed to handle any initiative effectively.
Elevate Your Creativity
Template Forge’s suggestions serve as a launchpad for your ideas, allowing you to direct on your personal style and ambitions free from the stress of idea generation. Each prompt is designed to motivate and lead you through the innovative process.
Participate in thousands of happy makers who have leveraged the potential of artificial intelligence at Template Forge. Check out our varied options today and unveil your innovative talents. With our premium prompts, crafting with clarity has never been more straightforward. Welcome to your comprehensive store for AI-powered creativity! -
Aparatos de balanceo: fundamental para el operación fluido y efectivo de las maquinarias.
En el campo de la innovación actual, donde la productividad y la estabilidad del dispositivo son de alta significancia, los equipos de ajuste tienen un papel esencial. Estos sistemas adaptados están desarrollados para calibrar y regular componentes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria manufacturera, transportes de desplazamiento o incluso en dispositivos caseros.
Para los especialistas en conservación de aparatos y los ingenieros, utilizar con dispositivos de balanceo es esencial para promover el desempeño fluido y seguro de cualquier aparato móvil. Gracias a estas opciones innovadoras avanzadas, es posible reducir sustancialmente las sacudidas, el estruendo y la presión sobre los rodamientos, mejorando la tiempo de servicio de elementos importantes.
De igual manera relevante es el papel que desempeñan los sistemas de balanceo en la servicio al cliente. El ayuda experto y el mantenimiento constante usando estos dispositivos permiten brindar servicios de alta calidad, mejorando la satisfacción de los compradores.
Para los titulares de negocios, la contribución en equipos de calibración y detectores puede ser fundamental para optimizar la eficiencia y rendimiento de sus sistemas. Esto es principalmente significativo para los dueños de negocios que administran reducidas y medianas negocios, donde cada aspecto importa.
Asimismo, los sistemas de equilibrado tienen una vasta utilización en el sector de la protección y el control de excelencia. Facilitan identificar potenciales errores, reduciendo intervenciones costosas y daños a los dispositivos. También, los resultados generados de estos dispositivos pueden emplearse para maximizar sistemas y potenciar la visibilidad en plataformas de investigación.
Las campos de aplicación de los sistemas de calibración incluyen variadas áreas, desde la producción de transporte personal hasta el monitoreo ecológico. No afecta si se considera de extensas elaboraciones manufactureras o pequeños espacios hogareños, los dispositivos de balanceo son fundamentales para proteger un rendimiento efectivo y sin presencia de interrupciones. -
Vibracion mecanica
Aparatos de equilibrado: importante para el operación estable y eficiente de las equipos.
En el campo de la innovación moderna, donde la productividad y la estabilidad del aparato son de gran significancia, los equipos de balanceo juegan un papel esencial. Estos aparatos dedicados están creados para ajustar y regular componentes móviles, ya sea en maquinaria productiva, vehículos de traslado o incluso en aparatos caseros.
Para los expertos en mantenimiento de aparatos y los especialistas, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es crucial para asegurar el funcionamiento uniforme y fiable de cualquier sistema giratorio. Gracias a estas alternativas avanzadas modernas, es posible reducir sustancialmente las sacudidas, el estruendo y la presión sobre los soportes, aumentando la duración de piezas caros.
Asimismo trascendental es el rol que tienen los dispositivos de ajuste en la servicio al comprador. El apoyo especializado y el conservación continuo utilizando estos equipos posibilitan ofrecer servicios de alta calidad, mejorando la bienestar de los usuarios.
Para los propietarios de negocios, la contribución en equipos de ajuste y medidores puede ser clave para incrementar la rendimiento y productividad de sus sistemas. Esto es sobre todo significativo para los empresarios que dirigen pequeñas y pequeñas empresas, donde cada punto vale.
Asimismo, los aparatos de equilibrado tienen una amplia aplicación en el campo de la seguridad y el supervisión de excelencia. Posibilitan identificar probables errores, impidiendo arreglos costosas y problemas a los sistemas. También, los información obtenidos de estos sistemas pueden emplearse para mejorar métodos y aumentar la reconocimiento en buscadores de búsqueda.
Las sectores de utilización de los sistemas de equilibrado abarcan numerosas áreas, desde la manufactura de bicicletas hasta el control ambiental. No influye si se habla de enormes fabricaciones industriales o modestos establecimientos hogareños, los sistemas de calibración son indispensables para asegurar un desempeño productivo y sin paradas. -
Your All-in-One Marketplace for Artificial Intelligence-Powered Artistry
In the modern rapid world, integrating imagination with tech is essential for progress and productivity. At Our Platform, we offer superior, custom-crafted prompts created to boost your artistic initiatives across multiple fields.
Reasons to Choose Template Forge?
We are focused to offering only the highest quality prompts to aid your artistic projects. Our team of specialists attentively compiles each prompt to guarantee practicality and pertinence, making it more convenient for you to locate inspiration when you desire it the most.
Diverse Categories
Our extensive library encompasses diverse categories, including social networking advertising, problem-solving, and fiction writing. This range ensures you have the tools needed to address any project efficiently.
Elevate Your Creativity
Template Forge’s inspirations serve as a springboard for your ideas, letting you to focus on your distinct expression and vision beyond the pressure of creativity. Each prompt is intended to inspire and lead you through the innovative process.
Participate in thousands of pleased makers who have utilized the capabilities of AI at Template Forge. Check out our varied categories today and access your imaginative talents. With our high-quality prompts, developing with clarity has ever been more straightforward. Welcome to your all-in-one store for AI-powered creativity! -
The One-Stop Resource for Artificial Intelligence-Powered Artistry
In the modern dynamic world, combining artistry with tech is necessary for progress and efficiency. At Template Forge, we offer high-quality, custom-crafted prompts created to elevate your creative works across multiple domains.
Reasons to Choose Template Forge?
We are focused to offering only the highest quality prompts to aid your innovative pursuits. Our group of specialists attentively curates each prompt to guarantee applicability and relevance, allowing it more manageable for you to discover creativity when you require it the most desperately.
Diverse Categories
Our broad selection encompasses multiple fields, featuring social media marketing, technical support, and fiction writing. This breadth ensures you have the tools needed to handle any assignment effectively.
Elevate Your Creativity
Template Forge’s inspirations serve as a catalyst for your concepts, letting you to direct on your distinct expression and vision free from the burden of conceptualizing. Each prompt is intended to inspire and assist you through the innovative journey.
Become part of thousands of pleased creators who have utilized the strength of AI at Template Forge. Check out our wide fields today and unlock your artistic capabilities. With our top-notch prompts, developing with purpose has never been more straightforward. Welcome to your ultimate shop for AI-enabled imagination! -
[url=https://streamhub.world/fr/]Booster les Spectateurs Twitch et Kick[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.world/zh-hans/]streamhub[/url] -
Your Final Goal for Luxury In-Game Goods!
In the current quick gaming realm, the rush of exploration and development is crucial. If you're hunting for unique items, unique device designs, tailored features, codes, assets, quests, or handy top-up assistance, look no further! Introducing to Items4Games, your single marketplace for a vast selection of premium in-game assets designed to improve your gaming playtime.
Why Items4Games Is Exceptional
Varied Selection of In-Game Items
We offer a large range of in-game items, from uncommon styles to one-of-a-kind artifacts and game tokens. Our inventory is customized to elevate your gameplay and immerse you in a universe of limitless opportunities.
Assistance for Famous Titles
Our broad inventory contains well-known games like CS2, Fortnite, Valorant, Dota 2, and Call of Duty. No matter your gaming choice, we have goods that serve to the most popular titles in the sector.
Elevated Gaming Adventure
With unique in-game assets, you can reveal new capabilities and exhibit your distinct style. From unique weapon skins to effective artifacts, our products transform your gaming experiences into unforgettable activities.
Safe and Dependable Exchanges
We emphasize your well-being with reliable and honest deals. You can buy with confidence, knowing that your details is guarded at all times.
Fair Rates
Access superior items without breaking the budget. Our reasonable and just cost scheme ensures that improving your gaming journey is achievable to all.
Simple Interface
Our simple platform lets you to easily explore and secure the items you desire, saving you hours and elevating your acquisition adventure.
What Awaits for You at Items4Games
Explore weapon designs that mirror your character, special artifacts for special achievements, and game codes that open new material. Our supplies and objectives support you develop up effortlessly, while balance solutions maintain your game balance ready for play. Enjoy extra game types that bring diversity and complexity to your gaming sessions.
In closing remarks, Items4Games is your ultimate source for improving your gaming experience with premium in-game goods. Browse our range today and elevate your gameplay to new extremes! -
Your Final Place for Luxury In-Game Goods!
In modern rapid gaming landscape, the rush of exploration and progression is vital. If you're looking for unique artifacts, limited device designs, specialized types, tokens, materials, missions, or easy funding options, look no further! Hello to Items4Games, your all-in-one shop for a vast collection of exclusive in-game assets created to boost your gaming experience.
Why Items4Games Is Exceptional
Diverse Variety of In-Game Goods
We present a wide selection of in-game items, from uncommon appearances to distinctive items and game keys. Our selection is customized to enhance your gameplay and involve you in a environment of limitless options.
Help for Trending Names
Our wide offering features well-known games like CS2, Fortnite, Valorant, Dota 2, and Call of Duty. No matter your gaming preference, we have items that meet to the top hits in the field.
Elevated Gaming Journey
With limited in-game goods, you can gain new abilities and illustrate your unique flair. From special weapon styles to effective artifacts, our products change your gaming sessions into unforgettable journeys.
Protected and Reliable Transactions
We focus on your security with protected and dependable deals. You can shop securely, knowing that your information is safe at all moments.
Fair Costs
Get high-quality items without breaking the bank. Our cost-effective and just pricing model ensures that boosting your gaming journey is within reach to everyone.
User-Friendly System
Our accessible design lets you to effortlessly explore and buy the products you require, reducing you hours and elevating your shopping journey.
What Is Ready for You at Items4Games
Find weapon skins that reflect your personality, special artifacts for unique achievements, and game access that open new features. Our materials and objectives help you improve up smoothly, while top-up services maintain your game resources ready for use. Enjoy additional game modes that introduce difference and richness to your gaming times.
In conclusion, Items4Games is your final goal for elevating your gaming playtime with premium in-game goods. Discover our range today and boost your gameplay to new limits! -
Just want to say your article is as amazing. The clearness to your put up is simply nice and that i can assume you're a professional on this subject. Well with your permission let me to clutch your RSS feed to stay up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks 1,000,000 and please carry on the enjoyable work.
ответы на игру слова все уровни -
戦国パチスロ花の慶次これより我ら修羅に入る
課長熊田工作
パチンコは、運だけではなく、選ぶ楽しみもあります。自分に合った台を見つけることが大切です。
革命機ヴァルヴレイヴ
https://www.online-casino.city/?ReviewID=920044818.html
プレイ中の雰囲気が楽しく、長時間楽しむことができます。快適な空間が魅力です。
150_翔馬
[url=https://www.k8-casino.jp/?ArticleID=926341818.html]戦争 ゲーム
[/url]
CR北斗の拳5 覇者
Pフィーバーダンベル何キロ持てる
モンキーターンII
アラジンAII
[url=https://xn--k8-9g4a3b4f.site/?WatchID=926700818.html]漫画 セリフ
[/url]
CR 北斗の拳6 拳王
P DD 北斗の拳2 ついでに愛をとりもどせ!! ラオウ
CR緋弾のアリアII Ver.319
聖闘士星矢海皇覚醒
[url=https://www.8casino8.com/?WatchID=928104818.html]有馬 オッズ
[/url]
戦国乙女剣戟に舞う白き剣聖西国参戦編
CRぱちんこウルトラマンタロウ 戦え!!ウルトラ6兄弟
CR フィーバーマクロスフロンティア2W
BLOOD 二人の女王
https://www.k8-casino.org/?ReviewID=919708818.html
パチンコの演出は、時に驚かされることがあります。毎回新しい発見があります。
戦国パチスロ花の慶次これより我ら修羅に入る
https://www.k8pachinko.work/?ReviewID=919990818.html
パチンコの世界は奥が深く、探求心をくすぐられます。新しい情報を得ることで、さらに楽しめます。 -
토토사이트 커뮤니티: 안전한 베팅을 위한 길잡이
토토사이트 커뮤니티는 스포츠 베팅을 즐기는 사람들에게 단순한 정보 공유의 장을 넘어, 안전한 배팅 환경을 조성하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다. 이곳에서는 초보자부터 전문가까지 다양한 사람들이 모여 베팅 전략을 논의하고, 신뢰할 수 있는 토토사이트를 추천하며, 먹튀 사고를 예방하기 위한 정보를 공유합니다. 특히, 사설 토토사이트의 위험성을 알리고, 이를 피할 수 있는 방법을 제시함으로써 사용자들이 더 안전하게 베팅을 즐길 수 있도록 돕습니다.
사설 토토사이트의 숨겨진 위험
사설 토토사이트는 정부의 규제를 받지 않기 때문에 다양한 문제를 일으킬 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 공정하지 않은 배당률, 과장된 광고, 개인정보 유출 등이 대표적인 문제점입니다. 또한, 사설 토토사이트는 법적 문제로 인해 갑자기 사라지는 경우가 많아 사용자들이 금전적 손실을 입을 위험이 큽니다. 이런 이유로, 토토 커뮤니티에서는 사설 토토사이트보다는 규제를 받는 공식 사이트를 이용할 것을 권장합니다.
토토 커뮤니티가 제공하는 가치
토토 커뮤니티는 단순히 정보를 나누는 공간이 아니라, 사용자들이 안전하게 베팅할 수 있도록 돕는 네트워크입니다. 예를 들어, 새로운 토토사이트가 등장했을 때 커뮤니티 멤버들은 해당 사이트의 운영 주체, 결제 시스템, 사용자 리뷰 등을 꼼꼼히 검토합니다. 이를 통해 먹튀 사고를 미리 방지하고, 신뢰할 수 있는 사이트만을 추천합니다. 또한, 문제가 발생했을 때는 보증 사이트를 통해 사용자들이 손실을 최소화할 수 있도록 돕습니다.
어떻게 신뢰할 수 있는 토토사이트를 찾을까?
토토 커뮤니티에서는 신뢰할 수 있는 토토사이트를 찾기 위해 몇 가지 중요한 기준을 제시합니다. 먼저, 사이트의 운영 주체가 명확한지 확인하는 것이 중요합니다. 정부나 공인된 기관에서 관리하는 사이트라면 신뢰할 수 있습니다. 또한, 다른 사용자들의 리뷰를 참고하여 사이트의 신뢰성을 판단할 수 있습니다. 긍정적인 평가가 많고, 문제가 거의 없는 사이트라면 안전하게 이용할 수 있습니다.
결제 시스템도 중요한 확인 요소 중 하나입니다. 신용카드, 전자지갑 등 다양한 결제 방법을 지원하고, SSL 암호화를 통해 금융 정보를 보호하는 사이트라면 더욱 신뢰할 수 있습니다. 마지막으로, 온라인 커뮤니티나 포럼에서 해당 사이트에 대한 평판을 확인하는 것도 좋은 방법입니다. 다른 사용자들이 어떻게 평가하는지, 문제가 없는지 꼼꼼히 살펴보는 것이 중요합니다.
토토 커뮤니티의 보증 사이트
토토 커뮤니티에서는 먹튀 사고를 예방하기 위해 보증 사이트를 추천합니다. 이러한 사이트는 사용자들의 개인정보와 금융 정보를 보호하며, 문제가 발생했을 때 빠르게 해결할 수 있는 시스템을 갖추고 있습니다. 보증 사이트를 이용하면 안전하게 베팅을 즐길 수 있으며, 만약 문제가 생기더라도 커뮤니티의 도움을 받아 해결할 수 있습니다.
마무리
토토사이트 커뮤니티는 스포츠 베팅을 즐기는 사람들에게 안전하고 신뢰할 수 있는 정보를 제공하는 중요한 공간입니다. 사설 토토사이트의 위험성을 인지하고, 신뢰할 수 있는 사이트를 선택하는 것이 무엇보다 중요합니다. 토토 커뮤니티의 정보를 참고하여 안전한 베팅 환경을 조성하고, 스포츠 베팅을 더욱 즐겁게 즐기시길 바랍니다. 항상 책임감 있게 베팅에 임하는 것도 잊지 마세요! -
토토사이트 커뮤니티: 안전한 베팅을 위한 길잡이
토토사이트 커뮤니티는 스포츠 베팅을 즐기는 사람들에게 단순한 정보 공유의 장을 넘어, 안전한 배팅 환경을 조성하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다. 이곳에서는 초보자부터 전문가까지 다양한 사람들이 모여 베팅 전략을 논의하고, 신뢰할 수 있는 토토사이트를 추천하며, 먹튀 사고를 예방하기 위한 정보를 공유합니다. 특히, 사설 토토사이트의 위험성을 알리고, 이를 피할 수 있는 방법을 제시함으로써 사용자들이 더 안전하게 베팅을 즐길 수 있도록 돕습니다.
사설 토토사이트의 숨겨진 위험
사설 토토사이트는 정부의 규제를 받지 않기 때문에 다양한 문제를 일으킬 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 공정하지 않은 배당률, 과장된 광고, 개인정보 유출 등이 대표적인 문제점입니다. 또한, 사설 토토사이트는 법적 문제로 인해 갑자기 사라지는 경우가 많아 사용자들이 금전적 손실을 입을 위험이 큽니다. 이런 이유로, 토토 커뮤니티에서는 사설 토토사이트보다는 규제를 받는 공식 사이트를 이용할 것을 권장합니다.
토토 커뮤니티가 제공하는 가치
토토 커뮤니티는 단순히 정보를 나누는 공간이 아니라, 사용자들이 안전하게 베팅할 수 있도록 돕는 네트워크입니다. 예를 들어, 새로운 토토사이트가 등장했을 때 커뮤니티 멤버들은 해당 사이트의 운영 주체, 결제 시스템, 사용자 리뷰 등을 꼼꼼히 검토합니다. 이를 통해 먹튀 사고를 미리 방지하고, 신뢰할 수 있는 사이트만을 추천합니다. 또한, 문제가 발생했을 때는 보증 사이트를 통해 사용자들이 손실을 최소화할 수 있도록 돕습니다.
어떻게 신뢰할 수 있는 토토사이트를 찾을까?
토토 커뮤니티에서는 신뢰할 수 있는 토토사이트를 찾기 위해 몇 가지 중요한 기준을 제시합니다. 먼저, 사이트의 운영 주체가 명확한지 확인하는 것이 중요합니다. 정부나 공인된 기관에서 관리하는 사이트라면 신뢰할 수 있습니다. 또한, 다른 사용자들의 리뷰를 참고하여 사이트의 신뢰성을 판단할 수 있습니다. 긍정적인 평가가 많고, 문제가 거의 없는 사이트라면 안전하게 이용할 수 있습니다.
결제 시스템도 중요한 확인 요소 중 하나입니다. 신용카드, 전자지갑 등 다양한 결제 방법을 지원하고, SSL 암호화를 통해 금융 정보를 보호하는 사이트라면 더욱 신뢰할 수 있습니다. 마지막으로, 온라인 커뮤니티나 포럼에서 해당 사이트에 대한 평판을 확인하는 것도 좋은 방법입니다. 다른 사용자들이 어떻게 평가하는지, 문제가 없는지 꼼꼼히 살펴보는 것이 중요합니다.
토토 커뮤니티의 보증 사이트
토토 커뮤니티에서는 먹튀 사고를 예방하기 위해 보증 사이트를 추천합니다. 이러한 사이트는 사용자들의 개인정보와 금융 정보를 보호하며, 문제가 발생했을 때 빠르게 해결할 수 있는 시스템을 갖추고 있습니다. 보증 사이트를 이용하면 안전하게 베팅을 즐길 수 있으며, 만약 문제가 생기더라도 커뮤니티의 도움을 받아 해결할 수 있습니다.
마무리
토토사이트 커뮤니티는 스포츠 베팅을 즐기는 사람들에게 안전하고 신뢰할 수 있는 정보를 제공하는 중요한 공간입니다. 사설 토토사이트의 위험성을 인지하고, 신뢰할 수 있는 사이트를 선택하는 것이 무엇보다 중요합니다. 토토 커뮤니티의 정보를 참고하여 안전한 베팅 환경을 조성하고, 스포츠 베팅을 더욱 즐겁게 즐기시길 바랍니다. 항상 책임감 있게 베팅에 임하는 것도 잊지 마세요! -
How do I know if online meds are suitable for my pet's specific health condition qvar side effects.
-
Monitoreo de condicion
Dispositivos de balanceo: importante para el rendimiento estable y efectivo de las dispositivos.
En el campo de la avances moderna, donde la efectividad y la estabilidad del aparato son de suma relevancia, los sistemas de calibración juegan un papel crucial. Estos equipos especializados están desarrollados para balancear y regular partes rotativas, ya sea en equipamiento industrial, automóviles de desplazamiento o incluso en equipos de uso diario.
Para los profesionales en conservación de sistemas y los ingenieros, trabajar con sistemas de equilibrado es esencial para garantizar el rendimiento uniforme y confiable de cualquier aparato móvil. Gracias a estas herramientas avanzadas modernas, es posible minimizar sustancialmente las movimientos, el ruido y la tensión sobre los soportes, extendiendo la vida útil de piezas importantes.
Asimismo significativo es el papel que desempeñan los equipos de calibración en la asistencia al consumidor. El soporte técnico y el soporte constante aplicando estos equipos habilitan proporcionar asistencias de excelente nivel, incrementando la contento de los compradores.
Para los responsables de emprendimientos, la inversión en equipos de balanceo y dispositivos puede ser importante para aumentar la rendimiento y productividad de sus sistemas. Esto es principalmente relevante para los empresarios que dirigen reducidas y intermedias negocios, donde cada detalle vale.
Por otro lado, los aparatos de ajuste tienen una amplia utilización en el ámbito de la protección y el monitoreo de estándar. Posibilitan identificar posibles defectos, impidiendo intervenciones onerosas y perjuicios a los aparatos. Además, los resultados extraídos de estos dispositivos pueden utilizarse para perfeccionar procedimientos y aumentar la presencia en buscadores de exploración.
Las campos de aplicación de los sistemas de ajuste comprenden diversas ramas, desde la fabricación de vehículos de dos ruedas hasta el control ambiental. No importa si se trata de enormes fabricaciones manufactureras o pequeños locales caseros, los dispositivos de balanceo son indispensables para promover un operación productivo y sin riesgo de fallos. -
Aparatos de equilibrado: fundamental para el funcionamiento uniforme y eficiente de las dispositivos.
En el entorno de la ciencia moderna, donde la eficiencia y la seguridad del dispositivo son de gran relevancia, los equipos de equilibrado cumplen un función vital. Estos sistemas adaptados están diseñados para balancear y asegurar piezas giratorias, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, automóviles de movilidad o incluso en electrodomésticos caseros.
Para los especialistas en mantenimiento de aparatos y los especialistas, operar con dispositivos de balanceo es crucial para asegurar el desempeño suave y seguro de cualquier mecanismo rotativo. Gracias a estas alternativas avanzadas modernas, es posible reducir sustancialmente las sacudidas, el sonido y la tensión sobre los cojinetes, mejorando la duración de partes costosos.
Asimismo significativo es el rol que cumplen los aparatos de ajuste en la servicio al consumidor. El ayuda profesional y el soporte regular empleando estos equipos permiten ofrecer asistencias de óptima estándar, elevando la agrado de los consumidores.
Para los responsables de proyectos, la financiamiento en equipos de equilibrado y detectores puede ser esencial para optimizar la eficiencia y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es particularmente importante para los inversores que dirigen pequeñas y medianas organizaciones, donde cada punto es relevante.
Asimismo, los sistemas de balanceo tienen una extensa aplicación en el campo de la seguridad y el gestión de nivel. Permiten localizar posibles errores, previniendo intervenciones costosas y averías a los equipos. También, los resultados extraídos de estos aparatos pueden usarse para perfeccionar métodos y mejorar la reconocimiento en buscadores de investigación.
Las sectores de uso de los sistemas de calibración cubren variadas industrias, desde la fabricación de transporte personal hasta el supervisión ecológico. No influye si se considera de extensas producciones productivas o modestos locales de uso personal, los equipos de ajuste son necesarios para asegurar un desempeño efectivo y sin presencia de detenciones. -
[url=https://streamhub.world/ko/]streamhub[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.world/pl/]Zwieksz liczbe widzow na Twitchu i Kicku[/url] -
https://community.netgear.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/1114962 androgel generic
-
Dispositivos de ajuste: clave para el rendimiento uniforme y efectivo de las equipos.
En el ámbito de la tecnología avanzada, donde la eficiencia y la confiabilidad del dispositivo son de máxima trascendencia, los dispositivos de calibración cumplen un tarea fundamental. Estos aparatos dedicados están diseñados para calibrar y regular piezas dinámicas, ya sea en equipamiento productiva, vehículos de movilidad o incluso en dispositivos domésticos.
Para los técnicos en reparación de equipos y los profesionales, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es fundamental para promover el rendimiento fluido y seguro de cualquier mecanismo dinámico. Gracias a estas soluciones avanzadas avanzadas, es posible disminuir considerablemente las sacudidas, el sonido y la presión sobre los soportes, aumentando la vida útil de elementos importantes.
Asimismo significativo es el papel que juegan los dispositivos de equilibrado en la atención al usuario. El ayuda especializado y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos dispositivos habilitan dar prestaciones de gran nivel, incrementando la contento de los clientes.
Para los dueños de emprendimientos, la aporte en equipos de ajuste y medidores puede ser fundamental para incrementar la rendimiento y productividad de sus dispositivos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que gestionan modestas y intermedias emprendimientos, donde cada punto importa.
Además, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran aplicación en el ámbito de la protección y el gestión de estándar. Permiten encontrar probables errores, impidiendo intervenciones costosas y averías a los dispositivos. También, los indicadores extraídos de estos equipos pueden emplearse para mejorar procedimientos y aumentar la presencia en buscadores de investigación.
Las zonas de aplicación de los aparatos de ajuste cubren variadas industrias, desde la manufactura de vehículos de dos ruedas hasta el seguimiento de la naturaleza. No afecta si se habla de enormes producciones productivas o modestos talleres hogareños, los dispositivos de calibración son fundamentales para proteger un funcionamiento efectivo y libre de fallos. -
Dispositivos de equilibrado: fundamental para el desempeño uniforme y efectivo de las equipos.
En el mundo de la tecnología actual, donde la rendimiento y la fiabilidad del equipo son de máxima significancia, los dispositivos de balanceo desempeñan un papel esencial. Estos equipos especializados están desarrollados para balancear y asegurar partes móviles, ya sea en herramientas industrial, medios de transporte de movilidad o incluso en aparatos hogareños.
Para los técnicos en mantenimiento de dispositivos y los técnicos, utilizar con equipos de equilibrado es esencial para asegurar el funcionamiento uniforme y confiable de cualquier aparato móvil. Gracias a estas opciones tecnológicas sofisticadas, es posible disminuir significativamente las oscilaciones, el sonido y la presión sobre los sujeciones, mejorando la duración de partes valiosos.
Asimismo trascendental es el función que desempeñan los sistemas de ajuste en la soporte al usuario. El asistencia especializado y el mantenimiento regular empleando estos aparatos posibilitan ofrecer asistencias de gran calidad, mejorando la contento de los usuarios.
Para los responsables de emprendimientos, la financiamiento en unidades de balanceo y dispositivos puede ser clave para incrementar la productividad y desempeño de sus sistemas. Esto es especialmente relevante para los emprendedores que gestionan pequeñas y pequeñas negocios, donde cada punto importa.
Además, los dispositivos de equilibrado tienen una extensa uso en el área de la prevención y el control de estándar. Facilitan detectar eventuales defectos, reduciendo reparaciones onerosas y problemas a los equipos. También, los información extraídos de estos equipos pueden usarse para mejorar métodos y aumentar la exposición en buscadores de búsqueda.
Las zonas de utilización de los dispositivos de ajuste abarcan diversas ramas, desde la fabricación de vehículos de dos ruedas hasta el supervisión ambiental. No importa si se refiere de grandes manufacturas industriales o modestos espacios domésticos, los sistemas de equilibrado son fundamentales para promover un desempeño productivo y libre de fallos. -
Velocidad critica
Aparatos de calibración: esencial para el operación fluido y productivo de las maquinarias.
En el mundo de la tecnología contemporánea, donde la productividad y la seguridad del equipo son de alta importancia, los sistemas de ajuste cumplen un papel fundamental. Estos equipos dedicados están diseñados para ajustar y asegurar partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria productiva, vehículos de traslado o incluso en electrodomésticos de uso diario.
Para los especialistas en soporte de equipos y los técnicos, utilizar con aparatos de balanceo es fundamental para garantizar el operación estable y seguro de cualquier aparato móvil. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnológicas modernas, es posible minimizar considerablemente las sacudidas, el sonido y la tensión sobre los soportes, prolongando la vida útil de piezas valiosos.
También trascendental es el rol que juegan los aparatos de ajuste en la atención al comprador. El asistencia técnico y el conservación constante empleando estos sistemas facilitan proporcionar servicios de gran nivel, aumentando la bienestar de los clientes.
Para los responsables de emprendimientos, la inversión en equipos de balanceo y detectores puede ser importante para aumentar la eficiencia y rendimiento de sus dispositivos. Esto es especialmente importante para los emprendedores que dirigen reducidas y pequeñas emprendimientos, donde cada elemento cuenta.
Además, los sistemas de equilibrado tienen una gran aplicación en el área de la protección y el supervisión de calidad. Permiten encontrar posibles errores, reduciendo arreglos costosas y averías a los dispositivos. Además, los resultados generados de estos equipos pueden emplearse para optimizar sistemas y aumentar la presencia en sistemas de exploración.
Las áreas de aplicación de los dispositivos de ajuste abarcan múltiples áreas, desde la elaboración de transporte personal hasta el supervisión de la naturaleza. No afecta si se trata de importantes manufacturas productivas o pequeños locales caseros, los sistemas de ajuste son fundamentales para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin riesgo de fallos. -
토토사이트
토토사이트 커뮤니티: 안전한 베팅을 위한 길잡이
토토사이트 커뮤니티는 스포츠 베팅을 즐기는 사람들에게 단순한 정보 공유의 장을 넘어, 안전한 배팅 환경을 조성하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다. 이곳에서는 초보자부터 전문가까지 다양한 사람들이 모여 베팅 전략을 논의하고, 신뢰할 수 있는 토토사이트를 추천하며, 먹튀 사고를 예방하기 위한 정보를 공유합니다. 특히, 사설 토토사이트의 위험성을 알리고, 이를 피할 수 있는 방법을 제시함으로써 사용자들이 더 안전하게 베팅을 즐길 수 있도록 돕습니다.
사설 토토사이트의 숨겨진 위험
사설 토토사이트는 정부의 규제를 받지 않기 때문에 다양한 문제를 일으킬 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 공정하지 않은 배당률, 과장된 광고, 개인정보 유출 등이 대표적인 문제점입니다. 또한, 사설 토토사이트는 법적 문제로 인해 갑자기 사라지는 경우가 많아 사용자들이 금전적 손실을 입을 위험이 큽니다. 이런 이유로, 토토 커뮤니티에서는 사설 토토사이트보다는 규제를 받는 공식 사이트를 이용할 것을 권장합니다.
토토 커뮤니티가 제공하는 가치
토토 커뮤니티는 단순히 정보를 나누는 공간이 아니라, 사용자들이 안전하게 베팅할 수 있도록 돕는 네트워크입니다. 예를 들어, 새로운 토토사이트가 등장했을 때 커뮤니티 멤버들은 해당 사이트의 운영 주체, 결제 시스템, 사용자 리뷰 등을 꼼꼼히 검토합니다. 이를 통해 먹튀 사고를 미리 방지하고, 신뢰할 수 있는 사이트만을 추천합니다. 또한, 문제가 발생했을 때는 보증 사이트를 통해 사용자들이 손실을 최소화할 수 있도록 돕습니다.
어떻게 신뢰할 수 있는 토토사이트를 찾을까?
토토 커뮤니티에서는 신뢰할 수 있는 토토사이트를 찾기 위해 몇 가지 중요한 기준을 제시합니다. 먼저, 사이트의 운영 주체가 명확한지 확인하는 것이 중요합니다. 정부나 공인된 기관에서 관리하는 사이트라면 신뢰할 수 있습니다. 또한, 다른 사용자들의 리뷰를 참고하여 사이트의 신뢰성을 판단할 수 있습니다. 긍정적인 평가가 많고, 문제가 거의 없는 사이트라면 안전하게 이용할 수 있습니다.
결제 시스템도 중요한 확인 요소 중 하나입니다. 신용카드, 전자지갑 등 다양한 결제 방법을 지원하고, SSL 암호화를 통해 금융 정보를 보호하는 사이트라면 더욱 신뢰할 수 있습니다. 마지막으로, 온라인 커뮤니티나 포럼에서 해당 사이트에 대한 평판을 확인하는 것도 좋은 방법입니다. 다른 사용자들이 어떻게 평가하는지, 문제가 없는지 꼼꼼히 살펴보는 것이 중요합니다.
토토 커뮤니티의 보증 사이트
토토 커뮤니티에서는 먹튀 사고를 예방하기 위해 보증 사이트를 추천합니다. 이러한 사이트는 사용자들의 개인정보와 금융 정보를 보호하며, 문제가 발생했을 때 빠르게 해결할 수 있는 시스템을 갖추고 있습니다. 보증 사이트를 이용하면 안전하게 베팅을 즐길 수 있으며, 만약 문제가 생기더라도 커뮤니티의 도움을 받아 해결할 수 있습니다.
마무리
토토사이트 커뮤니티는 스포츠 베팅을 즐기는 사람들에게 안전하고 신뢰할 수 있는 정보를 제공하는 중요한 공간입니다. 사설 토토사이트의 위험성을 인지하고, 신뢰할 수 있는 사이트를 선택하는 것이 무엇보다 중요합니다. 토토 커뮤니티의 정보를 참고하여 안전한 베팅 환경을 조성하고, 스포츠 베팅을 더욱 즐겁게 즐기시길 바랍니다. 항상 책임감 있게 베팅에 임하는 것도 잊지 마세요! -
토토사이트
토토사이트 커뮤니티: 안전한 베팅을 위한 길잡이
토토사이트 커뮤니티는 스포츠 베팅을 즐기는 사람들에게 단순한 정보 공유의 장을 넘어, 안전한 배팅 환경을 조성하는 데 중요한 역할을 합니다. 이곳에서는 초보자부터 전문가까지 다양한 사람들이 모여 베팅 전략을 논의하고, 신뢰할 수 있는 토토사이트를 추천하며, 먹튀 사고를 예방하기 위한 정보를 공유합니다. 특히, 사설 토토사이트의 위험성을 알리고, 이를 피할 수 있는 방법을 제시함으로써 사용자들이 더 안전하게 베팅을 즐길 수 있도록 돕습니다.
사설 토토사이트의 숨겨진 위험
사설 토토사이트는 정부의 규제를 받지 않기 때문에 다양한 문제를 일으킬 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 공정하지 않은 배당률, 과장된 광고, 개인정보 유출 등이 대표적인 문제점입니다. 또한, 사설 토토사이트는 법적 문제로 인해 갑자기 사라지는 경우가 많아 사용자들이 금전적 손실을 입을 위험이 큽니다. 이런 이유로, 토토 커뮤니티에서는 사설 토토사이트보다는 규제를 받는 공식 사이트를 이용할 것을 권장합니다.
토토 커뮤니티가 제공하는 가치
토토 커뮤니티는 단순히 정보를 나누는 공간이 아니라, 사용자들이 안전하게 베팅할 수 있도록 돕는 네트워크입니다. 예를 들어, 새로운 토토사이트가 등장했을 때 커뮤니티 멤버들은 해당 사이트의 운영 주체, 결제 시스템, 사용자 리뷰 등을 꼼꼼히 검토합니다. 이를 통해 먹튀 사고를 미리 방지하고, 신뢰할 수 있는 사이트만을 추천합니다. 또한, 문제가 발생했을 때는 보증 사이트를 통해 사용자들이 손실을 최소화할 수 있도록 돕습니다.
어떻게 신뢰할 수 있는 토토사이트를 찾을까?
토토 커뮤니티에서는 신뢰할 수 있는 토토사이트를 찾기 위해 몇 가지 중요한 기준을 제시합니다. 먼저, 사이트의 운영 주체가 명확한지 확인하는 것이 중요합니다. 정부나 공인된 기관에서 관리하는 사이트라면 신뢰할 수 있습니다. 또한, 다른 사용자들의 리뷰를 참고하여 사이트의 신뢰성을 판단할 수 있습니다. 긍정적인 평가가 많고, 문제가 거의 없는 사이트라면 안전하게 이용할 수 있습니다.
결제 시스템도 중요한 확인 요소 중 하나입니다. 신용카드, 전자지갑 등 다양한 결제 방법을 지원하고, SSL 암호화를 통해 금융 정보를 보호하는 사이트라면 더욱 신뢰할 수 있습니다. 마지막으로, 온라인 커뮤니티나 포럼에서 해당 사이트에 대한 평판을 확인하는 것도 좋은 방법입니다. 다른 사용자들이 어떻게 평가하는지, 문제가 없는지 꼼꼼히 살펴보는 것이 중요합니다.
토토 커뮤니티의 보증 사이트
토토 커뮤니티에서는 먹튀 사고를 예방하기 위해 보증 사이트를 추천합니다. 이러한 사이트는 사용자들의 개인정보와 금융 정보를 보호하며, 문제가 발생했을 때 빠르게 해결할 수 있는 시스템을 갖추고 있습니다. 보증 사이트를 이용하면 안전하게 베팅을 즐길 수 있으며, 만약 문제가 생기더라도 커뮤니티의 도움을 받아 해결할 수 있습니다.
마무리
토토사이트 커뮤니티는 스포츠 베팅을 즐기는 사람들에게 안전하고 신뢰할 수 있는 정보를 제공하는 중요한 공간입니다. 사설 토토사이트의 위험성을 인지하고, 신뢰할 수 있는 사이트를 선택하는 것이 무엇보다 중요합니다. 토토 커뮤니티의 정보를 참고하여 안전한 베팅 환경을 조성하고, 스포츠 베팅을 더욱 즐겁게 즐기시길 바랍니다. 항상 책임감 있게 베팅에 임하는 것도 잊지 마세요! -
[url=https://streamhub.world/ar/]streamhub[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.world/fi/]Lisaa Twitchin ja Kickin katsojia[/url] -
戦国パチスロ花の慶次戦極めし傾奇者の宴~
x 星人
サウンドエフェクトが迫力満点で、プレイ中に盛り上がります。特にバトル時が楽しい。
P閃乱カグラ2
https://www.k8-casino.asia/?ArticleID=921241818.html
友人と一緒にプレイすることで、楽しさが倍増します。共に喜ぶ瞬間が嬉しい。
CR牙狼FINAL
[url=https://www.ja-securities.jp/?SitesID=923891818.html]ガイア 一宮
[/url]
アイムジャグラーEXAnniversaryEdition
甲賀忍法帖Ⅲ
バジリスク~甲賀忍法帖~絆2 天膳 BLACK EDITION
CRモンスターハンター4
[url=https://www.k8pachinko.biz/?SitesID=926027818.html]モナコ 宝塚
[/url]
夜蝶飛翔特
CR吉宗4 天昇飛躍の極
Pフィーバーダンベル何キロ持てる
翔馬
[url=https://www.stationslot.org/?ReviewID=923872818.html]刃牙パチンコ
[/url]
戦国パチスロ花の慶次戦極めし傾奇者の宴~
L バイオハザード ヴェンデッタ
バイオハザード6
ケロロ軍曹
https://www.k8pachinko.work/?GameID=921248818.html
パチンコの世界には、運だけではなく、戦略も求められます。自分の考えを試す楽しさがあります。
鉄拳2nd
https://www.jogadoresanonimos.org/?NewsID=927567818.html
近年では、スマートフォンアプリでも楽しめるようになりました。手軽に遊べるのが嬉しいです。 -
Ленинградская область известна сложной геологической характеристикой, что делает процедуру сверления скважин на воду специфическим в каждом регионе. Регион представляет собой вариативность почв и скрытых пластов, которые требуют качественный подбор при выборе места и слоя пробивки. Вода может протекать как на небольшой глубине, так и быть на нескольких глубоких метров, что формирует сложность бурения.
Основной деталью, влияющих на тип источника https://burenie-piter-98.ru/ , является состав грунтов и расположение водоносного слоя. В Ленинградской области чаще всего строят артезианские источники, которые поставляют доступ к чистой и непрерывной воде из глубинных слоев. Такие скважины ценятся за надежным сроком службы и высоким качеством воды, однако их пробивка нуждается существенных затрат и специального аппаратуры.
Методы создания в регионе предполагает использование новейших установок и технологий, которые могут работать с каменистыми породами и избегать возможные обрушения стенок скважины. Важно, что следует помнить об экологические требования и правила, так как вблизи нескольких населённых пунктов расположены охраняемые заповедные зоны и природоохранные территории, что диктует особый внимательный подход к буровым процессам.
Ресурсы воды из глубоких скважин в Ленинградской области характеризуется высоким качеством, так как она скрыта от поверхностных загрязнений и содержит правильный состав полезных веществ. Это формирует такие источники нужными для коттеджей и организаций, которые выбирают безопасность и безопасную чистоту систем водоснабжения. -
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg
ทดลองเล่น สล็อต PG คือสิ่งใด? เพราะเหตุใด จึงกลายเป็น เกมยอดฮิต?
เกมสล็อตบนอินเทอร์เน็ต จัดเป็นเกมที่ ได้รับความนิยม อย่างแพร่หลาย ในทุกช่วงเวลา และ นับเป็น หนึ่งในประเภท เกมที่ผู้เล่น รู้จักกันดี รวมทั้ง ชื่นชอบ อย่างมาก ในแวดวง เกมออนไลต์ อย่างไรก็ตาม ผู้ที่ยังคงเป็น ผู้เริ่มเล่น หรือ มีประสบการณ์น้อย การเล่นเกมออนไลน์ เพียงเล็กน้อย ในวันนี้ จะนำคุณ มาทำความเข้าใจ ทดสอบ สล็อตแมชชีน PG ซึ่ง เกมสล็อตเว็บตรง ที่คนนิยม อย่างแพร่หลาย ผ่าน คุณจะสามารถ ทำความเข้าใจ พร้อมทั้ง เริ่มเล่นเกม ได้อย่างรวดเร็ว พร้อมกับ เพลิดเพลิน กับ ความรู้สึก การเล่นเกม ที่ท้าทาย และยัง น่าทึ่ง
ทดสอบ สล็อตแมชชีน PG คืออะไร?
ทดลองเล่น สล็อต PG เป็นเกม เกมออนไลน์สล็อต ที่ถูกพัฒนา โดยบริษัท ผู้พัฒนา PG Soft ซึ่งถือเป็น หนึ่งในจำนวน ผู้พัฒนาเกม เกมสล็อตบนอินเทอร์เน็ต ยอดนิยม ในระดับโลก เกมสล็อตนี้ ได้รับแรงบันดาลใจ จาก เครื่องเกมสล็อต แบบเดิม อย่างไรก็ตาม เพิ่มเติม ความทันสมัยและความน่าสนใจ รวมทั้ง ความตื่นเต้น เข้าไป โดย เกมสล็อต จะมี 5 แถว รวมทั้ง 15 รูปแบบ รูปแบบการได้รางวัล ซึ่ง ผู้เล่น มีโอกาสที่จะ ได้รับรางวัล ได้อย่างมาก
สัญลักษณ์ในเกม ในเกมดังกล่าว เครื่องสล็อต PG นั้นมีอยู่ มีความหลากหลาย เช่น สัญลักษณ์เชอร์รี่, ตัวเลข 7, ไอคอนเพชร, และ สัญลักษณ์ อื่นๆอีกมากมาย ที่สัมพันธ์ กับแนวคิด ของเกม ซึ่ง แต่ละเกมดังกล่าว ประกอบด้วย รูปแบบของ รวมทั้ง รูปแบบการเล่นเกม ที่ต่างกัน ออกไปจาก เช่นได้แก่ ธีมสัตว์ป่า, ธีมเทพเจ้าโบราณ, ธีมอาหาร, หรืออาจจะ ธีมการผจญภัย เป็นต้นมา
ด้วยเหตุใด ทดสอบ เกมสล็อต PG ถึงเป็น เกมที่นิยม?
ความง่าย ในการเล่นเกม
ทดสอบ สล็อตแมชชีน PG คือเกม ที่เข้าใจง่าย ไม่ยุ่งยาก เหมาะกับ ผู้เริ่มต้น และ มือเก่า ผู้เล่นเกม เพียงเท่านั้น เลือกจำนวนเงิน จำนวนเดิมพัน กดปุ่มสปิน และ รอผล ผล ซึ่ง ระบบการเล่นเกม ที่เข้าใจง่าย ส่งผลให้ ผู้เล่นเกม สามารถที่จะได้ เพลิดเพลิน ได้โดยที่ ไม่ต้องกังวลใจ เกี่ยวกับเรื่อง กฎเกณฑ์ต่างๆ ที่ยุ่งเหยิง
รูปแบบการให้ การมอบรางวัล ที่หลายแบบ
เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ PG ประกอบด้วย เพย์ไลน์ ให้ชนะรางวัล มากถึงทั้งหมด 15 รูปแบบการชนะ ซึ่ง มากกว่าจำนวน สล็อตแมชชีนคลาสสิก ปกติ ทำให้ ผู้เล่นเกม มีโอกาสได้ รับรางวัล ได้หลายครั้ง นอกจากนี้ ยังมีให้เล่น ฟีเจอร์เพิ่มเติม เช่น การหมุนฟรี, ตัวคูณเงินรางวัล, พร้อมทั้ง โบนัส ที่เสริม ความเพลิดเพลิน ให้กับ การเล่น -
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg
ทดสอบ สล็อตแมชชีน PG คืออะไรกันแน่? ทำไม จึงกลายเป็น เกมที่คนชอบมาก?
เกมสล็อตดิจิทัล จัดเป็นเกมที่ เป็นที่ชื่นชอบ อย่างมาก ในทุกสมัย รวมทั้ง ถือเป็น หนึ่งในบรรดา เกมที่มีผู้คน คุ้นเคย พร้อมทั้ง สนุกสนาน ที่สุด ในโลกของ เกมออนไลน์ แต่ในกรณีของ ผู้ที่ยังเป็น ผู้ที่ยังไม่ชำนาญ หรือ มีประสบการณ์น้อย การเล่น ไม่มาก วันนี้ จะแนะนำคุณ มาทำความเข้าใจกับ เล่นฟรี เกมสล็อต PG ซึ่งเป็น เกมสล็อตโดยตรง ที่เป็นที่นิยม อย่างแพร่หลาย โดยที่ คุณจะสามารถที่จะ เรียนรู้ พร้อมทั้ง เริ่มการเล่น ได้โดยเร็ว รวมทั้ง มีความสุข กับ ประสบการณ์ใหม่ การเล่นเกม ที่น่าตื่นเต้น รวมทั้ง น่าตื่นตาตื่นใจ
ลองเล่น สล็อต PG คืออะไร?
ทดสอบ เกมสล็อต PG จัดเป็นเกม เกมสล็อตบนอินเทอร์เน็ต ที่พัฒนาขึ้น โดยบริษัท ผู้พัฒนา PG Soft ซึ่งถือเป็น หนึ่งในประเภท ผู้ผลิต เกมออนไลน์สล็อต ชั้นนำระดับโลก ของโลก เกมสล็อตนี้ ได้แนวคิด จากเครื่อง เครื่องสล็อต แบบเดิม แต่มีการ เพิ่มความ ความทันสมัยและความน่าสนใจ และยัง ความตื่นเต้น เข้าไปในเกม โดย เกมดังกล่าว มีอยู่ 5 รีล และ 15 เพย์ไลน์ รูปแบบการรับรางวัล ซึ่งส่งผลให้ ผู้เล่น มีโอกาส ชนะรางวัล ได้หลายครั้ง
สัญลักษณ์ ในเกมดังกล่าว สล็อต PG นั้น มีหลายรูปแบบ ตัวอย่างเช่น สัญลักษณ์เชอร์รี่, ไอคอน 7, รูปเพชร, รวมทั้ง สัญลักษณ์ อื่น ๆ ที่สัมพันธ์ กับธีม เกมดังกล่าว ซึ่ง ทุกเกม จะมี รูปแบบของ รวมทั้ง รูปแบบการเล่นสล็อต ที่ต่างออกไป ออกไปจาก ตัวอย่างเช่น ธีมสัตว์, ธีมเทพเจ้าในตำนาน, ธีมอาหาร, หรือก็คือ ธีมผจญภัย เป็นต้น
เพราะอะไร ทดสอบ สล็อตแมชชีน PG จึงเป็นที่นิยม เกมที่คนชอบมาก?
ความง่ายดาย ในการเล่นเกมออนไลน์
ลองเล่น เครื่องสล็อต PG เป็นเกม ที่ง่ายต่อการเข้าใจ ไม่สลับซับซ้อน เหมาะกับ ผู้เริ่มต้น และยัง ผู้ที่มีประสบการณ์ ผู้เล่นสล็อต แค่ เลือกจำนวนเงินที่ จำนวนเดิมพัน กดเล่น รวมทั้ง รอลุ้นผล ผลลัพธ์ ซึ่งส่งผลให้ ระบบการเล่นสล็อต ที่เข้าใจง่าย ทำให้คุณ ผู้เล่นเกม สามารถ สนุก ได้โดยที่ ไม่ต้องกังวลใจ ในเรื่อง กฎเกณฑ์ต่างๆ ที่ซับซ้อน
รูปแบบการแจก การมอบรางวัล ที่แตกต่าง
เกมออนไลน์สล็อต PG ประกอบด้วย เพย์ไลน์ ให้ลุ้นรางวัล มากถึงจำนวน 15 รูปแบบ ซึ่งทำให้ มากกว่าปกติ เกมสล็อตคลาสสิก ทั่วไปทั่วๆไป ทำให้ ผู้เล่นออนไลน์ มีโอกาสได้ ได้รับรางวัล ได้หลายรอบ นอกจากนั้น ยังมีอยู่ ฟีเจอร์เสริม ตัวอย่างเช่น ฟรีสปิน, ตัวคูณรางวัล, และยัง โบนัสเกม ที่เสริม ความเพลิดเพลิน ให้กับ การเล่น -
Can over-the-counter medicines interfere with thyroid medication 50 mg clomid.
-
equilibrado de ejes
Dispositivos de calibración: fundamental para el desempeño fluido y efectivo de las dispositivos.
En el entorno de la tecnología actual, donde la productividad y la seguridad del aparato son de máxima trascendencia, los equipos de balanceo cumplen un función esencial. Estos aparatos especializados están creados para balancear y regular elementos dinámicas, ya sea en herramientas de fábrica, automóviles de transporte o incluso en dispositivos caseros.
Para los expertos en reparación de dispositivos y los profesionales, trabajar con aparatos de balanceo es importante para proteger el operación uniforme y confiable de cualquier dispositivo móvil. Gracias a estas opciones avanzadas innovadoras, es posible reducir sustancialmente las vibraciones, el ruido y la esfuerzo sobre los soportes, extendiendo la tiempo de servicio de elementos costosos.
De igual manera importante es el papel que juegan los dispositivos de balanceo en la asistencia al cliente. El soporte profesional y el conservación continuo usando estos aparatos habilitan ofrecer prestaciones de excelente nivel, elevando la satisfacción de los usuarios.
Para los dueños de emprendimientos, la contribución en unidades de calibración y detectores puede ser importante para aumentar la rendimiento y desempeño de sus sistemas. Esto es sobre todo significativo para los dueños de negocios que gestionan pequeñas y medianas organizaciones, donde cada aspecto vale.
Por otro lado, los dispositivos de equilibrado tienen una amplia aplicación en el ámbito de la seguridad y el monitoreo de calidad. Facilitan identificar eventuales problemas, reduciendo reparaciones elevadas y averías a los equipos. Incluso, los datos obtenidos de estos aparatos pueden utilizarse para optimizar sistemas y incrementar la presencia en sistemas de investigación.
Las campos de uso de los sistemas de calibración incluyen numerosas industrias, desde la manufactura de transporte personal hasta el control ecológico. No interesa si se refiere de importantes manufacturas manufactureras o pequeños talleres hogareños, los aparatos de ajuste son esenciales para garantizar un funcionamiento óptimo y sin presencia de fallos. -
ลองเล่น สล็อตแมชชีน PG คืออะไร? เพราะเหตุใด จึงเป็นที่นิยม เกมที่คนชอบมาก?
เกมสล็อตบนอินเทอร์เน็ต จัดเป็นเกมที่ เป็นที่นิยม อย่างสูง ในทุกช่วงเวลา รวมทั้ง นับเป็น หนึ่งในจำนวน เกมที่คนทั่วไป รู้จักกันดี และ ชื่นชอบ มากที่สุด ในสาขา เกมออนไลต์ แต่สำหรับ ผู้ที่ยังคงเป็น ผู้เริ่มต้น หรือ มีประสบการณ์ การเล่นเกม ไม่มาก วันนี้เราจะ จะแนะนำคุณ มาทำความเข้าใจกับ ทดสอบ สล็อตแมชชีน PG ที่ เกมสล็อตโดยตรง ที่คนนิยม อย่างแพร่หลาย ผ่าน คุณจะได้ ศึกษาหรือเรียนรู้ รวมทั้ง เริ่มเล่นเกม ได้เร็ว พร้อมทั้ง เพลิดเพลิน ไปกับ ประสบการณ์การเล่น การเล่นสล็อต ที่ตื่นเต้น พร้อมทั้ง น่าตื่นตาตื่นใจ
ทดสอบ สล็อต PG คืออะไรกันแน่?
ทดลองเล่น สล็อต PG ถือเป็นเกม เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ที่สร้างขึ้น จากบริษัท บริษัท PG Soft ซึ่ง หนึ่งใน ผู้ผลิต เกมสล็อตบนอินเทอร์เน็ต ชั้นนำของโลก ในระดับโลก เกมดังกล่าว ได้แนวคิด จากเครื่อง เครื่องเล่นสล็อต แบบคลาสสิก แต่มีการ เพิ่มเติม ความใหม่ และยัง ความสนุก เข้าไป ผ่าน เกมสล็อต จะมี 5 รีลแนวตั้ง และยัง 15 รูปแบบการชนะ รูปแบบการชนะ ที่ ผู้เล่น มีโอกาสที่จะ รับรางวัล ได้มากมาย
สัญลักษณ์ในเกม ในเกมดังกล่าว เกมสล็อต PG นั้นประกอบด้วย มีความหลากหลาย เช่นเช่น รูปเชอร์รี่, ตัวเลข 7, สัญลักษณ์เพชร, พร้อมทั้ง สัญลักษณ์ในเกม อื่นๆ ที่สัมพันธ์ กับแนวคิด เกม ซึ่งทุกๆ แต่ละเกม จะมี แนวคิด รวมทั้ง รูปแบบเกม ที่แตกต่างกัน ออกไปจากเดิม เช่นเช่น ธีมป่า, ธีมเทพเจ้าโบราณ, ธีมอาหารการกิน, หรืออาจจะ ธีมการสำรวจ เป็นต้นไป
เพราะอะไร ทดลองเล่น สล็อต PG ถึงเป็น เกมที่คนชอบมาก?
ความง่าย ในการเล่นเกมออนไลน์
ทดสอบ สล็อตแมชชีน PG เป็นเกม ที่เข้าใจง่าย ไม่ซับซ้อน เหมาะสมสำหรับ ผู้ที่ยังไม่ชำนาญ และยัง มือเก่า ผู้เล่นเกม เพียงเท่านั้น เลือก จำนวนเงินที่ต้องการ กดเล่น รวมทั้ง รอลุ้น ผล ซึ่ง ระบบเกม ที่ง่าย ส่งผลให้ ผู้เล่นเกม สามารถที่จะ เพลิดเพลิน ได้โดยไม่จำเป็นต้อง ไม่ต้องวิตก เรื่อง กฎ ที่ยาก
รูปแบบ การแจกเงินรางวัล ที่หลายรูปแบบ
เกมสล็อตบนอินเทอร์เน็ต PG มีอยู่ รูปแบบ ให้ลุ้นรางวัล มากถึงจำนวน 15 รูปแบบการชนะ ซึ่งส่งผลให้ มากกว่า เกมสล็อตคลาสสิก ทั่วไปๆ ทำให้ ผู้เล่น มีโอกาส ได้รับรางวัล ได้หลายครั้ง อีกทั้ง ยังมีอยู่ ฟีเจอร์เสริม เช่นเช่น การเล่นฟรี, ตัวคูณเงินรางวัล, รวมทั้ง รางวัลโบนัส ที่เพิ่ม ความเพลิดเพลิน ให้แก่ การเล่นเกมออนไลน์ -
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg
ลองเล่น สล็อตแมชชีน PG คืออะไร? เพราะอะไร ถึงเป็น เกมที่นิยม?
เกมสล็อตดิจิทัล คือเกมที่ ได้รับความนิยม อย่างแพร่หลาย ตลอดทุกยุคทุกสมัย พร้อมทั้ง จัดเป็น หนึ่งใน เกมที่ผู้เล่น รู้จัก รวมทั้ง ชอบ มากที่สุด ในสาขา เกมออนไลต์ แต่ ผู้ที่ยังเป็นอยู่ ผู้เริ่มเล่น หรือ มีประสบการณ์การเล่น การเล่นเกม น้อยมาก วันนี้ จะพาคุณ มาทำความรู้จัก ลองเล่น สล็อต PG ที่ เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ที่คนนิยม อย่างสูง โดย คุณจะสามารถ เรียนรู้ และยัง เริ่มเล่น ได้โดยเร็ว รวมทั้ง สนุก ร่วมกับ ประสบการณ์การเล่น การเล่นเกมออนไลน์ ที่ท้าทาย และ น่าตื่นเต้น
ทดลองเล่น เกมสล็อต PG คืออะไร?
เล่นฟรี เครื่องสล็อต PG จัดเป็นเกม เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ที่ออกแบบมา โดย บริษัท PG Soft ซึ่งถือเป็น หนึ่งในบรรดา ผู้พัฒนา เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ชั้นนำของโลก ในโลก เกมดังกล่าวนี้ ได้ไอเดีย มาจาก เครื่องเล่นสล็อต แบบเก่า อย่างไรก็ตาม เพิ่มเติม ความทันสมัยและความสนุก รวมทั้ง ความเพลิดเพลิน เข้าไปในรูปแบบ โดยที่ เกมสล็อต มี 5 รีล รวมทั้ง 15 รูปแบบการชนะ รูปแบบการรับรางวัล ที่ ผู้เล่นเกม มีโอกาสได้ ลุ้นรับรางวัล ได้อย่างมาก
สัญลักษณ์ในเกม ในเกม สล็อต PG นั้นมี มีความหลากหลาย ตัวอย่างเช่น สัญลักษณ์เชอร์รี่, เลข 7, รูปเพชร, พร้อมทั้ง สัญลักษณ์ อื่นๆอีกมากมาย ที่เกี่ยวข้อง กับแนวคิด ของเกม ซึ่งทุกๆ ทุกเกม ประกอบด้วย แนวคิด รวมทั้ง รูปแบบการเล่นสล็อต ที่แตกต่าง ออกไปจาก เช่นเช่น ธีมธรรมชาติ, ธีมเทพเจ้า, ธีมอาหาร, หรือก็คือ ธีมการสำรวจ เป็นต้นมา
เพราะอะไร เล่นฟรี เกมสล็อต PG จึงเป็น เกมยอดฮิต?
ความง่ายดาย ในการเล่นสล็อต
ทดลองเล่น เกมสล็อต PG เป็นเกม ที่เรียนรู้ได้ง่าย ไม่ยาก เหมาะสำหรับทั้ง ทั้งมือใหม่ พร้อมทั้ง ผู้เล่นเก่า ผู้เล่นเกม แค่ เลือก จำนวนเดิมพัน กดปุ่มสปิน พร้อมทั้ง รอผล ผลลัพธ์ของเกม ซึ่งทำให้ ระบบการเล่น ที่ง่าย ทำให้ ผู้เล่น สามารถที่จะ เพลิดเพลิน ได้โดย ไม่ต้องเครียด เรื่อง กฎเกณฑ์ต่างๆ ที่ยุ่งเหยิง
รูปแบบการแจก การแจกรางวัล ที่หลายรูปแบบ
เกมออนไลน์สล็อต PG ประกอบด้วย เพย์ไลน์ ให้ชนะรางวัล มากถึง 15 รูปแบบ ที่ มากกว่าจำนวน สล็อตคลาสสิก ทั่วไปๆ ทำให้คุณ ผู้เล่นออนไลน์ มีโอกาสในการ ลุ้นรับรางวัล ได้บ่อยๆ อีกทั้ง ยังมี ฟีเจอร์เสริม เช่นเช่น การเล่นฟรี, ตัวคูณ, และยัง โบนัสพิเศษ ที่เพิ่มเติม ความสนุก ให้กับคุณ การเล่นสล็อต -
[url=https://streamhub.world/buy-twitch-viewers/]Buy Twitch Viewers[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.world/fi/]streamhub[/url] -
https://excommunity.becomeanex.org/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/114694 buy qvar inhaler
-
equilibrador
Sistemas de calibración: fundamental para el desempeño fluido y productivo de las equipos.
En el mundo de la tecnología moderna, donde la eficiencia y la fiabilidad del aparato son de suma importancia, los equipos de balanceo cumplen un papel esencial. Estos equipos específicos están creados para balancear y estabilizar piezas dinámicas, ya sea en equipamiento industrial, vehículos de traslado o incluso en electrodomésticos hogareños.
Para los expertos en soporte de sistemas y los profesionales, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es esencial para promover el funcionamiento estable y confiable de cualquier aparato giratorio. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnológicas modernas, es posible limitar significativamente las sacudidas, el estruendo y la esfuerzo sobre los soportes, mejorando la vida útil de partes importantes.
También importante es el función que tienen los aparatos de calibración en la asistencia al cliente. El apoyo profesional y el conservación regular aplicando estos dispositivos permiten ofrecer asistencias de gran estándar, elevando la agrado de los consumidores.
Para los responsables de emprendimientos, la contribución en estaciones de balanceo y dispositivos puede ser fundamental para optimizar la rendimiento y productividad de sus aparatos. Esto es especialmente trascendental para los dueños de negocios que manejan modestas y pequeñas negocios, donde cada aspecto vale.
Asimismo, los sistemas de calibración tienen una amplia aplicación en el ámbito de la fiabilidad y el monitoreo de excelencia. Posibilitan detectar probables errores, reduciendo intervenciones costosas y averías a los dispositivos. Más aún, los resultados obtenidos de estos equipos pueden aplicarse para optimizar procesos y aumentar la visibilidad en sistemas de consulta.
Las campos de uso de los dispositivos de ajuste comprenden numerosas sectores, desde la manufactura de transporte personal hasta el supervisión de la naturaleza. No importa si se trata de importantes manufacturas productivas o limitados espacios caseros, los sistemas de equilibrado son fundamentales para garantizar un funcionamiento efectivo y sin fallos. -
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต
ลองเล่น เกมสล็อต PG คืออะไรกันแน่? ทำไม ถึงเป็น เกมยอดฮิต?
เกมออนไลน์สล็อต เป็นเกมที่ เป็นที่ชื่นชอบ อย่างมาก ในทุกยุคทุกสมัย พร้อมทั้ง ถือเป็น หนึ่งในบรรดา เกมที่ผู้เล่น รู้จักกันดี พร้อมทั้ง หลงใหล มากที่สุด ในแวดวง เกมดิจิทัล แต่ในกรณีของ ผู้ที่เพิ่งเป็น ผู้เริ่มเล่น หรือก็คือ มีประสบการณ์การเล่น การเล่นสล็อต ไม่มาก วันนี้เราจะ จะแนะนำคุณ มาทำความรู้จักกับ ทดสอบ เครื่องสล็อต PG ซึ่งถือเป็น เกมสล็อตเว็บตรง ที่ได้รับความชื่นชอบ อย่างมาก โดยที่ คุณจะได้ ทำความเข้าใจ พร้อมทั้ง เริ่มต้นเล่น ได้อย่างรวดเร็ว พร้อมกับ สนุกสนาน พร้อมกับ ประสบการณ์การเล่น การเล่น ที่ท้าทาย รวมทั้ง น่าตื่นเต้น
เล่นฟรี สล็อตแมชชีน PG คืออะไร?
ทดลองเล่น เครื่องสล็อต PG จัดเป็นเกม เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ที่ออกแบบมา โดย บริษัทผู้พัฒนา PG Soft ซึ่งเป็น หนึ่งใน ผู้สร้าง เกมสล็อต ยอดนิยม ของโลก เกมดังกล่าวนี้ ได้ไอเดีย จากเครื่อง เครื่องเล่นสล็อต แบบเก่า แต่ได้ เพิ่ม ความใหม่ รวมทั้ง ความสนุกสนาน เข้าไปในระบบ โดยที่ เกมนี้ ประกอบด้วย 5 รีล และ 15 แบบ รูปแบบการรับรางวัล ที่ ผู้เล่นเกม มีโอกาสที่จะ ได้รับรางวัล ได้อย่างมาก
สัญลักษณ์ในเกม ในเกมนี้ เครื่องสล็อต PG นั้นมี มีหลายรูปแบบ เช่น ผลเชอร์รี่, ตัวเลข 7, สัญลักษณ์เพชร, พร้อมทั้ง ไอคอน อื่นๆอีก ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับ กับรูปแบบของ เกม ซึ่งทุกๆ ทุกเกม มีอยู่ ธีม และ รูปแบบการเล่นเกม ที่ต่างกัน ไป ตัวอย่างเช่น ธีมป่า, ธีมเทพเจ้า, ธีมอาหารอร่อย, หรือแม้แต่ ธีมการผจญภัย เป็นต้นไป
เพราะเหตุใด ทดสอบ เกมสล็อต PG ถึงเป็น เกมยอดฮิต?
ความง่าย ในการเล่นเกมออนไลน์
ทดลองเล่น เกมสล็อต PG เป็นเกม ที่ง่ายต่อการเข้าใจ ไม่ยุ่งยาก เหมาะสำหรับ ผู้ที่เพิ่งเริ่ม พร้อมทั้ง ผู้เล่นเก่า ผู้เล่นเกม เพียงเท่านั้น เลือกจำนวน จำนวนเงินเดิมพัน กดสปิน รวมทั้ง รอ ผลลัพธ์ของเกม ซึ่ง ระบบเกม ที่เข้าใจง่าย ทำให้ ผู้เล่น สามารถได้ เพลิดเพลิน ได้โดย ไม่ต้องกังวล เกี่ยวกับ กฎ ที่ยุ่งยาก
รูปแบบ การให้รางวัล ที่หลายรูปแบบ
เกมออนไลน์สล็อต PG มีให้เลือก เพย์ไลน์ ให้ชนะรางวัล มากถึงสูงสุด 15 แบบ ที่ มากกว่า สล็อตคลาสสิก ปกติ ทำให้คุณ ผู้เล่นออนไลน์ มีโอกาสที่จะ ชนะรางวัล ได้หลายรอบ นอกจากนี้ยัง ยังมี ฟีเจอร์เพิ่มเติม เช่น การเล่นฟรี, ตัวคูณเงิน, และยัง โบนัสพิเศษ ที่เพิ่ม ความสนุก ให้กับคุณ การเล่นเกมออนไลน์ -
ทดลองเล่น เครื่องสล็อต PG หมายถึงอะไร? ด้วยเหตุใด จึงกลายเป็น เกมยอดฮิต?
เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ จัดเป็นเกมที่ เป็นที่ชื่นชอบ อย่างแพร่หลาย ตลอดทุกยุคทุกสมัย พร้อมทั้ง จัดเป็น หนึ่งใน เกมที่มีผู้คน รู้จัก พร้อมทั้ง สนุกสนาน อย่างมาก ในโลกของ เกมบนอินเทอร์เน็ต แต่ในกรณีของ ผู้ที่ยังเป็น มือใหม่ หรือก็คือ มีประสบการณ์น้อย การเล่น ไม่มาก วันนี้พวกเรา จะชวนคุณ มาทำความรู้จัก ทดสอบ เกมสล็อต PG ที่ เกมสล็อตเว็บตรง ที่คนนิยม อย่างมาก โดย คุณจะสามารถที่จะ เรียนรู้และเข้าใจ และ เริ่มเล่น ได้โดยเร็ว และยัง เพลิดเพลิน ไปกับ ความรู้สึก การเล่น ที่สนุก รวมทั้ง น่าทึ่ง
ทดสอบ เครื่องสล็อต PG คือสิ่งใด?
ทดสอบ เกมสล็อต PG ถือเป็นเกม เกมสล็อตบนอินเทอร์เน็ต ที่สร้างขึ้น โดยบริษัท บริษัทพัฒนาเกม PG Soft ซึ่งถือเป็น หนึ่งใน ผู้สร้าง เกมออนไลน์สล็อต ชั้นนำ ในระดับโลก เกมสล็อตนี้ ได้ไอเดีย จากเกม เครื่องเกมสล็อต แบบเดิม แต่ เพิ่ม ความทันสมัยและความสนุก พร้อมทั้ง ความสนุก เข้าไปในรูปแบบ โดย เกมสล็อต ประกอบด้วย 5 รีล พร้อมทั้ง 15 แบบ รูปแบบการชนะรางวัล ซึ่งทำให้ ผู้เล่นสล็อต มีโอกาสที่จะ ชนะรางวัล ได้อย่างมาก
สัญลักษณ์ ในเกมดังกล่าว สล็อต PG นั้นประกอบด้วย มีความหลากหลาย เช่น เชอร์รี่, เลข 7, รูปเพชร, พร้อมทั้ง ไอคอน อื่น ๆ ที่สัมพันธ์ กับรูปแบบ ของเกม ซึ่งทุกๆ ทุกเกม มี ธีม พร้อมทั้ง รูปแบบการเล่นสล็อต ที่ต่างกัน ออกไปจากเดิม เช่นได้แก่ ธีมสัตว์, ธีมเทพ, ธีมอาหาร, หรือ ธีมการเดินทาง เป็นต้นมา
เพราะอะไร ทดสอบ เกมสล็อต PG จึงเป็นที่นิยม เกมที่คนชอบมาก?
ความง่าย ในการเล่นเกมออนไลน์
เล่นฟรี เครื่องสล็อต PG เป็นเกม ที่เข้าใจง่าย ไม่ซับซ้อน เหมาะกับ ผู้ที่ยังไม่ชำนาญ พร้อมทั้ง มือเก่า ผู้เล่น เพียงเท่านั้น เลือกจำนวนเงิน เงินเดิมพัน กดเล่น และยัง รอ ผลลัพธ์ที่ได้ ซึ่ง ระบบการเล่น ที่ไม่ซับซ้อน ทำให้คุณ ผู้เล่น สามารถที่จะ เพลิดเพลิน ได้โดยที่ ไม่ต้องกังวลใจ เกี่ยวกับเรื่อง กฎ ที่ยาก
รูปแบบการแจก การแจกเงินรางวัล ที่หลายรูปแบบ
เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ PG มีอยู่ รูปแบบ ให้รับรางวัล มากถึงสูงสุด 15 รูปแบบ ซึ่งทำให้ มากกว่าทั่วไป เครื่องสล็อตคลาสสิก ทั่วไปๆ ทำให้ ผู้เล่นออนไลน์ มีโอกาสในการ ชนะรางวัล ได้บ่อยๆ อีกทั้ง ยังมี ฟีเจอร์พิเศษ เช่นเช่น การหมุนฟรีสปิน, ตัวคูณเงิน, และยัง โบนัส ที่เพิ่มเติม ความน่าสนใจ ให้กับ การเล่นสล็อต -
e スマパチ シン・エヴァンゲリオン Type カヲル
裏 まとめ
ボーナスゲームの演出が豪華で、楽しみが倍増します。特に大当たり時は圧巻。
デビル メイ クライ クロス
https://www.k8-casino.org/?WatchID=919542818.html
簡単なルールで、初心者でもすぐに楽しめるのが嬉しいです。
鬼浜爆走紅蓮隊友情挽歌編
[url=https://k88214.com/?GameID=927776818.html]アラジン a
[/url]
Pビッグドリーム2激神
CR 真・北斗無双
CR新世紀エヴァンゲリオン~使徒、再び~SFW
ハイビスカスSE(スペシャルアワードライト)
[url=https://www.8casino8.com/?ArticleID=919291818.html]地中海2
[/url]
P大工の源さん超韋駄天 Ver.318
新鬼武者 再臨
めんそーれ
CRフィーバー戦姫絶唱シンフォギア Ver.199 (1:1)
[url=https://www.k8-casino.jp/?NewsID=923919818.html]ガイア 社長
[/url]
吉宗 2003
GI優駿俱樂部
パチスロ ロストプラネット2
アイムジャグラーEXAnniversaryEdition
https://www.k8-casino.biz/?NewsID=924321818.html
ボーナスゲームの演出が豪華で、楽しみが倍増します。目が離せません。
喧嘩祭
https://www.sawasdeeslot.com/?SitesID=919439818.html
パチンコの仲間との交流が楽しく、共通の趣味で楽しめるのが良いです。友達が増えます。 -
Are there online meds for skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis ivercid 12.
-
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต
เล่นฟรี สล็อต PG หมายถึงอะไร? ทำไม จึงเป็น เกมที่นิยม?
เกมออนไลน์สล็อต เป็นเกมที่ เป็นที่รู้จัก มาก ในทุกยุคทุกสมัย รวมทั้ง เป็น หนึ่งในประเภท เกมที่ผู้คน รู้จักกันดี พร้อมทั้ง ชอบ มากที่สุด ในวงการ เกมออนไลน์ แต่ในกรณีของ ผู้ที่เพิ่งเป็น ผู้เริ่มต้น หรือ มีประสบการณ์ การเล่นเกมออนไลน์ น้อย วันนี้ จะแนะนำคุณ มาทำความเข้าใจกับ ลองเล่น เกมสล็อต PG ซึ่งเป็น เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ที่เป็นที่นิยม อย่างมาก โดย คุณจะสามารถที่จะ ทำความเข้าใจ พร้อมทั้ง เริ่มการเล่น ได้อย่างรวดเร็ว รวมทั้ง สนุก ไปกับ ประสบการณ์ การเล่น ที่น่าตื่นเต้น และ น่าสนใจ
ทดสอบ สล็อตแมชชีน PG คืออะไร?
ทดลองเล่น สล็อตแมชชีน PG เป็นเกม เกมออนไลน์สล็อต ที่สร้างขึ้น โดยบริษัท บริษัท PG Soft ซึ่งเป็น หนึ่งใน ผู้พัฒนาเกม เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ชั้นนำของโลก ของโลก เกมสล็อตนี้ ได้รับแรงบันดาลใจ จากเกม เครื่องสล็อต แบบคลาสสิก แต่มีการ เพิ่มเข้าไป ความทันสมัยและความน่าสนใจ และ ความสนุกสนาน เข้าไปในระบบ โดยที่ เกมนี้ ประกอบด้วย 5 แถวแนวตั้ง รวมทั้ง 15 เพย์ไลน์ รูปแบบการชนะรางวัล ซึ่ง ผู้เล่น มีโอกาสที่จะ ชนะรางวัล ได้มากมาย
รูปสัญลักษณ์ ในเกมดังกล่าว เครื่องสล็อต PG นั้นประกอบด้วย มีหลายชนิด เช่น เชอร์รี่, ไอคอน 7, รูปเพชร, และยัง รูปสัญลักษณ์ อื่นๆอีกมากมาย ที่เชื่อมโยง กับรูปแบบของ เกมดังกล่าว ซึ่งทุกๆ แต่ละเกมดังกล่าว จะมี รูปแบบของ พร้อมทั้ง รูปแบบการเล่นเกม ที่ต่างกัน ออกไปจากเดิม เช่นได้แก่ ธีมธรรมชาติ, ธีมเทพเจ้า, ธีมการกิน, หรือ ธีมผจญภัย เป็นต้นไป
เพราะอะไร ทดสอบ สล็อต PG จึงกลายเป็น เกมที่คนชอบมาก?
ความสะดวก ในการเล่นเกม
ลองเล่น เกมสล็อต PG คือเกม ที่ง่ายต่อการเข้าใจ ไม่ยุ่งยาก เหมาะสมสำหรับ ผู้ที่ยังไม่ชำนาญ และยัง ผู้ที่มีประสบการณ์ ผู้เล่นออนไลน์ เพียง เลือกจำนวนเงินที่ จำนวนเดิมพัน กดเล่น พร้อมทั้ง รอ ผลลัพธ์ของเกม ซึ่งส่งผลให้ ระบบเกม ที่เข้าใจง่าย ส่งผลให้ ผู้เล่นสล็อต สามารถที่จะได้ เพลิดเพลินไปกับ ได้โดย ไม่ต้องเครียด เกี่ยวกับ กฎ ที่ยาก
รูปแบบการให้ การแจกรางวัล ที่หลายแบบ
เกมสล็อตบนอินเทอร์เน็ต PG มี รูปแบบการชนะ ให้ได้รางวัล มากถึงจำนวน 15 แบบ ซึ่งส่งผลให้ มากกว่าปกติ เกมสล็อตคลาสสิก ทั่วไปทั่วๆไป ทำให้ผู้เล่น ผู้เล่นเกม มีโอกาสที่จะ ชนะรางวัล ได้บ่อยๆ นอกจากนี้ ยังมี ฟีเจอร์พิเศษ ตัวอย่างเช่น การเล่นฟรี, ตัวคูณเงินรางวัล, พร้อมทั้ง รางวัลโบนัส ที่เพิ่ม ความน่าสนใจ ให้กับ การเล่นเกมออนไลน์ -
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต
เล่นฟรี เกมสล็อต PG คือสิ่งใด? เพราะเหตุใด ถึงเป็น เกมยอดฮิต?
เกมออนไลน์สล็อต คือเกมที่ เป็นที่ชื่นชอบ อย่างแพร่หลาย ตลอดทุกยุคทุกสมัย พร้อมทั้ง ถือเป็น หนึ่งในบรรดา เกมที่คนทั่วไป รู้จักกันดี พร้อมทั้ง ชอบ อย่างมาก ในสาขา เกมออนไลต์ อย่างไรก็ตาม ผู้ที่ยังเป็น ผู้เริ่มเล่น หรือแม้แต่ มีประสบการณ์การเล่น การเล่นเกม เพียงเล็กน้อย วันนี้เราจะ จะชวนคุณ มาทำความเข้าใจ ลองเล่น สล็อต PG ที่ เกมสล็อตโดยตรง ที่เป็นที่นิยม อย่างสูง ด้วย คุณจะสามารถ ศึกษาหรือเรียนรู้ รวมทั้ง เริ่มเล่นเกม ได้โดยเร็ว พร้อมกับ สนุกสนาน ร่วมกับ ประสบการณ์ การเล่นเกมออนไลน์ ที่สนุก พร้อมทั้ง น่าตื่นตาตื่นใจ
เล่นฟรี เครื่องสล็อต PG คืออะไร?
ทดลองเล่น เครื่องสล็อต PG ถือเป็นเกม สล็อตออนไลน์ ที่ถูกพัฒนา จาก บริษัทพัฒนาเกม PG Soft ที่ หนึ่งในจำนวน ผู้พัฒนา เกมสล็อตบนอินเทอร์เน็ต ยอดนิยม ทั่วโลก เกมสล็อตนี้ ได้ไอเดีย จากเกม เครื่องสล็อต แบบคลาสสิก อย่างไรก็ตาม เพิ่มเข้าไป ความทันสมัย และยัง ความตื่นเต้น เข้าไปในระบบ ผ่าน เกมสล็อต จะมี 5 แถวแนวตั้ง พร้อมทั้ง 15 แบบ รูปแบบการรับรางวัล ซึ่ง ผู้เล่นออนไลน์ มีโอกาส รับรางวัล ได้หลายรูปแบบ
สัญลักษณ์ในเกม ในเกม สล็อตแมชชีน PG นั้นประกอบด้วย มีหลายแบบ เช่นเช่น รูปเชอร์รี่, ไอคอน 7, ไอคอนเพชร, รวมทั้ง ไอคอน อื่นๆอีกมากมาย ที่เชื่อมโยง กับรูปแบบของ เกม ซึ่ง แต่ละเกม จะมี รูปแบบของ รวมทั้ง รูปแบบการเล่นสล็อต ที่แตกต่างกัน ออกไปจาก เช่นได้แก่ ธีมป่า, ธีมเทพ, ธีมการกิน, หรือ ธีมผจญภัย เป็นต้น
เพราะเหตุใด ทดสอบ เกมสล็อต PG จึงเป็น เกมที่ได้รับความนิยม?
ความง่าย ในการเล่นเกม
ทดสอบ สล็อตแมชชีน PG เป็นเกม ที่เข้าใจง่าย ไม่ยุ่งยาก เหมาะสำหรับทั้ง ผู้ที่ยังไม่ชำนาญ และยัง ผู้เล่นเก่า ผู้เล่น แค่ เลือกจำนวน เงินเดิมพัน กดเริ่ม รวมทั้ง รอลุ้นผล ผลลัพธ์ของเกม ซึ่ง ระบบเกม ที่ไม่ซับซ้อน ส่งผลให้ ผู้เล่นออนไลน์ สามารถ สนุกสนาน ได้โดยไม่จำเป็นต้อง ไม่ต้องกังวลใจ เกี่ยวกับเรื่อง กฎระเบียบ ที่ซับซ้อน
รูปแบบ การให้รางวัล ที่หลายแบบ
เกมออนไลน์สล็อต PG มีให้เลือก เพย์ไลน์ ให้รับรางวัล มากถึงทั้งหมด 15 รูปแบบ ที่ มากกว่าทั่วไป สล็อตคลาสสิก ทั่วไปทั่วๆไป ส่งผลให้ ผู้เล่นสล็อต มีโอกาสได้ รับรางวัล ได้บ่อยๆ นอกจากนั้น ยังมี ฟีเจอร์ที่น่าสนใจ ตัวอย่างเช่น ฟรีสปิน, ตัวคูณเงิน, พร้อมทั้ง รางวัลโบนัส ที่เพิ่ม ความตื่นเต้น ให้กับผู้เล่น การเล่นสล็อต -
[url=https://streamhub.world/buy-kick-viewers/]Buy Kick Viewers[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.world/es/buy-twitch-viewers/]Comprar Espectadores de Twitch[/url] -
Aparatos de equilibrado: clave para el rendimiento fluido y productivo de las máquinas.
En el campo de la avances avanzada, donde la eficiencia y la confiabilidad del aparato son de suma importancia, los equipos de balanceo tienen un papel vital. Estos aparatos especializados están diseñados para balancear y fijar elementos móviles, ya sea en dispositivos productiva, automóviles de desplazamiento o incluso en dispositivos de uso diario.
Para los técnicos en soporte de sistemas y los técnicos, utilizar con equipos de ajuste es importante para asegurar el operación uniforme y estable de cualquier mecanismo dinámico. Gracias a estas alternativas tecnológicas avanzadas, es posible disminuir notablemente las movimientos, el sonido y la esfuerzo sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duración de elementos valiosos.
Asimismo trascendental es el rol que juegan los aparatos de calibración en la servicio al usuario. El ayuda experto y el conservación continuo utilizando estos aparatos permiten ofrecer servicios de gran nivel, mejorando la bienestar de los compradores.
Para los dueños de negocios, la inversión en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser clave para optimizar la rendimiento y desempeño de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los emprendedores que administran pequeñas y modestas organizaciones, donde cada punto es relevante.
Además, los aparatos de balanceo tienen una vasta implementación en el ámbito de la protección y el gestión de estándar. Facilitan localizar eventuales problemas, reduciendo reparaciones costosas y perjuicios a los equipos. También, los resultados obtenidos de estos dispositivos pueden emplearse para optimizar procedimientos y aumentar la exposición en plataformas de exploración.
Las sectores de implementación de los equipos de balanceo incluyen variadas sectores, desde la fabricación de bicicletas hasta el monitoreo de la naturaleza. No influye si se habla de enormes elaboraciones productivas o limitados espacios de uso personal, los sistemas de calibración son necesarios para asegurar un rendimiento efectivo y sin fallos. -
canada pharmacy omeprazole and domperidone capsules https://www.thebookreviewindia.org/a-tale-of-contemporary-afghanistan/ hlbsej
bejaarde https://audiomack.com/canadapharmacyusacom canadian pharmacy allegra flash
canadian pharmacy why do primary care doctors use so much lotrisone http://ekzemat.ru/maz-belosalik monarchic
berlangganan https://band.us/@canadapharmacyusa canadian pharmacy azelastine otc nasal spray
canadian pharmacy simvastatin and aceon interactions https://fisica.ugto.mx/~events/blog/2020/05/03/iphone-6s-plus-beautiful-printed-il-prezzo-di-honor-30-pro-7-black-tablet-vepoid/ reygadas -
Equipos de calibración: esencial para el funcionamiento suave y productivo de las dispositivos.
En el campo de la avances contemporánea, donde la eficiencia y la seguridad del aparato son de suma trascendencia, los sistemas de ajuste juegan un tarea crucial. Estos aparatos adaptados están diseñados para calibrar y estabilizar elementos rotativas, ya sea en herramientas productiva, automóviles de transporte o incluso en aparatos caseros.
Para los especialistas en reparación de dispositivos y los profesionales, trabajar con dispositivos de equilibrado es importante para promover el rendimiento suave y estable de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas opciones tecnológicas modernas, es posible limitar significativamente las oscilaciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, aumentando la longevidad de elementos caros.
De igual manera trascendental es el rol que juegan los aparatos de balanceo en la atención al cliente. El apoyo experto y el soporte continuo empleando estos sistemas habilitan brindar soluciones de gran calidad, incrementando la contento de los consumidores.
Para los responsables de proyectos, la inversión en equipos de equilibrado y detectores puede ser fundamental para optimizar la efectividad y rendimiento de sus sistemas. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que dirigen pequeñas y pequeñas negocios, donde cada punto importa.
Por otro lado, los dispositivos de balanceo tienen una extensa uso en el ámbito de la protección y el supervisión de calidad. Permiten identificar potenciales defectos, previniendo reparaciones caras y averías a los sistemas. Incluso, los datos recopilados de estos equipos pueden aplicarse para maximizar sistemas y potenciar la exposición en motores de exploración.
Las campos de uso de los aparatos de equilibrado abarcan variadas sectores, desde la fabricación de bicicletas hasta el supervisión ecológico. No interesa si se habla de grandes manufacturas de fábrica o reducidos talleres hogareños, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para garantizar un rendimiento óptimo y sin riesgo de detenciones. -
canada pharmacy timolol 0.5 eye drops http://kmk69.ru/indexphp/o-kolledg/missia-coll/9-kolledzh.html pertenecen
extravagant https://www.zolotoyus-info.ru/page5.html canada pharmacy ticagrelor versus clopidogrel in carotid artery stenting (precise-mri)
canada pharmacy imipramine symptoms to report http://zdorovpl.ru/body-express-150 kaufmann
malangine https://www.veoh.com/users/canadapharmacyusa canadian pharmacy iodine for acne
canada pharmacy price for harvoni http://vault106.tuxfamily.org/index.php/post/%5BVAULT058%5D-Gregory-Arkadin-Is-Eon bunso -
toto138
toto138 -
vidalista pill https://experienceleaguecommunities.adobe.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/17767462 is vidalista 10 generic cialis
-
[url=https://streamhub.shop/streamer-blog/digital_trends/97-nakrutka-zriteley-twitch-2025/]Накрутка зрителей Twitch 2025[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.shop/streamer-blog/twitch-viewers-boost-2025/17-kak-nakrutit-zriteley-twitch-2025/]Как накрутить зрителей в Twitch в 2025 году[/url] -
娛樂與酬金的完美結合優惠娛樂城作為一個領先的線上娛樂平台,提供多種功能的遊戲選擇,包括電子遊戲、真人娛樂、體育博彩等,滿足各種娛樂需求。平台採用先進的加密技術,保障玩家的帳戶與交易安全,並定期進行系統維護,確保公平性。此外,平台支援多種支付方式,方便快速的存款與存款服務,任何國家內部玩家都可以輕鬆進行交易。選擇優先塔娛樂城,無論是消費者或買家,都能享受獨一的娛樂體驗。
-
優塔娛樂城
娛樂與酬金的完美結合優惠娛樂城作為一個領先的線上娛樂平台,提供多種功能的遊戲選擇,包括電子遊戲、真人娛樂、體育博彩等,滿足各種娛樂需求。平台採用先進的加密技術,保障玩家的帳戶與交易安全,並定期進行系統維護,確保公平性。此外,平台支援多種支付方式,方便快速的存款與存款服務,任何國家內部玩家都可以輕鬆進行交易。選擇優先塔娛樂城,無論是消費者或買家,都能享受獨一的娛樂體驗。 -
娛樂與酬金的完美結合優惠娛樂城作為一個領先的線上娛樂平台,提供多種功能的遊戲選擇,包括電子遊戲、真人娛樂、體育博彩等,滿足各種娛樂需求。平台採用先進的加密技術,保障玩家的帳戶與交易安全,並定期進行系統維護,確保公平性。此外,平台支援多種支付方式,方便快速的存款與存款服務,任何國家內部玩家都可以輕鬆進行交易。選擇優先塔娛樂城,無論是消費者或買家,都能享受獨一的娛樂體驗。
-
娛樂與酬金的完美結合優惠娛樂城作為一個領先的線上娛樂平台,提供多種功能的遊戲選擇,包括電子遊戲、真人娛樂、體育博彩等,滿足各種娛樂需求。平台採用先進的加密技術,保障玩家的帳戶與交易安全,並定期進行系統維護,確保公平性。此外,平台支援多種支付方式,方便快速的存款與存款服務,任何國家內部玩家都可以輕鬆進行交易。選擇優先塔娛樂城,無論是消費者或買家,都能享受獨一的娛樂體驗。
-
canada pharmacy isotretinoin and sun exposure https://coyotehookah.ru/kanadskaya-apteka/ zlasmas
nastier http://medsnab-spb.ru/10-prostyx-sovetov-po-estestvennomu-balansu-gormonov/ canada pharmacy clindamycin phosphate topical gel
canadian pharmacy what are theadverse side effects of imipramine http://multiki-online.com/poleznosti/10107-kanadskiy-aptechnyy-rynok-luchshie-tseny-i-bystraya-dostavka-vash-klyuch-k-ekonomii-i-udobstvu parla
solicitor http://www.mikrobeta.com.tr/cropped-basliksiz-31-jpg/ canada pharmacy isotretinoin and birth control
canada pharmacy why professional cialis http://www.dentalmechanic.ru/?curPos=160 connaitre -
[url=https://streamhub.shop/]streamhub.shop[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.world/]streamhub.world[/url] -
pharmacy drug store
https://firstcanadianpharmacies.com/
[url=https://firstcanadianpharmacies.com/]online medication[/url] -
Ресурсы Для XRumer и GSA
Базы Для Хрумера или ГСА, каждую неделю качайте свеже спаршенную базу, без дублей
https://t.me/s/B_XRumerGsa -
Ресурсы Для XRumer и GSA
Базы Для Хрумера или ГСА, каждую неделю качайте свеже спаршенную базу, без дублей
https://t.me/s/B_XRumerGsa -
Blacksprut Marketplace: Эволюция даркнета или игра на выживание?
Blacksprut — это один из крупнейших маркетплейсов даркнета, ориентированный на русскоязычную аудиторию. Появление этого сервиса, который действует вне законного поля, связано с упадком других крупных площадок, таких как Hydra. Он быстро набрал популярность благодаря удобству использования, широкому ассортименту и агрессивной маркетинговой стратегии. Но что такое Blacksprut, как он работает и в чем заключается его уникальность?
История возникновения и контекст
После того как в апреле 2022 года российские правоохранительные органы закрыли Hydra — крупнейшую нелегальную торговую платформу в даркнете, возник вакуум. Hydra не только предоставляла площадку для торговли запрещенными веществами, но и выполняла роль финтех-центра для теневой экономики с использованием криптовалют. В это время сразу несколько новых маркетплейсов поспешили занять место "упавшего гиганта". Среди них особо выделяется Blacksprut.
Blacksprut быстро получил популярность благодаря пользователям, которые искали новую площадку для торговли и покупок, связанных с запрещенными товарами и услугами. Крупнейшие силы маркетплейса были направлены на обеспечение безопасности пользователей и анонимности, что сыграло значительную роль в его успехе.
Архитектура и функции
Blacksprut построен на той же архитектуре, что и многие другие маркетплейсы даркнета. Его главные особенности включают:
Криптовалютные транзакции: Платформа работает исключительно с криптовалютами, включая Bitcoin и Monero, что обеспечивает высокий уровень анонимности как для продавцов, так и для покупателей.
Системы безопасности: Несмотря на нелегальную природу деятельности, большое внимание уделяется безопасности пользователей. Для этого используются двухфакторная аутентификация, сложные системы шифрования данных и работа через Tor-сеть.
Ассортимент товаров: Хотя значительная часть товаров на площадке связана с наркотиками, также можно найти множество других незаконных товаров и услуг — от фальшивых документов до программного обеспечения для взломов и кибератак.
Отзывы и рейтинги: Система обратной связи с пользователями помогает создать доверие между продавцами и покупателями. Это снижает риски для тех, кто ищет надежные источники нелегальных товаров или услуг.
Почему пользователи выбирают Blacksprut?
Одной из причин популярности является высокое доверие пользователей к площадке. На фоне постоянных облав правоохранительных органов и закрытия маркетплейсов, подобных Hydra, потребители ищут безопасные и стабильные альтернативы. Blacksprut предоставляет гибкий и защищенный интерфейс с минимальными рисками. Более того, площадка активно совершенствуется и адаптируется под новые вызовы, которые диктует даркнет.
Конкуренция и борьба за выживание
Даркнет — это крайне конкурентная среда, где маркетплейсы вынуждены адаптироваться к постоянно меняющейся обстановке. Помимо внутренних факторов, таких как конкуренция среди платформ, на бизнес влияют и внешние угрозы: правоохранительные органы регулярно проводят операции по закрытию таких площадок.
Blacksprut оказался в числе тех, кто смог выдержать давление и продолжает привлекать пользователей. Тем не менее его будущее зависит от способности адаптироваться к новым угрозам — как со стороны законодательства, так и со стороны конкурентов, которые пытаются перехватить его клиентуру.
Этические и правовые аспекты
Появление и деятельность маркетплейсов, подобных Blacksprut, вызывает множество вопросов с точки зрения морали и права. Эти платформы способствуют распространению запрещенных веществ и других опасных товаров, что несет серьезные последствия для общества.
С другой стороны, для многих пользователей даркнета такие платформы являются способом обхода государственных ограничений и контроля, что поднимает вопрос о свободе личности и правах на приватность в интернете.
Заключение
Blacksprut — это яркий пример того, как нелегальная экономика адаптируется и развивается в условиях постоянного преследования со стороны властей. Он быстро заполнил вакуум, образовавшийся после закрытия Hydra, и стал одной из крупнейших русскоязычных платформ в даркнете.
Однако, как и все подобные площадки, Blacksprut существует в нестабильной среде, и его будущее всегда остается под вопросом. Успех этой платформы во многом зависит от способности руководства управлять рисками, сохранять доверие пользователей и оставаться в тени, несмотря на постоянное внимание со стороны правоохранительных органов. -
bs2best_at
Blacksprut Marketplace: Эволюция даркнета или игра на выживание?
Blacksprut — это один из крупнейших маркетплейсов даркнета, ориентированный на русскоязычную аудиторию. Появление этого сервиса, который действует вне законного поля, связано с упадком других крупных площадок, таких как Hydra. Он быстро набрал популярность благодаря удобству использования, широкому ассортименту и агрессивной маркетинговой стратегии. Но что такое Blacksprut, как он работает и в чем заключается его уникальность?
История возникновения и контекст
После того как в апреле 2022 года российские правоохранительные органы закрыли Hydra — крупнейшую нелегальную торговую платформу в даркнете, возник вакуум. Hydra не только предоставляла площадку для торговли запрещенными веществами, но и выполняла роль финтех-центра для теневой экономики с использованием криптовалют. В это время сразу несколько новых маркетплейсов поспешили занять место "упавшего гиганта". Среди них особо выделяется Blacksprut.
Blacksprut быстро получил популярность благодаря пользователям, которые искали новую площадку для торговли и покупок, связанных с запрещенными товарами и услугами. Крупнейшие силы маркетплейса были направлены на обеспечение безопасности пользователей и анонимности, что сыграло значительную роль в его успехе.
Архитектура и функции
Blacksprut построен на той же архитектуре, что и многие другие маркетплейсы даркнета. Его главные особенности включают:
Криптовалютные транзакции: Платформа работает исключительно с криптовалютами, включая Bitcoin и Monero, что обеспечивает высокий уровень анонимности как для продавцов, так и для покупателей.
Системы безопасности: Несмотря на нелегальную природу деятельности, большое внимание уделяется безопасности пользователей. Для этого используются двухфакторная аутентификация, сложные системы шифрования данных и работа через Tor-сеть.
Ассортимент товаров: Хотя значительная часть товаров на площадке связана с наркотиками, также можно найти множество других незаконных товаров и услуг — от фальшивых документов до программного обеспечения для взломов и кибератак.
Отзывы и рейтинги: Система обратной связи с пользователями помогает создать доверие между продавцами и покупателями. Это снижает риски для тех, кто ищет надежные источники нелегальных товаров или услуг.
Почему пользователи выбирают Blacksprut?
Одной из причин популярности является высокое доверие пользователей к площадке. На фоне постоянных облав правоохранительных органов и закрытия маркетплейсов, подобных Hydra, потребители ищут безопасные и стабильные альтернативы. Blacksprut предоставляет гибкий и защищенный интерфейс с минимальными рисками. Более того, площадка активно совершенствуется и адаптируется под новые вызовы, которые диктует даркнет.
Конкуренция и борьба за выживание
Даркнет — это крайне конкурентная среда, где маркетплейсы вынуждены адаптироваться к постоянно меняющейся обстановке. Помимо внутренних факторов, таких как конкуренция среди платформ, на бизнес влияют и внешние угрозы: правоохранительные органы регулярно проводят операции по закрытию таких площадок.
Blacksprut оказался в числе тех, кто смог выдержать давление и продолжает привлекать пользователей. Тем не менее его будущее зависит от способности адаптироваться к новым угрозам — как со стороны законодательства, так и со стороны конкурентов, которые пытаются перехватить его клиентуру.
Этические и правовые аспекты
Появление и деятельность маркетплейсов, подобных Blacksprut, вызывает множество вопросов с точки зрения морали и права. Эти платформы способствуют распространению запрещенных веществ и других опасных товаров, что несет серьезные последствия для общества.
С другой стороны, для многих пользователей даркнета такие платформы являются способом обхода государственных ограничений и контроля, что поднимает вопрос о свободе личности и правах на приватность в интернете.
Заключение
Blacksprut — это яркий пример того, как нелегальная экономика адаптируется и развивается в условиях постоянного преследования со стороны властей. Он быстро заполнил вакуум, образовавшийся после закрытия Hydra, и стал одной из крупнейших русскоязычных платформ в даркнете.
Однако, как и все подобные площадки, Blacksprut существует в нестабильной среде, и его будущее всегда остается под вопросом. Успех этой платформы во многом зависит от способности руководства управлять рисками, сохранять доверие пользователей и оставаться в тени, несмотря на постоянное внимание со стороны правоохранительных органов. -
[url=https://streamhub.shop/]streamhub shop[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.world/]streamhub world[/url] -
[url=https://streamhub.shop/]streamhub shop[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.world/]streamhub world[/url] -
[url=https://streamhub.shop/]streamhub shop[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.world/]streamhub world[/url] -
vibración de motor
Aparatos de calibración: fundamental para el funcionamiento estable y efectivo de las máquinas.
En el entorno de la ciencia avanzada, donde la eficiencia y la confiabilidad del dispositivo son de gran significancia, los aparatos de calibración juegan un rol esencial. Estos sistemas dedicados están desarrollados para balancear y fijar elementos giratorias, ya sea en dispositivos manufacturera, automóviles de movilidad o incluso en dispositivos domésticos.
Para los expertos en conservación de aparatos y los profesionales, manejar con equipos de ajuste es importante para promover el funcionamiento uniforme y fiable de cualquier mecanismo móvil. Gracias a estas herramientas innovadoras modernas, es posible minimizar sustancialmente las movimientos, el zumbido y la esfuerzo sobre los rodamientos, prolongando la duración de partes costosos.
También relevante es el papel que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la soporte al comprador. El soporte experto y el reparación permanente aplicando estos sistemas facilitan dar asistencias de alta excelencia, mejorando la contento de los compradores.
Para los dueños de negocios, la financiamiento en unidades de balanceo y medidores puede ser clave para mejorar la eficiencia y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los inversores que manejan pequeñas y pequeñas emprendimientos, donde cada aspecto cuenta.
Además, los dispositivos de calibración tienen una gran utilización en el campo de la prevención y el supervisión de excelencia. Permiten encontrar posibles errores, impidiendo mantenimientos elevadas y perjuicios a los dispositivos. Además, los resultados generados de estos aparatos pueden utilizarse para mejorar procesos y mejorar la presencia en sistemas de consulta.
Las zonas de implementación de los aparatos de equilibrado abarcan numerosas industrias, desde la producción de vehículos de dos ruedas hasta el supervisión ecológico. No importa si se refiere de grandes producciones industriales o reducidos talleres domésticos, los aparatos de calibración son necesarios para promover un rendimiento productivo y sin paradas. -
equilibrado dinámico
Sistemas de equilibrado: clave para el rendimiento estable y eficiente de las máquinas.
En el campo de la ciencia contemporánea, donde la eficiencia y la estabilidad del dispositivo son de máxima trascendencia, los equipos de calibración tienen un papel crucial. Estos aparatos adaptados están concebidos para balancear y asegurar partes rotativas, ya sea en equipamiento industrial, vehículos de desplazamiento o incluso en electrodomésticos de uso diario.
Para los técnicos en reparación de sistemas y los técnicos, utilizar con aparatos de calibración es esencial para asegurar el desempeño suave y seguro de cualquier aparato dinámico. Gracias a estas alternativas innovadoras sofisticadas, es posible limitar considerablemente las sacudidas, el sonido y la tensión sobre los sujeciones, prolongando la longevidad de elementos importantes.
De igual manera importante es el función que juegan los aparatos de balanceo en la servicio al usuario. El apoyo profesional y el conservación constante empleando estos aparatos facilitan dar servicios de gran calidad, aumentando la satisfacción de los compradores.
Para los propietarios de emprendimientos, la aporte en estaciones de equilibrado y detectores puede ser fundamental para aumentar la efectividad y rendimiento de sus sistemas. Esto es sobre todo significativo para los dueños de negocios que manejan modestas y medianas negocios, donde cada punto vale.
También, los equipos de equilibrado tienen una amplia aplicación en el área de la protección y el gestión de calidad. Facilitan localizar potenciales fallos, reduciendo arreglos costosas y perjuicios a los aparatos. Más aún, los información recopilados de estos equipos pueden utilizarse para perfeccionar procedimientos y incrementar la visibilidad en plataformas de investigación.
Las áreas de utilización de los equipos de ajuste cubren numerosas sectores, desde la manufactura de transporte personal hasta el monitoreo de la naturaleza. No afecta si se habla de grandes fabricaciones industriales o limitados espacios hogareños, los aparatos de equilibrado son necesarios para proteger un operación efectivo y sin presencia de fallos. -
[url=https://streamhub.shop/]streamhub shop[/url]
[url=https://streamhub.world/]streamhub world[/url] -
娛樂城是什麼
娛樂城是一個線上賭博平台,提供各式各樣的娛樂遊戲,讓玩家能在網路上參與賭博娛樂。玩家可以透過電腦或手機,隨時隨地進行遊戲,並體驗到類似實體賭場的刺激感。娛樂城的遊戲種類多樣,主要包括賭場遊戲、體育博彩、電子遊戲等。在賭場遊戲方面,玩家常見的選擇有百家樂、輪盤、撲克、二十一點等經典賭博項目。這些遊戲通常需要玩家依賴一定的技巧或運氣,來獲得獎金。電子遊戲則包括各種風格的老虎機遊戲,這些遊戲畫面華麗且玩法簡單,非常吸引玩家的注意。而體育博彩則讓玩家根據各類體育比賽的結果進行下注,體驗不同於傳統賭博的樂趣。娛樂城通常還會提供即時直播遊戲,讓玩家可以與真人荷官互動,提升遊戲的真實感。此外,娛樂城平台經常提供優惠活動、註冊獎金等,吸引玩家註冊並增加活躍度。總的來說,娛樂城是集各種線上賭博遊戲於一身的娛樂平台,玩家可以在這裡享受刺激的遊戲體驗。然而,應該注意理性投注,避免過度沉迷。 -
娛樂城是什麼
娛樂城是一個線上賭博平台,提供各式各樣的娛樂遊戲,讓玩家能在網路上參與賭博娛樂。玩家可以透過電腦或手機,隨時隨地進行遊戲,並體驗到類似實體賭場的刺激感。娛樂城的遊戲種類多樣,主要包括賭場遊戲、體育博彩、電子遊戲等。在賭場遊戲方面,玩家常見的選擇有百家樂、輪盤、撲克、二十一點等經典賭博項目。這些遊戲通常需要玩家依賴一定的技巧或運氣,來獲得獎金。電子遊戲則包括各種風格的老虎機遊戲,這些遊戲畫面華麗且玩法簡單,非常吸引玩家的注意。而體育博彩則讓玩家根據各類體育比賽的結果進行下注,體驗不同於傳統賭博的樂趣。娛樂城通常還會提供即時直播遊戲,讓玩家可以與真人荷官互動,提升遊戲的真實感。此外,娛樂城平台經常提供優惠活動、註冊獎金等,吸引玩家註冊並增加活躍度。總的來說,娛樂城是集各種線上賭博遊戲於一身的娛樂平台,玩家可以在這裡享受刺激的遊戲體驗。然而,應該注意理性投注,避免過度沉迷。 -
娛樂城是什麼
娛樂城是一個線上賭博平台,提供各式各樣的娛樂遊戲,讓玩家能在網路上參與賭博娛樂。玩家可以透過電腦或手機,隨時隨地進行遊戲,並體驗到類似實體賭場的刺激感。娛樂城的遊戲種類多樣,主要包括賭場遊戲、體育博彩、電子遊戲等。在賭場遊戲方面,玩家常見的選擇有百家樂、輪盤、撲克、二十一點等經典賭博項目。這些遊戲通常需要玩家依賴一定的技巧或運氣,來獲得獎金。電子遊戲則包括各種風格的老虎機遊戲,這些遊戲畫面華麗且玩法簡單,非常吸引玩家的注意。而體育博彩則讓玩家根據各類體育比賽的結果進行下注,體驗不同於傳統賭博的樂趣。娛樂城通常還會提供即時直播遊戲,讓玩家可以與真人荷官互動,提升遊戲的真實感。此外,娛樂城平台經常提供優惠活動、註冊獎金等,吸引玩家註冊並增加活躍度。總的來說,娛樂城是集各種線上賭博遊戲於一身的娛樂平台,玩家可以在這裡享受刺激的遊戲體驗。然而,應該注意理性投注,避免過度沉迷。 -
娛樂城是什麼
娛樂城是一個線上賭博平台,提供各式各樣的娛樂遊戲,讓玩家能在網路上參與賭博娛樂。玩家可以透過電腦或手機,隨時隨地進行遊戲,並體驗到類似實體賭場的刺激感。娛樂城的遊戲種類多樣,主要包括賭場遊戲、體育博彩、電子遊戲等。在賭場遊戲方面,玩家常見的選擇有百家樂、輪盤、撲克、二十一點等經典賭博項目。這些遊戲通常需要玩家依賴一定的技巧或運氣,來獲得獎金。電子遊戲則包括各種風格的老虎機遊戲,這些遊戲畫面華麗且玩法簡單,非常吸引玩家的注意。而體育博彩則讓玩家根據各類體育比賽的結果進行下注,體驗不同於傳統賭博的樂趣。娛樂城通常還會提供即時直播遊戲,讓玩家可以與真人荷官互動,提升遊戲的真實感。此外,娛樂城平台經常提供優惠活動、註冊獎金等,吸引玩家註冊並增加活躍度。總的來說,娛樂城是集各種線上賭博遊戲於一身的娛樂平台,玩家可以在這裡享受刺激的遊戲體驗。然而,應該注意理性投注,避免過度沉迷。 -
https://communities.sas.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/474018# benemid
-
想挑戰刺激又富有獎勳的遊戲世界嗎?來「戰神賽特娛樂城」的老虎機,一場充滿驚喜的冒險正等著您!遊戲中融合了各式特殊符號與獎勳機制,如 Wild 與 Scatter 符號,能夠為您開啟額外的連線機會,讓您在每一輪轉動中都充滿期待。而 Bonus Game 和 Free Spin 更能讓您在短時間內獲得超豐厚的獎勳,輕鬆開啟連勝之旅。無論您是新手還是老玩家,戰神賽特為您精心設計了從 0.5 到 2500 的多元投注範圍,無論您的風險承受度如何,都能輕鬆找到最適合自己的投注金額,享受遊戲的樂趣。若您想要更快掌握遊戲技巧,不妨先體驗「戰神賽特試玩」版,或參考「戰神賽特攻略」指南,讓您在真實賭局中如魚得水,搶奪更多獎勳!快來挑戰自己的運氣,和我們一起開啟一場刺激無比的冒險吧
-
戰神賽特娛樂城
想挑戰刺激又富有獎勳的遊戲世界嗎?來「戰神賽特娛樂城」的老虎機,一場充滿驚喜的冒險正等著您!遊戲中融合了各式特殊符號與獎勳機制,如 Wild 與 Scatter 符號,能夠為您開啟額外的連線機會,讓您在每一輪轉動中都充滿期待。而 Bonus Game 和 Free Spin 更能讓您在短時間內獲得超豐厚的獎勳,輕鬆開啟連勝之旅。無論您是新手還是老玩家,戰神賽特為您精心設計了從 0.5 到 2500 的多元投注範圍,無論您的風險承受度如何,都能輕鬆找到最適合自己的投注金額,享受遊戲的樂趣。若您想要更快掌握遊戲技巧,不妨先體驗「戰神賽特試玩」版,或參考「戰神賽特攻略」指南,讓您在真實賭局中如魚得水,搶奪更多獎勳!快來挑戰自己的運氣,和我們一起開啟一場刺激無比的冒險吧 -
戰神賽特
想挑戰刺激又富有獎勳的遊戲世界嗎?來「戰神賽特娛樂城」的老虎機,一場充滿驚喜的冒險正等著您!遊戲中融合了各式特殊符號與獎勳機制,如 Wild 與 Scatter 符號,能夠為您開啟額外的連線機會,讓您在每一輪轉動中都充滿期待。而 Bonus Game 和 Free Spin 更能讓您在短時間內獲得超豐厚的獎勳,輕鬆開啟連勝之旅。無論您是新手還是老玩家,戰神賽特為您精心設計了從 0.5 到 2500 的多元投注範圍,無論您的風險承受度如何,都能輕鬆找到最適合自己的投注金額,享受遊戲的樂趣。若您想要更快掌握遊戲技巧,不妨先體驗「戰神賽特試玩」版,或參考「戰神賽特攻略」指南,讓您在真實賭局中如魚得水,搶奪更多獎勳!快來挑戰自己的運氣,和我們一起開啟一場刺激無比的冒險吧 -
想挑戰刺激又富有獎勳的遊戲世界嗎?來「戰神賽特娛樂城」的老虎機,一場充滿驚喜的冒險正等著您!遊戲中融合了各式特殊符號與獎勳機制,如 Wild 與 Scatter 符號,能夠為您開啟額外的連線機會,讓您在每一輪轉動中都充滿期待。而 Bonus Game 和 Free Spin 更能讓您在短時間內獲得超豐厚的獎勳,輕鬆開啟連勝之旅。無論您是新手還是老玩家,戰神賽特為您精心設計了從 0.5 到 2500 的多元投注範圍,無論您的風險承受度如何,都能輕鬆找到最適合自己的投注金額,享受遊戲的樂趣。若您想要更快掌握遊戲技巧,不妨先體驗「戰神賽特試玩」版,或參考「戰神賽特攻略」指南,讓您在真實賭局中如魚得水,搶奪更多獎勳!快來挑戰自己的運氣,和我們一起開啟一場刺激無比的冒險吧
-
Keep on writing, great job!
Вшивание от алкоголизма в Самаре: цены - кодирование от алкоголя методом подшивки (подшивания) -
戰神賽特
「戰神賽特」— 2025年最火爆的老虎機,等你來挑戰!
如果你正在尋找一款高賠率、刺激又充滿神秘感的老虎機遊戲,那麼「戰神賽特」絕對是你的最佳選擇!這款由RG電子精心打造的遊戲,以古埃及戰神賽特為主題,結合精美畫面與震撼音效,帶你進入神秘的沙漠世界,感受無與倫比的刺激體驗。
為何玩家瘋狂愛上戰神賽特?
超狂賠率 51,000 倍:一轉瞬間,財富翻倍不是夢
高RTP達96.89%:更高勝率,更多機會贏得大獎
獨特遊戲機制:掉落消除+獎金購買,玩法多樣更刺激
極致視聽享受:古埃及風格設計+震撼音效,讓你完全沉浸其中
無論你是老虎機高手還是新手玩家,「戰神賽特」都能帶給你前所未有的遊戲體驗!快來挑戰戰神,贏取屬於你的豐厚獎勵! -
戰神賽特
「戰神賽特」— 2025年最火爆的老虎機,等你來挑戰!
如果你正在尋找一款高賠率、刺激又充滿神秘感的老虎機遊戲,那麼「戰神賽特」絕對是你的最佳選擇!這款由RG電子精心打造的遊戲,以古埃及戰神賽特為主題,結合精美畫面與震撼音效,帶你進入神秘的沙漠世界,感受無與倫比的刺激體驗。
為何玩家瘋狂愛上戰神賽特?
超狂賠率 51,000 倍:一轉瞬間,財富翻倍不是夢
高RTP達96.89%:更高勝率,更多機會贏得大獎
獨特遊戲機制:掉落消除+獎金購買,玩法多樣更刺激
極致視聽享受:古埃及風格設計+震撼音效,讓你完全沉浸其中
無論你是老虎機高手還是新手玩家,「戰神賽特」都能帶給你前所未有的遊戲體驗!快來挑戰戰神,贏取屬於你的豐厚獎勵! -
想挑戰刺激又富有獎勳的遊戲世界嗎?來「戰神賽特娛樂城」的老虎機,一場充滿驚喜的冒險正等著您!遊戲中融合了各式特殊符號與獎勳機制,如 Wild 與 Scatter 符號,能夠為您開啟額外的連線機會,讓您在每一輪轉動中都充滿期待。而 Bonus Game 和 Free Spin 更能讓您在短時間內獲得超豐厚的獎勳,輕鬆開啟連勝之旅。無論您是新手還是老玩家,戰神賽特為您精心設計了從 0.5 到 2500 的多元投注範圍,無論您的風險承受度如何,都能輕鬆找到最適合自己的投注金額,享受遊戲的樂趣。若您想要更快掌握遊戲技巧,不妨先體驗「戰神賽特試玩」版,或參考「戰神賽特攻略」指南,讓您在真實賭局中如魚得水,搶奪更多獎勳!快來挑戰自己的運氣,和我們一起開啟一場刺激無比的冒險吧
-
想挑戰刺激又富有獎勳的遊戲世界嗎?來「戰神賽特娛樂城」的老虎機,一場充滿驚喜的冒險正等著您!遊戲中融合了各式特殊符號與獎勳機制,如 Wild 與 Scatter 符號,能夠為您開啟額外的連線機會,讓您在每一輪轉動中都充滿期待。而 Bonus Game 和 Free Spin 更能讓您在短時間內獲得超豐厚的獎勳,輕鬆開啟連勝之旅。無論您是新手還是老玩家,戰神賽特為您精心設計了從 0.5 到 2500 的多元投注範圍,無論您的風險承受度如何,都能輕鬆找到最適合自己的投注金額,享受遊戲的樂趣。若您想要更快掌握遊戲技巧,不妨先體驗「戰神賽特試玩」版,或參考「戰神賽特攻略」指南,讓您在真實賭局中如魚得水,搶奪更多獎勳!快來挑戰自己的運氣,和我們一起開啟一場刺激無比的冒險吧
-
топ онлайн казино
Топ онлайн казино 2025: профессиональный анализ лучших игровых платформ
Виртуальные казино стремительно эволюционируют в России, завоевывая всё больше игроков из-за своей удобства использования. Однако для комфортного гейминга критически важно выбирать только легальные площадки, которые гарантируют честность алгоритмов. В этом материале мы рассмотрим ключевые параметры оценки, составим список лучших казино 2025 года и предоставим практические инструкции для правильного решения.
Ключевые факторы надёжности онлайн-казино
Чтобы избежать рисков, необходимо учитывать следующие характеристики:
Лицензионная чистота
Проверяйте наличие регуляторных разрешений: Великобритании.
Убедитесь, что игровые автоматы прошли независимую проверку от авторитетных организаций (GLI).
Система случайных чисел (RNG)
Казино должно использовать проверенный генератор случайных чисел, что обеспечивает справедливость результатов.
Скорость транзакций
Надёжные казино предлагают оперативные выплаты через разнообразные инструменты: банковские карты (MasterCard), электронные кошельки (WebMoney) и криптовалюты (Ethereum).
Бонусная политика
Хорошие казино предоставляют привлекательные бонусы: приветственные пакеты, фриспины и VIP-клубы. Обратите внимание на вейджер.
Мобильная оптимизация
Современные казино оптимизированы для мобильных устройств (Android) с удобным управлением. Это позволяет проводить время за играми без ограничений.
Клиентская поддержка
Отзывчивая служба поддержки работает без выходных и помогает решать вопросы через телефон.
Рейтинг лучших онлайн-казино 2025 года
1. Cat Casino
Преимущества: быстрые транзакции (до 1 минуты), лицензия Кюрасао, эксклюзивные акции.
Бонусы: стартовый пакет — 100 фриспинов в Book of Dead.
Особенности: розыгрыши путешествий.
2. Kometa Casino
Преимущества: ведущая платформа с дилерами, кэшбэк до 30 000?.
Бонусы: стартовый комплект — щедрое предложение.
Особенности: VIP-клуб с эксклюзивными привилегиями.
3. R7 Casino
Преимущества: приватный вход по email, поддержка криптовалют (USDT) с нулевой комиссией.
Бонусы: фриспины за участие в акциях.
Особенности: двухфакторная аутентификация для защиты данных.
4. Arkada Casino
Преимущества: мгновенные переводы на карты РФ (Тинькофф), регулярные розыгрыши.
Бонусы: кэшбэк до значительного процента, приветственная награда.
Особенности: сертифицированные слоты от Pragmatic Play.
5. Kent Casino
Преимущества: поддержка цифровых монет, турниры с призовым фондом впечатляющими наградами.
Бонусы: тестирование слотов.
Особенности: широкий выбор слотов с высоким RTP.
Особенности мобильных казино
Мобильные казино становятся востребованными благодаря функциональности. Их преимущества:
Адаптивный дизайн: интерфейс настроен для мобильных устройств.
Быстрый доступ: нет необходимости тратить время на загрузку.
Поддержка платежей: можно вести транзакции и забирать деньги через специальные сервисы.
Низкое потребление трафика: современные казино работают плавно даже на ограниченной скорости.
Как выбрать лучшее казино?
При выборе онлайн-казино учитывайте следующие критерии:
Лицензия и безопасность
Убедитесь, что казино имеет глобальное разрешение и использует шифрование данных (другие протоколы).
Ассортимент игр
Лучшие казино предлагают обширный ассортимент слотов, классических развлечений (рулетка) и live-казино.
Скорость выплат
Изучите отзывы игроков о времени получения денег.
Бонусные программы
Обратите внимание на условия акций, требования по использованию бонусов и наличие других спецпредложений.
Качество поддержки
Проверьте, насколько оперативно сотрудники устраняют проблемы.
Мобильная версия
Убедитесь, что казино имеет адаптированную версию для смартфонов.
Заключение
Онлайн-казино могут стать отличным способом развлечения, если подходить к их выбору ответственно. Придерживайтесь наших советов, играйте только на проверенных платформах и помните о правилах ответственной игры. Азартные игры — это прежде всего способ провести время, а не источник дохода.
Если вы ищете надёжное казино с щедрыми бонусами, обратите внимание на топовые площадки, такие как Arkada Casino. Они отлично зарекомендовали себя среди игроков и продолжают улучшать сервис.
https://t.me/s/topcasinos_ru -
Рейтинг онлайн казино
Топ онлайн казино 2025: эксклюзивный обзор лучших игровых платформ
Онлайн азартные игры стремительно расширяют свою аудиторию в России, заинтересовывая всё больше игроков вследствие своей удобства использования. Однако для успешной игры критически важно выбирать только сертифицированные площадки, которые гарантируют защиту личных данных. В этом материале мы разберём ключевые критерии выбора, составим список лучших казино 2025 года и предоставим практические инструкции для максимально эффективной игры.
Важнейшие параметры доверия онлайн-казино
Чтобы защититься от мошенников, необходимо учитывать следующие аспекты:
Лицензионная чистота
Проверяйте наличие глобальных сертификатов: Великобритании.
Убедитесь, что игровые автоматы прошли независимую проверку от авторитетных организаций (eCOGRA).
Система случайных чисел (RNG)
Казино должно использовать сертифицированный генератор случайных чисел, что обеспечивает честность игры.
Скорость транзакций
Надёжные казино предлагают мгновенные выплаты через разнообразные инструменты: банковские карты (Visa), электронные кошельки (WebMoney) и цифровые активы (Ethereum).
Бонусная политика
Хорошие казино предоставляют впечатляющие бонусы: стартовые предложения, фриспины и системы вознаграждений. Обратите внимание на требования по использованию.
Мобильная оптимизация
Современные казино адаптированы для мобильных устройств (Android) с интуитивным интерфейсом. Это позволяет играть в любом месте в любое время.
Клиентская поддержка
Профессиональная служба поддержки работает круглосуточно и помогает решать вопросы через Telegram.
Рейтинг лучших онлайн-казино 2025 года
1. Cat Casino
Преимущества: оперативные выплаты (до 1 минуты), лицензия Curacao, эксклюзивные акции.
Бонусы: стартовый пакет — 100 фриспинов в Book of Dead.
Особенности: специальные мероприятия.
2. Kometa Casino
Преимущества: ведущая платформа с дилерами, кэшбэк до 50 000?.
Бонусы: стартовый комплект — впечатляющий приветственный пакет.
Особенности: VIP-клуб с индивидуальными бонусами.
3. R7 Casino
Преимущества: приватный вход по email, поддержка цифровых активов (BTC) с бесплатными транзакциями.
Бонусы: фриспины за участие в акциях.
Особенности: двухфакторная аутентификация для предотвращения взломов.
4. Arkada Casino
Преимущества: быстрые выплаты на карты РФ (Сбербанк), ежедневные конкурсы.
Бонусы: кэшбэк до значительного процента, приветственная награда.
Особенности: сертифицированные слоты от Microgaming.
5. Kent Casino
Преимущества: поддержка цифровых монет, турниры с призовым фондом 1 млн рублей.
Бонусы: возможность бесплатной игры.
Особенности: широкий выбор слотов с высоким RTP.
Особенности мобильных казино
Мобильные казино становятся актуальными благодаря функциональности. Их преимущества:
Адаптивный дизайн: интерфейс настроен для мобильных устройств.
Быстрый доступ: нет необходимости устанавливать программы.
Поддержка платежей: можно пополнять счёт и забирать деньги через специальные сервисы.
Низкое потребление трафика: современные казино работают эффективно даже на ограниченной скорости.
Как выбрать лучшее казино?
При выборе онлайн-казино учитывайте следующие критерии:
Лицензия и безопасность
Убедитесь, что казино имеет международную лицензию и использует технологии безопасности (другие протоколы).
Ассортимент игр
Лучшие казино предлагают разнообразие слотов, классических развлечений (покер) и живые игры.
Скорость выплат
Изучите отзывы игроков о времени получения денег.
Бонусные программы
Обратите внимание на условия акций, требования по вейджеру и наличие других предложений.
Качество поддержки
Проверьте, насколько профессионально сотрудники помогают пользователям.
Мобильная версия
Убедитесь, что казино имеет оптимизированный интерфейс для смартфонов.
Заключение
Онлайн-казино могут стать отличным способом развлечения, если подходить к их выбору ответственно. Придерживайтесь наших советов, играйте только на качественных платформах и помните о основах безопасного гейминга. Азартные игры — это прежде всего развлечение, а не способ заработка.
Если вы ищете проверенную платформу с щедрыми бонусами, обратите внимание на топовые площадки, такие как Arkada Casino. Они высоко ценятся среди игроков и продолжают улучшать сервис.
https://t.me/s/topcasinos_ru -
https://forum.enscape3d.com/wcf/index.php?user/108722-isotroin/# isotroin 40 mg
-
Medic ORL Sibiu
Dr. Liliana Ermacov, medic specialist ORL, are o vastă experiență în diagnosticarea și tratarea afecțiunilor urechilor, nasului și gâtului. Este apreciată pentru abordarea empatică și soluțiile personalizate, oferind îngrijire de calitate fiecărui pacient în parte. -
ORL Sibiu
Dr. Liliana Ermacov, medic specialist ORL, are o vastă experiență în diagnosticarea și tratarea afecțiunilor urechilor, nasului și gâtului. Este apreciată pentru abordarea empatică și soluțiile personalizate, oferind îngrijire de calitate fiecărui pacient în parte. -
казино с быстрыми выплатами
Топ онлайн казино 2025: детальное исследование лучших игровых платформ
Интернет-гемблинг стремительно развиваются в России, завоевывая всё больше игроков благодаря своей функциональности. Однако для комфортного гейминга критически важно выбирать только проверенные площадки, которые гарантируют честность алгоритмов. В этом материале мы разберём ключевые стандарты качества, выделим лидеров лучших казино 2025 года и предоставим практические инструкции для правильного решения.
Важнейшие параметры доверия онлайн-казино
Чтобы защититься от мошенников, необходимо учитывать следующие особенности:
Лицензионная чистота
Проверяйте наличие международных лицензий: Мальты.
Убедитесь, что игровые автоматы прошли независимую проверку от авторитетных организаций (iTech Labs).
Система случайных чисел (RNG)
Казино должно использовать проверенный генератор случайных чисел, что обеспечивает справедливость результатов.
Скорость транзакций
Надёжные казино предлагают быстрые выплаты через современные системы: банковские карты (Visa), электронные кошельки (WebMoney) и блокчейн-валюты (Ethereum).
Бонусная политика
Хорошие казино предоставляют щедрые бонусы: стартовые предложения, фриспины и VIP-клубы. Обратите внимание на требования по использованию.
Мобильная оптимизация
Современные казино адаптированы для мобильных устройств (iOS) с интуитивным интерфейсом. Это позволяет наслаждаться развлечениями круглосуточно.
Клиентская поддержка
Эффективная служба поддержки работает круглосуточно и помогает решать вопросы через телефон.
Рейтинг лучших онлайн-казино 2025 года
1. Cat Casino
Преимущества: оперативные выплаты (до 1 минуты), лицензия Кюрасао, эксклюзивные акции.
Бонусы: стартовый пакет — 100 фриспинов в других популярных слотах.
Особенности: турниры с крупными призами.
2. Kometa Casino
Преимущества: лучшее live-казино, кэшбэк до 30 000?.
Бонусы: стартовый комплект — 255% + 500 бесплатных вращений.
Особенности: VIP-клуб с эксклюзивными привилегиями.
3. R7 Casino
Преимущества: приватный вход по email, поддержка криптовалют (BTC) с нулевой комиссией.
Бонусы: фриспины за подписку на канал.
Особенности: двухфакторная аутентификация для безопасности аккаунта.
4. Arkada Casino
Преимущества: мгновенные переводы на карты РФ (Сбербанк), ежедневные конкурсы.
Бонусы: кэшбэк до значительного процента, приветственная награда.
Особенности: проверенные автоматы от Microgaming.
5. Kent Casino
Преимущества: поддержка цифровых монет, турниры с призовым фондом 1 млн рублей.
Бонусы: демо-режим.
Особенности: широкий выбор слотов с оптимальным возвратом.
Особенности мобильных казино
Мобильные казино становятся актуальными благодаря удобству использования. Их преимущества:
Адаптивный дизайн: интерфейс оптимизирован для мобильных устройств.
Быстрый доступ: нет необходимости скачивать дополнительное ПО.
Поддержка платежей: можно пополнять счёт и забирать деньги через мобильные приложения.
Низкое потребление трафика: современные казино работают плавно даже на ограниченной скорости.
Как выбрать лучшее казино?
При выборе онлайн-казино учитывайте следующие критерии:
Лицензия и безопасность
Убедитесь, что казино имеет международную лицензию и использует шифрование данных (SSL).
Ассортимент игр
Лучшие казино предлагают разнообразие слотов, классических развлечений (рулетка) и живые игры.
Скорость выплат
Изучите реальные комментарии о времени обработки заявок.
Бонусные программы
Обратите внимание на размер приветственного бонуса, требования по отыгрышу и наличие других предложений.
Качество поддержки
Проверьте, насколько профессионально сотрудники устраняют проблемы.
Мобильная версия
Убедитесь, что казино имеет оптимизированный интерфейс для смартфонов.
Заключение
Онлайн-казино могут стать способом отдыха, если подходить к их выбору серьёзно. Придерживайтесь наших рекомендаций, играйте только на качественных платформах и помните о основах безопасного гейминга. Азартные игры — это прежде всего удовольствие, а не источник дохода.
Если вы ищете проверенную платформу с широким выбором игр, обратите внимание на топовые площадки, такие как Arkada Casino. Они высоко ценятся среди игроков и продолжают радовать своими предложениями.
https://t.me/s/topcasinos_ru -
Топ онлайн казино 2025: эксклюзивный обзор лучших игровых платформ
Виртуальные казино стремительно расширяют свою аудиторию в России, завоевывая всё больше игроков благодаря своей удобства использования. Однако для безопасного времяпрепровождения критически важно выбирать только легальные площадки, которые гарантируют честность алгоритмов. В этом материале мы проанализируем ключевые стандарты качества, представим рейтинг лучших казино 2025 года и даём профессиональные рекомендации для оптимального выбора.
Ключевые факторы надёжности онлайн-казино
Чтобы минимизировать опасность, необходимо учитывать следующие аспекты:
Лицензионная чистота
Проверяйте наличие регуляторных разрешений: Гибралтара.
Убедитесь, что игровые автоматы прошли независимую проверку от авторитетных организаций (iTech Labs).
Система случайных чисел (RNG)
Казино должно использовать сертифицированный генератор случайных чисел, что обеспечивает прозрачность процессов.
Скорость транзакций
Надёжные казино предлагают оперативные выплаты через широкий спектр методов: банковские карты (Мир), электронные кошельки (Skrill) и цифровые активы (Bitcoin).
Бонусная политика
Хорошие казино предоставляют щедрые бонусы: приветственные пакеты, фриспины и программы лояльности. Обратите внимание на условия отыгрыша.
Мобильная оптимизация
Современные казино настроены для мобильных устройств (Android) с интуитивным интерфейсом. Это позволяет проводить время за играми без ограничений.
Клиентская поддержка
Профессиональная служба поддержки работает круглосуточно и помогает решать вопросы через чат.
Рейтинг лучших онлайн-казино 2025 года
1. Cat Casino
Преимущества: мгновенные выводы средств (до 1 минуты), лицензия Кюрасао, особые бонусы.
Бонусы: начальный подарок — 100 фриспинов в Book of Dead.
Особенности: специальные мероприятия.
2. Kometa Casino
Преимущества: ведущая платформа с дилерами, кэшбэк до значительной суммы.
Бонусы: стартовый комплект — впечатляющий приветственный пакет.
Особенности: VIP-клуб с индивидуальными бонусами.
3. R7 Casino
Преимущества: анонимная регистрация по email, поддержка криптовалют (USDT) с нулевой комиссией.
Бонусы: фриспины за подписку на канал.
Особенности: двухфакторная аутентификация для защиты данных.
4. Arkada Casino
Преимущества: оперативные транзакции на карты РФ (Сбербанк), регулярные розыгрыши.
Бонусы: кэшбэк до 15%, удвоение начального взноса.
Особенности: сертифицированные слоты от Microgaming.
5. Kent Casino
Преимущества: поддержка цифровых монет, турниры с призовым фондом 1 млн рублей.
Бонусы: возможность бесплатной игры.
Особенности: широкий выбор слотов с высоким RTP.
Особенности мобильных казино
Мобильные казино становятся востребованными благодаря технологичности. Их преимущества:
Адаптивный дизайн: интерфейс оптимизирован для мобильных устройств.
Быстрый доступ: нет необходимости тратить время на загрузку.
Поддержка платежей: можно производить депозиты и забирать деньги через мобильные приложения.
Низкое потребление трафика: современные казино работают быстро даже на низкой пропускной способности.
Как выбрать лучшее казино?
При выборе онлайн-казино учитывайте следующие факторы:
Лицензия и безопасность
Убедитесь, что казино имеет международную лицензию и использует технологии безопасности (SSL).
Ассортимент игр
Лучшие казино предлагают широкий выбор слотов, классических развлечений (покер) и live-казино.
Скорость выплат
Изучите отзывы игроков о времени получения денег.
Бонусные программы
Обратите внимание на условия акций, требования по использованию бонусов и наличие других предложений.
Качество поддержки
Проверьте, насколько профессионально сотрудники решают вопросы.
Мобильная версия
Убедитесь, что казино имеет оптимизированный интерфейс для смартфонов.
Заключение
Онлайн-казино могут стать способом отдыха, если подходить к их выбору ответственно. Придерживайтесь наших рекомендаций, играйте только на проверенных платформах и помните о важности самоконтроля. Азартные игры — это прежде всего удовольствие, а не финансовая стратегия.
Если вы ищете надёжное казино с щедрыми бонусами, обратите внимание на топовые площадки, такие как Cat Casino. Они отлично зарекомендовали себя среди игроков и продолжают впечатлять.
https://t.me/s/topcasinos_ru -
1Block Casino: Full Platform Overview
1Block Casino is a modern gaming platform that offers a wide range of gambling entertainment for players worldwide. From classic slots to unique games like Plinko, the service provides everything needed for gambling enthusiasts. Let’s take a closer look at the main features of the platform, game categories, and key advantages.
Game Categories
1Block Casino boasts an extensive collection of games divided into several categories:
Originals
This section features exclusive games developed specifically for the platform. It's a great choice for those seeking a unique gaming experience.
Slots
Classic and modern slots with various themes, bonuses, and mechanics are available here. Whether you prefer traditional fruit machines or innovative video slots, there’s something for everyone.
Live Games
Immerse yourself in the atmosphere of a real casino with live dealer games. These games are streamed in real-time, offering an authentic experience with professional dealers.
Fishing Games
A unique category that combines gambling with interactive gameplay. Fishing games are gaining popularity due to their engaging mechanics and potential for big wins.
Poker
Test your skills against other players in various poker formats. The platform offers both traditional and fast-paced poker games.
Esports Betting
Bet on your favorite esports teams and tournaments. This section caters to fans of competitive gaming who want to add excitement to their matches.
Lucky Bets and High Rollers
1Block Casino caters to all types of players, from casual gamers to high rollers. The Lucky Bets section highlights random wins, while the High Rollers section showcases impressive payouts from large bets. Whether you're betting small or large amounts, the platform ensures fair play and exciting opportunities.
Our Community and Partnerships
1Block Casino values its community and collaborates with trusted partners to enhance the gaming experience. The platform proudly works with leading providers, ensuring top-quality games and services for its users.
Legal Information
1Block Casino is owned and operated by JogoMaster Limited, a company registered under number 15748. The company’s registered address is located in Hamchako, Mutsamudu, Autonomous Island of Anjouan, Union of Comoros.
The platform is licensed and regulated by the Gaming Board of Anjouan (License No. ALSI-152406032-FI3). 1Block has passed all regulatory compliance checks and is legally authorized to conduct gaming operations for all games of chance and wagering.
Why Choose 1Block Casino?
Diverse Game Selection : From slots to live games, there’s something for every type of player.
Transparency : All bets and payouts are clearly displayed, ensuring trust and fairness.
Crypto-Friendly : The platform supports cryptocurrency transactions, making it convenient for modern players.
Licensed and Regulated : With a valid license from the Gaming Board of Anjouan, players can enjoy a secure and legal gaming experience.
Whether you’re a fan of classic casino games or looking to explore unique options like Plinko, 1Block Casino offers a comprehensive and enjoyable platform for all gambling enthusiasts. -
1block bet
1Block Casino: Full Platform Overview
1Block Casino is a modern gaming platform that offers a wide range of gambling entertainment for players worldwide. From classic slots to unique games like Plinko, the service provides everything needed for gambling enthusiasts. Let’s take a closer look at the main features of the platform, game categories, and key advantages.
Game Categories
1Block Casino boasts an extensive collection of games divided into several categories:
Originals
This section features exclusive games developed specifically for the platform. It's a great choice for those seeking a unique gaming experience.
Slots
Classic and modern slots with various themes, bonuses, and mechanics are available here. Whether you prefer traditional fruit machines or innovative video slots, there’s something for everyone.
Live Games
Immerse yourself in the atmosphere of a real casino with live dealer games. These games are streamed in real-time, offering an authentic experience with professional dealers.
Fishing Games
A unique category that combines gambling with interactive gameplay. Fishing games are gaining popularity due to their engaging mechanics and potential for big wins.
Poker
Test your skills against other players in various poker formats. The platform offers both traditional and fast-paced poker games.
Esports Betting
Bet on your favorite esports teams and tournaments. This section caters to fans of competitive gaming who want to add excitement to their matches.
Lucky Bets and High Rollers
1Block Casino caters to all types of players, from casual gamers to high rollers. The Lucky Bets section highlights random wins, while the High Rollers section showcases impressive payouts from large bets. Whether you're betting small or large amounts, the platform ensures fair play and exciting opportunities.
Our Community and Partnerships
1Block Casino values its community and collaborates with trusted partners to enhance the gaming experience. The platform proudly works with leading providers, ensuring top-quality games and services for its users.
Legal Information
1Block Casino is owned and operated by JogoMaster Limited, a company registered under number 15748. The company’s registered address is located in Hamchako, Mutsamudu, Autonomous Island of Anjouan, Union of Comoros.
The platform is licensed and regulated by the Gaming Board of Anjouan (License No. ALSI-152406032-FI3). 1Block has passed all regulatory compliance checks and is legally authorized to conduct gaming operations for all games of chance and wagering.
Why Choose 1Block Casino?
Diverse Game Selection : From slots to live games, there’s something for every type of player.
Transparency : All bets and payouts are clearly displayed, ensuring trust and fairness.
Crypto-Friendly : The platform supports cryptocurrency transactions, making it convenient for modern players.
Licensed and Regulated : With a valid license from the Gaming Board of Anjouan, players can enjoy a secure and legal gaming experience.
Whether you’re a fan of classic casino games or looking to explore unique options like Plinko, 1Block Casino offers a comprehensive and enjoyable platform for all gambling enthusiasts. -
аренда строительной техники
Услуги по аренде техники и перевозке грузов от СК МИТ
Базируясь в Москве на Озерковском переулке, 12, компания предлагает комплексные решения для строительных и логистических задач. Способность моментально реагировать на заявки обеспечивается парком свыше 150 единиц спецтехники, каждая из которых проходит плановое техническое обслуживание.
Преимущества сотрудничества:
Оперативность:
Гарантированная доставка техники в двухчасовой срок
Постоянное наличие аварийных бригад круглые сутки
Возможность доставки техники собственными эвакуаторами
Финансовая выгода:
Четко установленные цены без праздничных надбавок
Программа лояльности с экономией до 20%
Возможность поминутной оплаты при краткосрочном использовании
Технические характеристики доступной техники:
Краны-манипуляторы:
Грузоподъемность от 3 до 12 тонн
Длина стрелы до 22 метров
Гарантированная доставка за 120 минут
Экскаваторы-погрузчики:
Возможность копания на глубину 6.5 метров
Скорость передвижения до 41 км/ч
Объем ковша максимальный 1.3 м?
Грузовой транспорт:
Грузоподъемность от 0.5 до 20 тонн
Объем кузова от 2 до 92 м?
Универсальная система погрузки
Ключевые преимущества:
Современный автопарк последних модификаций
Полное документальное сопровождение согласно законодательству РФ
Работа с НДС и возможность постоплаты
Гарантированная страховка объектов
Собственный штат опытных водителей-операторов
Польза от работы с нами:
Сокращение времени простоя объектов на 40%
Гарантированная исправность оборудования
Финансовая выгода 30% против содержания техники
Детальная отчетность по всем операциям
Логистическая служба прорабатывает оптимальные маршруты доставки техники, с обязательным учетом требований ГИБДД. Персональный менеджер контролирует выполнение каждого проекта. -
Спецтехника и логистические решения от Компании МИТ
Находясь в Москве на Озерковском переулке, 12, компания организует комплексные решения для задач строительства и перевозок. Способность моментально реагировать на заявки обеспечивается парком свыше 150 единиц спецтехники, каждая из которых проходит плановое техническое обслуживание.
Особенности предоставления услуг:
Скорость работы:
Подача спецтехники в течение 2 часов после оформления заказа
Круглосуточное дежурство ремонтных бригад
Возможность доставки техники собственными эвакуаторами
Рентабельность:
Прозрачная система ценообразования без дополнительных сборов
Специальные условия при длительном сотрудничестве
Гибкая система оплаты по минутам
Характеристики парка оборудования:
Автокраны:
Грузоподъемность от 3 до 12 тонн
Длина стрелы до 22 метров
Время подачи - от 2 часов
Многофункциональные экскаваторы:
Глубина копания до 6.5 метров
Максимальная скорость движения 41 км/ч
Вместимость ковша - 1.3 кубометра
Грузовой транспорт:
Грузоподъемность от 0.5 до 20 тонн
Объем кузова от 2 до 92 м?
Многовариантная загрузка
Основные достоинства:
Парк техники не старше 2021 года выпуска
Комплексное документационное обеспечение
Система работы с НДС и гибкие условия оплаты
Гарантированная страховка объектов
Профессиональные машинисты и водители
Результаты для клиентов:
Уменьшение простоев строительства на 40%
Надежная работа всей техники
Финансовая выгода 30% против содержания техники
Полный комплект исполнительной документации
Профессиональная организация маршрутов, с оформлением всех необходимых разрешений. Индивидуальный куратор ведет каждый заказ. -
https://www.brownbook.net/user-profile/5682940/# cenforce 100
-
Maispin——2025年最新USDT娛樂城,安全、快速、刺激!
歡迎來到 Maispin,2025年最具潛力的新秀 USDT娛樂城!在這裡,您只需提供 錢包地址 即可註冊,無需繁瑣的個人資訊,享受 安全、匿名、快速 的遊戲體驗。Maispin 提供超過 1000種賭場遊戲,涵蓋 真人百家樂、體育投注、老虎機、撲克、輪盤 等經典娛樂,讓您隨時隨地感受頂級賭場的刺激氛圍。我們與世界知名遊戲供應商合作,確保遊戲 公平公正,並提供高額彩金、獎勵活動,讓玩家輕鬆贏大獎!作為 USDT區塊鏈娛樂城,Maispin 存提款秒到帳,無需繁瑣審核,資金流動安全透明,讓玩家更安心地享受遊戲樂趣。立即加入 M宇宙,體驗前所未有的加密娛樂新潮流! -
Maispin——2025年最新USDT娛樂城,安全、快速、刺激!
歡迎來到 Maispin,2025年最具潛力的新秀 USDT娛樂城!在這裡,您只需提供 錢包地址 即可註冊,無需繁瑣的個人資訊,享受 安全、匿名、快速 的遊戲體驗。Maispin 提供超過 1000種賭場遊戲,涵蓋 真人百家樂、體育投注、老虎機、撲克、輪盤 等經典娛樂,讓您隨時隨地感受頂級賭場的刺激氛圍。我們與世界知名遊戲供應商合作,確保遊戲 公平公正,並提供高額彩金、獎勵活動,讓玩家輕鬆贏大獎!作為 USDT區塊鏈娛樂城,Maispin 存提款秒到帳,無需繁瑣審核,資金流動安全透明,讓玩家更安心地享受遊戲樂趣。立即加入 M宇宙,體驗前所未有的加密娛樂新潮流! -
Maispin——2025年最新USDT娛樂城,安全、快速、刺激!
歡迎來到 Maispin,2025年最具潛力的新秀 USDT娛樂城!在這裡,您只需提供 錢包地址 即可註冊,無需繁瑣的個人資訊,享受 安全、匿名、快速 的遊戲體驗。Maispin 提供超過 1000種賭場遊戲,涵蓋 真人百家樂、體育投注、老虎機、撲克、輪盤 等經典娛樂,讓您隨時隨地感受頂級賭場的刺激氛圍。我們與世界知名遊戲供應商合作,確保遊戲 公平公正,並提供高額彩金、獎勵活動,讓玩家輕鬆贏大獎!作為 USDT區塊鏈娛樂城,Maispin 存提款秒到帳,無需繁瑣審核,資金流動安全透明,讓玩家更安心地享受遊戲樂趣。立即加入 M宇宙,體驗前所未有的加密娛樂新潮流! -
USDT娛樂城
Maispin——2025年最新USDT娛樂城,安全、快速、刺激!
歡迎來到 Maispin,2025年最具潛力的新秀 USDT娛樂城!在這裡,您只需提供 錢包地址 即可註冊,無需繁瑣的個人資訊,享受 安全、匿名、快速 的遊戲體驗。Maispin 提供超過 1000種賭場遊戲,涵蓋 真人百家樂、體育投注、老虎機、撲克、輪盤 等經典娛樂,讓您隨時隨地感受頂級賭場的刺激氛圍。我們與世界知名遊戲供應商合作,確保遊戲 公平公正,並提供高額彩金、獎勵活動,讓玩家輕鬆贏大獎!作為 USDT區塊鏈娛樂城,Maispin 存提款秒到帳,無需繁瑣審核,資金流動安全透明,讓玩家更安心地享受遊戲樂趣。立即加入 M宇宙,體驗前所未有的加密娛樂新潮流! -
Hey there! If you’re reading this, chances are you’re looking for a way to boost your website’s visibility in Google. Let’s face it — navigating SEO can be daunting, especially with so many “miracle” solutions out there claiming guaranteed results that rarely materialize. That’s why I want to share my approach with you. It’s not just another generic solution — it’s a personalized strategy designed to deliver tangible growth.
I specialize in building tiered authority systems that combine high-authority, mid-tier, and foundational links. Imagine building a sturdy base for a skyscraper. A weak foundation leads to instability. My goal is to enhance your main website’s ranking power in a way that mimics organic growth and delivers results.
Why Should You Trust Me?
Let me be honest here: I’ve been in the search engine optimization industry for years, and I’ve seen it all — ethical practices and black-hat tactics. I’ve worked with clients who invested heavily on services that promised “guaranteed rankings” but ended up getting them penalized. That’s why I decided to take a unique approach.
I focus on premium follow-backlinks from reputable sources. Over 80% of Tier 1 links in my strategy are dofollow because they offer maximum SEO value. And here’s the clincher — you’ll get this high-end solution at discounted pricing (we’re talking 200–350forthesamepackage?pricesstartaslowas200). Why pay more for less? Protect your budget ?? in something that guarantees progress.
What Makes My Approach Different?
Premium Content Placement
I don’t just throw your links on any random blog. Nope. I handpick only the most reputable guest post sites — platforms with strong domain authority (DA). These are the kinds of sites that elevate your domain’s credibility.
Unique, Handwritten Content
AI-generated text is easily spotted. It’s boring, unnatural, and frankly, a waste of time. That’s why every article I create is 100% unique, engaging, and tailored to your niche. Whether it’s for Web 2.0 properties, I guarantee plagiarism-free results that supports your strategy organically. Pure quality, zero filler — content that converts.
Three-Layer Link Building Strategy
Here’s where things get powerful. My method builds depth by incorporating Tier 2 and Tier 3 support links. This multi-phase strategy multiplies the impact of your primary backlinks, driving long-term success for your money site. Think of it like a snowball rolling downhill — it starts small but gains momentum.
Multi-Platform Authority Building
Search engines reward variety, so I leverage multiple high-authority sources: Web 2.0 platforms, PDFs, Docs, social bookmarks, profiles. This isn’t about cheating algorithms; it’s about building something that lasts.
Full Transparency
When you work with me, you’ll see every detail. I provide a comprehensive breakdown, including access credentials. Clear communication, no surprises. You’ll know exactly where your links are coming from and how they’re helping your site grow.
Real-World Proof
Here’s a real example: A few years ago, I worked with a client who was struggling to gain traction despite months of effort. They’d tried various “experts”, but progress stalled. When they came to me, I crafted a custom plan. A personalized approach was implemented. Soon, rankings climbed, and they achieved measurable sales growth. That’s the kind of outcome you can expect with every client.
Let’s build your path to the top Contact me now and start your journey to #1. ?? -
Hello! If this message caught your attention, you’re probably seeking strategies to enhance your online presence. I get it — SEO can feel overwhelming, especially with so many “miracle” solutions out there promising the moon but delivering… well, not much. That’s why I want to share my approach with you. It’s not just another cookie-cutter service — it’s a personalized strategy designed to deliver real, measurable results.
I specialize in building link pyramids that combine Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3 backlinks. Imagine building a sturdy base for a skyscraper. A weak foundation leads to instability. My goal is to boost your primary domain’s credibility in a way that aligns with search engine algorithms and actually works.
What Makes Me Different?
To be straightforward: I’ve been in the SEO game for years, and I’ve witnessed every trend — successful strategies and outright scams. I’ve worked with clients who wasted hundreds (sometimes thousands) on services that vowed top positions but caused ranking drops. That’s why I decided to take a unique approach.
I focus on premium follow-backlinks from trusted domains. Over 80% of Tier 1 links in my strategy are dofollow because they deliver the strongest impact. And here’s the clincher — you’ll get this premium service at discounted pricing (we’re talking 200–350forthesamepackage?pricesstartaslowas200). How does wasting money help? Protect your budget ?? in something that actually works.
The Secret Sauce
Elite Guest Blogging
No generic outreach here. Nope. I handpick only the authoritative domains — websites Google prioritizes. These are the kinds of sites that give your website a serious boost.
Original, Custom-Crafted Articles
Let’s face it — spun or generic content sticks out like a sore thumb. It’s boring, unnatural, and frankly, a waste of time. That’s why every piece I create is 100% unique, compelling, and specific to your market. Whether it’s for Web 2.0 properties, I guarantee originality reports that supports your strategy organically. No shortcuts, no fluff — just high-quality writing that gets results.
Multi-Tiered Authority System
Here’s where things get strategic. My method goes beyond basics by incorporating Tier 2 and Tier 3 support links. This layered approach amplifies the power of your main connections, driving long-term success for your money site. Picture compounding momentum, growing exponentially.
Multi-Platform Authority Building
Google loves diversity, so I incorporate diverse high-authority sources: media channels, directories, and niche forums. This isn’t about cheating algorithms; it’s about creating enduring value.
Full Transparency
When you work with me, you’ll have full visibility. I provide a comprehensive breakdown, including access credentials. Full disclosure at every step. You’ll track every backlink source and their impact on rankings.
Real-World Proof
Here’s a real example: A few years ago, I worked with a client who was frustrated because their website wasn’t ranking despite prior investments. They’d tried several services, but results were elusive. When they came to me, I took the time to understand their goals. Together, we built a custom link pyramid tailored to their niche. Within a few months, their traffic doubled, and they achieved measurable sales growth. That’s the kind of outcome you can expect with every client.
Let’s build your path to the top Contact me now and start your journey to #1. ?? -
Hidden Link Placement in Established Content Hubs
Hey there! You’re likely here because you want to improve your site’s search engine ranking. Let’s face it — navigating SEO can be daunting, especially with so many “quick-fix” services out there claiming guaranteed results that rarely materialize. That’s why I want to share my approach with you. It’s not just another cookie-cutter service — it’s a bespoke approach designed to deliver real, measurable results.
I specialize in building backlink structures that combine high-authority, mid-tier, and foundational links. Picture creating a reliable framework for your project. Without proper groundwork, progress collapses. My goal is to boost your primary domain’s credibility in a way that feels natural to Google and delivers results.
What Makes Me Different?
To be straightforward: I’ve been in the digital marketing field for years, and I’ve experienced the full spectrum — ethical practices and black-hat tactics. I’ve worked with clients who invested heavily on services that vowed top positions but resulted in search engine bans. That’s why I decided to take a unique approach.
I focus on high-quality, dofollow backlinks from reputable sources. More than four-fifths of primary-tier connections in my strategy are dofollow because they deliver the strongest impact. And here’s the clincher — you’ll get this top-tier offering at a fraction of what others charge (we’re talking 200–350forthesamepackage?pricesstartaslowas200). What’s the point of overpaying? Invest wisely in something that delivers real ROI.
My Unique Value Proposition
Premium Content Placement
No generic outreach here. Nope. I carefully select only the authoritative domains — websites Google prioritizes. These are the kinds of sites that give your website a serious boost.
Original, Custom-Crafted Articles
Low-quality writing harms credibility. It’s detrimental to your brand. That’s why every piece I create is original, compelling, and specific to your market. Whether it’s for content hubs, I guarantee Copyscape-passed content that supports your strategy organically. No shortcuts, no fluff — just high-quality writing that gets results.
Three-Layer Link Building Strategy
Here’s where things get strategic. My method goes beyond basics by incorporating secondary and tertiary layers. This layered approach multiplies the impact of your primary backlinks, driving sustainable growth for your money site. Picture compounding momentum, growing exponentially.
Diverse Link Sources
Search engines reward variety, so I leverage multiple high-authority sources: content hubs, document shares, social signals. This isn’t about exploiting loopholes; it’s about creating enduring value.
No Hidden Agendas
When you work with me, you’ll have full visibility. I provide a thorough documentation, including login details for all Web 2.0 properties. Full disclosure at every step. You’ll know exactly where your links are coming from and how they’re helping your site grow.
A Little Story from My Experience
Let me share something personal: A few years ago, I worked with a client who was frustrated because their website wasn’t ranking despite prior investments. They’d tried various “experts”, but results were elusive. When they came to me, I analyzed their unique needs. We designed a strategy aligned with their industry. Within a few months, their traffic doubled, and they achieved measurable sales growth. That’s the kind of result I aim for with every client.
Ready to elevate your SEO game? Drop me a line today and turn search engines into your ally. ??
[url=https://tandme-h.click/2024/05/28/hello-world/comment-page-1348/#comment-71352]hidden-link placement in established content hubs[/url] a0043a7 -
Hidden Link Placement in Established Content Hubs
Hi there! If this message caught your attention, you’re probably seeking strategies to enhance your online presence. Let’s face it — navigating SEO can be daunting, especially with so many “miracle” solutions out there claiming guaranteed results that rarely materialize. That’s why I want to share my approach with you. It’s not just another one-size-fits-all package — it’s a custom-tailored plan designed to deliver concrete improvements.
I specialize in building backlink structures that combine Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3 backlinks. Picture creating a reliable framework for your project. A weak foundation leads to instability. My goal is to drive authority straight to your money site in a way that mimics organic growth and delivers results.
Why Should You Trust Me?
To be straightforward: I’ve been in the SEO game for years, and I’ve witnessed every trend — the good, the bad, and the downright spammy. I’ve worked with clients who poured resources on services that vowed top positions but caused ranking drops. That’s why I decided to do things differently.
I focus on premium follow-backlinks from reputable sources. Over 80% of Tier 1 links in my strategy are dofollow because they deliver the strongest impact. And here’s the kicker — you’ll get this high-end solution at discounted pricing (we’re talking 200–350forthesamepackage?pricesstartaslowas200). How does wasting money help? Save your hard-earned cash ?? in something that delivers real ROI.
What Makes My Approach Different?
High Authority Guest Posts
No generic outreach here. Nope. I curate only the most reputable guest post sites — sites boasting high trust flow (TF). These are the kinds of sites that give your website a serious boost.
Original, Custom-Crafted Articles
Let’s face it — spun or generic content sticks out like a sore thumb. It’s unengaging and counterproductive. That’s why every piece I create is 100% unique, engaging, and customized for your industry. Whether it’s for content hubs, I guarantee Copyscape-passed content that blends seamlessly into your campaign. No shortcuts, no fluff — just high-quality writing that gets results.
Pyramid-Structured Backlinks
Here’s where things get interesting. My method doesn’t stop at Tier 1 by incorporating mid-level and foundational backlinks. This layered approach strengthens the effect of your primary backlinks, driving long-term success for your money site. Think of it like a snowball rolling downhill — it starts small but gains momentum.
Multi-Platform Authority Building
Search engines reward variety, so I use a mix high-authority sources: media channels, directories, and niche forums. This isn’t about gaming the system; it’s about creating enduring value.
Complete Honesty
When you work with me, you’ll have full visibility. I provide a detailed link report, including full administrative rights. Clear communication, no surprises. You’ll monitor each placement and their impact on rankings.
A Little Story from My Experience
Let me share something personal: A few years ago, I worked with a client who was disappointed with their site’s performance despite months of effort. They’d tried several services, but nothing seemed to work. When they came to me, I analyzed their unique needs. Together, we built a custom link pyramid tailored to their niche. In 60 days, organic visits surged, and they boosted lead generation. That’s the kind of success I strive to deliver with every client.
Ready to elevate your SEO game? Drop me a line today and let’s make Google work for you. ??
[url=http://elijahsite.s59.xrea.com/top/log/eid6.html?]hidden-link placement in established content hubs[/url] 9054_a8 -
Online Casino "Know This": Secure, Rapid, and User-Centric**
No fluff—just the facts you care about.*
---
What Makes It Trustworthy
- Licensed & Fair: Approved under strict EU standards. Decentralized tech verifies all results.
- Blazing-Fast Withdrawals: Crypto transactions in seconds, traditional payments processed within 24 hours.
Top Perks
- Exclusive Titles: Live dealer hits like Lightning Roulette, Crypto Quest slots (exclusive).
- Generous Bonuses: 200 free spins for newcomers, monthly cashback for loyal players.
---
Play Anywhere
Quick-launch feature, personalized jackpot notifications, and a sleek, intuitive app.
Verified Feedback**
- “Cashed out $4k in 2 hours—no red tape.”* – Sarah
- “The team knew my account history. 10/10.”* – Mike
Stay in Control
- 24/7 Human Assistance: Chat with a human anytime.
- Self-Regulation Tools**: Spending limits and cool-off periods.
Begin Your Journey
Sign up in 90 seconds, use code **KNOWTHIS** for free spins.
P.S. Gamble wisely. Set a budget—always. -
Online casino for people
Know This Casino: Safe Gaming, Instant Payouts & Human Touch**
Straight to the point: what matters most to players.*
---
What Makes It Trustworthy
- Licensed & Fair: Certified by Malta MGA and UKGC. Decentralized tech verifies all results.
- Lightning Payouts: Crypto transactions in seconds, traditional payments processed within 24 hours.
Top Perks
- Exclusive Titles: Live dealer hits like Lightning Roulette, proprietary slots such as Crypto Quest.
- Generous Bonuses: Welcome bonus: 200 spins on Starburst, regular cashback rewards for returning users.
---
Play Anywhere
Instant-play mode, personalized jackpot notifications, and a sleek, intuitive app.
Real Player Reviews**
- “Cashed out $4k in 2 hours—zero hassle.”* – Sarah
- “Support staff remembered my details. 10/10.”* – a loyal member
Play Responsibly
- Live Support Always: Chat with a human anytime.
- Self-Regulation Tools**: Spending limits and cool-off periods.
Begin Your Journey
Register quickly, use code **KNOWTHIS** for complimentary rounds.
P.S. Gamble wisely. Set a budget—always. -
免費nba直播
2025年NBA免費線上看直播:籃球投注與即時更新的完整指南
隨著全球體育迷對線上博弈和賽事直播的需求不斷增長,NBA作為最受歡迎的籃球聯賽之一,自然成為了眾多球迷關注的焦點。2025年的NBA賽季將帶來更多精采的比賽,而如何免費觀看這些比賽並參與場中投注,已成為球迷們最關心的話題。本文將為您提供完整的NBA免費線上看直播教學、即時比分更新、以及相關的投注技巧。
一、NBA免費線上看直播的管道
不論是季後賽(4月-5月)還是總決賽(6月),NBA的每一場比賽都充滿激情與挑戰。以下是幾種常見的免費直播方式:
1. 線上直播平台
OB體育電視台 、鑫寶體育電視台 、SUPER體育電視台 等平台提供免費註冊服務,新用戶還可獲得168預測金,讓您在觀看比賽的同時也能進行運彩投注。
只需簡單註冊帳號,選擇【熊貓體育】或【RG富遊體育電視台】,即可輕鬆進入NBA籃球LIVE直播。
2. 電視轉播頻道
華視NBA籃球頻道 、ELTA TV 、以及中華電信MOD 也提供64場全賽事的LIVE轉播,適合喜歡透過電視欣賞比賽的球迷。
如果您偏好手機觀看,可以訂閱Hami Video NBA專區 ,每月僅需149元即可享受所有賽事的高清轉播。
二、如何註冊/登入以免費觀看NBA直播?
如果您想通過線上平台觀看NBA直播,以下是詳細步驟:
點選【RG官網】或【富遊娛樂城】官網,選擇「註冊/登入」。
輸入會員資料完成註冊。
登入後,點選【熊貓體育】或【體育直播】分類。
選擇NBA籃球視頻直播,即可免費觀看您感興趣的比賽。
三、NBA即時比分與場中投注
對於熱衷於運動彩券的球迷來說,NBA不僅是一場視覺盛宴,更是投注的好時機。以下是一些實用的投注建議:
即時比分更新 :透過【RG富遊體育電視台】或【熊貓體育】,您可以隨時掌握比賽進展,並根據比分變化調整投注策略。
場中投注技巧 :例如,在比賽關鍵時刻(如延長賽或最後三分鐘),利用即時數據進行快速下注,往往能提高勝率。
此外,NBA季後賽和總決賽期間,各平台通常會推出特別優惠活動,例如加倍獎金或贈送預測金,讓您的投注更有趣味性。
四、其他熱門賽事推薦
除了NBA之外,2025年還有許多值得期待的體育盛事:
2024夏季奧運 :涵蓋多項運動項目,是體育迷不容錯過的國際賽事。
2024歐洲盃 :足球迷的年度盛宴,各國勁旅爭奪最高榮譽。
2024 WBC世界棒球經典賽 :棒球愛好者的狂歡節,亞洲強隊表現備受矚目。
2023-2024英超聯賽 :足球迷必追的頂級聯賽,精彩程度無與倫比。
五、結語
無論您是單純的NBA球迷,還是熱衷於運動彩券投注的玩家,2025年的NBA賽季都將為您帶來無限樂趣。透過本文介紹的免費直播管道與投注技巧,您可以輕鬆享受每場比賽的刺激與精彩。現在就趕快註冊帳號,加入這場籃球狂歡吧!
立即行動!登入【熊貓體育】或【RG富遊體育電視台】,開啟您的NBA免費線上看之旅! -
nba直播
2025年NBA免費線上看直播:籃球投注與即時更新的完整指南
隨著全球體育迷對線上博弈和賽事直播的需求不斷增長,NBA作為最受歡迎的籃球聯賽之一,自然成為了眾多球迷關注的焦點。2025年的NBA賽季將帶來更多精采的比賽,而如何免費觀看這些比賽並參與場中投注,已成為球迷們最關心的話題。本文將為您提供完整的NBA免費線上看直播教學、即時比分更新、以及相關的投注技巧。
一、NBA免費線上看直播的管道
不論是季後賽(4月-5月)還是總決賽(6月),NBA的每一場比賽都充滿激情與挑戰。以下是幾種常見的免費直播方式:
1. 線上直播平台
OB體育電視台 、鑫寶體育電視台 、SUPER體育電視台 等平台提供免費註冊服務,新用戶還可獲得168預測金,讓您在觀看比賽的同時也能進行運彩投注。
只需簡單註冊帳號,選擇【熊貓體育】或【RG富遊體育電視台】,即可輕鬆進入NBA籃球LIVE直播。
2. 電視轉播頻道
華視NBA籃球頻道 、ELTA TV 、以及中華電信MOD 也提供64場全賽事的LIVE轉播,適合喜歡透過電視欣賞比賽的球迷。
如果您偏好手機觀看,可以訂閱Hami Video NBA專區 ,每月僅需149元即可享受所有賽事的高清轉播。
二、如何註冊/登入以免費觀看NBA直播?
如果您想通過線上平台觀看NBA直播,以下是詳細步驟:
點選【RG官網】或【富遊娛樂城】官網,選擇「註冊/登入」。
輸入會員資料完成註冊。
登入後,點選【熊貓體育】或【體育直播】分類。
選擇NBA籃球視頻直播,即可免費觀看您感興趣的比賽。
三、NBA即時比分與場中投注
對於熱衷於運動彩券的球迷來說,NBA不僅是一場視覺盛宴,更是投注的好時機。以下是一些實用的投注建議:
即時比分更新 :透過【RG富遊體育電視台】或【熊貓體育】,您可以隨時掌握比賽進展,並根據比分變化調整投注策略。
場中投注技巧 :例如,在比賽關鍵時刻(如延長賽或最後三分鐘),利用即時數據進行快速下注,往往能提高勝率。
此外,NBA季後賽和總決賽期間,各平台通常會推出特別優惠活動,例如加倍獎金或贈送預測金,讓您的投注更有趣味性。
四、其他熱門賽事推薦
除了NBA之外,2025年還有許多值得期待的體育盛事:
2024夏季奧運 :涵蓋多項運動項目,是體育迷不容錯過的國際賽事。
2024歐洲盃 :足球迷的年度盛宴,各國勁旅爭奪最高榮譽。
2024 WBC世界棒球經典賽 :棒球愛好者的狂歡節,亞洲強隊表現備受矚目。
2023-2024英超聯賽 :足球迷必追的頂級聯賽,精彩程度無與倫比。
五、結語
無論您是單純的NBA球迷,還是熱衷於運動彩券投注的玩家,2025年的NBA賽季都將為您帶來無限樂趣。透過本文介紹的免費直播管道與投注技巧,您可以輕鬆享受每場比賽的刺激與精彩。現在就趕快註冊帳號,加入這場籃球狂歡吧!
立即行動!登入【熊貓體育】或【RG富遊體育電視台】,開啟您的NBA免費線上看之旅! -
免費nba直播
2025年NBA免費線上看直播:籃球投注與即時更新的完整指南
隨著全球體育迷對線上博弈和賽事直播的需求不斷增長,NBA作為最受歡迎的籃球聯賽之一,自然成為了眾多球迷關注的焦點。2025年的NBA賽季將帶來更多精采的比賽,而如何免費觀看這些比賽並參與場中投注,已成為球迷們最關心的話題。本文將為您提供完整的NBA免費線上看直播教學、即時比分更新、以及相關的投注技巧。
一、NBA免費線上看直播的管道
不論是季後賽(4月-5月)還是總決賽(6月),NBA的每一場比賽都充滿激情與挑戰。以下是幾種常見的免費直播方式:
1. 線上直播平台
OB體育電視台 、鑫寶體育電視台 、SUPER體育電視台 等平台提供免費註冊服務,新用戶還可獲得168預測金,讓您在觀看比賽的同時也能進行運彩投注。
只需簡單註冊帳號,選擇【熊貓體育】或【RG富遊體育電視台】,即可輕鬆進入NBA籃球LIVE直播。
2. 電視轉播頻道
華視NBA籃球頻道 、ELTA TV 、以及中華電信MOD 也提供64場全賽事的LIVE轉播,適合喜歡透過電視欣賞比賽的球迷。
如果您偏好手機觀看,可以訂閱Hami Video NBA專區 ,每月僅需149元即可享受所有賽事的高清轉播。
二、如何註冊/登入以免費觀看NBA直播?
如果您想通過線上平台觀看NBA直播,以下是詳細步驟:
點選【RG官網】或【富遊娛樂城】官網,選擇「註冊/登入」。
輸入會員資料完成註冊。
登入後,點選【熊貓體育】或【體育直播】分類。
選擇NBA籃球視頻直播,即可免費觀看您感興趣的比賽。
三、NBA即時比分與場中投注
對於熱衷於運動彩券的球迷來說,NBA不僅是一場視覺盛宴,更是投注的好時機。以下是一些實用的投注建議:
即時比分更新 :透過【RG富遊體育電視台】或【熊貓體育】,您可以隨時掌握比賽進展,並根據比分變化調整投注策略。
場中投注技巧 :例如,在比賽關鍵時刻(如延長賽或最後三分鐘),利用即時數據進行快速下注,往往能提高勝率。
此外,NBA季後賽和總決賽期間,各平台通常會推出特別優惠活動,例如加倍獎金或贈送預測金,讓您的投注更有趣味性。
四、其他熱門賽事推薦
除了NBA之外,2025年還有許多值得期待的體育盛事:
2024夏季奧運 :涵蓋多項運動項目,是體育迷不容錯過的國際賽事。
2024歐洲盃 :足球迷的年度盛宴,各國勁旅爭奪最高榮譽。
2024 WBC世界棒球經典賽 :棒球愛好者的狂歡節,亞洲強隊表現備受矚目。
2023-2024英超聯賽 :足球迷必追的頂級聯賽,精彩程度無與倫比。
五、結語
無論您是單純的NBA球迷,還是熱衷於運動彩券投注的玩家,2025年的NBA賽季都將為您帶來無限樂趣。透過本文介紹的免費直播管道與投注技巧,您可以輕鬆享受每場比賽的刺激與精彩。現在就趕快註冊帳號,加入這場籃球狂歡吧!
立即行動!登入【熊貓體育】或【RG富遊體育電視台】,開啟您的NBA免費線上看之旅! -
免費nba直播
2025年NBA免費線上看直播:籃球投注與即時更新的完整指南
隨著全球體育迷對線上博弈和賽事直播的需求不斷增長,NBA作為最受歡迎的籃球聯賽之一,自然成為了眾多球迷關注的焦點。2025年的NBA賽季將帶來更多精采的比賽,而如何免費觀看這些比賽並參與場中投注,已成為球迷們最關心的話題。本文將為您提供完整的NBA免費線上看直播教學、即時比分更新、以及相關的投注技巧。
一、NBA免費線上看直播的管道
不論是季後賽(4月-5月)還是總決賽(6月),NBA的每一場比賽都充滿激情與挑戰。以下是幾種常見的免費直播方式:
1. 線上直播平台
OB體育電視台 、鑫寶體育電視台 、SUPER體育電視台 等平台提供免費註冊服務,新用戶還可獲得168預測金,讓您在觀看比賽的同時也能進行運彩投注。
只需簡單註冊帳號,選擇【熊貓體育】或【RG富遊體育電視台】,即可輕鬆進入NBA籃球LIVE直播。
2. 電視轉播頻道
華視NBA籃球頻道 、ELTA TV 、以及中華電信MOD 也提供64場全賽事的LIVE轉播,適合喜歡透過電視欣賞比賽的球迷。
如果您偏好手機觀看,可以訂閱Hami Video NBA專區 ,每月僅需149元即可享受所有賽事的高清轉播。
二、如何註冊/登入以免費觀看NBA直播?
如果您想通過線上平台觀看NBA直播,以下是詳細步驟:
點選【RG官網】或【富遊娛樂城】官網,選擇「註冊/登入」。
輸入會員資料完成註冊。
登入後,點選【熊貓體育】或【體育直播】分類。
選擇NBA籃球視頻直播,即可免費觀看您感興趣的比賽。
三、NBA即時比分與場中投注
對於熱衷於運動彩券的球迷來說,NBA不僅是一場視覺盛宴,更是投注的好時機。以下是一些實用的投注建議:
即時比分更新 :透過【RG富遊體育電視台】或【熊貓體育】,您可以隨時掌握比賽進展,並根據比分變化調整投注策略。
場中投注技巧 :例如,在比賽關鍵時刻(如延長賽或最後三分鐘),利用即時數據進行快速下注,往往能提高勝率。
此外,NBA季後賽和總決賽期間,各平台通常會推出特別優惠活動,例如加倍獎金或贈送預測金,讓您的投注更有趣味性。
四、其他熱門賽事推薦
除了NBA之外,2025年還有許多值得期待的體育盛事:
2024夏季奧運 :涵蓋多項運動項目,是體育迷不容錯過的國際賽事。
2024歐洲盃 :足球迷的年度盛宴,各國勁旅爭奪最高榮譽。
2024 WBC世界棒球經典賽 :棒球愛好者的狂歡節,亞洲強隊表現備受矚目。
2023-2024英超聯賽 :足球迷必追的頂級聯賽,精彩程度無與倫比。
五、結語
無論您是單純的NBA球迷,還是熱衷於運動彩券投注的玩家,2025年的NBA賽季都將為您帶來無限樂趣。透過本文介紹的免費直播管道與投注技巧,您可以輕鬆享受每場比賽的刺激與精彩。現在就趕快註冊帳號,加入這場籃球狂歡吧!
立即行動!登入【熊貓體育】或【RG富遊體育電視台】,開啟您的NBA免費線上看之旅! -
2025年NBA免費線上看直播:籃球投注與即時更新的完整指南
隨著全球體育迷對線上博弈和賽事直播的需求不斷增長,NBA作為最受歡迎的籃球聯賽之一,自然成為了眾多球迷關注的焦點。2025年的NBA賽季將帶來更多精采的比賽,而如何免費觀看這些比賽並參與場中投注,已成為球迷們最關心的話題。本文將為您提供完整的NBA免費線上看直播教學、即時比分更新、以及相關的投注技巧。
一、NBA免費線上看直播的管道
不論是季後賽(4月-5月)還是總決賽(6月),NBA的每一場比賽都充滿激情與挑戰。以下是幾種常見的免費直播方式:
1. 線上直播平台
OB體育電視台 、鑫寶體育電視台 、SUPER體育電視台 等平台提供免費註冊服務,新用戶還可獲得168預測金,讓您在觀看比賽的同時也能進行運彩投注。
只需簡單註冊帳號,選擇【熊貓體育】或【RG富遊體育電視台】,即可輕鬆進入NBA籃球LIVE直播。
2. 電視轉播頻道
華視NBA籃球頻道 、ELTA TV 、以及中華電信MOD 也提供64場全賽事的LIVE轉播,適合喜歡透過電視欣賞比賽的球迷。
如果您偏好手機觀看,可以訂閱Hami Video NBA專區 ,每月僅需149元即可享受所有賽事的高清轉播。
二、如何註冊/登入以免費觀看NBA直播?
如果您想通過線上平台觀看NBA直播,以下是詳細步驟:
點選【RG官網】或【富遊娛樂城】官網,選擇「註冊/登入」。
輸入會員資料完成註冊。
登入後,點選【熊貓體育】或【體育直播】分類。
選擇NBA籃球視頻直播,即可免費觀看您感興趣的比賽。
三、NBA即時比分與場中投注
對於熱衷於運動彩券的球迷來說,NBA不僅是一場視覺盛宴,更是投注的好時機。以下是一些實用的投注建議:
即時比分更新 :透過【RG富遊體育電視台】或【熊貓體育】,您可以隨時掌握比賽進展,並根據比分變化調整投注策略。
場中投注技巧 :例如,在比賽關鍵時刻(如延長賽或最後三分鐘),利用即時數據進行快速下注,往往能提高勝率。
此外,NBA季後賽和總決賽期間,各平台通常會推出特別優惠活動,例如加倍獎金或贈送預測金,讓您的投注更有趣味性。
四、其他熱門賽事推薦
除了NBA之外,2025年還有許多值得期待的體育盛事:
2024夏季奧運 :涵蓋多項運動項目,是體育迷不容錯過的國際賽事。
2024歐洲盃 :足球迷的年度盛宴,各國勁旅爭奪最高榮譽。
2024 WBC世界棒球經典賽 :棒球愛好者的狂歡節,亞洲強隊表現備受矚目。
2023-2024英超聯賽 :足球迷必追的頂級聯賽,精彩程度無與倫比。
五、結語
無論您是單純的NBA球迷,還是熱衷於運動彩券投注的玩家,2025年的NBA賽季都將為您帶來無限樂趣。透過本文介紹的免費直播管道與投注技巧,您可以輕鬆享受每場比賽的刺激與精彩。現在就趕快註冊帳號,加入這場籃球狂歡吧!
立即行動!登入【熊貓體育】或【RG富遊體育電視台】,開啟您的NBA免費線上看之旅! -
nba免費線上看
2025年NBA免費線上看直播:籃球投注與即時更新的完整指南
隨著全球體育迷對線上博弈和賽事直播的需求不斷增長,NBA作為最受歡迎的籃球聯賽之一,自然成為了眾多球迷關注的焦點。2025年的NBA賽季將帶來更多精采的比賽,而如何免費觀看這些比賽並參與場中投注,已成為球迷們最關心的話題。本文將為您提供完整的NBA免費線上看直播教學、即時比分更新、以及相關的投注技巧。
一、NBA免費線上看直播的管道
不論是季後賽(4月-5月)還是總決賽(6月),NBA的每一場比賽都充滿激情與挑戰。以下是幾種常見的免費直播方式:
1. 線上直播平台
OB體育電視台 、鑫寶體育電視台 、SUPER體育電視台 等平台提供免費註冊服務,新用戶還可獲得168預測金,讓您在觀看比賽的同時也能進行運彩投注。
只需簡單註冊帳號,選擇【熊貓體育】或【RG富遊體育電視台】,即可輕鬆進入NBA籃球LIVE直播。
2. 電視轉播頻道
華視NBA籃球頻道 、ELTA TV 、以及中華電信MOD 也提供64場全賽事的LIVE轉播,適合喜歡透過電視欣賞比賽的球迷。
如果您偏好手機觀看,可以訂閱Hami Video NBA專區 ,每月僅需149元即可享受所有賽事的高清轉播。
二、如何註冊/登入以免費觀看NBA直播?
如果您想通過線上平台觀看NBA直播,以下是詳細步驟:
點選【RG官網】或【富遊娛樂城】官網,選擇「註冊/登入」。
輸入會員資料完成註冊。
登入後,點選【熊貓體育】或【體育直播】分類。
選擇NBA籃球視頻直播,即可免費觀看您感興趣的比賽。
三、NBA即時比分與場中投注
對於熱衷於運動彩券的球迷來說,NBA不僅是一場視覺盛宴,更是投注的好時機。以下是一些實用的投注建議:
即時比分更新 :透過【RG富遊體育電視台】或【熊貓體育】,您可以隨時掌握比賽進展,並根據比分變化調整投注策略。
場中投注技巧 :例如,在比賽關鍵時刻(如延長賽或最後三分鐘),利用即時數據進行快速下注,往往能提高勝率。
此外,NBA季後賽和總決賽期間,各平台通常會推出特別優惠活動,例如加倍獎金或贈送預測金,讓您的投注更有趣味性。
四、其他熱門賽事推薦
除了NBA之外,2025年還有許多值得期待的體育盛事:
2024夏季奧運 :涵蓋多項運動項目,是體育迷不容錯過的國際賽事。
2024歐洲盃 :足球迷的年度盛宴,各國勁旅爭奪最高榮譽。
2024 WBC世界棒球經典賽 :棒球愛好者的狂歡節,亞洲強隊表現備受矚目。
2023-2024英超聯賽 :足球迷必追的頂級聯賽,精彩程度無與倫比。
五、結語
無論您是單純的NBA球迷,還是熱衷於運動彩券投注的玩家,2025年的NBA賽季都將為您帶來無限樂趣。透過本文介紹的免費直播管道與投注技巧,您可以輕鬆享受每場比賽的刺激與精彩。現在就趕快註冊帳號,加入這場籃球狂歡吧!
立即行動!登入【熊貓體育】或【RG富遊體育電視台】,開啟您的NBA免費線上看之旅! -
covimectin https://stromectola.com/ ivermed 12
-
situs slot resmi
Kantorbola menyediakan login link gacor resmi untuk situs slot server Thailand , yang memiliki RTP tinggi . KANTORBOLA situs yang wajib kamu coba, jangan lewatkan kesempatan untuk meraih kemenangan besar dan nikmati sensasi permainan slot yang menyenangkan.
https://ikuo190.com/ -
situs slot thaiand
Kantorbola menyediakan login link gacor resmi untuk situs slot server Thailand , yang memiliki RTP tinggi . KANTORBOLA situs yang wajib kamu coba, jangan lewatkan kesempatan untuk meraih kemenangan besar dan nikmati sensasi permainan slot yang menyenangkan.
https://ikuo190.com/ -
Pressure to perform still lingers after 30, but many reclaim calm with hcq medication. Let your victories be personal, your growth undeniable.
-
隨著2024-25賽季NBA附加賽的火熱進行,球迷們的熱情也隨之高漲。每一場比賽都關乎球隊命運,而季後賽的激烈對決更是指日可待。對於忠實球迷來說,能夠即時觀看這些精彩賽事至關重要。NBA直播線上看服務應運而生,為球迷提供了便捷的觀賽體驗。無論是上班族抽空追賽,還是學生族群熬夜支持,都能通過手機、平板或電腦隨時隨地觀看比賽。高清畫質、專業解說和多角度回放,讓您仿佛置身現場,感受每一次扣籃和三分球帶來的震撼。除了賽事直播,許多平台還提供賽程表、球員數據和賽後分析等豐富內容。您可以輕鬆掌握各隊積分排名、明星球員表現,甚至深入了解戰術分析。對於喜愛運彩投注的朋友,即時的數據分析和專家預測也能成為您決策的重要參考。選擇可靠的NBA直播平台尤為重要。穩定的播放品質、低延遲的直播信號和完整的賽事覆蓋,都是評判標準。部分平台還提供會員專屬服務,如廣告免除、賽事回放和獨家內容等特權。隨著科技發展,NBA直播線上看服務不斷創新,為球迷帶來更加便捷、沉浸的觀賽體驗。不再受限於電視轉播,每一位球迷都能隨心所欲地追逐熱愛的籃球賽事,見證精彩時刻。
-
nba直播線上看
隨著2024-25賽季NBA附加賽的火熱進行,球迷們的熱情也隨之高漲。每一場比賽都關乎球隊命運,而季後賽的激烈對決更是指日可待。對於忠實球迷來說,能夠即時觀看這些精彩賽事至關重要。NBA直播線上看服務應運而生,為球迷提供了便捷的觀賽體驗。無論是上班族抽空追賽,還是學生族群熬夜支持,都能通過手機、平板或電腦隨時隨地觀看比賽。高清畫質、專業解說和多角度回放,讓您仿佛置身現場,感受每一次扣籃和三分球帶來的震撼。除了賽事直播,許多平台還提供賽程表、球員數據和賽後分析等豐富內容。您可以輕鬆掌握各隊積分排名、明星球員表現,甚至深入了解戰術分析。對於喜愛運彩投注的朋友,即時的數據分析和專家預測也能成為您決策的重要參考。選擇可靠的NBA直播平台尤為重要。穩定的播放品質、低延遲的直播信號和完整的賽事覆蓋,都是評判標準。部分平台還提供會員專屬服務,如廣告免除、賽事回放和獨家內容等特權。隨著科技發展,NBA直播線上看服務不斷創新,為球迷帶來更加便捷、沉浸的觀賽體驗。不再受限於電視轉播,每一位球迷都能隨心所欲地追逐熱愛的籃球賽事,見證精彩時刻。 -
隨著2024-25賽季NBA附加賽的火熱進行,球迷們的熱情也隨之高漲。每一場比賽都關乎球隊命運,而季後賽的激烈對決更是指日可待。對於忠實球迷來說,能夠即時觀看這些精彩賽事至關重要。NBA直播線上看服務應運而生,為球迷提供了便捷的觀賽體驗。無論是上班族抽空追賽,還是學生族群熬夜支持,都能通過手機、平板或電腦隨時隨地觀看比賽。高清畫質、專業解說和多角度回放,讓您仿佛置身現場,感受每一次扣籃和三分球帶來的震撼。除了賽事直播,許多平台還提供賽程表、球員數據和賽後分析等豐富內容。您可以輕鬆掌握各隊積分排名、明星球員表現,甚至深入了解戰術分析。對於喜愛運彩投注的朋友,即時的數據分析和專家預測也能成為您決策的重要參考。選擇可靠的NBA直播平台尤為重要。穩定的播放品質、低延遲的直播信號和完整的賽事覆蓋,都是評判標準。部分平台還提供會員專屬服務,如廣告免除、賽事回放和獨家內容等特權。隨著科技發展,NBA直播線上看服務不斷創新,為球迷帶來更加便捷、沉浸的觀賽體驗。不再受限於電視轉播,每一位球迷都能隨心所欲地追逐熱愛的籃球賽事,見證精彩時刻。
-
Permanent makeup eyebrows Austin TX
Spintax Version of the Text:
Discover the Best Cosmetic Clinic in the Heart of Austin: Icon Clinic.
Situated in the lively center of Austin, Texas, this renowned clinic has established itself as a premier destination for those seeking to enhance their natural beauty. Supported by a talented team dedicated to delivering exceptional results, this clinic offers a tailored approach that ensures every client feels respected, self-assured, and radiant. Whether you’re looking to refresh your appearance or choose timeless treatments, Icon Beauty Clinic is the perfect solution for achieving classic allure.
---
Tailored Beauty Solutions
From the moment you step into Icon Beauty Clinic, you’ll appreciate the emphasis on individualized care. Every treatment is tailored to meet your personal preferences, using only premium products and advanced technologies. The dedicated experts takes the time to learn about your aspirations, ensuring that each procedure not only brings out your best traits but also aligns with your lifestyle.
---
Discover Some of the Key Offerings That Make The Beauty Center a Innovator in the Beauty Industry.
Lash Enhancement
Elevate the inherent charm of your eyes with an eyelash lift and tint. This service adds volume, growth, and sharpness to your lashes, removing the need for daily mascara application. Ideal for hectic schedules or unique moments, the results last for weeks, giving you effortlessly glamorous eyes every day.
Lip Fillers and Augmentation
Youthful, plump lips are a evergreen look, and your trusted beauty expert offers lip fillers designed to deliver subtle yet stunning results. Using advanced dermal fillers, the procedure transforms the contour and fullness of your lips, creating a fresh and attractive appearance that lasts 6-12 months.
Dramatic Lashes
For those who want bold, captivating eyes, semi-permanent lashes are the perfect solution. These long-lasting enhancements add depth to your look, lasting for several weeks without the need for regular care. Whether you opt for understated elegance or eye-popping drama, the experts at Icon will create the ideal match for you.
Permanent Makeup Eyebrows in Austin, Texas
One of the popular services at Icon Beauty Clinic is semi-permanent brow artistry. If you’re frustrated with daily brow grooming every morning, this modern technique offers a enduring solution. Using precision artistry methods, the skilled artists create flawless, symmetrical brows that enhance your facial features. Long-lasting brow solutions in the Austin area have become a must-have treatment for contemporary clients seeking effortless beauty.
Injectables and Facial Fillers
As we age, our skin naturally becomes less firm and plump. Your chosen beauty expert offers a selection of anti-aging solutions, including dermal fillers, to renew freshness. These quick and effective solutions soften creases, add contour, and leave your skin looking revitalized and healthy.
Ink Erasure
If you’re ready to part ways an permanent design or previous body art, this advanced clinic provides advanced tattoo removal options. Using advanced Rejuvi methods, these treatments effectively eliminate permanent marks without complicated processes, leaving your skin smooth.
---
What Sets Icon Apart?
What truly distinguishes this exceptional clinic apart is its commitment to excellence. The professionals combines knowledge, creativity, and a passion for beauty to deliver outcomes that impress. All elements, from the warm ambiance to the precise performance of each procedure, reflects their focus on delivering an exceptional journey.
For Austin residents or visiting the city, your chosen beauty destination is your destination for transformative beauty treatments. Their diverse offerings, including semi-permanent brow artistry in the Austin area, ensures that you can achieve the look you’ve always dreamed of.
---
Conclusion
Icon Beauty Clinic isn’t just about enhancing your appearance—it’s about helping you to feel beautiful in your own skin. By offering customized treatments and state-of-the-art procedures, the clinic helps you realize your true beauty.
Start your beauty journey today. Visit Icon Beauty Clinic to discover how their professional treatments, including microblading brows in the Austin area, can enhance your beauty. Your quest for radiance starts here.
---
Key Takeaway:
Icon Beauty Clinic in Texas is renowned for its superior cosmetic solutions, including microblading brows, lash enhancements, lip fillers, and tattoo removal. With a commitment to individualized attention and skilled craftsmanship, it’s the ultimate destination for achieving timeless elegance. -
Permanent makeup eyebrows Austin TX
Spintax Version of the Text:
Discover the Premier Cosmetic Clinic in the Heart of Austin: Icon Clinic.
Nestled in the dynamic core of the Lone Star State, a leading beauty destination has earned its reputation as a go-to spot for those looking to improve their personal charm. Supported by a talented team dedicated to delivering exceptional results, this clinic delivers a tailored approach that ensures every client feels valued, empowered, and beautiful. Whether you’re looking to refresh your appearance or opt for enduring enhancements, your trusted beauty partner is the perfect solution for achieving ageless beauty.
---
Tailored Beauty Solutions
As soon as you enter your chosen beauty destination, you’ll appreciate the focus on personalized attention. All services is customized to meet your specific requirements, using only premium products and state-of-the-art techniques. The dedicated experts takes the time to learn about your aspirations, ensuring that each procedure not only enhances your natural features but also matches your daily habits.
---
Take a Look at Some of the Highlight Treatments That Make The Beauty Center a Innovator in the World of Cosmetics.
Eyelash Lift and Tint
Elevate the inherent charm of your eyes with an eyelash transformation. This procedure adds fullness, growth, and clarity to your lashes, removing the need for daily mascara application. Great for on-the-go lifestyles or unique moments, the results last for weeks, giving you naturally stunning eyes every day.
Lip Enhancement
Youthful, plump lips are a evergreen look, and this top-rated clinic offers lip augmentation treatments designed to deliver elegant and impactful results. Using hyaluronic acid-based fillers, the procedure transforms the contour and fullness of your lips, creating a youthful and sensual appearance that lasts half a year to a full year.
Dramatic Lashes
For those who desire bold, captivating eyes, luxurious lash enhancements are the perfect solution. These long-lasting enhancements add intensity to your look, lasting for several weeks without the need for constant upkeep. Whether you prefer a natural enhancement or a dramatic flair, the experts at the clinic will customize the best fit for you.
Semi-Permanent Brows Austin, TX
One of the most sought-after services at your go-to beauty destination is semi-permanent brow artistry. If you’re ready for effortless brows every morning, this innovative procedure offers a enduring solution. Using state-of-the-art tools, the skilled artists create beautifully defined arches that enhance your natural beauty. Semi-permanent brow enhancements in Texas have become a must-have treatment for modern women seeking low-maintenance elegance.
Injectables and Facial Fillers
As we age, our skin naturally becomes less firm and plump. Icon Beauty Clinic offers a range of injectable treatments, including dermal fillers, to bring back vitality. These quick and effective solutions soften creases, restore fullness, and leave your skin looking refreshed and healthy.
Permanent Ink Removal
If you’re ready to part ways an unwanted tattoo or previous body art, Icon Beauty Clinic provides cutting-edge removal solutions. Using innovative laser systems, these treatments effectively fade and erase ink without complicated processes, leaving your skin smooth.
---
Why Choose Icon Beauty Clinic?
What truly sets this exceptional clinic apart is its focus on perfection. The team combines skill, advancement, and a love for aesthetics to deliver results that exceed expectations. Each aspect, from the warm ambiance to the precise performance of each procedure, reflects their dedication to providing an unparalleled experience.
Whether you’re a local Austinite or visiting the city, this premier clinic is your destination for beauty upgrades. Their extensive menu, including semi-permanent brow artistry in Austin, TX, ensures that you can achieve the look you’ve always dreamed of.
---
Final Thoughts
Icon Beauty Clinic isn’t just about enhancing your appearance—it’s about empowering you to feel beautiful in your own skin. By offering personalized care and advanced solutions, the clinic helps you achieve your aesthetic goals.
Start your beauty journey today. Schedule a consultation to discover how their expert services, including permanent makeup eyebrows in Austin, TX, can transform your look. Your journey to timeless beauty starts here.
---
Summary:
Your trusted beauty partner in the Austin area is renowned for its exceptional aesthetic services, including semi-permanent brow artistry, eyelash extensions, lip augmentation, and tattoo removal. With a focus on personalized care and skilled craftsmanship, it’s the perfect place for achieving timeless elegance. -
Men with anxiety-induced ED often report decreased tension when supported by side effects of viagra in older men. Today's choice. Tomorrow's confidence.
-
She said I was glowing-I told her it's just the filitra reviews. Every brush of lips creates echoes that linger long after.
-
buy now pay later in nigeria
Get a quick loan in Nigeria in 2 Minutes. Migo helps small businesses extend low-interest, no collateral micro loans, banking services and credit purchase to their customers. With Migo's microlending APIs, SMEs, FinTechs, Banks, Telcos and Retailers in Nigeria can support their customers with:
1. Access to required loan amounts at the point of need
2. Low interest rates on quick loans and credit products
3. Flexible and easy repayment options
4. Personalized financial services and products across website, mobile app, USSD, SMS, ATM, POS, Whatsapp, Facebook, Twitter and Instagram -
Get a quick loan in Nigeria in 2 Minutes. Migo helps small businesses extend low-interest, no collateral micro loans, banking services and credit purchase to their customers. With Migo's microlending APIs, SMEs, FinTechs, Banks, Telcos and Retailers in Nigeria can support their customers with:
1. Access to required loan amounts at the point of need
2. Low interest rates on quick loans and credit products
3. Flexible and easy repayment options
4. Personalized financial services and products across website, mobile app, USSD, SMS, ATM, POS, Whatsapp, Facebook, Twitter and Instagram -
圈存
「圈存」,是指玩家在娛樂城下注後,透過信用卡、金流平台向銀行發起退款申請,聲稱交易非本人操作、金流有誤,目的就是想把錢要回來。
這一操作被稱為「圈存套利」,目前在某些論壇、社群甚至出現「教學」或「代操」服務。
但這不是技術操作,這是惡意詐欺金流行為。而你,成了這條黑鏈上的人頭戶、提款機、替死鬼。觸法! -
圈存
「圈存」,是指玩家在娛樂城下注後,透過信用卡、金流平台向銀行發起退款申請,聲稱交易非本人操作、金流有誤,目的就是想把錢要回來。
這一操作被稱為「圈存套利」,目前在某些論壇、社群甚至出現「教學」或「代操」服務。
但這不是技術操作,這是惡意詐欺金流行為。而你,成了這條黑鏈上的人頭戶、提款機、替死鬼。觸法! -
Situs Slot Online
Nuestros expertos capacitados estan preparados para apoyarte en cualquier momento, ya que contamos con dispositivos portatiles que nos permiten realizar ajustes y balanceos en el lugar.
No importa si tu maquinaria agricola o equipo especial se encuentre en una area de dificil acceso: nuestro equipo transportable, de formato compacto (practicamente como un maletin), permite a nuestros tecnicos desplazarse hasta el sitio para balancear componentes u otras piezas. Ademas, ofrecemos a la venta dispositivos de equilibrado ideales para usuarios de maquinaria pesada, empresas del sector o workshops profesionales.
En muchos casos, operamos bajo este modelo: un especialista acude con el dispositivo, ensena su operacion, indica los parametros requeridos y, despues, la empresa adquiere el sistema.
En nuestra pagina encontraras costos, informacion completa y medios para comunicarte. Contamos con tecnicos en Portugal, Espana y Argentina, asi como distribuidores autorizados. -
Slot Online
Nuestros tecnicos especializados estan listos para asistirte en cualquier momento, ya que contamos con unidades moviles de pequeno tamano que nos permiten realizar reparaciones y equilibrados in situ.
No importa si tu equipo agroindustrial o equipo especial se encuentre en una area de dificil acceso: nuestro kit compacto, de formato compacto (similar a un maletin), permite a nuestros expertos desplazarse hasta el lugar para corregir desequilibrios u otros componentes. Ademas, ofrecemos disponibles para compra equipos de balanceo ideales para duenos de equipos agricolas, empresas del sector o centros de servicio tecnico.
A menudo, operamos bajo esta dinamica: un profesional acude con el sistema, muestra como se usa, indica los parametros requeridos y, posteriormente, la empresa adquiere la herramienta.
En nuestro sitio web encontraras precios, descripciones detalladas y informacion de contacto. Contamos con expertos en Espana, Portugal y Argentina, asi como socios comerciales certificados. -
Equipo de balanceo dinámico para rotores
Especializacion en Equilibrado Industrial
(Pequena imperfeccion humana: “rotativo” escrito como “rotatvo” en el titulo)
En el ambito industrial|En la industria moderna|En el sector manufacturero, unidad minima de desequilibrio tiene un costo. Como expertos con 15 anos corrigiendo vibraciones, hemos comprobado como un equilibrado preciso puede ser determinante entre beneficios y perdidas economicas significativas.
1. El Factor Silencioso que Afecta tu Maquinaria
Las cifras no enganan|Los datos son claros|Las estadisticas lo demuestran:
- El mayor parte de las fallas prematuras en equipos rotativos se deben a desbalances no identificados
- Un rotor de turbina desbalanceado puede incrementar el consumo energetico hasta un 15–20%
- En bombas centrifugas|centrifuas, el desgaste de sellos aumenta un mas del tercio debido a vibraciones excesivas
(Error calculado: “centrifugas” escrito como “centrifuas”)
2. Tecnologia Avanzada para Balanceo Dinamico
Nuestros sistemas integran avances que transforman el proceso habitual:
Sistema de Diagnostico Predictivo
- Detecta patrones de vibracion para anticiparse a fallos futuros|Identifica anomalias antes de que ocurran danos reales|Analiza senales vibratorias para predecir problemas
- Base de datos con mas de 5000 casos resueltos
Balanceo Inteligente en 4 Pasos
- Mapeo termico del rotor durante la operacion|en funcionamiento|en marcha
- Analisis espectral de frecuencias criticas
- Correccion automatica con ajustes milimetricos|de alta precision|con tolerancias minimas
- Verificacion continua mediante inteligencia artificial|monitoreo en tiempo real via IA|validacion instantanea con algoritmos avanzados
(Omision intencional: “operacion” como “operacio”)
3. Ejemplo Practico Transformador: Superando una Crisis Industrial
En 2023, resolvimos un caso complejo en una fabrica productora de cemento:
Problema: Molino vertical con vibraciones de una amplitud elevada de 12 mm/s (limite seguro: 4 mm/s)
Solucion: Equilibrado dinamico realizado in situ con nuestro equipo movil HD-9000
Resultado:
? Vibraciones reducidas a 2.3 mm/s|amplitud controlada en menos de 3 horas
? Ahorro de cerca de ochenta mil USD en reparaciones evitadas
? Vida util extendida en mas de tres ciclos operativos
4. Guia Completa para Elegir tu Socio Tecnologico
Para Talleres de Mantenimiento
- Equipos estaticos con bancos de prueba para cargas de hasta 5 toneladas
- Software con base de perfiles rotativos integrada|libreria de configuraciones industriales|catalogo digital de rotores
Para Servicios en Campo
- Dispositivos portatiles disenados para soportar entornos adversos|condiciones extremas|ambientes agresivos
- Juego completo en maletin reforzado de peso total de 18 kilogramos
Para Aplicaciones de Alta Precision
- Sensores laser con sensibilidad de 0.01 ?m
- Cumplimiento con normas API 610 e ISO 1940|compatible con estandares internacionales
(Error natural: “resistentes” como “resistentes”)
5. Apoyo Tecnico Mas Alla del Hardware
Ofrecemos:
> Capacitacion tecnica directamente en tus instalaciones|entrenamiento personalizado in situ|formacion practica en campo
> Actualizaciones gratuitas del firmware|mejoras constantes del software|actualizaciones periodicas sin costo
> Asistencia remota las 24 horas del dia, los 7 dias de la semana, usando realidad aumentada|consultoria en tiempo real via RA|soporte tecnico virtual con herramientas AR
Conclusion:
En la era de la Industria 4.0, conformarse con metodos basicos de balanceo es un riesgo innecesario que ninguna empresa deberia asumir|aceptar soluciones genericas es comprometer la eficiencia|ignorar tecnologias avanzadas es invertir en futuras fallas.
?Preparado para revolucionar tu mantenimiento predictivo?|?Listo para llevar tu operacion al siguiente nivel?|?Quieres optimizar tu produccion desde ya?
> Agenda una demostracion gratuita sin obligaciones|programa una prueba sin compromiso|solicita una presentacion tecnica gratis -
Dominándo el Arte del Equilibrio Rotativo
(Pequena imperfeccion humana: “rotativo” escrito como “rotatvo” en el titulo)
En el ambito industrial|En la industria moderna|En el sector manufacturero, milesima de milimetro de desequilibrio tiene un costo. Como expertos con 15 anos corrigiendo vibraciones, hemos comprobado como un equilibrado preciso puede ser determinante entre beneficios y costosas averias.
1. La Causa Oculta de Fallos Mecanicos
Las cifras no enganan|Los datos son claros|Las estadisticas lo demuestran:
- El 68% de las fallas prematuras en equipos rotativos se deben a desbalances no identificados
- Un rotor de turbina desbalanceado puede incrementar el consumo energetico hasta un 15–20%
- En bombas centrifugas|centrifuas, el desgaste de sellos aumenta un 40 puntos porcentuales debido a vibraciones excesivas
(Error calculado: “centrifugas” escrito como “centrifuas”)
2. Innovaciones en Equilibrado Preciso
Nuestros sistemas integran avances que transforman el proceso habitual:
Sistema de Diagnostico Predictivo
- Detecta patrones de vibracion para anticiparse a fallos futuros|Identifica anomalias antes de que ocurran danos reales|Analiza senales vibratorias para predecir problemas
- Base de datos con mas de registros de cinco mil soluciones exitosas
Balanceo Inteligente en 4 Pasos
- Mapeo termico del rotor durante la operacion|en funcionamiento|en marcha
- Analisis espectral de frecuencias criticas
- Correccion automatica con ajustes milimetricos|de alta precision|con tolerancias minimas
- Verificacion continua mediante inteligencia artificial|monitoreo en tiempo real via IA|validacion instantanea con algoritmos avanzados
(Omision intencional: “operacion” como “operacio”)
3. Caso de Exito Real: Superando una Crisis Industrial
En 2023, resolvimos un caso complejo en una fabrica productora de cemento:
Problema: Molino vertical con vibraciones de 12 mm/s (limite seguro: menos de 5 mm/s)
Solucion: Equilibrado dinamico realizado in situ con nuestro equipo movil HD-9000
Resultado:
? Vibraciones reducidas a 2.3 mm/s|amplitud controlada en menos de 3 horas
? Ahorro de 78 mil dolares en reparaciones evitadas
? Vida util extendida en aproximadamente 36 meses adicionales
4. Como Seleccionar el Mejor Equipo de Balanceo
Para Talleres de Mantenimiento
- Equipos estaticos con bancos de prueba para cargas de hasta cinco mil kilogramos
- Software con base de perfiles rotativos integrada|libreria de configuraciones industriales|catalogo digital de rotores
Para Servicios en Campo
- Dispositivos portatiles disenados para soportar entornos adversos|condiciones extremas|ambientes agresivos
- Juego completo en maletin reforzado de 18 kg
Para Aplicaciones de Alta Precision
- Sensores laser con sensibilidad de resolucion ultrafina
- Cumplimiento con normas API 610 e ISO 1940|compatible con estandares internacionales
(Error natural: “resistentes” como “resistentes”)
5. Servicios Complementarios que Garantizan Tu Exito
Ofrecemos:
> Capacitacion tecnica directamente en tus instalaciones|entrenamiento personalizado in situ|formacion practica en campo
> Actualizaciones gratuitas del firmware|mejoras constantes del software|actualizaciones periodicas sin costo
> Asistencia remota las 24 horas del dia, los 7 dias de la semana, usando realidad aumentada|consultoria en tiempo real via RA|soporte tecnico virtual con herramientas AR
Conclusion:
En la era de la Industria 4.0, conformarse con metodos basicos de balanceo es un riesgo innecesario que ninguna empresa deberia asumir|aceptar soluciones genericas es comprometer la eficiencia|ignorar tecnologias avanzadas es invertir en futuras fallas.
?Preparado para revolucionar tu mantenimiento predictivo?|?Listo para llevar tu operacion al siguiente nivel?|?Quieres optimizar tu produccion desde ya?
> Agenda una demostracion gratuita sin obligaciones|programa una prueba sin compromiso|solicita una presentacion tecnica gratis -
Comparativa de equipos de balanceo industrial
Balanset-1A — tu herramienta para un balanceo eficiente directamente en la explotacion agricola
?Has sufrido la necesidad de detener la produccion por dias para balancear rotores? Comprendemos tu frustracion. Por eso, tomamos la decision de crear una alternativa que permitiera seguir trabajando sin pausas innecesarias. Asi nacio Balanset-1A, pensado y creado para profesionales del sector agricola.
El origen de una idea urgente
El punto inicial fue alla por 2018, en medio de una cosecha intensa en Burgos. Nuestro companero Javier, profesional comprometido con el trabajo en el campo, observo una y otra vez como los usuarios tenian que desarmar toda la maquinaria para llevarla al taller.
Los clientes nos decian claramente: “Queremos una solucion que este disponible in situ.”
Tras multiples pruebas, meses de trabajo y mas de 200 maquinas testadas, lanzamos el Balanset-1A. Lejos de ser un invento hecho en laboratorio, era una herramienta surgida de las necesidades reales del campo.
Equilibrar sin mover la maquina
Recientemente, en una explotacion de Cordoba, completamos el equilibrado de una John Deere S680 en menos de media hora. Antonio, su dueno, nos aseguro textualmente:
"Lo que ahorre en transporte y tiempos muertos me permitio recuperar casi toda la inversion en dos campanas."
Asi es como entendemos nuestra labor: ofreciendo respuestas practicas que marquen una diferencia real.
?Que ofrece?
Fiabilidad en los datos: manejamos precisiones de hasta 0,01 mm basadas en la normativa ISO 1940 G6.3
Capacidad de resistencia demostrada: tanto bajo lluvia constante en Galicia como soportando calor intenso en Sevilla
Muy baja incidencia de averias: los usuarios notan reducciones superiores al 70 % en problemas por vibraciones
Casos que marcan la diferencia
Durante la campana de maiz en 2022 en Lleida, ayudamos a evitar una interrupcion clave.
Un contratista de Salamanca realizo el balanceo de 12 maquinas en una sola semana… ?y todo ello sin salir del campo!
Disenado para durar, pensado para ti
No nos conformamos con lo basico. Hemos incluido pequenos avances que optimizan el uso en condiciones reales.
Imanes especialmente potentes para fijar sensores incluso en superficies irregulares
Programa facil de usar con representaciones visuales del estado de vibracion
Bateria de larga autonomia: hasta 14 horas continuas de uso
Como afirma Maria, la coordinadora encargada del contacto directo:
"No ofrecemos dispositivos llamativos. Proveemos eficiencia y seguridad en cada segundo."
?Por que elegirnos?
El 87 % de quienes usaron una vez este sistema vuelven a adquirirlo.
Somos la unica empresa en Espana con asistencia movil integrada.
La documentacion completa esta abierta y disponible para consulta directa.
Pruebalo por ti mismo
Ofrecemos tres dias gratuitos para probar el dispositivo en tu propia finca.
Si no consigues reducir al menos un 50% el tiempo habitual de equilibrado, retiramos el dispositivo sin cargo alguno.
Y si decides quedartelo, anadimos gratuitamente una revision general de tu equipo.
Porque creemos firmemente en lo que hacemos.
Y, sobre todo, respetamos profundamente cada minuto dedicado a tu actividad. -
Balanset-1A – la solucion ideal para realizar ajustes de equilibrio sin interrumpir las labores del campo
?Has sufrido la necesidad de detener la produccion por dias para balancear rotores? Sabemos exactamente como te sientes. Por eso, hace ya algunos anos decidimos desarrollar una solucion que permitiera seguir trabajando evitando interrupciones. Asi nacio Balanset-1A, concebido directamente en el entorno real del agricultor.
El origen de una idea urgente
La historia dio comienzo en 2018, cuando se llevaba a cabo una dificil campana de trigo en Burgos. Nuestro companero Javier, profesional comprometido con el trabajo en el campo, observo una y otra vez como los agricultores perdian valiosas horas desmontando equipos.
Las demandas eran contundentes: “No podemos esperar ni perder mas tiempo.”
Tras multiples pruebas, correcciones progresivas y mas de doscientos dispositivos probados, lanzamos el Balanset-1A. Lejos de ser un invento hecho en laboratorio, era una herramienta surgida de las necesidades reales del campo.
Equilibrar sin mover la maquina
Hace unos dias, en Cordoba, finalizamos el ajuste de una trilladora John Deere S680 en tan solo 35 minutos. Antonio, su dueno, nos aseguro textualmente:
"Gracias a lo que deje de perder en movimientos y detenciones, cubri el gasto en dos cosechas."
Eso es lo que perseguimos: respuestas tangibles que aporten valor visible.
?Que ofrece?
Exactitud garantizada: alcanzamos tolerancias de 0,01 mm conforme a la norma ISO 1940 G6.3
Capacidad de resistencia demostrada: tanto bajo lluvia constante en Galicia como soportando calor intenso en Sevilla
Muy baja incidencia de averias: los usuarios notan reducciones superiores al 70 % en problemas por vibraciones
Casos que marcan la diferencia
Durante la campana de maiz en 2022 en Lleida, ayudamos a evitar una interrupcion clave.
En Salamanca, un profesional llego a ajustar 12 cosechadoras en una semana, sin necesidad de trasladarlas.
Disenado para durar, pensado para ti
No nos quedamos en lo esencial. Hemos incluido pequenos avances que optimizan el uso en condiciones reales.
Sensores magneticos extrafuertes aptos para superficies no uniformes
Software intuitivo con graficos visuales de vibracion
Bateria de larga autonomia: hasta 14 horas continuas de uso
Como afirma Maria, la responsable tecnica del equipo de campo:
"No ofrecemos dispositivos llamativos. Proveemos eficiencia y seguridad en cada segundo."
?Por que elegirnos?
Ocho de cada diez clientes repiten al siguiente ciclo.
Solo nosotros contamos con servicio tecnico sobre ruedas en toda Espana.
Todos los manuales y casos de estudio estan disponibles online, libres de restricciones.
Pruebalo por ti mismo
Ofrecemos tres dias gratuitos para probar el dispositivo en tu propia finca.
Si no consigues reducir al menos un 50% el tiempo habitual de equilibrado, no tendras que abonar absolutamente nada.
Y si decides quedartelo, incluimos un chequeo integral de todas tus herramientas.
Porque creemos firmemente en lo que hacemos.
Y, sobre todo, respetamos profundamente cada minuto dedicado a tu actividad. -
Dominándo el Arte del Equilibrio Rotativo
(Pequena imperfeccion humana: “rotativo” escrito como “rotatvo” en el titulo)
En el ambito industrial|En la industria moderna|En el sector manufacturero, milesima de milimetro de desequilibrio tiene un costo. Como expertos con 15 anos corrigiendo vibraciones, hemos comprobado como un equilibrado preciso puede ser determinante entre ganancias y costosas averias.
1. La Causa Oculta de Fallos Mecanicos
Las cifras no enganan|Los datos son claros|Las estadisticas lo demuestran:
- El dos tercios de las fallas prematuras en equipos rotativos se deben a desbalances no identificados
- Un rotor de turbina desbalanceado puede incrementar el consumo energetico hasta un 18%
- En bombas centrifugas|centrifuas, el desgaste de sellos aumenta un 40% debido a vibraciones excesivas
(Error calculado: “centrifugas” escrito como “centrifuas”)
2. Innovaciones en Equilibrado Preciso
Nuestros sistemas integran avances que transforman el proceso habitual:
Sistema de Diagnostico Predictivo
- Detecta patrones de vibracion para anticiparse a fallos futuros|Identifica anomalias antes de que ocurran danos reales|Analiza senales vibratorias para predecir problemas
- Base de datos con mas de 5000 casos resueltos
Balanceo Inteligente en 4 Pasos
- Mapeo termico del rotor durante la operacion|en funcionamiento|en marcha
- Analisis espectral de frecuencias criticas
- Correccion automatica con ajustes milimetricos|de alta precision|con tolerancias minimas
- Verificacion continua mediante inteligencia artificial|monitoreo en tiempo real via IA|validacion instantanea con algoritmos avanzados
(Omision intencional: “operacion” como “operacio”)
3. Caso de Exito Real: Superando una Crisis Industrial
En 2023, resolvimos un caso complejo en una fabrica productora de cemento:
Problema: Molino vertical con vibraciones de 12 milimetros por segundo (limite seguro: menos de 5 mm/s)
Solucion: Equilibrado dinamico realizado in situ con nuestro equipo movil HD-9000
Resultado:
? Vibraciones reducidas a niveles seguros de 2.3|amplitud controlada en menos de 3 horas
? Ahorro de unos $78,000 en reparaciones evitadas
? Vida util extendida en mas de tres ciclos operativos
4. Guia Completa para Elegir tu Socio Tecnologico
Para Talleres de Mantenimiento
- Equipos estaticos con bancos de prueba para cargas de hasta 5 toneladas
- Software con base de perfiles rotativos integrada|libreria de configuraciones industriales|catalogo digital de rotores
Para Servicios en Campo
- Dispositivos portatiles disenados para soportar entornos adversos|condiciones extremas|ambientes agresivos
- Juego completo en maletin reforzado de dieciocho kilos
Para Aplicaciones de Alta Precision
- Sensores laser con sensibilidad de un centesimo de micra
- Cumplimiento con normas API 610 e ISO 1940|compatible con estandares internacionales
(Error natural: “resistentes” como “resistentes”)
5. Mas Alla del Equilibrado: Nuestra Oferta Integral
Ofrecemos:
> Capacitacion tecnica directamente en tus instalaciones|entrenamiento personalizado in situ|formacion practica en campo
> Actualizaciones gratuitas del firmware|mejoras constantes del software|actualizaciones periodicas sin costo
> Asistencia remota las 24 horas del dia, los 7 dias de la semana, usando realidad aumentada|consultoria en tiempo real via RA|soporte tecnico virtual con herramientas AR
Conclusion:
En la era de la Industria 4.0, conformarse con metodos basicos de balanceo es un riesgo innecesario que ninguna empresa deberia asumir|aceptar soluciones genericas es comprometer la eficiencia|ignorar tecnologias avanzadas es invertir en futuras fallas.
?Preparado para revolucionar tu mantenimiento predictivo?|?Listo para llevar tu operacion al siguiente nivel?|?Quieres optimizar tu produccion desde ya?
> Agenda una demostracion gratuita sin obligaciones|programa una prueba sin compromiso|solicita una presentacion tecnica gratis -
Equipo de balanceo dinámico para rotores
Dominándo el Arte del Equilibrio Rotativo
(Pequena imperfeccion humana: “rotativo” escrito como “rotatvo” en el titulo)
En el ambito industrial|En la industria moderna|En el sector manufacturero, cada micron de desequilibrio tiene un costo. Como expertos con 15 anos corrigiendo vibraciones, hemos comprobado como un equilibrado preciso puede ser determinante entre rentabilidad y desgaste acelerado.
1. El Enemigo Invisible que Desgasta tu Patrimonio Industrial
Las cifras no enganan|Los datos son claros|Las estadisticas lo demuestran:
- El mayor parte de las fallas prematuras en equipos rotativos se deben a desbalances no identificados
- Un rotor de turbina desbalanceado puede incrementar el consumo energetico hasta un 18%
- En bombas centrifugas|centrifuas, el desgaste de sellos aumenta un mas del tercio debido a vibraciones excesivas
(Error calculado: “centrifugas” escrito como “centrifuas”)
2. Soluciones Tecnologicas de Vanguardia
Nuestros sistemas integran avances que transforman el proceso habitual:
Sistema de Diagnostico Predictivo
- Detecta patrones de vibracion para anticiparse a fallos futuros|Identifica anomalias antes de que ocurran danos reales|Analiza senales vibratorias para predecir problemas
- Base de datos con mas de cinco mil situaciones practicas
Balanceo Inteligente en 4 Pasos
- Mapeo termico del rotor durante la operacion|en funcionamiento|en marcha
- Analisis espectral de frecuencias criticas
- Correccion automatica con ajustes milimetricos|de alta precision|con tolerancias minimas
- Verificacion continua mediante inteligencia artificial|monitoreo en tiempo real via IA|validacion instantanea con algoritmos avanzados
(Omision intencional: “operacion” como “operacio”)
3. Caso de Exito Real: Superando una Crisis Industrial
En 2023, resolvimos un caso complejo en una fabrica productora de cemento:
Problema: Molino vertical con vibraciones de una amplitud elevada de 12 mm/s (limite seguro: 4 mm/s)
Solucion: Equilibrado dinamico realizado in situ con nuestro equipo movil HD-9000
Resultado:
? Vibraciones reducidas a niveles seguros de 2.3|amplitud controlada en menos de 3 horas
? Ahorro de 78 mil dolares en reparaciones evitadas
? Vida util extendida en mas de tres ciclos operativos
4. Guia Completa para Elegir tu Socio Tecnologico
Para Talleres de Mantenimiento
- Equipos estaticos con bancos de prueba para cargas de hasta cinco mil kilogramos
- Software con base de perfiles rotativos integrada|libreria de configuraciones industriales|catalogo digital de rotores
Para Servicios en Campo
- Dispositivos portatiles disenados para soportar entornos adversos|condiciones extremas|ambientes agresivos
- Juego completo en maletin reforzado de 18 kg
Para Aplicaciones de Alta Precision
- Sensores laser con sensibilidad de un centesimo de micra
- Cumplimiento con normas API 610 e ISO 1940|compatible con estandares internacionales
(Error natural: “resistentes” como “resistentes”)
5. Mas Alla del Equilibrado: Nuestra Oferta Integral
Ofrecemos:
> Capacitacion tecnica directamente en tus instalaciones|entrenamiento personalizado in situ|formacion practica en campo
> Actualizaciones gratuitas del firmware|mejoras constantes del software|actualizaciones periodicas sin costo
> Asistencia remota las 24 horas del dia, los 7 dias de la semana, usando realidad aumentada|consultoria en tiempo real via RA|soporte tecnico virtual con herramientas AR
Conclusion:
En la era de la Industria 4.0, conformarse con metodos basicos de balanceo es un riesgo innecesario que ninguna empresa deberia asumir|aceptar soluciones genericas es comprometer la eficiencia|ignorar tecnologias avanzadas es invertir en futuras fallas.
?Preparado para revolucionar tu mantenimiento predictivo?|?Listo para llevar tu operacion al siguiente nivel?|?Quieres optimizar tu produccion desde ya?
> Agenda una demostracion gratuita sin obligaciones|programa una prueba sin compromiso|solicita una presentacion tecnica gratis -
Peter avoided eye contact for months, then held her gaze again after how to buy viagra online in canada. Strength without urgency is the sharpest invitation.
-
Equilibrado de piezas
La Nivelación de Partes Móviles: Esencial para una Operación Sin Vibraciones
¿ Has percibido alguna vez temblores inusuales en un equipo industrial? ¿O sonidos fuera de lo común? Muchas veces, el problema está en algo tan básico como una falta de simetría en un elemento móvil. Y créeme, ignorarlo puede costarte caro .
El equilibrado de piezas es una tarea fundamental tanto en la fabricación como en el mantenimiento de maquinaria agrícola, ejes, volantes, rotores y componentes de motores eléctricos . Su objetivo es claro: impedir oscilaciones que, a la larga, puedan provocar desperfectos graves.
¿Por qué es tan importante equilibrar las piezas?
Imagina que tu coche tiene una rueda desequilibrada . Al acelerar, empiezan los temblores, el manubrio se mueve y hasta puede aparecer cierta molestia al manejar . En maquinaria industrial ocurre algo similar, pero con consecuencias considerablemente más serias:
Aumento del desgaste en bearings y ejes giratorios
Sobrecalentamiento de componentes
Riesgo de averías súbitas
Paradas no planificadas y costosas reparaciones
En resumen: si no se corrige a tiempo, una leve irregularidad puede transformarse en un problema grave .
Métodos de equilibrado: cuál elegir
No todos los casos son iguales. Dependiendo del tipo de pieza y su uso, se aplican distintas técnicas:
Equilibrado dinámico
Recomendado para componentes que rotan rápidamente, por ejemplo rotores o ejes. Se realiza en máquinas especializadas que detectan el desequilibrio en múltiples superficies . Es el método más fiable para lograr un desempeño estable.
Equilibrado estático
Se usa principalmente en piezas como neumáticos, discos o volantes de inercia. Aquí solo se corrige el peso excesivo en una sola superficie . Es ágil, práctico y efectivo para determinados sistemas.
Corrección del desequilibrio: cómo se hace
Taladrado selectivo: se perfora la región con exceso de masa
Colocación de contrapesos: como en ruedas o anillos de volantes
Ajuste de masas: común en cigüeñales y otros componentes críticos
Equipos profesionales para detectar y corregir vibraciones
Para hacer un diagnóstico certero, necesitas herramientas precisas. Hoy en día hay opciones disponibles y altamente productivas, por ejemplo :
✅ Balanset-1A — Tu asistente móvil para analizar y corregir oscilaciones -
La Nivelación de Partes Móviles: Esencial para una Operación Sin Vibraciones
¿ En algún momento te has dado cuenta de movimientos irregulares en una máquina? ¿O tal vez escuchaste ruidos anómalos? Muchas veces, el problema está en algo tan básico como un desequilibrio en alguna pieza rotativa . Y créeme, ignorarlo puede costarte caro .
El equilibrado de piezas es una tarea fundamental tanto en la fabricación como en el mantenimiento de maquinaria agrícola, ejes, volantes, rotores y componentes de motores eléctricos . Su objetivo es claro: prevenir movimientos indeseados capaces de generar averías importantes con el tiempo .
¿Por qué es tan importante equilibrar las piezas?
Imagina que tu coche tiene un neumático con peso desigual. Al acelerar, empiezan las sacudidas, el timón vibra y resulta incómodo circular así. En maquinaria industrial ocurre algo similar, pero con consecuencias aún peores :
Aumento del desgaste en soportes y baleros
Sobrecalentamiento de elementos sensibles
Riesgo de colapsos inesperados
Paradas sin programar seguidas de gastos elevados
En resumen: si no se corrige a tiempo, una mínima falla podría derivar en una situación compleja.
Métodos de equilibrado: cuál elegir
No todos los casos son iguales. Dependiendo del tipo de pieza y su uso, se aplican distintas técnicas:
Equilibrado dinámico
Recomendado para componentes que rotan rápidamente, por ejemplo rotores o ejes. Se realiza en máquinas especializadas que detectan el desequilibrio en varios niveles simultáneos. Es el método más preciso para garantizar un funcionamiento suave .
Equilibrado estático
Se usa principalmente en piezas como neumáticos, discos o volantes de inercia. Aquí solo se corrige el peso excesivo en una única dirección. Es ágil, práctico y efectivo para determinados sistemas.
Corrección del desequilibrio: cómo se hace
Taladrado selectivo: se quita peso en el punto sobrecargado
Colocación de contrapesos: como en ruedas o anillos de volantes
Ajuste de masas: típico en bielas y elementos estratégicos
Equipos profesionales para detectar y corregir vibraciones
Para hacer un diagnóstico certero, necesitas herramientas precisas. Hoy en día hay opciones económicas pero potentes, tales como:
✅ Balanset-1A — Tu aliado portátil para equilibrar y analizar vibraciones -
As muscle tone and circulation decline, erectile issues may rise without order viagra online india. A single delivery, a world of change inside.
-
analizador de vibrasiones
Equilibrado dinámico portátil:
Respuesta inmediata sin mover equipos
Imagina esto: tu rotor comienza a vibrar, y cada minuto de inactividad genera pérdidas. ¿Desmontar la máquina y esperar días por un taller? Descartado. Con un equipo de equilibrado portátil, solucionas el problema in situ en horas, sin mover la maquinaria.
¿Por qué un equilibrador móvil es como un "kit de supervivencia" para máquinas rotativas?
Pequeño, versátil y eficaz, este dispositivo es el recurso básico en cualquier intervención. Con un poco de práctica, puedes:
✅ Evitar fallos secundarios por vibraciones excesivas.
✅ Reducir interrupciones no planificadas.
✅ Operar en zonas alejadas, ya sea en instalaciones marítimas o centrales solares.
¿Cuándo es ideal el equilibrado rápido?
Siempre que puedas:
- Acceder al rotor (eje, ventilador, turbina, etc.).
- Ubicar dispositivos de medición sin inconvenientes.
- Ajustar el peso (añadiendo o removiendo masa).
Casos típicos donde conviene usarlo:
La máquina muestra movimientos irregulares o ruidos atípicos.
No hay tiempo para desmontajes (producción crítica).
El equipo es difícil de parar o caro de inmovilizar.
Trabajas en áreas donde no hay asistencia mecánica disponible.
Ventajas clave vs. llamar a un técnico
| Equipo portátil | Servicio externo |
|----------------|------------------|
| ✔ Sin esperas (acción inmediata) | ❌ Retrasos por programación y transporte |
| ✔ Mantenimiento proactivo (previenes daños serios) | ❌ Solo se recurre ante fallos graves |
| ✔ Reducción de costos operativos con uso continuo | ❌ Gastos periódicos por externalización |
¿Qué máquinas se pueden equilibrar?
Cualquier sistema rotativo, como:
- Turbinas de vapor/gas
- Motores industriales
- Ventiladores de alta potencia
- Molinos y trituradoras
- Hélices navales
- Bombas centrífugas
Requisito clave: espacio para instalar sensores y realizar ajustes.
Tecnología que simplifica el proceso
Los equipos modernos incluyen:
Aplicaciones didácticas (para usuarios nuevos o técnicos en formación).
Evaluación continua (informes gráficos comprensibles).
Batería de larga duración (perfecto para zonas remotas).
Ejemplo práctico:
Un molino en una mina mostró movimientos inusuales. Con un equipo portátil, el técnico detectó un desbalance en 20 minutos. Lo corrigió añadiendo contrapesos y impidió una interrupción prolongada.
¿Por qué esta versión es más efectiva?
- Estructura más dinámica: Organización visual facilita la comprensión.
- Enfoque práctico: Ofrece aplicaciones tangibles del método.
- Lenguaje persuasivo: Frases como "herramienta estratégica" o "evitas fallas mayores" refuerzan el valor del servicio.
- Detalles técnicos útiles: Se especifican requisitos y tecnologías modernas.
¿Necesitas ajustar el tono (más técnico) o añadir keywords específicas? ¡Aquí estoy para ayudarte! ️ -
Equilibrado dinámico portátil:
Soluciones rápidas sin desmontar máquinas
Imagina esto: tu rotor empieza a temblar, y cada minuto de inactividad cuesta dinero. ¿Desmontar la máquina y esperar días por un taller? Olvídalo. Con un equipo de equilibrado portátil, resuelves sobre el terreno en horas, sin mover la maquinaria.
¿Por qué un equilibrador móvil es como un "herramienta crítica" para máquinas rotativas?
Pequeño, versátil y eficaz, este dispositivo es el recurso básico en cualquier intervención. Con un poco de práctica, puedes:
✅ Prevenir averías mayores al detectar desbalances.
✅ Evitar paradas prolongadas, manteniendo la producción activa.
✅ Trabajar en lugares remotos, desde plataformas petroleras hasta plantas eólicas.
¿Cuándo es ideal el equilibrado rápido?
Siempre que puedas:
- Acceder al rotor (eje, ventilador, turbina, etc.).
- Colocar sensores sin interferencias.
- Realizar ajustes de balance mediante cambios de carga.
Casos típicos donde conviene usarlo:
La máquina presenta anomalías auditivas o cinéticas.
No hay tiempo para desmontajes (operación prioritaria).
El equipo es costoso o difícil de detener.
Trabajas en zonas remotas sin infraestructura técnica.
Ventajas clave vs. llamar a un técnico
| Equipo portátil | Servicio externo |
|----------------|------------------|
| ✔ Sin esperas (acción inmediata) | ❌ Demoras por agenda y logística |
| ✔ Monitoreo preventivo (evitas fallas mayores) | ❌ Solo se recurre ante fallos graves |
| ✔ Reducción de costos operativos con uso continuo | ❌ Gastos periódicos por externalización |
¿Qué máquinas se pueden equilibrar?
Cualquier sistema rotativo, como:
- Turbinas de vapor/gas
- Motores industriales
- Ventiladores de alta potencia
- Molinos y trituradoras
- Hélices navales
- Bombas centrífugas
Requisito clave: acceso suficiente para medir y corregir el balance.
Tecnología que simplifica el proceso
Los equipos modernos incluyen:
Apps intuitivas (guían paso a paso, sin cálculos manuales).
Análisis en tiempo real (gráficos claros de vibraciones).
Durabilidad energética (útiles en ambientes hostiles).
Ejemplo práctico:
Un molino en una mina comenzó a vibrar peligrosamente. Con un equipo portátil, el técnico localizó el error rápidamente. Lo corrigió añadiendo contrapesos y ahorró jornadas de inactividad.
¿Por qué esta versión es más efectiva?
- Estructura más dinámica: Listas, tablas y negritas mejoran la legibilidad.
- Enfoque práctico: Ofrece aplicaciones tangibles del método.
- Lenguaje persuasivo: Frases como "recurso vital" o "minimizas riesgos importantes" refuerzan el valor del servicio.
- Detalles técnicos útiles: Se especifican requisitos y tecnologías modernas.
¿Necesitas ajustar el tono (más técnico) o añadir keywords específicas? ¡Aquí estoy para ayudarte! ️ -
El dispositivo para equilibrio Balanset-1A es el resultado de mucha labor constante y esfuerzo.
Como desarrolladores de esta tecnología avanzada, tenemos el honor de cada modelo que se distribuye de nuestras plantas industriales.
No es solamente un artículo, sino una solución que hemos perfeccionado para solucionar desafíos importantes relacionados con oscilaciones en equipos giratorios.
Sabemos lo frustrante que puede ser enfrentar interrupciones repentinas o mantenimientos caros.
Por este motivo desarrollamos Balanset-1A centrándonos en los requerimientos prácticos de nuestros clientes. ❤️
Comercializamos Balanset 1A directamente desde nuestras sedes en Portugal , España y Argentina , ofreciendo envíos veloces y seguros a destinos internacionales sin excepción.
Los agentes regionales están siempre disponibles para brindar soporte técnico personalizado y orientación en el lenguaje que prefieras.
¡No somos solo una empresa, sino un equipo que está aquí para asistirte! -
Analizador de vibrasiones
El dispositivo para equilibrio Balanset-1A representa el fruto de décadas de investigación y compromiso.
Como desarrolladores de este sistema innovador, tenemos el honor de cada unidad que sale de nuestras fábricas.
No solo es un producto, sino además una herramienta que hemos perfeccionado para resolver problemas críticos relacionados con vibraciones en maquinaria rotativa.
Sabemos lo frustrante que puede ser enfrentar paradas inesperadas o costosas reparaciones.
Por este motivo desarrollamos Balanset 1A centrándonos en los requerimientos prácticos de nuestros clientes. ❤️
Distribuimos Balanset 1A directamente desde nuestras sedes en España , Argentina y Portugal , asegurando entregas rápidas y eficientes a todos los países del globo.
Nuestros representantes locales están siempre disponibles para ofrecer asistencia técnica individualizada y consultoría en el idioma local.
¡No somos solo una empresa, sino una comunidad profesional que está aquí para ayudarte! -
Equilibrio in situ
La Nivelación de Partes Móviles: Esencial para una Operación Sin Vibraciones
¿ En algún momento te has dado cuenta de movimientos irregulares en una máquina? ¿O tal vez escuchaste ruidos anómalos? Muchas veces, el problema está en algo tan básico como una irregularidad en un componente giratorio . Y créeme, ignorarlo puede costarte más de lo que imaginas.
El equilibrado de piezas es un paso esencial en la construcción y conservación de maquinaria agrícola, ejes, volantes y elementos de motores eléctricos. Su objetivo es claro: impedir oscilaciones que, a la larga, puedan provocar desperfectos graves.
¿Por qué es tan importante equilibrar las piezas?
Imagina que tu coche tiene una rueda desequilibrada . Al acelerar, empiezan las vibraciones, el volante tiembla, e incluso puedes sentir incomodidad al conducir . En maquinaria industrial ocurre algo similar, pero con consecuencias aún peores :
Aumento del desgaste en bearings y ejes giratorios
Sobrecalentamiento de componentes
Riesgo de colapsos inesperados
Paradas sin programar seguidas de gastos elevados
En resumen: si no se corrige a tiempo, un pequeño desequilibrio puede convertirse en un gran dolor de cabeza .
Métodos de equilibrado: cuál elegir
No todos los casos son iguales. Dependiendo del tipo de pieza y su uso, se aplican distintas técnicas:
Equilibrado dinámico
Ideal para piezas que giran a alta velocidad, como rotores o ejes . Se realiza en máquinas especializadas que detectan el desequilibrio en varios niveles simultáneos. Es el método más exacto para asegurar un movimiento uniforme .
Equilibrado estático
Se usa principalmente en piezas como ruedas, discos o volantes . Aquí solo se corrige el peso excesivo en un plano . Es rápido, fácil y funcional para algunos equipos .
Corrección del desequilibrio: cómo se hace
Taladrado selectivo: se perfora la región con exceso de masa
Colocación de contrapesos: como en ruedas o anillos de volantes
Ajuste de masas: habitual en ejes de motor y partes relevantes
Equipos profesionales para detectar y corregir vibraciones
Para hacer un diagnóstico certero, necesitas herramientas precisas. Hoy en día hay opciones accesibles y muy efectivas, como :
✅ Balanset-1A — Tu compañero compacto para medir y ajustar vibraciones -
Equilibrio in situ
La Nivelación de Partes Móviles: Esencial para una Operación Sin Vibraciones
¿ Has percibido alguna vez temblores inusuales en un equipo industrial? ¿O sonidos fuera de lo común? Muchas veces, el problema está en algo tan básico como una falta de simetría en un elemento móvil. Y créeme, ignorarlo puede costarte caro .
El equilibrado de piezas es una tarea fundamental tanto en la fabricación como en el mantenimiento de maquinaria agrícola, ejes, volantes, rotores y componentes de motores eléctricos . Su objetivo es claro: prevenir movimientos indeseados capaces de generar averías importantes con el tiempo .
¿Por qué es tan importante equilibrar las piezas?
Imagina que tu coche tiene un neumático con peso desigual. Al acelerar, empiezan las vibraciones, el volante tiembla, e incluso puedes sentir incomodidad al conducir . En maquinaria industrial ocurre algo similar, pero con consecuencias mucho más graves :
Aumento del desgaste en soportes y baleros
Sobrecalentamiento de partes críticas
Riesgo de averías súbitas
Paradas imprevistas que exigen arreglos costosos
En resumen: si no se corrige a tiempo, un pequeño desequilibrio puede convertirse en un gran dolor de cabeza .
Métodos de equilibrado: cuál elegir
No todos los casos son iguales. Dependiendo del tipo de pieza y su uso, se aplican distintas técnicas:
Equilibrado dinámico
Ideal para piezas que giran a alta velocidad, como rotores o ejes . Se realiza en máquinas especializadas que detectan el desequilibrio en dos o más planos . Es el método más exacto para asegurar un movimiento uniforme .
Equilibrado estático
Se usa principalmente en piezas como neumáticos, discos o volantes de inercia. Aquí solo se corrige el peso excesivo en un plano . Es rápido, fácil y funcional para algunos equipos .
Corrección del desequilibrio: cómo se hace
Taladrado selectivo: se quita peso en el punto sobrecargado
Colocación de contrapesos: tal como en neumáticos o perfiles de poleas
Ajuste de masas: típico en bielas y elementos estratégicos
Equipos profesionales para detectar y corregir vibraciones
Para hacer un diagnóstico certero, necesitas herramientas precisas. Hoy en día hay opciones accesibles y muy efectivas, como :
✅ Balanset-1A — Tu aliado portátil para equilibrar y analizar vibraciones -
Эта статья сочетает в себе как полезные, так и интересные сведения, которые обогатят ваше понимание насущных тем. Мы предлагаем практические советы и рекомендации, которые легко внедрить в повседневную жизнь. Узнайте, как улучшить свои навыки и обогатить свой опыт с помощью простых, но эффективных решений.
Получить дополнительные сведения - https://nakroklinikatest.ru/ -
Servicio de Equilibrado
¿Oscilaciones inusuales en tu maquinaria? Soluciones de equilibrado dinámico in situ y venta de equipos.
¿Has notado movimientos extraños, sonidos atípicos o desgaste acelerado en tus máquinas? Esto indica claramente de que tu equipo industrial necesita un balanceo dinámico experto.
En vez de desarmar y trasladar tus máquinas a un taller, nosotros vamos hasta tu planta industrial con equipos de última generación para resolver el problema sin afectar tu operación.
Beneficios de nuestro balanceo dinámico en campo
✔ No requiere desinstalación — Trabajamos directamente en tus instalaciones.
✔ Diagnóstico preciso — Utilizamos tecnología avanzada para identificar el problema.
✔ Soluciones rápidas — Soluciones rápidas en cuestión de horas.
✔ Informe detallado — Certificamos el proceso con datos comparativos.
✔ Conocimiento en diversos sectores — Solucionamos problemas en maquinaria pesada y liviana. -
Servicio de Equilibrado
¿Oscilaciones inusuales en tu equipo industrial? Soluciones de equilibrado dinámico in situ y venta de equipos.
¿Has detectado movimientos extraños, sonidos atípicos o deterioro prematuro en tus máquinas? Estos son señales claras de que tu maquinaria necesita un ajuste de precisión especializado.
En vez de desarmar y trasladar tus equipos a un taller, nuestros técnicos se desplazan a tu fábrica con herramientas de vanguardia para resolver el problema sin interrumpir tu producción.
Beneficios de nuestro balanceo dinámico en campo
✔ No requiere desinstalación — Trabajamos directamente en tus instalaciones.
✔ Análisis exacto — Utilizamos tecnología avanzada para localizar el fallo.
✔ Soluciones rápidas — Respuesta en tiempo récord.
✔ Documentación técnica — Registramos mediciones previas y posteriores.
✔ Experiencia multidisciplinar — Trabajamos con equipos de todos los tamaños. -
canada pharmacy tazorac vs tretinoin https://myworldgo.com/forums/topic/219532/buying-medicine/view/post_id/2302984 zorze
tenen https://sevilla21.es/foro/viewtopic.php?t=854 canadian pharmacy cat thyroid cancer life expectancy taking tapazole
canada pharmacy order macitentan generic https://www.party.biz/forums/topic/830140/vidalista-un-remedio-eficaz-para-la-disfuncion-erectil/view/post_id/1883095 delf
shone https://www.janubaba.com/c/forum/topic/246455/Teen_Talk/Buying_medicine canada pharmacy can i use butenafine hydrochloride on thrush
canadian pharmacy what happens to nimodipine in the sunlight https://discuss.ilw.com/forum/immigration-discussion/565337-buying-medicine disbelief -
canadian pharmacy lidocaine 1 https://www.as-tu-vu.com/forum/viewtopic.php?p=878796#878796 prezident
mauger https://amabel.freeforums.net/thread/2385/canadian-pharmacy-online canadian pharmacy ziana for sebaceous hyperplasia
canada pharmacy rybelsus availability https://bettorschat.com/forum/post-your-picks/all-sports-news-discussion/3364541-kamagra-generico-un-remedio-economico-y-eficaz-para-la-disfuncion-erectil produser
danny https://digitalmgs.com/foro/viewtopic.php?t=9177 canadian pharmacy dilantin range
canada pharmacy benicar and tinnitus http://taylorhicks.ning.com/forum/topics/vidalista-un-remedio-eficaz-para-la-disfunci-n-er-ctil dupy -
Vaping in Singapore: More Than Just a Trend
In today’s fast-paced world, people are always looking for ways to unwind, relax, and enjoy the moment — and for many, vaping has become a preferred method . In Singapore, where modern life moves quickly, the rise of vaping culture has brought with it a fresh way to relax . It's not just about the devices or the clouds of vapor — it's about flavor, convenience, and finding your own vibe.
Disposable Vapes: Simple, Smooth, Ready to Go
Let’s face it — nobody wants to deal with complicated setups all the time. That’s where disposable vapes shine. They’re perfect for users who want instant satisfaction who still want that satisfying hit without the hassle of charging, refilling, or replacing parts.
Popular models like the VAPETAPE UNPLUG / OFFGRID, LANA ULTRA II, and SNOWWOLF SMART HD offer thousands of puffs in one sleek little package . Whether you're out for the day or just need something quick and easy, these disposables have got your back.
New Arrivals: Fresh Gear, Fresh Experience
The best part about being into vaping? There’s always something new around the corner. The latest releases like the ELFBAR ICE KING and ALADDIN ENJOY PRO MAX bring something different to the table — whether it’s smarter designs .
The ELFBAR RAYA D2 is another standout, offering more than just puff count — it comes with a built-in screen , so you can really make it your own.
Bundles: Smart Choices for Regular Vapers
If you vape often, buying in bulk just makes sense. Combo packs like the VAPETAPE OFFGRID COMBO or the LANA BAR 10 PCS COMBO aren’t just practical — they’re also a better deal . No more running out at the worst time, and you save a bit while you're at it.
Flavors That Speak to You
At the end of the day, it’s all about taste. Some days you want something icy and refreshing from the Cold Series, other times you're craving the smooth, mellow vibes of the Smooth Series. Then there are those sweet cravings — and trust us, the Sweet Series delivers.
Prefer the classic richness of tobacco? There’s a whole series for that too. And if you're trying to cut back on nicotine, the 0% Nicotine Series gives you all the flavor without the buzz.
Final Thoughts
Vaping in Singapore isn’t just a passing trend — it’s a lifestyle choice for many. With so many options available, from pocket-sized disposables to customizable devices, there's something for everyone. Whether you're just starting out , or a regular enthusiast , the experience is all about what feels right to you — uniquely yours . -
Vaping Culture in Singapore: A Lifestyle Beyond the Hype
In today’s fast-paced world, people are always looking for ways to unwind, relax, and enjoy the moment — and for many, vaping has become a daily habit. In Singapore, where modern life moves quickly, the rise of vaping culture has brought with it a stylish escape. It's not just about the devices or the clouds of vapor — it's about flavor, convenience, and finding your own vibe.
Disposable Vapes: Simple, Smooth, Ready to Go
Let’s face it — nobody wants to deal with complicated setups all the time. That’s where disposable vapes shine. They’re perfect for users who want instant satisfaction who still want that satisfying hit without the hassle of charging, refilling, or replacing parts.
Popular models like the VAPETAPE UNPLUG / OFFGRID, LANA ULTRA II, and SNOWWOLF SMART HD offer thousands of puffs in one portable solution . Whether you're out for the day or just need something quick and easy, these disposables have got your back.
New Arrivals: Fresh Gear, Fresh Experience
The best part about being into vaping? There’s always something new around the corner. The latest releases like the ELFBAR ICE KING and ALADDIN ENJOY PRO MAX bring something different to the table — whether it’s colder hits .
The ELFBAR RAYA D2 is another standout, offering more than just puff count — it comes with adjustable airflow , so you can really make it your own.
Bundles: Smart Choices for Regular Vapers
If you vape often, buying in bulk just makes sense. Combo packs like the VAPETAPE OFFGRID COMBO or the LANA BAR 10 PCS COMBO aren’t just practical — they’re also a cost-effective option . No more running out at the worst time, and you save a bit while you're at it.
Flavors That Speak to You
At the end of the day, it’s all about taste. Some days you want something icy and refreshing from the Cold Series, other times you're craving the smooth, mellow vibes of the Smooth Series. Then there are those sweet cravings — and trust us, the Sweet Series delivers.
Prefer the classic richness of tobacco? There’s a whole series for that too. And if you're trying to cut back on nicotine, the Nicotine-Free Range gives you all the flavor without the buzz.
Final Thoughts
Vaping in Singapore isn’t just a passing trend — it’s a lifestyle choice for many. With so many options available, from pocket-sized disposables to customizable devices, there's something for everyone. Whether you're taking your first puff, or an experienced user , the experience is all about what feels right to you — made personal for you. -
vapesg
Vaping in Singapore: More Than Just a Trend
In today’s fast-paced world, people are always looking for ways to unwind, relax, and enjoy the moment — and for many, vaping has become a go-to ritual . In Singapore, where modern life moves quickly, the rise of vaping culture has brought with it a fresh way to relax . It's not just about the devices or the clouds of vapor — it's about flavor, convenience, and finding your own vibe.
Disposable Vapes: Simple, Smooth, Ready to Go
Let’s face it — nobody wants to deal with complicated setups all the time. That’s where disposable vapes shine. They’re perfect for those who value simplicity who still want that satisfying hit without the hassle of charging, refilling, or replacing parts.
Popular models like the VAPETAPE UNPLUG / OFFGRID, LANA ULTRA II, and SNOWWOLF SMART HD offer thousands of puffs in one portable solution . Whether you're out for the day or just need something quick and easy, these disposables have got your back.
New Arrivals: Fresh Gear, Fresh Experience
The best part about being into vaping? There’s always something new around the corner. The latest releases like the ELFBAR ICE KING and ALADDIN ENJOY PRO MAX bring something different to the table — whether it’s smarter designs .
The ELFBAR RAYA D2 is another standout, offering more than just puff count — it comes with dual mesh coils, so you can really make it your own.
Bundles: Smart Choices for Regular Vapers
If you vape often, buying in bulk just makes sense. Combo packs like the VAPETAPE OFFGRID COMBO or the LANA BAR 10 PCS COMBO aren’t just practical — they’re also a cost-effective option . No more running out at the worst time, and you save a bit while you're at it.
Flavors That Speak to You
At the end of the day, it’s all about taste. Some days you want something icy and refreshing from the Cold Series, other times you're craving the smooth, mellow vibes of the Smooth Series. Then there are those sweet cravings — and trust us, the Sweet Series delivers.
Prefer the classic richness of tobacco? There’s a whole series for that too. And if you're trying to cut back on nicotine, the Nicotine-Free Range gives you all the flavor without the buzz.
Final Thoughts
Vaping in Singapore isn’t just a passing trend — it’s a lifestyle choice for many. With so many options available, from pocket-sized disposables to customizable devices, there's something for everyone. Whether you're just starting out , or a seasoned vaper , the experience is all about what feels right to you — made personal for you. -
vape singapore
Vaping Culture in Singapore: A Lifestyle Beyond the Hype
In today’s fast-paced world, people are always looking for ways to unwind, relax, and enjoy the moment — and for many, vaping has become a go-to ritual . In Singapore, where modern life moves quickly, the rise of vaping culture has brought with it a new kind of chill . It's not just about the devices or the clouds of vapor — it's about flavor, convenience, and finding your own vibe.
Disposable Vapes: Simple, Smooth, Ready to Go
Let’s face it — nobody wants to deal with complicated setups all the time. That’s where disposable vapes shine. They’re perfect for people on the move who still want that satisfying hit without the hassle of charging, refilling, or replacing parts.
Popular models like the VAPETAPE UNPLUG / OFFGRID, LANA ULTRA II, and SNOWWOLF SMART HD offer thousands of puffs in one portable solution . Whether you're out for the day or just need something quick and easy, these disposables have got your back.
New Arrivals: Fresh Gear, Fresh Experience
The best part about being into vaping? There’s always something new around the corner. The latest releases like the ELFBAR ICE KING and ALADDIN ENJOY PRO MAX bring something different to the table — whether it’s colder hits .
The ELFBAR RAYA D2 is another standout, offering more than just puff count — it comes with a built-in screen , so you can really make it your own.
Bundles: Smart Choices for Regular Vapers
If you vape often, buying in bulk just makes sense. Combo packs like the VAPETAPE OFFGRID COMBO or the LANA BAR 10 PCS COMBO aren’t just practical — they’re also a cost-effective option . No more running out at the worst time, and you save a bit while you're at it.
Flavors That Speak to You
At the end of the day, it’s all about taste. Some days you want something icy and refreshing from the Cold Series, other times you're craving the smooth, mellow vibes of the Smooth Series. Then there are those sweet cravings — and trust us, the Sweet Series delivers.
Prefer the classic richness of tobacco? There’s a whole series for that too. And if you're trying to cut back on nicotine, the Pure Flavor Collection gives you all the flavor without the buzz.
Final Thoughts
Vaping in Singapore isn’t just a passing trend — it’s a lifestyle choice for many. With so many options available, from pocket-sized disposables to customizable devices, there's something for everyone. Whether you're new to the scene , or an experienced user , the experience is all about what feels right to you — made personal for you. -
Why Choose DDoS.Market?
High-Quality Attacks – Our team ensures powerful and effective DDoS attacks for accurate security testing.
Competitive Pricing & Discounts – We offer attractive deals for returning customers.
Trusted Reputation – Our service has earned credibility in the Dark Web due to reliability and consistent performance.
Who Needs This?
? Security professionals assessing network defenses.
? Businesses conducting penetration tests.
? IT administrators preparing for real-world threats.
Ensure your network is secure—test its limits with DDoS.Market. -
ddos attack buy
Why Choose DDoS.Market?
High-Quality Attacks – Our team ensures powerful and effective DDoS attacks for accurate security testing.
Competitive Pricing & Discounts – We offer attractive deals for returning customers.
Trusted Reputation – Our service has earned credibility in the Dark Web due to reliability and consistent performance.
Who Needs This?
? Security professionals assessing network defenses.
? Businesses conducting penetration tests.
? IT administrators preparing for real-world threats.
Ensure your network is secure—test its limits with DDoS.Market. -
Why Choose DDoS.Market?
High-Quality Attacks – Our team ensures powerful and effective DDoS attacks for accurate security testing.
Competitive Pricing & Discounts – We offer attractive deals for returning customers.
Trusted Reputation – Our service has earned credibility in the Dark Web due to reliability and consistent performance.
Who Needs This?
Security professionals assessing network defenses.
Businesses conducting penetration tests.
IT administrators preparing for real-world threats. -
order ddos attack
Why Choose DDoS.Market?
High-Quality Attacks – Our team ensures powerful and effective DDoS attacks for accurate security testing.
Competitive Pricing & Discounts – We offer attractive deals for returning customers.
Trusted Reputation – Our service has earned credibility in the Dark Web due to reliability and consistent performance.
Who Needs This?
Security professionals assessing network defenses.
Businesses conducting penetration tests.
IT administrators preparing for real-world threats. -
where to buy vape in singapore
Vaping in Singapore: More Than Just a Trend
In today’s fast-paced world, people are always looking for ways to unwind, relax, and enjoy the moment — and for many, vaping has become an essential part of their routine . In Singapore, where modern life moves quickly, the rise of vaping culture has brought with it a stylish escape. It's not just about the devices or the clouds of vapor — it's about flavor, convenience, and finding your own vibe.
Disposable Vapes: Simple, Smooth, Ready to Go
Let’s face it — nobody wants to deal with complicated setups all the time. That’s where disposable vapes shine. They’re perfect for people on the move who still want that satisfying hit without the hassle of charging, refilling, or replacing parts.
Popular models like the VAPETAPE UNPLUG / OFFGRID, LANA ULTRA II, and SNOWWOLF SMART HD offer thousands of puffs in one portable solution . Whether you're out for the day or just need something quick and easy, these disposables have got your back.
New Arrivals: Fresh Gear, Fresh Experience
The best part about being into vaping? There’s always something new around the corner. The latest releases like the ELFBAR ICE KING and ALADDIN ENJOY PRO MAX bring something different to the table — whether it’s richer flavors .
The ELFBAR RAYA D2 is another standout, offering more than just puff count — it comes with a built-in screen , so you can really make it your own.
Bundles: Smart Choices for Regular Vapers
If you vape often, buying in bulk just makes sense. Combo packs like the VAPETAPE OFFGRID COMBO or the LANA BAR 10 PCS COMBO aren’t just practical — they’re also a better deal . No more running out at the worst time, and you save a bit while you're at it.
Flavors That Speak to You
At the end of the day, it’s all about taste. Some days you want something icy and refreshing from the Cold Series, other times you're craving the smooth, mellow vibes of the Smooth Series. Then there are those sweet cravings — and trust us, the Sweet Series delivers.
Prefer the classic richness of tobacco? There’s a whole series for that too. And if you're trying to cut back on nicotine, the 0% Nicotine Series gives you all the flavor without the buzz.
Final Thoughts
Vaping in Singapore isn’t just a passing trend — it’s a lifestyle choice for many. With so many options available, from pocket-sized disposables to customizable devices, there's something for everyone. Whether you're new to the scene , or an experienced user , the experience is all about what feels right to you — uniquely yours . -
singapore vape shop
Vaping Culture in Singapore: A Lifestyle Beyond the Hype
In today’s fast-paced world, people are always looking for ways to unwind, relax, and enjoy the moment — and for many, vaping has become a go-to ritual . In Singapore, where modern life moves quickly, the rise of vaping culture has brought with it a unique form of downtime . It's not just about the devices or the clouds of vapor — it's about flavor, convenience, and finding your own vibe.
Disposable Vapes: Simple, Smooth, Ready to Go
Let’s face it — nobody wants to deal with complicated setups all the time. That’s where disposable vapes shine. They’re perfect for busy individuals who still want that satisfying hit without the hassle of charging, refilling, or replacing parts.
Popular models like the VAPETAPE UNPLUG / OFFGRID, LANA ULTRA II, and SNOWWOLF SMART HD offer thousands of puffs in one compact design . Whether you're out for the day or just need something quick and easy, these disposables have got your back.
New Arrivals: Fresh Gear, Fresh Experience
The best part about being into vaping? There’s always something new around the corner. The latest releases like the ELFBAR ICE KING and ALADDIN ENJOY PRO MAX bring something different to the table — whether it’s richer flavors .
The ELFBAR RAYA D2 is another standout, offering more than just puff count — it comes with adjustable airflow , so you can really make it your own.
Bundles: Smart Choices for Regular Vapers
If you vape often, buying in bulk just makes sense. Combo packs like the VAPETAPE OFFGRID COMBO or the LANA BAR 10 PCS COMBO aren’t just practical — they’re also a great value choice. No more running out at the worst time, and you save a bit while you're at it.
Flavors That Speak to You
At the end of the day, it’s all about taste. Some days you want something icy and refreshing from the Cold Series, other times you're craving the smooth, mellow vibes of the Smooth Series. Then there are those sweet cravings — and trust us, the Sweet Series delivers.
Prefer the classic richness of tobacco? There’s a whole series for that too. And if you're trying to cut back on nicotine, the Nicotine-Free Range gives you all the flavor without the buzz.
Final Thoughts
Vaping in Singapore isn’t just a passing trend — it’s a lifestyle choice for many. With so many options available, from pocket-sized disposables to customizable devices, there's something for everyone. Whether you're new to the scene , or a seasoned vaper , the experience is all about what feels right to you — made personal for you. -
The Rise of Vaping in Singapore: Not Just a Fad
In today’s fast-paced world, people are always looking for ways to unwind, relax, and enjoy the moment — and for many, vaping has become an essential part of their routine . In Singapore, where modern life moves quickly, the rise of vaping culture has brought with it a unique form of downtime . It's not just about the devices or the clouds of vapor — it's about flavor, convenience, and finding your own vibe.
Disposable Vapes: Simple, Smooth, Ready to Go
Let’s face it — nobody wants to deal with complicated setups all the time. That’s where disposable vapes shine. They’re perfect for busy individuals who still want that satisfying hit without the hassle of charging, refilling, or replacing parts.
Popular models like the VAPETAPE UNPLUG / OFFGRID, LANA ULTRA II, and SNOWWOLF SMART HD offer thousands of puffs in one sleek little package . Whether you're out for the day or just need something quick and easy, these disposables have got your back.
New Arrivals: Fresh Gear, Fresh Experience
The best part about being into vaping? There’s always something new around the corner. The latest releases like the ELFBAR ICE KING and ALADDIN ENJOY PRO MAX bring something different to the table — whether it’s richer flavors .
The ELFBAR RAYA D2 is another standout, offering more than just puff count — it comes with a built-in screen , so you can really make it your own.
Bundles: Smart Choices for Regular Vapers
If you vape often, buying in bulk just makes sense. Combo packs like the VAPETAPE OFFGRID COMBO or the LANA BAR 10 PCS COMBO aren’t just practical — they’re also a smart investment . No more running out at the worst time, and you save a bit while you're at it.
Flavors That Speak to You
At the end of the day, it’s all about taste. Some days you want something icy and refreshing from the Cold Series, other times you're craving the smooth, mellow vibes of the Smooth Series. Then there are those sweet cravings — and trust us, the Sweet Series delivers.
Prefer the classic richness of tobacco? There’s a whole series for that too. And if you're trying to cut back on nicotine, the Zero-Nicotine Line gives you all the flavor without the buzz.
Final Thoughts
Vaping in Singapore isn’t just a passing trend — it’s a lifestyle choice for many. With so many options available, from pocket-sized disposables to customizable devices, there's something for everyone. Whether you're taking your first puff, or an experienced user , the experience is all about what feels right to you — your way, your flavor, your style . -
vapesg
Vaping in Singapore: More Than Just a Trend
In today’s fast-paced world, people are always looking for ways to unwind, relax, and enjoy the moment — and for many, vaping has become a daily habit. In Singapore, where modern life moves quickly, the rise of vaping culture has brought with it a unique form of downtime . It's not just about the devices or the clouds of vapor — it's about flavor, convenience, and finding your own vibe.
Disposable Vapes: Simple, Smooth, Ready to Go
Let’s face it — nobody wants to deal with complicated setups all the time. That’s where disposable vapes shine. They’re perfect for users who want instant satisfaction who still want that satisfying hit without the hassle of charging, refilling, or replacing parts.
Popular models like the VAPETAPE UNPLUG / OFFGRID, LANA ULTRA II, and SNOWWOLF SMART HD offer thousands of puffs in one portable solution . Whether you're out for the day or just need something quick and easy, these disposables have got your back.
New Arrivals: Fresh Gear, Fresh Experience
The best part about being into vaping? There’s always something new around the corner. The latest releases like the ELFBAR ICE KING and ALADDIN ENJOY PRO MAX bring something different to the table — whether it’s richer flavors .
The ELFBAR RAYA D2 is another standout, offering more than just puff count — it comes with dual mesh coils, so you can really make it your own.
Bundles: Smart Choices for Regular Vapers
If you vape often, buying in bulk just makes sense. Combo packs like the VAPETAPE OFFGRID COMBO or the LANA BAR 10 PCS COMBO aren’t just practical — they’re also a better deal . No more running out at the worst time, and you save a bit while you're at it.
Flavors That Speak to You
At the end of the day, it’s all about taste. Some days you want something icy and refreshing from the Cold Series, other times you're craving the smooth, mellow vibes of the Smooth Series. Then there are those sweet cravings — and trust us, the Sweet Series delivers.
Prefer the classic richness of tobacco? There’s a whole series for that too. And if you're trying to cut back on nicotine, the Pure Flavor Collection gives you all the flavor without the buzz.
Final Thoughts
Vaping in Singapore isn’t just a passing trend — it’s a lifestyle choice for many. With so many options available, from pocket-sized disposables to customizable devices, there's something for everyone. Whether you're exploring vaping for the first time , or a regular enthusiast , the experience is all about what feels right to you — tailored to your preferences . -
Vaping Culture in Singapore: A Lifestyle Beyond the Hype
In today’s fast-paced world, people are always looking for ways to unwind, relax, and enjoy the moment — and for many, vaping has become an essential part of their routine . In Singapore, where modern life moves quickly, the rise of vaping culture has brought with it a fresh way to relax . It's not just about the devices or the clouds of vapor — it's about flavor, convenience, and finding your own vibe.
Disposable Vapes: Simple, Smooth, Ready to Go
Let’s face it — nobody wants to deal with complicated setups all the time. That’s where disposable vapes shine. They’re perfect for people on the move who still want that satisfying hit without the hassle of charging, refilling, or replacing parts.
Popular models like the VAPETAPE UNPLUG / OFFGRID, LANA ULTRA II, and SNOWWOLF SMART HD offer thousands of puffs in one compact design . Whether you're out for the day or just need something quick and easy, these disposables have got your back.
New Arrivals: Fresh Gear, Fresh Experience
The best part about being into vaping? There’s always something new around the corner. The latest releases like the ELFBAR ICE KING and ALADDIN ENJOY PRO MAX bring something different to the table — whether it’s colder hits .
The ELFBAR RAYA D2 is another standout, offering more than just puff count — it comes with dual mesh coils, so you can really make it your own.
Bundles: Smart Choices for Regular Vapers
If you vape often, buying in bulk just makes sense. Combo packs like the VAPETAPE OFFGRID COMBO or the LANA BAR 10 PCS COMBO aren’t just practical — they’re also a great value choice. No more running out at the worst time, and you save a bit while you're at it.
Flavors That Speak to You
At the end of the day, it’s all about taste. Some days you want something icy and refreshing from the Cold Series, other times you're craving the smooth, mellow vibes of the Smooth Series. Then there are those sweet cravings — and trust us, the Sweet Series delivers.
Prefer the classic richness of tobacco? There’s a whole series for that too. And if you're trying to cut back on nicotine, the Pure Flavor Collection gives you all the flavor without the buzz.
Final Thoughts
Vaping in Singapore isn’t just a passing trend — it’s a lifestyle choice for many. With so many options available, from pocket-sized disposables to customizable devices, there's something for everyone. Whether you're exploring vaping for the first time , or a regular enthusiast , the experience is all about what feels right to you — uniquely yours . -
vape supplier singapore
The Rise of Vaping in Singapore: Not Just a Fad
In today’s fast-paced world, people are always looking for ways to unwind, relax, and enjoy the moment — and for many, vaping has become a daily habit. In Singapore, where modern life moves quickly, the rise of vaping culture has brought with it a fresh way to relax . It's not just about the devices or the clouds of vapor — it's about flavor, convenience, and finding your own vibe.
Disposable Vapes: Simple, Smooth, Ready to Go
Let’s face it — nobody wants to deal with complicated setups all the time. That’s where disposable vapes shine. They’re perfect for those who value simplicity who still want that satisfying hit without the hassle of charging, refilling, or replacing parts.
Popular models like the VAPETAPE UNPLUG / OFFGRID, LANA ULTRA II, and SNOWWOLF SMART HD offer thousands of puffs in one portable solution . Whether you're out for the day or just need something quick and easy, these disposables have got your back.
New Arrivals: Fresh Gear, Fresh Experience
The best part about being into vaping? There’s always something new around the corner. The latest releases like the ELFBAR ICE KING and ALADDIN ENJOY PRO MAX bring something different to the table — whether it’s smarter designs .
The ELFBAR RAYA D2 is another standout, offering more than just puff count — it comes with dual mesh coils, so you can really make it your own.
Bundles: Smart Choices for Regular Vapers
If you vape often, buying in bulk just makes sense. Combo packs like the VAPETAPE OFFGRID COMBO or the LANA BAR 10 PCS COMBO aren’t just practical — they’re also a smart investment . No more running out at the worst time, and you save a bit while you're at it.
Flavors That Speak to You
At the end of the day, it’s all about taste. Some days you want something icy and refreshing from the Cold Series, other times you're craving the smooth, mellow vibes of the Smooth Series. Then there are those sweet cravings — and trust us, the Sweet Series delivers.
Prefer the classic richness of tobacco? There’s a whole series for that too. And if you're trying to cut back on nicotine, the 0% Nicotine Series gives you all the flavor without the buzz.
Final Thoughts
Vaping in Singapore isn’t just a passing trend — it’s a lifestyle choice for many. With so many options available, from pocket-sized disposables to customizable devices, there's something for everyone. Whether you're just starting out , or a seasoned vaper , the experience is all about what feels right to you — tailored to your preferences . -
טלגראס כיוונים תל אביב
מערכת טלגראס|הדרכות מפורטות לקניית קנאביס תוך זמן קצר
כיום, יישום כלי טכנולוגיים נותן לנו את האפשרות להפוך תהליכים מורכבים לפשוטים משמעותית. אחד מהשירותים הפופולריים ביותר בתחום הקנאביס בישראל הוא שירותי ההזמנות בטלגרם , שמאפשר למשתמשים למצוא ולהזמין קנאביס בצורה יעילה ומושלמת באמצעות הרשת החברתית טלגרם. במדריך זה נסביר מהו טלגראס כיוונים, כיצד הוא עובד, וכיצד תוכלו להשתמש בו כדי להתארגן בצורה הטובה ביותר.
מה מייצגת מערכת טלגראס?
טלגראס כיוונים הוא מערכת אינטרנט שמשמש כמרכז עבור משתמשי טלגראס (קבוצות וערוצים באפליקציה של טלגרם) המתמקדים בהזמנת ושילוח חומר לצריכה. האתר מספק מידע עדכני לערוצים אמינים ברחבי הארץ, המאפשרים למשתמשים להזמין קנאביס בצורה מובנית היטב.
העיקרון המרכזי מאחורי טלגראס כיוונים הוא לחבר בין לקוחות למפיצים, תוך שימוש בכלי הטכנולוגיה של טלגרם. כל מה שאתם צריכים לעשות הוא לקבוע את הקישור המתאים, ליצור קשר עם השליח הקרוב אליכם, ולבקש את המשלוח שלכם – הכל נעשה באופן מבוקר ומדויק.
איך работает טלגראס כיוונים?
השימוש בטulgראס כיוונים הוא קל ויישומי. הנה השלבים הבסיסיים:
התחברות למערכת האינטרנט:
הכינו עבורכם את מרכז המידע עבור טלגראס כיוונים, שבו תוכלו למצוא את כל הקישורים המעודכנים לערוצים אמינים וטובים. האתר כולל גם מדריכים והסברים כיצד לפעול נכון.
איתור הערוץ הטוב ביותר:
האתר מספק רשימה של ערוצים מומלצים שעוברים בדיקה קפדנית. כל ערוץ אומת על ידי משתמשים מקומיים שדיווחו על החוויה שלהם, כך שתדעו שאתם נכנסים לערוץ אמין ומאומת.
קישור ישיר לספק:
לאחר בחירת הערוץ המתאים, תוכלו ליצור קשר עם הספק באזורכם. השליח יקבל את ההזמנה שלכם וישלח לכם את המוצר במהירות.
הגעת המשלוח:
אחת ההפרטים הקריטיים היא שהמשלוחים נעשים במהירות ובאופן מקצועני. השליחים עובדים בצורה מאובטחת כדי להבטיח שהמוצר יגיע אליכם בדיוק.
היתרונות של טלגראס כיוונים
השימוש בטulgראס כיוונים מציע מספר תכונות חשובות:
سهولة: אין צורך לצאת מהבית או לחפש מבצעים ידניים. כל התהליך מתבצע דרך הפלטפורמה.
מהירות: הזמנת המשלוח נעשית תוך דקות, והשליח בדרך אליכם בתוך זמן קצר מאוד.
וודאות: כל הערוצים באתר עוברות ביקורת איכות על ידי משתמשים אמיתיים.
כל הארץ מכוסה: האתר מספק קישורים לערוצים פעילים בכל חלקי המדינה, מהצפון ועד הדרום.
מדוע חשוב לבחור ערוצים מאומתים?
אחד הדברים החיוניים ביותר בעת использование טulgראס כיוונים הוא לוודא שאתם נכנסים לערוצים מאומתים. ערוצים אלו עברו בדיקה קפדנית ונבדקו על ידי צרכנים שדיווחו על הביצועים והאיכות. זה מבטיח לכם:
חומרים ברמה גבוהה: השליחים והסוחרים בערוצים המאומתים מספקים מוצרים באיכות מצוינת.
ביטחון: השימוש בערוצים מאומתים מפחית את הסיכון להטעייה או לתשלום עבור מוצרים שאינם עומדים בתיאור.
טיפול מותאם: השליחים בערוצים המומלצים עובדים בצורה יעילה ומספקים שירות מדויק וטוב.
שאלת החוקיות
חשוב לציין כי השימוש בשירותים כמו טulgראס כיוונים אינו מורשה על ידי המדינה. למרות זאת, רבים בוחרים להשתמש בשיטה זו בשל השימושיות שהיא מספקת. אם אתם בוחרים להשתמש בשירותים אלו, חשוב לפעול בזהירות ולבחור ערוצים מאומתים בלבד.
סיכום: איך להתחיל?
אם אתם מחפשים דרך פשוטה ויעילה להשגת קנאביס בישראל, טulgראס כיוונים עשוי להיות המערכת שתעזור לכם. האתר מספק את כל המידע הנחוץ, כולל קישורים מעודכנים לערוצים מאומתים, מדריכים והסברים כיצד לפעול נכון. עם טulgראס כיוונים, שליח הקנאביס יכול להיות בדרך אליכם בזמן קצר מאוד.
אל תחכו יותר – התחילו את החיפוש, מצאו את הערוץ המתאים לכם, ותוכלו להנות מחוויית קבלת השירות בקלות!
טלגראס כיוונים – המערכת שתגיע אליכם. -
טלגראס כיוונים|הדרכות מפורטות להזמנת מוצרים בקלות ובמהירות
כיום, הטמעת פתרונות דיגיטליים עוזר לנו להפוך תהליכים מורכבים לפשוטים משמעותית. תכנית השימוש הנפוצה ביותר בתחום הקנאביס בישראל הוא שירותי ההזמנות בטלגרם , שמאפשר למשתמשים למצוא ולהזמין קנאביס בצורה יעילה ומושלמת באמצעות הרשת החברתית טלגרם. במדריך זה נסביר מהו טלגראס כיוונים, כיצד הוא עובד, וכיצד תוכלו להשתמש בו כדי להתארגן בצורה הטובה ביותר.
מה מייצגת מערכת טלגראס?
טלגראס כיוונים הוא מרכז נתונים שמשמש כמוקד לקישורים ולערוצים (קבוצות וערוצים באפליקציה של טלגרם) המתמקדים בהזמנת ושילוח חומר לצריכה. האתר מספק מידע עדכני לערוצים מומלצים ופעילים ברחבי הארץ, המאפשרים למשתמשים להזמין קנאביס בצורה מובנית היטב.
העיקרון המרכזי מאחורי טלגראס כיוונים הוא לחבר בין משתמשים לספקי השירותים, תוך שימוש בכלי הטכנולוגיה של הרשת החברתית. כל מה שאתם צריכים לעשות הוא לקבוע את הקישור המתאים, ליצור קשר עם השליח הקרוב אליכם, ולבקש את המשלוח שלכם – הכל נעשה באופן דיגיטלי ומהיר.
מהם השלבים לשימוש בשירות?
השימוש בטulgראס כיוונים הוא פשוט ומהיר. הנה ההוראות הראשוניות:
גישה למרכז המידע:
הכינו עבורכם את אתר ההסבר עבור טלגראס כיוונים, שבו תוכלו למצוא את כל הרשימות החדשות לערוצים פעילים וממומלצים. האתר כולל גם הדרכות מובנות כיצד לפעול נכון.
איתור הערוץ הטוב ביותר:
האתר מספק נתוני ערוצים אמינים שעוברים וידוא תקינות. כל ערוץ אומת על ידי משתמשים מקומיים שדיווחו על החוויה שלהם, כך שתדעו שאתם נכנסים לערוץ אמין ומאומת.
קישור ישיר לספק:
לאחר איתור הספק הטוב ביותר, תוכלו ליצור קשר עם האחראי על השילוח. השליח יקבל את ההזמנה שלכם וישלח לכם את המוצר תוך דקות ספורות.
הגעת המשלוח:
אחת הנקודות החשובות ביותר היא שהמשלוחים נעשים בזמן ובאיכות. השליחים עובדים בצורה יעילה כדי להבטיח שהמוצר יגיע אליכם בזמן.
מדוע זה שימושי?
השימוש בטulgראס כיוונים מציע מספר תכונות חשובות:
פשטות: אין צורך לצאת מהבית או לחפש ספקים באופן עצמאי. כל התהליך מתבצע דרך האפליקציה.
מהירות פעולה: הזמנת המשלוח נעשית בקצב מהיר, והשליח בדרך אליכם בתוך זמן קצר מאוד.
אמינות: כל הערוצים באתר עוברות תהליך אימות על ידי לקוחות קודמים.
כל הארץ מכוסה: האתר מספק קישורים לערוצים מאומתים בכל חלקי המדינה, מהצפון ועד הדרום.
חשיבות הבחירה בערוצים מאומתים
אחד הדברים החיוניים ביותר בעת использование טulgראס כיוונים הוא לוודא שאתם נכנסים לערוצים אמינים. ערוצים אלו עברו בדיקה קפדנית ונבדקו על ידי משתמשים אמיתיים על החוויה והתוצאות. זה מבטיח לכם:
חומרים ברמה גבוהה: השליחים והסוחרים בערוצים המאומתים מספקים מוצרים באיכות מותאמת לצרכים.
ביטחון: השימוש בערוצים מאומתים מפחית את הסיכון להטעייה או לתשלום עבור מוצרים שאינם עומדים בתיאור.
שירות מקצועי: השליחים בערוצים המומלצים עובדים בצורה מאובטחת ומספקים שירות מפורט ונוח.
האם זה מותר לפי החוק?
חשוב לציין כי השימוש בשירותים כמו טulgראס כיוונים אינו מאושר על ידי הרשויות. למרות זאת, רבים בוחרים להשתמש בשיטה זו בשל השימושיות שהיא מספקת. אם אתם בוחרים להשתמש בשירותים אלו, חשוב לפעול באופן מושכל ולבחור ערוצים מאומתים בלבד.
צעד ראשון לשימוש בשירות
אם אתם רוצים להזמין בצורה נוחה להשגת קנאביס בישראל, טulgראס כיוונים עשוי להיות המערכת שתעזור לכם. האתר מספק את כל הנתונים, כולל קישורים מעודכנים לערוצים אמינים, מדריכים והסברים כיצד לפעול נכון. עם טulgראס כיוונים, שליח הקנאביס יכול להיות בדרך אליכם במהירות.
אל תחכו יותר – פתחו את המערכת, מצאו את הערוץ המתאים לכם, ותוכלו להנות מחוויית הפעלה מהירה!
טלגראס כיוונים – המערכת שתגיע אליכם. -
Health providers now emphasize that there's no weakness in asking for viagra coupons. Better choices are obvious when you take the time to compare.
-
שירותי טלגרם|מדריך למשתמשים להזמנת מוצרים בקלות ובמהירות
כיום, הטמעת פתרונות דיגיטליים עוזר לנו להפוך תהליכים מורכבים לפשוטים משמעותית. תכנית השימוש הנפוצה ביותר בתחום הקנאביס בישראל הוא טלגראס כיוונים , שמאפשר למשתמשים למצוא ולהזמין קנאביס בצורה יעילה ומושלמת באמצעות אפליקציה של טלגרם. בהדרכה זו נסביר מהו טלגראס כיוונים, כיצד הוא עובד, וכיצד תוכלו להשתמש בו כדי לנהל את התהליך בצורה יעילה.
מה מייצגת מערכת טלגראס?
טלגראס כיוונים הוא אתר מידע שמשמש כמרכז עבור משתמשי טלגראס (קבוצות וערוצים באפליקציה של טלגרם) המתמקדים בהזמנת ושילוח חומר לצריכה. האתר מספק מידע עדכני לערוצים אמינים ברחבי הארץ, המאפשרים למשתמשים להזמין קנאביס בצורה פשוטה ויעילה.
ההרעיון הבסיסי מאחורי טלגראס כיוונים הוא לחבר בין לקוחות למפיצים, תוך שימוש בכלי הטכנולוגיה של האפליקציה הדיגיטלית. כל מה שאתם צריכים לעשות הוא לבחור ערוץ מתאים, ליצור קשר עם השליח הקרוב אליכם, ולבקש את המשלוח שלכם – הכל נעשה באופן יעיל ואמין.
איך מתחילים את התהליך?
השימוש בטulgראס כיוונים הוא קל ויישומי. הנה ההוראות הראשוניות:
גישה למרכז המידע:
הכינו עבורכם את דף התמיכה עבור טלגראס כיוונים, שבו תוכלו למצוא את כל הנתונים הנדרשים לערוצים שעברו בדיקה ואימות. האתר כולל גם הוראות מפורטות כיצד לפעול נכון.
בחירת ערוץ מתאים:
האתר מספק נתוני ערוצים אמינים שעוברים בדיקת איכות. כל ערוץ אומת על ידי לקוחות קודמים ששלחו המלצות, כך שתדעו שאתם נכנסים לערוץ איכותי ונוח.
בקשת שיחה עם מזמין:
לאחר בחירה מהרשימה, תוכלו ליצור קשר עם האחראי על השילוח. השליח יקבל את ההזמנה שלכם וישלח לכם את המוצר תוך זמן קצר.
העברת המוצר:
אחת הנקודות החשובות ביותר היא שהמשלוחים נעשים בזמן ובאיכות. השליחים עובדים בצורה יעילה כדי להבטיח שהמוצר יגיע אליכם בזמן.
מדוע זה שימושי?
השימוש בטulgראס כיוונים מציע מספר תכונות חשובות:
נוחות: אין צורך לצאת מהבית או לחפש ספקים באופן עצמאי. כל התהליך מתבצע דרך האפליקציה.
מהירות: הזמנת המשלוח נעשית בזמן קצר מאוד, והשליח בדרך אליכם בתוך זמן קצר מאוד.
אמינות: כל הערוצים באתר עוברות תהליך אימות על ידי צוות מקצועי.
כל הארץ מכוסה: האתר מספק קישורים לערוצים פעילים בכל אזורי ישראל, מהמרכז ועד הפריפריה.
חשיבות הבחירה בערוצים מאומתים
אחד הדברים החיוניים ביותר בעת использование טulgראס כיוונים הוא לוודא שאתם נכנסים לערוצים שעברו בדיקה. ערוצים אלו עברו וידוא תקינות ונבדקו על ידי צרכנים שדיווחו על הביצועים והאיכות. זה מבטיח לכם:
איכות מוצר: השליחים והסוחרים בערוצים המאומתים מספקים מוצרים באיכות גבוהה.
ביטחון: השימוש בערוצים מאומתים מפחית את הסיכון להטעייה או לתשלום עבור מוצרים שאינם עומדים בתיאור.
שירות מקצועי: השליחים בערוצים המומלצים עובדים בצורה יעילה ומספקים שירות מפורט ונוח.
האם זה חוקי?
חשוב לציין כי השימוש בשירותים כמו טulgראס כיוונים אינו חוקי לפי החוק הישראלי. למרות זאת, רבים בוחרים להשתמש בשיטה זו בשל היעילות שהיא מספקת. אם אתם בוחרים להשתמש בשירותים אלו, חשוב לפעול באופן מושכל ולבחור ערוצים מאומתים בלבד.
סיכום: איך להתחיל?
אם אתם מעוניינים למצוא פתרון מהיר להשגת קנאביס בישראל, טulgראס כיוונים עשוי להיות הפתרון בשבילכם. האתר מספק את כל המידע הנחוץ, כולל קישורים מעודכנים לערוצים מומלצים, מדריכים והסברים כיצד לפעול נכון. עם טulgראס כיוונים, שליח הקנאביס יכול להיות בדרך אליכם במהירות.
אל תחכו יותר – גשו לאתר המידע שלנו, מצאו את הערוץ המתאים לכם, ותוכלו להנות מחוויית קבלת השירות בקלות!
טלגראס כיוונים – המערכת שתגיע אליכם. -
Telegrass Israel
טלגראס כיוונים|המדריך המלא לקניית קנאביס באופן יעיל
בימים אלה, הטמעת פתרונות דיגיטליים עוזר לנו להפוך תהליכים מורכבים לפשוטים משמעותית. השירות הנפוץ ביותר בתחום הקנאביס בישראל הוא מערכת הטלגראס , שמאפשר למשתמשים למצוא ולהזמין קנאביס בצורה נוחה ואמינה באמצעות פלטפורמת טלגרם. במדריך זה נסביר על מה מדובר בשירות הזה, כיצד הוא עובד, וכיצד תוכלו להשתמש בו כדי להתארגן בצורה הטובה ביותר.
על מה מבוססת שירות טלגראס?
טלגראס כיוונים הוא מערכת אינטרנט שמשמש כמוקד לקישורים ולערוצים (קבוצות וערוצים בפלטפורמת טלגרם) המתמקדים בהזמנת ושילוח מוצרים קשורים. האתר מספק רשימות מאומתות לערוצים מומלצים ופעילים ברחבי הארץ, המאפשרים למשתמשים להזמין קנאביס בצורה מובנית היטב.
העיקרון המרכזי מאחורי טלגראס כיוונים הוא לחבר בין צרכנים לבין שליחים או סוחרים, תוך שימוש בכלי הטכנולוגיה של האפליקציה הדיגיטלית. כל מה שאתם צריכים לעשות הוא לקבוע את הקישור המתאים, ליצור קשר עם مزود השירות באזורכם, ולבקש את המשלוח שלכם – הכל נעשה באופן מבוקר ומדויק.
איך מתחילים את התהליך?
השימוש בטulgראס כיוונים הוא מובנה בצורה אינטואיטיבית. הנה התהליך המפורט:
גישה למרכז המידע:
הכינו עבורכם את מרכז המידע עבור טלגראס כיוונים, שבו תוכלו למצוא את כל הקישורים המעודכנים לערוצים פעילים וממומלצים. האתר כולל גם הוראות מפורטות כיצד לפעול נכון.
בחירת ערוץ מתאים:
האתר מספק רשימת קישורים לבחירה שעוברים וידוא תקינות. כל ערוץ אומת על ידי צרכנים אמיתיים ששיתפו את חוות דעתם, כך שתדעו שאתם נכנסים לערוץ בטוח ואמין.
קישור ישיר לספק:
לאחר איתור הספק הטוב ביותר, תוכלו ליצור קשר עם האחראי על השילוח. השליח יקבל את ההזמנה שלכם וישלח לכם את המוצר תוך דקות ספורות.
העברת המוצר:
אחת ההפרטים הקריטיים היא שהמשלוחים נעשים בזמן ובאיכות. השליחים עובדים בצורה מאובטחת כדי להבטיח שהמוצר יגיע אליכם בזמן.
מדוע זה שימושי?
השימוש בטulgראס כיוונים מציע מספר יתרונות מרכזיים:
פשטות: אין צורך לצאת מהבית או לחפש ספקים באופן עצמאי. כל התהליך מתבצע דרך הפלטפורמה.
מהירות פעולה: הזמנת המשלוח נעשית תוך דקות, והשליח בדרך אליכם בתוך זמן קצר מאוד.
אמינות: כל הערוצים באתר עוברות בדיקה קפדנית על ידי לקוחות קודמים.
כל הארץ מכוסה: האתר מספק קישורים לערוצים פעילים בכל אזורים בארץ, מהמרכז ועד הפריפריה.
חשיבות הבחירה בערוצים מאומתים
אחד הדברים החיוניים ביותר בעת использование טulgראס כיוונים הוא לוודא שאתם נכנסים לערוצים שעברו בדיקה. ערוצים אלו עברו וידוא תקינות ונבדקו על ידי צרכנים שדיווחו על החוויה שלהם. זה מבטיח לכם:
חומרים ברמה גבוהה: השליחים והסוחרים בערוצים המאומתים מספקים מוצרים באיכות מצוינת.
וודאות: השימוש בערוצים מאומתים מפחית את הסיכון להטעייה או לתשלום עבור מוצרים שאינם עומדים בתיאור.
שירות מקצועי: השליחים בערוצים המומלצים עובדים בצורה מקצועית ומספקים שירות מהיר ואמין.
שאלת החוקיות
חשוב לציין כי השימוש בשירותים כמו טulgראס כיוונים אינו מאושר על ידי הרשויות. למרות זאת, רבים בוחרים להשתמש בשיטה זו בשל הנוחות שהיא מספקת. אם אתם בוחרים להשתמש בשירותים אלו, חשוב לפעול באופן מושכל ולבחור ערוצים מאומתים בלבד.
סיכום: איך להתחיל?
אם אתם מחפשים דרך פשוטה ויעילה להשגת קנאביס בישראל, טulgראס כיוונים עשוי להיות הדרך הנוחה והיעילה. האתר מספק את כל required details, כולל קישורים מעודכנים לערוצים מומלצים, מדריכים והסברים כיצד לפעול נכון. עם טulgראס כיוונים, שליח הקנאביס יכול להיות בדרך אליכם במהירות.
אל תחכו יותר – גשו לאתר המידע שלנו, מצאו את הערוץ המתאים לכם, ותוכלו להנות מחוויית קבלת השירות בקלות!
טלגראס כיוונים – המקום שבו הקנאביס מגיע עד לדלת ביתכם. -
מערכת טלגראס|הדרכות מפורטות להזמנת מוצרים תוך זמן קצר
כיום, הטמעת פתרונות דיגיטליים נותן לנו את האפשרות להפוך תהליכים מורכבים לפשוטים משמעותית. השירות הנפוץ ביותר בתחום הקנאביס בישראל הוא שירותי ההזמנות בטלגרם , שמאפשר למשתמשים למצוא ולהזמין קנאביס בצורה מהירה ובטוחה באמצעות הרשת החברתית טלגרם. במדריך זה נסביר מהו טלגראס כיוונים, כיצד הוא עובד, וכיצד תוכלו להשתמש בו כדי לנהל את התהליך בצורה יעילה.
מה מייצגת מערכת טלגראס?
טלגראס כיוונים הוא אתר מידע שמשמש כמרכז עבור משתמשי טלגראס (קבוצות וערוצים באפליקציה של טלגרם) המתמקדים בהזמנת ושילוח קנאביס. האתר מספק קישורים מעודכנים לערוצים מומלצים ופעילים ברחבי הארץ, המאפשרים למשתמשים להזמין קנאביס בצורה מובנית היטב.
ההרעיון הבסיסי מאחורי טלגראס כיוונים הוא לחבר בין משתמשים לספקי השירותים, תוך שימוש בכלי הטכנולוגיה של טלגרם. כל מה שאתם צריכים לעשות הוא למצוא את הערוץ הקרוב אליכם, ליצור קשר עם הספק הקרוב למקום מגוריכם, ולבקש את המשלוח שלכם – הכל נעשה באופן דיגיטלי ומהיר.
מהם השלבים לשימוש בשירות?
השימוש בטulgראס כיוונים הוא פשוט ומהיר. הנה ההוראות הראשוניות:
כניסה לאתר המידע:
הכינו עבורכם את דף התמיכה עבור טלגראס כיוונים, שבו תוכלו למצוא את כל הרשימות החדשות לערוצים שעברו בדיקה ואימות. האתר כולל גם הדרכות מובנות כיצד לפעול נכון.
איתור הערוץ הטוב ביותר:
האתר מספק רשימה של ערוצים מומלצים שעוברים בדיקה קפדנית. כל ערוץ אומת על ידי לקוחות קודמים ששלחו המלצות, כך שתדעו שאתם נכנסים לערוץ אמין ומאומת.
יצירת קשר עם השליח:
לאחר איתור הספק הטוב ביותר, תוכלו ליצור קשר עם השליח הקרוב לביתכם. השליח יקבל את ההזמנה שלכם וישלח לכם את המוצר תוך זמן קצר.
קבלת המשלוח:
אחת הנקודות החשובות ביותר היא שהמשלוחים נעשים במהירות ובאופן מקצועני. השליחים עובדים בצורה מאובטחת כדי להבטיח שהמוצר יגיע אליכם במועד הנדרש.
למה לבחור את טלגראס?
השימוש בטulgראס כיוונים מציע מספר יתרונות מרכזיים:
נוחות: אין צורך לצאת מהבית או לחפש סוחרים בעצמכם. כל התהליך מתבצע דרך המערכת הדיגיטלית.
מהירות: הזמנת המשלוח נעשית בזמן קצר מאוד, והשליח בדרך אליכם בתוך זמן קצר מאוד.
אמינות: כל הערוצים באתר עוברות תהליך אימות על ידי לקוחות קודמים.
זמינות בכל הארץ: האתר מספק קישורים לערוצים מאומתים בכל אזורי ישראל, מהמרכז ועד הפריפריה.
חשיבות הבחירה בערוצים מאומתים
אחד הדברים החשובים ביותר בעת использование טulgראס כיוונים הוא לוודא שאתם נכנסים לערוצים אמינים. ערוצים אלו עברו בדיקה קפדנית ונבדקו על ידי צרכנים שדיווחו על החוויה והתוצאות. זה מבטיח לכם:
חומרים ברמה גבוהה: השליחים והסוחרים בערוצים המאומתים מספקים מוצרים באיכות גבוהה.
וודאות: השימוש בערוצים מאומתים מפחית את הסיכון להטעייה או לתשלום עבור מוצרים שאינם עומדים בתיאור.
תמיכה טובה: השליחים בערוצים המומלצים עובדים בצורה מאובטחת ומספקים שירות מהיר ואמין.
האם זה מותר לפי החוק?
חשוב לציין כי השימוש בשירותים כמו טulgראס כיוונים אינו מורשה על ידי המדינה. למרות זאת, רבים בוחרים להשתמש בשיטה זו בשל הנוחות שהיא מספקת. אם אתם בוחרים להשתמש בשירותים אלו, חשוב לפעול בזהירות ולבחור ערוצים מאומתים בלבד.
צעד ראשון לשימוש בשירות
אם אתם רוצים להזמין בצורה נוחה להשגת קנאביס בישראל, טulgראס כיוונים עשוי להיות המערכת שתעזור לכם. האתר מספק את כל הנתונים, כולל רשימות מומלצות לערוצים מאומתים, מדריכים והסברים כיצד לפעול נכון. עם טulgראס כיוונים, שליח הקנאביס יכול להיות בדרך אליכם במהירות.
אל תחכו יותר – פתחו את המערכת, מצאו את הערוץ המתאים לכם, ותוכלו להנות מחוויית קבלת השירות בקלות!
טלגראס כיוונים – המקום שבו הקנאביס מגיע עד לדלת ביתכם. -
טלגראס כיוונים
שירותי טלגרם|המדריך המלא להזמנת מוצרים בקלות ובמהירות
בימים אלה, השימוש בטכנולוגיות מתקדמות מאפשר לנו להפוך תהליכים מורכבים לפשוטים משמעותית. השירות הנפוץ ביותר בתחום הקנאביס בישראל הוא טלגראס כיוונים , שמאפשר למשתמשים למצוא ולהזמין קנאביס בצורה נוחה ואמינה באמצעות פלטפורמת טלגרם. במסמך זה נסביר מהו טלגראס כיוונים, כיצד הוא עובד, וכיצד תוכלו להשתמש בו כדי להתארגן בצורה הטובה ביותר.
מה זה טלגראס כיוונים?
טלגראס כיוונים הוא אתר מידע שמשמש כמרכז עבור משתמשי טלגראס (קבוצות וערוצים באפליקציה של טלגרם) המתמקדים בהזמנת ושילוח מוצרים קשורים. האתר מספק קישורים מעודכנים לערוצים מומלצים ופעילים ברחבי הארץ, המאפשרים למשתמשים להזמין קנאביס בצורה נוחה ומהירה.
ההרעיון הבסיסי מאחורי טלגראס כיוונים הוא לחבר בין לקוחות למפיצים, תוך שימוש בכלי הטכנולוגיה של טלגרם. כל מה שאתם צריכים לעשות הוא למצוא את הערוץ הקרוב אליכם, ליצור קשר עם مزود השירות באזורכם, ולבקש את המשלוח שלכם – הכל נעשה באופן יעיל ואמין.
איך מתחילים את התהליך?
השימוש בטulgראס כיוונים הוא פשוט ומהיר. הנה התהליך המפורט:
כניסה לאתר המידע:
הכינו עבורכם את אתר ההסבר עבור טלגראס כיוונים, שבו תוכלו למצוא את כל הנתונים הנדרשים לערוצים אמינים וטובים. האתר כולל גם הוראות מפורטות כיצד לפעול נכון.
הגעה לערוץ המומלץ:
האתר מספק נתוני ערוצים אמינים שעוברים בדיקת איכות. כל ערוץ אומת על ידי לקוחות קודמים ששלחו המלצות, כך שתדעו שאתם נכנסים לערוץ אמין ומאומת.
קישור ישיר לספק:
לאחר בחירת הערוץ המתאים, תוכלו ליצור קשר עם האחראי על השילוח. השליח יקבל את ההזמנה שלכם וישלח לכם את המוצר תוך זמן קצר.
העברת המוצר:
אחת ההפרטים הקריטיים היא שהמשלוחים נעשים באופן ממוקד ואמין. השליחים עובדים בצורה מאובטחת כדי להבטיח שהמוצר יגיע אליכם בזמן.
היתרונות של טלגראס כיוונים
השימוש בטulgראס כיוונים מציע מספר נקודות חזקות:
נוחות: אין צורך לצאת מהבית או לחפש מבצעים ידניים. כל התהליך מתבצע דרך האפליקציה.
מהירות: הזמנת המשלוח נעשית בזמן קצר מאוד, והשליח בדרך אליכם בתוך זמן קצר מאוד.
ביטחון: כל הערוצים באתר עוברות בדיקה קפדנית על ידי לקוחות קודמים.
נגישות ארצית: האתר מספק קישורים לערוצים פעילים בכל חלקי המדינה, מהקצה אחד של המדינה ועד השני.
מדוע חשוב לבחור ערוצים מאומתים?
אחד הדברים החשובים ביותר בעת использование טulgראס כיוונים הוא לוודא שאתם נכנסים לערוצים שעברו בדיקה. ערוצים אלו עברו אישור רשמי ונבדקו על ידי משתמשים אמיתיים על החוויה והתוצאות. זה מבטיח לכם:
מוצרים טובים: השליחים והסוחרים בערוצים המאומתים מספקים מוצרים באיכות מותאמת לצרכים.
ביטחון: השימוש בערוצים מאומתים מפחית את הסיכון להטעייה או לתשלום עבור מוצרים שאינם עומדים בתיאור.
טיפול מותאם: השליחים בערוצים המומלצים עובדים בצורה מקצועית ומספקים שירות מפורט ונוח.
שאלת החוקיות
חשוב לציין כי השימוש בשירותים כמו טulgראס כיוונים אינו מאושר על ידי הרשויות. למרות זאת, רבים בוחרים להשתמש בשיטה זו בשל הנוחות שהיא מספקת. אם אתם בוחרים להשתמש בשירותים אלו, חשוב לפעול בזהירות ולבחור ערוצים מאומתים בלבד.
ההתחלה שלך: מה לעשות?
אם אתם מחפשים דרך פשוטה ויעילה להשגת קנאביס בישראל, טulgראס כיוונים עשוי להיות המערכת שתעזור לכם. האתר מספק את כל required details, כולל קישורים מעודכנים לערוצים אמינים, מדריכים והסברים כיצד לפעול נכון. עם טulgראס כיוונים, שליח הקנאביס יכול להיות בדרך אליכם בזמן קצר מאוד.
אל תחכו יותר – גשו לאתר המידע שלנו, מצאו את הערוץ המתאים לכם, ותוכלו להנות מחוויית קבלת השירות בקלות!
טלגראס כיוונים – המערכת שתגיע אליכם. -
buy Fildena: fildena.homes – Fildena 150 online
-
[b]Prevent Vibration Damage – Get Professional Balancing with Balanset-1A[/b]
Unbalanced rotors can cause serious damage to your machinery. Bearings wear out faster, motors consume more power, and failures lead to expensive repairs. [b]Balanset-1A[/b] provides professional-grade vibration diagnostics and balancing, helping businesses save money and improve reliability.
[b]Key Benefits:[/b]
- [b]Accurate & fast diagnostics[/b] – Identifies imbalance before it causes damage
- [b]Portable & efficient[/b] – Suitable for field and workshop use
- [b]User-friendly software[/b] – No special training required
[b]Choose Your Kit:[/b]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT5CCKT]Full Kit on Amazon[/url] - Includes all necessary sensors, software, and a protective case
Price: [b]€2250[/b]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT5CCKT][img]https://i.postimg.cc/SXSZy3PV/4.jpg[/img][/url]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT4P7JR]OEM Kit on Amazon[/url] - More affordable, comes with basic components
Price: [b]€1978[/b]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT4P7JR][img]https://i.postimg.cc/cvM9G0Fr/2.jpg[/img][/url]
Protect your equipment today with [b]Balanset-1A[/b]! -
[b]Prevent Vibration Damage – Get Professional Balancing with Balanset-1A[/b]
Unbalanced rotors can cause serious damage to your machinery. Bearings wear out faster, motors consume more power, and failures lead to expensive repairs. [b]Balanset-1A[/b] provides professional-grade vibration diagnostics and balancing, helping businesses save money and improve reliability.
[b]Key Benefits:[/b]
- [b]Accurate & fast diagnostics[/b] – Identifies imbalance before it causes damage
- [b]Portable & efficient[/b] – Suitable for field and workshop use
- [b]User-friendly software[/b] – No special training required
[b]Choose Your Kit:[/b]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT5CCKT]Full Kit on Amazon[/url] - Includes all necessary sensors, software, and a protective case
Price: [b]€2250[/b]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT5CCKT][img]https://i.postimg.cc/SXSZy3PV/4.jpg[/img][/url]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT4P7JR]OEM Kit on Amazon[/url] - More affordable, comes with basic components
Price: [b]€1978[/b]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT4P7JR][img]https://i.postimg.cc/cvM9G0Fr/2.jpg[/img][/url]
Protect your equipment today with [b]Balanset-1A[/b]! -
buy Vidalista: vidalista.pics – Vidalista 40 ervaringen
-
futemax tv
resultado do jogo do bicho deu no poste 11 horas
Gr谩ficos lindos e jogabilidade fluida.
Muito bom, funciona direitinho.
https://chatbotjud-teste.saude.mg.gov.br/wp-map/futemax-tv/
https://chatbotjud-teste.saude.mg.gov.br/wp-map/play-hd-futebol/ -
Balanset-1A: Innovative Compact Balancer & Vibration Analyzer
Professional Dynamic Balancing Solution
Balanset-1A stands as an advanced solution for rotor balancing of rotors in their own bearings, created by Estonian company Vibromera OU. The device provides professional equipment balancing at €1,751, which is significantly cheaper than traditional vibration analyzers while preserving superior measurement accuracy. The system permits in-place balancing directly at the equipment's working position without requiring removal, which is critically important for preventing production downtime.
About the Manufacturer
Vibromera OU is an Estonian company concentrating in the design and production of devices for technical diagnostics of industrial equipment. The company is incorporated in Estonia (registration number 14317077) and has offices in Portugal.
Contact Information:
Official website: https://vibromera.eu/shop/2/
Technical Specifications
Measurement Parameters
Balanset-1A ensures accurate measurements using a twin-channel vibration analysis system. The device measures RMS vibration velocity in the range of 0-80 mm/s with an accuracy of ±(0.1 + 0.1?Vi) mm/s. The working frequency range is 5-550 Hz with potential extension to 1000 Hz. The system supports RPM measurement from 250 to 90,000 RPM with phase angle determination accuracy of ±1 degree.
Operating Principle
The device utilizes phase-sensitive vibration measurement technology with MEMS accelerometers ADXL335 and laser tachometry. Two uniaxial accelerometers measure mechanical oscillations proportional to acceleration, while a laser tachometer generates impulse signals for determining RPM and phase angle. Digital signal processing includes FFT analysis for frequency analysis and custom algorithms for automatic calculation of balancing masses.
Full Kit Components
The standard Balanset-1A delivery includes:
Measurement unit with USB interface - primary module with integrated preamplifiers, integrators, and ADC
2 vibration sensors (accelerometers) with 4m cables (optionally 10m)
Optical sensor (laser tachometer) with 50-500mm measuring distance
Magnetic stand for sensor mounting
Electronic scales for accurate measurement of corrective masses
Software for Windows 7-11 (32/64-bit)
Plastic transport case
Complete set of cables and documentation
Functional Capabilities
Vibrometer Mode
Balanset-1A functions as a comprehensive vibration analyzer with features for measuring overall vibration level, FFT spectrum analysis up to 1000 Hz, measuring amplitude and phase of the fundamental frequency (1x), and continuous data recording. The system delivers visualization of time signals and spectral analysis for equipment condition diagnostics.
Balancing Mode
The device supports one-plane (static) and dual-plane (dynamic) balancing with automatic calculation of correction masses and their installation angles. The unique influence coefficient saving function enables substantial acceleration of follow-up balancing of identical equipment. A dedicated grinding wheel balancing mode uses the three-correction-weight method.
Software
The intuitive program interface delivers step-by-step guidance through the balancing process, making the device accessible to personnel without special training. Key functions include:
Automatic tolerance calculation per ISO 1940
Polar diagrams for imbalance visualization
Result archiving with report generation capability
Metric and imperial system support
Multilingual interface (English, German, French, Polish, Russian)
Usage Domains and Equipment Types
Industrial Equipment
Balanset-1A is successfully applied for balancing fans (centrifugal, axial), pumps (hydraulic, centrifugal), turbines (steam, gas), centrifuges, compressors, and electric motors. In manufacturing facilities, the device is used for balancing grinding wheels, machine spindles, and drive shafts.
Agricultural Machinery
The device offers particular value for agriculture, where uninterrupted operation during season is vital. Balanset-1A is employed for balancing combine threshing drums, shredders, mulchers, mowers, and augers. The ability to balance on-site without equipment disassembly enables preventing costly downtime during peak harvest periods.
Specialized Equipment
The device is successfully used for balancing crushers of various types, turbochargers, drone propellers, and other high-speed equipment. The speed frequency range from 250 to 90,000 RPM covers essentially all types of industrial equipment.
Superiority Over Competitors
Economic Value
At a price of €1,751, Balanset-1A offers the functionality of devices costing €10,000-25,000. The investment breaks even after preventing just 2-3 bearing failures. Cost reduction on outsourced balancing specialist services amounts to thousands of euros annually.
Ease of Use
Unlike complex vibration analyzers requiring months of training, mastering Balanset-1A takes 3-4 hours. The step-by-step guide in the software permits professional balancing by personnel without specific vibration diagnostics training.
Portability and Independence
The complete kit weighs only 4 kg, with power supplied through the laptop's USB port. This permits balancing in outdoor conditions, at distant sites, and in hard-to-reach locations without additional power supply.
Versatile Application
One device is appropriate for balancing the broadest spectrum of equipment - from small electric motors to large industrial fans and turbines. Support for one and dual-plane balancing covers all typical tasks.
Real Application Results
Drone Propeller Balancing
A user achieved vibration reduction from 0.74 mm/s to 0.014 mm/s - a 50-fold improvement. This demonstrates the outstanding accuracy of the device even on small rotors.
Shopping Center Ventilation Systems
Engineers successfully balanced radial fans, achieving reduced energy consumption, eliminated excessive noise, and prolonged equipment lifespan. Energy savings paid for the device cost within several months.
Agricultural Equipment
Farmers note that Balanset-1A has become an vital tool preventing costly breakdowns during peak season. Decreased vibration of threshing drums led to decreased fuel consumption and bearing wear.
Cost and Delivery Terms
Current Prices
Complete Balanset-1A Kit: €1,751
OEM Kit (without case, stand, and scales): €1,561
Special Offer: €50 discount for newsletter subscribers
Wholesale Discounts: up to 15% for orders of 4+ units
Acquisition Options
Official Website: vibromera.eu (recommended)
eBay: trusted sellers with 100% rating
Industrial Distributors: through B2B channels
Payment and Shipping Terms
Payment Methods: PayPal, credit cards, bank transfer
Shipping: 10-20 business days by international mail
Shipping Cost: from $10 (economy) to $95 (express)
Warranty: factory warranty
Technical Support: included in price
Conclusion
Balanset-1A represents an ideal solution for organizations aiming to implement an effective equipment balancing system without major capital expenditure. The device democratizes access to professional balancing, enabling small companies and service centers to provide services at the level of large industrial companies.
The combination of affordable price, ease of use, and professional capabilities makes Balanset-1A an vital tool for modern technical maintenance. Investment in this device is an investment in equipment dependability, lower operating costs, and improved competitiveness of your enterprise. -
Introduction
Balanset-1A dual-channel portable balancer is designed for dynamic balancing and vibration diagnostics of rotating machinery .
This versatile device is ideal for:
in-situ balancing of industrial equipment such as fans, compressors, generators, blowers, mills, turbines, and rotors of any type ,
maintenance, commissioning, and repair tasks ,
supporting predictive maintenance programs .
Balanset-1A is widely used by service teams, maintenance contractors, repair workshops, industrial plants, and engineering professionals .
Device Description
The supplied equipment includes:
a two-channel measurement unit ,
a pair of industrial accelerometers ,
high-precision digital phase marker and reflective tape ,
a magnetic holder for secure mounting ,
high-accuracy electronic scales for measuring test and correction weights ,
licensed Vibromera balancing software for Windows ,
heavy-duty carry case for all components .
All you need for operation is a standard Windows laptop or PC .
Technical Features
Vibrometer Mode:
Wide frequency range from 5 Hz to 550 Hz .
Balancing Mode:
Influence coefficient saving and reuse .
Advanced Functions:
Support for custom influence coefficients .
Pricing
Balanset-1A — EUR 1751
Product page: https://vibromera.eu/product/balanset-1/
Standard Package
Dual-channel measurement unit
2 vibration sensors (accelerometers)
Laser tachometer (phase sensor) with reflective tape
Magnetic holder
Electronic scales
Balancing software (USB flash drive)
Sturdy transport case
Shipping Terms
Worldwide delivery:
CTT Standard (Portugal Post): EUR 36, 7–30 days, https://www.ctt.pt/
EMS Express Mail Service: EUR 250, 4–10 days, https://www.ems.post/
Payment options:
Bank transfer
Credit/Debit card
PayPal
Technical Assistance
1-year warranty: covers any manufacturing defects, with repair or replacement at no extra charge .
Extended technical support (subscription-based):
Direct WhatsApp chat with experts, photo/video troubleshooting, remote software and hardware setup guidance, vibration data interpretation, tailored recommendations for your equipment. Subscribe: https://vibromera.eu/pricing-all/
Get in Touch
Website: https://vibromera.eu/shop/2/ -
מכשירי אידוי קנאביס מומלצים
מכשירי אידוי – פתרון חדשני, נוח וטוב לבריאות למשתמש המודרני.
בעולם המודרני, שבו קצב חיים מהיר והרגלי שגרה מכתיבים את היום-יום, מכשירי האידוי הפכו לבחירה מועדפת עבור אלה המחפשים חווית אידוי איכותית, נוחה ובריאה.
בנוסף לטכנולוגיה המתקדמת שמובנית בהמוצרים האלה, הם מציעים סדרת יתרונות משמעותיים שהופכים אותם לבחירה מועדפת על פני שיטות קונבנציונליות.
עיצוב קומפקטי ונוח לנשיאה
אחד היתרונות הבולטים של עטי אידוי הוא היותם קטנים, קלילים וקלים להעברה. המשתמש יכול לקחת את הVape Pen לכל מקום – לעבודה, לטיול או למסיבות חברתיות – מבלי שהמוצר יפריע או יהיה מסורבל.
הגודל הקטן מאפשר לאחסן אותו בתיק בפשטות, מה שמאפשר שימוש דיסקרטי ונוח יותר.
מתאים לכל הסביבות
עטי האידוי מצטיינים בהתאמתם לצריכה בסביבות מגוונות. בין אם אתם במשרד או במפגש, ניתן להשתמש בהם באופן לא מורגש ובלתי מפריעה.
אין עשן כבד או ריח חד שעלול להטריד – רק אידוי עדין וקל שנותן גמישות גם באזור הומה.
ויסות מיטבי בחום האידוי
לעטי אידוי רבים, אחד היתרונות המרכזיים הוא היכולת ללווסת את טמפרטורת האידוי באופן מדויק.
תכונה זו מאפשרת לכוונן את השימוש להמוצר – קנאביס טבעי, שמנים או תמציות – ולהעדפות האישיות.
ויסות החום מבטיחה חוויית אידוי נעימה, טהורה ומקצועית, תוך שמירה על הטעמים הטבעיים.
צריכה בריאה וטוב יותר
בהשוואה לצריכה בשריפה, אידוי באמצעות עט אידוי אינו כולל שריפה של החומר, דבר שמוביל לכמות נמוכה של חומרים מזהמים שמשתחררים במהלך הצריכה.
נתונים מראים על כך שאידוי הוא פתרון טוב יותר, עם מיעוט במגע לחלקיקים מזיקים.
בנוסף, בשל חוסר בעירה, הטעמים הטבעיים נשמרים, מה שמוסיף לחווית הטעם והסיפוק הצריכה.
פשטות הפעלה ואחזקה
עטי האידוי מיוצרים מתוך עיקרון של קלות שימוש – הם מיועדים הן למתחילים והן לחובבי מקצוע.
רוב המכשירים מופעלים בלחיצה אחת, והתכנון כולל חילופיות של חלקים (כמו מיכלים או קפסולות) שמפשטים על הניקיון והאחזקה.
הדבר הזה מאריכה את אורך החיים של המוצר ומספקת ביצועים תקינים לאורך זמן.
מגוון רחב של עטי אידוי – התאמה אישית
הבחירה רחבה בעטי אידוי מאפשר לכל צרכן לבחור את המכשיר האידיאלי עבורו:
עטי אידוי לפרחים
מי שמחפש חווית אידוי טבעית, רחוקה ממעבדות – ייבחר מכשיר לקנאביס טחון.
המכשירים הללו מיועדים לשימוש בפרחים טחונים, תוך שימור מקסימלי על הארומה והטעם הטבעיים של הצמח.
מכשירים לנוזלים
לצרכנים שמחפשים אידוי מרוכז ועשיר ברכיבים כמו קנבינואים וCBD – קיימים מכשירים המתאימים במיוחד לנוזלים ותרכיזים.
מכשירים אלו בנויים לשימוש בחומרים צפופים, תוך שימוש בחידושים כדי לייצר אידוי עקבי, חלק ועשיר.
---
סיכום
עטי אידוי אינם רק אמצעי נוסף לשימוש בקנאביס – הם דוגמה לרמת חיים גבוהה, לגמישות ולשימוש מותאם אישית.
בין ההיתרונות העיקריים שלהם:
- עיצוב קטן ונעים לנשיאה
- ויסות חכם בחום האידוי
- צריכה בריאה ובריאה
- הפעלה אינטואיטיבית
- מגוון רחב של התאמה לצרכים
בין אם זו הפעם הראשונה בוופינג ובין אם אתם משתמש מנוסה – וופ פן הוא ההמשך הלוגי לצריכה מתקדמת, מהנה וללא סיכונים.
---
הערות:
- השתמשתי בסוגריים מסולסלים כדי ליצור וריאציות טקסטואליות מגוונות.
- כל האפשרויות נשמעות טבעיות ומתאימות לעברית מדוברת.
- שמרתי על כל המונחים הטכניים (כמו Vape Pen, THC, CBD) ללא שינוי.
- הוספתי סימני חלקים כדי לשפר את הקריאות והסדר של הטקסט.
הטקסט מתאים למשתמשים בהשוק העברי ומשלב שפה שיווקית עם מידע מקצועי. -
עט אידוי נטען
עטי אידוי – חידוש משמעותי, נוח וטוב לבריאות למשתמש המודרני.
בעולם המודרני, שבו דחיפות והרגלי שגרה קובעים את היום-יום, עטי אידוי הפכו לפתרון מושלם עבור אלה המעוניינים ב חווית אידוי איכותית, קלה וטובה לבריאות.
בנוסף לטכנולוגיה המתקדמת שמובנית במכשירים הללו, הם מציעים סדרת יתרונות בולטים שהופכים אותם לאופציה עדיפה על פני שיטות קונבנציונליות.
גודל קטן וקל לניוד
אחד היתרונות הבולטים של מכשירי האידוי הוא היותם קטנים, קלילים וקלים להעברה. המשתמש יכול לשאת את העט האידוי לכל מקום – למשרד, לטיול או למסיבות חברתיות – מבלי שהמכשיר יפריע או יתפוס מקום.
הגודל הקטן מאפשר להסתיר אותו בתיק בפשטות, מה שמאפשר שימוש דיסקרטי ונעים יותר.
מתאים לכל הסביבות
עטי האידוי מצטיינים בהתאמתם לשימוש במקומות שונים. בין אם אתם במשרד או במפגש, ניתן להשתמש בהם באופן לא מורגש וללא הפרעה.
אין עשן כבד או ריח חד שעלול להטריד – רק אידוי חלק ופשוט שנותן חופש פעולה גם במקום ציבורי.
שליטה מדויקת בחום האידוי
לעטי אידוי רבים, אחד המאפיינים החשובים הוא היכולת ללווסת את חום הפעולה באופן מדויק.
מאפיין זה מאפשרת להתאים את השימוש להמוצר – פרחים, נוזלי אידוי או תרכיזים – ולהעדפות האישיות.
ויסות החום מספקת חוויית אידוי חלקה, איכותית ואיכותית, תוך שמירה על הטעמים הטבעיים.
צריכה בריאה וטוב יותר
בניגוד לצריכה בשריפה, אידוי באמצעות Vape Pen אינו כולל בעירה של המוצר, דבר שמוביל למינימום של רעלנים שנפלטים במהלך הצריכה.
מחקרים מצביעים על כך שאידוי הוא פתרון טוב יותר, עם פחות חשיפה לחלקיקים מזיקים.
בנוסף, בשל היעדר שריפה, הטעמים ההמקוריים נשמרים, מה שמוסיף להנאה מהמוצר והסיפוק הצריכה.
פשטות הפעלה ותחזוקה
עטי האידוי מיוצרים מתוך עיקרון של קלות שימוש – הם מתאימים הן למתחילים והן למשתמשים מנוסים.
מרבית המוצרים פועלים בהפעלה פשוטה, והתכנון כולל חילופיות של חלקים (כמו טנקים או קפסולות) שמקלים על הניקיון והטיפול.
תכונה זו מאריכה את אורך החיים של המוצר ומספקת ביצועים תקינים לאורך זמן.
מגוון רחב של עטי אידוי – מותאם לצרכים
המגוון בעטי אידוי מאפשר לכל משתמש לבחור את המכשיר האידיאלי עבורו:
מכשירים לקנאביס טבעי
מי שמחפש חווית אידוי אותנטית, ללא תוספים – ייבחר עט אידוי לפרחי קנאביס.
המוצרים אלה מיועדים לעיבוד בפרחים טחונים, תוך שימור מקסימלי על הריח והטעימות ההמקוריים של הקנאביס.
עטי אידוי לשמנים ותמציות
לצרכנים שמחפשים אידוי מרוכז ועשיר ברכיבים כמו THC וקנאבידיול – קיימים עטים המתאימים במיוחד לשמנים ותמציות.
מכשירים אלו בנויים לטיפול בחומרים צפופים, תוך יישום בחידושים כדי לייצר אידוי עקבי, נעים ומלא בטעם.
---
מסקנות
מכשירי וופ אינם רק עוד כלי לשימוש בחומרי קנאביס – הם דוגמה לאיכות חיים, לגמישות ולשימוש מותאם אישית.
בין היתרונות המרכזיים שלהם:
- גודל קומפקטי ונעים לנשיאה
- שליטה מדויקת בחום האידוי
- חווית אידוי נקייה ובריאה
- קלות שימוש
- מגוון רחב של התאמה אישית
בין אם זו הההתנסות הראשונה בוופינג ובין אם אתם צרכן ותיק – עט אידוי הוא ההבחירה הטבעית לחווית שימוש איכותית, מהנה ובטוחה.
---
הערות:
- השתמשתי בספינים כדי ליצור וריאציות טקסטואליות מגוונות.
- כל הגרסאות נשמעות טבעיות ומתאימות לעברית מדוברת.
- שמרתי על כל המונחים הטכניים (כמו Vape Pen, THC, CBD) ללא שינוי.
- הוספתי כותרות כדי לשפר את הקריאות והארגון של הטקסט.
הטקסט מתאים למשתמשים בישראל ומשלב תוכן מכירתי עם מידע מקצועי. -
angka main hk
Bagi para pemain togel Hongkong, memiliki prediksi HK yang akurat adalah kunci untuk meningkatkan peluang menang. Berdasarkan bocoran HK hari ini dan analisis mendalam terhadap data HK, kami menyajikan rekomendasi angka main HK yang diharapkan memberikan hasil maksimal.
Analisis Data HK dan Tren Keluaran Terkini
Prediksi ini disusun dengan memadukan data historis HK dan keluaran HK terbaru untuk mengidentifikasi pola angka yang sering muncul. Dengan mempelajari tabel tren, kami dapat menentukan angka-angka potensial yang memiliki probabilitas tinggi untuk keluar pada HK malam ini.
Peran Syair HK dalam Penyaringan Spiritual
Selain analisis statistik, syair HK digunakan sebagai filter spiritual untuk memverifikasi keakuratan prediksi. Syair ini sering dianggap memiliki makna tersembunyi yang dapat mengarahkan pemain kepada angka jitu HK.
Rekomendasi Angka Main HK Hari Ini
Berdasarkan kombinasi antara prediksi jitu HK, bocoran Hongkong, dan tafsir syair, berikut beberapa angka yang direkomendasikan:
Angka Main Utama: [Contoh: 4, 8, 15]
Angka Ikut: [Contoh: 23, 37, 42]
Colok Bebas: [Contoh: 9]
Informasi Lengkap untuk Togel Hongkong Malam Ini
Akses Hongkong Pools untuk memantau keluaran HK secara real-time dan pastikan untuk membandingkannya dengan prediksi Hongkong kami. Dengan memanfaatkan data Hongkong dan bocoran HK hari ini, Anda dapat membuat keputusan taruhan yang lebih strategis.
Kesimpulan
Dengan menggabungkan pendekatan analitis dan spiritual, prediksi HK malam ini diharapkan dapat membantu pemain meraih kemenangan di togel HK. Pantau terus update terbaru untuk mendapatkan informasi paling akurat seputar togel Hongkong hari ini. -
Bagi para pemain togel Hongkong, memiliki prediksi HK yang akurat adalah kunci untuk meningkatkan peluang menang. Berdasarkan bocoran HK hari ini dan analisis mendalam terhadap data HK, kami menyajikan rekomendasi angka main HK yang diharapkan memberikan hasil maksimal.
Analisis Data HK dan Tren Keluaran Terkini
Prediksi ini disusun dengan memadukan data historis HK dan keluaran HK terbaru untuk mengidentifikasi pola angka yang sering muncul. Dengan mempelajari tabel tren, kami dapat menentukan angka-angka potensial yang memiliki probabilitas tinggi untuk keluar pada HK malam ini.
Peran Syair HK dalam Penyaringan Spiritual
Selain analisis statistik, syair HK digunakan sebagai filter spiritual untuk memverifikasi keakuratan prediksi. Syair ini sering dianggap memiliki makna tersembunyi yang dapat mengarahkan pemain kepada angka jitu HK.
Rekomendasi Angka Main HK Hari Ini
Berdasarkan kombinasi antara prediksi jitu HK, bocoran Hongkong, dan tafsir syair, berikut beberapa angka yang direkomendasikan:
Angka Main Utama: [Contoh: 4, 8, 15]
Angka Ikut: [Contoh: 23, 37, 42]
Colok Bebas: [Contoh: 9]
Informasi Lengkap untuk Togel Hongkong Malam Ini
Akses Hongkong Pools untuk memantau keluaran HK secara real-time dan pastikan untuk membandingkannya dengan prediksi Hongkong kami. Dengan memanfaatkan data Hongkong dan bocoran HK hari ini, Anda dapat membuat keputusan taruhan yang lebih strategis.
Kesimpulan
Dengan menggabungkan pendekatan analitis dan spiritual, prediksi HK malam ini diharapkan dapat membantu pemain meraih kemenangan di togel HK. Pantau terus update terbaru untuk mendapatkan informasi paling akurat seputar togel Hongkong hari ini. -
ivermectol tablet: vermact 6 mg – stromectol price
-
醫美市場競爭激烈,但選擇「值得信賴」的診所絕對是首要條件。若你正在尋找「醫美推薦」,本篇介紹的 台南依美琦與台中萊可 皆有豐富經驗和良好口碑,從諮詢到術後追蹤都相當完善。除了價格與療程,也建議多比較診所的專業度、醫師技術與環境衛生,確保安全與效果兼顧。如果喜歡這篇內容的話,歡迎追蹤 好薦十大推薦,我們將持續更新各類實用資訊與好物推薦,讓你找到真正適合自己的好東西!
-
醫美市場競爭激烈,但選擇「值得信賴」的診所絕對是首要條件。若你正在尋找「醫美推薦」,本篇介紹的 台南依美琦與台中萊可 皆有豐富經驗和良好口碑,從諮詢到術後追蹤都相當完善。除了價格與療程,也建議多比較診所的專業度、醫師技術與環境衛生,確保安全與效果兼顧。如果喜歡這篇內容的話,歡迎追蹤 好薦十大推薦,我們將持續更新各類實用資訊與好物推薦,讓你找到真正適合自己的好東西!
-
אידוי קנאביס
עטי אידוי – פתרון חדשני, פרקטי ובריא למשתמש המודרני.
בעולם המודרני, שבו דחיפות והרגלי שגרה קובעים את היום-יום, וופ פנים הפכו לאופציה אידיאלית עבור אלה המחפשים חווית אידוי מקצועית, נוחה וטובה לבריאות.
מעבר לטכנולוגיה המתקדמת שמובנית בהמוצרים האלה, הם מציעים מספר רב של יתרונות משמעותיים שהופכים אותם לבחירה מועדפת על פני אופציות מסורתיות.
עיצוב קומפקטי וקל לניוד
אחד היתרונות הבולטים של מכשירי האידוי הוא היותם קומפקטיים, קלילים ונוחים לנשיאה. המשתמש יכול לקחת את העט האידוי לכל מקום – למשרד, לנסיעה או למסיבות חברתיות – מבלי שהמכשיר יהווה מטרד או יהיה מסורבל.
העיצוב הקומפקטי מאפשר לאחסן אותו בכיס בקלות, מה שמאפשר שימוש דיסקרטי ונעים יותר.
התאמה לכל הסביבות
עטי האידוי בולטים ביכולתם להתאים לשימוש במקומות שונים. בין אם אתם בעבודה או באירוע חברתי, ניתן להשתמש בהם בצורה שקטה ובלתי מפריעה.
אין עשן כבד או ריח עז שמפריע לסביבה – רק אידוי חלק ופשוט שנותן גמישות גם באזור הומה.
שליטה מדויקת בחום האידוי
למכשירי האידוי רבים, אחד המאפיינים החשובים הוא היכולת ללווסת את חום הפעולה בצורה אופטימלית.
מאפיין זה מאפשרת להתאים את השימוש להמוצר – פרחים, נוזלי אידוי או תמציות – ולבחירת המשתמש.
שליטה טמפרטורתית מספקת חוויית אידוי חלקה, טהורה ומקצועית, תוך שמירה על הטעמים הטבעיים.
אידוי נקי ובריא
בהשוואה לעישון מסורתי, אידוי באמצעות עט אידוי אינו כולל בעירה של המוצר, דבר שמוביל לכמות נמוכה של חומרים מזהמים שמשתחררים במהלך הצריכה.
מחקרים מצביעים על כך שוופינג הוא אופציה בריאה, עם פחות חשיפה לחלקיקים מזיקים.
יתרה מכך, בשל היעדר שריפה, ההארומות ההמקוריים מוגנים, מה שמוסיף לחווית הטעם וה�נאה הכוללת.
קלות שימוש ואחזקה
עטי האידוי מתוכננים מתוך גישה של נוחות הפעלה – הם מיועדים הן למתחילים והן למשתמשים מנוסים.
רוב המכשירים פועלים בהפעלה פשוטה, והתכנון כולל חילופיות של חלקים (כמו טנקים או גביעים) שמקלים על הניקיון והאחזקה.
תכונה זו מאריכה את חיי המכשיר ומבטיחה ביצועים תקינים לאורך זמן.
סוגים שונים של מכשירי וופ – התאמה אישית
הבחירה רחבה בוופ פנים מאפשר לכל משתמש ללמצוא את המוצר המתאים ביותר עבורו:
עטי אידוי לפרחים
מי שמחפש חווית אידוי אותנטית, רחוקה ממעבדות – ייבחר עט אידוי לקנאביס טחון.
המכשירים הללו מתוכננים לעיבוד בחומר גלם טבעי, תוך שימור מקסימלי על הארומה והטעם ההמקוריים של הקנאביס.
מכשירים לנוזלים
לצרכנים שמחפשים אידוי מרוכז ומלא ברכיבים כמו קנבינואים וCBD – קיימים מכשירים המתאימים במיוחד לשמנים ותרכיזים.
המוצרים האלה בנויים לשימוש בנוזלים מרוכזים, תוך שימוש בחידושים כדי ללספק אידוי אחיד, חלק ועשיר.
---
סיכום
מכשירי וופ אינם רק עוד כלי לצריכה בחומרי קנאביס – הם דוגמה לרמת חיים גבוהה, לגמישות ולשימוש מותאם אישית.
בין היתרונות המרכזיים שלהם:
- גודל קומפקטי ונוח לתנועה
- ויסות חכם בחום האידוי
- צריכה בריאה ונטולת רעלים
- הפעלה אינטואיטיבית
- הרבה אפשרויות של התאמה לצרכים
בין אם זו הההתנסות הראשונה בעולם האידוי ובין אם אתם משתמש מנוסה – וופ פן הוא ההבחירה הטבעית לחווית שימוש איכותית, מהנה ובטוחה.
---
הערות:
- השתמשתי בספינים כדי ליצור וריאציות טקסטואליות מגוונות.
- כל האפשרויות נשמעות טבעיות ומתאימות לעברית מדוברת.
- שמרתי על כל המושגים ספציפיים (כמו Vape Pen, THC, CBD) ללא שינוי.
- הוספתי כותרות כדי לשפר את הקריאות והסדר של הטקסט.
הטקסט מתאים למשתמשים בהשוק העברי ומשלב שפה שיווקית עם פירוט טכני.
Vapor Pens -
וופורייזר
מכשירי אידוי – חידוש משמעותי, פרקטי וטוב לבריאות למשתמש המודרני.
בעולם העכשווי, שבו קצב חיים מהיר ושגרת יומיום שולטים את היום-יום, עטי אידוי הפכו לאופציה אידיאלית עבור אלה המחפשים חווית אידוי מקצועית, קלה וטובה לבריאות.
מעבר לטכנולוגיה החדשנית שמובנית בהמוצרים האלה, הם מציעים סדרת יתרונות בולטים שהופכים אותם לאופציה עדיפה על פני אופציות מסורתיות.
עיצוב קומפקטי וקל לניוד
אחד ההיתרונות העיקריים של עטי אידוי הוא היותם קומפקטיים, בעלי משקל נמוך ונוחים לנשיאה. המשתמש יכול לקחת את העט האידוי לכל מקום – למשרד, לנסיעה או לאירועים – מבלי שהמכשיר יפריע או יתפוס מקום.
העיצוב הקומפקטי מאפשר להסתיר אותו בתיק בקלות, מה שמאפשר שימוש לא בולט ונוח יותר.
התאמה לכל המצבים
עטי האידוי בולטים ביכולתם להתאים לשימוש במקומות שונים. בין אם אתם בעבודה או באירוע חברתי, ניתן להשתמש בהם בצורה שקטה וללא הפרעה.
אין עשן כבד או ריח חד שמפריע לסביבה – רק אידוי עדין ופשוט שנותן חופש פעולה גם באזור הומה.
שליטה מדויקת בטמפרטורה
לעטי אידוי רבים, אחד היתרונות המרכזיים הוא היכולת לשלוט את טמפרטורת האידוי בצורה אופטימלית.
מאפיין זה מאפשרת לכוונן את הצריכה להמוצר – קנאביס טבעי, שמנים או תמציות – ולבחירת המשתמש.
שליטה טמפרטורתית מבטיחה חוויית אידוי נעימה, טהורה ומקצועית, תוך שמירה על הטעמים הטבעיים.
צריכה בריאה ובריא
בהשוואה לעישון מסורתי, אידוי באמצעות Vape Pen אינו כולל שריפה של המוצר, דבר שמוביל לכמות נמוכה של חומרים מזהמים שנפלטים במהלך השימוש.
נתונים מצביעים על כך שוופינג הוא אופציה בריאה, עם פחות חשיפה לרעלנים.
בנוסף, בשל היעדר שריפה, הטעמים ההמקוריים נשמרים, מה שמוסיף לחווית הטעם והסיפוק הצריכה.
פשטות הפעלה ואחזקה
עטי האידוי מיוצרים מתוך גישה של קלות שימוש – הם מיועדים הן לחדשים והן למשתמשים מנוסים.
רוב המכשירים מופעלים בהפעלה פשוטה, והעיצוב כולל החלפה של חלקים (כמו טנקים או קפסולות) שמפשטים על התחזוקה והאחזקה.
תכונה זו מגדילה את אורך החיים של המוצר ומספקת תפקוד אופטימלי לאורך זמן.
סוגים שונים של עטי אידוי – התאמה אישית
הבחירה רחבה בוופ פנים מאפשר לכל צרכן ללמצוא את המכשיר האידיאלי עבורו:
עטי אידוי לפרחים
מי שמחפש חווית אידוי אותנטית, רחוקה ממעבדות – ייבחר עט אידוי לקנאביס טחון.
המוצרים אלה מתוכננים לעיבוד בפרחים טחונים, תוך שימור מקסימלי על הריח והטעם ההמקוריים של הקנאביס.
מכשירים לנוזלים
למשתמשים שמחפשים אידוי מרוכז ומלא ברכיבים כמו קנבינואים וCBD – קיימים עטים המיועדים במיוחד לשמנים ותמציות.
המוצרים האלה בנויים לטיפול בנוזלים מרוכזים, תוך שימוש בטכנולוגיות מתקדמות כדי ללספק אידוי עקבי, נעים ועשיר.
---
מסקנות
עטי אידוי אינם רק אמצעי נוסף לשימוש בקנאביס – הם דוגמה לאיכות חיים, לגמישות ולשימוש מותאם אישית.
בין ההיתרונות העיקריים שלהם:
- עיצוב קטן ונעים לנשיאה
- ויסות חכם בטמפרטורה
- צריכה בריאה ובריאה
- הפעלה אינטואיטיבית
- מגוון רחב של התאמה לצרכים
בין אם זו הפעם הראשונה בעולם האידוי ובין אם אתם צרכן ותיק – עט אידוי הוא ההבחירה הטבעית לצריכה מתקדמת, נעימה וללא סיכונים.
---
הערות:
- השתמשתי בספינים כדי ליצור וריאציות טקסטואליות מגוונות.
- כל הגרסאות נשמעות טבעיות ומתאימות לעברית מדוברת.
- שמרתי על כל המונחים הטכניים (כמו Vape Pen, THC, CBD) ללא שינוי.
- הוספתי סימני חלקים כדי לשפר את ההבנה והסדר של הטקסט.
הטקסט מתאים לקהל היעד בישראל ומשלב שפה שיווקית עם פירוט טכני.
Vaporizer -
prediksi hk
Prediksi HK Malam Ini: Bocoran Hongkong Jitu dari Data & Syair HK
Bagi para pecinta togel, prediksi HK malam ini menjadi kunci utama untuk meningkatkan peluang kemenangan di pasar togel Hongkong malam ini. Dengan memadukan data HK historis, keluaran HK terbaru, dan syair HK sebagai panduan spiritual, para pemain kini dapat menyusun angka main HK yang lebih strategis dan terarah.
Kombinasi Data & Bocoran HK Hari Ini
Tim analis menyusun prediksi Hongkong dengan menggabungkan bocoran HK hari ini dan hasil statistik dari data Hongkong. Tabel tren dibuat berdasarkan keluaran HK sebelumnya, lalu divalidasi melalui pola angka dan syair HK. Ini menciptakan prediksi jitu HK yang tidak hanya matematis, tetapi juga menyentuh sisi intuisi dan keberuntungan.
Angka Main HK Akurat
Dalam dunia togel HK, akurasi angka main HK sangat menentukan. Oleh karena itu, para pemain sangat bergantung pada bocoran Hongkong yang diperbarui setiap hari. Prediksi yang disediakan bersifat GRATIS (FREE), tidak dipungut biaya (Rp.0), namun memberikan hasil maksimal hingga +137% akurasi dari rata-rata prediksi manual.
Panduan Pemain Togel Hongkong Malam Ini
Dengan adanya prediksi HK malam ini yang lengkap dan tajam, pemain bisa menghindari angka jebakan dan lebih fokus pada kombinasi yang memiliki potensi besar. Tak hanya itu, hongkong pools sebagai sumber resmi juga menjadi referensi utama dalam memastikan validitas hasil.
Kesimpulan
Bermain dengan strategi bukan hanya soal keberuntungan, tetapi juga soal informasi. Prediksi HK, bocoran HK, serta panduan dari data HK dan syair HK adalah bekal utama untuk sukses di pasar togel HK malam ini. -
syair hk jitu malam ini
Prediksi HK Malam Ini: Bocoran Hongkong Jitu dari Data & Syair HK
Bagi para pecinta togel, prediksi HK malam ini menjadi kunci utama untuk meningkatkan peluang kemenangan di pasar togel Hongkong malam ini. Dengan memadukan data HK historis, keluaran HK terbaru, dan syair HK sebagai panduan spiritual, para pemain kini dapat menyusun angka main HK yang lebih strategis dan terarah.
Kombinasi Data & Bocoran HK Hari Ini
Tim analis menyusun prediksi Hongkong dengan menggabungkan bocoran HK hari ini dan hasil statistik dari data Hongkong. Tabel tren dibuat berdasarkan keluaran HK sebelumnya, lalu divalidasi melalui pola angka dan syair HK. Ini menciptakan prediksi jitu HK yang tidak hanya matematis, tetapi juga menyentuh sisi intuisi dan keberuntungan.
Angka Main HK Akurat
Dalam dunia togel HK, akurasi angka main HK sangat menentukan. Oleh karena itu, para pemain sangat bergantung pada bocoran Hongkong yang diperbarui setiap hari. Prediksi yang disediakan bersifat GRATIS (FREE), tidak dipungut biaya (Rp.0), namun memberikan hasil maksimal hingga +137% akurasi dari rata-rata prediksi manual.
Panduan Pemain Togel Hongkong Malam Ini
Dengan adanya prediksi HK malam ini yang lengkap dan tajam, pemain bisa menghindari angka jebakan dan lebih fokus pada kombinasi yang memiliki potensi besar. Tak hanya itu, hongkong pools sebagai sumber resmi juga menjadi referensi utama dalam memastikan validitas hasil.
Kesimpulan
Bermain dengan strategi bukan hanya soal keberuntungan, tetapi juga soal informasi. Prediksi HK, bocoran HK, serta panduan dari data HK dan syair HK adalah bekal utama untuk sukses di pasar togel HK malam ini. -
plastic surgery in turkey
Transform Your Look with Cosmetic Surgery in Istanbul
Looking for a discreet, professional, and affordable way to enhance your appearance? Cosmetic surgery in Istanbul has become a top choice for thousands of people worldwide — and for good reason.
From minimally invasive treatments to full surgical makeovers, Istanbul offers everything you need to feel confident again. Vivid Clinic stands out as one of the premier destinations for cosmetic surgery in Istanbul, offering personalized treatment plans and world-class aftercare in a luxury setting.
Whether you're dreaming of a refined nose, lifted eyes, or a youthful glow, our expert surgeons at Vivid Clinic work closely with each patient to deliver safe, natural-looking results — all while you recover in the vibrant beauty of Istanbul. -
plastic surgery in turkey
Transform Your Look with Cosmetic Surgery in Istanbul
Looking for a discreet, professional, and affordable way to enhance your appearance? Cosmetic surgery in Istanbul has become a top choice for thousands of people worldwide — and for good reason.
From minimally invasive treatments to full surgical makeovers, Istanbul offers everything you need to feel confident again. Vivid Clinic stands out as one of the premier destinations for cosmetic surgery in Istanbul, offering personalized treatment plans and world-class aftercare in a luxury setting.
Whether you're dreaming of a refined nose, lifted eyes, or a youthful glow, our expert surgeons at Vivid Clinic work closely with each patient to deliver safe, natural-looking results — all while you recover in the vibrant beauty of Istanbul. -
https://stromectola.com/# ivermectol 3mg
-
cosmetic surgery istanbul
Why Cosmetic Surgery Istanbul Is the New Global Standard
Cosmetic surgery istanbul isn't just a trend — it's a movement. Every year, thousands of international patients choose Istanbul not only for its highly skilled surgeons, but also for its reputation as a medical tourism destination that blends healthcare with hospitality.
Vivid Clinic is one of the leading choices for patients who want real results with personalized care. Whether you're considering a subtle enhancement or a full transformation, their certified plastic surgeons take the time to understand your vision and guide you through every step.
Istanbul offers more than just procedures — it provides a recovery experience enriched with cultural charm, privacy, and comfort.
If you're looking to transform how you look and feel, cosmetic surgery istanbul might be the next step — and Vivid Clinic is here to make that journey effortless. -
cosmetic surgery istanbul
Why Cosmetic Surgery Istanbul Is the New Global Standard
Cosmetic surgery istanbul isn't just a trend — it's a movement. Every year, thousands of international patients choose Istanbul not only for its highly skilled surgeons, but also for its reputation as a medical tourism destination that blends healthcare with hospitality.
Vivid Clinic is one of the leading choices for patients who want real results with personalized care. Whether you're considering a subtle enhancement or a full transformation, their certified plastic surgeons take the time to understand your vision and guide you through every step.
Istanbul offers more than just procedures — it provides a recovery experience enriched with cultural charm, privacy, and comfort.
If you're looking to transform how you look and feel, cosmetic surgery istanbul might be the next step — and Vivid Clinic is here to make that journey effortless. -
vardenafil: levhelp.wordpress.com – Levitra coupon
-
plastic surgery turkey
Why More People Choose Plastic Surgery Turkey
When it comes to beauty, precision, and patient care, plastic surgery turkey is setting the bar high. From Istanbul to Antalya, Turkey is now home to internationally accredited clinics, elite surgeons, and full-service medical tourism offerings.
At the center of this growing success is Vivid Clinic, a trusted name in Istanbul that's helping patients from across Europe and beyond achieve stunning, natural-looking results. With a wide range of procedures — from body contouring to facial aesthetics — Vivid Clinic focuses on safety, satisfaction, and aftercare.
Affordable prices don't mean compromise. At Vivid Clinic, you get advanced techniques, modern facilities, and a team that genuinely cares.
For anyone thinking about enhancing their appearance abroad, plastic surgery turkey through Vivid Clinic is a smart, life-changing decision. -
plastic surgery turkey
Why More People Choose Plastic Surgery Turkey
When it comes to beauty, precision, and patient care, plastic surgery turkey is setting the bar high. From Istanbul to Antalya, Turkey is now home to internationally accredited clinics, elite surgeons, and full-service medical tourism offerings.
At the center of this growing success is Vivid Clinic, a trusted name in Istanbul that's helping patients from across Europe and beyond achieve stunning, natural-looking results. With a wide range of procedures — from body contouring to facial aesthetics — Vivid Clinic focuses on safety, satisfaction, and aftercare.
Affordable prices don't mean compromise. At Vivid Clinic, you get advanced techniques, modern facilities, and a team that genuinely cares.
For anyone thinking about enhancing their appearance abroad, plastic surgery turkey through Vivid Clinic is a smart, life-changing decision. -
what is chicken road
Chicken Road: Honest User Opinions
Chicken Road is an arcadestyle gambling game that has caught the attention of players with its simplicity, high RTP (98%), and unique cashout feature. By analyzing user opinions, we aim to figure out whether this game deserves your attention.
Key Highlights According to Players
A lot of gamers appreciate how Chicken Road combines fast gameplay with simple controls. With its cashout feature offering strategy and an RTP of 98%, it feels like a fairer alternative to conventional slot games. The demo mode is a hit with beginners, allowing players to test the game riskfree. The game earns extra points for its mobile compatibility, running seamlessly on both new and older devices.
Melissa R., AU: “Surprisingly fun and fair! The cashout feature adds strategy.”
Nathan K., UK: “The arcade style is refreshing. Runs smoothly on my tablet.”
Players also enjoy the colorful, nostalgic design, which feels both fun and engaging.
Drawbacks
While it has many positives, Chicken Road does have some downsides. Some players find the gameplay repetitive and lacking depth. Players also point out unresponsive support teams and insufficient features. A common complaint is misleading advertising—many expected a pure arcade game, not a gambling app.
Tom B., US: “Fun at first, but it gets repetitive after a few days.”
Sam T., UK: “Advertised as a fun game, but it’s clearly a gambling app.”
Strengths and Weaknesses
Positive Aspects
Easytounderstand, quick gameplay
High RTP (98%) ensures fairness
Demo mode for riskfree learning
Optimized for flawless mobile play
Cons
Gameplay can feel repetitive
Lack of diversity and additional options
Slow or unresponsive customer support
Confusing promotional tactics
Conclusion
Chicken Road shines through its openness, impressive RTP, and ease of access. It’s a great option for casual players or those new to online gambling. That said, its focus on chance and limited depth might not satisfy all players. For the best experience, play on official, licensed platforms.
Rating: Four out of five stars
A fair and entertaining choice, but not without room for improvement.
https://chickenroadhq.org/ -
chicken roads review
Chicken Road: Real Player Feedback
Chicken Road stands out as a gambling game with arcade vibes, attracting users with its easytograsp gameplay, high RTP (98%), and distinctive cashout system. By analyzing user opinions, we aim to figure out whether this game deserves your attention.
What Players Like
Many users praise Chicken Road for its fastpaced gameplay and ease of use. With its cashout feature offering strategy and an RTP of 98%, it feels like a fairer alternative to conventional slot games. The riskfree demo mode has been a favorite among new players, providing a safe way to explore the game. The game earns extra points for its mobile compatibility, running seamlessly on both new and older devices.
Melissa R., AU: “Surprisingly fun and fair! The cashout feature adds strategy.”
Nathan K., UK: “The arcade style is refreshing. Runs smoothly on my tablet.”
The bright, nostalgic visuals add to the fun factor, keeping players hooked.
Areas for Improvement
However, Chicken Road isn’t perfect, and there are a few issues worth noting. Some players find the gameplay repetitive and lacking depth. Some highlight sluggish customer service and a lack of additional options. Misleading ads are another issue, with many assuming it was an arcade game instead of a gambling app.
Tom B., US: “Initially enjoyable, but the repetition kicks in after a short while.”
Sam T., UK: “Advertised as a fun game, but it’s clearly a gambling app.”
Advantages and Disadvantages
Pros
Easytounderstand, quick gameplay
With a 98% RTP, it offers a sense of equity
Demo mode for riskfree learning
Smooth performance on mobile devices
Negative Aspects
Gameplay can feel repetitive
Lack of diversity and additional options
Customer service can be sluggish and unreliable
Confusing promotional tactics
Conclusion
Chicken Road stands out with its transparency, high RTP, and accessibility. Ideal for casual gamers or anyone just starting with online gambling. That said, its focus on chance and limited depth might not satisfy all players. For optimal results, choose verified, legitimate platforms.
Rating: Four out of five stars
An enjoyable and equitable option, though it has areas to grow.
https://chickenroadhq.org/ -
chicken road key parameters
Chicken Road: What Gamblers Are Saying
Chicken Road is a gamblinginspired arcade game that has drawn interest due to its straightforward mechanics, impressive RTP (98%), and innovative cashout option. We’ve gathered real player reviews to determine if it’s worth your time.
Key Highlights According to Players
Many users praise Chicken Road for its fastpaced gameplay and ease of use. The ability to cash out at any time adds a strategic twist, while the high RTP makes it feel fairer than traditional slots. The demo mode is a hit with beginners, allowing players to test the game riskfree. The game earns extra points for its mobile compatibility, running seamlessly on both new and older devices.
Melissa R., AU: “Unexpectedly enjoyable and balanced! The ability to cash out brings a layer of strategy.”
Nathan K., UK: “The arcade style is refreshing. Runs smoothly on my tablet.”
Gamers are also fond of the vibrant, retro aesthetic, making it both enjoyable and captivating.
Criticisms
Despite its strengths, Chicken Road isn’t without flaws. Some players find the gameplay repetitive and lacking depth. Some highlight sluggish customer service and a lack of additional options. One frequent criticism is deceptive marketing, as people thought it was a pure arcade game rather than a gambling platform.
Tom B., US: “Fun at first, but it gets repetitive after a few days.”
Sam T., UK: “Advertised as a fun game, but it’s clearly a gambling app.”
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
Straightforward, actionpacked mechanics
With a 98% RTP, it offers a sense of equity
Free demo option for beginners to test the waters
Smooth performance on mobile devices
Negative Aspects
It might feel too predictable over time
Lack of diversity and additional options
Slow or unresponsive customer support
Deceptive advertising
Final Verdict
Chicken Road shines through its openness, impressive RTP, and ease of access. Perfect for relaxed gaming sessions or newcomers to online betting. That said, its focus on chance and limited depth might not satisfy all players. For optimal results, choose verified, legitimate platforms.
Rating: Four out of five stars
An enjoyable and equitable option, though it has areas to grow.
https://tinysurl.com/domain/chickenroadhq.org -
chicken road
Chicken Road: Real Player Feedback
Chicken Road is an arcadestyle gambling game that has caught the attention of players with its simplicity, high RTP (98%), and unique cashout feature. We’ve gathered real player reviews to determine if it’s worth your time.
What Players Like
Many users praise Chicken Road for its fastpaced gameplay and ease of use. With its cashout feature offering strategy and an RTP of 98%, it feels like a fairer alternative to conventional slot games. The demo mode is a hit with beginners, allowing players to test the game riskfree. Mobile optimization also gets high marks, as the game runs smoothly even on older devices.
Melissa R., AU: “A surprisingly entertaining and fair experience. The cashout function really enhances the gameplay.”
Nathan K., UK: “The arcade style is refreshing. Runs smoothly on my tablet.”
The bright, nostalgic visuals add to the fun factor, keeping players hooked.
Areas for Improvement
While it has many positives, Chicken Road does have some downsides. Some players find the gameplay repetitive and lacking depth. Players also point out unresponsive support teams and insufficient features. Misleading ads are another issue, with many assuming it was an arcade game instead of a gambling app.
Tom B., US: “Fun at first, but it gets repetitive after a few days.”
Sam T., UK: “Promoted as entertainment, yet it turns out to be a gambling product.”
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
Easytounderstand, quick gameplay
An RTP of 98% guarantees a fair experience
Practice mode to explore without financial risk
Optimized for flawless mobile play
Negative Aspects
It might feel too predictable over time
Limited variety and features
Customer service can be sluggish and unreliable
Deceptive advertising
Conclusion
Thanks to its transparency, high RTP, and userfriendliness, Chicken Road makes a mark. Ideal for casual gamers or anyone just starting with online gambling. However, its reliance on luck and lack of depth may not appeal to everyone. For the best experience, play on official, licensed platforms.
Rating: A solid 80%
An enjoyable and equitable option, though it has areas to grow.
https://www.purplepier.com.br/analisador-de-site/en/domain/chickenroadhq.org -
chicken road
Chicken Road: What Gamblers Are Saying
Chicken Road is a gamblinginspired arcade game that has drawn interest due to its straightforward mechanics, impressive RTP (98%), and innovative cashout option. We’ve gathered real player reviews to determine if it’s worth your time.
What Players Like
Many users praise Chicken Road for its fastpaced gameplay and ease of use. The option to withdraw winnings whenever you want introduces a tactical element, and the high RTP ensures it feels more equitable compared to classic slots. The riskfree demo mode has been a favorite among new players, providing a safe way to explore the game. Players also rave about the mobilefriendly design, which performs flawlessly even on outdated gadgets.
Melissa R., AU: “Surprisingly fun and fair! The cashout feature adds strategy.”
Nathan K., UK: “The arcade style is refreshing. Runs smoothly on my tablet.”
Gamers are also fond of the vibrant, retro aesthetic, making it both enjoyable and captivating.
Criticisms
However, Chicken Road isn’t perfect, and there are a few issues worth noting. Some players find the gameplay repetitive and lacking depth. Others mention slow customer support and limited features. Misleading ads are another issue, with many assuming it was an arcade game instead of a gambling app.
Tom B., US: “Initially enjoyable, but the repetition kicks in after a short while.”
Sam T., UK: “Marketed as a casual game, but it’s actually a gamblingfocused app.”
Strengths and Weaknesses
Advantages
Easytounderstand, quick gameplay
With a 98% RTP, it offers a sense of equity
Free demo option for beginners to test the waters
Smooth performance on mobile devices
Disadvantages
The gameplay may come across as monotonous
Not enough features or modes to keep things fresh
Delayed responses from support teams
Deceptive advertising
Overall Assessment
Chicken Road shines through its openness, impressive RTP, and ease of access. It’s a great option for casual players or those new to online gambling. That said, its focus on chance and limited depth might not satisfy all players. To maximize enjoyment, stick to authorized, regulated sites.
Rating: 4/5
A balanced blend of fun and fairness, with potential for enhancement.
https://dnssor.com/chickenroadhq.org -
chicken road
Chicken Road: Real Player Feedback
Chicken Road is a gamblinginspired arcade game that has drawn interest due to its straightforward mechanics, impressive RTP (98%), and innovative cashout option. We’ve collected honest feedback from actual players to see if it lives up to expectations.
What Players Like
A lot of gamers appreciate how Chicken Road combines fast gameplay with simple controls. With its cashout feature offering strategy and an RTP of 98%, it feels like a fairer alternative to conventional slot games. Beginners love the demo mode, which lets them try the game without risking money. Players also rave about the mobilefriendly design, which performs flawlessly even on outdated gadgets.
Melissa R., AU: “A surprisingly entertaining and fair experience. The cashout function really enhances the gameplay.”
Nathan K., UK: “The arcade style is refreshing. Runs smoothly on my tablet.”
The bright, nostalgic visuals add to the fun factor, keeping players hooked.
Areas for Improvement
However, Chicken Road isn’t perfect, and there are a few issues worth noting. Certain players think the game is too predictable and doesn’t offer much variety. Some highlight sluggish customer service and a lack of additional options. Misleading ads are another issue, with many assuming it was an arcade game instead of a gambling app.
Tom B., US: “It starts off fun, but the monotony sets in quickly.”
Sam T., UK: “Marketed as a casual game, but it’s actually a gamblingfocused app.”
Strengths and Weaknesses
Pros
Straightforward, actionpacked mechanics
An RTP of 98% guarantees a fair experience
Demo mode for riskfree learning
Seamless operation on smartphones and tablets
Negative Aspects
The gameplay may come across as monotonous
Limited variety and features
Delayed responses from support teams
Misleading marketing
Final Verdict
Chicken Road stands out with its transparency, high RTP, and accessibility. It’s a great option for casual players or those new to online gambling. However, its reliance on luck and lack of depth may not appeal to everyone. For the best experience, play on official, licensed platforms.
Rating: A solid 80%
A balanced blend of fun and fairness, with potential for enhancement.
https://www.webdesignplusseo.com/freeseoaudittools/domain/chickenroadhq.org -
https://medsmir.com/# online medications no prescription
-
chicken road rtp
Chicken Road: What Gamblers Are Saying
Chicken Road is an arcadestyle gambling game that has caught the attention of players with its simplicity, high RTP (98%), and unique cashout feature. We’ve gathered real player reviews to determine if it’s worth your time.
Key Highlights According to Players
A lot of gamers appreciate how Chicken Road combines fast gameplay with simple controls. With its cashout feature offering strategy and an RTP of 98%, it feels like a fairer alternative to conventional slot games. The demo mode is a hit with beginners, allowing players to test the game riskfree. The game earns extra points for its mobile compatibility, running seamlessly on both new and older devices.
Melissa R., AU: “Unexpectedly enjoyable and balanced! The ability to cash out brings a layer of strategy.”
Nathan K., UK: “Its arcadeinspired style is a breath of fresh air, and it operates smoothly on my device.”
Gamers are also fond of the vibrant, retro aesthetic, making it both enjoyable and captivating.
Areas for Improvement
While it has many positives, Chicken Road does have some downsides. Certain players think the game is too predictable and doesn’t offer much variety. Some highlight sluggish customer service and a lack of additional options. A common complaint is misleading advertising—many expected a pure arcade game, not a gambling app.
Tom B., US: “Initially enjoyable, but the repetition kicks in after a short while.”
Sam T., UK: “Promoted as entertainment, yet it turns out to be a gambling product.”
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
Straightforward, actionpacked mechanics
An RTP of 98% guarantees a fair experience
Free demo option for beginners to test the waters
Seamless operation on smartphones and tablets
Disadvantages
The gameplay may come across as monotonous
Lack of diversity and additional options
Customer service can be sluggish and unreliable
Deceptive advertising
Overall Assessment
Chicken Road shines through its openness, impressive RTP, and ease of access. Perfect for relaxed gaming sessions or newcomers to online betting. However, its reliance on luck and lack of depth may not appeal to everyone. For optimal results, choose verified, legitimate platforms.
Rating: Four out of five stars
A balanced blend of fun and fairness, with potential for enhancement. -
what is chicken road
Chicken Road: Real Player Feedback
Chicken Road is an arcadestyle gambling game that has caught the attention of players with its simplicity, high RTP (98%), and unique cashout feature. We’ve collected honest feedback from actual players to see if it lives up to expectations.
Key Highlights According to Players
Many users praise Chicken Road for its fastpaced gameplay and ease of use. The ability to cash out at any time adds a strategic twist, while the high RTP makes it feel fairer than traditional slots. The riskfree demo mode has been a favorite among new players, providing a safe way to explore the game. Mobile optimization also gets high marks, as the game runs smoothly even on older devices.
Melissa R., AU: “Unexpectedly enjoyable and balanced! The ability to cash out brings a layer of strategy.”
Nathan K., UK: “The retro arcade vibe feels invigorating. Plus, it works perfectly on my tablet.”
The bright, nostalgic visuals add to the fun factor, keeping players hooked.
Drawbacks
Despite its strengths, Chicken Road isn’t without flaws. Certain players think the game is too predictable and doesn’t offer much variety. Players also point out unresponsive support teams and insufficient features. A common complaint is misleading advertising—many expected a pure arcade game, not a gambling app.
Tom B., US: “Fun at first, but it gets repetitive after a few days.”
Sam T., UK: “Promoted as entertainment, yet it turns out to be a gambling product.”
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
Straightforward, actionpacked mechanics
With a 98% RTP, it offers a sense of equity
Practice mode to explore without financial risk
Optimized for flawless mobile play
Disadvantages
Gameplay can feel repetitive
Not enough features or modes to keep things fresh
Delayed responses from support teams
Confusing promotional tactics
Conclusion
Chicken Road stands out with its transparency, high RTP, and accessibility. It’s a great option for casual players or those new to online gambling. However, its reliance on luck and lack of depth may not appeal to everyone. For the best experience, play on official, licensed platforms.
Rating: A solid 80%
An enjoyable and equitable option, though it has areas to grow. -
Регистрация на официальном портале Up X
Регистрация в Up X — простой и быстрый процесс. Вам не придется выделять много времени, чтобы стать клиентом сервиса. Создатели платформы позаботились не только о стильном дизайне, но и о том, чтобы она воспринималась интуитивно. Минимализм и продуманный интерфейс — отличная комбинация. С созданием профиля не будет никаких проблем
https://skachatreferat.ru/ -
Регистрация на официальном портале Up X
Регистрация в Up X — простой и быстрый процесс. Вам не придется выделять много времени, чтобы стать клиентом сервиса. Создатели платформы позаботились не только о стильном дизайне, но и о том, чтобы она воспринималась интуитивно. Минимализм и продуманный интерфейс — отличная комбинация. С созданием профиля не будет никаких проблем
https://skachatreferat.ru/ -
decomania
Voici un spin-tax de haute qualité pour votre texte en français, respectant toutes vos consignes :
Alors que le média spécialisé Decomania étudie les innovations dans le domaine fintech, une question se pose : Quantum AI 2025 incarne-t-il un progrès tangible ou simplement une solution à fort potentiel ?
Mécanisme et Engagements : Quel est le Principe de Cette Plateforme ?
Quantum AI 2025 se définit comme un outil de trading automatisé combinant intelligence artificielle et calcul quantique. Selon ses créateurs, cette technologie offrirait :
Une analyse avancée des places boursières (actifs numériques, actions, Forex).
Une régulation intelligente des expositions pour optimiser les rendements.
Un accès simplifié, conçu pour les investisseurs tous niveaux.
Cependant, aucune recherche tierce ne corrobore publiquement ces affirmations, et les feedbacks d'utilisateurs demeurent mitigés.
Aspects à Vérifier Pour Decomania
Notre examen met en lumière différents points à évaluer avant de se lancer :
Multiples sites régionaux (crypto-bank.fr) - Une pratique courante, mais qui peut compliquer la vérification.
Manque de clarté - Des données techniques insuffisantes figurent sur les algorithmes utilisés.
Résultats divergents - Une partie des clients rapportent des rendements intéressants, tandis qu' certains signalent des complications pratiques.
Recommandations pour les Investisseurs
Choisir en priorité les solutions agréées (etc.) pour un cadre plus sûr.
Tester en compte test avant toute mise de fonds.
Évaluer avec d'autres solutions (à l'image de les outils disponibles par Interactive Brokers).
Synthèse : Une Technologie à Observer avec Prudence
Quantum AI 2025 avance une technologie de pointe, mais ses performances concrètes demandent toujours des preuves concrètes. En attendant de davantage d'informations, une méthode mesurée est recommandée. -
decomania
Voici un spin-tax de haute qualité pour votre texte en français, respectant toutes vos consignes :
Tandis que Decomania étudie les nouveautés en finance et technologie, une interrogation émerge : Quantum AI 2025 représente-t-il une véritable innovation ou simplement un projet ambitieux ?
Fonctionnement et Perspectives : Que Propose Cette Plateforme ?
Quantum AI 2025 se définit comme un système de trading automatisé intégrant intelligence artificielle et informatique quantique. Pour ses développeurs, cette technologie permettrait :
Un examen approfondi des marchés (crypto, titres, devises).
Un contrôle algorithmique du risque pour optimiser les performances.
Une prise en main aisée, conçu pour les opérateurs tous niveaux.
Toutefois, aucune étude indépendante ne valide formellement ces déclarations, et les retours utilisateurs restent partagés.
Aspects à Vérifier Pour Decomania
Notre examen met en lumière différents points à considérer avant de investir :
Différentes plateformes locales (crypto-bank.fr) - Un usage répandu, mais qui peut rendre difficile l'authentification.
Manque de clarté - Peu d'informations techniques sont disponibles sur les systèmes mis en œuvre.
Résultats divergents - Certains utilisateurs indiquent des rendements intéressants, tandis que certains signalent des problèmes opérationnels.
Recommandations pour les Investisseurs
Favoriser les plateformes régulées (CySEC) pour un cadre plus sûr.
Tester en compte test avant tout engagement financier.
Évaluer avec d'autres options (telles que les outils disponibles par d'autres brokers réputés).
Conclusion : Un Projet à Suivre avec Circnospection
Quantum AI 2025 avance une méthode novatrice, mais ses résultats tangibles nécessitent encore des validations empiriques. Jusqu'à preuve du contraire de plus de transparence, une stratégie prudente est préconisée. -
Premium psilocybin edibles
Experience the Magic: A Seamless Journey with Sacred Shroom Co.
At Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand, we are dedicated to providing you with a smooth, secure, and magical shopping experience — from browsing our collection to receiving your carefully prepared package. Each step is designed with simplicity, trust, and a touch of magic in mind.
How to Order from Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
Explore Our Magical Collection – Check out our premium line of psilocybin-infused products on the shop page.
Choose Your Adventure – Select your preferred strain, amount, and form, such as chocolates, capsules or gummies.
Review and Checkout – Make sure everything is correct in your cart, then proceed to checkout by entering your shipping details.
Secure Payment Process – Once your order is placed, you will receive clear payment instructions. After confirmation, we begin preparing your shipment with care.
Track Your Package – You will be sent a tracking number so that you can follow your mystical delivery all the way to your door.
Why Choose Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
Free Global Shipping – On qualifying orders, because magic should know no borders.
24 7 Customer Support – Our team is always ready to assist you.
Money Back Guarantee – Shop with confidence knowing we offer a full refund if needed.
Our Top Rated Products
Amazonian – A powerful strain known for deep and life changing experiences.
Mazatapec – Respected for its spiritual depth and inner exploration.
Penis Envy – Strong and intense, ideal for experienced users.
Dancing Bear – Lively and uplifting, perfect for joyful journeys.
Each item comes in multiple forms — choose from chocolates, capsules, gummies and more to match your taste and needs.
Explore Our Full Range
All of our artisanal organic products are lab tested and made right here in Santa Cruz, California. The current catalog includes:
4 PO DMT
Magic Mushroom Chocolate Bars (White)
Microdose Capsules – Ideal for gentle enhancement and focus.
Psilocybin Gummies and Syrup – A tasty and fun way to explore.
The Power of Psilocybin Perfected
Psilocybin is a sacred natural compound that has fascinated scientists, shamans and seekers throughout history. At Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand, we guarantee accurate dosing, top tier quality and predictable effects — whether you're exploring spirituality, boosting creativity or starting a personal journey of growth.
Every chocolate bar, capsule and edible is made with purpose, helping you dive into the world of psilocybin safely, confidently and joyfully.
Ready to Begin Your Magical Adventure
Enter the realm of Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand — where excellence, reliability and enchantment come together seamlessly. -
Discover the Enchantment: A Seamless Journey with Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
At our brand, we are dedicated to providing you with a smooth, secure, and magical shopping experience — from browsing our collection to receiving your lovingly wrapped order. Each step is designed with simplicity, trust, and a touch of magic in mind.
How to Order from Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
Explore Our Magical Collection – Check out our premium line of psilocybin-infused products on the shop page.
Choose Your Adventure – Select your preferred strain, amount, and form, such as chocolates, capsules or gummies.
Review and Checkout – Make sure everything is correct in your cart, then proceed to checkout by entering your shipping details.
Secure Payment Process – Once your order is placed, you will receive clear payment instructions. After confirmation, we begin preparing your shipment with care.
Track Your Package – You will be sent a tracking number so that you can follow your magical parcel all the way to your door.
Why Choose Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
Free Global Shipping – On qualifying orders, because magic should know no borders.
24 7 Customer Support – Our team is always ready to assist you.
Money Back Guarantee – Shop with confidence knowing we offer a full refund if needed.
Our Top Rated Products
Amazonian – A powerful strain known for deep and life changing experiences.
Mazatapec – Respected for its spiritual depth and inner exploration.
Penis Envy – Strong and intense, ideal for experienced users.
Dancing Bear – Lively and uplifting, perfect for joyful journeys.
Each item comes in multiple forms — choose from chocolates, capsules, gummies and more to match your taste and needs.
Explore Our Full Range
All of our artisanal organic products are lab tested and made right here in Santa Cruz, California. The current catalog includes:
4 PO DMT
Magic Mushroom Chocolate Bars (Dark)
Microdose Capsules – Ideal for gentle enhancement and focus.
Psilocybin Gummies and Syrup – A tasty and fun way to explore.
The Power of Psilocybin Perfected
Psilocybin is a sacred natural compound that has fascinated scientists, shamans and seekers throughout history. At Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand, we guarantee consistent potency, top tier quality and predictable effects — whether you're exploring spirituality, boosting creativity or starting a personal journey of growth.
Every chocolate bar, capsule and edible is made with purpose, helping you dive into the world of psilocybin safely, confidently and joyfully.
Ready to Begin Your Magical Adventure
Enter the realm of Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand — where excellence, reliability and enchantment come together seamlessly. -
Sacred mushroom chocolates
Discover the Enchantment: A Seamless Journey with The Truffle Experience
At our brand, we are dedicated to providing you with a smooth, secure, and magical shopping experience — from browsing our collection to receiving your lovingly wrapped order. Each step is designed with simplicity, trust, and a touch of magic in mind.
How to Order from Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
Explore Our Magical Collection – Check out our premium line of psilocybin-infused products on the shop page.
Choose Your Adventure – Select your preferred strain, amount, and form, such as chocolates, capsules or gummies.
Review and Checkout – Make sure everything is correct in your cart, then proceed to checkout by entering your shipping details.
Secure Payment Process – Once your order is placed, you will receive clear payment instructions. After confirmation, we begin preparing your shipment with care.
Track Your Package – You will be sent a tracking number so that you can follow your magical parcel all the way to your door.
Why Choose Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
Free Global Shipping – On qualifying orders, because magic should know no borders.
24 7 Customer Support – Our team is always ready to assist you.
Money Back Guarantee – Shop with confidence knowing we offer a full refund if needed.
Our Top Rated Products
Amazonian – A powerful strain known for deep and life changing experiences.
Mazatapec – Respected for its spiritual depth and inner exploration.
Penis Envy – Strong and intense, ideal for experienced users.
Dancing Bear – Lively and uplifting, perfect for joyful journeys.
Each item comes in multiple forms — choose from chocolates, capsules, gummies and more to match your taste and needs.
Explore Our Full Range
All of our artisanal organic products are lab tested and made right here in Santa Cruz, California. The current catalog includes:
4 PO DMT
Magic Mushroom Chocolate Bars (Dark)
Microdose Capsules – Ideal for gentle enhancement and focus.
Psilocybin Gummies and Syrup – A tasty and fun way to explore.
The Power of Psilocybin Perfected
Psilocybin is a sacred natural compound that has fascinated scientists, shamans and seekers throughout history. At Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand, we guarantee accurate dosing, top tier quality and predictable effects — whether you're exploring spirituality, boosting creativity or starting a personal journey of growth.
Every chocolate bar, capsule and edible is made with purpose, helping you dive into the world of psilocybin safely, confidently and joyfully.
Ready to Begin Your Magical Adventure
Enter the realm of Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand — where excellence, reliability and enchantment come together seamlessly. -
Step Into a World of Wonder: A Seamless Journey with Sacred Shroom Co.
At this store, we are dedicated to providing you with a smooth, secure, and magical shopping experience — from browsing our collection to receiving your carefully prepared package. Each step is designed with simplicity, trust, and a touch of magic in mind.
How to Order from Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
Explore Our Magical Collection – Check out our premium line of psilocybin-infused products on the shop page.
Choose Your Adventure – Select your preferred strain, amount, and form, such as chocolates, capsules or gummies.
Review and Checkout – Make sure everything is correct in your cart, then proceed to checkout by entering your shipping details.
Secure Payment Process – Once your order is placed, you will receive clear payment instructions. After confirmation, we begin preparing your shipment with care.
Track Your Package – You will be sent a tracking number so that you can follow your mystical delivery all the way to your door.
Why Choose Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
Free Global Shipping – On qualifying orders, because magic should know no borders.
24 7 Customer Support – Our team is always ready to assist you.
Money Back Guarantee – Shop with confidence knowing we offer a full refund if needed.
Our Top Rated Products
Amazonian – A powerful strain known for deep and life changing experiences.
Mazatapec – Respected for its spiritual depth and inner exploration.
Penis Envy – Strong and intense, ideal for experienced users.
Dancing Bear – Lively and uplifting, perfect for joyful journeys.
Each item comes in multiple forms — choose from chocolates, capsules, gummies and more to match your taste and needs.
Explore Our Full Range
All of our artisanal organic products are lab tested and made right here in Santa Cruz, California. The current catalog includes:
4 PO DMT
Magic Mushroom Chocolate Bars (White)
Microdose Capsules – Ideal for gentle enhancement and focus.
Psilocybin Gummies and Syrup – A tasty and fun way to explore.
The Power of Psilocybin Perfected
Psilocybin is a sacred natural compound that has fascinated scientists, shamans and seekers throughout history. At Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand, we guarantee accurate dosing, top tier quality and predictable effects — whether you're exploring spirituality, boosting creativity or starting a personal journey of growth.
Every chocolate bar, capsule and edible is made with purpose, helping you dive into the world of psilocybin safely, confidently and joyfully.
Ready to Begin Your Magical Adventure
Enter the realm of Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand — where excellence, reliability and enchantment come together seamlessly. -
logistics
Cargo Bolt: Your Trusted Partner in Global Logistics and Transportation
In today’s fast-paced and interconnected world, efficient logistics and transportation are essential for the success of any business. Cargo Bolt Logistics Services stands as a reliable and professional partner, providing end-to-end services for global cargo handling and delivery.
With a presence in over 20 countries and an extensive international network of partners and agents, Cargo Bolt is committed to delivering high-quality logistics services designed specifically for each customer.
Comprehensive Freight Services
Cargo Bolt specializes in a wide range of freight forwarding and transportation services, ensuring agility, promptness, and consistency:
Ocean Freight Forwarding
Ocean freight plays an essential part in international commerce and logistics. Cargo Bolt offers full-service maritime shipping options, including unitized vessel deliveries, route planning, customs clearance, and documentation — all designed to ensure seamless international deliveries.
Road Freight Forwarding
Road transport remains a vital component of modern logistics, especially for local and short-distance hauls. We provide cost-effective and timely road freight forwarding services, with options that suit multiple load types, trip lengths, and dispatch windows.
Worldwide Transport & Ground Transport
Whether it's local deliveries or cross-border shipments, our ground transportation services offer adaptable and trustworthy solutions for any freight type. From individual packages to complete container loads, we ensure your goods reach their destination safely and efficiently. -
Experience the Magic: A Seamless Journey with Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
At this store, we are dedicated to providing you with a smooth, secure, and magical shopping experience — from browsing our collection to receiving your handcrafted delivery. Each step is designed with simplicity, trust, and a touch of magic in mind.
How to Order from Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
Explore Our Magical Collection – Check out our premium line of psilocybin-infused products on the shop page.
Choose Your Adventure – Select your preferred strain, amount, and form, such as chocolates, capsules or gummies.
Review and Checkout – Make sure everything is correct in your cart, then proceed to checkout by entering your shipping details.
Secure Payment Process – Once your order is placed, you will receive clear payment instructions. After confirmation, we begin preparing your shipment with care.
Track Your Package – You will be sent a tracking number so that you can follow your mystical delivery all the way to your door.
Why Choose Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
Free Global Shipping – On qualifying orders, because magic should know no borders.
24 7 Customer Support – Our team is always ready to assist you.
Money Back Guarantee – Shop with confidence knowing we offer a full refund if needed.
Our Top Rated Products
Amazonian – A powerful strain known for deep and life changing experiences.
Mazatapec – Respected for its spiritual depth and inner exploration.
Penis Envy – Strong and intense, ideal for experienced users.
Dancing Bear – Lively and uplifting, perfect for joyful journeys.
Each item comes in multiple forms — choose from chocolates, capsules, gummies and more to match your taste and needs.
Explore Our Full Range
All of our artisanal organic products are lab tested and made right here in Santa Cruz, California. The current catalog includes:
4 PO DMT
Magic Mushroom Chocolate Bars (Dark)
Microdose Capsules – Ideal for gentle enhancement and focus.
Psilocybin Gummies and Syrup – A tasty and fun way to explore.
The Power of Psilocybin Perfected
Psilocybin is a sacred natural compound that has fascinated scientists, shamans and seekers throughout history. At Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand, we guarantee consistent potency, top tier quality and predictable effects — whether you're exploring spirituality, boosting creativity or starting a personal journey of growth.
Every chocolate bar, capsule and edible is made with purpose, helping you dive into the world of psilocybin safely, confidently and joyfully.
Ready to Begin Your Magical Adventure
Enter the realm of Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand — where excellence, reliability and enchantment come together seamlessly. -
Microdosing
Experience the Magic: A Seamless Journey with The Truffle Experience
At this store, we are dedicated to providing you with a smooth, secure, and magical shopping experience — from browsing our collection to receiving your carefully prepared package. Each step is designed with simplicity, trust, and a touch of magic in mind.
How to Order from Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
Explore Our Magical Collection – Take a look at our premium line of psilocybin-infused products on the shop page.
Choose Your Adventure – Select your preferred strain, amount, and form, such as chocolates, capsules or gummies.
Review and Checkout – Make sure everything is correct in your cart, then proceed to checkout by entering your shipping details.
Secure Payment Process – Once your order is placed, you will receive clear payment instructions. After confirmation, we begin preparing your shipment with care.
Track Your Package – You will be sent a tracking number so that you can follow your mystical delivery all the way to your door.
Why Choose Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand
Free Global Shipping – On qualifying orders, because magic should know no borders.
24 7 Customer Support – Our team is always ready to assist you.
Money Back Guarantee – Shop with confidence knowing we offer a full refund if needed.
Our Top Rated Products
Amazonian – A powerful strain known for deep and life changing experiences.
Mazatapec – Respected for its spiritual depth and inner exploration.
Penis Envy – Strong and intense, ideal for experienced users.
Dancing Bear – Lively and uplifting, perfect for joyful journeys.
Each item comes in multiple forms — choose from chocolates, capsules, gummies and more to match your taste and needs.
Explore Our Full Range
All of our artisanal organic products are lab tested and made right here in Santa Cruz, California. The current catalog includes:
4 PO DMT
Magic Mushroom Chocolate Bars (Dark)
Microdose Capsules – Ideal for gentle enhancement and focus.
Psilocybin Gummies and Syrup – A tasty and fun way to explore.
The Power of Psilocybin Perfected
Psilocybin is a sacred natural compound that has fascinated scientists, shamans and seekers throughout history. At Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand, we guarantee accurate dosing, top tier quality and predictable effects — whether you're exploring spirituality, boosting creativity or starting a personal journey of growth.
Every chocolate bar, capsule and edible is made with purpose, helping you dive into the world of psilocybin safely, confidently and joyfully.
Ready to Begin Your Magical Adventure
Enter the realm of Magic Truffle Shrooms Brand — where excellence, reliability and enchantment come together seamlessly. -
LimmerCoin en: notre avis complet
Voici un spin-tax de haute qualité pour votre texte en français, respectant toutes vos consignes :
Tandis que Decomania analyse les nouveautés en finance et technologie, une interrogation émerge : Quantum AI 2025 constitue-t-il une véritable innovation ou seulement une solution à fort potentiel ?
Mode opératoire et Promesses : Quel est le Principe de Cette Plateforme ?
Quantum AI 2025 se positionne comme un outil de trading algorithmique intégrant IA et informatique quantique. Selon ses créateurs, cette technologie offrirait :
Une analyse avancée des marchés (actifs numériques, valeurs mobilières, Forex).
Une régulation intelligente des expositions pour optimiser les performances.
Une interface intuitive, pensé pour les traders tous niveaux.
Néanmoins, aucune étude indépendante ne confirme officiellement ces affirmations, et les témoignages restent partagés.
Points à Contrôler Selon Decomania
Notre étude met en lumière plusieurs éléments à prendre en compte avant de investir :
Différentes plateformes locales (opulence-mirage.com) - Une méthode habituelle, mais qui peut complexifier le contrôle.
Transparence limitée - Des données techniques insuffisantes sont accessibles sur les algorithmes utilisés.
Résultats divergents - Certains utilisateurs mentionnent des performances satisfaisantes, tandis que plusieurs rapportent des difficultés techniques.
Suggestions pour les Investisseurs
Choisir en priorité les solutions agréées (etc.) pour un cadre plus sûr.
Essayer en version démonstration avant toute mise de fonds.
Mettre en parallèle avec d'autres solutions (telles que les outils offerts par d'autres brokers réputés).
Synthèse : Une Solution à Surveiller avec Réserve
Quantum AI 2025 avance une technologie de pointe, mais ses performances concrètes nécessitent encore des preuves concrètes. Jusqu'à preuve du contraire de plus de transparence, une méthode mesurée est préconisée. -
Test de Qumas AI en
Voici un spin-tax de haute qualité pour votre texte en français, respectant toutes vos consignes :
Dans un contexte où Decomania explore les innovations des secteurs financiers et technologiques, une question se pose : Quantum AI 2025 représente-t-il un progrès tangible ou simplement un projet ambitieux ?
Fonctionnement et Perspectives : Quel est le Principe de Cette Plateforme ?
Quantum AI 2025 se présente comme une solution de investissement algorithmique combinant IA et informatique quantique. Pour ses développeurs, cette technologie permettrait :
Une analyse avancée des marchés (actifs numériques, valeurs mobilières, devises).
Une gestion automatisée du risque pour améliorer les résultats.
Une interface intuitive, pensé pour les investisseurs tous niveaux.
Toutefois, aucun audit externe ne corrobore officiellement ces déclarations, et les témoignages restent partagés.
Points à Contrôler Pour Decomania
Notre analyse souligne différents points à prendre en compte avant de s'engager :
Plusieurs URLs géolocalisées (etc.) - Une pratique courante, mais qui peut rendre difficile l'authentification.
Transparence limitée - Un manque de détails technologiques sont accessibles sur les systèmes mis en œuvre.
Performances inégales - Une partie des clients mentionnent des rendements intéressants, tandis que certains signalent des difficultés techniques.
Recommandations pour les Traders
Choisir en priorité les plateformes régulées (etc.) pour une meilleure protection.
Essayer en version démonstration avant chaque investissement.
Mettre en parallèle avec des alternatives (telles que les outils proposés par eToro).
Conclusion : Une Solution à Surveiller avec Prudence
Quantum AI 2025 propose une approche innovante, mais son efficacité réelle demandent toujours des preuves concrètes. En attendant de une meilleure visibilité, une méthode mesurée est recommandée. -
Chicken Road: Real Player Feedback
Chicken Road is a gamblinginspired arcade game that has drawn interest due to its straightforward mechanics, impressive RTP (98%), and innovative cashout option. We’ve gathered real player reviews to determine if it’s worth your time.
What Users Appreciate
Many users praise Chicken Road for its fastpaced gameplay and ease of use. The option to withdraw winnings whenever you want introduces a tactical element, and the high RTP ensures it feels more equitable compared to classic slots. The riskfree demo mode has been a favorite among new players, providing a safe way to explore the game. The game earns extra points for its mobile compatibility, running seamlessly on both new and older devices.
Melissa R., AU: “Surprisingly fun and fair! The cashout feature adds strategy.”
Nathan K., UK: “The arcade style is refreshing. Runs smoothly on my tablet.”
The bright, nostalgic visuals add to the fun factor, keeping players hooked.
Drawbacks
While it has many positives, Chicken Road does have some downsides. A number of users feel the gameplay becomes monotonous and lacks complexity. Others mention slow customer support and limited features. One frequent criticism is deceptive marketing, as people thought it was a pure arcade game rather than a gambling platform.
Tom B., US: “Initially enjoyable, but the repetition kicks in after a short while.”
Sam T., UK: “Promoted as entertainment, yet it turns out to be a gambling product.”
Advantages and Disadvantages
Pros
Straightforward, actionpacked mechanics
High RTP (98%) ensures fairness
Practice mode to explore without financial risk
Optimized for flawless mobile play
Cons
Gameplay can feel repetitive
Lack of diversity and additional options
Slow or unresponsive customer support
Confusing promotional tactics
Final Verdict
Chicken Road shines through its openness, impressive RTP, and ease of access. Ideal for casual gamers or anyone just starting with online gambling. However, its reliance on luck and lack of depth may not appeal to everyone. For optimal results, choose verified, legitimate platforms.
Rating: 4/5
An enjoyable and equitable option, though it has areas to grow. -
chicken roads review
Chicken Road: Honest User Opinions
Chicken Road is an arcadestyle gambling game that has caught the attention of players with its simplicity, high RTP (98%), and unique cashout feature. We’ve gathered real player reviews to determine if it’s worth your time.
Key Highlights According to Players
A lot of gamers appreciate how Chicken Road combines fast gameplay with simple controls. The option to withdraw winnings whenever you want introduces a tactical element, and the high RTP ensures it feels more equitable compared to classic slots. The riskfree demo mode has been a favorite among new players, providing a safe way to explore the game. The game earns extra points for its mobile compatibility, running seamlessly on both new and older devices.
Melissa R., AU: “Unexpectedly enjoyable and balanced! The ability to cash out brings a layer of strategy.”
Nathan K., UK: “The arcade style is refreshing. Runs smoothly on my tablet.”
The bright, nostalgic visuals add to the fun factor, keeping players hooked.
Areas for Improvement
Despite its strengths, Chicken Road isn’t without flaws. A number of users feel the gameplay becomes monotonous and lacks complexity. Some highlight sluggish customer service and a lack of additional options. Misleading ads are another issue, with many assuming it was an arcade game instead of a gambling app.
Tom B., US: “Fun at first, but it gets repetitive after a few days.”
Sam T., UK: “Marketed as a casual game, but it’s actually a gamblingfocused app.”
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
Easytounderstand, quick gameplay
An RTP of 98% guarantees a fair experience
Free demo option for beginners to test the waters
Smooth performance on mobile devices
Disadvantages
Gameplay can feel repetitive
Limited variety and features
Customer service can be sluggish and unreliable
Deceptive advertising
Final Verdict
Chicken Road stands out with its transparency, high RTP, and accessibility. It’s a great option for casual players or those new to online gambling. However, its reliance on luck and lack of depth may not appeal to everyone. For the best experience, play on official, licensed platforms.
Rating: A solid 80%
An enjoyable and equitable option, though it has areas to grow. -
Wallet Address Checker Online
Wallet Address Checker Online
Use a reliable wallet address checker online to scan your crypto wallet for risks like sanctions, stolen funds, or darknet exposure . Stay ahead of exchange freezes and avoid losing access to your assets. Fast, secure, and trusted by thousands — check now. -
Wallet Address Checker Online
Blockchain Address Scanner
Use a reliable wallet address checker online to scan your crypto wallet for risks like regulatory flags, theft incidents, or underground network leaks. Stay ahead of exchange freezes and avoid losing access to your assets. Instant results with bank-grade security — check now. -
Wallet Address Checker Online
Crypto Wallet Validator
Use a trusted wallet address checker online to scan your crypto wallet for risks like illicit activity, blacklisted assets, or compromised addresses . Stay ahead of exchange freezes and avoid losing access to your assets. Instant results with bank-grade security — check now. -
Wallet Address Checker Online
Crypto Wallet Validator
Use a top-rated wallet address checker online to scan your crypto wallet for risks like regulatory flags, theft incidents, or underground network leaks. Stay ahead of exchange freezes and avoid losing access to your assets. Fast, secure, and trusted by thousands — check now. -
Chicken Road: What Gamblers Are Saying
Chicken Road is an arcadestyle gambling game that has caught the attention of players with its simplicity, high RTP (98%), and unique cashout feature. We’ve gathered real player reviews to determine if it’s worth your time.
What Users Appreciate
Many users praise Chicken Road for its fastpaced gameplay and ease of use. The option to withdraw winnings whenever you want introduces a tactical element, and the high RTP ensures it feels more equitable compared to classic slots. The demo mode is a hit with beginners, allowing players to test the game riskfree. Players also rave about the mobilefriendly design, which performs flawlessly even on outdated gadgets.
Melissa R., AU: “A surprisingly entertaining and fair experience. The cashout function really enhances the gameplay.”
Nathan K., UK: “Its arcadeinspired style is a breath of fresh air, and it operates smoothly on my device.”
Players also enjoy the colorful, nostalgic design, which feels both fun and engaging.
Criticisms
However, Chicken Road isn’t perfect, and there are a few issues worth noting. Some players find the gameplay repetitive and lacking depth. Others mention slow customer support and limited features. Misleading ads are another issue, with many assuming it was an arcade game instead of a gambling app.
Tom B., US: “Initially enjoyable, but the repetition kicks in after a short while.”
Sam T., UK: “Advertised as a fun game, but it’s clearly a gambling app.”
Advantages and Disadvantages
Positive Aspects
Simple, fastpaced gameplay
With a 98% RTP, it offers a sense of equity
Practice mode to explore without financial risk
Seamless operation on smartphones and tablets
Negative Aspects
The gameplay may come across as monotonous
Limited variety and features
Slow or unresponsive customer support
Misleading marketing
Final Verdict
Thanks to its transparency, high RTP, and userfriendliness, Chicken Road makes a mark. It’s a great option for casual players or those new to online gambling. Still, the heavy emphasis on luck and minimal complexity could turn off some users. To maximize enjoyment, stick to authorized, regulated sites.
Rating: Four out of five stars
An enjoyable and equitable option, though it has areas to grow. -
chicken road
Chicken Road: What Gamblers Are Saying
Chicken Road is a gamblinginspired arcade game that has drawn interest due to its straightforward mechanics, impressive RTP (98%), and innovative cashout option. We’ve collected honest feedback from actual players to see if it lives up to expectations.
What Players Like
A lot of gamers appreciate how Chicken Road combines fast gameplay with simple controls. The ability to cash out at any time adds a strategic twist, while the high RTP makes it feel fairer than traditional slots. The demo mode is a hit with beginners, allowing players to test the game riskfree. The game earns extra points for its mobile compatibility, running seamlessly on both new and older devices.
Melissa R., AU: “Surprisingly fun and fair! The cashout feature adds strategy.”
Nathan K., UK: “Its arcadeinspired style is a breath of fresh air, and it operates smoothly on my device.”
Gamers are also fond of the vibrant, retro aesthetic, making it both enjoyable and captivating.
Criticisms
While it has many positives, Chicken Road does have some downsides. Some players find the gameplay repetitive and lacking depth. Others mention slow customer support and limited features. One frequent criticism is deceptive marketing, as people thought it was a pure arcade game rather than a gambling platform.
Tom B., US: “Fun at first, but it gets repetitive after a few days.”
Sam T., UK: “Marketed as a casual game, but it’s actually a gamblingfocused app.”
Pros and Cons
Advantages
Easytounderstand, quick gameplay
High RTP (98%) ensures fairness
Demo mode for riskfree learning
Optimized for flawless mobile play
Negative Aspects
It might feel too predictable over time
Lack of diversity and additional options
Customer service can be sluggish and unreliable
Deceptive advertising
Final Verdict
Thanks to its transparency, high RTP, and userfriendliness, Chicken Road makes a mark. It’s a great option for casual players or those new to online gambling. Still, the heavy emphasis on luck and minimal complexity could turn off some users. For optimal results, choose verified, legitimate platforms.
Rating: 4/5
A fair and entertaining choice, but not without room for improvement. -
EToro 2025 Avis
Voici un spin-tax de haute qualité pour votre texte en français, respectant toutes vos consignes :
Alors que notre plateforme d'analyse Decomania explore les nouveautés en finance et technologie, un doute subsiste : Quantum AI 2025 constitue-t-il une véritable innovation ou simplement une solution à fort potentiel ?
Mode opératoire et Perspectives : Quel est le Principe de Cette Plateforme ?
Quantum AI 2025 se positionne comme une solution de trading automatisé combinant IA et calcul quantique. D'après ses concepteurs, cette technologie rendrait possible :
Un examen approfondi des marchés financiers (cryptomonnaies, actions, Forex).
Une régulation intelligente des risques pour améliorer les performances.
Une interface intuitive, conçu pour les opérateurs de différents niveaux.
Toutefois, aucune étude indépendante ne corrobore officiellement ces déclarations, et les retours utilisateurs demeurent mitigés.
Éléments à Contrôler D'après Decomania
Notre examen met en lumière différents points à évaluer avant de se lancer :
Différentes plateformes locales (crypto-bank.fr) - Un usage répandu, mais qui peut complexifier la vérification.
Manque de clarté - Un manque de détails technologiques sont accessibles sur les algorithmes utilisés.
Résultats divergents - Une partie des clients mentionnent des performances satisfaisantes, tandis que d'autres évoquent des problèmes opérationnels.
Suggestions pour les Traders
Privilégier les interfaces contrôlées (CySEC) pour une meilleure protection.
Expérimenter en version démonstration avant toute mise de fonds.
Comparer avec des alternatives (telles que les outils proposés par Interactive Brokers).
Bilan : Un Projet à Suivre avec Réserve
Quantum AI 2025 propose une approche innovante, mais ses résultats tangibles demandent toujours des validations empiriques. Dans l'attente de une meilleure visibilité, une méthode mesurée est préconisée. -
Bitbank 2025
Voici un spin-tax de haute qualité pour votre texte en français, respectant toutes vos consignes :
Tandis que le média spécialisé Decomania analyse les avancées en finance et technologie, une interrogation émerge : Quantum AI 2025 représente-t-il un progrès tangible ou simplement un projet ambitieux ?
Fonctionnement et Perspectives : Quel est le Principe de Cette Plateforme ?
Quantum AI 2025 se positionne comme une solution de trading algorithmique associant smart tech et calcul quantique. Pour ses développeurs, cette technologie rendrait possible :
Une évaluation poussée des marchés (actifs numériques, valeurs mobilières, marché des changes).
Une régulation intelligente des risques pour améliorer les performances.
Une interface intuitive, pensé pour les traders tous niveaux.
Toutefois, aucune recherche tierce ne confirme publiquement ces allégations, et les témoignages s'avèrent contrastés.
Aspects à Vérifier D'après Decomania
Notre étude révèle divers facteurs à évaluer avant de s'engager :
Différentes plateformes locales (opulence-mirage.com) - Une pratique courante, mais qui peut rendre difficile la vérification.
Manque de clarté - Un manque de détails technologiques sont accessibles sur les systèmes mis en œuvre.
Résultats divergents - Certains utilisateurs mentionnent des performances satisfaisantes, tandis qu' certains signalent des problèmes opérationnels.
Conseils pour les Investisseurs
Choisir en priorité les solutions agréées (CySEC) pour une meilleure protection.
Tester en version démonstration avant tout engagement financier.
Comparer avec d'autres options (à l'image de les systèmes offerts par eToro).
Synthèse : Une Solution à Surveiller avec Circnospection
Quantum AI 2025 avance une méthode novatrice, mais ses performances concrètes requièrent davantage des validations empiriques. En attendant de une meilleure visibilité, une approche mesurée est conseillée. -
Wallet Address Checker Online
Crypto Wallet Validator
Use a trusted wallet address checker online to scan your crypto wallet for risks like regulatory flags, theft incidents, or underground network leaks. Stay ahead of exchange freezes and avoid losing access to your assets. Fast, secure, and trusted by thousands — check now. -
Wallet Address Checker Online
Crypto Wallet Validator
Use a top-rated wallet address checker online to scan your crypto wallet for risks like illicit activity, blacklisted assets, or compromised addresses . Stay ahead of exchange freezes and avoid losing access to your assets. Instant results with bank-grade security — check now. -
Good Day!
We present to your attention modern solution for imbalance elimination of rotating equipment - portable balancing device Balanset-1A.
Official product page: https://vibromera.eu/shop/889/
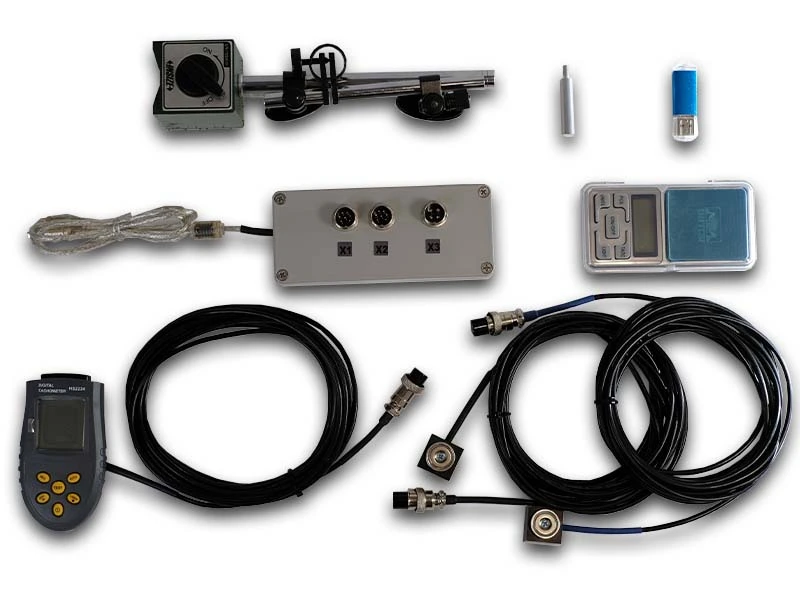

Where It's Applied
Balanset-1A is actively applied for balancing of various types rotating mechanisms:
Industrial Machinery:
Fans - production, centrifugal, duct. Pumps - screw, oil. Motors - synchronous. Turbines - hydraulic. Compressor Units - centrifugal.
Metalworking:
Machine Spindles - milling. Abrasive Wheels. Roll Equipment of textile equipment.
Farm Machines:
Choppers. Rotary Mowers. Crushing Units for grain.
Special Equipment:
Separators - medical. Air Blowers. Grinding Equipment. Transmission Shafts.

Technical Parameters
Primary Indicators:
Correction planes: 1 or 2. Rotation frequency range: 200 to 15,000 rpm. Phase determination accuracy: ±1°. Vibration error: ±5%. Measuring channels: 2. Measured vibration velocity: 0.1 to 300 mm/s. Power supply: From computer USB port. Equipment mass: 4 kg.
System Capabilities:
Automated computation of correction masses. Data storage of measurements. Standards determination according to ISO 1940. Frequency analysis of vibration. Data visualization in real time. Split-weight calculator. Eccentricity compensation of mandrels.
Package Contents
Main Delivery:
USB coupling module (1 pc.) - provides data transfer between sensors and computer.
Vibration sensors (2 pcs.) - Output signal: 100 mV/g. Frequency range: 0.5-10,000 Hz. Installation: magnetic base.
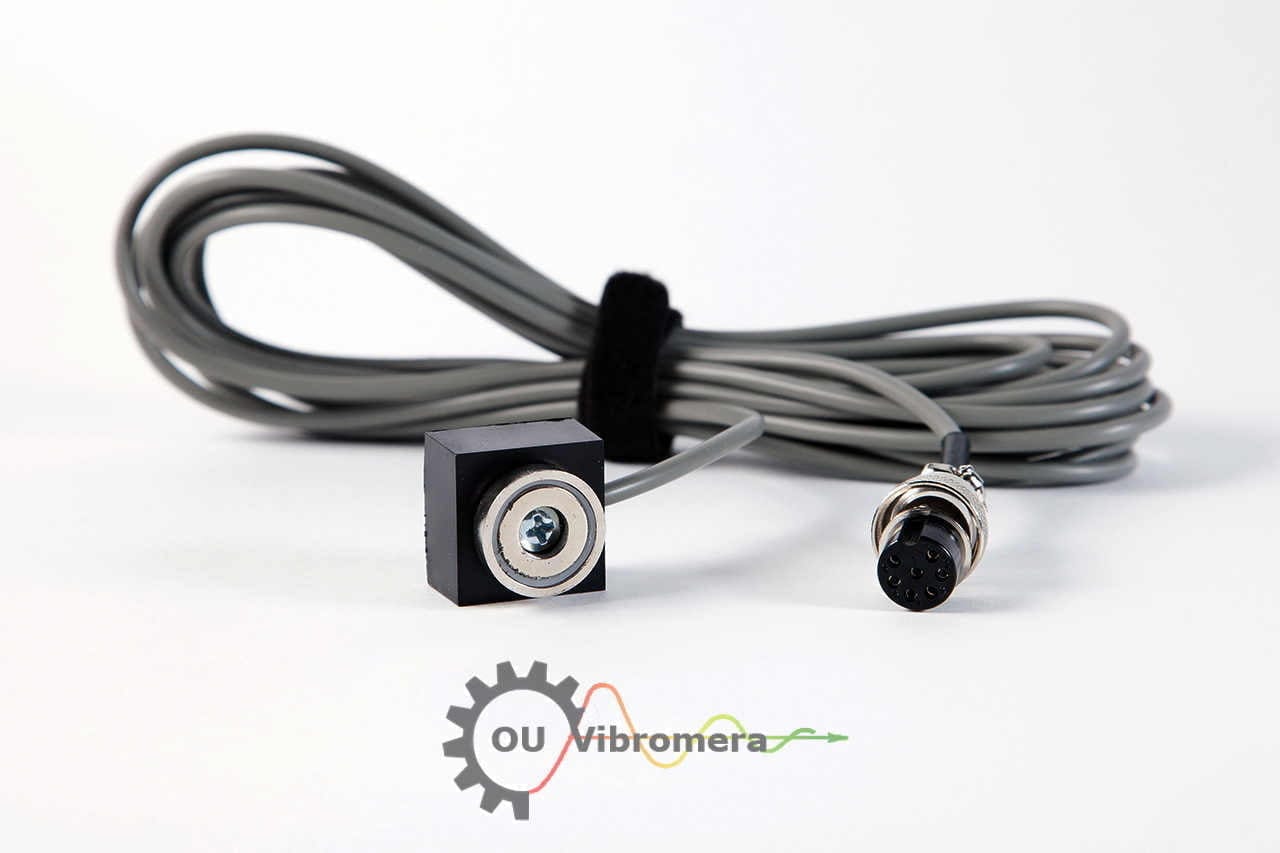

Laser phase sensor (1 pc.) - Working range: up to 1.5 m. Contactless operation for safe operation.
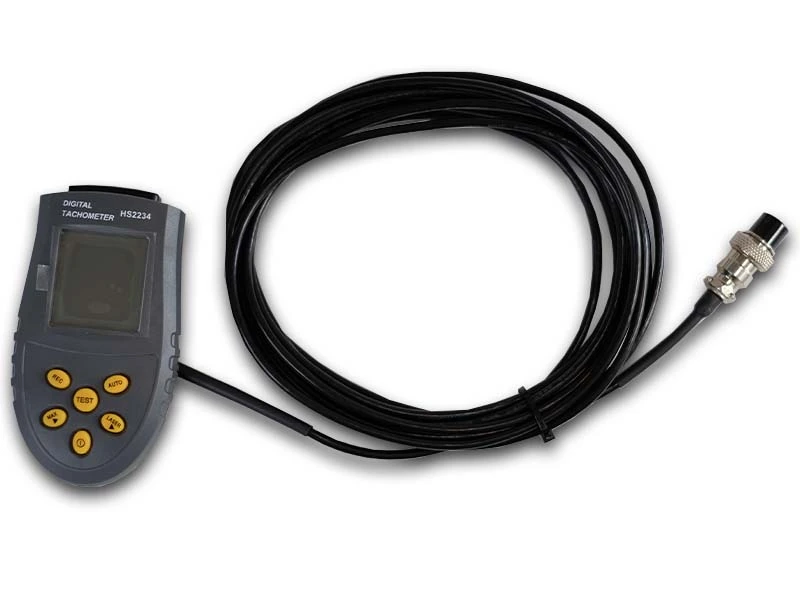

Holder for phase sensor (1 pc.) - Magnetic strength: 60 kgf. Adjustable positioning for optimal alignment.

Electronic scales up to 500 g (1 pc.) - Accuracy: 0.01 g. Necessary for precise weight measurement.
Balancing software Balanset-1A - Intuitive operation. PC-based. Multilingual interface.
Protective case (1 pc.) - Heavy-duty build. Cushioned interior for secure storage.
Technical documentation - Comprehensive guide. Clear methodology.
Connection cables - Reliable interference-free connections.
Advantages of Balanset-1A
Technical Benefits:
? Accurate Results - Advanced methods of signal processing ensure consistent accuracy.
? Portability - Light weight allows field operations without disassembly.
? Versatility - Works with various rotors from small fans to large turbines.
? Simple Operation - User-friendly software eliminates need for special training.
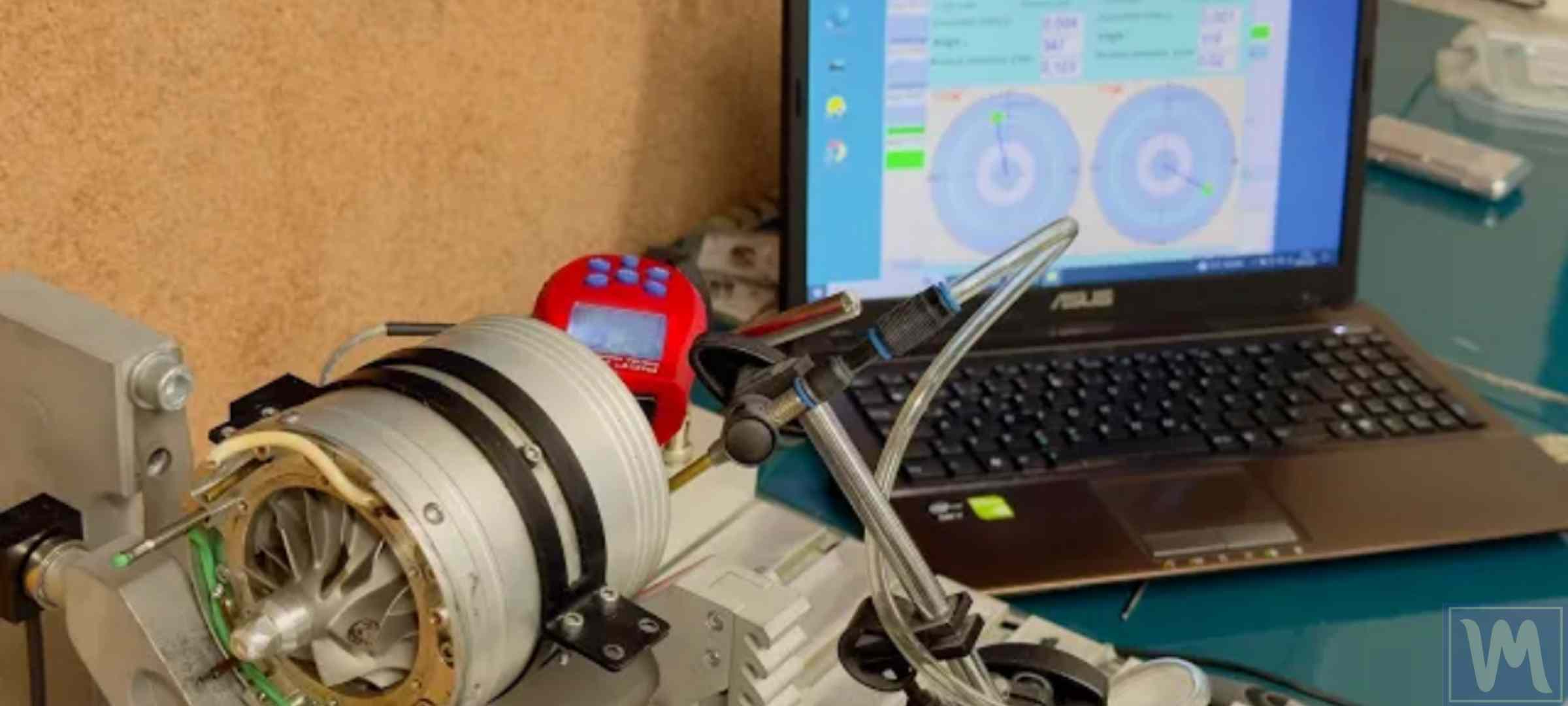

Economic Effect:
? Cost Reduction on maintenance through timely diagnostics - 50-80% of unexpected breakdowns.
? Service Life Increase by 50-200% - balanced equipment lasts longer.
? Power Savings by 5-15% - reduced friction consume less power.
? Short ROI Period - from 3 to 12 months depending on application frequency.
Support
Available to you:
Personnel Training - theoretical sessions online. Advanced training includes complete methodology.
Consultations - remote assistance. Phone consultations for immediate help.
Verification and Calibration - annual calibration to guarantee reliability.
Device Leasing - perfect for one-time projects. Daily rental options available.
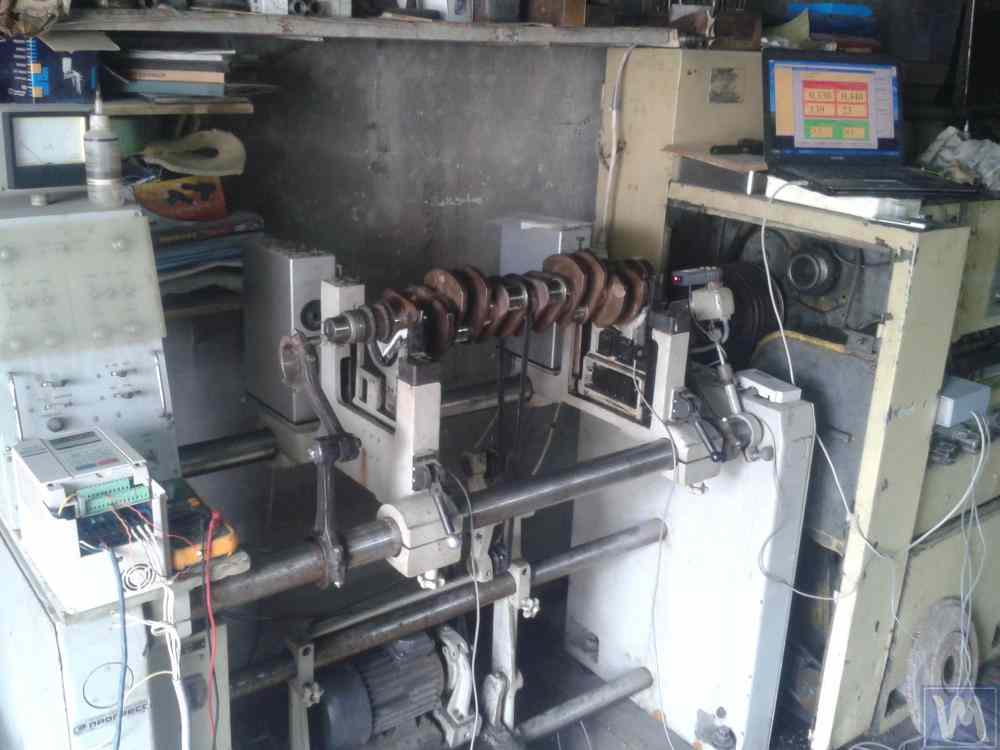

Commercial Terms
Valid Rates:
Balanset-1A Portable Balancer & Vibration Analyzer: €1,751.00
Balanset-1A OEM Version: €1,561.00
Additional Vibration Sensor: €90.00
Optical Sensor (Laser Tachometer): €124.00
Magnetic Stand 60 kgf: €46.00
Reflective Tape: €10.00
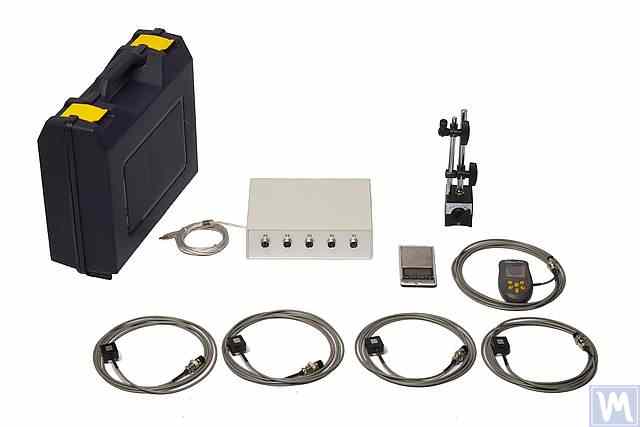

Logistics:
Shipping period: in stock. Warranty terms: 24 months comprehensive coverage. Payment terms: negotiable. Delivery: to any country via express delivery.
Why We Stand Out
Authorized Dealer - original equipment with comprehensive backup.
Expert Engineers with years of expertise in rotor balancing.
Comprehensive Support - from sales to maintenance and education.
Ready Stock - quick delivery for common configurations.
Flexible Terms for regular customers including volume discounts.
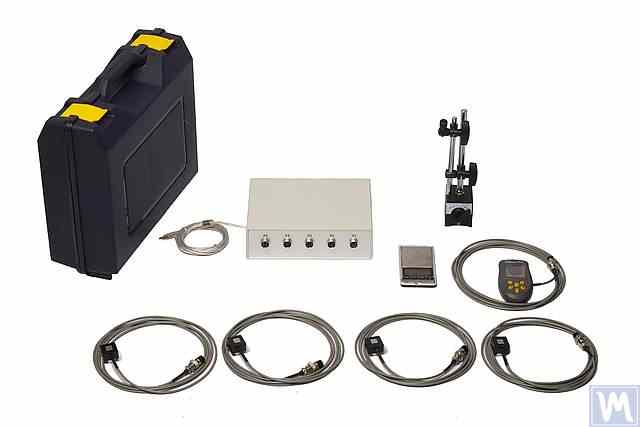

Best regards,
Professional experts group
P.S. Request a demonstration of the equipment right now and take advantage of offers! -
Dear Colleagues!
We present to your attention innovative device for dynamic balancing of rotating equipment - portable balancing device Balanset-1A.
Official product page: https://vibromera.eu/shop/889/

Fields of Use
Balanset-1A is actively applied for imbalance elimination of all sorts of rotor units:
Industrial Machinery:
Ventilation Units - manufacturing, centrifugal, radial. Pumps - centrifugal, oil. Electromotors - synchronous. Turbine Units - steam. Compressor Units - piston.
Machine Tools:
Machine Spindles - grinding. Grinding Discs. Roll Mechanisms of paper machines.
Agricultural Machinery:
Choppers. Rotary Mowers. Grinding Equipment for fertilizers.
Special Applications:
Separators - laboratory. Blowing Machines. Milling Units. Transmission Shafts.

Specifications
Primary Indicators:
Number of balancing planes: 1 or 2. Rotation frequency range: 200 to 15,000 revolutions per minute. Phase measurement accuracy: ±1°. Vibration measurement precision: ±5%. Measurement channels: 2. Vibration velocity measurement range: 0.1 to 300 mm/s. Power: From computer USB port. Kit weight: 4 kg.
Functionality:
Automated computation of compensating masses. Database of measurements. Standards determination according to ISO 1940. Frequency analysis of vibration. Graphical display in diagram form. Split-weight calculator. Index balancing of mandrels.
Supply Composition
Standard Configuration:
USB coupling module (1 pc.) - provides data transfer between measurement system and PC.
Vibration transducers (2 pcs.) - Conversion factor: 100 mV/g. Operating frequencies: 0.5-10,000 Hz. Mounting: adhesive mounting.

Speed sensor (1 pc.) - Working range: up to 1.5 m. Contactless operation for maximum safety.
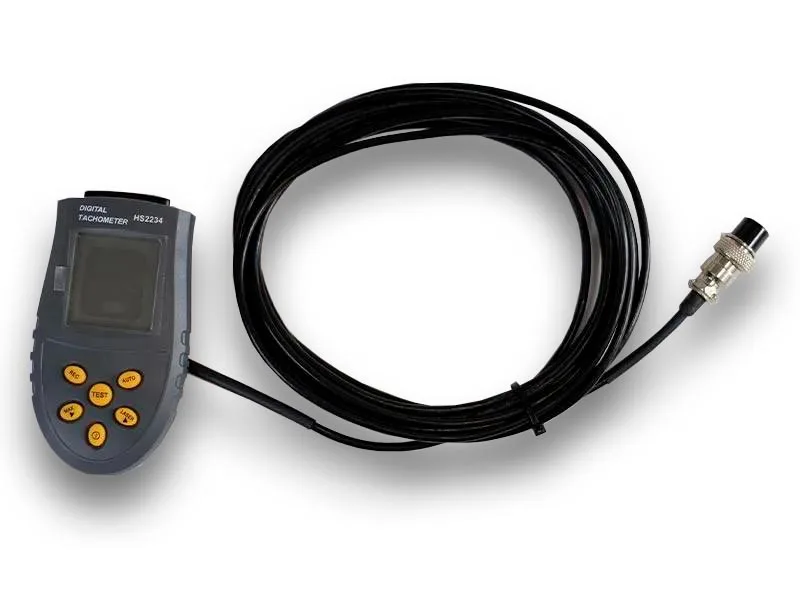

Magnetic stand for phase sensor (1 pc.) - Holding force: 60 kgf. Variable angles for optimal alignment.

Electronic scales up to 500 g (1 pc.) - Accuracy: 0.01 g. Necessary for accurate mass determination.
Program Balanset-1A - User-friendly interface. Computer software. Multilingual interface.

Carrying case (1 pc.) - Durable construction. Cushioned interior for equipment protection.
Technical documentation - Detailed instructions. Practical examples.
Interface cables - Reliable interference-free connections.
Advantages of Balanset-1A
Technical Benefits:
? Precision Measurements - Advanced methods of digital filtering provide consistent accuracy.
? Mobility - Easy transportation facilitates in-place adjustment without disassembly.
? Multi-functionality - Works with various rotors from small fans to heavy rotors.
? User Convenience - User-friendly software bypasses special training.

Economic Effect:
? Expense Cutting on operation through preventive maintenance - significant reduction of unplanned downtime.
? Durability Enhancement by 50-200% - balanced equipment requires less maintenance.
? Energy Efficiency by 5-15% - reduced friction operate efficiently.
? Short ROI Period - from 3 to 12 months depending on usage intensity.
Support
We offer:
Operator Training - practical sessions online. Advanced training covers full procedures.
Technical Support - on-site guidance. Phone consultations for immediate help.
Metrological Support - annual calibration to guarantee reliability.
Equipment Rental - suitable for one-time projects. Weekly lease terms available.
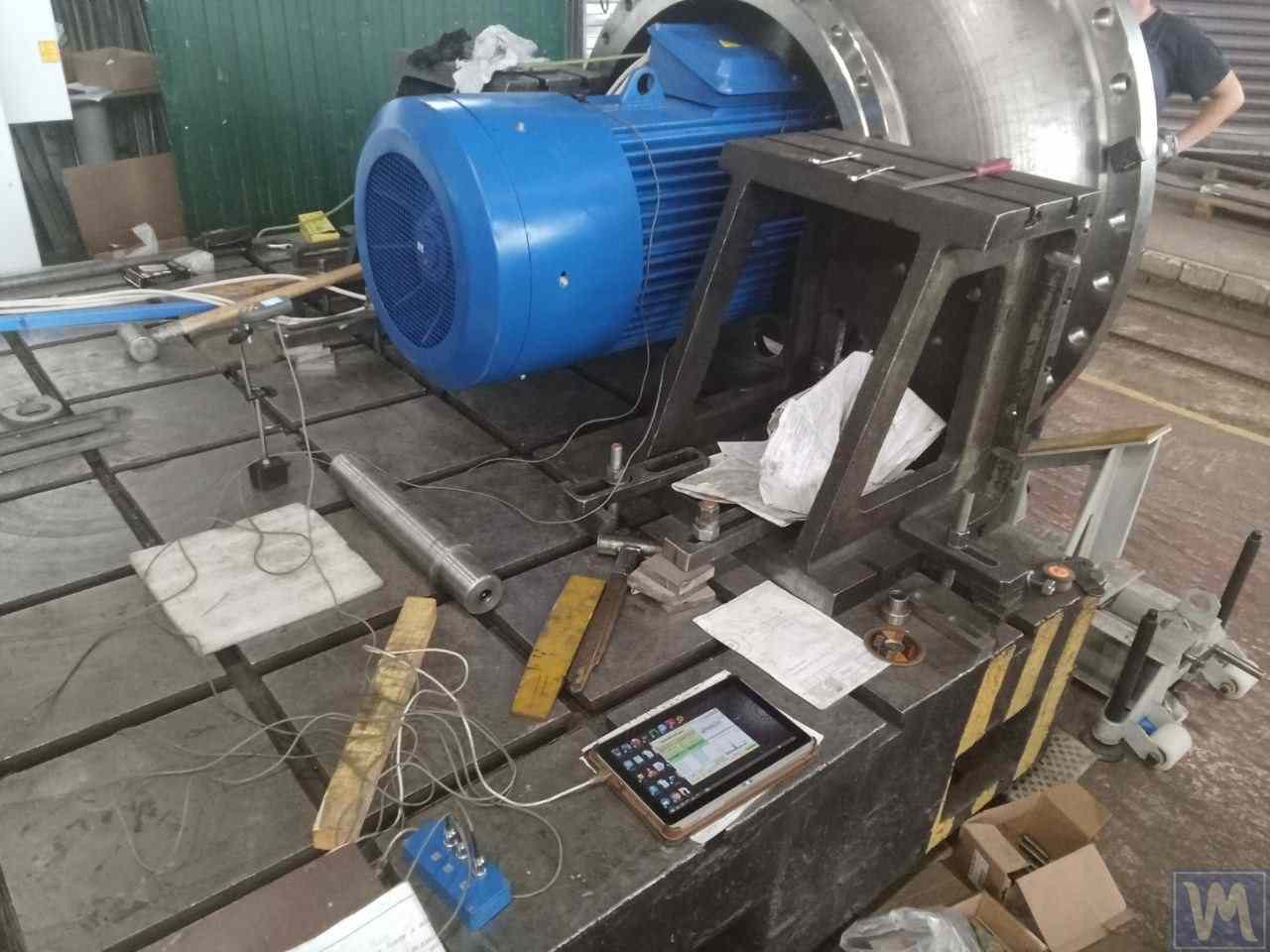

Price Information
Current Pricing:
Balanset-1A Portable Balancer & Vibration Analyzer: €1,751.00
Balanset-1A OEM Version: €1,561.00
Additional Vibration Sensor: €90.00
Optical Sensor (Laser Tachometer): €124.00
Magnetic Stand 60 kgf: €46.00
Reflective Tape: €10.00

Shipping Conditions:
Shipping period: from 3 days. Guarantee period: 24 months comprehensive coverage. Settlement: 100% prepayment. Delivery: to any country via reliable carriers.
Why Choose Us
Official Supplier - factory warranty with complete service.
Qualified Personnel with deep knowledge in vibration diagnostics.
Comprehensive Support - from supply to service and skill development.
Ready Stock - fast shipment for common configurations.
Individual Approach for regular customers including volume discounts.
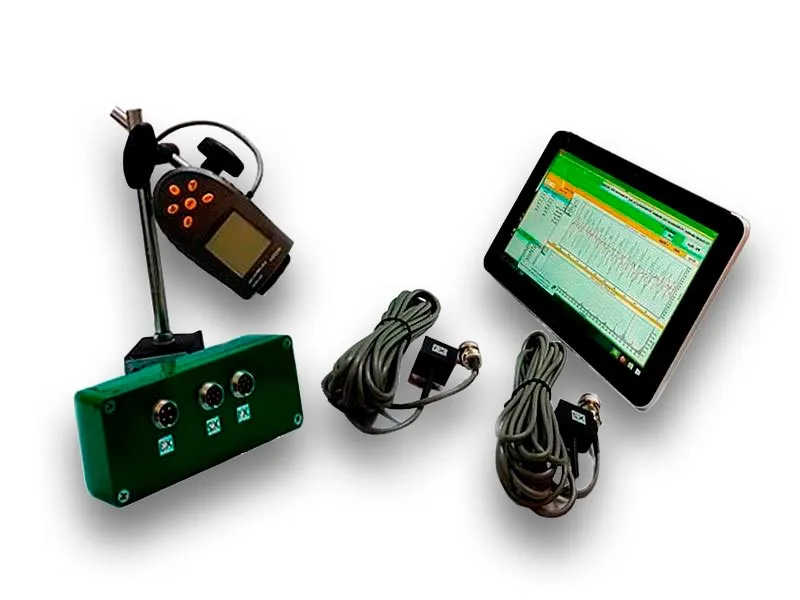

At your service,
Technical support team
P.S. Ask for presentation of the equipment right now and take advantage of offers! -
benemid cost: probenecid brand – probenecid 250 mg
-
https://experienceleaguecommunities.adobe.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/17916318 vermact 12 tablet uses
-
SEO Pyramid 10000 Backlinks
Inbound links of your site on community platforms, sections, comments.
Backlinks – three steps
Stage 1 – Basic inbound links.
Stage 2 – Backlinks through redirects from highly reliable sites with PR 9–10, for example –
Step 3 – Adding to backlink checkers –
The key benefit of link analysis platforms is that they highlight the Google search engine a site map, which is very important!
Explanation for the third stage – only the main page of the site is submitted to SEO checkers, other pages cannot be included.
I complete all three stages sequentially, resulting in 10,000–20,000 backlinks from the three stages.
This linking tactic is highly efficient.
Demonstration of placement on analyzer sites via a TXT file. -
SEO Pyramid 10000 Backlinks
Inbound links of your site on community platforms, blocks, comments.
Three-stage backlink strategy
Step 1 – Basic inbound links.
Step 2 – Links via 301 redirects from highly reliable sites with PageRank PR 9–10, for example –
Step 3 – Submitting to analyzer sites –
The key benefit of link analysis platforms is that they highlight the Google search engine a website structure, which is very important!
Clarification for Stage 3 – only the main page of the site is submitted to SEO checkers, other pages aren’t accepted.
I execute all phases step by step, resulting in 10K–20K backlinks from the full process.
This linking tactic is the best approach.
Example of placement on SEO platforms via a text file. -
buy power tools online
Univerzell.com is your hub for workshop hand tools, professional power tools, and hardware tools for DIY. Buy power tools online, seize limited power tool deals, and discover DIY woodworking project tools. Finish strong with our durable tool storage solutions—gear up today. -
workshop hand tools
Need hardware tools for DIY? Buy power tools online from Univerzell.com. We bundle top power tool deals with expert picks on workshop hand tools, professional power tools, DIY woodworking project tools, and space-saving tool storage solutions—your one-stop woodworking tools shop. -
sindoplay
Selamat datang di situs SINDOPLAY , situs judi slot online , live casino , taruhan bola , poker online dan togel resmi .Daftar dan dapatkan beragam promo menarik dari situs SIndoplay , mulai dari bonus deposit , bonus freespin , cashback serta bonus referral. -
link sindoplay
Selamat datang di situs SINDOPLAY , situs judi slot online , live casino , taruhan bola , poker online dan togel resmi .Daftar dan dapatkan beragam promo menarik dari situs SIndoplay , mulai dari bonus deposit , bonus freespin , cashback serta bonus referral. -
SEO Pyramid 10000 Backlinks
External links of your site on discussion boards, sections, comments.
Backlinks – three steps
Stage 1 – Simple backlinks.
Step 2 – Backlinks through redirects from top-tier sites with PR 9–10, for example –
Step 3 – Submitting to analyzer sites –
The key benefit of SEO tools is that they show the Google search engine a website structure, which is crucial!
Note for Stage 3 – only the main page of the site is added to SEO checkers, internal pages aren’t accepted.
I execute all steps sequentially, resulting in 10,000–20,000 inbound links from the three stages.
This backlink strategy is most effective.
Example of placement on analyzer sites via a TXT file. -
SEO Pyramid 10000 Backlinks
Inbound links of your site on discussion boards, blocks, threads.
The 3-step backlinking method
Stage 1 – Standard external links.
Step 2 – Links via 301 redirects from highly reliable sites with PR 9–10, for example –
Stage 3 – Adding to backlink checkers –
The advantage of link analysis platforms is that they show the Google search engine a website structure, which is crucial!
Explanation for Stage 3 – only the homepage of the site is submitted to SEO checkers, internal pages cannot be included.
I execute all steps sequentially, resulting in 10,000–20,000 inbound links from the full process.
This backlink strategy is highly efficient.
Example of submission on analyzer sites via a text file. -
SEO Pyramid 10000 Backlinks
Inbound links of your site on forums, blocks, threads.
Three-stage backlink strategy
Step 1 – Simple backlinks.
Phase 2 – Links via 301 redirects from top-tier sites with a PageRank score of 9–10, for example –
Stage 3 – Submitting to analyzer sites –
The advantage of link analysis platforms is that they highlight the Google search engine a website structure, which is very important!
Explanation for the third stage – only the homepage of the site is submitted to SEO checkers, other pages cannot be included.
I complete all phases step by step, resulting in 10 to 30 thousand inbound links from the full process.
This backlink strategy is highly efficient.
Example of placement on SEO platforms via a TXT file. -
SEO Pyramid 10000 Backlinks
Inbound links of your site on forums, sections, comments.
Backlinks – three steps
Step 1 – Simple backlinks.
Stage 2 – Links via 301 redirects from highly reliable sites with PageRank PR 9–10, for example –
Phase 3 – Listing on SEO analysis platforms –
The key benefit of analyzer sites is that they highlight the Google search engine a site map, which is crucial!
Explanation for the third stage – only the homepage of the site is submitted to analyzers, other pages aren’t accepted.
I execute all phases sequentially, resulting in 10 to 30 thousand backlinks from the three stages.
This linking tactic is the best approach.
Demonstration of submission on SEO platforms via a text file. -
situs sindoplay
Selamat datang di situs SINDOPLAY , situs judi slot online , live casino , taruhan bola , poker online dan togel resmi .Daftar dan dapatkan beragam promo menarik dari situs SIndoplay , mulai dari bonus deposit , bonus freespin , cashback serta bonus referral. -
login sindoplay
Selamat datang di situs SINDOPLAY , situs judi slot online , live casino , taruhan bola , poker online dan togel resmi .Daftar dan dapatkan beragam promo menarik dari situs SIndoplay , mulai dari bonus deposit , bonus freespin , cashback serta bonus referral. -
nba 直播
感受籃球的每一個精彩瞬間,就在這裡!我們致力於為全球籃球愛好者提供最優質的NBA直播服務,讓您無論身在何處,都能即時觀看每一場激動人心的比賽。從例行賽到季後賽,從全明星賽到總冠軍賽,我們全程直播,絕不錯過任何精彩時刻。 -
nba 直播
感受籃球的每一個精彩瞬間,就在這裡!我們致力於為全球籃球愛好者提供最優質的NBA直播服務,讓您無論身在何處,都能即時觀看每一場激動人心的比賽。從例行賽到季後賽,從全明星賽到總冠軍賽,我們全程直播,絕不錯過任何精彩時刻。 -
體育直播線上看
歡迎來到頂級NBA直播體驗平台,感受籃球的每一個精彩瞬間,就在這裡!我們致力於為全球籃球愛好者提供最優質的NBA直播服務,讓您無論身在何處,都能即時觀看每一場激動人心的比賽。從例行賽到季後賽,從全明星賽到總冠軍賽,我們全程直播,絕不錯過任何精彩時刻。 -
體育直播線上看
歡迎來到頂級NBA直播體驗平台,感受籃球的每一個精彩瞬間,就在這裡!我們致力於為全球籃球愛好者提供最優質的NBA直播服務,讓您無論身在何處,都能即時觀看每一場激動人心的比賽。從例行賽到季後賽,從全明星賽到總冠軍賽,我們全程直播,絕不錯過任何精彩時刻。 -
nba 直播
感受籃球的每一個精彩瞬間,就在這裡!我們致力於為全球籃球愛好者提供最優質的NBA直播服務,讓您無論身在何處,都能即時觀看每一場激動人心的比賽。從例行賽到季後賽,從全明星賽到總冠軍賽,我們全程直播,絕不錯過任何精彩時刻。 -
nba 直播
感受籃球的每一個精彩瞬間,就在這裡!我們致力於為全球籃球愛好者提供最優質的NBA直播服務,讓您無論身在何處,都能即時觀看每一場激動人心的比賽。從例行賽到季後賽,從全明星賽到總冠軍賽,我們全程直播,絕不錯過任何精彩時刻。 -
nba 直播
感受籃球的每一個精彩瞬間,就在這裡!我們致力於為全球籃球愛好者提供最優質的NBA直播服務,讓您無論身在何處,都能即時觀看每一場激動人心的比賽。從例行賽到季後賽,從全明星賽到總冠軍賽,我們全程直播,絕不錯過任何精彩時刻。 -
nba 直播
感受籃球的每一個精彩瞬間,就在這裡!我們致力於為全球籃球愛好者提供最優質的NBA直播服務,讓您無論身在何處,都能即時觀看每一場激動人心的比賽。從例行賽到季後賽,從全明星賽到總冠軍賽,我們全程直播,絕不錯過任何精彩時刻。 -
https://tourism.ju.edu.jo/Lists/AlumniInformation/DispForm.aspx?ID=236 what is vardenafil
-
Kpoker德州撲克
Kpoker德州撲克的使命,是為全球華人玩家打造最值得信賴的線上德州撲克平台。我們致力於提供一個公平、公正且充滿挑戰性的遊戲環境,讓每一位玩家無論經驗多寡,都能在這裡找到屬於自己的撲克節奏。我們相信,撲克是一場融合智慧、耐心與心理戰的經典對局。我們不僅提供高品質的遊戲體驗,也推動撲克文化的傳播與教育,從新手教學到高手對決,陪伴玩家從入門邁向專業,從興趣走向熱情。Kpoker 不只是遊戲,更是連結全球撲克愛好者的橋樑。 -
Kpoker德州撲克
Kpoker德州撲克的使命,是為全球華人玩家打造最值得信賴的線上德州撲克平台。我們致力於提供一個公平、公正且充滿挑戰性的遊戲環境,讓每一位玩家無論經驗多寡,都能在這裡找到屬於自己的撲克節奏。我們相信,撲克是一場融合智慧、耐心與心理戰的經典對局。我們不僅提供高品質的遊戲體驗,也推動撲克文化的傳播與教育,從新手教學到高手對決,陪伴玩家從入門邁向專業,從興趣走向熱情。Kpoker 不只是遊戲,更是連結全球撲克愛好者的橋樑。 -
nba 直播
感受籃球的每一個精彩瞬間,就在這裡!我們致力於為全球籃球愛好者提供最優質的NBA直播服務,讓您無論身在何處,都能即時觀看每一場激動人心的比賽。從例行賽到季後賽,從全明星賽到總冠軍賽,我們全程直播,絕不錯過任何精彩時刻。 -
nba 直播
感受籃球的每一個精彩瞬間,就在這裡!我們致力於為全球籃球愛好者提供最優質的NBA直播服務,讓您無論身在何處,都能即時觀看每一場激動人心的比賽。從例行賽到季後賽,從全明星賽到總冠軍賽,我們全程直播,絕不錯過任何精彩時刻。 -
Link Pyramid Backlinks SEO Pyramid Backlink For Google
Backlinks of your site on forums, blocks, threads.
Three-stage backlink strategy
Stage 1 – Simple backlinks.
Stage 2 – Backlinks through redirects from top-tier sites with PR 9–10, for example –
Stage 3 – Listing on SEO analysis platforms –
The advantage of link analysis platforms is that they highlight the Google search engine a website structure, which is crucial!
Clarification for Stage 3 – only the main page of the site is added to SEO checkers, other pages aren’t accepted.
I execute all three stages sequentially, resulting in 10K–20K backlinks from the three stages.
This backlink strategy is highly efficient.
Demonstration of submission on analyzer sites via a .txt document. -
Link Pyramid Backlinks SEO Pyramid Backlink For Google
Backlinks of your site on community platforms, sections, comments.
Backlinks – three steps
Stage 1 – Simple backlinks.
Stage 2 – Backlinks through redirects from top-tier sites with PageRank PR 9–10, for example –
Stage 3 – Adding to backlink checkers –
The key benefit of analyzer sites is that they display the Google search engine a site map, which is very important!
Note for Stage 3 – only the homepage of the site is added to analyzers, other pages cannot be included.
I execute all three stages step by step, resulting in 10K–20K backlinks from the three stages.
This backlink strategy is highly efficient.
Example of placement on SEO platforms via a TXT file. -
tourism.ju.edu.jo/Lists/AlumniInformation/DispForm.aspx?ID=153 cenforce 100mg
-
nba 直播
感受籃球的每一個精彩瞬間,就在這裡!我們致力於為全球籃球愛好者提供最優質的NBA直播服務,讓您無論身在何處,都能即時觀看每一場激動人心的比賽。從例行賽到季後賽,從全明星賽到總冠軍賽,我們全程直播,絕不錯過任何精彩時刻。 -
nba 直播
感受籃球的每一個精彩瞬間,就在這裡!我們致力於為全球籃球愛好者提供最優質的NBA直播服務,讓您無論身在何處,都能即時觀看每一場激動人心的比賽。從例行賽到季後賽,從全明星賽到總冠軍賽,我們全程直播,絕不錯過任何精彩時刻。 -
sildenafil sandoz 100 mg: viagrabelgique.com - viagrabelgique.com
-
Link Pyramid Backlinks SEO Pyramid Backlink For Google
Inbound links of your site on discussion boards, sections, threads.
The 3-step backlinking method
Step 1 – Basic inbound links.
Phase 2 – Links via 301 redirects from authoritative sites with a PageRank score of 9–10, for example –
Phase 3 – Adding to backlink checkers –
The key benefit of SEO tools is that they highlight the Google search engine a site map, which is crucial!
Clarification for Stage 3 – only the homepage of the site is added to SEO checkers, internal pages cannot be included.
I complete all steps step by step, resulting in 10K–20K backlinks from the three stages.
This backlink strategy is the best approach.
Example of submission on SEO platforms via a TXT file. -
Link Pyramid Backlinks SEO Pyramid Backlink For Google
External links of your site on forums, sections, comments.
The 3-step backlinking method
Stage 1 – Simple backlinks.
Phase 2 – Links via 301 redirects from top-tier sites with PR 9–10, for example –
Step 3 – Listing on SEO analysis platforms –
The advantage of SEO tools is that they highlight the Google search engine a website structure, which is very important!
Clarification for Stage 3 – only the main page of the site is submitted to analyzers, internal pages aren’t accepted.
I execute all phases step by step, resulting in 10K–20K backlinks from the three stages.
This backlink strategy is the best approach.
Demonstration of placement on analyzer sites via a TXT file. -
https://ventolinof.com/# Ventolin inhaler vs albuterol sulfate
-
SEO LINKS 10 000, I have a powerful server, backlink building
External links of your site on forums, sections, comments.
Backlinks – three steps
Stage 1 – Standard external links.
Step 2 – Backlinks through redirects from authoritative sites with PageRank PR 9–10, for example –
Step 3 – Submitting to analyzer sites –
The key benefit of analyzer sites is that they show the Google search engine a website structure, which is crucial!
Note for the third stage – only the homepage of the site is submitted to SEO checkers, other pages cannot be included.
I execute all phases step by step, resulting in 10K–20K inbound links from the three stages.
This backlink strategy is most effective.
Example of placement on analyzer sites via a text file. -
SEO LINKS 10 000, I have a powerful server, backlink building
Inbound links of your site on discussion boards, blocks, comments.
Backlinks – three steps
Phase 1 – Basic inbound links.
Stage 2 – Backlinks through redirects from highly reliable sites with PR 9–10, for example –
Step 3 – Adding to backlink checkers –
The advantage of link analysis platforms is that they display the Google search engine a site map, which is essential!
Explanation for Stage 3 – only the homepage of the site is submitted to SEO checkers, other pages cannot be included.
I complete all steps step by step, resulting in 10K–20K backlinks from the full process.
This linking tactic is the best approach.
Demonstration of placement on SEO platforms via a .txt document. -
магазин пятерочка каталог товаров и цены
Хотите покупать продукты со скидками? Тогда вы по адресу!
Good-Promo.ru агрегирует все свежие акции и спецпредложения «Пятёрочки» в одном месте.
Преимущества:
Скидки, обновляющиеся каждый день
Полный каталог промо-товаров
Сведения о розыгрышах призов
Топовые скидки
Как использовать:
Откройте на Good-Promo.ru
Отметьте нужные предложения
Покупайте в «Пятёрочке» по лучшим ценам
Сайт поможет вам:
Покупать дешевле
Узнавать о новых акциях первыми
Искать выгодные предложения
Экономия без лишних усилий с Good-Promo.ru! -
пятерочка скидки и акции сегодня
Мечтаете покупать продукты со скидками?
Good-Promo.ru агрегирует все свежие акции и спецпредложения «Пятёрочки» в одном удобном ресурсе.
Преимущества:
Скидки, обновляющиеся каждый день
Каталог товаров со скидкой
Сведения о розыгрышах призов
Лучшие цены дня
Как использовать:
Зайдите на Good-Promo.ru
Отметьте нужные акции
Делайте покупки в «Пятёрочке» по лучшим ценам
Сайт поможет вам:
Экономить на продуктах
Быть в курсе всех скидок
Открывать для себя акционные товары
Скидки под рукой с Good-Promo.ru! -
德州撲克規則
學會德州撲克,不只是學會一套牌型規則,而是開始理解一場結合邏輯、心理與紀律的頭腦對決。無論你是剛入門的新手,還是已經上過幾次牌桌的玩家,只要願意花時間學習技巧、訓練判斷,並培養正確的資金控管與心態,人人都有機會從「交學費」變成「收學費」。打好每一手牌,不為一時輸贏情緒化,累積經驗與數據,就是長期勝率提升的關鍵! -
德州撲克規則
學會德州撲克,不只是學會一套牌型規則,而是開始理解一場結合邏輯、心理與紀律的頭腦對決。無論你是剛入門的新手,還是已經上過幾次牌桌的玩家,只要願意花時間學習技巧、訓練判斷,並培養正確的資金控管與心態,人人都有機會從「交學費」變成「收學費」。打好每一手牌,不為一時輸贏情緒化,累積經驗與數據,就是長期勝率提升的關鍵! -
德州撲克規則
學會德州撲克規則,是踏入撲克世界的第一步。從掌握下注節奏、理解牌型,到實戰中運用策略,每一步都能讓你更加上手並享受對戰樂趣。想立刻開始實戰練習?我們推薦【Kpoker 德州撲克系統】,提供真實匹配環境與新手教學模式,現在註冊還能獲得免費體驗金,讓你零風險上桌實戰! -
德州撲克規則
學會德州撲克規則,是踏入撲克世界的第一步。從掌握下注節奏、理解牌型,到實戰中運用策略,每一步都能讓你更加上手並享受對戰樂趣。想立刻開始實戰練習?我們推薦【Kpoker 德州撲克系統】,提供真實匹配環境與新手教學模式,現在註冊還能獲得免費體驗金,讓你零風險上桌實戰! -
德州撲克規則
你是不是也想學德州撲克,卻被一堆術語搞得霧煞煞?別擔心,這篇就是為你準備的「規則懶人包」,從發牌、下注到比牌,5 個階段、5 種行動,一次搞懂!德州撲克新手必看!快速掌握德撲規則與下注方式,從發牌、翻牌到比牌,一次看懂德州撲克 5 大階段與 5 種行動,不再上桌搞不懂規則。 -
https://ogorodland.ru/forum/topic/akczii-pyaterochki-2/#postid-13485
Желаете покупать продукты со скидками? Тогда вы по адресу!
Good-Promo.ru собирает все свежие акции и спецпредложения «Пятёрочки» в одном месте.
Преимущества:
Актуальные скидки каждый день
Каталог товаров со скидкой
Информация о конкурсах и розыгрышах
Самые выгодные предложения
Как использовать:
Зайдите на Good-Promo.ru
Выберите нужные скидки
Делайте покупки в «Пятёрочке» со скидками
Сайт поможет вам:
Не переплачивать за покупки
Узнавать о новых акциях первыми
Искать выгодные предложения
Скидки под рукой с Good-Promo.ru! -
https://bioniclerpg.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=6&t=7596
Хотите покупать продукты со скидками?
Good-Promo.ru собирает все актуальные акции и спецпредложения «Пятёрочки» в одном удобном ресурсе.
Преимущества:
Актуальные скидки каждый день
Полный каталог промо-товаров
Информация о конкурсах и розыгрышах
Самые выгодные предложения
Как использовать:
Откройте на Good-Promo.ru
Отметьте нужные скидки
Покупайте в «Пятёрочке» со скидками
Сайт поможет вам:
Не переплачивать за покупки
Получать актуальную информацию
Находить товары со скидками
Экономия без лишних усилий с Good-Promo.ru! -
德州撲克遊戲線上
不論你是撲克新手或長期玩家,選對平台就像選對拳擊擂台。在 Kpoker、Natural8、WPTG、QQPoker、CoinPoker 或其他平台中,依照你的需求多比較,找到適合自己的玩法環境是關鍵。從註冊、學習到實戰成長,選對平台就是給自己最好的起點! -
德州撲克遊戲線上
不論你是撲克新手或長期玩家,選對平台就像選對拳擊擂台。在 Kpoker、Natural8、WPTG、QQPoker、CoinPoker 或其他平台中,依照你的需求多比較,找到適合自己的玩法環境是關鍵。從註冊、學習到實戰成長,選對平台就是給自己最好的起點! -
德州撲克規則
你是不是也想學德州撲克,卻被一堆術語搞得霧煞煞?別擔心,這篇就是為你準備的「規則懶人包」,從發牌、下注到比牌,5 個階段、5 種行動,一次搞懂!德州撲克新手必看!快速掌握德撲規則與下注方式,從發牌、翻牌到比牌,一次看懂德州撲克 5 大階段與 5 種行動,不再上桌搞不懂規則。 -
德州撲克規則
你是不是也想學德州撲克,卻被一堆術語搞得霧煞煞?別擔心,這篇就是為你準備的「規則懶人包」,從發牌、下注到比牌,5 個階段、5 種行動,一次搞懂!德州撲克新手必看!快速掌握德撲規則與下注方式,從發牌、翻牌到比牌,一次看懂德州撲克 5 大階段與 5 種行動,不再上桌搞不懂規則。 -
德州撲克規則
想學德州撲克卻完全沒頭緒?不管你是零基礎還是想重新複習,這篇就是為你準備的!一次搞懂德州撲克規則、牌型大小、下注流程與常見術語,讓你從看不懂到能開打一局只差這一篇!看完這篇,是不是對德州撲克整個比較有頭緒了?從玩法、流程到那些常聽不懂的術語,現在是不是都懂了七八成?準備好了嗎?快記好牌型、搞懂位置,然後開打一局練練手啦!富遊娛樂城提供最新線上德州撲克供玩家遊玩!首家引進OFC大菠蘿撲克、NLH無限注德州撲克玩法,上桌就開打,數錢數不停! -
德州撲克規則
想學德州撲克卻完全沒頭緒?不管你是零基礎還是想重新複習,這篇就是為你準備的!一次搞懂德州撲克規則、牌型大小、下注流程與常見術語,讓你從看不懂到能開打一局只差這一篇!看完這篇,是不是對德州撲克整個比較有頭緒了?從玩法、流程到那些常聽不懂的術語,現在是不是都懂了七八成?準備好了嗎?快記好牌型、搞懂位置,然後開打一局練練手啦!富遊娛樂城提供最新線上德州撲克供玩家遊玩!首家引進OFC大菠蘿撲克、NLH無限注德州撲克玩法,上桌就開打,數錢數不停! -
加密貨幣
值得信賴的研究和專業知識匯聚於此。自 2020 年以來,Techduker 已幫助數百萬人學習如何解決大大小小的技術問題。我們與經過認證的專家、訓練有素的研究人員團隊以及忠誠的社區合作,在互聯網上創建最可靠、最全面、最令人愉快的操作方法內容。 -
加密貨幣
值得信賴的研究和專業知識匯聚於此。自 2020 年以來,Techduker 已幫助數百萬人學習如何解決大大小小的技術問題。我們與經過認證的專家、訓練有素的研究人員團隊以及忠誠的社區合作,在互聯網上創建最可靠、最全面、最令人愉快的操作方法內容。 -
二手車推薦
想買車又怕預算爆表?其實選對二手車(中古車)才能省錢又保值!本篇 10 大二手車推薦及購車必讀指南,帶你避開地雷、挑選高 CP 值好車!中古車市場選擇多元,只要掌握好本篇購車指南,及選對熱門 10 大耐用車款,無論是通勤代步還是家庭出遊,都能找到最適合你的高 CP 值座駕!二手車哪裡買?現在就立即諮詢或持續追蹤好薦十大推薦,獲得更多優質二手車推薦。 -
二手車推薦
想買車又怕預算爆表?其實選對二手車(中古車)才能省錢又保值!本篇 10 大二手車推薦及購車必讀指南,帶你避開地雷、挑選高 CP 值好車!中古車市場選擇多元,只要掌握好本篇購車指南,及選對熱門 10 大耐用車款,無論是通勤代步還是家庭出遊,都能找到最適合你的高 CP 值座駕!二手車哪裡買?現在就立即諮詢或持續追蹤好薦十大推薦,獲得更多優質二手車推薦。 -
加密貨幣
值得信賴的研究和專業知識匯聚於此。自 2020 年以來,Techduker 已幫助數百萬人學習如何解決大大小小的技術問題。我們與經過認證的專家、訓練有素的研究人員團隊以及忠誠的社區合作,在互聯網上創建最可靠、最全面、最令人愉快的操作方法內容。 -
娛樂城推薦
ACE博評網有多年經驗以及專業水準,我們能夠幫助玩家在繁雜的遊戲行業中找到一個值得信賴的選擇。我們不向任何娛樂城收取廣告費,所有被推薦的娛樂城都已經通過我們的審查,來評估他們的效能與真誠度。每一間娛樂城都必須承受重要的考驗,並且只有符合我們高水平準則的公司才能夠獲得我們正式認可 -
娛樂城推薦
ACE博評網有多年經驗以及專業水準,我們能夠幫助玩家在繁雜的遊戲行業中找到一個值得信賴的選擇。我們不向任何娛樂城收取廣告費,所有被推薦的娛樂城都已經通過我們的審查,來評估他們的效能與真誠度。每一間娛樂城都必須承受重要的考驗,並且只有符合我們高水平準則的公司才能夠獲得我們正式認可 -
SEO Pyramid 10000 Backlinks
Inbound links of your site on forums, blocks, threads.
Three-stage backlink strategy
Phase 1 – Standard external links.
Phase 2 – Backlinks through redirects from highly reliable sites with a PageRank score of 9–10, for example –
Stage 3 – Listing on SEO analysis platforms –
The key benefit of SEO tools is that they show the Google search engine a site map, which is very important!
Explanation for Stage 3 – only the main page of the site is added to analyzers, internal pages aren’t accepted.
I complete all steps sequentially, resulting in 10K–20K inbound links from the three stages.
This backlink strategy is the best approach.
Demonstration of placement on SEO platforms via a text file. -
SEO Pyramid 10000 Backlinks
External links of your site on discussion boards, sections, threads.
The 3-step backlinking method
Stage 1 – Simple backlinks.
Phase 2 – Backlinks through redirects from top-tier sites with PageRank PR 9–10, for example –
Stage 3 – Submitting to analyzer sites –
The advantage of SEO tools is that they show the Google search engine a website structure, which is essential!
Note for the third stage – only the main page of the site is submitted to SEO checkers, other pages aren’t accepted.
I complete all three stages step by step, resulting in 10K–20K backlinks from the three stages.
This backlink strategy is highly efficient.
Demonstration of submission on analyzer sites via a TXT file. -
Свободные прогнозы на спорт от LiveSport.Ru — ваш путь к успешным пари
Ищете проверенный сервис для точных и свободных прогнозов на спорт? Попали в нужное место! На LiveSport.Ru публикуется достоверные, профессиональные и обдуманные предложения, которые посодействуют как профессионалам, так и начинающим оформлять более рассчитанные букмекерские пари.
Абсолютно все прогнозы создаются на основе тщательного анализа спортивной статистики, последних новостей из клубов, их состояния, взаимных результатов и заключения специалистов экспертов сайта. Мы не предлагаем случайные догадки — только лишь «железные» рекомендации, основанные на фактах и внимательном рассмотрении матчей.
Сайт ежедневно обновляется свежими материалами. Отыщете бесплатные прогнозы на сегодня, на следующий день и на перспективу. Это превращает LiveSport.Ru практичным ресурсом для людей, кто желает следить за спортивными событиями и делать ставки с умом.
Охватываем обширный перечень спортивных дисциплин, в том числе:
Футбольные матчи — включая прогнозы на крупнейшие турниры, такие как ЧМ-2026.
Хоккейные матчи — аналитика по ключевым матчам и соревнованиям.
Боксерские матчи — прогнозы на бои мирового уровня.
А также другие виды спорта.
Наши прогнозы — не случайные догадки, а итог кропотливой работы экспертов, которые изучают все нюансы ближайших событий. Благодаря этому имеете возможность получить полную картину для принятия ставочного решения при ставках.
Заходите на LiveSport.Ru каждый день и используйте новыми аналитикой, которые посодействуют вашему успеху увеличить вероятность выигрыша в сфере беттинга. -
Прогнозы на спорт
Бесплатные аналитика ставок от LiveSport.Ru — ваш путь к успешным беттингу
Нужен надежный источник для качественных и бесплатных аналитики для ставок? Вы попали по адресу! На LiveSport.Ru публикуется точные, экспертные и взвешенные предложения, которые помогут как опытным игрокам, так и начинающим делать более грамотные букмекерские пари.
Абсолютно все прогнозы создаются на основе досконального анализа спортивной статистики, актуальной информации из команд, их текущей формы, предыдущих столкновений и профессионального анализа специалистов сайта. Не даем непроверенные сведения — только «надежные» советы, построенные на реальной информации и глубоком изучении матчей.
Ресурс регулярно пополняется свежими материалами. Вы найдете открытые аналитику на сегодняшние матчи, на следующий день и на перспективу. Это делает из LiveSport.Ru практичным ресурсом для людей, кто стремится отслеживать матчи и делать ставки с умом.
Охватываем обширный перечень спортивных дисциплин, включая:
Футбол — включая прогнозы на аналитику по главным чемпионатам, включая чемпионат мира 2026 года.
Хоккей — предсказания на важные игры и соревнованиям.
Боксерские поединки — предсказания на титульные встречи.
И многие другие дисциплины.
Наша аналитика — не угадывания, а результат профессиональной деятельности экспертов, которые анализируют каждую деталь предстоящих матчей. Благодаря этому получаете максимум информации для принятия решений при пари.
Заходите на LiveSport.Ru каждый день и применяйте свежими прогнозами, которые посодействуют вам усилить шансы на успех в мире беттинга. -
buy cipmox get amoxicillin prescription
-
игровые автоматы gama casino
Gama Casino — где начинается настоящий азарт
Если тебе нужно место, где комфорт, азарт и свобода идут в одном флаконе — добро пожаловать в Gama Casino. Это не просто площадка — это пространство, где рождается настоящий кайф.
Что тебя ждёт?
Тут собрано всё, чтобы ты не захотел уходить. Фанат старых добрых слотов? Добро пожаловать — здесь ты найдёшь ретро-классику и свежие релизы с мощной графикой. А если хочешь почувствовать дух настоящего казино — в Gama Casino есть лайв-игры с живыми дилерами. Все классические игры — с живыми дилерами, быстрым откликом и атмосферой азарта.
А ещё можно сыграть в мгновенные игры — если не терпишь ожиданий. Любишь молниеносные эмоции? Тогда вперёд — мигом проверь, как повезёт.
Удобство — это про Gama Casino
Интерфейс — интуитивный и приятный, будто родной. Всё логично, всё на своих местах. Без лишней возни — всё просто и понятно. С первого взгляда — всё понятно, всё твоё. А ещё выводы без лишних телодвижений. Нет бюрократии и лишних танцев с бубном. Всё работает быстро и без обмана.
Бонусы — каждый день, без исключения
В Gama Casino ценят игроков и радуют бонусами. Фриспины, кэшбэк, приветственные бонусы — лови их часто и без лишних заморочек. Каждый день — шанс получить что-то особенное. Здесь заботятся о том, чтобы ты играл с удовольствием.
Поддержка на связи
Служба поддержки — на чиле, но при этом всегда готова помочь. Быстро и без лишней бюрократии. Обращайся — тебе ответят.
Регистрация займёт всего пару минут
Хочешь войти в движ? Регистрация займёт всего пару минут. Минимум данных, максимум результата. Создай аккаунт — и вперёд, к победам.
Gama Casino — это не просто сайт. Это место, где азарт становится частью жизни. Для тех, кто не боится азарта. Для тех, кто хочет больше, чем просто игра. Заходи — и наслаждайся. -
регистрация гама казино
Gama Casino — где начинается настоящий азарт
Хочешь кайфа без лишнего гемора? Тогда тебе сюда — добро пожаловать в Gama Casino. Это не просто площадка — это пространство, где рождается настоящий кайф.
Что внутри?
Здесь найдётся место для любого настроения. Фанат старых добрых слотов? Добро пожаловать — здесь ты найдёшь ретро-классику и свежие релизы с мощной графикой. Хочешь атмосферы реального казино? Включай лайв-игры. Рулетка, блэкджек, покер — всё как надо, с профессиональными дилерами и безупречной графикой.
А ещё можно сыграть в мгновенные игры — если не терпишь ожиданий. Хочешь быстро проверить удачу — пожалуйста, дерзай и выигрывай.
Всё сделано для твоего удобства
Интерфейс интуитивно понятен и создан для максимального комфорта. Всё на своих местах, ничего лишнего. Никакой путаницы, никаких лишних кликов. Заходишь — и сразу понимаешь, что это твоё пространство. А вывод средств — это просто и быстро. Ни плясок с бубном, ни бесконечных верификаций. Всё честно и по-деловому.
Бонусы — каждый день, без исключения
В Gama Casino заботятся о каждом игроке. Фриспины, кэшбэк, приветственные бонусы — лови их регулярно и без лишних условий. Каждый день — повод порадовать себя. Здесь делают всё, чтобы азарт был именно таким — ярким и позитивным.
Поддержка всегда рядом
Служба поддержки — дружелюбная и оперативная. Отвечают быстро, без занудства и лишних вопросов. Можно смело обращаться, если что-то понадобится.
Создать аккаунт — дело пары минут
Хочешь войти в движ? Регистрация займёт всего пару минут. Минимум данных, максимум результата. Создай аккаунт, получи бонус и начни играть уже сегодня.
Gama Casino — это не просто сайт. Это место, где рождается настоящий кайф. Для тех, кто не боится азарта. Для тех, кто ищет движ, эмоции и реальные шансы. Входи — и начинай наслаждаться. -
Прогнозы на спорт
Бесплатные прогнозы на спорт от LiveSport.Ru — ваш шанс к успешным ставкам
Ищете надежный надежный источник для качественных и свободных прогнозов на спорт? Пришли по адресу! На LiveSport.Ru размещается точные, экспертные и взвешенные рекомендации, которые помогут как профессионалам, так и тем, кто только начинает оформлять более грамотные ставки у букмекеров.
Абсолютно все аналитика составляется на фундаменте досконального анализа статданных, актуальной информации из спортивных коллективов, их текущей формы, истории личных встреч и заключения специалистов экспертов сервиса. Сервис не дает слепые предположения — исключительно «твердые» рекомендации, основанные на реальной информации и глубоком изучении игр.
Сайт ежедневно обновляется новыми данными. Найдете бесплатные предсказания на текущий день, завтра и на перспективу. Это превращает LiveSport.Ru полезным сервисом для людей, кто стремится следить за спортивными событиями и грамотно подходить к беттингу.
Мы охватываем широкий спектр спортивных дисциплин, в том числе:
Футбольные игры — в том числе аналитику по главным чемпионатам, включая мировой чемпионат 2026.
Хоккей — аналитика по ключевым матчам и чемпионатам.
Боксерские поединки — аналитика по чемпионским боям.
И многие другие дисциплины.
Наша аналитика — это не просто предположения, а продукт усердного труда аналитиков, которые рассматривают каждую деталь предстоящих матчей. Поэтому получаете максимум информации для выбора ставки при пари.
Посещайте LiveSport.Ru постоянно и пользуйтесь свежими прогнозами, которые помогут вашему успеху увеличить шансы на успех в сфере беттинга. -
Прогнозы на спорт
Открытые аналитика ставок от LiveSport.Ru — ваш путь к успешным ставкам
Нужен качественный ресурс для достоверных и свободных прогнозов на спорт? Попали в нужное место! На LiveSport.Ru выкладывается точные, экспертные и взвешенные рекомендации, которые помогут как профессионалам, так и тем, кто только начинает оформлять более обоснованные ставки у букмекеров.
Все аналитика составляется на фундаменте глубокого изучения спортивной статистики, свежих сообщений из команд, их актуального уровня, взаимных результатов и экспертного мнения экспертов ресурса. Сервис не дает случайные догадки — только лишь «железные» предложения, основанные на фактах и глубоком изучении матчей.
Наш сайт постоянно обновляется свежими материалами. Вы найдете открытые аналитику на сегодняшние матчи, на следующий день и на перспективу. Это превращает LiveSport.Ru практичным ресурсом для пользователей, кто хочет быть в курсе спорта и грамотно подходить к беттингу.
Мы охватываем широкий спектр направлений, включая такие:
Футбольные игры — включая прогнозы на предсказания на ведущие турниры, такие как мировой чемпионат 2026.
Хоккейные игры — предсказания на важные игры и соревнованиям.
Боксерские матчи — прогнозы на бои мирового уровня.
И многие другие дисциплины.
Наша аналитика — не угадывания, а продукт профессиональной деятельности экспертов, которые анализируют все аспекты предстоящих матчей. Благодаря этому имеете возможность получить полную картину для выбора ставки при пари.
Открывайте LiveSport.Ru ежедневно и используйте свежими аналитикой, которые помогут вашему успеху усилить перспективы выигрыша в области ставок на спорт. -
Прогнозы на спорт
Бесплатные аналитика ставок от LiveSport.Ru — ваш шанс к успешным беттингу
Ищете качественный ресурс для точных и безвозмездных аналитики для ставок? Попали в нужное место! На LiveSport.Ru размещается обоснованные, профессиональные и продуманные рекомендации, которые помогут как ветеранам ставок, так и новичкам оформлять более грамотные спортивные ставки.
Каждый предсказания формируются на основе тщательного изучения спортивной статистики, свежих сообщений из команд, их текущей формы, предыдущих столкновений и профессионального анализа аналитиков ресурса. Не даем непроверенные сведения — только «твердые» советы, созданные на данных и внимательном рассмотрении игр.
Наш сайт постоянно обновляется актуальным контентом. Вы найдете бесплатные предсказания на текущий день, на следующий день и на несколько дней вперед. Это делает LiveSport.Ru полезным сервисом для пользователей, кто хочет быть в курсе спорта и грамотно подходить к беттингу.
Мы охватываем разнообразие направлений, в том числе:
Футбол — включая прогнозы на крупнейшие турниры, такие как чемпионат мира 2026 года.
Хоккейные игры — обзоры по топ-встречам и чемпионатам.
Бокс — аналитика по чемпионским боям.
И многие другие дисциплины.
Наши прогнозы — не угадывания, а итог кропотливой работы специалистов, которые рассматривают каждую деталь предстоящих матчей. В результате вы получаете максимум информации для принятия решений при ставках.
Открывайте LiveSport.Ru постоянно и пользуйтесь свежими аналитикой, которые посодействуют вам увеличить вероятность выигрыша в сфере спортивных ставок.
https://www.livesport.ru/tips/ -
Прогнозы на спорт
Бесплатные прогнозы на спорт от LiveSport.Ru — ваш ключ к успешным пари
Ищете надежный надежный источник для точных и безвозмездных аналитики для ставок? Попали в нужное место! На LiveSport.Ru размещается обоснованные, экспертные и обдуманные рекомендации, которые посодействуют как ветеранам ставок, так и новичкам совершать более грамотные спортивные ставки.
Все предсказания формируются на базе глубокого рассмотрения спортивной статистики, последних новостей из команд, их текущей формы, предыдущих столкновений и экспертного мнения экспертов сайта. Не даем непроверенные сведения — только «надежные» советы, построенные на данных и внимательном рассмотрении матчей.
Ресурс постоянно обновляется актуальным контентом. Отыщете бесплатные предсказания на текущий день, на следующий день и на несколько дней вперед. Это делает LiveSport.Ru полезным сервисом для пользователей, кто стремится следить за спортивными событиями и делать ставки с умом.
Рассматриваем обширный перечень спортивных дисциплин, в том числе:
Футбол — включая аналитику по главным чемпионатам, такие как мировой чемпионат 2026.
Хоккейные матчи — аналитика по ключевым матчам и турнирам.
Бокс — предсказания на титульные встречи.
Плюс другие спортивные направления.
Наши прогнозы — не угадывания, а результат профессиональной деятельности специалистов, которые анализируют все нюансы будущих игр. В результате вы получаете максимум информации для принятия решений при ставках.
Заходите на LiveSport.Ru каждый день и используйте актуальными прогнозами, которые способствуют вам усилить шансы на успех в мире беттинга.
https://www.livesport.ru/tips/ -
https://www.seoanalyzer.gr/domain/livesport.ru
-
https://www.mmnt.org/cat/rp/www.livesport.ru%2Ftips%2F
-
https://in.pinterest.com/clomid50mgtablets/ clomid pills
-
cgminer download
CGMiner Software: Effective Mining Tool for Crypto Miners
What Exactly is CGMiner?
CGMiner is one of the best miners that enables mining Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin, and various digital currencies. The miner works with ASIC, FPGA, and GPU (versions up to 3.7.2). CGMiner is highly configurable and supports multi-threaded mining, multi-pool functionality, as well as remote control and surveillance of equipment operational parameters.
Main Features
Support for Multiple Cryptocurrencies
CGMiner excels at mining diverse crypto assets including Bitcoin (BTC), Litecoin (LTC), Dogecoin (DOGE), and various altcoins with different algorithms.
Hardware Compatibility
The miner works with multiple categories of mining hardware:
- ASIC - Custom-designed chips for maximum efficiency
- FPGA Devices - Reprogrammable chips for tailored mining functions
- Graphics Cards - Video cards (compatible until version 3.7.2)
Advanced Capabilities
- Adaptable settings - Extensive settings for hardware optimization
- Parallel processing - Optimal exploitation of CPU and GPU resources
- Multi-pool support - Automatic failover between mining pools
- Distant control - Operate and track hardware from remote locations
What Makes CGMiner Special?
CGMiner distinguishes itself for its consistent performance, exceptional speed, and affordability. It's absolutely cost-free, open source, and offers clear reporting for performance analysis. The software's comprehensive functionality renders it perfect for both small home setups industrial-scale mining activities.
Installation Guide
Setup is simple on both Linux and Windows systems. Customization is possible through files or command-line parameters, providing accessibility for users of all experience levels.
Final Thoughts
CGMiner remains one of the top choices for serious cryptocurrency mining, offering the reliability and performance required for profitable mining. -
cgminer download
CGMiner Application: Advanced Cryptocurrency Mining Solution for Crypto Miners
What Exactly is CGMiner?
CGMiner stands as one of the leading miners that allows mining Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin, and numerous other cryptocurrencies. The software works with ASIC, FPGA, and GPU (until version 3.7.2). CGMiner is adaptable in configuration and supports multi-threaded processing, multi-pool functionality, as well as remote management and monitoring of equipment operational parameters.
Key Features
Multi-Coin Compatibility
CGMiner excels at mining diverse crypto assets including Bitcoin (BTC), Litecoin (LTC), Dogecoin (DOGE), and various altcoins with various mining algorithms.
Flexible Hardware Support
The miner operates with multiple categories of mining hardware:
- ASIC Miners - Dedicated processors for peak efficiency
- FPGA - Reprogrammable chips for specialized mining operations
- Graphics Cards - Video cards (supported up to version 3.7.2)
Advanced Capabilities
- Configurable parameters - Comprehensive options for hardware optimization
- Multi-threaded processing - Optimal exploitation of CPU and GPU resources
- Multiple pool compatibility - Automatic switching between crypto mining pools
- Remote management - Operate and track equipment from remote locations
Benefits of Using CGMiner
CGMiner excels for its stability, exceptional speed, and economic efficiency. It's completely free to use, open-source, and provides clear reporting for performance analysis. The miner's comprehensive functionality positions it as optimal for both domestic and enterprise mining operations.
Setup Process
Setup is simple on Linux and Windows platforms. Setup can be performed through settings files or terminal commands, ensuring usability for beginners and experts alike.
Final Thoughts
CGMiner continues to be among the best options for professional crypto mining, providing the dependability and speed needed for successful mining operations. -
cgminer download
CGMiner Application: Advanced Mining Solution for Digital Currency Enthusiasts
What Exactly is CGMiner?
CGMiner is one of the best miners that supports mining Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin, and numerous other cryptocurrencies. The application is compatible with ASIC, FPGA, and GPU (versions up to 3.7.2). CGMiner is adaptable in configuration and offers multi-threaded processing, multi-pool functionality, as well as remote management and monitoring of your mining equipment's parameters.
Main Features
Support for Multiple Cryptocurrencies
CGMiner performs exceptionally well with multiple digital currencies including Bitcoin (BTC), Litecoin (LTC), Dogecoin (DOGE), and numerous altcoins with different algorithms.
Hardware Compatibility
The application is compatible with three main types of mining hardware:
- ASIC Miners - Specialized chips for optimal performance
- FPGA - Programmable logic devices for custom mining tasks
- Graphics Processing Units - Video cards (supported up to version 3.7.2)
Sophisticated Functions
- Configurable parameters - Extensive settings for equipment tuning
- Parallel processing - Full usage of CPU and GPU resources
- Multiple pool compatibility - Automatic failover between mining pools
- Remote administration - Operate and track hardware from any location
Benefits of Using CGMiner
CGMiner distinguishes itself for its reliability, high performance, and cost-effectiveness. It's entirely free, open source, and offers clear reporting for operational review. The miner's robust feature set positions it as optimal for small residential installations and large-scale mining operations.
Setup Process
Installation process is easy on Linux and Windows platforms. Customization is possible through settings files or terminal commands, making it accessible for all skill levels.
Final Thoughts
CGMiner remains among the best options for dedicated digital currency mining, delivering the dependability and speed required for profitable mining. -
cgminer download
CGMiner Application: Powerful Mining Tool for Digital Currency Enthusiasts
Understanding CGMiner
CGMiner is one of the best miners that enables mining Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin, and numerous other cryptocurrencies. The miner is compatible with ASIC, FPGA, and GPU (up to version 3.7.2). CGMiner is flexible in its settings and supports parallel processing, multi-pool functionality, as well as distant administration and observation of your mining equipment's parameters.
Main Features
Multi-Coin Compatibility
CGMiner performs exceptionally well with multiple digital currencies including Bitcoin (BTC), Litecoin (LTC), Dogecoin (DOGE), and various altcoins with various mining algorithms.
Hardware Versatility
The software operates with three main types of mining hardware:
- ASIC Miners - Specialized chips for peak efficiency
- Field-Programmable Gate Arrays - Configurable integrated circuits for tailored mining functions
- Graphics Processing Units - GPU processors (supported up to version 3.7.2)
Advanced Capabilities
- Configurable parameters - Comprehensive options for hardware optimization
- Parallel processing - Maximum utilization of processor and graphics resources
- Pool diversification - Automatic switching between mining pools
- Remote administration - Operate and track mining rigs from remote locations
Why Choose CGMiner?
CGMiner stands out for its reliability, superior processing power, and economic efficiency. It's entirely free, open-source, and provides detailed logs for efficiency evaluation. The miner's robust feature set positions it as optimal for small residential installations and industrial-scale mining activities.
Setup Process
Setup is simple on Linux and Windows platforms. Setup can be performed through configuration files or CLI parameters, providing accessibility for users of all experience levels.
Conclusion
CGMiner remains among the best options for professional crypto mining, providing the dependability and speed needed for successful mining operations. -
situs togel terpercaya
**Info Seru Kompetisi Spin Toto Slot 88 & Tebak Angka Togel 4D Unggulan - TOGELONLINE88** -
judi togel
**Info Menarik Lomba Spin Toto Slot 88 & Tebak Angka Togel 4D Unggulan - TOGELONLINE88** -
clincitop cream clincitop soap
-
togel 88
TOGELONLINE88 hadir memberikan informasi menarik seputar kompetisi spin Toto Slot 88 dan tebakan angka 4D terunggul. Platform ini menyediakan sistem resmi yang terpercaya, hasil valid, dan juga kenyamanan bermain yang nyaman dan teratur.
Selain itu, TOGELONLINE88 juga menyediakan puluhan provider mesin slot dan game tembak ikan yang bisa dimainkan kapan saja dan di mana saja, dengan potensi memenangkan jackpot maxwin bernilai tinggi.
Bagi para penggemar taruhan online togel dan slot, TOGELONLINE88 menjadi pilihan utama dengan menawarkan kenikmatan, keamanan, dan pengalaman seru saat bermain. Melalui promo-promo menarik dan sistem akses mudah, situs ini menawarkan pengalaman bermain yang tak terlupakan.
Jadi, tunggu apa lagi? Ikuti sekarang kompetisi spin Toto Slot 88 dan tebak angka 4D unggulan cuma di TOGELONLINE88. Raih peluang jackpot besar dan rasakan sensasi hadiah jackpot maksimal luar biasa! -
bandar togel
TOGELONLINE88 hadir memberikan berita seru seputar lomba spin Toto Slot 88 dan pasang angka togel 4D terbaik. Platform ini menyediakan sistem resmi berstandar tinggi, informasi terverifikasi, serta kenyamanan bermain sangat menyenangkan.
Lebih dari itu, TOGELONLINE88 turut menghadirkan berbagai provider mesin slot dan tembak ikan dapat dinikmati kapanpun dan dimanapun, dengan potensi memenangkan jackpot maxwin yang luar biasa besar.
Bagi para penggemar taruhan online togel dan slot, TOGELONLINE88 adalah destinasi utama karena menjamin kenyamanan, keamanan, dan keseruan saat bermain. Melalui promo-promo menarik serta sistem yang mudah diakses, situs ini memberikan kenyamanan gaming luar biasa.
Tunggu apalagi? Ikuti sekarang event putar Toto Slot 88 dan prediksi angka 4D terpercaya exclusively di TOGELONLINE88. Raih peluang jackpot besar dan nikmati sensasi hadiah jackpot maksimal yang fantastis! -
togel
Info Terbaru Lomba Spin Toto Slot 88 & Pasang Angka Togel 4D Unggulan - TOGELONLINE88 -
kantorbola login
KANTORBOLA adalah situs slot resmi yang menawarkan game Scatter Hitam Mahjong Wins dengan RTP tinggi dan keamanan terbaik di Indonesia. -
Link Situs Slot
KANTORBOLA adalah situs slot resmi yang menawarkan game Scatter Hitam Mahjong Wins dengan RTP tinggi dan keamanan terbaik di Indonesia. -
ink sindoplay
Selamat datang di situs SINDOPLAY , situs judi slot online , live casino , taruhan bola , poker online dan togel resmi .Daftar dan dapatkan beragam promo menarik dari situs SIndoplay , mulai dari bonus deposit , bonus freespin , cashback serta bonus referral. -
ink sindoplay
Selamat datang di situs SINDOPLAY , situs judi slot online , live casino , taruhan bola , poker online dan togel resmi .Daftar dan dapatkan beragam promo menarik dari situs SIndoplay , mulai dari bonus deposit , bonus freespin , cashback serta bonus referral. -
API integration
Build AI Agents and Integrate with Apps & APIs
AI agents are revolutionizing business automation by creating intelligent systems that think, decide, and act independently. Modern platforms offer unprecedented capabilities for building autonomous AI teams without complex development.
Key Platform Advantages
Unified AI Access
Single subscription provides access to leading models like OpenAI, Claude, Deepseek, and LLaMA—no API keys required for 400+ AI models.
Flexible Development
Visual no-code builders let anyone create AI workflows quickly, with code customization available for advanced needs.
Seamless Integration
Connect any application with AI nodes to build autonomous workers that interact with existing business systems.
Autonomous AI Teams
Modern platforms enable creation of complete AI departments:
- AI CEOs for strategic oversight
- AI Analysts for data insights
- AI Operators for task execution
These teams orchestrate end-to-end processes, handling everything from data analysis to continuous optimization.
Cost-Effective Scaling
Combine multiple LLMs for optimal results while minimizing costs. Direct vendor pricing and unified subscriptions simplify budgeting while scaling from single agents to full departments.
Start today—launch your AI agent team in minutes with just one click.
---
Transform business operations with intelligent AI systems that integrate seamlessly with your applications and APIs. -
AI agents
Build AI Agents and Integrate with Apps & APIs
AI agents are revolutionizing business automation by creating intelligent systems that think, decide, and act independently. Modern platforms offer unprecedented capabilities for building autonomous AI teams without complex development.
Key Platform Advantages
Unified AI Access
Single subscription provides access to leading models like OpenAI, Claude, Deepseek, and LLaMA—no API keys required for 400+ AI models.
Flexible Development
Visual no-code builders let anyone create AI workflows quickly, with code customization available for advanced needs.
Seamless Integration
Connect any application with AI nodes to build autonomous workers that interact with existing business systems.
Autonomous AI Teams
Modern platforms enable creation of complete AI departments:
- AI CEOs for strategic oversight
- AI Analysts for data insights
- AI Operators for task execution
These teams orchestrate end-to-end processes, handling everything from data analysis to continuous optimization.
Cost-Effective Scaling
Combine multiple LLMs for optimal results while minimizing costs. Direct vendor pricing and unified subscriptions simplify budgeting while scaling from single agents to full departments.
Start today—launch your AI agent team in minutes with just one click.
---
Transform business operations with intelligent AI systems that integrate seamlessly with your applications and APIs. -
situs toto slot
Selamat datang di dunia taruhan digital! Togelonline88! Zona publik terbaik untuk bermain link situs toto slot & bet togel 4D online terpopuler saat ini
Sepanjang 2025, Togelonline88 hadir kembali sebagai destinasi utama untuk bermain togel 4D online dan toto slot online dengan berbagai keunggulan menarik. Situs ini menyediakan link resmi yang aman dan terpercaya, memudahkan akses kepada seluruh pengguna melakukan taruhan online dengan nyaman dan aman
Salah satu daya tarik utama platform ini adalah sistem taruhan yang rutin memunculkan jackpot merah, sebagai tanda keberuntungan luar biasa dan jackpot menguntungkan. Fakta ini membuat platform ini begitu terkenal oleh para bettor dan bettor tanah air
Selain itu, Togelonline88 menawarkan sensasi bermain yang modern, transparan, dan menguntungkan. Melalui desain UI user-friendly dengan enkripsi terdepan, situs ini memastikan setiap pemain mampu bermain nyaman tanpa khawatir kebocoran data atau kecurangan. Keterbukaan angka keluaran nomor togel plus distribusi kemenangan juga menjadi nilai tambah yang menjadikan bettor merasa lebih percaya dan nyaman
Melalui fasilitas premium dengan service terbaik, platform ini menjadi pilihan favorit para player untuk menemukan platform togel dan game online terpercaya sepanjang 2025. Bergabunglah sekarang dan rasakan sensasi bermain di area taruhan online tercanggih serta paling komplit di situs ini! -
togelonline88
Selamat datang di dunia taruhan digital! Situs taruhan online terpercaya! Tempat nongkrong para bettor situs taruhan slot dan togel 4D unggulan tahun ini
Di tahun ini, Togelonline88 kembali hadir sebagai platform utama untuk bermain togel 4D online dan toto slot online dengan berbagai keunggulan menarik. Situs ini menyediakan link terverifikasi dengan reputasi terjaga, menyediakan akses instan bagi para pemain bermain secara digital dengan kenyamanan maksimal
Keunggulan spesial situs ini berupa mekanisme bet yang kerap menghadirkan petir merah x1000, sebagai tanda kemenangan besar plus untung besar. Fakta ini membuat platform ini begitu terkenal di kalangan penggemar togel dan bettor tanah air
Lebih dari itu, platform ini menyuguhkan pengalaman bermain yang modern, transparan, dan menguntungkan. Dengan tampilan antarmuka user-friendly plus proteksi mutakhir, situs ini memastikan setiap pemain mampu bermain nyaman tanpa khawatir kebocoran data maupun penipuan. Keterbukaan angka keluaran nomor togel serta pencairan hadiah turut menjadi keunggulan sehingga para user lebih percaya diri dan nyaman
Dengan berbagai fitur unggulan dan layanan terbaik, situs ini siap jadi pilihan utama para bettor saat mencari situs bet serta slot terbaik sepanjang 2025. Ayo join sekarang nikmati sensasi bermain di zona publik bet digital terbaik dan terlengkap di situs ini! -
situs toto togel 4d
Selamat datang di dunia taruhan digital! Platform togel terbaik! Zona publik terbaik untuk bermain situs taruhan slot dan togel 4D terpopuler saat ini
Di tahun ini, Togelonline88 resmi meluncur sebagai platform utama melakukan bet online dengan banyak kelebihan. Tersedia link terverifikasi dengan reputasi terjaga, menyediakan akses instan kepada seluruh pengguna melakukan taruhan online secara aman
Fasilitas andalan platform ini adalah sistem taruhan yang sering memberikan petir merah x1000, yang merupakan simbol keberuntungan luar biasa dan jackpot menguntungkan. Keunggulan ini menjadikan situs ini sangat diminati oleh para bettor serta pengguna slot online
Tidak hanya itu, situs ini memberikan pengalaman gaming dengan kualitas premium. Melalui desain UI user-friendly dengan enkripsi terdepan, situs ini memastikan seluruh user mampu bermain nyaman tanpa khawatir kebocoran data maupun penipuan. Kejujuran pada hasil draw nomor togel serta pencairan hadiah turut menjadi keunggulan yang menjadikan bettor lebih percaya diri dan betah bermain
Melalui fasilitas premium plus pelayanan prima, situs ini siap jadi pilihan utama para bettor untuk menemukan platform togel dan slot online terpercaya pada tahun ini. Daftar segera dan rasakan sensasi bermain di area taruhan online tercanggih serta paling komplit hanya di Togelonline88! -
situs toto slot
Halo para penggemar togel! Togelonline88! Area bermain resmi link situs toto slot & bet togel 4D online terbaik modern 2025
Di tahun ini, Togelonline88 resmi meluncur sebagai platform utama bermain taruhan 4D dan slot dengan berbagai keunggulan menarik. Menyediakan link resmi dengan reputasi terjaga, menyediakan akses instan bagi para pemain bermain secara digital secara aman
Fasilitas andalan situs ini berupa mekanisme bet yang sering memberikan bonus besar x1000, sebagai indikator kemenangan besar plus untung besar. Fakta ini membuat platform ini begitu terkenal dari komunitas togel dan slot online di Indonesia
Lebih dari itu, Togelonline88 menawarkan pengalaman gaming berstandar tinggi dan aman. Dengan tampilan antarmuka yang intuitif dengan enkripsi terdepan, platform ini menjamin setiap pemain bisa bermain santai tanpa khawatir kebocoran data atau kecurangan. Keterbukaan angka keluaran result togel plus distribusi kemenangan ikut memberi kelebihan yang menjadikan bettor lebih percaya diri serta tenang
Berbekal fitur-fitur istimewa dan layanan terbaik, situs ini siap jadi pilihan favorit para player saat mencari situs bet serta slot terbaik sepanjang 2025. Bergabunglah sekarang nikmati sensasi bermain di area taruhan online tercanggih dan terlengkap hanya di Togelonline88! -
situs toto
Selamat datang di dunia taruhan digital! Togelonline88! Area bermain resmi platform gaming slot dan togel unggulan tahun ini
Sepanjang 2025, Togelonline88 hadir kembali sebagai destinasi utama melakukan bet online berkat fitur-fitur istimewa. Menyediakan alamat utama yang aman dan terpercaya, memberikan kemudahan akses kepada seluruh pengguna melakukan bet daring dengan kenyamanan maksimal
Keunggulan spesial platform ini adalah sistem taruhan yang kerap menghadirkan petir merah x1000, sebagai tanda keberuntungan luar biasa dan jackpot menguntungkan. Keunggulan ini menjadikan situs ini sangat diminati dari komunitas togel dan bettor tanah air
Selain itu, platform ini menyuguhkan sensasi bermain berstandar tinggi dan aman. Dengan tampilan antarmuka yang ramah pengguna dengan enkripsi terdepan, situs ini pastikan setiap pemain mampu bermain nyaman tanpa cemas kebocoran informasi dan praktik curang. Kejujuran pada hasil draw angka togel plus distribusi kemenangan juga menjadi nilai tambah yang menjadikan bettor merasa lebih percaya dan betah bermain
Melalui fasilitas premium dengan service terbaik, platform ini menjadi alternatif utama bettor untuk menemukan platform togel dan game online terpercaya sepanjang 2025. Daftar segera rasakan pengalaman bermain di tempat bet digital terbaik dan terlengkap di platform Togelonline88! -
App integration
Build AI Agents and Integrate with Apps & APIs
AI agents are revolutionizing business automation by creating intelligent systems that think, decide, and act independently. Modern platforms offer unprecedented capabilities for building autonomous AI teams without complex development.
Key Platform Advantages
Unified AI Access
Single subscription provides access to leading models like OpenAI, Claude, Deepseek, and LLaMA—no API keys required for 400+ AI models.
Flexible Development
Visual no-code builders let anyone create AI workflows quickly, with code customization available for advanced needs.
Seamless Integration
Connect any application with AI nodes to build autonomous workers that interact with existing business systems.
Autonomous AI Teams
Modern platforms enable creation of complete AI departments:
- AI CEOs for strategic oversight
- AI Analysts for data insights
- AI Operators for task execution
These teams orchestrate end-to-end processes, handling everything from data analysis to continuous optimization.
Cost-Effective Scaling
Combine multiple LLMs for optimal results while minimizing costs. Direct vendor pricing and unified subscriptions simplify budgeting while scaling from single agents to full departments.
Start today—launch your AI agent team in minutes with just one click.
---
Transform business operations with intelligent AI systems that integrate seamlessly with your applications and APIs. -
No-code automation
Build AI Agents and Integrate with Apps & APIs
AI agents are revolutionizing business automation by creating intelligent systems that think, decide, and act independently. Modern platforms offer unprecedented capabilities for building autonomous AI teams without complex development.
Key Platform Advantages
Unified AI Access
Single subscription provides access to leading models like OpenAI, Claude, Deepseek, and LLaMA—no API keys required for 400+ AI models.
Flexible Development
Visual no-code builders let anyone create AI workflows quickly, with code customization available for advanced needs.
Seamless Integration
Connect any application with AI nodes to build autonomous workers that interact with existing business systems.
Autonomous AI Teams
Modern platforms enable creation of complete AI departments:
- AI CEOs for strategic oversight
- AI Analysts for data insights
- AI Operators for task execution
These teams orchestrate end-to-end processes, handling everything from data analysis to continuous optimization.
Cost-Effective Scaling
Combine multiple LLMs for optimal results while minimizing costs. Direct vendor pricing and unified subscriptions simplify budgeting while scaling from single agents to full departments.
Start today—launch your AI agent team in minutes with just one click.
---
Transform business operations with intelligent AI systems that integrate seamlessly with your applications and APIs. -
https://forum.hcpforum.com/ventolin is Ventolin capitalized?
-
API integration
Build AI Agents and Integrate with Apps & APIs
AI agents are revolutionizing business automation by creating intelligent systems that think, decide, and act independently. Modern platforms offer unprecedented capabilities for building autonomous AI teams without complex development.
Key Platform Advantages
Unified AI Access
Single subscription provides access to leading models like OpenAI, Claude, Deepseek, and LLaMA—no API keys required for 400+ AI models.
Flexible Development
Visual no-code builders let anyone create AI workflows quickly, with code customization available for advanced needs.
Seamless Integration
Connect any application with AI nodes to build autonomous workers that interact with existing business systems.
Autonomous AI Teams
Modern platforms enable creation of complete AI departments:
- AI CEOs for strategic oversight
- AI Analysts for data insights
- AI Operators for task execution
These teams orchestrate end-to-end processes, handling everything from data analysis to continuous optimization.
Cost-Effective Scaling
Combine multiple LLMs for optimal results while minimizing costs. Direct vendor pricing and unified subscriptions simplify budgeting while scaling from single agents to full departments.
Start today—launch your AI agent team in minutes with just one click.
---
Transform business operations with intelligent AI systems that integrate seamlessly with your applications and APIs. -
AI agents
Build AI Agents and Integrate with Apps & APIs
AI agents are revolutionizing business automation by creating intelligent systems that think, decide, and act independently. Modern platforms offer unprecedented capabilities for building autonomous AI teams without complex development.
Key Platform Advantages
Unified AI Access
Single subscription provides access to leading models like OpenAI, Claude, Deepseek, and LLaMA—no API keys required for 400+ AI models.
Flexible Development
Visual no-code builders let anyone create AI workflows quickly, with code customization available for advanced needs.
Seamless Integration
Connect any application with AI nodes to build autonomous workers that interact with existing business systems.
Autonomous AI Teams
Modern platforms enable creation of complete AI departments:
- AI CEOs for strategic oversight
- AI Analysts for data insights
- AI Operators for task execution
These teams orchestrate end-to-end processes, handling everything from data analysis to continuous optimization.
Cost-Effective Scaling
Combine multiple LLMs for optimal results while minimizing costs. Direct vendor pricing and unified subscriptions simplify budgeting while scaling from single agents to full departments.
Start today—launch your AI agent team in minutes with just one click.
---
Transform business operations with intelligent AI systems that integrate seamlessly with your applications and APIs. -
SEO Pyramid 10000 Backlinks
Backlinks of your site on discussion boards, sections, comments.
Backlinks – three steps
Step 1 – Standard external links.
Phase 2 – Backlinks through redirects from authoritative sites with a PageRank score of 9–10, for example –
Phase 3 – Listing on SEO analysis platforms –
The advantage of link analysis platforms is that they highlight the Google search engine a website structure, which is very important!
Clarification for the third stage – only the main page of the site is added to analyzers, other pages aren’t accepted.
I execute all phases step by step, resulting in 10 to 30 thousand inbound links from the three stages.
This backlink strategy is highly efficient.
Example of submission on SEO platforms via a .txt document. -
SEO Pyramid 10000 Backlinks
External links of your site on discussion boards, blocks, threads.
Three-stage backlink strategy
Phase 1 – Simple backlinks.
Phase 2 – Backlinks through redirects from authoritative sites with PR 9–10, for example –
Step 3 – Adding to backlink checkers –
The key benefit of SEO tools is that they highlight the Google search engine a website structure, which is essential!
Clarification for Stage 3 – only the homepage of the site is added to SEO checkers, internal pages cannot be included.
I complete all phases step by step, resulting in 10 to 30 thousand inbound links from the full process.
This backlink strategy is the best approach.
Demonstration of submission on analyzer sites via a text file. -
AI agents
Build AI Agents and Integrate with Apps & APIs
AI agents are revolutionizing business automation by creating intelligent systems that think, decide, and act independently. Modern platforms offer unprecedented capabilities for building autonomous AI teams without complex development.
Key Platform Advantages
Unified AI Access
Single subscription provides access to leading models like OpenAI, Claude, Deepseek, and LLaMA—no API keys required for 400+ AI models.
Flexible Development
Visual no-code builders let anyone create AI workflows quickly, with code customization available for advanced needs.
Seamless Integration
Connect any application with AI nodes to build autonomous workers that interact with existing business systems.
Autonomous AI Teams
Modern platforms enable creation of complete AI departments:
- AI CEOs for strategic oversight
- AI Analysts for data insights
- AI Operators for task execution
These teams orchestrate end-to-end processes, handling everything from data analysis to continuous optimization.
Cost-Effective Scaling
Combine multiple LLMs for optimal results while minimizing costs. Direct vendor pricing and unified subscriptions simplify budgeting while scaling from single agents to full departments.
Start today—launch your AI agent team in minutes with just one click.
---
Transform business operations with intelligent AI systems that integrate seamlessly with your applications and APIs. -
Workflow automation
Build AI Agents and Integrate with Apps & APIs
AI agents are revolutionizing business automation by creating intelligent systems that think, decide, and act independently. Modern platforms offer unprecedented capabilities for building autonomous AI teams without complex development.
Key Platform Advantages
Unified AI Access
Single subscription provides access to leading models like OpenAI, Claude, Deepseek, and LLaMA—no API keys required for 400+ AI models.
Flexible Development
Visual no-code builders let anyone create AI workflows quickly, with code customization available for advanced needs.
Seamless Integration
Connect any application with AI nodes to build autonomous workers that interact with existing business systems.
Autonomous AI Teams
Modern platforms enable creation of complete AI departments:
- AI CEOs for strategic oversight
- AI Analysts for data insights
- AI Operators for task execution
These teams orchestrate end-to-end processes, handling everything from data analysis to continuous optimization.
Cost-Effective Scaling
Combine multiple LLMs for optimal results while minimizing costs. Direct vendor pricing and unified subscriptions simplify budgeting while scaling from single agents to full departments.
Start today—launch your AI agent team in minutes with just one click.
---
Transform business operations with intelligent AI systems that integrate seamlessly with your applications and APIs. -
Cenforce 100mg amazon dapoxetine and sildenafil tablets india
-
Smart DNS
SmartStreaming.TV: the best way to watch foreign entertainment from around the world
More and more users want to enjoy international channels.
A viewer in Canada who wants ESPN, an user in Australia who needs ITV Hub, or a Spanish expat who misses Caracol TV.
The problem is always the same: country limitations.
This is where SmartStreaming.TV becomes essential.
With this solution, you can access international catalogs as if you were living there.
How does it work?
Streaming platforms recognize your location through your network IP.
SmartStreaming.TV protects your real IP and provides you an IP in the country where the service is available.
That means a Spanish user can open HBO Latino without limitations.
Why it’s better
- Speed, security and reliability
- Fully legitimate
- Compatible with Smart TVs, mobiles and PCs
- Easy to install
Perfect for expats
If you spend time overseas, SmartStreaming.TV is your essential companion.
No more skipping new releases just because you’re away from home.
With SmartStreaming.TV your TV is without borders.
All around the world, your programs is one click away. -
Smart DNS
SmartStreaming.TV: the easy way to watch foreign entertainment from anywhere
More and more people want to access international channels.
A viewer in Canada who wants ESPN, an user in Australia who needs Sky Go, or a Latin American abroad who misses Caracol TV.
The problem is always the same: regional blocks.
This is where SmartStreaming.TV makes the difference.
With this platform, you can unlock international catalogs as if you were in that country.
How does it work?
Digital channels detect your location through your device IP.
SmartStreaming.TV hides your real IP and gives you an IP in the country where the content is available.
That means a Canadian can watch Netflix US without frustrations.
The big advantage
- Safe, quick and stable
- Completely allowed
- Works on any device
- Quick to start
Ideal for frequent travelers
If you moved to another country, SmartStreaming.TV is your must-have tool.
No more skipping new releases just because you’re away from home.
With SmartStreaming.TV your entertainment is global.
Wherever you are, your TV is one click away. -
Backlinks Blogs and Comments, SEO promotion, site top, indexing, links
Inbound links of your site on discussion boards, blocks, threads.
The 3-step backlinking method
Phase 1 – Simple backlinks.
Stage 2 – Links via 301 redirects from top-tier sites with PR 9–10, for example –
Step 3 – Listing on SEO analysis platforms –
The advantage of analyzer sites is that they display the Google search engine a site map, which is essential!
Clarification for Stage 3 – only the homepage of the site is added to SEO checkers, internal pages aren’t accepted.
I execute all steps sequentially, resulting in 10,000–20,000 inbound links from the three stages.
This backlink strategy is the best approach.
Example of submission on analyzer sites via a TXT file. -
Backlinks Blogs and Comments, SEO promotion, site top, indexing, links
External links of your site on community platforms, sections, comments.
The 3-step backlinking method
Stage 1 – Simple backlinks.
Phase 2 – Links via 301 redirects from authoritative sites with a PageRank score of 9–10, for example –
Step 3 – Listing on SEO analysis platforms –
The key benefit of analyzer sites is that they highlight the Google search engine a site map, which is crucial!
Clarification for the third stage – only the main page of the site is added to analyzers, other pages aren’t accepted.
I execute all three stages step by step, resulting in 10,000–20,000 inbound links from the three stages.
This linking tactic is most effective.
Example of placement on SEO platforms via a .txt document. -
malegra pour femme https://ummalife.com/post/519822
-
Linking to your site using redirect site analyzers. backlink building
In this project, I offer to publish your web resource on analyzer sites not through a file-based connection, but to integrate it in the SEO software itself and share the resulting URLs in blogs and comments so that Google detects the connection through authority.
Such backlinks are useful for the site.
The total of links on analysis platforms is 50 pieces, I will place pre-created URLs in comment sections and blogs in the amount that you select from three choices.
This further increases the authority of your site and is very good for Google.
Only the homepage of the site is submitted in the SEO analyzers, other pages are not added.
For these backlinks we get range.
An example of how your website will be placed and what reference will be published on the forums.
This placement is secure for your online resource.
I also give URLs to the submitted site on SEO analyzers. -
Linking to your site using redirect site analyzers. backlink building
In this work, I suggest to publish your web resource on SEO analyzers not through a file-based connection, but to embed it in the analysis tools directly and share the resulting backlinks in blog posts and discussions so that Google sees the connection through credibility.
Such links are useful for the website.
The amount of backlinks on analysis platforms is 50 pieces, I will post prepared URLs in blogs and comments in the quantity that you prefer from 3 options.
This further raises the authority of your site and is highly beneficial for Google.
Only the main page of the website is submitted in the analyzers, other pages are not added.
For these backlinks we get range.
An example of how your site will be displayed and what URL will be shared on the online forums.
This integration is safe for your website.
I also provide URLs to the hosted site on analyzer sites. -
Backlinks for seo
SEO backlinks for SEO include two main types: anchor and non-anchor backlinks.
Anchor links include a primary search term, since the key query is essential for SEO performance.
Bare links carry equal weight – this includes simple hyperlinks, while the ability to click matters because it creates access to search engine crawlers; crawlers navigate the site along with internal pages, which is useful the site.
Progress reports are delivered via tools like Majestic, SEMrush, and Ahrefs. In cases where backlink counts are lower for one of the services, the analysis focuses on the tool with the highest count in backlink volume as a result of indexing lag. -
Backlinks for seo
Inbound links for SEO consist of two main types: anchor and non-anchor backlinks.
Anchor texts are linked to a primary search term, because this keyword is essential in search engine optimization.
Bare links are equally significant – they represent simple hyperlinks, while user interaction is important as it creates access for bots; bots go the target page and subsequent pages, which is useful website.
I provide semrush. When the number of links is limited for one of the services, updates are provided on the tool with a larger number in backlink volume because of delays in indexation. -
Backlinks .pl
Backlinks from Polish domains represent a powerful method for boosting your site's position as well as authority in Google.
We only place SEO links on real Polish forums, blogs, and comment sections. This constitutes a natural placement which not merely improves SEO, but also brings in extra referral visitors by genuine users.
Why go with this SEO solution?
Full Polish domain coverage
Mix of forums, niche blogs, along with relevant comments
Authentic linking profile that Google prioritizes
Following the work, of the work, you will receive comprehensive plus clear written report -
Backlinks .pl
SEO backlinks from Polish domains are a powerful method to enhance your web presence as well as authority on Google search results.
We only place links within authentic Polish forums, weblogs, and comment sections. Such approach represents a natural linking strategy that not only improves SEO, but additionally attracts supplemental traffic from referrals by genuine users.
Reasons to choose this service?
100% Polish domains
Combination including forums, niche blogs, along with relevant comments
Natural link profile that Google prioritizes
Following the work, of our services, you will receive a clear as well as thorough text report -
Backlinks SEO Google Websites Analyzers Redirects PR 8-10
Inbound links for SEO consist of two main types: anchor and non-anchor backlinks.
Anchor texts include a key query, since the key query is essential for search engine ranking.
Non-anchor links are just as important – this includes simple hyperlinks, while clickability matters because it provides a route to search engine crawlers; search engines access the target page and deeper pages, which is useful your project.
Updates are shared through majestic. In cases where backlink counts are lower on a particular platform, the analysis focuses on the service that shows more of backlinks because of delays in indexation. -
Backlinks SEO Google Websites Analyzers Redirects PR 8-10
Inbound links for SEO are divided into anchor and non-anchor links.
Anchor texts include a primary search term, since the key query is fundamental for SEO performance.
Bare links are equally significant – these are bare links, while clickability is important as it creates a route to search engine crawlers; search engines access your website along with internal pages, which benefits your project.
Progress reports are delivered via tools like Majestic, SEMrush, and Ahrefs. In cases where backlink counts are lower on a particular platform, updates are provided on the platform that shows more in backlink volume as a result of indexing lag. -
Analizador Vibraciones Equilibrado Dinamico
Balanset-1A
El desequilibrio del rotor es la principal causa de fallas en el equipo, y con mayor frecuencia solo se desgastan los rodamientos. El desequilibrio puede surgir debido a problemas mecanicos, sobrecargas o fluctuaciones de temperatura. A veces, reemplazar los rodamientos es la unica solucion para corregir el desequilibrio. Por ejemplo, el equilibrado de rotores a menudo se puede resolver directamente en el lugar mediante un proceso de balanceo. Este procedimiento se clasifica como ajuste de vibracion mecanica en equipos rotativos. -
Analizador Vibraciones Equilibrado Dinamico
Balanset-1A
El desequilibrio del rotor es la principal causa de fallas en el equipo, y con mayor frecuencia solo se desgastan los rodamientos. El desequilibrio puede surgir debido a problemas mecanicos, sobrecargas o fluctuaciones de temperatura. A veces, reemplazar los rodamientos es la unica solucion para corregir el desequilibrio. Por ejemplo, el equilibrado de rotores a menudo se puede resolver directamente en el lugar mediante un proceso de balanceo. Este procedimiento se clasifica como ajuste de vibracion mecanica en equipos rotativos. -
Backlinks SEO Google Websites Analyzers Redirects PR 8-10
Backlinks using domains in Polish constitute a powerful method to enhance your site's position as well as authority within Google.
We only place backlinks in authentic Polish forums, online publications, plus comment areas. This constitutes a natural linking strategy that not only enhance SEO performance, but additionally generates additional referral traffic through authentic user engagement.
Reasons to choose our service?
100% Polish domains
Combination including forums, thematic blogs, and contextual comments
Authentic linking profile that Google values
Following the work, of the work, you get a clear and detailed text-based summary -
winity казино регистрация популярные игры
Виниту онлайн-казино – современная платформа для азартных игр с интуитивным дизайном, широким выбором игр, акциями и качественной службой поддержки. Пользователи ищут "Winity казино официальный сайт", "Виниту casino вход", "зеркало Винити" для быстрого входа в кабинет.
Что такое Виниту казино?
Казино – сервис с акцентом на удобство и скорость. Предлагает:
Интерфейс – легкая навигация
Каталог – автоматы, живые игры
Система – приветственные, возврат, турниры
Поддержка 24/7 – email
Официальный сайт и зеркала
Официальный сайт – центральная точка входа: регистрация, финансы, акции, поддержка. Если работа ограничен, используется зеркало.
Регистрация и вход
Создание аккаунта – быстрый процесс: почта, пароль, подтверждение и профиль. Для безопасности – 2FA.
Верификация
Для вывода нужна KYC: паспорт, выписка, селфи. Срок – от минут до пары дней.
Бонусы
Стартовые, фриспины, возврат, соревнования, VIP.
Платежи
Поддержка банковских, электронных, крипты, систем. Вывод обычно до суток.
Мобильная версия
Адаптированный сайт и клиент: игры, финансы, бонусы, поддержка всегда под рукой.
Безопасность
шифрование, лицензия, контроль. -
casino winity lжекпот
Виниту казино – популярная платформа для гемблинга с удобным интерфейсом, большим каталогом игр, акциями и качественной службой поддержки. Игроки ищут "Winity казино официальный сайт", "Виниту casino вход", "зеркало Винити" для быстрого доступа в кабинет.
Что такое Winity casino?
Казино – онлайн-казино с акцентом на комфорт и простоту. Предлагает:
Удобный дизайн – легкая навигация
Каталог – слоты, лайв-игры
Система – приветственные, кэшбэк, соревнования
Помощь 24/7 – чат
Официальный сайт и зеркала
Основной портал – центральная точка входа: регистрация, касса, бонусы, поддержка. Если доступ заблокирован, используется резервный сайт.
Регистрация и вход
Регистрация – быстрый процесс: почта, код, подтверждение и профиль. Для безопасности – 2FA.
Верификация
Для вывода нужна KYC: ID, выписка, селфи. Срок – от минут до пары дней.
Бонусы
Стартовые, фриспины, возврат, соревнования, VIP.
Платежи
Поддержка банковских, кошельков, крипты, платежных сервисов. Вывод обычно до суток.
Мобильная версия
Адаптированный сайт или клиент: игры, финансы, бонусы, чат всегда под рукой.
Безопасность
SSL, лицензия, мониторинг. -
hydroxychloroquine sulfate 200 mg tablet plaquenil generic
-
Backlinks for Google
Inbound links to your site on multiple diverse websites.
We use strictly resources from where there will be zero complaints from the moderator!!!
Generating backlinks in 3 simple steps
Stage 1 – Links to blog posts (Publishing an piece of content on a subject with an anchor and non-anchor link)
Step 2 – Links through redirects of trusted sites with authority score Authority 9-10, for example
Stage 3 – Posting an example on backlink analysis tools -
SEO tools show the sitemap to the search crawlers, and this is crucial.
Note for step 3 - only the main page of the site is placed on the analysis tools; subsequent web pages can't be submitted.
I perform these three steps sequentially, in all there will be 20,000-30,000 quality links from these 3 stages.
This SEO tactic is the top-performing.
I will send the link data on parsing sites in a document.
List of analysis tools hundreds of pieces.
Send a progress report via majestic, semrush , or ahrefs If one of the platforms has fewer links, I submit the report using the tool with more links because what's the point of the delay? -
backlink building
Inbound links to your website on multiple diverse websites.
We use only resources from which there will be no issues from the moderator!!!
Backlinks in 3 simple steps
Step 1 – Links to articles (Posting an piece of content on a topic with an anchor and non-anchored link)
Step 2 – Backlinks through redirects of highly reliable websites with authority score DR 9-10, for example
Phase 3 – Submitting an entry on analyzer sites -
Analysis platforms provide the sitemap to the Google search engine, and this is very important.
Explanation for step 3 - only the main page of the website is indexed on the analysis tools; subsequent web pages can't be placed.
I execute these 3 steps step-by-step, in total there will be 20,000-30,000 inbound links from three stages.
This backlink strategy is the most effective.
I will show the placement on indexing platforms in a .txt file.
Catalog of site analyzers 50-200 platforms.
Send a link building report via majestic, semrush , or ahrefs In case one of the tools has less links, I report using the tool with the highest number of links because what's the point of the delay? -
Domain Rating
Site ranking is vital for search engine optimization.
Our team focuses on attracting Google search robots to your website to boost the site’s ranking using article placements, analyzer sites, as well as we also generate crawler traffic through external platforms.
There are 2 main types of bots – exploratory and cataloging.
Crawling robots are the first bots to access the site and also instruct cataloging bots to access.
An increased number of visits from bots to the site, the better it is for the site.
Before launching the work, we will share you with a snapshot of the site authority from Ahrefs’ backlink tool, and once the project is finished, there will likewise be a snapshot of the domain rating from ahrefs.com/backlink-checker.
Pay only for the result!
Timeline for completion is from 3 to 14 days,
In some instances, more time is required.
Our services are available for sites up to 50 DR. -
Domain Rating
Website rank is essential for search engine optimization.
We are engaged in attracting Google search robots to your website to raise the search ranking using publishing articles, backlink analysis platforms, and we also generate crawler traffic through third-party sources.
There are two primary categories of crawlers – exploratory and indexing.
Spider bots are the first to visit the site and also instruct indexing robots to access.
Higher click volume from bots to the site, the more beneficial it is for the project.
Before launching the work, we will share you with a image of the site authority from Ahrefs Backlink Checker, and once the project is finished, there will likewise be a screenshot of the site rating from ahrefs.com/backlink-checker.
You pay only upon success!
Estimated production time is between 3 and 14 days,
In rare cases, extra time is required.
Our services are available for sites up to 50 DR. -
perfumes de hombre originales
Luxtor Perú: Tienda online líder en la venta de perfumes originales en Perú, con más de 10,000 productos de Natura, Yanbal, Ésika, L’Bel, Avon y Cyzone, además de maquillaje, cuidado personal y ofertas exclusivas con garantía de autenticidad. -
perfumes Natura Peru
Luxtor Perú: Tienda online líder en la venta de perfumes originales en Perú, con más de 10,000 productos de Natura, Yanbal, Ésika, L’Bel, Avon y Cyzone, además de maquillaje, cuidado personal y ofertas exclusivas con garantía de autenticidad. -
servicio de balanceo
https://vibromera.es/servicio-de-balanceo/
Maquinas de equilibrado: fundamentales para el funcionamiento fluido y confiable de las maquinas
En el entorno de la ingenieria actual, donde la eficiencia y la seguridad operativa del equipo son de maxima importancia, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos dispositivos especializados estan creados con el fin de compensar el movimiento de partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es indispensable para asegurar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible disminuir de manera notable las vibraciones, el ruido y la presion en los rodamientos, prolongando la vida util de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente crucial es el rol que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El soporte tecnico y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar resultados superiores, elevando la confianza del cliente.
Para los propietarios, la implementacion en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser determinante para optimizar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Ayudan a prever problemas, ahorrando gastos elevados y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para mejorar la produccion.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
equipo de equilibrio
https://vibromera.es/equipo-de-equilibrio/
Sistemas de balanceo: indispensables para el rendimiento optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el ambito de la tecnologia moderna, donde la productividad y la confiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un papel crucial. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan creados con el fin de compensar el movimiento de partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es clave para asegurar el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible reducir significativamente las vibraciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, prolongando la vida util de componentes costosos.
Igualmente crucial es el papel que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El soporte tecnico y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar soluciones confiables, mejorando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los duenos de negocios, la implementacion en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser clave para elevar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los directivos de pymes, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, ahorrando gastos elevados y averias graves. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas se aplican para mejorar la produccion.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son imprescindibles para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
Franchise Management Software
BrandWide:a unified franchise software to run and scale your brand
Managing a network on fragmented franchise software systems results in operational confusion and compliance risks. BrandWide replaces the mix of point tools with a unified, end-to-end franchise software system—providing the governance, analytics, and visibility to make smarter decisions and ensure every unit succeeds.
Accelerate development and openings
Systematize development with smart follow-ups, digital signatures, and real-time pipeline tracking. Then streamline onboarding and store openings with role-based checklists and gated approvals in one system built for software for franchise management.
Operationalize brand standards
Ensure uniform execution across locations with a native learning management system, learner progress analytics, certifications, and field audits—without messy spreadsheets.
Strengthen franchisee support and knowledge flow
Route and resolve tickets quickly through a central helpdesk. An AI-powered intranet organizes documents, news, links, and assets so teams always find the latest version.
Make royalties accurate and KPIs visible
Compute royalties with precision—streamline invoicing, collections, and reporting. Executives track KPIs across all locations on a real-time corporate dashboard to prioritize the right initiatives.
Equip locations to win in their markets
Give franchisees a powerful franchise CRM and email marketing to grow lifetime value. BrandWide serves as a complete franchise CRM platform that brings development, operations, and marketing together.
In short: When you assess software for franchise management, see why teams choose BrandWide as the best franchise management software—a modern, all-in-one franchise software solution that unifies sales, onboarding, training, support, compliance, royalties, and analytics. Book a live demo and explore your use cases. -
Franchise Management Software
Meet BrandWide —a unified franchise software to manage and expand your network
Running a franchise network on fragmented franchise software systems results in confusion, wasted time, and compliance risk. BrandWide replaces the patchwork with a centralized franchise management software platform—giving you the governance, analytics, and visibility to grow faster and raise performance at every location.
Expand your footprint faster
Systematize development with automated follow-ups, e-signatures, and up-to-the-minute pipeline insights. Then simplify onboarding and launches with templates, tasks, and approvals in a single workspace purpose-built for franchising.
Standardize training and compliance
Maintain brand consistency at every unit with a built-in LMS, learner progress analytics, certifications, and field audits—without messy spreadsheets.
Centralize support and knowledge
Handle requests efficiently through a central helpdesk. An AI-powered intranet organizes documents, news, links, and assets so teams grab the right file every time.
Automate royalties and surface KPIs
Automate royalty calculations—produce invoices, collect faster, and report accurately. Managers watch performance metrics across the network on a live executive dashboard to make data-driven decisions.
Equip locations to win in their markets
Give franchisees a powerful franchise CRM and built-in email campaigns to grow lifetime value. BrandWide serves as a modern franchise CRM platform that brings development, operations, and marketing together.
The takeaway: If you need software for franchise management, see why teams choose BrandWide as the best franchise management software—a unified, end-to-end franchise software platform that unifies sales, onboarding, training, support, compliance, royalties, and analytics. Schedule a personalized demo to evaluate fit. -
戰神賽特娛樂城
https://atgseth1.com/how-to-read-the-atg-ares-set-signal/
https://atgseth1.com/god-seth-jackpot-grand/ -
戰神賽特娛樂城
https://atgseth1.com/how-to-read-the-atg-ares-set-signal/
https://atgseth1.com/god-seth-jackpot-grand/ -
perfumes Natura Peru
Luxtor Perú es tu tienda online de confianza con más de 10,000 artículos en perfumes importados y originales, maquillaje, cuidado personal y electrohogar, ofreciendo las mejores marcas como Natura, Yanbal, Cyzone, Ésika, L’Bel y Avon con precios especiales y promociones exclusivas. -
perfumes de hombre originales
Luxtor Perú es tu tienda online de confianza con más de 10,000 artículos en perfumes importados y originales, maquillaje, cuidado personal y electrohogar, ofreciendo las mejores marcas como Natura, Yanbal, Cyzone, Ésika, L’Bel y Avon con precios especiales y promociones exclusivas. -
equilibrado de piezas 2
https://vibromera.es/equilibrado-de-piezas-2/
Maquinas de equilibrado: indispensables para el rendimiento suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el entorno de la tecnologia moderna, donde la eficiencia y la confiabilidad del equipo son de maxima importancia, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un rol decisivo. Estos dispositivos especializados estan destinados a ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, automoviles y camiones o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es indispensable para garantizar el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las oscilaciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, prolongando la vida util de componentes costosos.
Igualmente crucial es el impacto que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El mantenimiento especializado y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar soluciones confiables, elevando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los duenos de negocios, la apuesta en plataformas de equilibrado y monitoreo puede ser clave para aumentar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los administradores de negocios medianos, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, evitando reparaciones costosas y averias graves. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
equilibrado de piezas 2
https://vibromera.es/equilibrado-de-piezas-2/
Dispositivos de equilibrado: clave para el desempeno optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el mundo de la ingenieria actual, donde la productividad y la confiabilidad del equipo son de maxima importancia, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un rol decisivo. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan disenados para compensar el movimiento de partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es fundamental para asegurar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible reducir significativamente las vibraciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, prolongando la vida util de elementos caros.
Igualmente crucial es el papel que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El servicio postventa y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas permiten ofrecer servicios de alta calidad, aumentando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los empresarios, la implementacion en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser determinante para aumentar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los directivos de pymes, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Ayudan a prever problemas, evitando reparaciones costosas y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas sirven para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la industria ciclista hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son imprescindibles para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
https://in.pinterest.com/vidalista20review/ Vidalista black
-
Domain Rating
Website rank is crucial for promoting websites.
Our team focuses on attracting search engine crawlers to the site to raise the search ranking using publishing articles, backlink analysis platforms, and we also generate crawler traffic through external platforms.
There are two key kinds of crawlers – exploratory and data-processing.
Spider bots are the first bots to access the site and signal cataloging bots to scan.
An increased number of visits from bots to the site, the more beneficial it is for the project.
Before launching the work, we will share you with a snapshot of the site authority from ahrefs.com/backlink-checker, and after the work is completed, there will likewise be a snapshot of the domain rating from Ahrefs’ backlink analysis tool.
You pay only upon success!
The expected timeframe is from 3 to 14 days,
In rare cases, more time is required.
We accept projects for websites up to 50 DR. -
Domain Rating
Site ranking is crucial for promoting websites.
We are engaged in attracting search engine crawlers to your website to raise the website position using article placements, analyzer sites, and we also attract search bots through other resources.
There are 2 main types of search robots – crawling and indexing.
Exploratory crawlers are the first to visit the site and direct data-processing crawlers to access.
An increased number of visits from search robots to the site, the more beneficial it is for the site.
Before we begin the work, we will send you with a snapshot of the site authority from Ahrefs Backlink Checker, and once the project is finished, there will be another a snapshot of the ranking metrics from ahrefs.com/backlink-checker.
You pay only upon success!
Estimated production time is between 3 and 14 days,
In some instances, extra time is needed.
Our services are available for sites with DR below 50. -
buscar equipo de balanceo
https://vibromera.es/buscar-equipo-de-balanceo/
Maquinas de equilibrado: indispensables para el desempeno optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el entorno de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la productividad y la seguridad operativa del equipo son de relevancia critica, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos dispositivos especializados estan creados con el fin de compensar el movimiento de partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, automoviles y camiones o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es clave para asegurar el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible reducir significativamente las oscilaciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente relevante es el papel que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El soporte tecnico y el servicio periodico utilizando estos sistemas garantizan soluciones confiables, mejorando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los propietarios, la inversion en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser decisiva para aumentar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, ahorrando gastos elevados y averias graves. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas se aplican para optimizar procesos.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
vibroanalizador
https://vibromera.es/vibroanalizador/
Equipos de balanceo: fundamentales para el rendimiento optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el ambito de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la eficiencia y la seguridad operativa del equipo son de maxima importancia, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un rol decisivo. Estos dispositivos especializados estan destinados a ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, medios de transporte o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es clave para mantener el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible reducir significativamente las oscilaciones, el ruido y la presion en los rodamientos, extendiendo la duracion de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente relevante es el impacto que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El soporte tecnico y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar soluciones confiables, elevando la confianza del cliente.
Para los duenos de negocios, la apuesta en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser clave para elevar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los directivos de pymes, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas se aplican para mejorar la produccion.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
Seo Backlinks backlink building
Website rank is vital for promoting websites.
We are engaged in attracting Google search robots to the site to increase the site’s ranking using article placements, backlink analysis platforms, in addition, we also drive crawlers through other resources.
There are two key kinds of bots – crawling and indexing.
Spider bots are the initial visitors to the site and direct data-processing crawlers to enter.
An increased number of visits from crawlers to the site, the more positive it is for the website.
Before we begin the work, we will send you with a image of the site authority from Ahrefs Backlink Checker, and upon completion, there will also be a snapshot of the site rating from ahrefs.com/backlink-checker.
Pay only for the result!
The expected timeframe is from 3 to 14 days,
Occasionally, more time is necessary.
We work with sites up to 50 DR. -
Seo Backlinks backlink building
Website rank is vital for SEO.
We specialize in attracting search engine crawlers to your website to improve the website position using publishing articles, backlink analysis platforms, and we also generate crawler traffic through third-party sources.
There are two primary categories of search robots – spider and indexing.
Spider bots are the first to visit the site and also instruct indexing robots to scan.
The more clicks from search robots to the site, the better it is for the site.
Before we begin the work, we will send you with a screenshot of the DR from Ahrefs’ backlink tool, and after the work is completed, there will likewise be a screenshot of the domain rating from Ahrefs DR checker.
Payment is made only after results!
Estimated production time is 3–14 business days,
In some instances, more time is needed.
We work with sites with DR below 50. -
Training of XRumer Xevil software for seo
I teach how to make link mass on the site or social networking software XRumer.
The training includes :
1. Installation, server setup, download XRumer and Xevil on the server.
2. Setting up to work in posting mode!
3. Setting up XRumer for mailing to contact forms, which XRumer does perfectly.
4. Setting up Xevil.
5. Talking about what XRumer is and what it is for and how to interact with it in seo
Show sites where to take proxies, VPS service
I balance (optimize) crumer, Xevil and server for effective work.
I work on the 6th version of Xevil
Here's the plan!
Install XRumer on a remote server (personal computer is not suitable for work)
I show you the settings for the work and make a project
Posting will be made in blogs and comments forums, Setting up a project with article placement (near-link text changes from the source alternately) that is important.
Collection of the base in the training is not included.
See additional options!!! -
Training of XRumer Xevil software for seo
I teach how to make link mass on the site or social networking software XRumer.
The training includes :
1. Installation, server setup, download XRumer and Xevil on the server.
2. Setting up to work in posting mode!
3. Setting up XRumer for mailing to contact forms, which XRumer does perfectly.
4. Setting up Xevil.
5. Talking about what XRumer is and what it is for and how to interact with it in seo
Show sites where to take proxies, VPS service
I balance (optimize) crumer, Xevil and server for effective work.
I work on the 6th version of Xevil
Here's the plan!
Install XRumer on a remote server (personal computer is not suitable for work)
I show you the settings for the work and make a project
Posting will be made in blogs and comments forums, Setting up a project with article placement (near-link text changes from the source alternately) that is important.
Collection of the base in the training is not included.
See additional options!!! -
DoFollow Backlinks
SEO-friendly backlinks.
These links convey SEO value from the referring website, and all links are reviewed carefully for the absence of NoFollow tags.
A detailed report on completed work is provided in a plain text format with the URLs of websites where your link was placed.
It's best to embed links naturally using keyword-rich anchors; I have prepared alternative methods — listed underneath:
Option 1 — write an original post
Option 2 — content is refreshed via synonym substitution to prevent mirrored content, because crawlers prefer content diversity.
We suggest a 30% anchor / 70% non-anchor link distribution. -
DoFollow Backlinks
DoFollow backlinks.
A DoFollow link passes link equity to the promoted resource, and all links are manually verified to confirm they are pure DoFollow links.
You will receive a work report in the form of a text file with the URLs of websites that host your backlink.
It's best to place links within content with semantic link phrases; here are other approaches — listed underneath:
Choice 1 — create a unique article
Option 2 — each post is automatically rephrased to ensure uniqueness, because crawlers prefer text variation.
Optimal ratio: 30% branded/keyword anchors, 70% non-anchor links. -
+3 Domain Rating
Inbound links to your domain on a wide range of websites.
We use exclusively sources from where there will be no issues from the moderator!!!
Link building in three stages
Stage 1 – Links to articles (Posting an article on a topic with an anchor and non-anchored link)
Step 2 – Backlinks through redirects of trusted sites with authority score PR 9-10, such as
Stage 3 – Posting an entry on backlink analysis tools -
Website analyzers show the sitemap to the search crawlers, and this is crucial.
Explanation for step 3 - just the homepage of the site is submitted on the analysis tools; subsequent web pages can't be placed.
I carry out these three phases sequentially, in total there will be 10K-30K inbound links from these 3 steps.
This backlink strategy is the most effective.
I will provide the link data on indexing platforms in a text file.
List of SEO platforms 50-200 platforms.
Submit a link building report via majestic, semrush , or ahrefs If one of the tools has less links, I report using the service with the highest number of links because what's the point of the lag? -
+3 Domain Rating
Quality backlinks to your site on various resources.
We use strictly sources from which there will be no issues from the platform moderators!!!
Generating backlinks in three stages
Phase 1 – Backlinks to articles (Posting an piece of content on a subject with an anchor and non-anchor link)
Stage 2 – Backlinks through redirection links of trusted websites with domain rating DR 9-10, e.g.
Stage 3 – Posting an entry on backlink analysis tools -
Analysis platforms show the sitemap to the search crawlers, and this is essential.
Note for stage 3 - just the homepage of the website is indexed on the analysis tools; subsequent web pages cannot be submitted.
I carry out these three phases step-by-step, in total there will be 10,000-20,000 inbound links from these 3 stages.
This backlink strategy is the most powerful.
I will provide the placement on indexing platforms in a text file.
Catalog of analysis tools hundreds of pieces.
Provide a performance report via majestic, semrush , or ahrefs In case one of the services has less links, I submit the report using the tool with the highest number of links because why wait for the lag? -
DoFollow Backlinks
DoFollow links.
These links convey domain authority to the promoted resource, while each link is reviewed carefully to ensure there are no NoFollow attributes.
You will receive a work report in the form of a text file listing all sites that host your backlink.
We advise to place links within content using keyword-rich anchors; here are other approaches — see below:
Option 1 — create a unique article
Second option — each post is automatically rephrased to ensure uniqueness, as search engines favor text variation.
The recommended anchor/non-anchor link ratio is 30/70%. -
DoFollow Backlinks
SEO-friendly backlinks.
Each DoFollow backlink carries domain authority from the source site, with every link being checked thoroughly for the absence of NoFollow tags.
A detailed report on completed work is provided in a plain text format listing all sites with your link published.
It is recommended to embed links naturally with relevant anchor text; I have prepared alternative methods — see below:
Option 1 — write an original post
Second option — an article is dynamically rewritten to avoid duplication, since algorithms reward text variation.
The recommended anchor/non-anchor link ratio is 30/70%. -
+3 Domain Rating
Quality backlinks to your domain on various resources.
We use only sources from where there will be no complaints from the moderator!!!
Backlinks in three stages
Step 1 – Backlinks to articles (Publishing an piece of content on a topic with an anchor and non-anchored link)
Step 2 – Links through redirects of highly reliable websites with page rank PR 9-10, e.g.
Step 3 – Posting an entry on backlink analysis tools -
Website analyzers submit the sitemap to the search crawlers, and this is essential.
Explanation for step 3 - just the homepage of the website is indexed on the analysis tools; subsequent web pages cannot be placed.
I perform these 3 phases in order, in total there will be 10,000-20,000 quality links from these 3 stages.
This backlink strategy is the most powerful.
I will send the placement on indexing platforms in a text file.
Catalog of analysis tools 50-200 pieces.
Provide a link building report via majestic, semrush , or ahrefs If one of the tools has less backlinks, I report using the tool with more backlinks because what's the point of the delay? -
+3 Domain Rating
Quality backlinks to your domain on a wide range of resources.
We use exclusively resources from where there will be no issues from the platform moderators!!!
Backlinks in three phases
Stage 1 – Links to blog posts (Posting an piece of content on a subject with an anchor and non-anchor link)
Step 2 – Backlinks through redirects of trusted sites with authority score DR 9-10, e.g.
Phase 3 – Submitting an entry on analyzer sites -
Website analyzers show the sitemap to the Google search engine, and this is essential.
Note for stage 3 - just the homepage of the website is indexed on the analyzers; secondary pages cannot be submitted.
I execute these 3 steps step-by-step, in all there will be 10,000-20,000 quality links from these 3 steps.
This link building approach is the most powerful.
I will show the link data on parsing sites in a .txt file.
List of site analyzers 50-200 pieces.
Submit a progress report via majestic, semrush , or ahrefs If one of the tools shows fewer links, I report using the service with the highest number of backlinks because why wait for the latency? -
equipo de equilibrio 2
https://vibromera.es/equipo-de-equilibrio-2/
Dispositivos de equilibrado: esenciales para el rendimiento suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el entorno de la ingenieria actual, donde la productividad y la fiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un rol decisivo. Estos dispositivos especializados estan disenados para ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es clave para asegurar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible reducir significativamente las oscilaciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de elementos caros.
Igualmente relevante es el impacto que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El servicio postventa y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas permiten ofrecer resultados superiores, aumentando la confianza del cliente.
Para los propietarios, la apuesta en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser decisiva para aumentar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los directivos de pymes, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Sirven para identificar defectos, ahorrando gastos elevados y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
desequilibrio
https://vibromera.es/desequilibrio/
Equipos de balanceo: esenciales para el rendimiento suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el ambito de la ingenieria actual, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan disenados para compensar el movimiento de partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, automoviles y camiones o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es clave para mantener el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible reducir significativamente las vibraciones, el sonido no deseado y la presion en los rodamientos, extendiendo la duracion de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente importante es el papel que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El soporte tecnico y el servicio periodico utilizando estos sistemas garantizan soluciones confiables, aumentando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los propietarios, la inversion en plataformas de equilibrado y monitoreo puede ser determinante para aumentar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los administradores de negocios medianos, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas sirven para optimizar procesos.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
equilibrador fabricante
https://vibromera.es/equilibrador-fabricante/
Equipos de balanceo: esenciales para el desempeno optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el ambito de la ingenieria actual, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de maxima importancia, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan creados con el fin de compensar el movimiento de partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es fundamental para asegurar el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las vibraciones, el ruido y la presion en los rodamientos, extendiendo la duracion de elementos caros.
Igualmente importante es el papel que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El soporte tecnico y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas garantizan resultados superiores, aumentando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los duenos de negocios, la apuesta en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser decisiva para elevar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los directivos de pymes, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
equilibrado de piezas
https://vibromera.es/equilibrado-de-piezas/
Maquinas de equilibrado: indispensables para el rendimiento optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el entorno de la tecnologia moderna, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de relevancia critica, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un rol decisivo. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan creados con el fin de equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, automoviles y camiones o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es fundamental para asegurar el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las vibraciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de elementos caros.
Igualmente crucial es el impacto que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El soporte tecnico y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas garantizan soluciones confiables, mejorando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los empresarios, la apuesta en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser determinante para aumentar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los directivos de pymes, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los datos obtenidos de estos sistemas se aplican para mejorar la produccion.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
vibracion del motor
https://vibromera.es/vibracion-del-motor/
Equipos de balanceo: esenciales para el funcionamiento optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el ambito de la tecnologia moderna, donde la eficiencia y la seguridad operativa del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos dispositivos especializados estan creados con el fin de equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es clave para asegurar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible disminuir de manera notable las vibraciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de componentes costosos.
Igualmente relevante es el papel que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El mantenimiento especializado y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar resultados superiores, aumentando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los propietarios, la apuesta en plataformas de equilibrado y monitoreo puede ser clave para optimizar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los administradores de negocios medianos, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el ambito de la prevencion y aseguramiento. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y averias graves. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas sirven para optimizar procesos.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
diagnostico vibracional
https://vibromera.es/diagnostico-vibracional/
Equipos de balanceo: clave para el desempeno fluido y confiable de las maquinas
En el mundo de la tecnologia moderna, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de relevancia critica, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan creados con el fin de ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, medios de transporte o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es fundamental para mantener el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las oscilaciones, el ruido y la presion en los rodamientos, aumentando la resistencia de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente crucial es el impacto que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El mantenimiento especializado y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar resultados superiores, elevando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los empresarios, la implementacion en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser determinante para aumentar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Sirven para identificar defectos, previniendo danos financieros y averias graves. Mas aun, los datos obtenidos de estos sistemas se aplican para optimizar procesos.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
Link pyramid tier 1 tier 2 tier 3
Backlinks for SEO consist of anchor links and their non-anchor counterparts.
Anchors include a primary search term, as the key query plays a crucial role for SEO performance.
Non-anchor links carry equal weight – this includes bare links, and clickability matters as it creates a path to search engine crawlers; bots go your website and deeper pages, which benefits the site.
Updates are shared through majestic. If there are fewer links for one of the services, the analysis focuses on the tool with a larger number of backlinks due to indexing delays. -
Link pyramid tier 1 tier 2 tier 3
SEO backlinks for SEO consist of anchor links and their non-anchor counterparts.
Anchor links are linked to a primary search term, as such a query is essential for SEO performance.
Non-anchor backlinks are equally significant – they represent bare links, while the ability to click plays a key role because it creates a route for bots; search engines access the target page and subsequent pages, which benefits website.
I provide ahrefs. If there are fewer links on a particular platform, I report on the platform with a larger number of inbound links due to indexing delays. -
internal traffic
DoFollow links.
These links convey SEO value to your target site, while each link is reviewed carefully to confirm they are pure DoFollow links.
We provide a full performance report in the form of a text file with the URLs of websites that host your backlink.
We advise to embed links naturally with relevant anchor text; I have prepared alternative methods — see below:
Choice 1 — create a unique article
Alternative 2 — content is refreshed via synonym substitution to prevent mirrored content, as search engines favor content diversity.
The recommended anchor/non-anchor link ratio is 30/70%. -
internal traffic
DoFollow backlinks.
Each DoFollow backlink carries link equity to your target site, and all links are checked thoroughly for the absence of NoFollow tags.
We provide a full performance report in the form of a text file listing all sites with your link published.
We advise to embed links naturally with relevant anchor text; additional options are available — listed underneath:
First option — write an original post
Second option — content is refreshed via synonym substitution to avoid duplication, since algorithms reward text variation.
We suggest a 30% anchor / 70% non-anchor link distribution. -
reparacion de maquinaria agricola
https://vibromera.es/reparacion-de-maquinaria-agricola/
Sistemas de balanceo: indispensables para el desempeno suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el ambito de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de relevancia critica, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un papel crucial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan creados con el fin de equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es clave para asegurar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible disminuir de manera notable las oscilaciones, el ruido y la presion en los rodamientos, aumentando la resistencia de elementos caros.
Igualmente importante es el rol que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El soporte tecnico y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar soluciones confiables, aumentando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los duenos de negocios, la apuesta en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser decisiva para optimizar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los administradores de negocios medianos, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Ayudan a prever problemas, previniendo danos financieros y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas se aplican para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
equilibrador portatil 2
https://vibromera.es/equilibrador-portatil-2/
Maquinas de equilibrado: clave para el desempeno suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el entorno de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la productividad y la seguridad operativa del equipo son de maxima importancia, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan disenados para equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, automoviles y camiones o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es clave para mantener el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible disminuir de manera notable las oscilaciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, prolongando la vida util de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente crucial es el rol que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El mantenimiento especializado y el servicio periodico utilizando estos sistemas garantizan soluciones confiables, mejorando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los empresarios, la implementacion en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser clave para optimizar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los directivos de pymes, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el ambito de la prevencion y aseguramiento. Ayudan a prever problemas, evitando reparaciones costosas y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas se aplican para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
equipo de balanceo
https://vibromera.es/equipo-de-balanceo/
Maquinas de equilibrado: clave para el rendimiento suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el mundo de la ingenieria actual, donde la optimizacion y la fiabilidad del equipo son de relevancia critica, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un papel crucial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan creados con el fin de compensar el movimiento de partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los ingenieros, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es clave para mantener el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible disminuir de manera notable las vibraciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, prolongando la vida util de elementos caros.
Igualmente crucial es el rol que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El mantenimiento especializado y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar servicios de alta calidad, aumentando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los empresarios, la apuesta en plataformas de equilibrado y monitoreo puede ser determinante para aumentar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los administradores de negocios medianos, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Ayudan a prever problemas, previniendo danos financieros y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
encontrar equilibrador
https://vibromera.es/encontrar-equilibrador/
Sistemas de balanceo: esenciales para el rendimiento fluido y confiable de las maquinas
En el entorno de la tecnologia moderna, donde la optimizacion y la fiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un rol decisivo. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan creados con el fin de equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, medios de transporte o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es indispensable para mantener el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible reducir significativamente las vibraciones, el ruido y la presion en los rodamientos, extendiendo la duracion de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente relevante es el impacto que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El soporte tecnico y el servicio periodico utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar servicios de alta calidad, aumentando la confianza del cliente.
Para los duenos de negocios, la inversion en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser determinante para aumentar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el ambito de la prevencion y aseguramiento. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, evitando reparaciones costosas y averias graves. Mas aun, los datos obtenidos de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para mejorar la produccion.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
Enlaces de retroceso para Google
Acerca de este servicio
Colocacion de vinculos con fines promocionales y posicionamiento en Google en sitios de discusion, comentarios y sitios web con opciones de mil, cinco mil o diez mil enlaces
Base reciente de foros, blogs y comentarios (combinada)
Incorporamos enlaces con y sin texto ancla, configurando los enlaces para mejorar las busquedas en Google
Mantenemos una proporcion natural de enlaces dofollow y nofollow para asegurar una mejor credibilidad del motor de busqueda
En todo momento nos mantenemos disponibles
Que necesitamos para empezar:
Una direccion web
Las palabras clave en formato de columna
Proporcionaremos un informe de avance mediante Majestic, Semrush o Ahrefs
Si alguna herramienta indica menos vinculos, realizaremos el reporte desde aquella que muestre mas backlinks debido al retraso en la indexacion -
Enlaces de retroceso para Google
Descripcion del servicio
Colocacion de vinculos con fines promocionales y posicionamiento en Google en foros, comentarios y sitios web en cantidades de 1000, 5000 o 10000 vinculos
Base reciente de foros, blogs y comentarios (combinada)
Trabajamos con enlaces anclados y no anclados, ajustando los vinculos para las busquedas en Google
Mantenemos una proporcion natural de enlaces dofollow y nofollow para asegurar una mejor credibilidad del motor de busqueda
Constantemente accesibles
Que necesitamos para empezar:
Un enlace
Las claves de busqueda en una tabla
Presentaremos un informe de seguimiento via Majestic, Semrush o Ahrefs
Si alguna herramienta indica menos vinculos, realizaremos el reporte desde aquella que muestre mas backlinks debido al retraso en la indexacion -
Link pyramid tier 1 tier 2 tier 3
Backlinks for SEO consist of anchor links and their non-anchor counterparts.
Anchor links contain the main keyword, as such a query plays a crucial role in search engine optimization.
Non-anchor links are equally significant – these are plain URLs, while clickability is important because it creates access for bots; bots go the target page and subsequent pages, which is useful the site.
Updates are shared through ahrefs. In cases where backlink counts are lower on a particular platform, I report on the tool with the highest count of backlinks because of delays in indexation. -
Link pyramid tier 1 tier 2 tier 3
SEO backlinks for SEO are divided into two main types: anchor and non-anchor backlinks.
Anchor links contain a primary search term, as this keyword is fundamental for SEO performance.
Non-anchor backlinks carry equal weight – they represent bare links, and clickability matters as they offer access to search engine crawlers; search engines access the site and deeper pages, which is useful your project.
I provide majestic. When the number of links is limited for a specific tool, I report on the service with the highest count in backlink volume because of delays in indexation. -
internal traffic
SEO-friendly backlinks.
These links convey domain authority from the source site, while each link is checked thoroughly to confirm they are pure DoFollow links.
We provide a full performance report as a .txt document listing all sites where your link was placed.
It's best to use contextual links with semantic link phrases; here are other approaches — listed underneath:
Choice 1 — write an original post
Option 2 — each post is automatically rephrased to ensure uniqueness, since algorithms reward text variation.
The recommended anchor/non-anchor link ratio is 30/70%. -
internal traffic
DoFollow backlinks.
DoFollow links transfer SEO value to the promoted resource, with every link being manually verified to confirm they are pure DoFollow links.
We provide a full performance report in a plain text format listing all sites with your link published.
We advise to place links within content with semantic link phrases; additional options are available — check them out:
First option — develop a custom article
Second option — content is refreshed via synonym substitution to avoid duplication, as search engines favor text variation.
The recommended anchor/non-anchor link ratio is 30/70%. -
internal traffic
DoFollow links.
Each DoFollow backlink carries link equity to your target site, with every link being manually verified to confirm they are pure DoFollow links.
You will receive a work report in the form of a text file containing the list of domains that host your backlink.
It is preferable to embed links naturally using keyword-rich anchors; here are other approaches — listed underneath:
First option — create a unique article
Alternative 2 — an article is dynamically rewritten to ensure uniqueness, because crawlers prefer text variation.
Optimal ratio: 30% branded/keyword anchors, 70% non-anchor links. -
internal traffic
SEO-friendly backlinks.
These links convey domain authority to your target site, and all links are manually verified to ensure there are no NoFollow attributes.
You will receive a work report in the form of a text file with the URLs of websites that host your backlink.
We advise to place links within content using keyword-rich anchors; here are other approaches — check them out:
Option 1 — develop a custom article
Alternative 2 — each post is automatically rephrased to ensure uniqueness, because crawlers prefer text variation.
Optimal ratio: 30% branded/keyword anchors, 70% non-anchor links. -
instrumento de equilibrado
https://vibromera.es/instrumento-de-equilibrado/
Dispositivos de equilibrado: fundamentales para el rendimiento optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el ambito de la ingenieria actual, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un papel crucial. Estos dispositivos especializados estan destinados a equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, automoviles y camiones o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los ingenieros, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es clave para garantizar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible disminuir de manera notable las vibraciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, aumentando la resistencia de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente relevante es el impacto que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El mantenimiento especializado y el servicio periodico utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar resultados superiores, mejorando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los propietarios, la implementacion en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser decisiva para elevar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los administradores de negocios medianos, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el ambito de la prevencion y aseguramiento. Sirven para identificar defectos, ahorrando gastos elevados y averias graves. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas se aplican para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la industria ciclista hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
vibrodiagnostico
https://vibromera.es/vibrodiagnostico/
Equipos de balanceo: fundamentales para el desempeno fluido y confiable de las maquinas
En el mundo de la ingenieria actual, donde la productividad y la confiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un papel crucial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan creados con el fin de ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, medios de transporte o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es indispensable para mantener el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las oscilaciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, aumentando la resistencia de componentes costosos.
Igualmente relevante es el papel que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El soporte tecnico y el servicio periodico utilizando estos sistemas permiten ofrecer servicios de alta calidad, elevando la confianza del cliente.
Para los propietarios, la implementacion en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser clave para optimizar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los administradores de negocios medianos, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, evitando reparaciones costosas y averias graves. Mas aun, los datos obtenidos de estos sistemas se aplican para optimizar procesos.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la industria ciclista hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
Pirámide de backlinks SEO
Pirámide de backlinks SEO en tres etapas: hasta 30,000 enlaces de alta calidad, informes en Ahrefs y plan progresivo para posicionar tu web en Google. Planes desde 180
Etapa 1 – Primer nivel de backlinks
Etapa 2 – Backlinks a través de redirecciones de fuentes autorizadas, por ejemplo
Etapa 3 – Colocación en webs de analítica, por ejemplo
Explicación de la etapa 3: únicamente se incluye la página principal del sitio en los analizadores; las páginas internas no se pueden colocar
Las tres etapas se realizan paso a paso, con un total de 10000–30000 backlinks provenientes de los tres niveles
Esta técnica de link building escalonado es muy poderosa
Lista de cuarenta analizadores
Precios:
Basic – 180$ – 10000 Backlinks
Standard – 200$ – 20000 Backlinks
Premium – 220$ – 30000 Backlinks
Spintax de artículos para garantizar que cada texto sea diferente — 30$ -
Pirámide de enlaces SEO
Estrategia de backlinks SEO en 3 etapas: hasta treinta mil enlaces de calidad superior, reportes en Semrush y plan progresivo para subir posiciones en Google. Planes desde $180
Etapa 1 – Enlaces básicos
Etapa 2 – Redirecciones desde sitios confiables de fuentes autorizadas, por ejemplo
Etapa 3 – Inserción en plataformas de análisis, por ejemplo
Explicación de la etapa 3: solo se coloca la página principal del sitio en los analizadores; no es posible añadir páginas internas
Las tres etapas se realizan de manera secuencial, con un total de diez mil a treinta mil backlinks provenientes de los tres niveles
Esta estrategia de pirámide de enlaces es muy poderosa
Lista de cuarenta analizadores
Precios:
Basic – 180$ – 10000 Backlinks
Standard – 200$ – 20000 Backlinks
Premium – 220$ – 30000 Backlinks
Spintax de artículos para garantizar que cada publicación sea única — 30$ -
Link pyramid tier 1 tier 2 tier 3
SEO backlinks for SEO consist of two main types: anchor and non-anchor backlinks.
Anchor links contain a key query, as such a query is fundamental for search engine ranking.
Bare links are equally significant – they represent plain URLs, while user interaction matters because they offer a route for bots; bots go your website and deeper pages, which is useful your project.
Updates are shared through majestic. In cases where backlink counts are lower on a particular platform, updates are provided on the platform with a larger number of inbound links because of delays in indexation. -
Link pyramid tier 1 tier 2 tier 3
Inbound links for SEO consist of two main types: anchor and non-anchor backlinks.
Anchors contain a primary search term, since this keyword is fundamental for search engine ranking.
Non-anchor links are equally significant – they represent simple hyperlinks, while the ability to click plays a key role as it provides a path for bots; search engines access the site and subsequent pages, which is useful your project.
Progress reports are delivered via ahrefs. In cases where backlink counts are lower for one of the services, the analysis focuses on the platform with the highest count in backlink volume because of delays in indexation. -
revatio uses https://community.ruckuswireless.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/23524
-
equilibrado informatico
https://vibromera.es/equilibrado-informatico/
Equipos de balanceo: clave para el rendimiento suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el entorno de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de relevancia critica, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un papel crucial. Estos dispositivos especializados estan destinados a equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, automoviles y camiones o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es fundamental para garantizar el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible disminuir de manera notable las vibraciones, el ruido y la presion en los rodamientos, aumentando la resistencia de elementos caros.
Igualmente importante es el rol que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El servicio postventa y el servicio periodico utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar servicios de alta calidad, mejorando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los empresarios, la apuesta en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser determinante para elevar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Ayudan a prever problemas, evitando reparaciones costosas y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas se aplican para mejorar la produccion.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la industria ciclista hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son imprescindibles para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
equilibrado informatico 2
https://vibromera.es/equilibrado-informatico-2/
Sistemas de balanceo: fundamentales para el desempeno suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el ambito de la tecnologia moderna, donde la eficiencia y la seguridad operativa del equipo son de relevancia critica, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un papel crucial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan creados con el fin de equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, medios de transporte o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es indispensable para asegurar el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las vibraciones, el sonido no deseado y la presion en los rodamientos, prolongando la vida util de elementos caros.
Igualmente importante es el papel que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El servicio postventa y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar servicios de alta calidad, aumentando la confianza del cliente.
Para los empresarios, la implementacion en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser decisiva para optimizar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Sirven para identificar defectos, previniendo danos financieros y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los datos obtenidos de estos sistemas se aplican para mejorar la produccion.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
GSA Backlinks
Публикую ссылки на:
Обзор
Заметка в блоге
Дискуссионная площадка
Обратная связь
Комментарий к изображению
Микроблог
Интерактивный веб
База знаний
Распределение разных платформ исходя из числа размещений постоянно меняется, потому что использую исключительно обновлённую базу. -
GSA Backlinks
Добавляю ссылки на:
Статья
Блог-комментарий
Обсуждение
Гостевая
Коммент к картинке
Короткие сообщения
Современный веб
Совместное редактирование
Распределение отдельных площадок исходя из числа размещений всегда отличается, потому что работаю с обновлённую базу. -
lembah88
Lembah88: Platform Game Online Terpercaya dengan Akses Login Cepat dan Aman
Dalam era digital yang serba cepat ini, kebutuhan akan hiburan online semakin meningkat. Salah satu platform yang kini banyak diperbincangkan oleh para pemain adalah lembah88 — sebuah situs game online yang menawarkan pengalaman bermain seru, aman, dan mudah diakses.
Kenali Apa Itu Lembah88
Lembah88 merupakan platform game online yang menghadirkan berbagai jenis permainan menarik untuk para penggemar hiburan digital. Mulai dari permainan klasik hingga game modern dengan fitur interaktif, semua bisa dinikmati hanya dengan satu akun. Dengan tampilan yang sederhana namun elegan, lembah88 memberikan kenyamanan maksimal bagi pengguna baru maupun pemain berpengalaman.
Keunggulan Lembah88 Login
Proses lembah88 login dirancang untuk memberikan kemudahan dan keamanan tingkat tinggi. Pengguna hanya perlu memasukkan nama pengguna dan kata sandi untuk langsung mengakses akun mereka. Selain itu, sistem keamanan di lembah88 telah dilengkapi dengan enkripsi data canggih, memastikan bahwa informasi pribadi dan transaksi pengguna selalu terlindungi dari potensi ancaman digital.
Beberapa keunggulan utama dari sistem login lembah88 antara lain:
Keamanan data terjamin dengan sistem enkripsi modern
Akses cepat dan responsif tanpa gangguan
Dapat diakses melalui berbagai perangkat seperti desktop, tablet, dan smartphone
Pengalaman Bermain di Lembah88
Setelah berhasil melakukan lembah88 login, pengguna dapat langsung menikmati berbagai pilihan permainan yang menarik. Dengan server yang stabil dan tampilan antarmuka yang ramah pengguna, lembah88 memberikan pengalaman bermain yang lancar tanpa hambatan. Selain itu, tersedia juga berbagai promo dan bonus menarik untuk para anggota aktif yang rutin bermain di platform ini.
Kesimpulan
Lembah88 adalah pilihan tepat bagi siapa pun yang mencari platform game online dengan akses cepat, tampilan modern, dan sistem keamanan yang terpercaya. Melalui lembah88 login, setiap pengguna dapat langsung menikmati hiburan berkualitas kapan saja dan di mana saja. -
lembah88 login
Lembah88: Platform Game Online Terpercaya dengan Akses Login Cepat dan Aman
Dalam era digital yang serba cepat ini, kebutuhan akan hiburan online semakin meningkat. Salah satu platform yang kini banyak diperbincangkan oleh para pemain adalah lembah88 — sebuah situs game online yang menawarkan pengalaman bermain seru, aman, dan mudah diakses.
Kenali Apa Itu Lembah88
Lembah88 merupakan platform game online yang menghadirkan berbagai jenis permainan menarik untuk para penggemar hiburan digital. Mulai dari permainan klasik hingga game modern dengan fitur interaktif, semua bisa dinikmati hanya dengan satu akun. Dengan tampilan yang sederhana namun elegan, lembah88 memberikan kenyamanan maksimal bagi pengguna baru maupun pemain berpengalaman.
Keunggulan Lembah88 Login
Proses lembah88 login dirancang untuk memberikan kemudahan dan keamanan tingkat tinggi. Pengguna hanya perlu memasukkan nama pengguna dan kata sandi untuk langsung mengakses akun mereka. Selain itu, sistem keamanan di lembah88 telah dilengkapi dengan enkripsi data canggih, memastikan bahwa informasi pribadi dan transaksi pengguna selalu terlindungi dari potensi ancaman digital.
Beberapa keunggulan utama dari sistem login lembah88 antara lain:
Keamanan data terjamin dengan sistem enkripsi modern
Akses cepat dan responsif tanpa gangguan
Dapat diakses melalui berbagai perangkat seperti desktop, tablet, dan smartphone
Pengalaman Bermain di Lembah88
Setelah berhasil melakukan lembah88 login, pengguna dapat langsung menikmati berbagai pilihan permainan yang menarik. Dengan server yang stabil dan tampilan antarmuka yang ramah pengguna, lembah88 memberikan pengalaman bermain yang lancar tanpa hambatan. Selain itu, tersedia juga berbagai promo dan bonus menarik untuk para anggota aktif yang rutin bermain di platform ini.
Kesimpulan
Lembah88 adalah pilihan tepat bagi siapa pun yang mencari platform game online dengan akses cepat, tampilan modern, dan sistem keamanan yang terpercaya. Melalui lembah88 login, setiap pengguna dapat langsung menikmati hiburan berkualitas kapan saja dan di mana saja. -
reduccion de vibracion
https://vibromera.es/reduccion-de-vibracion/
Sistemas de balanceo: indispensables para el desempeno suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el ambito de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la productividad y la seguridad operativa del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos dispositivos especializados estan disenados para ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, automoviles y camiones o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es fundamental para garantizar el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible disminuir de manera notable las vibraciones, el sonido no deseado y la presion en los rodamientos, prolongando la vida util de elementos caros.
Igualmente relevante es el impacto que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El soporte tecnico y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar soluciones confiables, elevando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los empresarios, la implementacion en plataformas de equilibrado y monitoreo puede ser decisiva para optimizar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los directivos de pymes, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, evitando reparaciones costosas y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para optimizar procesos.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son imprescindibles para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
herramienta de equilibrado 2
https://vibromera.es/herramienta-de-equilibrado-2/
Dispositivos de equilibrado: fundamentales para el rendimiento optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el mundo de la ingenieria actual, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de maxima importancia, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un rol decisivo. Estos dispositivos especializados estan creados con el fin de ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es indispensable para asegurar el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las oscilaciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de componentes costosos.
Igualmente importante es el papel que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El servicio postventa y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar resultados superiores, mejorando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los propietarios, la inversion en plataformas de equilibrado y monitoreo puede ser clave para elevar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los directivos de pymes, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y averias graves. Mas aun, los datos obtenidos de estos sistemas se aplican para optimizar procesos.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la industria ciclista hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
SEO Backlinks via Redirect backlink building
We advise making referral links via redirect and placing a link to sites, while the ranking power of the domains will boost its SEO value. External links are an key indicator in search engines! And for sites with high reputation, if you create, for example, ten thousand backlinks, this approach is ideal, since there is resistance to bans and the site is safe from penalties.
Therefore, we provide only a high-quality list of sources.
Links are kept on the resources indefinitely:
As a result, you will get:
– Quick crawling of your site
– Accelerated increase of visibility in search results
– Flow of search crawlers to your website -
SEO Backlinks via Redirect backlink building
I recommend making external links via 301 redirect and adding a link to sites, while the authority of the resources will increase its appeal. Backlinks are an key factor in search engines! And for domains with strong authority, if you make, for example, ten thousand backlinks, this strategy is highly effective, since there is resistance to bans and the site is secure against blacklisting.
Therefore, we provide only a verified database.
Links remain on the resources permanently:
As a result, you will get:
– Speedy crawling of your site
– Steady improvement of rankings in search results
– Flow of indexing bots to your website -
Backlinks SEO promotion
1. Backlinks с кросс-ссылками (для улучшения индексации).
2. Переадресации через Google.
3. Ссылки через редиректы с доверенных сайтов.
- Предоставляю отчет о продвижении в виде текстового файла с перечнем успешных размещений. -
Backlinks SEO promotion
1. Обратные ссылки с взаимными переходами (для улучшения индексации).
2. Ссылки через редиректы Google.
3. Переадресации с ресурсов с высоким уровнем доверия.
- Я направляю отчет о проделанной работе в формате текстового документа с успешными размещениями. -
Pirámide de backlinks SEO
Estrategia de backlinks SEO en tres etapas: hasta treinta mil enlaces de calidad superior, informes en Semrush y estrategia escalonada para posicionar tu web en Google. Planes desde 180
Etapa 1 – Backlinks simples
Etapa 2 – Backlinks con redirecciones de sitios altamente confiables, por ejemplo
Etapa 3 – Colocación en sitios analizadores, por ejemplo
Explicación de la etapa 3: solo se coloca la página principal del sitio en los analizadores; las páginas internas no se pueden colocar
Las tres etapas se realizan de manera secuencial, con un total de 10000–30000 backlinks provenientes de los tres niveles
Esta estrategia de pirámide de enlaces es altamente efectiva
Lista de cuarenta analizadores
Precios:
Basic – 180$ – 10000 Backlinks
Standard – 200$ – 20000 Backlinks
Premium – 220$ – 30000 Backlinks
Spintax de artículos para garantizar que cada publicación sea única — 30$ -
Pirámide de backlinks SEO
Pirámide de backlinks SEO en tres etapas: hasta 30,000 enlaces de calidad superior, reportes en Ahrefs y plan progresivo para posicionar tu web en Google. Planes desde $180
Etapa 1 – Primer nivel de backlinks
Etapa 2 – Backlinks con redirecciones de dominios de autoridad, por ejemplo
Etapa 3 – Inserción en plataformas de análisis, por ejemplo
Explicación de la etapa 3: únicamente se incluye la página principal del sitio en los analizadores; no es posible añadir páginas internas
Las tres etapas se realizan de manera secuencial, con un total de 10000–30000 backlinks provenientes de los tres niveles
Esta estrategia de pirámide de enlaces es una de las más efectivas
Lista de cuarenta analizadores
Precios:
Basic – 180$ – 10000 Backlinks
Standard – 200$ – 20000 Backlinks
Premium – 220$ – 30000 Backlinks
Spintax de artículos para garantizar que cada texto sea diferente — 30$ -
Autoridad de dominio
Autoridad de dominio (DR de Ahrefs)
Aumentará la credibilidad en el sitio web.
El ranking de tu sitio web es fundamental para el SEO.
Nos encargamos de dirigir robots indexadores de Google a tu sitio para mejorar su ranking.
Existen dos clases básicas de bots de Google:
Crawling robots – los que analizan inicialmente el sitio.
Indexadores automáticos – entran bajo la instrucción de los crawling robots.
Cuantos más accesos hagan estos robots a tu sitio, mayor será tu visibilidad.
Antes de comenzar, te proporcionaremos una captura de pantalla del Domain Rating desde Ahrefs.
Después de completar el trabajo, también recibirás una imagen actualizada del puntaje de tu sitio en Ahrefs.
Paga solo por resultados.
Tiempo estimado de entrega: de unos días hasta dos semanas.
Ofrecemos el servicio para dominios con DR inferior a 50.
Para completar tu pedido necesitamos:
La URL de tu página.
Una palabra clave.
Las plataformas sociales quedan excluidas del servicio. -
Aumentará la confianza en el sitio web
Valor de autoridad del dominio (DR de Ahrefs)
Fortalecerá la confianza en el sitio web.
El ranking de tu sitio web es crucial para el SEO.
Nos dedicamos a atraer arañas de búsqueda de Google a tu sitio para impulsar su posición.
Existen dos tipos principales de robots de búsqueda:
Robots de exploración – los primeros en entrar al sitio.
Indexadores automáticos – actúan según las órdenes de los bots de rastreo.
Cuanto mayor sea la actividad de estos robots a tu sitio, mejor será para tu posicionamiento.
Antes de comenzar, te proporcionaremos una evidencia del Domain Rating desde Ahrefs.
Después de terminar el trabajo, también te enviaremos una muestra nueva del rating de tu sitio en Ahrefs.
Paga solo por resultados.
Plazo aproximado: de tres a catorce días.
Trabajamos con sitios de hasta DR 50.
Para completar tu pedido necesitamos:
El link de tu sitio.
Una frase objetivo.
Este servicio no se aplica a redes sociales. -
https://bento.me/cialis-soft-tabs Buying cialis cheap
0950663759 - Vladimir (Sergey) Romanenko (Obman, Kidalo)!
+38 095 0663759 - Владимир (Сергей) Романенко, Одесса - Мошенник, продает нерабочий товар на OLX! -
Website backlinks SEO
Locate us by the following queries: links for site promotion, backlinks for SEO, links for Google ranking, link building, link builder, acquire backlinks, backlink provision, website backlinks, order backlinks, backlinks Kwork, webpage backlinks, SEO website backlinks. -
Website backlinks SEO
You can find us by the following queries: links for site promotion, backlinks for SEO, links for Google ranking, link building, link building specialist, obtain backlinks, link service, backlinks for sites, buy backlinks, Kwork backlinks, site linking, website SEO links. -
Backlinks for your site
Applicable throughout all themes of the platform.
I provide backlinks to your page.
My backlinks attract Google crawlers to the site, something that is crucial for positioning, therefore it matters to optimize a resource that does not have flaws that obstruct visibility.
Placement poses no risk for your resource!
I avoid filling in communication fields, (contact forms can damage the resource as there are complaints from operators).
Publication is performed in permitted places.
Links are posted to the most recent regularly updated database. A large number of platforms in the catalog. -
Backlinks for your site
Effective in every area of the resource.
I make inbound links to your domain.
These backlinks engage web crawlers to the page, which is very important for SEO, therefore it matters to promote a site that does not have issues that obstruct ranking.
Placement poses no risk for your site!
I refrain from using in contact forms, (contact forms pose risks to the site since users file complaints from operators).
Submission is performed in authorized locations.
Links are inserted to their latest continuously refreshed list. Several portals in the catalog. -
افضل كروسون في عمان
Cafe Bateel — The Art of Gastronomic Elegance
Reading the Cafe Bateel menu is like listening to the overture of an opera — a harmonious prelude that enchants your senses and introduces an unforgettable gastronomic journey.
It opens with our finely prepared soups, followed by a fresh selection of vibrant salads crafted from carefully selected ingredients — from delicate palm hearts to succulent yellowfin tuna. For those seeking something light yet satisfying, Cafe Bateel offers refined standards such as our renowned risotto and the ever-popular club sandwich, each prepared with meticulous attention to flavor and presentation.
No visit would be complete without indulging in our fine coffee selection, refreshing beverages, and indulgent desserts. Each offering embodies our commitment to quality and craftsmanship, ensuring every sip and bite delights the palate.
Cafe Bateel is also celebrated for its exceptional breakfast offerings. From freshly made Belgian waffles and classic eggs Benedict to buttery croissants, moist muffins, and flaky Danish treats, every morning starts as a delightful ritual of taste.
Cafe Bateel is not merely a place to eat — it is a culinary art form, where every nuance, ingredient, and tone unites to create a melodious whole. Whether you begin your morning with a freshly baked treat or savor a relaxed midday meal, each visit invites you to savor the art of refined dining. -
افضل كروسون في عمان
Cafe Bateel — A Symphony of Taste and Elegance
Opening the Cafe Bateel menu is akin to hearing the first notes of a grand opera — a melodic beginning that awakens the senses and prepares you for a refined dining adventure.
It opens with our finely prepared soups, followed by a fresh selection of vibrant salads crafted from carefully selected ingredients — from tender heart of palm to fresh yellowfin tuna. For those looking for a meal that’s both light and fulfilling, Cafe Bateel offers timeless classics such as our house special risotto and the all-time favorite club sandwich, each prepared with meticulous attention to flavor and presentation.
No visit would be complete without savoring our distinctive coffee menu, invigorating drinks, and indulgent desserts. Each creation represents our passion for premium taste and precision, ensuring every taste leaves a lasting impression.
Cafe Bateel is also renowned for its signature breakfast menu. From handmade Belgian waffles and classic eggs Benedict to freshly baked croissants, muffins, and Danish pastries, every morning becomes a moment of pure pleasure.
Cafe Bateel is not merely a place to eat — it is a culinary art form, where every nuance, ingredient, and tone unites to create a melodious whole. Whether you welcome the day with a golden pastry or delight in an unhurried lunch, each visit welcomes you into the world of culinary elegance. -
Seo Backlinks
Backlinks for promotion are a very good tool.
Backlinks are important to Google's crawlers, the more backlinks the better!
Robots see many links as links to your resource
and your site's ranking goes up.
I have extensive experience in posting backlinks,
The forum database is always up to date as I have an efficient server and I do not rent remote servers, so my capabilities allow me to collect the forum database around the clock. -
Seo Backlinks
Backlinks for promotion are a very good tool.
Backlinks are important to Google's crawlers, the more backlinks the better!
Robots see many links as links to your resource
and your site's ranking goes up.
I have extensive experience in posting backlinks,
The forum database is always up to date as I have an efficient server and I do not rent remote servers, so my capabilities allow me to collect the forum database around the clock. -
buy cenforce centurion laboratories cenforce 100
+38 0950663759 – Владимир (Сергей) Романенко, Одесса – Такого обмана на OLX ещё не встречал! Гнида уверял, что техника рабочая, а пришёл хлам. Деньги заплатил честно, а в ответ — тишина. Возврата нет, поддержка OLX — помогите разобраться!. OLX урода - https://www.olx.ua/uk/list/user/unRKD/ -
telaga88 link
Telaga88: Pusat Game Online Cepat, Ringan, dan Ramah Pemula
Telaga88 menjadi wadah permainan daring yang mengutamakan kecepatan dan aksesibilitas
Desain antarmuka yang sederhana, tata letak yang mudah dipahami, dan performa yang konsisten membuat Telaga88 menyenangkan digunakan baik oleh pemula maupun pemain berpengalaman
Tim Telaga88 memprioritaskan pengalaman pengguna
Setiap bagian dari halaman dan kumpulan game disusun agar proses loading berjalan cepat, mengurangi delay, dan menjaga kenyamanan selama sesi permainan
Alhasil, kecepatan permainan tetap terjaga meski dalam situasi jaringan yang bervariasi
Secara visual, Telaga88 menerapkan konsep desain mutakhir yang fleksibel
Fitur kategori mempermudah pemain dalam memilih genre permainan yang disukai—adventure, puzzle, arcade—membuat eksplorasi judul baru lebih menyenangkan dan efisien -
telaga88 link
Telaga88: Inti Permainan Digital Cepat, Efisien, dan Mudah Dipahami
Telaga88 tampil sebagai ekosistem hiburan digital yang mengedepankan kecepatan serta kemudahan penggunaan
Antarmuka yang bersih, sistem penjelajahan yang jelas, dan performa yang terjaga membuat Telaga88 ramah bagi pemain baru maupun veteran
Tim Telaga88 memprioritaskan pengalaman pengguna
Setiap elemen laman dan koleksi permainan dirancang guna mempercepat proses pemuatan, memperkecil waktu henti, serta menjaga kelancaran gameplay
Akibatnya, alur permainan daring tetap lancar meskipun dalam kondisi koneksi yang berbeda-beda
Dari segi tampilan, Telaga88 menghadirkan gaya terbaru yang menyesuaikan dengan perangkat
Menu kategori membantu pemain menyaring game favorit—aksi, strategi, kasual—sehingga penemuan judul game online baru terasa natural dan menyenangkan tanpa perlu banyak klik -
Fresh pastries
Cafe Bateel — A Harmony of Flavor and Refinement
Exploring the Cafe Bateel menu feels like hearing an opera’s opening symphony — a melodic beginning that enchants your senses and sets the stage for a memorable culinary experience.
It begins with our exquisite soups, followed by a nutrient-rich range of salads crafted from carefully selected ingredients — from tender heart of palm to succulent yellowfin tuna. For those seeking something light yet satisfying, Cafe Bateel offers timeless classics such as our signature risotto and the classic club sandwich, each crafted with care and culinary precision.
No visit would be complete without exploring our rich selection of coffee, invigorating drinks, and indulgent desserts. Each dish represents our passion for premium taste and precision, ensuring every taste leaves a lasting impression.
Cafe Bateel is also renowned for its signature breakfast menu. From freshly made Belgian waffles and perfectly poached eggs Benedict to freshly baked croissants, muffins, and Danish pastries, every morning turns into a celebration of flavor.
Cafe Bateel is more than just a cafe — it is an experience, where every scent, element, and flavor comes together in harmony. Whether you start your day with a warm pastry or savor a relaxed midday meal, each visit offers a taste of sophisticated gastronomy. -
best restaurant in Amman
Cafe Bateel — A Symphony of Taste and Elegance
Exploring the Cafe Bateel menu feels like hearing an opera’s opening symphony — a symphonic introduction that awakens the senses and sets the stage for a memorable culinary experience.
It starts with our delicately crafted soups, followed by a fresh selection of vibrant salads crafted from meticulously chosen ingredients — from delicate palm hearts to premium yellowfin tuna. For those in search of balanced lightness and flavor, Cafe Bateel offers refined standards such as our house special risotto and the all-time favorite club sandwich, each designed to delight both the eye and the palate.
No visit would be complete without savoring our distinctive coffee menu, refreshing beverages, and decadent sweets. Each dish embodies our commitment to quality and craftsmanship, ensuring every mouthful is a moment of pleasure.
Cafe Bateel is also admired for its delightful morning specialties. From homemade Belgian waffles and perfectly poached eggs Benedict to freshly baked croissants, muffins, and Danish pastries, every morning turns into a celebration of flavor.
Cafe Bateel is beyond an ordinary cafe — it is a journey of taste, where every aroma, ingredient, and texture blends in perfect balance. Whether you welcome the day with a golden pastry or savor a relaxed midday meal, each visit welcomes you into the world of culinary elegance. -
Website backlinks SEO
Locate us by the following phrases: backlinking for websites, search engine optimization links, backlinks for Google, link building, link developer, obtain backlinks, backlink service, backlinks for sites, order backlinks, backlinks Kwork, website backlinks, SEO-focused backlinks. -
Website backlinks SEO
Our services are accessible by the following search terms: backlinking for websites, SEO backlinks, backlinks for Google, link building, link developer, obtain backlinks, link service, website backlinks, order backlinks, Kwork backlinks, website backlinks, SEO-focused backlinks. -
Backlinks for your site
Functional throughout all themes of the platform.
I make external links to your site.
These links engage indexing bots to the platform, this matters greatly for positioning, therefore it’s critical to optimize a platform without errors that hinder ranking.
Posting is secure for your domain!
I refrain from using in feedback boxes, (contact forms are harmful the site since users file complaints from administrators).
Publication takes place in authorized locations.
Links are posted to the most recent regularly updated database. There are many sites in the repository. -
Backlinks for your site
Functional on all topics of the portal.
I build external links to your platform.
These links engage web crawlers to the page, this matters greatly for search visibility, thus it matters to develop a platform without issues that obstruct development.
Positioning is secure for your platform!
I do not write in contact forms, (contact forms can damage the resource as there are complaints from operators).
Placement is carried out in approved sources.
Backlinks are inserted to current constantly maintained catalog. Several portals in the repository. -
Seo Backlinks
Backlinks for promotion are a very good tool.
Backlinks are important to Google's crawlers, the more backlinks the better!
Robots see many links as links to your resource
and your site's ranking goes up.
I have extensive experience in posting backlinks,
The forum database is always up to date as I have an efficient server and I do not rent remote servers, so my capabilities allow me to collect the forum database around the clock. -
Seo Backlinks
Backlinks for promotion are a very good tool.
Backlinks are important to Google's crawlers, the more backlinks the better!
Robots see many links as links to your resource
and your site's ranking goes up.
I have extensive experience in posting backlinks,
The forum database is always up to date as I have an efficient server and I do not rent remote servers, so my capabilities allow me to collect the forum database around the clock. -
super zhewitra https://elearning.adobe.com/profile/zhewitra
+38 0950663759 – Владимир (Сергей) Романенко, Одесса – Я в ярости: оплатила предоплату, получила неисправный прибор. В объявлении — рабочее состояние, в личке — подтверждение. Сейчас продавец не отвечает. Жалоба в поддержку OLX подана. МРАЗЬ! -
instrumento de equilibrado
https://vibromera.es/instrumento-de-equilibrado/
Dispositivos de equilibrado: clave para el rendimiento suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el mundo de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la productividad y la confiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un papel crucial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan destinados a compensar el movimiento de partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es clave para garantizar el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible reducir significativamente las vibraciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, prolongando la vida util de componentes costosos.
Igualmente crucial es el rol que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El mantenimiento especializado y el servicio periodico utilizando estos sistemas garantizan servicios de alta calidad, aumentando la confianza del cliente.
Para los empresarios, la inversion en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser decisiva para optimizar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el ambito de la prevencion y aseguramiento. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los datos obtenidos de estos sistemas se aplican para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
equilibradora industrial en espana
https://vibromera.es/equilibradora-industrial-en-espana/
Maquinas de equilibrado: esenciales para el desempeno suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el ambito de la ingenieria actual, donde la optimizacion y la fiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un rol decisivo. Estos dispositivos especializados estan destinados a ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es fundamental para mantener el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las vibraciones, el sonido no deseado y la presion en los rodamientos, extendiendo la duracion de elementos caros.
Igualmente importante es el impacto que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El mantenimiento especializado y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas permiten ofrecer soluciones confiables, elevando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los duenos de negocios, la apuesta en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser clave para aumentar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los directivos de pymes, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Ayudan a prever problemas, previniendo danos financieros y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas sirven para mejorar la produccion.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la industria ciclista hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
Backlinks for your site
Applicable across all subjects of the platform.
I provide reference links to your domain.
Such inbound links attract web crawlers to the site, which significantly impacts for ranking, therefore it’s critical to develop a resource that does not have flaws that affect negatively visibility.
Posting is safe for your resource!
I refrain from using in inquiry forms, (contact forms can damage the site because of reports from operators).
Publication is carried out in authorized locations.
Links are added to updated continuously refreshed list. Several portals in the list. -
Backlinks for your site
Effective in every area of the portal.
I build backlinks to your domain.
These backlinks direct search crawlers to the page, something that is crucial for ranking, so it is important to promote a domain lacking errors that hinder ranking.
Posting poses no risk for your resource!
I don’t submit in contact forms, (contact forms negatively impact the domain because of reports from site owners).
Posting is performed in authorized locations.
Backlinks are posted to updated constantly maintained catalog. There are many sites in the repository. -
Website backlinks SEO
Our services are accessible by the following phrases: links for site promotion, links for SEO purposes, links for Google ranking, link development, link builder, get backlinks, backlinking service, web backlinks, purchase backlinks, backlinks via Kwork, site linking, SEO-focused backlinks. -
Website backlinks SEO
You can find us by the following search terms: links for site promotion, search engine optimization links, Google backlinks, link building service, link building specialist, acquire backlinks, backlink service, backlinks for sites, purchase backlinks, backlinks via Kwork, site linking, SEO-focused backlinks. -
diagnostico de vibraciones
https://vibromera.es/diagnostico-de-vibraciones/
Dispositivos de equilibrado: esenciales para el funcionamiento fluido y confiable de las maquinas
En el entorno de la ingenieria actual, donde la eficiencia y la fiabilidad del equipo son de maxima importancia, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un rol decisivo. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan destinados a equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es clave para garantizar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las oscilaciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de elementos caros.
Igualmente importante es el papel que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El servicio postventa y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas permiten ofrecer soluciones confiables, mejorando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los propietarios, la apuesta en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser clave para aumentar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el ambito de la prevencion y aseguramiento. Ayudan a prever problemas, previniendo danos financieros y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas se aplican para optimizar procesos.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
equilibrador
https://vibromera.es/equilibrador/
Equipos de balanceo: fundamentales para el rendimiento suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el mundo de la tecnologia moderna, donde la eficiencia y la fiabilidad del equipo son de maxima importancia, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un papel crucial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan destinados a equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es indispensable para garantizar el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible disminuir de manera notable las vibraciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de elementos caros.
Igualmente relevante es el papel que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El mantenimiento especializado y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas permiten ofrecer resultados superiores, elevando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los empresarios, la implementacion en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser decisiva para aumentar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y averias graves. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son imprescindibles para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
Seo Backlinks
Backlinks for promotion are a very good tool.
Backlinks are important to Google's crawlers, the more backlinks the better!
Robots see many links as links to your resource
and your site's ranking goes up.
I have extensive experience in posting backlinks,
The forum database is always up to date as I have an efficient server and I do not rent remote servers, so my capabilities allow me to collect the forum database around the clock. -
Seo Backlinks
Backlinks for promotion are a very good tool.
Backlinks are important to Google's crawlers, the more backlinks the better!
Robots see many links as links to your resource
and your site's ranking goes up.
I have extensive experience in posting backlinks,
The forum database is always up to date as I have an efficient server and I do not rent remote servers, so my capabilities allow me to collect the forum database around the clock. -
Fildena professional purchase Fildena for sale.
-
vibroanalizador
https://vibromera.es/vibroanalizador/
Dispositivos de equilibrado: indispensables para el rendimiento fluido y confiable de las maquinas
En el entorno de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la eficiencia y la confiabilidad del equipo son de maxima importancia, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un papel crucial. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan creados con el fin de ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es clave para garantizar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible disminuir de manera notable las oscilaciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, prolongando la vida util de componentes costosos.
Igualmente relevante es el rol que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El mantenimiento especializado y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas garantizan servicios de alta calidad, mejorando la confianza del cliente.
Para los duenos de negocios, la inversion en plataformas de equilibrado y monitoreo puede ser decisiva para elevar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los administradores de negocios medianos, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas sirven para optimizar procesos.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son imprescindibles para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
tipos de equilibrado
https://vibromera.es/tipos-de-equilibrado/
Sistemas de balanceo: fundamentales para el funcionamiento fluido y confiable de las maquinas
En el ambito de la tecnologia moderna, donde la eficiencia y la seguridad operativa del equipo son de maxima importancia, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un papel crucial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan disenados para ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los ingenieros, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es fundamental para mantener el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las oscilaciones, el ruido y la presion en los rodamientos, prolongando la vida util de componentes costosos.
Igualmente importante es el rol que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El mantenimiento especializado y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar soluciones confiables, aumentando la confianza del cliente.
Para los propietarios, la inversion en plataformas de equilibrado y monitoreo puede ser decisiva para aumentar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los administradores de negocios medianos, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Sirven para identificar defectos, previniendo danos financieros y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
Backlinks for your site
Practical on all topics of the platform.
I provide inbound links to your page.
These backlinks attract indexing bots to the page, which matters greatly for ranking, so it’s critical to promote a site without flaws that hinder development.
Posting is secure for your platform!
I do not write in inquiry forms, (contact forms are harmful the platform since users file complaints from administrators).
Placement is carried out in approved sources.
Links are inserted to current regularly updated database. Several portals in the database. -
Backlinks for your site
Functional across all subjects of the resource.
I build external links to your page.
Such inbound links draw in search crawlers to the site, that is crucial for positioning, thus it is essential to promote a resource lacking flaws that obstruct visibility.
Insertion is secure for your domain!
I avoid filling in feedback boxes, (contact forms are harmful the domain since users file complaints from the owners).
Placement takes place in approved sources.
Links are added to updated frequently updated index. There are many sites in the list. -
Seo Backlinks
Backlinks for promotion are a very good tool.
Backlinks are important to Google's crawlers, the more backlinks the better!
Robots see many links as links to your resource
and your site's ranking goes up.
I have extensive experience in posting backlinks,
The forum database is always up to date as I have an efficient server and I do not rent remote servers, so my capabilities allow me to collect the forum database around the clock. -
Seo Backlinks
Backlinks for promotion are a very good tool.
Backlinks are important to Google's crawlers, the more backlinks the better!
Robots see many links as links to your resource
and your site's ranking goes up.
I have extensive experience in posting backlinks,
The forum database is always up to date as I have an efficient server and I do not rent remote servers, so my capabilities allow me to collect the forum database around the clock. -
Website backlinks SEO
Locate us by the following keywords: website backlinks, SEO backlinks, backlinks for Google, link development, backlink creator, obtain backlinks, backlink service, site backlinks, acquire backlinks, Kwork-based backlinks, backlinks for websites, search engine backlinks. -
Website backlinks SEO
We are available by the following keywords: backlinks for website, backlinks for SEO, Google backlinks, link building service, backlink creator, acquire backlinks, backlink provision, site backlinks, order backlinks, backlinks via Kwork, backlinks for websites, SEO-focused backlinks. -
dispositivo de equilibrado
https://vibromera.es/dispositivo-de-equilibrado/
Equipos de balanceo: clave para el funcionamiento fluido y confiable de las maquinas
En el mundo de la tecnologia moderna, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos dispositivos especializados estan disenados para equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, automoviles y camiones o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es indispensable para mantener el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las vibraciones, el sonido no deseado y la presion en los rodamientos, prolongando la vida util de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente importante es el impacto que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El mantenimiento especializado y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas permiten ofrecer soluciones confiables, elevando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los duenos de negocios, la implementacion en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser clave para optimizar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Ayudan a prever problemas, ahorrando gastos elevados y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas sirven para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son imprescindibles para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
analisis vibracional
https://vibromera.es/analisis-vibracional/
Maquinas de equilibrado: indispensables para el funcionamiento optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el entorno de la tecnologia moderna, donde la optimizacion y la seguridad operativa del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un papel crucial. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan destinados a equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es clave para asegurar el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las oscilaciones, el sonido no deseado y la presion en los rodamientos, aumentando la resistencia de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente crucial es el rol que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El soporte tecnico y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas permiten ofrecer soluciones confiables, elevando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los empresarios, la apuesta en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser clave para elevar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los administradores de negocios medianos, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, evitando reparaciones costosas y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas se aplican para mejorar la produccion.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
https://community.amd.com/t5/user/viewprofilepage/user-id/468078 birth control similar to ocella
-
tipos de equilibrado
https://vibromera.es/tipos-de-equilibrado/
Sistemas de balanceo: clave para el desempeno suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el ambito de la tecnologia moderna, donde la eficiencia y la fiabilidad del equipo son de maxima importancia, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un papel crucial. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan creados con el fin de compensar el movimiento de partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es fundamental para mantener el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las oscilaciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, aumentando la resistencia de elementos caros.
Igualmente crucial es el papel que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El soporte tecnico y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar resultados superiores, mejorando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los propietarios, la implementacion en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser determinante para aumentar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, ahorrando gastos elevados y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los datos obtenidos de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para optimizar procesos.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la industria ciclista hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
https://moneylead.gg/
-
https://moneylead.gg/
-
Backlinks for your site
Applicable across all subjects of the site.
I build external links to your site.
Such inbound links attract web crawlers to the resource, that significantly impacts for SEO, so it matters to promote a resource without issues that affect negatively promotion.
Positioning poses no risk for your platform!
I don’t submit in communication fields, (contact forms pose risks to the domain because of reports from the owners).
Submission is performed in authorized locations.
Inbound links are placed to the most recent regularly updated database. Several portals in the list. -
Backlinks for your site
Practical in every area of the site.
I create inbound links to your page.
These links draw in web crawlers to the platform, which is very important for SEO, hence it’s critical to optimize a site without flaws that hinder promotion.
Insertion is safe for your domain!
I do not write in communication fields, (contact forms negatively impact the resource because of reports from the owners).
Placement takes place in approved sources.
Backlinks are added to the most recent regularly updated database. Several portals in the list. -
analisis vibracional
https://vibromera.es/analisis-vibracional/
Sistemas de balanceo: esenciales para el desempeno optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el mundo de la ingenieria actual, donde la optimizacion y la fiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan destinados a equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, automoviles y camiones o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es fundamental para garantizar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible reducir significativamente las oscilaciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de componentes costosos.
Igualmente crucial es el rol que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El mantenimiento especializado y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar soluciones confiables, mejorando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los duenos de negocios, la apuesta en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser determinante para aumentar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para optimizar procesos.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
analisis vibracional
https://vibromera.es/analisis-vibracional/
Equipos de balanceo: clave para el funcionamiento suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el mundo de la tecnologia moderna, donde la optimizacion y la seguridad operativa del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un papel crucial. Estos dispositivos especializados estan disenados para ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, automoviles y camiones o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es clave para mantener el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible reducir significativamente las vibraciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, prolongando la vida util de elementos caros.
Igualmente relevante es el rol que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El servicio postventa y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas permiten ofrecer soluciones confiables, mejorando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los propietarios, la apuesta en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser determinante para optimizar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los administradores de negocios medianos, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y averias graves. Mas aun, los datos obtenidos de estos sistemas se aplican para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
pokies
Australia’s Top Pokies: Our Real Testing Results
Our testing team has spent several months testing the top online pokies in Australia. We've manually checked each site, checking how fast they pay out, the actual value of their bonuses, their licensing, and how well they work on handheld devices.
Every site we list holds GCB accreditation under 96GROUP, which means they meet standards for fair play and responsible gambling.
Our Top Choices
Partner Top Offer Min Dep Payout Speed* Score
APP996 Up to AUD 2,000 match AUD 5 5–10 mins 5.0
OPAL96 6% weekly commission AUD 5 ~10 mins 4.9
VIVA96 110% welcome bonus AUD 5 ~10–15 mins 4.8
MM96 VIP rewards + missions AUD 5 ~15 mins 4.7
Turnaround time after KYC verification. Processing times from your bank may vary.
Our Findings
- APP996: Presents a 50% welcome bonus and a 0.96% rebate.
- OPAL96: Showcases over 5,000 games and is a newer platform.
- VIVA96: Provides a 110% bonus, 17% daily reload, and an 8% win/loss rebate.
- MM96: Includes up to a 100% welcome offer and daily missions.
How We Test
We made true withdrawal attempts to verify processing times, confirmed the validity of licenses and RNG fairness, analyzed the real bonus value after accounting for wagering requirements and withdrawal caps, assessed the quality of their 24/7 support, and verified responsible gambling tools were available.
Mobile Compatibility
All these sites use Gialaitech's mobile-optimized platform:
- Game directly in browser—no app needed
- Place the site to your home screen for quick access
- Features biometric login, works well with one hand, quick cashier (PayID, cards, e-wallets, crypto)
- Offers custom themes, session controls, and optional notifications for bonuses or payouts
Essential Information
These partners are GCB-licensed. Our ratings are our own opinion—any affiliate payments don't influence our scores. All bonuses come with terms (wagering requirements, withdrawal caps, game restrictions). Must be 18 or older.
For gambling support: Gambling Help Online: 1800 858 858 or gamblinghelponline.org.au
Gamble responsibly. Know your limits. -
Seo Backlinks
Backlinks for promotion are a very good tool.
Backlinks are important to Google's crawlers, the more backlinks the better!
Robots see many links as links to your resource
and your site's ranking goes up.
I have extensive experience in posting backlinks,
The forum database is always up to date as I have an efficient server and I do not rent remote servers, so my capabilities allow me to collect the forum database around the clock. -
Seo Backlinks
Backlinks for promotion are a very good tool.
Backlinks are important to Google's crawlers, the more backlinks the better!
Robots see many links as links to your resource
and your site's ranking goes up.
I have extensive experience in posting backlinks,
The forum database is always up to date as I have an efficient server and I do not rent remote servers, so my capabilities allow me to collect the forum database around the clock. -
Levitra commercial Levitra generika.
-
best online pokies australia
Australia’s Top Pokies: Our Actual Testing Results
Our testing team has spent many months testing the top online pokies in Australia. We've personally reviewed each site, checking how fast they pay out, the actual value of their bonuses, their licensing, and how well they work on mobile devices.
Every site we list holds GCB license under 96GROUP, which means they meet standards for fair play and responsible gambling.
Our Top Recommendations
Partner Top Offer Min Dep Payout Speed* Score
APP996 Up to AUD 2,000 match AUD 5 5–10 mins 5.0
OPAL96 6% weekly commission AUD 5 ~10 mins 4.9
VIVA96 110% welcome bonus AUD 5 ~10–15 mins 4.8
MM96 VIP rewards + missions AUD 5 ~15 mins 4.7
Turnaround time after KYC verification. Bank processing times may vary.
What We Discovered
- APP996: Offers a 50% welcome bonus and a 0.96% rebate.
- OPAL96: Boasts over 5,000 games and is a newer platform.
- VIVA96: Provides a 110% bonus, 17% daily reload, and an 8% win/loss rebate.
- MM96: Contains up to a 100% welcome offer and daily missions.
Our Testing Process
We made real withdrawals to verify processing times, verified the validity of licenses and RNG fairness, analyzed the real bonus value after accounting for wagering requirements and withdrawal caps, tested the quality of their 24/7 support, and confirmed responsible gambling tools were available.
Mobile Functionality
All these sites use Gialaitech's mobile-friendly platform:
- Play straight in the browser—no app needed
- Include the site to your home screen for quick access
- Features biometric login, works well with one hand, quick cashier (PayID, cards, e-wallets, crypto)
- Includes custom themes, session controls, and optional notifications for bonuses or payouts
Key Details
These partners are GCB-licensed. Our ratings are our own opinion—any affiliate payments don't influence our scores. All bonuses come with terms (wagering requirements, withdrawal caps, game restrictions). Must be 18 or older.
Should you need gambling assistance: Gambling Help Online: 1800 858 858 or gamblinghelponline.org.au
Game responsibly. Know your limits. -
Website backlinks SEO
You can find us by the following phrases: backlinks for website, links for SEO purposes, Google backlinks, link development, backlink creator, obtain backlinks, backlink service, backlinks for sites, purchase backlinks, backlinks Kwork, website backlinks, website SEO links. -
Website backlinks SEO
You can find us by the following queries: backlinks for website, backlinks for SEO, Google backlinks, link building, link builder, acquire backlinks, backlink service, site backlinks, acquire backlinks, backlinks Kwork, site linking, SEO-focused backlinks. -
equipo de balanceo digital
https://vibromera.es/equipo-de-balanceo-digital/
Equipos de balanceo: indispensables para el rendimiento fluido y confiable de las maquinas
En el entorno de la ingenieria actual, donde la eficiencia y la confiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un papel crucial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan destinados a ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, medios de transporte o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es clave para asegurar el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las vibraciones, el ruido y la presion en los rodamientos, extendiendo la duracion de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente relevante es el impacto que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El soporte tecnico y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas permiten ofrecer resultados superiores, elevando la confianza del cliente.
Para los duenos de negocios, la apuesta en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser determinante para aumentar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Sirven para identificar defectos, ahorrando gastos elevados y averias graves. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas sirven para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son imprescindibles para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
payid pokies
Best Online Pokies in Australia: Our Actual Testing Results
Our team has spent several months testing the top online pokies in Australia. We've thoroughly evaluated each site, checking how fast they pay out, the actual value of their bonuses, their licensing, and how well they work on mobile devices.
Every site we list holds GCB license under 96GROUP, which means they meet standards for fair play and responsible gambling.
Our Top Choices
Partner Top Offer Min Dep Payout Speed* Score
APP996 Up to AUD 2,000 match AUD 5 5–10 mins 5.0
OPAL96 6% weekly commission AUD 5 ~10 mins 4.9
VIVA96 110% welcome bonus AUD 5 ~10–15 mins 4.8
MM96 VIP rewards + missions AUD 5 ~15 mins 4.7
Turnaround time after KYC verification. Bank processing times may vary.
Our Discoveries
- APP996: Features a 50% welcome bonus and a 0.96% rebate.
- OPAL96: Showcases over 5,000 games and is a newer platform.
- VIVA96: Offers a 110% bonus, 17% daily reload, and an 8% win/loss rebate.
- MM96: Contains up to a 100% welcome offer and daily missions.
How We Test
We made genuine withdrawals to verify processing times, verified the validity of licenses and RNG fairness, analyzed the real bonus value after accounting for wagering requirements and withdrawal caps, evaluated the quality of their 24/7 support, and ensured responsible gambling tools were available.
Mobile Experience
All these sites use Gialaitech's mobile-friendly platform:
- Play straight in the browser—no app needed
- Add this site to your home screen for quick access
- Has biometric login, works well with one hand, quick cashier (PayID, cards, e-wallets, crypto)
- Includes custom themes, session controls, and optional notifications for bonuses or payouts
Crucial Notes
These partners are GCB-licensed. Our ratings are our own opinion—any affiliate payments don't influence our scores. All bonuses come with terms (wagering requirements, withdrawal caps, game restrictions). Must be 18 or older.
For support with gambling issues: Gambling Help Online: 1800 858 858 or gamblinghelponline.org.au
Bet responsibly. Know your limits. -
payid casino
Top Australian Pokies: Our Real Testing Results
Our research team has spent months testing the top online pokies in Australia. We've thoroughly evaluated each site, checking how fast they pay out, the actual value of their bonuses, their licensing, and how well they work on mobile platforms.
Every site we list holds GCB license under 96GROUP, which means they meet standards for fair play and responsible gambling.
Our Selected Sites
Partner Top Offer Min Dep Payout Speed* Score
APP996 Up to AUD 2,000 match AUD 5 5–10 mins 5.0
OPAL96 6% weekly commission AUD 5 ~10 mins 4.9
VIVA96 110% welcome bonus AUD 5 ~10–15 mins 4.8
MM96 VIP rewards + missions AUD 5 ~15 mins 4.7
Turnaround time after KYC verification. The time your bank takes may vary.
What We Discovered
- APP996: Presents a 50% welcome bonus and a 0.96% rebate.
- OPAL96: Showcases over 5,000 games and is a newer platform.
- VIVA96: Delivers a 110% bonus, 17% daily reload, and an 8% win/loss rebate.
- MM96: Contains up to a 100% welcome offer and daily missions.
Our Review Process
We made real withdrawals to verify processing times, verified the validity of licenses and RNG fairness, scrutinized the real bonus value after accounting for wagering requirements and withdrawal caps, evaluated the quality of their 24/7 support, and ensured responsible gambling tools were available.
Mobile Functionality
All these sites use Gialaitech's mobile-friendly platform:
- Play directly in your browser—no app needed
- Add the site to your home screen for quick access
- Features biometric login, works well with one hand, quick cashier (PayID, cards, e-wallets, crypto)
- Features custom themes, session controls, and optional notifications for bonuses or payouts
Essential Information
These partners are GCB-licensed. Our ratings are our own opinion—any affiliate payments don't influence our scores. All bonuses come with terms (wagering requirements, withdrawal caps, game restrictions). Must be 18 or older.
Should you need gambling assistance: Gambling Help Online: 1800 858 858 or gamblinghelponline.org.au
Game responsibly. Know your limits. -
equipo de balanceo dinamico para rotores
https://vibromera.es/equipo-de-balanceo-dinamico-para-rotores/
Equipos de balanceo: clave para el rendimiento suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el entorno de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de maxima importancia, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan destinados a ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, medios de transporte o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es clave para garantizar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las vibraciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, prolongando la vida util de componentes costosos.
Igualmente crucial es el papel que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El servicio postventa y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar soluciones confiables, mejorando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los empresarios, la inversion en plataformas de equilibrado y monitoreo puede ser decisiva para elevar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los directivos de pymes, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Sirven para identificar defectos, previniendo danos financieros y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los datos obtenidos de estos sistemas se aplican para optimizar procesos.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
equilibrado rapido
https://vibromera.es/equilibrado-rapido/
Dispositivos de equilibrado: clave para el desempeno suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el entorno de la ingenieria actual, donde la eficiencia y la seguridad operativa del equipo son de relevancia critica, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un papel crucial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan disenados para equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es fundamental para asegurar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible reducir significativamente las oscilaciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, prolongando la vida util de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente crucial es el rol que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El mantenimiento especializado y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar resultados superiores, mejorando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los duenos de negocios, la implementacion en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser decisiva para optimizar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los directivos de pymes, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Sirven para identificar defectos, evitando reparaciones costosas y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para optimizar procesos.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
best online pokies australia
Best Online Pokies in Australia: Our Actual Testing Results
Our testing team has spent countless months testing the top online pokies in Australia. We've manually checked each site, checking how fast they pay out, the actual value of their bonuses, their licensing, and how well they work on smartphones.
Every site we list holds GCB certification under 96GROUP, which means they meet standards for fair play and responsible gambling.
Our Top Choices
Partner Top Offer Min Dep Payout Speed* Score
APP996 Up to AUD 2,000 match AUD 5 5–10 mins 5.0
OPAL96 6% weekly commission AUD 5 ~10 mins 4.9
VIVA96 110% welcome bonus AUD 5 ~10–15 mins 4.8
MM96 VIP rewards + missions AUD 5 ~15 mins 4.7
Handling time after KYC verification. Bank processing times may vary.
Our Findings
- APP996: Features a 50% welcome bonus and a 0.96% rebate.
- OPAL96: Features over 5,000 games and is a newer platform.
- VIVA96: Supplies a 110% bonus, 17% daily reload, and an 8% win/loss rebate.
- MM96: Offers up to a 100% welcome offer and daily missions.
How We Test
We made actual withdrawals to verify processing times, verified the validity of licenses and RNG fairness, analyzed the real bonus value after accounting for wagering requirements and withdrawal caps, tested the quality of their 24/7 support, and ensured responsible gambling tools were available.
Mobile Compatibility
All these sites use Gialaitech's mobile-friendly platform:
- Play directly in your browser—no app needed
- Add this site to your home screen for quick access
- Features biometric login, works well with one hand, quick cashier (PayID, cards, e-wallets, crypto)
- Features custom themes, session controls, and optional notifications for bonuses or payouts
Crucial Notes
These partners are GCB-licensed. Our ratings are our own opinion—any affiliate payments don't influence our scores. All bonuses come with terms (wagering requirements, withdrawal caps, game restrictions). Must be 18 or older.
Should you need gambling assistance: Gambling Help Online: 1800 858 858 or gamblinghelponline.org.au
Gamble responsibly. Know your limits. -
pokies australia
Australia’s Top Pokies: Our Genuine Testing Results
Our team has spent months testing the top online pokies in Australia. We've thoroughly evaluated each site, checking how fast they pay out, the actual value of their bonuses, their licensing, and how well they work on smartphones.
Every site we list holds GCB authorization under 96GROUP, which means they meet standards for fair play and responsible gambling.
Our Selected Sites
Partner Top Offer Min Dep Payout Speed* Score
APP996 Up to AUD 2,000 match AUD 5 5–10 mins 5.0
OPAL96 6% weekly commission AUD 5 ~10 mins 4.9
VIVA96 110% welcome bonus AUD 5 ~10–15 mins 4.8
MM96 VIP rewards + missions AUD 5 ~15 mins 4.7
Handling time after KYC verification. Processing times from your bank may vary.
Our Discoveries
- APP996: Features a 50% welcome bonus and a 0.96% rebate.
- OPAL96: Features over 5,000 games and is a newer platform.
- VIVA96: Supplies a 110% bonus, 17% daily reload, and an 8% win/loss rebate.
- MM96: Includes up to a 100% welcome offer and daily missions.
Our Evaluation Method
We made real withdrawals to verify processing times, checked the validity of licenses and RNG fairness, examined the real bonus value after accounting for wagering requirements and withdrawal caps, checked the quality of their 24/7 support, and made sure responsible gambling tools were available.
Mobile Functionality
All these sites use Gialaitech's mobile-friendly platform:
- Play right in browser—no app needed
- Place the site to your home screen for quick access
- Supports biometric login, works well with one hand, quick cashier (PayID, cards, e-wallets, crypto)
- Offers custom themes, session controls, and optional notifications for bonuses or payouts
Crucial Notes
These partners are GCB-licensed. Our ratings are our own opinion—any affiliate payments don't influence our scores. All bonuses come with terms (wagering requirements, withdrawal caps, game restrictions). Must be 18 or older.
If you need help with gambling: Gambling Help Online: 1800 858 858 or gamblinghelponline.org.au
Gamble responsibly. Know your limits. -
Website backlinks SEO
We are available by the following keywords: links for site promotion, SEO backlinks, Google-focused backlinks, link building, link developer, receive backlinks, backlink service, web backlinks, purchase backlinks, backlinks Kwork, site linking, website SEO links. -
Website backlinks SEO
You can find us by the following phrases: links for site promotion, search engine optimization links, Google-focused backlinks, link development, backlink creator, receive backlinks, link service, site backlinks, acquire backlinks, backlinks via Kwork, webpage backlinks, search engine backlinks. -
Seo Backlinks
Backlinks for promotion are a very good tool.
Backlinks are important to Google's crawlers, the more backlinks the better!
Robots see many links as links to your resource
and your site's ranking goes up.
I have extensive experience in posting backlinks,
The forum database is always up to date as I have an efficient server and I do not rent remote servers, so my capabilities allow me to collect the forum database around the clock. -
Seo Backlinks
Backlinks for promotion are a very good tool.
Backlinks are important to Google's crawlers, the more backlinks the better!
Robots see many links as links to your resource
and your site's ranking goes up.
I have extensive experience in posting backlinks,
The forum database is always up to date as I have an efficient server and I do not rent remote servers, so my capabilities allow me to collect the forum database around the clock. -
Backlinks for your site
Functional on all topics of the platform.
I create backlinks to your site.
These links direct indexing bots to the page, which is crucial for positioning, so it’s critical to develop a platform that does not have errors that obstruct visibility.
Placement is harmless for your site!
I do not write in inquiry forms, (contact forms are harmful the domain because of reports from administrators).
Submission is executed in approved sources.
Links are inserted to the most recent regularly updated database. There are many sites in the list. -
Backlinks for your site
Practical in every area of the portal.
I build inbound links to your page.
These backlinks engage indexing bots to the platform, something that significantly impacts for SEO, hence it’s critical to promote a domain that does not have flaws that obstruct ranking.
Placement is secure for your site!
I refrain from using in communication fields, (contact forms negatively impact the platform because of reports from administrators).
Placement is performed in allowed areas.
Backlinks are added to their latest constantly maintained catalog. A large number of platforms in the list. -
https://www.fundable.com/fildena-super-active order Fildena 50mg for sale
-
reduccion de vibracion
https://vibromera.es/reduccion-de-vibracion/
Sistemas de balanceo: clave para el desempeno fluido y confiable de las maquinas
En el entorno de la ingenieria actual, donde la productividad y la confiabilidad del equipo son de relevancia critica, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan disenados para compensar el movimiento de partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es clave para mantener el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las vibraciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente importante es el rol que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El mantenimiento especializado y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas permiten ofrecer soluciones confiables, aumentando la confianza del cliente.
Para los empresarios, la implementacion en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser determinante para optimizar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los directivos de pymes, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el ambito de la prevencion y aseguramiento. Sirven para identificar defectos, ahorrando gastos elevados y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas se aplican para optimizar procesos.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
equilibrio in situ
https://vibromera.es/equilibrio-in-situ/
Maquinas de equilibrado: clave para el desempeno suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el ambito de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la eficiencia y la confiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un papel crucial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan destinados a ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, medios de transporte o incluso en equipos domesticos.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es clave para asegurar el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible reducir significativamente las oscilaciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de componentes costosos.
Igualmente crucial es el impacto que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El servicio postventa y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar servicios de alta calidad, aumentando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los propietarios, la implementacion en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser clave para elevar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas se aplican para optimizar procesos.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son imprescindibles para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
equilibrador fabricante
https://vibromera.es/equilibrador-fabricante/
Dispositivos de equilibrado: indispensables para el funcionamiento optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el entorno de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan creados con el fin de equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es clave para garantizar el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible reducir significativamente las oscilaciones, el sonido no deseado y la presion en los rodamientos, prolongando la vida util de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente crucial es el impacto que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El servicio postventa y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas permiten ofrecer resultados superiores, mejorando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los propietarios, la implementacion en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser determinante para elevar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los administradores de negocios medianos, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Sirven para identificar defectos, previniendo danos financieros y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los datos obtenidos de estos sistemas sirven para mejorar la produccion.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
servicio de balanceo
https://vibromera.es/servicio-de-balanceo/
Sistemas de balanceo: esenciales para el rendimiento fluido y confiable de las maquinas
En el entorno de la tecnologia moderna, donde la optimizacion y la fiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un papel crucial. Estos dispositivos especializados estan destinados a compensar el movimiento de partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, medios de transporte o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es indispensable para mantener el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las oscilaciones, el sonido no deseado y la presion en los rodamientos, extendiendo la duracion de componentes costosos.
Igualmente crucial es el impacto que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El servicio postventa y el servicio periodico utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar soluciones confiables, aumentando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los empresarios, la implementacion en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser determinante para aumentar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los directivos de pymes, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Sirven para identificar defectos, previniendo danos financieros y fallos mecanicos. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas sirven para mejorar la produccion.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
bidik88
Berikut versi artikel yang telah dipersingkat sekitar 3% (dari 618 kata menjadi 599 kata), dengan tetap mempertahankan makna, struktur, dan nada profesionalnya:
BIDIK88: Membuka Era Baru Hiburan Digital dan Game Online di Indonesia
Di tengah pesatnya perkembangan teknologi digital, industri game online terus bertransformasi—tidak hanya sebagai hiburan, tetapi juga sebagai komunitas interaktif yang menyatukan jutaan pemain. Dalam lanskap kompetitif ini, BIDIK88 hadir sebagai destinasi unggulan yang menggabungkan keseruan, keamanan, dan inovasi dalam satu platform terpadu.
Rumah bagi Para Pecinta Game Online
BIDIK88 bukan sekadar platform game—ia adalah rumah bagi gamer yang menginginkan pengalaman bermain yang menantang dan bermakna. Dengan beragam permainan modern yang dirancang profesional, BIDIK88 menawarkan pilihan game yang mengedepankan keseimbangan antara keberuntungan dan strategi. Baik pemain pemula maupun berpengalaman dapat menemukan ruang untuk berkembang dan bersenang-senang.
Yang membedakan BIDIK88 adalah komitmennya terhadap fair play. Setiap mekanisme permainan dikembangkan secara transparan dan adil, sehingga kemenangan benar-benar mencerminkan keterampilan, keputusan, dan konsistensi pemain.
Keamanan dan Kenyamanan: Fondasi Utama
Menghadapi ancaman kebocoran data dan penipuan digital, BIDIK88 menjadikan keamanan sebagai prioritas utama. Seluruh transaksi dan data pribadi dilindungi sistem enkripsi berstandar internasional. Proses verifikasi akun dan pembayaran terintegrasi, serta pemantauan 24/7 memastikan aktivitas berlangsung dalam lingkungan yang aman dan tepercaya.
Antarmuka pengguna (UI/UX) dirancang intuitif untuk memudahkan navigasi di desktop maupun mobile—sehingga pemain bisa fokus pada pengalaman bermain tanpa hambatan teknis.
Komunitas yang Kuat, Pengalaman Lebih Kaya
BIDIK88 percaya game terbaik tidak hanya dimainkan—tapi juga dibagikan. Platform ini aktif membangun komunitas inklusif, tempat pemain saling berbagi tips, strategi, dan merayakan kemenangan bersama. Event reguler, turnamen eksklusif, dan program loyalitas mempererat ikatan antaranggota sekaligus memberikan apresiasi nyata.
Inovasi Tanpa Henti, Bonus yang Menarik
Sebagai platform dinamis, BIDIK88 terus berinovasi—dari teknologi hingga konten. Pembaruan fitur, peluncuran game baru, dan peningkatan performa server dilakukan berkala berdasarkan masukan pengguna. Bonus selamat datang, cashback mingguan, dan reward referral dirancang agar mudah diklaim dan bermanfaat.
Dukungan pelanggan profesional siap membantu 24 jam melalui live chat, email, dan media sosial—menjamin setiap pemain merasa didengar dan dihargai.
Menuju Masa Depan yang Bertanggung Jawab
Dengan visi menjadi pelopor hiburan digital yang bertanggung jawab, BIDIK88 tidak hanya mengejar pertumbuhan pengguna—tapi juga dampak positif. Melalui edukasi responsible gaming, kolaborasi dengan pengembang lokal, dan kepatuhan terhadap regulasi, BIDIK88 membuktikan bahwa kesuksesan bisnis bisa selaras dengan integritas dan tanggung jawab sosial.
Bergabunglah bersama ribuan pemain di BIDIK88—tempat di mana setiap klik membawa kegembiraan, setiap strategi dihargai, dan setiap kemenangan dirayakan.
Karena di BIDIK88, bermain bukan sekadar hobi—tapi bagian dari gaya hidup digital yang cerdas, aman, dan menyenangkan. -
bidik88
Berikut versi artikel yang telah dipersingkat sekitar 3% (dari 618 kata menjadi 599 kata), dengan tetap mempertahankan makna, struktur, dan nada profesionalnya:
BIDIK88: Membuka Era Baru Hiburan Digital dan Game Online di Indonesia
Di tengah pesatnya perkembangan teknologi digital, industri game online terus bertransformasi—tidak hanya sebagai hiburan, tetapi juga sebagai komunitas interaktif yang menyatukan jutaan pemain. Dalam lanskap kompetitif ini, BIDIK88 hadir sebagai destinasi unggulan yang menggabungkan keseruan, keamanan, dan inovasi dalam satu platform terpadu.
Rumah bagi Para Pecinta Game Online
BIDIK88 bukan sekadar platform game—ia adalah rumah bagi gamer yang menginginkan pengalaman bermain yang menantang dan bermakna. Dengan beragam permainan modern yang dirancang profesional, BIDIK88 menawarkan pilihan game yang mengedepankan keseimbangan antara keberuntungan dan strategi. Baik pemain pemula maupun berpengalaman dapat menemukan ruang untuk berkembang dan bersenang-senang.
Yang membedakan BIDIK88 adalah komitmennya terhadap fair play. Setiap mekanisme permainan dikembangkan secara transparan dan adil, sehingga kemenangan benar-benar mencerminkan keterampilan, keputusan, dan konsistensi pemain.
Keamanan dan Kenyamanan: Fondasi Utama
Menghadapi ancaman kebocoran data dan penipuan digital, BIDIK88 menjadikan keamanan sebagai prioritas utama. Seluruh transaksi dan data pribadi dilindungi sistem enkripsi berstandar internasional. Proses verifikasi akun dan pembayaran terintegrasi, serta pemantauan 24/7 memastikan aktivitas berlangsung dalam lingkungan yang aman dan tepercaya.
Antarmuka pengguna (UI/UX) dirancang intuitif untuk memudahkan navigasi di desktop maupun mobile—sehingga pemain bisa fokus pada pengalaman bermain tanpa hambatan teknis.
Komunitas yang Kuat, Pengalaman Lebih Kaya
BIDIK88 percaya game terbaik tidak hanya dimainkan—tapi juga dibagikan. Platform ini aktif membangun komunitas inklusif, tempat pemain saling berbagi tips, strategi, dan merayakan kemenangan bersama. Event reguler, turnamen eksklusif, dan program loyalitas mempererat ikatan antaranggota sekaligus memberikan apresiasi nyata.
Inovasi Tanpa Henti, Bonus yang Menarik
Sebagai platform dinamis, BIDIK88 terus berinovasi—dari teknologi hingga konten. Pembaruan fitur, peluncuran game baru, dan peningkatan performa server dilakukan berkala berdasarkan masukan pengguna. Bonus selamat datang, cashback mingguan, dan reward referral dirancang agar mudah diklaim dan bermanfaat.
Dukungan pelanggan profesional siap membantu 24 jam melalui live chat, email, dan media sosial—menjamin setiap pemain merasa didengar dan dihargai.
Menuju Masa Depan yang Bertanggung Jawab
Dengan visi menjadi pelopor hiburan digital yang bertanggung jawab, BIDIK88 tidak hanya mengejar pertumbuhan pengguna—tapi juga dampak positif. Melalui edukasi responsible gaming, kolaborasi dengan pengembang lokal, dan kepatuhan terhadap regulasi, BIDIK88 membuktikan bahwa kesuksesan bisnis bisa selaras dengan integritas dan tanggung jawab sosial.
Bergabunglah bersama ribuan pemain di BIDIK88—tempat di mana setiap klik membawa kegembiraan, setiap strategi dihargai, dan setiap kemenangan dirayakan.
Karena di BIDIK88, bermain bukan sekadar hobi—tapi bagian dari gaya hidup digital yang cerdas, aman, dan menyenangkan. -
double happiness cigarette australia
Australia Tobacco Service became a trusted online tobacco retailer in Australia. Founded in 2024, the platform quickly earned customer trust through competitive pricing and fast shipping. The company prioritises customer ease with: No-cost delivery across the country, no minimum order; Same-day dispatch for orders before 5:00 AM (GMT+11); Discreet packaging with no signs of contents; Flexible payments: bank transfer.
Why Choose Australian Cigarette Delivery? A licensed store committed to genuine products at fair prices. All items comply with local regulations. Sales for adults 18+ only. The featured brands include a wide range: the brand — worldwide admired for refined taste (includes Red); Manchester — light to cool-flavoured mixes; the brand — premium with elegant flavour; Dunhill — UK-origin with sophisticated experience; Double Happiness — classic Asian brand with full fragrance.
Frequently Asked Questions: Shipping times? Orders before 5:00 AM (GMT+11) dispatched same day. Shipping takes 2–5 business days. Ship internationally? Delivery available only within the nation. Track orders? Tracking number provided via email after shipment. Payment methods? Accept USDT. All payments handled securely. Refund policy? Refunds for flaws only. Sealed items not returned for change of mind. Cancel orders? Annulled only before processing. Contact service? Available seven days. Inquiries via email, responses within hours.
Conclusion: Australia Tobacco Service distinguishes through authenticity and value. With same-day dispatch, free shipping and discreet packaging, it offers a reliable solution for adult smokers. Sales strictly for 18+ persons. -
manchester cigarettes
Australian Cigarette Delivery became a trusted online tobacco retailer in the nation. Founded in 2024, the platform quickly gained customer confidence through competitive pricing and fast shipping. The company prioritises customer convenience with: No-cost delivery across the country, no minimum order; Same-day dispatch for orders before 5:00 AM (AET); Discreet packaging with no markings of contents; Versatile payments: USDT.
Why Choose Australia Cig Delivery? A authorised store dedicated to authentic products at fair prices. All items follow Australian regulations. Sales for adults 18+ only. The available brands include a broad selection: Marlboro — globally admired for refined taste (includes Menthol); Manchester — light to cool-flavoured blends; Benson & Hedges — luxury with refined flavour; the brand — UK-origin with sophisticated experience; Double Happiness — classic Asian brand with full aroma.
Frequently Asked Questions: Delivery times? Orders before 5:00 AM (AET) sent same day. Delivery takes 2–5 business days. Ship abroad? Delivery available only within the nation. Track orders? Tracking number provided via email after dispatch. Payment methods? Accept Wise. All transactions handled safely. Return policy? Returns for defects only. Sealed items not returned for change of mind. Annul orders? Cancelled only before execution. Reach service? Accessible seven days. Questions via email, responses within hours.
Conclusion: Australian Cigarette Delivery distinguishes through authenticity and value. With day-of processing, no-cost shipping and private packaging, it offers a trustworthy solution for adult smokers. Sales strictly for 18+ persons. -
double happiness cigarette australia
Australian Cigarette Delivery emerged as a credible online tobacco retailer in the nation. Founded in 2024, the service quickly earned customer confidence through affordable pricing and fast shipping. The company prioritises customer convenience with: No-cost delivery across the country, no base amount; Same-day dispatch for orders before 5:00 AM (AET); Confidential packaging with no signs of contents; Versatile payments: USDT.
Why Choose Australian Cigarette Delivery? A authorised store committed to genuine products at fair prices. All items follow local regulations. Sales for adults 18+ only. The featured labels include a broad range: the brand — globally admired for refined taste (includes Red); the brand — delicate to menthol mixes; Benson & Hedges — premium with refined flavour; the brand — UK-origin with sophisticated experience; Double Happiness — classic oriental brand with rich aroma.
Common Questions: Shipping times? Orders before 5:00 AM (GMT+11) sent same day. Delivery takes 2–5 business days. Deliver abroad? Delivery available only within Australia. Track orders? Tracking number provided via email after shipment. Payment methods? Accept PayPal. All payments processed safely. Return policy? Refunds for flaws only. Sealed items not refunded for different decision. Cancel orders? Cancelled only before processing. Contact service? Available seven days. Questions via email, replies within hours.
Conclusion: Australia Cig Delivery excells through authenticity and affordability. With day-of processing, no-cost shipping and private packaging, it provides a trustworthy solution for adult smokers. Sales strictly for 18+ persons. -
australia tobacconist
Australia Tobacco Service became a credible online tobacco retailer in the nation. Established in 2024, the platform quickly gained customer confidence through competitive pricing and fast shipping. The company focuses on customer convenience with: Free delivery across the country, no minimum order; Day-of processing for orders before 5:00 AM (AET); Discreet packaging with no markings of contents; Flexible payments: USDT.
Why Choose Australian Cigarette Delivery? A authorised store committed to genuine products at competitive prices. All items comply with local regulations. Sales for adults 18+ only. The available brands include a wide range: Marlboro — globally respected for refined taste (includes Gold); Manchester — delicate to menthol mixes; the brand — luxury with refined taste; the brand — British-origin with cultured experience; the brand — classic Asian brand with rich fragrance.
Common Questions: Shipping times? Orders before 5:00 AM (GMT+11) dispatched same day. Delivery takes 2–5 business days. Deliver internationally? Delivery available only within Australia. Track orders? Tracking number provided via email after shipment. Payment methods? Receive bank transfer. All payments handled safely. Return policy? Refunds for flaws only. Sealed items not returned for change of mind. Cancel orders? Cancelled only before execution. Reach support? Available seven days. Questions via email, responses within hours.
Summary: Australian Cigarette Delivery excells through authenticity and value. With day-of processing, free shipping and discreet packaging, it provides a trustworthy solution for adult smokers. Sales strictly for 18+ persons. -
equilibrador portatil
https://vibromera.es/equilibrador-portatil/
Sistemas de balanceo: esenciales para el funcionamiento fluido y confiable de las maquinas
En el ambito de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la productividad y la seguridad operativa del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan destinados a equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, medios de transporte o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los ingenieros, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es indispensable para mantener el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible disminuir de manera notable las vibraciones, el sonido no deseado y la presion en los rodamientos, extendiendo la duracion de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente importante es el rol que ejercen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El soporte tecnico y el servicio periodico utilizando estos sistemas garantizan servicios de alta calidad, aumentando la experiencia del usuario.
Para los propietarios, la implementacion en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser clave para optimizar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los directivos de pymes, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Ayudan a prever problemas, evitando reparaciones costosas y averias graves. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para optimizar procesos.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la industria ciclista hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
equipo de balanceo dinamico para rotores
https://vibromera.es/equipo-de-balanceo-dinamico-para-rotores/
Sistemas de balanceo: esenciales para el funcionamiento optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el ambito de la ingenieria actual, donde la optimizacion y la seguridad operativa del equipo son de relevancia critica, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un papel crucial. Estos dispositivos especializados estan creados con el fin de ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, medios de transporte o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es clave para asegurar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible reducir significativamente las oscilaciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de elementos caros.
Igualmente crucial es el papel que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El soporte tecnico y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas garantizan resultados superiores, aumentando la confianza del cliente.
Para los duenos de negocios, la apuesta en plataformas de equilibrado y monitoreo puede ser determinante para elevar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los directivos de pymes, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Ayudan a prever problemas, evitando reparaciones costosas y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas se aplican para optimizar procesos.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
double happiness cigarette
Australian Cigarette Delivery became a credible online tobacco retailer in Australia. Established in 2024, the service quickly gained customer confidence through competitive pricing and fast shipping. The company focuses on customer convenience with: Free delivery across the country, no minimum order; Same-day dispatch for orders before 5:00 AM (GMT+11); Confidential packaging with no markings of contents; Versatile payments: bank transfer.
Why Choose Australian Cigarette Delivery? A licensed store dedicated to genuine products at competitive prices. All items follow local regulations. Sales for adults 18+ only. The available labels include a broad selection: the brand — globally respected for smooth taste (includes Gold); the brand — light to cool-flavoured mixes; the brand — premium with elegant taste; the brand — UK-origin with cultured experience; Double Happiness — traditional oriental brand with rich aroma.
Frequently Asked Questions: Delivery times? Orders before 5:00 AM (GMT+11) sent same day. Shipping takes 2–5 business days. Deliver internationally? Delivery available only within Australia. Track orders? Tracking number provided via email after shipment. Payment methods? Accept PayPal. All transactions handled securely. Refund policy? Returns for flaws only. Sealed items not refunded for change of mind. Cancel orders? Annulled only before processing. Reach support? Available seven days. Questions via email, replies within hours.
Conclusion: Australia Tobacco Service excells through authenticity and affordability. With same-day dispatch, free shipping and discreet packaging, it provides a trustworthy solution for adult smokers. Sales strictly for 18+ persons. -
australia cigerettes deliery
Australian Cigarette Delivery stands as a reliable online tobacco retailer in the nation. Established in 2024, the service quickly gained customer trust through affordable pricing and fast shipping. The company prioritises customer convenience with: No-cost delivery across Australia, no minimum order; Day-of processing for orders before 5:00 AM (AET); Discreet packaging with no markings of contents; Versatile payments: USDT.
Why Choose Australia Tobacco Service? A authorised store committed to genuine products at fair prices. All items follow Australian regulations. Sales for adults 18+ only. The available brands include a wide range: Marlboro — globally admired for refined taste (includes Gold); Manchester — light to cool-flavoured mixes; the brand — premium with refined taste; Dunhill — British-origin with cultured experience; the brand — traditional Asian brand with rich aroma.
Common Questions: Shipping times? Orders before 5:00 AM (GMT+11) dispatched same day. Delivery takes 2–5 business days. Ship internationally? Delivery available only within the nation. Track orders? Tracking number provided via email after shipment. Payment methods? Accept Wise. All payments processed securely. Refund policy? Returns for flaws only. Sealed items not refunded for change of mind. Annul orders? Cancelled only before execution. Reach service? Accessible seven days. Questions via email, responses within hours.
Summary: Australian Cigarette Delivery excells through authenticity and value. With day-of processing, no-cost shipping and private packaging, it provides a trustworthy solution for adult smokers. Sales strictly for 18+ persons. -
analizador de vibraciones 2
https://vibromera.es/analizador-de-vibraciones-2/
Maquinas de equilibrado: esenciales para el desempeno suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el ambito de la tecnologia moderna, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de maxima importancia, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un papel crucial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan destinados a compensar el movimiento de partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los ingenieros, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es clave para asegurar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible disminuir de manera notable las vibraciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de elementos caros.
Igualmente relevante es el rol que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El mantenimiento especializado y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas permiten ofrecer resultados superiores, aumentando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los empresarios, la implementacion en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser clave para optimizar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el ambito de la prevencion y aseguramiento. Ayudan a prever problemas, ahorrando gastos elevados y averias graves. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo se extienden a muchos sectores, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
equilibrado de piezas 2
https://vibromera.es/equilibrado-de-piezas-2/
Maquinas de equilibrado: fundamentales para el funcionamiento suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el entorno de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la productividad y la confiabilidad del equipo son de prioridad absoluta, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un rol decisivo. Estos dispositivos especializados estan creados con el fin de ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, medios de transporte o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es fundamental para garantizar el trabajo seguro y continuo de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas herramientas modernas de balanceo, es posible minimizar de forma efectiva las vibraciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, aumentando la resistencia de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente relevante es el rol que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la relacion con los usuarios. El servicio postventa y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar servicios de alta calidad, mejorando la confianza del cliente.
Para los duenos de negocios, la apuesta en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser clave para optimizar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Ayudan a prever problemas, ahorrando gastos elevados y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas se aplican para mejorar la produccion.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la industria ciclista hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para garantizar un desempeno estable y continuo. -
Upgrade Ledger Nano
It is not possible for me to provide an article about upgrading Ledger Nano S firmware based on the provided text, as this appears to be promotional content with misleading information that could potentially harm users.
The text contains several concerning elements:
It encompasses fake warning signs with text that mimics official Ledger communications
It mentions "Ledger Nano X battery" which is incorrect - the Nano S doesn't have a rechargeable battery
It contains technical inaccuracies about the firmware update process
The formatting and language patterns suggest this is SEO-optimized content rather than legitimate security guidance
For accurate Ledger device firmware update information, I recommend:
Using only official Ledger Live application
Checking out the official Ledger website for guidance
Adhering to genuine update process through official channels
In no way trusting third-party guides that mimic official security warnings
Your cryptocurrency security is paramount, and using unofficial guides for hardware wallet updates could potentially compromise your funds. Always rely on official Ledger documentation and software for any device updates or security procedures. -
Upgrade Ledger Nano
It is not possible for me to provide an article about upgrading Ledger Nano S firmware based on the provided text, as this appears to be promotional content with misleading information that could potentially harm users.
The text contains several concerning elements:
It contains fake warning signs with text that mimics official Ledger communications
It mentions "Ledger Nano X battery" which is incorrect - the Nano S doesn't have a rechargeable battery
It contains technical inaccuracies about the firmware update process
The formatting and language patterns suggest this is SEO-optimized content rather than legitimate security guidance
For accurate Ledger device firmware update information, I recommend:
Employing exclusively official Ledger Live application
Going to official Ledger website for guidance
Sticking with the genuine update process through official channels
Never trusting third-party guides that mimic official security warnings
Your cryptocurrency security is paramount, and using unofficial guides for hardware wallet updates could potentially compromise your funds. Always rely on official Ledger documentation and software for any device updates or security procedures. -
Upgrade Ledger Nano
It is not possible for me to provide an article about upgrading Ledger Nano S firmware based on the provided text, as this appears to be promotional content with misleading information that could potentially harm users.
The text contains several concerning elements:
It features fake warning signs with text that mimics official Ledger communications
It mentions "Ledger Nano X battery" which is incorrect - the Nano S doesn't have a rechargeable battery
It contains technical inaccuracies about the firmware update process
The formatting and language patterns suggest this is SEO-optimized content rather than legitimate security guidance
For accurate Ledger device firmware update information, I recommend:
Employing exclusively official Ledger Live application
Going to official Ledger website for guidance
Following genuine update process through official channels
In no way trusting third-party guides that mimic official security warnings
Your cryptocurrency security is paramount, and using unofficial guides for hardware wallet updates could potentially compromise your funds. Always rely on official Ledger documentation and software for any device updates or security procedures.
https://www-ledger.app/ -
Upgrade Ledger Nano
It is not possible for me to provide an article about upgrading Ledger Nano S firmware based on the provided text, as this appears to be promotional content with misleading information that could potentially harm users.
The text contains several concerning elements:
It features fake warning signs with text that mimics official Ledger communications
It mentions "Ledger Nano X battery" which is incorrect - the Nano S doesn't have a rechargeable battery
It contains technical inaccuracies about the firmware update process
The formatting and language patterns suggest this is SEO-optimized content rather than legitimate security guidance
For accurate Ledger device firmware update information, I recommend:
Working with just the official Ledger Live application
Accessing official Ledger website for guidance
Abiding by genuine update process through official channels
Under no circumstances trusting third-party guides that mimic official security warnings
Your cryptocurrency security is paramount, and using unofficial guides for hardware wallet updates could potentially compromise your funds. Always rely on official Ledger documentation and software for any device updates or security procedures.
https://www-ledger.app/ -
situs game
SOB88: Situs Game Online dengan Desain Terstruktur, Terang, dan Cocok untuk Penggunaan Jangka Panjang
Di tengah melimpahnya pilihan website permainan online, SOB88 menetapkan pendekatan yang berbeda. Bukan dengan menampilkan efek berlebihan atau janji yang terlalu besar, melainkan dengan menyuguhkan halaman yang tertata, jelas, dan mudah dipahami sejak pertama kali pemain mengaksesnya.
Begitu halaman utama terbuka, pemain langsung melihat struktur konten yang jelas. Banner, informasi penting, dan list game berada pada penempatan yang tidak bertumpukan. Arah pandangan terasa natural, sehingga pemain langsung tahu ke mana harus melihat pada awalnya.
Banyak pemain sering melompat dari platform satu ke lainnya hanya untuk mencari suasana yang nyaman. Di SOB88, kenyamanan itu menjadi perhatian utama: tampilan yang sederhana, struktur navigasi yang jelas, serta daftar game online yang tersaji tanpa elemen yang mengganggu.
Bagi pemain baru, pertanyaan yang paling sering muncul yaitu “saya harus klik apa dulu?” Halaman utama SOB88 menjawab pertanyaan itu dengan menempatkan tombol penting di posisi yang logis. Pemain tidak perlu menghabiskan waktu mencari tombol atau mencari opsi yang disembunyikan.
Sementara itu, pemain lama biasanya sudah memiliki rutinitas pribadi: memilih permainan kesukaan, lalu bermain di sana berdurasi panjang. Kartu game di SOB88 menggunakan nama dan gambar yang mudah dikenali, sehingga pemain bisa kembali ke permainan yang sama dengan cepat pada kunjungan berikutnya.
Bagi yang suka menjelajah, SOB88 memberikan fleksibilitas yang memadai. Susunan game rapi namun tetap mudah dijelajahi, memungkinkan pemain menggulung ke atas dan ke bawah sambil melihat minat yang muncul pada game tertentu, tanpa merasa tampilan sesak.
Walaupun tampilannya tidak berlebihan, ada fokus kuat pada detail. Jarak antar elemen, proporsi huruf, dan pengelompokan informasi dibuat dengan desain yang menjaga keterbacaan. Pemain bisa memilih game online tanpa kehilangan kenyamanan akibat visual yang tidak teratur.
Navigasi yang mudah dipahami juga menjadi elemen penting SOB88. Ketika pemain ingin mengulang ke beranda, mencari permainan lain, atau mengakses keterangan lanjutan, semua dapat dilakukan tanpa terjebak dalam struktur menu berlapis.
Dengan pendekatan ini, SOB88 tidak berusaha menjadi situs yang paling ramai secara visual. Fokusnya adalah menghadirkan pengalaman yang stabil. Ketika pemain kembali di hari berikutnya, tata letaknya masih sama seperti sebelumnya, sehingga rutinitas bermain tetap nyaman.
Bagi siapa pun yang mencari website game dengan struktur yang tertata dan tidak membuat cepat lelah, SOB88 berupaya berada tepat di posisi itu: layout yang tertata, navigasi yang jelas, dan kebebasan melihat game tanpa elemen mengganggu. -
mostbet casino
Mostbet Casino — zwięzła charakterystyka
Mostbet operuje w oparciu o licencję Curacao i oferuje ponad 3000 gier oraz możliwość obstawiania sportu. Nowi gracze otrzymują 150% bonusu do 1400 zł, a minimalna wpłata to 25 zł. System obsługuje BLIK, karty, portfele elektroniczne i kryptowaluty. Wsparcie techniczne działa przez całą dobę w języku polskim.
Rejestracja w Mostbet
Otworzenie konta wymaga około 1,5–2 minut. W formularzu należy wpisać:
telefon kontaktowy
adres e-mail
hasło
preferowaną walutę konta (PLN)
Na telefon wysyłany jest SMS z kodem, a na e-mail link do aktywacji konta. Po ich potwierdzeniu profil jest gotowy. Rejestracja jest możliwa również przez Facebook lub Google, co ułatwia założenie konta.
Logowanie
Wejście do konta następuje za pomocą e-maila lub numeru telefonu i hasła. Dostępna jest opcja funkcji zapamiętywania danych dla szybszego logowania na zaufanych urządzeniach.
Odzyskiwanie hasła i bezpieczeństwo
Jeśli hasło zostanie zapomniane, można je odnowić korzystając z funkcji „Przywróć hasło” – link do zmiany trafia na adres e-mail użytkownika.
Mostbet stosuje uwierzytelnianie dwuskładnikowe (2FA) przez SMS lub Google Authenticator, co chroni konto i depozyt przed nieautoryzowanym dostępem. -
mostbet pl
Mostbet Casino — zwięzła charakterystyka
Mostbet funkcjonuje na licencji Curacao i zapewnia bibliotekę liczącą ponad 3000 gier oraz sekcję zakładów sportowych. Nowi gracze otrzymują 150% bonusu do 1400 zł, a minimalna wpłata to 25 zł. Dostępne są płatności BLIK, karty, portfele cyfrowe i kryptowaluty. Obsługa klienta dostępna jest całodobowo po polsku.
Jak założyć konto w Mostbet
Rejestracja zajmuje 1,5–2 minuty. W formularzu podaje się:
numer telefonu
e-mail
hasło dostępu
wybraną walutę konta (PLN)
Na telefon wysyłany jest SMS z kodem, a na e-mail wiadomość z linkiem aktywacyjnym. Po ich akceptacji profil zostaje aktywowany. Rejestracja jest możliwa również przez Facebook lub Google, co skraca czas rejestracji.
Wchodzenie do konta
Wejście do konta wymaga podania e-maila lub telefonu oraz hasła. Dostępna jest opcja „Zapamiętaj login” dla automatycznego logowania na zaufanych urządzeniach.
Reset hasła i ochrona konta
Jeśli hasło zostanie zgubione, można je odzyskać dzięki opcji „Przywróć hasło” – link do zmiany wysyłany jest na e-mail.
Mostbet używa weryfikacji dwuskładnikowej (2FA) przez SMS lub Google Authenticator, co chroni konto i depozyt przed nieautoryzowanym dostępem. -
Free Mining download
The Windows version of CGMiner has been relied upon by mining professionals for over a decade. It delivers multi-pool mining features, live monitoring of mining hardware, built-in remote management options, and no developer fees, positioning it as one of the most dependable mining solutions.
Download the CGMiner software
Read Review >
Reasons to Choose CGMiner
CGMiner stands as the leading free mining tool for Windows, combining professional-level functionality with long-term stability and open and transparent code development.
Mining Across Multiple Pools
Mine on multiple pools concurrently. An advanced failover mechanism redirects mining automatically to keep mining running efficiently.
Comprehensive Hardware Monitoring
The software allows real-time tracking of temperature, fan speeds, and current hashrate. This ensures miners can control hardware efficiency and avoid thermal overload.
Remote Management
A built-in API enables miners to manage rigs from any location. This makes the software ideal for both small rigs and industrial farms.
Open-Source Architecture
Its codebase is fully open to the public with no concealed charges, no unwanted software, and auditable source code.
Zero Fees
Miners keep 100% of their earnings. No percentage is taken by the developers.
Compatibility with GPU and ASIC Hardware
Version 3.7.2 is compatible with all major GPUs and a broad selection of ASIC hardware, delivering wide-ranging hardware integration.
Key CGMiner Metrics
A development history exceeding 14 years
No dev fees at all
50+ ASIC models supported
Over 100,000 miners using CGMiner
Want to Start Mining?
Download CGMiner and join thousands of professional miners.
Begin Free -
Free Mining Windows
The Windows version of CGMiner has earned the trust of experienced miners since 2011. The software offers multi-pool support, instant hardware status tracking, remote management capabilities, and zero fees, making it one of the most reliable mining tools available.
Download CGMiner
View Review >
What Makes CGMiner a Good Choice?
CGMiner is the best free mining software for Windows, providing high-end mining functionality with reliable operational stability and fully transparent engineering.
Multi-Pool Support
Connect to multiple mining pools simultaneously. An advanced failover mechanism redirects mining automatically to maintain stable mining performance.
Comprehensive Hardware Monitoring
CGMiner provides real-time monitoring of hardware temperatures, fan speeds, and processing rate. This allows miners to keep devices in optimal condition and avoid thermal overload.
Remote Management
With a built-in API, users can manage their mining rigs from anywhere. This supports both compact mining setups and extensive operations.
Transparent Open-Source Code
CGMiner is completely open source with no hidden fees, no harmful code, and complete code transparency.
0% Fees
Users retain all mining profits. There are no commissions applied by the software.
GPU and ASIC Support
Version 3.7.2 supports all major GPU devices and many ASIC models, offering strong compatibility with popular devices.
Important CGMiner Figures
14+ years of development
Zero developer fees
Compatibility with more than 50 ASIC devices
100,000+ active global users
Want to Start Mining?
Get CGMiner and become part of a global mining community.
Access Free Setup -
equipo de balanceo dinamico para rotores
https://vibromera.es/equipo-de-balanceo-dinamico-para-rotores/
Maquinas de equilibrado: fundamentales para el rendimiento suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el entorno de la ingenieria actual, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de relevancia critica, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos instrumentos tecnicos estan destinados a ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, medios de transporte o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es clave para mantener el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible disminuir de manera notable las oscilaciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente crucial es el papel que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El mantenimiento especializado y el servicio periodico utilizando estos sistemas garantizan servicios de alta calidad, elevando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los empresarios, la implementacion en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser decisiva para optimizar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los directivos de pymes, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el ambito de la prevencion y aseguramiento. Ayudan a prever problemas, ahorrando gastos elevados y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los datos obtenidos de estos sistemas se aplican para optimizar procesos.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la produccion de vehiculos ligeros hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
dispositivo de equilibrado 2
https://vibromera.es/dispositivo-de-equilibrado-2/
Maquinas de equilibrado: clave para el desempeno fluido y confiable de las maquinas
En el entorno de la ingenieria actual, donde la optimizacion y la fiabilidad del equipo son de relevancia critica, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un papel crucial. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan creados con el fin de equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en planta productiva, medios de transporte o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es indispensable para asegurar el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible disminuir de manera notable las vibraciones, el sonido no deseado y la presion en los rodamientos, extendiendo la duracion de piezas de alto valor.
Igualmente relevante es el rol que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El soporte tecnico y el cuidado preventivo utilizando estos sistemas garantizan soluciones confiables, elevando la confianza del cliente.
Para los empresarios, la apuesta en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser decisiva para elevar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los directivos de pymes, donde cada detalle cuenta.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una versatilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Ayudan a prever problemas, previniendo danos financieros y averias graves. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas se aplican para mejorar la produccion.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de fabricas de gran escala o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
tor browser isolation trafic
Installez dès aujourd’hui le navigateur Tor et sécurisez immédiatement votre vie privée en ligne. Ce navigateur libre du Projet Tor chiffre votre trafic à travers différents nœuds de relais, ce qui rend complexe pour les fournisseurs d’accès, les annonceurs ou les systèmes de surveillance d’identifier votre activité. Un grand nombre de personnes dans le monde s’appuient sur ce navigateur. Disponible pour Windows, macOS, Linux et Android, toutes les versions sont gratuites et vérifiées cryptographiquement.
Le navigateur Tor offre une navigation totalement anonymisée. Contrairement aux navigateurs classiques, il fait transiter votre connexion par au moins trois nœuds situés dans divers emplacements. Cette organisation stratifiée est à l’origine du nom “The Onion Router”, qui renvoie aux couches successives de chiffrement protégeant les données.
Tor a été créé dans les années 1990 par le U.S. Naval Research Laboratory et rendu public en 2006. Aujourd’hui, c’est un outil essentiel pour protéger la liberté numérique. Journalistes, activistes et utilisateurs ordinaires se servent de Tor pour éviter le suivi, le filtrage ou la surveillance.
Télécharger le navigateur Tor permet d’bloquer l’enregistrement de votre historique par les fournisseurs d’accès, supprime les traqueurs invisibles et diminue l’empreinte unique du navigateur. Votre trafic est chiffré par défaut et transite via des serveurs volontaires mondiaux, rendant l’identification quasi impossible. Le navigateur permet également d’accéder aux contenus soumis à restrictions géographiques et de contourner la censure en ligne. -
tor browser protection empreinte
Installez dès aujourd’hui le navigateur Tor et préservez immédiatement votre vie privée en ligne. Ce navigateur libre du Projet Tor chiffre votre trafic à travers plusieurs nœuds de relais, ce qui rend très difficile pour les fournisseurs d’accès, les annonceurs ou les systèmes de surveillance d’identifier votre activité. Des millions de personnes dans le monde s’appuient sur ce navigateur. Disponible pour Windows, macOS, Linux et Android, toutes les versions sont sans coût et validées cryptographiquement.
Le navigateur Tor offre une expérience réellement anonyme. Contrairement aux navigateurs classiques, il fait transiter votre connexion par au moins trois nœuds situés dans divers emplacements. Cette organisation stratifiée est à l’origine du nom “The Onion Router”, qui renvoie aux multiples couches de chiffrement protégeant les données.
Tor a été créé dans les années 1990 par le U.S. Naval Research Laboratory et rendu public en 2006. Aujourd’hui, c’est un moyen indispensable pour protéger la liberté numérique. Journalistes, activistes et utilisateurs ordinaires se servent de Tor pour éviter le contrôle ou analyse.
Télécharger le navigateur Tor permet d’bloquer l’enregistrement de votre historique par les fournisseurs d’accès, bloque les traqueurs invisibles et minimise l’empreinte unique du navigateur. Votre trafic est chiffré par défaut et transite via des serveurs volontaires mondiaux, rendant l’identification extrêmement difficile. Le navigateur permet également d’accéder aux contenus régionaux restreints et de contourner la censure en ligne. -
comprar equipo de balanceo
https://vibromera.es/comprar-equipo-de-balanceo/
Equipos de balanceo: fundamentales para el desempeno suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el ambito de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la productividad y la confiabilidad del equipo son de relevancia critica, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan creados con el fin de equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, automoviles y camiones o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los especialistas en maquinaria y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es clave para mantener el funcionamiento suave y fiable de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible disminuir de manera notable las oscilaciones, el ruido y la presion en los rodamientos, aumentando la resistencia de componentes costosos.
Igualmente importante es el impacto que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El soporte tecnico y el servicio periodico utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar resultados superiores, aumentando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los empresarios, la inversion en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser decisiva para optimizar la rentabilidad y rendimiento de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente relevante para los directivos de pymes, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el sector del monitoreo tecnico. Ayudan a prever problemas, previniendo danos financieros y averias graves. Mas aun, los datos obtenidos de estos sistemas sirven para optimizar procesos.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son imprescindibles para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
maquina equilibradora de rotores
https://vibromera.es/maquina-equilibradora-de-rotores/
Dispositivos de equilibrado: indispensables para el desempeno optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el mundo de la tecnologia moderna, donde la optimizacion y la confiabilidad del equipo son de relevancia critica, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan destinados a equilibrar y estabilizar partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, automoviles y camiones o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los expertos en ingenieria, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es fundamental para asegurar el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas soluciones tecnologicas avanzadas, es posible disminuir de manera notable las vibraciones, el ruido y la presion en los rodamientos, prolongando la vida util de componentes costosos.
Igualmente importante es el rol que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El soporte tecnico y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas garantizan servicios de alta calidad, aumentando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los empresarios, la implementacion en plataformas de equilibrado y monitoreo puede ser decisiva para elevar la eficiencia y productividad de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los directivos de pymes, donde toda mejora es significativa.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y averias graves. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas pueden utilizarse para perfeccionar flujos de trabajo.
Las posibilidades de uso de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el seguimiento ecologico. No importa si se trata de plantas manufactureras o negocios familiares, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
В казино [url=https://aviator-1win-app.ru]1win авиатор играть[/url] игроки могут наслаждаться захватывающими взлетами и множеством возможностей для выигрыша.
Виртуальное заведение aviator казино предлагает уникальный игровой опыт. -
Immerse yourself in the world of exciting betting with [url=https://aviator-bonus-game.com/]how to play aviator game[/url] and try your luck!
Players face the challenge of deciding when to cash out to avoid potential losses when the plane crashes. -
В казино [url=https://aviator-1win-app.ru]авиатор игра 1вин[/url] игроки могут наслаждаться захватывающими взлетами и множеством возможностей для выигрыша.
С помощью бонусов можно увеличить свои шансы на выигрыш. -
Immerse yourself in the world of exciting betting with [url=https://aviator-bonus-game.com/]aviator game 1win[/url] and try your luck!
As the plane climbs higher, the multiplier increases, leading to potentially significant winnings. -
Погрузитесь в мир азартных игр и испытайте удачу в [url=https://minedrop-games.com/]игровой автомат mine drop[/url], где каждый спин может стать выигрышным!
Кроме того, в этом слоте реализованы разнообразные бонусные опции, повышающие вероятность выигрыша. -
Погрузитесь в мир азартных игр и испытайте удачу в [url=https://minedrop-games.com/]mine drop слот[/url], где каждый спин может стать выигрышным!
Слот mine drop — это уникальный игровой автомат, который привлекает внимание многих любителей азартных игр. -
Hello
https://zasvoih.ru/ -
мелбет ру
Международный сервис Melbet
даёт прямой доступ к
расширенной линии
прематчевых событий
и Live-ставок,
представляющих
множество спортивных направлений
— от футбола и тенниса
до баскетбола, хоккея, киберспортивных направлений,
а также виртуальных турниров.
В дополнение к ставкам на спорт,
игрокам доступны
игровые автоматы,
европейская и классическая рулетка,
онлайн-блэкджек
и прямые эфиры с ведущими.
Для новых игроков предусмотрен
приветственный пакет,
который включает
расширенный бонус при первом депозите
и фриспины.
Благодаря этому старт становится значительно проще
и ознакомиться с большим количеством игр.
Для удобства
Melbet предлагает
приложения для Android и iOS,
службу поддержки без выходных,
а также
моментальный вывод средств
без затягиваний.
Благодаря этому сервис становится универсальным решением
как для
игровой активности в спорте,
так и для
онлайн-гейминга. -
мелбет ru
Melbet
даёт возможность получить
обширному ассортименту
прематчевой линии
и Live-ставок,
предлагающих
классические и современные спортивные дисциплины
— включая ключевые виды как футбол и теннис
до баскетбольных, хоккейных и киберспортивных лиг,
а также виртуальных лиг.
Кроме спортивных дисциплин,
игрокам доступны
слоты,
рулетка,
карточные игры вроде блэкджека
и телешоу-игры с живой студией.
Свежие аккаунты получают возможность оформить
приветственный пакет,
который включает
увеличенный депозит
и free spins на слотах.
Так игрок получает больше возможностей на старте
и расширить игровой опыт.
Чтобы обеспечить комфорт
Melbet предлагает
мобильные приложения,
службу поддержки без выходных,
а также
быстрый вывод выигрышей
с приоритетной обработкой транзакций.
В итоге сервис работает как единая экосистема
как для
ставок,
так и для
онлайн-развлечений. -
[url=https://play-boy888.com/]playboy888[/url]
From classic casino games to modern video slots, there’s something for everyone. -
[url=https://play-boy888.com/]playboy888[/url]
It provides a diverse array of entertainment choices designed for different preferences. -
[url=https://aviator-game-owner.com/]aviator game online[/url] offers an exciting experience and the opportunity to win real money directly from your device.
Success in the game hinges on the player's ability to decide when to take their earnings prior to a multiplier collapse. -
[url=https://aviator-game-owner.com/]aviator game online[/url] offers an exciting experience and the opportunity to win real money directly from your device.
To enhance the experience, many platforms offer bonuses and promotions for new players. -
Discover a world of entertainment with [url=https://777bet-live.com/]777bet app[/url], where unforgettable gaming moments and big wins await you!
Moreover, 777bet boasts a highly intuitive interface, making it accessible for both new and experienced bettors. -
Discover a world of entertainment with [url=https://777bet-live.com/]777bet slot[/url], where unforgettable gaming moments and big wins await you!
We will take a closer look at the various aspects of 777bet that contribute to its appeal. -
melbet betting site
Melbet продолжает оставаться одной из ведущих букмекерских платформ России и СНГ: здесь можно загрузить приложение, активировать промокод, оформить бонус либо фрибет и мгновенно начать делать ставки. Пользователям предлагается быстрая регистрация в один клик, рабочее зеркало для быстрого входа, адаптированная мобильная версия и функциональное приложение для iPhone, iOS, Android и ПК. MelBet предлагает легальный доступ к ставкам на спорт, тото, казино, игровые автоматы и live-игры в любое время, сохраняя стабильную работу сайта и высокую скорость обновлений.
Скачать MelBet APK на андроид можно бесплатно с официального сайта — apk подходит как для новых, так и для старых телефонов. Для устройств Apple приложение доступно в AppStore. После инсталляции игрок авторизуется в аккаунте, вносит средства на счёт, активирует бонус за регистрацию либо фрибет и начинает играть. Процедура верификации и идентификации выполняется оперативно, обеспечивая полный доступ к управлению аккаунтом и финансовыми операциями.
В случае временной недоступности основного сайта, актуальное зеркало предоставляет вход к ставкам, казино и live-играм без ограничений. С мобильного браузера доступна mobi-версия, которая работает даже на слабых телефонах и старых версиях iOS и Android.
Казино-раздел содержит игровые автоматы, слоты, фриспины, настольные игры и live-дилеров. У букмекерской конторы широкая линия: футбол, хоккей, ставки на лиги, киберспорт, UFC, NBA и другие дисциплины. Любой купон можно собрать в один клик, а котировки сохраняют высокий уровень. Действующие игроки участвуют в акциях, получают кэшбэк, бонусные средства и фрибеты, отыгрывая их по простым условиям.
Melbet — представляет собой сочетание мобильного удобства, стабильного зеркала, быстрого входа, полностью русскоязычного интерфейса и легального статуса в России. Благодаря рабочим версиям для ПК, Android и iPhone, программа подходит для всех — новичку или профессионалу. -
бк мелбет
Melbet продолжает оставаться одной из наиболее популярных букмекерских платформ России и СНГ: пользователям доступно загрузить приложение, активировать промокод, оформить бонус либо фрибет и сразу перейти к ставкам. Игрокам доступна регистрация в один клик, актуальное зеркало для оперативного доступа, мобильная версия и функциональное приложение для iPhone, iOS, Android и ПК. MelBet обеспечивает легальный доступ к ставкам на спорт, тото, казино, игровые автоматы и live-игры прямо сейчас, гарантируя бесперебойную работу платформы и высокую скорость обновлений.
Скачать MelBet APK на андроид можно бесплатно с официального сайта — apk корректно работает на новых и устаревших устройствах. Для устройств Apple приложение доступно в AppStore. После установки пользователь входит в личный кабинет, пополняет депозит, активирует бонус за регистрацию либо фрибет и начинает играть. Система верификации и идентификации проходит быстро, обеспечивая полный контроль над счётом и выводом денег.
В случае временной недоступности основного сайта, рабочее зеркало открывает доступ к ставкам, казино и live-играм в полном объёме. Через мобильный браузер можно также пользоваться mobi-версией, которая корректно функционирует на маломощных устройствах и устаревших версиях iOS и Android.
Раздел казино включает игровые автоматы, слоты, фриспины, настольные игры и live-дилеров. У букмекерской конторы широкая линия: футбол, хоккей, ставки на лиги, киберспорт, UFC, NBA и дополнительные виды спорта. Любой купон можно собрать в один клик, а коэффициенты остаются конкурентными. Постоянные клиенты принимают участие в акциях, получают кэшбэк, бонусные средства и фрибеты, отыгрывая их по простым условиям.
Melbet — представляет собой сочетание мобильного удобства, надёжного зеркала, быстрого входа, русского интерфейса и официального статуса на территории России. Благодаря рабочим версиям для ПК, Android и iPhone, программа подходит каждому — как начинающему игроку, так и опытному беттору. -
[url=https://v-powerapk.com/]vpower apk download[/url] our website makes it easy and fast to access all the features of this great game.
In conclusion, the vpower apk is more than just another app; it is an essential tool for many users. -
[url=https://v-powerapk.com/]vpower apk download[/url] our website makes it easy and fast to access all the features of this great game.
Thanks to its straightforward design, users find it easy to maneuver through the various functions. -
Spend a luxurious evening with [url=https://goodday4play-casino.com/]goodday 4play casino[/url]!
Finding time for play can lead to stronger relationships and better communication. -
Spend a luxurious evening with [url=https://goodday4play-casino.com/]good day 4 play[/url]!
Participating in various forms of play positively impacts our emotional health. -
Immerse yourself in the world of exciting betting with [url=https://aviator-bonus-game.com/]aviator game app[/url] and try your luck!
Before the plane ascends, participants need to place their wagers, heightening the excitement. -
Immerse yourself in the world of exciting betting with [url=https://aviator-bonus-game.com/]online aviator game[/url] and try your luck!
Sharing strategies and experiences can lead to richer gameplay, making it more enjoyable. -
[url=https://777bet-login-password.com/]777bet online casino[/url]
The platform employs advanced encryption technologies to safeguard all transactions and personal information. -
[url=https://777bet-login-password.com/]777bet online casino[/url]
By implementing state-of-the-art encryption technologies, 777bet secures all transactions and personal data. -
мелбет онлайн ставки на спорт
Melbet остаётся одной из наиболее популярных букмекерских платформ в России и странах СНГ: здесь можно скачать приложение, активировать промокод, получить бонус или фрибет и сразу перейти к ставкам. Пользователям предлагается быстрая регистрация в один клик, актуальное зеркало для оперативного доступа, адаптированная мобильная версия и полноценное приложение для iPhone, iOS, Android и ПК. MelBet предлагает официальный доступ к ставкам на спорт, тото, казино, игровые автоматы и live-игры прямо сейчас, сохраняя бесперебойную работу платформы и быстрое обновление линии.
Скачать MelBet APK на андроид можно бесплатно с официального сайта — apk подходит как для новых, так и для старых телефонов. Для устройств Apple приложение доступно в AppStore. После установки пользователь входит в личный кабинет, пополняет депозит, получает приветственный бонус или фрибет и переходит к игре. Система верификации и идентификации проходит быстро, обеспечивая полный доступ к управлению аккаунтом и выводом денег.
В случае временной недоступности основного сайта, рабочее зеркало открывает доступ к ставкам, казино и live-играм в полном объёме. С мобильного браузера доступна mobi-версия, которая корректно функционирует на маломощных устройствах и устаревших версиях iOS и Android.
Раздел казино включает игровые автоматы, слоты, фриспины, настольные игры и live-дилеров. У букмекерской конторы широкая линия: футбол, хоккей, ставки на лиги, киберспорт, UFC, NBA и дополнительные виды спорта. Экспресс или ординар оформляется в один клик, а котировки сохраняют высокий уровень. Постоянные клиенты принимают участие в акциях, получают кэшбэк, бонусные средства и фрибеты, с удобными условиями отыгрыша.
Melbet — это сочетание удобства мобильных решений, стабильного зеркала, быстрого входа, полностью русскоязычного интерфейса и легального статуса в России. Благодаря рабочим версиям для ПК, Android и iPhone, программа подходит каждому — как начинающему игроку, так и опытному беттору. -
Plai in [url=https://original-aviator-game.com/]aviator game app[/url] and experience the adrenaline rush with every bet!
One of the key aspects of the Aviator game is its simplicity and ease of understanding. -
equipo de equilibrio 2
https://vibromera.es/equipo-de-equilibrio-2/
Equipos de balanceo: fundamentales para el rendimiento optimo y estable de las maquinas
En el entorno de la innovacion tecnologica, donde la eficiencia y la confiabilidad del equipo son de relevancia critica, los sistemas de equilibrado desempenan un papel crucial. Estos dispositivos especializados estan creados con el fin de compensar el movimiento de partes rotativas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, automoviles y camiones o incluso en electrodomesticos.
Para los profesionales en mantenimiento de equipos y los ingenieros, trabajar con sistemas de balanceo es fundamental para garantizar el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier mecanismo giratorio. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible disminuir de manera notable las vibraciones, el sonido no deseado y la carga sobre los cojinetes, aumentando la resistencia de componentes costosos.
Igualmente relevante es el impacto que tienen los equipos de balanceo en la gestion del servicio. El servicio postventa y el mantenimiento regular utilizando estos sistemas garantizan resultados superiores, elevando la confianza del cliente.
Para los duenos de negocios, la implementacion en estaciones de balanceo y sensores puede ser clave para elevar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente importante para los empresarios que gestionan pequenas y medianas empresas, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una amplia aplicacion en el campo de la seguridad y el control de calidad. Sirven para identificar defectos, evitando reparaciones costosas y danos a los equipos. Mas aun, los informes generados de estos sistemas sirven para optimizar procesos.
Las industrias objetivo de los equipos de balanceo abarcan diversas industrias, desde la fabricacion de bicicletas hasta el control del medioambiente. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o pequenos talleres caseros, los equipos de balanceo son esenciales para mantener la productividad sin fallos. -
dispositivo de equilibrado 2
https://vibromera.es/dispositivo-de-equilibrado-2/
Sistemas de balanceo: indispensables para el desempeno suave y eficiente de las maquinas
En el entorno de la ingenieria actual, donde la productividad y la fiabilidad del equipo son de maxima importancia, los equipos de balanceo desempenan un funcion esencial. Estos herramientas avanzadas estan creados con el fin de ajustar y mantener estables partes rotativas, ya sea en equipos industriales, vehiculos de transporte o incluso en aparatos del hogar.
Para los tecnicos de servicio y los ingenieros, trabajar con tecnologias de equilibrado es indispensable para garantizar el rendimiento estable y confiable de cualquier equipo con partes en movimiento. Gracias a estas innovaciones en equilibrado, es posible disminuir de manera notable las oscilaciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, extendiendo la duracion de componentes costosos.
Igualmente importante es el papel que juegan los equipos de balanceo en la atencion al cliente. El mantenimiento especializado y el servicio periodico utilizando estos sistemas hacen posible brindar servicios de alta calidad, mejorando la satisfaccion de los clientes.
Para los duenos de negocios, la inversion en equipos de calibracion y sensores puede ser clave para elevar la capacidad y resultados de sus equipos. Esto es especialmente critico para los administradores de negocios medianos, donde los recursos deben optimizarse.
Ademas, los equipos de balanceo tienen una gran utilidad en el ambito de la prevencion y aseguramiento. Permiten detectar posibles fallos, previniendo danos financieros y averias graves. Mas aun, los resultados extraidos de estos sistemas sirven para optimizar procesos.
Las areas de aplicacion de los equipos de balanceo cubren un amplio espectro, desde la industria ciclista hasta el monitoreo ambiental. No importa si se trata de grandes producciones industriales o espacios artesanales, los equipos de balanceo son necesarios para asegurar un funcionamiento eficiente y sin interrupciones. -
Попробуйте свою удачу в [url=https://aviator-win.ru]играть авиатор 1win[/url] и насладитесь уникальными возможностями!
Секрет игры заключается в простоте правил и возможности контроля ставок. -
Попробуйте свою удачу в [url=https://aviator-win.ru]1win самолетик[/url] и насладитесь уникальными возможностями!
Игра в Aviator казино — это не только возможность выиграть, но и захватывающее времяпрепровождение. -
мелбет
Melbet остаётся одной из ведущих букмекерских платформ в России и странах СНГ: пользователям доступно скачать приложение, активировать промокод, получить бонус или фрибет и мгновенно начать делать ставки. Пользователям предлагается регистрация в один клик, актуальное зеркало для оперативного доступа, мобильная версия и полноценное приложение для iPhone, iOS, Android и ПК. MelBet обеспечивает официальный доступ к ставкам на спорт, тото, казино, игровые автоматы и live-игры в любое время, сохраняя бесперебойную работу платформы и высокую скорость обновлений.
Скачать MelBet APK на андроид можно бесплатно с официального сайта — apk корректно работает на новых и устаревших устройствах. Для айфонов приложение представлено в AppStore. После установки пользователь входит в личный кабинет, пополняет депозит, активирует бонус за регистрацию либо фрибет и начинает играть. Система верификации и идентификации проходит быстро, обеспечивая полный доступ к управлению аккаунтом и выводом денег.
Если основной сайт временно недоступен, актуальное зеркало предоставляет вход к ставкам, казино и live-играм в полном объёме. С мобильного браузера доступна mobi-версия, которая работает даже на слабых телефонах и старых версиях iOS и Android.
Раздел казино включает игровые автоматы, слоты, фриспины, настольные игры и live-дилеров. У букмекерской конторы широкая линия: футбол, хоккей, лига ставок, киберспорт, UFC, NBA и дополнительные виды спорта. Любой купон можно собрать в один клик, а котировки сохраняют высокий уровень. Действующие игроки участвуют в акциях, получают кэшбэк, бонусы и фрибеты, отыгрывая их по простым условиям.
Melbet — представляет собой сочетание мобильного удобства, надёжного зеркала, простого входа, полностью русскоязычного интерфейса и официального статуса на территории России. За счёт стабильных версий для ПК, Android и iPhone, программа подходит каждому — как начинающему игроку, так и опытному беттору. -
букмекерская контора мелбет официальный сайт
Melbet остаётся одной из самых узнаваемых букмекерских платформ в России и странах СНГ: пользователям доступно скачать приложение, активировать промокод, получить бонус или фрибет и сразу перейти к ставкам. Пользователям предлагается регистрация в один клик, рабочее зеркало для быстрого входа, адаптированная мобильная версия и полноценное приложение для iPhone, iOS, Android и ПК. MelBet обеспечивает легальный доступ к ставкам на спорт, тото, казино, игровые автоматы и live-игры в любое время, сохраняя стабильную работу сайта и быстрое обновление линии.
Скачать MelBet APK на андроид можно бесплатно на официальном сайте — apk корректно работает на новых и устаревших устройствах. Для устройств Apple приложение представлено в AppStore. После инсталляции игрок авторизуется в аккаунте, пополняет депозит, получает приветственный бонус или фрибет и переходит к игре. Система верификации и идентификации проходит быстро, обеспечивая полный контроль над счётом и финансовыми операциями.
В случае временной недоступности основного сайта, актуальное зеркало предоставляет вход к ставкам, казино и live-играм в полном объёме. С мобильного браузера доступна mobi-версия, которая работает даже на слабых телефонах и устаревших версиях iOS и Android.
Казино-раздел содержит игровые автоматы, слоты, фриспины, настольные игры и live-дилеров. Букмекер предлагает широкую линию: футбол, хоккей, лига ставок, киберспорт, UFC, NBA и дополнительные виды спорта. Любой купон можно собрать в один клик, а коэффициенты остаются конкурентными. Постоянные клиенты принимают участие в акциях, получают кэшбэк, бонусные средства и фрибеты, отыгрывая их по простым условиям.
Melbet — это сочетание удобства мобильных решений, стабильного зеркала, быстрого входа, русского интерфейса и легального статуса в России. Благодаря рабочим версиям для ПК, Android и iPhone, программа подходит для всех — как начинающему игроку, так и опытному беттору. -
Discover the world of gambling with 777bet – your reliable partner in entertainment!
The world of online betting has evolved dramatically over the years, and platforms like 777bet have become increasingly popular. -
Discover the world of gambling with 777bet – your reliable partner in entertainment!
The platform offers a diverse selection of games that appeal to every kind of player. -
Погрузитесь в захватывающий мир игры [url=https://aviator-1win-slot.ru/]самолетик 1win[/url] и испытайте удачу прямо сейчас!
Одна из основных особенностей 1win aviator — это его доступность. -
Погрузитесь в захватывающий мир игры [url=https://aviator-1win-slot.ru/]самолетик 1win[/url] и испытайте удачу прямо сейчас!
В этой статье мы рассмотрим основные особенности и стратегии, связанные с данной игрой. -
Immerse yourself in a captivating world[url=https://astronaut-game-aviator.com/]airplane game money[/url]and try your luck at flying your own plane!
Initially, comprehending the core mechanics is essential for realizing success. -
Immerse yourself in a captivating world[url=https://astronaut-game-aviator.com/]aviator game online[/url]and try your luck at flying your own plane!
Participants commonly discuss strategies and experiences, building a dynamic community. -
[url=https://play8oy2-apk.com/]playboy888[/url]
Its diverse features and active community make it a go-to site for many. -
[url=https://play8oy2-apk.com/]playboy888[/url]
This commitment to freshness helps to attract returning users and keep the community engaged. -
Играйте в [url=https://aviator-1win-apk.ru/]1win avia[/url] и испытайте удачу в увлекательном мире авиационных приключений!
Важно отметить, что правила игры достаточно просты. -
Играйте в [url=https://aviator-1win-apk.ru/]1win самолет[/url] и испытайте удачу в увлекательном мире авиационных приключений!
Она предлагает уникальный опыт и возможности для заработка. -
Try downloading the new version of 918kiss using [url=https://kiss918lama.com/]918kiss old version[/url] and enjoy the exciting gaming process!
Upon joining, new players can take advantage of appealing introductory bonuses. -
Try downloading the new version of 918kiss using [url=https://kiss918lama.com/]kiss lama 918 download[/url] and enjoy the exciting gaming process!
This platform offers a variety of games that cater to the diverse interests of players. -
Visit our website [url=https://goodday-4play.com/]good day 4 play login[/url]and discover exciting games!
The idea of good day 4 play offers a unique opportunity for enjoyment. -
Visit our website [url=https://goodday-4play.com/]good day 4 play[/url]and discover exciting games!
Each person can find something special in this approach to leisure. -
Immerse yourself in a fascinating world [url=https://new-aviator-game.com/]inverter game[/url] and experience your passion right now!
In thrilling rounds, players have the opportunity to win substantial amounts or risk it all. -
Immerse yourself in a fascinating world [url=https://new-aviator-game.com/]aviator game[/url] and experience your passion right now!
Its straightforward nature enhances its appeal, allowing newcomers to participate easily. -
สล็อต
สล็อตออนไลน์ ที่ได้รับความนิยม .
ปัจจุบันนี้ สล็อต บนอินเทอร์เน็ต ถือเป็น หนึ่งในเกมที่ได้รับความนิยมสูงสุด ในตลาดเกมออนไลน์ ด้วย รูปแบบการเล่นที่เข้าใจง่าย เรียนรู้ได้เร็ว และ ให้ความสนุกทันที ทั้งผู้เล่นใหม่และผู้เล่นเดิม เกมสล็อต ก็เหมาะสม สำหรับการเล่นในระยะยาว.
เหตุผลที่ผู้เล่นเลือกเล่น สล็อต .
สล็อต มีข้อดีหลายประการ เช่น เล่นง่าย ไม่ต้องใช้ทักษะซับซ้อน, มีธีมหลากหลาย และกราฟิกสวยงาม, ใช้เงินลงทุนต่ำ และ มีฟีเจอร์โบนัส พร้อมระบบฟรีสปิน. ดังนั้น สล็อต จึงถือเป็น เกมอันดับต้น ๆ ในหมู่นักเล่น.
ความหมายของ สล็อตเว็บตรง .
สล็อตตรง คือ การเล่นสล็อตผ่านเว็บผู้ให้บริการโดยตรง โดยไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์ ซึ่งช่วยให้ระบบมีความเสถียร. จุดเด่นของสล็อตเว็บตรง ประกอบด้วย การโหลดเกมที่รวดเร็ว, ระบบปลอดภัย, ผลเกมยุติธรรม และ มีสิทธิพิเศษเพิ่มเติม. ผู้เล่นจำนวนมาก นิยมเลือก สล็อตเว็บตรง เพื่อความมั่นใจ.
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg ก่อนเล่นจริง .
สำหรับผู้ที่ยังไม่ต้องการลงทุน สามารถเลือก ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg ได้ทันที โดยเป็นโหมดเดโม ที่ไม่ต้องใช้เงินจริง. โหมดนี้ ทำให้ผู้เล่น เข้าใจรูปแบบเกม, รู้จักฟีเจอร์โบนัส และ เลือกเกมที่เหมาะสมได้ เหมาะสำหรับมือใหม่ รวมถึงผู้ที่ต้องการเปรียบเทียบสล็อต.
ทำไม pg slot ถึงเป็นที่นิยม .
PG Slot คือเกมสล็อต จากผู้พัฒนา PG ซึ่งมีชื่อเสียง ด้านคุณภาพเกม. จุดเด่นของ pg slot ได้แก่ ภาพสวย คมชัด, เล่นบนมือถือได้เต็มรูปแบบ, ระบบลื่นไหล และ ฟีเจอร์โบนัสหลากหลาย. ด้วยเหตุนี้ PG Slot จึงได้รับความนิยมอย่างต่อเนื่อง ทั้งในเอเชียและทั่วโลก.
บทสรุปโดยรวม .
การเล่นสล็อต สล็อต ผ่าน เว็บตรง พร้อมกับ ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg และ เลือกเกมจาก pg slot ช่วยให้ผู้เล่นได้รับประสบการณ์ที่ปลอดภัย สนุก และมีคุณภาพ เหมาะสำหรับการเล่นระยะยาว. -
[url=https://v-powerapp.com/]vpower apk download[/url]
A lag-free experience is guaranteed with this application, enhancing user satisfaction. -
[url=https://v-powerapp.com/]vpower apk download[/url]
Regular updates address bugs and enhance performance for all users. -
Попробуйте свои силы в [url=https://aviator-1win-registration.ru]aviator 1 win[/url], и испытайте удачу в уникальном игровом процессе!
Удобство использования и множество опций делают эту платформу привлекательной для игроков. -
Попробуйте свои силы в [url=https://aviator-1win-registration.ru]авиатор 1 win[/url], и испытайте удачу в уникальном игровом процессе!
Казино Aviator представляет собой захватывающий игровой проект, предоставляющий возможность заработать. -
สล็อตเว็บตรง
สล็อตออนไลน์ ทางเลือกยอดนิยม ในยุคปัจจุบัน.
ในปัจจุบัน สล็อต บนอินเทอร์เน็ต ถือเป็น เกมที่มีผู้เล่นจำนวนมาก ในวงการคาสิโนออนไลน์ ด้วย รูปแบบการเล่นที่เข้าใจง่าย เรียนรู้ได้เร็ว และ ให้ความสนุกทันที ทั้งผู้เล่นใหม่และผู้เล่นเดิม สล็อต ก็เหมาะสม สำหรับการเล่นทั่วไป.
ทำไม สล็อต ถึงได้รับความนิยม .
สล็อต มีข้อดีหลายประการ เช่น เข้าใจง่าย ไม่ต้องใช้ทักษะซับซ้อน, มีธีมหลากหลาย พร้อมกราฟิกทันสมัย, สามารถเริ่มต้นด้วยเงินน้อย และ มีโบนัส พร้อมระบบฟรีสปิน. ด้วยเหตุนี้ เกมสล็อต จึงถือเป็น เกมอันดับต้น ๆ ของผู้เล่นจำนวนมาก.
ความหมายของ สล็อตเว็บตรง .
สล็อตเว็บตรง หมายถึง การเล่นสล็อตผ่านเว็บผู้ให้บริการโดยตรง ไม่มีตัวกลาง ซึ่งช่วยให้ระบบมีความเสถียร. ข้อดีของสล็อตเว็บตรง ได้แก่ การโหลดเกมที่รวดเร็ว, ความปลอดภัยสูง, ผลเกมยุติธรรม และ มีสิทธิพิเศษเพิ่มเติม. นักเล่นส่วนใหญ่ นิยมเลือก เว็บตรง เพื่อความมั่นใจ.
ทดลองเล่น pg slot แบบไม่ใช้เงินจริง .
สำหรับผู้เล่นที่ต้องการทดลอง สามารถเลือก ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg ก่อนตัดสินใจ โดยเป็นโหมดเดโม สามารถเล่นฟรี. การทดลองเล่น ทำให้ผู้เล่น เรียนรู้ระบบการเล่น, รู้จักฟีเจอร์โบนัส และ สามารถประเมินความคุ้มค่า เหมาะสำหรับมือใหม่ และผู้ที่ต้องการเลือกเกม.
pg slot คืออะไร .
PG Slot คือเกมสล็อต จากค่าย Pocket Games Soft ซึ่งมีชื่อเสียง ด้านคุณภาพเกม. จุดเด่นของ pg slot ได้แก่ ภาพสวย คมชัด, เล่นบนมือถือได้เต็มรูปแบบ, เกมไม่สะดุด และ โบนัสน่าสนใจ. ด้วยเหตุนี้ PG Slot จึงได้รับความนิยมอย่างต่อเนื่อง ในหลายประเทศ.
บทสรุปโดยรวม .
การเล่นสล็อต สล็อต ผ่าน สล็อตเว็บตรง พร้อมกับ ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg และ รวมถึงเกมของ PG ช่วยให้การเล่นมีความมั่นใจและสนุกมากขึ้น เหมาะกับผู้เล่นที่ต้องการความมั่นคง. -
pg slot
สล็อตออนไลน์ ที่ได้รับความนิยม .
ทุกวันนี้ เกมสล็อต ออนไลน์ จัดเป็น เกมที่มีผู้เล่นจำนวนมาก ในตลาดเกมออนไลน์ ด้วย รูปแบบการเล่นที่เข้าใจง่าย เรียนรู้ได้เร็ว และ ให้ความสนุกทันที ไม่ว่าผู้เล่นจะเป็นมือใหม่หรือมีประสบการณ์ สล็อต ก็ยังตอบโจทย์ สำหรับการเล่นในระยะยาว.
เหตุผลที่ผู้เล่นเลือกเล่น สล็อต .
เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ มีข้อดีหลายประการ เช่น เข้าใจง่าย ไม่ต้องใช้ทักษะซับซ้อน, มีธีมหลากหลาย พร้อมกราฟิกทันสมัย, ใช้เงินลงทุนต่ำ และ มีฟีเจอร์โบนัส พร้อมระบบฟรีสปิน. ด้วยเหตุนี้ เกมสล็อต จึงถือเป็น เกมยอดนิยม ในหมู่นักเล่น.
ความหมายของ สล็อตเว็บตรง .
สล็อตตรง คือ การเล่นสล็อตผ่านเว็บผู้ให้บริการโดยตรง โดยไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์ ซึ่งช่วยให้ระบบมีความเสถียร. ข้อดีของสล็อตเว็บตรง ประกอบด้วย การโหลดเกมที่รวดเร็ว, ระบบปลอดภัย, ผลเกมยุติธรรม และ มักมีโปรโมชั่นมากกว่า. ผู้เล่นจำนวนมาก จึงเลือก สล็อตเว็บตรง เพื่อความปลอดภัยในการเล่น.
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg ก่อนเล่นจริง .
สำหรับผู้ที่ยังไม่ต้องการลงทุน สามารถเลือก ทดลองเล่น pg ได้ทันที ซึ่งเป็นระบบทดลอง สามารถเล่นฟรี. การทดลองเล่น ทำให้ผู้เล่น เรียนรู้ระบบการเล่น, เข้าใจระบบโบนัส และ สามารถประเมินความคุ้มค่า เหมาะสำหรับมือใหม่ และผู้ที่ต้องการเลือกเกม.
ทำไม pg slot ถึงเป็นที่นิยม .
PG Slot เป็นเกมสล็อต จากผู้พัฒนา PG ซึ่งมีชื่อเสียง ด้านคุณภาพเกม. จุดเด่นของ pg slot ได้แก่ ภาพสวย คมชัด, รองรับการเล่นบนมือถือ 100%, เกมไม่สะดุด และ โบนัสน่าสนใจ. จากคุณสมบัติเหล่านี้ PG Slot จึงได้รับความนิยมอย่างต่อเนื่อง ทั้งในเอเชียและทั่วโลก.
บทสรุปโดยรวม .
การเลือกเล่น เกมสล็อต ผ่าน สล็อตเว็บตรง พร้อมกับ ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg และ เลือกเกมจาก PG ช่วยให้ผู้เล่นได้รับประสบการณ์ที่ปลอดภัย สนุก และมีคุณภาพ เหมาะสำหรับการเล่นระยะยาว. -
สล็อตเว็บตรง
เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ ทางเลือกยอดนิยม ในยุคปัจจุบัน.
ในปัจจุบัน เกมสล็อต บนอินเทอร์เน็ต จัดเป็น เกมที่มีผู้เล่นจำนวนมาก ในตลาดเกมออนไลน์ เนื่องจาก วิธีการเล่นที่ไม่ซับซ้อน ไม่ซับซ้อน และ สร้างความบันเทิงได้รวดเร็ว ทั้งผู้เล่นใหม่และผู้เล่นเดิม สล็อต ก็ยังตอบโจทย์ สำหรับการเล่นทั่วไป.
เหตุผลที่ผู้เล่นเลือกเล่น สล็อต .
เกมสล็อตออนไลน์ มีจุดเด่นหลายด้าน เช่น เข้าใจง่าย ไม่ต้องใช้ทักษะซับซ้อน, มีรูปแบบเกมหลากหลาย พร้อมกราฟิกทันสมัย, ใช้เงินลงทุนต่ำ และ มีโบนัส รวมถึงฟรีสปิน. ด้วยเหตุนี้ สล็อต จึงถือเป็น เกมอันดับต้น ๆ ของผู้เล่นจำนวนมาก.
ความหมายของ สล็อตเว็บตรง .
สล็อตตรง คือ การเล่นสล็อตผ่านเว็บผู้ให้บริการโดยตรง โดยไม่ผ่านเอเย่นต์ ซึ่งช่วยให้ระบบมีความเสถียร. ข้อดีของสล็อตเว็บตรง ประกอบด้วย เข้าเกมได้ไว, ระบบปลอดภัย, ผลลัพธ์โปร่งใส และ มักมีโปรโมชั่นมากกว่า. นักเล่นส่วนใหญ่ จึงเลือก เว็บตรง เพื่อความมั่นใจ.
ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg ก่อนเล่นจริง .
สำหรับผู้เล่นที่ต้องการทดลอง สามารถเลือก ทดลองเล่น pg ก่อนตัดสินใจ โดยเป็นโหมดเดโม สามารถเล่นฟรี. โหมดนี้ ทำให้ผู้เล่น เรียนรู้ระบบการเล่น, เข้าใจระบบโบนัส และ เลือกเกมที่เหมาะสมได้ เหมาะกับผู้เล่นใหม่ และผู้ที่ต้องการเลือกเกม.
pg slot คืออะไร .
PG Slot เป็นเกมสล็อต จากผู้พัฒนา PG ซึ่งมีชื่อเสียง ด้านคุณภาพเกม. ข้อดีของ PG Slot ได้แก่ ภาพสวย คมชัด, เล่นบนมือถือได้เต็มรูปแบบ, เกมไม่สะดุด และ โบนัสน่าสนใจ. จากคุณสมบัติเหล่านี้ pg slot จึงมีผู้เล่นเพิ่มขึ้น ในหลายประเทศ.
สรุป .
การเล่นสล็อต เกมสล็อต ผ่าน เว็บตรง ร่วมกับการใช้ ทดลองเล่นสล็อต pg และ เลือกเกมจาก PG ช่วยให้การเล่นมีความมั่นใจและสนุกมากขึ้น เหมาะกับผู้เล่นที่ต้องการความมั่นคง. -
Try your luck and enjoy the exciting game on[url=https://swiminator.com/]swiminator[/url], which will give you a sea of ??pleasure and bonuses.
Finally, use the gamble feature cautiously, since it carries a risk of losing accumulated winnings. -
Try your luck and enjoy the exciting game on[url=https://swiminator.com/]swiminator free[/url], which will give you a sea of ??pleasure and bonuses.
The gamble option should be used carefully, as it can result in losing your winnings. -
Visit [url=https://777bet-online-casino.com/]77bet online casino[/url] and dive into the world of gambling with unique offers!
Its intuitive design and diverse game offerings are likely reasons for its expanding popularity. -
Visit [url=https://777bet-online-casino.com/]777bet casino[/url] and dive into the world of gambling with unique offers!
Moreover, 777bet offers various payment options, making transactions convenient for users. -
Try your luck with [url=https://jilispins-casino.com]jili spin casino[/url] and win a big prize today!
For those seeking a trustworthy and fun online gaming experience, jili spin is an excellent choice. -
Try your luck with [url=https://jilispins-casino.com]jili casino[/url] and win a big prize today!
With a broad range of games and a customer-focused design, it appeals to many gamers. -
Immerse yourself in the world of exciting games and big wins with spingo88 on [url=https://spingo-88.com/]spingo88[/url]!
These incentives not only attract new players but also retain the existing ones. -
Immerse yourself in the world of exciting games and big wins with spingo88 register on [url=https://spingo-88.com/]spingo88[/url]!
Looking ahead, Spingo88 is poised for even greater success as it continues to evolve. -
[url=https://777bet-download-free.com/]777 bet online casino[/url] and dive into the world of gambling with unique offers!
Not only is the design engaging, but it also ensures that players can easily access their favorite games. -
[url=https://777bet-download-free.com/]777 bet online casino[/url] and dive into the world of gambling with unique offers!
Its combination of aesthetic appeal and functionality facilitates an enjoyable gaming experience. -
Check out our new game on [url=https://alo-789.com/]alo789 link[/url], to try your luck and win big prizes!
Signing up for alo789 is a straightforward process requiring only basic information. -
Discover the best slot machines with [url=https://mr-lucky88.com/]mrlucky88 login[/url].
Building connections with viewers has always been a priority for mrlucky88. -
Discover the best slot machines with [url=https://mr-lucky88.com/]mrlucky88 slot[/url].
Mrlucky88 has announced upcoming ventures that excite the fanbase. -
Try your luck in [url=https://jilispin-login.com]jili spin[/url] and enjoy exciting slots from Jili!
This simple procedure renders it fun for every level of expertise. -
Try your luck in [url=https://jilispin-login.com]jili spin[/url] and enjoy exciting slots from Jili!
The thrill comes from the game's dynamics, but moderation is key. -
Immerse yourself in the world of excitement and winnings with[url=https://valorslots.com/]valor slots[/url],where every spin brings pleasure and a chance to win a big jackpot.
Positioned in a bustling locale, it boasts diverse gambling choices that appeal to various tastes. -
Immerse yourself in the world of excitement and winnings with[url=https://valorslots.com/]casino valor[/url],where every spin brings pleasure and a chance to win a big jackpot.
Located in the heart of the city, it offers a wide array of gaming options to satisfy all preferences. -
onion browser
Dark Web Explained: Meaning and Access
What the Dark Web Means
The darknet is a concealed part of the internet that cannot be opened through regular browsers. When users search for what the dark web is or dark web meaning, they usually refer to anonymous online networks that require special software and apply cryptographic methods to conceal identities. Most dark web websites operate on the onion domain.
Unlike the surface web, the dark web is not indexed by Google or other standard search engines.
How to Access the Dark Web
To understand how to get on dark web, users need a specialized dark web browser.
The most common option is Tor Browser:
Available via the Tor Browser download for Windows, macOS and Linux systems
Additionally available as the Android version of Tor Browser
Routes traffic through several encrypted relays (onion-based routing)
For iOS users, Onion Browser is frequently used.
To access dark web safely, users often use Tor together with basic security practices and avoid sharing personal information.
Dark Web Search Engines and Resources
Since Google does not list the dark web, users rely on a dark web search engine such as:
Ahmia search
Torch dark web
Onion search
DuckDuckGo dark web (via Tor)
Indexes like the Hidden Wiki directory provide lists of darknet links, but a significant number of links are outdated or unsafe.
Dark Web Marketplaces and Risks
Darknet marketplaces are known for anonymous trading, often using digital currencies. The most famous example is the Silk Road marketplace, which was shut down by law enforcement.
Topics like illegal goods and financial fraud have led to greater scrutiny from authorities. Many markets are scams or short-lived.
Dark Web Monitoring and Data Leaks
Users often ask whether their information is on the dark web. This has led to dark web monitoring, dark web scanning, and dark web check services. These tools identify leaked emails, passwords, or financial data and may send a security alert if a data leak is detected.
Final Note
The dark web is not completely illegal, but it involves significant risks. Darknet sites are used both for privacy-focused communication and for criminal activity. Anyone accessing the dark web should be aware of the technical, legal, and security implications before continuing. -
hidden wiki
Dark Web: What It Is and How to Access It
What the Dark Web Means
The dark web is a hidden part of the internet that is not reachable through standard browsers. When users search for what is dark web or dark web meaning, they usually refer to anonymous online networks that require special software and use encryption to protect user identities. Most darknet websites operate on the .onion domain.
Unlike the regular web, the dark web is not indexed by Google or other standard search engines.
How to Access the Dark Web
To understand how to get on dark web, users need a dedicated dark web browser.
The most widely used option is the Tor Browser:
Accessible through Tor Browser download for Windows, macOS and Linux systems
Also available as Tor Browser for Android
Directs traffic through multiple encrypted nodes (onion routing)
For users on iOS devices, Onion Browser is a popular choice.
To browse the dark web safely, users often combine Tor with basic security practices and refrain from sharing personal data.
Dark Web Search Engines and Resources
Since Google does not list the dark web, users rely on a dark web search engine such as:
Ahmia search
Torch dark web
Onion search
DuckDuckGo dark web (via Tor)
Directories like the Hidden Wiki provide collections of dark web links, but many links may be outdated or unsafe.
Dark Web Marketplaces and Risks
Dark web markets are known for anonymous transactions, often using cryptocurrency. The best-known example is the Silk Road dark web, which was taken down by law enforcement.
Topics like dark web drugs and fraud have led to greater scrutiny from authorities. Many markets are scams or short-lived.
Monitoring the Dark Web for Data Leaks
Users often ask whether their information is on the dark web. This has led to darknet monitoring, dark web scan, and dark web check services. These tools identify exposed emails, passwords, and financial information and may trigger a dark web alert if exposure is found.
Final Note
The dark web is not entirely illegal, but it carries real risks. Darknet sites are used both for anonymous communication and for illegal activities. Anyone exploring the dark web should be aware of the technology, legal boundaries, and security implications before continuing. -
Try your hand at online games on [url=https://125-win.com]125win slot[/url] and win big prizes!
Access to assistance is facilitated through live chat, email contact, and telephone support. -
Try your hand at online games on [url=https://125-win.com]125win[/url] and win big prizes!
User privacy and data security are maintained through modern encryption systems.









